Dominic Y. Leung, MBBS, PhD; Melissa Leung, MBBS, PhD Department of Cardiology, Liverpool Hospital, University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia
|
|
|
- Debra Hodge
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Heart Metab. (2017) 73:18-23 Early detection of left ventricular dysfunction in diabetes Dominic Y. Leung, MBBS, PhD; Melissa Leung, MBBS, PhD Department of Cardiology, Liverpool Hospital, University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia Correspondence: Professor Dominic Leung, Department of Cardiology, Liverpool Hospital, Locked Bag, 7103, Liverpool BC, NSW 1871, Australia Abstract Patients with type 2 diabetes are at risk of developing left ventricular (LV) dysfunction and heart failure. Symptoms associated with LV dysfunction in these patients, especially in the early stages, may be minimal or attributed to other noncardiac factors. LV dysfunction in diabetes is multifactorial, but there is evidence of the specific entity of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Although a direct relationship between glycemic control and LV function has not been firmly established, there is increasing evidence to suggest that poor glycemic control is associated with LV dysfunction and that improving glycemic control improves LV function. A high index of suspicion is necessary in managing these patients. Echocardiography is a noninvasive, widely available imaging tool that provides comprehensive assessment of cardiac structure and function. Exercise echocardiography allows detection of coronary disease and assessment of LV diastolic reserve. A multifaceted approach targeting all vascular risk factors in the management of LV dysfunction in these patients is essential. A specific treatment for diabetic cardiomyopathy is still lacking, but optimizing glycemic control and aldosterone antagonism may be beneficial, and trials are currently underway. Early detection of LV dysfunction allows identification of at-risk patients and timely intervention, which could ultimately improve patient outcome in this condition, which is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. L Heart Metab. 2017;73:18-23 Keywords: cardiomyopathy; diabetes; echocardiography Introduction The prevalence of obesity is skyrocketing in both developing and developed countries. This is accompanied by a corresponding increase in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Patients with type 2 diabetes have a high prevalence of heart failure, both undiagnosed and diagnosed, and left ventricular (LV) dysfunction. 1 In these patients, although LV dysfunction and heart failure may be attributed to common comorbidities, such as hypertension, obesity, and coronary disease, there is evidence for the distinct clinical entity of diabetic cardiomyopathy. 2 The spectrum of the disease may range from LV diastolic dysfunction in the early stage 3 to systolic dysfunction and overt LV dysfunction and advanced heart failure. The diagnosis of heart failure and LV dysfunction in these patients is often delayed. LV diastolic and systolic dysfunction may be subclinical, and early symptoms of exercise intolerance may be subtle and attributed to lack of physical fitness. Nevertheless, early detection of LV dysfunction in these high-risk 18
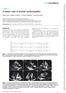
2 Heart Metab. (2017) 73:18-23 Leung and Leung Fig. 1 Evaluation of a 66-year-old man with type 2 diabetes who complained of dyspnea on exertion found left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy, but normal LV ejection fraction. LV global longitudinal strain (GLS) was impaired at -13.2% (Panel A). The patient had grade 1 diastolic dysfunction with a mitral E/A ratio <0.5 at rest (Panel B) and a septal e velocity of 6 cm/s (Panel C). Abbreviations: 4-ch, 4-chamber view; ANT_SEPT, anteroseptal; APLAX, apical long axis view; AVC_AUTO, aortic valve closure detected automatically; GLPS_A4C, global longitudinal peak strain, apical 4-chamber view; GLPS_LAX, global longitudinal peak strain, apical long axis view; HR, heart rate; HR_ApLAX, heart rate during acquisition of the apical long axis view; INF, inferior; LAT, lateral; POST, posterior; SEPT, septal. 19
3 Leung and Leung Heart Metab. (2017) 73:18-23 patients is important; timely, aggressive, multifaceted management is the key to ameliorating the otherwise devastating consequences of diabetic heart disease. Echocardiography in detection of left ventricular dysfunction Echocardiography is a versatile, noninvasive, and widely available imaging tool for the assessment of LV structure and function and has been most commonly used in the detection of LV dysfunction. LV ejection fraction is an insensitive marker for early detection of LV dysfunction. Mitral E- and A-wave, and tissue Doppler e -wave velocities are measures of LV diastolic function. An elevated mitral E/e velocity ratio is a reliable marker of elevated LV filling pressures, commonly seen in patients with LV dysfunction and heart failure. Echocardiographic strain deformation imaging allows a sensitive, angle-independent, and site-specific assessment of LV systolic function, and assessment of LV global longitudinal strain is superior to ejection fraction in the detection of early diabetic heart disease. 4 Moreover, LV global longitudinal strain has incremental prognostic value over ejection fraction in a wide range of cardiovascular diseases. Exercise echocardiography is a well-accepted, accurate, and noninvasive test for inducible ischemia, allowing detection of coronary artery disease. It also allows assessment of LV filling pressures at rest and after exercise. 5 As an example, Figure 1 and Figure 2 depict an exercise echocardiographic evaluation of a type 2 diabetes patient with dyspnea on exertion. The Strong Heart Study demonstrated that heart failure was very prevalent in patients with diabetes despite normal ejection fraction. 6 Fang et al found subclinical LV systolic and diastolic dysfunction in a large proportion of patients with type 2 diabetes without ischemia or hypertrophy. 7 Compared with age-matched controls, asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes had impaired LV longitudinal systolic, as well as diastolic, function. 4 In a recent study of 105 patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes, we found that these patients have impaired LV diastolic and systolic function and elevated LV filling pressures despite normal LV ejection fraction and LV mass. 8 The underlying pathophysiological mechanisms of diabetic cardiomyopathy are multifactorial and may include microvascular disease, endothelial dysfunction, autonomic dysfunction, hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, insulin resistance and other metabolic disturbances, myocardial interstitial fibrosis, and myocardial steatosis. 2 Obesity, common in patients with diabetes, may also lead to LV dysfunction. We have demonstrated impaired coronary microvascular function in patients with diabetes in the absence of epicardial coronary stenosis. 9 As cardiac extracellular matrix plays an active role in modulating cardiac function, myocardial fibrosis has been suggested as one of the important mechanisms of LV dysfunction in diabetes. 2 Although hyperglycemia is the primary metabolic disturbance in diabetes, the relationship between glycemic control and cardiac function is unclear. Some studies have shown poor glycemic control to be associated with abnormal LV relaxation, elevated filling pressures, and impaired systolic contraction. 7 Patients who had poorly controlled diabetes in the Strong Heart Study were found to have abnormal LV relaxation. 10 In 120 patients with type 2 diabetes, peak systolic strain was independently associated with glycated hemoglobin (HbA 1c ) levels, whereas septal e velocities were related more to age and hypertension and not to glycemic control. 7 However, a number of other studies have demonstrated no association between glycemic control and ventricular function. The relationship between prevailing glycemic control and LV function may be more complicated and affected by multiple factors, including duration of diabetes, presence and control of other vascular risk factors, medications, body weight, and others that are known to have an impact on LV function. Impact of improving glycemic control on left ventricular function A few studies have examined the effect that improved glycemic control has on LV function. von Bibra et al showed that intensive glycemic control with insulin improved LV diastolic, but not systolic, function. 11 However, others did not demonstrate improvements, despite better glycemic control. 12 Most of these studies examined improved glycemic control over short periods of time, which may not have been sufficient to effect any detectable changes in LV function. We 20
