CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT
|
|
|
- Dylan Holmes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT Diane E. Spicer, BS, PA(ASCP) University of Florida Dept. of Pediatric Cardiology Curator Van Mierop Cardiac Archive This lecture is given with special thanks to Professor RH Anderson, my mentor and my friend. Without his spectacular research and images of both human and mouse embryos, this lecture would not have been possible.
2 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT What s new? CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT An understanding of the elementary facts of human and comparative embryology is essential to an intelligent grasp of the ontogenetic problems of congenital cardiac disease. Maude Abbott Atlas of Congenital Cardiac Disease American Heart Association, New York, 1936
3 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT Do we need to change? In the past, most theories of morphogenesis were based on fanciful interpretation of normal development We are now able to demonstrate the anatomic and molecular changes that take place during cardiac development This now permits us to base our inferences on evidence, rather than speculation
4 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT It used to be thought that all components of the postnatal heart were contained within the initial linear heart tube In reality, new material is added at the arterial and venous poles from the second heart field. The initial tube, derived from the first heart field, forms little more than the definitive left ventricle
5 Mouse embryo 9 somites Myosin LC
6 Growth at arterial pole Putative left ventricle Growth at venous pole Mouse embryo E8.5 9 somites
7 Outflow tract Developing left ventricle Developing right ventricle Atrioventricular canal Mouse embryo E somites Atrial component
8 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT How are the chambers formed? By expansion from the cavity of the primary heart tube Ballooning Atrial segment the appendages Ventricular segment the apical components
9
10 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT Does this permit us to understand the basis of cardiac isomerism? The chambers develop under the influence of the laterality genes Pitx2c produces morphologically leftness Lefty-1 and nodal stop this gene from reaching the right side
11 Morphologically left Morphologically right Mouse embryo E8.5 9 somites
12 L L R R R L Mouse embryo E somites
13 Mouse embryonic day 13.5
14 Pitx2 Knock-out mouse Bilateral morphologically right appendages
15 Lefty-1 Knock-out mouse Bilateral morphologically left appendages
16 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT Cardiac isomerism It is only the appendages that show evidence of isomerism The venoatrial connections are variable, as are the remainder of the cardiac components All require description, along with the remaining systems of organs
17 What about the venoatrial connections? CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT It is often stated that there is a common wall between the coronary sinus and the left atrium, which is produced by formation of a sinuatrial fold In reality, the left sinus horn possesses its own walls from the outset of development. It becomes incorporated into the left atrioventricular groove as it becomes the coronary sinus
18 Mouse embryo 13 somites Primary atrium
19 Mouse embryo 13 somites Gut Dorsal mesocardium Right sinus horn Left sinus horn
20 Mouse embryonic day 10.5 Left atrium Right atrium Venous valves
21 Mouse embryonic day 11.5 Left atrium Left ventricle Left sinus horn
22 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT Formation of the pulmonary vein It is often stated that the pulmonary vein takes its origin from the systemic venous sinus (or sinus venosus ) In reality, the pulmonary vein develops from a midline strand in the pharyngeal mesenchyme. It canalises so as to open into the developing left ventricle through the remaining attachments of the dorsal mesocardium
23 Systemic venous sinus to right atrium Mouse embryo Embryonic day 10.5 Opening of pulmonary vein
24 SVS LSH Human embryo Carnegie stage 14 Coloured to show NKX 2.5
25 SVS LSH Human embryo Carnegie stage 14 Coloured to show TBX 18
26 Human embryo Carnegie stage 14 Left atrium Left sinus horn
27 Pulmonary venous component Left superior caval vein Left atrium Human embryo post-septation
28 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT Mechanisms of atrial septation Most textbooks still show growth of a secondary atrial septum (the septum secundum ) from the atrial roof, which overlaps cranially the primary atrial septum In reality, the so-called septum secundum is a cranial interatrial fold. It is not formed until the pulmonary veins are remodelled to form the atrial roof. The true second septum forms the anteroinferior buttress of the atrial septum
29 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT Atrial septation It is transfer of the systemic venous tributaries to the right side of the primary atrial chamber that sets the scene for subsequent septation
30 Secondary foramen Primary septum Mesenchymal cap Primary foramen Systemic venous sinus Inferior AV cushion Mouse - Embryonic day 11.5
31 Vestibular spine Primary septum Mesenchymal cap Primary foramen Inferior AV cushion Mouse - Embryonic day 11.5
32 Vestibular spine Pulmonary vein Mouse - Embryonic day 11.5
33 Mouse - Embryonic day 13.5 Secondary foramen Primary septum Vestibular spine Mesenchymal cap Inferior AV cushion Superior AV cushion
34 Breakdown at atrial roof Primary septum Oval foramen Secondary septum Mouse - Embryonic day 14.5
35 Primary septum & cap Growth of primary septum Cranial perforations Primary foramen Reducing primary foramen Systemic venous sinus to right Dorsal mesocardium Pulmonary vein
36 Growth of vestibular spine Breakdown cranially Primary septum Superior interatrial fold Oval foramen Closure of primary foramen Oval fossa Anteroinferior buttress
37 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT Right pulmonary veins Left pulmonary veins Superior interatrial fold Anterior-inferior muscular buttress Oval fossa Mitral valve Tricuspid valve
38 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT ASD - Secundum type Vestibular ASD MV MV TV TV
39 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT The definitive atrial septum The floor of the oval fossa is derived from the primary atrial septum The so-called septum secundum is the superior interatrial fold The antero-inferior buttress is a true second septal component Perforations within the oval fossa are ostium secundum defects, but reflect abnormal formation of the primary septum
