HYPOTHALAMIC OBESE AND NON OBESE RATS EXPRESS A SIMILAR FUNCTIONAL MUSCARINIC M 3 SUBTYPE IN THE CONDUCTANCE ARTERY
|
|
|
- Jacob Gilbert
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN Vol 3, Issue 2, 211 Research Article HYPOTHALAMIC OBESE AND NON OBESE RATS EXPRESS A SIMILAR FUNCTIONAL MUSCARINIC M 3 SUBTYPE IN THE CONDUCTANCE ARTERY LETYCIA LONGHI SCOLARO 1, JÚLIO CEZAR DE OLIVEIRA 2, PAULO CEZAR DE FREITAS MATHIAS 2 AND WILSON ALVES DO PRADO 1* 1Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutic and 2 Department of Cell Biology and Genetics, State University of Maringá, Paraná, Brazil waprado@uem.br Received: 14 Aug 21, Revised and Accepted: 18 Sep 21 ABSTRACT The substantial homology between the genomes of rodents and humans has made hypothalamic obese rats, obtained by neonatal treatment with monosodium L glutamate (MSG), a good tool for studying the effects of obesity on the functional characteristics of muscarinic receptors. The affinity of muscarinic receptors for quinuclynidyl benzylate is increased in cells in the central nervous system in MSG obese rats, and the population of M3 receptors expressed in pancreatic islets isolated from non obese rat transitions toward the M2 subtype in MSG obese animals. We investigated whether neonatal treatment with MSG could also modify the M3 muscarinic receptor subtype that is expressed in vascular tissues of rats. The EC% values for acetylcholine induced relaxation in obese and non obese rats were similar in the intact aortic ring preparations precontracted with norepinephrine. Atropine, 1,1 dimethyl 4 diphenylacetoxypiperidinium iodide (4 DAMP), and pirenzepine induced similar parallel rightward shifts of the log [concentration] response curve of acetylcholine induced relaxation in preparations isolated from both types of animals. The pa2 values for atropine, 4 DAMP, and pirenzepine in obese animals were not different from controls. Methoctramine did not produce any effect on the log [concentration] response curve for acetylcholine in obese and non obese rats. MSG does not modify the muscarinic receptor subtype expressed in the conductance artery of rats. Keywords: Muscarinic receptors, aorta, obesity, monosodium L glutamate, arterial blood pressure INTRODUCTION Obesity is associated with a spectrum of metabolic and cardiovascular disorders [1] and may be induced in animals by neuroendocrine, dietary, or genetic changes [2]. Although the studies performed with such animal models have shown that the central nervous system regulates energy expenditure and food intake, the mechanisms by which hypothalamic injury leads to obesity are not fully understood [2]. However, the obesity induced by hypothalamic injury is known to not be caused by an increase in food intake [2]. The substantial homology between the genomes of rodents and humans have made these animal models a good tool for studying the effects of obesity on different biological parameters [2], such as the arterial blood pressure and the responsiveness of vascular tissues to activation by different drugs. Thus, it has been verified that the neonatal treatment of rat with monosodium L glutamate (MSG), a condition that produces obese animal (hypothalamic obese rat or MSG obese rat), lowers the responsiveness of both α adrenergic receptors and angiotensin II receptors in vascular tissues in these animals [3]. Moreover, it has been proposed that the neonatal treatment of rats with MSG could alter the expression of muscarinic receptors in different tissues in these animals, as it was verified that the population of M3 muscarinic receptor subtypes transitions toward the M2 subtype in pancreatic islets isolated from MSG obese rats [4], and the number of muscarinic receptors, as well as the affinity of such receptors for quinuclynidyl benzylate, are increased in cells of the central nervous system in MSG obese animals [5]. Although vascular muscarinic receptors are well established to not be activated under physiological conditions (i.e., the absence of cholinergic innervation and the absence of acetylcholine molecules in the blood), the activation of such receptors by different cholinomimetic drugs significantly reduces arterial blood pressure under therapeutic conditions [6]. The endothelial M3 receptor is well known to be the main subtype of muscarinic receptor involved in acetylcholine induced endothelium dependent relaxation in aortic ring preparations isolated from spontaneously hypertensive rats [7] and non hypertensive animals [8]. However, unknown is whether the obesity produced by neonatal treatment of rats with MSG modifies the specific muscarinic receptor subtypes that are expressed in vascular tissue in such animals, or whether the muscarinic receptors in the vessels of MSG obese rats are less or more responsive to activation by acetylcholine than in non obese animals. Since information about vascular muscarinic receptors expressed in MSGobese rats could be useful for managing therapeutic procedures in obese patients, the responsiveness of vascular muscarinic receptors to activation by acetylcholine, and the subtype of vascular muscarinic receptors expressed in aortic ring preparations isolated from MSG obese rats were evaluated in the current study. METHODS Drugs Monosodium L glutamate, acetylcholine, pirenzepine, methoctramine, 1,1 dimethyl 4 diphenylacetoxypiperidinium iodide (4 DAMP), and norepinephrine were obtained from Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA). Animals and obesity The Ethical Committee for Animal Experiments of the State University of Maringa approved the animal protocols. Neonate male Wistar rats were subcutaneously injected during the first 5 days of life with MSG (4 g/kg body weight). Control animals received equimolar saline solution. Both animal groups were weaned on postnatal day 21. All animals were housed under a 12 h/12 h light/dark cycle (7: to 19: h) and controlled temperature (21 ± 2 C). Water and standard rodent chow (Nuvital, Curitiba, Brazil) were available ad libitum. Retroperitoneal, perigonadal, and subcutaneous fat pads were removed, washed, and weighed to estimate obesity induced by MSG treatment. The Lee index (body weight [g] 1/3/nasal anal length [cm] 1) was calculated as a predictor of obesity in MSG rats. Arterial blood pressure When 9 days old, rats from both groups were anesthetized with sodium pentobarbital (45 mg/kg, i.p.) and urethane (6 mg/kg, i.p.). A polyethylene catheter (PE 1) containing heparinized saline ( IU heparin/ml.9%) was introduced into the femoral artery to permit the recording of mean arterial blood pressure (MLT38/D transducer) in each animal on a computer equipped with Powerlab chart software (AD Instruments, Pty, Ltd., Castle Hill, NSW, Australia). In vitro preparations After obtaining the arterial pressure values for each rat, the animals were subjected to medial laparotomy, and the thoracic aorta was
2 Int J Pharm Pharm Sci, Vol 3, Issue 2, 211, immediately excised. The vessel was cut into 3 mm rings and gently dissected free of fat and connective tissue. Rings were then mounted into 3 ml organ baths filled with oxygenated (95% O2, 5% CO2) Krebs buffer (118 mmol/l NaCl, 4. mmol/l KCl, 2.5 mmol/l CaCl2, 1.2 mmol/l MgSO4, mmol/l NaHCO3, 1.2 mmol/l KH2PO4,.3 mmol/l EDTA, and 11 mmol/l glucose) at 37 C, and the ph of the solution was maintained at 7.4. The aortic ring preparation was connected to strain gauges (Grass, FT 3), and isometric tension was recorded on a computer equipped with Powerlab chart software (AD Instruments, Pty, Ltd., Castle Hill, NSW, Australia). After the rings were allowed to equilibrate for 1 h, the preparations were gradually stretched to an optimal resting tension (1 g). The endothelium was considered to be functionally intact when the addition of acetylcholine (1. μm) produced 1% relaxation (return of tension to values recorded before any previous contraction of rings) of the precontraction induced by norepinephrine (1 nm). After the resting tension stabilized, norepinephrine (1 nm) was administered to induce a rapid increase in vascular tone, which was followed by stable vasoconstriction (tonic contraction). Acetylcholine (.1 1. μm) was then added to the bath. Norepinephrine was the drug chosen to produce vessel precontraction because it is an endogenous agonist and when compared with epinephrine has a higher affinity for α adrenergic receptors [9]. The norepinephrine concentration we used had produced about % of the maximal tension in isolated rat aortic ring preparations devoid of endothelium [1]. In the experiments with atropine, pirenzepine, methoctramine, and 4 DAMP, each antimuscarinic agent was administered 15 sec after norepinephrine. The lowest concentration of each antimuscarinic drug able to produce a small rightward shift in the dose effect curve produced by acetylcholine was determined, and the multiple dose values were used to obtain the others