Debanding and repair of ventricular septal defect: a new technique for older patients
|
|
|
- Madeline McKenzie
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thorax, 1979, 34, Debanding and repair of ventricular septal defect: a new technique for older patients P LAURIDSEN, A UHRENHOLDT, AND I H RYGG From the Department of Thoracic Surgery R and Cardiovascular Laboratory of Medical Department B Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, Denmark ABSTRACT Between October 1972 and April patients underwent definitive repair of a ventricular septal defect (VSD) and reconstruction of the pulmonary artery at the banding site. This report presents pre- and post-operative haemodynamic data in 12 patients, seven to 22 years after banding (mean 13-4). Banding of the pulmonary artery was performed before the age of 6 months (mean 4). The indications were increased pulmonary blood flow and intractable heart failure. As we had previously become dissatisfied with patch angioplasty of the main pulmonary artery, we introduced a new technique in this group of excising the site of the band and anastomosing the pulmonary artery end-to-end. The gradient between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery was abolished completely in nine cases and reduced to below 30 mmhg in the remaining three patients. This technique is used only in older patients in whom the banding has persisted for a long time. In children under 2 years of age we usually remove the band and dilate the pulmonary The beneficial effects of banding of the pulmonary nique comprising resection of the banding site artery in infants with severe congestive heart with end-to-end anastomosis of the main pulmonary artery and closure of the ventricular septal failure caused by ventricular septal defect (VSD) (isolated or in combination with other cardiac defect. This paper deals with the haemodynamic anomalies) are well established (Muller and results. Dammann, 1952). The extensive study by Hunt et al (1971) showed a three-fold haemodynamic Patients gain: (1) reduction in the pulmonary artery pressure; (2) reduction of excessive pulmonary The indications for banding of the pulmonary blood flow; and (3) reduction of the pulmonary artery were increased pulmonary blood flow and resistance towards normal with possible-prevention pulmonary hypertension resulting in heart failure of the progression of pulmonary vascular obstructive disease. 1959). intractable to medical treatment (Therkelsen et al, Palliative banding of the pulmonary artery is These infants were banded by Therkelsen at followed later by a corrective operation at which Queen Louise's Children's Hospital, Copenhagen, the VSD is closed and the band removed. Almost during the years , where he banded in all one-half of the patients in whom this is performed 47 babies with VSD (Therkelsen, 1968). They need a patch in the pulmonary artery to relieve a were kept under observation and not referred for fixed stenosis at the banding site (Hunt et al, 1971) surgical correction until increasing cyanosis appeared. Thus we have a series of extraordinarily and despite this a gradient caused by the posterior crest may persist in some patients. long observation times after banding. In the present group of patients in whom definitive repair was performed so late after the first trolled by pressure measurement, and a systolic The degree of banding was in every case con- operation very severe fibrosis was found at the pressure peripheral to the band of 40 mmhg was banding site. Accordingly, to avoid residual aimed at. Despite this high degree of narrowing stenosis after debanding we used a different tech- the patients were in excellent condition and cy- 531
2 532 anosis was moderate up to the time of correction. Between October 1972 and April patients underwent definitive repair of the VSD and reconstruction of the pulmonary artery at the banding site with the technique described below. The table shows details of the 12 (six male, six female) patients at follow-up who were aged 8-22 years (mean 14-6). The pulmonary artery banding was performed before the age of 6 months (mean 4) in all cases. Details of the 12 patients at the time of follow-up Case Agelsex Age at Banding Observation banding (mo) period (yr) time (months) 1 11 F M M F M F F F M F M M Mean 14*6 years 4 months 13 4 years 11 3 months The banding persisted for seven to 22 years (mean 13*4). Cardiac catheterisation was performed before debanding in all cases. The postoperative observation time has varied from one to 28 months (mean 11-3). There were two operative deaths, and one patient has not been recatheterised. Twelve patients are included in the follow-up study. They underwent cardiac catheterisation before banding, before total repair, and after debanding. Operative technique The new technique involves excision of the banded area and an end-to-end anastomosis of the pulmonary artery (fig 1). The band was positioned on the main pulmonary artery between the pulmonary artery bifurcation and the pulmonary valve in all cases. In the same period we had four cases where the band had slipped out to the bifurcation, and a patch repair was used. In a fifth case where the band had resulted in narrowing of both branches of the pulmonary artery we proceeded with the new technique. This was an error, and led to one of the two operative deaths. The band consisted of umbilical tape threaded through a silicone tube. There was severe fibrous reaction in the region of the band in all cases. Infundibular resection was performed in all Resected segment P Lauridsen, A Uhrenholdt, and I H Rygg Fig 1 New technique for relieving obstruction after banding. Segment is excised and end-to-end anastomosis performed. patients to relieve the acquired infundibular stenosis. The VSD was closed with a Dacron prosthesis. Results The systolic pressure in the pulmonary artery decreased from a mean value of 68 mmhg (SD 10) before to 24 mmhg (SD 6-9) after banding (fig 2). This is statistically significant (P<O0001). Debanding and VSD closure caused a slight but inconstant increase in the systolic pulmonary artery pressure to 27 mmhg (SD 7 3). The right ventricular systolic pressure showed a striking reduction from a mean value of 103 mmhg (SD 1X5) before to a mean value of 36 mmhg (SD 10-4) after debanding (P<0001) (fig 3). Complete normalisation was obtained in only seven patients as five patients still had values between 45 and 55 mmhg. There was no significant change in the mean right ventricular pressure before and after debanding. The pressure gradient across the pulmonary band varied between 42 and 105 mmhg (mean 80 mmhg (SD 16.8)) and after debanding the mean was 8-4 mmhg (SD 8-6) (fig 4). Before banding four patients had varying degrees of left to right shunt (fig 5). After the second operation the VSD was completely closed in nine patients while minor left to right shunts remained in three. Debanding caused the heart to increase slightly in size from a mean value of 412 ml/2 body surface area (Jonsell, 1939) (SD 73-9) to 443 ml/2 body surface area (SD 68). The
3 Debanding and repair of ventricular septal defect: a new technique for older patients patient with the largest heart had tricuspid incompetence and a small residual VSD after the operation. This patient also had the highest enddiastolic pressure in the right ventricle (fig 6). Pre- banding Post - banding Post-correction Fig 2 Pulmonary artery systolic pressure before banding, after banding, and after definitive repair j ] IF Right ventricle (mmhg) systolic Pre- banding Post-bandng Post- correction Fig 3 Right ventricular systolic pressure before banding, after banding, and after definitive repair. Ten patients were asymptomatic after correction. One patient noticed dyspnoea on slight to moderate exercise and another complained of periodic oppression in the chest, not provoked by exercise. Seven of the patients were maintained on a small dose of digoxin in the early postoperative period after debanding. None of the patients were receiving cardiac drugs before the debanding. Before debanding the electrocardiogram showed moderate to severe right-sided hypertrophy in ten patients and right bundle-branch block in two. After debanding all patients had right bundlebranch block except for one patient with complete heart block. Microscopy of the resected infundibular muscle showed myocardial fibrosis and degenerative changes in the myocardial cells. There was severe fibrosis at the site of the pulmonary artery banding and calcium deposits in the arterial wall were found in several cases. Two patients developed complete heart block after correction, one of whom died. Pulmanary (mmhg) artery gradient Post - binding Post -correct ion Fig 4 Pulmonary artery gradient after banding and after definitive repair. 533