40 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT Ventricular septation Some suggest that the ventricular septum is developed with a component derived from the septum of the atrioventricular canal, and another component representing the conal septum In reality, the definitive ventricular septum has only muscular and membranous components. There are no inlet and outlet components
41 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT Ventricular septation The apical muscular ventricular septum develops concomitant with the ballooning of the ventricular apical components from the inlet and outlet parts of the ventricular loop When first formed, the developing heart exhibits double inlet to the developing left ventricle, and double outlet from the developing right ventricle So as to close the ventricular septum, there must be transfer of the inlet of the right ventricle, and the outlet of the left ventricle
42 Outflow tract Developing left ventricle Developing right ventricle Atrioventricular canal Mouse embryo E somites Atrial component
43 Embryonic mouse E10.5 Outflow tract Atrioventricular canal Right ventricle Left ventricle
44 Ventricular septation CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT The processes of transfer were elucidated by a study in which it proved possible to track the fate of a ring of cells surrounding the initial embryonic interventricular communication Lamers WH, Wessels A, Verbeek FJ, Moorman AFM, Virágh S, Wenink ACG, Gittenberger-de Groot AC, Anderson RH. New findings concerning ventricular septation in the human heart. Implications for maldevelopment. Circulation 1992;86:
45 Human embryo Carnegie stage 13 Left atrium Right atrium Left ventricle Right ventricle
46 Right atrium Part of the ring marks the crest of the muscular ventricular septum Right ventricle Left ventricle Human embryo Carnegie stage 16
47 Embryonic day 11.5 Still double outlet Right atrium Developing right ventricle
48 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT The story thus far Atrioventricular canal initially drains exclusively to developing left ventricle Expansion of canal produces connection between right atrium and developing right ventricle At this stage, outflow tract is supported exclusively by developing right ventricle Necessary to transfer aorta to left ventricle before heart can be properly septated
49 Interventricular communication Aortic root Line of putative ventricular septation Left ventricle Embryonic day 12.5
50 Previous interventricular communication Line of putative ventricular septation Later on embryonic day 12.5
51 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT LA Aorta LV RA Tetralogy of Fallot RV
52 Aortic root Initial interventricular communication is now left ventricular outflow tract End of embryonic day 12.5
53 End of embryonic day 12.5 Muscularising infundibulum Tubercles fusing to wall aorta into left ventricle
54 Embryonic day 15.5 Muscularised infundibulum Membranous septum
55 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT The definitive ventricular septum Has only apical muscular and membranous components The postero-inferior part of the septum separates the right ventricular inlet from the left ventricular outlet The subpulmonary infundibulum is a free-standing muscular sleeve
56 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT LA PV RV AV RA LV LV RV
57 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT Formation of the outflow tracts It is usual to describe the developing outflow tract in terms of the truncus and conus It is also frequently stated that the outflow cushions form an aortopulmonary septal complex Better to analyse in tripartite fashion, showing that the cushions separate the arterial roots and outflow tracts, rather than the intrapericardial arterial trunks
58 Distal Intermediate Proximal Developing right ventricle
59 Aortic sac Distal OFT Left atrium Left ventricle Mouse early E11.5
60 Mouse early E11.5 Parietal cushion 4 6 Non-myocardial walls Septal cushion
61 Mouse early E11.5 Intrapericardial aorta Intrapericardial pulm. trunk
62 Mouse mid E11.5 Aortopulmonary foramen Intrapericardial aorta
63 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT The distal outflow tract Is separated to form the intrapericardial components of the aorta and pulmonary trunk by growth of the aortopulmonary septum from the dorsal wall of the aortic sac The protrusion fuses with the distal ends of the outflow cushions to close the embryonic aortopulmonary foramen
64 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT Aorta RAA LAA Pulm. valve Aortic valve Pulm. valve
65 Embryonic day 12.5 Oblique cut through intermediate part of outflow tract Pulmonary root Aortic root Right atrium
66 Embryonic day 12.5 Pulmonary root Cushions fused centrally Unfused peripherally Aortic root
67 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT The intermediate outflow tract The distal cushions, along with the intercalated cushions, excavate to form the leaflets of the arterial valves The central parts of the cushions fuse to septate the arterial roots, but then attenuate as the roots separate one from the other
68 Aortic root Columns of condensed mesenchyme Unfused proximal cushions Embryonic day 12.5
69 Mouse day 13.5 Aorta Right atrium Right ventricle Closing interventricular foramen
70 DEVELOPMENT OF OUTFLOW TRACT Aortic sac
71 DEVELOPMENT OF OUTFLOW TRACT Intrapericardial arterial trunks Extrapericardial arterial trunks Valves & sinuses Ventricular outflow tracts
72 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT The outflow tract Is best described in terms of proximal, intermediate, and distal components The aortopulmonary septum separates the distal part into the intrapericardial arterial trunks Description in terms of truncus and conus does not legislate for formation of arterial roots
73 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT The bottom line The recent advances in visualising the developing heart now permit us to describe the changes in evidence-based fashion The findings now provide the basis for understanding the morphogenesis of congenital cardiac malformations
74 Thank you for your attention. CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT
Development of the Heart
 Development of the Heart Thomas A. Marino, Ph.D. Temple University School of Medicine Stages of Development of the Heart 1. The horseshoe-shaped pericardial cavity. 2. The formation of the single heart
