Upper extremity deep vein thrombosis (UEDVT) is an
|
|
|
- Christina Deirdre Murphy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Update Article Upper Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis S Malhotra*, VPS Punia** Abstract Upper extremity deep vein thrombosis (UEDVT) is a rare thrombotic disorder (1-4% or all DVT), but it has a potential for considerable morbidity in the form of pulmonary embolism, persistent upper extremity pain and swelling, superior vena cava syndrome and loss of vascular access. Newer noninvasive methods such as duplex ultrasound and magnetic resonance angiography facilitate early diagnosis. Early catheter directed thrombolysis followed by anticoagulation prevent long-term sequalae. INTRODUCTION Upper extremity deep vein thrombosis (UEDVT) is an increasingly important clinical entity with potential for considerable morbidity. Pulmonary embolism (PE) is present in upto one-third of patients with UEDVT. 1 When compared with the lower extremities, the venous pathways of the upper extremities are less likely to develop thrombus because of increased flow, gravitation effects and the absence of stasis. There are fewer valves in the upper extremities, and no counterpart to the soleal veins in the lower extremities is found. 2 The exact incidence of deep venous thrombosis of the upper extremities is unknown. A prevalence of two cases per 1000 hospital admissions 3 has been reported in a recent series. UEDVT accounts for approximately 2% of all cases of deep vein thrombosis. Originally described by Paget in 1875 and Van Schroetter in 1884, it was long felt to be a disorder associated with either trauma or spontaneous thrombogenesis occurring after streneous exercise or profound hyperabduction of the arm. Recently there is increasing incidence directly related to use of central venous catheters for cancer chemotherapy, bone marrow transplantation, dialysis and parenteral nutrition. 4 Pathogenesis Upper extremity deep vein thrombosis (UEDVT) most commonly refers to thrombosis of the axillary and/or subclavian veins. It can be classified as primary or secondary on the basis of pathogenesis (Table 1). Primary Thrombosis Primary UEDVT is a rare disorder (2 per person per year)..5 This term refers to effort thrombosis which is also *Specialist; ** Sr. Specialist, Department of Medicine, VMMC and Safdarjang Hospital, New Delhi Received : ; Revised : ; Re-revised : ; Accepted : Table 1: Causes of upper extremity DVT I Primary A. Traumatic * Effort thrombosis * Blood vessel injury B. Increased distal venous pressure *` Cervical ribs * Long transverse processes of cervical spine * Musculofascial bands of subclavius muscle and costoclavicular ligament * Clavicular or 1st rib anomalies D. Hypercoagulable state * Antiphospholipid antibodies * Factor V Leiden * Antithrombin III deficiency * Protein C & S deficiency * Prothrombin gene mutation * Hyperhomocystinemia * Pregnancy and oral contraceptive use II Secondary A. Central venous catheters B. Malignant disease * Lymphoma/Leukaemia * Pancreas cancer * Breast cancer * Chest disorders lung, pleura and oesophagus * Gastrointestinal tract C. Pacemakers D. Intravenous Drug Abuse III Idiopathic may be associated with occult cancer known as Paget Schroetter syndrome and includes patients with idiopathic UEDVT. Patients with Paget Schroetter syndrome develop spontaneous UEDVT usually in the dominant arm with physical activities such as rowing, wrestling, weight lifting and painting which involve abduction or hyperabduction of the upper extremity. The pathogenesis 6 involves a combination of exertion causing microtrauma of the vessel intima with activation of the coagulation cascade with cessation of venous flow from a reflex valsalva maneuver. JAPI VOL. 52 MARCH
2 Thoracic outlet obstruction refers to compression of subclavian vein at its point of exit at the thoracic inlet. This intermittent positional extrinsic vein compression can be produced 7 by cervical ribs, long transverse process of the cervical spine, musculofascial bands and clavicular or first rib anomalies. In contrast to Paget Schroetter syndrome, idiopathic UEDVT may have no known trigger or obvious underlying disease. In one study, 8 one-fourth of patients were associated with occult cancer and developed lung cancer or lymphoma within one year of follow up. The prevalence of hypercoagulable states in patients with UEDVT is uncertain. The yield of these tests is highest in those with idiopathic disease, a positive family history and recurrent DVT or pregnancy loss. A recent study 9 has shown that presence of lupus anticoagulant or anticardiolipin antibodies (27%) was the most frequent finding. The other abnormalities that have been found include factor V leiden, prothrombin gene mutation, hyperhomocystinaemia and rarely deficiency of protein C, protein S and antithrombin- III. Secondary Thrombosis Secondary UEDVT accounts for most cases of thrombosis. Majority of patients (33-60%) of UEDVT are asymptomatic and only fewer than 3% patients on central venous catheters and pacemakers develop clinically evident UEDVT. Malignant disease was present in 63% of patients with known DVT of the upper extremities in a recent series. 5 The incidence of DVT increased in those cancer patients who had central venous catheters. Catheter-induced vessel wall damage and impedance of blood flow through veins may be the predisposing cause in such cases. 11 Those patients who had implanted permanent pacemakers 12 with prior use of temporary pacemakers and low left ventricular ejection fractions (less than 40%) had a much higher incidence of venous thrombosis. Symptomas and Signs Axillary or subclavian vein thrombosis may be completely asymptomatic or patients complain of vague shoulder or neck discomfort and arm oedema. If thrombosis causes obstruction of superior vena cava, patients complain of facial oedema, head fullness, blurred vision, vertigo and dyspnea. Patients with thoracic outlet obstruction usually have pain that radiates into the fourth and fifth digits via the medial arm and forearm. Adson test is done in which the examiner extends the patients, arm on the affected side while the patient extends the neck and rotates the head towards the same side. The test is positive if there is weakening of the radial pulse with deep inspiration which suggests compression of the subclavian artery. Physical examination may reveal fever due to thrombosis, underlying septic infection or presence of malignancy. A high index of suspicion in those with arm and hand oedema and dilated cutaneous veins over the chest or upper arm, can clinch the diagnosis. The signs and symptoms (Table 2) of Table 2 : Signs and symptoms of UEDVT Symptoms Signs 1. Axillary or * Shoulder or neck * Supraclavicular fullness subclavian vein discomfort * Palpable cord thrombosis * Arm or hand * Arm or hand oedema oedema * Cyanosed extremity * Dilated vein * Jugular vein distention 2. Throacic outlet * Pain rediating * Brachial plexus syndrome to arm/forearm tenderness * Hand weakness * Arm or hand atrophy * Positive Adson test UEDVT are, however, non-specific and have to be differentiated 13 from lymphoedema, neoplasms, muscle injury and superficial vein thrombosis. DIAGNOSIS 1. Duplex Ultrasound : This is the initial imaging test of choice for diagnosing UEDVT because this is a non-invasive and reproducible technique with high sensitivity and specificity for assessment of cephalic, axillary and subclavian veins. But since jugular vein is best assessed by compression ultrasonography and brachiocephalic vein is visible only on venography and magnetic resonance angiography, this modality cannot be used. Non-compressibility 14 of venous segment, intraluminal thrombus and flow abnormality are sufficient for the diagnosis of DVT of the upper extremities. 2. Contrast Venography : This procedure involves injection of 30 ml contrast in the antecubital vein or distal arm vein of the affected extremity and subsequently digital subtraction images of the brachial, axillary, subclavian and superior caval veins are obtained at a rate of one frame per second. Although venography demonstrates the venous anatomy very well, technical difficulty can occur in cannulating the vein in an oedematous arm. The various reactions produced by iodinated contrast agents circumvent its routine use in clinical practice. Hence venography should be used only if suspicion for clot remains high despite a negative ultrasound. 3. Magnetic Resonance Angiography : This is an accurate, noninvasive method for detecting thromhus in the central thoracic veins such as SVC and brachiocephalic vein. This method correlates extremely well with venography 16 and provides complete evaluation of central collaterals and blood flow. 4. CT Scan : Although this method has injection of contrast 13 and requires injection of contrast agent, it has the ability to detect central thrombus especially in brachiocephalic vein thrombosis. It can also detect the presence of extrinsic vessel compression. COMPLICATIONS AND PROGNOSIS Recent studies have shown that complications of deep JAPI VOL. 52 MARCH 2004