dose effect curves necessary to infer the pa2 values (GraphPad Prism version 3.2 for Windows, GraphPad Software ) for the antimuscarinic agents [11; 12]. Data analysis Data were analyzed using Student s t test or analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test. Values of p <.5 were considered statistically significant. RESULTS Obesity and arterial blood pressure The MSG obese animals had a Lee index and retroperitoneal, perigonadal, and subcutaneous fat values that were significantly (p<.5) higher than those in non obese rats (Table 1). Mean arterial blood pressure in obese animals was not significantly (p>.5) different from that found in non obese animals (Table 1). EC values for acetylcholine The EC values for acetylcholine in the intact aortic ring preparations precontracted with norepinephrine (1 nm) in obese (2.27 ±.26 nm, n = 35) and non obese (2.37 ±.32 nm, n = 35) animals were not significantly different (p >.5) (Fig. 1). pa2 values for muscarinic antagonist Atropine (12.5,., and 2. nm, n = 4), 4 DAMP (.,., and 1. nm, n = 4), and pirenzepine (1., 1., and 1. µm, n = 4) caused a parallel rightward displacement of the log [concentration] response curve for acetylcholine in MSG obese and non obese rats (Fig. 2). The pa2 values ( log M) for atropine, 4 DAMP, and pirenzepine for the relaxing effect induced by acetylcholine were similar (p >.5) in obese and non obese rats (Table 2). Methoctramine (until 1 µm) did not produce any effect on the log [concentration] response curve for acetylcholine in MSG obese and non obese rats (data not shown). Responsiveness of α adrenergic receptors A decreased responsiveness of α adrenergic receptors to norepinephrine induced effect was detected in the vascular tissue of MSG obese rats (Table 3). Table 1: Effects of MSG neonatal treatment in adult rats Control (n = 22) MSG (n = 3) Mean arterial blood pressure (mmhg) 94.4 ± ± 3. Lee index 33.2 ± ± 1.84* Retroperitoneal fat (g/1 g) 1.3 ± ±.7* Perigonadal fat (g/1 g).9 ± ±.6* Subcutaneous fat (g/1 g) 1.3 ± ±.15* Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of 22 to 3 experiments obtained from non obese (control) and MSG obese (MSG) rats. The Lee index and the various fats are described in the Methods. *p <.5, significant difference from control (Student s t test). A 28
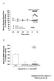
3 Int J Pharm Pharm Sci, Vol 3, Issue 2, 211, B Fig. 1: (A) Relaxing effect produced by acetylcholine (ACh, 1 8 to 1 6 M) in intact rat aortic ring preparations isolated from MSG obese rats and precontracted with 1 nm norepinephrine (Nor). The wash indicates an exchange of nutrient solution containing Nor and ACh by drug free Krebs buffer. (B) The percentage (%) of relaxing effect produced by acetylcholine (ACh) in intact rat aortic ring preparations in MSG obese (, n = 35) and non obese (, n = 35) rats precontracted with 1 8 M norepinephrine. Symbols indicate mean ± SEM of 35 experiments. The EC values (mean ± SEM) for ACh were similar (p >.5) in MSG obese rats (2.27 ± M) and non obese rats (2.37 ± M). NON-obese ATROPINE MSG-obese 1 1 PIRENZEPINE 1 1 log[ach](m) 4-DAMP 29
4 Int J Pharm Pharm Sci, Vol 3, Issue 2, 211, Fig. 2: Competitive antagonism by atropine ( 12.5 nm, nm, 2 nm), pirenzepine ( 1µM, 1 µm, 1 µm), and 4 DAMP ( nm, nm, 1 nm) of the relaxing effect produced by acetylcholine (ACh) in the aortic ring preparations in rats precontracted with 1 nm norepinephrine. The preparations were isolated from non obese and MSG obese rats. Symbols indicate mean ± SEM of 4 to 12 experiments. Table 2: pa2 and slope values for atropine, pirenzepine, and 4 DAMP in intact aortic ring preparations in MSG obese and non obese rats precontracted with norepinephrine (1 nm). Non obese MSG obese Slope pa2 ( log M) Slope pa2 ( log M) Atropine.9 ±.2 1. ± ± ±.1 Pirenzepine 1.2 ± ± ± ±.1 4 DAMP.9 ± ± ± ±.1 Values are expressed as mean ± SEM of 11 to 12 observations. pa2 and slope were obtained using Arunlakshana and Schild methods for slope equal to unity. Data were subjected to ANOVA. Table 3: Maximal tension produced by norepinephrine (1 nm) and interval (ΔT) of time for norepinephrine to produce its maximal effect in aortic ring preparations in MSG obese and non obese rats. NON obese MSG Obese Maximal tension (N),284 ±,1,224 ±,2* T (min) 2.4 ± ±.2 Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of 15 to 2 observations. *p <.5, significant difference from control (non obese rats; Student s t test). DISCUSSION MSG treated neonatal rats developed obesity in adulthood. The parameters that were used to infer obesity in the present study produced data similar to those previously reported [4]. However, it was recorded in the current study that the muscarinic receptor subtype inducing vascular relaxation did not transition toward another muscarinic receptor subtype in MSG obese animals. Although such a conclusion conflicts with previous results observed in pancreatic cells [4], the results are consistent with data showing that the pa2 values found for atropine, pirenzepine, and 4 DAMP in the aortic ring preparations isolated from MSG obese rats were not different from those found in the preparations isolated from nonobese animals. The muscarinic receptor subtype in vascular tissue in MSG obese and non obese animal was determined to be the M3 subtype. The order of affinity found for both groups of animals was atropine > 4 DAMP >> pirenzepine. Methoctramine did not produce any effect on the concentration effect curve induced by acetylcholine in either group of animals. The order of affinity found in the present study is similar to the orders of affinity reported for other tissues expressing M3 muscarinic receptors [7; 13; 14; 15], and the pa2 value for 4 DAMP was consistent with activation of a homologous population of M3 muscarinic receptors [7]. Therefore, MSG treatment appears to induce changes in the population of muscarinic receptors in a specific tissue, if such tissue already naturally expresses more than one muscarinic receptor subtype. This might be the case for pancreatic cells in rats, in which both M1 and M3 muscarinic receptors are abundant [16], and MSG treatment induces changes that determine the functional expression of another muscarinic receptor subtype (M2) in such tissues [4]. The present study also showed that MSG treatment did not produce any change in the potency of acetylcholine in inducing endothelium dependent relaxation. The EC values for acetylcholine and the maximal reduction in tension produced by the cholinomimetic were similar in aortic ring preparations isolated from MSG obese rats and non obese animals. Furthermore, the present data indicate that M3 muscarinic receptors exhibit preserved functional characteristics in MSG obese rats. In contrast, neonatal MSG treatment in rats has been hypothesized to decrease the responsiveness of the cardiovascular system, particularly in response to α adrenergic stimulation when phenylephrine is intravenously administered in awake MSG obese rats [3], or when the functional activity of vascular tissue is evaluated with the use of perfusion techniques and direct norepinephrine administration in the catheterized vascular tissue of such animals [17]. Although the results of the present study were obtained with the use of a different type of bioassay, the decreased responsiveness of α adrenergic receptors was also detected in the vascular tissue of MSG obese animals. The maximum constrictor effect induced by norepinephrine in the aortic ring preparations from MSG obese rats was significantly (p <.5) lower than that found in preparations isolated from non obese animals. The reduced responsiveness of vascular tissues to α adrenergic activation recorded in the aortic ring preparation isolated from MSG obese animals was unlikely to have influenced the data obtained with the use of acetylcholine in such preparations. Under such conditions, one would expect that the 3
