Heart Development. Origins of congenital heart defects Properties of cardiac progenitor cells. Robert G. Kelly
|
|
|
- Thomasine Anthony
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ESC CBCS Summer School on Cardiovascular Sciences Heart Development 19th June 2013 Origins of congenital heart defects Properties of cardiac progenitor cells Robert G. Kelly
2 Animal models of heart development
3
4 Tinman/Nkx2.5 expression in different species In situ hybridisation Harvey 1996 Dev Biol 178:203-16
5
6
7 Heart Development From the cardiac crescent to the embryonic heart Second heart field cardiac progenitor cells Cardiac septation and chamber morphogenesis Conduction system and epicardial development
8 Specifying cardiac fate in the early embryo Inductive signals Baf60c-Gata4 Tbx5 Harvey 2002 Nat Rev Genet 3: Mef2c, Nkx2.5, Hand, Isl1 Muscle gene activation Beating heart muscle Kirby 2007 Cardiac Development Takeuchi and Bruneau 2009 Nature 459: Ieda et al 2010 Cell 142:375-86
9 From the cardiac crescent to the embryonic heart
10 The right ventricle and outflow tract are added progressively to the elongating heart tube E8.25 E9.25 DiI labeling, 24hr embryo culture
11 The second heart field Cardiac crescent Second heart field Outflow tract Right ventricle Parmacek and Epstein 2005 Cell 120:
12 Transcriptional programs in the first and second heart field lacz Transgenic mice Olson 2006 Science 313:
13 Clonal analysis in the embryonic heart: evidence for the existence of two myocardial lineages c actin nlaacz c actin nlacz Meilhac et al., 2004 Dev Cell 6:685-98
14 Cardiac progenitor cell lineages Second heart field First heart field Martin-Puig, Wang and Chien 2008, Cell Stem Cell 2:320-31
15 Gene expression in the second heart field Wildtype Isl1 -/- Isl1 E8.5 Isl1-Cre Rosa26-Stop-lacZ Stop Cai et al Dev Cell 5: Fgf10 E8.5 Fgf10 lacz Pitx2c
16 Tbx1: DiGeorge Syndrome candidate gene expressed in the second heart field Tbx1 Tbx1 +/- Tbx1 -/- Chen et al Circ Res 105: Fgf10 lacz
17 The second heart field and conotruncal congenital heart defects Di Felice and Zummo 2009 Trends Cardiovasc Med 19:130-5
18 The second heart field and cardiac neural crest cells Wnt1-Cre R26R Fgf10 lacz Jiang et al Development 127: Hutson and Kirby, 2007 Sem Cell Dev Biol Neural crest Mesoderm
19 Ablation of the cardiac neural crest impairs second heart field development Endoderm/ ectoderm Neural crest cells Yelbuz et al, 2002 Circulation 106: Second heart field progenitor cells Heart tube extension Outflow tract septation
20 Signaling pathways controling second heart field development
21 Regulation of second heart field differentiation by micrornas Wang et al 2010 Dev Cell 19:903-12
22 Fgf8 is required for second heart field and outflow tract development Ilagan et al Development 133: Reifers et al Development 126:225-35
23 ltbp3 MF20 Zhou et al 2011 Nature 474:645-8
24 Second heart field contribution at the venous pole of the heart ISL1 NKX2.5 Briggs et al 2012 Differentiation 84:117-30
25 Second heart field contribution to atrial and AV septation Hoffman et al 2009 Development 136:
26 The second heart field is part of a cardiocraniofacial developmental field Isl1-Cre R26R b-gal MF20 Nathan et al Development 135:
27 A common lineage relationship between head muscles and SHF-derived myocardium Tbx1 +/- Tbx1 -/- Kelly et al Hum Mol Genet 13: c actin nlaacz c actin nlacz Jaw muscles Right Ventricle Facial expression muscles Arterial pole Lescroart et al 2010 Development 137:
28 Heart Development From the cardiac crescent to the embryonic heart Second heart field cardiac progenitor cells Cardiac septation and chamber morphogenesis Conduction system and epicardial development
29 Cardiac chamber formation: the ballooning model Moorman and Christoffels Physiol Rev 84:
30 Differential gene expression during chamber formation ANF/Nppa 700bp promoter nlacz Habets et al Genes Dev 16:
31 A T-box gene network regulates chamber formation ANF/Nppa Tbx5 Activator Tbx2 Repressor ANF/Nppa promoter lacz activity Habets et al Genes Dev 16:
32 A T-box gene network regulates chamber formation Wildtype Tbx2 -/- Hoogaars et al Cell Mol Life Sci 64: ANF/Nppa Harrelson et al Development 131,
33 A T-box gene network regulates chamber formation Wildtype Tbx20 -/- ANF Tbx2 Singh et al Circ Res 105:442-52
34 Conduction system development Tbx3 Cx40 V AVC A V AVC A SA node AV node Bundle branches Purkinje fibres Tbx3 Central conduction system: AV node Cx40 GFP Purkinje fibre network
35 Clonal analysis of the origin of the ventricular conduction system c actin nlaacz c actin nlacz GFP X-Gal Mixed clone Unmixed clone Unmixed Mixed Number of Clusters cells 5-8 cells 9-16 cells cells cells cells Nu m ber of ß - gal- positive cells per clu ster >129 cells Biphasic development of the conduction system specification from a common progenitor followed by outgrowth Miquerol et al Circ Res 107:153-61
36
37 Purkinje fibre hypoplasia in Nkx2.5 haploinsufficient hearts Cx40 egfp Cx40 egfp ;Nkx2.5 +/- Meysen et al Dev Biol 303:740-51
38 The epicardium regulates ventricular growth RXR -/- Wessels and Sedmera, 2003 Physiol. Genomics 15:
39 Fate of the epicardium and origin of the coronary vasculature Endocardium is a major source of coronary endothelial cells Chien et al Science 322: Epicardial-derived cells Cardiac fibroblasts Smooth muscle cells? Myocardium? Coronary endothelial cells Wu et al Cell 151:
40 Heart Development The second heart field is a population of cardiac progenitor cells in pharyngeal mesoderm Perturbation of second heart field development results in congenital heart anomalies Chamber formation and conduction system development are regulated by a network of T-box transcription factors The epicardium is required for myocardial growth and coronary smooth muscle development
