Cardiomyopathy in Myotonic Dystrophy. A Light and Electron Microscopic Study of the Myocardium
|
|
|
- Bennett Brown
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cardiomyopathy in Myotonic Dystrophy A Light and Electron Microscopic Study of the Myocardium Nobuyuki TANAKA, M.D., Hiromitsu TANAKA, M.D., Motohiko TAKEDA, M.D., Tatsuru NIIMURA, M.D., Takuya KANEHISA, M.D., and Shin-ichi TERASHI, M.D.* SUMMARY A case of 31-year-old woman with myotonic dystrophy who developed only slight cardiac symptoms has been reported. Light and electron microscopic study was performed on myocardium obtained with endomyocardial biopsy. Light microscopy revealed a considerable degree of fatty infiltration in the myocardium, slight interstitial fibrosis and degenerated myocardial cells. On electron microscopy, marked mitochondriosis and a small number of vacuoles consisting of single limiting membrane and indefinite content low in electron density were observed. Peculiar intranuclear structure and myofibrils showing partial over-contraction and indistinct Z band were also present, and these findings were discussed comparing with the previous reports. Endomyocardial biopsy seemed to be very useful to detect the myocardial changes even in the early stage of this disease, and the electron microscopic examination of the myocardium may provide the finding which is pathognomonic for the development of the cardiomyopathy in myotonic dystrophy. Additional Indexing Words: Myotonic dystrophy Cardiomyopathy Endomyocardial biopsy Fatty infiltration Electron micrograph of myocardium Mitochondriosis Sarcoplasmic reticulum YOTONIC dystrophy is a heredo-familial disorder characterized by myotonia, atrophy of the muscles, dysfunction in different endocrine glands and dystrophic signs in other tissues including baldness and cataracts. Griffith1) was the first to focus attention on the heart in myotonic dystrophy. In 1911, he described a patient with pulse rate of 30 to 46 per minute. Since that time an increasing number of reports have appeared describing From the First Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Kagoshima University, Kagoshima. * First Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Kagoshima University, Kagoshima. Received for publication February 13,
2 Vol.14 No.3 CARDIOMYOPATHY IN MYOTONIC DYSTROPHY 203 cardiac abnormalities in myotonic dystrophy, such as electrocardiographic changes3),4),7) and hypotension.6) Few histopathological studies of the heart, however, have been reported and only 2 cases were examined for heart ante mortem. In 1964, Petkovich, Dunn and Reed8) described the light microscopic findings of the myocardium provided at the time of long-term pacemaker implantation. Besides, the electron microscopic examination of the myocardium in myotonic dystrophy was first reported by Bulloch et al9) in In 1962, Konno and Sakakibara10) devised a special form of endomyocardial bioptome, and the endomyocardial biopsy using this bioptome has been reported to be safe and dependable.11) Recently, we had the opportunity to observe a 31-year-old woman of myotonic dystrophy who exhibited slight exertional dyspnea and monofocal ventricular premature beats. This report deals with light and electron microscopic findings of the myocardium obtained with endomyocardial biopsy of the right ventricle. CASE REPORT A 31-year-old woman was admitted to Kagoshima University Hospitl with the complaints of slight exertional palpitation and dyspnea on September 4, In 1945, at the age of 6, she developed grasping myotonia. Her menstruation has been very irregular from the time of menarche at the age of 14. She married at the age of 27 and had 2 pregnancies which resulted in spontaneous abortion at 3 and 4 months' gestation, respectively. Palpitation and slight dyspnea on exertion appeared in 1952, at the age of 13. In 1968, about 1 year before admission she noticed bilateral cataracts. She has had cold intolerance and caught a cold frequently. Family pedigree is shown in Fig. 1. Her father has myotonia, cataracts, muscular atrophy and baldness. One of her brother developed myotonia and muscular atrophy. She has 2 paternal uncles who have frontal baldness. One of her paternal cousins has myotonia and baldness. On physical examination, she appeared almost healthy except for bilateral cataracts and slight muscular atrophy in the neck. Pulse rate was 66 per minute and occasional premature beats were present. Blood pressure was 106/80mmHg in the upper limbs. The heart and the lung were clear on percussion and auscultation. Hepato-splenomegaly, abdominal mass and pretibial edema were not observed. Grasping myotonia was apparently present. The percussion myotonia was clearly demonstrated in the hand and the tongue. Muscular atrophy and weekness were dominant in sternomastoids and in the muscles of the forearm. Other neurological examinations remained normal. The peripheral blood counts, urinalysis, serum electrolytes, serum creatine and creatinine, s-got and -GPT, serum CPK, total and fractional proteins, blood sugar and immunoglobulin analysis were all within normal limits. The serum cholesterol was 319mg/ml. Triosorb test was 30% and the basal metabolic rate
3 204 TANAKA, ET AL. Jap. Heart J. May, 1973 shown Fig. 1. The family pedigree. The patient reported in this paper is by arrow. Fig. 2. Chest X-ray photogram.