5 Int J Pharm Pharm Sci, Vol 3, Issue 2, 211, vasodilator effect and EC value for acetylcholine would be altered in preparations isolated from obese animals. Additionally, the mean arterial blood pressure in anesthetized MSG obese rats was slightly lower than, but not significantly (p >.5) different from, that found in non obese animals. Although these results were obtained with the use of anesthetized animals, the data are consistent with a previous study in which arterial pressure was measured in awaked MSGobese animals [3]. Altogether, the present data show that the vascular responsiveness of α adrenergic receptors is reduced in aortic rings preparations isolated from MSG obese rats, but neonatal MSG treatment does not alter the functional characteristics and muscarinic receptor subtype that is naturally expressed in vascular tissues in rats. The present findings may have clinical significance and may help understand and control the effects of drugs on arterial blood pressure in obese patients. REFERENCES 1. Hsueh WA, Buchanan TA. Obesity and hypertension. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 1994; 23: Von Diemem V, Trindade EN, Trindade MRC. Experimental model to induce obesity in rats. Acta Cir Bras 26; 21: Tokarev D, Kristová V, Kriska M, Jezová D. Treatment of neonatal rats with monosodium glutamate attenuates the cardiovascular reactivity to phenylephrine and angiotensin II. Physiol Res 1997; 46: Grassiolli S, Gravena C, de Freitas Mathias PC. Muscarinic M2 receptor is active on pancreatic islets from hypothalamic obese rat. Eur J Pharmacol 27; 556: Ortuño Sahagún D, Beas Zárate C, Adame Gonzalez G, Feria Velasco A. Effect of L glutamate on cholinergic neurotransmission in various brain regions and during the development of rats, when administered perinatally. Neurochem Int 1997; 31: Brown JH, Taylor P. Muscarinic receptor agonists and antagonists. In: Brunton LL, Lazo JS, Parker KL, editors. Goodman and Gilman s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics, New York: McGraw Hill; 26, p Boulanger CM, Morrison KJ, Vanhoutte PM. Mediation by M3 muscarinic receptors of both endothelium dependent contraction and relaxation to acetylcholine in the aorta of the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Br J Pharmacol 1994; 112: Sawyer BD, Bymaster FP, Calligaro DO, Falcone J, Mitch CH, Ward JS, et al. Direct pharmacological comparison of the muscarinic receptors mediating relaxation and contraction in the rabbit thoracic aorta. Gen Pharmacol 1999; 32: Westfall TC, Westfall DP, 26. Adrenergic agonists and antagonists. In: Brunton LL, Lazo JS, Parker KL, editors. Goodman and Gilman s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics, New York: McGraw Hill; 26, p Testai L, Silvio C, Ammar B, Luisa P, Vincenzo C, Martinotti E. Vasorelaxant effects of the chloroformic crude extract of Bupleurm fruticosum L. (Umbelliferae) roots on rat thoracic aorta. J Ethnopharmacol ; 96: Kenakin TP. Pharmacologic analysis of drug receptor interaction, 2rd ed. New York: Raven Press; Arunlakshana O, Schild HO. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother 1959; 14: McCormack DG, Mak JC, Minette P, Barnes PJ. Muscarinic receptor subtypes mediating vasodilation in the pulmonary artery. Eur J Pharmacol 1988; 158: Michel AD, Stefanich E, Whiting RL. Direct labelling of rat M3 muscarinic receptors by [ 3 H]4DAMP. Eur J Pharmacol 1989; 166: Alonso MJ, Arribas S, Marin J, Balfagon G, Salaices M. Presynaptic M2 muscarinic receptors on noradrenergic nerve endings and endothelium derived M3 receptors in cat cerebral arteries. Brain Res 1991; 567: Iismaa TP, Kerr EA, Wilson JR, Carpenter L, Sims N, Biden TJ. Quantitative and functional characterization of muscarinic receptor subtypes in insulin secreting cell lines and rat pancreatic islets. Diabetes 2; 49: Kristova V, Kriska M, Babal P, Jezova D. Early postnatal glutamate treatment results in altered vascular responsiveness to serotonin and noradrenaline in adult rats. Endocr Regul 1998; 32:
Relaxation responses of aortic rings from salt-loaded high calcium fed rats to potassium chloride, calcium chloride and magnesium sulphate
 Pathophysiology 4 (1998) 275 280 Relaxation responses of aortic rings from salt-loaded high calcium fed rats to potassium chloride, calcium chloride and magnesium sulphate B.J. Adegunloye, O.A. Sofola
Pathophysiology 4 (1998) 275 280 Relaxation responses of aortic rings from salt-loaded high calcium fed rats to potassium chloride, calcium chloride and magnesium sulphate B.J. Adegunloye, O.A. Sofola
EFFECT OF ANTIMUSCARINIC AGENTS ON THE CONTRACTILE
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1981), 73,829-835 EFFECT OF ANTIMUSCARINIC AGENTS ON THE CONTRACTILE RESPONSES TO CHOLINOMIMETICS IN THE RAT ANOCOCCYGEUS MUSCLE SHEILA A. DOGGRELL Department of Pharmacology & Clinical
Br. J. Pharmac. (1981), 73,829-835 EFFECT OF ANTIMUSCARINIC AGENTS ON THE CONTRACTILE RESPONSES TO CHOLINOMIMETICS IN THE RAT ANOCOCCYGEUS MUSCLE SHEILA A. DOGGRELL Department of Pharmacology & Clinical
Reactivity of the isolated perfused rat tail vascular bed
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1997) 30: 891-895 Perfused rat tail vascular bed ISSN 0100-879X 891 Reactivity of the isolated perfused rat tail vascular bed A.S. França, L.V. Rossoni,
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1997) 30: 891-895 Perfused rat tail vascular bed ISSN 0100-879X 891 Reactivity of the isolated perfused rat tail vascular bed A.S. França, L.V. Rossoni,
Effect of ageing on ƒ 1A-adrenoceptor mechanisms in rabbit. Issei TAKAYANAGI, Mann MORIYA and Katsuo KOIKE
 J. Smooth Muscle Res. 28: 63-68, 1992. Effect of ageing on ƒ 1A-adrenoceptor mechanisms in rabbit isolated bronchial preparations Issei TAKAYANAGI, Mann MORIYA and Katsuo KOIKE Department of Chemical Pharmacology,
J. Smooth Muscle Res. 28: 63-68, 1992. Effect of ageing on ƒ 1A-adrenoceptor mechanisms in rabbit isolated bronchial preparations Issei TAKAYANAGI, Mann MORIYA and Katsuo KOIKE Department of Chemical Pharmacology,
Pharmacologyonline 2: (2008) Newsletter Deepraj and Nandakumar
 INVESTIGATION OF ISOLATED GOAT ILEUM PREPARATION FOR THE SUITABILITY AS A TEACHING AID FOR UNDER GRADUATE AND POST GRADUATE PRACTICALS Deepraj Paul, K.Nandakumar DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY, P.E.S COLLEGE
INVESTIGATION OF ISOLATED GOAT ILEUM PREPARATION FOR THE SUITABILITY AS A TEACHING AID FOR UNDER GRADUATE AND POST GRADUATE PRACTICALS Deepraj Paul, K.Nandakumar DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY, P.E.S COLLEGE
Differential responses to endothelial dependent relaxation of the thoracic and abdominal aorta from male Sprague-Dawley rats
 Niger. J. Physiol. Sci. 27(December 12) 117 122 www.njps.com.ng Differential responses to endothelial dependent relaxation of the thoracic and abdominal aorta from male Sprague-Dawley rats 1 Oloyo, Ahmed
Niger. J. Physiol. Sci. 27(December 12) 117 122 www.njps.com.ng Differential responses to endothelial dependent relaxation of the thoracic and abdominal aorta from male Sprague-Dawley rats 1 Oloyo, Ahmed
Chronotropic and Inotropic Effects of 3 Kinds of Alpha-Adrenergic Blockers on the Isolated Dog Atria
 Chronotropic and Inotropic Effects of 3 Kinds of Alpha-Adrenergic Blockers on the Isolated Dog Atria Shigetoshi CHIBA, M.D., Yasuyuki FURUKAWA, M.D., and Hidehiko WATANABE, M.D. SUMMARY Using the isolated
Chronotropic and Inotropic Effects of 3 Kinds of Alpha-Adrenergic Blockers on the Isolated Dog Atria Shigetoshi CHIBA, M.D., Yasuyuki FURUKAWA, M.D., and Hidehiko WATANABE, M.D. SUMMARY Using the isolated
Prenatal hypoxia causes long-term alterations in vascular endothelin-1 function in aged male but not female offspring
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 Supplementary information for: Prenatal hypoxia causes long-term alterations in vascular endothelin-1 function in aged male but not female offspring Stephane L Bourque,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 Supplementary information for: Prenatal hypoxia causes long-term alterations in vascular endothelin-1 function in aged male but not female offspring Stephane L Bourque,
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(3): Research Article. Partial agonistic property of new isolated natural compounds
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(3):1294-1298 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Partial agonistic property of new isolated natural
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(3):1294-1298 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Partial agonistic property of new isolated natural
Evidence for a Role of Cyclic AMP and Endothelium in Rat Aortic Relaxation
 6 The Open Circulation and Vascular Journal, 2011, 4, 6-11 Open Access Evidence for a Role of Cyclic AMP and Endothelium in Rat Aortic Relaxation Induced by R-PIA Gonzalo Allende* and Salvador Acevedo
6 The Open Circulation and Vascular Journal, 2011, 4, 6-11 Open Access Evidence for a Role of Cyclic AMP and Endothelium in Rat Aortic Relaxation Induced by R-PIA Gonzalo Allende* and Salvador Acevedo
Advanced Receptor Psychopharmacology
 Advanced Receptor Psychopharmacology Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc. 2017 Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc., Rockville, MD February 2017 Lundbeck,
Advanced Receptor Psychopharmacology Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc. 2017 Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc., Rockville, MD February 2017 Lundbeck,
A NEW TYPE OF DRUG ENHANCEMENT: INCREASED MAXIMUM RESPONSE TO CUMULATIVE NORADREN- ALINE IN THE ISOLATED RAT VAS DEFERENS
 Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 33, 171-176. A NEW TYPE OF DRUG ENHANCEMENT: NCREASED MAXMUM RESPONSE TO CUMULATVE NORADREN- ALNE N THE SOLATED RAT VAS DEFERENS BY A. BARNETT, D. D. GREENHOUSE AND R..
Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 33, 171-176. A NEW TYPE OF DRUG ENHANCEMENT: NCREASED MAXMUM RESPONSE TO CUMULATVE NORADREN- ALNE N THE SOLATED RAT VAS DEFERENS BY A. BARNETT, D. D. GREENHOUSE AND R..
2. Langendorff Heart
 2. Langendorff Heart 2.1. Principle Langendorff heart is one type of isolated perfused heart which is widely used for biochemical, physiological, morphological and pharmacological researches. It provides
2. Langendorff Heart 2.1. Principle Langendorff heart is one type of isolated perfused heart which is widely used for biochemical, physiological, morphological and pharmacological researches. It provides
Properties of Pressure
 OBJECTIVES Overview Relationship between pressure and flow Understand the differences between series and parallel circuits Cardiac output and its distribution Cardiac function Control of blood pressure
OBJECTIVES Overview Relationship between pressure and flow Understand the differences between series and parallel circuits Cardiac output and its distribution Cardiac function Control of blood pressure
PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE ANOCOCCYGEUS MUSCLE OF
 Br. J. Pharmac. (198). 71, 35-4 PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDY OF TH ANOCOCCYGUS MUSCL OF TH DOG A.R. DHPOUR, M.A. KHOYI, H. KOUTCHKI & M.R. ZARRINDAST Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, University
Br. J. Pharmac. (198). 71, 35-4 PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDY OF TH ANOCOCCYGUS MUSCL OF TH DOG A.R. DHPOUR, M.A. KHOYI, H. KOUTCHKI & M.R. ZARRINDAST Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, University
Peptides-Derived from Thai Rice Bran Improve Hemodynamics and Induce Vasorelaxation in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats
 Peptides-Derived from Thai Rice Bran Improve Hemodynamics and Induce Vasorelaxation in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats Orachorn Boonla 1, Phattharaphon Tuangpolkrung 1, Poungrat Pakdeechote 1, Upa Kukongviriyapan
Peptides-Derived from Thai Rice Bran Improve Hemodynamics and Induce Vasorelaxation in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats Orachorn Boonla 1, Phattharaphon Tuangpolkrung 1, Poungrat Pakdeechote 1, Upa Kukongviriyapan
THE CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF ERGOMETRINE IN THE EXPERIMENTAL ANIMAL IN VIVO AND IN VITRO
 Br. J. Anaesth. (1974), 46, 473 THE CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF ERGOMETRINE IN THE EXPERIMENTAL ANIMAL IN VIVO AND IN VITRO M. R. WASSEF, H. LAL AND BARBARA J. PLEUVRY SUMMARY The cardiovascular effects
Br. J. Anaesth. (1974), 46, 473 THE CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF ERGOMETRINE IN THE EXPERIMENTAL ANIMAL IN VIVO AND IN VITRO M. R. WASSEF, H. LAL AND BARBARA J. PLEUVRY SUMMARY The cardiovascular effects
ambrisentan, bosentan, BQ788, endothelin-1, ET A receptors, ET B receptor-mediated clearance mechanism, ET B receptors, macitentan, sarafotoxin S6c
 Received: 9 October 2017 Accepted: 23 October 2017 DOI: 10.1002/prp2.374 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Distortion of K B estimates of endothelin-1 ET A and ET B receptor antagonists in pulmonary arteries: Possible
Received: 9 October 2017 Accepted: 23 October 2017 DOI: 10.1002/prp2.374 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Distortion of K B estimates of endothelin-1 ET A and ET B receptor antagonists in pulmonary arteries: Possible
Drug Receptor Interactions and Pharmacodynamics
 Drug Receptor Interactions and Pharmacodynamics Dr. Raz Mohammed MSc Pharmacology School of Pharmacy 22.10.2017 Lec 6 Pharmacodynamics definition Pharmacodynamics describes the actions of a drug on the
Drug Receptor Interactions and Pharmacodynamics Dr. Raz Mohammed MSc Pharmacology School of Pharmacy 22.10.2017 Lec 6 Pharmacodynamics definition Pharmacodynamics describes the actions of a drug on the
Hawthorn Extract - Viable Treatment for Cardiovascular Disease or Unscrupulous Herbal Supplement?
 Grand Valley State University ScholarWorks@GVSU Student Summer Scholars Undergraduate Research and Creative Practice 2010 Hawthorn Extract - Viable Treatment for Cardiovascular Disease or Unscrupulous
Grand Valley State University ScholarWorks@GVSU Student Summer Scholars Undergraduate Research and Creative Practice 2010 Hawthorn Extract - Viable Treatment for Cardiovascular Disease or Unscrupulous
EVIDENCE FOR CATECHOLAMINE-DEPLETING ACTION OF FLUOXETlNE
 indian J Physiol Pharmacol 1994; 38(3) : 169-173 EVIDENCE FOR CATECHOLAMINE-DEPLETING ACTION OF FLUOXETlNE MILIND R. PATIL, MILAN C. SATIA, ANITA A. MEHTA AND RAMESH K. GOYAL * Department of Pharmacology,
indian J Physiol Pharmacol 1994; 38(3) : 169-173 EVIDENCE FOR CATECHOLAMINE-DEPLETING ACTION OF FLUOXETlNE MILIND R. PATIL, MILAN C. SATIA, ANITA A. MEHTA AND RAMESH K. GOYAL * Department of Pharmacology,
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
RAPID COMMUNICATION. Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension
 Physiol. Res. 40:367-371,1991 RAPID COMMUNICATION Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension V. HAMPL, J. HERGET Department of Physiology, 2nd Medical School,
Physiol. Res. 40:367-371,1991 RAPID COMMUNICATION Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension V. HAMPL, J. HERGET Department of Physiology, 2nd Medical School,
The effect of L-arginine on guinea-pig and rabbit airway smooth muscle function in vitro
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1998) 31: 811-818 L-arginine on airway smooth muscle ISSN -879X 811 The effect of L-arginine on guinea-pig and rabbit airway smooth muscle function
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1998) 31: 811-818 L-arginine on airway smooth muscle ISSN -879X 811 The effect of L-arginine on guinea-pig and rabbit airway smooth muscle function
Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition
 Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition Chapter 3 Pharmacology of the Autonomic Nervous System Multimedia Directory Slide 19 Slide 37 Slide 38 Slide 39 Slide 40 Slide 41 Slide 42 Slide 43
Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition Chapter 3 Pharmacology of the Autonomic Nervous System Multimedia Directory Slide 19 Slide 37 Slide 38 Slide 39 Slide 40 Slide 41 Slide 42 Slide 43
Yuan et al., Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. (2014) 11(4):
 IZALPININ FROM FRUITS OF ALPINIA OXYPHYLLA WITH ANTAGONISTIC ACTIVITY AGAINST THE RAT BLADDER CONTRACTILITY 120 Yuan Yuan 1,5#, Yin-Feng Tan 2,3,4#, Peng Xu 2,3,4, Hailong Li 2,3,4, Yong-Hui Li 2,3,4,
IZALPININ FROM FRUITS OF ALPINIA OXYPHYLLA WITH ANTAGONISTIC ACTIVITY AGAINST THE RAT BLADDER CONTRACTILITY 120 Yuan Yuan 1,5#, Yin-Feng Tan 2,3,4#, Peng Xu 2,3,4, Hailong Li 2,3,4, Yong-Hui Li 2,3,4,
PHARMACODYNAMICS II QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS OF DRUGS. Ali Alhoshani, B.Pharm, Ph.D. Office: 2B 84
 PHARMACODYNAMICS II QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS OF DRUGS Ali Alhoshani, B.Pharm, Ph.D. ahoshani@ksu.edu.sa Office: 2B 84 Quantitative aspects of drugs By the end of this lecture, you should: Determine quantitative
PHARMACODYNAMICS II QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS OF DRUGS Ali Alhoshani, B.Pharm, Ph.D. ahoshani@ksu.edu.sa Office: 2B 84 Quantitative aspects of drugs By the end of this lecture, you should: Determine quantitative
Module Objectives: Why to study Organic Pharmaceutical Chemistry? 24-Oct-17
 1 2 Useful Info: Students are encouraged to visit the faculty website: http://pharmacy.uokerbala.edu.iq/ And most importantly the e-learning website: http://elearning.uokerbala.edu.iq Nevertheless, feel
1 2 Useful Info: Students are encouraged to visit the faculty website: http://pharmacy.uokerbala.edu.iq/ And most importantly the e-learning website: http://elearning.uokerbala.edu.iq Nevertheless, feel
Effect of cocaine on the affinity of a-adrenoceptors for noradrenaline
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 139-143. Effect of cocaine on the affinity of a-adrenoceptors for noradrenaline I. R. INNES AND R. MAILHOT* Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Faculty of Medicine,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 139-143. Effect of cocaine on the affinity of a-adrenoceptors for noradrenaline I. R. INNES AND R. MAILHOT* Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Faculty of Medicine,
