Percutaneous Revascularization of Sole Arch Artery for Severe Cerebral Ischemia Resulting from Takayasu Arteritis
|
|
|
- Philip Potter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Percutaneous Revascularization of Sole Arch Artery for Severe Cerebral Ischemia Resulting from Takayasu Arteritis Sanjay Tyagi, MD, Mohit D. Gupta, MD, Praveen Singh, MD, Devendra Shrimal, MD, and M.P. Girish, MD PURPOSE: Takayasu arteritis (TA) is a rare form of inflammatory arteriopathy affecting the aorta and its major branches. Obstructive lesions of all arch vessels may lead to disabling neurologic symptoms. There is limited experience with endovascular revascularization in this situation. The present report describes immediate and follow-up results with stent-supported angioplasty of severely stenosed single patent arch arteries. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Angioplasty and stent placement were performed in 10 consecutive patients with TA (age, years; mean, 28.3 y 4.1) with cerebrovascular symptoms caused by severe stenotic lesions of supraaortic (ie, carotid, vertebral, and brachiocephalic) arteries. RESULTS: Angioplasty was attempted in 12 stenotic lesions: carotid (n 8), vertebral (n 2), and brachiocephalic (n 2). Eight lesions were discrete and four were diffuse. Balloon angioplasty and stent implantation were performed successfully in all patients. The luminal diameter increased from 0.84 mm 0.6 to 5.6 mm 0.7 (P <.001), and the diameter of stenosis was reduced from 81.1% 6.8% to 1.7% 3.3% (P <.001). No immediate procedure-related complication or neurologic deficits occurred. The symptoms improved in all patients. On follow-up (mean, 25 months 7; range, 3 49 months), eight patients were asymptomatic and two patients with diffuse stenosis had recurrence of neurologic symptoms. These patients had in-stent restenosis of the carotid artery, which was successfully treated with cutting balloon angioplasty. CONCLUSION: Stent-supported angioplasty of a sole supraaortic artery in TA is safe and effective and provides good symptomatic relief in patients with multiple stenoocclusive lesions of arch arteries. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2008; 19: Abbreviation: TA Takayasu arteritis TAKAYASU arteritis (TA) is an uncommon chronic, progressive inflammatory disease affecting the aorta, its major branches, and sometimes the pulmonary arteries (1). Stenosis and occlusion of supraaortic arteries is common. The subclavian artery is From the Department of Cardiology, G. B. Pant Hospital and Maulana Azad Medical College, Suite 125, First Floor Academic Building, New Delhi , India. Received January 14, 2008; final revision received September 5, 2008; accepted September 14, Address correspondence to S.T.; drsanjaytyagi@vsnl.com None of the authors have identified a conflict of interest. SIR, 2008 DOI: /j.jvir most frequently involved, followed by proximal segments of the brachiocephalic, carotid, and vertebral arteries; and the disease may manifest as brain and retinal ischemia (2). As a result of the slow, progressive nature of the disease, collateral vessel formation is common. Therefore, symptoms of cerebral ischemia are most often associated with obstructive lesions of multiple arch vessels. It may manifest as fainting spells on standing, altered sensorium, seizures, vertigo (especially when looking upward), or visual disturbance (2 4). Medical management with glucocorticoids and immunosuppressive agents is ineffective in reducing stenosis in the chronic phase. Diffuse, proximal, and multifocal involvement of the arch vessels in this disease makes surgical revascularization difficult. Surgical repair of stenoocclusive lesions at the origin of arch vessels is much more complex and requires an intrathoracic approach, as opposed to endarterectomy of cervical carotid bifurcation stenosis in atherosclerosis. Lesions in aortoarteritis are distinctly characterized by more diffuse involvement and require higher balloon pressures to dilate, with more residual stenosis and a higher restenosis rate (5). Angioplasty has emerged as the initial mode of treatment for aorta, renal, and subclavian artery stenosis caused by aortoarteritis (3,4,6). However, the role of this technique in the treatment of carotid, brachiocephalic, and vertebral artery lesions is limited to few reports 1699
2 1700 Revascularization of Arch Artery for Ischemia in Takayasu Arteritis December 2008 JVIR (7 9). We attempted to achieve palliation of cerebral symptoms by angioplasty of a sole severely stenotic arch artery to improve cerebral blood flow while avoiding a totally occluded artery. We report our initial and follow-up results of angioplasty and stent placement in the proximal carotid, vertebral, and brachiocephalic arteries. MATERIALS AND METHODS We retrospectively analyzed all patients with TA who presented to our institution between January 2000 and June 2006 (N 14) with symptoms suggestive of severe cerebral ischemia. The diagnosis of TA was based on clinical, laboratory, and angiographic findings as established by the Aortitis Syndrome Research Committee of Japan (10). There were four male subjects and six female subjects whose ages ranged from 11 to 42 years (mean, 28.3 y 4.1). Three patients had recurrent syncope and seven had presyncope as a presenting symptom. One patient had associated seizures. Three of these patients also reported blurring of vision. Four patients were in the active phase of disease, as evidenced by an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate. C-reactive protein was also increased in two of these patients. These four patients were administered glucocorticoids before their angioplasty procedures, but angioplasty was not delayed for more than 1 week in these patients as they had severe symptoms. A baseline angiographic study was performed to determine the extent of vascular disease. Patients underwent diagnostic aortic arch and abdominal aortography via a femoral approach under local anesthesia. Selective angiography of the stenosed artery was then performed to localize the site and extent of vessel involvement and distal circulation. Stenoses less than 2 cm in length were classified as discrete and those 2 cm or longer as diffuse. Angioplasty was performed in 10 patients for artery with severe stenosis ( 70%), and angioplasty was not attempted in vessels with total occlusion. Patients with subclavian artery angioplasty are not included in this series. Four patients with occlusion of all arch vessels were referred for surgical revascularization and are not included in this study. For the intervention, a 7-F, 90-cmlong Shuttle Flexor sheath (Cook, Bloomington, Indiana) was advanced over a 5-F cerebral diagnostic catheter into the proximal portion of the stenosed artery. Intravenous heparin (5,000 IU) was administered to maintain an activated clotting time of seconds during the procedure. The stenotic lesion was crossed with a floppy-tipped inch coronary guide wire, taking care not to enter the intracranial segment of the artery. The lesions were initially dilated with a monorail balloon 4 6 mm in diameter. The balloon was inflated for seconds with diluted contrast medium until the waist on the balloon disappeared or the rated burst pressure of the balloon was reached. Peripheral cutting balloons (4 6 mm diameter; Boston Scientific, Natick, Massachusetts) were used in four patients for initial dilation during the latter half of the study after these balloons became available. After balloon dilation, angiogram was obtained to assess the results. Balloon-expandable stents (5 7 mm in diameter; Express Vascular; Boston Scientific) were implanted in nine lesions, and self-expandable 7 9-mm nitinol stents (Smart Stent; Cordis, Miami Lakes, Florida) were implanted in three lesions. If the result was suboptimal after stent deployment, postdilation was performed with a high-pressure noncompliant balloon. No distal or proximal protection device was employed because these lesions are fibrotic, firm, and nonulcerated. All patients were given aspirin 150 mg/d and clopidogrel or ticlopidine daily for at least 3 days before the intervention, and this combination antiplatelet regimen was continued for 6 months. Thereafter, only aspirin 150 mg/d was given. Patients with evidence of disease activity as suggested by increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate were given oral steroids. Angioplasty was considered to be technically successful if the residual stenosis was less than 20% of the luminal diameter with at least a 50% increase compared with the pretreatment diameter. Patients were followed up at 1 month after treatment and then after 6 months, 12 months, and yearly. At each of these visits, independent neurologic examination was carried out by a neurologist. We recorded all procedure-related complications; transient ischemic attacks; nondisabling, disabling, and fatal strokes in the vertebrobasilar or carotid territory; myocardial infarctions; and deaths from any cause. The degree of residual stenosis immediately after endovascular treatment was measured on a posttreatment catheter angiogram. Patients were further followed up with Doppler ultrasound (US) examination at 6 months with or without catheter angiography in all patients. Approval for the study from the institutional ethical board was obtained, and after informed consent was obtained, repeat angiographic study was performed after 6 months in nine patients. One patient did not give consent for invasive follow-up study. Restenosis was defined by the presence of more than 50% restenosis on a follow-up angiogram. A cutting balloon 5 7 mm in diameter was passed over a inch guide wire and positioned across the stenosis. Two to three dilations with a cutting balloon at 6 8 atm for seconds were used to dilate the restenosis. The size of the cutting balloon was selected according to the diameter of the adjacent normal vessel. The cutting balloon was rotated between dilations. RESULTS Fourteen patients had severe involvement of arch arteries on aortograms. Four patients had total occlusion of all four arch vessels. These patients were sent for bypass graft surgery, as distal vessels are often patent in these patients despite proximal occlusion. Ten patients had total occlusion of three arch vessels along with a severe stenotic lesion in the only patent supraaortic vessel (ie, carotid, vertebral, or innominate). These patients were treated by stent-supported angioplasty and were prospectively followed up. Angioplasty was attempted on 12 lesions: carotid (n 8; 66.6%), vertebral (n 2; 16.6%), and brachiocephalic (n 2; 16.6%). Two patients who underwent brachiocephalic artery angioplasty also underwent carotid angioplasty (n 1) and vertebral artery dilation (n 1). Eight lesions were discrete (ie, 2 cm) and four were diffuse (ie, 2 cm). A peripheral cutting balloon was used in four cases, and balloon inflation at high pressure
