Coexistence of asymmetric septal hypertrophy and aortic valve disease in adults
|
|
|
- Rosalind Sharp
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thorax, 1979, 34, Coexistence of asymmetric septal hypertrophy and aortic valve disease in adults M V J RAJ, V SRINIVAS, I M GRAHAM, AND D W EVANS From the Regional Cardiac Unit, Papworth Hospital, Papworth Everard, Cambridge CB3 8RE, UK ABSTRACT Echocardiography detected asymmetric septal hypertrophy (ASH) in five of 200 adults being assessed for aortic valve surgery. Four of these were among 119 patients with dominant aortic stenosis, which was severe in three. ASH was confirmed at the time of aortic valve replacement in two of these patients; the third declined operation. The finding of ASH in only one of 81 patients with free aortic reflux is consistent with chance association. While the same explanation could apply to the higher prevalence in those with aortic stenosis, it may be that a long-standing pressure overload can trigger inappropriate septal hypertrophy in predisposed individuals. Brock (1957) recorded subaortic hypertrophy in association with hypertension and postulated its development in response to chronic left ventricular pressure load from aortic valvar stenosis. Hurst and Logue (1966) suggested, on the basis of operative and necropsy data, that it might be present in about 10% of those with aortic valve disease. Another necropsy study (Parker et al, 1969) yielded ten instances of subaortic hypertrophy in association with aortic valve stenosis. In echocardiography we now have a sensitive method for detecting excessive (asymmetric) septal hypertrophy (ASH) during life (Henry etal, 1973). We used it to screen a series of patients undergoing investigation with a view to aortic valve replacement and report our findings with respect to dominance of pressure or volume load on the left ventricle. Patients and methods Echocardiography was carried out in 220 adults undergoing assessment for aortic valve replacement. Technically satisfactory records could not be obtained from 20 of them. The remaining 200 patients (74 women, 126 men) form the basis of this study. Their ages ranged from 18 to 67 years (mean 47). None gave a family history suggestive of cardiomyopathy. One hundred and nineteen patients had dominant aortic stenosis. Their symptoms and some aetiological details are shown in table 1. Their peak systolic-left ventricular-systemic arterial 91 pressure gradients, estimated echocardiographically (Bennett et al, 1975) in all, and measured at cardiac catheterisation in 55, ranged from 20 to 100 mmhg. Of the 118 with gradients higher than 40 mmhg 117 had pressures of a similar order recorded at operation. One, with a valvar gradient of 100 mmhg at rest, refused the offer of surgical help. Table patients with dominant aortic stenosis Age yr (mean 47) Sex Men 72 Women 47 Aetiology Congenital 3 Calcific 112 Unknown 4 Symptoms Dyspnoea 110 Angina 82 Syncope or faintness 40 Congestive heart failure 4 Of the 81 patients who had free aortic reflux, of varied aetiology, which was thought to be the basis of their symptoms (table 2), 80 underwent aortic valve replacement. In one the investigations showed only moderately severe reflux, with coexisting ASH, and operation was not advised. The echocardiograms were recorded with the patients supine, using a Cl 1 transducer with an Ekoline 20 ultrasonoscope and a Cambridge photographic recorder. Echocardiograms showed both
2 92 Table 2 81 patients with aortic reflux Age yr (mean 46) Sex Men 54 Women 27 Aetiology Rheumatic 67 Bacterial 6 Syphilitic 2 Aortic dissection 1 Rickettsial carditis 1 Unknown 4 Symptoms Dyspnoea 8 1 Angina 20 Syncope or faintness 12 Congestive heart failure 10 M V J Raj, V Srinivas, I M Graham, and D W Evans surfaces of the interventricular septum (IVS), the posterior basal left ventricular wall (PLVW), and the peak excursion of the mitral leaflets (fig 1). Diastolic IVS and PLVW thickness was measured at a point in the cardiac cycle immediately before atrial systole. The left ventricular internal diamensions in systole (Ds) and diastole (Dd) were also measured. Mean circumferential fibre shortening velocity (Vcf) was calculated by the method of Cooper et al (1972). The chief echocardiographic criterion used for diagnosing ASH in this study was an IVS: PLVW thickness ratio in excess of 1-3: 1 (Henry et al. 1973). Systolic anterior movement of the mitral N. 23 mm D '" D ~'' / Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 February Downloaded from PLVW 16 mmr IL 67 yrs Fig 1 Echocardiogram showing IVS and PLVW thickness and left ventricular internal dimensions at peak.systole and end diastole. ASH is present in this case. on 18 April 2019 by guest. Protected by copyright.
3 Coexistence of asymmetric septal hypertrophy and aortic valve disease in adults valve (SAM), high Vcf, and small left ventricular cavity (Shah et al, 1969) were also sought. Results Table 3 shows the numbers, sex distribution, and echocardiographic findings in those with dominant aortic stenosis and table 4 in those with aortic reflux. Four patients with dominant stenosis (three women aged 63, 64, and 67 and one man aged 53) were found to have IVS: PLVW ratios higher than 1-3: 1. All four exhibited typical SAM of the anterior mitral leaflet (fig 2), though in one only after inhalation of amyl nitrite. Retrograde left ventricular catheterisation showed systolic aortic valvar gradients of 20, 65, 75, and 100 mmhg, without subvalvar gradients, and showed ventriculographic features of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in all four. The patient with the gradient of 100 mmhg declined operation. Excessive septal hypertrophy was confirmed at the time of aortic valve replacement in the other two with critical stenosis, and a myotomy was carried out in one. Table 3 Age and sex distribution and echocardiographic findings in subjects with aortic stenosis IVS/PLVW Wall ratio <1 3 >1 3 No Men 71 1 Women 44 3 Range Mean Range Mean Age (yr) IVs (mm) PLVW (mm) IVS/PLVW Ds(mm) Dd(mm) Vcf(sec -) SAM Absent Present