3 venous thrombosis of upper extremity occur frequently. 13 Pulmonary embolism (8-36%) is most often asymptomatic. Acute presentation is more often seen in a setting of catheter related DVT with underlying malignancy compared to those with effort related thrombosis of the subclavian veins. Sometimes recurrent thromboembolism can present with pulmonary hypertension and right heart failure and may be fatal. In some cases catheter removal and fibrinolytic therapy may predispose to breakup of fibrin emboli and cause pulmonary embolism. Post-thrombotic syndrome (upto 50% cases) caused by venous hypertension can vary from mild oedema with little discomfort to severe limb swelling associated with pain and ulceration. Recurrent thrombosis (2-15%) after cessation of anticoagulation treatment is most frequent in Paget Schroetter syndrome and a recent series 18 has shown that the recurrence rate can be markedly reduced by early use (less than 7 days) of catheter directed thrombolysis together with first rib resection. The other reported complications (Table 3) are rare but loss of vascular access can be a practical problem since it prevents administration of essential medication and nutrition. Table 3 : Reported complications of UEDVT 1. Chronic venous insufficiency * Pain * Swelling 2. Venous gangrene 3. Superior vena cava syndrome 4. Catheter infection 5. Acute pulmonary embolism 6. Recurrent pulmonary embolization * Pulmonary hypertension * Right sided heart failure 7. Thoracic duct obstruction * Chylous pleural effusion * Chylous pericardial effusion 8. Brachial plexopathy The case fatality rate for untreated UEDVT can be as high as 10%, a rate similar to that seen with pulmonary embolism originating from the lower extremities. TREATMENT There is no consensus on treatment of UEDVT because of difficulty in obtaining adequate number of patients for a good prospective study. Firstly only diagnosis and initiation of treatment before the thrombus becomes organized is vital to the successful outcome of treatment. Secondly 19 because the underlying cause of primary UEDVT is usually an anatomic abnormality, surgical decompression of the subclavian vein is essential to prevent recurrent thrombosis. Hence a multidisciplinary treatment strategy including both medical and surgical management is needed. The various treatment modalities (Table 4) available have to be individualized in each patient. The symptomatic management includes anterior elevation of the affected Table 4 : Treatment options for UEDVT Limb elevation Graduated compression arm sleeve Anticoagulation * Unfractionated heparin as bridge to warfarin * Low molecular weight heparin as bridge to wafarin * Low molecular weight heparin as monotherapy Catheter directed thrombolysis Suction thrombectomy Vein stenting Surgical thrombectomy Thoracic outlet decompression * Surgery * Physical therapy Superior vena cava filter extremity, best rest and heat. In cases of secondary UEDVT, removal or correction of the predisposing cause (central catheter, infection, IV drug abuse) is important. Anticoagulation Anticoagulation is the mainstay of therapy. It facilitates the patency of venous collaterals and retards the propagation of the thrombus, although clot lysis is affected very little. Typically, unfractionated heparin is used as a bridge to warfarin therapy. Low molecular weight heparin as a bridge may be safe and effective for out-patient treatment and for reducing the duration of hospitalization. A recent meta analysis 20 has shown low molecular weight heparin and unfractionated heparin to be equivalent with respect to efficacy and major bleeding but low molecular weight heparin was associated with a 25% reduction in relative risk of death in venous thromboembolism compared to unfractionated heparin. Warfarin therapy should be continued for at least 6 months and probably longer in those with coagulation abnormality with a goal INR of 2.0 to 3.0. Patients who have received only symptomatic treatment and no anticoagulation have a high incidence of recurrent symptoms and long term disability from chronic venous hypertension in the upper limbs. Thrombolysis In the upper limbs, lytic therapy restores early venous patency, minimizes damage to vessel endothelium and reduces risk of post-thrombotic syndrome which is characterised by chronic arm aching and swelling. Catheter directed thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plaminogen activator (rtpa) 13 as a continuous infusion of 1-2 mg/hour for at least 8 hours or reteplase at a dose 21 of 1.0 unit/hour, in a recent study, have been able to achieve thrombolytic success in 92% of patients on follow up serial venography. The best candidates for thrombolysis are young healthy patients with primary UEDVT presenting within the first week after thrombosis, patients with symptomatic SVC syndrome and those who require insertion of mandatory central venous catheter. JAPI VOL. 52 MARCH
4 Suction Thrombectomy Percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy with devices such as the angiojet 21 is often used in combination with thrombolytics. This procedure can rapidly extract large quantities of thrombus, within 5 days after initial occlusion and thereby reduce the dose and duration of thrombolytic therapy. Surgery The importance of eradicating vein compression in patients with primary UEDVT has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of recurrent thrombosis and long term mobidity. After successful thrombolysis repeat venography of patients is preformed with the shoulder in an abducted position. Those patient showing venous compression on venography should have surgical resection of part of the first rib or clavicle 13 and lysis of dense adhesions around the subclavian veins. Angioplasty and Vein Stenting Those patients with residual stricture after surgery and thrombolytic therapy require balloon venoplasty and stenting (52% in a recent study) to ensure maintenance of patency. 18 Surgical Thrombectomy This procedure restores venous patency but is invasive, carries the risk of general anaesthesia and may be complicated by pneumothorax and brachial plexus damage. Hence this technique should be reserved for refractory cases or who have an infected thrombus as a cause of bacteraemia. 18 Physical Therapy A structured programme 13 to loosen muscles around the subclavian vein, weight loss in the obese and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may obviate the need for surgery. Those with neurological symptoms require several months of physical therapy before improvement is noted. Superior Vena Cava Filters Patients in whom anticoagulation is contraindicated, has failed or created complications, those who are poor surgical risk and those who are at risk for pulmonary embolism can benefit. CONCLUSION In primary effort thrombosis of subclavian veins, most investigators favour using thrombolytic therapy for patients presenting within first 7 days of venous thrombosis. This is followed by heparin therapy as a bridge to warfarin therapy till patient reaches on INR of Subsequently resection of first rib or clavicle is done to reduce the recurrences. Catheter associated subclavian vein thrombosis (secondary) is best prevented by giving low dose warfarin (1 mg) beginning three days before catheter placement. Since these patients have significant co-morbidity, thrombolytics should be used very cautiously. Surgery is reserved for patients with recurrent vein thrombosis despite lytic therapy and endoluminal stent placement should be used in those with residual stricture after balloon venoplasty. REFERENCES 1. Prandoni P, Polistena I, Bernardi E, et al. Upper extremity deep vein thrombosis. Risk factors, diagnosis and complication. Arch Intern Med 1997;157: Hill SE, Berry RE. Subclavian vein thrombosis: A continuing challenge. Surg 1990;108: Kroger K, Schelo C, Gocke C, et al. Colour Doppler sonographic diagnosis of upper limb venous thrombosis. Clin Sci (London) 1998;94: Hurattas MC, Wright DJ, Fenton AH, et al. Changing concepts of deep venous thrombosis of the upper extremity. Report of a series and review of the literature. Surgery 1988;104: Lindblad B, Tengborn L, Bergqvist D. Deep vein thrombosis of the axillary subclavian veins: epidemiologic data, effects of different types of treatment and late sequelae. Eur J Vasc Surg 1988;2: Zell L, Kindermann W, Marschall R, et al. Paget Schroetter syndrome in sports activities: case study and literature review. Angiology 2001;52: Parziale JR, Akelman E Weiss AP, et al. Throacic outlet syndrome. Am J Orthop 2000;29: Girolami A, Prandoni P, Zanon E, et al. Venous thrombosis of upper limbs are more frequently associated with occult cancer as compared with those of lower limbs. Blood Coag Fibrinol 1999;10: Leebeek RW, Standhouders NA, Van Stein D. Coagulation abnormalities in deep venous thrombosis of the upper extremity. Am J Haematol 2001;67: Henk-Jan Baarslag, Edwin JR. Prospective study of colour Duplex ultrasonography compared with contrast venography in patients suspected of having DVT of upper extremities. Ann Intern Med 2002;136: Luciani A, Clement O, Halimi P, et al. Catheter related upper extremity deep venous thrombosis in cancer patients: a prospective study based on Doppler US. Radiology 2001;344: Da Costa SS, Scalabrini NA, Costa R, et al. Incidence and risk factors of upper extremity deep vein lesions after permanent transvenous pacemaker implant: A 6 month follow up prospective study. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2002;25: Hylton V, Goldhaber Z. Upper extremity deep vein thrombosis. Circulation 2002;106: Lensing AW, Buuer HR, Prandoni P, et al. Contrast venography, the gold standard for the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis: improvement in observer agreement. Throm Haemost 1992;67: Hartnell GG, Hughes LA, Finn JP, et al. Magnetic resonance Angiography of the central chest veins: a new gold standard Chest 1995;107: Jefferson Jones, Ichabod L Balkcom, Robert K Wormar Pulmonary embolus after treatment for subclavian-axillary vel thrombosis. Post Graduate Medicine 1987;82: Urshel HC, Razzuk MA. Paget Schroetter syndrome: what is the best management? Ann Thorac Surg 2000;69: Gregory A, Vaturo, Richard J Repeat. Non lower extremity deep vein thrombosis. Emergency Medicine Clinics of North JAPI VOL. 52 MARCH 2004