Development of the Heart Thomas A. Marino, Ph.D. Temple University School of Medicine Stages of Development of the Heart 1. The horseshoe-shaped pericardial cavity. 2. The formation of the single heart
Through the 20th century, knowledge of the events occurring during cardiac development was
 806 * Anatomy DEVELOPMENT OF THE HEART: (1) FORMATION OF THE CARDIAC CHAMBERS AND ARTERIAL TRUNKS Antoon Moorman, Sandra Webb, Nigel A Brown, Wouter Lamers, Robert H Anderson See end of article for authors
806 * Anatomy DEVELOPMENT OF THE HEART: (1) FORMATION OF THE CARDIAC CHAMBERS AND ARTERIAL TRUNKS Antoon Moorman, Sandra Webb, Nigel A Brown, Wouter Lamers, Robert H Anderson See end of article for authors
Embryology of the Heart
 *Page 1A: Embryology of the Heart Human embryonic disc is divided into three layers: ectoderm, intraembryonic mesoderm, and endoderm. The embryonic disc lies between the amniotic cavity and the primary
*Page 1A: Embryology of the Heart Human embryonic disc is divided into three layers: ectoderm, intraembryonic mesoderm, and endoderm. The embryonic disc lies between the amniotic cavity and the primary
In the first part of our review of cardiac development,
 Anatomy DEVELOPMENT OF THE HEART: (2) SEPTATION OF THE ATRIUMS AND VENTRICLES Robert H Anderson, Sandra Webb, Nigel A Brown, Wouter Lamers, Antoon Moorman See end of article for authors affiliations c
Anatomy DEVELOPMENT OF THE HEART: (2) SEPTATION OF THE ATRIUMS AND VENTRICLES Robert H Anderson, Sandra Webb, Nigel A Brown, Wouter Lamers, Antoon Moorman See end of article for authors affiliations c
Most cardiologists would probably consider that, during their training, they had received
 104 * Anatomy DEVELOPMENT AND STRUCTURE OF THE ATRIAL SEPTUM c DEVELOPMENT Correspondence to: Professor RH Anderson, Cardiac Unit, Institute of Child Health, 30 Guilford Street, London WC1N 1EH, UK; r.anderson@ich.ucl.ac.uk
104 * Anatomy DEVELOPMENT AND STRUCTURE OF THE ATRIAL SEPTUM c DEVELOPMENT Correspondence to: Professor RH Anderson, Cardiac Unit, Institute of Child Health, 30 Guilford Street, London WC1N 1EH, UK; r.anderson@ich.ucl.ac.uk
Segmental Analysis. Gautam K. Singh, M.D. Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis
 Segmental Analysis Gautam K. Singh, M.D. Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis Segmental Analysis Segmental Analysis: From Veins to Ventricles Segmental Approach to Evaluation of Congenital
Segmental Analysis Gautam K. Singh, M.D. Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis Segmental Analysis Segmental Analysis: From Veins to Ventricles Segmental Approach to Evaluation of Congenital
Development of the heart
 Development of the heart Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Early Development of the Circulatory System Appears in the middle of the third week, when the
Development of the heart Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Early Development of the Circulatory System Appears in the middle of the third week, when the
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval
 When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
Anatomy of Atrioventricular Septal Defect (AVSD)
 Surgical challenges in atrio-ventricular septal defect in grown-up congenital heart disease Anatomy of Atrioventricular Septal Defect (AVSD) S. Yen Ho Professor of Cardiac Morphology Royal Brompton and
Surgical challenges in atrio-ventricular septal defect in grown-up congenital heart disease Anatomy of Atrioventricular Septal Defect (AVSD) S. Yen Ho Professor of Cardiac Morphology Royal Brompton and
Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease
 Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease Sally Dunwoodie s.dunwoodie@victorchang.edu.au Developmental and Stem Cell Biology Division Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute for the heart of Australia...
Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease Sally Dunwoodie s.dunwoodie@victorchang.edu.au Developmental and Stem Cell Biology Division Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute for the heart of Australia...
W.S. O The University of Hong Kong
 W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Objectives: Describe early angiogenesis. Describe the heart tube formation. Describe the partitioning into a 4- chambered heart. List the formation of heart valves and
W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Objectives: Describe early angiogenesis. Describe the heart tube formation. Describe the partitioning into a 4- chambered heart. List the formation of heart valves and
W.S. O. School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong
 W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong Objectives: Describe early angiogenesis. Describe the heart tube formation. Describe the partitioning into a 4- chambered heart. List the formation
W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong Objectives: Describe early angiogenesis. Describe the heart tube formation. Describe the partitioning into a 4- chambered heart. List the formation
Atrial Septal Defects
 Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
Blood supply of the Heart & Conduction System. Dr. Nabil Khouri
 Blood supply of the Heart & Conduction System Dr. Nabil Khouri Arterial supply of Heart Right coronary artery Left coronary artery 3 Introduction: Coronary arteries - VASAVASORUM arising from aortic sinuses
Blood supply of the Heart & Conduction System Dr. Nabil Khouri Arterial supply of Heart Right coronary artery Left coronary artery 3 Introduction: Coronary arteries - VASAVASORUM arising from aortic sinuses
The Cardiovascular System (Part I) 黃敏銓 解剖學暨細胞生物學研究所
 The Cardiovascular System (Part I) 黃敏銓 解剖學暨細胞生物學研究所 1 Congenital heart defects (CHDs) 台灣兒童心臟學會 Sinus venarum Membranous septum Conus arteiosus (infundibulum) Aortic vestibule The Cardiovascular System
The Cardiovascular System (Part I) 黃敏銓 解剖學暨細胞生物學研究所 1 Congenital heart defects (CHDs) 台灣兒童心臟學會 Sinus venarum Membranous septum Conus arteiosus (infundibulum) Aortic vestibule The Cardiovascular System
Anomalous Systemic Venous Connection Systemic venous anomaly
 World Database for Pediatric and Congenital Heart Surgery Appendix B: Diagnosis (International Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Codes (IPCCC) and definitions) Anomalous Systemic Venous Connection Systemic
World Database for Pediatric and Congenital Heart Surgery Appendix B: Diagnosis (International Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Codes (IPCCC) and definitions) Anomalous Systemic Venous Connection Systemic
the Cardiovascular System I
 the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
"Lecture Index. 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development.