Table 4 Age and sex distribution and eclhocardiographic findings in subjects with aortic reflux IIVS/PL VW Wall ratio <1*3 >1*3 No 80 1 Men 54 0 Women 26 1 Range Mean Age IVs (mm) PLVW (mm) IVS/PLVW Ds (mm) Dd (mm) Vcf(sec 1) 06-1*8 1*4 1*6 SAM Absent Present One woman (aged 63) with aortic reflux was found to have an IVS: PLVW ratio in excess of 1-3: 1. Her echocardiogram also showed typical SAM and cardioangiography confirmed asymmetric hypertrophy while suggesting that her aortic reflux was not severe enough to require aortic valve replacement. All 195 patients without echocardiographic evidence of ASH were operated on, and no evidence of unusual septal hypertrophy was noted. Discussion Nanda et al (1974) pioneered the use of echocardiography for detecting idiopathic subaortic stenosis coexisting with aortic valve disease. We used the technique in an attempt to establish the prevalence of excessive asymmetric septal hypertrophy in a series of patients undergoing assessment with a view to aortic valve replacement. Since Henry et al (1973) had suggested that in adults without right ventricular hypertension an IVS: PLVW ratio in excess of 1 3 offers a sufficient basis for the diagnosis, we used this criterion in our study. Popp (1976) subsequently suggested that a ratio in excess of 1-5: 1 is necessary. Had we used that criterion, we would have failed to identify two examples of ASH (subsequently confirmed by ventriculography and at operation) in association with disease of the aortic valve. In a still more recent study (Chahine et al, 1977), which pointed the lack of any pathognomonic feature, three patients finally considered to have hypertrophic cardiomyopathy had echocardiographic IVS: PLVW ratios between 1 0 and 1 2. Only three of the patients in this study had coexistent ASH and disease of the aortic valve severe enough to require operation. On this evidence, the prevalence of ASH in adults with critical aortic stenosis may be of the order of 2 5%. The figure rises to 3-4% if the patient with a peak systolic gradient of 20 mmhg (and resting left ventricular pressure circa 160 mmhg) is included. Others have noted coexistence of ASH with aortic stenosis, and with systemic hypertension and coarctation of the aorta (Moreyra et al, 1970; Block et al, 1973; Feizi and Emanuel, 1975). The possibility exists that frequent or sustained excessive pressure loads may trigger inappropriate (asymmetric) ventricular hypertrophy in predisposed individuals. Alternatively, the association may be coincidental; however, in our series none of the four patients with ASH gave a family history suggestive of cardiomyopathy. Among the 81 patients with aortic reflux, only one was found to have coexisting ASH. This 93
4 94 M V J Raj, V Srinivas, I M Graham, and D W Evans Fig. 2 Echocardiogram of patient with moderate aortic reflux, illustrating SAM of the anterior mitral leaflet (A ML). association was probably coincidental, although ASH has been detected in association with other volume-overload conditions such as thyrotoxic heart disease, persistent ductus arteriosus, and ventricular septal defect (Symons et al, 1974; Feizi and Emanuel, 1975; Larter et al, 1976). We thank Dr H A Fleming for allowing us to study some of his patients and Mr B B Milstein and Mr T A H English for the surgical observations. References Bennett, D H, Evans, D W, and Raj, M V J (1975). Echocardiographic left ventricular dimensions in pressure and volume overload. Their use in assessing aortic stenosis. British Heart Journal, 37, Block, P C, Powell, W J, jun, Dinsmore, R E, and Goldblatt, A (1973). Coexistent fixed congenital and idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis. American Journal of Cardiology, 31, Brock, R (1957). Functional obstruction of the left ventricle. Guy's Hospital Reports, 106, Chahine, R A, Raizner, A E, Ishimori, T, and Montero, A C (1977). Echocardiographic, haemodynamic, and angiographic correlations in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. British Heart Journal, 39, Cooper, R H, O'Rourke, R A, Karliner, J S, Peterson, K L, and Leopold, G R (1972). Comparison of ultrasound and cineangiographic measurements of the mean rate of circumferential fiber shortening in man. Circulation, 46, Feizi, 0, and Emanuel, R (1975). Echocardiographic spectrum of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. British Heart Journal, 37, Henry, W L, Clark, C E, and Epstein, S E (1973). Asymmetric septal hypertrophy (ASH). The unifying link in IHSS disease spectrum. Circulation, 47,
5 Coexistence of asymmetric septal hypertrophy and aortic valve disease in adults Hurst, J W, and Logue, R B (1966). The Heart, Arteries and Veins, p 579. McGraw Hill, New York. Larter, W E, Allen, H D, Sahn, D J, and Golberg, S J (1976). The asymmetrically hypertrophied septum, further differentiation of its causes. Circulation, 53, Moreyra, E, Knibbe, P, and Brest, A N (1970). Hypertension and muscular subaortic stenosis. Chest, 57, Nanda, N C, Gramiak, R, Shah, P M, Stewart, S, and De Weese, J A (1974). Echocardiography in the diagnosis of idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis coexisting with aortic valve disease. Circulation, 50, 752. Parker, D P, Kaplan, M A, and Connolly, J E (1969). Coexistent aortic valvular and functional hypertrophic subaortic stenosis. Clinical, physiologic and angiographic aspects. A merican Journal of Cardiology, 24, Popp, R L (1976). Echocardiographic assessment of cardiac disease. Circulation, 54, Shah, P M, Gramiak, R, and Kramer, D H (1969). Ultrasound localisation of left ventricular outflow obstruction in hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy. Circulation, 40, Symons, C, Richardson, P J, and Feizi, 0 (1974). Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and hyperthyroidism; a report of three cases. Thorax, 29, Requests for reprints to: Dr D W Evans, Regional Cardiac Unit, Papworth Hospital, Papworth Everard, Cambridge CB3 8RE. 95 Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 February Downloaded from on 18 April 2019 by guest. Protected by copyright.