5 America 2001;19: Dolovich LR, Ginsberg JS, Douketis JD, et al. A meta analvsis comparing low molecular weight heparin with unfractionated heparin in the treatment of venous thromboembolism. Arch Intern Med 2000;161: Castaneda R, Li R, Young K, et al. Catheter directed thrombolysis in deep venous thrombosis with use of reteplase. Immediate results and complications from a pilot study. J Vasc Intern Radiol 2002;13: Kasirajan K, Gray B, Ouriel K. Percutaneous angiojet thrombectomy in the management of extensive deep venous thrombosis. J Vasc Intern Radiol 2001;12: Obituary Dr. PJ Geevarghese Dr. PJ Geevarghese, eminent diabetologist of international reputation and one of the pioneers of diabetes research in India passed away on at the age of 78 following subarachnoid haemorrhage. He was the President, Kerala Diabetes Foundation and executive patron of RSSDI (Research Society for Study of Diabetes in India). He was formerly Director and Professor of Medicine at Medical College, Kottayam and during his long tenure in Government service has graced almost all the then medical colleges in Kerala. In addition he has been visiting Professor at foreign university schools of New York, Marseilles and California. He has done a lot of research work on Pancreatic Diabetes which won international recognition and has authored many monographs like Pancreatic Diabetes (1968), Calcific Paancreatitis and Diabetes in Tropics (1992), A Handbook for Diabetics (8 editions) and Recent Progress in Clinical Diabetes (2002). A spiritual book Holy Trinity and the Apostolic Church was also written by him. After retirement he was practising as Consultant Diabetologist at St. Mary s Diabetes Centre and Krishna Nursing Home in Cochin. During his long and fruitful career, Prof. Geevarghese has been President, Scientific Section, Diabetic Association of India and Indian Society of Pancreatology. He has received a number of awards like Boehringer-Knoll Award, Silver Jubilee Oration Award by Trivandrum Medical College, and the Lifetime Dedication to Diabetes Care award by Novo-Nordisk. R Sajith Kumar Secretary, API Kerala Announcement Second Madras Diabetes Research Foundation (MDRF) - American Diabetes Association (ADA), Postgraduate Course on Diabetes, at Chennai, India, September The second MDRF- ADA Postgraduate Course on Diabetes will be held from 24th to 26th September 2004 at Chennai, India. The meeting will be hosted by the Madras Diabetes Research Foundation, Chennai. For further details contact : Prof V Mohan, MD, Ph D, D Sc, Madras Diabetes Research Foundation, No. 4 Conran Smith Road, Gopalapuram, Chennai , India. Phone : (91 44) , , , Fax : (91 44) , mvdsc@vsnl.com Also visit our website at for details regarding registration charges etc. JAPI VOL. 52 MARCH
Upper Extremity Venous Duplex. Michigan Sonographers Society Fall Ultrasound Symposium October 15, 2016
 Upper Extremity Venous Duplex Michigan Sonographers Society Fall Ultrasound Symposium October 15, 2016 Patricia A. (Tish) Poe, BA RVT FSVU Director of Quality Assurance Navix Diagnostix Patricia A. Poe
Upper Extremity Venous Duplex Michigan Sonographers Society Fall Ultrasound Symposium October 15, 2016 Patricia A. (Tish) Poe, BA RVT FSVU Director of Quality Assurance Navix Diagnostix Patricia A. Poe
Treatment of acute thrombosis of axillo-subclavian vein
 Treatment of acute thrombosis of axillo-subclavian vein Yang Jin Park Vascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine CASE A 32-year-old male patient 3-day history of
Treatment of acute thrombosis of axillo-subclavian vein Yang Jin Park Vascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine CASE A 32-year-old male patient 3-day history of
Surgical approach for DVT. Division of Vascular Surgery Department of Surgery Seoul National University College of Medicine
 Surgical approach for DVT Seung-Kee Min Division of Vascular Surgery Department of Surgery Seoul National University College of Medicine Treatment Options for Venous Thrombosis Unfractionated heparin &
Surgical approach for DVT Seung-Kee Min Division of Vascular Surgery Department of Surgery Seoul National University College of Medicine Treatment Options for Venous Thrombosis Unfractionated heparin &
Paget-Schroetter Syndrome in the Young and Active
 Paget-Schroetter Syndrome in the Young and Active Viju Vijaysadan, MD, Aphrodite M. Zimmerman, MS, and Rafael E. Pajaro, MD We report this case of effort thrombosis of the upper extremity (Paget-Schroetter
Paget-Schroetter Syndrome in the Young and Active Viju Vijaysadan, MD, Aphrodite M. Zimmerman, MS, and Rafael E. Pajaro, MD We report this case of effort thrombosis of the upper extremity (Paget-Schroetter
Upper-extremity deep vein thrombosis (UEDVT) is an
 Current Perspective Upper-Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis Hylton V. Joffe, MD; Samuel Z. Goldhaber, MD Upper-extremity deep vein thrombosis (UEDVT) is an increasingly important clinical entity with potential
Current Perspective Upper-Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis Hylton V. Joffe, MD; Samuel Z. Goldhaber, MD Upper-extremity deep vein thrombosis (UEDVT) is an increasingly important clinical entity with potential
Pseudothrombosis of the Subclavian Vein
 416507JDMXXX10.1177/8756479311416507Wash ko et al.journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Pseudothrombosis of the Subclavian Vein Journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography 27(5) 231 235 The Author(s) 2011
416507JDMXXX10.1177/8756479311416507Wash ko et al.journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Pseudothrombosis of the Subclavian Vein Journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography 27(5) 231 235 The Author(s) 2011
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
 Disclosures None relevant to this discussion The Management of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: Acute Charles Eichler MD Professor, Department of Surgery Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University
Disclosures None relevant to this discussion The Management of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: Acute Charles Eichler MD Professor, Department of Surgery Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University
Interventional Treatment VTE: Radiologic Approach
 Interventional Treatment VTE: Radiologic Approach Hae Giu Lee, MD Professor, Dept of Radiology Seoul St. Mary s Hospital The Catholic University of Korea Introduction Incidence High incidence: 250,000-1,000,000/year
Interventional Treatment VTE: Radiologic Approach Hae Giu Lee, MD Professor, Dept of Radiology Seoul St. Mary s Hospital The Catholic University of Korea Introduction Incidence High incidence: 250,000-1,000,000/year
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME (T.O.S.) Prof J van Marle
 THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME (T.O.S.) Prof J van Marle 1. Definition Clinical syndrome caused by compression of the neurovascular bundle as it passes through the thoracic outlet, a narrow space bordered by
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME (T.O.S.) Prof J van Marle 1. Definition Clinical syndrome caused by compression of the neurovascular bundle as it passes through the thoracic outlet, a narrow space bordered by
Paget-Schrötter Syndrome and the Thoracic Outlet. Carl Aschkenasi September 6, 2001
 Paget-Schrötter Syndrome and the Thoracic Outlet Carl Aschkenasi September 6, 2001 1 Our Patient: Acute onset left arm pain J.B. is a 44 yo male lawyer Has had a hx of occasional mild L arm pain on exertion
Paget-Schrötter Syndrome and the Thoracic Outlet Carl Aschkenasi September 6, 2001 1 Our Patient: Acute onset left arm pain J.B. is a 44 yo male lawyer Has had a hx of occasional mild L arm pain on exertion
4/3/2014. Disclosures. Venous Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: Our Approach and Results. Paget Schroetter Syndrome. Paget Schroetter Syndrome.