4 Vol.14 CARDIOMYOPATHY IN MYOTONIC DYSTROPHY 205 No.3 Fig. 3. Electrocardiogram showing occasional monofocal ventricular premature beats and increased R/S ratio in V1. was -21%. The 24-hour 131I-uptake was 14% and wasn't increased by TSH administration. Urinary excretion of 17-OHCS and 17-KS were 2.1mg/day and 2.2 to 5.8mg/day, respectively. The corticotropin response test disclosed 35% decrease of eosinophiles, however, urinary 17-OHCS level remained unchanged. The basal body temperature curve was low and flat and the administration of gonadotropin revealed no response. But the menstruation had occurred after the administration of estrogen and progesterone. The heart silhouette was slightly hyposthenic and languid as shown in Fig. 2 but the cardio-thoracic ratio was just within normal limit. The electrocardiogram represented in Fig. 3 revealed normal sinus rhythm and occasional monofocal ventricular premature beats. In all leads, P waves were low and PQ interval was 0.18sec. Master's two step test was negative. Right heart catheterization revealed mean pulmonary wedge pressure of 4.0mmHg, pulmonary arterial pressure of 14/9mmHg, and right ventricular pressure of 11/0mmHg. The cardiac output calculated with Fick's method was 5,500ml/min and the stroke volume was 68.7ml. Electromyographic study disclosed typical myotonic pattern and "diver-bomber" effect characteristic of myotonic dystrophy. MATERIALS AND METHODS Endomyocardial Biopsy: Endomyocardial biopsy was performed according to the Konno's technique.10),11) The endomyocardial bioptome was inserted into the right ventricle via the right saphenous vein and the specimen was obtained without any side effects. Electron Microscopy: The myocardial tissues obtained were cut into smaller pieces on ice and fixed with 2% osmium tetroxide in 0.1M phosphate buffer (ph 7.4) for 1 hour. After rapid dehydration with increasing concentrations of ethanol, the tissues were subjected to Epon embedding. Porter-Blum ultramicrotome, Ivan S arvall Inc, was used for cutting the blocks and the sections were stained with uranyl acetate and lead acetate. Electron micrographs were taken with JEM type-7 electron microscope. Light Microscopy: Light microscopic examination of the skeletal muscle and the heart muscle was carried out after staining with hematoxylin-eosin and Mal - lory-azan stains according to the usual method.
5 206 TANAKA, ET AL. Jap. Heart J. May, 1973 RESULTS Light Microscopy of the Skeletal Muscle: Biopsy specimen of the right quadriceps femoris muscle shown in Fig. 4 represented a small number of atrophic muscle fibers and central migration of nuclei. The quantity of interstitial connective tissues and sarcolemmal nuclei remained normal. Necro- ~160). Fig. 4. Light micrograph of the skeletal muscle (Hematoxylin and eosin, Fig. 5. Light micrograph of the myocardium showing marked fatty infiltration and degenerative myocardial cells with granular sarcoplasma and small vacuolation (Hematoxylin and eosin, ~100).
6 Vol.14 No.3 CARDIOMYOPATHY IN MYOTONIC DYSTROPHY 207 tic muscle debris, fatty infiltration and ring fibers were not present. Light Microscopy of the Myocardium: Marked fatty infiltration and slight interstitial fibrosis were present in the myocardium, and the remaining myocardial fibers differed in size as shown in Fig. 5. Adjoining the fatty infiltration, there were degenerated myocytes having granular sarcoplasma and small vacuolation. The endocardial and subendocardial tissues appeared to be normal. Myocardial necrosis, lipofuscin deposit and cellular infiltration were not observed. Electron Microscopy of the Myocardium: With increased number of mitochondria, a small number of vacuoles which were bounded with single limiting membrane resembling the findings described by Bulloch et al and contained indefinite substance which was low in electron density were present as shown in Fig. 6. It was, however, difficult to ascertain the original structure of the vacuoles from which they derived. Marked mitochondriosis was present in places, especially in the circumferences of nuclei as shown in Fig. 7, Fig. 6. Electron micrograph of the myocardium showing increased num - ber of mitochondria and a small number of vacuoles (V) consist of single limiting membrane and indefinite content which is low in electron density.
7 208 TANAKA, ET AL. Jap. Heart J. May, 1973 Fig. 7. Long section of myocardium showing perinuclear proliferation of mitochondria. The intercalated discs, end-to-end junction (EJ) seems to be bound tightly but side-to-side junction (SJ) is apparently distended. still the gross structure of each mitochondria seemed to retain its normal configuration. The basic structure of myofibrils appeared to be normal except for partial over-contraction of the myofibrils and few indistinct Z lines as represented in Figs. 6 and 8. A peculiar intranuclear figure and perinuclear proliferation of electron dense lysosome were observed as shown in Fig. 9. DISCUSSION Some histopathological studies on the heart in myotonic dystrophy have appeared in the literature. Berthold12) reviewed the literature on pathological anatomy of 45 patients with myotonic dystrophy. Of 29 cases examined on heart histologically, 14 cases had normal hearts or only slight changes in the hearts. Fifteen cases, on the other hand, revealed pathological findings in the hearts including myocardial atrophy, proliferation of interstitial connective tissues and perinuclear pigments. Orndahl et al7) reported 4 autopsy cases
