chronic inflammation and focal calcification. The postoperative course was benign, and the patient currently is
|
|
|
- Arlene Moore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mycotic Aortic Aneurysm in Children Jacob Bergsland, M.D, Akira Kawaguchi, M.D., J. Michel Roland, M.D., Daniel R. Pieroni, M.D., and S. Subramanian, M.D. ABSTRACT Mycotic aneurysms of the aorta are uncommon in babies and children. Prior to the development of antibiotics, most mycotic aneurysms were seen secondary to bacterial endocarditis, but this is now uncommon. Instead, more cases have been reported as complications of umbilical artery catheters in newborns. We have seen five cases of mycotic aneurysms in children, two of them secondary to umbilical artery catheters. One patient had coarctation of the aorta, and the other patients had different sources of infection. Three patients were treated surgically by us with good results after antibiotic therapy. One patient died of sepsis before the aneurysm was diagnosed. The fifth patient was treated elsewhere and now has a recurrent aneurysm. We think a combination of aggressive medical and early surgical therapy may save a high percentage of these patients. Mycotic aortic aneurysm is an uncommon, frequently fatal condition occasionally seen in children. Within the last decade, several cases have been reported to occur after insertion of umbilical artery catheters. The clinical picture is usually dominated by sepsis, and many cases are still first diagnosed at postmortem examination. Angiography should be done early if this condition is suspected. Aggressive antibiotic therapy followed by early operative intervention may save many of the patients. Aneurysms detected later in the course should be operated on as soon as possible, since rupture of the aneurysm is unpredictable. Umbilical artery catheterization is a major risk factor, and strict technique is required when using these devices. The following case reports present our experience with 5 children with mycotic aortic aneurysm. Material and Methods Patient 1 A male infant was born at term after a normal pregnancy. Mild respiratory distress developed and was treated with constant positive airway pressure for three days. An umbilical artery catheter was used to monitor his condition. When the patient was 5 days old, Staphylococcus aureus septicemia developed. He was treated with antibiotics, and the umbilical artery catheter was removed. The patient responded well, but two weeks From the Departments of Cardiology and Cardiovascular Surgery, Chddren s Hospital, Buffalo, NY. Accepted for publication Aug 10, Address reprint requests to Dr. Subramanian, Division of Cardiovascular Surgery, 219 Bryant St, Buffalo, NY later a mediastinal mass was noted on chest roentgenogram. Angiography revealed multiple aortic aneurysms. A cardiovascular surgery consultant considered the aneurysms inoperable. At 6 months of age, the patient was doing well and was referred to the Children s Hospital of Buffalo. A repeat angiogram was made; the major findings are shown in Figures 1 and 2. At operation, the aneurysms were resected using one high thoracic and one thoracoabdominal incision. The aorta was cross-clamped intermittently, and the aneurysms resected one by one. Primary lateral closure was done without using graft material. Pathological examination of the aorta revealed chronic inflammation, and a culture grew enterococci. The postoperative course was benign. Currently the patient is doing well and has no signs of recurrence. Patient 2 A full-term male infant in a severely cyanotic condition was transferred to the Children s Hospital of Buffalo one day after birth. An umbilical artery catheter was inserted for monitoring. Heart catheterization showed transposition of the great arteries and patent ductus arteriosus. Balloon septostomy was performed, and the patient s condition improved markedly. The umbilical artery catheter was removed after two days, since the patient was doing well. Two days later, however, he became septic. Cultures of blood and umbilical secretions and from the tip of the catheter all grew S. aureus. In spite of appropriate antibiotic therapy, the patient continued to be febrile. A new upper mediastinal mass on the left side was now seen on the chest roentgenogram (Fig 3). The patient died after a continued downhill course. Postmortem examination revealed transposition of the great arteries, large septic thrombi in the right ventricle, septic emboli in the anterior descending coronary artery, and two large septic aneurysms at the level of the patent ductus arteriosus. This had also been the location of the tip of the umbilical artery catheter. Patient 3 A female infant was born at term and was well until she was 12 months old. At that time, a septic illness developed after a measles vaccination. The patient was treated with antibiotics. A large pericardial effusion was diagnosed, and a tap revealed straw-colored fluid. The results of culture were negative. She did well and was next seen eight years later for a cough. Calcifications in the ascending aorta were noted on routine chest roentgenograms. Cardiac catheterization and aortography showed a large aneurysm of the ascending aorta (Fig 4) but was otherwise normal. 314
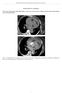
2 315 Bergsland et al: Mycotic Aneurysms in Children Fig 1. (Patient 1. ) Thoracic aortogram showing a huge aneurysm of the descending aorta. Resection was done on cardiopulmonary bypass after dense adhesions of the pericardium were taken down. The golf ball-sized aneurysm was sitting 1cm above the aortic ring and ended just before the innominate artery. The defect was repaired with a Dacron patch. Pathological examination revealed an aortic aneurysm with chronic inflammation and focal calcification. The postoperative course was benign, and the patient currently is doing well. COMMENT. In spite of the negative results of cultures during the patient s febrile illness, we consider the clinical course and pathological findings typical for a mycotic aneurysm. Patient 4 A female infant was born at term after an uncomplicated pregnancy. She was well until the age of 4 years at which time S. aureus septicemia developed. The source of the sepsis was unknown. The patient had a heart murmur, and it was thought she might have had bacterial endocarditis. She was treated successfully with antibiotics. When the patient was 7 years old, a routine examination revealed a large, pulsatile mass in the abdomen. An angiogram showed an abdominal aortic aneurysm (Fig 5). The results of cardiac catheterization were normal. At operation, the aneurysm was found below the inferior mesenteric artery. Aneurysmectomy was done and a 13 mm bifurcation Dacron graft used for replacement. Pathological examination showed intimal thickening and inflammatory changes. Fig 2. (Patient 1. ) Abdominal aortogram showing two abdominal aortic arrows) and two left iliac aneurysms (white arrows). The patient is asymptomatic 12 years after operation. A repeat angiogram showed mild stenosis of the distal anastomosis. Patient 5 A 3x-year-old boy who was a Jehovah s Witness was admitted to another hospital with bacterial endocarditis caused by S. aureus. He was known to have coarctation of the aorta. He was treated with appropriate antibiotics, but peripheral emboli and continued sepsis worsened his condition. An enlarging mass was seen in the upper mediastinum on chest roentgenograms. Emergency right heart catheterization and angiography were done and revealed a large, leaking aneurysm of the descending aorta just distal to a juxtaductal coarctation. The aortic valve could not be seen well, but a two-dimensional echocardiogram showed a bicuspid aortic valve with vegetations. The patient underwent a left thoracotomy. The aneurysm was 7 cm in diameter and grossly infected. The aorta was clamped and opened opposite to the perfora-
