Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) In Primary Care Supporting early detection and consistent management
|
|
|
- Shannon Sparks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) In Primary Care Supporting early detection and consistent management Responding to AKI Warning Stage Test Results for Adults in Primary Care: Best Practice Guidance
2 AKI in Primary Care AKI: Context and focus for primary care Definition, staging and association with acute illness Implications for patients, the NHS and primary care AKI: Detection in primary care Identifying patients at risk of AKI Interpreting AKI warning stage test results within clinical context AKI: Management in primary care Think Kidneys Think Cause, Think Drugs, Think Fluid Status, Think Review When to consider admission and / or renal referral
3 AKI in Primary Care AKI: Context and focus for primary care Definition, staging and association with acute illness Implications for patients, the NHS and primary care AKI: Detection in primary care Identifying patients at risk of AKI Interpreting AKI warning stage test results within clinical context AKI: Management in primary care Think Kidneys Think Cause, Think Drugs, Think Fluid Status, Think Review When to consider admission and / or renal referral
4 AKI: Context and focus for primary care What is AKI? A sudden reduction in kidney function ( usually coincides with onset of acute illness) Why is AKI important? Associated with adverse outcomes for patients ( consider AKI an acute illness severity marker) Common ( more than 1 / 2 million people in England develop AKI every year) Why has a national Think Kidneys campaign been established to raise AKI awareness? Public 1 and Healthcare Professional 2 awareness of AKI is poor UK Study (2009) found deficiencies in AKI care were common - including delayed AKI recognition 3 1 Ipsos MORI Survey (2014). Understanding what the public know about their kidneys and what they do. 2 Muniraju et al (2012). Diagnosis and management of acute kidney injury. Clinical Medicine 12(3): NCEPOD Report (2009). Acute Kidney Injury: Adding Insult to Injury.
5 AKI: Context and focus for primary care Why are primary care teams being alerted to AKI? Many patients in community are at risk of AKI ( require prompt review when acutely unwell) Most AKI occurs in community ( 2 / 3 of hospital AKI cases begin pre-hospital admission) 1 What can primary care teams do to reduce patient harm caused by AKI? 1. Raise AKI awareness and limit AKI risk ( AKI often asymptomatic further delaying AKI detection) 2. Promote prompt AKI detection ( consider AKI early during acute illness episodes) 3. Initiate simple interventions early ( increase chance of recovery / reduce treatment costs) 4. Perform post-aki review ( detect new or progressive CKD +/- restart drugs suspended during AKI) 1 Selby et al. (2012). Defining the Cause of Death in Hospitalised Patients with AKI. PLoS ONE. 7 (11): e
6 AKI in primary care AKI: Context and focus for primary care Definition, staging and association with acute illness Implications for patients, the NHS and primary care AKI: Detection in primary care Identifying patients at risk of AKI Interpreting AKI warning stage test results within clinical context AKI: Management in primary care Think Kidneys Think Cause, Think Drugs, Think Fluid Status, Think Review When to consider admission and / or renal referral
7 AKI: Definition, Staging and Association with Acute Illness AKI definition AKI is a clinical and biochemical syndrome reflecting abrupt kidney dysfunction AKI is not a primary disease nor a diagnosis AKI is a heterogeneous syndrome with various causes and variable outcomes AKI staging AKI stage is determined by acute changes to serum creatinine and / or urine output AKI usually occurs secondary to acute illness ( commonly sepsis) Identifying underlying acute illness causing AKI is key to establishing primary diagnosis Treating underlying acute illness key to treating most AKI
8 AKI Definition (Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes, KDIGO criteria 1 ) AKI Definition Serum Creatinine 2 Urine Output 4 Increase in serum creatinine by >26 mol/l 48 hrs Increase in serum creatinine by 1.5 times baseline 3 which is known or presumed to have occurred within previous 7 days 1 Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney International Supplement 2012;2(1): Urine volume <0.5 ml/kg/hr for 6 hrs 2 Note serum creatinine changes and not estimated GFR (egfr) define AKI (as egfr is not a reliable indicator of true GFR during unsteady clinical states associated with AKI) Drug dosing should not be based upon egfr during AKI episodes. 2 Note timescale of creatinine change is central to AKI definition if no recent preceding blood test then incorporate clinical context to determine if creatinine change likely to have occurred during preceding week (ie. acutely ). 3 Baseline creatinine value should be considered as the patient s usual creatinine when clinically well determine by reviewing patient s previous blood results within clinical context. Assume normal baseline if no previous blood tests. 4 In practice urine output criteria can only be applied to hospitalised patients who are catheterised - but a reliable history of low or absent urine output should alert the clinician to the possibility of AKI.