 Disclosures No relevant financial relationships with commercial interests Venous Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: Our Approach and Julie A. Freischlag, M.D. Vice Chancellor for Human Health Sciences Dean of the
Disclosures No relevant financial relationships with commercial interests Venous Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: Our Approach and Julie A. Freischlag, M.D. Vice Chancellor for Human Health Sciences Dean of the
CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM. Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow
 CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Common cause of death and disability 50% hospital-acquired
CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Common cause of death and disability 50% hospital-acquired
SAMPLE CHAPTERS UNESCO-EOLSS MANAGEMENT OF SUBCLAVIAN VEIN THROMBOSIS KNOWN AS PAGET-SCHROETTER SYNDROME
 MANAGEMENT OF SUBCLAVIAN VEIN THROMBOSIS KNOWN AS PAGETSCHROETTER SYNDROME J. Ernesto Molina University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Minnesota, U.S.A. Keywords: Thoracic outlet, Venous disease Contents 1.
MANAGEMENT OF SUBCLAVIAN VEIN THROMBOSIS KNOWN AS PAGETSCHROETTER SYNDROME J. Ernesto Molina University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Minnesota, U.S.A. Keywords: Thoracic outlet, Venous disease Contents 1.
5/5/15. Overview. Deep vein thrombosis of the upper extremity (UEDVT) Classification of UEDVT Epidemiology. Primary UEDVT.
 Deep vein thrombosis of the upper extremity (UEDVT) Hong H. Keo, MD, MSc Angiologie Kantonsspital Aarau 07.05.2015 06. Symposium venöse Insuff. und arterielle Gefässerkr. Glarus Overview Epidemiology Classification/Risk
Deep vein thrombosis of the upper extremity (UEDVT) Hong H. Keo, MD, MSc Angiologie Kantonsspital Aarau 07.05.2015 06. Symposium venöse Insuff. und arterielle Gefässerkr. Glarus Overview Epidemiology Classification/Risk
Early View Article: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form.
 : Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: Journal of Case Reports and Images in Medicine Type of Article: Case Report Title: Use of new oral
: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: Journal of Case Reports and Images in Medicine Type of Article: Case Report Title: Use of new oral
Venous thrombosis is common and often occurs spontaneously, but it also frequently accompanies medical and surgical conditions, both in the community
 Venous Thrombosis Venous Thrombosis It occurs mainly in the deep veins of the leg (deep vein thrombosis, DVT), from which parts of the clot frequently embolize to the lungs (pulmonary embolism, PE). Fewer
Venous Thrombosis Venous Thrombosis It occurs mainly in the deep veins of the leg (deep vein thrombosis, DVT), from which parts of the clot frequently embolize to the lungs (pulmonary embolism, PE). Fewer
Learning Objectives for Rotations in Vascular Surgery Year 3 Basic Clerkship
 Learning Objectives for Rotations in Vascular Surgery Year 3 Basic Clerkship CLINICAL PROBLEMS IN VASCULAR SURGERY 1. ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSM A 70 year old man presents in the emergency department with
Learning Objectives for Rotations in Vascular Surgery Year 3 Basic Clerkship CLINICAL PROBLEMS IN VASCULAR SURGERY 1. ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSM A 70 year old man presents in the emergency department with
NOTE: Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Risk Factors
 Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is the formation of a blood clot, known as a thrombus, in the deep leg vein. It is a very serious condition that can cause permanent damage to the
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is the formation of a blood clot, known as a thrombus, in the deep leg vein. It is a very serious condition that can cause permanent damage to the
Michael Meuse, M.D. Vascular and Interventional Radiology
 Michael Meuse, M.D. Vascular and Interventional Radiology Iliac Vein Compression Syndrome Left CIV compressed by right CIA Virchow 1851: DVT L>R May and Thurner 1954: venous spurs Cockett and Thomas 1965:
Michael Meuse, M.D. Vascular and Interventional Radiology Iliac Vein Compression Syndrome Left CIV compressed by right CIA Virchow 1851: DVT L>R May and Thurner 1954: venous spurs Cockett and Thomas 1965:
Risk stratification and incidence of acute complications in upper extremity deep vein thrombosis (UEDVT) patients.