Pulmonary valve echo motion in pulmonary
 British HeartJournal, I975, 37, ii84-ii90. Pulmonary valve echo motion in pulmonary regurgitation' Arthur E. Weyman, James C. Dillon, Harvey Feigenbaum, and Sonia Chang From the Department of Medicine,
British HeartJournal, I975, 37, ii84-ii90. Pulmonary valve echo motion in pulmonary regurgitation' Arthur E. Weyman, James C. Dillon, Harvey Feigenbaum, and Sonia Chang From the Department of Medicine,
Valvar aortic stenosis with unusual features
 326 Case reports CRAPP, A.R., Powls, J., CLARK, C., KEIGHLEY, M.R.B. & ALEXANDER-WILLIAMS, J. (1975) Postoperative pseudomembranous colitis. (Correspondence) British Medical Journal, 3, 227. KEATING, J.P.,
326 Case reports CRAPP, A.R., Powls, J., CLARK, C., KEIGHLEY, M.R.B. & ALEXANDER-WILLIAMS, J. (1975) Postoperative pseudomembranous colitis. (Correspondence) British Medical Journal, 3, 227. KEATING, J.P.,
Idiopathic Hypertrophic Subaortic Stenosis and Mitral Stenosis
 CASE REPORTS Idiopathic Hypertrophic Subaortic Stenosis and Mitral Stenosis Martin J. Nathan, M.D., Roman W. DeSanctis, M.D., Mortimer J. Buckley, M.D., Charles A. Sanders, M.D., and W. Gerald Austen,
CASE REPORTS Idiopathic Hypertrophic Subaortic Stenosis and Mitral Stenosis Martin J. Nathan, M.D., Roman W. DeSanctis, M.D., Mortimer J. Buckley, M.D., Charles A. Sanders, M.D., and W. Gerald Austen,
MITRAL STENOSIS. Joanne Cusack
 MITRAL STENOSIS Joanne Cusack BSE Breakdown Recognition of rheumatic mitral stenosis Qualitative description of valve and sub-valve calcification and fibrosis Measurement of orifice area by planimetry
MITRAL STENOSIS Joanne Cusack BSE Breakdown Recognition of rheumatic mitral stenosis Qualitative description of valve and sub-valve calcification and fibrosis Measurement of orifice area by planimetry
Index of subjects. effect on ventricular tachycardia 30 treatment with 101, 116 boosterpump 80 Brockenbrough phenomenon 55, 125
 145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
found that some patients without stenotic lesions had blood velocity or pressure measurement across the
 Br Heart J 1985; 53: 640-4 Increased blood velocities in the heart and great vessels of patients with congenital heart disease An assessment of their significance in the absence of valvar stenosis STANLEY
Br Heart J 1985; 53: 640-4 Increased blood velocities in the heart and great vessels of patients with congenital heart disease An assessment of their significance in the absence of valvar stenosis STANLEY
Echocardiographic findings in persistent truncus
 British HeartJournal, I974, 36, 732-736. Echocardiographic findings in persistent truncus arteriosus in a young adult Premindra A. N. Chandraratna, Udayan Bhaduri, Benjamin B. Littman, and Frank J. Hildner
British HeartJournal, I974, 36, 732-736. Echocardiographic findings in persistent truncus arteriosus in a young adult Premindra A. N. Chandraratna, Udayan Bhaduri, Benjamin B. Littman, and Frank J. Hildner
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Congenitally bicuspid aortic valves
 British Heart Journal, 1978, 40, 1402-1407 Congenitally bicuspid aortic valves Clinicogenetic study of 41 families RICHARD EMANUEL, RONALD WITHERS, KAY O'BRIEN, PETER ROSS1, AND OZGEN FEIZI2 From the National
British Heart Journal, 1978, 40, 1402-1407 Congenitally bicuspid aortic valves Clinicogenetic study of 41 families RICHARD EMANUEL, RONALD WITHERS, KAY O'BRIEN, PETER ROSS1, AND OZGEN FEIZI2 From the National
Case # 1. Page: 8. DUKE: Adams
 Case # 1 Page: 8 1. The cardiac output in this patient is reduced because of: O a) tamponade physiology O b) restrictive physiology O c) coronary artery disease O d) left bundle branch block Page: 8 1.
Case # 1 Page: 8 1. The cardiac output in this patient is reduced because of: O a) tamponade physiology O b) restrictive physiology O c) coronary artery disease O d) left bundle branch block Page: 8 1.
Inspiratory Right Ventricular Outflow Obstruction in a Patient with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
 Case Reports Inspiratory Right Ventricular Outflow Obstruction in a Patient with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Kazufumi TSUCHIHASHI, M.D., Akihito TSUCHIDA, M.D., Nobuichi HIKITA, M.D., Shuji YONEKURA, M.D.,
Case Reports Inspiratory Right Ventricular Outflow Obstruction in a Patient with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Kazufumi TSUCHIHASHI, M.D., Akihito TSUCHIDA, M.D., Nobuichi HIKITA, M.D., Shuji YONEKURA, M.D.,
Medical Policy and and and and
 ARBenefits Approval: 10/12/2011 Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Revision Date: Code(s): 93799, Unlisted cardiovascular service or procedure Medical Policy Title: Percutaneous Transluminal Septal Myocardial
ARBenefits Approval: 10/12/2011 Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Revision Date: Code(s): 93799, Unlisted cardiovascular service or procedure Medical Policy Title: Percutaneous Transluminal Septal Myocardial
Anaesthesia for non-cardiac surgery in patients left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO)
 Anaesthesia for non-cardiac surgery in patients left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO) Dr. Siân Jaggar Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Brompton Hospital London UK Congenital Cardiac Services
Anaesthesia for non-cardiac surgery in patients left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO) Dr. Siân Jaggar Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Brompton Hospital London UK Congenital Cardiac Services
Aortic root and left atrial wall motion
 British Heart Journal, 1977, 39, 1082-1087 Aortic root and left atrial wall motion An echocardiographic study GONES AKGtYN AND CLIVE LAYTON1 From the Cardiac Department, The London Hospital, London The
British Heart Journal, 1977, 39, 1082-1087 Aortic root and left atrial wall motion An echocardiographic study GONES AKGtYN AND CLIVE LAYTON1 From the Cardiac Department, The London Hospital, London The
The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors:
 Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
Echocardiographic measurement of right ventricular
 Br Heart Jf 1980; 44: 55-61 Echocardiographic measurement of right ventricular wall thickness in adults by anterior approach TSUKASA TSUDA, TOSHITAMI SAWAYAMA, NOBUYOSHI KAWAI,* TAKAKAZU KATOH, SHOSO NEZUO,
Br Heart Jf 1980; 44: 55-61 Echocardiographic measurement of right ventricular wall thickness in adults by anterior approach TSUKASA TSUDA, TOSHITAMI SAWAYAMA, NOBUYOSHI KAWAI,* TAKAKAZU KATOH, SHOSO NEZUO,
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
PULMONARY VALVE ECHOCARDIOiGRAM IN THE EVALUATION OF PULMONARY ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION IN THE PRESENCE OF INTRACARDIAC SHUNTS
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 41 No. 3 September 1986 PULMONARY VALVE ECHOCARDIOiGRAM IN THE EVALUATION OF PULMONARY ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION IN THE PRESENCE OF INTRACARDIAC SHUNTS FONG CHEE YEE K. T. SINGHAM SUMMARY
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 41 No. 3 September 1986 PULMONARY VALVE ECHOCARDIOiGRAM IN THE EVALUATION OF PULMONARY ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION IN THE PRESENCE OF INTRACARDIAC SHUNTS FONG CHEE YEE K. T. SINGHAM SUMMARY
Congenital Heart Defects
 Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT
 ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS
 Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING
 PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by the fact that a murmur was heard at birth?
 HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
Muscular (hypertrophic) subaortic stenosis (hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy): the evidence for true obstruction
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (1986) 62, 531-536 Muscular (hypertrophic) subaortic stenosis (hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy): the evidence for true obstruction to left ventricular outflow E. Douglas
Postgraduate Medical Journal (1986) 62, 531-536 Muscular (hypertrophic) subaortic stenosis (hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy): the evidence for true obstruction to left ventricular outflow E. Douglas
Septal Myectomy, Papillary Muscle Resection, and Mitral Valve Replacement for Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy: A Case Report
 Case Report Septal Myectomy, Papillary Muscle Resection, and Mitral Valve Replacement for Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy: A Case Report Junichiro Takahashi, MD, 1 Yutaka Wakamatsu, MD, 1 Jun Okude,
Case Report Septal Myectomy, Papillary Muscle Resection, and Mitral Valve Replacement for Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy: A Case Report Junichiro Takahashi, MD, 1 Yutaka Wakamatsu, MD, 1 Jun Okude,
B-scan ultrasonography in idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis1 Study of left ventricular outflow tract and
 British Heart Jrournal, 1976, 38, 595-604. B-scan ultrasonography in idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis1 Study of left ventricular outflow tract and mechanism of obstruction Michael V. Cohen, Louis
British Heart Jrournal, 1976, 38, 595-604. B-scan ultrasonography in idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis1 Study of left ventricular outflow tract and mechanism of obstruction Michael V. Cohen, Louis
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Echocardiography in Discrete Subaortic Stenosis
 Echocardiography in Discrete Subaortic Stenosis STEVEN K. KRUEGER, M.D., JAMES W. FRENCH, M.D., F.A.C.C., ALAN D. FORKER, M.D., F.A.C.C., CHRISTOPHER C. CAUDILL, M.D., F.A.C.C., AND RICHARD L. Popp, M.D.,
Echocardiography in Discrete Subaortic Stenosis STEVEN K. KRUEGER, M.D., JAMES W. FRENCH, M.D., F.A.C.C., ALAN D. FORKER, M.D., F.A.C.C., CHRISTOPHER C. CAUDILL, M.D., F.A.C.C., AND RICHARD L. Popp, M.D.,
Cardiac ultrasound protocols
 Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
Valvular Heart Disease
 Valvular Heart Disease MITRAL STENOSIS Pathophysiology rheumatic fever. calcific degeneration, malignant carcinoid disease, congenital mitral stenosis. SLE. The increased pressure gradient across the mitral
Valvular Heart Disease MITRAL STENOSIS Pathophysiology rheumatic fever. calcific degeneration, malignant carcinoid disease, congenital mitral stenosis. SLE. The increased pressure gradient across the mitral
December 2018 Tracings
 Tracings Tracing 1 Tracing 4 Tracing 1 Answer Tracing 4 Answer Tracing 2 Tracing 5 Tracing 2 Answer Tracing 5 Answer Tracing 3 Tracing 6 Tracing 3 Answer Tracing 6 Answer Questions? Contact Dr. Nelson
Tracings Tracing 1 Tracing 4 Tracing 1 Answer Tracing 4 Answer Tracing 2 Tracing 5 Tracing 2 Answer Tracing 5 Answer Tracing 3 Tracing 6 Tracing 3 Answer Tracing 6 Answer Questions? Contact Dr. Nelson
Echocardiography in the evaluation of the cyanotic
 British Heart-Journal, 1974, 36, I54-I66. Echocardiography in the evaluation of the cyanotic newborn infant Michael J. Godman, Poolin Tham, and B. S. Langford Kidd From the Department of Cardiology, Hospitalfor
British Heart-Journal, 1974, 36, I54-I66. Echocardiography in the evaluation of the cyanotic newborn infant Michael J. Godman, Poolin Tham, and B. S. Langford Kidd From the Department of Cardiology, Hospitalfor
Cardiomyopathy Consequences. function of the myocardium for any reason. This is a serious disease in which the heart muscle
 Becki Simmons Cardiomyopathy Consequences Cardiomyopathy, which literally means "heart muscle disease," is the deterioration of the function of the myocardium for any reason. This is a serious disease
Becki Simmons Cardiomyopathy Consequences Cardiomyopathy, which literally means "heart muscle disease," is the deterioration of the function of the myocardium for any reason. This is a serious disease
Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers MANAGEMENT
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers MANAGEMENT
Common Codes for ICD-10
 Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
Syncope Due to Intracavitary Left Ventricular Obstruction Secondary to Giant Esophageal Hiatus Hernia
 American Journal of Medical Case Reports, 2017, Vol. 5, No. 4, 89-93 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajmcr/5/4/4 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajmcr-5-4-4 Syncope Due to Intracavitary
American Journal of Medical Case Reports, 2017, Vol. 5, No. 4, 89-93 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajmcr/5/4/4 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajmcr-5-4-4 Syncope Due to Intracavitary
Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction
 Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction Department of Paediatrics Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction Subvalvular aortic stenosis Aortic Stenosis Supravalvular aortic stenosis Aortic Coarctation
Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction Department of Paediatrics Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction Subvalvular aortic stenosis Aortic Stenosis Supravalvular aortic stenosis Aortic Coarctation
The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors:
 Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
pulmonary valve on, 107 pulmonary valve vegetations on, 113
 INDEX Adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy, 176 Amyloidosis, 160-161 echocardiographic abnormalities in, 160 intra-mural tumors similar to, 294 myocardial involvement in, 160-161 two-dimensional echocardiography
INDEX Adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy, 176 Amyloidosis, 160-161 echocardiographic abnormalities in, 160 intra-mural tumors similar to, 294 myocardial involvement in, 160-161 two-dimensional echocardiography
Rest and Exercise Echocardiography in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Determinants of Exercise Peak Gradient and Predictors of Outcome
 Rest and Exercise Echocardiography in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Determinants of Exercise Peak Gradient and Predictors of Outcome G. Deswarte, AS. Polge, N. Lamblin, A. Millaire, M. Richardson, C. Bauters,