3 316 The Annals of Thoracic Surgery Vol 37 No 4 April 1984 Fig 3. (Patient 2.) Chest roentgenogram made one week after removal of umbilical artery catheter. The large mass (arrows) in the superior mediustinum corresponded to the location of the tip of the umbilical artery catheter that M S removed. Fig 5. (Patient 4. ) Abdominal aortogram showing large abdominal aortic aneurysm (arrows). tion. The necrotic part of the aortic wall was excised, and primary closure was done from the inside of the aorta. Then a subclavian angioplasty was performed to enlarge the lumen. The patient recovered. Four years later, the patient was seen in our hospital for evaluation. A two-dimensional echocardiogram showed a bicuspid, thickened aortic valve. Cardiac catheterization revealed an aortic valve gradient of 100 mm Hg. A recurrent aneurysm in the area of the previous coarctation was seen on angiography (Fig 6). A computed tomographic scan of the chest showed the size of the aneurysm to be 20 mm. With the patient on cardiopulmonary bypass, aortic valvotomy was performed. He did well postoperatively. Blood pressure was controlled to avoid rupture of the aneurysm. Because of the family's refusal to accept blood transfusion, the child was discharged on a regimen of iron medication. At that time, resection of the aortic aneurysm was planned for one to two months later. Comment Fig 4. (Patient 3. ) Lateral aortogram showing posterior location of large ascending aortic aneurysm (arrows). Mycotic aneurysms of the aorta are uncommon, especially in children with an undiseased aorta. In 1923, a survey by Stengel and Woelferth [l]found 217 patients with mycotic aneurysms, sixty-six of which were located in the aorta. Only 14 of the 217 patients were children. Of the patients, 187 had evidence of endocarditis; other types of bacterial infections were present in 30.With the
4 317 Bergsland et al: Mycotic Aneurysms in Children Fig 6. (Patient 5.) Anterior aortogram showing large aneuysm at site of previous coarctation. The right subclavian artery takes off aberrantly from the aneu y sm (arrow). development of effective antibiotics, these causes of mycotic aneurysm may be seen less frequently. However, they still occur, as in our Patients 3 and 4 and as reported by several authors [2-71. Coarctation of the aorta is known to predispose to bacterial endocarditis [S] and development of mycotic aneurysm [2], especially if there is a coexistent bicuspid aortic valve. The use of umbilical artery catheters in newborns has created a new group at risk for development of mycotic aortic aneurysms or pseudoaneurysms ( The diagnosis of mycotic aneurysm of the aorta is often difficult. In the acute stage, sepsis usually dominates the clinical picture. A chest roentgenogram and a good clinical examination of the abdomen are important. A computed tomographic scan and ultrasonogram are helpful [5], but aortography will be required in most instances for accurate anatomical delineation. Many cases of mycotic aneurysm are still not diagnosed before postmortem examination (9, 111, as in our Patient 2. Other patients have been explored for mediastinal masses thought to be tumors [14], sometimes with catastrophic results [6, 71. The clinical course is unpredictable. The patient may die early of uncontrolled sepsis [9, 10, 131. If he or she survives the septic stage, rupture is a danger that is always present. Parkhurst and Decker [15] found a 50% incidence of rupture in their 12 patients. Rupture may occur rapidly in spite of appropriate antibiotic therapy [13]. Other aneurysms may not rupture for years, as in 2 of our patients. Spontaneous cure by thrombosis has been reported in a patient with a thoracic aortic aneurysm without any treatment [16]. Previously, treatment was limited to ligation and excision of mycotic aneurysms of the peripheral arteries [l]. The optimal treatment today is antibiotic therapy followed by early operative intervention [13]. If operation is done too early, bacteria may still be present and the insertion of prosthetic graft material could cause postoperative reinfection [17]. Our first patient was operated on six months after the initial sepsis, but the results of culture of the aneurysm tissues were positive even though there was no gross infection. Graft material was not required, and this may have prevented reinfection. Operation without use of graft material has been done successfully as early as four days after initiation of antibiotic therapy, and the result was good [MI. In patients requiring very early operation at a stage at which active infection is uncontrolled, the situation is more difficult. A foreign body should not be utilized in the area of infection, and it may be necessary to ligate the proximal and distal aorta and perform an extraanatomical bypass. In Patient 5 who was operated on elsewhere, operation could not be delayed since the aneurysm was leaking. The aneurysm was grossly infected. It was excised and the coarctation repaired by a subclavian angioplasty. This method has been used with apparent success in a patient with an infected Dacron patch after coarctation repair [19], but in our patient, the aneurysm recurred and reoperation has become necessary. References 1. Stengel A, Woelferth CC: Mycotic (bacterial) aneurysms of intravascular origin. Arch Intern Med 31:527, Fricker FI, Park SC, Neches WH, et al: Aneurysm of the aorta in children. Chest 76:305, Javett SN, Kahn E: Rupture of a mycotic aneurysm of the thoracic aorta. Arch Dis Child 27:294, Mitchell RG, Claireaux AE: Mycotic aneurysm of the abdominal aorta. Arch Dis Child 27147, Rose JS, Hotson WC, Levin DC: Abdominal aortic aneurysm in childhood. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 123:708, Siege1 MJ, McAlister WH: Aortic aneurysms in children. Radiology 132:615, Wood BP, Young LW, Elbadawi NA: Primary mycotic aneurysm in infancy and childhood. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 118:109, Campbell M: Natural history of coarctation of the aorta. Br Heart J 32:633, Colclough AB, Barson A]: Infantile aortic aneurysm complicating umbilical arterial catheterization. Arch Dis Child 56795, Faer MJ, Taybi H: Mycotic aortic aneurysm in premature infants. Radiology 125:177, Rais J, Finnstroem 0, Wesstroem G: Aortic aneurysm developing after umbilical artery catheterization. Acta Paediatr Scand 65:495, Spangler JG, Kleinberg F, Fulton RE, et al: False aneurysm of the descending aorta. Am J Dis Child 131:1258, 1977
5 318 The Annals of Thoracic Surgery Vol 37 No 4 April Thompson TR, Tilleli J, Johnson DE, et al: Umbilical artery catheterization complicated by mycotic aortic aneurysm in neonates. Adv Pediatr 27275, Cliff MM, Soulen RL, Finestone AJ: Mycotic aneurysm: a challenge and a clue. Arch Intern Med , Parkhurst GF, Decker JP Bacterial aortitis and mycotic aneurysm of the aorta. Am J Pathol31:821, Barker WF: Mycotic aneurysm. Ann Surg 139:84, Bennett DE: Primary mycotic aneurysms of the aorta. Arch Surg 94:758, Malloy MH, Nichols MM: False abdominal aortic aneurysm: an unusual complication of umbilical arterial catheterization for exchange transfusion. J Pediatr 90:285, Kirsh MM, Percy 8, Spooner E: Management of pseudoaneurysm following patch grafting for coarctation of the aorta. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 74536, 1977 Notice from the American Board of Thoracic Surgery The American Board of Thoracic Surgery will begin its recertification process in Diplomates interested in participating in this examination should maintain a documented list of the cardiothoracic operations they performed during the year prior to application for recertification. They should also keep a record of their attendance at thoracic surgical meetings and other continuing medical education activities for the two years prior to application for recertification. In place of a cognitive examination, candidates for recertification will be required to complete both the general thoracic and cardiac portions of the SESATS (Self-Educationklf-Assessment in Thoracic Surgery) I1 Syllabus. Diplomates whose 10-year certificates will expire in 1986 may begin the recertification process in Their new certificate will be dated 10 years from the time of expiration of the original certificate. Pecertification is also open to any Diplomate with an unlimited certificate. The deadline for submission of applications is July 1, A recertification brochure outlining the rules and requirements for recertification in thoracic surgery is available on request from the American Board of Thoracic Surgery, E Seven Mile Rd, Detroit, MI
Aneurysm of the Aorta in Children*
 Aneurysm of the Aorta in Children* Frederick T. Fricker, M.D.; Sang C. Park, M.D.; William H. Neches, M.D.; 00 Robert A.!lfathews, M.D.; and David B. Lerlwrg, M.D., F.C.C.P. Seven children with aortic
Aneurysm of the Aorta in Children* Frederick T. Fricker, M.D.; Sang C. Park, M.D.; William H. Neches, M.D.; 00 Robert A.!lfathews, M.D.; and David B. Lerlwrg, M.D., F.C.C.P. Seven children with aortic
CASE REPORTS. Surgical Treatment of Mycotic Aneurysm Associated with Coarctation of the Aorta. H. Newland Oldham, Jr., M.D., Joseph F. Phillips, M.D.