41 Heart Development bibliography and meetings Cardiac Development, 2008, ML Kirby, Oxford Heart Development and Regeneration, 2009, N Rosenthal and RP Harvey, Academic Press Bruneau BG. The developmental genetics of congenital heart disease. Nature : Miquerol L, Kelly RG. Organogenesis of the vertebrate heart. WIRES Dev Biol /wdev.68 Cardiovascular Research Spotlight issue on Cardiac Development, July 2011 ESC WG on Development, Anatomy and Pathology Annual meeting Berlin, September 2013 Weinstein Cardiovascular Development Meeting, USA EU FP7 Cardio GeNet
Heart Development. Robert G. Kelly Developmental Biology Institute of Marseilles - Luminy
 ESC CBCS Summer School on Cardiovascular Sciences 15th June 2011 Heart Development Robert G. Kelly Developmental Biology Institute of Marseilles - Luminy Animal models of heart development Tinman/Nkx2.5
ESC CBCS Summer School on Cardiovascular Sciences 15th June 2011 Heart Development Robert G. Kelly Developmental Biology Institute of Marseilles - Luminy Animal models of heart development Tinman/Nkx2.5
Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease
 Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease Sally Dunwoodie s.dunwoodie@victorchang.edu.au Developmental and Stem Cell Biology Division Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute for the heart of Australia...
Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease Sally Dunwoodie s.dunwoodie@victorchang.edu.au Developmental and Stem Cell Biology Division Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute for the heart of Australia...
Normal formation of a 4-chambered heart is critically
 Right Ventricular Myocardium Derives From the Anterior Heart Field Stéphane Zaffran, Robert G. Kelly, Sigolène M. Meilhac, Margaret E. Buckingham, Nigel A. Brown Abstract The mammalian heart develops from
Right Ventricular Myocardium Derives From the Anterior Heart Field Stéphane Zaffran, Robert G. Kelly, Sigolène M. Meilhac, Margaret E. Buckingham, Nigel A. Brown Abstract The mammalian heart develops from
"Lecture Index. 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development.
 "Lecture Index 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development. 5) Septation and Maturation. 6) Changes in Blood Flow during Development.
"Lecture Index 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development. 5) Septation and Maturation. 6) Changes in Blood Flow during Development.
Development of the Heart
 Development of the Heart Thomas A. Marino, Ph.D. Temple University School of Medicine Stages of Development of the Heart 1. The horseshoe-shaped pericardial cavity. 2. The formation of the single heart
Development of the Heart Thomas A. Marino, Ph.D. Temple University School of Medicine Stages of Development of the Heart 1. The horseshoe-shaped pericardial cavity. 2. The formation of the single heart
Molecular and genetic basis of congenital conotruncal heart defects Rana, M.S.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Molecular and genetic basis of congenital conotruncal heart defects Rana, M.S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Rana, M. S. (2014). Molecular
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Molecular and genetic basis of congenital conotruncal heart defects Rana, M.S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Rana, M. S. (2014). Molecular
Supplementary Figure 1. A microarray screen of organizers compared to non-organizer tissue reveals a putative organizer gene set.
 Supplementary Figure 1. A microarray screen of organizers compared to non-organizer tissue reveals a putative organizer gene set. (a, b) Venn diagrams of 31 enriched (a) and 17 depleted (b) genes significantly
Supplementary Figure 1. A microarray screen of organizers compared to non-organizer tissue reveals a putative organizer gene set. (a, b) Venn diagrams of 31 enriched (a) and 17 depleted (b) genes significantly
Arterial pole progenitors interpret opposing FGF/BMP signals to proliferate or differentiate
 AND STEM CELLS RESEARCH ARTICLE 3001 Development 137, 3001-3011 (2010) doi:10.1242/dev.051565 2010. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Arterial pole progenitors interpret opposing FGF/BMP signals
AND STEM CELLS RESEARCH ARTICLE 3001 Development 137, 3001-3011 (2010) doi:10.1242/dev.051565 2010. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Arterial pole progenitors interpret opposing FGF/BMP signals
Cardiac precursor cells are located bilaterally as 2 symmetrical
 Cellular Biology Asymmetric Fate of the Posterior Part of the Second Heart Field Results in Unexpected Left/Right Contributions to Both Poles of the Heart Jorge N. Domínguez, Sigolène M. Meilhac, Yvette
Cellular Biology Asymmetric Fate of the Posterior Part of the Second Heart Field Results in Unexpected Left/Right Contributions to Both Poles of the Heart Jorge N. Domínguez, Sigolène M. Meilhac, Yvette
Clonal analysis reveals common lineage relationships between head muscles and second heart field derivatives in the mouse embryo
 RESEARCH ARTICLE 3269 Development 137, 3269-3279 (2010) doi:10.1242/dev.050674 2010. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Clonal analysis reveals common lineage relationships between head muscles
RESEARCH ARTICLE 3269 Development 137, 3269-3279 (2010) doi:10.1242/dev.050674 2010. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Clonal analysis reveals common lineage relationships between head muscles
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY. Transcriptional Regulation of the Hand1 Gene in the Developing Mouse Conceptus. Dana Rae Rourke-Sim A THESIS
 UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY Transcriptional Regulation of the Hand1 Gene in the Developing Mouse Conceptus by Dana Rae Rourke-Sim A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT OF
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY Transcriptional Regulation of the Hand1 Gene in the Developing Mouse Conceptus by Dana Rae Rourke-Sim A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT OF
