Research Article Total Bolus Extraction Method Improves Arterial Image Quality in Dynamic CTAs Derived from Whole-Brain CTP Data
|
|
|
- Charlotte Carr
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BioMed Research International, Article ID , 6 pages Research Article Total Bolus Extraction Method Improves Arterial Image Quality in Dynamic CTAs Derived from Whole-Brain CTP Data Elyas Ghariq, 1 Adriënne M. Mendrik, 2 Peter W. A. Willems, 1 Raoul M. S. Joemai, 1 Eidrees Ghariq, 3 Evert-jan Vonken, 4 Matthias J. P. van Osch, 1,3 and Marianne A. A. van Walderveen 1 1 Department of Radiology, Leiden University Medical Center, Albinusdreef 2, 2333 ZA Leiden, The Netherlands 2 Image Sciences Institute, University Medical Center Utrecht, Heidelberglaan 100, 3584 CX Utrecht, The Netherlands 3 Department of Radiology, C.J. Gorter Center for High Field MRI, Leiden University Medical Center, Albinusdreef 2, 2333 ZA Leiden, The Netherlands 4 Department of Radiology, University Medical Center Utrecht, Heidelberglaan 100, 3584 CX Utrecht, The Netherlands Correspondence should be addressed to Adriënne M. Mendrik; a.m.mendrik@umcutrecht.nl Received 25 April 2014; Revised 17 June 2014; Accepted 26 June 2014; Published 16 July 2014 Academic Editor: Alessandro Cianfoni Copyright 2014 Elyas Ghariq et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Background and Purposes. The 320-detector row CT scanner enables visualization of whole-brain hemodynamic information (dynamic CT angiography (CTA) derived from CT perfusion scans). However, arterial image quality in dynamic CTA (dcta) is inferior to arterial image quality in standard CTA. This study evaluates whether the arterial image quality can be improved by using a total bolus extraction (ToBE) method. Materials and Methods. DCTAs of 15 patients, who presented with signs of acute cerebral ischemia, were derived from 320-slice CT perfusion scans using both the standard subtraction method and the proposed ToBE method. Two neurointerventionalists blinded to the scan type scored the arterial image quality on a 5-point scale in the 4D dctas in consensus. Arteries were divided into four categories: (I) large extradural, (II) intradural (large, medium, and small), (III) communicating arteries, and (IV) cerebellar and ophthalmic arteries. Results. Quality of extradural and intradural arterieswas significantly higher in the ToBE dctas than in the standard dctas (extradural P = 0.001, large intradural P < 0.001, medium intradural P < 0.001, and small intradural P < 0.001). Conclusion.The4DdCTAsderivedwiththetotalbolusextraction(ToBE) method provide hemodynamic information combined with improved arterial image quality as compared to standard 4D dctas. 1. Introduction Cerebral computed tomography perfusion (CTP) scans are acquired in patients with acute stroke [1] or subarachnoid hemorrhage [2]. Although there is some debate [2 5] about the prognostic value of CT perfusion, many studies [1, 2, 6 9] have shown that it provides valuable information about the cerebral hemodynamics, especially with the introduction of 320-slice CT scanners (16 cm coverage) that enable the acquisition of whole-brain CTP scans and provide an option to derive 4D dynamic CT angiography (dcta) images from the CTP scans [9 12]. These 4D dcta images show great potential for the assessment of collaterals [13], the measurement of cerebral circulation times [14], and arteriovenous shunting lesion assessment [15]. However, it has been shown that the 4D dctas have inferior quality compared to standard 3D CTA scans [16]. Therefore, cerebral arteries, and in particular arteries with a small diameter, are more difficult to assess. Several methods have been proposed to derive vascular information from CTP scans [17 19]ofwhichsomearewith a quality comparable to standard 3D CTA [19, 20]. However, these methods do not provide full 4D dynamic CTA images but instead provide a 3D image showing the vasculature. Therefore, even though the arterial image quality is good, the hemodynamic information available in the 4D dcta images is lost. In this paper, we propose a total bolus extraction (ToBE) method to derive 4D dctas from CTP scans in which the hemodynamic information is preserved. We performed an observer study in which two neurointerventionalists scored the image quality of the intracranial arteries in 30
2 2 BioMed Research International anonymized and randomized dctas (15 standard and 15 ToBE dctas). The observers were blind to the type of dcta that was presented to them. Our hypothesis is that the ToBE method will improve the arterial image quality in the 4D dctas derived from the 4D CTP scans compared to the standard method to derive 4D dctas. 2. Materials and Methods 2.1. Patients. Fifteen patients (4 males, 11 females; average age of 70.2 years, range years) were included from alargeprospectivemulticenterobservationalcohortstudy. ThiscohortstudyevaluatesthepredictivevalueofCTPand CTA on the clinical and radiological outcome measures of patients presenting with symptoms of acute ischemic stroke. On admission, all patients underwent an unenhanced CT and a CTP study of the brain using Toshiba Aquilion ONE 320-slice CT scanner (Toshiba Medical Systems, Otawara, Japan). Inclusion criteria were age >18 years, onset of stroke symptoms <9 hours, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) 2, and informed consent from patient or family. Exclusion criteria were known renal failure and contrast allergy CTP Scan Acquisition Protocol. CTP studies were acquired during injection of 50 ml of contrast agent (IOMERON 400, BRACCO Imaging Europe) with a flow rate of5ml/sfollowedby40mlsalinesolutionwithaflowrateof 4 ml/s using an antecubital placed intravenous line. A total of24volumescanswereacquired(slicethickness:0.5mm, slice interval: 0.5 mm) with a total scan time of around three and a half minutes. The CTP acquisition procedure consisted of a mask volume (5 seconds after start of contrast agent administration), followed by a 10-second delay, 4 early arterial volumes (80 ma, 80 kv), 6 full dose arterial volumes (300mA,80kV),and3latearterialvolumeswithaninterscan delay (ISD) of 2 seconds (160 ma, 80 kv). Next, 4 venous volumes (ISD of 5 seconds) and 6 delayed volumes starting at 90 seconds (ISD of 30 seconds) were obtained (130 ma, 80 kv) Postprocessing Standard 4D Dynamic CTA. The standard 4D dctas were derived from the 320-slice CTPs on a postprocessing workstation (Vitrea fx, Vital Images, Minnetonka, USA). This software subtracts the first unenhanced volume of the CTP study from the subsequent contrast enhanced volumes to ensure that only vessels remain visible. From the resulting dcta, the volume with the highest arterial contrast (arterial phase) was selected for quality analysis of the arteries ToBE 4D Dynamic CTA. ToBE dctas were derived from the 320-slice CTPs by employing the total bolus extraction method developed in the UMC Utrecht, The Netherlands. This method is based on a method proposed by Mendrik et al. [18, 20] that derives 3D angiograms from CTP data. These 3D angiograms (vessel enhanced volumes) were derived from the CTP data by quantifying the total change in Hounsfield units (HU) over all temporal volumes (total bolus), using the absolute area under the first temporal derivative curve as described in [18]. For this study, dynamic information extracted from the original CTPdatawasaddedtothe3Dangiograms,tocreatethe ToBE dctas, as follows: a Gaussian temporal filter (σ = 1 sec) was applied to the original CTP data to reduce noise. Subsequently, the time-intensity curves in the filtered CTP data were normalized to values between zero and one, by detectingthebaselineandmaximum,andmultipliedby the 3D angiogram. An automatically generated skull mask was used to mask possible registration artifacts. From the resulting ToBE dcta, the volume with the highest arterial contrast (arterial phase) was chosen for quality analysis of the arteries Quality Analysis. A total of 30 (15 standard dctas, 15 ToBE dctas) maximum intensity projections (MIPs) were created, anonymized, and randomized. Quality analysis of thearteriesonthesemip-ctaswasdonebytwoneurointerventionalists in consensus. Arteries were divided into four subcategories: (I) large extradural arteries (internal carotid arteries (ICAs) and vertebral arteries (VAs)); (II) intradural arteries: large intradural arteries (basilar artery (BA), first segments of anterior cerebral artery (A1), middle cerebral artery (M1), and posterior cerebral artery (P1)), medium sized intradural arteries (A2, P2, and P3), and small sized intradural arteries (A3, A4, M2, M3, M4, and P4); (III) communicating arteries (anterior communicating (Acom) and posterior communicating (Pcom) arteries); and (IV) cerebellar (superior cerebellar artery (SCA) and anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA)) and ophthalmic arteries. A 5-point analogue scoring system (5 = good quality, 1 = poor quality) was used for evaluation of image quality of thefollowingarteries:va,ica,ba,sca,aica,ophthalmic artery,a1,acom,a2,m1,p1,p2,pcom,andp3.thefollowing image quality characteristics were evaluated: arterial contrast, arterial contour sharpness, and regularity and impression of contrast to background noise ratio. Since segments of small intradural arteries (A3, A4, M3, M4, and P4) contain several peripheral branches, it is nearly impossible to provide an overall quality score for each individual vessel segment. Therefore the observers had to indicate whether 3 or more peripheral branches in each vessel segment were visible or not, with respect to the aforementioned image quality characteristics. This binary (>3 branches visible yes/no) scoring system is also used for the M2 segment of MCA, since this segment also divides into several branches directly after its division from the M1 segment; for this reason, the M2 segment is defined and scored as a small intradural artery in this study (although in terms of vessel diameter the M2 segment would be categorized in the group of medium sized intradural arteries). The cerebellar and ophthalmic arteries were scored as a separate group on the 5-point scale and no distinction between small and medium sized arteries was made. The reason for this is that the ramifications of the cerebellar and ophthalmic arteries are less well defined and balanced as compared to the small sized intradural arteries,
3 BioMed Research International 3 Table 1: Results of the observer study on arterial image quality in standard dynamic CTAs (dctas) and the proposed ToBE dynamic CTAs derived from 15 4D CT perfusion scans. The scores are presented as mean (standard deviation) over all 15 images and were scored on a 5-point scale (5 = good quality, 1 = poor quality) for all arteries, except the small intradural arteries. The small intradural arteries are presented as the number of scans with >3 visible small artery branches/total number of small arteries assessed (ratio in percentage; standard error). Category Standard dctas ToBE dctas Test results Large extradural arteries 4.5 (0.7) 4.9 (0.4) P=0.001 Intradural arteries Large 4.4 (1.0) 4.7 (0.7) P<0.001 Medium 3.7 (1.1) 4.4 (0.8) P<0.001 Small 104/180 (57.8%; 3.7%) 159/180 (88.3%; 2.4%) P<0.001 Cerebellar and ophthalmic arteries 2.5 (1.6) 2.9 (1.7) P = Communicating arteries 2.7 (1.8) 2.9 (1.9) P = 0.10 Significant, Wilcoxon Signed Rank statistical test. Significant, McNemar statistical test. 3D CTA standard 4D dcta ToBE 4D dcta Figure 1: Illustration (maximum intensity projections over a 15 mm axial slab) of the image quality of the arteries in the dynamic 4D CTAs compared to the 3D CTA. The arrows indicate the arteries that show improved arterial image quality in the ToBE 4D dcta compared to the standard 4D dcta. The 3D CTA can be used as a reference. and the arteries lack proximal divisions (e.g., the ophthalmic artery branches only when it crosses over the optic nerve). The communicating arteries were scored separately on the 5-point scale as well, because they can vary considerably in presence and size, due to, for example, aplasia, hypoplasia, or fetal continuation of the posterior cerebral artery, which complicates the classification of these arteries as medium or small Statistical Analysis. To compare the arterial image quality in the standard dctas and the ToBE dctas, paired nonparametric statistical tests were used. For the small intracerebral arteries, the McNemar test was used and the Wilcoxon Signed Rank test was used for the remaining arteries. The statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS 18 software package (IBM SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). A significance level of α = was chosen after Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. 3. Results The results of the observer study are presented in Table 1. Some arteries were excluded from the statistical evaluation due to the following findings: ICA occlusion (2), BA occlusion (1), A1 occlusion (1), AICA occlusion (3), ophthalmic arteryocclusion(3),andpcomaplasia(4).thefinalclinical diagnoses included transient ischemic attack (4) and cerebral ischemia (7). In 4 patients, the definite diagnosis remained uncertain.theresultsshowthatthearterialimagequalityin the ToBE dctas was scored significantly higher than arterial image quality in the standard dctas for the large extradural andthelargeandmediumintraduralarteries.thenumber of visible artery branches of the small intradural arteries also improved significantly in the ToBE dctas compared to the standard dctas. Although the mean scores for the communicating arteries and cerebellar and ophthalmic arteries were slightly higher in the ToBE dctas compared to the standard dctas, this difference was not significant. Figure 1 illustrates
4 4 BioMed Research International standard 4D dcta ToBE 4D dcta Figure 2: Illustration of the arterial phase in the dynamic CTAs derived from the CTP data. The arterial phase (whole-brain maximum intensity projection) is shown of both the standard and ToBE dctas of three of the evaluated 15 subjects. The arrows indicate locations where the ToBE dctas show improved visualization of the arteries. standard 4D dcta ToBE 4D dcta Figure 3: Zoomed in subimages of the arterial phase in one of the evaluated subjects in both the standard 4D dynamic CTA (dcta) and the proposed ToBE 4D dcta. the quality of the evaluated arterial phase in the 4D dctas compared to the 3D CT angiography (CTA) scan. Figure 2 shows three examples of the improved arterial image quality in the arterial phase of the ToBE dcta as compared to the standard dcta. Figure 3 shows a zoomed in subimage to illustrate the enhancement of the small arteries. 4. Discussion The 320-slice CT scanner has introduced whole head coverage in a single rotation enabling acquisition of whole-brain CT perfusion (CTP) scans at a high temporal resolution. Consequently, whole-brain 4D dynamic CTAs (dctas) can