9 AKI Staging (Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes, KDIGO criteria 1 ) AKI Stage Serum Creatinine Urine Output Stage 1 Increase in serum creatinine by >26 mol/l 48 hrs OR an increase in serum creatinine by 1.5 x baseline 2 urine output <0.5mL/kg/hr for 6-12hrs Stage 2 Increase in serum creatinine by 2 x baseline 2 urine output <0.5mL/kg/h for 12hrs Stage 3 Increase in serum creatinine by 3 x baseline 2 OR an increase in serum creatinine by 1.5 baseline to > 354 mol/l urine output <0.3mL/kg/h for 24hrs OR anuria for 12 h 2 When creatinine change is known or presumed to have occurred within previous 7 days 1 Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney International Supplement 2012;2(1):1 138.
10 AKI as a patient safety barometer associated with acute illness Acutely Unwell Patient BIDIRECTIONAL RELATIONSHIP CRP HR BP Creatinine AKI Deteriorating Patient Temp Urine output BIDIRECTIONAL RELATIONSHIP Prompt recognition and good management of AKI requires and often reflects Prompt recognition and good management of acutely unwell patients
11 AKI in primary care AKI: Context and focus Definition, staging and association with acute illness Implications for patients, the NHS and primary care AKI: Detection in primary care Identifying patients at risk of AKI Interpreting AKI warning stage test results within clinical context AKI: Management in primary care Think Kidneys Think Cause, Think Drugs, Think Fluid Status, Think Review When to consider admission and / or renal referral
12 AKI Patient Implications: Independently associated with adverse acute and chronic outcomes AKI associated with increased patient mortality Odds of death AKI severity in UK Study 1 Other studies show association with death persists if Acute and chronic co-morbidities accounted for 2 Patients followed up post discharge / longer term 3 1 Selby N. et al. (2012). Use of Electronic Results Reporting to Diagnose and Monitor AKI in Hospitalized Patients. CJASN. 7: Chertow et al. (2005). Acute Kidney Injury, Mortality, Length of Stay, and Costs in Hospitalized Patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 16: Coca et al. (2012). Chronic kidney disease after acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Int. 81,
13 AKI Patient Implications: Independently associated with adverse acute and chronic outcomes Independently associated with adverse acute and chronic outcomes AKI associated with increased patient morbidity Meta-analysis shows AKI is risk factor for CKD 1 Pooled hazard adjusted ratios for CKD post-aki 1 CKD also associated with risk of end-stage renal failure 1, cardiovascular disease and death 2 1 Coca et al. (2012). Chronic kidney disease after acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Int. 81, Chronic Kidney disease Consortium (2010). Association of egfr and albuminuria with all-cause & cardiovascular mortality. Lancet 375:
14 AKI NHS Implications: Significant additional impact on Healthcare Resources AKI commonly complicates acute illness and hospital admissions AKI associated with 25.4% of unselected emergency admissions to a large UK acute hospital Trust 1 AKI increases duration and complexity of acute illness AKI increases length of hospital stay (LOS) 1 : AKI group LOS almost 3x higher than non AKI group (10 vs 4 days) 1 AKI group more often required critical care beds (8.1% vs 1.7%) 1 AKI associated with complex treatments such as dialysis ( may be required permanently) AKI significantly increases healthcare costs as a consequence of these complications 1 Challiner et al. (2014). Incidence and consequence of AKI in unselected emergency admissions to a large acute UK hospital trust. BMC Nephrology. 15:84
15 AKI aspirations for primary care teams Primary care teams well located to:- 1. Raise AKI awareness and limit AKI risk in at risk patient groups 2. Detect AKI and deliver simple interventions early ( to limit AKI severity and duration) 3. Undertake post AKI review to a. Detect new or worsening Chronic Kidney Disease post AKI b. Restart drugs suspended during AKI ( especially if prognostic benefit) c. Limit risk of further AKI ( patient / carer advice where appropriate)
16 AKI and primary care: Prompt detection and management Two National AKI Patient Safety Alerts aim to promote AKI care in the community Mandates national automated AKI detection system to generate AKI warning alerts alongside blood tests Pilot studies indicate Full Time Equivalent GP expects about one AKI e-alert every 1-2 months (> 1 / 2 likely AKI Stage 1) Health care staff should be signposted to Think Kidneys AKI resources (hyperlinks to relevant resources at foot of slides) Resources include AKI guidelines to support appropriate response to AKI warning alerts by Primary Care Teams THINK KIDNEYS Resource: Full Primary Care AKI Guidelines LINK