 "Lecture Index 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development. 5) Septation and Maturation. 6) Changes in Blood Flow during Development.
"Lecture Index 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development. 5) Septation and Maturation. 6) Changes in Blood Flow during Development.
6. Development of circulatory system II. Cardiac looping. Septation of atria and ventricles. Common heart malformations.
 6. Development of circulatory system II. Cardiac looping. Septation of atria and ventricles. Common heart malformations. Formation of heart tube paired endothelial-lined heart tube is formed from blood
6. Development of circulatory system II. Cardiac looping. Septation of atria and ventricles. Common heart malformations. Formation of heart tube paired endothelial-lined heart tube is formed from blood
Notes: 1)Membranous part contribute in the formation of small portion in the septal cusp.
 Embryology 9 : Slide 16 : There is a sulcus between primitive ventricular and bulbis cordis that will disappear gradually and lead to the formation of one chamber which is called bulboventricular chamber.
Embryology 9 : Slide 16 : There is a sulcus between primitive ventricular and bulbis cordis that will disappear gradually and lead to the formation of one chamber which is called bulboventricular chamber.
human anatomy 2016 lecture thirteen Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 Heart The heart is a hollow muscular organ that is somewhat pyramid shaped and lies within the pericardium in the mediastinum. It is connected at its base to the great blood vessels but otherwise lies
Heart The heart is a hollow muscular organ that is somewhat pyramid shaped and lies within the pericardium in the mediastinum. It is connected at its base to the great blood vessels but otherwise lies
Development and teratology of cardiovascular and lymphatic systems. Repetition: Muscle tissue
 Development and teratology of cardiovascular and lymphatic systems Repetition: Muscle tissue Beginning of the cardiovascular system development the 3rd week: Hemangiogenesis (day 15 16) blood islets (insulae
Development and teratology of cardiovascular and lymphatic systems Repetition: Muscle tissue Beginning of the cardiovascular system development the 3rd week: Hemangiogenesis (day 15 16) blood islets (insulae
Chapter 4: The thoracic cavity and heart. The Heart
 Chapter 4: The thoracic cavity and heart The thoracic cavity is divided into right and left pleural cavities by a central partition, the mediastinum. The mediastinum is bounded behind by the vertebral
Chapter 4: The thoracic cavity and heart The thoracic cavity is divided into right and left pleural cavities by a central partition, the mediastinum. The mediastinum is bounded behind by the vertebral
Heart & vascular system I. Dawei Dong
 Heart & vascular system I Dawei Dong Lecture goal Learn the basics of heart and vascular development. Development of Heart, Blood, and Blood Vessels LEARNING GOALS: 1. explain the early development of
Heart & vascular system I Dawei Dong Lecture goal Learn the basics of heart and vascular development. Development of Heart, Blood, and Blood Vessels LEARNING GOALS: 1. explain the early development of
Congenital Heart Defects
 Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Middle mediastinum---- heart & pericardium. Dep. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hongying
 Middle mediastinum---- heart & pericardium Dep. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Subdivisions of the mediastinum Contents of Middle mediastinum Heart Pericardium: a serous sac enclosing
Middle mediastinum---- heart & pericardium Dep. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Subdivisions of the mediastinum Contents of Middle mediastinum Heart Pericardium: a serous sac enclosing
Appendix A.1: Tier 1 Surgical Procedure Terms and Definitions
 Appendix A.1: Tier 1 Surgical Procedure Terms and Definitions Tier 1 surgeries AV Canal Atrioventricular Septal Repair, Complete Repair of complete AV canal (AVSD) using one- or two-patch or other technique,
Appendix A.1: Tier 1 Surgical Procedure Terms and Definitions Tier 1 surgeries AV Canal Atrioventricular Septal Repair, Complete Repair of complete AV canal (AVSD) using one- or two-patch or other technique,
Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016
 1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
FUNCTIONALLY SINGLE VENTRICLE
 MORPHOLOGICAL DETERMINANTS VI TRAN EuroEcho, Budapest, 7 th December 2011 DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST: I have nothing to declare What is the functionally single ventricle? The heart that is incapable
MORPHOLOGICAL DETERMINANTS VI TRAN EuroEcho, Budapest, 7 th December 2011 DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST: I have nothing to declare What is the functionally single ventricle? The heart that is incapable
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart
 LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
Segmental approach to normal and abnormal situs arrangement - Echocardiography -
 Segmental approach to normal and abnormal situs arrangement - Echocardiography - Jan Marek Great Ormond Street Hospital & Institute of Cardiovascular Sciences, University College London No disclosures
Segmental approach to normal and abnormal situs arrangement - Echocardiography - Jan Marek Great Ormond Street Hospital & Institute of Cardiovascular Sciences, University College London No disclosures
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT
 ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
THE VESSELS OF THE HEART
 1 THE VESSELS OF THE HEART The vessels of the heart include the coronary arteries, which supply the heart and the veins and lymph vessels, which drain the heart. THE CORONARY ARTERIES These are the blood
1 THE VESSELS OF THE HEART The vessels of the heart include the coronary arteries, which supply the heart and the veins and lymph vessels, which drain the heart. THE CORONARY ARTERIES These are the blood
Cardiac Catheterization Cases Primary Cardiac Diagnoses Facility 12 month period from to PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient)
 PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART
 ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
Pulmonary Valve Morphology in Patients with Bicuspid Aortic Valves
 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-018-1807-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pulmonary Valve Morphology in Patients with Bicuspid Aortic Valves Wilke M. C. Koenraadt 1 Margot M. Bartelings 2 Adriana C. Gittenberger de Groot
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-018-1807-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pulmonary Valve Morphology in Patients with Bicuspid Aortic Valves Wilke M. C. Koenraadt 1 Margot M. Bartelings 2 Adriana C. Gittenberger de Groot
The problems that exist when considering the anatomic variability between the channels that permit interventricular shunting
 Cardiology in the Young (2015), 25, 15 28 Cambridge University Press, 2014 doi:10.1017/s1047951114000869 Review Article The problems that exist when considering the anatomic variability between the channels
Cardiology in the Young (2015), 25, 15 28 Cambridge University Press, 2014 doi:10.1017/s1047951114000869 Review Article The problems that exist when considering the anatomic variability between the channels
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Cardiac ultrasound protocols
 Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
When to close an Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) in adulthood?