3 Volume 19 Number 12 Tyagi et al 1701 ( 10 atm) was used for initial dilation in eight lesions. Patients who underwent cutting balloon angioplasty had better dilation with less dissection at lower pressure (6 8 atm) compared with balloon angioplasty. All lesions could be successfully dilated, with a variable degree of intimal tearing at the site of angioplasty. Stent implantation was performed in all patients, as the artery that had been treated with angioplasty was the sole major supply to the brain. Balloon-expandable stents were implanted in nine short-segment/ostial lesions, and self-expandable nitinol stents were implanted in three long-segment nonostial lesions. After angioplasty and stent implantation, the minimal luminal diameter increased from 0.84 mm 0.6 to 5.6 mm 0.7 (P.001), and the stenosis diameter was reduced from 81.1% 6.8% to 1.7% 3.3% (P.001; Figs 1,2). There were no procedure-related complications. No transient or permanent neurologic deficits occurred. All patients had relief of symptoms after successful angioplasty. During follow-up of 3 49 months (mean, 25 months 7), Doppler US was performed in all patients. It showed restenosis in two patients. Repeat angiographic study was performed in nine patients. One patient did not give consent for invasive follow-up study. Mild intimal hyperplasia was seen in all five patients with discrete stenosis at the time of angioplasty. Two of four patients with diffuse lesions (50%) developed restenosis. These two patients had recurrence of symptoms in the form of dizziness after 1 year. Both these patients were successfully treated with cutting balloon angioplasty. The stenosis could be effectively relieved without significant dissection with this technique. All patients continue to be free of neurologic symptoms. DISCUSSION TA is a chronic idiopathic inflammatory disease that affects large and medium-sized arteries. Clinical features reflect limb or organ ischemia resulting from stenosis or obliteration of the involved arteries. The inflammatory stage of the disease is treated with corticosteroids with the aim to arrest progression of existing lesions and prevent new lesions (11). In most Figure 1. (a) Selective angiogram of the brachiocephalic artery shows severe stenosis of the brachiocephalic artery and the origin of the right vertebral artery. The right carotid artery has long severe diffuse stenosis. Arch aortogram in this patient shows total occlusion of the left carotid and subclavian arteries. (b) Selective angiogram of brachiocephalic artery after angioplasty and stent implantation shows marked improvement in the lumen of the brachiocephalic and vertebral arteries. The patient had relief from recurrent syncope. Figure 2. (a) Selective angiogram shows severe long-segment stenosis of the right common carotid artery. The patient s vertebral, left common carotid, and left subclavian arteries were totally occluded, and the patient had recurrent syncope. (b) Angiogram shows marked improvement of the carotid artery lumen after angioplasty and selfexpandable nitinol stent placement. His symptoms were also relieved. patients, who present with chronicstage disease with severe stenosis and organ ischemia, revascularization is required (12). Lesions are often multifocal and often involve the ostium, producing irregularity, stenosis, or even total occlusion. Unlike atherosclerotic lesions, the vessels are firm, scarred, nonulcerated, and fibrotic (7). Carotid artery involvement in TA is common (6% 69%), with the left side more commonly involved than the right (13). Lupi-Herrera et al (14) showed that 6.8% of these patients developed hemiplegia and 4.5% had loss of vision at a mean follow-up of 33.2 months 37 (14). Cerebrovascular events contribute to 20% of the cases of mortality in these patients. Carotid artery bypass graft creation in this disease is associated with high rates of morbidity, mortality, cranial nerve injury, anastomotic narrowing, graft occlusion, and aneurysm formation. There may also be sudden increases in intracranial blood pressure after ca-
4 1702 Revascularization of Arch Artery for Ischemia in Takayasu Arteritis December 2008 JVIR rotid reconstruction, which may lead to cerebral hemorrhage. Severe and risky postoperative cerebral edema or ischemic reperfusion syndrome is encountered in approximately 10% of patients who are treated with surgical revascularization (12). Carotid angioplasty and stent placement are being evaluated in the treatment of carotid artery stenosis. However, most data have come from patients with atherosclerotic carotid artery involvement (15,16). The experience with carotid angioplasty in TA is limited (6 9,13,17). Our experience shows that carotid angioplasty and stent placement in patients with TA can be performed with excellent immediate and intermediateterm results. The excellent immediate results in this series could be a result of case selection with the exclusion of cases of total occlusion along with the use of cutting balloons and highpressure balloons for predilation of stenotic lesions (5). A majority of lesions dilated (75%) were short-segment lesions. The best results were obtained in short focal lesions. Long lesions tend to have incomplete dilation and are associated with a higher rate of restenosis (7). Angioplasty of a chronically occluded carotid artery is associated with a low initial success rate and high chances of restenosis. In TA, higher balloon inflation pressures are often required for dilation as a result of transmural fibrosis. In our limited experience, dilation with a cutting balloon proved to be safe and effective for initial dilation and treatment of in-stent restenosis. Balloons on the blade may help to overcome the hoop stress, leading to better dilation at lower pressures. Cerebral protection devices are not required in these nonatherosclerotic fibrotic lesions because atheroembolization is unlikely (5). Balloon-expandable stents were preferred in the present series because of their high radial strength and positioning ability, as these stenoses often involve the ostium. Self-expandable nitinol stents were preferred for long lesions away from the ostium. As the stenotic artery was the sole major supply to the brain, stents were used to enhance the safety of the procedure, which is analogous to left main coronary artery angioplasty. Balloon inflation was performed for a short duration (10 15 seconds), as longer inflation times may lead to convulsions resulting from cerebral ischemia, as other arch vessels are occluded. In aortic arteritis, stenosis of the extracranial vertebral artery is not infrequent. Kerr et al (10) reported incidences as high as 20% 40% in certain patient populations. There is a clear relationship between vertebral artery insufficiency and posterior circulation ischemia, but this is not commonly recognized because most patients can tolerate occlusion of one of the two vertebral arteries (18,19). The clinical significance of vertebral artery stenosis in aortoarteritis is underestimated in clinical practice. Surgical revascularization of an atherosclerotic vertebral artery is associated with relatively high rates of mortality (4.2%) and complications (10% 20%) such as nerve injury, as access to its origin is difficult, and pulmonary problems occur as a result of thoracotomy (20). Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty has emerged as an effective, safer therapeutic alternative to operative revascularization of proximal vertebral artery stenosis. To date there are approximately 150 reported cases of endovascular treatment with primary stent placement for extracranial vertebral artery stenosis. Most of these cases were atherosclerotic, and only few cases involved TA (8,21). These early reports have shown high technical success rates with incidences of complications (eg, minor stroke or transient ischemic attack) less than 3% and no related deaths during short-term follow-up. Angiography of the posterior and anterior circulation is required before angioplasty is performed. Special attention must also be paid to collateral supply from the contralateral vertebral artery, as well as the carotid artery, from which collateral vessels may reconstitute the distal vertebral artery in cases of vertebral occlusion or severe stenosis. The presence of bilateral disease and diffuse disease in arch vessels is associated with a higher risk of neurologic complications. Late presentation permitted palliative endovascular revascularization. Detection of cases at an earlier stage of disease ie, before total occlusion occurs could have enabled more complete revascularization by angioplasty of other stenotic arteries before the occlusive phase. The present series describes patients with TA with severe cerebrovascular symptoms in whom angioplasty and primary stent placement were performed to treat severe arch vessel stenosis. Although the present analysis is limited by its retrospective nature, small number of study subjects, and relatively short follow-up period, it shows that endoluminal stent placement of carotid and vertebral artery lesions is safe and effective and produces marked relief of symptoms and durable results, as evidenced by the low recurrence rate. It may be a suitable alternative to surgery in a select subgroup of patients, as it is associated with lower morbidity rates, good success rates, and shorter periods of hospitalization. However, further studies are needed to better define the role of endovascular treatment in such cases. References 1. Hotchi M. Pathological studies on Takayasu arteritis. Heart Vessels Suppl 1992; 7: Takahashi JC, Sakai N, Manaka H, et al. Multiple supra-aortic stent placement for Takayasu arteritis: extensive revascularization and two-year follow-up. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2002; 23: Tyagi S, Kaul UA, Nair M, et al. Balloon angioplasty of the aorta in Takayasu s arteritis: initial and long term results. Am Heart J 1992; 124: Tyagi S, Singh B, Kaul UA, et al. Balloon angioplasty for renovascular hypertension in Takayasu s arteritis. Am Heart J 1993; 25: Tyagi S, Verma PK, Gambhir DS, et al. Early and long-term results of subclavian angioplasty in aortoarteritis (Takayasu disease): comparison with atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 1998; 21: Min PK, Park S, Jung JH, et al. Endovascular therapy combined with immunosuppressive treatment for occlusive arterial disease in patients with Takayasu s arteritis. J Endovasc Ther 2005; 12: Hodgins GN, Dutton JN. Subclavian and carotid angioplasties for Takayasu arteritis. J Can Assoc Radiol 1982; 33: Joseph G, Pati PK, Mathews P. Multivessel cutting balloon angioplasty in a patient with type iii nonspecific aortoarteritis. Indian Heart J 2003; 55: Rath PC, Lakshmi G, Henry M. Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty using a cutting balloon for stenosis of
5 Volume 19 Number 12 Tyagi et al 1703 the arch vessels in aortoarteritis. Indian Heart J 2004; 56: Inada K, Swashima Y, Okada A, et al. Aortitis syndrome: the diagnostic criteria. Genai Iryo 1976; 8: Kerr GS. Takayasu arteritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 1995; 21: Wang ZG, Gu YQ, Wang SL, et al. Management of cerebral ischemia due to Takayasu s arteritis. Chinese Med J 2002; 115: Bali HK, Bhargava M, Bhatta YK, et al. Single stage bilateral common carotid artery stent placement in a patient of Takayasu arteritis. Neurol India 2001; 49: Lupi-Herrera E, Sanches-Torres G, Marcoshamer J, et al. Takayasu arteritis: clinical study of 107 cases. Am Heart J 1977; 83: Mathur A, Roubin GS, Iyer SS, et al. Predictors of stroke complicating carotid artery stenting. Circulation 1998; 97: Loftus IM, Thompson MM. The role of carotid stenting. J Endovasc Ther 2007; 14: Murakami R, Korogi Y, Matsuno Y, et al. Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty for carotid artery stenosis in Takayasu arteritis: persistent benefit over 10 years. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 1997; 20: Rocha-Singh K. Vertebral artery stenting: ready for prime time? Cathet Cardiovasc Interv 2001; 54: Chastain HD, Campbell MS, Iyer S, et al. Extracranial vertebral artery stent placement in-hospital and follow-up results. J Neurosurg 1999; 91: Higashida RT, Tsai FY, Halbach W, et al. Transluminal angioplasty for atherosclerotic disease of the vertebral and basilar arteries. J Neurosurg 1993; 78: Ko YG, Park S, Kim JY, et al. Percutaneous interventional treatment of extracranial vertebral artery stenosis with coronary stent. Yonsei Med J 2004; 45:
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Endovascular Therapies for Extracranial Vertebral Artery Disease File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: endovascular_therapies_for_extracranial_vertebral_artery_disease
Corporate Medical Policy Endovascular Therapies for Extracranial Vertebral Artery Disease File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: endovascular_therapies_for_extracranial_vertebral_artery_disease
9 : , cutting balloon 9 : , PTA cutting balloon. bruit. 4 cutting balloon. WBC 5300 µl CRP 0.1 ESR. Hb 11.8 A G. X CT Fig.
 9 : 659-663, 2000 4 cutting balloon 29 bruit angiography 4 cutting balloon cutting balloon 9 : 659-663, 2000 PTA cutting balloon 4 cutting balloon 765-0001 2-1-1 2000 7 12 2000 9 26 29 18 1999 3 bruit
9 : 659-663, 2000 4 cutting balloon 29 bruit angiography 4 cutting balloon cutting balloon 9 : 659-663, 2000 PTA cutting balloon 4 cutting balloon 765-0001 2-1-1 2000 7 12 2000 9 26 29 18 1999 3 bruit
Subclavian and Vertebral Artery Angioplasty - Vertebro-basilar Insufficiency: Clinical Aspects and Diagnosis
 HOSPITAL CHRONICLES 2008, 3(3): 136 140 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Subclavian and Vertebral Artery Angioplasty - Vertebro-basilar Insufficiency: Clinical Aspects and Diagnosis Antonios Polydorou, MD Hemodynamic
HOSPITAL CHRONICLES 2008, 3(3): 136 140 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Subclavian and Vertebral Artery Angioplasty - Vertebro-basilar Insufficiency: Clinical Aspects and Diagnosis Antonios Polydorou, MD Hemodynamic
Subclavian artery Stenting
 Subclavian artery Stenting Etiology Atherosclerosis Takayasu s arteritis Fibromuscular dysplasia Giant Cell Arteritis Radiation-induced Vascular Injury Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Neurofibromatosis Incidence
Subclavian artery Stenting Etiology Atherosclerosis Takayasu s arteritis Fibromuscular dysplasia Giant Cell Arteritis Radiation-induced Vascular Injury Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Neurofibromatosis Incidence
SCAI Fall Fellows Course Subclavian/Innominate Case Presentation
 SCAI Fall Fellows Course 2012 Subclavian/Innominate Case Presentation Daniel J. McCormick DO, FACC, FSCAI Director, Cardiovascular Interventional Therapy Pennsylvania Hospital University of Pennsylvania
SCAI Fall Fellows Course 2012 Subclavian/Innominate Case Presentation Daniel J. McCormick DO, FACC, FSCAI Director, Cardiovascular Interventional Therapy Pennsylvania Hospital University of Pennsylvania
CAROTID ARTERY ANGIOPLASTY
 CAROTID ARTERY ANGIOPLASTY Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical Coverage Guideline
CAROTID ARTERY ANGIOPLASTY Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical Coverage Guideline
CIC Edizioni Internazionali. original article
 G Chir Vol. 36 - n. 4 - pp. 161-167 July-August 2015 The results of treatment in renal artery stenosis due to Takayasu disease: comparison between surgery, angioplasty, and stenting. A monocentrique retrospective
G Chir Vol. 36 - n. 4 - pp. 161-167 July-August 2015 The results of treatment in renal artery stenosis due to Takayasu disease: comparison between surgery, angioplasty, and stenting. A monocentrique retrospective
Overview of Subclavian & Innominate Artery Interventions
 TCT 2016 Washington, DC, USA Tuesday November 1st, 2016 Peripheral vascular interventions Overview of Subclavian & Innominate Artery Interventions Dr Jacques Busquet Vascular & Endovascular Surgery Paris,
TCT 2016 Washington, DC, USA Tuesday November 1st, 2016 Peripheral vascular interventions Overview of Subclavian & Innominate Artery Interventions Dr Jacques Busquet Vascular & Endovascular Surgery Paris,
Vivek R. Deshmukh, MD Director, Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery Chairman, Department of Neurosurgery Providence Brain and Spine
 Vivek R. Deshmukh, MD Director, Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery Chairman, Department of Neurosurgery Providence Brain and Spine Institute The Oregon Clinic Disclosure I declare that neither
Vivek R. Deshmukh, MD Director, Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery Chairman, Department of Neurosurgery Providence Brain and Spine Institute The Oregon Clinic Disclosure I declare that neither
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service
 M AY. 6. 2011 10:37 A M F D A - C D R H - O D E - P M O N O. 4147 P. 1 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue Document Control
M AY. 6. 2011 10:37 A M F D A - C D R H - O D E - P M O N O. 4147 P. 1 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue Document Control
Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke
 Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
Occlusion of All Four Extracranial Vessels With Minimal Clinical Symptomatology. Case Report
 Occlusion of All Four Extracranial Vessels With Minimal Clinical Symptomatology. Case Report BY JIRI J. VITEK, M.D., JAMES H. HALSEY, JR., M.D., AND HOLT A. McDOWELL, M.D. Abstract: Occlusion of All Four
Occlusion of All Four Extracranial Vessels With Minimal Clinical Symptomatology. Case Report BY JIRI J. VITEK, M.D., JAMES H. HALSEY, JR., M.D., AND HOLT A. McDOWELL, M.D. Abstract: Occlusion of All Four
Aortic arch pathology. Cerebral ischemia following carotid artery stenosis.
