CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage
|
|
|
- Irene Small
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
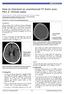
1 CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage RD Magazine, 39, 458, Dr M Igra Radiology SPR Leeds General Infirmary Dr I Djoukhadar Research fellow Wolfson Molecular Imaging Centre University of Manchester Dr T Goddard Consultant neuroradiologist Leeds General Infirmary Introduction Spontaneous intracranial haemorrhage constitutes only 15% 1 of acute stroke but remains the most devastating form, with a death and severe disability rate of more than 75%. 2,3 Prompt identification of a structural vascular abnormality, or lack of it, is a major factor in improving the clinical management of these patients and ultimately their outcomes. Digital subtraction angiography (DS) has been the gold standard imaging technique allowing for a detailed assessment of the circle of Willis. However, it is an invasive examination carrying significant risks (1% stroke rate) to the patient, 4 is time consuming and requires a certain level of experience limiting its availability. The wide availability of CT angiography, on the other hand, coupled with the introduction of multi-detector row CT angiography (MDCT) and the improved post processing techniques, has resulted in an increased use of CT as an imaging tool for the assessment of the intracranial vascular structure. CT angiography techniques and role CT angiography is proving to be a suitable alternative method of assessing the cerebral vessels. This is due to its non-invasive nature, lower radiation dose, 5 wide availability and the ability to perform the examination in conjunction with non-contrast CT. The introduction of multi-detector row CT angiography has revolutionised the CT technique with its quicker acquisition times and improved post-processing image quality. Following image acquisition, the volumetric data is transferred to a working station for further processing. In our institution this includes multi-planar reformation (MPR) with 1mm thickness in multiple planes, thin slab maximum intensity projections (MIP) and volume rendered technique (VRT) algorithm. systematic and thorough approach is adopted in reviewing all the images. The main role of CT is to identify the culprit vascular lesion and assess treatment options. With respect to aneurysms, this is achieved by examining the following features: size, shape, location in relation to the haemorrhage, calcification, number of vessels involved and the presence of any other lesions or anatomical variants. Subarachnoid haemorrhage In our institution, once an unenhanced CT has demonstrated subarachnoid haemorrhage (SH), a CT is usually acquired in the same setting, saving the patient and the medical team an extra visit to the radiology department. Intracranial aneurysms are responsible for most cases of SH, approaching 90%. 6 In addition to identifying the aneurysm, the radiologist should look for certain features including location of the aneurysm in relation to the blood (figure 1), neck size, number of vessels incorporated within the aneurysm and the presence of vasospasm. Occasionally, in the presence of multiple aneurysms, it might not be possible to identify the culprit lesion and the neuro-interventionist will need to treat more than one lesion (figure 2). Many authors have published data indicating the high sensitivity and specificity of CT in detecting acutely ruptured intracranial aneurysms. Using MDCT, gid et al 7 quote a 98% sensitivity and 100% specificity for the detection of aneurysm. Similar results are also published by Sideman, Lourenco and yyny meta-analysis by Westerlaan et al 11 showed a specificity of 99% for ruptured aneurysms and a sensitivity of 92%. Despite these impressive rates, CT lags slightly behind conventional DS and can occasionally yield false negatives, especially in cases of tiny aneurysms measuring less than 2mm 12 and ones that are close to bony structures. 13 In late SH presentation, the accuracy of unenhanced CT and lumbar puncture sensitivity and accuracy drop significantly. CT is a very powerful tool in assessment of this subgroup of patients. negative unenhanced CT and CT can exclude aneurysmal SH with a post-test probability of 99%. 14 s interpretation is user dependent, technological advances coupled with increased familiarity with the investigation should yield greater detection rates. systematic approach to assessing the arterial tree, its branches and Table 1 CT angiography to aneurysm therapy chart.
2 MIPs in three orthogonal planes with different postprocessing techniques should be implemented to ensure aneurysm detection. rteriovenous vascular malformation VM are another well-recognised cause of SH and intracerebral haemorrhage. The main modality for imaging these abnormalities is DS as it allows for dynamic assessment. However, when an VM is encountered on CT, certain radiological features should be actively assessed to try and stratify the risk of recurrent haemorrhage. Venous pouches or intra-nidal aneurysms (figure 3) confer a higher risk for VM rupture and can cause a diagnostic dilemma due to their wide range and locations; hence identification of these lesions is essential. Sanelli et al 12,15 demonstrated that, while DS remains the gold standard, CT has an important role to play in the initial diagnostic vascular assessment. CT can assess both arterial supply of the nidus as well as its venous drainage, and is also useful in stereotactic localisation. recent study showed that CT was more sensitive (87%) than MRI and MR (83% and 87% respectively) at identifying ruptured VMs, and that sensitivity was 100% for VMs larger than 3cm. 16 They also showed that associated aneurysms were best detected with CT, compared to these other imaging modalities. lthough conventional cerebral angiography remains the modality of choice for the diagnosis of dural arteriovenous fistula, CT can be useful with certain imaging features suggestive of the diagnosis. For example, tortuous feeding arteries with dilated cortical draining veins and dilated external carotid artery branches are recognised imaging features (figure 4). Lobar haemorrhage Multiple structural abnormalities can cause isolated intracerebral lobar haemorrhage. These include aneurysms, VM as well as dural fistulae. The decision to investigate patients with an intracerebral haematoma using CT varies widely from one institution to another. In our unit, a multidisciplinary approach is followed, with each case assessed on an individual basis. Factors affecting the decision to investigate further include: patient age, haemorrhage location and the presence of risk factors such as hypertension. 