 When to close an Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) in adulthood? Philippe ALDEBERT Hôpital de la Timone, CHU Marseille Département de cardiologie pédiatrique et congénitale médico-chirurgical Abbott Incidence
When to close an Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) in adulthood? Philippe ALDEBERT Hôpital de la Timone, CHU Marseille Département de cardiologie pédiatrique et congénitale médico-chirurgical Abbott Incidence
CARDIAC ANATOMY. David McGiffin Director of Cardiothoracic Surgery and Transplantation Alfred Health, Melbourne
 CARDIAC ANATOMY David McGiffin Director of Cardiothoracic Surgery and Transplantation Alfred Health, Melbourne Outline The aorto-ventricular unit The mitral valve Interior of the right ventricle Aorto-ventricular
CARDIAC ANATOMY David McGiffin Director of Cardiothoracic Surgery and Transplantation Alfred Health, Melbourne Outline The aorto-ventricular unit The mitral valve Interior of the right ventricle Aorto-ventricular
THE NORMAL AND ABNORMAL INTER-ATRIAL SEPTUM
 THE NORMAL AND ABNORMAL INTER-ATRIAL SEPTUM BY REGINALD HUDSON From the Institute of Cardiology and National Heart Hospital Received April 5, 1954 This paper is an elementary study of the normal and abnormal
THE NORMAL AND ABNORMAL INTER-ATRIAL SEPTUM BY REGINALD HUDSON From the Institute of Cardiology and National Heart Hospital Received April 5, 1954 This paper is an elementary study of the normal and abnormal
Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract'
 Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract' ROBERT WALMSLEY British Heart Journal, 1979, 41, 263-267 From the Department of Anatomy and Experimental Pathology, The University, St Andrews, Scotland SUMMARY
Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract' ROBERT WALMSLEY British Heart Journal, 1979, 41, 263-267 From the Department of Anatomy and Experimental Pathology, The University, St Andrews, Scotland SUMMARY
Anatomy of the Heart. Figure 20 2c
 Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
Circulatory system. Lecture #2
 Circulatory system Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs
Circulatory system Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13}
 Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
Introduction to Anatomy. Dr. Maher Hadidi. Bayan Yanes. April/9 th /2013
 Introduction to Anatomy Dr. Maher Hadidi Bayan Yanes 27 April/9 th /2013 KEY POINTS: 1) Right side of the heart 2) Papillary muscles 3) Left side of the heart 4) Comparison between right and left sides
Introduction to Anatomy Dr. Maher Hadidi Bayan Yanes 27 April/9 th /2013 KEY POINTS: 1) Right side of the heart 2) Papillary muscles 3) Left side of the heart 4) Comparison between right and left sides
Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital
 Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital VSD is one of the most common congenital cardiac abnormalities in the newborn. It can occur as an isolated finding or in combination
Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital VSD is one of the most common congenital cardiac abnormalities in the newborn. It can occur as an isolated finding or in combination
By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE
 By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE Introduction CHDs are abnormalities of the heart or great vessels that are present at birth. Common type of heart disease
By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE Introduction CHDs are abnormalities of the heart or great vessels that are present at birth. Common type of heart disease
Anatomy lab -1- Imp note: papillary muscle Trabeculae Carneae chordae tendineae
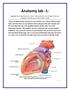 Anatomy lab -1- Imp note: the arrangement of this sheet is different than the lab recording, it has been arranged in a certain way to make it easier to study. When you open the left ventricle you can see
Anatomy lab -1- Imp note: the arrangement of this sheet is different than the lab recording, it has been arranged in a certain way to make it easier to study. When you open the left ventricle you can see
Atrioventricular Canal (Septal) Defects. Norman H Silverman MD. D Sc (Med),FACC, FAHA
 Atrioventricular Canal (Septal) Defects Norman H Silverman MD. D Sc (Med),FACC, FAHA Embryology of the A-V Canal Looping NHS. Formation of the Atrial Septum Embryology of the A-V Canal NHS. Development
Atrioventricular Canal (Septal) Defects Norman H Silverman MD. D Sc (Med),FACC, FAHA Embryology of the A-V Canal Looping NHS. Formation of the Atrial Septum Embryology of the A-V Canal NHS. Development
The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3-
 1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
6. HEART AND CIRCULATORY SYSTEM I
 6. HEART AND CIRCULATORY SYSTEM I Dr. Taube P. Rothman P&S 12-520 Tpr2@columbia.edu 212-305-7930 RECOMMENDED READING: Larsen Human Embryology, 3rd Edition, pp. 195-199; 157-169 top left; 172-174; bottom
6. HEART AND CIRCULATORY SYSTEM I Dr. Taube P. Rothman P&S 12-520 Tpr2@columbia.edu 212-305-7930 RECOMMENDED READING: Larsen Human Embryology, 3rd Edition, pp. 195-199; 157-169 top left; 172-174; bottom
Supplementary Figure S1 Enlarged coronary artery branches in Edn1-knockout mice. a-d, Coronary angiography by ink injection in wild-type (a, b) and
 Supplementary Figure S1 Enlarged coronary artery branches in Edn1-knockout mice. a-d, Coronary angiography by ink injection in wild-type (a, b) and Edn1-knockout (Edn1-KO) (c, d) hearts. The boxed areas