4 Cardiac shunts Pre- banding Post-banding Post-correction Fig 5 Before banding all patients had arteriovenous shunts. After definitive repair nine patients had no shunt and three had minor arteriovenous shunts. Necropsy findings Two patients died in the immediate postoperative period. The first, a 4-year-old boy, was operated on in June Surgical heart block resulted, and temporary pacing wires were attached to the right ventricle. He remained in low cardiac output, developed renal failure, and died on the second day. Necropsy showed that the VSD was closed and that there was a wide pulmonary artery at the former banding site. Microscopy showed myocardial hypertrophy, subendocardial bleeding, and necrosis in the septum where the VSD patch was inserted. The second, a 9-year-old boy, was operated on in October The band had migrated close to the bifurcation of the pulmonary artery resulting in stenosis of both pulmonary arterial branches. There was also severe fibrosis around the band. It was decided to proceed with excision of the band, but the anastomosis of the main pulmonary artery to the pulmonary artery branches were very difficult, and the bypass time was five hours. After termination of the extracorporeal circulation the right ventricular pressure was at systemic level. The patient died a few hours later from cardiac failure. At necropsy the VSD was closed, and there was some stenosis of the anastomosis be- P Lauridsen, A Uhrenholdt, and I H Rygg 600 Heart size Post- banding Post - correction Fig 6 Heart size before definitive repair and at time of follow-up. tween the main pulmonary artery and the bifurcation. Discussion Banding of the pulmonary artery has been used for palliative treatment of excessive pulmonary blood flow secondary to VSD when it is an isolated lesion or when combined with other malformations, such as transposition of the great vessel, truncus arteriosus, or coarctation of the aorta (Hunt et al, 1971). The operative mortality has been about 15% (Therkelsen et al, 1959; Stark et al, 1969; Patel et al, 1973), but in recent years 3% (Trusler and Mustard, 1972) in cases with minor associated defects. Despite continued medical treatment congestive heart failure and recurrent pneumonia can still be a problem after pulmonary artery banding (Dobell et al, 1973; Stark et al, 1969; Hunt et al, 1971). This has not been the case in the present group. At the time of definitive intracardiac repair the band presents technical problems as a patch enlargement is often necessary to relieve the stenosis at the band site or the I.
5 Debanding and repair of ventricular septal defect: a new technique for older patients branch stenosis resulting from migration of the band to the bifurcation (Hunt et al, 1970). The operative mortality has been about 20% (Stark et al, 1969; Patel et al, 1973; Kirklin et al, 1976; Seybold-Epting et al, 1976) at the time of definitive repair. Residual systolic gradients across the debanded area of greater than 30 mmhg have been recorded in 30% of patients (Stark et al, 1969). Our early experience of debanding was similar and stimulated us to search for a more effective technique for debanding. Since October 1972 we have used the present technique (fig 1) in all cases where the band was still located on the main pulmonary In cases where the band has migrated peripherally causing fibrous stenosis of the right and left branches complete resection should probably not be performed because this makes the operation difficult, as we found in one of our cases who died. In such cases we have recently preferred patch repair with pericardium or with glutaraldehyde preserved pig pericardium. In contrast to most other reports, our patients have undergone definitive intracardiac repair and debanding rather late. The mean banding period was 13*3 years (SD 3 8). This probably accounted for the presence of secondary muscular hypertrophy necessitating infundibular resection in every case. Hunt et al (1970) found acquired infundibular stenosis in three of their eight patients, but it was of no haemodynamic significance. In their cases the debanding was performed four to eight years (mean five) after banding. They noted thickening of the pulmonary valve cusps resulting in mild valvar stenosis in seven cases. Small minor left to right shunts persist in three of the surviving patients, one of whom also has tricuspid incompetence and cardiomegaly. A major increase in heart size after repair suggests that there is some additional cardiac disease. Our cases show that patients banded in infancy can develop almost normally and tolerate a severe degree of artificial supravalvar stenosis, which does not change in size and which does not interfere with normal development of the pulmonary valves. From our results we conclude that debanding by excision of the banded segment can be performed with no significant residual pulmonary gradient and is a satisfactory method when the banding period has been unusually long. This method should be reserved for cases where the band is located in the middle of the main pulmonary Our present policy is to undertake primary repair of isolated VSDs. We reserve banding for patients with VSDs and complicating cardiac disease, and proceed to debanding and definitive repair two years later. At this age excision of the band site is usually unnecessary as the pulmonary artery can be dilated after removal of the band. References 535 Dobell, A R C, Murphy, D A, Poirier, N L, and Gibbons, J E (1973). The pulmonary artery after debanding. Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, 65, Hunt, C E, Formanek, G, Castaneda, A, and Moller, J H (1970). Closure of ventricular septal defect and removal of pulmonary arterial band. American Journal of Cardiology, 26, Hunt, C E, Formanek, G, Levine, M A, Castaneda, A, and Moller, J H (1971). Banding of the pulmonary artery: results in 111 children. Circulation, 43, Jonsell, S (1939). A method for the determination of the heart size by teleroentgenography. (A Heart Volume Index). Acta Radiologica, 20, Kirklin, J W, Appelbaum, A, and Bargeron, L M (1976). Primary repair versus banding for ventricular septal defects in infants. In The Child with Congenital Heart Disease after Surgery, edited by B S L Kidd, and R D Rowe, pp 3-9. Futura, New York. Muller, W H, and Dammann, J F (1952). The treatment of certain congenital malformations of the heart by the creation of pulmonic stenosis to reduce pulmonary hypertension and excessive pulmonary blood flow. Surgery, Gynecology and Obstetrics, 95, Patel, R G, Ihenacho, H N C, Abrams, L D, Astley, R, Parsons, C G, Roberts, K D, and Singh, S P (1973). Pulmonary artery banding and subsequent repair in ventricular septal defect. British Heart Journal, 35, Seybold-Epting, W, Reul, G J, Hallman, G L, and Cooley, D A (1976). Repair of ventricular septal defect after pulmonary artery banding. Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, 71, Stark, J, Aberdeen, E, Waterston, D J, Bonham-Carter, R E, and Tynan, M (1969). Pulmonary artery constriction (banding): A report of 146 cases. Surgery, 65, Therkelsen, F, Gammelgaard, P A, and Boesen, I (1959). Ventricular septal defects in infants treated with various modifications of the Dammann-Muller operation. Acta Chirurgica Scandinavica, suppl, 245, Therkelsen, F (1968). Congenital cardiac diseases in infants. Diseases of the Chest, 53, Trusler, G A, and Mustard, W T (1972). A method of banding the pulmonary artery for large isolated ventricular septal defect with and without transposition of the great arteries. Annals of Thoracic Surgery, 13, Requests for reprints to: Dr P Lauridsen, Department of Thoracic Surgery, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen.
