Relaxant Effects of Matrine on Aortic Smooth Muscles of Guinea Pigs 1
|
|
|
- Ami Lynch
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BIOMEDICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES 22, (2009) Relaxant Effects of Matrine on Aortic Smooth Muscles of Guinea Pigs 1 JIE ZHENG #, PING ZHENG #, XU ZHOU *, LIN YAN #, RU ZHOU #, XUE-YAN FU + #, +, 2, AND GUI-DONG DAI # Department of Pharmacology; * Department of Physiology, School of Basic Medical Science; + Ningxia Research Institute of Medicine & Pharmacy, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan , Ningxia, China Objective To determine whether matrine, a kind of traditional Chinese medicinal alkaloid, can relax the aortic smooth muscles isolated from guinea pigs and to investigate the mechanism of its relaxant effects. Methods Phenylephrine or potassium chloride concentration-dependent relaxation response of aortic smooth muscles to matrine was studied in the precontracted guinea pigs. Results Matrine ( mol/l mol/l) relaxed the endothelium-denuded aortic rings pre-contracted sub-maximally with phenylephrine, in a concentration-dependent manner, and its pre-incubation ( mol/l) produced a significant rightward shift in the phenylephrine dose-response curve, but had no effects on the potassium chloride-induced contraction. The anti-contractile effect of matrine was not reduced by the highly selective ATP-dependent K + channel blocker glibenclamide (10-5 mol/l), either by the non-selective K + channel blocker tetraethylammonium (10-3 mol/l), or by the β-antagonist propranolol (10-5 mol/l). In either normal or Ca 2+ -free bathing medium, the phenylephrine-induced contraction was attenuated by matrine ( mol/l), indicating that the vasorelaxation was due to inhibition of intracellular and extracellular Ca 2+ mobilization. Conclusion Matrine inhibits phenylephrine-induced contractions by inhibiting activation of α-adrenoceptor and interfering with the release of intracellular Ca 2+ and the influx of extracellular Ca 2+. Key words: Matrine; Aorta; Vascular smooth muscle; Relaxation; Guinea-pigs; Calcium INTRODUCTION Matrine, a major quinoilizidine alkaloid with four-loop and molecular formula of C 15 H 24 N 2 O (Fig. 1), is extracted from Sophora alopecuroides L, a Chinese medicinal plant, and has been intensively studied for its pleiotropic effects on cardiovascular diseases [1]. It has been shown that matrine inhibits ventricular arrhythmia induced by aconitine, barium chloride or coronary ligation in rats, and reduces the incidence of atrium fibrillation produced by calcium chloride-acetylcholine mixture in mice [2-4]. The mechanism of matrine s anti-arrhythmic action might be associated with the prolonged action potential by blocking multiple potassium currents and by increasing intracellular calcium through promoting extracellular calcium flow into intracellular calcium, and has nothing to do with the release of intracellular calcium from ventricular myocytes [5-9]. Matrine can prevent myocardial hypertrophy and pathologic switching of myosin heavy chain isoform mediated by norepinephrine, thus reversing cardiac remodeling induced by norepinephrine, and so inhibits cardiac fibrosis stimulated by angiotensin II by suppressing cultured neonatal cardiac fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis [10-11]. It was reported that matrine inhibits angiotensin II-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and calcium overload [12-13]. We recently reported that the protective effect of matrine on myocardial infarction in hypercholesterolemia rats was due to its ability to decrease the total serum cholesterol and triglycerin level, to enhance the activities of anti-oxidative enzymes, and to maintain the stability of myocardial cellular membranes [14] (Fig. 1). FIG. 1. Chemical structure of matrine. Since no report is available about the effect of 1 This work was supported by the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in Universities of the Ministry of Education of China (NCET ), Ningxia Natural Science Foundation (NZ0782), and Ningxia Academic Scientific Research Program ( ). 2 Correspondence should be addressed to Professor Gui-Dong DAI, Fax: Tel: daiguidong@163.com Biographical note of the first author: Jie ZHENG, female, born in 1976, MS, majoring in cardiovascular pharmacology zhengjie@163.com /2009 CN /Q Copyright 2009 by China CDC 327
2 328 ZHENG ET AL. matrine on vasomotion, the present study aims to investigate the relaxant effects of matrine on vascular smooth muscle in order to gain insights into its mode of action. Animals MATERIAL AND METHODS Guinea pigs, weighing 250±30 g, were supplied by the Animal Center of Ningxia Medical University (Ningxia, China). The animals were housed individually in cages under hygienic conditions in a 12 h light and dark cycle at 22±3 and 45%±10% humidity, with free access to standard rat diet and water. The study was approved by the Animal Center of Ningxia Medical University. Reagents Matrine with a purity>99% was purchased from Ningxia Bauhinia Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Glibenclamide, tetraethylammonium, and acetylcholine were purchased from Sigma Chemical Co. Phenylephrine was purchased from Shanghai Harvest Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and propranolol from Changzhou Siyao Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Glibenclamide was initially dissolved in dimethyl sulphoxide and further diluted in Krebs solution to the proper final concentration. The final concentration of dimethyl sulphoxide in the solution did not exceed 0.1%. Matrine, tetraethylammonium, acetylcholine, phenylephrine, and propranolol were dissolved in Krebs solution. Experimental Protocols Guinea pigs were sacrificed by a blow on the back of head followed by exsanguination under running water. The thoracic aorta was rapidly isolated and cleaned from adherent connective tissues. When endothelium-denuded tissue was used, the endothelial lining was mechanically removed by gently rubbing against a syringe needle. Then the thoracic aorta was cut into 3-4 mm long rings. Several rings cut from the same artery were studied in parallel. The rings were suspended between two stainless steel L-shaped hooks in a 10 ml organ chamber containing warmed (37 ) and oxygenated (95% O2 and 5% CO 2 ) Krebs solution. The Krebs solution contained the following compositions (in mmol/l): NaCl, 25.5 NaHCO 3, 4.3 KCl, 1.2 KH 2 PO 4, 1.2 MgSO 4, 2.5 CaCl 2, and 11.0 glucose. One hook was fixed at the organ bath while the other was connected to a force transducer. Rings were equilibrated for 60 min under 2 g of resting tension. During this time, the rings were washed with Krebs solution every 15 min. The tension of rings was continuously monitored by Chengdu Taimen BL-420E+Data Acquisition & Analysis System (Chengdu, China) and recorded on computer. At the end of a 60-min equilibration period, the viabilities of vessel specimens were checked with phenylephrine (10-5 mol/l), and preparations developing a tension less than 1 g were discarded [15]. The absence of endothelium was assessed prior to experiment by treating a phenylephrine-precontracted aortic ring with acetylcholine (10-5 mol/l). Rings giving a 10% reduction in phenylephrine-induced tone when treated with acetylcholine were regarded as being endothelium-denuded [16]. Examination of Effect of Matrine on Vasoconstrictions with Phenylephrine or Potassium Chloride The isolated aortic rings were exposed to matrine ( mol/l) or the Krebs solution for 15 min. Phenylephrine ( mol/l) or potassium chloride ( mol/l) was cumulatively added into the organ bath at a min interval. The effect of matrine on isolated aortic rings was always detected in parallel. Relaxant Effect of Matrine on Vascular Smooth Muscle of Aortic Rings The experiment was performed to evaluate the effect of matrine on guinea pig aortic rings precontracted submaximally (70%-80%) with contractile agents, phenylephrine (10-5 mol/l) and potassium chloride ( mol/l) acting by different mechanisms. Increasing concentrations of matrine ( mol/l) were administered cumulatively at 4-7 min interval when the contractions to phenylephrine or potassium chloride reached a plateau. Examination of Effect of Gilbenclamide, Tetraethylammonium and Propranolol Pretreatments on Matrine-induced Vasorelaxation The aortic rings were incubated with gilbenclamide (10-5 mol/l), tetraethylammonium chloride (10-3 mol/l) and propranolol (10-5 mol/l) for 30 min or 15 min before phenylephrine (10-5 mol/l) was administered. The role of K + channel and β-antagonist activation in matrine-induced vasorelaxation was evaluated. Examination of Effect of Matrine on Calcium Flux Four aortic rings, taken from the same animal, were separately put into a 10 ml tissue bath as previously described [16-17]. Two preparations were washed with modified Krebs solution, into which calcium was omitted and mol/l EDTA was
3 MATRINE ON AORTIC SMOOTH MUSCLES 329 added (calcium-free). The other two preparations were washed with normal Krebs solution. After 10- min incubation, submaximal contractions to phenylephrine (10-5 mol/l) (C1) occurred in the four preparations. When the contractions reached their peak, the preparations were washed three times with normal Krebs solution and incubated for 10 min. Matrine ( mol/l) was then added into one of the calcium-free and normal preparations for 10 min and vehicle was added into the control before the second transient contraction was evoked by phenylephrine (C2) (Fig. 4A). A ratio of the responses to phenylephrine was obtained ((C2/C1) 100%) (Fig. 4B). Statistical Analysis Data were expressed as x ± s. Statistical analysis was performed with ANOVA. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS Effect of Matrine on Cumulative Concentrationresponse Curve for Phenylephrine or Potassium Chloride After pretreatment with matrine ( mol/l), the concentration-response curve for phenylephrine was shifted rightward and the maximal rate of inhibition was reduced to 77.45%, whereas the concentration-response curve for potassium chloride was shifted otherwise and the maximal rate of inhibition remained unreduced (Fig. 2). Effect of Matrine on Vascular Smooth Muscle of Aortic Rings Matrine ( mol/l) relaxed the vascular smooth muscle of aortic rings in a concentration-dependent manner. The maximal relaxation induced by matrine was 58.3%. However, matrine ( mol/l) had no dilatation-effect on aortic rings (Fig. 3A). Effect of Cumulative Concentration-response Curves for Gilbenclamide, Tetraethylammonium, and Propranolol on Matrine-induced Relaxation The incubation of aortic rings with highly selective ATP-dependent K + channel blocker glibenclamide, non-selective K + channel blocker tetraethylammonium and β-antagonist propranolol failed to modify the relaxant effect of matrine ( mol/l). The maximal relaxation values for glibenclamide, tetraethylammonium, and propranolol was 56.3%±7.8%, 54.6%±6.3%, and 59.1%±11.8%, respectively (Fig. 3B-D). Effect of Matrine on Phenylephrine-induced Contractions in Ca 2+ -free and Normal Ca 2+ Medium Matrine ( mol/l) significantly decreased the phenylephrine-induced contractions in both normal and Ca 2+ -free Krebs solutions. The ratios were 57.9%±30% (n=8) and 36.7%±17% (n=8), as compared with their controls (110.1%±24.6% vs 83.2%±27.1%, Fig. 4B). DISCUSSION In the present study, matrine pretreatment shifted the concentration-response curve for phenylephrine rightward, but exerted no effect on the concentration-response curve for potassium chloride. Additionally, matrine relaxed the vascular smooth muscle of aortic rings in a concentration-dependent manner. It is well known that the cellular mechanism of contraction involved in response to potassium FIG. 2. Effect of matrine on aortic smooth muscle contraction curves for potassium chloride (A) and phenylephrine (B). The data are represented as x ± s (n=8). * P<0.05, ** P<0.01 vs control.