17,2 For example, in an over 60-year-old hypertensive patient with a basal ganglionic haemorrhage, the yield of further CT will be limited. In 2009, Yoon et al 18 compared the accuracy of MDCT against conventional DS in 78 patients. CT successfully detected the underlying vascular abnormalities in all but one patient (a 4mm VM) with no false positive cases. The authors concluded that MDCT is a promising investigation in the assessment of lobar ICH but does not replace DS in all patients. Primary intracranial haemorrhage refers to a spontaneous haemorrhage where an underlying structural abnormality is not identified. In addition to the obvious exclusion value of CT, there is a potentially important prognostic value too. Over the last two decades there have been an increasing number of publications relating to the spot sign in CT. The concept has evolved but most authors refer to the spot sign as tiny areas of enhancement in the haematoma on CT source data. 19 lmandoz et al 20 proposed a scoring system reflecting certain imaging parameters including the number, maximum axial dimension and Hounsfield unit attenuation values of the spot sign. It is important to remember that the spot sign is mainly used in primary intracranial haemorrhage cases and its application in secondary haemorrhage is less clear. Recently, rouwers et al reviewed the available literature highlighting the consistent ability of the spot sign in predicting haematoma expansion, functional outcome and mortality. 21 Conclusion The increasing use of CT can be attributed to its noninvasive nature, wide availability and lower dose when compared with DS. In addition, when reviewed by an experienced operator (figure 5), CT is a highly sensitive and specific investigation and should be use as a gatekeeper limiting the need for DS. References 1. Qureshi I et al. Spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. N Engl J Med 2001;344(19): Zhu X L, Chan M S, Poon W S. Spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage: Which patients need diagnostic cerebral angiography? prospective study of 206 cases and review of the literature. Stroke 1997;28(7): Willinsky R et al. Neurologic complications of cerebral angiography: Prospective analysis of 2,899 procedures and review of the literature. Radiology 2003;227(2): Hankey G J, Warlow C P, Molyneux J. Complications of cerebral angiography for patients with mild carotid territory ischaemia being considered for carotid endarterectomy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1990;(7)53: Manninen L et al. comparison of radiation exposure between diagnostic CT and DS examinations of cerebral and cervicocerebral vessels. m J Neuroradiol 2012;33(11): Kirkpatrick P J. Subarachnoid haemorrhage and intracranial aneurysms: what neurologists need to know. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2002; 73(Suppl1):i gid R et al. cute subarachnoid hemorrhage: Using 64-slice multidetector CT angiography to triage patients treatment. Neuroradiology 2006; 48(11): Sidman R, Connolly E, Lemke T. Subarachnoid hemorrhage diagnosis: Lumbar puncture is still needed when the computed tomography scan is normal. cad Emerg Med 1996;3(9): Lourenco P et al. Does 16-detector computed tomography improve detection of non-traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage in the emergency department? J Emerg Med 2009;36(2): yyny R L et al. Sensitivity of noncontrast cranial computed tomography for the emergency department diagnosis of subarachnoid hemorrhage. nn Emerg Med 2008;51(6): Westerlaan H E et al. Intracranial aneurysms in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage: CT angiography as a primary examination tool for diagnosis systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiology 2011;258(1): Sanelli P C et al. CT angiography in the evaluation of cerebrovascular diseases. m J Roentgenol 2005;184(1): Seruga T, unc G, Klein G E. Helical high-resolution volume-rendered 3- dimensional computer tomography angiography in the detection of intracranial aneurysms. J Neuroimaging 2001;11(3): McCormack R F, Hutson. Can computed tomography angiography of the brain replace lumbar puncture in the evaluation of acute-onset headache after a negative noncontrast cranial computed tomography scan? cad Emerg Med 2010;17(4): Sanelli P C, Mifsud M J, Stieg P E. Role of CT angiography in guiding management decisions of newly diagnosed and residual arteriovenous malformations. m J Roentgenol 2004;183(4): Gross, Frerichs K U, Du R. Sensitivity of CT angiography, T2- weighted MRI, and magnetic resonance angiography in detecting cerebral arteriovenous malformations and associated aneurysms. J Clin Neurosci 2012; 19(8): Halpin S F et al. Prospective evaluation of cerebral angiography and computed tomography in cerebral haematoma. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1994;57(10): Yoon D Y et al. Multidetector row CT angiography in spontaneous lobar intracerebral hemorrhage; a prospective comparison with conventional angiography. m J Neuroradiol 2009;30(5): Tanaka H et al. Initial experience with helical CT and 3D reconstruction in therapeutic planning of cerebral VMs; comparison with 3D time-offlight MR and digital subtraction angiography. J Comput ssist Tomogr 1997;21(5): Romero J M et al. ccuracy of CT angiography for the diagnosis of vascular abnormalities causing intraparenchymal hemorrhage in young patients. Emerg Radiol 2009;16(3): rouwers H et al. Clinical applications of the computed tomography angiography spot sign in acute intracerebral hemorrhage: review. Stroke 2012;43(12):
3 Figures 1 and 1 () Unenhanced CT brain showing predominantly posterior fossa haemorrhage suggesting a posterior circulation aneurysm. () CT confirms a tiny left posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysm (2mm). Haematoma Haematoma Figures 2 and 2 xial () and coronal () CT angiography images demonstrating multiple vascular abnormalities. 1. VM in the left temporal region. 2. Left middle cerebral artery aneurysm, this is the culprit abnormality given the surrounding hematoma (red arrow). 3. Small and incidental right middle cerebral artery aneurysm.
4 C D Figures 3, 3, 3C and 3D () Unenhanced CT brain demonstrating large intraventricular haemorrhage and a small adjacent left corona radiata haemorrhage. () CT reveals a large left frontal VM. (C) CT also show a tiny aneurysm intimately related to the parenchymal haemorrhage. (D) 3D reconstructed images of a conventional angiogram showing the aneurysmal lesion within the VM. Figures 4 and 4 () CT showing a right cerebellar tortuous vessels and, interestingly, the right temporal artery is enlarged raising concerns for a dural fistula. () Conventional cerebral angiogram confirming a dural arteriovenous fistula.