Supplementary Figure S1 Enlarged coronary artery branches in Edn1-knockout mice. a-d, Coronary angiography by ink injection in wild-type (a, b) and Edn1-knockout (Edn1-KO) (c, d) hearts. The boxed areas
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart
 Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Among the congenital defects of the heart diagnosed
 Atrial Septal Defect: Anatomoechocardiographic Correlation Luis Muñóz-Castellanos, MD, Nilda Espinola-Zavaleta, MD, PhD, Magdalena Kuri-Nivón, MD, José Francisco Ruíz, MD, and Candace Keirns, MD, Mexico
Atrial Septal Defect: Anatomoechocardiographic Correlation Luis Muñóz-Castellanos, MD, Nilda Espinola-Zavaleta, MD, PhD, Magdalena Kuri-Nivón, MD, José Francisco Ruíz, MD, and Candace Keirns, MD, Mexico
Heart Anatomy. 7/5/02 Stephen G Davenport 1
 Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
was judged subjectively. The left ventricle was considered to be slightly hypoplastic when the cardiac
 British Heart J7ournal, 1976, 38, 1124-1132. Double outlet right ventricle Study of 27 cases A. H. Cameron, F. Acerete, M. Quero, and M. C. Castro From the Department of Patlology, Children's Hospital,
British Heart J7ournal, 1976, 38, 1124-1132. Double outlet right ventricle Study of 27 cases A. H. Cameron, F. Acerete, M. Quero, and M. C. Castro From the Department of Patlology, Children's Hospital,
Transposition of the Great Arteries Preoperative Diagnostic Considerations. John Simpson Evelina Children s Hospital London, UK
 Transposition of the Great Arteries Preoperative Diagnostic Considerations John Simpson Evelina Children s Hospital London, UK Areas to be covered Definitions Scope of occurrence of transposition of the
Transposition of the Great Arteries Preoperative Diagnostic Considerations John Simpson Evelina Children s Hospital London, UK Areas to be covered Definitions Scope of occurrence of transposition of the
Congenital Heart Disease: Physiology and Common Defects
 Congenital Heart Disease: Physiology and Common Defects Jamie S. Sutherell, M.D, M.Ed. Associate Professor, Pediatrics Division of Cardiology Director, Medical Student Education in Pediatrics Director,
Congenital Heart Disease: Physiology and Common Defects Jamie S. Sutherell, M.D, M.Ed. Associate Professor, Pediatrics Division of Cardiology Director, Medical Student Education in Pediatrics Director,
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Part 1
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
Organogenesis Part 2. V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm VI. Endoderm VII. Development of the Tetrapod Limb VIII. Sex Determination. V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm
 Organogenesis Part 2 V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm VI. Endoderm VII. Development of the Tetrapod Limb VIII. Sex Determination V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm chordamesoderm paraxial mesoderm intermediate mesoderm
Organogenesis Part 2 V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm VI. Endoderm VII. Development of the Tetrapod Limb VIII. Sex Determination V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm chordamesoderm paraxial mesoderm intermediate mesoderm
Although it has been suggested by some 1 that failure of. Mechanisms of Deficient Cardiac Septation in the Mouse With Trisomy 16
 Mechanisms of Deficient Cardiac Septation in the Mouse With Trisomy 16 Sandra Webb, Robert H. Anderson, Wouter H. Lamers, Nigel A. Brown Abstract It used to be thought that the atrioventricular septum
Mechanisms of Deficient Cardiac Septation in the Mouse With Trisomy 16 Sandra Webb, Robert H. Anderson, Wouter H. Lamers, Nigel A. Brown Abstract It used to be thought that the atrioventricular septum
List of Videos. Video 1.1
 Video 1.1 Video 1.2 Video 1.3 Video 1.4 Video 1.5 Video 1.6 Video 1.7 Video 1.8 The parasternal long-axis view of the left ventricle shows the left ventricular inflow and outflow tract. The left atrium
Video 1.1 Video 1.2 Video 1.3 Video 1.4 Video 1.5 Video 1.6 Video 1.7 Video 1.8 The parasternal long-axis view of the left ventricle shows the left ventricular inflow and outflow tract. The left atrium
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome
 Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
Concomitant procedures using minimally access
 Surgical Technique on Cardiac Surgery Concomitant procedures using minimally access Nelson Santos Paulo Cardiothoracic Surgery, Centro Hospitalar de Vila Nova de Gaia, Oporto, Portugal Correspondence to:
Surgical Technique on Cardiac Surgery Concomitant procedures using minimally access Nelson Santos Paulo Cardiothoracic Surgery, Centro Hospitalar de Vila Nova de Gaia, Oporto, Portugal Correspondence to:
2. right heart = pulmonary pump takes blood to lungs to pick up oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide
 A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
Fetal Echocardiography and the Routine Obstetric Sonogram
 JDMS 23:143 149 May/June 2007 143 Fetal Echocardiography and the Routine Obstetric Sonogram SHELLY ZIMBELMAN, RT(R)(CT), RDMS, RDCS ASAD SHEIKH, MD, RDCS Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the most common
JDMS 23:143 149 May/June 2007 143 Fetal Echocardiography and the Routine Obstetric Sonogram SHELLY ZIMBELMAN, RT(R)(CT), RDMS, RDCS ASAD SHEIKH, MD, RDCS Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the most common