4 330 ZHENG ET AL. FIG. 3. Effects of matrine on aortic smooth muscle contractions induced phenylephrine and potassium chloride (A), glibenclamide (B), tetraethylammonium (C), and propranolol (D). The data are shown as x ± s, ** P<0.01 vs control. FIG. 4. Effect of matrine on phenylephrine-induced aortic smooth muscle contractions in experimental protocol (A) and in normal calcium and calcium-free Krebs solutions (B). Vertical bars represent x ± s, ** P<0.01 vs control.
5 MATRINE ON AORTIC SMOOTH MUSCLES 331 chloride and phenylephrine is different. Since potassium chloride-induced contraction results from the influx of Ca 2+ on membrane, the smooth muscle will be depolarized in high external K +, thereby opening voltage-dependent Ca 2+ channels, with the potassium equilibrium potential shifted and the influx of calcium leading contractions [17-19]. The increased vascular tone caused by addition of phenylephrine to guinea-pig aortic rings is due to the activation of α 1 -adrenoceptors [17,20]. Since matrine has been found to have direct and selective antagonizing effects on α-adrenoceptors, we examined phenylephrineinduced contractions of smooth muscle of aortic rings. Calcium signaling is an important factor for vascular tone and contractility [21-22]. It has been reported that phenylephrine-induced aortic smooth muscle contraction is due to the activation of α 1 -adrenoceptors leading to intracellular calcium release via the activation of inositol phosphate cascade and extracellular calcium influx via the receptor-operated Ca 2+ channels, and that contractions to phenylephrine in a normal calcium bathing medium are dependent upon intracellular and extracellular calcium mobilization, whereas, in calcium free conditions, the response to phenylephrine is attributed to intracellular calcium [16-17]. The important finding of the present study is that matrine significantly decreases phenylephrine-induced contractions in both normal and Ca 2+ -free Krebs solutions, suggesting that it inhibits phenylephrine-induced contractions by interfering with both the release of intracellular Ca 2+ and the influx of extracellular Ca 2+. In this study, we used different inhibitors to determine the mechanism of matrine s relaxation of smooth muscle or aortic rings in guinea pigs. The cardiovascular system is widely innervated by sympathetic sensory nerves and their receptors. Stimulation of α 1 receptors characteristically produces vasoconstriction and increases peripheral resistance and blood pressure [23]. Conversely, stimulation of β 2 receptors characteristically produces vasodilatation [24]. In order to test the contribution of β 2 -adrenoceptors to the concentration-dependent matrine-induced vasorelaxation of the guinea-pig aortic smooth muscles, propranolol, a β-adrenergic antagonist, has been used [24-26]. In the present study, propranolol did not inhibit the relaxation of guinea-pig aortic smooth muscles, demonstrating that β 2 -adrenoceptor mediated vaso-relaxation was not involved in the pathway. Activation of K + channels plays an essential role in the regulation of vascular smooth muscles [15,17]. Opening of K + channels leads to dilation of vascular smooth muscles by hyperpolarizing the membrane [15]. In the present study, glibenclamide and tetraethylammonium were used respectively to analyze whether K + channels mediate relaxation of matrine-evoked guinea-pig aortic smooth muscle. Glibenclamide is a highly selective inhibitor of ATP-sensitive K + channels [27-28]. In our study, glibenclamide pretreatment did not inhibit the relaxant effects of matrine on guinea-pig aortic smooth muscles. As a non-selective K + channel inhibitor, tetraethylammonium can block most K + channels [27]. The concentration of tetraethylammonium used in the present study was sufficient to block K + channels, which is consistent with the reported findings [25], but actually the relaxation of aortic smooth muscles induced by matrine was not affected at such a concentration, which suggested that K + channels might not be involved in matrine-induced relaxation of the aortic muscle of guinea pigs. In conclusion, matrine can inhibit phenylephrineinduced contractions by interfering with the release of intracellular Ca 2+ and the influx of extracellular Ca 2+ by blocking α 1 receptor. REFERENCES 1. Xing H B, Liu S F (1987). Effects of matrine on myocardial contraction and arrhythmia in isolated heart atria. Acta Pharmacol Sin 8(6), Shan H, Yang B, Zhou Y, et al. (2004). Effects of matrine on aconitine-induced electrophysiological changes in rat ventricular myocytes. J Chin Pharmaceut Sci 13(3), Huang C, Xie S, Huang S, Gao G (2002). Experimental studies of antiarrhythmic effects of matrine. J Dalian Med Univer 24(3), (In Chinese). 4. Zhang B H, Wang N S, Li X J, et al. (1990). Anti-arrhythmic effects of matrine. Acta Pharmacol Sin 11(3), Zhou Y, Xu C, Shan H, et al. (2007). Inhibition of matrine on potassium currents in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. J Pharmacol Toxicol 21(3), (In Chinese) 6. Xie H, Wen H, Gao Y, et al. (2004). Effects of matrine on action potentials and contractile force in guinea pig papillary muscles. Pharmacol Bull 20(2), (In Chinese) 7. Yang B, Li B, Zhou Y, et al. (2004). Inhibitory effects of matrine, E-4031, dofetilide and RP58866 on inward rectifier potassium current in rabbit ventricular myocytes. J Pharmacol Toxicol 18(6), (In Chinese) 8. Ai J, Gao H, He S, et al. (2001). Effects of matrine, artemisinin, and tetrandrine on cytosolic [Ca 2+ ] i in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Acta Pharmacol Sin 22(6), Ai J, Gao H, Wang Y (2000). Effects of matrine on in single guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J Harbin Med Univer 34(4), (In Chinese) 10. Ruan C, He Z, Jin C, et al. (2002). Effect of matrine on norepinephrine-induced hypertrophy and expression of myosin heavy chain genes in cultured rat cardiomyocytes. J Clin Cardiol 18(4), (In Chinese) 11. Wu K, Ouyang J, Wang B, et al. (2003). Influence of matrine on the preliferation and collagen synthesis of cultured neonatal rat cardiac fibroblast stimulated by angiotensin II. Med J Wuhan Univer 24(3), (In Chinese)