8 Vol.14 CARDIOMYOPATHY IN MYOTONIC DYSTROPHY 209 No.3 Fig. 8. Long section of myocardium. Partially over-contracted myofibrils are seen. aged 39, 47, 53, and 62. They stated that the histological changes might be well correlated to the degree of atherosclerosis in the coronary arteries. However, a 60-year-old patient with myotonic dystrophy described by Cannon13) had minimally atherosclerotic coronary vessels and histologically normal bilateral ventricles. De Wind and Jones,5) reviewing 98 cases of myotonic dystrophy, excluded the atherosclerois as the prime cause of cardiomyopathy in this disease. Payne and Greenfield, 4) and Fisch and Evans2) also reached the similar conclusion. In our case, a 31-year-old woman, the myocardial lesion could not be attributed to atherosclerosis. The fatty infiltration and fibrosis of the myocardium seem to be the most common histopathological findings described by many authors as summarized in Table I. Some of the authors reported additional findings such as vacuolar degeneration and splitting of the myocardial fibers,14) interstitial edema and fibrosis,12) cell infiltration in the stroma8) and variation in size of the myocardial fibers. Consequently, in the patients of myotonic dystrophy, the myocardial involvements, when present, are one of or the combination of the dif-
9 210 TANAKA, ET AL. Jap. Heart J. M ay, 1973 Fig. 9. A peculiar intranuclear structure (P) and electron dense lysosomes (L) are represented. Table I. Histopathological Findings on Myocardium in Myotonic Dystrophy Previously Reported
10 Vol.14 No.3 CARDIOMYOPATHY IN MYOTONIC DYSTROPHY 211 ferent histological changes as described avobe. However, these histological findings were considered to be not pathognomonic but nonspecific for cardiomyopathy in myotonic dystrophy. In this case, the myocardial specimen obtained with endomyocardial biopsy disclosed similar histological changes such as fatty infiltration and myocardial degeneration, and these findings seemed to be sufficient to understand the cardiac symptoms including exertional palpitation and ventricular premature beats. It is noteworthy that a considerable degree of myocardial involvements were present in the patient who had only slight skeletal muscle lesion. However, Petkovich4) and Thomson15) considered that the similar pathological process which involved the skeletal muscle might be responsible for the development of the cardiomyopathy in myotonic dystrophy. Bulloch et al9) reported the first and the only 1 case of myotonic dystrophy whose myocardium was examined by electron microscopy as well as light microscopy. They stated that the sarcoplasmic reticulum might be the site of early pathological change in myocardium, and that myocardial biopsy in the early stage of this disease would be of great interest in attempting to identify an early structural lesion. The endomyocardial biopsy afforded us a chance to examine the heart muscle exhibiting only slight cardiac symptoms. The presence of vacuolation and indistinct Z lines resembled the findings described by Bulloch et al. The structure of the vacuoles in our case did'nt indicate double limiting membranes and lamellated electron dense rings (myeline figures) as described by them, but consisted of single limiting membrane and dim content low in electron density. It is difficult to identify the primary structure of the vacuoles, however, we considered that the dilated tubules of the endoplasmic reticulum might be the primary structure of the vacuoles as seen from the location of the vacuoles and their single limiting membrane. Proliferation of mitochondria and peculiar intranuclear figure observed in our case were not reported by Bulloch et al. In spite of marked mitochondriosis, the mitochondrial structure was well maintained and the mitochondrial ghosts and sarcoplasmic debris were not observed in our case. In order to verify the primary site and nature of cardiomyopathy in myotonic dystrophy, it is necessary to accumulate many electron microscopic examinations on myocardium in an early stage of the disease with the aid of endomyocardial biopsy. Furthermore, it is well known fact that the myotonic dystrophy is frequently complicated by dysfunctions in different endocrine glands as reported in this paper. Therefore, to understand the exact pathological process of the development of cardiomyopathy in this disease, it also seems to be important to deliberate on the effects of the hormonal disorders on myocardium.16)-18)
11 212 TANAKA, ET AL. Jap. Heart J. May, 1973 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We wish to thank Dr. K. Kawamura, the Third Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Kyoto, for his kind criticism on electron microscopic findings on myocardium. REFERENCES 1. Griffith TW: Quart J Med 5: 229, Fisch C, Evans PV : New Eng J Med 251: 527, Fisch C: Am Heart J 41: 525, Payne CA, Greenfield JC: Am Heart J 65: 436, De Wind LT, Jones RJ: JAMA 144: 229, Spillane JD: Brit Heart J 13: 343, Orndahl G: Acta Med Scand 176: 479, Petkovich NJ, Dunn M, Reed W: Am Heart J 68: 391, Bulloch RT, Davis, JL, Hara M: Arch Path 84: 130, Sakakibara S, Konno S: Jap Heart J 3: 537, Konno S, Sakakibara S: Bulletin of the Heart Institute, 1, Berthold H: Deutsch Zeitschr Nervenheilkunde 178: 374, Cannon PJ: Am J Med 32: 765, Hozumi T: Naika 27: 178, 1971 (in Japanese) 15. Thomson AMP: J Path Bact 96: 285, Douglass RC, Jacobson SD: J Clin Endocrin 17: 1354, Goodof II: J Clin Endocrin 4: 30, McFadden PM, Berenson GS: Circulation 45: 808, 1972
Glycogen Aggregates in Cardiac Muscle Cell: A Cytopathological Study on Endomyocardial Biopsies
 Arch. histol. jap., Vol. 45, No. 4 (1982) p. 347-354 Glycogen Aggregates in Cardiac Muscle Cell: A Cytopathological Study on Endomyocardial Biopsies Kazumasa MIURA, Tohru IZUMI, Junichi FUKUDA, Masaru
Arch. histol. jap., Vol. 45, No. 4 (1982) p. 347-354 Glycogen Aggregates in Cardiac Muscle Cell: A Cytopathological Study on Endomyocardial Biopsies Kazumasa MIURA, Tohru IZUMI, Junichi FUKUDA, Masaru
IN recent years heart disease with eosinophilia has been called "eosinohilic
 A Case of Eosinophilic Heart Disease Diagnosed by Endomyocardial Biopsy Findings Hajime KAWAGOSHI, M.D., Masami SHIMIZU, M.D., Tetsuo SUEMATSU, M.D., Norihiko SUGIHARA, M.D., Yoshihito KITA, M.D., Kuniyoshi
A Case of Eosinophilic Heart Disease Diagnosed by Endomyocardial Biopsy Findings Hajime KAWAGOSHI, M.D., Masami SHIMIZU, M.D., Tetsuo SUEMATSU, M.D., Norihiko SUGIHARA, M.D., Yoshihito KITA, M.D., Kuniyoshi
BIOCHEMICAL INVESTIGATIONS IN THE DIAGNOSTICS OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISORDERS. As. MARUSHCHAK M.I.