5 BioMed Research International 5 be derived from these CTP scans that provide information on the cerebral hemodynamics. Unfortunately, the arterial image quality of these 4D dctas has been shown to be inferior to 3D CTA [14]. In this paper, we proposed the total bolus extraction (ToBE) method as an alternative to the standard subtraction-based method to derive 4D dctas from CTP scans. The standard method subtracts the first unenhanced volume of the CTP scan from each of the subsequent volumes to derive the dcta image, which increases noise and could decrease the arterial image quality. The ToBE method uses all volumes available in the CTP scan to retrieve the total amount of available contrast for each vessel (total bolus), after which the hemodynamic information from the CTP scan is added by showing the corresponding percentage of the total bolus at each point in time. Our hypothesis was that the ToBE method would improve the arterial image quality in 4D dctas compared to the standard method. Our observer study confirmed this hypothesis for the large extradural arteries and the intradural arteries. In these arteries, the image quality improved significantly. The quality of the communicating arteries and cerebellar and ophthalmic arteries showed slight improvements as well, but these were not significant. The improved arterial image quality in the ToBE dctas was especially prominent for the small intracranial arteries. Therefore, ToBE dctas could have the potential to improve detection of small-artery pathologies, for example, vasculitis, small distal aneurysms, and small shunting lesions, as compared to standard dctas, since Siebert et al. [16] reported that the evaluation of the medium and small intracranial arteries in standard dctas is limited, due to the inferior quality compared to 3D CTA. Although the results of our study are promising, there are some limitations. First, in this study we did not compare the arterial image quality of the ToBE 4D dcta with the arterial image quality of standard 3D CTA. We cannot therefore be certain that the ToBE 4D CTA would have the potential to replace the 3D CTA in the diagnostic work-up of ischemic stroke patients and thus may limit radiation exposure to patients. This comparison will be the subject of future studies. Second, we did not include patients with pathology of small arteries; we cannot therefore be sure that improvement of image quality of small cerebral arteries by applying the ToBE method is sufficient for detecting pathologies in these arteries. The arterial image quality improved, but further research in patients with pathologies of small arteries should assess whether the small arteries are indeed diagnostic. Third, a relatively small number of patients were used to evaluate the ToBEmethod.Finally,theskullmaskthatwasusedforthe ToBE method introduced some artifacts in the arteries near the cranial base, that were not present in the standard dctas, sincethismethoddoesnotuseskullmasking.asolution to this problem would be to use the ToBE method without bone masking, since bone is automatically suppressed [18, 20]. However, in this study we used the bone mask to suppress high intensities that could result from small misalignments of the sequential CTP volumes and might reduce depiction of arteries. Improving the registration method could resolve this limitation, which is a subject for further research. Despite these limitations, the ToBE dctas showed improved image quality of especially the small intracranial arteries as compared to the standard dctas. The clinical significance of the improved image quality of the small intracranial arteries needs to be validated in patients with small vessel pathology, for example, compared to digital subtraction angiography as a reference standard. 5. Conclusion In conclusion, this study showed that 4D dynamic CTAs derived from 320-slice CTP scans using the total bolus extraction(tobe)methodshowimprovedimagequalityof the large extradural and all intradural arteries as compared to standard 4D dynamic CTAs derived using the subtraction method.arterialimagequalityimprovementswereespecially prominent in the small intradural arteries. The 4D ToBE dynamic CTAs derived from the CTP scans combine valuable hemodynamic information with improved arterial image quality. Abbreviations ToBE: Total bolus extraction method Acom: Anterior communicating artery Pcom: Posterior communicating arteries AICA: Anterior inferior cerebellar artery SCA: Superior cerebellar artery dcta: Dynamic 4D whole-brain CT angiograms derived from CTP scans. Conflict of Interests The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper. References [1] G. Zhu, P. Michel, A. Aghaebrahim et al., Computed tomography workup of patients suspected of acute ischemic stroke: perfusion computed tomography adds value compared with clinical evaluation, noncontrast computed tomography, and computed tomography angiogram in terms of predicting outcome, Stroke,vol.44,no.4,pp ,2013. [2] C.H.P.Cremers,I.C.vanderSchaaf,E.Wensinketal., CT perfusion and delayed cerebral ischemia in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism,vol.34,no.2,pp , [3] M. Goyal, B. K. Menon, and C. P. Derdeyn, Perfusion imaging in acute ischemic stroke: let us improve the science before changing clinical practice, Radiology,vol.266,no.1,pp.16 21, [4] M. Sharma and D. M. Pelz, CT perfusion in acute stroke: added value or waste of time? Stroke, vol. 44, no. 9, articlee115, [5] M. Wintermark, G. Zhu, J. T. Patrie, and P. Michel, Response to letter regarding article, CT perfusion in acute stroke: added value or waste of time?, Stroke, vol. 44, p. e116, 2013.
6 6 BioMed Research International [6] A. P.-H. Huang, J.-C. Tsai, L.-T. Kuo et al., Clinical application of perfusion computed tomography in neurosurgery, Neurosurgery,vol.120,no.2,pp ,2014. [7] P. Kan, K. V. Snyder, M. J. Binning, A. H. Siddiqui, L. N. Hopkins, and E. I. Levy, Computed tomography (CT) perfusion in the treatment of acute stroke., World Neurosurgery,vol.74,no. 6, pp , [8] R.E.Latchaw,M.J.Alberts,M.H.Levetal., Recommendations for imaging of acute ischemic stroke: a scientific statement from the american heart association, Stroke, vol. 40, no. 11, pp , [9] K. V. Snyder, M. Mokin, and V. E. Bates, Neurologic applications of whole-brain volumetric multidetector computed tomography, Neurologic Clinics,vol.32,no.1,pp ,2014. [10] R. Klingebiel, E. Siebert, S. Diekmann et al., 4-D imaging in cerebrovascular disorders by using 320-Slice CT. Feasibility and preliminary clinical experience, Academic Radiology, vol. 16, no. 2, pp , [11] W. W. Orrison Jr., K. V. Snyder, L. N. Hopkins et al., Wholebrain dynamic CT angiography and perfusion imaging, Clinical Radiology, vol. 66, no. 6, pp , [12] E. J. Salomon, J. Barfett, P. W. A. Willems, S. Geibprasert, S. Bacigaluppi, and T. Krings, Dynamic CT angiography and CT perfusion employing a 320-detector row CT: protocol and current clinical applications, Clinical Neuroradiology, vol.19, no. 3, pp , [13] B.K.Menon,B.O Brien,A.Bivardetal., Assessmentofleptomeningeal collaterals using dynamic CT angiography in patients with acute ischemic stroke, Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism,vol.33,no.3,pp ,2013. [14] E. Siebert, S. Diekmann, F. Masuhr et al., Measurement of cerebral circulation times using dynamic whole-brain CTangiography: feasibility and initial experience, Neurological Sciences,vol.33,no.4,pp ,2012. [15] P. A. Brouwer, T. Bosman, M. A. A. Van Walderveen, T. Krings, A. A. Leroux, and P. W. A. Willems, Dynamic 320-section CT angiography in cranial arteriovenous shunting lesions, American Neuroradiology,vol.31,no.4,pp , [16] E. Siebert, G. Bohner, M. Dewey et al., 320-Slice CT neuroimaging: initial clinical experience and image quality evaluation, British Radiology, vol. 82, no. 979, pp , [17] H. A. F. Gratama van Andel, H. W. Venema, C. B. Majoie, G. J. Den Heeten, C. A. Grimbergen, and G. J. Streekstra, Intracranial CT angiography obtained from a cerebral CT perfusion examination, Medical Physics, vol. 36, no. 4, pp , [18] A. Mendrik, E. Vonken, B. Van Ginneken et al., Automatic segmentation of intracranial arteries and veins in four-dimensional cerebral CT perfusion scans, Medical Physics,vol.37,no.6,pp , [19] E. J. Smit, E. Vonken, I. C. van der Schaaf et al., Timinginvariant reconstruction for deriving high-quality CT angiographic data from cerebral CT perfusion data, Radiology, vol. 263, no. 1, pp , [20] A. M. Mendrik, E. P. A. Vonken, G. A. P. De Kort et al., Improved arterial visualization in cerebral CT perfusionderived arteriograms compared with standard CT angiography: a visual assessment study, The American Neuroradiology,vol.33,no.11,pp ,2012.