6 332 ZHENG ET AL. 12. He L, Li Y, Yang L, et al. (1999). Function of matrine to Ang II-induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cell and changes of ultrastructure. Acta Universit Trad Med Sin Pharmacol Shanghai 13(4), (In Chinese) 13. Li Y, He L, Yang L, et al. (2000). Intervention of matrine on calcium overload in Ang II-induced vascular smooth muscle cells. Acta Universit Trad Med Sin Pharmacol Shanghai 14(1), (In Chinese) 14. Yang C, Zheng P, Wang X, et al. (2008). Cardioprotective effect of matrine on myocardial ischemia in hypercholesterolemia rats. Trad Herb Drug 39(6), (In Chinese) 15. Soares P M, Lima R F, de Freitas Pires A, et al. (2007). Effects of anethole and structural analogues on the contractility of rat isolated aorta: Involvement of voltage-dependent Ca 2+ -channels. Life Sci 81(13), Ford W R, Broadley K J (1999). Effects of adenosine receptor agonists on induction of contractions to phenylephrine of guinea-pig aorta mediated via intra- or extracellular calcium. Gen Pharmacol 33(2), Chen C X, Kwan C Y (2001). Endothelium-independent vasorelaxation by leonurine, a plant alkaloid purified from Chinese motherwort. Life Sci 68(8), Chan S S, Cheng T Y, Lin G (2007). Relaxation effects of ligustilide and senkyunolide A, two main constituents of Ligusticum chuanxiong, in rat isolated aorta. J Ethnopharmacol 111(3), Tammaro P, Smith A L, Hutchings S R, et al. (2004). Pharmacological evidence for a key role of voltage-gated K + channels in the function of rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Br J Pharmacol 143(2), van Breemen C, Saida K (1989). Cellular mechanisms regulating [Ca 2+ ] i smooth muscle. Annu Rev Physiol 51, Akata, T (2007). Cellular and molecular mechanisms regulating vascular tone. Part 1: basic mechanisms controlling cytosolic Ca 2+ concentration and the Ca 2+ -dependent regulation of vascular tone. J Anesth 21(2), Akata T (2007). Cellular and molecular mechanisms regulating vascular tone. Part 2: regulatory mechanisms modulating Ca 2+ mobilization and/or myofilament Ca 2+ sensitivity in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Anesth 21(2), Graham R M, Perez D M, Hwa J, et al. (1996). Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes. Molecular structure, function, and signaling. Circ Res 78(5), O'Rourke S T (2007). Antianginal actions of Beta-adrenoceptor antagonists. Am J Pharm Educ 71(5), Yanaga A, Goto H, Nakagawa T, et al. (2006). Cinnamaldehyde induces endothelium-dependent and independent vasorelaxant action on isolated rat aorta. Aorta Biol Pharm Bull 29(12), Bernstein D, Fajardo G, Zhao M, et al. (2005). Differential cardioprotective/cardiotoxic effects mediated by beta-adrenergic receptor subtypes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 289(6), Sönmez Uydeş-Doğan B, Topal G, Takir S, et al. (2005). Relaxant effects of pravastatin, atorvastatin and cerivastatin on isolated rat aortic rings. Life Sci 76(15), Kinoshita H, Ishikawa T, Hatano Y (2000). Role of K + channels in augmented relaxations to sodium nitroprusside induced by mexiletine in rat aortas. Anesthesiology 92(3), (Received December 20, 2008 Accepted May 26, 2009)
Relaxation responses of aortic rings from salt-loaded high calcium fed rats to potassium chloride, calcium chloride and magnesium sulphate
 Pathophysiology 4 (1998) 275 280 Relaxation responses of aortic rings from salt-loaded high calcium fed rats to potassium chloride, calcium chloride and magnesium sulphate B.J. Adegunloye, O.A. Sofola
Pathophysiology 4 (1998) 275 280 Relaxation responses of aortic rings from salt-loaded high calcium fed rats to potassium chloride, calcium chloride and magnesium sulphate B.J. Adegunloye, O.A. Sofola
This laboratory exercise uses a simple preparation and a straightforward
 LABORATORY DEMONSTRATION OF VASCULAR SMOOTH MUSCLE FUNCTION USING RAT AORTIC RING SEGMENTS Rayna J. Gonzales, Rebecca W. Carter, and Nancy L. Kanagy Vascular Physiology Group, Department of Cell Biology
LABORATORY DEMONSTRATION OF VASCULAR SMOOTH MUSCLE FUNCTION USING RAT AORTIC RING SEGMENTS Rayna J. Gonzales, Rebecca W. Carter, and Nancy L. Kanagy Vascular Physiology Group, Department of Cell Biology
Effect of ageing on ƒ 1A-adrenoceptor mechanisms in rabbit. Issei TAKAYANAGI, Mann MORIYA and Katsuo KOIKE
 J. Smooth Muscle Res. 28: 63-68, 1992. Effect of ageing on ƒ 1A-adrenoceptor mechanisms in rabbit isolated bronchial preparations Issei TAKAYANAGI, Mann MORIYA and Katsuo KOIKE Department of Chemical Pharmacology,
J. Smooth Muscle Res. 28: 63-68, 1992. Effect of ageing on ƒ 1A-adrenoceptor mechanisms in rabbit isolated bronchial preparations Issei TAKAYANAGI, Mann MORIYA and Katsuo KOIKE Department of Chemical Pharmacology,
Hawthorn Extract - Viable Treatment for Cardiovascular Disease or Unscrupulous Herbal Supplement?
 Grand Valley State University ScholarWorks@GVSU Student Summer Scholars Undergraduate Research and Creative Practice 2010 Hawthorn Extract - Viable Treatment for Cardiovascular Disease or Unscrupulous
Grand Valley State University ScholarWorks@GVSU Student Summer Scholars Undergraduate Research and Creative Practice 2010 Hawthorn Extract - Viable Treatment for Cardiovascular Disease or Unscrupulous
Effects of Total Alkaloids in Buxus microphylla Leaves on Aorta Smooth Muscle of Rats and Their Mechanisms
 136 Zhang HQ et al. Chinese Herbal Medicines, 212, 4(2): 136-141 Effects of Total Alkaloids in Buxus microphylla Leaves on Aorta Smooth Muscle of Rats and Their Mechanisms ZHANG Hui-qin 1, LIU Yan-yan
136 Zhang HQ et al. Chinese Herbal Medicines, 212, 4(2): 136-141 Effects of Total Alkaloids in Buxus microphylla Leaves on Aorta Smooth Muscle of Rats and Their Mechanisms ZHANG Hui-qin 1, LIU Yan-yan
Mechanisms of simvastatin-induced vasodilatation of rat superior mesenteric arteries
 BIOMEDICAL REPORTS 5: 491-496, 2016 Mechanisms of simvastatin-induced vasodilatation of rat superior mesenteric arteries YULONG CHEN 1,2*, HONGMEI ZHANG 3*, HUANHUAN LIU 2 and AILAN CAO 1,4 1 Shaanxi Pharmaceutical
BIOMEDICAL REPORTS 5: 491-496, 2016 Mechanisms of simvastatin-induced vasodilatation of rat superior mesenteric arteries YULONG CHEN 1,2*, HONGMEI ZHANG 3*, HUANHUAN LIU 2 and AILAN CAO 1,4 1 Shaanxi Pharmaceutical
Assessment of pro-arrhythmic effects using Pluricyte Cardiomyocytes. on the ACEA xcelligence RTCA CardioECR
 Assessment of pro-arrhythmic effects using Pluricyte Cardiomyocytes on the ACEA xcelligence RTCA CardioECR Application Note Version 2.1 / March 2018 Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Assessment of pro-arrhythmic
Assessment of pro-arrhythmic effects using Pluricyte Cardiomyocytes on the ACEA xcelligence RTCA CardioECR Application Note Version 2.1 / March 2018 Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Assessment of pro-arrhythmic
Journal of Ningxia Medical University DMEM F12 GIBCO. 2mm mm 4mm 2mm vitrification group 10mm. 4mm 2mm VG 3
 34 9 2012 9 Journal of Ningxia Medical University 869 1674-6309 2012 09-0869 - 03 FSH 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 1. 750004 2. 054000 3. 750001 FSH FSH 20 5mm 4mm 2mm 10mm 4mm 2mm 10μg FSH ml - 1 4. 5h FSH 1 2 -
34 9 2012 9 Journal of Ningxia Medical University 869 1674-6309 2012 09-0869 - 03 FSH 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 1. 750004 2. 054000 3. 750001 FSH FSH 20 5mm 4mm 2mm 10mm 4mm 2mm 10μg FSH ml - 1 4. 5h FSH 1 2 -
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment
 Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Sulfur dioxide relaxes rat aorta by endothelium-dependent and. -independent mechanisms
 Sulfur dioxide relaxes rat aorta by endothelium-dependent and -independent mechanisms Yang-Kai WANG 1 #, An-Jing REN 1 #, Xiang-Qun YANG 1, Li-Gang WANG 1, Wei-Fang RONG 3, Chao-Shu TANG 4, Wen-Jun YUAN
Sulfur dioxide relaxes rat aorta by endothelium-dependent and -independent mechanisms Yang-Kai WANG 1 #, An-Jing REN 1 #, Xiang-Qun YANG 1, Li-Gang WANG 1, Wei-Fang RONG 3, Chao-Shu TANG 4, Wen-Jun YUAN
Arrhythmias. Simple-dysfunction cause abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium.