Pulmonary Artery Debanding
 Surgical Considerations A. Robert Cordell, M.D., Robert C. McKone, M.D., and M. Amjad Bhatti, M.D. ABSTRACT Thirty-five infants underwent pulmonary artery banding for cardiac defects producing excessive
Surgical Considerations A. Robert Cordell, M.D., Robert C. McKone, M.D., and M. Amjad Bhatti, M.D. ABSTRACT Thirty-five infants underwent pulmonary artery banding for cardiac defects producing excessive
Management of Infants with Large Ventricular Septa1 Defects
 THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY Journal of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association VOLUME 15 * NUMBER * FEBRUARY 1973 Management of Infants with Large Ventricular
THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY Journal of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association VOLUME 15 * NUMBER * FEBRUARY 1973 Management of Infants with Large Ventricular
AORTIC COARCTATION. Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta
 AORTIC COARCTATION Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta Definition: Aortic coarctation is a congenital narrowing of the aorta, usually located after the left subclavian artery, near the ductus or the ligamentum
AORTIC COARCTATION Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta Definition: Aortic coarctation is a congenital narrowing of the aorta, usually located after the left subclavian artery, near the ductus or the ligamentum
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome
 Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
Anomalous muscle bundle of the right ventricle
 British Heart Journal, 1978, 40, 1040-1045 Anomalous muscle bundle of the right ventricle Its recognition and surgical treatment M. D. LI, J. C. COLES, AND A. C. McDONALD From the Department of Paediatrics,
British Heart Journal, 1978, 40, 1040-1045 Anomalous muscle bundle of the right ventricle Its recognition and surgical treatment M. D. LI, J. C. COLES, AND A. C. McDONALD From the Department of Paediatrics,
SURGICAL TREATMENT AND OUTCOME OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE
 SURGICAL TREATMENT AND OUTCOME OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Mr. W. Brawn Birmingham Children s Hospital. Aims of surgery The aim of surgery in congenital heart disease is to correct or palliate the heart
SURGICAL TREATMENT AND OUTCOME OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Mr. W. Brawn Birmingham Children s Hospital. Aims of surgery The aim of surgery in congenital heart disease is to correct or palliate the heart
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD)
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016
 1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
Pulmonary artery banding in congenital heart disease
 Thorax (1968), 23, 385. Pulmonary artery banding in congenital heart disease associated with pulmonary hypertension J.-M. REID, R. S. BARCLAY, E. N. COLEMAN, J. G. STEVENSON, T. M. WELSH, AND N. McSWAN
Thorax (1968), 23, 385. Pulmonary artery banding in congenital heart disease associated with pulmonary hypertension J.-M. REID, R. S. BARCLAY, E. N. COLEMAN, J. G. STEVENSON, T. M. WELSH, AND N. McSWAN
Reconstruction of right ventricular outflow with a valved homograft conduit
 Thorax (1974), 29, 617. Reconstruction of right ventricular outflow with a valved homograft conduit D. J. WHEATLEY, S. PRUSTY, and D. N. ROSS Department of Surgery, National Heart Hospital, London WI Wheadey,
Thorax (1974), 29, 617. Reconstruction of right ventricular outflow with a valved homograft conduit D. J. WHEATLEY, S. PRUSTY, and D. N. ROSS Department of Surgery, National Heart Hospital, London WI Wheadey,
LEFT VENTRICULAR OUTFLOW OBSTRUCTION WITH A VSD: OPTIONS FOR SURGICAL MANAGEMENT
 LEFT VENTRICULAR OUTFLOW OBSTRUCTION WITH A VSD: OPTIONS FOR SURGICAL MANAGEMENT 10-13 March 2017 Ritz Carlton, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Zohair AlHalees, MD Consultant, Cardiac Surgery Heart Centre LEFT VENTRICULAR
LEFT VENTRICULAR OUTFLOW OBSTRUCTION WITH A VSD: OPTIONS FOR SURGICAL MANAGEMENT 10-13 March 2017 Ritz Carlton, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Zohair AlHalees, MD Consultant, Cardiac Surgery Heart Centre LEFT VENTRICULAR
Pulmonarv Arterv Plication: with Type I Trunms Arteriosus. A New S&gical Procedure for Small Infants
 Pulmonarv Arterv Plication: A New S&gical Procedure for Small Infants with Type I Trunms Arteriosus S. Bert Litwin, M.D., and David Z. Friedberg, M.D. ABSTRACT A new technique is reported for constriction
Pulmonarv Arterv Plication: A New S&gical Procedure for Small Infants with Type I Trunms Arteriosus S. Bert Litwin, M.D., and David Z. Friedberg, M.D. ABSTRACT A new technique is reported for constriction
The Rastelli procedure has been traditionally used for repair
 En-bloc Rotation of the Truncus Arteriosus A Technique for Complete Anatomic Repair of Transposition of the Great Arteries/Ventricular Septal Defect/Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction or Double
En-bloc Rotation of the Truncus Arteriosus A Technique for Complete Anatomic Repair of Transposition of the Great Arteries/Ventricular Septal Defect/Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction or Double
14 Valvular Stenosis
 14 Valvular Stenosis 14-1. Valvular Stenosis unicuspid valve FIGUE 14-1. This photograph shows severe valvular stenosis as it occurs in a newborn. There is a unicuspid, horseshoe-shaped leaflet with a
14 Valvular Stenosis 14-1. Valvular Stenosis unicuspid valve FIGUE 14-1. This photograph shows severe valvular stenosis as it occurs in a newborn. There is a unicuspid, horseshoe-shaped leaflet with a
Myocardial Ischemia in Infants
 THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY Journal of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association VOLUME 8 NUMBER 5 NOVEMBER 1969. * Myocardial Ischemia in Infants Its Role in Three
THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY Journal of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association VOLUME 8 NUMBER 5 NOVEMBER 1969. * Myocardial Ischemia in Infants Its Role in Three
Indications for the Brock operation in current
 Thorax (1973), 28, 1. Indications for the Brock operation in current treatment of tetralogy of Fallot H. R. MATTHEWS and R. H. R. BELSEY Department of Thoracic Surgery, Frenchay Hospital, Bristol It is
Thorax (1973), 28, 1. Indications for the Brock operation in current treatment of tetralogy of Fallot H. R. MATTHEWS and R. H. R. BELSEY Department of Thoracic Surgery, Frenchay Hospital, Bristol It is
Appendix A.1: Tier 1 Surgical Procedure Terms and Definitions
 Appendix A.1: Tier 1 Surgical Procedure Terms and Definitions Tier 1 surgeries AV Canal Atrioventricular Septal Repair, Complete Repair of complete AV canal (AVSD) using one- or two-patch or other technique,