 Important: -Subclavian Steal Syndrome -Cerebral ischemia Aortic arch pathology. Cerebral ischemia following carotid artery stenosis. Mina Aubeed & Alba Hernández Pinilla Aortic arch pathology Common arch
Important: -Subclavian Steal Syndrome -Cerebral ischemia Aortic arch pathology. Cerebral ischemia following carotid artery stenosis. Mina Aubeed & Alba Hernández Pinilla Aortic arch pathology Common arch
Takayasu s Arteritis: A Case Report With Global Arterial Involvement
 1 Case Report Takayasu s Arteritis: A Case Report With Global Arterial Involvement Waqas Ahmed, Zeeshan Ahmad* From Shifa International Hospital H-8/4, Islamabad, Pakistan Correspondence: Dr Waqas Ahmed,
1 Case Report Takayasu s Arteritis: A Case Report With Global Arterial Involvement Waqas Ahmed, Zeeshan Ahmad* From Shifa International Hospital H-8/4, Islamabad, Pakistan Correspondence: Dr Waqas Ahmed,
2017 Cardiology Survival Guide
 2017 Cardiology Survival Guide Chapter 2: Angioplasty/Atherectomy/Stent The term angioplasty literally means "blood vessel repair." During an angioplasty procedure, the physician inserts a catheter, with
2017 Cardiology Survival Guide Chapter 2: Angioplasty/Atherectomy/Stent The term angioplasty literally means "blood vessel repair." During an angioplasty procedure, the physician inserts a catheter, with
RadRx Your Prescription for Accurate Coding & Reimbursement Copyright All Rights Reserved.
 Interventional Radiology Coding Case Studies Prepared by Stacie L. Buck, RHIA, CCS-P, RCC, CIRCC, AAPC Fellow President & Senior Consultant Week of November 19, 2018 Abdominal Aortogram, Bilateral Runoff
Interventional Radiology Coding Case Studies Prepared by Stacie L. Buck, RHIA, CCS-P, RCC, CIRCC, AAPC Fellow President & Senior Consultant Week of November 19, 2018 Abdominal Aortogram, Bilateral Runoff
Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Abnormalities after Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty and Stenting for Intracranial Atherosclerotic Disease
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:385 389, February 2005 Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Abnormalities after Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty and Stenting for Intracranial Atherosclerotic Disease Tomoyuki Tsumoto
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:385 389, February 2005 Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Abnormalities after Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty and Stenting for Intracranial Atherosclerotic Disease Tomoyuki Tsumoto
Non Atheromatous Lesions Fibromuscular Dysplasia. Rod Samuelson, MD Babak Jahromi,, MD Elad Levy, MD Adnan Siddiqui,, PhD, MD Nick Hopkins, MD
 Non Atheromatous Lesions Fibromuscular Dysplasia Rod Samuelson, MD Babak Jahromi,, MD Elad Levy, MD Adnan Siddiqui,, PhD, MD Nick Hopkins, MD Presenter Disclosure Information L. Nelson Hopkins MD FINANCIAL
Non Atheromatous Lesions Fibromuscular Dysplasia Rod Samuelson, MD Babak Jahromi,, MD Elad Levy, MD Adnan Siddiqui,, PhD, MD Nick Hopkins, MD Presenter Disclosure Information L. Nelson Hopkins MD FINANCIAL
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Safety of Latest-Generation Self-expanding Stents in Patients With NASCET-Ineligible Severe Symptomatic Extracranial Internal Carotid Artery Stenosis Italo Linfante, MD; Joshua A.
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Safety of Latest-Generation Self-expanding Stents in Patients With NASCET-Ineligible Severe Symptomatic Extracranial Internal Carotid Artery Stenosis Italo Linfante, MD; Joshua A.
Advances in the treatment of posterior cerebral circulation symptomatic disease
 Advances in the treatment of posterior cerebral circulation symptomatic disease Athanasios D. Giannoukas MD, MSc(Lond.), PhD(Lond.), FEBVS Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine, School of Health
Advances in the treatment of posterior cerebral circulation symptomatic disease Athanasios D. Giannoukas MD, MSc(Lond.), PhD(Lond.), FEBVS Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine, School of Health
Although moyamoya disease, a rare cerebrovascular occlusive
 Renal Artery Lesions in Patients With Moyamoya Disease Angiographic Findings Ichiro Yamada, MD; Yoshiro Himeno, MD; Yoshiharu Matsushima, MD; Hitoshi Shibuya, MD Background and Purpose Renal artery lesions
Renal Artery Lesions in Patients With Moyamoya Disease Angiographic Findings Ichiro Yamada, MD; Yoshiro Himeno, MD; Yoshiharu Matsushima, MD; Hitoshi Shibuya, MD Background and Purpose Renal artery lesions
Comparison Of Primary Long Stenting Versus Primary Short Stenting For Long Femoropopliteal Artery Disease (PARADE)
 Comparison Of Primary Long Stenting Versus Primary Short Stenting For Long Femoropopliteal Artery Disease (PARADE) Young-Guk Ko, M.D. Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University Health System,
Comparison Of Primary Long Stenting Versus Primary Short Stenting For Long Femoropopliteal Artery Disease (PARADE) Young-Guk Ko, M.D. Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University Health System,
Guidelines for Ultrasound Surveillance
 Guidelines for Ultrasound Surveillance Carotid & Lower Extremity by Ian Hamilton, Jr, MD, MBA, RPVI, FACS Corporate Medical Director BlueCross BlueShield of Tennessee guidelines for ultrasound surveillance
Guidelines for Ultrasound Surveillance Carotid & Lower Extremity by Ian Hamilton, Jr, MD, MBA, RPVI, FACS Corporate Medical Director BlueCross BlueShield of Tennessee guidelines for ultrasound surveillance
Extracranial Carotid Artery Stenting With or Without Distal Protection Device
 Extracranial Carotid Artery Stenting With or Without Distal Protection Device Eak-Kyun Shin MD. Professor of Medicine Division of Cardiology, Heart Center, Gil Medical Center Gacheon Medical School Incheon,
Extracranial Carotid Artery Stenting With or Without Distal Protection Device Eak-Kyun Shin MD. Professor of Medicine Division of Cardiology, Heart Center, Gil Medical Center Gacheon Medical School Incheon,
Management of Ruptures Complicating Angioplasty and Stenting of Supraaortic Arteries: Report of Two Cases and a Review of the Literature
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:2057 2061, November/December 2003 Case Report Management of Ruptures Complicating Angioplasty and Stenting of Supraaortic Arteries: Report of Two Cases and a Review of the Literature
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:2057 2061, November/December 2003 Case Report Management of Ruptures Complicating Angioplasty and Stenting of Supraaortic Arteries: Report of Two Cases and a Review of the Literature
Current Role of Renal Artery Stenting in Patients with Renal Artery Stenosis
 Current Role of Renal Artery Stenting in Patients with Renal Artery Stenosis Young-Guk Ko, M.D. Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Etiology Fibromuscular
Current Role of Renal Artery Stenting in Patients with Renal Artery Stenosis Young-Guk Ko, M.D. Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Etiology Fibromuscular
O ne quarter of strokes occur in the posterior
 586 PAPER Vertebral artery origin angioplasty and primary stenting: safety and restenosis rates in a prospective series G C Cloud, F Crawley, A Clifton, DJHMcCabe, M M Brown, H S Markus... See end of article
586 PAPER Vertebral artery origin angioplasty and primary stenting: safety and restenosis rates in a prospective series G C Cloud, F Crawley, A Clifton, DJHMcCabe, M M Brown, H S Markus... See end of article
Patients with symptomatic atherosclerotic stenosis of the
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH B. Du E.H.C. Wong W.-J. Jiang Long-Term Outcome of Tandem Stenting for Stenoses of the Intracranial Vertebrobasilar Artery and Vertebral Ostium BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Patients with symptomatic
ORIGINAL RESEARCH B. Du E.H.C. Wong W.-J. Jiang Long-Term Outcome of Tandem Stenting for Stenoses of the Intracranial Vertebrobasilar Artery and Vertebral Ostium BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Patients with symptomatic
How to manage the left subclavian and left vertebral artery during TEVAR
 How to manage the left subclavian and left vertebral artery during TEVAR Jürg Schmidli Chief of Vascular Surgery Inselspital Hamburg 2017 Dept Cardiovascular Surgery, Bern, Switzerland Disclosure No Disclosures