7 MEDIATORS of INFLAMMATION The Scientific World Journal Gastroenterology Research and Practice Diabetes Research International Endocrinology Immunology Research Disease Markers Submit your manuscripts at BioMed Research International PPAR Research Obesity Ophthalmology Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Stem Cells International Oncology Parkinson s Disease Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine AIDS Behavioural Neurology Research and Treatment Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity
Case Report Tortuous Common Carotid Artery: A Report of Four Cases Observed in Cadaveric Dissections
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2016, Article ID 2028402, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2028402 Case Report Tortuous Common Carotid Artery: A Report of Four Cases Observed in Cadaveric Dissections
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2016, Article ID 2028402, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2028402 Case Report Tortuous Common Carotid Artery: A Report of Four Cases Observed in Cadaveric Dissections
Clinical Study Circle of Willis Variants: Fetal PCA
 Stroke Research and Treatment Volume 2013, Article ID 105937, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/105937 Clinical Study Circle of Willis Variants: Fetal PCA Amir Shaban, 1 Karen C. Albright, 2,3,4,5
Stroke Research and Treatment Volume 2013, Article ID 105937, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/105937 Clinical Study Circle of Willis Variants: Fetal PCA Amir Shaban, 1 Karen C. Albright, 2,3,4,5
Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT
 Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT Poster No.: C-9 Congress: ECR 5 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nakadate, Y. Iwasa, M. Kishino, U. Tateishi;
Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT Poster No.: C-9 Congress: ECR 5 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nakadate, Y. Iwasa, M. Kishino, U. Tateishi;
Case Report Asymptomatic Pulmonary Vein Stenosis: Hemodynamic Adaptation and Successful Ablation
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2016, Article ID 4979182, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4979182 Case Report Asymptomatic Pulmonary Vein Stenosis: Hemodynamic Adaptation and Successful Ablation
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2016, Article ID 4979182, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4979182 Case Report Asymptomatic Pulmonary Vein Stenosis: Hemodynamic Adaptation and Successful Ablation
Case Report Ocular Symptomatology, Management, and Clinical Outcome of a Giant Intracranial Aneurysm
 Volume 2012, Article ID 643965, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/643965 Case Report Ocular Symptomatology, Management, and Clinical Outcome of a Giant Intracranial Aneurysm Chryssa Terzidou, 1 Georgios Dalianis,
Volume 2012, Article ID 643965, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/643965 Case Report Ocular Symptomatology, Management, and Clinical Outcome of a Giant Intracranial Aneurysm Chryssa Terzidou, 1 Georgios Dalianis,
Subtraction CT Angiography with Controlled- Orbit Helical Scanning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:291 295, February 1998 Subtraction CT Angiography with Controlled- Orbit Helical Scanning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms Satoshi Imakita, Yoshitaka Onishi, Tokihiro Hashimoto,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:291 295, February 1998 Subtraction CT Angiography with Controlled- Orbit Helical Scanning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms Satoshi Imakita, Yoshitaka Onishi, Tokihiro Hashimoto,
B-Flow, Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Assessment of Carotid Stenosis: Comparison with 64-MD-CT Angiography
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 805-809, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net B-Flow, Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Assessment of Carotid Stenosis: Comparison with
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 805-809, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net B-Flow, Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Assessment of Carotid Stenosis: Comparison with
CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage
 CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage RD Magazine, 39, 458, 29-30 Dr M Igra Radiology SPR Leeds General Infirmary Dr I Djoukhadar Research fellow Wolfson Molecular
CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage RD Magazine, 39, 458, 29-30 Dr M Igra Radiology SPR Leeds General Infirmary Dr I Djoukhadar Research fellow Wolfson Molecular
Hrushchak N.M. The Pharma Innovation Journal 2014; 3(9): 38-42
 2014; 3(9): 38-42 ISSN: 2277-7695 TPI 2014; 3(9): 38-42 2013 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 10-10-2014 Accepted: 23-11-2014 Ivano-Frankivsk national medical university Kalush regional hospital.
2014; 3(9): 38-42 ISSN: 2277-7695 TPI 2014; 3(9): 38-42 2013 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 10-10-2014 Accepted: 23-11-2014 Ivano-Frankivsk national medical university Kalush regional hospital.
Peter I. Kalmar, 1 Peter Oberwalder, 2 Peter Schedlbauer, 1 Jürgen Steiner, 1 and Rupert H. Portugaller Introduction. 2.
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 714914, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/714914 Case Report Secondary Aortic Dissection after Endoluminal Treatment of an Intramural Hematoma of the
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 714914, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/714914 Case Report Secondary Aortic Dissection after Endoluminal Treatment of an Intramural Hematoma of the
Comparison of Five Major Recent Endovascular Treatment Trials
 Comparison of Five Major Recent Endovascular Treatment Trials Sample size 500 # sites 70 (100 planned) 316 (500 planned) 196 (833 estimated) 206 (690 planned) 16 10 22 39 4 Treatment contrasts Baseline
Comparison of Five Major Recent Endovascular Treatment Trials Sample size 500 # sites 70 (100 planned) 316 (500 planned) 196 (833 estimated) 206 (690 planned) 16 10 22 39 4 Treatment contrasts Baseline
Case Report Computed Tomography Angiography Successfully Used to Diagnose Postoperative Systemic-Pulmonary Artery Shunt Narrowing
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2011, Article ID 802643, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/802643 Case Report Computed Tomography Angiography Successfully Used to Diagnose Postoperative Systemic-Pulmonary Artery
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2011, Article ID 802643, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/802643 Case Report Computed Tomography Angiography Successfully Used to Diagnose Postoperative Systemic-Pulmonary Artery
Research Article The Value of Cerebral CT Angiography with Low Tube Voltage in Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms
 BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 876796, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/876796 Research Article The Value of Cerebral CT Angiography with Low Tube Voltage in Detection of Intracranial
BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 876796, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/876796 Research Article The Value of Cerebral CT Angiography with Low Tube Voltage in Detection of Intracranial
Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 6434623, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6434623 Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male Jordan Nepute,
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 6434623, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6434623 Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male Jordan Nepute,
Whole brain CT perfusion imaging using increased sampling intervals: A pilot study
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 14: 2643-2649, 2017 Whole brain CT perfusion imaging using increased sampling intervals: A pilot study GUOQUAN CAO, WEIJIAN CHEN, HOUZHANG SUN, XIANZHONG GUO, YUNJUN
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 14: 2643-2649, 2017 Whole brain CT perfusion imaging using increased sampling intervals: A pilot study GUOQUAN CAO, WEIJIAN CHEN, HOUZHANG SUN, XIANZHONG GUO, YUNJUN
Case Report Three-Dimensional Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Enhancing Stone/Stent Contrasting and Stone Visualization in Urolithiasis
 Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 646087, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/646087 Case Report Three-Dimensional Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Enhancing Stone/Stent Contrasting
Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 646087, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/646087 Case Report Three-Dimensional Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Enhancing Stone/Stent Contrasting
Variations of the cerebellar arteries at CT angiography
 DOI 10.1007/s00276-013-1208-z Original Article Variations of the cerebellar arteries at CT angiography Yeliz Pekcevik Ridvan Pekcevik Received: 28 July 2013 / Accepted: 14 September 2013 / Published online:
DOI 10.1007/s00276-013-1208-z Original Article Variations of the cerebellar arteries at CT angiography Yeliz Pekcevik Ridvan Pekcevik Received: 28 July 2013 / Accepted: 14 September 2013 / Published online:
Baris Beytullah Koc, 1 Martijn Schotanus, 1 Bob Jong, 2 and Pieter Tilman Introduction. 2. Case Presentation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 7898090, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7898090 Case Report The Role of Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI in a Child with Sport-Induced Avascular
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 7898090, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7898090 Case Report The Role of Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI in a Child with Sport-Induced Avascular
Research Article Comparison of Colour Duplex Ultrasound with Computed Tomography to Measure the Maximum Abdominal Aortic Aneurysmal Diameter
 International Vascular Medicine, Article ID 574762, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/574762 Research Article Comparison of Colour Duplex Ultrasound with Computed Tomography to Measure the Maximum
International Vascular Medicine, Article ID 574762, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/574762 Research Article Comparison of Colour Duplex Ultrasound with Computed Tomography to Measure the Maximum
Posterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysms with Common Carotid Artery Occlusion: A Report of Two Cases
 Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 371 375 Online March 3, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2016-0114 Posterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysms with Common Carotid Artery Occlusion: A Report of Two Cases
Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 371 375 Online March 3, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2016-0114 Posterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysms with Common Carotid Artery Occlusion: A Report of Two Cases
Different CT perfusion algorithms in the detection of delayed. cerebral ischemia (DCI) after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
 Neuroradiology (2015) 57:469 474 DOI 10.1007/s00234-015-1486-8 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY Different CT perfusion algorithms in the detection of delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