 BIOCHEMICAL INVESTIGATIONS IN THE DIAGNOSTICS OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISORDERS As. MARUSHCHAK M.I. Heart attack symptoms Acute MI Measurement of cardiac enzyme levels Measure cardiac enzyme levels at regular
BIOCHEMICAL INVESTIGATIONS IN THE DIAGNOSTICS OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISORDERS As. MARUSHCHAK M.I. Heart attack symptoms Acute MI Measurement of cardiac enzyme levels Measure cardiac enzyme levels at regular
A Case of Alternating Bundle Branch Block in Combination With Intra-Hisian Block
 A Case of Alternating Bundle Branch Block in Combination With IntraHisian Block Yukie OGURA, 1 MD, Junichi KATO, 1 MD, Yuji OGAWA, 1 MD, Takahiro SHIOKOSHI, 1 MD, Toru KITAOKA, 1 MD, Takahide SUZUKI, 1
A Case of Alternating Bundle Branch Block in Combination With IntraHisian Block Yukie OGURA, 1 MD, Junichi KATO, 1 MD, Yuji OGAWA, 1 MD, Takahiro SHIOKOSHI, 1 MD, Toru KITAOKA, 1 MD, Takahide SUZUKI, 1
Cardiac findings in myotonia atrophica
 University of Nebraska Medical Center DigitalCommons@UNMC MD Theses College of Medicine 5-1-1969 Cardiac findings in myotonia atrophica Dee R. Mattley University of Nebraska Medical Center Follow this
University of Nebraska Medical Center DigitalCommons@UNMC MD Theses College of Medicine 5-1-1969 Cardiac findings in myotonia atrophica Dee R. Mattley University of Nebraska Medical Center Follow this
Electron Microscopical Findings in Hypertrophied Human Ventricle
 Brit. Heart J., 1969, 31, 200. Electron Microscopical Findings in Hypertrophied Human Ventricle K. DOWLATSHAHI AND A. C. HUNT From the Cardiac Unit, Royal Infirmary, Bristol, and the Department of Pathology,
Brit. Heart J., 1969, 31, 200. Electron Microscopical Findings in Hypertrophied Human Ventricle K. DOWLATSHAHI AND A. C. HUNT From the Cardiac Unit, Royal Infirmary, Bristol, and the Department of Pathology,
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function
 Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
The Heart. The Heart A muscular double pump. The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits
 C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
(D) (E) (F) 6. The extrasystolic beat would produce (A) increased pulse pressure because contractility. is increased. increased
 Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 18 Part A The Cardiovascular System 1/19/16 1 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Similarities of Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle RMP Ion concentration Deploarization Action Potential Repolarization
Chapter 18 Part A The Cardiovascular System 1/19/16 1 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Similarities of Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle RMP Ion concentration Deploarization Action Potential Repolarization
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
A Case Showing Atrial Dissociation and Other Various Kinds of Arrhythmias
 A Case Showing Atrial Dissociation and Other Various Kinds of Arrhythmias Shigeru KAWAGOE, M.D., Keiichi HASHIMOTO, M.D., Hirokazu HAYAKAWA, M.D., and Eiichi KIMURA, M.D. SUMMARY A case is reported in
A Case Showing Atrial Dissociation and Other Various Kinds of Arrhythmias Shigeru KAWAGOE, M.D., Keiichi HASHIMOTO, M.D., Hirokazu HAYAKAWA, M.D., and Eiichi KIMURA, M.D. SUMMARY A case is reported in
ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF MELANIN-PHAGOCYTOSIS BY CUTANEOUS VESSELS IN CELLULAR BLUE NEVUS*
 THE JOURNAL 05' INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkinl Co. Vol. 62, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF MELANIN-PHAGOCYTOSIS BY CUTANEOUS VESSELS IN CELLULAR
THE JOURNAL 05' INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkinl Co. Vol. 62, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF MELANIN-PHAGOCYTOSIS BY CUTANEOUS VESSELS IN CELLULAR
Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders
 Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders - importance of early and ongoing treatment, management and available able medications. Dr Bo Remenyi Department of Cardiology The
Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders - importance of early and ongoing treatment, management and available able medications. Dr Bo Remenyi Department of Cardiology The
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System. The heart. The heart is a double pump. A quick note on arteries vs. veins. = the muscular pump of the CV system
 Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
PRACTICAL ROADMAP. MUSCLE WJ van der Spuy
 PRACTICAL ROADMAP MUSCLE WJ van der Spuy MUSCLE Skeletal (striated) Cardiac (striated) Smooth Identification based on Fiber size, shape and presence/absence of branching Number, shape and position of nuclei
PRACTICAL ROADMAP MUSCLE WJ van der Spuy MUSCLE Skeletal (striated) Cardiac (striated) Smooth Identification based on Fiber size, shape and presence/absence of branching Number, shape and position of nuclei
O unaffected siblings. MYOTONIA CONGENITA (THOMSEN'S DISEASE) 1N A CHINESE FAMILY
 Vol. 10, No. 2. SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL 111 June, 1969. MYOTONIA CONGENITA (THOMSEN'S DISEASE) 1N A CHINESE FAMILY By J. S. Cheah, M.B., B.S., M.R.A.C.P. and B. H. Toh, Ms., B.S., (Department of Medicine,
Vol. 10, No. 2. SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL 111 June, 1969. MYOTONIA CONGENITA (THOMSEN'S DISEASE) 1N A CHINESE FAMILY By J. S. Cheah, M.B., B.S., M.R.A.C.P. and B. H. Toh, Ms., B.S., (Department of Medicine,
Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Anatomy of the Heart (See lab handout for terms list) A. Describe the size, shape and location of the heart B. Describe the structure and function of the pericardium
Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Anatomy of the Heart (See lab handout for terms list) A. Describe the size, shape and location of the heart B. Describe the structure and function of the pericardium
Muscle Physiology. Dr. Ebneshahidi Ebneshahidi
 Muscle Physiology Dr. Ebneshahidi Skeletal Muscle Figure 9.2 (a) Functions of the muscular system 1. Locomotion body movements are due to skeletal muscle contraction. 2. Vasoconstriction and vasodilatation
Muscle Physiology Dr. Ebneshahidi Skeletal Muscle Figure 9.2 (a) Functions of the muscular system 1. Locomotion body movements are due to skeletal muscle contraction. 2. Vasoconstriction and vasodilatation
Following viral myocarditis, which athlete can re-enter his active sports career?