 Arrhythmias Simple-dysfunction cause abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium. However, in clinic it present as a complex family of disorders that show variety of symptoms, for
Arrhythmias Simple-dysfunction cause abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium. However, in clinic it present as a complex family of disorders that show variety of symptoms, for
Cardiac Drugs: Chapter 9 Worksheet Cardiac Agents. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate.
 Complete the following. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate. 2. drugs affect the force of contraction and can be either positive or negative. 3.
Complete the following. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate. 2. drugs affect the force of contraction and can be either positive or negative. 3.
Differential responses to endothelial dependent relaxation of the thoracic and abdominal aorta from male Sprague-Dawley rats
 Niger. J. Physiol. Sci. 27(December 12) 117 122 www.njps.com.ng Differential responses to endothelial dependent relaxation of the thoracic and abdominal aorta from male Sprague-Dawley rats 1 Oloyo, Ahmed
Niger. J. Physiol. Sci. 27(December 12) 117 122 www.njps.com.ng Differential responses to endothelial dependent relaxation of the thoracic and abdominal aorta from male Sprague-Dawley rats 1 Oloyo, Ahmed
Ncardia. Assessment of pro-arrhythmic effects in Pluricyte Cardiomyocytes. using the Axion BioSystems Maestro TM MEA system
 Ncardia Stem cell experts Assessment of pro-arrhythmic effects in Pluricyte Cardiomyocytes using the Axion BioSystems Maestro TM MEA system Application note Version 2.0 Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Assessment
Ncardia Stem cell experts Assessment of pro-arrhythmic effects in Pluricyte Cardiomyocytes using the Axion BioSystems Maestro TM MEA system Application note Version 2.0 Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Assessment
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents Question No. 1 of 10 1. Vascular smooth muscle contraction is triggered by a rise in. Question #01 (A) Luminal calcium (B) Extracellular calcium (C) Intracellular
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents Question No. 1 of 10 1. Vascular smooth muscle contraction is triggered by a rise in. Question #01 (A) Luminal calcium (B) Extracellular calcium (C) Intracellular
Supplemental Figure I
 Supplemental Figure I Kl ( mmol/l)-induced Force orta M (mn) 1 (mn) 1 Supplemental Figure I. Kl-induced contractions. and, Kl ( mmol/l)-induced contractions of the aorta () and those of mesenteric arteries
Supplemental Figure I Kl ( mmol/l)-induced Force orta M (mn) 1 (mn) 1 Supplemental Figure I. Kl-induced contractions. and, Kl ( mmol/l)-induced contractions of the aorta () and those of mesenteric arteries
Arrhythmias. 1. beat too slowly (sinus bradycardia). Like in heart block
 Arrhythmias It is a simple-dysfunction caused by abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium. The heart is designed in such a way that allows it to generate from the SA node electrical
Arrhythmias It is a simple-dysfunction caused by abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium. The heart is designed in such a way that allows it to generate from the SA node electrical
Fundamentals of Pharmacology for Veterinary Technicians Chapter 8
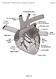 Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
Effect of cocaine on the affinity of a-adrenoceptors for noradrenaline
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 139-143. Effect of cocaine on the affinity of a-adrenoceptors for noradrenaline I. R. INNES AND R. MAILHOT* Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Faculty of Medicine,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 139-143. Effect of cocaine on the affinity of a-adrenoceptors for noradrenaline I. R. INNES AND R. MAILHOT* Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Faculty of Medicine,
In Vivo Animal Models of Heart Disease. Why Animal Models of Disease? Timothy A Hacker, PhD Department of Medicine University of Wisconsin-Madison
 In Vivo Animal Models of Heart Disease Timothy A Hacker, PhD Department of Medicine University of Wisconsin-Madison Why Animal Models of Disease? Heart Failure (HF) Leading cause of morbidity and mortality
In Vivo Animal Models of Heart Disease Timothy A Hacker, PhD Department of Medicine University of Wisconsin-Madison Why Animal Models of Disease? Heart Failure (HF) Leading cause of morbidity and mortality
Histamine Develops Homologous Desensitization under Ca 2+ -free Conditions with Increase in Basal Tone in Smooth Muscle of Guinea Pig Taenia Caeci
 YAKUGAKU ZASSHI 130(3) 451 455 (2010) 2010 The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan 451 Notes Histamine Develops Homologous Desensitization under Ca 2+ -free Conditions with Increase in Basal Tone in Smooth
YAKUGAKU ZASSHI 130(3) 451 455 (2010) 2010 The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan 451 Notes Histamine Develops Homologous Desensitization under Ca 2+ -free Conditions with Increase in Basal Tone in Smooth
The Effects of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) on the Spontaneously Beating Isolated Auricles of the Rabbit Heart
 The Effects of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) on the Spontaneously Beating Isolated Auricles of the Rabbit Heart Pages with reference to book, From 216 To 219 A. Shabbir Ali Bhatti ( Department
The Effects of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) on the Spontaneously Beating Isolated Auricles of the Rabbit Heart Pages with reference to book, From 216 To 219 A. Shabbir Ali Bhatti ( Department
Calcium-dependent mechanisms mediate the vasorelaxant effects of Tridax procumbens
 DOI 1.1515/jbcpp-213-3 J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 214; 25(2): 161 166 Hussein M. Salahdeen, Gbolahan O. Idowu, Omoniyi K. Yemitan, Babatunde A. Murtala and Abdul-Rasak A. Alada Calcium-dependent mechanisms
DOI 1.1515/jbcpp-213-3 J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 214; 25(2): 161 166 Hussein M. Salahdeen, Gbolahan O. Idowu, Omoniyi K. Yemitan, Babatunde A. Murtala and Abdul-Rasak A. Alada Calcium-dependent mechanisms
Circulation. Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications. Venous Return. Arterial flow. Regulation of Cardiac Output.