 CASE REPORTS Surgical Treatment of Mycotic Aneurysm Associated with Coarctation of the Aorta H. Newland Oldham, Jr., M.D., Joseph F. Phillips, M.D., Paul H. Jewett, M.D., and James T. Chen, M.D. ABSTRACT
CASE REPORTS Surgical Treatment of Mycotic Aneurysm Associated with Coarctation of the Aorta H. Newland Oldham, Jr., M.D., Joseph F. Phillips, M.D., Paul H. Jewett, M.D., and James T. Chen, M.D. ABSTRACT
AORTIC COARCTATION. Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta
 AORTIC COARCTATION Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta Definition: Aortic coarctation is a congenital narrowing of the aorta, usually located after the left subclavian artery, near the ductus or the ligamentum
AORTIC COARCTATION Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta Definition: Aortic coarctation is a congenital narrowing of the aorta, usually located after the left subclavian artery, near the ductus or the ligamentum
Our Experiences With Adult Type Aortic Coarctation
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 7 Number 2 Our Experiences With Adult Type Aortic Coarctation E Duran, S Canbaz, M Acipayam, O Gur, O Karaca Citation E Duran,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 7 Number 2 Our Experiences With Adult Type Aortic Coarctation E Duran, S Canbaz, M Acipayam, O Gur, O Karaca Citation E Duran,
Right-Sided Bacterial Endocarditis
 New Concepts in the Treatment of the Uncontrollable Infection Agustin Arbulu, M.D., Ali Kafi, M.D., Norman W. Thorns, M.D., and Robert F. Wilson, M.D. ABSTRACT Our experience with 25 patients with right-sided
New Concepts in the Treatment of the Uncontrollable Infection Agustin Arbulu, M.D., Ali Kafi, M.D., Norman W. Thorns, M.D., and Robert F. Wilson, M.D. ABSTRACT Our experience with 25 patients with right-sided
Pseudoaneurysm of the Thoracic Aorta: A Late Complication of Umbilical Artery Catheterization
 CASE REPORTS Pseudoaneurysm of the Thoracic Aorta: A Late Complication of Umbilical Artery Catheterization Michael L. Wynn, M.D., Marshall Rowen, M.D., Ralph W. Rucker, M.D., Donald R. Sperling, M.D.,
CASE REPORTS Pseudoaneurysm of the Thoracic Aorta: A Late Complication of Umbilical Artery Catheterization Michael L. Wynn, M.D., Marshall Rowen, M.D., Ralph W. Rucker, M.D., Donald R. Sperling, M.D.,
ROLE OF CONTRAST ENHANCED MR ANGIOGRAPHY IN AORTIC COARCTATION
 ROLE OF CONTRAST ENHANCED MR ANGIOGRAPHY IN AORTIC COARCTATION By Adel El Badrawy, Ahmed Abdel Razek, Nermin Soliman, Hala El Marsafawy *, Sameh Amer** From Radiodiagnosis, Pediatric Cardiology* & Cardiothoracic
ROLE OF CONTRAST ENHANCED MR ANGIOGRAPHY IN AORTIC COARCTATION By Adel El Badrawy, Ahmed Abdel Razek, Nermin Soliman, Hala El Marsafawy *, Sameh Amer** From Radiodiagnosis, Pediatric Cardiology* & Cardiothoracic
Management of Ascending Aortic
 Management of Ascending Aortic Aneurysm Complicating Coarctation of the Aorta Ramanathan Sampath, M.D., William N. O'Connor, M.D., Jacqueline A. Noonan, M.D., and Edward P. Todd, M.D., Ph.D. ABSTRACT Four
Management of Ascending Aortic Aneurysm Complicating Coarctation of the Aorta Ramanathan Sampath, M.D., William N. O'Connor, M.D., Jacqueline A. Noonan, M.D., and Edward P. Todd, M.D., Ph.D. ABSTRACT Four
AORTIC DISSECTIONS Current Management. TOMAS D. MARTIN, MD, LAT Professor, TCV Surgery Director UF Health Aortic Disease Center University of Florida
 AORTIC DISSECTIONS Current Management TOMAS D. MARTIN, MD, LAT Professor, TCV Surgery Director UF Health Aortic Disease Center University of Florida DISCLOSURES Terumo Medtronic Cook Edwards Cryolife AORTIC
AORTIC DISSECTIONS Current Management TOMAS D. MARTIN, MD, LAT Professor, TCV Surgery Director UF Health Aortic Disease Center University of Florida DISCLOSURES Terumo Medtronic Cook Edwards Cryolife AORTIC
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Debate in Management of native COA; Balloon Versus Surgery
 Debate in Management of native COA; Balloon Versus Surgery Dr. Amira Esmat, El Tantawy, MD Professor of Pediatrics Consultant Pediatric Cardiac Interventionist Faculty of Medicine Cairo University 23/2/2017
Debate in Management of native COA; Balloon Versus Surgery Dr. Amira Esmat, El Tantawy, MD Professor of Pediatrics Consultant Pediatric Cardiac Interventionist Faculty of Medicine Cairo University 23/2/2017
CT of Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Stuart S. Sagel, M.D.
 CT of Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Stuart S. Sagel, M.D. Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms Atherosclerotic Dissection Penetrating ulcer Mycotic Inflammatory (vasculitis) Traumatic Aortic Imaging Options Catheter
CT of Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Stuart S. Sagel, M.D. Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms Atherosclerotic Dissection Penetrating ulcer Mycotic Inflammatory (vasculitis) Traumatic Aortic Imaging Options Catheter
Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery Aneurysm
 Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery William S. Stoney, M.D., William C. Alford, Jr., M.D., George R. Burrus, M.D., and Clarence S. Thomas, Jr., M.D. ABSTRACT Ten patients with aneurysm of an aberrant right
Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery William S. Stoney, M.D., William C. Alford, Jr., M.D., George R. Burrus, M.D., and Clarence S. Thomas, Jr., M.D. ABSTRACT Ten patients with aneurysm of an aberrant right
AORTIC DISSECTION. DISSECTING ANEURYSMS OF THE AORTA or CLASSIFICATION
 DISSECTING ANEURYSMS OF THE AORTA or AORTIC DISSECTION CLASSIFICATION DeBakey classified aortic dissections into types I, II, and III :- Type I dissection the tear site originates in the ascending aorta,
DISSECTING ANEURYSMS OF THE AORTA or AORTIC DISSECTION CLASSIFICATION DeBakey classified aortic dissections into types I, II, and III :- Type I dissection the tear site originates in the ascending aorta,
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome
 Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
In 1980, Bex and associates 1 first introduced the initial
 Technique of Aortic Translocation for the Management of Transposition of the Great Arteries with a Ventricular Septal Defect and Pulmonary Stenosis Victor O. Morell, MD, and Peter D. Wearden, MD, PhD In
Technique of Aortic Translocation for the Management of Transposition of the Great Arteries with a Ventricular Septal Defect and Pulmonary Stenosis Victor O. Morell, MD, and Peter D. Wearden, MD, PhD In
Anatomy & Physiology
 1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
Ascending Aortic Associated Aortic. Aneurysms with Regurgitation. Koger K. Stenlund, M.D., Charles K. Peterson, M.D.
 Ascending Aortic Associated Aortic Aneurysms with Regurgitation Hovald K. Helseth, M.D., John J. Haglin, M.D., Koger K. Stenlund, M.D., Charles K. Peterson, M.D., and David W. Gauger, M.D. ABSTRACT A safe
Ascending Aortic Associated Aortic Aneurysms with Regurgitation Hovald K. Helseth, M.D., John J. Haglin, M.D., Koger K. Stenlund, M.D., Charles K. Peterson, M.D., and David W. Gauger, M.D. ABSTRACT A safe
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial
 An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
Case Report International Journal of Basic and Clinical Studies (IJBCS) 2013;1(1): Elbey MA et al.