Neuroradiology (2015) 57:469 474 DOI 10.1007/s00234-015-1486-8 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY Different CT perfusion algorithms in the detection of delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
Case Report Formation of a Tunnel under the Major Hepatic Vein Mouths during Removal of IVC Tumor Thrombus
 Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 129632, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/129632 Case Report Formation of a Tunnel under the Major Hepatic Vein Mouths during Removal of IVC Tumor Thrombus
Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 129632, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/129632 Case Report Formation of a Tunnel under the Major Hepatic Vein Mouths during Removal of IVC Tumor Thrombus
Research Article Predictions of the Length of Lumbar Puncture Needles
 Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, Article ID 732694, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/732694 Research Article Predictions of the Length of Lumbar Puncture Needles Hon-Ping Ma, 1,2
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, Article ID 732694, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/732694 Research Article Predictions of the Length of Lumbar Puncture Needles Hon-Ping Ma, 1,2
Case Report A Rare Case of Near Complete Regression of a Large Cervical Disc Herniation without Any Intervention Demonstrated on MRI
 Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 832765, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/832765 Case Report A Rare Case of Near Complete Regression of a Large Cervical Disc Herniation without Any Intervention
Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 832765, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/832765 Case Report A Rare Case of Near Complete Regression of a Large Cervical Disc Herniation without Any Intervention
Assessment of Vasospasm and Delayed Cerebral Ischemia after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Current concepts and Value of CT Perfusion and CT Angiography
 Assessment of Vasospasm and Delayed Cerebral Ischemia after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Current concepts and Value of CT Perfusion and CT Angiography Poster No.: C-2563 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational
Assessment of Vasospasm and Delayed Cerebral Ischemia after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Current concepts and Value of CT Perfusion and CT Angiography Poster No.: C-2563 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational
Blood Supply. Allen Chung, class of 2013
 Blood Supply Allen Chung, class of 2013 Objectives Understand the importance of the cerebral circulation. Understand stroke and the types of vascular problems that cause it. Understand ischemic penumbra
Blood Supply Allen Chung, class of 2013 Objectives Understand the importance of the cerebral circulation. Understand stroke and the types of vascular problems that cause it. Understand ischemic penumbra
Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections in Patients with Hydrocephalus
 The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 461896, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/461896 Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections
The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 461896, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/461896 Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections
Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling
 Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
Case Report Spontaneous Rapid Resolution of Acute Epidural Hematoma in Childhood
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 956849, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/956849 Case Report Spontaneous Rapid Resolution of Acute Epidural Hematoma in Childhood Ismail GülGen, 1
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 956849, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/956849 Case Report Spontaneous Rapid Resolution of Acute Epidural Hematoma in Childhood Ismail GülGen, 1
Tom Eisele, Benedikt M. Muenz, and Grigorios Korosoglou. Department of Cardiology & Vascular Medicine, GRN Hospital Weinheim, Weinheim, Germany
 Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 7376457, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7376457 Case Report Successful Endovascular Repair of an Iatrogenic Perforation of the Superficial
Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 7376457, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7376457 Case Report Successful Endovascular Repair of an Iatrogenic Perforation of the Superficial
Multisection CT Venography of the Dural Sinuses and Cerebral Veins by Using Matched Mask Bone Elimination
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:787 791, May 2004 Case Report Multisection CT Venography of the Dural Sinuses and Cerebral Veins by Using Matched Mask Bone Elimination Charles B. L. M. Majoie, Marcel van Straten,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:787 791, May 2004 Case Report Multisection CT Venography of the Dural Sinuses and Cerebral Veins by Using Matched Mask Bone Elimination Charles B. L. M. Majoie, Marcel van Straten,
Whole brain CT perfusion maps with paradoxical low mean transit time to predict infarct core
 Whole brain CT perfusion maps with paradoxical low mean transit time to predict infarct core Poster No.: B-292 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Topic: Neuro Authors: S. Chakraborty, M. E. Ahmad,
Whole brain CT perfusion maps with paradoxical low mean transit time to predict infarct core Poster No.: B-292 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Topic: Neuro Authors: S. Chakraborty, M. E. Ahmad,
CT perfusion in Moyamoya disease
 CT perfusion in Moyamoya disease Poster No.: C-1726 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. C. Lam, C. P. Tsang, K. K. Wong, R. LEE ; HK, Hong Kong/HK Keywords: Hemodynamics / Flow dynamics,
CT perfusion in Moyamoya disease Poster No.: C-1726 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. C. Lam, C. P. Tsang, K. K. Wong, R. LEE ; HK, Hong Kong/HK Keywords: Hemodynamics / Flow dynamics,
Devendra V. Kulkarni, Rahul G. Hegde, Ankit Balani, and Anagha R. Joshi. 2. Case Report. 1. Introduction
 Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 614647, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/614647 Case Report A Rare Case of Pulmonary Atresia with Ventricular Septal Defect with a Right Sided Aortic Arch and
Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 614647, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/614647 Case Report A Rare Case of Pulmonary Atresia with Ventricular Septal Defect with a Right Sided Aortic Arch and
Case Report A Unique Case of Left Second Supernumerary and Left Third Bifid Intrathoracic Ribs with Block Vertebrae and Hypoplastic Left Lung
 Volume 2013, Article ID 620120, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/620120 Case Report A Unique Case of Left Second Supernumerary and Left Third Bifid Intrathoracic Ribs with Block Vertebrae and Hypoplastic
Volume 2013, Article ID 620120, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/620120 Case Report A Unique Case of Left Second Supernumerary and Left Third Bifid Intrathoracic Ribs with Block Vertebrae and Hypoplastic
SVD+ Dynamic Volume CT:
 SVD+ Dynamic Volume CT: Delay Insensitive Brain Perfusion Analysis Erin Angel, PhD Manager, CT Clinical Science Toshiba America Medical Systems, Inc. SVD+ Dynamic Volume CT: Delay Insensitive Brain Perfusion
SVD+ Dynamic Volume CT: Delay Insensitive Brain Perfusion Analysis Erin Angel, PhD Manager, CT Clinical Science Toshiba America Medical Systems, Inc. SVD+ Dynamic Volume CT: Delay Insensitive Brain Perfusion
ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE. Current Treatment Approaches for Acute Ischemic Stroke
 ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Current Treatment Approaches for Acute Ischemic Stroke EARLY MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Rapid identification of a stroke Immediate EMS transport to nearest stroke center
ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Current Treatment Approaches for Acute Ischemic Stroke EARLY MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Rapid identification of a stroke Immediate EMS transport to nearest stroke center
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE
 IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
Applicable Neuroradiology
 For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
Isolated Cranial Nerve-III Palsy Secondary to Perimesencephalic Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
 Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Department of Medicine Isolated Cranial Nerve-III Palsy Secondary to Perimesencephalic Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Hussam A. Yacoub MD Lehigh Valley Health
Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Department of Medicine Isolated Cranial Nerve-III Palsy Secondary to Perimesencephalic Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Hussam A. Yacoub MD Lehigh Valley Health
Case Conference: Neuroradiology. Case 1: Tumor Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures
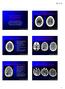 Case Conference: Neuroradiology Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures David E. Rex, MD, PhD Stanford University Hospital Department of Radiology Case 1: Tumor Most likely gangiloglioma, oligodendroglioma,
Case Conference: Neuroradiology Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures David E. Rex, MD, PhD Stanford University Hospital Department of Radiology Case 1: Tumor Most likely gangiloglioma, oligodendroglioma,
Department of Internal Medicine, Saitama Citizens Medical Center, Saitama , Japan
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8790347, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8790347 Case Report GuideLiner Catheter Use for Percutaneous Intervention Involving Anomalous Origin of
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8790347, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8790347 Case Report GuideLiner Catheter Use for Percutaneous Intervention Involving Anomalous Origin of
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 4
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 4 Strokes and infarcts K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 4 Strokes and infarcts K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
CT angiography (CTA) becomes more and more important
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH B.F. Tomandl T. Hammen E. Klotz H. Ditt B. Stemper M. Lell Bone-Subtraction CT Angiography for the Evaluation of Intracranial Aneurysms PURPOSE: CT angiography (CTA) has been established
ORIGINAL RESEARCH B.F. Tomandl T. Hammen E. Klotz H. Ditt B. Stemper M. Lell Bone-Subtraction CT Angiography for the Evaluation of Intracranial Aneurysms PURPOSE: CT angiography (CTA) has been established
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA
 99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA As described in Chapter 12, time of flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is commonly utilized in the evaluation of the circle of Willis. TOF MRA allows depiction
99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA As described in Chapter 12, time of flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is commonly utilized in the evaluation of the circle of Willis. TOF MRA allows depiction
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Table 1.Summary of 12 Patients with Brain Death and Deep Coma: Clinical Findings Patients No. Age/Sex Underlying Cause Study No.