 Risk stratification and incidence of acute complications in upper extremity deep vein thrombosis (UEDVT) patients. Dr. Santosh Yatam Ganesh MBBS, MPH., Mentors: Dr. Khalid J. Qazi MD, MACP., Dr. Paul Anain
Risk stratification and incidence of acute complications in upper extremity deep vein thrombosis (UEDVT) patients. Dr. Santosh Yatam Ganesh MBBS, MPH., Mentors: Dr. Khalid J. Qazi MD, MACP., Dr. Paul Anain
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center
 Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
Ultrasound-enhanced, catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Ultrasound-enhanced, catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism A pulmonary embolism (PE) is
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Ultrasound-enhanced, catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism A pulmonary embolism (PE) is
Upper Extremity Venous Duplex Evaluation
 VASCULARTECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Upper Extremity Venous Duplex Evaluation This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society for Vascular Ultrasound
VASCULARTECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Upper Extremity Venous Duplex Evaluation This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society for Vascular Ultrasound
Vascular Surgery and Transplant Unit University of Catania. Pierfrancesco Veroux
 Vascular Surgery and Transplant Unit University of Catania Pierfrancesco Veroux Bologna-Palazzo dei Congressi, 23 Ottobre 2017 Disclosure Speaker name: Prof. Pierfrancesco Veroux I have the following potential
Vascular Surgery and Transplant Unit University of Catania Pierfrancesco Veroux Bologna-Palazzo dei Congressi, 23 Ottobre 2017 Disclosure Speaker name: Prof. Pierfrancesco Veroux I have the following potential
Venous interventions in DVT
 Venous interventions in DVT Sriram Narayanan Chief of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, Tan Tock Seng Hospital A/Prof of Surgery, National University of Singapore ANTI-COAGULATION LMWH Warfarin x 6m Acute
Venous interventions in DVT Sriram Narayanan Chief of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, Tan Tock Seng Hospital A/Prof of Surgery, National University of Singapore ANTI-COAGULATION LMWH Warfarin x 6m Acute
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT
 DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
Case Report Recurrent Upper Extremity Thrombosis Associated with Overactivity: A Case of Delayed Diagnosis of Paget-Schroetter Syndrome
 Hindawi Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 8764903, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8764903 Case Report Recurrent Upper Extremity Thrombosis Associated with Overactivity: A
Hindawi Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 8764903, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8764903 Case Report Recurrent Upper Extremity Thrombosis Associated with Overactivity: A
Disclosures. DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Questions To Ask. Dr. Susanna Shin - DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) None
 Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism
 Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Summary Number 68 Overview Venous thromboembolism
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Summary Number 68 Overview Venous thromboembolism
Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine
 Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine Venous thromboembolism: pulmonary embolism (PE) deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 1% of all patients admitted to hospital 5% of in-hospital mortality
Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine Venous thromboembolism: pulmonary embolism (PE) deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 1% of all patients admitted to hospital 5% of in-hospital mortality
AV ACESS COMPLICATIONS. Ass. Prof. Dr. Habas
 AV ACESS COMPLICATIONS Ass. Prof. Dr. Habas COMPLICATION AVF IS CONSIDERED A MINOR PROCEDURE INCIDENCE OF COMPLICATION- 20-27% MANY A COMPLICATION LEADS TO FAILURE OF FISTULA LOSS OF SITE AND VEIN FOR
AV ACESS COMPLICATIONS Ass. Prof. Dr. Habas COMPLICATION AVF IS CONSIDERED A MINOR PROCEDURE INCIDENCE OF COMPLICATION- 20-27% MANY A COMPLICATION LEADS TO FAILURE OF FISTULA LOSS OF SITE AND VEIN FOR
Pulmonary Emboli without Leg Symptoms, May-Thurner syndrome. Case Report and Review
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 9 Number 2 Pulmonary Emboli without Leg Symptoms, May-Thurner syndrome. Case Report and Review A Hamo, M Alyaseen, F Alkhankan, T Gress Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 9 Number 2 Pulmonary Emboli without Leg Symptoms, May-Thurner syndrome. Case Report and Review A Hamo, M Alyaseen, F Alkhankan, T Gress Citation
Pulmonary Embolism. Pulmonary Embolism. Pulmonary Embolism. PE - Clinical
 Pulmonary embolus - a practical approach to investigation and treatment Sam Janes Wellcome Senior Fellow and Respiratory Physician, University College London Background Diagnosis Treatment Common: 50 cases
Pulmonary embolus - a practical approach to investigation and treatment Sam Janes Wellcome Senior Fellow and Respiratory Physician, University College London Background Diagnosis Treatment Common: 50 cases
Treatment of Axillosubclavian Vein Thrombosis: A Novel Technique for Rapid Removal of Clot Using Low-Dose Thrombolysis
 J ENDOVASC THER 733 RAPID COMMUNICATION Treatment of Axillosubclavian Vein Thrombosis: A Novel Technique for Rapid Removal of Clot Using Low-Dose Thrombolysis Frank R. Arko, MD; Paul Cipriano, MD; Eugene
J ENDOVASC THER 733 RAPID COMMUNICATION Treatment of Axillosubclavian Vein Thrombosis: A Novel Technique for Rapid Removal of Clot Using Low-Dose Thrombolysis Frank R. Arko, MD; Paul Cipriano, MD; Eugene
ACR Appropriateness Criteria Suspected Lower Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis EVIDENCE TABLE
 . Fowkes FJ, Price JF, Fowkes FG. Incidence of diagnosed deep vein thrombosis in the general population: systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 003; 5():-5.. Hamper UM, DeJong MR, Scoutt LM. Ultrasound
. Fowkes FJ, Price JF, Fowkes FG. Incidence of diagnosed deep vein thrombosis in the general population: systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 003; 5():-5.. Hamper UM, DeJong MR, Scoutt LM. Ultrasound
Not all Leg DVT s are the Same: Which Patients Benefit from Interventional Therapy? Case 1:
 12/16/2015 Not all Leg DVT s are the Same: Which Patients Benefit from Interventional Therapy? Constantino S.Peña, FSIR, FSCCT, FAHA Interventional Radiologist Medical Director, Vascular Imaging Miami
12/16/2015 Not all Leg DVT s are the Same: Which Patients Benefit from Interventional Therapy? Constantino S.Peña, FSIR, FSCCT, FAHA Interventional Radiologist Medical Director, Vascular Imaging Miami
DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients. David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center
 DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center Overview Pathophysiology of DVT Epidemiology and risk factors for DVT in the
DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center Overview Pathophysiology of DVT Epidemiology and risk factors for DVT in the
Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Patient Information
 Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Patient Information A Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and a Pulmonary Embolism (PE) are both disorders of unwanted blood clotting. Unwanted blood clots can occur
Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Patient Information A Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and a Pulmonary Embolism (PE) are both disorders of unwanted blood clotting. Unwanted blood clots can occur
ESIM 2014 Clinical Case Presentation Israel. Ben-Sasson Maayan Bnei-Zion medical center Haifa
 ESIM 2014 Clinical Case Presentation Israel Ben-Sasson Maayan Bnei-Zion medical center Haifa Presentation A 24 YO male,a ping-pong player, presented to the ER with acute onset of right upper extremity
ESIM 2014 Clinical Case Presentation Israel Ben-Sasson Maayan Bnei-Zion medical center Haifa Presentation A 24 YO male,a ping-pong player, presented to the ER with acute onset of right upper extremity
Risk factors for DVT. Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism. Anticoagulation (cont d) Diagnosis 1/5/2018. Ahmed Mahmoud, MD
 Risk factors for DVT Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Risk factors for DVT Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism. Ahmed Mahmoud, MD
 Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Risk factors for DVT Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Risk factors for DVT Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
University Journal of Medicine and Medical Specialities
 ISSN 2455-2852 2018, Vol. 4(5) Imaging Assessment of Vascular Thoracic Outlet Syndrome BALAJI A AYYAMPERUMAL Department of Radio Diagnosis,MADRAS MEDICAL COLLEGE AND GOVERNMENT GENERAL HOSPITAL Abstract
ISSN 2455-2852 2018, Vol. 4(5) Imaging Assessment of Vascular Thoracic Outlet Syndrome BALAJI A AYYAMPERUMAL Department of Radio Diagnosis,MADRAS MEDICAL COLLEGE AND GOVERNMENT GENERAL HOSPITAL Abstract
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Mismetti P, Laporte S, Pellerin O, Ennezat P-V, Couturaud F, Elias A, et al. Effect of a retrievable inferior vena cava filter plus anticoagulation vs anticoagulation alone
Supplementary Online Content Mismetti P, Laporte S, Pellerin O, Ennezat P-V, Couturaud F, Elias A, et al. Effect of a retrievable inferior vena cava filter plus anticoagulation vs anticoagulation alone
Iliofemoral DVT: Miminizing Post-Thrombotic Syndrome
 Iliofemoral DVT: Miminizing Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Catherine K. Chang, MD FACS Vascular Surgery San Diego Southern California Permanente Medical Group Acute Deep Venous Thrombosis Incidence & Outcomes
Iliofemoral DVT: Miminizing Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Catherine K. Chang, MD FACS Vascular Surgery San Diego Southern California Permanente Medical Group Acute Deep Venous Thrombosis Incidence & Outcomes
COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 16 December 1999 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON CLINICAL
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 16 December 1999 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON CLINICAL
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM
 PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM International Consensus Statement 2013 Guidelines According to Scientific Evidence Developed under the auspices of the: Cardiovascular Disease Educational
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM International Consensus Statement 2013 Guidelines According to Scientific Evidence Developed under the auspices of the: Cardiovascular Disease Educational
Intervention for Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolus
 Intervention for Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolus Michael R. Jaff, DO Paul and Phyllis Fireman Endowed Chair in Vascular Medicine Massachusetts General Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard
Intervention for Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolus Michael R. Jaff, DO Paul and Phyllis Fireman Endowed Chair in Vascular Medicine Massachusetts General Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard
EKOS. Interventional Vascular 3 February, Imagine where we can go.