Potassium-Induced Release of Endothelium- Derived Relaxing Factor From Canine Femoral Arteries
 1098 Potassium-Induced Release of Endothelium- Derived Relaxing Factor From Canine Femoral Arteries Gabor M. Rubanyi and Paul M. Vanhoutte Downloaded from http://ahajournals.org by on January 13, 2019
1098 Potassium-Induced Release of Endothelium- Derived Relaxing Factor From Canine Femoral Arteries Gabor M. Rubanyi and Paul M. Vanhoutte Downloaded from http://ahajournals.org by on January 13, 2019
Pharmacology. Biomedical Sciences. Dynamics Kinetics Genetics. School of. Dr Lindsey Ferrie
 Pharmacology Dynamics Kinetics Genetics Dr Lindsey Ferrie lindsey.ferrie@ncl.ac.uk MRCPsych Neuroscience and Psychopharmacology School of Biomedical Sciences Dynamics What the drug does to the body What
Pharmacology Dynamics Kinetics Genetics Dr Lindsey Ferrie lindsey.ferrie@ncl.ac.uk MRCPsych Neuroscience and Psychopharmacology School of Biomedical Sciences Dynamics What the drug does to the body What
Action of drugs on denervated myoepithelial cells of salivary glands
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 73-79. Action of drugs on denervated myoepithelial cells of salivary glands N. EMMELIN AND A. THULIN Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden Summary 1. The pressure
Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 73-79. Action of drugs on denervated myoepithelial cells of salivary glands N. EMMELIN AND A. THULIN Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden Summary 1. The pressure
INTERACTION DRUG BODY
 INTERACTION DRUG BODY What the drug does to the body What the body does to the drug Receptors - intracellular receptors - membrane receptors - Channel receptors - G protein-coupled receptors - Tyrosine-kinase
INTERACTION DRUG BODY What the drug does to the body What the body does to the drug Receptors - intracellular receptors - membrane receptors - Channel receptors - G protein-coupled receptors - Tyrosine-kinase
Cooling effects on nitric oxide production by rabbit ear and femoral arteries during cholinergic stimulation
 Br. J. Pharmacol. (1994), 113, 55-554 '." Macmillan Press Ltd, 1994 Cooling effects on nitric oxide production by rabbit ear and femoral arteries during cholinergic stimulation N. Fernandez, L. Monge,
Br. J. Pharmacol. (1994), 113, 55-554 '." Macmillan Press Ltd, 1994 Cooling effects on nitric oxide production by rabbit ear and femoral arteries during cholinergic stimulation N. Fernandez, L. Monge,
The Journal of Veterinary Medical Science
 Advance Publication The Journal of Veterinary Medical Science Accepted Date: Nov 0 J-STAGE Advance Published Date: Nov 0 FULL PAPER Pharmacology Eukaryotic elongation factor kinase inhibitor, A inhibits
Advance Publication The Journal of Veterinary Medical Science Accepted Date: Nov 0 J-STAGE Advance Published Date: Nov 0 FULL PAPER Pharmacology Eukaryotic elongation factor kinase inhibitor, A inhibits
Studies on the effects of viprostol in isolated small blood vessels and thoracic aorta of the rat
 Br. J. Pharmacol. (1988), 93, 613-617 Studies on the effects of viprostol in isolated small blood vessels and thoracic aorta of the rat Fong M. Lai, Tarak Tanikella, Agnes Cobuzzi & Peter Cervoni Cardiovascular
Br. J. Pharmacol. (1988), 93, 613-617 Studies on the effects of viprostol in isolated small blood vessels and thoracic aorta of the rat Fong M. Lai, Tarak Tanikella, Agnes Cobuzzi & Peter Cervoni Cardiovascular
Sulfur dioxide relaxes rat aorta by endothelium-dependent and. -independent mechanisms
 Sulfur dioxide relaxes rat aorta by endothelium-dependent and -independent mechanisms Yang-Kai WANG 1 #, An-Jing REN 1 #, Xiang-Qun YANG 1, Li-Gang WANG 1, Wei-Fang RONG 3, Chao-Shu TANG 4, Wen-Jun YUAN
Sulfur dioxide relaxes rat aorta by endothelium-dependent and -independent mechanisms Yang-Kai WANG 1 #, An-Jing REN 1 #, Xiang-Qun YANG 1, Li-Gang WANG 1, Wei-Fang RONG 3, Chao-Shu TANG 4, Wen-Jun YUAN
Physiology and pharmacology of smooth muscle contractions a brief introduction
 SimVessel: Physiology and pharmacology of smooth muscle contractions a brief introduction The virtual SimVessel Laboratory is for recordings of smooth muscle contractions of small muscle stripes of different
SimVessel: Physiology and pharmacology of smooth muscle contractions a brief introduction The virtual SimVessel Laboratory is for recordings of smooth muscle contractions of small muscle stripes of different
Effects and mechanisms of Fenofibrate on the secretion of vascular endothelial contraction factors in hypertensive rats
 Effects and mechanisms of Fenofibrate on the secretion of vascular endothelial contraction factors in hypertensive rats Y. Zhu 1, H.-S. Wang 1, X.-M. Li 1 and C. Qu 2 1 Department of Cardiac Surgery, General
Effects and mechanisms of Fenofibrate on the secretion of vascular endothelial contraction factors in hypertensive rats Y. Zhu 1, H.-S. Wang 1, X.-M. Li 1 and C. Qu 2 1 Department of Cardiac Surgery, General
Clonidine Inhibits Phenylephrine-Induced Contraction of Rat Thoracic Aortae by
 Pharmacology & Pharmacy, 2017, 8, 172-188 http://www.scirp.org/journal/pp ISSN Online: 2157-9431 ISSN Print: 2157-9423 Clonidine Inhibits Phenylephrine-Induced Contraction of Rat Thoracic Aortae by Competitive
Pharmacology & Pharmacy, 2017, 8, 172-188 http://www.scirp.org/journal/pp ISSN Online: 2157-9431 ISSN Print: 2157-9423 Clonidine Inhibits Phenylephrine-Induced Contraction of Rat Thoracic Aortae by Competitive
MODIFICATIONS BY PROPRANOLOL OF THE RESPONSE OF ISOLATED RABBIT ATRIA TO ENDOGENOUS AND EXOGENOUS NORADRENALINE
 Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 32, 539-545. MODIFICATIONS BY PROPRANOLOL OF THE RESPONSE OF ISOLATED RABBIT ATRIA TO ENDOGENOUS AND EXOGENOUS NORADRENALINE BY K. SHIMAMOTO AND N. TODA From the Department
Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 32, 539-545. MODIFICATIONS BY PROPRANOLOL OF THE RESPONSE OF ISOLATED RABBIT ATRIA TO ENDOGENOUS AND EXOGENOUS NORADRENALINE BY K. SHIMAMOTO AND N. TODA From the Department
I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors. Chapter 9. Autonomic Motor Nerves. Autonomic Neurons. Autonomic Ganglia. Autonomic Neurons 9/19/11
 Chapter 9 I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Autonomic
Chapter 9 I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Autonomic
Relaxant Effects of Matrine on Aortic Smooth Muscles of Guinea Pigs 1
 BIOMEDICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES 22, 327-332 (2009) www.besjournal.com Relaxant Effects of Matrine on Aortic Smooth Muscles of Guinea Pigs 1 JIE ZHENG #, PING ZHENG #, XU ZHOU *, LIN YAN #, RU ZHOU
BIOMEDICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES 22, 327-332 (2009) www.besjournal.com Relaxant Effects of Matrine on Aortic Smooth Muscles of Guinea Pigs 1 JIE ZHENG #, PING ZHENG #, XU ZHOU *, LIN YAN #, RU ZHOU
The Autonomic Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology
 The Autonomic Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology 1 After studying the endocrine system you should be able to: 1. Describe the organization of the nervous system. 2. Compare and contrast
The Autonomic Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology 1 After studying the endocrine system you should be able to: 1. Describe the organization of the nervous system. 2. Compare and contrast
hypoxic pulmonary hypertension
 Br. J. Pharmacol. (1992), 17, 47-413 '." Macmillan Press Ltd, 1992 Reduced relaxant potency of nitroprusside on pulmonary artery preparations taken from rats during the development of hypoxic pulmonary
Br. J. Pharmacol. (1992), 17, 47-413 '." Macmillan Press Ltd, 1992 Reduced relaxant potency of nitroprusside on pulmonary artery preparations taken from rats during the development of hypoxic pulmonary
The Antihypertensive Effect of Sesame Seed-derived Products
 Bulletin of saka University of Pharmaceutical Sciences 1 (2007) Brief Reviews *,a b c The Antihypertensive Effect of Sesame Seed-derived Products Daisuke NAKAN, *, a Yoshinobu KIS, b Yasuo MATSUMURA c