5 C D Figures 5-D CT and initially CT was interpreted as negative. Figure 5E Conventional cerebral angiogram showing aneurysm in the right distal internal carotid artery. Figure 5F On retrospective review of CT, the lesion was present but difficult to see. E F
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
UPSTATE Comprehensive Stroke Center. Neurosurgical Interventions Satish Krishnamurthy MD, MCh
 UPSTATE Comprehensive Stroke Center Neurosurgical Interventions Satish Krishnamurthy MD, MCh Regional cerebral blood flow is important Some essential facts Neurons are obligatory glucose users Under anerobic
UPSTATE Comprehensive Stroke Center Neurosurgical Interventions Satish Krishnamurthy MD, MCh Regional cerebral blood flow is important Some essential facts Neurons are obligatory glucose users Under anerobic
Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT
 Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT Poster No.: C-9 Congress: ECR 5 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nakadate, Y. Iwasa, M. Kishino, U. Tateishi;
Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT Poster No.: C-9 Congress: ECR 5 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nakadate, Y. Iwasa, M. Kishino, U. Tateishi;
The "filling defect" sign helps localise the site of intracranial aneurysm rupture on an unenhanced CT
 The "filling defect" sign helps localise the site of intracranial aneurysm rupture on an unenhanced CT Poster No.: C-3380 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit Neuro
The "filling defect" sign helps localise the site of intracranial aneurysm rupture on an unenhanced CT Poster No.: C-3380 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit Neuro
Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis
 Original article: Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis Dr. Rajneesh Gour 1, Dr. S. N. Ghosh 2, Dr. Sumit Deb 3 1Dept.Of Surgery,Chirayu Medical College & Research Centre,
Original article: Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis Dr. Rajneesh Gour 1, Dr. S. N. Ghosh 2, Dr. Sumit Deb 3 1Dept.Of Surgery,Chirayu Medical College & Research Centre,
Epidemiology And Treatment Of Cerebral Aneurysms At An Australian Tertiary Level Hospital
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 Number 2 Epidemiology And Treatment Of Cerebral Aneurysms At An Australian Tertiary Level Hospital A Granger, R Laherty Citation A Granger, R Laherty.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 Number 2 Epidemiology And Treatment Of Cerebral Aneurysms At An Australian Tertiary Level Hospital A Granger, R Laherty Citation A Granger, R Laherty.
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography of Neurovascular Lesions in Pediatric Patients
 ngiography of Neurovascular Lesions in Pediatric Patients Pediatric Imaging Pictorial Essay M E E N T U R I L I M G I N G JR 2006; 186:75 84 0361 803X/06/1861 75 merican Roentgen Ray Society Y O John M.
ngiography of Neurovascular Lesions in Pediatric Patients Pediatric Imaging Pictorial Essay M E E N T U R I L I M G I N G JR 2006; 186:75 84 0361 803X/06/1861 75 merican Roentgen Ray Society Y O John M.
Imaging of Moya Moya Disease
 Abstract Imaging of Moya Moya Disease Pages with reference to book, From 181 To 185 Rashid Ahmed, Hurnera Ahsan ( Liaquat National Hospital, Karachi. ) Moya Moya disease is a rare disease causing occlusion
Abstract Imaging of Moya Moya Disease Pages with reference to book, From 181 To 185 Rashid Ahmed, Hurnera Ahsan ( Liaquat National Hospital, Karachi. ) Moya Moya disease is a rare disease causing occlusion
Imaging of Cerebrovascular Disease
 Imaging of Cerebrovascular Disease A Practical Guide Val M. Runge, MD Editor-in-Chief of Investigative Radiology Institute for Diagnostic, Interventional, and Pediatric Radiology Inselspital, University
Imaging of Cerebrovascular Disease A Practical Guide Val M. Runge, MD Editor-in-Chief of Investigative Radiology Institute for Diagnostic, Interventional, and Pediatric Radiology Inselspital, University
CLEAR III TRIAL : UPDATE ON SURGICAL MATTERS THAT MATTER
 CLEAR III TRIAL : UPDATE ON SURGICAL MATTERS THAT MATTER CLEAR Surgical Center Team July 2011 Trial Enrollment Status Updates Insert latest enrollment update chart from most recent CLEAR newsletter Imaging
CLEAR III TRIAL : UPDATE ON SURGICAL MATTERS THAT MATTER CLEAR Surgical Center Team July 2011 Trial Enrollment Status Updates Insert latest enrollment update chart from most recent CLEAR newsletter Imaging
Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
Methods. Yahya Paksoy, Bülent Oğuz Genç, and Emine Genç. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24: , August 2003
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I
 NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED BRAIN IMAGING METHODS Plain film radiography Ultrasonography (US) Computer tomography (CT) Magnetic resonance imaging
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED BRAIN IMAGING METHODS Plain film radiography Ultrasonography (US) Computer tomography (CT) Magnetic resonance imaging
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases
 How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
Multislice CT Angiography of Cerebral Aneurysms in Nontraumatic Subarachnoid and Intraparenchymal Haemorrhage
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 80, No. 2, June: 173-178, 2012 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Multislice CT Angiography of Cerebral Aneurysms in Nontraumatic Subarachnoid and Intraparenchymal Haemorrhage
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 80, No. 2, June: 173-178, 2012 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Multislice CT Angiography of Cerebral Aneurysms in Nontraumatic Subarachnoid and Intraparenchymal Haemorrhage
Role of the Radiologist
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Blunt Cerebrovascular Injuries NORDTER Consensus Conference October 22-24, 2007 Clint W. Sliker, M.D. University of Maryland Medical Center R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center
Diagnosis and Treatment of Blunt Cerebrovascular Injuries NORDTER Consensus Conference October 22-24, 2007 Clint W. Sliker, M.D. University of Maryland Medical Center R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center
Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Subtraction CT Angiography with Controlled- Orbit Helical Scanning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:291 295, February 1998 Subtraction CT Angiography with Controlled- Orbit Helical Scanning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms Satoshi Imakita, Yoshitaka Onishi, Tokihiro Hashimoto,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:291 295, February 1998 Subtraction CT Angiography with Controlled- Orbit Helical Scanning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms Satoshi Imakita, Yoshitaka Onishi, Tokihiro Hashimoto,
EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS
 Arteriovenous fistula after radiosurgery for multiple CAVM EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Chao-Bao Luo, Wan-Yuo Guo, Michael
Arteriovenous fistula after radiosurgery for multiple CAVM EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Chao-Bao Luo, Wan-Yuo Guo, Michael
Case Report 1. CTA head. (c) Tele3D Advantage, LLC
 Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
The standard examination to evaluate for a source of subarachnoid
 Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3478 ORIGINAL RESEARCH INTERVENTIONAL Use of CT Angiography and Digital Subtraction Angiography in Patients with Ruptured Cerebral Aneurysm: Evaluation of a Large
Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3478 ORIGINAL RESEARCH INTERVENTIONAL Use of CT Angiography and Digital Subtraction Angiography in Patients with Ruptured Cerebral Aneurysm: Evaluation of a Large
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula
 A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
Dilemma in Imaging Diagnosis, Endovascular Management and Complications
 Vascular anomaly at the craniocervical junction presenting with sub arachnoid hemorrhage: Dilemma in Imaging Diagnosis, Endovascular Management and Complications Ajeet 1* 1. Department of Radiology, St
Vascular anomaly at the craniocervical junction presenting with sub arachnoid hemorrhage: Dilemma in Imaging Diagnosis, Endovascular Management and Complications Ajeet 1* 1. Department of Radiology, St
Benefit of cone-beam computed tomography angiography in acute management of angiographically undetectable ruptured arteriovenous malformations
 J Neurosurg 119:1015 1020, 2013 AANS, 2013 Benefit of cone-beam computed tomography angiography in acute management of angiographically undetectable ruptured arteriovenous malformations Clinical article
J Neurosurg 119:1015 1020, 2013 AANS, 2013 Benefit of cone-beam computed tomography angiography in acute management of angiographically undetectable ruptured arteriovenous malformations Clinical article
Subtraction Helical CT Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vessels: Technical Considerations and Preliminary Experience
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:451 455, March 2003 Subtraction Helical CT Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vessels: Technical Considerations and Preliminary Experience Vijayam K. Jayakrishnan, Philip M.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:451 455, March 2003 Subtraction Helical CT Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vessels: Technical Considerations and Preliminary Experience Vijayam K. Jayakrishnan, Philip M.
T HE blood supply of cerebral arteriovenous malformations is often extensive
 NOVEMBER, 1974 ROENTGENOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS OF THE OCCIPITAL LOBE* By B. TODD TROOST, M.D.,t and THOMAS H. NEWTON, M.D4 T HE blood supply of cerebral arteriovenous malformations
NOVEMBER, 1974 ROENTGENOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS OF THE OCCIPITAL LOBE* By B. TODD TROOST, M.D.,t and THOMAS H. NEWTON, M.D4 T HE blood supply of cerebral arteriovenous malformations
Guideline scope Subarachnoid haemorrhage caused by a ruptured aneurysm: diagnosis and management
 0 0 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Subarachnoid haemorrhage caused by a ruptured aneurysm: diagnosis and management The Department of Health and Social Care in England
0 0 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Subarachnoid haemorrhage caused by a ruptured aneurysm: diagnosis and management The Department of Health and Social Care in England
Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) with retrograde
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Cortical Venous Drainage: Incidence, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose
ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Cortical Venous Drainage: Incidence, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
A New Trend in Vascular Imaging: the Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Sequence
 A New Trend in Vascular Imaging: the Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Sequence Poster No.: C-1347 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Hodel, A. GUILLONNET, M. Rodallec, S. GERBER, R. 1
A New Trend in Vascular Imaging: the Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Sequence Poster No.: C-1347 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Hodel, A. GUILLONNET, M. Rodallec, S. GERBER, R. 1
Fundamentals, Techniques, Pitfalls, and Limitations of MDCT Interpretation and Measurement
 Fundamentals, Techniques, Pitfalls, and Limitations of MDCT Interpretation and Measurement 3 rd Annual Imaging & Physiology Summit November 20-21, 21, 2009 Seoul, Korea Wm. Guy Weigold, MD, FACC Cardiovascular
Fundamentals, Techniques, Pitfalls, and Limitations of MDCT Interpretation and Measurement 3 rd Annual Imaging & Physiology Summit November 20-21, 21, 2009 Seoul, Korea Wm. Guy Weigold, MD, FACC Cardiovascular
Case 37 Clinical Presentation
 Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
Case 9799 Stanford type A aortic dissection: US and CT findings
 Case 9799 Stanford type A aortic dissection: US and CT findings Accogli S, Aringhieri G, Scalise P, Angelini G, Pancrazi F, Bemi P, Bartolozzi C Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, University
Case 9799 Stanford type A aortic dissection: US and CT findings Accogli S, Aringhieri G, Scalise P, Angelini G, Pancrazi F, Bemi P, Bartolozzi C Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, University
Vascular Malformations
 Vascular Malformations LTC Robert Shih Chief of Neuroradiology Walter Reed Medical Center Special thanks to LTC Alice Smith (retired) Disclosures: None. This presentation reflects the personal views of
Vascular Malformations LTC Robert Shih Chief of Neuroradiology Walter Reed Medical Center Special thanks to LTC Alice Smith (retired) Disclosures: None. This presentation reflects the personal views of
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Am Coll Radiol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 June 24.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Am Coll Radiol. 2010 January ; 7(1): 73 76. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2009.06.015. Cerebral Aneurysms Janet C. Miller, DPhil, Joshua A.