 Treatment of Interrupted Aorta in Adult Patients; a Challenge Both in Surgery and Transcatheter Intervention Mehmet Ali Elbey MD 1, Ahmet Caliskan MD 2, Ferhat Isık MD 1, Faruk Ertas MD 1, Mehmet Serdar
Treatment of Interrupted Aorta in Adult Patients; a Challenge Both in Surgery and Transcatheter Intervention Mehmet Ali Elbey MD 1, Ahmet Caliskan MD 2, Ferhat Isık MD 1, Faruk Ertas MD 1, Mehmet Serdar
Inflow Occlusion for Semilunar Valve Stenosis
 Inflow Occlusion for Semilunar Valve Stenosis Robert M. Sade, M.D., Fred A. Crawford, M.D., and Arno R. Hohn, M.D ABSTRACT Twenty-nine patients have had valvotomy with inflow occlusion since 1975 at our
Inflow Occlusion for Semilunar Valve Stenosis Robert M. Sade, M.D., Fred A. Crawford, M.D., and Arno R. Hohn, M.D ABSTRACT Twenty-nine patients have had valvotomy with inflow occlusion since 1975 at our
SURGICAL TREATMENT AND OUTCOME OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE
 SURGICAL TREATMENT AND OUTCOME OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Mr. W. Brawn Birmingham Children s Hospital. Aims of surgery The aim of surgery in congenital heart disease is to correct or palliate the heart
SURGICAL TREATMENT AND OUTCOME OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Mr. W. Brawn Birmingham Children s Hospital. Aims of surgery The aim of surgery in congenital heart disease is to correct or palliate the heart
Post-Op Aorta: Differentiating Normal Post-Op vs. Complications. Linda C. Chu, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Johns Hopkins University
 Post-Op Aorta: Differentiating Normal Post-Op vs. Complications Linda C. Chu, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Johns Hopkins University No disclosures Disclosures Goals and Objectives To review CT technique
Post-Op Aorta: Differentiating Normal Post-Op vs. Complications Linda C. Chu, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Johns Hopkins University No disclosures Disclosures Goals and Objectives To review CT technique
Update on Acute Aortic Syndrome
 SUNDAY Update on Acute Aortic Syndrome Diana Litmanovich, MD Learning objectives To be familiar with the definition, natural history, and imaging findings of acute aortic syndrome, including: I. Aortic
SUNDAY Update on Acute Aortic Syndrome Diana Litmanovich, MD Learning objectives To be familiar with the definition, natural history, and imaging findings of acute aortic syndrome, including: I. Aortic
Acute Aortic Syndromes
 Acute Aortic Syndromes Carole J. Dennie, MD Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Background Non-Traumatic Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Carole Dennie MD FRCPC Associate Professor of Radiology and Cardiology
Acute Aortic Syndromes Carole J. Dennie, MD Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Background Non-Traumatic Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Carole Dennie MD FRCPC Associate Professor of Radiology and Cardiology
CORONARY arteriovenous fistulas are uncommon, but their detection has. Rupture of a Giant Saccular Aneurysm of Coronary Arteriovenous Fistulas
 Rupture of a Giant Saccular Aneurysm of Coronary Arteriovenous Fistulas Masahiro ITO, MD, Makoto KODAMA, MD, Makihiko SAEKI, 1 MD, Hiroshi FUKUNAGA, MD, Tomoji GOTO, 2 MD, Hidenori INOUE, 2 MD, Shigetaka
Rupture of a Giant Saccular Aneurysm of Coronary Arteriovenous Fistulas Masahiro ITO, MD, Makoto KODAMA, MD, Makihiko SAEKI, 1 MD, Hiroshi FUKUNAGA, MD, Tomoji GOTO, 2 MD, Hidenori INOUE, 2 MD, Shigetaka
Unusual Causes of Aortic Regurgitation. Case 1
 Unusual Causes of Aortic Regurgitation Judy Hung, MD Cardiology Division Massachusetts General Hospital Boston, MA No Disclosures Case 1 54 year old female with h/o cerebral aneurysm and vascular malformation
Unusual Causes of Aortic Regurgitation Judy Hung, MD Cardiology Division Massachusetts General Hospital Boston, MA No Disclosures Case 1 54 year old female with h/o cerebral aneurysm and vascular malformation
CASE REPORT. Mycotic Aneurysm of Ascending Aorta Due to Sarcina Lutea. G. A. Lopez, M.D., and A. R. C. Dobell, M.D.
 CASE REPORT Mycotic Aneurysm of Ascending Aorta Due to Sarcina Lutea G. A. Lopez, M.D., and A. R. C. Dobell, M.D. ABSTRACT A patient developed a mycotic aneurysm of the aortic suture line after aortic
CASE REPORT Mycotic Aneurysm of Ascending Aorta Due to Sarcina Lutea G. A. Lopez, M.D., and A. R. C. Dobell, M.D. ABSTRACT A patient developed a mycotic aneurysm of the aortic suture line after aortic
The arterial switch operation has been the accepted procedure
 The Arterial Switch Procedure: Closed Coronary Artery Transfer Edward L. Bove, MD The arterial switch operation has been the accepted procedure for the repair of transposition of the great arteries (TGA)
The Arterial Switch Procedure: Closed Coronary Artery Transfer Edward L. Bove, MD The arterial switch operation has been the accepted procedure for the repair of transposition of the great arteries (TGA)
Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement
 Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement of Severe Segmental Coronary Artery Occlusion Operative Technique Rene G. Favaloro, M.D. D irect operation on the coronary artery has been performed in 180 patients
Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement of Severe Segmental Coronary Artery Occlusion Operative Technique Rene G. Favaloro, M.D. D irect operation on the coronary artery has been performed in 180 patients
14 Valvular Stenosis
 14 Valvular Stenosis 14-1. Valvular Stenosis unicuspid valve FIGUE 14-1. This photograph shows severe valvular stenosis as it occurs in a newborn. There is a unicuspid, horseshoe-shaped leaflet with a
14 Valvular Stenosis 14-1. Valvular Stenosis unicuspid valve FIGUE 14-1. This photograph shows severe valvular stenosis as it occurs in a newborn. There is a unicuspid, horseshoe-shaped leaflet with a
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD)
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
Portal vein catheterization and selective angiography in diagnosis of total anomalous pulmonary venous connexion
 British Heart journal, 974, 36, 155-59. Portal vein catheterization and selective angiography in diagnosis of total anomalous pulmonary venous connexion Michael Tynan, D. Behrendt, W. Urquhart, and G.
British Heart journal, 974, 36, 155-59. Portal vein catheterization and selective angiography in diagnosis of total anomalous pulmonary venous connexion Michael Tynan, D. Behrendt, W. Urquhart, and G.
Aortography in Fallot's Tetralogy and Variants
 Brit. Heart J., 1969, 31, 146. Aortography in Fallot's Tetralogy and Variants SIMON REES AND JANE SOMERVILLE From The Institute of Cardiology and National Heart Hospital, London W.J In patients with Fallot's
Brit. Heart J., 1969, 31, 146. Aortography in Fallot's Tetralogy and Variants SIMON REES AND JANE SOMERVILLE From The Institute of Cardiology and National Heart Hospital, London W.J In patients with Fallot's
12 th Annual West Virginia ACC Meeting April 8, 2017
 12 th Annual West Virginia ACC Meeting April 8, 2017 Rameez Sayyed, M.D., FACC, FSCAI Associate professor of Medicine Program Director for interventional cardiology Marshall University Joan C. Edwards
12 th Annual West Virginia ACC Meeting April 8, 2017 Rameez Sayyed, M.D., FACC, FSCAI Associate professor of Medicine Program Director for interventional cardiology Marshall University Joan C. Edwards
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTL MTERIL Marie erna, Martin Kocher, Rohit Philip Thomas. cute aorta, overview of acute T findings and endovascular treatment options (doi: 10.5507/bp.2016.060) Fig. 1. : Non-enhanced T, hemopericardium
SUPPLEMENTL MTERIL Marie erna, Martin Kocher, Rohit Philip Thomas. cute aorta, overview of acute T findings and endovascular treatment options (doi: 10.5507/bp.2016.060) Fig. 1. : Non-enhanced T, hemopericardium
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
Current treatment of Aortic Aneurysms and Dissections. Adam Keefer, MD, FACS Sean Hislop, MD, FACS
 Current treatment of Aortic Aneurysms and Dissections Adam Keefer, MD, FACS Sean Hislop, MD, FACS Patient 1 69 year old well-educated man with reoccurring pain in his upper abdomen and a pulsatile mass.