Bulletin of saka University of Pharmaceutical Sciences 1 (2007) Brief Reviews *,a b c The Antihypertensive Effect of Sesame Seed-derived Products Daisuke NAKAN, *, a Yoshinobu KIS, b Yasuo MATSUMURA c
TITLE: Alcohol Intoxication Impact on Outcome from Traumatic Injury
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-06-1-0236 TITLE: Alcohol Intoxication Impact on Outcome from Traumatic Injury PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Patricia Molina, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Louisiana State University
AD Award Number: W81XWH-06-1-0236 TITLE: Alcohol Intoxication Impact on Outcome from Traumatic Injury PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Patricia Molina, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Louisiana State University
E ects of indoramin in rat vas deferens and aorta: concomitant a 1 -adrenoceptor and neuronal uptake blockade
 British Journal of Pharmacology (1999) 127, 1832 ± 1836 ã 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bjp E ects of indoramin in rat vas deferens and aorta:
British Journal of Pharmacology (1999) 127, 1832 ± 1836 ã 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bjp E ects of indoramin in rat vas deferens and aorta:
Ch 9. The Autonomic Nervous System
 Ch 9 The Autonomic Nervous System SLOs Review the organization of the ANS Describe how neural regulation of smooth and cardiac muscles differs from that of skeletal muscles Describe the structure and innervation
Ch 9 The Autonomic Nervous System SLOs Review the organization of the ANS Describe how neural regulation of smooth and cardiac muscles differs from that of skeletal muscles Describe the structure and innervation
Pharmacological analysis of muscarinic receptors coupled to oxyntic cell secretion in the mouse stomach
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1985), 86, 601-607 Pharmacological analysis of muscarinic receptors coupled to oxyntic cell secretion in the mouse stomach J.W. Black & N.P. Shankley The Rayne Institute, King's College
Br. J. Pharmac. (1985), 86, 601-607 Pharmacological analysis of muscarinic receptors coupled to oxyntic cell secretion in the mouse stomach J.W. Black & N.P. Shankley The Rayne Institute, King's College
Streptozotocin Diabetes-Induced Changes in Aorta, Peripheral Nerves and Stomach of Wistar Rats
 Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1999), 18, Focus Issue, 155 162 155 Streptozotocin Diabetes-Induced Changes in Aorta, Peripheral Nerves and Stomach of Wistar Rats R. SOTNÍKOVÁ, V. NosÁĽovÁ, M. ŠTEFEK, S. ŠTOLC,
Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1999), 18, Focus Issue, 155 162 155 Streptozotocin Diabetes-Induced Changes in Aorta, Peripheral Nerves and Stomach of Wistar Rats R. SOTNÍKOVÁ, V. NosÁĽovÁ, M. ŠTEFEK, S. ŠTOLC,
Chapter 14 Blood Vessels, Blood Flow and Pressure Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 14 Blood Vessels, Blood Flow and Pressure Exam Study Questions 14.1 Physical Law Governing Blood Flow and Blood Pressure 1. How do you calculate flow rate? 2. What is the driving force of blood
Chapter 14 Blood Vessels, Blood Flow and Pressure Exam Study Questions 14.1 Physical Law Governing Blood Flow and Blood Pressure 1. How do you calculate flow rate? 2. What is the driving force of blood
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Keri Muma Bio 6 Organization of the Nervous System Efferent Division Somatic Nervous System Voluntary control Effector = skeletal muscles Muscles must be excited by a motor neuron
Autonomic Nervous System Keri Muma Bio 6 Organization of the Nervous System Efferent Division Somatic Nervous System Voluntary control Effector = skeletal muscles Muscles must be excited by a motor neuron
Lujain Hamdan. Ayman Musleh & Yahya Salem. Mohammed khatatbeh
 12 Lujain Hamdan Ayman Musleh & Yahya Salem Mohammed khatatbeh the last lecture, we have studied the differences between the two divisions of the ANS: sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways which work
12 Lujain Hamdan Ayman Musleh & Yahya Salem Mohammed khatatbeh the last lecture, we have studied the differences between the two divisions of the ANS: sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways which work
Basics of Pharmacology
 Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
Pharmacodynamics. Dr. Alia Shatanawi
 Pharmacodynamics Dr. Alia Shatanawi Drug Receptor Interactions Sep-17 Dose response relationships Graduate dose-response relations As the dose administrated to single subject or isolated tissue is increased,
Pharmacodynamics Dr. Alia Shatanawi Drug Receptor Interactions Sep-17 Dose response relationships Graduate dose-response relations As the dose administrated to single subject or isolated tissue is increased,
Effects of metabolic inhibitors on contraction of rabbit detrusor muscle
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1968), 34, 493-498. Effects of metabolic inhibitors on contraction of rabbit detrusor muscle D. M. PATON Department of Pharmacology, Utniversity of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada 1.
Br. J. Pharmac. (1968), 34, 493-498. Effects of metabolic inhibitors on contraction of rabbit detrusor muscle D. M. PATON Department of Pharmacology, Utniversity of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada 1.
PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work!
 PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work Drug: a chemical that affects physiological function in a specific way. Endogenous substances: hormones, neurotransmitters, antibodies, genes. Exogenous substances:
PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work Drug: a chemical that affects physiological function in a specific way. Endogenous substances: hormones, neurotransmitters, antibodies, genes. Exogenous substances:
This laboratory exercise uses a simple preparation and a straightforward
 LABORATORY DEMONSTRATION OF VASCULAR SMOOTH MUSCLE FUNCTION USING RAT AORTIC RING SEGMENTS Rayna J. Gonzales, Rebecca W. Carter, and Nancy L. Kanagy Vascular Physiology Group, Department of Cell Biology
LABORATORY DEMONSTRATION OF VASCULAR SMOOTH MUSCLE FUNCTION USING RAT AORTIC RING SEGMENTS Rayna J. Gonzales, Rebecca W. Carter, and Nancy L. Kanagy Vascular Physiology Group, Department of Cell Biology
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
 2. MATERIALS AND METHODS 2.1 Materials [ 3 H]-Digoxin (37Ci/mmol) was purchased from Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences Inc. (Boston, USA) and [U- 14 C]-Sucrose (660mCi/mmol) was purchased from Amersham Bioscience
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS 2.1 Materials [ 3 H]-Digoxin (37Ci/mmol) was purchased from Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences Inc. (Boston, USA) and [U- 14 C]-Sucrose (660mCi/mmol) was purchased from Amersham Bioscience
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS):
 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): ANS is the major involuntary, unconscious, automatic portion of the nervous system. involuntary voluntary The motor (efferent)portion of the ANS is the major pathway for
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): ANS is the major involuntary, unconscious, automatic portion of the nervous system. involuntary voluntary The motor (efferent)portion of the ANS is the major pathway for
Role of GABA B Receptor and L-Arg in GABA- Induced Vasorelaxation in Non-diabetic and Streptozotocin- Induced Diabetic Rat Vessels
 Iranian Biomedical Journal 19 (2): 91-95 (April 2015) DOI: 10.6091/ibj.1461.2015 Role of GABA B Receptor and L-Arg in GABA- Induced Vasorelaxation in Non-diabetic and Streptozotocin- Induced Diabetic Rat
Iranian Biomedical Journal 19 (2): 91-95 (April 2015) DOI: 10.6091/ibj.1461.2015 Role of GABA B Receptor and L-Arg in GABA- Induced Vasorelaxation in Non-diabetic and Streptozotocin- Induced Diabetic Rat
General organization of central and peripheral components of the nervous system
 General organization of central and peripheral components of the nervous system Today we are focusing on the ANS Part of ANS?? Life depends on the innervation of the viscera... all the rest is biological