17 AKI and Primary Care: Post AKI review AKI also associated with adverse long term outcomes Pooled hazard adjusted ratios for End-Stage Renal Failure (ESRF) post-aki 1 Renal Health: AKI is associated with new or worsening CKD, including ESRF especially if severe or multi-hit AKI in 1. Elderly patients 2. Patients with diabetes 3. Patients with pre-existing CKD General Health: Drugs with prognostic long term benefit (eg ACE-I for heart failure) may be suspended in clinical context of acute illness and AKI long term prognostic benefit of such drugs lost if not restarted post AKI 1 Coca et al. (2012). Chronic kidney disease after acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Int. 81,
18 Post AKI reviews consider:- AKI and Primary Care: Post AKI review 1. Monitoring for new or worsening CKD especially if creatinine has not returned to baseline or other CKD risk factors. NICE guidelines advocate monitoring renal function for 3 years post AKI. 2. Restarting drugs with prognostic benefit once clinical context improves and stabilises / acute illness resolved unless compelling contraindication to drug remains (or ongoing AKI risk > drug benefit). 3. Onward drug adjustments tailored to chronic disease and acute clinical context ( see 2 next slides) 4. Patient / carer advice to limit further AKI episodes ( utilise AKI Patient Leaflets, links below) Encourage early medical contact to assess blood pressure, renal function and medications if a. Acutely unwell b. Unable to maintain good fluid intake c. Reduced urine output noted THINK KIDNEYS Resources: Restarting drugs LINK, Sick Day Guidance for Drugs LINK, Patient Advice Leaflets for those who have sustained AKI LINK and those at persistent risk of AKI LINK
19 Clinical Context and ACE-Inhibitors Current Clinical Context Unstable Clinical Context Long term ACE-I Sepsis therapy or other of proven acute illness Hypovolaemia prognostic benefit in True such or relative patient hypotension groups? Assess Heart Failure Diabetes Mellitus Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic Clinical Context AKI Risk Threshold to suspend ACE-I / ARB (+/- other anti-hypertensives if BP low) During Same unstable patient context groups such drugs may 1. at Worsen high risk renal of perfusion AKI if 2. Magnify acutely AKI unwell severity / duration
20 Current Clinical Context Stable Clinical Context Recovery from acute illness / clinically stable Restoration of volume / BP Clinical Context and ACE-Inhibitors Threshold to resume ACE-I / ARB Post AKI / Renal function stabilised Try to restart drug if strong indication Review patient & bloods 1-2 weeks See resource below but generally: Heart Failure Diabetes Mellitus Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic Clinical Context Prognostic benefit of ACE-I / ARB Initial creatinine rise 30% often OK If creatinine rise 30% / progressive: 1. Suspend drug and review patient 2. Consider renal opinion 3. If indication for ACE-I is heart failure consider cardiology opinion THINK KIDNEYS RESOURCE: ACE-Inhibitor and diuretic use in Primary Care LINK
21 ACE-I / ARB initiation or dose up-titration in Primary Care 1. Ensure clinical context is stable consider patient sick day advice. 2. Use Immediate pre-treatment creatinine as baseline creatinine. 3. Arrange repeat blood tests within 1-2 weeks. Serum creatinine rise > 15% but < 30% from baseline 1. Continue drug but arrange to re-assess clinical status, BP and bloods within 1-2 weeks. 2. Consider other BP-lowering drugs if sbp <120, including diuretics if evidence of hypovolaemia. 3. Continue drug if creatinine stabilises on repeat testing (< 30% above pre-treatment baseline). Continuing ACE-I in chronic heart failure sometimes may be overall beneficial even if creatinine rise > 30% Initial Assessment Serum creatinine rise > 30% from baseline 1. Promptly re-assess clinical, fluid and BP status. 2. Consider other BP-lowering drugs if sbp <120, including diuretics if evidence of hypovolaemia. 3. Repeat bloods 5-7 days if renal function remains > 30% despite above measures: 1. Stop drug and consider local renal opinion 2. If indication for drug is heart failure also obtain advice from local heart failure team THINK KIDNEYS RESOURCE: ACE-Inhibitor and diuretic use in Primary Care LINK THINK KIDNEYS RESOURCE: Patient Sick Day Guidance for Drugs LINK
22 AKI in primary care AKI: Context and focus Definition, staging and causes Implications for patients, the NHS and primary care AKI: Detection in primary care Identifying patients at risk of AKI Interpreting AKI warning stage test results within clinical context AKI: Management in primary care Think Kidneys Think Cause, Think Drugs, Think Fluid Status, Think Review When to consider admission and / or renal referral