 3 9 5 Table 1.Summary of 12 Patients with Brain Death and Deep Coma: Clinical Findings Patients No. Age/Sex Underlying Cause Study No. Brain Stem Reflex EEG Clinical Diagnosis 01 40/M Trauma 01 ECS Brain
3 9 5 Table 1.Summary of 12 Patients with Brain Death and Deep Coma: Clinical Findings Patients No. Age/Sex Underlying Cause Study No. Brain Stem Reflex EEG Clinical Diagnosis 01 40/M Trauma 01 ECS Brain
Case Report Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis in Isolated Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy
 Volume 2016, Article ID 5184196, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5184196 Case Report Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis in Isolated Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy Sanjay Khaladkar, Avadhesh
Volume 2016, Article ID 5184196, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5184196 Case Report Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis in Isolated Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy Sanjay Khaladkar, Avadhesh
Lung Perfusion Analysis New Pathways in Lung Imaging. Case Study Brochure PLA 309 Hospital
 Lung Perfusion Analysis New Pathways in Lung Imaging Case Study Brochure PLA 309 Hospital http://www.toshibamedicalsystems.com Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation 2012 all rights reserved. Design and specifications
Lung Perfusion Analysis New Pathways in Lung Imaging Case Study Brochure PLA 309 Hospital http://www.toshibamedicalsystems.com Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation 2012 all rights reserved. Design and specifications
Subtraction Helical CT Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vessels: Technical Considerations and Preliminary Experience
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:451 455, March 2003 Subtraction Helical CT Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vessels: Technical Considerations and Preliminary Experience Vijayam K. Jayakrishnan, Philip M.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:451 455, March 2003 Subtraction Helical CT Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vessels: Technical Considerations and Preliminary Experience Vijayam K. Jayakrishnan, Philip M.
Blunt Carotid Injury- CT Angiography is Adequate For Screening. Kelly Knudson, M.D. UCHSC April 3, 2006
 Blunt Carotid Injury- CT Angiography is Adequate For Screening Kelly Knudson, M.D. UCHSC April 3, 2006 CT Angiography vs Digital Subtraction Angiography Blunt carotid injury screening is one of the very
Blunt Carotid Injury- CT Angiography is Adequate For Screening Kelly Knudson, M.D. UCHSC April 3, 2006 CT Angiography vs Digital Subtraction Angiography Blunt carotid injury screening is one of the very
Validation of CT Perfusion Imaging Against Invasive Angiography and FFR on a 320-MDCT Scanner
 Validation of CT Perfusion Imaging Against Invasive Angiography and FFR on a 320-MDCT Scanner Zhen Qian, Gustavo Vasquez, Sarah Rinehart, Parag Joshi, Eric Krivitsky, Anna Kalynych, Dimitri Karmpaliotis,
Validation of CT Perfusion Imaging Against Invasive Angiography and FFR on a 320-MDCT Scanner Zhen Qian, Gustavo Vasquez, Sarah Rinehart, Parag Joshi, Eric Krivitsky, Anna Kalynych, Dimitri Karmpaliotis,
Case Report 1. CTA head. (c) Tele3D Advantage, LLC
 Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Case Report Optic Disk Pit with Sudden Central Visual Field Scotoma
 Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 1423481, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1423481 Case Report Optic Disk Pit with Sudden Central Visual Field Scotoma Nikol Panou
Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 1423481, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1423481 Case Report Optic Disk Pit with Sudden Central Visual Field Scotoma Nikol Panou
Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography
 Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography Kazumi Kimura, Yoichiro Hashimoto, Teruyuki Hirano, Makoto Uchino, and Masayuki Ando PURPOSE: To determine
Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography Kazumi Kimura, Yoichiro Hashimoto, Teruyuki Hirano, Makoto Uchino, and Masayuki Ando PURPOSE: To determine
Imaging of Moya Moya Disease
 Abstract Imaging of Moya Moya Disease Pages with reference to book, From 181 To 185 Rashid Ahmed, Hurnera Ahsan ( Liaquat National Hospital, Karachi. ) Moya Moya disease is a rare disease causing occlusion
Abstract Imaging of Moya Moya Disease Pages with reference to book, From 181 To 185 Rashid Ahmed, Hurnera Ahsan ( Liaquat National Hospital, Karachi. ) Moya Moya disease is a rare disease causing occlusion
UPDATES IN INTRACRANIAL INTERVENTION Jordan Taylor DO Metro Health Neurology 2015
 UPDATES IN INTRACRANIAL INTERVENTION Jordan Taylor DO Metro Health Neurology 2015 NEW STUDIES FOR 2015 MR CLEAN ESCAPE EXTEND-IA REVASCAT SWIFT PRIME RECOGNIZED LIMITATIONS IV Alteplase proven benefit
UPDATES IN INTRACRANIAL INTERVENTION Jordan Taylor DO Metro Health Neurology 2015 NEW STUDIES FOR 2015 MR CLEAN ESCAPE EXTEND-IA REVASCAT SWIFT PRIME RECOGNIZED LIMITATIONS IV Alteplase proven benefit
Research Article Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms and Coronary Artery Disease in a Small Country with High Cardiovascular Burden
 ISRN Cardiology, Article ID 825461, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/825461 Research Article Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms and Coronary Artery Disease in a Small Country with High Cardiovascular Burden
ISRN Cardiology, Article ID 825461, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/825461 Research Article Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms and Coronary Artery Disease in a Small Country with High Cardiovascular Burden
[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]
![[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD] [(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]](/thumbs/89/98619893.jpg) 2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
Neuroradiology. of Stroke and Headaches
 Neuroradiology of Stroke and Headaches Learning Objec:ves 1. Iden:fy T1 and T2 sequences 2. Recall the normal anatomy of the intracranial circula:on 3. Apply appropriate CT and MR imaging of the brain
Neuroradiology of Stroke and Headaches Learning Objec:ves 1. Iden:fy T1 and T2 sequences 2. Recall the normal anatomy of the intracranial circula:on 3. Apply appropriate CT and MR imaging of the brain
Multislice CT Angiography of Cerebral Aneurysms in Nontraumatic Subarachnoid and Intraparenchymal Haemorrhage
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 80, No. 2, June: 173-178, 2012 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Multislice CT Angiography of Cerebral Aneurysms in Nontraumatic Subarachnoid and Intraparenchymal Haemorrhage
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 80, No. 2, June: 173-178, 2012 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Multislice CT Angiography of Cerebral Aneurysms in Nontraumatic Subarachnoid and Intraparenchymal Haemorrhage
Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
Stroke Treatment Beyond Traditional Time Windows. Rishi Gupta, MD, MBA
 Stroke Treatment Beyond Traditional Time Windows Rishi Gupta, MD, MBA Director, Stroke and Neurocritical Care Endovascular Neurosurgery Wellstar Health System THE PAST THE PRESENT 2015 American Heart Association/American
Stroke Treatment Beyond Traditional Time Windows Rishi Gupta, MD, MBA Director, Stroke and Neurocritical Care Endovascular Neurosurgery Wellstar Health System THE PAST THE PRESENT 2015 American Heart Association/American
External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas
 External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas Report of two cases HARVEY L. LEVINE, M.D., ERNEST J. FERmS, M.D., AND EDWARD L. SPATZ, M.D. Departments of Radiology, Neurology, and Neurosurgery,