 Following viral myocarditis, which athlete can re-enter his active sports career? ESC Congress 2011 Paris F. Carré University Rennes 1-Pontchaillou Hospital Inserm U642, Rennes - F-35000 The author declares
Following viral myocarditis, which athlete can re-enter his active sports career? ESC Congress 2011 Paris F. Carré University Rennes 1-Pontchaillou Hospital Inserm U642, Rennes - F-35000 The author declares
Title. Author(s)KANAGAWA, Hiroshi; ISHIKAWA, Tsune; KAWATA, Keiichir. CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 13(1): Issue Date
 Title A CASE OF CANINE TESTICULAR SERTOLI CELL TUMOR Author(s)KANAGAWA, Hiroshi; ISHIKAWA, Tsune; KAWATA, Keiichir CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 13(1): 11-1 Issue Date 1965-03 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.13.1.11
Title A CASE OF CANINE TESTICULAR SERTOLI CELL TUMOR Author(s)KANAGAWA, Hiroshi; ISHIKAWA, Tsune; KAWATA, Keiichir CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 13(1): 11-1 Issue Date 1965-03 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.13.1.11
NEUROCARDIOLOGY NEUROCARDIOLOGY
 NEUROCARDIOLOGY JON BRILLMAN, M.D CHAIRMAN EMERITUS, DEPARTMENT OF NEUROLOGY ALLEGHENY GENERAL HOSPITAL PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY DREXEL UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF MEDICINE, ALLEGHENY CAMPUS 1 SUD SUDDEN DEATH
NEUROCARDIOLOGY JON BRILLMAN, M.D CHAIRMAN EMERITUS, DEPARTMENT OF NEUROLOGY ALLEGHENY GENERAL HOSPITAL PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY DREXEL UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF MEDICINE, ALLEGHENY CAMPUS 1 SUD SUDDEN DEATH
Disturbances of Circulation. Histopathology Lab #2 (Web)
 Disturbances of Circulation Histopathology Lab #2 (Web) Paul Hanna Winter 2015 Slide #96 History: pig was fine in the morning & found dead in the afternoon there was ~100 mls of clear fluid in the pericardial
Disturbances of Circulation Histopathology Lab #2 (Web) Paul Hanna Winter 2015 Slide #96 History: pig was fine in the morning & found dead in the afternoon there was ~100 mls of clear fluid in the pericardial
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
FAMILIAL CARDIOMEGALY
 FAMILIAL CARDIOMEGALY BY R. T. GAUNT AND M. A. LECUTIER From the Departments of Pathology and Medicine, Royal Hospital, Chesterfield Received July 9, 1955 William Evans (1949) described a series of cases
FAMILIAL CARDIOMEGALY BY R. T. GAUNT AND M. A. LECUTIER From the Departments of Pathology and Medicine, Royal Hospital, Chesterfield Received July 9, 1955 William Evans (1949) described a series of cases
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II. Lab #5: Physiology of the Cardiovascular System For Labs Associated With Dr. Thompson s Lectures
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Lab #5: Physiology of the Cardiovascular System For Labs Associated With Dr. Thompson s Lectures References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Lab #5: Physiology of the Cardiovascular System For Labs Associated With Dr. Thompson s Lectures References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Heart 2
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart 2 PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Cardiac muscle Striated Short Wide Branched Interconnected Skeletal muscle Striated Long Narrow Cylindrical PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Intercalated
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart 2 PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Cardiac muscle Striated Short Wide Branched Interconnected Skeletal muscle Striated Long Narrow Cylindrical PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Intercalated
*Generating blood pressure *Routing blood: separates. *Ensuring one-way blood. *Regulating blood supply *Changes in contraction
 *Generating blood pressure *Routing blood: separates pulmonary and systemic circulations *Ensuring one-way blood flow: valves *Regulating blood supply *Changes in contraction rate and force match blood
*Generating blood pressure *Routing blood: separates pulmonary and systemic circulations *Ensuring one-way blood flow: valves *Regulating blood supply *Changes in contraction rate and force match blood
SESSION IV: MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS PULMONARY PATHOLOGY I. December 5, 2012
 SESSION IV: MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS PULMONARY PATHOLOGY I December 5, 2012 FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic and pathophysiologic changes in various conditions
SESSION IV: MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS PULMONARY PATHOLOGY I December 5, 2012 FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic and pathophysiologic changes in various conditions
Blood must move! 4/15/2014. Heart Basics
 What is the CARDIOVASCULAR system? The cardiovascular system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from different places in the body. The Heart has the job of pumping these things around the body.
What is the CARDIOVASCULAR system? The cardiovascular system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from different places in the body. The Heart has the job of pumping these things around the body.
Topics to be Covered. Cardiac Measurements. Distribution of Blood Volume. Distribution of Pulmonary Ventilation & Blood Flow
 Topics to be Covered MODULE F HEMODYNAMIC MONITORING Cardiac Output Determinants of Stroke Volume Hemodynamic Measurements Pulmonary Artery Catheterization Control of Blood Pressure Heart Failure Cardiac
Topics to be Covered MODULE F HEMODYNAMIC MONITORING Cardiac Output Determinants of Stroke Volume Hemodynamic Measurements Pulmonary Artery Catheterization Control of Blood Pressure Heart Failure Cardiac
Cellular Pathology. Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018
 Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Cardiac Pathophysiology
 Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
Human Anatomy and Physiology- Problem Drill 04: Tissues of the Body
 Human Anatomy and Physiology- Problem Drill 04: Tissues of the Body Question No. 1 of 10 A biopsy sample is obtained from a lesion on the right cheek of a male patient. A technician in the histology lab
Human Anatomy and Physiology- Problem Drill 04: Tissues of the Body Question No. 1 of 10 A biopsy sample is obtained from a lesion on the right cheek of a male patient. A technician in the histology lab
Electrophysiological and Histological Correlations in Two Cases of Complete Heart Block
 Electrophysiological and Histological Correlations in Two Cases of Complete Heart Block Shin-ichiro OHKAWA, M.D., Satoru MATSUSHITA, M.D., Keiji UEDA, M.D., Hiroshi MATSUO, M.D.,* and Masaya SUGIURA, M.D.
Electrophysiological and Histological Correlations in Two Cases of Complete Heart Block Shin-ichiro OHKAWA, M.D., Satoru MATSUSHITA, M.D., Keiji UEDA, M.D., Hiroshi MATSUO, M.D.,* and Masaya SUGIURA, M.D.