23 AKI in Primary Care: Patients at risk of AKI in Community Situation Specific - Exposure Any acutely unwell patient is at acute risk of AKI AKI vigilance in clinically unstable, especially if Hypovolaemia, dehydration, reduced oral intake Absolute hypotension (sbp < 90 mmhg) Relative hypotension ( 40 mmhg from baseline BP) Sepsis Recent operation or iodinated contrast scan NSAIDs, BP-lowering ± diuretic drug use 1week Patient Specific - Susceptibility Many patients remain at persistent AKI risk AKI vigilance in at risk communities Older age patients (especially with polypharmacy) Co-morbidities (eg. CKD, DM & Heart Failure) Psycho-social setting (eg. In care home, mobility / dementia unable to self regulate fluid intake) Consider risk reduction strategies in such groups promote self care (or carers) to avoid dehydration similar advice / resources as for "Post AKI review THINK KIDNEYS Resource: Advice on communities at risk of AKI LINK 23
24 AKI in primary care AKI: Context and focus Definition, staging and causes Implications for patients, the NHS and primary care AKI: Detection in primary care Identifying patients at risk of AKI Interpreting AKI warning stage test results within clinical context AKI: Management in primary care Think Kidneys Think Cause, Think Drugs, Think Fluid Status, Think Review When to consider admission and / or renal referral
25 Interpreting AKI warning stage test results in Primary Care: Clinical context is Key A national automated AKI detection system aims to improve early recognition of AKI Presentation of AKI warning alerts depends upon Pathology System used, examples below: Alert system relies upon computerised interpretation of blood results in isolation from clinical context AKI is not merely a biochemical finding do not rely upon alert system to detect all AKI cases Always review current and previous blood results within clinical context in order to validate AKI alert
26 Interpreting AKI warning stage test results in Primary Care: Clinical context is Key A positive AKI alert simply alerts clinician to possibility of AKI false positives can occur (see table below) A negative AKI alert does not always rule out AKI false negatives can occur (see table below) False positive examples Recent Pregnancy: Creatinine falls during pregnancy creatinine rise expected / normal post delivery. Drugs (eg. trimethoprim) inhibiting tubular creatinine secretion: Can cause creatinine rise whilst GFR stable. Recent IV fluid: spuriously low baseline creatinine. False negatives example Previous AKI within last year: Algorithm may calculate spuriously high baseline creatinine for patient. If alert unexpected and stable clinical context consider repeating bloods within 48-72hrs to determine whether any creatinine changes are truly dynamic (AKI) or relatively stable / false positive. If no alert issued though high clinical suspicion of AKI / acute illness it especially important for clinician to review current and previous blood results before ruling out AKI. THINK KIDNEYS Resource: Further guidance on page 7 of Primary Care AKI Guidelines LINK
27 Interpreting AKI warning stage test results in Primary Care: Infrastructure & Process Any automated detection system is only effective if leads to timely and appropriate intervention Detection Alert Intervention Detection system does not issue interruptive alert and in isolation does not ensure timely intervention Correct effective utilisation of automated AKI system thus requires clinicians:- 1. Actively review alerts within clinical context in timely fashion Practices should ensure clinicians reviewing alerts know reason why blood tests were taken Particular challenge if results reviewed by out of hours services 2. Respond to alerts and clinical context with timely intervention Think Kidneys Primary Care Resource includes recommended alert response times ( next slide) THINK KIDNEYS Resource: Full Primary Care AKI Guidelines LINK
28 Table 1: Recommended response times to AKI Warning Stage Test Results for Adults in Primary Care In order AKI to Warning utilise this Stage Also table Test consider Result correctly if other first determine features present pre-test to probability prompt Clinical Context earlier that Within review creatinine Which / hospital rise Blood reflects Test admission Taken true AKI by considering Confirm or refute automated AKI Test Result by LOW Pre-test Probability of AKI HIGH Pre-test Probability of AKI comparing 1. What patient s was clinical current context creatinine when against the blood test was Stable taken? Clinical Context 3. Are factors present to suggest Context acute of Acute kidney Illness dysfunction? patient s baseline creatinine Stable Clinical Context Unstable Clinical Context Clinical Features Biochemical Features Chronic disease AKI / drug Warning monitoring Stage 1 Assessment Consider of acute clinical illness review 72 hours of e-alert Consider clinical review 24 hours of e-alert Current creatinine> 1.5 x baseline level Reduced urine output Creatinine rise from recent baseline If AKI confirmed manage as per table 2 Likely Stage 1 AKI manage as per table 2 (Assume (or creatinine unstable rise clinical >26 mol/l context 48 if hrs) clinical context unknown) Patient unwell Further creatinine rise on repeat test 2. Are risk factors for AKI present? 