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Am Coll Radiol. 2010 January ; 7(1): 73 76. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2009.06.015. Cerebral Aneurysms Janet C. Miller, DPhil, Joshua A.
MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases
 833 MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases D. Dormont 1 F. Gelbert 2 E. Assouline 2 D. Reizine 2 A. Helias 2 M. C. Riche 2 J. Chiras 1 J. Sories 1 J. J. Merland
833 MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases D. Dormont 1 F. Gelbert 2 E. Assouline 2 D. Reizine 2 A. Helias 2 M. C. Riche 2 J. Chiras 1 J. Sories 1 J. J. Merland
Applicable Neuroradiology
 For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
ORIGINAL ARTICLE COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY EVALUATION OF SPONTANEOUS INTRACRANIAL HAEMORRHAGE
 Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 4, pp 647-652, April, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 4, pp 647-652, April, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Dural Arteriovenous Malformations and Fistulae (DAVM S DAVF S)
 Jorge Guedes Campos NEUROIMAGING DEPARTMENT HOSPITAL SANTA MARIA UNIVERSITY OF LISBON PORTUGAL DEFINITION region of arteriovenous shunting confined to a leaflet of packymeninges often adjacent to a major
Jorge Guedes Campos NEUROIMAGING DEPARTMENT HOSPITAL SANTA MARIA UNIVERSITY OF LISBON PORTUGAL DEFINITION region of arteriovenous shunting confined to a leaflet of packymeninges often adjacent to a major
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
Time-resolved Magnetic Resonance Angiography for assessment of recanalization after coil embolization of visceral artery aneurysms
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2013; 78(1): 64-68 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.883769 CASE REPORT Received: 2012.09.29 Accepted: 2013.01.15 Time-resolved Magnetic Resonance Angiography for assessment of recanalization
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2013; 78(1): 64-68 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.883769 CASE REPORT Received: 2012.09.29 Accepted: 2013.01.15 Time-resolved Magnetic Resonance Angiography for assessment of recanalization
Transarterial Embolisation of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations
 Transarterial Embolisation of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations How Few Can You Do? G. WIKHOLM, C. LUNDQVIST*, P. SVENDSEN Section of Interventional Neuroradiology, Department of Radiology, * Department
Transarterial Embolisation of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations How Few Can You Do? G. WIKHOLM, C. LUNDQVIST*, P. SVENDSEN Section of Interventional Neuroradiology, Department of Radiology, * Department
Cerebral Aneurysms: Accuracy of 320 Detector Row Nonsubtracted and Subtracted Volumetric CT Angiography for Diagnosis 1
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Wenhua Chen, MD Wei
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Wenhua Chen, MD Wei
Neurosurgical decision making in structural lesions causing stroke. Dr Rakesh Ranjan MS, MCh, Dip NB (Neurosurgery)
 Neurosurgical decision making in structural lesions causing stroke Dr Rakesh Ranjan MS, MCh, Dip NB (Neurosurgery) Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Every year, an estimated 30,000 people in the United States experience
Neurosurgical decision making in structural lesions causing stroke Dr Rakesh Ranjan MS, MCh, Dip NB (Neurosurgery) Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Every year, an estimated 30,000 people in the United States experience
Distal anterior cerebral artery (DACA) aneurysms are. Case Report
 248 Formos J Surg 2010;43:248-252 Distal Anterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysm: an Infrequent Cause of Transient Ischemic Attack Followed by Diffuse Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Report of a Case Che-Chuan Wang
248 Formos J Surg 2010;43:248-252 Distal Anterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysm: an Infrequent Cause of Transient Ischemic Attack Followed by Diffuse Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Report of a Case Che-Chuan Wang
Angioarchitecture of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations and the Risk of Bleeding: An Analysis of Patients in Northeastern Malaysia
 Brief Communication Angioarchitecture of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations and the Risk of Bleeding: An Analysis of Patients in Northeastern Malaysia Shibani KanDai 1, Mohd Shafie abdullah 1, Nyi Nyi naing
Brief Communication Angioarchitecture of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations and the Risk of Bleeding: An Analysis of Patients in Northeastern Malaysia Shibani KanDai 1, Mohd Shafie abdullah 1, Nyi Nyi naing
Sciences, Sri Ramachandra Medical College and Research Institute, Chennai, India.
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Devara K V A, 1 Joseph S, 2 Uppu S C. 3 Spontaneous Subarachnoid Haemorrhage Due to Coarctation of Aorta and 1 Department of Radiology, Medall Healthcare Private Ltd, King
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Devara K V A, 1 Joseph S, 2 Uppu S C. 3 Spontaneous Subarachnoid Haemorrhage Due to Coarctation of Aorta and 1 Department of Radiology, Medall Healthcare Private Ltd, King
Role of Computed Tomography in Evaluation of Cerebrovascular Accidents.