Effects of sitagliptin on cardiac metabolism in mice
 Effects of sitagliptin on cardiac metabolism in mice M. Lenski, J.-C. Reil, M. Böhm, U. Laufs Saarland University Hospital Department of Internal Medicine III, Cardiology Homburg - Germany Disclosures
Effects of sitagliptin on cardiac metabolism in mice M. Lenski, J.-C. Reil, M. Böhm, U. Laufs Saarland University Hospital Department of Internal Medicine III, Cardiology Homburg - Germany Disclosures
Cardiovascular system
 BIO 301 Human Physiology Cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System: consists of the heart plus all the blood vessels transports blood to all parts of the body in two 'circulations': pulmonary (lungs)
BIO 301 Human Physiology Cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System: consists of the heart plus all the blood vessels transports blood to all parts of the body in two 'circulations': pulmonary (lungs)
ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Cardiovascular System
 ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP QUIT ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Cardiovascular System 2007 Ontario Base Hospital Group ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Cardiovascular System AUTHORS Mike Muir AEMCA, ACP, BHSc Paramedic Program
ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP QUIT ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Cardiovascular System 2007 Ontario Base Hospital Group ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Cardiovascular System AUTHORS Mike Muir AEMCA, ACP, BHSc Paramedic Program
1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI).
 1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI). 5- cardiogenic shock (massive MIs >40% of the left ventricle)
1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI). 5- cardiogenic shock (massive MIs >40% of the left ventricle)
GENERAL HISTOLOGY 4. Muscular Tissue
 Biology-232 GENERAL HISTOLOGY 4. Muscular Tissue Dr. Manal Othman Anatomy Department CMMS, AGU Responsible for MOST types of BODY MOVEMENT Made up of groups of elongated MUSCLE cells with contractile filaments
Biology-232 GENERAL HISTOLOGY 4. Muscular Tissue Dr. Manal Othman Anatomy Department CMMS, AGU Responsible for MOST types of BODY MOVEMENT Made up of groups of elongated MUSCLE cells with contractile filaments
Reports. infrastructure of cataract in myotonic dystrophy. JOSEPH ESHACHIAN,*
 infrastructure of cataract in myotonic dystrophy. JOSEPH ESHACHIAN,* WAYNE F. MARCH,* WILLIAM GOOSSENS,** AND NANCY S. RAFFERTY.** Four cataractous lenses from patients with myotonic dystrophy were studied
infrastructure of cataract in myotonic dystrophy. JOSEPH ESHACHIAN,* WAYNE F. MARCH,* WILLIAM GOOSSENS,** AND NANCY S. RAFFERTY.** Four cataractous lenses from patients with myotonic dystrophy were studied
Female Carrier of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Presenting With Secondary Dilated Cardiomyopathy : A Case Report
 J Cardiol 2001 ; 38: 35 40 Duchenne 1 Female Carrier of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Presenting With Secondary Dilated Cardiomyopathy : A Case Report Shigeki Kiyoaki Toru Kenji Kojiro HIRAMATSU, MD MAEKAWA,
J Cardiol 2001 ; 38: 35 40 Duchenne 1 Female Carrier of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Presenting With Secondary Dilated Cardiomyopathy : A Case Report Shigeki Kiyoaki Toru Kenji Kojiro HIRAMATSU, MD MAEKAWA,
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system. What are the function of the cardiovascular system? Arteries and arterioles:
 5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM There are three primary closed cycles: 1) Cardiac circulation pathway of blood within the heart 2) Pulmonary circulation blood from the heart to lungs and back 3) Systemic
THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM There are three primary closed cycles: 1) Cardiac circulation pathway of blood within the heart 2) Pulmonary circulation blood from the heart to lungs and back 3) Systemic
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells. Special Reference to the Well-Developed Agranular Endoplasmic Reticulum
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 58(4-6) : 583-594, March 1982 Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells in the Nasal Respiratory Epithelium of the Rat, with Special Reference to the Well-Developed
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 58(4-6) : 583-594, March 1982 Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells in the Nasal Respiratory Epithelium of the Rat, with Special Reference to the Well-Developed
Two Cardiology Zebras ERIC MARTIN MD
 Two Cardiology Zebras ERIC MARTIN MD Disclosures Bayer Gilead Sciences NIH Vascular Dynamics, In. Employer Iowa Heart Center/Mercy Des Moines Zebra # 1 History CC: 52-year-old man seen in consultation
Two Cardiology Zebras ERIC MARTIN MD Disclosures Bayer Gilead Sciences NIH Vascular Dynamics, In. Employer Iowa Heart Center/Mercy Des Moines Zebra # 1 History CC: 52-year-old man seen in consultation
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 20 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Learn about the components of the cardiovascular system
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 20 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Learn about the components of the cardiovascular system
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
PERMANENT PACEMAKERS AND IMPLANTABLE DEFIBRILLATORS Considerations for intensivists
 PERMANENT PACEMAKERS AND IMPLANTABLE DEFIBRILLATORS Considerations for intensivists Craig A. McPherson, MD, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Constantine Manthous, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Clinical
PERMANENT PACEMAKERS AND IMPLANTABLE DEFIBRILLATORS Considerations for intensivists Craig A. McPherson, MD, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Constantine Manthous, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Clinical
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY
 RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
Microanatomy of Muscles. Anatomy & Physiology Class
 Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
III./10.4. Diagnosis. Introduction. A.) Laboratory tests. Laboratory tests, electrophysiology, muscle biopsy, genetic testing, imaging techniques
 III./10.4. Diagnosis Laboratory tests, electrophysiology, muscle biopsy, genetic testing, imaging techniques After studying this chapter, you will become familiar with the most commonly used diagnostic
III./10.4. Diagnosis Laboratory tests, electrophysiology, muscle biopsy, genetic testing, imaging techniques After studying this chapter, you will become familiar with the most commonly used diagnostic
4/11/2017. Cardiomyopathy. John Steuter, MD Bryan Heart. Disclosures. No Conflicts. Cardiomyopathy. WHO Classification
 Cardiomyopathy John Steuter, MD Bryan Heart Disclosures No Conflicts Cardiomyopathy WHO Classification Anatomy & physiology of the LV 1. Dilated Enlarged Systolic dysfunction 2. Hypertrophic Thickened
Cardiomyopathy John Steuter, MD Bryan Heart Disclosures No Conflicts Cardiomyopathy WHO Classification Anatomy & physiology of the LV 1. Dilated Enlarged Systolic dysfunction 2. Hypertrophic Thickened
Ultrastructural studies of human cutaneous nerve
 J. clin. Path. (1965), 18, 188 Ultrastructural studies of human cutaneous nerve with special reference to lamellated cell inclusions and vacuole-containing cells MARJORE J. EVANS, J. B. FNEAN, AND A. L.