4. Are additional factors present to prompt early review? Consider clinical review 24 hours of e-alert Consider clinical review 6 hours of e-alert AKI Warning Stage 2 Chronic AKI Risk Factors Acute AKI If AKI Risk confirmed Factors manage Patient as per Factors table 2 Likely Stage Clinical 2 AKI / manage Biochemical as per table factors 2 Current creatinine> 2 x baseline level Chronic Kidney Disease Acute illness Stage 4 or 5 CKD Patient unwell Chronic Heart AKI Failure Warning / Liver Stage Disease 3 New drug started Kidney transplant recipient Serum K+ 6.0 mmol/l Consider clinical review 6 hours of e-alert Consider Immediate Admission Current creatinine> 3 x baseline level Diabetes Mellitus Poor oral If fluid AKI confirmed intake consider Frail admission / co-morbidities Likely intrinsic Stage 3 AKI kidney disease (or creatinine> 1.5 x baseline and > 354 mol/l) Cognitive / Neurological Disease Recent previous AKI Urinary tract obstruction Providing access to salient clinical data when taking blood tests via laboratory forms, medical records or handover will support timely appropriate response especially when alert reviewed by out of hours GP unfamiliar with patient
29 AKI in primary care AKI: Context and focus Definition, staging and causes Implications for patients, the NHS and primary care AKI: Detection in primary care Identifying patients at risk of AKI Interpreting AKI warning stage test results within clinical context AKI: Management in primary care Think Kidneys Think Cause, Think Drugs, Think Fluid Status, Think Review When to consider admission and / or renal referral
30 Common causes of AKI in Primary Care: Pre-renal and Post Renal AKI AKI: Pre-renal Renal Insults Kidney function requires adequate renal perfusion 80-90% of all AKI due to acute illness causing a significant / sustained reduction in renal perfusion:- Vasodilatation and hypotension due to sepsis ECV loss due to diarrhoea & vomiting, or bleeding Hypotension due to acute heart failure Some drugs may magnify AKI during such states AKI: Post-renal Renal Insults Kidney function requires adequate urine drainage threshold for early renal USS in patients reporting urine output, especially if unwell +/- history of :- Males with enlarged prostates Renal calculi Pelvic or abdominal masses Delays relieving obstruction may magnify AKI THINK KIDNEYS Resource: AKI & Drugs Guideline LINK
31 AKI Causes: Pre-renal and Post-renal account for majority of AKI Addressing these 4 common drivers of AKI will address majority (> 90%) of AKI Volume depletion Drugs Sepsis MOST AKI Obstruction Intrinsic kidney disease is a less common cause of AKI But important not to miss
32 AKI Causes: When to suspect Intrinsic Renal Disease Intrinsic Renal Disease is a less common cause of AKI ( 5%) Important not to miss may benefit from early renal referral Group of disorders reflecting toxin and / or immune-mediated kidney damage Urine dip often key to diagnosis protein ± blood on dip should raise suspicion of intrinsic disease Myeloma and Tubulo-Interstitial Nephritis (TIN) exceptions can be present with normal urine dip Especially consider intrinsic renal disease as cause of AKI if:- 1. No common / obvious cause for AKI (ie. sepsis, volume depletion, drugs or obstruction) and / or 2. Urine dip +ve for protein +/- blood and / or 3. Clinical features of nephritis or systemic disease causing AKI present ( see next slide)
33 AKI Causes: When to suspect Intrinsic Renal Disease Clinical Clues and Screening for intrinsic renal disease in AKI Clinical context Potential diagnosis Example screening tests Rash +/- arthralgia SLE, vasculitis, HSP, cryoglobulinaemia ANA, ANCA, complement Haemoptysis Anti-GBM disease, vasculitis Anti-GBM Ab, ANCA Crush injury / long lie Rhabdomyolysis Creatine kinase Haemolysis & platelets Thrombotic microangiopathy (TTP, HUS) Blood film, LDH Severe hypertension Malignant hypertension Fundoscopy Vascular intervention Cholesterol embolisation Complement, eosinophils Recent chemotherapy Tumour lysis syndrome Uric acid level Ca 2+ +/- bone pain Multiple myeloma Myeloma screen Recently started new drug AKI National Programme Tubulo-Interstitial Introducing the Think Kidneys Nephritis campaign (TIN) Karen Thomas Eosinophils (not always) 33