4 Heart Metab. (2017) 73:18-23 Leung and Leung Fig. 2 Evaluation of a 66-year-old man with type 2 diabetes who complained of dyspnea on exertion (see also Fig. 1) found a dilated left atrium (Panel A), with a maximum left atrial volume of 51 ml/m2. On exercise echocardiography, no inducible ischemia was found. Immediately after exercise, the mitral E/A ratio reversed and became >1 (Panel B). The septal e velocity decreased to 5 cm/s, leading to a significantly higher E/e ratio; this indicates elevated LV filling pressures and limited LV diastolic reserve, explaining the exertional dyspnea. Abbreviations: A2C, apical 2-chamber; A-L, area-length; LAEDV, left atrial end diastolic volume; LAAd, left atrial area; LALd, left atrial longitudinal dimension. 21
5 Leung and Leung Heart Metab. (2017) 73:18-23 recruited 105 patients with suboptimally controlled type 2 diabetes; during a 12-month follow-up period, we optimized treatment aimed to improve their metabolic control. Improved glycemic control led to improvement in LV diastolic and systolic function, and both the magnitude of the improvement and the final glycemic control affected LV function at follow-up. Worsened glycemic control actually led to further deterioration of LV systolic function. 8 Patients with diabetes are often overweight and obesity itself is also linked to LV dysfunction. In support of this concept, weight loss has been shown to lead to improved LV function. 13 The impact of improving glycemic control on LV function may be mediated through the beneficial effects of weight loss on LV function. However, in another study, we demonstrated that both improved glycemic control and weight loss had incremental additive benefits on LV function. 14 Effort intolerance in diabetes Early stages of LV dysfunction in diabetes may be associated with little or no symptoms. Effort intolerance is usually the first manifestation. Unfortunately, effort intolerance may be attributed to body weight or lack of physical fitness. Coronary artery disease may be another underlying cause. Evaluation of LV function at rest may not be adequate in patients with diabetes. Therefore, examining the response of the left ventricle to exercise may yield further diagnostic information. Diastolic reserve is the ability of LV filling pressures to remain normal with exercise and tachycardia. Impaired diastolic reserve is seen in the early stages of LV diastolic dysfunction in diabetes. Patients with diabetes have an impaired diastolic reserve, and elevated LV filling pressures with exercise manifest an exertional dyspnea even without inducible myocardial ischemia. 5 Exercise echocardiography, by allowing assessment of LV diastolic reserve, is a useful tool to unmask diastolic and systolic dysfunction to evaluate patients with exertional dyspnea. Improving glycemic control is also associated with an improvement in exercise tolerance in these patients. 8 Treatment of left ventricular dysfunction in diabetes Treatment of LV dysfunction in diabetes requires a multifaceted approach. Early detection of LV dysfunction in these patients allows identification of atrisk patients and early intervention. As these patients often have multiple comorbidities, a comprehensive approach to the management of all vascular risk factors is essential. Aggressive blood pressure lowering, treating hypercholesterolemia to target, and optimization of body weight are all important parts of management. Optimization of glycemic control may also lead to improvement in LV systolic and diastolic function and exercise tolerance. A specific therapeutic agent for diabetic cardiomyopathy is still lacking. Aldosterone antagonism, which reduces cardiac extracellular matrix turnover, improves symptoms and outcomes in advanced systolic heart failure and after acute myocardial infarction. Aldosterone antagonism has also been shown to improve LV function in dilated and hypertensive cardiomyopathy 15 and metabolic syndrome with regression in markers of myocardial fibrosis. 16 Trials evaluating the impact of specific aldosterone antagonism on LV systolic and diastolic function in patients with type 2 diabetes are ongoing. 17 Conclusions LV dysfunction and heart failure are prevalent in patients with diabetes. Hypertension, coronary artery disease, and obesity are common comorbidities and may also cause LV dysfunction. Diabetic cardiomyopathy is considered a distinct entity. LV dysfunction in these patients may be associated with little or no symptoms, with exertional dyspnea a common, though nonspecific, symptom. LV function is linked to glycemic control, and early detection of LV dysfunction is important. Echocardiography, combined with exercise testing, allows comprehensive assessment of LV morphology, systolic and diastolic function at rest and after stress, and exclusion of coronary artery disease. A multifaceted approach targeting all vascular risk factors in the management of LV dysfunction in these patients is essential. A specific treatment for diabetic cardiomyopathy is still lacking, but aldosterone antagonists may be beneficial. Timely intervention may improve patient outcome for such a condition, which is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. L REFERENCES 1. Boonman-de Winter LJ, Rutten FH, et al. High prevalence of previously unknown heart failure and left ventricular dysfunction 22
6 Heart Metab. (2017) 73:18-23 Leung and Leung in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2012;55: Fang ZY, Prins JB, Marwick TH. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: evidence, mechanisms, and therapeutic implications. Endocr Rev. 2004;25: Marwick TH. Diabetic heart disease. Postgrad Med J. 2008;84: Ng AC, Delgado V, Bertini M, et al. Findings from left ventricular strain and strain rate imaging in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Cardiol. 2009;104: Leung M, Phan V, Whatmough M, Heritier S, Wong VW, Leung DY. Left ventricular diastolic reserve in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Open Heart. 2015;2:e Devereux RB, Roman MJ, Liu JE, et al. Congestive heart failure despite normal left ventricular systolic function in a population-based sample: the Strong Heart Study. Am J Cardiol. 2000;86: Fang ZY, Schull-Meade R, Downey M, Prins J, Marwick TH. Determinants of subclinical diabetic heart disease. Diabetologia. 2005;48: Leung M, Wong VW, Hudson M, Leung DY. Impact of improved glycemic control on cardiac function in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016;9:e Leung M, Leung DY. Coronary microvascular function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. EuroIntervention. 2016;11: Liu JE, Palmieri V, Roman MJ, et al. The impact of diabetes on left ventricular filling pattern in normotensive and hypertensive adults: the Strong Heart Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001;37: von Bibra H, Hansen A, Dounis V, Bystedt T, Malmberg K, Rydén L. Augmented metabolic control improves myocardial diastolic function and perfusion in patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes. Heart. 