 EKOS Interventional Vascular 3 February, 2015 Imagine where we can go. Forward-looking statement This presentation and information communicated verbally to you may contain certain projections and other
EKOS Interventional Vascular 3 February, 2015 Imagine where we can go. Forward-looking statement This presentation and information communicated verbally to you may contain certain projections and other
Sinus and Cerebral Vein Thrombosis
 Sinus and Cerebral Vein Thrombosis A Summary Sinus and cerebral vein clots are uncommon. They can lead to severe headaches, confusion, and stroke-like symptoms. They may lead to bleeding into the surrounding
Sinus and Cerebral Vein Thrombosis A Summary Sinus and cerebral vein clots are uncommon. They can lead to severe headaches, confusion, and stroke-like symptoms. They may lead to bleeding into the surrounding
DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO IMPROVING CLINICAL OUTCOMES
 DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO IMPROVING CLINICAL OUTCOMES Jose M. Borromeo M.D. Vascular Surgeon Iowa Heart Center Disclosures: AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals Cook CVRx LeMaitre Vascular,
DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO IMPROVING CLINICAL OUTCOMES Jose M. Borromeo M.D. Vascular Surgeon Iowa Heart Center Disclosures: AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals Cook CVRx LeMaitre Vascular,
Sonography Evaluation of the Upper Extremity Venous System Evaluation for Deep and Superficial Venous Thrombosis
 Sonography Evaluation of the Upper Extremity Venous System Evaluation for Deep and Superficial Venous Thrombosis Wayne C Leonhardt, BA, RDMS, RVT Mission Imaging Asheville, North Carolina Disclosure Information
Sonography Evaluation of the Upper Extremity Venous System Evaluation for Deep and Superficial Venous Thrombosis Wayne C Leonhardt, BA, RDMS, RVT Mission Imaging Asheville, North Carolina Disclosure Information
A A U
 PVD Venous AUC Rating Sheet 2nd Round 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Median I NI MADM Rating Agree Disagree Upper Extremity Venous Evaluation Table 1. Venous Duplex of the Upper Extremities for Patency
PVD Venous AUC Rating Sheet 2nd Round 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Median I NI MADM Rating Agree Disagree Upper Extremity Venous Evaluation Table 1. Venous Duplex of the Upper Extremities for Patency
Pharmaco-mechanical techniques stand alone procedures? Peter Neglén, MD, PhD SP Vascular Center Limassol Cyprus
 Pharmaco-mechanical techniques stand alone procedures? Peter Neglén, MD, PhD SP Vascular Center Limassol Cyprus Faculty Disclosure Peter Neglén, M.D., Ph.D Stockholder/Founder of Veniti, Inc. Member, Medical
Pharmaco-mechanical techniques stand alone procedures? Peter Neglén, MD, PhD SP Vascular Center Limassol Cyprus Faculty Disclosure Peter Neglén, M.D., Ph.D Stockholder/Founder of Veniti, Inc. Member, Medical
DOPPLER ULTRASOUND OF DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS
 TOKUDA HOSPITAL SOFIA DOPPLER ULTRASOUND OF DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS MILENA STANEVA, MD, PhD Department of vascular surgery and angiology Venous thromboembolic disease continues to cause significant morbidity
TOKUDA HOSPITAL SOFIA DOPPLER ULTRASOUND OF DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS MILENA STANEVA, MD, PhD Department of vascular surgery and angiology Venous thromboembolic disease continues to cause significant morbidity
Case 1. Your diagnosis
 Case 1 44-year-old midwife presented with intermittent pins and needles in the little and ring fingers with blanching. Symptoms were exacerbated by cold exposure. Your diagnosis Diagnosis Hypothenar syndrome
Case 1 44-year-old midwife presented with intermittent pins and needles in the little and ring fingers with blanching. Symptoms were exacerbated by cold exposure. Your diagnosis Diagnosis Hypothenar syndrome
PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL
 CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL Since French internist Armand Trousseau reported the occurrence of mysterious thrombotic disorders in cancer patients in the mid-19th century, the link
CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL Since French internist Armand Trousseau reported the occurrence of mysterious thrombotic disorders in cancer patients in the mid-19th century, the link
Inferior Vena Cava Filter for DVT
 Inferior Vena Cava Filter for DVT Deep Vein Thrombosis A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in a deep vein. This is a serious condition that occurs more often than you might think. If
Inferior Vena Cava Filter for DVT Deep Vein Thrombosis A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in a deep vein. This is a serious condition that occurs more often than you might think. If
Percutaneously Inserted AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy for the Treatment of Filter-Related. Iliocaval Thrombosis
 Percutaneously Inserted AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy for the Treatment of Filter-Related Iliocaval Thrombosis Faiz D. Francis, DO; Gianvito Salerno, MD; Sabbah D. Butty, MD Abstract In the setting of
Percutaneously Inserted AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy for the Treatment of Filter-Related Iliocaval Thrombosis Faiz D. Francis, DO; Gianvito Salerno, MD; Sabbah D. Butty, MD Abstract In the setting of
PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
 PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide a diagnostic algorithm and treatment options for patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE). BACKGROUND: Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide a diagnostic algorithm and treatment options for patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE). BACKGROUND: Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
 Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Cristina Sola, BSN, RN-BC Nurse Manager Department of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery McGovern Medical School The University of Texas Science Center at Houston Memorial Hermann
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Cristina Sola, BSN, RN-BC Nurse Manager Department of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery McGovern Medical School The University of Texas Science Center at Houston Memorial Hermann
Innovative Endovascular Approach to Pulmonary Embolism by Ultrasound Enhanced Thrombolysis. Prof. Ralf R.Kolvenbach MD,PhD,FEBVS
 Innovative Endovascular Approach to Pulmonary Embolism by Ultrasound Enhanced Thrombolysis Prof. Ralf R.Kolvenbach MD,PhD,FEBVS Catheter-based thrombolysis Local administration of lytic agent Higher local
Innovative Endovascular Approach to Pulmonary Embolism by Ultrasound Enhanced Thrombolysis Prof. Ralf R.Kolvenbach MD,PhD,FEBVS Catheter-based thrombolysis Local administration of lytic agent Higher local
Prevention and management of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) John Fletcher Wound Care Association of New South Wales
 Prevention and management of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) John Fletcher Wound Care Association of New South Wales Merimbula, 6 th November 2010 University of Sydney Department of Surgery Westmead Hospital
Prevention and management of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) John Fletcher Wound Care Association of New South Wales Merimbula, 6 th November 2010 University of Sydney Department of Surgery Westmead Hospital
Pulmonary Thromboembolism
 Pulmonary Thromboembolism James Allen, MD Epidemiology of Pulmonary Embolism 1,500,000 new cases per year in the United States Often asymptomatic 300,000 deaths per year DVT or PE present in 10% of ICU
Pulmonary Thromboembolism James Allen, MD Epidemiology of Pulmonary Embolism 1,500,000 new cases per year in the United States Often asymptomatic 300,000 deaths per year DVT or PE present in 10% of ICU
4/23/2009. September 15, 2008
 The Current Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis: Are We Doing Enough? George H. Meier, MD Professor and Chief Division of Vascular Surgery University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Cincinnati, Ohio
The Current Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis: Are We Doing Enough? George H. Meier, MD Professor and Chief Division of Vascular Surgery University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Cincinnati, Ohio
Recurrent Pulmonary Embolism From Left Subclavian Thrombosis: A Case Report
 J Cardiol 2000 ; 36: 191 196 Recurrent Pulmonary Embolism From Left Subclavian Thrombosis: A Case Report Junji Makoto Tetsunori Hideo Junko Toshihide Kunihide Toshio KAWAGOE, MD TAKENAGA, MD ISHIKAWA,
J Cardiol 2000 ; 36: 191 196 Recurrent Pulmonary Embolism From Left Subclavian Thrombosis: A Case Report Junji Makoto Tetsunori Hideo Junko Toshihide Kunihide Toshio KAWAGOE, MD TAKENAGA, MD ISHIKAWA,
Sample page. POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your trusted coding partner for 32 years. Visit optum360coding.com.