34 THINK KIDNEYS Resource: AKI & Drugs Guidelines LINK Table 2: Management of AKI in Primary Care "Think" Cause "Think" Medication "Think" Fluids "Think" Review History of acute Illness? Think Review Sepsis patient Think within Hypotension clinical context History of acute Illness? Intrinsic renal disease Think Sepsis (E.g. vasculitis)? Think Hypotension Urinary tract obstruction? Positive Urinalysis? UTI symptoms absent? Multisystem symptoms? Think intrinsic disease Urinary Tract Symptoms? Palpable bladder? Consider urgent USS Think obstruction Any medication which could Review drugs exacerbate AKI? within clinical context Consider Could drug withholding: be driving AKI? Think NSAIDs suspend drug? eg NSAIDs Diuretics BP drugs if low BP Antihypertensive Diuretics if dehydrated medication Could drug accumulate? Any medication Think change which dose? may eg accumulate Diabetic and medication cause harm during Digoxin AKI? Opiates / gabapentin Any Could new medication new drug cause that may AKI? be causing Think AKI causes (E.g. drug of TIN induced? eg tubulo-interstitial NSAIDs, antibiotics nephritis)? Proton pump inhibitors What is the patient s volume status? Tailor fluid advice to clinical context If hypovolaemic, can the patient If hypovolemic consider if increase oral fluids? Urine output +/- BP low? Can patient drink more? When did the patient last pass Are IV fluids required? urine? If fluid overloaded consider If risk of lung oedema? Is patient passing urine? Are diuretics indicated? Does the patient need acute Time next review to admission? clinical & chemical context If not, Consider when early will you review review? (< 12 hours) +/- admission if Have Patient you ensured unwell handover? Stage 3 AKI K + >6.5 (not haemolysed) Risk of lung oedema Consider repeating bloods:- 72 hrs for stage 1 AKI 24 hrs for stage 2 AKI 12 hrs for stage 3 AKI and Ensure clinical context for repeat bloods handed over to those reviewing results
35 Contact Think Kidneys How to find out more Karen Thomas Think Kidneys Programme Manager UK Renal Registry Teresa Wallace Think Kidneys Programme Coordinator UK Renal Registry Richard Fluck National Clinical Director for Renal NHS England Joan Russell Head of Patient Safety NHS England Ron Cullen Director UK Renal Registry
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines. AKI guidelines for primary care
 Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines AKI guidelines for primary care Contents: Flow Diagram: Recommended response time to AKI warning stage test results for adults in primary care 2 Table
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines AKI guidelines for primary care Contents: Flow Diagram: Recommended response time to AKI warning stage test results for adults in primary care 2 Table
Doncaster & Bassetlaw. AKI guidelines for primary care
 Doncaster & Bassetlaw AKI guidelines for primary care Contents: FLOW DIAGRAM: MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH AKI DETECTED IN PRIMARY CARE... 2 FLOW DIAGRAM: MANAGEMENT OF HYPERKALAEMIA.... 3 FLOW DIAGRAM:
Doncaster & Bassetlaw AKI guidelines for primary care Contents: FLOW DIAGRAM: MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH AKI DETECTED IN PRIMARY CARE... 2 FLOW DIAGRAM: MANAGEMENT OF HYPERKALAEMIA.... 3 FLOW DIAGRAM:
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education
 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education Year Three Developed Summer 2017 Objectives Understand Acute Kidney Injury and its relevance to patient care. Brief revision of the Anatomy and physiology
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education Year Three Developed Summer 2017 Objectives Understand Acute Kidney Injury and its relevance to patient care. Brief revision of the Anatomy and physiology
Acute Kidney Injury 2
 South West Cardiovascular Strategic Clinical Network Acute Kidney Injury 2 Audit review meeting 18/07/2014 Redwood Education Centre Author: Summary of results: Dr Preetham Boddana Consultant Nephrologist
South West Cardiovascular Strategic Clinical Network Acute Kidney Injury 2 Audit review meeting 18/07/2014 Redwood Education Centre Author: Summary of results: Dr Preetham Boddana Consultant Nephrologist
Nephrology. 3 rd Year Revision Session 06/05/17 Cathal Hannan
 Nephrology 3 rd Year Revision Session 06/05/17 Cathal Hannan Aims Acute Kidney Injury-recognition and management Sample OSCE Station Clinically relevant renal physiology Aetiology of Chronic Kidney Disease
Nephrology 3 rd Year Revision Session 06/05/17 Cathal Hannan Aims Acute Kidney Injury-recognition and management Sample OSCE Station Clinically relevant renal physiology Aetiology of Chronic Kidney Disease
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
Liverpool experience of Community AKI care
 Liverpool experience of Community AKI care Shahed Ahmed Consultant Nephrologist and Honorary Lecturer Royal Liverpool University Hospital shahed.ahmed@rlbuht.nhs.uk Is AKI really a problem? 100000, deaths
Liverpool experience of Community AKI care Shahed Ahmed Consultant Nephrologist and Honorary Lecturer Royal Liverpool University Hospital shahed.ahmed@rlbuht.nhs.uk Is AKI really a problem? 100000, deaths
WEEK. MPharm Programme. Acute Kidney Injury. Alan M. Green MPHM13: Acute Kidney Injury. Slide 1 of 47
 MPharm Programme Acute Kidney Injury Alan M. Green 2017 Slide 1 of 47 Overview Renal Function What is it? Why does it matter? What causes it? Who is at risk? What can we (Pharmacists) do? How do you recognise