2004;90: Jarnert C, Landstedt-Hallin L, Malmberg K, et al. A randomized trial of the impact of strict glycaemic control on myocardial diastolic function and perfusion reserve: a report from the DADD (Diabetes mellitus And Diastolic Dysfunction) study. Eur J Heart Fail. 2009;11: Cuspidi C, Rescaldani M, Tadic M, Sala C, Grassi G. Effects of bariatric surgery on cardiac structure and function: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Hypertension. 2013;27: Leung M, Wong VW, Durmush E, Phan V, Xie M, Leung DY. Cardiac dysfunction in type II diabetes: a bittersweet, weighty problem, or both? Acta Diabetol. 2017;54: Mottram PM, Haluska B, Leano R, Cowley D, Stowasser M, Marwick TH. Effect of aldosterone antagonism on myocardial dysfunction in hypertensive patients with diastolic heart failure. Circulation. 2004;110: Kosmala W, Przewlocka-Kosmala M, Szczepanik-Osadnik H, et al. A randomized study of the beneficial effects of aldosterone antagonism on LV function, structure, and fibrosis markers in metabolic syndrome. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011;4: Leung M, Wong VW, Heritier S, Mihailidou AS, Leung DY. Rationale and design of a randomized trial on the impact of aldosterone antagonism on cardiac structure and function in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013;12:
LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION
 LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION Jamilah S AlRahimi Assistant Professor, KSU-HS Consultant Noninvasive Cardiology KFCC, MNGHA-WR Introduction LV function assessment in Heart Failure:
LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION Jamilah S AlRahimi Assistant Professor, KSU-HS Consultant Noninvasive Cardiology KFCC, MNGHA-WR Introduction LV function assessment in Heart Failure:
Weight Loss with Sleeve Gastrectomy in Obese Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Impact on Cardiac Function
 OBES SURG (2016) 26:321 326 DOI 10.1007/s11695-015-1748-x ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTIONS Weight Loss with Sleeve Gastrectomy in Obese Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Impact on Cardiac Function Melissa Leung 1,2 & Mikey
OBES SURG (2016) 26:321 326 DOI 10.1007/s11695-015-1748-x ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTIONS Weight Loss with Sleeve Gastrectomy in Obese Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Impact on Cardiac Function Melissa Leung 1,2 & Mikey
Diabetes and Heart Failure
 Diabetes and Heart Failure A common and fatal combination A Aspects on epidemiology, prognosis diagnosis and therapy Lars Rydén Department of Medicine Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden Diabetes and
Diabetes and Heart Failure A common and fatal combination A Aspects on epidemiology, prognosis diagnosis and therapy Lars Rydén Department of Medicine Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden Diabetes and
The Impact of Autonomic Neuropathy on Left Ventricular Function in Normotensive Type 1 Diabetic Patients: a Tissue Doppler Echocardiographic Study
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online November 13, 2007 The Impact of Autonomic Neuropathy on Left Ventricular Function in Normotensive Type 1 Diabetic Patients: a Tissue Doppler Echocardiographic
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online November 13, 2007 The Impact of Autonomic Neuropathy on Left Ventricular Function in Normotensive Type 1 Diabetic Patients: a Tissue Doppler Echocardiographic
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea
 Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Echocardiographic and Doppler Assessment of Cardiac Functions in Patients of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2002; 3(2): 164-8 Echocardiographic and Doppler Assessment of Cardiac Functions in Patients of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Rajesh Rajput*, Jagdish**, SB Siwach***, A
ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2002; 3(2): 164-8 Echocardiographic and Doppler Assessment of Cardiac Functions in Patients of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Rajesh Rajput*, Jagdish**, SB Siwach***, A
Diastology State of The Art Assessment
 Diastology State of The Art Assessment Dr. Mohammad AlGhamdi Assistant professor, KSAU-HS Consultant Cardiologist King AbdulAziz Cardiac Center Ministry of National Guard Health Affairs Diagnostic Clinical
Diastology State of The Art Assessment Dr. Mohammad AlGhamdi Assistant professor, KSAU-HS Consultant Cardiologist King AbdulAziz Cardiac Center Ministry of National Guard Health Affairs Diagnostic Clinical
Left atrial function. Aliakbar Arvandi MD
 In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
Hypertensive heart disease and failure
 Hypertensive heart disease and failure Prof. Dr. Alan Fraser Cardiff University The heart in hypertension Pathophysiology of LV adaptation Regional development of hypertrophy Stress testing - inducible
Hypertensive heart disease and failure Prof. Dr. Alan Fraser Cardiff University The heart in hypertension Pathophysiology of LV adaptation Regional development of hypertrophy Stress testing - inducible
Diabetes and the Heart
 Diabetes and the Heart Association of Specialty Professors April 4, 2013 Jorge Plutzky, MD Co-Director, Preventive Cardiology Director, The Lipid Clinic Cardiovascular Division Brigham and Women s Hospital
Diabetes and the Heart Association of Specialty Professors April 4, 2013 Jorge Plutzky, MD Co-Director, Preventive Cardiology Director, The Lipid Clinic Cardiovascular Division Brigham and Women s Hospital
Is normal ejection fraction equivalent to normal systolic function?
 Is normal ejection fraction equivalent to normal systolic function? D. Vinereanu University of Medicine, Bucharest, Romania EAE course, Bucharest No 2 nd criterion (out of 3) for the diagnosis of HFNEF:
Is normal ejection fraction equivalent to normal systolic function? D. Vinereanu University of Medicine, Bucharest, Romania EAE course, Bucharest No 2 nd criterion (out of 3) for the diagnosis of HFNEF:
HFPEF Echo with Strain vs. MRI T1 Mapping
 HFPEF Echo with Strain vs. MRI T1 Mapping Erik Schelbert, MD MS Director, Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Assistant Professor of Medicine Heart & Vascular Institute University of Pittsburgh Disclosures
HFPEF Echo with Strain vs. MRI T1 Mapping Erik Schelbert, MD MS Director, Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Assistant Professor of Medicine Heart & Vascular Institute University of Pittsburgh Disclosures
Νεότερα ςτην Υπερηχοκαρδιογραφία. Βαςίλειοσ Καμπερίδησ Clinical research fellow in Cardiology
 Νεότερα ςτην Υπερηχοκαρδιογραφία Βαςίλειοσ Καμπερίδησ Clinical research fellow in Cardiology Disclosures ESC training grant EACVI research grant HCS training grant ELIKAR research grant Evolution of Echocardiography
Νεότερα ςτην Υπερηχοκαρδιογραφία Βαςίλειοσ Καμπερίδησ Clinical research fellow in Cardiology Disclosures ESC training grant EACVI research grant HCS training grant ELIKAR research grant Evolution of Echocardiography
2/2/2011. Strain and Strain Rate Imaging How, Why and When? Movement vs Deformation. Doppler Myocardial Velocities. Movement. Deformation.
 Strain and Strain Rate Imaging How, Why and When? João L. Cavalcante, MD Advanced Cardiac Imaging Fellow Cleveland Clinic Foundation Disclosures: No conflicts of interest Movement vs Deformation Movement
Strain and Strain Rate Imaging How, Why and When? João L. Cavalcante, MD Advanced Cardiac Imaging Fellow Cleveland Clinic Foundation Disclosures: No conflicts of interest Movement vs Deformation Movement
When is strain assessment mandatory?