 Circulation Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications Two systems Pulmonary (low pressure) Systemic (high pressure) Aorta 120 mmhg Large arteries 110 mmhg Arterioles 40 mmhg Arteriolar capillaries
Circulation Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications Two systems Pulmonary (low pressure) Systemic (high pressure) Aorta 120 mmhg Large arteries 110 mmhg Arterioles 40 mmhg Arteriolar capillaries
Drug Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease
 Drug Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine, The University of Jordan November, 2014 Categories of Ischemic Heart Disease Fixed "Stable, Effort Angina Variant
Drug Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine, The University of Jordan November, 2014 Categories of Ischemic Heart Disease Fixed "Stable, Effort Angina Variant
Acta Physiologica Sinica
 , 1999 4, 51 (2), 187 192 187 Acta Physiologica Sinica 3 1998204222 1998206203 3 (No139500052) 3 3, 221002 3 3 3 3 3 (, 200031) ( Ito), 28 d (H28, 6 h/ d), Ito (16118 4161 6132 1135 pa/ pf, P < 0105),
, 1999 4, 51 (2), 187 192 187 Acta Physiologica Sinica 3 1998204222 1998206203 3 (No139500052) 3 3, 221002 3 3 3 3 3 (, 200031) ( Ito), 28 d (H28, 6 h/ d), Ito (16118 4161 6132 1135 pa/ pf, P < 0105),
Electrophysiologic effects of capsaicin on pacemaker cells in sinoatrial nodes of rabbits
 826 2003, Acta Pharmacologica Sinica Chinese Pharmacological Society Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica Chinese Academy of Sciences http://www.chinaphar.com Electrophysiologic effects of capsaicin on
826 2003, Acta Pharmacologica Sinica Chinese Pharmacological Society Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica Chinese Academy of Sciences http://www.chinaphar.com Electrophysiologic effects of capsaicin on
Potassium-Induced Release of Endothelium- Derived Relaxing Factor From Canine Femoral Arteries
 1098 Potassium-Induced Release of Endothelium- Derived Relaxing Factor From Canine Femoral Arteries Gabor M. Rubanyi and Paul M. Vanhoutte Downloaded from http://ahajournals.org by on January 13, 2019
1098 Potassium-Induced Release of Endothelium- Derived Relaxing Factor From Canine Femoral Arteries Gabor M. Rubanyi and Paul M. Vanhoutte Downloaded from http://ahajournals.org by on January 13, 2019
Effects and mechanisms of Fenofibrate on the secretion of vascular endothelial contraction factors in hypertensive rats
 Effects and mechanisms of Fenofibrate on the secretion of vascular endothelial contraction factors in hypertensive rats Y. Zhu 1, H.-S. Wang 1, X.-M. Li 1 and C. Qu 2 1 Department of Cardiac Surgery, General
Effects and mechanisms of Fenofibrate on the secretion of vascular endothelial contraction factors in hypertensive rats Y. Zhu 1, H.-S. Wang 1, X.-M. Li 1 and C. Qu 2 1 Department of Cardiac Surgery, General
HYPERTENSION: Sustained elevation of arterial blood pressure above normal o Systolic 140 mm Hg and/or o Diastolic 90 mm Hg
 Lecture 39 Anti-Hypertensives B-Rod BLOOD PRESSURE: Systolic / Diastolic NORMAL: 120/80 Systolic = measure of pressure as heart is beating Diastolic = measure of pressure while heart is at rest between
Lecture 39 Anti-Hypertensives B-Rod BLOOD PRESSURE: Systolic / Diastolic NORMAL: 120/80 Systolic = measure of pressure as heart is beating Diastolic = measure of pressure while heart is at rest between
Adrenergic regulation of the rapid component of delayed rectifier K+ currents in guinea pig cardiomyocytes
 Original Article Adrenergic regulation of the rapid component of delayed rectifier K+ currents in guinea pig cardiomyocytes en Wang, Xiao-Yan Min, i-i Pang, Jin Qian, Di Xu, Yan Guo Department of Geriatric
Original Article Adrenergic regulation of the rapid component of delayed rectifier K+ currents in guinea pig cardiomyocytes en Wang, Xiao-Yan Min, i-i Pang, Jin Qian, Di Xu, Yan Guo Department of Geriatric
In the name of GOD. Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension
 In the name of GOD Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension 44 Presentation outline: Cardiovascular diseases Acute myocardial infarction Animal models for myocardial
In the name of GOD Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension 44 Presentation outline: Cardiovascular diseases Acute myocardial infarction Animal models for myocardial
10/23/2017. Muscular pump Two atria Two ventricles. In mediastinum of thoracic cavity 2/3 of heart's mass lies left of midline of sternum
 It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
WRITER TRISTAN WALKER TABLE OF CONTENTS. The Basics of cardiac pharmacology 2007
 WRITER TRISTAN WALKER TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. WHAT ARE THE MAJOR CLASSES OF CARDIAC DRUGS?...2 2. HOW DO THEY WORK?...3 3. CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE PEDIATRIC PATIENT...7 4. SUMMARY TABLE...10 REFERENCES...14
WRITER TRISTAN WALKER TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. WHAT ARE THE MAJOR CLASSES OF CARDIAC DRUGS?...2 2. HOW DO THEY WORK?...3 3. CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE PEDIATRIC PATIENT...7 4. SUMMARY TABLE...10 REFERENCES...14
-adrenergic receptor subtypes blockade on the rat myocardium inotropy
 Research Article The effect of -adrenergic receptor subtypes blockade on the rat myocardium inotropy Insaf Ilkhamovich Khabibrakhmanov*, Nafisa Ilgizovna Ziшatdinova, Timur Lvovich Zefirov ABSTRACT Aim:
Research Article The effect of -adrenergic receptor subtypes blockade on the rat myocardium inotropy Insaf Ilkhamovich Khabibrakhmanov*, Nafisa Ilgizovna Ziшatdinova, Timur Lvovich Zefirov ABSTRACT Aim:
Evidence for a Role of Cyclic AMP and Endothelium in Rat Aortic Relaxation
 6 The Open Circulation and Vascular Journal, 2011, 4, 6-11 Open Access Evidence for a Role of Cyclic AMP and Endothelium in Rat Aortic Relaxation Induced by R-PIA Gonzalo Allende* and Salvador Acevedo
6 The Open Circulation and Vascular Journal, 2011, 4, 6-11 Open Access Evidence for a Role of Cyclic AMP and Endothelium in Rat Aortic Relaxation Induced by R-PIA Gonzalo Allende* and Salvador Acevedo
Electrophysiological effects of haloperidol on isolated rabbit Purkinje fibers and guinea pigs papillary muscles under normal and simulated ischemia
 Acta Pharmacol Sin 2007 Aug; 28 (8): 1155 1160 Short communication Electrophysiological effects of haloperidol on isolated rabbit Purkinje fibers and guinea pigs papillary muscles under normal and simulated
Acta Pharmacol Sin 2007 Aug; 28 (8): 1155 1160 Short communication Electrophysiological effects of haloperidol on isolated rabbit Purkinje fibers and guinea pigs papillary muscles under normal and simulated
Relaxation mechanisms of neferine on the rabbit corpus cavernosum tissue in vitro
 Asian J Androl 2007; 9 (6): 795 800 DOI: 10.1111/j.1745-7262.2007.00321.x www.asiaandro.com. Original Article. Relaxation mechanisms of neferine on the rabbit corpus cavernosum tissue in vitro Jun Chen
Asian J Androl 2007; 9 (6): 795 800 DOI: 10.1111/j.1745-7262.2007.00321.x www.asiaandro.com. Original Article. Relaxation mechanisms of neferine on the rabbit corpus cavernosum tissue in vitro Jun Chen
Cardiac Properties MCQ
 Cardiac Properties MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Cardiac Valves: a- Prevent backflow of blood from the ventricles to the atria during
Cardiac Properties MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Cardiac Valves: a- Prevent backflow of blood from the ventricles to the atria during
Effects of Temperature, Stretch, and Various Drug Treatments on the
 Nicole Rodi Bio 235: Animal Physiology Heart Muscle Lab Report 10/24/2014 Effects of Temperature, Stretch, and Various Drug Treatments on the Cardiac Muscle Activity of Rana pipiens Abstract Mechanical
Nicole Rodi Bio 235: Animal Physiology Heart Muscle Lab Report 10/24/2014 Effects of Temperature, Stretch, and Various Drug Treatments on the Cardiac Muscle Activity of Rana pipiens Abstract Mechanical
We also tested the hypothesis that the inhibitory effects of etomidate and ketamine involved a decrease in
 Anesthesiology 2003; 98:104 13 2003 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Inhibitory Effects of Etomidate and Ketamine on Adenosine Triphosphate Sensitive Potassium
Anesthesiology 2003; 98:104 13 2003 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Inhibitory Effects of Etomidate and Ketamine on Adenosine Triphosphate Sensitive Potassium
CKD Satellite Symposium
 CKD Satellite Symposium Recommended Therapy by Heart Failure Stage AHA/ACC Task Force on Practice Guideline 2001 Natural History of Heart Failure Patients surviving % Mechanism of death Sudden death 40%
CKD Satellite Symposium Recommended Therapy by Heart Failure Stage AHA/ACC Task Force on Practice Guideline 2001 Natural History of Heart Failure Patients surviving % Mechanism of death Sudden death 40%
PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE ANOCOCCYGEUS MUSCLE OF
 Br. J. Pharmac. (198). 71, 35-4 PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDY OF TH ANOCOCCYGUS MUSCL OF TH DOG A.R. DHPOUR, M.A. KHOYI, H. KOUTCHKI & M.R. ZARRINDAST Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, University
Br. J. Pharmac. (198). 71, 35-4 PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDY OF TH ANOCOCCYGUS MUSCL OF TH DOG A.R. DHPOUR, M.A. KHOYI, H. KOUTCHKI & M.R. ZARRINDAST Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, University
The Effects of Extracellular Calcium Removal on Sino-atrial Node Cells Treated with Potassium-depleted Solutions
 Short Communication Japanese Journal of Physiology, 36, 403-409, 1986 The Effects of Extracellular Calcium Removal on Sino-atrial Node Cells Treated with Potassium-depleted Solutions Shun-ichi MIYAMAE
Short Communication Japanese Journal of Physiology, 36, 403-409, 1986 The Effects of Extracellular Calcium Removal on Sino-atrial Node Cells Treated with Potassium-depleted Solutions Shun-ichi MIYAMAE
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 11 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Autonomic Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 533 through 552 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words! Work
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 11 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Autonomic Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 533 through 552 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words! Work
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
Chapter 14. Agents used in Cardiac Arrhythmias