Appendix A.1: Tier 1 Surgical Procedure Terms and Definitions Tier 1 surgeries AV Canal Atrioventricular Septal Repair, Complete Repair of complete AV canal (AVSD) using one- or two-patch or other technique,
Stenosis of Pulmonary Veins
 Stenosis of Pulmonary Veins Report of a Patient Corrected Surgically Yasunaru Kawashima, M.D., Takeshi Ueda, M.D., Yasuaki Naito, M.D, Eiji Morikawa, M.D., and Hisao Manabe, M.D. ABSTRACT A 15-year-old
Stenosis of Pulmonary Veins Report of a Patient Corrected Surgically Yasunaru Kawashima, M.D., Takeshi Ueda, M.D., Yasuaki Naito, M.D, Eiji Morikawa, M.D., and Hisao Manabe, M.D. ABSTRACT A 15-year-old
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
In 1980, Bex and associates 1 first introduced the initial
 Technique of Aortic Translocation for the Management of Transposition of the Great Arteries with a Ventricular Septal Defect and Pulmonary Stenosis Victor O. Morell, MD, and Peter D. Wearden, MD, PhD In
Technique of Aortic Translocation for the Management of Transposition of the Great Arteries with a Ventricular Septal Defect and Pulmonary Stenosis Victor O. Morell, MD, and Peter D. Wearden, MD, PhD In
THE SOUNDS AND MURMURS IN TRANSPOSITION OF THE
 Brit. Heart J., 25, 1963, 748. THE SOUNDS AND MURMURS IN TRANSPOSITION OF THE GREAT VESSELS BY BERTRAND WELLS From The Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London W. C.J Received April 18,
Brit. Heart J., 25, 1963, 748. THE SOUNDS AND MURMURS IN TRANSPOSITION OF THE GREAT VESSELS BY BERTRAND WELLS From The Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London W. C.J Received April 18,
Congenital Heart Defects
 Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Aorticopulmonary septal defect
 British HeartJournal, I974, 36, 630-635. Aorticopulmonary septal defect An experience with I7 patients Leonard C. Blieden' and James H. Moller From the Department of Pediatrics, University of Minnesota,
British HeartJournal, I974, 36, 630-635. Aorticopulmonary septal defect An experience with I7 patients Leonard C. Blieden' and James H. Moller From the Department of Pediatrics, University of Minnesota,
Anatomy of the coronary arteries in transposition
 Thorax, 1978, 33, 418-424 Anatomy of the coronary arteries in transposition of the great arteries and methods for their transfer in anatomical correction MAGDI H YACOUB AND ROSEMARY RADLEY-SMITH From Harefield
Thorax, 1978, 33, 418-424 Anatomy of the coronary arteries in transposition of the great arteries and methods for their transfer in anatomical correction MAGDI H YACOUB AND ROSEMARY RADLEY-SMITH From Harefield
5.8 Congenital Heart Disease
 5.8 Congenital Heart Disease Congenital heart diseases (CHD) refer to structural or functional heart diseases, which are present at birth. Some of these lesions may be discovered later. prevalence of Chd
5.8 Congenital Heart Disease Congenital heart diseases (CHD) refer to structural or functional heart diseases, which are present at birth. Some of these lesions may be discovered later. prevalence of Chd
Debate in Management of native COA; Balloon Versus Surgery
 Debate in Management of native COA; Balloon Versus Surgery Dr. Amira Esmat, El Tantawy, MD Professor of Pediatrics Consultant Pediatric Cardiac Interventionist Faculty of Medicine Cairo University 23/2/2017
Debate in Management of native COA; Balloon Versus Surgery Dr. Amira Esmat, El Tantawy, MD Professor of Pediatrics Consultant Pediatric Cardiac Interventionist Faculty of Medicine Cairo University 23/2/2017
Congenital heart disease. By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics
 Congenital heart disease By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics What is the most striking clinical finding in this child? Learning objectives By the end of this lecture, final year student should be able
Congenital heart disease By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics What is the most striking clinical finding in this child? Learning objectives By the end of this lecture, final year student should be able
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 46 No. 4 December 1991
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 46 No. 4 December 1991 aneurysms ofthe sinus of valsalva R. J eyamalar. MBBS, IvIRCP. Lecturer P. Kannan, MBBS,MRCP. Associate Professor Dept. of Medicine, University Hospital, 59100
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 46 No. 4 December 1991 aneurysms ofthe sinus of valsalva R. J eyamalar. MBBS, IvIRCP. Lecturer P. Kannan, MBBS,MRCP. Associate Professor Dept. of Medicine, University Hospital, 59100
The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists
 Mayo Clinic & British Cardiovascular Society at the Royal College of Physicians, London : 21-23-October 2013 Cases-Controversies-Updates 2013 The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists Michael Rubens Royal Brompton
Mayo Clinic & British Cardiovascular Society at the Royal College of Physicians, London : 21-23-October 2013 Cases-Controversies-Updates 2013 The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists Michael Rubens Royal Brompton
Perimembranous VSD: When Do We Ask For A Surgical Closure? LI Xin. Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery Queen Mary Hospital Hong Kong
 Perimembranous VSD: When Do We Ask For A Surgical Closure? LI Xin Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery Queen Mary Hospital Hong Kong Classification (by Kirklin) I. Subarterial (10%) Outlet, conal, supracristal,
Perimembranous VSD: When Do We Ask For A Surgical Closure? LI Xin Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery Queen Mary Hospital Hong Kong Classification (by Kirklin) I. Subarterial (10%) Outlet, conal, supracristal,
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) with absent pulmonary valve
 Repair of Tetralogy of Fallot with Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Karl F. Welke, MD, and Ross M. Ungerleider, MD, MBA Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) with absent pulmonary valve syndrome (APVS) occurs in 5%
Repair of Tetralogy of Fallot with Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Karl F. Welke, MD, and Ross M. Ungerleider, MD, MBA Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) with absent pulmonary valve syndrome (APVS) occurs in 5%
PULMONARY ARTERY STENTING AFfER TOTAL SURGICAL CORRECTION OF RIGHT VENTRICULAR OUTFLOW TRACT OBSTRUCTIVE LESIONS
 Articles 5 PULMONARY ARTERY STENTING AFfER TOTAL SURGICAL CORRECTION OF RIGHT VENTRICULAR OUTFLOW TRACT OBSTRUCTIVE LESIONS SAMEH ARAB, MD; ERIC ROSENTHAL, MD, MRCP; SHAKEEL QURESHI, MB, MRCP; MICHAEL
Articles 5 PULMONARY ARTERY STENTING AFfER TOTAL SURGICAL CORRECTION OF RIGHT VENTRICULAR OUTFLOW TRACT OBSTRUCTIVE LESIONS SAMEH ARAB, MD; ERIC ROSENTHAL, MD, MRCP; SHAKEEL QURESHI, MB, MRCP; MICHAEL
Surgical Treatment for Double Outlet Right Ventricle. Masakazu Nakao Consultant, Paediatric Cardiothoracic Surgery