MPharm Programme Acute Kidney Injury Alan M. Green 2017 Slide 1 of 47 Overview Renal Function What is it? Why does it matter? What causes it? Who is at risk? What can we (Pharmacists) do? How do you recognise
ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY FOCUS ON OBSTETRICS DONNA HIGGINS, CLINICAL NURSE EDUCATOR, NORTHERN LINCOLNSHIRE HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST
 ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY FOCUS ON OBSTETRICS DONNA HIGGINS, CLINICAL NURSE EDUCATOR, NORTHERN LINCOLNSHIRE HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST AIMS & OBJECTIVES Review the functions of the kidney Identify renal
ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY FOCUS ON OBSTETRICS DONNA HIGGINS, CLINICAL NURSE EDUCATOR, NORTHERN LINCOLNSHIRE HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST AIMS & OBJECTIVES Review the functions of the kidney Identify renal
An Introduction to Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) An Education Package for Healthcare Professionals in Medical Directorates
 An Introduction to Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) An Education Package for Healthcare Professionals in Medical Directorates STH Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Project 1 What is Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)? AKI is
An Introduction to Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) An Education Package for Healthcare Professionals in Medical Directorates STH Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Project 1 What is Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)? AKI is
The role of the Nephrologist in Acute Kidney Injury. Rebecca Brown Consultant Nephrologist Royal Liverpool University Hospital
 The role of the Nephrologist in Acute Kidney Injury Rebecca Brown Consultant Nephrologist Royal Liverpool University Hospital Overview Impact of AKI Need for change Who needs a Nephrologist Are we making
The role of the Nephrologist in Acute Kidney Injury Rebecca Brown Consultant Nephrologist Royal Liverpool University Hospital Overview Impact of AKI Need for change Who needs a Nephrologist Are we making
London Strategic Clinical Networks. Quality Standard. Version 1.0 (2015)
 London Strategic Clinical Networks Quality Standard Version 1.0 (2015) Supporting the delivery of equitable, high quality AKI care through collaboration www.londonaki.net @LondonAKI Overview The management
London Strategic Clinical Networks Quality Standard Version 1.0 (2015) Supporting the delivery of equitable, high quality AKI care through collaboration www.londonaki.net @LondonAKI Overview The management
Northern Devon Healthcare NHS Trust. Acute Kidney Injury. Presenter
 Acute Kidney Injury Presenter Housekeeping Northern Devon Healthcare NHS Trust To respect confidentiality within the group unless it is necessary to address a current concern about the safety of an adult
Acute Kidney Injury Presenter Housekeeping Northern Devon Healthcare NHS Trust To respect confidentiality within the group unless it is necessary to address a current concern about the safety of an adult
ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY A PRIMER FOR PRIMARY CARE PHYSICIANS. Myriam Farah, MD, FRCPC
 ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY A PRIMER FOR PRIMARY CARE PHYSICIANS Myriam Farah, MD, FRCPC Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Nephrology, University of British Columbia November 2016 1. How to recognize acute
ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY A PRIMER FOR PRIMARY CARE PHYSICIANS Myriam Farah, MD, FRCPC Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Nephrology, University of British Columbia November 2016 1. How to recognize acute
AKI: definitions, detection & pitfalls. Jon Murray
 AKI: definitions, detection & pitfalls Jon Murray Previous conventional definition Acute renal failure (ARF) An abrupt and sustained decline in renal excretory function due to a reduction in glomerular
AKI: definitions, detection & pitfalls Jon Murray Previous conventional definition Acute renal failure (ARF) An abrupt and sustained decline in renal excretory function due to a reduction in glomerular
Plenary presentations 1
 Wessex Cardiovascular Strategic Clinical Network Acute Kidney Injury Launch Event Wednesday 15 April 2015, 10.00 16.30 Plenary presentations 1 Wessex Acute Kidney Injury Clinical Forum Dr Mark Uniacke
Wessex Cardiovascular Strategic Clinical Network Acute Kidney Injury Launch Event Wednesday 15 April 2015, 10.00 16.30 Plenary presentations 1 Wessex Acute Kidney Injury Clinical Forum Dr Mark Uniacke
Acute Kidney Injury shared guidance
 Acute Kidney Injury shared guidance Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Fluid balance assessment (NICE CG 169) Assess the patient s likely fluid and electrolyte needs 1.History previous limited intake, thirst, abnormal