How to manage the left subclavian and left vertebral artery during TEVAR Jürg Schmidli Chief of Vascular Surgery Inselspital Hamburg 2017 Dept Cardiovascular Surgery, Bern, Switzerland Disclosure No Disclosures
Endovascular treatment for pseudoocclusion of the internal carotid artery
 Endovascular treatment for pseudoocclusion of the internal carotid artery Daqiao Guo, Xiao Tang, Weiguo Fu Institute of Vascular Surgery, Fudan University, Department of Vascular Surgery, Zhongshan Hospital
Endovascular treatment for pseudoocclusion of the internal carotid artery Daqiao Guo, Xiao Tang, Weiguo Fu Institute of Vascular Surgery, Fudan University, Department of Vascular Surgery, Zhongshan Hospital
Malperfusion Syndromes Type B Aortic Dissection with Malperfusion
 Malperfusion Syndromes Type B Aortic Dissection with Malperfusion Jade S. Hiramoto, MD, MAS April 27, 2012 Associated with early mortality Occurs when there is end organ ischemia secondary to aortic branch
Malperfusion Syndromes Type B Aortic Dissection with Malperfusion Jade S. Hiramoto, MD, MAS April 27, 2012 Associated with early mortality Occurs when there is end organ ischemia secondary to aortic branch
Cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome after carotid angioplasty
 case report Cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome after carotid angioplasty Zoran Miloševič 1, Bojana Žvan 2, Marjan Zaletel 2, Miloš Šurlan 1 1 Institute of Radiology, 2 University Neurology Clinic, University
case report Cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome after carotid angioplasty Zoran Miloševič 1, Bojana Žvan 2, Marjan Zaletel 2, Miloš Šurlan 1 1 Institute of Radiology, 2 University Neurology Clinic, University
Updated Society for Vascular Surgery guidelines for management of extracranial carotid disease: Executive summary
 SOCIETY FOR VASCULAR SURGERY DOCUMENT Updated Society for Vascular Surgery guidelines for management of extracranial carotid disease: Executive summary John J. Ricotta, MD, a Ali AbuRahma, MD, FACS, b
SOCIETY FOR VASCULAR SURGERY DOCUMENT Updated Society for Vascular Surgery guidelines for management of extracranial carotid disease: Executive summary John J. Ricotta, MD, a Ali AbuRahma, MD, FACS, b
Intro: Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Basic understanding of interventional radiology. Gain knowledge of key terms and phrases
 Slide 1 Intro: PRESENTED BY: Selena M. Moore, AAS, CCS, CPC HIMS Physician Liaison Coder This is a modified/updated presentation that was originally written by: Rosemary Waligorski, RHIT, CCS, RCC and
Slide 1 Intro: PRESENTED BY: Selena M. Moore, AAS, CCS, CPC HIMS Physician Liaison Coder This is a modified/updated presentation that was originally written by: Rosemary Waligorski, RHIT, CCS, RCC and
BC Vascular Day. Contents. November 3, Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 2 3. Peripheral Arterial Disease 4 6. Deep Venous Thrombosis 7 8
 BC Vascular Day Contents Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 2 3 November 3, 2018 Peripheral Arterial Disease 4 6 Deep Venous Thrombosis 7 8 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Conservative Management Risk factor modification
BC Vascular Day Contents Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 2 3 November 3, 2018 Peripheral Arterial Disease 4 6 Deep Venous Thrombosis 7 8 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Conservative Management Risk factor modification
The learning curve associated with intracranial angioplasty and stenting: analysis from a single center
 Original Article Page 1 of 7 The learning curve associated with intracranial angioplasty and stenting: analysis from a single center Peiquan Zhou, Guang Zhang, Zhiyong Ji, Shancai Xu, Huaizhang Shi Department
Original Article Page 1 of 7 The learning curve associated with intracranial angioplasty and stenting: analysis from a single center Peiquan Zhou, Guang Zhang, Zhiyong Ji, Shancai Xu, Huaizhang Shi Department
SAMMPRIS. Stenting and Aggressive Medical Management for Preventing Recurrent Stroke and Intracranial Stenosis. Khalil Zahra, M.D
 SAMMPRIS Stenting and Aggressive Medical Management for Preventing Recurrent Stroke and Intracranial Stenosis Khalil Zahra, M.D Major points Patients with recent TIA or stroke and intra-cranial artery
SAMMPRIS Stenting and Aggressive Medical Management for Preventing Recurrent Stroke and Intracranial Stenosis Khalil Zahra, M.D Major points Patients with recent TIA or stroke and intra-cranial artery
Predictors of restenosis and cardiovascular events in patients undergoing percutaneous angioplasty for subclavian/innominate artery stenosis
 Predictors of restenosis and cardiovascular events in patients undergoing percutaneous angioplasty for subclavian/innominate artery stenosis Tadeusz Przewlocki, Anna Kablak Ziembicka, Piotr Pieniazek,
Predictors of restenosis and cardiovascular events in patients undergoing percutaneous angioplasty for subclavian/innominate artery stenosis Tadeusz Przewlocki, Anna Kablak Ziembicka, Piotr Pieniazek,
Lower Extremity Endovascular Revascularization Codes
 Lower Extremity Endovascular Update: AAPC National Long Beach, CA April 4, 2011 Presented by: David Zielske, MD, CIRCC, CPC H, CCC, CCS, RCC Lower Extremity Endovascular Revascularization Codes 37220 37235
Lower Extremity Endovascular Update: AAPC National Long Beach, CA April 4, 2011 Presented by: David Zielske, MD, CIRCC, CPC H, CCC, CCS, RCC Lower Extremity Endovascular Revascularization Codes 37220 37235
Case Report 1. CTA head. (c) Tele3D Advantage, LLC
 Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Stent placement for vertebral artery occlusive disease: preliminary clinical experience
 Neurosurg Focus 5 (4):Article 15, 1998 Stent placement for vertebral artery occlusive disease: preliminary clinical experience Richard D. Fessler, M.D., Ajay K. Wakhloo, M.D., Ph.D., Giuseppe Lanzino,
Neurosurg Focus 5 (4):Article 15, 1998 Stent placement for vertebral artery occlusive disease: preliminary clinical experience Richard D. Fessler, M.D., Ajay K. Wakhloo, M.D., Ph.D., Giuseppe Lanzino,
타카야수혈관염환자에서발생한관상동맥-쇄골하동맥도류증후군
 대한내과학회지 : 제 91 권제 1 호 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.3904/kjm.2016.91.1.37 타카야수혈관염환자에서발생한관상동맥-쇄골하동맥도류증후군 성균관대학교의과대학 1 삼성서울병원내과, 심장뇌혈관병원 2 순환기내과, 3 흉부외과, 4 영상의학과 김민선 1 백남영 1 최승혁 2 김욱성 3 김성목 4 전평 4 김덕경 2 Coronary-subclavian
대한내과학회지 : 제 91 권제 1 호 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.3904/kjm.2016.91.1.37 타카야수혈관염환자에서발생한관상동맥-쇄골하동맥도류증후군 성균관대학교의과대학 1 삼성서울병원내과, 심장뇌혈관병원 2 순환기내과, 3 흉부외과, 4 영상의학과 김민선 1 백남영 1 최승혁 2 김욱성 3 김성목 4 전평 4 김덕경 2 Coronary-subclavian
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty and Stenting for Pulmonary Stenosis Due to Takayasu s Arteritis: Clinical Outcome and Four-year Follow-up
 Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty and Stenting for Pulmonary Stenosis Due to Takayasu s Arteritis: Clinical Outcome and Four-year Follow-up Address for correspondence: Liu Zhi-Hong, MD Center for Pulmonary
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty and Stenting for Pulmonary Stenosis Due to Takayasu s Arteritis: Clinical Outcome and Four-year Follow-up Address for correspondence: Liu Zhi-Hong, MD Center for Pulmonary
Neuro-Vascular Intervention AAPC Regional Conference Springfield, MA
 Neuro-Vascular Intervention AAPC Regional Conference Springfield, MA October 8, 2010 1 Presented by: David Zielske, MD,CIRCC, CPC H, CCC, CCS, RCC General Recommendations for Physician Dictations State
Neuro-Vascular Intervention AAPC Regional Conference Springfield, MA October 8, 2010 1 Presented by: David Zielske, MD,CIRCC, CPC H, CCC, CCS, RCC General Recommendations for Physician Dictations State
Contemporary management of brachiocephalic occlusive disease. TM Sullivan Minneapolis, MN
 Contemporary management of brachiocephalic occlusive disease TM Sullivan Minneapolis, MN WL Gore & Associates Disclosures Meeting organizer (SOAR) CR Bard Chair, CEC Bolster trial Veryan National PI, MIMICS
Contemporary management of brachiocephalic occlusive disease TM Sullivan Minneapolis, MN WL Gore & Associates Disclosures Meeting organizer (SOAR) CR Bard Chair, CEC Bolster trial Veryan National PI, MIMICS
Beyond Stenosis Severity: Top 5 Important Duplex Characteristics to Identify in a Patient with Carotid Disease