 for Double Outlet Right Ventricle Masakazu Nakao Consultant, Paediatric Cardiothoracic Surgery 1 History Intraventricular tunnel (Kawashima) First repair of Taussig-Bing anomaly (Kirklin) Taussig-Bing
for Double Outlet Right Ventricle Masakazu Nakao Consultant, Paediatric Cardiothoracic Surgery 1 History Intraventricular tunnel (Kawashima) First repair of Taussig-Bing anomaly (Kirklin) Taussig-Bing
Supplemental Table 1. ICD-9 Codes for Diagnoses and Procedures
 Supplemental Table 1. ICD-9 Codes for Diagnoses and Procedures ICD-9 Code Description Heart Failure 402.01 Malignant hypertensive heart disease with heart failure 402.11 Benign hypertensive heart disease
Supplemental Table 1. ICD-9 Codes for Diagnoses and Procedures ICD-9 Code Description Heart Failure 402.01 Malignant hypertensive heart disease with heart failure 402.11 Benign hypertensive heart disease
Anatomy & Physiology
 1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
Surgical management of tricuspid
 Surgical management of tricuspid Thorax (1969), 24, 239. atresia P. B. DEVERALL, J. C. R. LINCOLN, E. ABERDEEN, R. E. BONHAM-CARTER, AND D. J. WATERSTON From the Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond
Surgical management of tricuspid Thorax (1969), 24, 239. atresia P. B. DEVERALL, J. C. R. LINCOLN, E. ABERDEEN, R. E. BONHAM-CARTER, AND D. J. WATERSTON From the Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond
Congenital Cardiac Anomalies
 Congenital Cardiac Anomalies One-Stage Repair in Infancy Donald B. Doty, M.D., Ronald M. Lauer, M.D., and J. L. Ehrenhaft, M.D. ABSTRACT A proposed preferred treatment plan consisting of one-stage operative
Congenital Cardiac Anomalies One-Stage Repair in Infancy Donald B. Doty, M.D., Ronald M. Lauer, M.D., and J. L. Ehrenhaft, M.D. ABSTRACT A proposed preferred treatment plan consisting of one-stage operative
A teenager with tetralogy of fallot becomes a soccer player
 ISSN 1507-6164 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.889440 Received: 2013.06.06 Accepted: 2013.07.10 Published: 2013.09.23 A teenager with tetralogy of fallot becomes a soccer player Authors Contribution: Study Design A
ISSN 1507-6164 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.889440 Received: 2013.06.06 Accepted: 2013.07.10 Published: 2013.09.23 A teenager with tetralogy of fallot becomes a soccer player Authors Contribution: Study Design A
Coarctation of the aorta is a congenital narrowing of the
 Operative Risk Factors and Durability of Repair of Coarctation of the Aorta in the Neonate Walter H. Merrill, MD, Steven J. Hoff, MD, James R. Stewart, MD, Charles C. Elkins, MD, Thomas P. Graham, [r,
Operative Risk Factors and Durability of Repair of Coarctation of the Aorta in the Neonate Walter H. Merrill, MD, Steven J. Hoff, MD, James R. Stewart, MD, Charles C. Elkins, MD, Thomas P. Graham, [r,
Tricuspid valve surgery in patients with a systemic right ventricle
 Tricuspid valve surgery in patients with a systemic right ventricle Roderick Scherptong, Hubert Vliegen, Michiel Winter, Barbara Mulder, Ernst van der Wall, Dave Koolbergen, Mark Hazekamp Eduard Holman,
Tricuspid valve surgery in patients with a systemic right ventricle Roderick Scherptong, Hubert Vliegen, Michiel Winter, Barbara Mulder, Ernst van der Wall, Dave Koolbergen, Mark Hazekamp Eduard Holman,
Balloon valvuloplasty and angioplasty in congenital
 Br Heart J 1985; 54: 285-9 Balloon valvuloplasty and angioplasty in congenital heart disease GRAHAM A H MILLER From the Brompton Hospital, London SUMMARY Balloon dilatation valvuloplasty was performed
Br Heart J 1985; 54: 285-9 Balloon valvuloplasty and angioplasty in congenital heart disease GRAHAM A H MILLER From the Brompton Hospital, London SUMMARY Balloon dilatation valvuloplasty was performed
The Arterial Switch Operation for Transposition of the Great Arteries
 The Arterial Switch Operation for Transposition of the Great Arteries Jan M. Quaegebeur, M.D., Ph.D. A Journey of 60 Years Transposition of the Great Arteries First description: M. BAILLIE The morbid anatomy
The Arterial Switch Operation for Transposition of the Great Arteries Jan M. Quaegebeur, M.D., Ph.D. A Journey of 60 Years Transposition of the Great Arteries First description: M. BAILLIE The morbid anatomy
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS 993 THE NATURAL HISTORY OF CERTAIN CONGENITAL CARDIOVASCULAR MALFORMATIONS. Alexander S. Nadas, M.D.
 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS 993 tnicular overload is the major problem and left ventricular failure occurs. Since for many years the importance of hepatomegaly in the diagnosis of cardiac failure has
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS 993 tnicular overload is the major problem and left ventricular failure occurs. Since for many years the importance of hepatomegaly in the diagnosis of cardiac failure has
Congenital heart disease in the neonate: results of
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1983, 58, 137-141 Congenital heart disease in the neonate: results of surgical treatment E L BOVE, C BULL, J STARK, M DE LEVAL, F J Thoracic Unit, The Hospitalfor Sick
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1983, 58, 137-141 Congenital heart disease in the neonate: results of surgical treatment E L BOVE, C BULL, J STARK, M DE LEVAL, F J Thoracic Unit, The Hospitalfor Sick
Ostium primum defects with cleft mitral valve
 Thorax (1965), 20, 405. VIKING OLOV BJORK From the Department of Thoracic Surgery, University Hospital, Uppsala, Sweden Ostium primum defects are common; by 1955, 37 operated cases had been reported by
Thorax (1965), 20, 405. VIKING OLOV BJORK From the Department of Thoracic Surgery, University Hospital, Uppsala, Sweden Ostium primum defects are common; by 1955, 37 operated cases had been reported by
Repair of very severe tricuspid regurgitation following detachment of the tricuspid valve
 OPEN ACCESS Images in cardiology Repair of very severe tricuspid regurgitation following detachment of the tricuspid valve Ahmed Mahgoub 1, Hassan Kamel 2, Walid Simry 1, Hatem Hosny 1, * 1 Aswan Heart
OPEN ACCESS Images in cardiology Repair of very severe tricuspid regurgitation following detachment of the tricuspid valve Ahmed Mahgoub 1, Hassan Kamel 2, Walid Simry 1, Hatem Hosny 1, * 1 Aswan Heart
PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS (PDA)
 PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS (PDA) It is a channel that connect the pulmonary artery with the descending aorta (isthumus part). It results from the persistence of patency of the fetal ductus arteriosus after
PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS (PDA) It is a channel that connect the pulmonary artery with the descending aorta (isthumus part). It results from the persistence of patency of the fetal ductus arteriosus after
Adult Congenital Heart Disease T S U N ` A M I!