Resident cardiac stem cells: how to find and use them
 Resident cardiac stem cells: how to find and use them G. Hasenfuß Cardiology and Pneumology Heart Research Center Göttingen Georg-August-University Göttingen Definition: Stem cell Selfrenewal Stem cell
Resident cardiac stem cells: how to find and use them G. Hasenfuß Cardiology and Pneumology Heart Research Center Göttingen Georg-August-University Göttingen Definition: Stem cell Selfrenewal Stem cell
W.S. O The University of Hong Kong
 W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Objectives: Describe early angiogenesis. Describe the heart tube formation. Describe the partitioning into a 4- chambered heart. List the formation of heart valves and
W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Objectives: Describe early angiogenesis. Describe the heart tube formation. Describe the partitioning into a 4- chambered heart. List the formation of heart valves and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10188 Supplementary Figure 1. Embryonic epicardial genes are down-regulated from midgestation stages and barely detectable post-natally. Real time qrt-pcr revealed a significant down-regulation
doi:10.1038/nature10188 Supplementary Figure 1. Embryonic epicardial genes are down-regulated from midgestation stages and barely detectable post-natally. Real time qrt-pcr revealed a significant down-regulation
Journal of Developmental Biology ISSN
 J. Dev. Biol. 2014, 2, 50-71; doi:10.3390/jdb2010050 Review OPEN ACCESS Journal of Developmental Biology ISSN 2221-3759 www.mdpi.com/journal/jdb/ Retinoids and Cardiac Development Stéphane Zaffran *, Nicolas
J. Dev. Biol. 2014, 2, 50-71; doi:10.3390/jdb2010050 Review OPEN ACCESS Journal of Developmental Biology ISSN 2221-3759 www.mdpi.com/journal/jdb/ Retinoids and Cardiac Development Stéphane Zaffran *, Nicolas
Material and Methods Production and analysis of -gal+ clones Immunostaining Optical projection tomography Statistical analysis
 Material and Methods Production and analysis of β-gal+ clones The α-cardiac actin nlaacz/+ and Cx40 egfp mouse lines used in this study were genotyped as previously reported 1, 2. Double transgenic knock-in
Material and Methods Production and analysis of β-gal+ clones The α-cardiac actin nlaacz/+ and Cx40 egfp mouse lines used in this study were genotyped as previously reported 1, 2. Double transgenic knock-in
The cardiomyocyte is the fundamental work unit of the. Myocardial Lineage Development
 This Review is part of a thematic series on Developmental Biology, which includes the following articles: Signaling Pathways Controlling Second Heart Field Development [Circ Res. 2009;104:933 942] Heart
This Review is part of a thematic series on Developmental Biology, which includes the following articles: Signaling Pathways Controlling Second Heart Field Development [Circ Res. 2009;104:933 942] Heart
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval
 When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT
 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT Diane E. Spicer, BS, PA(ASCP) University of Florida Dept. of Pediatric Cardiology Curator Van Mierop Cardiac Archive This lecture is given with special thanks to
CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT Diane E. Spicer, BS, PA(ASCP) University of Florida Dept. of Pediatric Cardiology Curator Van Mierop Cardiac Archive This lecture is given with special thanks to
Retinoic Acid Regulates Differentiation of the Secondary Heart Field and TGFb-Mediated Outflow Tract Septation
 Short Article Retinoic Acid Regulates Differentiation of the Secondary Heart Field and TGFb-Mediated Outflow Tract Septation Peng Li, 1 Mohammad Pashmforoush, 1 and Henry M. Sucov 1, * 1 Broad Center for
Short Article Retinoic Acid Regulates Differentiation of the Secondary Heart Field and TGFb-Mediated Outflow Tract Septation Peng Li, 1 Mohammad Pashmforoush, 1 and Henry M. Sucov 1, * 1 Broad Center for
Maoqing Ye, Yan Yin, Kazumi Fukatsu, and Paul Grossfeld
 Evidence That Deletion of ETS-1, a Gene in the Jacobsen Syndrome (11q-) Cardiac Critical Region, Causes Congenital Heart Defects through Impaired Cardiac Neural Crest Cell Function 52 Maoqing Ye, Yan Yin,
Evidence That Deletion of ETS-1, a Gene in the Jacobsen Syndrome (11q-) Cardiac Critical Region, Causes Congenital Heart Defects through Impaired Cardiac Neural Crest Cell Function 52 Maoqing Ye, Yan Yin,
Chapter 2 Molecular Mechanisms of Cardiac Development
 Chapter 2 Molecular Mechanisms of Cardiac Development Patricia Roche, Michael P. Czubryt and Jeffrey T. Wigle Abstract The heart is the first organ to develop in order to supply the ever-increasing metabolic
Chapter 2 Molecular Mechanisms of Cardiac Development Patricia Roche, Michael P. Czubryt and Jeffrey T. Wigle Abstract The heart is the first organ to develop in order to supply the ever-increasing metabolic
Congenital heart defects occur in almost 1% of live births,
 Review Signaling Pathways Controlling Second Heart Field Development Francesca Rochais, Karim Mesbah, Robert G. Kelly Abstract Insight into the mechanisms underlying congenital heart defects and the use
Review Signaling Pathways Controlling Second Heart Field Development Francesca Rochais, Karim Mesbah, Robert G. Kelly Abstract Insight into the mechanisms underlying congenital heart defects and the use
Morphogenesis of the right ventricle requires myocardial expression of Gata4
 Research article Morphogenesis of the right ventricle requires myocardial expression of Gata4 Elisabeth M. Zeisberg, 1,2 Qing Ma, 3 Amy L. Juraszek, 3,4 Kelvin Moses, 5 Robert J. Schwartz, 5 Seigo Izumo,
Research article Morphogenesis of the right ventricle requires myocardial expression of Gata4 Elisabeth M. Zeisberg, 1,2 Qing Ma, 3 Amy L. Juraszek, 3,4 Kelvin Moses, 5 Robert J. Schwartz, 5 Seigo Izumo,
Development of the Pacemaker Tissues of the Heart. Vincent M. Christoffels, Gertien J. Smits, Andreas Kispert, Antoon F. M.