 When is strain assessment mandatory? Geneviève Derumeaux University of Lyon France Presenter Disclosure Information Geneviève Derumeaux When is strain assessment mandatory? DISCLOSURE INFORMATION: None
When is strain assessment mandatory? Geneviève Derumeaux University of Lyon France Presenter Disclosure Information Geneviève Derumeaux When is strain assessment mandatory? DISCLOSURE INFORMATION: None
A STUDY OF LEFT VENTRICULAR DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERTENSION Ravi Keerthy M 1
 A STUDY OF LEFT VENTRICULAR DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERTENSION Ravi Keerthy M 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ravi Keerthy M. A Study of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Hypertension. Journal of
A STUDY OF LEFT VENTRICULAR DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERTENSION Ravi Keerthy M 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ravi Keerthy M. A Study of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Hypertension. Journal of
Selected age-associated changes in the cardiovascular system
 Selected age-associated changes in the cardiovascular system Tamara Harris, M.D., M.S. Chief, Interdisciplinary Studies of Aging Acting Co-Chief, Laboratory of Epidemiology and Population Sciences Intramural
Selected age-associated changes in the cardiovascular system Tamara Harris, M.D., M.S. Chief, Interdisciplinary Studies of Aging Acting Co-Chief, Laboratory of Epidemiology and Population Sciences Intramural
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False?
 Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
Advanced imaging of the left atrium - strain, CT, 3D, MRI -
 Advanced imaging of the left atrium - strain, CT, 3D, MRI - Monica Rosca, MD Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania Declaration of interest: I have nothing to declare Case
Advanced imaging of the left atrium - strain, CT, 3D, MRI - Monica Rosca, MD Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania Declaration of interest: I have nothing to declare Case
The importance of left atrium in LV diastolic function
 II Baltic Heart Failure Meeting and Congress of Latvian Society of Cardiology The importance of left atrium in LV diastolic function Dr. Artem Kalinin Eastern Clinical University Hospital Riga 30.09.2010.
II Baltic Heart Failure Meeting and Congress of Latvian Society of Cardiology The importance of left atrium in LV diastolic function Dr. Artem Kalinin Eastern Clinical University Hospital Riga 30.09.2010.
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
 ESC Congress 2011, Paris Imaging Unusual Causes of Cardiomyopathy Restrictive Cardiomyopathy Kazuaki Tanabe, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Chair, Division of Cardiology Izumo, Japan I Have No Disclosures
ESC Congress 2011, Paris Imaging Unusual Causes of Cardiomyopathy Restrictive Cardiomyopathy Kazuaki Tanabe, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Chair, Division of Cardiology Izumo, Japan I Have No Disclosures
Μαρία Μπόνου Διευθύντρια ΕΣΥ, ΓΝΑ Λαϊκό
 Μαρία Μπόνου Διευθύντρια ΕΣΥ, ΓΝΑ Λαϊκό Diastolic HF DD: Diastolic Dysfunction DHF: Diastolic HF HFpEF: HF with preserved EF DD Pathophysiologic condition: impaired relaxation, LV compliance, LV filling
Μαρία Μπόνου Διευθύντρια ΕΣΥ, ΓΝΑ Λαϊκό Diastolic HF DD: Diastolic Dysfunction DHF: Diastolic HF HFpEF: HF with preserved EF DD Pathophysiologic condition: impaired relaxation, LV compliance, LV filling
Strain and Strain Rate Imaging How, Why and When?
 Strain and Strain Rate Imaging How, Why and When? João L. Cavalcante, MD Advanced Cardiac Imaging Fellow Cleveland Clinic Foundation Disclosures: No conflicts of interest Movement vs Deformation Movement
Strain and Strain Rate Imaging How, Why and When? João L. Cavalcante, MD Advanced Cardiac Imaging Fellow Cleveland Clinic Foundation Disclosures: No conflicts of interest Movement vs Deformation Movement
Echocardiographic study of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in normotensive asymptomatic type II diabetes mellitus
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. VI (July. 2015), PP 39-43 www.iosrjournals.org Echocardiographic study of left ventricular
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. VI (July. 2015), PP 39-43 www.iosrjournals.org Echocardiographic study of left ventricular
Elevated LV filling pressure is a major determinant of cardiac symptoms and
 LEFT VENTRICULAR FILLING PRESSURE, DIASTOLIC FUNCTION, AND HEART RATE PATRIZIO LANCELLOTTI, MD, PhD, FESC PERSPECTIVES Author affiliations: University of Liège hospital, GIGA Cardiovascular Science, Heart
LEFT VENTRICULAR FILLING PRESSURE, DIASTOLIC FUNCTION, AND HEART RATE PATRIZIO LANCELLOTTI, MD, PhD, FESC PERSPECTIVES Author affiliations: University of Liège hospital, GIGA Cardiovascular Science, Heart
Objectives. Diastology: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. LV Diastolic Function: Introduction. LV Diastolic Function: Introduction
 Objectives Diastology: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. Jacobo Kirsch, MD Cardiopulmonary Imaging, Section Head Division of Radiology Cleveland Clinic Florida Weston, FL To review the physiology and
Objectives Diastology: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. Jacobo Kirsch, MD Cardiopulmonary Imaging, Section Head Division of Radiology Cleveland Clinic Florida Weston, FL To review the physiology and
Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors
 Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Heart Failure
 Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Heart Failure Francesco Paneni, MD, PhD, FESC Cardiology Unit Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Cardiology University Hospital Zurich Switzerland francesco.paneni@gmail.com
Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Heart Failure Francesco Paneni, MD, PhD, FESC Cardiology Unit Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Cardiology University Hospital Zurich Switzerland francesco.paneni@gmail.com
Diastolic Heart Function: Applying the New Guidelines Case Studies
 Diastolic Heart Function: Applying the New Guidelines Case Studies Mitral Regurgitation The New ASE William Guidelines: A. Zoghbi Role MD, of FASE, 2D/3D MACCand CMR Professor and Chairman, Department
Diastolic Heart Function: Applying the New Guidelines Case Studies Mitral Regurgitation The New ASE William Guidelines: A. Zoghbi Role MD, of FASE, 2D/3D MACCand CMR Professor and Chairman, Department
Advanced Multi-Layer Speckle Strain Permits Transmural Myocardial Function Analysis in Health and Disease:
 Advanced Multi-Layer Speckle Strain Permits Transmural Myocardial Function Analysis in Health and Disease: Clinical Case Examples Jeffrey C. Hill, BS, RDCS Echocardiography Laboratory, University of Massachusetts
Advanced Multi-Layer Speckle Strain Permits Transmural Myocardial Function Analysis in Health and Disease: Clinical Case Examples Jeffrey C. Hill, BS, RDCS Echocardiography Laboratory, University of Massachusetts
HFpEF. April 26, 2018
 HFpEF April 26, 2018 (J Am Coll Cardiol 2017;70:2476 86) HFpEF 50% or more (40-71%) of patients with CHF have preserved LV systolic function. HFpEF is an increasingly frequent hospital discharge. Outcomes
HFpEF April 26, 2018 (J Am Coll Cardiol 2017;70:2476 86) HFpEF 50% or more (40-71%) of patients with CHF have preserved LV systolic function. HFpEF is an increasingly frequent hospital discharge. Outcomes
Diagnosis is it really Heart Failure?