 Adult Congenital Heart Disease T S U N ` A M I! Erwin Oechslin, MD, FRCPC, FESC Director, Congenital Cardiac Centre for Adults University Health Network Peter Munk Cardiac Centre / Toronto General Hospital
Adult Congenital Heart Disease T S U N ` A M I! Erwin Oechslin, MD, FRCPC, FESC Director, Congenital Cardiac Centre for Adults University Health Network Peter Munk Cardiac Centre / Toronto General Hospital
Surgical treatment of ventricular septal defect
 Thorax (1965), 20, 278. VIKING OLOV BJORK From the Department of Thoracic Surgery, University Hospital, Uppsala, Sweden Since the first report of direct vision closure of ventricular septal defects in
Thorax (1965), 20, 278. VIKING OLOV BJORK From the Department of Thoracic Surgery, University Hospital, Uppsala, Sweden Since the first report of direct vision closure of ventricular septal defects in
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts
 Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Hypoplasia of the aortic root1 The problem of aortic valve replacement
 Hypoplasia of the aortic root1 The problem of aortic valve replacement ROWAN NICKS, T. CARTMILL, and L. BERNSTEIN Department of Cardio-thoracic Surgery and the Hallstrom Institute of Cardiology, the Royal
Hypoplasia of the aortic root1 The problem of aortic valve replacement ROWAN NICKS, T. CARTMILL, and L. BERNSTEIN Department of Cardio-thoracic Surgery and the Hallstrom Institute of Cardiology, the Royal
Patent ductus arteriosus PDA
 Patent ductus arteriosus PDA Is connecting between the aortic end just distal to the origin of the LT sub clavian artery& the pulmonary artery at its bifurcation. Female/male ratio is 2:1 and it is more
Patent ductus arteriosus PDA Is connecting between the aortic end just distal to the origin of the LT sub clavian artery& the pulmonary artery at its bifurcation. Female/male ratio is 2:1 and it is more
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Echocardiography in Adult Congenital Heart Disease
 Echocardiography in Adult Congenital Heart Disease Michael Vogel Kinderherz-Praxis München CHD missed in childhood Subsequent lesions after repaired CHD Follow-up of cyanotic heart disease CHD missed in
Echocardiography in Adult Congenital Heart Disease Michael Vogel Kinderherz-Praxis München CHD missed in childhood Subsequent lesions after repaired CHD Follow-up of cyanotic heart disease CHD missed in
Common Defects With Expected Adult Survival:
 Common Defects With Expected Adult Survival: Bicuspid aortic valve :Acyanotic Mitral valve prolapse Coarctation of aorta Pulmonary valve stenosis Atrial septal defect Patent ductus arteriosus (V.S.D.)
Common Defects With Expected Adult Survival: Bicuspid aortic valve :Acyanotic Mitral valve prolapse Coarctation of aorta Pulmonary valve stenosis Atrial septal defect Patent ductus arteriosus (V.S.D.)
By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE
 By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE Introduction CHDs are abnormalities of the heart or great vessels that are present at birth. Common type of heart disease
By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE Introduction CHDs are abnormalities of the heart or great vessels that are present at birth. Common type of heart disease
CongHeartDis.doc. Андрій Миколайович Лобода
 CongHeartDis.doc Андрій Миколайович Лобода 2015 Зміст 3 Зміст Зміст 4 A child with tetralogy of Fallot is most likely to exhibit: -Increased pulmonary blood flow -Increased pressure in the right ventricle
CongHeartDis.doc Андрій Миколайович Лобода 2015 Зміст 3 Зміст Зміст 4 A child with tetralogy of Fallot is most likely to exhibit: -Increased pulmonary blood flow -Increased pressure in the right ventricle
COMBINED CONGENITAL SUBAORTIC STENOSIS AND INFUNDIBULAR PULMONARY STENOSIS*
 COMBINED CONGENITAL SUBAORTIC STENOSIS AND INFUNDIBULAR PULMONARY STENOSIS* BY HENRY N. NEUFELD,t PATRICK A. ONGLEY, AND JESSE E. EDWARDS From the Sections of Pa?diatrics and Pathological Anatomy, Mayo
COMBINED CONGENITAL SUBAORTIC STENOSIS AND INFUNDIBULAR PULMONARY STENOSIS* BY HENRY N. NEUFELD,t PATRICK A. ONGLEY, AND JESSE E. EDWARDS From the Sections of Pa?diatrics and Pathological Anatomy, Mayo
S. Bert Litwin, MD. Preface
 Preface Because of the wide variety of anomalies encountered in congenital heart surgery, a broad understanding of the pathologic anatomy of defects is vitally important to the surgeon. More than in many
Preface Because of the wide variety of anomalies encountered in congenital heart surgery, a broad understanding of the pathologic anatomy of defects is vitally important to the surgeon. More than in many
Congenital heart disease: When to act and what to do?
 Leading Article Congenital heart disease: When to act and what to do? Duminda Samarasinghe 1 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2010; 39: 39-43 (Key words: Congenital heart disease) Congenital heart disease
Leading Article Congenital heart disease: When to act and what to do? Duminda Samarasinghe 1 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2010; 39: 39-43 (Key words: Congenital heart disease) Congenital heart disease
Index. cardiology.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACHD. See Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD), 503 512 across life span prevalence of, 504 506
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACHD. See Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD), 503 512 across life span prevalence of, 504 506
Congenital Heart Disease An Approach for Simple and Complex Anomalies
 Congenital Heart Disease An Approach for Simple and Complex Anomalies Michael D. Pettersen, MD Director, Echocardiography Rocky Mountain Hospital for Children Denver, CO None Disclosures 1 ASCeXAM Contains
Congenital Heart Disease An Approach for Simple and Complex Anomalies Michael D. Pettersen, MD Director, Echocardiography Rocky Mountain Hospital for Children Denver, CO None Disclosures 1 ASCeXAM Contains
Notes by Sandra Dankwa 2009 HF- Heart Failure DS- Down Syndrome IE- Infective Endocarditis ET- Exercise Tolerance. Small VSD Symptoms -asymptomatic
 Congenital Heart Disease: Notes. Condition Pathology PC Ix Rx Ventricular septal defect (VSD) L R shuntsdefect anywhere in the ventricle, usually perimembranous (next to the tricuspid valve) 30% 1)small
Congenital Heart Disease: Notes. Condition Pathology PC Ix Rx Ventricular septal defect (VSD) L R shuntsdefect anywhere in the ventricle, usually perimembranous (next to the tricuspid valve) 30% 1)small
Coarctation of the aorta
 T H E P E D I A T R I C C A R D I A C S U R G E R Y I N Q U E S T R E P O R T Coarctation of the aorta In the normal heart, blood flows to the body through the aorta, which connects to the left ventricle
T H E P E D I A T R I C C A R D I A C S U R G E R Y I N Q U E S T R E P O R T Coarctation of the aorta In the normal heart, blood flows to the body through the aorta, which connects to the left ventricle
Conduit Reconstruction of Right Ventricular Outflow Tract
 Conduit Reconstruction of Right Ventricular Outflow Tract Experience with 17 Patients E. Ross Kyger, 111, M.D., Luigi Chiariello, M.D., Grady L. Hallman, M.D., and Denton A. Cooley, M.D. ABSTRACT Evaluation
Conduit Reconstruction of Right Ventricular Outflow Tract Experience with 17 Patients E. Ross Kyger, 111, M.D., Luigi Chiariello, M.D., Grady L. Hallman, M.D., and Denton A. Cooley, M.D. ABSTRACT Evaluation