External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas Report of two cases HARVEY L. LEVINE, M.D., ERNEST J. FERmS, M.D., AND EDWARD L. SPATZ, M.D. Departments of Radiology, Neurology, and Neurosurgery,
Volumetric Perfusion CT Using Prototype 256 Detector Row CT Scanner: Preliminary Study with Healthy Porcine Model V
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2536 2541, November/December 2005 Technical Note Volumetric Perfusion CT Using Prototype 256 Detector Row CT Scanner: Preliminary Study with Healthy Porcine Model V Shinichiro
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2536 2541, November/December 2005 Technical Note Volumetric Perfusion CT Using Prototype 256 Detector Row CT Scanner: Preliminary Study with Healthy Porcine Model V Shinichiro
Effect of dose reduction on image quality and diagnostic performance in coronary computed tomography angiography
 Int J Cardiovasc Imaging (2013) 29:453 461 DOI 10.1007/s10554-012-0096-3 ORIGINAL PAPER Effect of dose reduction on image quality and diagnostic performance in coronary computed tomography angiography
Int J Cardiovasc Imaging (2013) 29:453 461 DOI 10.1007/s10554-012-0096-3 ORIGINAL PAPER Effect of dose reduction on image quality and diagnostic performance in coronary computed tomography angiography
TABLES. Table 1 Terminal vessel aneurysms. Table. Aneurysm location. Bypass flow** Symptoms Strategy Bypass recipient. Age/ Sex.
 Table TABLES Table 1 Terminal vessel aneurysms Age/ Sex Aneurysm location Symptoms Strategy Bypass recipient Recipient territory Recipient territory flow* Cut flow Bypass flow** Graft Patent postop F/U
Table TABLES Table 1 Terminal vessel aneurysms Age/ Sex Aneurysm location Symptoms Strategy Bypass recipient Recipient territory Recipient territory flow* Cut flow Bypass flow** Graft Patent postop F/U
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
320-slice CT neuroimaging: initial clinical experience and image quality evaluation
 The British Journal of Radiology, 82 (2009), 561 570 320-slice CT neuroimaging: initial clinical experience and image quality evaluation 1 E SIEBERT, MD, 1 G BOHNER, MD, 2 M DEWEY, MD, 3 F MASUHR, MD,
The British Journal of Radiology, 82 (2009), 561 570 320-slice CT neuroimaging: initial clinical experience and image quality evaluation 1 E SIEBERT, MD, 1 G BOHNER, MD, 2 M DEWEY, MD, 3 F MASUHR, MD,
The ejournal of the European Society of Minimally Invasive Neurological Therapy
 The ejournal of the European Society of Minimally Invasive Neurological Therapy Diagnostic performance of contrast enhanced magnetic resonance presenting with subarachnoid haemorrhage Willem van Zwam,
The ejournal of the European Society of Minimally Invasive Neurological Therapy Diagnostic performance of contrast enhanced magnetic resonance presenting with subarachnoid haemorrhage Willem van Zwam,
Paediatric cerebrovascular CT angiography towards better image quality
 Original Article Paediatric cerebrovascular CT angiography towards better image quality Stefanie C. Thust, Wui Khean Kling Chong, Roxana Gunny, Asif Mazumder, Marius Poitelea, Anna Welsh, Ash Ederies,
Original Article Paediatric cerebrovascular CT angiography towards better image quality Stefanie C. Thust, Wui Khean Kling Chong, Roxana Gunny, Asif Mazumder, Marius Poitelea, Anna Welsh, Ash Ederies,
Case Report Successful Implantation of a Coronary Stent Graft in a Peripheral Vessel
 Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 725168, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/725168 Case Report Successful Implantation of a Coronary Stent Graft in a Peripheral Vessel Alexander
Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 725168, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/725168 Case Report Successful Implantation of a Coronary Stent Graft in a Peripheral Vessel Alexander
Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
Case Report A Rare Case of Complete Stent Fracture, Coronary Arterial Transection, and Pseudoaneurysm Formation Induced by Repeated Stenting
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2015, Article ID 192853, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/192853 Case Report A Rare Case of Complete Stent Fracture, Coronary Arterial Transection, and Pseudoaneurysm
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2015, Article ID 192853, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/192853 Case Report A Rare Case of Complete Stent Fracture, Coronary Arterial Transection, and Pseudoaneurysm
Vivek R. Deshmukh, MD Director, Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery Chairman, Department of Neurosurgery Providence Brain and Spine
 Vivek R. Deshmukh, MD Director, Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery Chairman, Department of Neurosurgery Providence Brain and Spine Institute The Oregon Clinic Disclosure I declare that neither
Vivek R. Deshmukh, MD Director, Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery Chairman, Department of Neurosurgery Providence Brain and Spine Institute The Oregon Clinic Disclosure I declare that neither
Medical Policy. MP Computed Tomography Perfusion Imaging of the Brain
 Medical Policy MP 6.01.49 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 6.01.49 Last Review: 09/28/2017 Effective Date: 09/28/2017 Section: Radiology Related Policies 2.01.54 Endovascular Procedures for Intracranial Arterial Disease
Medical Policy MP 6.01.49 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 6.01.49 Last Review: 09/28/2017 Effective Date: 09/28/2017 Section: Radiology Related Policies 2.01.54 Endovascular Procedures for Intracranial Arterial Disease
Role of the Radiologist
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Blunt Cerebrovascular Injuries NORDTER Consensus Conference October 22-24, 2007 Clint W. Sliker, M.D. University of Maryland Medical Center R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center
Diagnosis and Treatment of Blunt Cerebrovascular Injuries NORDTER Consensus Conference October 22-24, 2007 Clint W. Sliker, M.D. University of Maryland Medical Center R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center
MR imaging at 3.0 tesla of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by neurovascular compression
 MR imaging at 3.0 tesla of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by neurovascular compression Poster No.: C-1281 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nishihara 1, T. Noguchi 1, H. Irie 1, K. Sasaguri
MR imaging at 3.0 tesla of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by neurovascular compression Poster No.: C-1281 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nishihara 1, T. Noguchi 1, H. Irie 1, K. Sasaguri
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
Conference Paper Antithrombotic Therapy in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes: Biological Markers and Personalized Medicine
 Conference Papers in Medicine, Article ID 719, pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/13/719 Conference Paper Antithrombotic Therapy in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes: Biological Markers and Personalized
Conference Papers in Medicine, Article ID 719, pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/13/719 Conference Paper Antithrombotic Therapy in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes: Biological Markers and Personalized
Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2508 2513, November/December 2005 Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2508 2513, November/December 2005 Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
Clinical Study Metastasectomy of Pulmonary Metastases from Osteosarcoma: Prognostic Factors and Indication for Repeat Metastasectomy
 Respiratory Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 570314, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/570314 Clinical Study Metastasectomy of Pulmonary Metastases from Osteosarcoma: Prognostic Factors and Indication