Rest and Exercise Echocardiography in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Determinants of Exercise Peak Gradient and Predictors of Outcome G. Deswarte, AS. Polge, N. Lamblin, A. Millaire, M. Richardson, C. Bauters,
Comparison of echocardiography and radiology in the diagnosis of aortic root dilatation in Marfan's syndrome and in syphilis
 Thorax, 1980, 35, 467-471 Comparison of echocardiography and radiology in the diagnosis of aortic root dilatation in Marfan's syndrome and in syphilis NICHOLAS G KOUNIS AND K CONSTANTINIDIS From the Cardiac
Thorax, 1980, 35, 467-471 Comparison of echocardiography and radiology in the diagnosis of aortic root dilatation in Marfan's syndrome and in syphilis NICHOLAS G KOUNIS AND K CONSTANTINIDIS From the Cardiac
Echocardiographic Evaluation of the Cardiomyopathies. Stephanie Coulter, MD, FACC, FASE April, 2016
 Echocardiographic Evaluation of the Cardiomyopathies Stephanie Coulter, MD, FACC, FASE April, 2016 Cardiomyopathies (CMP) primary disease intrinsic to cardiac muscle Dilated CMP Hypertrophic CMP Infiltrative
Echocardiographic Evaluation of the Cardiomyopathies Stephanie Coulter, MD, FACC, FASE April, 2016 Cardiomyopathies (CMP) primary disease intrinsic to cardiac muscle Dilated CMP Hypertrophic CMP Infiltrative
Echocardiography in the evaluation of the cyanotic
 British Heart-Journal, 1974, 36, I54-I66. Echocardiography in the evaluation of the cyanotic newborn infant Michael J. Godman, Poolin Tham, and B. S. Langford Kidd From the Department of Cardiology, Hospitalfor
British Heart-Journal, 1974, 36, I54-I66. Echocardiography in the evaluation of the cyanotic newborn infant Michael J. Godman, Poolin Tham, and B. S. Langford Kidd From the Department of Cardiology, Hospitalfor
Extreme pulmonary hypertension caused by mitral valve disease
 British Heart Journal, I975, 37, 74-78. Extreme pulmonary hypertension caused by mitral valve disease Natural history and results of surgery C. Ward and B. W. Hancock From the Cardio-Thoracic Unit, Northern
British Heart Journal, I975, 37, 74-78. Extreme pulmonary hypertension caused by mitral valve disease Natural history and results of surgery C. Ward and B. W. Hancock From the Cardio-Thoracic Unit, Northern
Muscle dynamics in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (1986) 62, 545-551 Muscle dynamics in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Roando F. Alvares and John F. Goodwin Division ofcardiovascular Diseases, Hammersmith Hospital, London W12,
Postgraduate Medical Journal (1986) 62, 545-551 Muscle dynamics in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Roando F. Alvares and John F. Goodwin Division ofcardiovascular Diseases, Hammersmith Hospital, London W12,
Changes in Left Atrial Size in Patients with Lone Atrial Fibrillation
 Clin. Cardiol. 14,652-656 (1991) Changes in Left Atrial Size in Patients with Lone Atrial Fibrillation GUILLERMO SOSA SUAREZ, M.D., SIEVEN LAMPERT, M.D., F.A.C.C., SHMUEL RAVID, M.D., BERNARD LOWN, M.D.,
Clin. Cardiol. 14,652-656 (1991) Changes in Left Atrial Size in Patients with Lone Atrial Fibrillation GUILLERMO SOSA SUAREZ, M.D., SIEVEN LAMPERT, M.D., F.A.C.C., SHMUEL RAVID, M.D., BERNARD LOWN, M.D.,
How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto
 How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto Introduction Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common genetic cardiomyopathy,
How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto Introduction Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common genetic cardiomyopathy,
EVALUATION OF PREGNANT PATIENTS WITH HEART DISEASE. Karen Stout, MD University of Washington Seattle Children s Seattle, WA
 EVALUATION OF PREGNANT PATIENTS WITH HEART DISEASE Karen Stout, MD University of Washington Seattle Children s Seattle, WA CASE PRESENTATION 24 year old woman with aortic regurgitation referred for evaluation
EVALUATION OF PREGNANT PATIENTS WITH HEART DISEASE Karen Stout, MD University of Washington Seattle Children s Seattle, WA CASE PRESENTATION 24 year old woman with aortic regurgitation referred for evaluation
PRACTICAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN THE ADULT with Doppler and color-doppler flow imaging
 PRACTICAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN THE ADULT with Doppler and color-doppler flow imaging PRACTICAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN THE ADULT with Doppler and color-doppler flow imaging by J.P.M. HAMER Thoraxcentre, Department
PRACTICAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN THE ADULT with Doppler and color-doppler flow imaging PRACTICAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN THE ADULT with Doppler and color-doppler flow imaging by J.P.M. HAMER Thoraxcentre, Department
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW
 PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
echocardiographic measures of left ventricular
 Br Heart J 1986; 55: 155-61 Comparison of electrocardiographic and echocardiographic measures of left ventricular hypertrophy in the assessment of aortic stenosis MARK DANCY From the Department of Cardiology,
Br Heart J 1986; 55: 155-61 Comparison of electrocardiographic and echocardiographic measures of left ventricular hypertrophy in the assessment of aortic stenosis MARK DANCY From the Department of Cardiology,
Relation of isovolumic relaxation to left ventricular
 British Heart Journal, 1979, 42, 51-56 Relation of isovolumic relaxation to left ventricular wall movement in man W. CHN AND D. GIBSON From the Department of Cardiology, Bromptont Hospital, London SUMMARY
British Heart Journal, 1979, 42, 51-56 Relation of isovolumic relaxation to left ventricular wall movement in man W. CHN AND D. GIBSON From the Department of Cardiology, Bromptont Hospital, London SUMMARY
Echocardiography of Cardiac Valves in
 Echocardiography of Cardiac Valves in Pericardial Effusion NAVN C. NANDA, M.D., RAYMOND GRAMAK, M.D., AND CHARLES M. GROSS, M.D. SUMMARY Nine adult patients with large pericardial effusions (PE) demonstrated
Echocardiography of Cardiac Valves in Pericardial Effusion NAVN C. NANDA, M.D., RAYMOND GRAMAK, M.D., AND CHARLES M. GROSS, M.D. SUMMARY Nine adult patients with large pericardial effusions (PE) demonstrated
Comparability of M mode echocardiographic long axis and short axis left ventricular function derivatives
 Br Heart J 1986;56:445-9 Comparability of M mode echocardiographic long axis and short axis left ventricular function derivatives P G D'ARBELA,* Z M SILAYAN,* J M BLANDt From the *Cardiology Section, Department
Br Heart J 1986;56:445-9 Comparability of M mode echocardiographic long axis and short axis left ventricular function derivatives P G D'ARBELA,* Z M SILAYAN,* J M BLANDt From the *Cardiology Section, Department