 Beyond Stenosis Severity: Top 5 Important Duplex Characteristics to Identify in a Patient with Carotid Disease Jan M. Sloves RVT, RCS, FASE Technical Director New York Cardiovascular Associates Disclosures
Beyond Stenosis Severity: Top 5 Important Duplex Characteristics to Identify in a Patient with Carotid Disease Jan M. Sloves RVT, RCS, FASE Technical Director New York Cardiovascular Associates Disclosures
There are multiple endovascular options for treatment
 Peripheral Rotablator Atherectomy: The Below-the-Knee Approach to Address Calcium Head On Peripheral Rotablator s front-cutting, diamond-tipped burr provides stable rotation in calcified lesions. BY SONYA
Peripheral Rotablator Atherectomy: The Below-the-Knee Approach to Address Calcium Head On Peripheral Rotablator s front-cutting, diamond-tipped burr provides stable rotation in calcified lesions. BY SONYA
Recommendations for Follow-up After Vascular Surgery Arterial Procedures SVS Practice Guidelines
 Recommendations for Follow-up After Vascular Surgery Arterial Procedures 2018 SVS Practice Guidelines vsweb.org/svsguidelines About the guidelines Published in the July 2018 issue of Journal of Vascular
Recommendations for Follow-up After Vascular Surgery Arterial Procedures 2018 SVS Practice Guidelines vsweb.org/svsguidelines About the guidelines Published in the July 2018 issue of Journal of Vascular
Carotid Artery Stenting (CAS) Pathophysiology. Technical Considerations. Plaque characteristics: relevant concepts. CAS and CEA
 Carotid Artery Stenting (CAS) Carotid Artery Stenting for Stroke Risk Reduction Matthew A. Corriere MD, MS, RPVI Assistant Professor of Surgery Department of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Rationale:
Carotid Artery Stenting (CAS) Carotid Artery Stenting for Stroke Risk Reduction Matthew A. Corriere MD, MS, RPVI Assistant Professor of Surgery Department of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Rationale:
Turbo-Power. Laser atherectomy catheter. The standard. for ISR
 Turbo-Power Laser atherectomy catheter The standard for ISR Vaporize the ISR challenge In-stent restenosis (ISR) Chance of recurring 7 115,000 + /year (U.S.) 1-6 Repeated narrowing of the arteries after
Turbo-Power Laser atherectomy catheter The standard for ISR Vaporize the ISR challenge In-stent restenosis (ISR) Chance of recurring 7 115,000 + /year (U.S.) 1-6 Repeated narrowing of the arteries after
CAROTID ARTERY ANGIOPLASTY
 CAROTID ARTERY ANGIOPLASTY Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and
CAROTID ARTERY ANGIOPLASTY Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and
Clinical Study Endovascular Recanalization for Chronic Symptomatic Intracranial Vertebral Artery Total Occlusion
 Minimally Invasive Surgery, Article ID 949585, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/949585 Clinical Study Endovascular Recanalization for Chronic Symptomatic Intracranial Vertebral Artery Total Occlusion
Minimally Invasive Surgery, Article ID 949585, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/949585 Clinical Study Endovascular Recanalization for Chronic Symptomatic Intracranial Vertebral Artery Total Occlusion
Durability of percutaneous transluminal angioplasty for obstructive lesions of proximal subclavian artery: Long-term results
 From the Society for Vascular Surgery Durability of percutaneous transluminal angioplasty for obstructive lesions of proximal subclavian artery: Long-term results Jean-Paul P. M. de Vries, MD, PhD, a L.
From the Society for Vascular Surgery Durability of percutaneous transluminal angioplasty for obstructive lesions of proximal subclavian artery: Long-term results Jean-Paul P. M. de Vries, MD, PhD, a L.
Index. interventional.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACAS (Asymptomatic Carotid Atherosclerosis Study), 65 66 ACST (Asymptomatic Carotid Surgery Trial), 6 7, 65, 75 Age factors, in carotid
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACAS (Asymptomatic Carotid Atherosclerosis Study), 65 66 ACST (Asymptomatic Carotid Surgery Trial), 6 7, 65, 75 Age factors, in carotid
Treatment Considerations for Carotid Artery Stenosis. Danielle Zielinski, RN, MSN, ACNP Rush University Neurosurgery
 Treatment Considerations for Carotid Artery Stenosis Danielle Zielinski, RN, MSN, ACNP Rush University Neurosurgery 4.29.2016 There is no actual or potential conflict of interest in regards to this presentation
Treatment Considerations for Carotid Artery Stenosis Danielle Zielinski, RN, MSN, ACNP Rush University Neurosurgery 4.29.2016 There is no actual or potential conflict of interest in regards to this presentation
SAMPLE EDITION PELVIC AND LOWER EXTREMITY ARTERIES WITH ENDOVASCULAR REVASCULARIZATION. Cardiovascular Illustrations and Guidelines
 Cardiovascular Illustrations and Guidelines PELVIC AND LOWER EXTREMITY ARTERIES WITH ENDOVASCULAR REVASCULARIZATION ANGIOPLASTY INTRAVASCULAR STENT PLACEMENT ATHERECTOMY For Fem-Pop Territory Angioplasty
Cardiovascular Illustrations and Guidelines PELVIC AND LOWER EXTREMITY ARTERIES WITH ENDOVASCULAR REVASCULARIZATION ANGIOPLASTY INTRAVASCULAR STENT PLACEMENT ATHERECTOMY For Fem-Pop Territory Angioplasty
RadRx Your Prescription for Accurate Coding & Reimbursement Copyright All Rights Reserved.
 Interventional Radiology Coding Case Studies Prepared by Stacie L. Buck, RHIA, CCS-P, RCC, CIRCC, AAPC Fellow President & Senior Consultant Week of June 4, 2018 Thrombolysis, Thrombectomy & Angioplasty
Interventional Radiology Coding Case Studies Prepared by Stacie L. Buck, RHIA, CCS-P, RCC, CIRCC, AAPC Fellow President & Senior Consultant Week of June 4, 2018 Thrombolysis, Thrombectomy & Angioplasty
Takayasu disease Is it still a room for intervention? NO YES. BUT
 Takayasu disease Is it still a room for intervention? NO YES. BUT Z. Tazi Mezalek Internal Medicine Department Mohammed V University Ibn Sina Hospital - Rabat - Maroc Disclosure Speaker name: TAZI MEZALEK
Takayasu disease Is it still a room for intervention? NO YES. BUT Z. Tazi Mezalek Internal Medicine Department Mohammed V University Ibn Sina Hospital - Rabat - Maroc Disclosure Speaker name: TAZI MEZALEK
Left Subclavian Artery Stenosis in Coronary Artery Bypass: Prevalence and Revascularization Strategies
 Left Subclavian Artery Stenosis in Coronary Artery Bypass: Prevalence and Revascularization Strategies Ho Young Hwang, MD, Jin Hyun Kim, MD, Whal Lee, MD, PhD, Jae Hyung Park, MD, PhD, and Ki-Bong Kim,
Left Subclavian Artery Stenosis in Coronary Artery Bypass: Prevalence and Revascularization Strategies Ho Young Hwang, MD, Jin Hyun Kim, MD, Whal Lee, MD, PhD, Jae Hyung Park, MD, PhD, and Ki-Bong Kim,
Hybrid Coronary Artery Revascularization for Takayasu Arteritis with Major Visceral Collateral Circulation from the Left Internal Thoracic Artery
 Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2017;50:105-109 ISSN: 2233-601X (Print) ISSN: 2093-6516 (Online) CASE REPORT https://doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2017.50.2.105 Hybrid Coronary Artery Revascularization for Takayasu
Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2017;50:105-109 ISSN: 2233-601X (Print) ISSN: 2093-6516 (Online) CASE REPORT https://doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2017.50.2.105 Hybrid Coronary Artery Revascularization for Takayasu
New Trials in Progress: ACT 1. Jon Matsumura, MD Cannes, France June 28, 2008
 New Trials in Progress: ACT 1 Jon Matsumura, MD Cannes, France June 28, 2008 Faculty Disclosure I disclose the following financial relationships: Consultant, CAS training director, and/or research grants
New Trials in Progress: ACT 1 Jon Matsumura, MD Cannes, France June 28, 2008 Faculty Disclosure I disclose the following financial relationships: Consultant, CAS training director, and/or research grants
Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) of the renal arteries Angiographic features and therapeutic options
 Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) of the renal arteries Angiographic features and therapeutic options Poster No.: C-0630 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. I. Ringe, B. Meyer, F. Wacker,
Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) of the renal arteries Angiographic features and therapeutic options Poster No.: C-0630 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. I. Ringe, B. Meyer, F. Wacker,
Catheter Interventions for Kawasaki Disease: Current Concepts and Future Directions