General organization of central and peripheral components of the nervous system Today we are focusing on the ANS Part of ANS?? Life depends on the innervation of the viscera... all the rest is biological
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(5):468-472 Study on the anticonvulsant activity of Pentazocine
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(5):468-472 Study on the anticonvulsant activity of Pentazocine
ca2-adrenoceptor-mediated responses in the rabbit isolated pulmonary artery
 Br. J. Pharmacol. (1993), 18, 155-161 d" Macmillan Press Ltd, 1993 Influences of the endothelium and hypoxia on ac- and ca2-adrenoceptor-mediated responses in the rabbit isolated pulmonary artery 'Margaret
Br. J. Pharmacol. (1993), 18, 155-161 d" Macmillan Press Ltd, 1993 Influences of the endothelium and hypoxia on ac- and ca2-adrenoceptor-mediated responses in the rabbit isolated pulmonary artery 'Margaret
Vascular action of the hypoglycaemic agent gliclazide in diabetic rabbits
 Diabetologia (1998) 41: 9--15 Springer-Verlag 1998 Vascular action of the hypoglycaemic agent gliclazide in diabetic rabbits P. J. Pagano 1, M. C. Griswold 1, D. Ravel 2, R. A. Cohen 1 1 Vascular Biology
Diabetologia (1998) 41: 9--15 Springer-Verlag 1998 Vascular action of the hypoglycaemic agent gliclazide in diabetic rabbits P. J. Pagano 1, M. C. Griswold 1, D. Ravel 2, R. A. Cohen 1 1 Vascular Biology
Myocardial Opiate Receptors
 Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 1982, 1, 447-452 Myocardial Opiate Receptors M. E. SAXON, G. R. IVANITSKY, F. F. BELOYARTSEV, V. G. SAFRONOVA, YU. M. KOKOZ and A. A. FREYDIN Institute of Biological Physics, Academy
Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 1982, 1, 447-452 Myocardial Opiate Receptors M. E. SAXON, G. R. IVANITSKY, F. F. BELOYARTSEV, V. G. SAFRONOVA, YU. M. KOKOZ and A. A. FREYDIN Institute of Biological Physics, Academy
A comparison of the sensitivities of innervated and denervated rat vasa deferentia to agonist drugs
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 39, 748-754. A comparison of the sensitivities of innervated and denervated rat vasa deferentia to agonist drugs A. T. BIRMINGHAM*, G. PATRSON AND J. W6JCICKIt Department of Pharmacology,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 39, 748-754. A comparison of the sensitivities of innervated and denervated rat vasa deferentia to agonist drugs A. T. BIRMINGHAM*, G. PATRSON AND J. W6JCICKIt Department of Pharmacology,
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Alia Shatnawi
 number 11 Done by Lojayn Salah Corrected by Doctor Alia Shatnawi The last thing we talked about in the previous lecture was the effect of a drug at a particular dose, and we took this equation: E= Emax
number 11 Done by Lojayn Salah Corrected by Doctor Alia Shatnawi The last thing we talked about in the previous lecture was the effect of a drug at a particular dose, and we took this equation: E= Emax
Lujain Hamdan. Tamer Barakat. Faisal Mohammad
 17 Lujain Hamdan Tamer Barakat Faisal Mohammad Review : Summary of synaptic transmission: 1) Action potential arrives to presynaptic terminals of a nerve and causes depolarization by opening Ca 2+ voltage-gated
17 Lujain Hamdan Tamer Barakat Faisal Mohammad Review : Summary of synaptic transmission: 1) Action potential arrives to presynaptic terminals of a nerve and causes depolarization by opening Ca 2+ voltage-gated
Histamine Develops Homologous Desensitization under Ca 2+ -free Conditions with Increase in Basal Tone in Smooth Muscle of Guinea Pig Taenia Caeci
 YAKUGAKU ZASSHI 130(3) 451 455 (2010) 2010 The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan 451 Notes Histamine Develops Homologous Desensitization under Ca 2+ -free Conditions with Increase in Basal Tone in Smooth
YAKUGAKU ZASSHI 130(3) 451 455 (2010) 2010 The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan 451 Notes Histamine Develops Homologous Desensitization under Ca 2+ -free Conditions with Increase in Basal Tone in Smooth
Structure and organization of blood vessels
 The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
Effects of Aging and Hypertension on Endothelium-Dependent Vascular Relaxation in Rat Carotid Artery
 892 Effects of Aging and Hypertension on Endothelium-Dependent Vascular Relaxation in Rat Carotid Artery Kazuhiro Hongo, MD, Tadayoshi Nakagomi, MD, Neal F. Kassell, MD, Tomio Sasaki, MD, Michael Lehman,
892 Effects of Aging and Hypertension on Endothelium-Dependent Vascular Relaxation in Rat Carotid Artery Kazuhiro Hongo, MD, Tadayoshi Nakagomi, MD, Neal F. Kassell, MD, Tomio Sasaki, MD, Michael Lehman,
Analysis of AVP functions via V1a and V1b receptors with knockout mice. Akito Tanoue
 Analysis of AVP functions via V1a and V1b receptors with knockout mice Akito Tanoue Department of Pharmacology, National Research Institute for Child Health and Development Arginine-Vasopressin (AVP) is
Analysis of AVP functions via V1a and V1b receptors with knockout mice Akito Tanoue Department of Pharmacology, National Research Institute for Child Health and Development Arginine-Vasopressin (AVP) is
Differential antagonism of the negative inotropic effect
 Br. J. Pharmacol. (1989), 96, 96-912 Differential antagonism of the negative inotropic effect of gentamicin by calcium ions, Bay K 8644 and isoprenaline in canine ventricular muscle: comparison with cobalt
Br. J. Pharmacol. (1989), 96, 96-912 Differential antagonism of the negative inotropic effect of gentamicin by calcium ions, Bay K 8644 and isoprenaline in canine ventricular muscle: comparison with cobalt
Introduction to Autonomic
 Part 2 Autonomic Pharmacology 3 Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology FUNCTIONS OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM The autonomic nervous system (Figure 3 1) is composed of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
Part 2 Autonomic Pharmacology 3 Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology FUNCTIONS OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM The autonomic nervous system (Figure 3 1) is composed of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
Part 3:Strategies for successful aging. Avoiding disease with physical activity
 Part 3:Strategies for successful aging Avoiding disease with physical activity Causes of disability and disease with aging Causes of death for old individuals Atherosclerosis (CHD) CNS-vascular accidents
Part 3:Strategies for successful aging Avoiding disease with physical activity Causes of disability and disease with aging Causes of death for old individuals Atherosclerosis (CHD) CNS-vascular accidents
Interrelationship between Angiotensin Catecholamines. Tatsuo SATO, M.D., Masaru MAEBASHI, M.D., Koji GOTO, M.D., and Kaoru YOSHINAGA, M.D.
 Interrelationship between Angiotensin and Catecholamines Tatsuo SATO, M.D., Masaru MAEBASHI, M.D., Koji GOTO, M.D., and Kaoru YOSHINAGA, M.D. SUMMARY Urinary catecholamines were measured with an attempt
Interrelationship between Angiotensin and Catecholamines Tatsuo SATO, M.D., Masaru MAEBASHI, M.D., Koji GOTO, M.D., and Kaoru YOSHINAGA, M.D. SUMMARY Urinary catecholamines were measured with an attempt
The role of angiotensin II (AngII) in maintaining
 AJH 1999;12:705 715 Chronic Captopril Administration Decreases Vasodilator Responses in Skeletal Muscle Arterioles Jefferson C. Frisbee, David S. Weber, and Julian H. Lombard Changes in arteriolar reactivity
AJH 1999;12:705 715 Chronic Captopril Administration Decreases Vasodilator Responses in Skeletal Muscle Arterioles Jefferson C. Frisbee, David S. Weber, and Julian H. Lombard Changes in arteriolar reactivity
A CENTRAL NORADRENERGIC MECHANISM RESPONSIBLE FOR MODULATION OF THE ARTERIAL BARORECEPTOR REFLEX IN CATS
 www.kopfinstruments.com A CENTRAL NORADRENERGIC MECHANISM RESPONSIBLE FOR MODULATION OF THE ARTERIAL BARORECEPTOR REFLEX IN CATS V. S. EREMEEV, Ph.D. R. S. KHRUSTALEVA, Ph.D. V. A. TSYRLIN, Ph.D. Yu. I.
www.kopfinstruments.com A CENTRAL NORADRENERGIC MECHANISM RESPONSIBLE FOR MODULATION OF THE ARTERIAL BARORECEPTOR REFLEX IN CATS V. S. EREMEEV, Ph.D. R. S. KHRUSTALEVA, Ph.D. V. A. TSYRLIN, Ph.D. Yu. I.