 ESC Congress Munich - 25-29 August 2012 Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction From Bench to Bedside Diagnosis is it really Heart Failure? Prof. Burkert Pieske Department of Cardiology Med.University
ESC Congress Munich - 25-29 August 2012 Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction From Bench to Bedside Diagnosis is it really Heart Failure? Prof. Burkert Pieske Department of Cardiology Med.University
Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension
 ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
Cardiac hypertrophy : differentiating disease from athlete
 Cardiac hypertrophy : differentiating disease from athlete Ario Soeryo Kuncoro, MD, Cardiologist Echocardiography Division, National Cardiovascular Centre Harapan Kita-Jakarta Departement of Cardiology
Cardiac hypertrophy : differentiating disease from athlete Ario Soeryo Kuncoro, MD, Cardiologist Echocardiography Division, National Cardiovascular Centre Harapan Kita-Jakarta Departement of Cardiology
Effect of Heart Rate on Tissue Doppler Measures of E/E
 Cardiology Department of Bangkok Metropolitan Administration Medical College and Vajira Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand Abstract Background: Our aim was to study the independent effect of heart rate (HR) on
Cardiology Department of Bangkok Metropolitan Administration Medical College and Vajira Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand Abstract Background: Our aim was to study the independent effect of heart rate (HR) on
Three-dimensional Wall Motion Tracking:
 Three-dimensional Wall Motion Tracking: A Novel Echocardiographic Method for the Assessment of Ventricular Volumes, Strain and Dyssynchrony Jeffrey C. Hill, BS, RDCS, FASE Jennifer L. Kane, RCS Gerard
Three-dimensional Wall Motion Tracking: A Novel Echocardiographic Method for the Assessment of Ventricular Volumes, Strain and Dyssynchrony Jeffrey C. Hill, BS, RDCS, FASE Jennifer L. Kane, RCS Gerard
Mechanisms of heart failure with normal EF Arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial coupling. What is the pathophysiology at presentation?
 Mechanisms of heart failure with normal EF Arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial coupling What is the pathophysiology at presentation? Ventricular-arterial coupling elastance Central arterial pressure
Mechanisms of heart failure with normal EF Arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial coupling What is the pathophysiology at presentation? Ventricular-arterial coupling elastance Central arterial pressure
Diastolic Dysfunction: Hypertension to Hypertrophy to Heart Failure
 Diastolic Dysfunction: Hypertension to Hypertrophy to Heart Failure Dr. Shelley Zieroth FRCPC Assistant Professor, Cardiology, University of Manitoba Director of Cardiac Transplant and Heart Failure Clinics
Diastolic Dysfunction: Hypertension to Hypertrophy to Heart Failure Dr. Shelley Zieroth FRCPC Assistant Professor, Cardiology, University of Manitoba Director of Cardiac Transplant and Heart Failure Clinics
Diastolic Heart Failure (HFpEF) Felix J. Rogers, DO, FACOI April 29, 2018
 Diastolic Heart Failure (HFpEF) Felix J. Rogers, DO, FACOI April 29, 2018 Case presentation MSO, an 81 year old woman was admitted to HFWH because of progressive dyspnea and difficult to control hypertension
Diastolic Heart Failure (HFpEF) Felix J. Rogers, DO, FACOI April 29, 2018 Case presentation MSO, an 81 year old woman was admitted to HFWH because of progressive dyspnea and difficult to control hypertension
Chamber Quantitation Guidelines: What is New?
 Chamber Quantitation Guidelines: What is New? Roberto M Lang, MD J AM Soc Echocardiogr 2005; 18:1440-1463 1 Approximately 10,000 citations iase in itune Cardiac Chamber Quantification: What is New? Database
Chamber Quantitation Guidelines: What is New? Roberto M Lang, MD J AM Soc Echocardiogr 2005; 18:1440-1463 1 Approximately 10,000 citations iase in itune Cardiac Chamber Quantification: What is New? Database
Strain Imaging: Myocardial Mechanics Simplified and Applied
 9/28/217 Strain Imaging: Myocardial Mechanics Simplified and Applied John Gorcsan III, MD Professor of Medicine Director of Clinical Research Division of Cardiology VECTORS OF CONTRACTION Shortening Thickening
9/28/217 Strain Imaging: Myocardial Mechanics Simplified and Applied John Gorcsan III, MD Professor of Medicine Director of Clinical Research Division of Cardiology VECTORS OF CONTRACTION Shortening Thickening
Diastolic Function Assessment Practical Ways to Incorporate into Every Echo
 Diastolic Function Assessment Practical Ways to Incorporate into Every Echo Jae K. Oh, MD Echo Hawaii 2018 2018 MFMER 3712003-1 Learning Objectives My presentation will help you to Appreciate the importance
Diastolic Function Assessment Practical Ways to Incorporate into Every Echo Jae K. Oh, MD Echo Hawaii 2018 2018 MFMER 3712003-1 Learning Objectives My presentation will help you to Appreciate the importance
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
 Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy From Genetics to ECHO Alexandra A Frogoudaki Second Cardiology Department ATTIKON University Hospital Athens University Athens, Greece EUROECHO 2010, Copenhagen, 11/12/2010
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy From Genetics to ECHO Alexandra A Frogoudaki Second Cardiology Department ATTIKON University Hospital Athens University Athens, Greece EUROECHO 2010, Copenhagen, 11/12/2010
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging. Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE
 Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None a. Turn the wall filters on and turn down the receiver gain. b. Turn
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None a. Turn the wall filters on and turn down the receiver gain. b. Turn
How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto
 How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto Introduction Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common genetic cardiomyopathy,
How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto Introduction Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common genetic cardiomyopathy,
An Integrated Approach to Study LV Diastolic Function
 An Integrated Approach to Study LV Diastolic Function Assoc. Prof. Adriana Ilieşiu, FESC University of Medicine Carol Davila Bucharest, Romania LV Diastolic Dysfunction impaired relaxation (early diastole)
An Integrated Approach to Study LV Diastolic Function Assoc. Prof. Adriana Ilieşiu, FESC University of Medicine Carol Davila Bucharest, Romania LV Diastolic Dysfunction impaired relaxation (early diastole)
Heart Failure: The Frequent, Forgotten and often Fatal Complication of Type 2 Diabetes
 Heart Failure: The Frequent, Forgotten and often Fatal Complication of Type 2 Diabetes DAVID S. H. BELL CHAIRMAN BELL, DSH. DIABETES CARE(2003)26:2433-41. Speaker s Bureau: AstraZeneca Novo Nordisk Janssen
Heart Failure: The Frequent, Forgotten and often Fatal Complication of Type 2 Diabetes DAVID S. H. BELL CHAIRMAN BELL, DSH. DIABETES CARE(2003)26:2433-41. Speaker s Bureau: AstraZeneca Novo Nordisk Janssen
Left ventricular systolic and diastolic dysfunction in asymptomatic, normotensive type 2 diabetes mellitus
 World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
Fetal cardiac function: what to use and does it make a difference?