 REVIEW DOI 10.4070/kcj.2011.41.2.53 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright 2011 The Korean Society of Cardiology Open Access Catheter Interventions for Kawasaki Disease: Current Concepts
REVIEW DOI 10.4070/kcj.2011.41.2.53 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright 2011 The Korean Society of Cardiology Open Access Catheter Interventions for Kawasaki Disease: Current Concepts
Case 37 Clinical Presentation
 Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
Acute dissections of the descending thoracic aorta (Debakey
 Endovascular Treatment of Acute Descending Thoracic Aortic Dissections Nimesh D. Desai, MD, PhD, and Joseph E. Bavaria, MD Acute dissections of the descending thoracic aorta (Debakey type III or Stanford
Endovascular Treatment of Acute Descending Thoracic Aortic Dissections Nimesh D. Desai, MD, PhD, and Joseph E. Bavaria, MD Acute dissections of the descending thoracic aorta (Debakey type III or Stanford
An Overview of Post-EVAR Endoleaks: Imaging Findings and Management. Ravi Shergill BSc Sean A. Kennedy MD Mark O. Baerlocher MD FRCPC
 An Overview of Post-EVAR Endoleaks: Imaging Findings and Management Ravi Shergill BSc Sean A. Kennedy MD Mark O. Baerlocher MD FRCPC Disclosure Slide Mark O. Baerlocher: Current: Consultant for Boston
An Overview of Post-EVAR Endoleaks: Imaging Findings and Management Ravi Shergill BSc Sean A. Kennedy MD Mark O. Baerlocher MD FRCPC Disclosure Slide Mark O. Baerlocher: Current: Consultant for Boston
Two Cases of Carotid Artery Stenting Combined Balloon- and Self-expanding Stent for the Spontaneous Internal Carotid Artery Dissections
 Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 437 442 Online June 13, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.tn.2016-0059 Two Cases of Carotid Artery Stenting Combined Balloon- and Self-expanding Stent for the Spontaneous
Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 437 442 Online June 13, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.tn.2016-0059 Two Cases of Carotid Artery Stenting Combined Balloon- and Self-expanding Stent for the Spontaneous
BY VINCENT V. TRUONG, MD, AND ALEX ABOU-CHEBL, MD
 Intracranial Angioplasty and Stenting Assessing the need for continued clinical exploration of the safety, efficacy, and durability of intracranial interventions. BY VINCENT V. TRUONG, MD, AND ALEX ABOU-CHEBL,
Intracranial Angioplasty and Stenting Assessing the need for continued clinical exploration of the safety, efficacy, and durability of intracranial interventions. BY VINCENT V. TRUONG, MD, AND ALEX ABOU-CHEBL,
Introduction. Risk factors of PVD 5/8/2017
 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CLINICAL FEATURES OF PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE Dr. Muhamad Zabidi Ahmad Radiologist and Section Chief, Radiology, Oncology and Nuclear Medicine Section, Advanced Medical and Dental
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CLINICAL FEATURES OF PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE Dr. Muhamad Zabidi Ahmad Radiologist and Section Chief, Radiology, Oncology and Nuclear Medicine Section, Advanced Medical and Dental
Carotid Stenosis (carotid artery disease)
 1 Carotid Stenosis (carotid artery disease) Overview Carotid stenosis is a narrowing of the carotid arteries, the two major arteries that carry oxygenrich blood from the heart to the brain. Also called
1 Carotid Stenosis (carotid artery disease) Overview Carotid stenosis is a narrowing of the carotid arteries, the two major arteries that carry oxygenrich blood from the heart to the brain. Also called
Repair of Intracranial Vessel Perforation with Onyx-18 Using an Exovascular Retreating Catheter Technique
 Repair of Intracranial Vessel Perforation with Onyx-18 Using an Exovascular Retreating Catheter Technique Michael Horowitz M.D. Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Background Iatrogenic intraprocedural rupture rates
Repair of Intracranial Vessel Perforation with Onyx-18 Using an Exovascular Retreating Catheter Technique Michael Horowitz M.D. Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Background Iatrogenic intraprocedural rupture rates
Effect of Intravascular Ultrasound- Guided vs. Angiography-Guided Everolimus-Eluting Stent Implantation: the IVUS-XPL Randomized Clinical Trial
 Effect of Intravascular Ultrasound- Guided vs. Angiography-Guided Everolimus-Eluting Stent Implantation: the IVUS-XPL Randomized Clinical Trial Myeong-Ki Hong, MD. PhD on behalf of the IVUS-XPL trial investigators
Effect of Intravascular Ultrasound- Guided vs. Angiography-Guided Everolimus-Eluting Stent Implantation: the IVUS-XPL Randomized Clinical Trial Myeong-Ki Hong, MD. PhD on behalf of the IVUS-XPL trial investigators
Dissection of descending aorta treated by stent-graft implantation in a patient with Marfan syndrome
 Case Report 1 Dissection of descending aorta treated by stent-graft implantation in a patient with Marfan syndrome Marat. ripov, Ildar Z. bdyldaev, Semen D. Chevgun, ektur S. Daniyarov, Dinara. Toktosunova,
Case Report 1 Dissection of descending aorta treated by stent-graft implantation in a patient with Marfan syndrome Marat. ripov, Ildar Z. bdyldaev, Semen D. Chevgun, ektur S. Daniyarov, Dinara. Toktosunova,
Total occlusion at ostial Left internal mammary graft with successful angioplasty and longterm patency result
 DOI 10.7603/s40602-014-0017-x ASEAN Heart Journal http://www.aseanheartjournal.org/ Vol. 22, no. 1, 116 121 (2014) ISSN: 2315-4551 Case Report Total occlusion at ostial Left internal mammary graft with
DOI 10.7603/s40602-014-0017-x ASEAN Heart Journal http://www.aseanheartjournal.org/ Vol. 22, no. 1, 116 121 (2014) ISSN: 2315-4551 Case Report Total occlusion at ostial Left internal mammary graft with
Challenges. 1. Sizing. 2. Proximal landing zone 3. Distal landing zone 4. Access vessels 5. Spinal cord ischemia 6. Endoleak
 Disclosure I have the following potential conflicts of interest to report: Consulting: Medtronic, Gore Employment in industry Stockholder of a healthcare company Owner of a healthcare company Other(s)
Disclosure I have the following potential conflicts of interest to report: Consulting: Medtronic, Gore Employment in industry Stockholder of a healthcare company Owner of a healthcare company Other(s)
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Am Coll Radiol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 June 24.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Am Coll Radiol. 2010 January ; 7(1): 73 76. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2009.06.015. Cerebral Aneurysms Janet C. Miller, DPhil, Joshua A.
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Am Coll Radiol. 2010 January ; 7(1): 73 76. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2009.06.015. Cerebral Aneurysms Janet C. Miller, DPhil, Joshua A.
Volume 3 (2017) Issue 11 ISSN Abstract. Keywords. Introduction. Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports
 Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 3 (2017) Issue 11 ISSN 2379-1039 Arterial bypass surgery and stenting to enable clot retrieval: A case of an acute ischaemic stroke in a patient with
Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 3 (2017) Issue 11 ISSN 2379-1039 Arterial bypass surgery and stenting to enable clot retrieval: A case of an acute ischaemic stroke in a patient with
Slide 1. Slide 2 Conflict of Interest Disclosure. Slide 3 Stroke Facts. The Treatment of Intracranial Stenosis. Disclosure
 Slide 1 The Treatment of Intracranial Stenosis Helmi Lutsep, MD Vice Chair and Dixon Term Professor, Department of Neurology, Oregon Health & Science University Chief of Neurology, VA Portland Health Care
Slide 1 The Treatment of Intracranial Stenosis Helmi Lutsep, MD Vice Chair and Dixon Term Professor, Department of Neurology, Oregon Health & Science University Chief of Neurology, VA Portland Health Care
Primary to non-coronary IVUS
 codes 2018 2018 codes Primary to non-coronary IVUS Page 2 All coding, coverage, billing and payment information provided herein by Philips is gathered from third-party sources and is subject to change.
codes 2018 2018 codes Primary to non-coronary IVUS Page 2 All coding, coverage, billing and payment information provided herein by Philips is gathered from third-party sources and is subject to change.
Abdominal Exam: The examination of the abdomen used by physicians to detect an abdominal aortic aneurysm.