Exercise 6: Cardiovascular Physiology: Activity 4: Examining the Effects of Chemical Modifiers on Heart Rate Lab Report
 Name: Rafael Paolo H Aquino Exercise 6: Cardiovascular Physiology: Activity 4: Examining the Effects of Chemical Modifiers on Heart Rate Lab Report Pre-lab Quiz Results You scored 100% by answering 4 out
Name: Rafael Paolo H Aquino Exercise 6: Cardiovascular Physiology: Activity 4: Examining the Effects of Chemical Modifiers on Heart Rate Lab Report Pre-lab Quiz Results You scored 100% by answering 4 out
PHARMACODYNAMICS II. The total number of receptors, [R T ] = [R] + [AR] + [BR] (A = agonist, B = antagonist, R = receptors) = T. Antagonist present
![PHARMACODYNAMICS II. The total number of receptors, [R T ] = [R] + [AR] + [BR] (A = agonist, B = antagonist, R = receptors) = T. Antagonist present PHARMACODYNAMICS II. The total number of receptors, [R T ] = [R] + [AR] + [BR] (A = agonist, B = antagonist, R = receptors) = T. Antagonist present](/thumbs/73/69197936.jpg) Pharmacology Semester 1 page 1 of 5 PHARMACODYNAMICS II Antagonists Are structurally similar to the binding site of a receptor and thus show affinity towards the receptor. However, they have zero intrinsic
Pharmacology Semester 1 page 1 of 5 PHARMACODYNAMICS II Antagonists Are structurally similar to the binding site of a receptor and thus show affinity towards the receptor. However, they have zero intrinsic
Enhancement of Peripheral Alpha-Receptor Stimulation by Blockade of "Silent" Beta Receptors
 Enhancement of Peripheral Alpha-Receptor Stimulation by Blockade of "Silent" Beta Receptors By Thomas F. Burks, Ph.D., and Theodore Cooper, M.D., Ph.D. ABSTRACT Evidence is presented for the existence
Enhancement of Peripheral Alpha-Receptor Stimulation by Blockade of "Silent" Beta Receptors By Thomas F. Burks, Ph.D., and Theodore Cooper, M.D., Ph.D. ABSTRACT Evidence is presented for the existence
Calcium-dependent mechanisms mediate the vasorelaxant effects of Tridax procumbens
 DOI 1.1515/jbcpp-213-3 J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 214; 25(2): 161 166 Hussein M. Salahdeen, Gbolahan O. Idowu, Omoniyi K. Yemitan, Babatunde A. Murtala and Abdul-Rasak A. Alada Calcium-dependent mechanisms
DOI 1.1515/jbcpp-213-3 J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 214; 25(2): 161 166 Hussein M. Salahdeen, Gbolahan O. Idowu, Omoniyi K. Yemitan, Babatunde A. Murtala and Abdul-Rasak A. Alada Calcium-dependent mechanisms
Title: Contractions of the mouse prostate elicited by acetylcholine are mediated by M 3 muscarinic
 JPET Fast This Forward. article has not Published been copyedited on and September formatted. The 1, final 2011 version as may DOI:10.1124/jpet.111.186841 differ from this version. :Wd deeedd d Title:
JPET Fast This Forward. article has not Published been copyedited on and September formatted. The 1, final 2011 version as may DOI:10.1124/jpet.111.186841 differ from this version. :Wd deeedd d Title:
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 11 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Autonomic Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 533 through 552 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words! Work
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 11 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Autonomic Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 533 through 552 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words! Work
January 25, Introduction to Pharmacology
 January 25, 2015 Introduction to Pharmacology Edward Fisher, Ph.D., R.Ph. Professor and Associate Dean for Academic Affairs Director MS Clinical Psychopharmacology University of Hawaii at Hilo College
January 25, 2015 Introduction to Pharmacology Edward Fisher, Ph.D., R.Ph. Professor and Associate Dean for Academic Affairs Director MS Clinical Psychopharmacology University of Hawaii at Hilo College
Pharmacological Assessment of the In Vitro Functional Selectivity of Aclidinium Bromide at M 3 and M 2 Muscarinic Receptors in Human Tissue
 Pulm Ther (2015) 1:103 107 DOI 10.1007/s41030-015-0003-x BRIEF REPORT Pharmacological Assessment of the In Vitro Functional Selectivity of Aclidinium Bromide at M 3 and M 2 Muscarinic Receptors in Human
Pulm Ther (2015) 1:103 107 DOI 10.1007/s41030-015-0003-x BRIEF REPORT Pharmacological Assessment of the In Vitro Functional Selectivity of Aclidinium Bromide at M 3 and M 2 Muscarinic Receptors in Human
The Nervous System and Metabolism
 = P1: JZP 8 The Nervous System and Metabolism Dendrites Cell body Axon (may be sheathed in myelin) Nucleus Axonal terminals (synapses) Figure 8.1 Basic structure of a nerve cell (neuron). CH 3_ CH 3 CH
= P1: JZP 8 The Nervous System and Metabolism Dendrites Cell body Axon (may be sheathed in myelin) Nucleus Axonal terminals (synapses) Figure 8.1 Basic structure of a nerve cell (neuron). CH 3_ CH 3 CH
Adrenergic agonists Sympathomimetic drugs. ANS Pharmacology Lecture 4 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy/University of Sulaimani
 Adrenergic agonists Sympathomimetic drugs ANS Pharmacology Lecture 4 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy/University of Sulaimani 2017-2018 Adrenergic agonists The adrenergic drugs affect receptors that
Adrenergic agonists Sympathomimetic drugs ANS Pharmacology Lecture 4 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy/University of Sulaimani 2017-2018 Adrenergic agonists The adrenergic drugs affect receptors that
VASCULAR DYSFUNCTION IN THE -GALACTOSIDASE A-KNOCKOUT MOUSE IS AN ENDOTHELIAL CELL-, PLASMA MEMBRANE-BASED DEFECT
 Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology (2008) 35, 1156 1163 doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2008.04984.x Blackwell Endothelial-based JL Park et Publishing al. defect Asiain Fabry disease VASCULAR
Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology (2008) 35, 1156 1163 doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2008.04984.x Blackwell Endothelial-based JL Park et Publishing al. defect Asiain Fabry disease VASCULAR
The average potassium content during the last 5. solids. This average decrease of 2.2 meq. per 100. initial potassium content of the arteries.
 THE EFFECT OF NOR-EPINEPHRINE ON THE ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION OF ARTERIAL SMOOTH MUSCLE' By LOUIS TOBIAN 2 AND ADACIE FOX (From the Departments of Pharmacology and Internal Medicine, Southwesters Medical
THE EFFECT OF NOR-EPINEPHRINE ON THE ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION OF ARTERIAL SMOOTH MUSCLE' By LOUIS TOBIAN 2 AND ADACIE FOX (From the Departments of Pharmacology and Internal Medicine, Southwesters Medical
Faculty of Science, Mahidol University
 1 Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Course Syllabus and Lesson Plan Principles of Drug Action (SCBM 451) Academic Year 2018 August 21 th September 13 th, 2018 Course code SCBM 451 Total credit 2 (2-0-4)
1 Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Course Syllabus and Lesson Plan Principles of Drug Action (SCBM 451) Academic Year 2018 August 21 th September 13 th, 2018 Course code SCBM 451 Total credit 2 (2-0-4)
Supplementary Figure 1: Steviol and stevioside potentiate TRPM5 in a cell-free environment. (a) TRPM5 currents are activated in inside-out patches
 Supplementary Figure 1: Steviol and stevioside potentiate TRPM5 in a cell-free environment. (a) TRPM5 currents are activated in inside-out patches during application of 500 µm Ca 2+ at the intracellular
Supplementary Figure 1: Steviol and stevioside potentiate TRPM5 in a cell-free environment. (a) TRPM5 currents are activated in inside-out patches during application of 500 µm Ca 2+ at the intracellular
Capsaicin (3.3 mmol/l)
 A 18 16 14 1 8 6 4 Vehicle BCTC (.8 mmol/l) Sensory deafferentation Time (min) Capsaicin (3.3 mmol/l) N=3 4 * P
A 18 16 14 1 8 6 4 Vehicle BCTC (.8 mmol/l) Sensory deafferentation Time (min) Capsaicin (3.3 mmol/l) N=3 4 * P
Chapter 16. APR Enhanced Lecture Slides
 Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
48 HYPERTENSION VOL 7, No 1, JANUARY-FEBRUARY 1985
 48 HYPERTENSON VOL 7, No 1, JANUARY-FEBRUARY 1985 stricter responses were evoked by electrical stimulation of the renal nerves via platinum electrodes with the use of parameters that activate adrenergic
48 HYPERTENSON VOL 7, No 1, JANUARY-FEBRUARY 1985 stricter responses were evoked by electrical stimulation of the renal nerves via platinum electrodes with the use of parameters that activate adrenergic
Actions of prostaglandin F20 on the splenic vascular and capsular smooth muscle in the dog
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 41, 1-7 Actions of prostaglandin F20 on the splenic vascular and capsular smooth muscle in the dog B. N. DAVIES ADi P. G. WITHRINGTON Department of Physiology, Medical College of
Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 41, 1-7 Actions of prostaglandin F20 on the splenic vascular and capsular smooth muscle in the dog B. N. DAVIES ADi P. G. WITHRINGTON Department of Physiology, Medical College of