Current treatment of Aortic Aneurysms and Dissections Adam Keefer, MD, FACS Sean Hislop, MD, FACS Patient 1 69 year old well-educated man with reoccurring pain in his upper abdomen and a pulsatile mass.
Assessing Cardiac Anatomy With Digital Subtraction Angiography
 485 JACC Vol. 5, No. I Assessing Cardiac Anatomy With Digital Subtraction Angiography DOUGLAS S., MD, FACC Cleveland, Ohio The use of intravenous digital subtraction angiography in the assessment of patients
485 JACC Vol. 5, No. I Assessing Cardiac Anatomy With Digital Subtraction Angiography DOUGLAS S., MD, FACC Cleveland, Ohio The use of intravenous digital subtraction angiography in the assessment of patients
ANEURYSM OF THE ASCENDING AORTA SIMULATING RIGHT ATRIAL DILATATION*
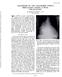 OCTOBER, 1969 ANEURYSM OF THE ASCENDING AORTA SIMULATING RIGHT ATRIAL DILATATION* \ ATE HAVE recently encountered I, V patients with cardiomegaly in whom the frontal, lateral and oblique roentgenograms
OCTOBER, 1969 ANEURYSM OF THE ASCENDING AORTA SIMULATING RIGHT ATRIAL DILATATION* \ ATE HAVE recently encountered I, V patients with cardiomegaly in whom the frontal, lateral and oblique roentgenograms
account for 10% to 15% of all traffic fatalities majority fatal at the scene 50% who survive the initial injury die in the first 24 hours 90% die
 account for 10% to 15% of all traffic fatalities majority fatal at the scene 50% who survive the initial injury die in the first 24 hours 90% die within the first month if aorta not repaired 30-90% overall
account for 10% to 15% of all traffic fatalities majority fatal at the scene 50% who survive the initial injury die in the first 24 hours 90% die within the first month if aorta not repaired 30-90% overall
CASE REPORTS. False Aneurysm After Ligation of a Patent Ductus Arteriosus
 CASE REPORTS False Aneurysm After Ligation of a Patent Ductus Arteriosus Jens G. Rosenkrantz, M.D., Leslie L. Kelminson, M.D., Bruce C. Paton, M.R.C.P., F.R.C.S., and John H. K. Vogel, M.D. T e development
CASE REPORTS False Aneurysm After Ligation of a Patent Ductus Arteriosus Jens G. Rosenkrantz, M.D., Leslie L. Kelminson, M.D., Bruce C. Paton, M.R.C.P., F.R.C.S., and John H. K. Vogel, M.D. T e development
Case 47 Clinical Presentation
 93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
Morbidity Audit and Logbook Tool SNOMED Board Reporting Terms for SET and IMG Vascular Surgery AMPUTATION AORTA
 SNOMED s for SET and IMG Vascular Surgery AMPUTATION Amputation above-knee Amputation of leg through tibia and fibula Amputation of the foot Amputation of toe Through knee amputation Ray amputation of
SNOMED s for SET and IMG Vascular Surgery AMPUTATION Amputation above-knee Amputation of leg through tibia and fibula Amputation of the foot Amputation of toe Through knee amputation Ray amputation of
Surgical treatment of aneurysmal changes in the ascending aorta
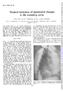 Thcrax (1966), 21, 240. Surgical treatment of aneurysmal changes in the ascending aorta VIKING OLOV BJORK AND LARS BJORK Fronit thle Depart-tneiet.s of Tlioracic Surgery and Diagnostic Radiology, University
Thcrax (1966), 21, 240. Surgical treatment of aneurysmal changes in the ascending aorta VIKING OLOV BJORK AND LARS BJORK Fronit thle Depart-tneiet.s of Tlioracic Surgery and Diagnostic Radiology, University
Optimal repair of acute aortic dissection
 Optimal repair of acute aortic dissection Dept. of Vascular Surgery, The 2nd Xiang-Yale Hospital, Central-South University, China Hunan Major Vessels Diseases Clinical Center Chang Shu Email:changshu01@yahoo.com
Optimal repair of acute aortic dissection Dept. of Vascular Surgery, The 2nd Xiang-Yale Hospital, Central-South University, China Hunan Major Vessels Diseases Clinical Center Chang Shu Email:changshu01@yahoo.com
Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia
 Marshall University Marshall Digital Scholar Internal Medicine Faculty Research Spring 5-2004 Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia Ellen A. Thompson
Marshall University Marshall Digital Scholar Internal Medicine Faculty Research Spring 5-2004 Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia Ellen A. Thompson
False Aneurvsm and Pseudo-False Aneurysm of the Left qentricle: ~tiology, Pathology; Diagnosis, and Operative Management
 False Aneurvsm and Pseudo-False Aneurysm of the Left qentricle: ~tiology, Pathology; Diagnosis, and Operative Management S. Stewart, M.D., R. Huddle, M.D., I. Stuard, M.D., B. F. Schreiner, M.D., and J.
False Aneurvsm and Pseudo-False Aneurysm of the Left qentricle: ~tiology, Pathology; Diagnosis, and Operative Management S. Stewart, M.D., R. Huddle, M.D., I. Stuard, M.D., B. F. Schreiner, M.D., and J.
Management of Acute Aortic Syndromes. M. Grabenwoger, MD Dept. of Cardiovascular Surgery Hospital Hietzing, Vienna, Austria
 Management of Acute Aortic Syndromes M. Grabenwoger, MD Dept. of Cardiovascular Surgery Hospital Hietzing, Vienna, Austria I have nothing to disclose. Acute Aortic Syndromes Acute Aortic Dissection Type
Management of Acute Aortic Syndromes M. Grabenwoger, MD Dept. of Cardiovascular Surgery Hospital Hietzing, Vienna, Austria I have nothing to disclose. Acute Aortic Syndromes Acute Aortic Dissection Type
IMAGES. in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2005 Jan-Mar; 7(1): 12 17. PMCID: PMC3232568 Stent implantation for coarctation facilitated by the anterograde trans-septal approach N Sreeram and
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2005 Jan-Mar; 7(1): 12 17. PMCID: PMC3232568 Stent implantation for coarctation facilitated by the anterograde trans-septal approach N Sreeram and
Case Reports The following case reports illustrate some of the ways in which staplers have proved useful in operations for aneurysms of the aorta.