 This article is part of a new thematic series on Mechanisms of Pacemaking in the Heart, which includes the following articles: Be Still, My Beating Heart Never! [2010;106:238 239] Development of the Pacemaker
This article is part of a new thematic series on Mechanisms of Pacemaking in the Heart, which includes the following articles: Be Still, My Beating Heart Never! [2010;106:238 239] Development of the Pacemaker
Introduction to Fetal Medicine: Genetics and Embryology
 Introduction to Fetal Medicine: Genetics and Embryology Question: What do cancer biology, molecular biology, neurobiology, cell biology developmental biology and reproductive biology, all have in common?
Introduction to Fetal Medicine: Genetics and Embryology Question: What do cancer biology, molecular biology, neurobiology, cell biology developmental biology and reproductive biology, all have in common?
Second heart field and the development of the outflow tract in human embryonic heart
 The Japanese Society of Developmental Biologists Develop. Growth Differ. (2013) 55, 359 367 doi: 10.1111/dgd.12050 Original Article Second heart field and the development of the outflow tract in human
The Japanese Society of Developmental Biologists Develop. Growth Differ. (2013) 55, 359 367 doi: 10.1111/dgd.12050 Original Article Second heart field and the development of the outflow tract in human
AN ABSTRACT OF THE THESIS OF. Shachi Bhatt for the degree of Master of Science in Genetics presented on June 10, 2008.
 AN ABSTRACT OF THE THESIS OF Shachi Bhatt for the degree of Master of Science in Genetics presented on June 10, 2008. Title: Role of Pitx2 in regulation of Cardiac Remodelling. Abstract approved: Chrissa
AN ABSTRACT OF THE THESIS OF Shachi Bhatt for the degree of Master of Science in Genetics presented on June 10, 2008. Title: Role of Pitx2 in regulation of Cardiac Remodelling. Abstract approved: Chrissa
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Science. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2010 July 2.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Science. 2009 October 16; 326(5951): 426 429. doi:10.1126/science.1177350. Generation of Functional Ventricular Heart Muscle from
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Science. 2009 October 16; 326(5951): 426 429. doi:10.1126/science.1177350. Generation of Functional Ventricular Heart Muscle from
Molecular Medicine. Tbx1 Coordinates Addition of Posterior Second Heart Field Progenitor Cells to the Arterial and Venous Poles of the Heart
 Molecular Medicine Tbx1 Coordinates Addition of Posterior Second Heart Field Progenitor Cells to the Arterial and Venous Poles of the Heart M. Sameer Rana,* Magali Théveniau-Ruissy,* Christopher De Bono,
Molecular Medicine Tbx1 Coordinates Addition of Posterior Second Heart Field Progenitor Cells to the Arterial and Venous Poles of the Heart M. Sameer Rana,* Magali Théveniau-Ruissy,* Christopher De Bono,
Organogenesis Part 2. V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm VI. Endoderm VII. Development of the Tetrapod Limb VIII. Sex Determination. V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm
 Organogenesis Part 2 V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm VI. Endoderm VII. Development of the Tetrapod Limb VIII. Sex Determination V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm chordamesoderm paraxial mesoderm intermediate mesoderm
Organogenesis Part 2 V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm VI. Endoderm VII. Development of the Tetrapod Limb VIII. Sex Determination V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm chordamesoderm paraxial mesoderm intermediate mesoderm
The Multiple Phases and Faces of Wnt Signaling During Cardiac Differentiation and Development
 This Review is the introduction of a new thematic series on Wnts in Cardiovascular Development and Disease, which includes the following articles: An Updated Overview on Wnt Signaling Pathways: A Prelude
This Review is the introduction of a new thematic series on Wnts in Cardiovascular Development and Disease, which includes the following articles: An Updated Overview on Wnt Signaling Pathways: A Prelude
Introduction to Fetal Medicine: Genetics and Embryology
 Introduction to Fetal Medicine: Genetics and Embryology Question: What do cancer biology, molecular biology, neurobiology, cell biology developmental biology and reproductive biology, all have in common?
Introduction to Fetal Medicine: Genetics and Embryology Question: What do cancer biology, molecular biology, neurobiology, cell biology developmental biology and reproductive biology, all have in common?
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
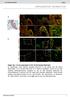 Suppl. Fig. 1 in vivo expression of ISL1 in the human fetal heart. a, Hematoxylin eosin staining showing structures of left atrium and left atrium appendage (*) of a human fetal heart at 11 weeks of gestation.
Suppl. Fig. 1 in vivo expression of ISL1 in the human fetal heart. a, Hematoxylin eosin staining showing structures of left atrium and left atrium appendage (*) of a human fetal heart at 11 weeks of gestation.