 17 th International Conference on Prenatal Diagnosis and Therapy Lisbon, June 2013 Fetal cardiac function: what to use and does it make a difference? Fàtima Crispi Department of Maternal-Fetal Medicine,
17 th International Conference on Prenatal Diagnosis and Therapy Lisbon, June 2013 Fetal cardiac function: what to use and does it make a difference? Fàtima Crispi Department of Maternal-Fetal Medicine,
Left Ventricular Function In Subclinical Hypothyroidism
 Clinical Proceedings. 2016;12(1):13-19 Original Article Left Ventricular Function In Subclinical Hypothyroidism NK Thulaseedharan, P Geetha, TM Padmaraj Department of Internal Medicine, Govt. Medical College
Clinical Proceedings. 2016;12(1):13-19 Original Article Left Ventricular Function In Subclinical Hypothyroidism NK Thulaseedharan, P Geetha, TM Padmaraj Department of Internal Medicine, Govt. Medical College
Highlights from EuroEcho 2009 Echo in cardiomyopathies
 Highlights from EuroEcho 2009 Echo in cardiomyopathies Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania ESC Congress 2010 Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy To determine the differences
Highlights from EuroEcho 2009 Echo in cardiomyopathies Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania ESC Congress 2010 Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy To determine the differences
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging
 Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 1 Objective way with which to quantify the minor amplitude and temporal
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 1 Objective way with which to quantify the minor amplitude and temporal
Heart Failure in Women: Dr Goh Ping Ping Cardiologist Asian Heart & Vascular Centre
 Heart Failure in Women: More than EF? Dr Goh Ping Ping Cardiologist Asian Heart & Vascular Centre Overview Review pathophysiology as it relates to diagnosis and management Rational approach to workup:
Heart Failure in Women: More than EF? Dr Goh Ping Ping Cardiologist Asian Heart & Vascular Centre Overview Review pathophysiology as it relates to diagnosis and management Rational approach to workup:
THE DIASTOLIC STRESS TEST: A NEW CLINICAL TOOL? THE CONCEPT OF DIASTOLIC RESERVE
 Thierry C. Gillebert University of Ghent ESC Education Committee THE DIASTOLIC STRESS TEST: A NEW CLINICAL TOOL? THE CONCEPT OF DIASTOLIC RESERVE 1 Case: Ann, 63 years Suffered from metabolic syndrome
Thierry C. Gillebert University of Ghent ESC Education Committee THE DIASTOLIC STRESS TEST: A NEW CLINICAL TOOL? THE CONCEPT OF DIASTOLIC RESERVE 1 Case: Ann, 63 years Suffered from metabolic syndrome
Echocardiography in endocrine disorders
 Echocardiography in endocrine disorders Tamás Forster University of Szeged, Hungary Declaration of interest: Nothing to declare related to this topic Endocrine disorders n Excess hormone secretion n Hormone
Echocardiography in endocrine disorders Tamás Forster University of Szeged, Hungary Declaration of interest: Nothing to declare related to this topic Endocrine disorders n Excess hormone secretion n Hormone
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging
 Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 1 Objective way with which to quantify the minor amplitude and temporal
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 1 Objective way with which to quantify the minor amplitude and temporal
Objectives. Systolic Heart Failure: Definitions. Heart Failure: Historical Perspective 2/7/2009
 Objectives Diastolic Heart Failure and Indications for Echocardiography in the Asian Population Damon M. Kwan, MD UCSF Asian Heart & Vascular Symposium 02.07.09 Define diastolic heart failure and differentiate
Objectives Diastolic Heart Failure and Indications for Echocardiography in the Asian Population Damon M. Kwan, MD UCSF Asian Heart & Vascular Symposium 02.07.09 Define diastolic heart failure and differentiate
Index of subjects. effect on ventricular tachycardia 30 treatment with 101, 116 boosterpump 80 Brockenbrough phenomenon 55, 125
 145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
PRESENTER DISCLOSURE INFORMATION. There are no potential conflicts of interest regarding current presentation
 PRESENTER DISCLOSURE INFORMATION There are no potential conflicts of interest regarding current presentation Better synchrony and diastolic function for septal versus apical right ventricular permanent
PRESENTER DISCLOSURE INFORMATION There are no potential conflicts of interest regarding current presentation Better synchrony and diastolic function for septal versus apical right ventricular permanent
Cardiovascular Imaging Stress Echo
 Cardiovascular Imaging Stress Echo Theodora A Zaglavara, MD, PhD Cardiac Imaging Department INTERBALKAN MEDICAL CENTER Thessaloniki GREECE Evolution of Stress Echo: From Innovation to a Widely Established
Cardiovascular Imaging Stress Echo Theodora A Zaglavara, MD, PhD Cardiac Imaging Department INTERBALKAN MEDICAL CENTER Thessaloniki GREECE Evolution of Stress Echo: From Innovation to a Widely Established
How to Assess Diastolic Dysfunction?
 How to Assess Diastolic Dysfunction? Fausto J Pinto, MD, PhD, FESC, FACC, FASE Lisbon University Dyastolic Dysfunction Impaired relaxation Elevated filling pressures Ischemic heart disease Cardiomyopathies
How to Assess Diastolic Dysfunction? Fausto J Pinto, MD, PhD, FESC, FACC, FASE Lisbon University Dyastolic Dysfunction Impaired relaxation Elevated filling pressures Ischemic heart disease Cardiomyopathies
Basic Approach to the Echocardiographic Evaluation of Ventricular Diastolic Function
 Basic Approach to the Echocardiographic Evaluation of Ventricular Diastolic Function J A F E R A L I, M D U N I V E R S I T Y H O S P I T A L S C A S E M E D I C A L C E N T E R S T A F F C A R D I O T
Basic Approach to the Echocardiographic Evaluation of Ventricular Diastolic Function J A F E R A L I, M D U N I V E R S I T Y H O S P I T A L S C A S E M E D I C A L C E N T E R S T A F F C A R D I O T
Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right ventricular sinusoids
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 1990 Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 1990 Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right
Rotation: Echocardiography: Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE)
 Rotation: Echocardiography: Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE) Rotation Format and Responsibilities: Fellows rotate in the echocardiography laboratory in each clinical year. Rotations during the first
Rotation: Echocardiography: Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE) Rotation Format and Responsibilities: Fellows rotate in the echocardiography laboratory in each clinical year. Rotations during the first
A classic case of amyloid cardiomyopathy
 Images in... A classic case of amyloid cardiomyopathy Hayan Jouni, 1 William G Morice, 2 S Vincent Rajkumar, 3 Joerg Herrmann 4 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Images in... A classic case of amyloid cardiomyopathy Hayan Jouni, 1 William G Morice, 2 S Vincent Rajkumar, 3 Joerg Herrmann 4 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Prof. Samir Morcos Rafla Alexandria Univ. Cardiology Dept.