 Use of Stapling Instruments in Surgery for Aneurysms of the Aorta M. Arisan Ergin, M.D., James V. O'Connor, M.D., Carlos Blanche, M.D., and Randall B. Griepp, M.D. ABSTRACT Since their inception, surgical
Use of Stapling Instruments in Surgery for Aneurysms of the Aorta M. Arisan Ergin, M.D., James V. O'Connor, M.D., Carlos Blanche, M.D., and Randall B. Griepp, M.D. ABSTRACT Since their inception, surgical
BILLING BULLETIN. Re: Interventional Cardiology. Bulletin #: 1. Date Issued: November 10, Background
 BILLING BULLETIN Re: Interventional Cardiology Bulletin #: 1 Date Issued: November 10, 2016 Background This Billing Bulletin provides billing guidance when submitting claims to Manitoba Health, Seniors
BILLING BULLETIN Re: Interventional Cardiology Bulletin #: 1 Date Issued: November 10, 2016 Background This Billing Bulletin provides billing guidance when submitting claims to Manitoba Health, Seniors
Infected Lower Extremity Aneurysms C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD
 Infected Lower Extremity Aneurysms C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD University Hospital of Brooklyn Department of Surgery History 52F c PMHx of HTN, asthma p/w fever, malaise s/p one week of ABx for presumed
Infected Lower Extremity Aneurysms C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD University Hospital of Brooklyn Department of Surgery History 52F c PMHx of HTN, asthma p/w fever, malaise s/p one week of ABx for presumed
Descending aorta replacement through median sternotomy
 Descending aorta replacement through median sternotomy Mitrev Z, Anguseva T, Belostotckij V, Hristov N. Special hospital for surgery Filip Vtori Skopje - Makedonija June, 2010 Cardiosurgery - Skopje 1
Descending aorta replacement through median sternotomy Mitrev Z, Anguseva T, Belostotckij V, Hristov N. Special hospital for surgery Filip Vtori Skopje - Makedonija June, 2010 Cardiosurgery - Skopje 1
The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3-
 1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS (PDA)
 PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS (PDA) It is a channel that connect the pulmonary artery with the descending aorta (isthumus part). It results from the persistence of patency of the fetal ductus arteriosus after
PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS (PDA) It is a channel that connect the pulmonary artery with the descending aorta (isthumus part). It results from the persistence of patency of the fetal ductus arteriosus after
ABERRANT RIGHT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY AND CALCIFIED ANEURYSM OF. Jose Rubio-Alvarez, Juan Sierra-Quiroga, Belen Adrio Nazar and Javier Garcia Carro.
 ABERRANT RIGHT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY AND CALCIFIED ANEURYSM OF KOMMERELL S DIVERTICULUM : AN ALTERNATIVE APPROACH. Jose Rubio-Alvarez, Juan Sierra-Quiroga, Belen Adrio Nazar and Javier Garcia Carro. Department
ABERRANT RIGHT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY AND CALCIFIED ANEURYSM OF KOMMERELL S DIVERTICULUM : AN ALTERNATIVE APPROACH. Jose Rubio-Alvarez, Juan Sierra-Quiroga, Belen Adrio Nazar and Javier Garcia Carro. Department
The Rastelli procedure has been traditionally used for repair
 En-bloc Rotation of the Truncus Arteriosus A Technique for Complete Anatomic Repair of Transposition of the Great Arteries/Ventricular Septal Defect/Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction or Double
En-bloc Rotation of the Truncus Arteriosus A Technique for Complete Anatomic Repair of Transposition of the Great Arteries/Ventricular Septal Defect/Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction or Double
Clotted false lumen: reappraisal of indications for
 Thorax, 1981, 36, 194-199 Clotted false lumen: reappraisal of indications for medical management of acute aortic dissection C J SANDERSON, STUART RICH, POLLY A BEERE, C E ANAGNOSTOPOULOS, JAMES M LEVETT,
Thorax, 1981, 36, 194-199 Clotted false lumen: reappraisal of indications for medical management of acute aortic dissection C J SANDERSON, STUART RICH, POLLY A BEERE, C E ANAGNOSTOPOULOS, JAMES M LEVETT,
Indications of Coronary Angiography Dr. Shaheer K. George, M.D Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University 2014
 Indications of Coronary Angiography Dr. Shaheer K. George, M.D Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University 2014 Indications for cardiac catheterization Before a decision to perform an invasive procedure such
Indications of Coronary Angiography Dr. Shaheer K. George, M.D Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University 2014 Indications for cardiac catheterization Before a decision to perform an invasive procedure such
Hybrid Repair of a Complex Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysm
 Hybrid Repair of a Complex Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysm Virendra I. Patel MD MPH Assistant Professor of Surgery Massachusetts General Hospital Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Disclosure
Hybrid Repair of a Complex Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysm Virendra I. Patel MD MPH Assistant Professor of Surgery Massachusetts General Hospital Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Disclosure
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease
 Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Procedure (TAVI)
 Page 1 of 5 Procedure (TAVI) Introduction Aortic stenosis (AS) is a common heart valve problem associated with heart failure and death. Surgical valve repair or replacement is recommended if AS patients
Page 1 of 5 Procedure (TAVI) Introduction Aortic stenosis (AS) is a common heart valve problem associated with heart failure and death. Surgical valve repair or replacement is recommended if AS patients
Acute Type B dissection. Closure of the infra diaphragmatic tear: how and when?
 Acute Type B dissection. Closure of the infra diaphragmatic tear: how and when? Prof. Olgierd Rowiński II Department of Clinical Radiology Medical University of Warsaw Disclosure Speaker name: Olgierd
Acute Type B dissection. Closure of the infra diaphragmatic tear: how and when? Prof. Olgierd Rowiński II Department of Clinical Radiology Medical University of Warsaw Disclosure Speaker name: Olgierd
Likes ML, Johnston TA. Gastric pseudoaneurysm in the setting of Loey s Dietz Syndrome. Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2012;14(3):1-5
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Likes ML, Johnston TA. Gastric pseudoaneurysm in the setting of Loey s Dietz Syndrome. Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2012;14(3):1-5 University of Washington, Pediatrics, Seattle
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Likes ML, Johnston TA. Gastric pseudoaneurysm in the setting of Loey s Dietz Syndrome. Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2012;14(3):1-5 University of Washington, Pediatrics, Seattle
Free Esophageal Perforation Following Hybrid Visceral Debranching and Distal Endograft Extension to Repair a Ruptured Thoracoabdominal Aortic
 Free Esophageal Perforation Following Hybrid Visceral Debranching and Distal Endograft Extension to Repair a Ruptured Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysm History A 56-year-old gentleman, who had been referred
Free Esophageal Perforation Following Hybrid Visceral Debranching and Distal Endograft Extension to Repair a Ruptured Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysm History A 56-year-old gentleman, who had been referred
Vascular Intervention
 10 : 389-393, 2001 B Vascular Intervention 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 3 2 1 1997 7 2000 4 B 29 19 10 50 84 66.1 stent graft S/G primary entry stenting S/G 12 4 2 1 1 40 mm 8 1 MOF 1 endoleak + 11 91.6% 10 stenting
10 : 389-393, 2001 B Vascular Intervention 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 3 2 1 1997 7 2000 4 B 29 19 10 50 84 66.1 stent graft S/G primary entry stenting S/G 12 4 2 1 1 40 mm 8 1 MOF 1 endoleak + 11 91.6% 10 stenting
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Residual Right=to-Left Shunt Following Repair of Atrial Septal Defect
 Residual Right=to-Left Shunt Following Repair of Atrial Septal Defect Susan J. Desnick, Ph.D., M.D., William A. Neal, M.D., Demetre M. Nicoloff, M.D., and James H. Moller, M.D. ABSTRACT Information about
Residual Right=to-Left Shunt Following Repair of Atrial Septal Defect Susan J. Desnick, Ph.D., M.D., William A. Neal, M.D., Demetre M. Nicoloff, M.D., and James H. Moller, M.D. ABSTRACT Information about
An Overview of Post-EVAR Endoleaks: Imaging Findings and Management. Ravi Shergill BSc Sean A. Kennedy MD Mark O. Baerlocher MD FRCPC
 An Overview of Post-EVAR Endoleaks: Imaging Findings and Management Ravi Shergill BSc Sean A. Kennedy MD Mark O. Baerlocher MD FRCPC Disclosure Slide Mark O. Baerlocher: Current: Consultant for Boston
An Overview of Post-EVAR Endoleaks: Imaging Findings and Management Ravi Shergill BSc Sean A. Kennedy MD Mark O. Baerlocher MD FRCPC Disclosure Slide Mark O. Baerlocher: Current: Consultant for Boston
Surgical implications of right aortic arch with isolation of left subclavian artery'
 British Heart journal, I975, 37, 93I-936. Surgical implications of right aortic arch with isolation of left subclavian artery' L. Rodriguez,2 T. Izukawa, C. A. F. MoEs, G. A. Trusler, and W. G. Williams
British Heart journal, I975, 37, 93I-936. Surgical implications of right aortic arch with isolation of left subclavian artery' L. Rodriguez,2 T. Izukawa, C. A. F. MoEs, G. A. Trusler, and W. G. Williams
Coronary Artery from the Wrong Sinus of Valsalva: A Physiologic Repair Strategy
 Coronary Artery from the Wrong Sinus of Valsalva: A Physiologic Repair Strategy Tom R. Karl, MS, MD he most commonly reported coronary artery malformation leading to sudden death in children and young
Coronary Artery from the Wrong Sinus of Valsalva: A Physiologic Repair Strategy Tom R. Karl, MS, MD he most commonly reported coronary artery malformation leading to sudden death in children and young
DR Turner, JA Vincent, and ML Epstein. Isolated right pulmonary artery discontinuity. Images Paediatr Cardiol Jul-Sep; 2(3):
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images PMCID: PMC3232486 Isolated right pulmonary artery discontinuity DR Turner, MD, * JA Vincent, ** and ML Epstein *** * Senior Fellow, Division of Cardiology, Children's
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images PMCID: PMC3232486 Isolated right pulmonary artery discontinuity DR Turner, MD, * JA Vincent, ** and ML Epstein *** * Senior Fellow, Division of Cardiology, Children's
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS 993 THE NATURAL HISTORY OF CERTAIN CONGENITAL CARDIOVASCULAR MALFORMATIONS. Alexander S. Nadas, M.D.