 Glossary of Terms Abdominal Exam: The examination of the abdomen used by physicians to detect an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Angiogram: A diagnostic test requiring the insertion of a catheter into an artery
Glossary of Terms Abdominal Exam: The examination of the abdomen used by physicians to detect an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Angiogram: A diagnostic test requiring the insertion of a catheter into an artery
Disclosures. CREST Trial: Summary. Lecture Outline 4/16/2015. Cervical Atherosclerotic Disease
 Disclosures Your Patient Has Carotid Bulb Stenosis and a Tandem Intracranial Stenosis: How Do SAMMPRIS and Other Evidence Inform Your Treatment? UCSF Vascular Symposium 2015 Steven W. Hetts, MD Associate
Disclosures Your Patient Has Carotid Bulb Stenosis and a Tandem Intracranial Stenosis: How Do SAMMPRIS and Other Evidence Inform Your Treatment? UCSF Vascular Symposium 2015 Steven W. Hetts, MD Associate
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis 2017 Edition
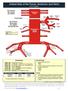 Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
Michael Horowitz, MD Pittsburgh, PA
 Michael Horowitz, MD Pittsburgh, PA Introduction Cervical Artery Dissection occurs by a rupture within the arterial wall leading to an intra-mural Hematoma. A possible consequence is an acute occlusion
Michael Horowitz, MD Pittsburgh, PA Introduction Cervical Artery Dissection occurs by a rupture within the arterial wall leading to an intra-mural Hematoma. A possible consequence is an acute occlusion
Outcome and cost comparison of percutaneous transluminal renal angioplasty, renal arterial stent placement, and renal arterial bypass grafting
 Outcome and cost comparison of percutaneous transluminal renal angioplasty, renal arterial stent placement, and renal arterial bypass grafting Xue F Y, Bettmann M A, Langdon D R, Wivell W A Record Status
Outcome and cost comparison of percutaneous transluminal renal angioplasty, renal arterial stent placement, and renal arterial bypass grafting Xue F Y, Bettmann M A, Langdon D R, Wivell W A Record Status
Limitations of Other Embolic Protection Devices - Filters. Carotid Stenting with Flow Reversal. Limitations of Distal Occlusion
 Carotid Stenting with Flow Reversal Marc Schermerhorn, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Beth Israel Deaconess Center Boston, MA Limitations of Other Embolic Protection Devices - Filters
Carotid Stenting with Flow Reversal Marc Schermerhorn, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Beth Israel Deaconess Center Boston, MA Limitations of Other Embolic Protection Devices - Filters
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
Comparison of Five Major Recent Endovascular Treatment Trials
 Comparison of Five Major Recent Endovascular Treatment Trials Sample size 500 # sites 70 (100 planned) 316 (500 planned) 196 (833 estimated) 206 (690 planned) 16 10 22 39 4 Treatment contrasts Baseline
Comparison of Five Major Recent Endovascular Treatment Trials Sample size 500 # sites 70 (100 planned) 316 (500 planned) 196 (833 estimated) 206 (690 planned) 16 10 22 39 4 Treatment contrasts Baseline
Basilar artery stenosis with bilateral cerebellar strokes on coumadin
 Qaisar A. Shah, MD Patient Profile 68 years old female with a history of; Basilar artery stenosis with bilateral cerebellar strokes on coumadin Diabetes mellitus Hyperlipidemia Hypertension She developed
Qaisar A. Shah, MD Patient Profile 68 years old female with a history of; Basilar artery stenosis with bilateral cerebellar strokes on coumadin Diabetes mellitus Hyperlipidemia Hypertension She developed
Ultrasound Imaging of The Posterior Circulation
 Ultrasound Imaging of The Posterior Circulation Michigan Sonographers Society 2 Nd Annual Fall Vascular Conference Larry N. Raber RDMS-RVT Clinical Manager General Ultrasound/Neurovascular Laboratory Cleveland
Ultrasound Imaging of The Posterior Circulation Michigan Sonographers Society 2 Nd Annual Fall Vascular Conference Larry N. Raber RDMS-RVT Clinical Manager General Ultrasound/Neurovascular Laboratory Cleveland
Small in-stent Low Density on CT Angiography after Carotid Artery Stenting
 www.centauro.it Interventional Neuroradiology 14 (Suppl. 2): 41-46, 2008 Small in-stent Low Density on CT Angiography after Carotid Artery Stenting MIKA OKAHARA 1, HIRO KIYOSUE 2, JUNJI KASHIWAGI 1, SHINYA
www.centauro.it Interventional Neuroradiology 14 (Suppl. 2): 41-46, 2008 Small in-stent Low Density on CT Angiography after Carotid Artery Stenting MIKA OKAHARA 1, HIRO KIYOSUE 2, JUNJI KASHIWAGI 1, SHINYA
Nicolas Bianchi M.D. May 15th, 2012
 Nicolas Bianchi M.D. May 15th, 2012 New concepts in TIA Differential Diagnosis Stroke Syndromes To learn the new definitions and concepts on TIA as a condition of high risk for stroke. To recognize the
Nicolas Bianchi M.D. May 15th, 2012 New concepts in TIA Differential Diagnosis Stroke Syndromes To learn the new definitions and concepts on TIA as a condition of high risk for stroke. To recognize the
Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography
 Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography Kazumi Kimura, Yoichiro Hashimoto, Teruyuki Hirano, Makoto Uchino, and Masayuki Ando PURPOSE: To determine
Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography Kazumi Kimura, Yoichiro Hashimoto, Teruyuki Hirano, Makoto Uchino, and Masayuki Ando PURPOSE: To determine
Copyright HMP Communications
 Ocelot With Wildcat in a Complicated Superficial Femoral Artery Chronic Total Occlusion Soundos K. Moualla, MD, FACC, FSCAI; Richard R. Heuser, MD, FACC, FACP, FESC, FSCAI From Phoenix Heart Center, Phoenix,
Ocelot With Wildcat in a Complicated Superficial Femoral Artery Chronic Total Occlusion Soundos K. Moualla, MD, FACC, FSCAI; Richard R. Heuser, MD, FACC, FACP, FESC, FSCAI From Phoenix Heart Center, Phoenix,
Case Report Endovascular treatment of subclavian artery stenosis complicated with subclavian artery aneurysms: a case report
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(10):20401-20405 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0016290 Case Report Endovascular treatment of subclavian artery stenosis complicated with subclavian artery aneurysms: a case
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(10):20401-20405 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0016290 Case Report Endovascular treatment of subclavian artery stenosis complicated with subclavian artery aneurysms: a case
Coronary angiography and PCI
 Coronary arteries Coronary angiography and PCI Samo Granda, Franjo Naji Department of Cardiology Clinical department of internal medicine University clinical centre Maribor Coronary arteries Atherosclerosis
Coronary arteries Coronary angiography and PCI Samo Granda, Franjo Naji Department of Cardiology Clinical department of internal medicine University clinical centre Maribor Coronary arteries Atherosclerosis
The MAIN-COMPARE Study
 Long-Term Outcomes of Coronary Stent Implantation versus Bypass Surgery for the Treatment of Unprotected Left Main Coronary Artery Disease Revascularization for Unprotected Left MAIN Coronary Artery Stenosis:
Long-Term Outcomes of Coronary Stent Implantation versus Bypass Surgery for the Treatment of Unprotected Left Main Coronary Artery Disease Revascularization for Unprotected Left MAIN Coronary Artery Stenosis:
Surgical Treatment of Carotid Disease
 Department of Cardiothoracic & Vascular Surgery McGovern Medical School / The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston Surgical Treatment of Carotid Disease The Old, the New, and the Future
Department of Cardiothoracic & Vascular Surgery McGovern Medical School / The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston Surgical Treatment of Carotid Disease The Old, the New, and the Future
Brain Attack. Strategies in the Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: Neuroscience Clerkship. Case Medical Center
 Brain Attack Strategies in the Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: Neuroscience Clerkship Stroke is a common and devastating disorder Third leading antecedent of death in American men, and second among
Brain Attack Strategies in the Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: Neuroscience Clerkship Stroke is a common and devastating disorder Third leading antecedent of death in American men, and second among
Carotid Revascularization
 Options for Carotid Disease Carotid Revascularization Wayne Causey, MD 2 nd Year Vascular Surgery Fellow Best medical therapy, Carotid Endarterectomy, and Carotid Stenting Who benefits from best medical
Options for Carotid Disease Carotid Revascularization Wayne Causey, MD 2 nd Year Vascular Surgery Fellow Best medical therapy, Carotid Endarterectomy, and Carotid Stenting Who benefits from best medical
Percutaneous Approaches to Aortic Disease in 2018
 Percutaneous Approaches to Aortic Disease in 2018 Wendy Tsang, MD, SM Assistant Professor, University of Toronto Toronto General Hospital, University Health Network Case 78 year old F Lower CP and upper
Percutaneous Approaches to Aortic Disease in 2018 Wendy Tsang, MD, SM Assistant Professor, University of Toronto Toronto General Hospital, University Health Network Case 78 year old F Lower CP and upper