Formation of the heart involves a wondrous and
 A genetic blueprint for cardiac development Deepak Srivastava* & Eric N. Olson* insight progress *Department of Molecular Biology and Department of Pediatrics, University of Texas, Southwestern Medical
A genetic blueprint for cardiac development Deepak Srivastava* & Eric N. Olson* insight progress *Department of Molecular Biology and Department of Pediatrics, University of Texas, Southwestern Medical
Supplementary Figure S1 Enlarged coronary artery branches in Edn1-knockout mice. a-d, Coronary angiography by ink injection in wild-type (a, b) and
 Supplementary Figure S1 Enlarged coronary artery branches in Edn1-knockout mice. a-d, Coronary angiography by ink injection in wild-type (a, b) and Edn1-knockout (Edn1-KO) (c, d) hearts. The boxed areas
Supplementary Figure S1 Enlarged coronary artery branches in Edn1-knockout mice. a-d, Coronary angiography by ink injection in wild-type (a, b) and Edn1-knockout (Edn1-KO) (c, d) hearts. The boxed areas
Pregestational Diabetes and Congenital Heart Defects: Role of Reactive Oxygen Species
 Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository November 2014 Pregestational Diabetes and Congenital Heart Defects: Role of Reactive Oxygen Species Hoda Moazzen The
Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository November 2014 Pregestational Diabetes and Congenital Heart Defects: Role of Reactive Oxygen Species Hoda Moazzen The
Author's personal copy
 Developmental Biology 351 (2011) 62 69 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Hand2 function in second heart field progenitors
Developmental Biology 351 (2011) 62 69 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Hand2 function in second heart field progenitors
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
CHAPTER 8 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR DEVELOPMENT OF THE HEART
 163 CHAPTER 8 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR DEVELOPMENT OF THE HEART Miguel Torres and Silvia Martín-Puig INTRODUCTION / 163 CARDIAC EMBRYOGENESIS / 163 Allocation and Specification of Cardiac Progenitors during
163 CHAPTER 8 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR DEVELOPMENT OF THE HEART Miguel Torres and Silvia Martín-Puig INTRODUCTION / 163 CARDIAC EMBRYOGENESIS / 163 Allocation and Specification of Cardiac Progenitors during
Circulation. Sinoatrial (SA) Node. Atrioventricular (AV) Node. Cardiac Conduction System. Cardiac Conduction System. Linked to the nervous system
 Circulation Cardiac Conduction System AHS A H S Your body resembles a large roadmap. There are routes or arteries that take you downtown to the heart of the city and veins that take you to the outskirts
Circulation Cardiac Conduction System AHS A H S Your body resembles a large roadmap. There are routes or arteries that take you downtown to the heart of the city and veins that take you to the outskirts
Cardiac Cycle. Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time.
 The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Role of Tbx3 in conduction system development Bakker, M.L. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Role of Tbx3 in conduction system development Bakker, M.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Bakker, M. L. (2012). Role of Tbx3 in conduction
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Role of Tbx3 in conduction system development Bakker, M.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Bakker, M. L. (2012). Role of Tbx3 in conduction
Heart Fields: Spatial Polarity and Temporal Dynamics
 THE ANATOMICAL RECORD 297:175 182 (2014) Heart Fields: Spatial Polarity and Temporal Dynamics RADWAN ABU-ISSA* Department of Natural Sciences, University of Michigan-Dearborn, Michigan ABSTRACT In chick
THE ANATOMICAL RECORD 297:175 182 (2014) Heart Fields: Spatial Polarity and Temporal Dynamics RADWAN ABU-ISSA* Department of Natural Sciences, University of Michigan-Dearborn, Michigan ABSTRACT In chick
W.S. O. School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong
 W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong Objectives: Describe early angiogenesis. Describe the heart tube formation. Describe the partitioning into a 4- chambered heart. List the formation
W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong Objectives: Describe early angiogenesis. Describe the heart tube formation. Describe the partitioning into a 4- chambered heart. List the formation
Through the 20th century, knowledge of the events occurring during cardiac development was
 806 * Anatomy DEVELOPMENT OF THE HEART: (1) FORMATION OF THE CARDIAC CHAMBERS AND ARTERIAL TRUNKS Antoon Moorman, Sandra Webb, Nigel A Brown, Wouter Lamers, Robert H Anderson See end of article for authors
806 * Anatomy DEVELOPMENT OF THE HEART: (1) FORMATION OF THE CARDIAC CHAMBERS AND ARTERIAL TRUNKS Antoon Moorman, Sandra Webb, Nigel A Brown, Wouter Lamers, Robert H Anderson See end of article for authors
Development of the heart
 Development of the heart Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Early Development of the Circulatory System Appears in the middle of the third week, when the
Development of the heart Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Early Development of the Circulatory System Appears in the middle of the third week, when the
Developmental Biology
 Developmental Biology 353 (2011) 266 274 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Hox genes define distinct progenitor sub-domains
Developmental Biology 353 (2011) 266 274 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Hox genes define distinct progenitor sub-domains
ISSN: CODEN Code: PIHNBQ ZDB-Number: IC Journal No: Vol. 2 No Online Available at
 Received: 13-05-2013 Accepted: 16-06-2013 ISSN: 2277-7695 CODEN Code: PIHNBQ ZDB-Number: 2663038-2 IC Journal No: 7725 Vol. 2 No. 5 2013 Online Available at www.thepharmajournal.com THE PHARMA INNOVATION
Received: 13-05-2013 Accepted: 16-06-2013 ISSN: 2277-7695 CODEN Code: PIHNBQ ZDB-Number: 2663038-2 IC Journal No: 7725 Vol. 2 No. 5 2013 Online Available at www.thepharmajournal.com THE PHARMA INNOVATION