J. clin. Path. (1965), 18, 188 Ultrastructural studies of human cutaneous nerve with special reference to lamellated cell inclusions and vacuole-containing cells MARJORE J. EVANS, J. B. FNEAN, AND A. L.
Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*)
 Hiroshima Journal of Medical Sciences Vol. 31, No. 1, March, 1982 HJIM 31-6 31 Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*) Yoshinori KAWAGUCHI, Eishi KITTAKA, Yoshito TANAKA, Takeo TANAKA
Hiroshima Journal of Medical Sciences Vol. 31, No. 1, March, 1982 HJIM 31-6 31 Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*) Yoshinori KAWAGUCHI, Eishi KITTAKA, Yoshito TANAKA, Takeo TANAKA
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease
 Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1 -
 Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Matters of the Heart: Comprehensive Cardiology SARAH BEANLANDS RN BSCN MSC
 Matters of the Heart: Comprehensive Cardiology SARAH BEANLANDS RN BSCN MSC Who am I? Class Outline Gross anatomy of the heart Trip around the heart Micro anatomy: cellular and tissue level Introduction
Matters of the Heart: Comprehensive Cardiology SARAH BEANLANDS RN BSCN MSC Who am I? Class Outline Gross anatomy of the heart Trip around the heart Micro anatomy: cellular and tissue level Introduction
Myocardial Infarction
 Myocardial Infarction MI = heart attack Defined as necrosis of heart muscle resulting from ischemia. A very significant cause of death worldwide. of these deaths, 33% -50% die before they can reach the
Myocardial Infarction MI = heart attack Defined as necrosis of heart muscle resulting from ischemia. A very significant cause of death worldwide. of these deaths, 33% -50% die before they can reach the
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 09a Lab Activity
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 09a Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: http://www.fallingpixel.com/products/33817/mains/0000-malemuscular_1.jpg The Muscular System The main function of the muscular
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 09a Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: http://www.fallingpixel.com/products/33817/mains/0000-malemuscular_1.jpg The Muscular System The main function of the muscular
HISTORY. Question: How do you interpret the patient s history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: 45-year-old man.
 HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
Serum Cardiac Troponin T in Cardiac Amyloidosis: Serial Observations in Five Patients
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2006, 208, 163-167 ctnt in Cardiac Amyloidosis 163 Serum Cardiac Troponin T in Cardiac Amyloidosis: Serial Observations in Five Patients Case Report TAKAO KATO, YUKIHITO SATO, KAZUYA
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2006, 208, 163-167 ctnt in Cardiac Amyloidosis 163 Serum Cardiac Troponin T in Cardiac Amyloidosis: Serial Observations in Five Patients Case Report TAKAO KATO, YUKIHITO SATO, KAZUYA
Histology of the Cardiac System. Dr. Nabil Khoury Anatomy Department
 Histology of the Cardiac System Dr. Nabil Khoury Anatomy Department Objectives 1. Identify the 3 layers of the heart endocardium, myocardium, epicardium 2. Differentiate cardiacmuscle 3. Define intercalated
Histology of the Cardiac System Dr. Nabil Khoury Anatomy Department Objectives 1. Identify the 3 layers of the heart endocardium, myocardium, epicardium 2. Differentiate cardiacmuscle 3. Define intercalated
Index of subjects. effect on ventricular tachycardia 30 treatment with 101, 116 boosterpump 80 Brockenbrough phenomenon 55, 125
 145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
Anatomy of the Heart
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System
 Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Arrhythmias. Pulmonary Artery
 Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM IN ENDOMYOCARDIAL FIBROSIS
 BY From the Department of Medicine, Makerere College, and Mulago Hospital, Kampala, Uganda Received May 11, 1959 Endomyocardial fibrosis is an important cause of heart failure in this part of Africa. The
BY From the Department of Medicine, Makerere College, and Mulago Hospital, Kampala, Uganda Received May 11, 1959 Endomyocardial fibrosis is an important cause of heart failure in this part of Africa. The
Cardiac arrhythmias. Janusz Witowski. Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences. J. Witowski
 Cardiac arrhythmias Janusz Witowski Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences A 68-year old man presents to the emergency department late one evening complaining of increasing
Cardiac arrhythmias Janusz Witowski Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences A 68-year old man presents to the emergency department late one evening complaining of increasing
The cardiovascular system
 The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
Chapter 10 -Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 10 -Muscle Tissue Muscles: 1. Overview of Muscle Tissue A. Review 5 functions of muscle tissue. B. Review the 5 properties of muscle tissue. WHICH do they share with nervous tissue? (2, plus the
Chapter 10 -Muscle Tissue Muscles: 1. Overview of Muscle Tissue A. Review 5 functions of muscle tissue. B. Review the 5 properties of muscle tissue. WHICH do they share with nervous tissue? (2, plus the
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Approximately the size of your fist Location. Pericardial physiology
 Heart Anatomy Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Wednesday, March 28, 2012 Muscle
Heart Anatomy Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Wednesday, March 28, 2012 Muscle
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
TRANSIENT LEFT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK -
 Vol. 11, No. 2. June, 1970. SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL TRANSIENT LEFT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK - A CASE REPORT 86 By L.S. Chew (Medical Unit III, General Hospital, Singapore) INTRODUCTION It is generally believed
Vol. 11, No. 2. June, 1970. SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL TRANSIENT LEFT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK - A CASE REPORT 86 By L.S. Chew (Medical Unit III, General Hospital, Singapore) INTRODUCTION It is generally believed
Chapter 12. Capillaries. Circulation. The circulatory system connects with all body tissues
 Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Case 1 Organ Set 3. Case 1 (for Organ Sets 1 3) 10/2/2015 CARIOVASCULAR II LABORATORY
 MHD I CRIOVSCULR II LORTORY 0/5/5 Case Organ Set Organ Set 2 Organ Set 3 Case (for Organ Sets 3) 72 year old man with a history of diabetes mellitus type 2, HTN, and hyperlipidemia presents with progressive
MHD I CRIOVSCULR II LORTORY 0/5/5 Case Organ Set Organ Set 2 Organ Set 3 Case (for Organ Sets 3) 72 year old man with a history of diabetes mellitus type 2, HTN, and hyperlipidemia presents with progressive
Muscle Tissue. General concepts. Classification of muscle. I. Functional classification is based on the type of neural control.
 Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Cardiac Muscle Tissue. Cardiac Muscle Tissue
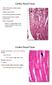 Walls of the heart (cardia: heart); myocardium. Cardiac muscle fibers not as densely packed as skeletal cardiac muscle tissue is highly vascularized Other components; dense C.T. septa, larger blood vessels,
Walls of the heart (cardia: heart); myocardium. Cardiac muscle fibers not as densely packed as skeletal cardiac muscle tissue is highly vascularized Other components; dense C.T. septa, larger blood vessels,
Chapter 18 - Heart. I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity)
 Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM AND RESPONSES TO EXERCISE Mr. S. Kelly PSK 4U North Grenville DHS THE HEART: A REVIEW Cardiac muscle = myocardium Heart divided into two sides, 4 chambers (L & R) RS: pulmonary
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM AND RESPONSES TO EXERCISE Mr. S. Kelly PSK 4U North Grenville DHS THE HEART: A REVIEW Cardiac muscle = myocardium Heart divided into two sides, 4 chambers (L & R) RS: pulmonary
Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS
 Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS You have 50 minutes to complete this test packet. One 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet is allowed, along with 1 non-programmable calculator dedicated to computation.
Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS You have 50 minutes to complete this test packet. One 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet is allowed, along with 1 non-programmable calculator dedicated to computation.
Circulatory System Function Move circulatory fluid (blood) around body Gas Transport Nutrient Transport Excretory Product Transport
 Lecture 37 Introduction to Circulation BY DR QAZI IMTIAZ RASOOL OBJECTIVES Functions of the Heart Generating blood pressure Routing blood: separates pulmonary and systemic circulations Ensuring one-way
Lecture 37 Introduction to Circulation BY DR QAZI IMTIAZ RASOOL OBJECTIVES Functions of the Heart Generating blood pressure Routing blood: separates pulmonary and systemic circulations Ensuring one-way
Myocardial Infarction: Left Ventricular Failure
 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY 93 Case 17 Myocardial Infarction: Left Ventricular Failure Marvin Zimmerman is a 52-year-old construction manager who is significantly overweight. Despite his physician's repeated
CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY 93 Case 17 Myocardial Infarction: Left Ventricular Failure Marvin Zimmerman is a 52-year-old construction manager who is significantly overweight. Despite his physician's repeated
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart -
 Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Aberrant atrial conduction Unrecognized electrocardiographic entity'
 British Heart journal, I972, 34, 34I-346. Aberrant atrial conduction Unrecognized electrocardiographic entity' Edward K. Chung From Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, West Virginia University
British Heart journal, I972, 34, 34I-346. Aberrant atrial conduction Unrecognized electrocardiographic entity' Edward K. Chung From Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, West Virginia University
Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis
 Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis 8 Arrhythmia Code No. Description 8002 Marked rhythm irregularity 8110 Sinus rhythm 8102 Sinus arrhythmia 8108 Marked sinus arrhythmia 8120 Sinus tachycardia
Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis 8 Arrhythmia Code No. Description 8002 Marked rhythm irregularity 8110 Sinus rhythm 8102 Sinus arrhythmia 8108 Marked sinus arrhythmia 8120 Sinus tachycardia
Pathology of Hypertension
 2016-03-07 Pathology of Hypertension Honghe Zhang honghezhang@zju.edu.cn Tel:88208199 Department of Pathology ❶ Genetic predisposition ❷ Dietary factors ❸ Environmental factors ❹ Others Definition and
2016-03-07 Pathology of Hypertension Honghe Zhang honghezhang@zju.edu.cn Tel:88208199 Department of Pathology ❶ Genetic predisposition ❷ Dietary factors ❸ Environmental factors ❹ Others Definition and
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) An Autopsy Case of Acute Intermitte Murase, Kunihiko; Makiyama, Kazuya; Nonaka, Shigeru Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37 Issue Date 1992-12-25
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) An Autopsy Case of Acute Intermitte Murase, Kunihiko; Makiyama, Kazuya; Nonaka, Shigeru Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37 Issue Date 1992-12-25
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 6, 2016,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 6, 2016, 4612 4617 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) STUDY ON PATHOMORPHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN 21 CASES OF CANINE DILATED CARDIOMYOPATHY
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 6, 2016, 4612 4617 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) STUDY ON PATHOMORPHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN 21 CASES OF CANINE DILATED CARDIOMYOPATHY
The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the cardiovascular system.
 LAB 3: THE MUSCLE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the cardiovascular system. The cases we will cover are: A. Atherosclerosis Refer to virtual slide p_8, should
LAB 3: THE MUSCLE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the cardiovascular system. The cases we will cover are: A. Atherosclerosis Refer to virtual slide p_8, should
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1
 ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
BIOL 219 Spring Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System
 1 BIOL 219 Spring 2013 Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System Outline: Components of the CV system Heart anatomy Layers of the heart wall Pericardium Heart chambers, valves, blood vessels, septum Atrioventricular
1 BIOL 219 Spring 2013 Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System Outline: Components of the CV system Heart anatomy Layers of the heart wall Pericardium Heart chambers, valves, blood vessels, septum Atrioventricular
Appropriate Use Criteria for Initial Transthoracic Echocardiography in Outpatient Pediatric Cardiology (scores listed by Appropriate Use rating)
 Appropriate Use Criteria for Initial Transthoracic Echocardiography in Outpatient Pediatric Cardiology (scores listed by Appropriate Use rating) Table 1: Appropriate indications (median score 7-9) Indication
Appropriate Use Criteria for Initial Transthoracic Echocardiography in Outpatient Pediatric Cardiology (scores listed by Appropriate Use rating) Table 1: Appropriate indications (median score 7-9) Indication