 2018 Complete Guide for Interventional Radiology An in-depth guide to interventional radiology coding, billing, and reimbursement for facilities and physicians POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your
2018 Complete Guide for Interventional Radiology An in-depth guide to interventional radiology coding, billing, and reimbursement for facilities and physicians POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your
Case Report Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis in Isolated Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy
 Volume 2016, Article ID 5184196, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5184196 Case Report Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis in Isolated Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy Sanjay Khaladkar, Avadhesh
Volume 2016, Article ID 5184196, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5184196 Case Report Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis in Isolated Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy Sanjay Khaladkar, Avadhesh
Resident Teaching Conference 3/12/2010
 Resident Teaching Conference 3/12/2010 Goals Definition and Classification of Acute Limb Ischemia Clinical Assessment of the Vascular Patient History and Physical Diagnostic Modalities Management of Acute
Resident Teaching Conference 3/12/2010 Goals Definition and Classification of Acute Limb Ischemia Clinical Assessment of the Vascular Patient History and Physical Diagnostic Modalities Management of Acute
Meissner MH, Gloviczki P, Comerota AJ, Dalsing MC, Eklof BG, Gillespie DL, et al. J Vasc Surg. 2012;55:
 Early thrombus removal strategies for acute deep venous thrombosis: Clinical Practice Guidelines of the Society for Vascular Surgery and the American Venous Forum Meissner MH, Gloviczki P, Comerota AJ,
Early thrombus removal strategies for acute deep venous thrombosis: Clinical Practice Guidelines of the Society for Vascular Surgery and the American Venous Forum Meissner MH, Gloviczki P, Comerota AJ,
How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT?
 How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT? Dr. Nihar Ranjan Pradhan M.S., DNB (Vascular Surgery), FVES(UK) Consultant Vascular Surgeon Apollo Hospital, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad (Formerly Faculty in
How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT? Dr. Nihar Ranjan Pradhan M.S., DNB (Vascular Surgery), FVES(UK) Consultant Vascular Surgeon Apollo Hospital, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad (Formerly Faculty in
I-Ming Chen, MD. Endovascular Stenting for Palliative Treatment of Superior Vena Cava Syndrome in End-Stage Lung Cancer
 Endovascular Stenting for Palliative Treatment of Superior Vena Cava Syndrome in End-Stage Lung Cancer I-Ming Chen, MD Division of CardioVascular Surgery Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan (Live
Endovascular Stenting for Palliative Treatment of Superior Vena Cava Syndrome in End-Stage Lung Cancer I-Ming Chen, MD Division of CardioVascular Surgery Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan (Live
Thrombolysis in PE. Outline. Disclosure. Overview on Pulmonary Embolism. Hot Topics in Emergency Medicine 2012 Midyear Clinical Meeting
 Disclosure Thrombolysis in PE Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP reports no relevant financial relationships. Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP Outline 55 YOF presents to ED with SOB PMH of DVT + noncompliance
Disclosure Thrombolysis in PE Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP reports no relevant financial relationships. Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP Outline 55 YOF presents to ED with SOB PMH of DVT + noncompliance
2013 Coding Changes. Diagnostic Radiology. Nuclear Medicine
 2013 Coding Changes The principal coding changes affecting Radiologists in 2013 occur in the Interventional Radiology Section of the AMA/CPT Manual. As in the past, we continue to see the Relative Update
2013 Coding Changes The principal coding changes affecting Radiologists in 2013 occur in the Interventional Radiology Section of the AMA/CPT Manual. As in the past, we continue to see the Relative Update
Proper Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE)
 Proper Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Whal Lee, M.D. Seoul National University Hospital Department of Radiology 2 nd EFORT Asia Symposium, 3 rd November 2010, Taipei DVT - Risk Factors Previous
Proper Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Whal Lee, M.D. Seoul National University Hospital Department of Radiology 2 nd EFORT Asia Symposium, 3 rd November 2010, Taipei DVT - Risk Factors Previous
Venous Thrombosis. Magnitude of the Problem. DVT 2 Million PE 600,000. Death 60,000. Estimated Cost of VTE Care $1.5 Billion/year.
 Venous Thrombosis Magnitude of the Problem DVT 2 Million Postthrombotic Syndrome 800,000 PE 600,000 Death 60,000 Silent PE 1 Million Pulmonary Hypertension 30,000 Estimated Cost of VTE Care $1.5 Billion/year
Venous Thrombosis Magnitude of the Problem DVT 2 Million Postthrombotic Syndrome 800,000 PE 600,000 Death 60,000 Silent PE 1 Million Pulmonary Hypertension 30,000 Estimated Cost of VTE Care $1.5 Billion/year
Dr. prakruthi Dept. of anaesthesiology, Rrmch, bangalore
 CENTRAL VENOUS CATHETERIZATION Dr. prakruthi Dept. of anaesthesiology, Rrmch, bangalore OBJECTIVES Introduction Indications and Contraindications Complications Technique Basic principles Specifics by Site
CENTRAL VENOUS CATHETERIZATION Dr. prakruthi Dept. of anaesthesiology, Rrmch, bangalore OBJECTIVES Introduction Indications and Contraindications Complications Technique Basic principles Specifics by Site
Introduction to the Native Arteriovenous Fistula: A primer for medical students and radiology residents
 Introduction to the Native Arteriovenous Fistula: A primer for medical students and radiology residents Jesus Contreras, D.O. PGY-4 John Yasmer, D.O. Department of Radiology No Disclosures Objectives Introduce
Introduction to the Native Arteriovenous Fistula: A primer for medical students and radiology residents Jesus Contreras, D.O. PGY-4 John Yasmer, D.O. Department of Radiology No Disclosures Objectives Introduce
Compression of neural or vascular structures within the
 Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: Transaxillary Approach Margaret Clarke Tracci, MD, JD Compression of neural or vascular structures within the constrained space of the thoracic outlet may give rise to 3 separate
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: Transaxillary Approach Margaret Clarke Tracci, MD, JD Compression of neural or vascular structures within the constrained space of the thoracic outlet may give rise to 3 separate
Prevention of thrombosis
 Prevention of thrombosis Massimo Lamperti MD, MBA Chief of General Anaesthesia Department Anaesthesiology Institute Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Clinical Professor of Anaesthesiology Cleveland Clinic Lerner
Prevention of thrombosis Massimo Lamperti MD, MBA Chief of General Anaesthesia Department Anaesthesiology Institute Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Clinical Professor of Anaesthesiology Cleveland Clinic Lerner
Carotid Doppler: Doppler wave forms obtained from the common, external and internal carotid arteries. As well as the vertebral and subclavian
 Competency Carotid Doppler: Doppler wave forms obtained from the common, external and internal carotid arteries. As well as the vertebral and subclavian arteries. Preferred angle is 60 degrees or less.
Competency Carotid Doppler: Doppler wave forms obtained from the common, external and internal carotid arteries. As well as the vertebral and subclavian arteries. Preferred angle is 60 degrees or less.