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Role of Tbx3 in conduction system development Bakker, M.L. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Role of Tbx3 in conduction system development Bakker, M.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Bakker, M. L. (2012). Role of Tbx3 in conduction
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Role of Tbx3 in conduction system development Bakker, M.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Bakker, M. L. (2012). Role of Tbx3 in conduction
Hand1 regulates cardiomyocyte proliferation versus differentiation in the developing heart
 AND DISEASE RESEARCH ARTICLE 4595 Development 133, 4595-4606 (2006) doi:10.1242/dev.02625 Hand1 regulates cardiomyocyte proliferation versus differentiation in the developing heart Catherine A. Risebro
AND DISEASE RESEARCH ARTICLE 4595 Development 133, 4595-4606 (2006) doi:10.1242/dev.02625 Hand1 regulates cardiomyocyte proliferation versus differentiation in the developing heart Catherine A. Risebro
1 General Introduction
 1 General Introduction chapter 1 Congenital heart disease is the most common birth defect with an estimated incidence of six per 1000 live born children. 1 Several mechanisms may underlie congenital heart
1 General Introduction chapter 1 Congenital heart disease is the most common birth defect with an estimated incidence of six per 1000 live born children. 1 Several mechanisms may underlie congenital heart
The Cardiovascular System
 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
Programming and reprogramming a human heart cell
 Review Focus: Induced Pluripotency & Cellular Reprogramming Programming and reprogramming a human heart cell Makoto Sahara 1,2,*, Federica Santoro 1 & Kenneth R Chien 1,2,** Abstract The latest discoveries
Review Focus: Induced Pluripotency & Cellular Reprogramming Programming and reprogramming a human heart cell Makoto Sahara 1,2,*, Federica Santoro 1 & Kenneth R Chien 1,2,** Abstract The latest discoveries
Congenital heart malformations, resulting from mistakes in the
 mirna-processing enzyme Dicer is necessary for cardiac outflow tract alignment and chamber septation Ankur Saxena a,b and Clifford J. Tabin a,1 a Department of Genetics, Harvard Medical School, Boston,
mirna-processing enzyme Dicer is necessary for cardiac outflow tract alignment and chamber septation Ankur Saxena a,b and Clifford J. Tabin a,1 a Department of Genetics, Harvard Medical School, Boston,
Hepatogenesis I Liver development
 Hepatogenesis I Liver development HB 308 George Yeoh Room 2.59 MCS Building yeoh@cyllene.uwa.edu.au Topics Early liver development Tissue interaction - role of morphogens and cytokines Liver enriched transcription
Hepatogenesis I Liver development HB 308 George Yeoh Room 2.59 MCS Building yeoh@cyllene.uwa.edu.au Topics Early liver development Tissue interaction - role of morphogens and cytokines Liver enriched transcription
Introduction to Anatomy. Dr. Maher Hadidi. Bayan Yanes. April/9 th /2013
 Introduction to Anatomy Dr. Maher Hadidi Bayan Yanes 27 April/9 th /2013 KEY POINTS: 1) Right side of the heart 2) Papillary muscles 3) Left side of the heart 4) Comparison between right and left sides
Introduction to Anatomy Dr. Maher Hadidi Bayan Yanes 27 April/9 th /2013 KEY POINTS: 1) Right side of the heart 2) Papillary muscles 3) Left side of the heart 4) Comparison between right and left sides
Middle mediastinum---- heart & pericardium. Dep. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hongying
 Middle mediastinum---- heart & pericardium Dep. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Subdivisions of the mediastinum Contents of Middle mediastinum Heart Pericardium: a serous sac enclosing
Middle mediastinum---- heart & pericardium Dep. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Subdivisions of the mediastinum Contents of Middle mediastinum Heart Pericardium: a serous sac enclosing
Tbx20 is essential for cardiac chamber differentiation and
 Research article 2697 Tbx20 is essential for cardiac chamber differentiation and repression of Tbx2 Manvendra K. Singh 1, Vincent M. Christoffels 2, José M. Dias 3, Mark-Oliver Trowe 1, Marianne Petry
Research article 2697 Tbx20 is essential for cardiac chamber differentiation and repression of Tbx2 Manvendra K. Singh 1, Vincent M. Christoffels 2, José M. Dias 3, Mark-Oliver Trowe 1, Marianne Petry
Molecular regulation of heart formation has fascinated biologists
 Review Molecular Regulation of Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Sharon L. Paige, Karolina Plonowska, Adele Xu, Sean M. Wu Abstract: The heart is the first organ to form during embryonic development. Given
Review Molecular Regulation of Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Sharon L. Paige, Karolina Plonowska, Adele Xu, Sean M. Wu Abstract: The heart is the first organ to form during embryonic development. Given
During the past decade, our understanding of the development
 Review article franklin h. epstein lecture Franklin H. Epstein, M.D., served the New England Journal of Medicine for more than 20 years. A keen clinician, accomplished researcher, and outstanding teacher,
Review article franklin h. epstein lecture Franklin H. Epstein, M.D., served the New England Journal of Medicine for more than 20 years. A keen clinician, accomplished researcher, and outstanding teacher,
CNS Developmental. Anke van Eekelen, PhD. Telethon Institute for Child Health Research
 CNS Developmental Anke van Eekelen, PhD Telethon Institute for Child Health Research (Some slides are modified versions of Prof. Alan Harvey s Neuroscience lecture at ANHB and Dr. Joanne Britto s Dev Neuroscience
CNS Developmental Anke van Eekelen, PhD Telethon Institute for Child Health Research (Some slides are modified versions of Prof. Alan Harvey s Neuroscience lecture at ANHB and Dr. Joanne Britto s Dev Neuroscience
Cardiac Conduction System
 Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
CV Anatomy Quiz. Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green
 CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
Fibroblast growth factors and Hedgehogs: at the heart of the epicardial signaling center