Surgical Management of TOF in Adults. Dr Flora Tsang Associate Consultant Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery Queen Mary Hospital
 Surgical Management of TOF in Adults Dr Flora Tsang Associate Consultant Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery Queen Mary Hospital Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) in Adults Most common cyanotic congenital heart
Surgical Management of TOF in Adults Dr Flora Tsang Associate Consultant Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery Queen Mary Hospital Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) in Adults Most common cyanotic congenital heart
Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital
 Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital VSD is one of the most common congenital cardiac abnormalities in the newborn. It can occur as an isolated finding or in combination
Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital VSD is one of the most common congenital cardiac abnormalities in the newborn. It can occur as an isolated finding or in combination
Surgical Treatment for Atrioventricular Septal Defect. Masakazu Nakao Consultant, Paediatric Cardiothoracic Surgery
 Surgical Treatment for Atrioventricular Septal Defect Masakazu Nakao Consultant, Paediatric Cardiothoracic Surgery 1 History Rastelli classification (Rastelli) Pulmonary artery banding (Muller & Dammann)
Surgical Treatment for Atrioventricular Septal Defect Masakazu Nakao Consultant, Paediatric Cardiothoracic Surgery 1 History Rastelli classification (Rastelli) Pulmonary artery banding (Muller & Dammann)
THE SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF
 POSTGRAD. MED. J. (I961), 37, 659 THE SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF FALLOT'S TETRALOGY FALLOT'S tetralogy is a condition of cyanotic congenital heart disease associated with pulmonary stenosis and a ventricular
POSTGRAD. MED. J. (I961), 37, 659 THE SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF FALLOT'S TETRALOGY FALLOT'S tetralogy is a condition of cyanotic congenital heart disease associated with pulmonary stenosis and a ventricular
The need for right ventricular outflow tract reconstruction
 Polytetrafluoroethylene Bicuspid Pulmonary Valve Implantation James A. Quintessenza, MD The need for right ventricular outflow tract reconstruction and pulmonary valve replacement is increasing for many
Polytetrafluoroethylene Bicuspid Pulmonary Valve Implantation James A. Quintessenza, MD The need for right ventricular outflow tract reconstruction and pulmonary valve replacement is increasing for many
Notes: 1)Membranous part contribute in the formation of small portion in the septal cusp.
 Embryology 9 : Slide 16 : There is a sulcus between primitive ventricular and bulbis cordis that will disappear gradually and lead to the formation of one chamber which is called bulboventricular chamber.
Embryology 9 : Slide 16 : There is a sulcus between primitive ventricular and bulbis cordis that will disappear gradually and lead to the formation of one chamber which is called bulboventricular chamber.
Anatomy lab -1- Imp note: papillary muscle Trabeculae Carneae chordae tendineae
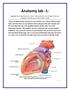 Anatomy lab -1- Imp note: the arrangement of this sheet is different than the lab recording, it has been arranged in a certain way to make it easier to study. When you open the left ventricle you can see
Anatomy lab -1- Imp note: the arrangement of this sheet is different than the lab recording, it has been arranged in a certain way to make it easier to study. When you open the left ventricle you can see
Cardiac Catheterization Cases Primary Cardiac Diagnoses Facility 12 month period from to PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient)
 PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
The modified Konno procedure, or subaortic ventriculoplasty,
 Modified Konno Procedure for Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction David P. Bichell, MD The modified Konno procedure, or subaortic ventriculoplasty, first described by Cooley and Garrett in1986, 1
Modified Konno Procedure for Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction David P. Bichell, MD The modified Konno procedure, or subaortic ventriculoplasty, first described by Cooley and Garrett in1986, 1
Structural heart disease in the newborn
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1979, 54, 281-285 Structural heart disease in the newborn Changing profile: comparison of 1975 with 1965 TERUO IZUKAWA, H. CONNOR MULHOLLAND, RICHARD D. ROWE, DAVID H.
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1979, 54, 281-285 Structural heart disease in the newborn Changing profile: comparison of 1975 with 1965 TERUO IZUKAWA, H. CONNOR MULHOLLAND, RICHARD D. ROWE, DAVID H.
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Double Outlet Right Ventricle with Anterior and Left-Sided Aorta and Subpulmonary Ventricular Septal Defect
 Case Report Double Outlet Right Ventricle with Anterior and Left-Sided rta and Subpulmonary Ventricular Septal Defect Luciana Braz Peixoto, Samira Morhy Borges Leal, Carlos Eduardo Suaide Silva, Sandra
Case Report Double Outlet Right Ventricle with Anterior and Left-Sided rta and Subpulmonary Ventricular Septal Defect Luciana Braz Peixoto, Samira Morhy Borges Leal, Carlos Eduardo Suaide Silva, Sandra
2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso
 2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Most common cardiac malformation 25-30 % Types of VSD: According to position perimembranous, inlet, muscular. According to size small, medium, large.
2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Most common cardiac malformation 25-30 % Types of VSD: According to position perimembranous, inlet, muscular. According to size small, medium, large.
Paediatric Cardiology. Acyanotic CHD. Prof F F Takawira
 Paediatric Cardiology Acyanotic CHD Prof F F Takawira Aetiology Chromosomal Down syndrome, T13, T18 Genetic syndromes (gene defects) Velo-Cardio-facial (22 del) Genetic syndromes (undefined aetiology)
Paediatric Cardiology Acyanotic CHD Prof F F Takawira Aetiology Chromosomal Down syndrome, T13, T18 Genetic syndromes (gene defects) Velo-Cardio-facial (22 del) Genetic syndromes (undefined aetiology)
Uptofate Study Summary
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Uptofate Study Summary Acyanotic Atrial septal defect Ventricular septal defect Patent foramen ovale Patent ductus arteriosus Aortic coartation Pulmonary stenosis Cyanotic Tetralogy
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Uptofate Study Summary Acyanotic Atrial septal defect Ventricular septal defect Patent foramen ovale Patent ductus arteriosus Aortic coartation Pulmonary stenosis Cyanotic Tetralogy
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
Paediatrics Revision Session Cardiology. Emma Walker 7 th May 2016
 Paediatrics Revision Session Cardiology Emma Walker 7 th May 2016 Cardiovascular Examination! General:! Make it fun!! Change how you act depending on their age! Introduction! Introduce yourself & check
Paediatrics Revision Session Cardiology Emma Walker 7 th May 2016 Cardiovascular Examination! General:! Make it fun!! Change how you act depending on their age! Introduction! Introduce yourself & check