 Obesity as a risk factor for Atrial Fibrillation Prof. Samir Morcos Rafla Alexandria Univ. Cardiology Dept. CardioAlex 2010 smrafla@hotmail.com 1 Obesity has reached epidemic proportions in the United
Obesity as a risk factor for Atrial Fibrillation Prof. Samir Morcos Rafla Alexandria Univ. Cardiology Dept. CardioAlex 2010 smrafla@hotmail.com 1 Obesity has reached epidemic proportions in the United
Abstract nr AHA, Chicago November European Heart Journal Cardiovascular Imaging, in press. Nr Peter Blomstrand
 Left Ventricular Diastolic Function Assessed by Echocardiography and Tissue Doppler Imaging is a strong Predictor of Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Peter Blomstrand, Martin
Left Ventricular Diastolic Function Assessed by Echocardiography and Tissue Doppler Imaging is a strong Predictor of Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Peter Blomstrand, Martin
Common Codes for ICD-10
 Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
Echocardiography for the Electrophysiologist: Day-to-day practice. Emmanuel Fares, MD
 Echocardiography for the Electrophysiologist: Day-to-day practice Emmanuel Fares, MD EP and pacing service, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Cairo University Agenda Role of echo in arrhythmia management:
Echocardiography for the Electrophysiologist: Day-to-day practice Emmanuel Fares, MD EP and pacing service, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Cairo University Agenda Role of echo in arrhythmia management:
Strain/Untwisting/Diastolic Suction
 What Is Diastole and How to Assess It? Strain/Untwisting/Diastolic Suction James D. Thomas, M.D., F.A.C.C. Cardiovascular Imaging Center Department of Cardiology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland,
What Is Diastole and How to Assess It? Strain/Untwisting/Diastolic Suction James D. Thomas, M.D., F.A.C.C. Cardiovascular Imaging Center Department of Cardiology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland,
Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function
 Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman
Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman
VECTORS OF CONTRACTION
 1/3/216 Strain, Strain Rate, and Torsion: Myocardial Mechanics Simplified and Applied VECTORS OF CONTRACTION John Gorcsan, MD University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA Shortening Thickening Twisting No
1/3/216 Strain, Strain Rate, and Torsion: Myocardial Mechanics Simplified and Applied VECTORS OF CONTRACTION John Gorcsan, MD University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA Shortening Thickening Twisting No
Left ventricular diastolic function and filling pressure in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
 Left ventricular diastolic function and filling pressure in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy Bucharest, Romania My conflicts of interest: I have
Left ventricular diastolic function and filling pressure in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy Bucharest, Romania My conflicts of interest: I have
A study of left ventricular dysfunction and hypertrophy by various diagnostic modalities in normotensive type 2 diabetes mellitus patients
 Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 8:102-106 A study of left ventricular dysfunction and hypertrophy by various
Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 8:102-106 A study of left ventricular dysfunction and hypertrophy by various
Presenter: Steven Brust, HCS-D, HCS-H Product Manager, Home Health Coding Center
 Presenter: Steven Brust, HCS-D, HCS-H Product Manager, Home Health Coding Center Pinpoint & properly assign the appropriate heart failure codes Left- vs. Right-sided Left ventricular failure (LVF) may
Presenter: Steven Brust, HCS-D, HCS-H Product Manager, Home Health Coding Center Pinpoint & properly assign the appropriate heart failure codes Left- vs. Right-sided Left ventricular failure (LVF) may
HYPERTROPHY: Behind the curtain. V. Yotova St. Radboud Medical University Center, Nijmegen
 HYPERTROPHY: Behind the curtain V. Yotova St. Radboud Medical University Center, Nijmegen Disclosure of interest: none Relative wall thickness (cm) M 0.22 0.42 0.43 0.47 0.48 0.52 0.53 F 0.24 0.42 0.43
HYPERTROPHY: Behind the curtain V. Yotova St. Radboud Medical University Center, Nijmegen Disclosure of interest: none Relative wall thickness (cm) M 0.22 0.42 0.43 0.47 0.48 0.52 0.53 F 0.24 0.42 0.43
Aortic valve Stenosis: Insights in the evaluation of LV function. Erwan DONAL Cardiologie CHU Rennes
 Aortic valve Stenosis: Insights in the evaluation of LV function Erwan DONAL Cardiologie CHU Rennes erwan.donal@chu-rennes.fr Preload Afterload Myocardial Fiber Shortening Circumferential Longitudinal
Aortic valve Stenosis: Insights in the evaluation of LV function Erwan DONAL Cardiologie CHU Rennes erwan.donal@chu-rennes.fr Preload Afterload Myocardial Fiber Shortening Circumferential Longitudinal
LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital
 LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital LV inflow across MV LV LV outflow across AV LV LV geometric changes Pressure overload
LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital LV inflow across MV LV LV outflow across AV LV LV geometric changes Pressure overload
Diastolic Function: What the Sonographer Needs to Know. Echocardiographic Assessment of Diastolic Function: Basic Concepts 2/8/2012
 Diastolic Function: What the Sonographer Needs to Know Pat Bailey, RDCS, FASE Technical Director Beaumont Health System Echocardiographic Assessment of Diastolic Function: Basic Concepts Practical Hints
Diastolic Function: What the Sonographer Needs to Know Pat Bailey, RDCS, FASE Technical Director Beaumont Health System Echocardiographic Assessment of Diastolic Function: Basic Concepts Practical Hints
Michigan Society of Echocardiography 30 th Year Jubilee
 Michigan Society of Echocardiography 30 th Year Jubilee Stress Echocardiography in Valvular Heart Disease Moving Beyond CAD Karthik Ananthasubramaniam, MD FRCP (Glas) FACC FASE FASNC Associate Professor
Michigan Society of Echocardiography 30 th Year Jubilee Stress Echocardiography in Valvular Heart Disease Moving Beyond CAD Karthik Ananthasubramaniam, MD FRCP (Glas) FACC FASE FASNC Associate Professor
Aortic Root Dilatation as a Marker of Subclinical Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Patients with Cardiovascular Risk Factors
 The Journal of International Medical Research 2011; 39: 64 70 Aortic Root Dilatation as a Marker of Subclinical Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Patients with Cardiovascular Risk Factors H MASUGATA,
The Journal of International Medical Research 2011; 39: 64 70 Aortic Root Dilatation as a Marker of Subclinical Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Patients with Cardiovascular Risk Factors H MASUGATA,
L ecocardiografia nello Scompenso Cardiaco Acuto e cronico: vecchi dogmi e nuovi trends.
 V SESSIONE SCOMPENSO CARDIACO 2015 Genova, 13-14 Novembre 2015 L ecocardiografia nello Scompenso Cardiaco Acuto e cronico: vecchi dogmi e nuovi trends. Gian Paolo Bezante, MD, FACC UOC Clinica di Malattie
V SESSIONE SCOMPENSO CARDIACO 2015 Genova, 13-14 Novembre 2015 L ecocardiografia nello Scompenso Cardiaco Acuto e cronico: vecchi dogmi e nuovi trends. Gian Paolo Bezante, MD, FACC UOC Clinica di Malattie
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW
 PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
Review of Cardiac Imaging Modalities in the Renal Patient. George Youssef
 Review of Cardiac Imaging Modalities in the Renal Patient George Youssef ECHO Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) assessment Diastolic dysfunction Stress ECHO Cardiac CT angiography Echocardiography - positives
Review of Cardiac Imaging Modalities in the Renal Patient George Youssef ECHO Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) assessment Diastolic dysfunction Stress ECHO Cardiac CT angiography Echocardiography - positives
Conflict of interest: none declared
 The value of left ventricular global longitudinal strain assessed by three-dimensional strain imaging in the early detection of anthracycline-mediated cardiotoxicity C. Mornoş, A. Ionac, D. Cozma, S. Pescariu,
The value of left ventricular global longitudinal strain assessed by three-dimensional strain imaging in the early detection of anthracycline-mediated cardiotoxicity C. Mornoş, A. Ionac, D. Cozma, S. Pescariu,
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We. ACHD Patients
 Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Left Atrial Volume:?Physiologic Model for Cardiovascular Disease Risk.