 Review Fibroblast growth factors and Hedgehogs: at the heart of the epicardial signaling center Kory J. Lavine and David M. Ornitz Department of Developmental Biology, Washington University School of Medicine,
Review Fibroblast growth factors and Hedgehogs: at the heart of the epicardial signaling center Kory J. Lavine and David M. Ornitz Department of Developmental Biology, Washington University School of Medicine,
The heart & Cardiovascular system
 The heart & Cardiovascular system The heart s continuous pulse create a base for our understanding of rhythms in everyday life. Bonnie Bainbridge Cohen The heart constantly beats throughout our lives never
The heart & Cardiovascular system The heart s continuous pulse create a base for our understanding of rhythms in everyday life. Bonnie Bainbridge Cohen The heart constantly beats throughout our lives never
Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology
 Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology 60 (2013) 129 141 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/yjmcc
Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology 60 (2013) 129 141 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/yjmcc
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function
 Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
Review. Endocardial and Epicardial Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transitions in Heart Development and Disease
 Review Endocardial and Epicardial Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transitions in Heart Development and Disease Alexander von Gise, William T. Pu Abstract: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) converts
Review Endocardial and Epicardial Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transitions in Heart Development and Disease Alexander von Gise, William T. Pu Abstract: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) converts
Heart 3: Organogenesis, CHD, prenatal circulation
 Heart 3: Organogenesis, CHD, prenatal circulation Heart development Development of vasculature Pathogenesis of CHD Prenatal circulation and its remodeling after birth David Sedmera Charles University First
Heart 3: Organogenesis, CHD, prenatal circulation Heart development Development of vasculature Pathogenesis of CHD Prenatal circulation and its remodeling after birth David Sedmera Charles University First
HCN4 Dynamically Marks the First Heart Field and Conduction System Precursors
 HCN4 Dynamically Marks the First Heart Field and Conduction System Precursors Xingqun Liang 1, 2, Gang Wang 1, Lizhu Lin 1, Jennifer Lowe 1, Qingquang Zhang 2, Lei Bu 1, Yihan Chen 2, Ju Chen 1, Yunfu
HCN4 Dynamically Marks the First Heart Field and Conduction System Precursors Xingqun Liang 1, 2, Gang Wang 1, Lizhu Lin 1, Jennifer Lowe 1, Qingquang Zhang 2, Lei Bu 1, Yihan Chen 2, Ju Chen 1, Yunfu
Role Of Nitric Oxide In Embryonic Heart Development And Adult Aortic Valve Disease
 Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository June 2014 Role Of Nitric Oxide In Embryonic Heart Development And Adult Aortic Valve Disease Yin Liu The University
Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository June 2014 Role Of Nitric Oxide In Embryonic Heart Development And Adult Aortic Valve Disease Yin Liu The University
Since Robert Gross inaugurated pediatric cardiac surgery. Congenital Heart Disease Compendium. Cardiac Regeneration. Lessons From Development
 Congenital Heart Disease Compendium Circulation Research Compendium on Congenital Heart Disease Congenital Heart Disease: The Remarkable Journey From the Post-Mortem Room to Adult Clinics Perspective on
Congenital Heart Disease Compendium Circulation Research Compendium on Congenital Heart Disease Congenital Heart Disease: The Remarkable Journey From the Post-Mortem Room to Adult Clinics Perspective on
Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin
 Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin sections from sham-operated adult hearts (a and i) and
Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin sections from sham-operated adult hearts (a and i) and
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
Moore-Morris et al. Supplemental Table 1.
 Moore-Morris et al. Supplemental Table. In vivo echocardiographic assessment of cardiac size and function following transaortic constriction (T) at 7d and 8d. SHM 7d N=6 T 7d N=5 SHM 8d N= T 8d N=6 W,
Moore-Morris et al. Supplemental Table. In vivo echocardiographic assessment of cardiac size and function following transaortic constriction (T) at 7d and 8d. SHM 7d N=6 T 7d N=5 SHM 8d N= T 8d N=6 W,
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
6. Development of circulatory system II. Cardiac looping. Septation of atria and ventricles. Common heart malformations.
 6. Development of circulatory system II. Cardiac looping. Septation of atria and ventricles. Common heart malformations. Formation of heart tube paired endothelial-lined heart tube is formed from blood
6. Development of circulatory system II. Cardiac looping. Septation of atria and ventricles. Common heart malformations. Formation of heart tube paired endothelial-lined heart tube is formed from blood
Full file at
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What electrical event must occur for atrial kick to occur? 1) A) Atrial repolarization B) Ventricular
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What electrical event must occur for atrial kick to occur? 1) A) Atrial repolarization B) Ventricular
The Cardiovascular System (Heart)
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
Dr David Begley Papworth Hospital, Cambridge HRUK Certificate of Accreditation Course: Core Heart Rhythm Congress 2011
 Dr David Begley Papworth Hospital, Cambridge HRUK Certificate of Accreditation Course: Core Heart Rhythm Congress 2011 The AV node is the soul of the heart, and whoever understands its anatomy and electrophysiology
Dr David Begley Papworth Hospital, Cambridge HRUK Certificate of Accreditation Course: Core Heart Rhythm Congress 2011 The AV node is the soul of the heart, and whoever understands its anatomy and electrophysiology
Stem cells: units of development and regeneration. Fernando D. Camargo Ph.D. Whitehead Fellow Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research.