Surgical Management Of TAPVR. Daniel A. Velez, M.D. Congenital Cardiac Surgeon Phoenix Children s Hospital
 Surgical Management Of TAPVR Daniel A. Velez, M.D. Congenital Cardiac Surgeon Phoenix Children s Hospital No Disclosures Goals Review the embryology and anatomy Review Surgical Strategies for repair Discuss
Surgical Management Of TAPVR Daniel A. Velez, M.D. Congenital Cardiac Surgeon Phoenix Children s Hospital No Disclosures Goals Review the embryology and anatomy Review Surgical Strategies for repair Discuss
Breakout Session: Transesophageal Echocardiography
 Breakout Session: Transesophageal Echocardiography Doris Ockert, MD Andrew Schroeder, MD University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health Jutta Novalija, MD, PhD Medical College of Wisconsin
Breakout Session: Transesophageal Echocardiography Doris Ockert, MD Andrew Schroeder, MD University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health Jutta Novalija, MD, PhD Medical College of Wisconsin
A SURGEONS' GUIDE TO CARDIAC DIAGNOSIS
 A SURGEONS' GUIDE TO CARDIAC DIAGNOSIS PART II THE CLINICAL PICTURE DONALD N. ROSS B. Sc., M. B., CH. B., F. R. C. S. CONSULTANT THORACIC SURGEON GUY'S HOSPITAL, LONDON WITH 53 FIGURES Springer-Verlag
A SURGEONS' GUIDE TO CARDIAC DIAGNOSIS PART II THE CLINICAL PICTURE DONALD N. ROSS B. Sc., M. B., CH. B., F. R. C. S. CONSULTANT THORACIC SURGEON GUY'S HOSPITAL, LONDON WITH 53 FIGURES Springer-Verlag
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray
 Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
CARDIAC AND CORONARY ARTERY ANATOMY NO DISCLOSURES. Axial Anatomy of Heart. Axial Anatomy of Heart. Axial Anatomy of Heart
 CARDIAC AND CORONARY ARTERY ANATOMY NO DISCLOSURES NASCI MEETING, ORLANDO FLORIDA 2009 KOSTAKI G. BIS, MD, FACR DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL Royal Oak, Michigan OBJECTIVES CARDIAC
CARDIAC AND CORONARY ARTERY ANATOMY NO DISCLOSURES NASCI MEETING, ORLANDO FLORIDA 2009 KOSTAKI G. BIS, MD, FACR DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL Royal Oak, Michigan OBJECTIVES CARDIAC
Chapter 18 - Heart. I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity)
 Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
Congenital Heart Disease: a Pictorial Illustration of Putting Segmental Approach into Practice
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:205-211 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.4.205 Congenital Heart Disease: a Pictorial Illustration of Putting Segmental Approach into Practice Tse Hang
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:205-211 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.4.205 Congenital Heart Disease: a Pictorial Illustration of Putting Segmental Approach into Practice Tse Hang
CV Anatomy Quiz. Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green
 CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE. Papworth Hospital NHS Trust INTRODUCTION. Jakub Kadlec/Catherine Sudarshan INTRODUCTION
 Slide 1 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Jakub Kadlec/Catherine Sudarshan NHS Trust Slide 2 INTRODUCTION Most common congenital illness in the newborn Affects about 4 9 / 1000 full-term live births in the UK 1.5
Slide 1 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Jakub Kadlec/Catherine Sudarshan NHS Trust Slide 2 INTRODUCTION Most common congenital illness in the newborn Affects about 4 9 / 1000 full-term live births in the UK 1.5
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
ANATOMY. lecture#: Date : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi
 ANATOMY 28 lecture#: Date : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Superior vena -=- Blood inflow part is rough and outflow part is smooth. - _Arch of aorta Pulmonary trunk Tricuspid valve Right auricle Right atrium
ANATOMY 28 lecture#: Date : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Superior vena -=- Blood inflow part is rough and outflow part is smooth. - _Arch of aorta Pulmonary trunk Tricuspid valve Right auricle Right atrium
Development of the Heart *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46673 1 Development of the Heart * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m46673 1 Development of the Heart * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
Anatomic echocardiographic correlates: an introduction to normal and congenitally malformed hearts
 Heart 2001;86(Suppl II):ii3 ii11 ii3 National Heart & Lung Institute, Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, and Royal Brompton and Harefield NHS Trust, London, UK SY Ho K P McCarthy M Josen
Heart 2001;86(Suppl II):ii3 ii11 ii3 National Heart & Lung Institute, Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, and Royal Brompton and Harefield NHS Trust, London, UK SY Ho K P McCarthy M Josen
Anatomy of Atrial and Ventricular Septal Defects
 Anatomy of Atrial and Ventricular Septal Defects SIEW YEN HO, PH.D., F.R.C.PATH, KAREN P. MCCARTHY, B.Sc., and MICHAEL RIGBY, M.D. From the Paediatrics, National Heart & Lung Institute, Imperial College
Anatomy of Atrial and Ventricular Septal Defects SIEW YEN HO, PH.D., F.R.C.PATH, KAREN P. MCCARTHY, B.Sc., and MICHAEL RIGBY, M.D. From the Paediatrics, National Heart & Lung Institute, Imperial College
Anatomy of the coronary arteries in transposition