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2017.3.2.RD10 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Role of Computed Tomography in Evaluation of Cerebrovascular Accidents. Rishikant Sinha 1, Ahmad Rizwan Karim 2
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2017.3.2.RD10 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Role of Computed Tomography in Evaluation of Cerebrovascular Accidents. Rishikant Sinha 1, Ahmad Rizwan Karim 2
Overview of imaging modalities for cerebral aneurysms
 Overview of imaging modalities for cerebral aneurysms Soroush Zaghi BIDMC PCE: Radiology August 2008 (Images from BIDMC, PACS.) Our Patient: Presentation Our patient is a 57 y/o woman who reports blowing
Overview of imaging modalities for cerebral aneurysms Soroush Zaghi BIDMC PCE: Radiology August 2008 (Images from BIDMC, PACS.) Our Patient: Presentation Our patient is a 57 y/o woman who reports blowing
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
ACUTE PANCREATITIS: NEW CLASSIFICATION OF AN OLD FOE. T Barrow, A Nasrullah, S Liong, V Rudralingam, S A Sukumar
 ACUTE PANCREATITIS: NEW CLASSIFICATION OF AN OLD FOE T Barrow, A Nasrullah, S Liong, V Rudralingam, S A Sukumar LEARNING OBJECTIVES q Through a series of cases illustrate the updated Atlanta symposium
ACUTE PANCREATITIS: NEW CLASSIFICATION OF AN OLD FOE T Barrow, A Nasrullah, S Liong, V Rudralingam, S A Sukumar LEARNING OBJECTIVES q Through a series of cases illustrate the updated Atlanta symposium
Brain Arteriovenous Malformations Endovascular Therapy and Associated Therapeutic Protocols Jorge Guedes Cabral de Campos
 Endovascular Therapy and Associated Therapeutic Protocols Jorge Guedes Cabral de Campos Neuroradiology Department Hospital de Santa Maria University of Lisbon CEREBRAL AVM CLINICAL / EPIDEMIOLOGY Brain
Endovascular Therapy and Associated Therapeutic Protocols Jorge Guedes Cabral de Campos Neuroradiology Department Hospital de Santa Maria University of Lisbon CEREBRAL AVM CLINICAL / EPIDEMIOLOGY Brain
Spontaneous ICH accounts for 10% 15% of cases
 J Neurosurg 117:761 766, 2012 Computed tomography angiography: improving diagnostic yield and cost effectiveness in the initial evaluation of spontaneous nonsubarachnoid intracerebral hemorrhage Clinical
J Neurosurg 117:761 766, 2012 Computed tomography angiography: improving diagnostic yield and cost effectiveness in the initial evaluation of spontaneous nonsubarachnoid intracerebral hemorrhage Clinical
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations. Bs. Nguyễn Ngọc Pi Doanh- Bs Đặng Ngọc Dũng Khoa Ngoại Thần Kinh
 Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations Bs. Nguyễn Ngọc Pi Doanh- Bs Đặng Ngọc Dũng Khoa Ngoại Thần Kinh Stroke Vascular Malformations of the Brain Epidemiology: - Incidence: 0.1%,
Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations Bs. Nguyễn Ngọc Pi Doanh- Bs Đặng Ngọc Dũng Khoa Ngoại Thần Kinh Stroke Vascular Malformations of the Brain Epidemiology: - Incidence: 0.1%,
New Frontiers in Intracerebral Hemorrhage
 New Frontiers in Intracerebral Hemorrhage Ryan Hakimi, DO, MS Director, Neuro ICU Director, Inpatient Neurology Services Greenville Health System Clinical Associate Professor Department of Medicine (Neurology)
New Frontiers in Intracerebral Hemorrhage Ryan Hakimi, DO, MS Director, Neuro ICU Director, Inpatient Neurology Services Greenville Health System Clinical Associate Professor Department of Medicine (Neurology)
From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is a Stroke? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is a Stroke? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair
Blunt Carotid Injury- CT Angiography is Adequate For Screening. Kelly Knudson, M.D. UCHSC April 3, 2006
 Blunt Carotid Injury- CT Angiography is Adequate For Screening Kelly Knudson, M.D. UCHSC April 3, 2006 CT Angiography vs Digital Subtraction Angiography Blunt carotid injury screening is one of the very
Blunt Carotid Injury- CT Angiography is Adequate For Screening Kelly Knudson, M.D. UCHSC April 3, 2006 CT Angiography vs Digital Subtraction Angiography Blunt carotid injury screening is one of the very
Neuroradiology MR Protocols
 Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 6434623, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6434623 Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male Jordan Nepute,
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 6434623, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6434623 Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male Jordan Nepute,
Introduction. Abstract. Michael Yannes 1, Jennifer V. Frabizzio, MD 1, and Qaisar A. Shah, MD 1 1
 Reversal of CT hypodensity after acute ischemic stroke Michael Yannes 1, Jennifer V. Frabizzio, MD 1, and Qaisar A. Shah, MD 1 1 Abington Memorial Hospital in Abington, Pennsylvania Abstract We report
Reversal of CT hypodensity after acute ischemic stroke Michael Yannes 1, Jennifer V. Frabizzio, MD 1, and Qaisar A. Shah, MD 1 1 Abington Memorial Hospital in Abington, Pennsylvania Abstract We report
Keywords: angiography, CTA, cerebral aneurysm, diagnostic yield, subarachnoid haemorrhage.
 Original research Volume 58 (1) 2011 A retrospective review of multi-slice CT and DSA reports in patients with non-traumatic subarachnoid haemorrhage and the resultant diagnostic yield of aneurysms E Marshall
Original research Volume 58 (1) 2011 A retrospective review of multi-slice CT and DSA reports in patients with non-traumatic subarachnoid haemorrhage and the resultant diagnostic yield of aneurysms E Marshall
Postoperative Assessment of Extracranial Intracranial Bypass by Time- Resolved 3D Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography Using Parallel Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2243 2247, October 2005 Postoperative Assessment of Extracranial Intracranial Bypass by Time- Resolved 3D Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography Using Parallel Imaging Kazuhiro Tsuchiya,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2243 2247, October 2005 Postoperative Assessment of Extracranial Intracranial Bypass by Time- Resolved 3D Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography Using Parallel Imaging Kazuhiro Tsuchiya,
Diagnostic Cerebral Angiography in Spontaneous Intracranial Haemorrhage: A Guide for Developing Countries
 Original Article Diagnostic Cerebral Angiography in Spontaneous Intracranial Haemorrhage: A Guide for Developing Countries Ishak Abu Bakar, Ibrahim Lutfi Shuaib, Abdul Rahman Mohd Ariff, Nyi Nyi Naing
Original Article Diagnostic Cerebral Angiography in Spontaneous Intracranial Haemorrhage: A Guide for Developing Countries Ishak Abu Bakar, Ibrahim Lutfi Shuaib, Abdul Rahman Mohd Ariff, Nyi Nyi Naing
with susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine
 Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Angel J. Lacerda MD PhD, Daisy Abreu MD, Julio A. Díaz MD, Sandro Perez MD, Julio C Martin MD, Daiyan Martin MD.