Valvular Heart Disease: Assessment and Timing of Intervention. Graham Cole Consultant Cardiologist Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust
 Valvular Heart Disease: Assessment and Timing of Intervention Graham Cole Consultant Cardiologist Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust Disclosures: Speaker fee: Bayer Acknowledgements: Matt Shun-Shin
Valvular Heart Disease: Assessment and Timing of Intervention Graham Cole Consultant Cardiologist Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust Disclosures: Speaker fee: Bayer Acknowledgements: Matt Shun-Shin
Echocardiographic Features of Supravalvular Aortic Stenosis
 Echocardiographic Features of Supravalvular Aortic Stenosis By JAMES L. BOLEN, M. D., RICHARD L. Popp, M.D., AND JAMES W. FRENCH, M.D. SUMMARY A method for the echocardiographic detection of supravalvular
Echocardiographic Features of Supravalvular Aortic Stenosis By JAMES L. BOLEN, M. D., RICHARD L. Popp, M.D., AND JAMES W. FRENCH, M.D. SUMMARY A method for the echocardiographic detection of supravalvular
Infirmary and the Westmorland County Hospital. A total of 305 subjects (152 male, 153 female) were. the Coronary Care Unit were excluded from this
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (April 1980) 56, 221-228 The use of cross-sectional echocardiography in a general hospital ALLEN K. BROWN F.R.C.P. VALERIE ANDERSON M.B., Ch.B. Cardiac Investigation Department,
Postgraduate Medical Journal (April 1980) 56, 221-228 The use of cross-sectional echocardiography in a general hospital ALLEN K. BROWN F.R.C.P. VALERIE ANDERSON M.B., Ch.B. Cardiac Investigation Department,
Managing Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy with Imaging. Gisela C. Mueller University of Michigan Department of Radiology
 Managing Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy with Imaging Gisela C. Mueller University of Michigan Department of Radiology Disclosures Gadolinium contrast material for cardiac MRI Acronyms Afib CAD Atrial fibrillation
Managing Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy with Imaging Gisela C. Mueller University of Michigan Department of Radiology Disclosures Gadolinium contrast material for cardiac MRI Acronyms Afib CAD Atrial fibrillation
Uncommon Doppler Echocardiographic Findings of Severe Pulmonic Insufficiency
 Uncommon Doppler Echocardiographic Findings of Severe Pulmonic Insufficiency Rahul R. Jhaveri, MD, Muhamed Saric, MD, PhD, FASE, and Itzhak Kronzon, MD, FASE, New York, New York Background: Two-dimensional
Uncommon Doppler Echocardiographic Findings of Severe Pulmonic Insufficiency Rahul R. Jhaveri, MD, Muhamed Saric, MD, PhD, FASE, and Itzhak Kronzon, MD, FASE, New York, New York Background: Two-dimensional
Congenital Heart Malformations Associated with Disproportionate Ventricular Septal Thickening
 Congenital Heart Malformations Associated with Disproportionate Ventricular Septal Thickening By BARRY J. MARON, M.D., JESSE E. EDWARDS, M.D., VICTOR J. FERRANS, M. D., Ph. D., CHESTER E. CLARK, M. D.,
Congenital Heart Malformations Associated with Disproportionate Ventricular Septal Thickening By BARRY J. MARON, M.D., JESSE E. EDWARDS, M.D., VICTOR J. FERRANS, M. D., Ph. D., CHESTER E. CLARK, M. D.,
Rotational excursion of heart in massive pericardial effusion studied by phased-array echocardiography
 British Heart journal, 1979, 41, 513-521 Rotational excursion of heart in massive pericardial effusion studied by phased-array echocardiography HIROHIDE MATSUO, MASAYUKI MATSUMOTO, YASUHIKO HAMANAKA, TATSUHIKO
British Heart journal, 1979, 41, 513-521 Rotational excursion of heart in massive pericardial effusion studied by phased-array echocardiography HIROHIDE MATSUO, MASAYUKI MATSUMOTO, YASUHIKO HAMANAKA, TATSUHIKO
Treatment of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy in Bruce B. Reid, MD
 Treatment of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy in 2017 Bruce B. Reid, MD Disclosures I have no conflicts of interest to disclose I will not be discussing any off label medications and/or devices Objectives 1)
Treatment of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy in 2017 Bruce B. Reid, MD Disclosures I have no conflicts of interest to disclose I will not be discussing any off label medications and/or devices Objectives 1)
Case 47 Clinical Presentation
 93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
By the end of this session, the student should be able to:
 Valvular Heart disease HVD By Dr. Ashraf Abdelfatah Deyab VHD- Objectives By the end of this session, the student should be able to: Define and classify valvular heart disease. Enlist the causes of acquired
Valvular Heart disease HVD By Dr. Ashraf Abdelfatah Deyab VHD- Objectives By the end of this session, the student should be able to: Define and classify valvular heart disease. Enlist the causes of acquired
Management of Congenital Aortic Stenosis
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1970, 45, 201. Management of Congenital Aortic Stenosis JOHN M. REID, ERIC N. COLEMAN, and JOHN G. STEVENSON From the University Department of Child Health; the Department
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1970, 45, 201. Management of Congenital Aortic Stenosis JOHN M. REID, ERIC N. COLEMAN, and JOHN G. STEVENSON From the University Department of Child Health; the Department
Influence of RAAS inhibition on outflow tract obstruction in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 5 RAAS inhibitors should be avoided if possible in patients with obstructive HCM Influence of RAAS inhibition on outflow tract obstruction in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Katrin Witzel,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 5 RAAS inhibitors should be avoided if possible in patients with obstructive HCM Influence of RAAS inhibition on outflow tract obstruction in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Katrin Witzel,
Debanding and repair of ventricular septal defect: a new technique for older patients
 Thorax, 1979, 34, 531-53 5 Debanding and repair of ventricular septal defect: a new technique for older patients P LAURIDSEN, A UHRENHOLDT, AND I H RYGG From the Department of Thoracic Surgery R and Cardiovascular
Thorax, 1979, 34, 531-53 5 Debanding and repair of ventricular septal defect: a new technique for older patients P LAURIDSEN, A UHRENHOLDT, AND I H RYGG From the Department of Thoracic Surgery R and Cardiovascular
Surgical treatment of congenital valvular