 Chapter 14 Agents used in Cardiac Arrhythmias Cardiac arrhythmia Approximately 50% of post-myocardial infarction fatalities result from ventricular tachycarida (VT) or ventricular fibrillation (VF). These
Chapter 14 Agents used in Cardiac Arrhythmias Cardiac arrhythmia Approximately 50% of post-myocardial infarction fatalities result from ventricular tachycarida (VT) or ventricular fibrillation (VF). These
11/10/2014. Muscular pump Two atria Two ventricles. In mediastinum of thoracic cavity 2/3 of heart's mass lies left of midline of sternum
 It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(3): Research Article. Partial agonistic property of new isolated natural compounds
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(3):1294-1298 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Partial agonistic property of new isolated natural
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(3):1294-1298 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Partial agonistic property of new isolated natural
Structure and organization of blood vessels
 The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
Cardiovascular Physiology. Heart Physiology. Introduction. The heart. Electrophysiology of the heart
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology Introduction The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and two vascular systems, the systemic and pulmonary circulations. The heart pumps blood through
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology Introduction The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and two vascular systems, the systemic and pulmonary circulations. The heart pumps blood through
Equivalent Cardioprotection Induced by Ischemic and Hypoxic Preconditioning
 Original Cardiovascular 229 Equivalent Cardioprotection Induced by Ischemic and Hypoxic Preconditioning Xujin Xiang 1 Haixia Lin 2 Jin Liu 1 Zeyan Duan 1 1 Department of Anesthesiology, West China Hospital,
Original Cardiovascular 229 Equivalent Cardioprotection Induced by Ischemic and Hypoxic Preconditioning Xujin Xiang 1 Haixia Lin 2 Jin Liu 1 Zeyan Duan 1 1 Department of Anesthesiology, West China Hospital,
Role of Ion Fluxes in Hydrogen Peroxide Pulmonary Vasoconstriction
 Physiol. Res. 44: 31-3 7, 1995 Role of Ion Fluxes in Hydrogen Peroxide Pulmonary Vasoconstriction J. W ILHELM, J. H E R G E T 1 Department of Medical Chemistry and Biochemistry and department of Physiology,
Physiol. Res. 44: 31-3 7, 1995 Role of Ion Fluxes in Hydrogen Peroxide Pulmonary Vasoconstriction J. W ILHELM, J. H E R G E T 1 Department of Medical Chemistry and Biochemistry and department of Physiology,
Drug Receptor Interactions and Pharmacodynamics
 Drug Receptor Interactions and Pharmacodynamics Dr. Raz Mohammed MSc Pharmacology School of Pharmacy 22.10.2017 Lec 6 Pharmacodynamics definition Pharmacodynamics describes the actions of a drug on the
Drug Receptor Interactions and Pharmacodynamics Dr. Raz Mohammed MSc Pharmacology School of Pharmacy 22.10.2017 Lec 6 Pharmacodynamics definition Pharmacodynamics describes the actions of a drug on the
Peptides-Derived from Thai Rice Bran Improve Hemodynamics and Induce Vasorelaxation in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats
 Peptides-Derived from Thai Rice Bran Improve Hemodynamics and Induce Vasorelaxation in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats Orachorn Boonla 1, Phattharaphon Tuangpolkrung 1, Poungrat Pakdeechote 1, Upa Kukongviriyapan
Peptides-Derived from Thai Rice Bran Improve Hemodynamics and Induce Vasorelaxation in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats Orachorn Boonla 1, Phattharaphon Tuangpolkrung 1, Poungrat Pakdeechote 1, Upa Kukongviriyapan
Chronotropic and Inotropic Effects of 3 Kinds of Alpha-Adrenergic Blockers on the Isolated Dog Atria
 Chronotropic and Inotropic Effects of 3 Kinds of Alpha-Adrenergic Blockers on the Isolated Dog Atria Shigetoshi CHIBA, M.D., Yasuyuki FURUKAWA, M.D., and Hidehiko WATANABE, M.D. SUMMARY Using the isolated
Chronotropic and Inotropic Effects of 3 Kinds of Alpha-Adrenergic Blockers on the Isolated Dog Atria Shigetoshi CHIBA, M.D., Yasuyuki FURUKAWA, M.D., and Hidehiko WATANABE, M.D. SUMMARY Using the isolated
*Generating blood pressure *Routing blood: separates. *Ensuring one-way blood. *Regulating blood supply *Changes in contraction
 *Generating blood pressure *Routing blood: separates pulmonary and systemic circulations *Ensuring one-way blood flow: valves *Regulating blood supply *Changes in contraction rate and force match blood
*Generating blood pressure *Routing blood: separates pulmonary and systemic circulations *Ensuring one-way blood flow: valves *Regulating blood supply *Changes in contraction rate and force match blood
Inhibition of ATP-sensitive potassium channels attenuates propofol-induced vasorelaxation
 Inhibition of ATP-sensitive potassium channels attenuates propofol-induced vasorelaxation Chen-Fuh Lam, Pei-Jung Chang, Yung-An Chen, Chin-Yi Yeh and Yu-Chuan Tsai Propofol (2,6-diisopropylphenol) is an
Inhibition of ATP-sensitive potassium channels attenuates propofol-induced vasorelaxation Chen-Fuh Lam, Pei-Jung Chang, Yung-An Chen, Chin-Yi Yeh and Yu-Chuan Tsai Propofol (2,6-diisopropylphenol) is an
1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias
 1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias Only need to know drugs discussed in class At the end of this section you should
1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias Only need to know drugs discussed in class At the end of this section you should
The dihydropyridine class of calcium channel. 1975; Fleckenstein, 1983). In contrast to the dihydropyridine
 Br. J. Pharmacol. (1988), 93, 994-14 Pressor responses induced by Bay K 8644 involve both release of adrenal catecholamines and calcium channel activation 'Suzanne Moreland, Mary P. Ushay, *S. David Kimball,
Br. J. Pharmacol. (1988), 93, 994-14 Pressor responses induced by Bay K 8644 involve both release of adrenal catecholamines and calcium channel activation 'Suzanne Moreland, Mary P. Ushay, *S. David Kimball,
The dynamic regulation of blood vessel caliber
 INVITED BASIC SCIENCE REVIEW The dynamic regulation of blood vessel caliber Colleen M. Brophy, MD, Augusta, Ga BACKGROUND The flow of blood to organs is regulated by changes in the diameter of the blood
INVITED BASIC SCIENCE REVIEW The dynamic regulation of blood vessel caliber Colleen M. Brophy, MD, Augusta, Ga BACKGROUND The flow of blood to organs is regulated by changes in the diameter of the blood
Previous experimental evidence indicates that some cardiovascular
 Report Downloaded from http://circres.ahajournals.org/ by guest on July 1, 2018 Autocrine Stimulation of Cardiac Na -Ca 2 Exchanger Currents by Endogenous Endothelin Released by Angiotensin II Ernesto
Report Downloaded from http://circres.ahajournals.org/ by guest on July 1, 2018 Autocrine Stimulation of Cardiac Na -Ca 2 Exchanger Currents by Endogenous Endothelin Released by Angiotensin II Ernesto
ANTI - ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS
 ANTI - ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS CARDIAC ACTION POTENTIAL K Out Balance Ca in/k out Na in K Out GENERATION OF ARRHYTHMIAS Four mechanisms of arrhythmia generation; Increased normal automaticity Abnormal automaticity
ANTI - ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS CARDIAC ACTION POTENTIAL K Out Balance Ca in/k out Na in K Out GENERATION OF ARRHYTHMIAS Four mechanisms of arrhythmia generation; Increased normal automaticity Abnormal automaticity
High Ca Content of Pacemaker Tissues in the Frog Heart
 Short Communication Japanese Journal of Physiology, 34, 1117-1121,1984 High Ca Content of Pacemaker Tissues in the Frog Heart Yasuichiro FUKUDA Department of Physiology II, School of Medicine, Chiba University,
Short Communication Japanese Journal of Physiology, 34, 1117-1121,1984 High Ca Content of Pacemaker Tissues in the Frog Heart Yasuichiro FUKUDA Department of Physiology II, School of Medicine, Chiba University,
Diphasic Effects of Astragalus membranaceus BUNGE (Leguminosae) on Vascular Tone in Rat Thoracic Aorta
 1450 Biol. Pharm. Bull. 28(8) 1450 1454 (2005) Vol. 28, No. 8 Diphasic Effects of Astragalus membranaceus BUNGE (Leguminosae) on Vascular Tone in Rat Thoracic Aorta Bi-Qi ZHANG, a Shen-Jiang HU,*,a,d Li-Hong
1450 Biol. Pharm. Bull. 28(8) 1450 1454 (2005) Vol. 28, No. 8 Diphasic Effects of Astragalus membranaceus BUNGE (Leguminosae) on Vascular Tone in Rat Thoracic Aorta Bi-Qi ZHANG, a Shen-Jiang HU,*,a,d Li-Hong
Hypertension. Penny Mosley MRPharmS
 Hypertension Penny Mosley MRPharmS Outline of presentation Introduction to hypertension Physiological control of arterial blood pressure What determines our bp? What determines the heart rate? What determines
Hypertension Penny Mosley MRPharmS Outline of presentation Introduction to hypertension Physiological control of arterial blood pressure What determines our bp? What determines the heart rate? What determines
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 CARDIAC MYOCYTE PHYSIOLOGY [CARDIOLOGY]
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 CARDIAC MYOCYTE PHYSIOLOGY [CARDIOLOGY] QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 CARDIAC MYOCYTE PHYSIOLOGY [CARDIOLOGY]](/thumbs/96/126998162.jpg) QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 CARDIAC MYOCYTE PHYSIOLOGY [CARDIOLOGY] Learning Objectives: Describe the ionic basis of action potentials in cardiac contractile and autorhythmic cells Explain the relationship
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 CARDIAC MYOCYTE PHYSIOLOGY [CARDIOLOGY] Learning Objectives: Describe the ionic basis of action potentials in cardiac contractile and autorhythmic cells Explain the relationship
Drug Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease
 Drug Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan November, 2017 Categories of Ischemic Heart Disease Fixed "Stable, Effort Angina Variant
Drug Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan November, 2017 Categories of Ischemic Heart Disease Fixed "Stable, Effort Angina Variant
Receptors Families. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Receptors Families Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Receptor Families 1. Ligand-gated ion channels 2. G protein coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-linked
Receptors Families Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Receptor Families 1. Ligand-gated ion channels 2. G protein coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-linked
Where are the normal pacemaker and the backup pacemakers of the heart located?