 Thorax, 1978, 33, 418-424 Anatomy of the coronary arteries in transposition of the great arteries and methods for their transfer in anatomical correction MAGDI H YACOUB AND ROSEMARY RADLEY-SMITH From Harefield
Thorax, 1978, 33, 418-424 Anatomy of the coronary arteries in transposition of the great arteries and methods for their transfer in anatomical correction MAGDI H YACOUB AND ROSEMARY RADLEY-SMITH From Harefield
Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart
 Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart Name Date Period 1. The "double pump" function of the heart includes the right side, which serves as the circuit pump, while the left side
Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart Name Date Period 1. The "double pump" function of the heart includes the right side, which serves as the circuit pump, while the left side
CMR for Congenital Heart Disease
 CMR for Congenital Heart Disease * Second-line tool after TTE * Strengths of CMR : tissue characterisation, comprehensive access and coverage, relatively accurate measurements of biventricular function/
CMR for Congenital Heart Disease * Second-line tool after TTE * Strengths of CMR : tissue characterisation, comprehensive access and coverage, relatively accurate measurements of biventricular function/
Large Arteries of Heart
 Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Figure 10.1A Transparency Master 79
 Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
Cardiology Fellowship Manual. Goals & Objectives -Cardiac Imaging- 1 P a g e
 Cardiology Fellowship Manual Goals & Objectives -Cardiac Imaging- 1 P a g e UNIV. OF NEBRASKA CHILDREN S HOSPITAL & MEDICAL CENTER DIVISION OF CARDIOLOGY FELLOWSHIP PROGRAM CARDIAC IMAGING ROTATION GOALS
Cardiology Fellowship Manual Goals & Objectives -Cardiac Imaging- 1 P a g e UNIV. OF NEBRASKA CHILDREN S HOSPITAL & MEDICAL CENTER DIVISION OF CARDIOLOGY FELLOWSHIP PROGRAM CARDIAC IMAGING ROTATION GOALS
The radial procedure was developed as an outgrowth
 The Radial Procedure for Atrial Fibrillation Takashi Nitta, MD The radial procedure was developed as an outgrowth of an alternative to the maze procedure. The atrial incisions are designed to radiate from
The Radial Procedure for Atrial Fibrillation Takashi Nitta, MD The radial procedure was developed as an outgrowth of an alternative to the maze procedure. The atrial incisions are designed to radiate from
ISUOG Basic Training. Obtaining & Interpreting Heart Views Correctly Alfred Abuhamad, USA. Basic training. Editable text here
 ISUOG Basic Training Obtaining & Interpreting Heart Views Correctly Alfred Abuhamad, USA Learning Objectives 6, 7 & 8 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe how to assess cardiac situs
ISUOG Basic Training Obtaining & Interpreting Heart Views Correctly Alfred Abuhamad, USA Learning Objectives 6, 7 & 8 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe how to assess cardiac situs
Vasculature and innervation of the heart. A. Bendelic Human Anatomy Department
 Vasculature and innervation of the heart A. Bendelic Human Anatomy Department Plan: 1. Arterial blood supply of the heart. Coronary arteries 2. Venous drainage of the heart. Cardiac veins 3. Innervation
Vasculature and innervation of the heart A. Bendelic Human Anatomy Department Plan: 1. Arterial blood supply of the heart. Coronary arteries 2. Venous drainage of the heart. Cardiac veins 3. Innervation
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to:
 The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
Anatomy of the atrial septum and interatrial communications
 Review Article Anatomy of the atrial septum and interatrial communications Nitha Naqvi 1, Karen P. McCarthy 2, Siew Yen Ho 2 1 Paediatric Cardiology, 2 Cardiac Morphology, Royal Brompton Hospital, Imperial
Review Article Anatomy of the atrial septum and interatrial communications Nitha Naqvi 1, Karen P. McCarthy 2, Siew Yen Ho 2 1 Paediatric Cardiology, 2 Cardiac Morphology, Royal Brompton Hospital, Imperial
The role of intraoperative TOE in congenital cardiac surgery
 The role of intraoperative TOE in congenital cardiac surgery Justiaan Swanevelder Dept of Anaesthesia Groote Schuur and Red Cross War Memorial Children s Hospitals University of Cape Town, South Africa
The role of intraoperative TOE in congenital cardiac surgery Justiaan Swanevelder Dept of Anaesthesia Groote Schuur and Red Cross War Memorial Children s Hospitals University of Cape Town, South Africa
ANATDMY. lecture # : Date : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi
 ANATDMY 27 lecture # : Date : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Pericardium A double-walled fibroserous conical-shaped sac, within middle mediastinum. Enclose the heart and roots of its large vessels. Vagus nerves
ANATDMY 27 lecture # : Date : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Pericardium A double-walled fibroserous conical-shaped sac, within middle mediastinum. Enclose the heart and roots of its large vessels. Vagus nerves
Communication of Mitral Valve with Both Ventricles Associated with Double Outlet Right Ventricle
 Communication of Mitral Valve with Both Ventricles Associated with Double Outlet Right Ventricle By RAJENTDRA TANDON, M.D., JAMES H. MOLLR, MD, AND JESSE E. EDWARDS, M.D. SUMMARY A rare case of an infant
Communication of Mitral Valve with Both Ventricles Associated with Double Outlet Right Ventricle By RAJENTDRA TANDON, M.D., JAMES H. MOLLR, MD, AND JESSE E. EDWARDS, M.D. SUMMARY A rare case of an infant