 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS 993 tnicular overload is the major problem and left ventricular failure occurs. Since for many years the importance of hepatomegaly in the diagnosis of cardiac failure has
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS 993 tnicular overload is the major problem and left ventricular failure occurs. Since for many years the importance of hepatomegaly in the diagnosis of cardiac failure has
Following Mitral Valve Replacement
 Re air of a Subvalvular Le rt Ventricular Aneurysm Following Mitral Valve Replacement Darryl J. Sutorius, M.D., James A. Helmsworth, M.D., James A. Majeski, Ph.D., M.D., and Stephen F. Miller, M.D. ABSTRACT
Re air of a Subvalvular Le rt Ventricular Aneurysm Following Mitral Valve Replacement Darryl J. Sutorius, M.D., James A. Helmsworth, M.D., James A. Majeski, Ph.D., M.D., and Stephen F. Miller, M.D. ABSTRACT
Diseases of the aorta
 Diseases of the aorta Aneurysm, dissection and aortitis are the main pathologies (Fig. 18.79 ). data:text/html;charset=utf-8,%3ch2%20id%3d%22cc5a0836d6aa490ca26dd7c15632b559%22%20style%3d%22margin%3a%201.3em%200px%200.5em%3b%20padding%3a%200px%3b%20border%3a%200px%3b%20font-fa
Diseases of the aorta Aneurysm, dissection and aortitis are the main pathologies (Fig. 18.79 ). data:text/html;charset=utf-8,%3ch2%20id%3d%22cc5a0836d6aa490ca26dd7c15632b559%22%20style%3d%22margin%3a%201.3em%200px%200.5em%3b%20padding%3a%200px%3b%20border%3a%200px%3b%20font-fa
CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY
 Volume 107, Number 4 April 1994 The Journal of THORACIC AND CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY Cardiac and Pulmonary Transplantation Risk factors for graft failure associated with pulmonary hypertension after pediatric
Volume 107, Number 4 April 1994 The Journal of THORACIC AND CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY Cardiac and Pulmonary Transplantation Risk factors for graft failure associated with pulmonary hypertension after pediatric
Anomalous muscle bundle of the right ventricle
 British Heart Journal, 1978, 40, 1040-1045 Anomalous muscle bundle of the right ventricle Its recognition and surgical treatment M. D. LI, J. C. COLES, AND A. C. McDONALD From the Department of Paediatrics,
British Heart Journal, 1978, 40, 1040-1045 Anomalous muscle bundle of the right ventricle Its recognition and surgical treatment M. D. LI, J. C. COLES, AND A. C. McDONALD From the Department of Paediatrics,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Cantrell s pentalogy: an unusual midline defect
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Cantrell s pentalogy: an unusual midline defect October 2004 2 Cevey-Macherel MN, Meijboom EJ, Di Bernardo S, Truttmann AC, Division of Neonatology and Division of Pediatric
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Cantrell s pentalogy: an unusual midline defect October 2004 2 Cevey-Macherel MN, Meijboom EJ, Di Bernardo S, Truttmann AC, Division of Neonatology and Division of Pediatric
Partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection to superior
 Cavo-Atrial Anastomosis Technique for Partial Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection to the Superior Vena Cava The Warden Procedure Robert A. Gustafson, MD Partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection
Cavo-Atrial Anastomosis Technique for Partial Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection to the Superior Vena Cava The Warden Procedure Robert A. Gustafson, MD Partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection
Case 8036 Multiple penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers
 Case 8036 Multiple penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers Santiago I, Seco M, Curvo-Semedo L Section: Cardiovascular Published: 2010, Feb. 22 Patient: 78 year(s), male Clinical History A 78-year-old hypertensive
Case 8036 Multiple penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers Santiago I, Seco M, Curvo-Semedo L Section: Cardiovascular Published: 2010, Feb. 22 Patient: 78 year(s), male Clinical History A 78-year-old hypertensive
Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism
 Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism Aneurysms, overview = congenital or acquired dilations of blood vessels or the heart True aneurysms -involve all three layers of the artery (intima, media, and
Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism Aneurysms, overview = congenital or acquired dilations of blood vessels or the heart True aneurysms -involve all three layers of the artery (intima, media, and
Complete Proximal Occlusion of All Three Main Coronary Arteries Complicated With a Left Main Coronary Aneurysm: A Case Report
 J Cardiol 2004 Nov; 44 5 : 201 205 Complete Proximal Occlusion of All Three Main Coronary Arteries Complicated With a Left Main Coronary Aneurysm: A Case Report Takatoshi Hiroshi Akira Takahiro Masayasu
J Cardiol 2004 Nov; 44 5 : 201 205 Complete Proximal Occlusion of All Three Main Coronary Arteries Complicated With a Left Main Coronary Aneurysm: A Case Report Takatoshi Hiroshi Akira Takahiro Masayasu
Left ventricle pseudoaneurysm as late postoperative complication of a large apical aneurysm
 CASE REPORT Left ventricle pseudoaneurysm as late postoperative complication of a large apical aneurysm Mariana M. Floria 1, 4, Carmen Elena Pleșoianu 2, 4, Michel Buche 3, Baudouin Marchandise 4, Erwin
CASE REPORT Left ventricle pseudoaneurysm as late postoperative complication of a large apical aneurysm Mariana M. Floria 1, 4, Carmen Elena Pleșoianu 2, 4, Michel Buche 3, Baudouin Marchandise 4, Erwin
Disclosures: Acute Aortic Syndrome. A. Michael Borkon, M.D. Director of CV Surgery Mid America Heart Institute Saint Luke s Hospital Kansas City, MO
 Acute Aortic Syndrome Disclosures: A. Michael Borkon, M.D. Director of CV Surgery Mid America Heart Institute Saint Luke s Hospital Kansas City, MO No financial relationships to disclose 1 Acute Aortic
Acute Aortic Syndrome Disclosures: A. Michael Borkon, M.D. Director of CV Surgery Mid America Heart Institute Saint Luke s Hospital Kansas City, MO No financial relationships to disclose 1 Acute Aortic
We present the case of an asymptomatic, 75-year-old
 Images in Cardiovascular Medicine Asymptomatic Rupture of the Left Ventricle Lech Paluszkiewicz, MD; Stefan Ożegowski, MD; Mohammad Amin Parsa, MD; Jan Gummert, PhD, MD We present the case of an asymptomatic,
Images in Cardiovascular Medicine Asymptomatic Rupture of the Left Ventricle Lech Paluszkiewicz, MD; Stefan Ożegowski, MD; Mohammad Amin Parsa, MD; Jan Gummert, PhD, MD We present the case of an asymptomatic,
A Loeys-Dietz Patient with a Trans-Atlantic Odyssey. Repeated Aortic Root Surgery ending with a Huge Left Main Coronary Aneurysm 4
 1 2 3 A Loeys-Dietz Patient with a Trans-Atlantic Odyssey Repeated Aortic Root Surgery ending with a Huge Left Main Coronary Aneurysm 4 5 6 7 8 9 Thierry Carrel 1, Florian Schoenhoff 1 and Duke Cameron
1 2 3 A Loeys-Dietz Patient with a Trans-Atlantic Odyssey Repeated Aortic Root Surgery ending with a Huge Left Main Coronary Aneurysm 4 5 6 7 8 9 Thierry Carrel 1, Florian Schoenhoff 1 and Duke Cameron
Primary to non-coronary IVUS
 codes 2018 2018 codes Primary to non-coronary IVUS Page 2 All coding, coverage, billing and payment information provided herein by Philips is gathered from third-party sources and is subject to change.