 CASE 9 A 68-year-old woman presents to the emergency center with shortness of breath, light-headedness, and chest pain described as being like an elephant sitting on her chest. She is diagnosed with a
CASE 9 A 68-year-old woman presents to the emergency center with shortness of breath, light-headedness, and chest pain described as being like an elephant sitting on her chest. She is diagnosed with a
RAPID COMMUNICATION. Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension
 Physiol. Res. 40:367-371,1991 RAPID COMMUNICATION Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension V. HAMPL, J. HERGET Department of Physiology, 2nd Medical School,
Physiol. Res. 40:367-371,1991 RAPID COMMUNICATION Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension V. HAMPL, J. HERGET Department of Physiology, 2nd Medical School,
The effect of L-arginine on guinea-pig and rabbit airway smooth muscle function in vitro
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1998) 31: 811-818 L-arginine on airway smooth muscle ISSN -879X 811 The effect of L-arginine on guinea-pig and rabbit airway smooth muscle function
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1998) 31: 811-818 L-arginine on airway smooth muscle ISSN -879X 811 The effect of L-arginine on guinea-pig and rabbit airway smooth muscle function
Mr. Eknath Kole M.S. Pharm (NIPER Mohali)
 M.S. Pharm (NIPER Mohali) Drug Class Actions Therapeutic Uses Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Other Quinidine IA -Binds to open and inactivated Na+ -Decreases the slope of Phase 4 spontaneous depolarization
M.S. Pharm (NIPER Mohali) Drug Class Actions Therapeutic Uses Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Other Quinidine IA -Binds to open and inactivated Na+ -Decreases the slope of Phase 4 spontaneous depolarization
Feasibility of Leadless Cardiac Pacing Using Injectable. Magnetic Microparticles
 Supplementary Information for Feasibility of Leadless Cardiac Pacing Using Injectable Magnetic Microparticles Menahem Y. Rotenberg, Hovav Gabay, Yoram Etzion and Smadar Cohen. Correspondence to: scohen@bgu.ac.il,
Supplementary Information for Feasibility of Leadless Cardiac Pacing Using Injectable Magnetic Microparticles Menahem Y. Rotenberg, Hovav Gabay, Yoram Etzion and Smadar Cohen. Correspondence to: scohen@bgu.ac.il,
Different Effects of Verapamil on Cytosolic Ca 2+ and Contraction in Norepinephrine-Stimulated Vascular Smooth Muscle
 Japan. J. Pharmacol. 55, 35-42 (1991) Different Effects of Verapamil on Cytosolic Ca 2+ and Contraction in Norepinephrine-Stimulated Vascular Smooth Muscle Hideaki Karaki, Koichi Sato and Hiroshi Ozaki
Japan. J. Pharmacol. 55, 35-42 (1991) Different Effects of Verapamil on Cytosolic Ca 2+ and Contraction in Norepinephrine-Stimulated Vascular Smooth Muscle Hideaki Karaki, Koichi Sato and Hiroshi Ozaki
Assessment of pro-arrhythmic effects using Pluricyte Cardiomyocytes on the ACEA xcelligence RTCA CardioECR
 Assessment of pro-arrhythmic effects using Pluricyte Cardiomyocytes on the ACEA xcelligence RTCA CardioECR Version 1.2 CONTENTS Getting started... 3 Technical support and training... 3 1. Introduction...
Assessment of pro-arrhythmic effects using Pluricyte Cardiomyocytes on the ACEA xcelligence RTCA CardioECR Version 1.2 CONTENTS Getting started... 3 Technical support and training... 3 1. Introduction...
1. Cardiomyocytes and nonmyocyte. 2. Extracellular Matrix 3. Vessels שאלה 1. Pathobiology of Heart Failure Molecular and Cellular Mechanism
 Pathobiology of Heart Failure Molecular and Cellular Mechanism Jonathan Leor Neufeld Cardiac Research Institute Tel-Aviv University Sheba Medical Center, Tel-Hashomer שאלה 1 התא הנפוץ ביותר (75%~) בלב
Pathobiology of Heart Failure Molecular and Cellular Mechanism Jonathan Leor Neufeld Cardiac Research Institute Tel-Aviv University Sheba Medical Center, Tel-Hashomer שאלה 1 התא הנפוץ ביותר (75%~) בלב
PHYSIOLOGY MeQ'S (Morgan) All the following statements related to blood volume are correct except for: 5 A. Blood volume is about 5 litres. B.
 PHYSIOLOGY MeQ'S (Morgan) Chapter 5 All the following statements related to capillary Starling's forces are correct except for: 1 A. Hydrostatic pressure at arterial end is greater than at venous end.
PHYSIOLOGY MeQ'S (Morgan) Chapter 5 All the following statements related to capillary Starling's forces are correct except for: 1 A. Hydrostatic pressure at arterial end is greater than at venous end.
Ginkgo biloba extract postconditioning reduces myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury
 Ginkgo biloba extract postconditioning reduces myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury K. Ran 1, D.-L. Yang 1, Y.-T. Chang 1, K.-M. Duan 2, Y.-W. Ou 2, H.-P. Wang 3 and Z.-J. Li 1 1 Department of Anesthesiology,
Ginkgo biloba extract postconditioning reduces myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury K. Ran 1, D.-L. Yang 1, Y.-T. Chang 1, K.-M. Duan 2, Y.-W. Ou 2, H.-P. Wang 3 and Z.-J. Li 1 1 Department of Anesthesiology,
Chapter 9. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Cardiac Arrhythmias. Define electrical therapy
 Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
hypoxic pulmonary hypertension
 Br. J. Pharmacol. (1992), 17, 47-413 '." Macmillan Press Ltd, 1992 Reduced relaxant potency of nitroprusside on pulmonary artery preparations taken from rats during the development of hypoxic pulmonary
Br. J. Pharmacol. (1992), 17, 47-413 '." Macmillan Press Ltd, 1992 Reduced relaxant potency of nitroprusside on pulmonary artery preparations taken from rats during the development of hypoxic pulmonary
Physiology sheet #2. The heart composed of 3 layers that line its lumen and cover it from out side, these layers are :
 Physiology sheet #2 * We will talk in this lecture about cardiac muscle physiology, the mechanism and the energy sources of their contraction and intracellular calcium homeostasis. # Slide 4 : The heart
Physiology sheet #2 * We will talk in this lecture about cardiac muscle physiology, the mechanism and the energy sources of their contraction and intracellular calcium homeostasis. # Slide 4 : The heart
gravid rat myometrial activity
 Research Paper Effect of functional modulation of Ca 2+ -activated Cl - currents on gravid rat myometrial activity P. G. Adaikan, A. Adebiyi ABSTRACT Departments of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, National
Research Paper Effect of functional modulation of Ca 2+ -activated Cl - currents on gravid rat myometrial activity P. G. Adaikan, A. Adebiyi ABSTRACT Departments of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, National
The Action of Sevoflurane on Vascular Smooth Muscle of Isolated Mesenteric Resistance Arteries (Part 1)
 1426 Anesthesiology 2000; 92:1426 40 2000 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. The Action of Sevoflurane on Vascular Smooth Muscle of Isolated Mesenteric Resistance
1426 Anesthesiology 2000; 92:1426 40 2000 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. The Action of Sevoflurane on Vascular Smooth Muscle of Isolated Mesenteric Resistance
FIBER TYPES - oxidative metabolism is the main form here - ATPase activity is relatively low
 Cardiac Muscle Physiology Special characteristics of cardiac muscle - Branching and interdigitating cells - At their ends, they are connected by INTERCALATED DISCS - The discs are always at the Z-lines
Cardiac Muscle Physiology Special characteristics of cardiac muscle - Branching and interdigitating cells - At their ends, they are connected by INTERCALATED DISCS - The discs are always at the Z-lines
PETER. I. AZIBA * and OKUNOLA M. C.l Departments Of Pharmacology* And Physiology 1, College of Medicine, University of lbadan, Nigeria.