Congenital Heart Disease: Physiology and Common Defects
 Congenital Heart Disease: Physiology and Common Defects Jamie S. Sutherell, M.D, M.Ed. Associate Professor, Pediatrics Division of Cardiology Director, Medical Student Education in Pediatrics Director,
Congenital Heart Disease: Physiology and Common Defects Jamie S. Sutherell, M.D, M.Ed. Associate Professor, Pediatrics Division of Cardiology Director, Medical Student Education in Pediatrics Director,
Surgical treatment of congenital valvular
 Thorax (1976), 31, 398. Surgical treatment of congenital valvular aortic stenosis LUIGI CHIARIELLO, PETER VLAD, and S. SUBRAMANIAN Departments of Paediatric Cardiology and Cardiovascular Surgery, Children's
Thorax (1976), 31, 398. Surgical treatment of congenital valvular aortic stenosis LUIGI CHIARIELLO, PETER VLAD, and S. SUBRAMANIAN Departments of Paediatric Cardiology and Cardiovascular Surgery, Children's
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT
 ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
Coexistence of asymmetric septal hypertrophy and aortic valve disease in adults
 Thorax, 1979, 34, 91-95 Coexistence of asymmetric septal hypertrophy and aortic valve disease in adults M V J RAJ, V SRINIVAS, I M GRAHAM, AND D W EVANS From the Regional Cardiac Unit, Papworth Hospital,
Thorax, 1979, 34, 91-95 Coexistence of asymmetric septal hypertrophy and aortic valve disease in adults M V J RAJ, V SRINIVAS, I M GRAHAM, AND D W EVANS From the Regional Cardiac Unit, Papworth Hospital,
Pulmonary Valve Replacement
 Pulmonary Valve Replacement with Fascia Lata J. C. R. Lincoln, F.R.C.S., M. Geens, M.D., M. Schottenfeld, M.D., and D. N. Ross, F.R.C.S. ABSTRACT The purpose of this paper is to describe a technique of
Pulmonary Valve Replacement with Fascia Lata J. C. R. Lincoln, F.R.C.S., M. Geens, M.D., M. Schottenfeld, M.D., and D. N. Ross, F.R.C.S. ABSTRACT The purpose of this paper is to describe a technique of
Congenitally Corrected Transposition of the Great Arteries (cctga or l-loop TGA)
 Congenitally Corrected Transposition of the Great Arteries (cctga or l-loop TGA) Mary Rummell, MN, RN, CPNP, CNS Clinical Nurse Specialist, Pediatric Cardiology/Cardiac Surgery Doernbecher Children s Hospital,
Congenitally Corrected Transposition of the Great Arteries (cctga or l-loop TGA) Mary Rummell, MN, RN, CPNP, CNS Clinical Nurse Specialist, Pediatric Cardiology/Cardiac Surgery Doernbecher Children s Hospital,
CMR for Congenital Heart Disease
 CMR for Congenital Heart Disease * Second-line tool after TTE * Strengths of CMR : tissue characterisation, comprehensive access and coverage, relatively accurate measurements of biventricular function/
CMR for Congenital Heart Disease * Second-line tool after TTE * Strengths of CMR : tissue characterisation, comprehensive access and coverage, relatively accurate measurements of biventricular function/
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts
 Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE. Papworth Hospital NHS Trust INTRODUCTION. Jakub Kadlec/Catherine Sudarshan INTRODUCTION
 Slide 1 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Jakub Kadlec/Catherine Sudarshan NHS Trust Slide 2 INTRODUCTION Most common congenital illness in the newborn Affects about 4 9 / 1000 full-term live births in the UK 1.5
Slide 1 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Jakub Kadlec/Catherine Sudarshan NHS Trust Slide 2 INTRODUCTION Most common congenital illness in the newborn Affects about 4 9 / 1000 full-term live births in the UK 1.5
MRI (AND CT) FOR REPAIRED TETRALOGY OF FALLOT
 MRI (AND CT) FOR REPAIRED TETRALOGY OF FALLOT Linda B Haramati MD, MS Departments of Radiology and Medicine Bronx, New York OUTLINE Pathogenesis Variants Initial surgical treatments Basic MR protocols
MRI (AND CT) FOR REPAIRED TETRALOGY OF FALLOT Linda B Haramati MD, MS Departments of Radiology and Medicine Bronx, New York OUTLINE Pathogenesis Variants Initial surgical treatments Basic MR protocols
Cases in Adult Congenital Heart Disease
 Cases in Adult Congenital Heart Disease Sabrina Phillips, MD FACC FASE Associate Professor of Medicine The University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center No Disclosures I Have Palpitations 18 Year old Man
Cases in Adult Congenital Heart Disease Sabrina Phillips, MD FACC FASE Associate Professor of Medicine The University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center No Disclosures I Have Palpitations 18 Year old Man
An anterior aortoventriculoplasty, known as the Konno-
 The Konno-Rastan Procedure for Anterior Aortic Annular Enlargement Mark E. Roeser, MD An anterior aortoventriculoplasty, known as the Konno-Rastan procedure, is a useful tool for the cardiac surgeon. Originally,
The Konno-Rastan Procedure for Anterior Aortic Annular Enlargement Mark E. Roeser, MD An anterior aortoventriculoplasty, known as the Konno-Rastan procedure, is a useful tool for the cardiac surgeon. Originally,
Chapter 13 Worksheet Code It
 Class: Date: Chapter 13 Worksheet 3 2 1 Code It True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. A cardiac catheterization diverts blood from the heart to the aorta. 2. Selective vascular
Class: Date: Chapter 13 Worksheet 3 2 1 Code It True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. A cardiac catheterization diverts blood from the heart to the aorta. 2. Selective vascular
Pulmonary valve echo motion in pulmonary
 British HeartJournal, I975, 37, ii84-ii90. Pulmonary valve echo motion in pulmonary regurgitation' Arthur E. Weyman, James C. Dillon, Harvey Feigenbaum, and Sonia Chang From the Department of Medicine,
British HeartJournal, I975, 37, ii84-ii90. Pulmonary valve echo motion in pulmonary regurgitation' Arthur E. Weyman, James C. Dillon, Harvey Feigenbaum, and Sonia Chang From the Department of Medicine,
Surgical implications of right aortic arch with isolation of left subclavian artery'
 British Heart journal, I975, 37, 93I-936. Surgical implications of right aortic arch with isolation of left subclavian artery' L. Rodriguez,2 T. Izukawa, C. A. F. MoEs, G. A. Trusler, and W. G. Williams
British Heart journal, I975, 37, 93I-936. Surgical implications of right aortic arch with isolation of left subclavian artery' L. Rodriguez,2 T. Izukawa, C. A. F. MoEs, G. A. Trusler, and W. G. Williams
'circular shunt'1. CASE 1 Shortly after birth a 36-hour-old, full-term infant girl showed cyanosis and dyspnoea. Physical
 Pulmonary atresia with left ventricularright atrial communication: basis for 'circular shunt'1 Thorax (1966), 21, 83. KENNETH L. JUE, GEORGE NOREN, AND JESSE E. EDWARDS From the Departments of Paediatrics
Pulmonary atresia with left ventricularright atrial communication: basis for 'circular shunt'1 Thorax (1966), 21, 83. KENNETH L. JUE, GEORGE NOREN, AND JESSE E. EDWARDS From the Departments of Paediatrics
Congenital Heart Disease
 Congenital Heart Disease Mohammed Alghamdi, MD, FRCPC, FAAP, FACC Associate Professor and Consultant Pediatric Cardiology, Cardiac Science King Fahad Cardiac Centre King Saud University INTRODUCTION CHD
Congenital Heart Disease Mohammed Alghamdi, MD, FRCPC, FAAP, FACC Associate Professor and Consultant Pediatric Cardiology, Cardiac Science King Fahad Cardiac Centre King Saud University INTRODUCTION CHD