 Thorax (1976), 31, 398. Surgical treatment of congenital valvular aortic stenosis LUIGI CHIARIELLO, PETER VLAD, and S. SUBRAMANIAN Departments of Paediatric Cardiology and Cardiovascular Surgery, Children's
Thorax (1976), 31, 398. Surgical treatment of congenital valvular aortic stenosis LUIGI CHIARIELLO, PETER VLAD, and S. SUBRAMANIAN Departments of Paediatric Cardiology and Cardiovascular Surgery, Children's
Aortic Stenosis and Perioperative Risk With Non-cardiac Surgery
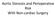 Aortic Stenosis and Perioperative Risk With Non-cardiac Surgery Aortic stenosis (AS) is characterized as a high-risk index for cardiac complications during non-cardiac surgery. A critical analysis of old
Aortic Stenosis and Perioperative Risk With Non-cardiac Surgery Aortic stenosis (AS) is characterized as a high-risk index for cardiac complications during non-cardiac surgery. A critical analysis of old
Effects of Amyl Nitrite in Aortic Valvular and Muscular Subaortic Stenosis
 Effects of Amyl Nitrite in Aortic Valvular and Muscular Subaortic Stenosis By E. W. HANCOCK, M.D., AND W. C. FoWKES, M.D. From the Department of Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto,
Effects of Amyl Nitrite in Aortic Valvular and Muscular Subaortic Stenosis By E. W. HANCOCK, M.D., AND W. C. FoWKES, M.D. From the Department of Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto,
Pre-participation Screening for the Prevention of sudden Cardiac Death in Young Athletes. Thomas W. Allen, DO, MPH
 Pre-participation Screening for the Prevention of sudden Cardiac Death in Young Athletes Thomas W. Allen, DO, MPH Cardiovascular disorders are the leading cause of sudden death in young athletes accounting
Pre-participation Screening for the Prevention of sudden Cardiac Death in Young Athletes Thomas W. Allen, DO, MPH Cardiovascular disorders are the leading cause of sudden death in young athletes accounting
AORTIC COARCTATION. Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta
 AORTIC COARCTATION Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta Definition: Aortic coarctation is a congenital narrowing of the aorta, usually located after the left subclavian artery, near the ductus or the ligamentum
AORTIC COARCTATION Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta Definition: Aortic coarctation is a congenital narrowing of the aorta, usually located after the left subclavian artery, near the ductus or the ligamentum
Cardiomyopathy. Jeff Grubbe MD FACP, Chief Medical Director, Allstate Life & Retirement
 Cardiomyopathy Jeff Grubbe MD FACP, Chief Medical Director, Allstate Life & Retirement Nebraska Home Office Life Underwriters Association March 20, 2018 1 Cardiomyopathy A myocardial disorder in which
Cardiomyopathy Jeff Grubbe MD FACP, Chief Medical Director, Allstate Life & Retirement Nebraska Home Office Life Underwriters Association March 20, 2018 1 Cardiomyopathy A myocardial disorder in which
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD)
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Hypertension in Aortic Valve Disease
 Hypertension in Aortic Valve Disease Hanna M. Nosseir MRCP, FRCP Head of Cardiology department Galaa Military Medical Complex Aortic stenosis: Introduction Arterial hypertension and aortic stenosis are
Hypertension in Aortic Valve Disease Hanna M. Nosseir MRCP, FRCP Head of Cardiology department Galaa Military Medical Complex Aortic stenosis: Introduction Arterial hypertension and aortic stenosis are
HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY (HCM) PRESENTED AS UNSTABLE ANGINA COMPLICATED BY SERIOUS VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS CASE REPORT AND REVIEW LITERATURE
 HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY (HCM) PRESENTED AS UNSTABLE ANGINA COMPLICATED BY SERIOUS VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS CASE REPORT AND REVIEW LITERATURE Lusyun Kumar Yadav * and Jin li Jun Department of Cardiology,
HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY (HCM) PRESENTED AS UNSTABLE ANGINA COMPLICATED BY SERIOUS VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS CASE REPORT AND REVIEW LITERATURE Lusyun Kumar Yadav * and Jin li Jun Department of Cardiology,
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in infants of poor1y-controlled diabetic mothers
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1981, 56, 258-263 Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in infants of poor1y-controlled diabetic mothers HENRY L HALLIDAY Children's Hospital, San Francisco, and Royal Maternity
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1981, 56, 258-263 Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in infants of poor1y-controlled diabetic mothers HENRY L HALLIDAY Children's Hospital, San Francisco, and Royal Maternity
New Therapies for the Heart Patient. Wilson They said "There's nothing more that can be done." Robert Federici MD, Presbyterian Heart
 New Therapies for the Heart Patient Wilson 2016 They said "There's nothing more that can be done." Robert Federici MD, Presbyterian Heart Disclosure Boston Scientific Physician Proctor for CTO's, Clinical
New Therapies for the Heart Patient Wilson 2016 They said "There's nothing more that can be done." Robert Federici MD, Presbyterian Heart Disclosure Boston Scientific Physician Proctor for CTO's, Clinical
Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016
 1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
Aortic stenosis (AS) is common with the aging population.
 New Insights Into the Progression of Aortic Stenosis Implications for Secondary Prevention Sanjeev Palta, MD; Anita M. Pai, MD; Kanwaljit S. Gill, MD; Ramdas G. Pai, MD Background The risk factors affecting
New Insights Into the Progression of Aortic Stenosis Implications for Secondary Prevention Sanjeev Palta, MD; Anita M. Pai, MD; Kanwaljit S. Gill, MD; Ramdas G. Pai, MD Background The risk factors affecting
Cardiac Catheterization Cases Primary Cardiac Diagnoses Facility 12 month period from to PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient)
 PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
Cardiac Conditions in Sport & Exercise. Cardiac Conditions in Sport. USA - Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD) Dr Anita Green. Sudden Cardiac Death
 Cardiac Conditions in Sport & Exercise Dr Anita Green Cardiac Conditions in Sport Sudden Cardiac Death USA - Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD)
Cardiac Conditions in Sport & Exercise Dr Anita Green Cardiac Conditions in Sport Sudden Cardiac Death USA - Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD)
marked increase in thickness of walls of heart in patient with HCM.