Approach to Thrombosis
 Approach to Thrombosis Theera Ruchutrakool, M.D. Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Faculty of Medicine Mahidol University Approach to Thrombosis Thrombosis: thrombus formation
Approach to Thrombosis Theera Ruchutrakool, M.D. Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Faculty of Medicine Mahidol University Approach to Thrombosis Thrombosis: thrombus formation
Expanding Horizons: AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy at UTHealth
 Expanding Horizons: AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy at UTHealth Naveed Saqib, MD Assistant Professor Department of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery McGovern Medical School The University of Texas Science
Expanding Horizons: AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy at UTHealth Naveed Saqib, MD Assistant Professor Department of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery McGovern Medical School The University of Texas Science
Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism
 Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism Gregory Piazza Benjamin Hohlfelder Samuel Z. Goldhaber Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism Gregory Piazza Cardiovascular Division Harvard Medical School Brigham and
Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism Gregory Piazza Benjamin Hohlfelder Samuel Z. Goldhaber Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism Gregory Piazza Cardiovascular Division Harvard Medical School Brigham and
Jordan M. Garrison, MD FACS, FASMBS
 Jordan M. Garrison, MD FACS, FASMBS Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Near or Complete obstruction of > 1 Peripheral Artery Peripheral Venous reflux Disease Varicose Veins Chronic Venous Stasis Ulcer Disease
Jordan M. Garrison, MD FACS, FASMBS Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Near or Complete obstruction of > 1 Peripheral Artery Peripheral Venous reflux Disease Varicose Veins Chronic Venous Stasis Ulcer Disease
Bare Metal Stents vs Stent Grafts
 Bare Metal Stents vs Stent Grafts ASDIN 12th Annual Scientific Meeting Phoenix, AZ, February 20, 2016 Dirk Hentschel, MD Director, Interventional Nephrology Brigham and Women s Hospital Disclosure Consultant:
Bare Metal Stents vs Stent Grafts ASDIN 12th Annual Scientific Meeting Phoenix, AZ, February 20, 2016 Dirk Hentschel, MD Director, Interventional Nephrology Brigham and Women s Hospital Disclosure Consultant:
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21764 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mos, Inge Christina Maria Title: A more granular view on pulmonary embolism Issue
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21764 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mos, Inge Christina Maria Title: A more granular view on pulmonary embolism Issue
The Evidence Base for Treating Acute DVT
 The Evidence Base for Treating Acute DVT Mr Chung Sim Lim Consultant Vascular Surgeon and Honorary Lecturer Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust and University College London NIHR UCLH Biomedical Research
The Evidence Base for Treating Acute DVT Mr Chung Sim Lim Consultant Vascular Surgeon and Honorary Lecturer Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust and University College London NIHR UCLH Biomedical Research
Chronic Iliocaval Venous Occlusive Disease
 none Chronic Iliocaval Venous Occlusive Disease David Rigberg, M.D. Clinical Professor of Surgery Division of Vascular Surgery University of California Los Angeles Chronic Venous Occlusive Disease Chronic
none Chronic Iliocaval Venous Occlusive Disease David Rigberg, M.D. Clinical Professor of Surgery Division of Vascular Surgery University of California Los Angeles Chronic Venous Occlusive Disease Chronic
BC Vascular Day. Contents. November 3, Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 2 3. Peripheral Arterial Disease 4 6. Deep Venous Thrombosis 7 8
 BC Vascular Day Contents Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 2 3 November 3, 2018 Peripheral Arterial Disease 4 6 Deep Venous Thrombosis 7 8 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Conservative Management Risk factor modification
BC Vascular Day Contents Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 2 3 November 3, 2018 Peripheral Arterial Disease 4 6 Deep Venous Thrombosis 7 8 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Conservative Management Risk factor modification
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/19768 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Langevelde, Kirsten van Title: Are pulmonary embolism and deep-vein thrombosis
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/19768 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Langevelde, Kirsten van Title: Are pulmonary embolism and deep-vein thrombosis
ENDOVASCULAR THERAPIES FOR ACUTE STROKE
 ENDOVASCULAR THERAPIES FOR ACUTE STROKE Cerebral Arteriogram Cerebral Anatomy Cerebral Anatomy Brain Imaging Acute Ischemic Stroke (AIS) Therapy Main goal is to restore blood flow and improve perfusion
ENDOVASCULAR THERAPIES FOR ACUTE STROKE Cerebral Arteriogram Cerebral Anatomy Cerebral Anatomy Brain Imaging Acute Ischemic Stroke (AIS) Therapy Main goal is to restore blood flow and improve perfusion
J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49:
 Online publication August 27, 2009 1 2 J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49: 247 254 deep vein thrombosis, thrombolytic therapy, catheter-directed thrombolysis, inferior vena cava filter, pulmonary thromboembolism
Online publication August 27, 2009 1 2 J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49: 247 254 deep vein thrombosis, thrombolytic therapy, catheter-directed thrombolysis, inferior vena cava filter, pulmonary thromboembolism
A case of pacing lead induced clinical superior vena cava syndrome: a case report Mukesh Singh 1,2 * and Sabry K Talab 1
 Open Access Case report A case of pacing lead induced clinical superior vena cava syndrome: a case report Mukesh Singh 1,2 * and Sabry K Talab 1 Addresses: 1 Department of Medicine, Blackpool Victoria
Open Access Case report A case of pacing lead induced clinical superior vena cava syndrome: a case report Mukesh Singh 1,2 * and Sabry K Talab 1 Addresses: 1 Department of Medicine, Blackpool Victoria
Intravenous Catheter Complications
 Vascular Access Device-Related Infection Inadequate skin antisepsis prior to VAD insertion Acute onset of fever, chills, and hypotension. No other apparent source of Notify Prescriber immediately Obtain
Vascular Access Device-Related Infection Inadequate skin antisepsis prior to VAD insertion Acute onset of fever, chills, and hypotension. No other apparent source of Notify Prescriber immediately Obtain
EFFORT THROMBOSIS OF THE SUBCLAVIAN VEIN IN ATHLETES
 SPORTS SURGERY EFFORT THROMBOSIS OF THE SUBCLAVIAN VEIN IN ATHLETES Written by Vladimir Resanovic and Aleksandar Resanovic, Serbia Upper-extremity deep venous thrombosisis is a potentially life-threatening
SPORTS SURGERY EFFORT THROMBOSIS OF THE SUBCLAVIAN VEIN IN ATHLETES Written by Vladimir Resanovic and Aleksandar Resanovic, Serbia Upper-extremity deep venous thrombosisis is a potentially life-threatening
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis 2017 Edition
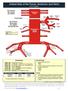 Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC
 Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC 1 st workshop: update to VTE guidelines in 2016 2 nd workshop: VTE controversies + new horizons André Roussin MD, FRCP, CSPQ CHUM
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC 1 st workshop: update to VTE guidelines in 2016 2 nd workshop: VTE controversies + new horizons André Roussin MD, FRCP, CSPQ CHUM
Vascular Injuries in the Throwing Shoulder MLB Winter Meeting 2015
 Neurovascular Problems in the Throwing Athlete s Shoulder Professor, Department of Orthopedics Head, Section of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Team Physician, Chicago White Sox and Bulls Chief Medical Editor,
Neurovascular Problems in the Throwing Athlete s Shoulder Professor, Department of Orthopedics Head, Section of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Team Physician, Chicago White Sox and Bulls Chief Medical Editor,
Venous Thrombo-Embolism. John de Vos Consultant Haematologist RSCH
 Venous Thrombo-Embolism John de Vos Consultant Haematologist RSCH overview The statistics Pathogenesis Prophylaxis Treatment Agent Duration Incidental VTE Recurrence of VTE IVC filters CVC related thrombosis
Venous Thrombo-Embolism John de Vos Consultant Haematologist RSCH overview The statistics Pathogenesis Prophylaxis Treatment Agent Duration Incidental VTE Recurrence of VTE IVC filters CVC related thrombosis
Deep Vein Thrombosis
 Deep Vein Thrombosis Introduction Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in a vein. This condition can affect men and women of any age and race. DVT is a potentially serious condition. If not treated,
Deep Vein Thrombosis Introduction Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in a vein. This condition can affect men and women of any age and race. DVT is a potentially serious condition. If not treated,