 Angel J. Lacerda MD PhD, Daisy Abreu MD, Julio A. Díaz MD, Sandro Perez MD, Julio C Martin MD, Daiyan Martin MD. Introduction: Spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage (SICH) represents one of the most severe
Angel J. Lacerda MD PhD, Daisy Abreu MD, Julio A. Díaz MD, Sandro Perez MD, Julio C Martin MD, Daiyan Martin MD. Introduction: Spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage (SICH) represents one of the most severe
Benign brain lesions
 Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Dynamic 3D MR Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vascular Malformations at 3T: A Technical Note
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:630 634, March 2005 Technical Note Dynamic 3D MR Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vascular Malformations at 3T: A Technical Note S. Ziyeh, R. Strecker, A. Berlis, J. Weber,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:630 634, March 2005 Technical Note Dynamic 3D MR Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vascular Malformations at 3T: A Technical Note S. Ziyeh, R. Strecker, A. Berlis, J. Weber,
Perioperative Management Of Extra-Ventricular Drains (EVD)
 Perioperative Management Of Extra-Ventricular Drains (EVD) Dr. Vijay Tarnal MBBS, FRCA Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Neuroanesthesiology Division of Head & Neck Anesthesiology Michigan Medicine
Perioperative Management Of Extra-Ventricular Drains (EVD) Dr. Vijay Tarnal MBBS, FRCA Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Neuroanesthesiology Division of Head & Neck Anesthesiology Michigan Medicine
Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis
 Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis Spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak is an important and underdiagnosed cause of new onset headache that is treatable. Cerebrospinal fluid
Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis Spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak is an important and underdiagnosed cause of new onset headache that is treatable. Cerebrospinal fluid
Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes
 Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes By Sheila Smith, MD Swedish Medical Center 1 Disclosures I have no disclosures 2 Course Objectives Review significance and differential
Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes By Sheila Smith, MD Swedish Medical Center 1 Disclosures I have no disclosures 2 Course Objectives Review significance and differential
CT of the Head, Spine, and Cerebral Vessels
 CT of the Head, Spine, and Cerebral Vessels Objectives Determine specific imaging plane used to acquire or reformat CT scan, i.e. sagittal, coronal, transverse, and offaxis or oblique. Assess and evaluate
CT of the Head, Spine, and Cerebral Vessels Objectives Determine specific imaging plane used to acquire or reformat CT scan, i.e. sagittal, coronal, transverse, and offaxis or oblique. Assess and evaluate
Renal vascular evaluation with 64 Multislice Computerized Tomography Daniela Stoisa, Fabrizzio E. Galiano, Andrés Quaranta, Roberto L.
 Renal vascular evaluation with 64 Multislice Computerized Tomography Daniela Stoisa, Fabrizzio E. Galiano, Andrés Quaranta, Roberto L. Villavicencio Footnote Diagnóstico Médico Oroño. Bv. Oroño 1515. 2000.
Renal vascular evaluation with 64 Multislice Computerized Tomography Daniela Stoisa, Fabrizzio E. Galiano, Andrés Quaranta, Roberto L. Villavicencio Footnote Diagnóstico Médico Oroño. Bv. Oroño 1515. 2000.
Anatomic Evaluation of the Circle of Willis: MR Angiography versus Intraarterial Digital Subtraction Angiography
 Anatomic Evaluation of the Circle of Willis: MR Angiography versus Intraarterial Digital Subtraction Angiography K. W. Stock, S. Wetzel, E. Kirsch, G. Bongartz, W. Steinbrich, and E. W. Radue PURPOSE:
Anatomic Evaluation of the Circle of Willis: MR Angiography versus Intraarterial Digital Subtraction Angiography K. W. Stock, S. Wetzel, E. Kirsch, G. Bongartz, W. Steinbrich, and E. W. Radue PURPOSE:
Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature Ashish Kumar Dwivedi, Pradeep Kumar,
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature Ashish Kumar Dwivedi, Pradeep Kumar,
Marc Norman, Ph.D. - Do Not Use without Permission 1. Cerebrovascular Accidents. Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry
 Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
Time-Dependent Test Characteristics of Head Computed Tomography in Patients Suspected of Nontraumatic Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
 Time-Dependent Test Characteristics of Head Computed Tomography in Patients Suspected of Nontraumatic Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Daan Backes, MSc; Gabriel J.E. Rinkel, MD; Hans Kemperman, PhD; Francisca H.H.
Time-Dependent Test Characteristics of Head Computed Tomography in Patients Suspected of Nontraumatic Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Daan Backes, MSc; Gabriel J.E. Rinkel, MD; Hans Kemperman, PhD; Francisca H.H.