 Surgical Management of Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy Hani K. Najm MD, Msc, FRCSC, FRCS (Glasg Glasg), FACC, FESC President of Saudi Heart Association King Abdulaziz Cardiac Centre Riyadh, Saudi
Surgical Management of Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy Hani K. Najm MD, Msc, FRCSC, FRCS (Glasg Glasg), FACC, FESC President of Saudi Heart Association King Abdulaziz Cardiac Centre Riyadh, Saudi
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome
 Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
The Management of HOCM: What are the Surgical Options
 The Management of HOCM: What are the Surgical Options Konstadinos A Plestis, MD System Chief of Cardiac Thoracic and Vascular Surgery Main Line Health Care System Professor Sidney Kimmel Medical College
The Management of HOCM: What are the Surgical Options Konstadinos A Plestis, MD System Chief of Cardiac Thoracic and Vascular Surgery Main Line Health Care System Professor Sidney Kimmel Medical College
Mitral Valve Disease. Prof. Sirchak Yelizaveta Stepanovna
 Mitral Valve Disease Prof. Sirchak Yelizaveta Stepanovna Fall 2008 Mitral Valve Stenosis Lecture Outline Mitral Stenosis Mitral Regurgitation Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical features Diagnostic testing
Mitral Valve Disease Prof. Sirchak Yelizaveta Stepanovna Fall 2008 Mitral Valve Stenosis Lecture Outline Mitral Stenosis Mitral Regurgitation Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical features Diagnostic testing
Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract'
 Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract' ROBERT WALMSLEY British Heart Journal, 1979, 41, 263-267 From the Department of Anatomy and Experimental Pathology, The University, St Andrews, Scotland SUMMARY
Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract' ROBERT WALMSLEY British Heart Journal, 1979, 41, 263-267 From the Department of Anatomy and Experimental Pathology, The University, St Andrews, Scotland SUMMARY
Echocardiographic Patterns of Pulmonic Valve Motion with Pulmonary Hypertension
 Echocardiographic Patterns of Pulmonic Valve Motion with Pulmonary Hypertension By ARTHUR E. WEYMAN, M.D., JAMES C. DILLON, M.D., HARVEY FEIGENBAUM, M.D., AND SONIA CHANG, B.A. SUMMARY Echocardiographic
Echocardiographic Patterns of Pulmonic Valve Motion with Pulmonary Hypertension By ARTHUR E. WEYMAN, M.D., JAMES C. DILLON, M.D., HARVEY FEIGENBAUM, M.D., AND SONIA CHANG, B.A. SUMMARY Echocardiographic
Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital
 Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital VSD is one of the most common congenital cardiac abnormalities in the newborn. It can occur as an isolated finding or in combination
Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital VSD is one of the most common congenital cardiac abnormalities in the newborn. It can occur as an isolated finding or in combination
Anomalous muscle bundle of the right ventricle
 British Heart Journal, 1978, 40, 1040-1045 Anomalous muscle bundle of the right ventricle Its recognition and surgical treatment M. D. LI, J. C. COLES, AND A. C. McDONALD From the Department of Paediatrics,
British Heart Journal, 1978, 40, 1040-1045 Anomalous muscle bundle of the right ventricle Its recognition and surgical treatment M. D. LI, J. C. COLES, AND A. C. McDONALD From the Department of Paediatrics,
Echocardiographic visualization of the anatomic causes of mitral regurgitation
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (May 1982) 58, 257-263 PAPERS Echocardiographic visualization of the anatomic causes of mitral regurgitation resulting from myocardial infarction ROBERT M. DONALDSON M.R.C.P.
Postgraduate Medical Journal (May 1982) 58, 257-263 PAPERS Echocardiographic visualization of the anatomic causes of mitral regurgitation resulting from myocardial infarction ROBERT M. DONALDSON M.R.C.P.
ORIGINAL PAPER. R. C. Steggerda & J. C. Balt & K. Damman & M. P. van den Berg & J. M. ten Berg
 Neth Heart J (2013) 21:504 509 DOI 10.1007/s12471-013-0453-4 ORIGINAL PAPER Predictors of outcome after alcohol septal ablation in patients with hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy. Special interest
Neth Heart J (2013) 21:504 509 DOI 10.1007/s12471-013-0453-4 ORIGINAL PAPER Predictors of outcome after alcohol septal ablation in patients with hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy. Special interest
An Appraisal of Mitral Valve Echocardiograms Mimicking Mitral Stenosis in Conditions with Right Ventricular Pressure Overload
 An Appraisal of Mitral Valve Echocardiograms Mimicking Mitral Stenosis in Conditions with Right Ventricular Pressure Overload By LAMBERT P. MOLAURIN, M.D., THOMAS C. GIBSON, M.R.C.P., WiNFRuwD WAIDER,
An Appraisal of Mitral Valve Echocardiograms Mimicking Mitral Stenosis in Conditions with Right Ventricular Pressure Overload By LAMBERT P. MOLAURIN, M.D., THOMAS C. GIBSON, M.R.C.P., WiNFRuwD WAIDER,
Cardiac hypertrophy and how it may break an athlete s heart e the Cypriot case
 Eur J Echocardiography (2005) 6, 301e307 Cardiac hypertrophy and how it may break an athlete s heart e the Cypriot case C.E. Chee a,1, C.P. Anastassiades a,1, A.G. Antonopoulos b, A.A. Petsas b, L.C. Anastassiades
Eur J Echocardiography (2005) 6, 301e307 Cardiac hypertrophy and how it may break an athlete s heart e the Cypriot case C.E. Chee a,1, C.P. Anastassiades a,1, A.G. Antonopoulos b, A.A. Petsas b, L.C. Anastassiades
Age and body surface area related normal upper and lower limits of M mode echocardiographic measurements and left ventricular volume and
 276 Br Heart _' 1994;72:276-280 MEASUREMENT University Departments of Medical Cardiology and Child Health, Glasgow F U Huwez A B Houston J Watson S McLaughlin P W Macfarlane Correspondence to: Dr P W Macfarlane,
276 Br Heart _' 1994;72:276-280 MEASUREMENT University Departments of Medical Cardiology and Child Health, Glasgow F U Huwez A B Houston J Watson S McLaughlin P W Macfarlane Correspondence to: Dr P W Macfarlane,
Radiology of the respiratory/cardiac diseases (part 2)
 Cardiology Cycle - Lecture 6 436 Teams Radiology of the respiratory/cardiac diseases (part 2) Objectives Done By Team Leaders: Khalid Alshehri Hanin Bashaikh Team Members: Leena Alwakeel Aroob Alhuthail
Cardiology Cycle - Lecture 6 436 Teams Radiology of the respiratory/cardiac diseases (part 2) Objectives Done By Team Leaders: Khalid Alshehri Hanin Bashaikh Team Members: Leena Alwakeel Aroob Alhuthail
Effect of the Geometry of the Left Ventricle
 EF AD LV GEOMETRY/Dumesnil and Shoucri 91 Rearranging equation 2 and solving for the activity yields =C u * T S e-ud (I - eut) (3) If the activity within the left ventricle is treated as a point source
EF AD LV GEOMETRY/Dumesnil and Shoucri 91 Rearranging equation 2 and solving for the activity yields =C u * T S e-ud (I - eut) (3) If the activity within the left ventricle is treated as a point source