 - Mr. J. Biomed. Res. 2(1), 1999: 23-27 Original rtide EFFECTS OF DRUGS ND IONIC VRITIONS ON CONTRCTIONS OF RT SMOOTH MUSCLES PETER. I. ZIB * and OKUNOL M. C.l Departments Of Pharmacology* nd Physiology
- Mr. J. Biomed. Res. 2(1), 1999: 23-27 Original rtide EFFECTS OF DRUGS ND IONIC VRITIONS ON CONTRCTIONS OF RT SMOOTH MUSCLES PETER. I. ZIB * and OKUNOL M. C.l Departments Of Pharmacology* nd Physiology
Original Article. Introduction
 Original Article The Effects of Na Movement on Surgical Myocardial Protection: The Role of the Na + -H + Exchange System and Na-Channel in the Development of Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury Ke-Xiang Liu,
Original Article The Effects of Na Movement on Surgical Myocardial Protection: The Role of the Na + -H + Exchange System and Na-Channel in the Development of Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury Ke-Xiang Liu,
Skeletal Muscle Contraction 4/11/2018 Dr. Hiwa Shafiq
 Skeletal Muscle Contraction 4/11/2018 Dr. Hiwa Shafiq Skeletal Muscle Fiber About 40 per cent of the body is skeletal muscle, and 10 per cent is smooth and cardiac muscle. Skeletal muscles are composed
Skeletal Muscle Contraction 4/11/2018 Dr. Hiwa Shafiq Skeletal Muscle Fiber About 40 per cent of the body is skeletal muscle, and 10 per cent is smooth and cardiac muscle. Skeletal muscles are composed
MODIFICATIONS BY PROPRANOLOL OF THE RESPONSE OF ISOLATED RABBIT ATRIA TO ENDOGENOUS AND EXOGENOUS NORADRENALINE
 Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 32, 539-545. MODIFICATIONS BY PROPRANOLOL OF THE RESPONSE OF ISOLATED RABBIT ATRIA TO ENDOGENOUS AND EXOGENOUS NORADRENALINE BY K. SHIMAMOTO AND N. TODA From the Department
Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 32, 539-545. MODIFICATIONS BY PROPRANOLOL OF THE RESPONSE OF ISOLATED RABBIT ATRIA TO ENDOGENOUS AND EXOGENOUS NORADRENALINE BY K. SHIMAMOTO AND N. TODA From the Department
Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay on the XF24 Analyzer
 Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay on the XF24 Analyzer Mitochondria oxidize a variety of fuels to generate ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. Cells can utilize fatty acid, glucose and amino acids as their
Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay on the XF24 Analyzer Mitochondria oxidize a variety of fuels to generate ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. Cells can utilize fatty acid, glucose and amino acids as their
PKC, Ca 2+, and Myogenic Constriction
 PKC, Ca 2+, and Myogenic Constriction Matt Childrey Journal Review of: Alterations in PKC signaling underlie enhanced myogenic tone in exercise-trained porcine coronary resistance arteries by: D.H. Korzick,
PKC, Ca 2+, and Myogenic Constriction Matt Childrey Journal Review of: Alterations in PKC signaling underlie enhanced myogenic tone in exercise-trained porcine coronary resistance arteries by: D.H. Korzick,
HYPOTHALAMIC OBESE AND NON OBESE RATS EXPRESS A SIMILAR FUNCTIONAL MUSCARINIC M 3 SUBTYPE IN THE CONDUCTANCE ARTERY
 International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN- 9-1491 Vol 3, Issue 2, 211 Research Article HYPOTHALAMIC OBESE AND NON OBESE RATS EXPRESS A SIMILAR FUNCTIONAL MUSCARINIC M 3 SUBTYPE
International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN- 9-1491 Vol 3, Issue 2, 211 Research Article HYPOTHALAMIC OBESE AND NON OBESE RATS EXPRESS A SIMILAR FUNCTIONAL MUSCARINIC M 3 SUBTYPE
Cardiac Output 1 Fox Chapter 14 part 1
 Vert Phys PCB3743 Cardiac Output 1 Fox Chapter 14 part 1 T. Houpt, Ph.D. Regulation of Heart & Blood Pressure Keep Blood Pressure constant if too low, not enough blood (oxygen, glucose) reaches tissues
Vert Phys PCB3743 Cardiac Output 1 Fox Chapter 14 part 1 T. Houpt, Ph.D. Regulation of Heart & Blood Pressure Keep Blood Pressure constant if too low, not enough blood (oxygen, glucose) reaches tissues
Yin Xia 1,2 and Raouf A. Khalil 1 1
 Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 31: H1851 H1865, 16. First published May 3, 16; doi:1.1152/ajpheart.876.15. nancy-associated adaptations in [Ca 2 ] i -dependent and Ca 2 sensitization mechanisms of venous
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 31: H1851 H1865, 16. First published May 3, 16; doi:1.1152/ajpheart.876.15. nancy-associated adaptations in [Ca 2 ] i -dependent and Ca 2 sensitization mechanisms of venous
In addition to energy storage, adipose tissue secretes a significant number of
 Perivascular adipose tissue modulates vascular function in the human internal thoracic artery Yu-Jing Gao, MD, PhD, a Zhao-hua Zeng, MD, a Kevin Teoh, MD, b Arya M. Sharma, MD, PhD, c Labib Abouzahr, MD,
Perivascular adipose tissue modulates vascular function in the human internal thoracic artery Yu-Jing Gao, MD, PhD, a Zhao-hua Zeng, MD, a Kevin Teoh, MD, b Arya M. Sharma, MD, PhD, c Labib Abouzahr, MD,
Ischaemic Preconditioning prevents the differentiation induced by ischaemia/reperfusion injury of rat cardiac fibroblast to myofibroblast
 Ischaemic Preconditioning prevents the differentiation induced by ischaemia/reperfusion injury of rat cardiac fibroblast to myofibroblast Kartika Pertiwi1 and Lisa Chilton2 1: Biology Education Department,
Ischaemic Preconditioning prevents the differentiation induced by ischaemia/reperfusion injury of rat cardiac fibroblast to myofibroblast Kartika Pertiwi1 and Lisa Chilton2 1: Biology Education Department,
The Journal of Veterinary Medical Science
 Advance Publication The Journal of Veterinary Medical Science Accepted Date: Nov 0 J-STAGE Advance Published Date: Nov 0 FULL PAPER Pharmacology Eukaryotic elongation factor kinase inhibitor, A inhibits
Advance Publication The Journal of Veterinary Medical Science Accepted Date: Nov 0 J-STAGE Advance Published Date: Nov 0 FULL PAPER Pharmacology Eukaryotic elongation factor kinase inhibitor, A inhibits
Vasorelaxant effects of the potassium channel opener SR on the isolated human saphenous vein and rat aorta
 Brazilian Vasorelaxant Journal effects of Medical of SR 4763 and Biological Research (2) 33: 961-966 ISSN -879X 961 Vasorelaxant effects of the potassium channel opener SR 4763 on the isolated human saphenous
Brazilian Vasorelaxant Journal effects of Medical of SR 4763 and Biological Research (2) 33: 961-966 ISSN -879X 961 Vasorelaxant effects of the potassium channel opener SR 4763 on the isolated human saphenous
Treatment of T Angina reatment of By Ali Alalawi
 Treatment of Angina By Ali Alalawi Determinants of Oxygen Demand Need to improve ratio of: Coronary blood flow / cardiac work Or Cardiac O2 Supply / Cardiac Requirement Coronary Circulation vs Other Circulation
Treatment of Angina By Ali Alalawi Determinants of Oxygen Demand Need to improve ratio of: Coronary blood flow / cardiac work Or Cardiac O2 Supply / Cardiac Requirement Coronary Circulation vs Other Circulation