Imaging in gastric cancer
 Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage
 July 2013 A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage John Dickson, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup
July 2013 A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage John Dickson, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup
Ultrasound diagnostics of a spontaneous arteriovenous fistula of the head and neck
 Case report Cite as: Zakharkina MV, Chechetkin O, Krotenkova MV, Konovalov RN: Ultrasound diagnostics of a spontaneous arteriovenous fistula of the head and neck.. Submitted: 29.03.2017 ccepted: 24.05.2017
Case report Cite as: Zakharkina MV, Chechetkin O, Krotenkova MV, Konovalov RN: Ultrasound diagnostics of a spontaneous arteriovenous fistula of the head and neck.. Submitted: 29.03.2017 ccepted: 24.05.2017
B. CT protocols for the spine
 B. CT protocols for the spine Poster No.: A-003 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Invited Speaker Topic: Neuro Authors: B. Tins; Oswestry/UK Keywords: CT, spine, diagnostic imaging protocol DOI: 10.1594/ecr2010/A-003
B. CT protocols for the spine Poster No.: A-003 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Invited Speaker Topic: Neuro Authors: B. Tins; Oswestry/UK Keywords: CT, spine, diagnostic imaging protocol DOI: 10.1594/ecr2010/A-003
A.J. Hauer Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae
 A.J. Hauer 27-06-2018 Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae Dural arteriovenous fistulae (davfs) epidemiology Pathological anastomoses (within the dural leaflets) between meningeal arteries and dural
A.J. Hauer 27-06-2018 Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae Dural arteriovenous fistulae (davfs) epidemiology Pathological anastomoses (within the dural leaflets) between meningeal arteries and dural
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT
 Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2508 2513, November/December 2005 Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2508 2513, November/December 2005 Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
Paediatric cerebrovascular CT angiography towards better image quality
 Original Article Paediatric cerebrovascular CT angiography towards better image quality Stefanie C. Thust, Wui Khean Kling Chong, Roxana Gunny, Asif Mazumder, Marius Poitelea, Anna Welsh, Ash Ederies,
Original Article Paediatric cerebrovascular CT angiography towards better image quality Stefanie C. Thust, Wui Khean Kling Chong, Roxana Gunny, Asif Mazumder, Marius Poitelea, Anna Welsh, Ash Ederies,
Specialised Services Policy: CP22. Stereotactic Radiosurgery
 Specialised Services Policy: CP22 Document Author: Assistant Director of Planning Executive Lead: Director of Planning ad Performance Approved by: Management Group Issue Date: 01 July 2015 Review Date:
Specialised Services Policy: CP22 Document Author: Assistant Director of Planning Executive Lead: Director of Planning ad Performance Approved by: Management Group Issue Date: 01 July 2015 Review Date:
Dr. Shakir Husain MD, DM, FINR Consultant & Chief of Services Department of NeuroEndoVascular Therapy & Stroke. Program Director
 EGAS MUNIZ FELLOWSHIP INTERVENTIONAL NEUROLOGY & STROKE Neurointervention is fast becoming an important subspecialty of neurosciences. There are many unexplored dimensions of these techniques, which may
EGAS MUNIZ FELLOWSHIP INTERVENTIONAL NEUROLOGY & STROKE Neurointervention is fast becoming an important subspecialty of neurosciences. There are many unexplored dimensions of these techniques, which may
I ntracranial haemorrhage is the main cause of morbidity and
 294 PAPER Concurrent arterial aneurysms in brain arteriovenous malformations with haemorrhagic presentation C Stapf, J P Mohr, J Pile-Spellman, R R Sciacca, A Hartmann, H C Schumacher, H Mast... See end
294 PAPER Concurrent arterial aneurysms in brain arteriovenous malformations with haemorrhagic presentation C Stapf, J P Mohr, J Pile-Spellman, R R Sciacca, A Hartmann, H C Schumacher, H Mast... See end
Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke
 Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
A review: Prediction model for the incidence rate of intracerebral hemorrhage
 2nd Information Technology and Mechatronics Engineering Conference (ITOEC 2016) A review: Prediction model for the incidence rate of intracerebral hemorrhage Kaikai Yin1, a, Le Zhang1, b *, Hua Feng2,c,
2nd Information Technology and Mechatronics Engineering Conference (ITOEC 2016) A review: Prediction model for the incidence rate of intracerebral hemorrhage Kaikai Yin1, a, Le Zhang1, b *, Hua Feng2,c,
Acute abdominal venous thromboses- the hyperdense noncontrast CT sign
 Acute abdominal venous thromboses- the hyperdense noncontrast CT sign Poster No.: C-1095 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Goldstein, K. Jhaveri; Toronto, ON/CA Keywords: Abdomen,
Acute abdominal venous thromboses- the hyperdense noncontrast CT sign Poster No.: C-1095 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Goldstein, K. Jhaveri; Toronto, ON/CA Keywords: Abdomen,
lek Magdalena Puławska-Stalmach
 lek Magdalena Puławska-Stalmach tytuł pracy: Kliniczne i radiologiczne aspekty tętniaków wewnątrzczaszkowych a wybór metody leczenia Summary An aneurysm is a localized, abnormal distended lumen of the
lek Magdalena Puławska-Stalmach tytuł pracy: Kliniczne i radiologiczne aspekty tętniaków wewnątrzczaszkowych a wybór metody leczenia Summary An aneurysm is a localized, abnormal distended lumen of the
Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction (UPJO) syndrome: imaging with Multidetector CT (MDCT) prior to minimally invasive treatment
 Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction (UPJO) syndrome: imaging with Multidetector CT (MDCT) prior to minimally invasive treatment Poster No.: C-1753 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E.
Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction (UPJO) syndrome: imaging with Multidetector CT (MDCT) prior to minimally invasive treatment Poster No.: C-1753 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E.
Bilaga 4 till rapport 1 (17)
 Bilaga 4 Tabeller, beskrivning av studier Bilaga 4 till rapport 1 (17) Bilddiagnostik vid misstanke om total hjärninfarkt en systematisk litteraturöversikt, rapport 282 (2018) SBU Statens beredning för
Bilaga 4 Tabeller, beskrivning av studier Bilaga 4 till rapport 1 (17) Bilddiagnostik vid misstanke om total hjärninfarkt en systematisk litteraturöversikt, rapport 282 (2018) SBU Statens beredning för
It has been demonstrated that postmortem MDCT, or virtual
 Published April 5, 2012 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2966 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.B. Smith G.E. Lattin Jr P. Berran H.T. Harcke Common and Expected Postmortem CT Observations Involving the Brain: Mimics of Antemortem
Published April 5, 2012 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2966 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.B. Smith G.E. Lattin Jr P. Berran H.T. Harcke Common and Expected Postmortem CT Observations Involving the Brain: Mimics of Antemortem