 Left Atrial Volume:?Physiologic Model for Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Dr Gitura Muriuki Physician Kenyatta National Hospital Aging Epidemic US approx 35m 65yrs plus. Fastest growing cohort 80s. Comorbidities
Left Atrial Volume:?Physiologic Model for Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Dr Gitura Muriuki Physician Kenyatta National Hospital Aging Epidemic US approx 35m 65yrs plus. Fastest growing cohort 80s. Comorbidities
Chapter 52 Diastolic Stress Echocardiography
 Chapter 52 Diastolic Stress Echocardiography SATISH C. GOVIND AASHA S. GOPAL ANATOLI KIOTSEKOGLOU SAMIR K. SAHA PHYSIOLOGY OF DIASTOLE Left ventricular (LV) diastole can typically be defined as a phase
Chapter 52 Diastolic Stress Echocardiography SATISH C. GOVIND AASHA S. GOPAL ANATOLI KIOTSEKOGLOU SAMIR K. SAHA PHYSIOLOGY OF DIASTOLE Left ventricular (LV) diastole can typically be defined as a phase
Carlos Eduardo Suaide Silva, Luiz Darcy Cortez Ferreira, Luciana Braz Peixoto, Claudia Gianini Monaco, Manuel Adán Gil, Juarez Ortiz
 Silva et al Original Article Arq Bras Cardiol Study of the Myocardial Contraction and Relaxation Velocities through Doppler Tissue Imaging Echocardiography. A New Alternative in the Assessment of the Segmental
Silva et al Original Article Arq Bras Cardiol Study of the Myocardial Contraction and Relaxation Velocities through Doppler Tissue Imaging Echocardiography. A New Alternative in the Assessment of the Segmental
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine
 MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2013; 8(3): 285-289 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine STATE-OF-THE-ART Diastolic Heart Failure in Hypertension: Possible Preventive Benefits of Nebivolol Beyond
MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2013; 8(3): 285-289 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine STATE-OF-THE-ART Diastolic Heart Failure in Hypertension: Possible Preventive Benefits of Nebivolol Beyond
Assessing the Impact on the Right Ventricle
 Advances in Tricuspid Regurgitation Congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Munich, August 25-29, 2012 Assessing the Impact on the Right Ventricle Stephan Rosenkranz, MD Clinic III for Internal
Advances in Tricuspid Regurgitation Congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Munich, August 25-29, 2012 Assessing the Impact on the Right Ventricle Stephan Rosenkranz, MD Clinic III for Internal
Ref 1. Ref 2. Ref 3. Ref 4. See graph
 Ref 1 Ref 2 Ref 3 1. Ages 6-23 y/o 2. Significant LVM differences by gender 3. For males 95 th percentiles: a. LVM/BSA = 103 b. LVM/height = 100 4. For females 95 th percentiles: a. LVM/BSA = 84 b. LVM/height
Ref 1 Ref 2 Ref 3 1. Ages 6-23 y/o 2. Significant LVM differences by gender 3. For males 95 th percentiles: a. LVM/BSA = 103 b. LVM/height = 100 4. For females 95 th percentiles: a. LVM/BSA = 84 b. LVM/height
Myocardial Creatinkinase as a Possible Predictor. of Myocardial Changes in Children. with Biciuspid Aortic Valve
 Biological Markers and Guided Therapy, Vol. 1, 2014, no. 2, 79-83 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/bmgt.2014.479 Myocardial Creatinkinase as a Possible Predictor of Myocardial Changes
Biological Markers and Guided Therapy, Vol. 1, 2014, no. 2, 79-83 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/bmgt.2014.479 Myocardial Creatinkinase as a Possible Predictor of Myocardial Changes
Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease
 Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease L. Youngmin Eun, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine The potential advantage of ultrasound
Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease L. Youngmin Eun, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine The potential advantage of ultrasound
ECHO HAWAII. Role of Stress Echo in Valvular Heart Disease. Not only ischemia! Cardiomyopathy. Prosthetic Valve. Diastolic Dysfunction
 Role of Stress Echo in Valvular Heart Disease ECHO HAWAII January 15 19, 2018 Kenya Kusunose, MD, PhD, FASE Tokushima University Hospital Japan Not only ischemia! Cardiomyopathy Prosthetic Valve Diastolic
Role of Stress Echo in Valvular Heart Disease ECHO HAWAII January 15 19, 2018 Kenya Kusunose, MD, PhD, FASE Tokushima University Hospital Japan Not only ischemia! Cardiomyopathy Prosthetic Valve Diastolic
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 4, April ISSN Left ventricle function in systemic
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 4, April-2015 1536 Left ventricle function in systemic hypertension from M-Mode to speckle tracking echocardiography Noha Hassanin
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 4, April-2015 1536 Left ventricle function in systemic hypertension from M-Mode to speckle tracking echocardiography Noha Hassanin
Segmental Tissue Doppler Image-Derived Tei Index in Patients With Regional Wall Motion Abnormalities
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2010.40.3.114 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2010 The Korean Society of Cardiology Open Access Segmental Tissue Doppler Image-Derived Tei Index
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2010.40.3.114 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2010 The Korean Society of Cardiology Open Access Segmental Tissue Doppler Image-Derived Tei Index
TO LEFT VENTRICULAR DIASTOLIC FUNCTION IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS AND WITHOUT OVERT HEART DISEASE
 1 Department of Cardiology, Babol University of Medical Sciences, Iran 2 Department of Endocrinology, Babol University of Medical Sciences, Iran Professional Paper Received: November 4, 2006 Accepted:
1 Department of Cardiology, Babol University of Medical Sciences, Iran 2 Department of Endocrinology, Babol University of Medical Sciences, Iran Professional Paper Received: November 4, 2006 Accepted:
Natural History and Echo Evaluation of Aortic Stenosis
 Natural History and Echo Evaluation of Aortic Stenosis Prof. Patrizio LANCELLOTTI, MD, PhD Heart Valve Clinic, University of Liège, CHU Sart Tilman, Liège, BELGIUM AORTIC STENOSIS First valvular disease
Natural History and Echo Evaluation of Aortic Stenosis Prof. Patrizio LANCELLOTTI, MD, PhD Heart Valve Clinic, University of Liège, CHU Sart Tilman, Liège, BELGIUM AORTIC STENOSIS First valvular disease