codes 2018 2018 codes Primary to non-coronary IVUS Page 2 All coding, coverage, billing and payment information provided herein by Philips is gathered from third-party sources and is subject to change.
Patent ductus arteriosus PDA
 Patent ductus arteriosus PDA Is connecting between the aortic end just distal to the origin of the LT sub clavian artery& the pulmonary artery at its bifurcation. Female/male ratio is 2:1 and it is more
Patent ductus arteriosus PDA Is connecting between the aortic end just distal to the origin of the LT sub clavian artery& the pulmonary artery at its bifurcation. Female/male ratio is 2:1 and it is more
Aortic arch pathology. Cerebral ischemia following carotid artery stenosis.
 Important: -Subclavian Steal Syndrome -Cerebral ischemia Aortic arch pathology. Cerebral ischemia following carotid artery stenosis. Mina Aubeed & Alba Hernández Pinilla Aortic arch pathology Common arch
Important: -Subclavian Steal Syndrome -Cerebral ischemia Aortic arch pathology. Cerebral ischemia following carotid artery stenosis. Mina Aubeed & Alba Hernández Pinilla Aortic arch pathology Common arch
Cardiac surgery Closure of defect of artrioventicular septum using dual prosthesis patches
 CARDIOLOGY / CARDIOTHORACIC SURGERY PROCEDURES PROCEDURE A ( RM 4401 - RM 4800 ) 1 General procedures Replacement of aortic valve (including valvuloplasty) 2 General procedures Replacement of mitral valve
CARDIOLOGY / CARDIOTHORACIC SURGERY PROCEDURES PROCEDURE A ( RM 4401 - RM 4800 ) 1 General procedures Replacement of aortic valve (including valvuloplasty) 2 General procedures Replacement of mitral valve
Surgical Repair Is Safe and Effective After Unsuccessful Balloon Angioplasty of Native Coarctation of the Aorta
 389 Surgical Repair Is Safe and Effective After Unsuccessful Balloon Angioplasty of Native Coarctation of the Aorta L. LUANN MINICH, MD, ROBERT H. BEEKMAN Ill, MD, FACC, ALBERT P. ROCCHINI, MD, KATHLEEN
389 Surgical Repair Is Safe and Effective After Unsuccessful Balloon Angioplasty of Native Coarctation of the Aorta L. LUANN MINICH, MD, ROBERT H. BEEKMAN Ill, MD, FACC, ALBERT P. ROCCHINI, MD, KATHLEEN
Mesenteric vascular insufficiency and claudication following acute dissecting thoracic aortic aneurysm
 Mesenteric vascular insufficiency and claudication following acute dissecting thoracic aortic aneurysm Thomas H. Cogbill, M.D., A. Erik Gundersen, M.D., and Renato TraveUi, M.D., La Crosse, Wisc. Mesenteric
Mesenteric vascular insufficiency and claudication following acute dissecting thoracic aortic aneurysm Thomas H. Cogbill, M.D., A. Erik Gundersen, M.D., and Renato TraveUi, M.D., La Crosse, Wisc. Mesenteric
PAEDIATRIC EMQs. Andrew A Mallick Paediatrics.info.
 PAEDIATRIC EMQs Andrew A Mallick Paediatrics.info www.paediatrics.info Paediatric EMQs Paediatrics.info First published in the United Kingdom in 2012. While the advice and information in this book is believed
PAEDIATRIC EMQs Andrew A Mallick Paediatrics.info www.paediatrics.info Paediatric EMQs Paediatrics.info First published in the United Kingdom in 2012. While the advice and information in this book is believed
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) with absent pulmonary valve
 Repair of Tetralogy of Fallot with Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Karl F. Welke, MD, and Ross M. Ungerleider, MD, MBA Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) with absent pulmonary valve syndrome (APVS) occurs in 5%
Repair of Tetralogy of Fallot with Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Karl F. Welke, MD, and Ross M. Ungerleider, MD, MBA Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) with absent pulmonary valve syndrome (APVS) occurs in 5%
IMAGING the AORTA. Mirvat Alasnag FACP, FSCAI, FSCCT, FASE June 1 st, 2011
 IMAGING the AORTA Mirvat Alasnag FACP, FSCAI, FSCCT, FASE June 1 st, 2011 September 11, 2003 Family is asking $67 million in damages from two doctors Is it an aneurysm? Is it a dissection? What type of
IMAGING the AORTA Mirvat Alasnag FACP, FSCAI, FSCCT, FASE June 1 st, 2011 September 11, 2003 Family is asking $67 million in damages from two doctors Is it an aneurysm? Is it a dissection? What type of
Surgical Procedures and Complications
 Radiological Society of North America, RSNA 2013 Refresher Course Program: Vascular Track Surgical Procedures and Complications Learning objectives Outline RC 112 : Key Concepts: Surgical Procedures and
Radiological Society of North America, RSNA 2013 Refresher Course Program: Vascular Track Surgical Procedures and Complications Learning objectives Outline RC 112 : Key Concepts: Surgical Procedures and
Transcatheter closure of right coronary artery fistula to the right ventricle
 Case Report Transcatheter closure of right coronary artery fistula to the right ventricle Abstract Coronary artery fistula (CAF) is an uncommon anomaly usually congenital but can be acquired. Although,
Case Report Transcatheter closure of right coronary artery fistula to the right ventricle Abstract Coronary artery fistula (CAF) is an uncommon anomaly usually congenital but can be acquired. Although,
Case Report DOUGLAS H. KING, MD, JAMES C. HUHTA, MD, HOWARD P. GUTGESELL, MD, FACC, DAVID A. OTT, MD*
 lacc Vol. 4, No.2 August 198'
lacc Vol. 4, No.2 August 198'
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