Respiratory Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 570314, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/570314 Clinical Study Metastasectomy of Pulmonary Metastases from Osteosarcoma: Prognostic Factors and Indication
Protocol variation analysis of whole brain CT perfusion in acute ischemic stroke
 UNLV Theses, Dissertations, Professional Papers, and Capstones 12-2010 Protocol variation analysis of whole brain CT perfusion in acute ischemic stroke Peter T. Heiberger University of Nevada, Las Vegas
UNLV Theses, Dissertations, Professional Papers, and Capstones 12-2010 Protocol variation analysis of whole brain CT perfusion in acute ischemic stroke Peter T. Heiberger University of Nevada, Las Vegas
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE
 IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula
 A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
Clinical Study Endovascular Recanalization for Chronic Symptomatic Intracranial Vertebral Artery Total Occlusion
 Minimally Invasive Surgery, Article ID 949585, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/949585 Clinical Study Endovascular Recanalization for Chronic Symptomatic Intracranial Vertebral Artery Total Occlusion
Minimally Invasive Surgery, Article ID 949585, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/949585 Clinical Study Endovascular Recanalization for Chronic Symptomatic Intracranial Vertebral Artery Total Occlusion
Computed tomographic pulmonary angiography procedures: Contrast media dilution from the venous to the systemic circulation
 Computed tomographic pulmonary angiography procedures: Contrast media dilution from the venous to the systemic circulation Petter Bugge Askeland Project thesis at the Faculty of Medicine UNIVERSITETET
Computed tomographic pulmonary angiography procedures: Contrast media dilution from the venous to the systemic circulation Petter Bugge Askeland Project thesis at the Faculty of Medicine UNIVERSITETET
Case Report Preoperative Assessment of Anomalous Right Coronary Artery Arising from the Main Pulmonary Artery
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2011, Article ID 642126, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/642126 Case Report Preoperative Assessment of Anomalous Right Coronary Artery Arising from the Main Pulmonary Artery Marshall
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2011, Article ID 642126, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/642126 Case Report Preoperative Assessment of Anomalous Right Coronary Artery Arising from the Main Pulmonary Artery Marshall
From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is a Stroke? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is a Stroke? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair
Case Report Anomalous Left Main Coronary Artery: Case Series of Different Courses and Literature Review
 Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 380952, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/380952 Case Report Anomalous Left Main Coronary Artery: Case Series of Different Courses and Literature
Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 380952, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/380952 Case Report Anomalous Left Main Coronary Artery: Case Series of Different Courses and Literature
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Case Report Successful Closed Reduction of a Lateral Elbow Dislocation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5934281, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5934281 Case Report Successful Closed Reduction of a Lateral Elbow Dislocation Kenya Watanabe, Takuma
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5934281, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5934281 Case Report Successful Closed Reduction of a Lateral Elbow Dislocation Kenya Watanabe, Takuma
Can sufficient preoperative information of intracranial aneurysms be obtained by using 320-row detector CT angiography alone?
 Jpn J Radiol (2013) 31:600 607 DOI 10.1007/s11604-013-0228-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Can sufficient preoperative information of intracranial aneurysms be obtained by using 320-row detector CT angiography alone?
Jpn J Radiol (2013) 31:600 607 DOI 10.1007/s11604-013-0228-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Can sufficient preoperative information of intracranial aneurysms be obtained by using 320-row detector CT angiography alone?
Stroke Imaging Basics. Jeremy Hopkin M.D.
 Stroke Imaging Basics Jeremy Hopkin M.D. Goals Introduce the basic physical properties of imaging used in stroke. Understand why each modality is used in the setting of stroke. Understand some strengths
Stroke Imaging Basics Jeremy Hopkin M.D. Goals Introduce the basic physical properties of imaging used in stroke. Understand why each modality is used in the setting of stroke. Understand some strengths
Case Report Crossed Renal Ectopia without Fusion An Unusual Cause of Acute Abdominal Pain: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 728531, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/728531 Case Report Crossed Renal Ectopia without Fusion An Unusual Cause of Acute Abdominal Pain: A Case Report D. P. Ramaema,
Case Reports in Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 728531, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/728531 Case Report Crossed Renal Ectopia without Fusion An Unusual Cause of Acute Abdominal Pain: A Case Report D. P. Ramaema,
Postoperative Assessment of Extracranial Intracranial Bypass by Time- Resolved 3D Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography Using Parallel Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2243 2247, October 2005 Postoperative Assessment of Extracranial Intracranial Bypass by Time- Resolved 3D Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography Using Parallel Imaging Kazuhiro Tsuchiya,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2243 2247, October 2005 Postoperative Assessment of Extracranial Intracranial Bypass by Time- Resolved 3D Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography Using Parallel Imaging Kazuhiro Tsuchiya,
Field Strength. Regional Perfusion Imaging (RPI) matches cerebral arteries to flow territories
 Field Strength Changing how the world looks at MR. Regional Perfusion Imaging (RPI) matches cerebral arteries to flow territories Research groups in Utrecht, Baltimore and Singapore collaborate on this
Field Strength Changing how the world looks at MR. Regional Perfusion Imaging (RPI) matches cerebral arteries to flow territories Research groups in Utrecht, Baltimore and Singapore collaborate on this
Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature Ashish Kumar Dwivedi, Pradeep Kumar,
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature Ashish Kumar Dwivedi, Pradeep Kumar,
A STUDY OF CIRCLE OF WILLIS BY MR ANGIOGRAPHY
 Original Research Article A STUDY OF CIRCLE OF WILLIS BY MR ANGIOGRAPHY Vishal Madhukar Tekale * 1, Medha Vijay Ambiye 2. ABSTRACT International Journal of Anatomy and Research, Int J Anat Res 2016, Vol
Original Research Article A STUDY OF CIRCLE OF WILLIS BY MR ANGIOGRAPHY Vishal Madhukar Tekale * 1, Medha Vijay Ambiye 2. ABSTRACT International Journal of Anatomy and Research, Int J Anat Res 2016, Vol
Emergency Department Stroke Registry Indicator Specifications 2018 Report Year (07/01/2017 to 06/30/2018 Discharge Dates)
 2018 Report Year (07/01/2017 to 06/30/2018 Discharge Dates) Summary of Changes I62.9 added to hemorrhagic stroke ICD-10-CM diagnosis code list (table 3) Measure Description Methodology Rationale Measurement
2018 Report Year (07/01/2017 to 06/30/2018 Discharge Dates) Summary of Changes I62.9 added to hemorrhagic stroke ICD-10-CM diagnosis code list (table 3) Measure Description Methodology Rationale Measurement