 Stem cells: units of development and regeneration Fernando D. Camargo Ph.D. Whitehead Fellow Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Concepts 1. Embryonic vs. adult stem cells 2. Hematopoietic stem
Stem cells: units of development and regeneration Fernando D. Camargo Ph.D. Whitehead Fellow Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Concepts 1. Embryonic vs. adult stem cells 2. Hematopoietic stem
The sinoatrial node (SAN) is the pacemaker of the heart
 Molecular Pathway for the Localized Formation of the Sinoatrial Node Mathilda T. M. Mommersteeg, Willem M. H. Hoogaars, Owen W. J. Prall, Corrie de Gier-de Vries, Cornelia Wiese, Danielle E. W. Clout,
Molecular Pathway for the Localized Formation of the Sinoatrial Node Mathilda T. M. Mommersteeg, Willem M. H. Hoogaars, Owen W. J. Prall, Corrie de Gier-de Vries, Cornelia Wiese, Danielle E. W. Clout,
Lab 16. The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels. Laboratory Objectives
 Lab 16 The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels Laboratory Objectives Describe the anatomical structures of the heart to include the pericardium, chambers, valves, and major vessels. Describe
Lab 16 The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels Laboratory Objectives Describe the anatomical structures of the heart to include the pericardium, chambers, valves, and major vessels. Describe
A GATA-dependent right ventricular enhancer controls dhand transcription in the developing heart
 Development 127, 5331-5341 (2000) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2000 DEV3263 5331 A GATA-dependent right ventricular enhancer controls dhand transcription in the developing
Development 127, 5331-5341 (2000) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2000 DEV3263 5331 A GATA-dependent right ventricular enhancer controls dhand transcription in the developing
Vertebrate Limb Patterning
 Vertebrate Limb Patterning What makes limb patterning an interesting/useful developmental system How limbs develop Key events in limb development positioning and specification initiation of outgrowth establishment
Vertebrate Limb Patterning What makes limb patterning an interesting/useful developmental system How limbs develop Key events in limb development positioning and specification initiation of outgrowth establishment
The HEART. What is it???? Pericardium. Heart Facts. This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep
 This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
Congenital valve defects occur in 2% to 3% of the
 Molecular Medicine The FGF-BMP Signaling Axis Regulates Outflow Tract Valve Primordium Formation by Promoting Cushion Neural Crest Cell Differentiation Jue Zhang, Julia Y.F. Chang, Yanqing Huang, Xiang
Molecular Medicine The FGF-BMP Signaling Axis Regulates Outflow Tract Valve Primordium Formation by Promoting Cushion Neural Crest Cell Differentiation Jue Zhang, Julia Y.F. Chang, Yanqing Huang, Xiang
HAND Proteins: Molecular Mediators of Cardiac Development and Congenital Heart Disease Deepak Srivastava
 HAND Proteins: Molecular Mediators of Cardiac Development and Congenital Heart Disease Deepak Srivastava Congenital heart defects are the clinical manifestation of anomalies in embryonic cardiac development.
HAND Proteins: Molecular Mediators of Cardiac Development and Congenital Heart Disease Deepak Srivastava Congenital heart defects are the clinical manifestation of anomalies in embryonic cardiac development.
The Cardiovascular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
the Cardiovascular System I
 the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
The T-Box transcription factor Tbx5 is required for the patterning and maturation of the murine cardiac conduction system
 Research article Development and disease 4107 The T-Box transcription factor Tbx5 is required for the patterning and maturation of the murine cardiac conduction system Ivan P. G. Moskowitz 1,2, Anne Pizard
Research article Development and disease 4107 The T-Box transcription factor Tbx5 is required for the patterning and maturation of the murine cardiac conduction system Ivan P. G. Moskowitz 1,2, Anne Pizard
Ventricular Anatomy for the Electrophysiologist (Part I)
 SPECIAL REVIEW Ventricular Anatomy for the Electrophysiologist (Part I) ABSTRACT Anatomy of the conduction system for electrophysiologists is reviewed in two parts. This first part details the historical
SPECIAL REVIEW Ventricular Anatomy for the Electrophysiologist (Part I) ABSTRACT Anatomy of the conduction system for electrophysiologists is reviewed in two parts. This first part details the historical
Fate of the mammalian cardiac neural crest
 Development 127, 1607-1616 (2000) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2000 DEV4300 1607 Fate of the mammalian cardiac neural crest Xiaobing Jiang 1,3, David H. Rowitch 4, *, Philippe
Development 127, 1607-1616 (2000) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2000 DEV4300 1607 Fate of the mammalian cardiac neural crest Xiaobing Jiang 1,3, David H. Rowitch 4, *, Philippe
Anatomy of Atrioventricular Septal Defect (AVSD)
 Surgical challenges in atrio-ventricular septal defect in grown-up congenital heart disease Anatomy of Atrioventricular Septal Defect (AVSD) S. Yen Ho Professor of Cardiac Morphology Royal Brompton and
Surgical challenges in atrio-ventricular septal defect in grown-up congenital heart disease Anatomy of Atrioventricular Septal Defect (AVSD) S. Yen Ho Professor of Cardiac Morphology Royal Brompton and
Heart. Heart 2-Tunica media: middle layer (media ='middle') muscle fibers (smooth or cardiac).
 t. innermost lumenal General Circulatory system heart and blood vessels walls have 3 layers (inside to outside) 1-Tunica interna: aka tunica intima layer--lumenal layer epithelium--endothelium simple squamous
t. innermost lumenal General Circulatory system heart and blood vessels walls have 3 layers (inside to outside) 1-Tunica interna: aka tunica intima layer--lumenal layer epithelium--endothelium simple squamous
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart
 LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