Acute Kidney Injury shared guidance Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Fluid balance assessment (NICE CG 169) Assess the patient s likely fluid and electrolyte needs 1.History previous limited intake, thirst, abnormal
Acute Kidney Injury in The Acute Oncology Patient
 Acute Kidney Injury in The Acute Oncology Patient Dr Andrew Lewington BSc MEd MD FRCP Consultant Renal Physician/Honorary Senior Lecturer Leeds Teaching Hospitals Definition Definitions and terminology
Acute Kidney Injury in The Acute Oncology Patient Dr Andrew Lewington BSc MEd MD FRCP Consultant Renal Physician/Honorary Senior Lecturer Leeds Teaching Hospitals Definition Definitions and terminology
ACB National Audit: Acute Kidney Injury. Jamie West Peterborough City Hospital June 2016
 ACB National Audit: Acute Kidney Injury Jamie West Peterborough City Hospital June 2016 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Pre-renal: Dehydration Haemorrhage Fluid loss Sepsis Acute cardiac failure Intrinsic: Glomerular
ACB National Audit: Acute Kidney Injury Jamie West Peterborough City Hospital June 2016 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Pre-renal: Dehydration Haemorrhage Fluid loss Sepsis Acute cardiac failure Intrinsic: Glomerular
London Strategic Clinical Networks. My AKI. Guidance for patients with, or recovering from, acute kidney injury
 London Strategic Clinical Networks My AKI Guidance for patients with, or recovering from, acute kidney injury Supporting the delivery of equitable, high quality AKI care through collaboration www.londonaki.net
London Strategic Clinical Networks My AKI Guidance for patients with, or recovering from, acute kidney injury Supporting the delivery of equitable, high quality AKI care through collaboration www.londonaki.net
Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males
 Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males Clinical presentation For patients in care homes see UTI in adults where IV Antibiotics in the community may be appropriate (under development) History and
Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males Clinical presentation For patients in care homes see UTI in adults where IV Antibiotics in the community may be appropriate (under development) History and
Bulletin Independent prescribing information for NHS Wales
 Bulletin Independent prescribing information for NHS Wales October 2017 Chronic kidney disease Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a long-term irreversible deterioration in the function of the kidneys, often
Bulletin Independent prescribing information for NHS Wales October 2017 Chronic kidney disease Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a long-term irreversible deterioration in the function of the kidneys, often
Acute Kidney Injury. Patient Information Leaflet
 Acute Kidney Injury Patient Information Leaflet What is Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)? Acute Kidney injury is a rapid fall in kidney function in a person who has become unwell. It can happen over hours or
Acute Kidney Injury Patient Information Leaflet What is Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)? Acute Kidney injury is a rapid fall in kidney function in a person who has become unwell. It can happen over hours or
Preventing Acute Kidney Injury
 Preventing Acute Kidney Injury Dr Andy Lewington MSc Clin Ed FRCP Consultant Nephrologist/Honorary Clinical Associate Professor Director of Undergraduate Medical Education Leeds Teaching Hospitals A.J.P.Lewington@leeds.ac.uk
Preventing Acute Kidney Injury Dr Andy Lewington MSc Clin Ed FRCP Consultant Nephrologist/Honorary Clinical Associate Professor Director of Undergraduate Medical Education Leeds Teaching Hospitals A.J.P.Lewington@leeds.ac.uk
CKD and risk management : NICE guideline
 CKD and risk management : NICE guideline 2008-2014 Shahed Ahmed Consultant Nephrologist shahed.ahmed@rlbuht.nhs.uk Key points : Changing parameters of CKD and NICE guidance CKD and age related change of
CKD and risk management : NICE guideline 2008-2014 Shahed Ahmed Consultant Nephrologist shahed.ahmed@rlbuht.nhs.uk Key points : Changing parameters of CKD and NICE guidance CKD and age related change of
Learning Objectives. How big is the problem? ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY
 ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY Karen Innocent, DNP, RN, CRNP, ANP-BC, CMSRN Executive Director, Continuing Education Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc May 2016 Orlando FL Learning Objectives Identify the risk factors and
ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY Karen Innocent, DNP, RN, CRNP, ANP-BC, CMSRN Executive Director, Continuing Education Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc May 2016 Orlando FL Learning Objectives Identify the risk factors and
Faculty/Presenter Disclosure
 CSI for CKD Unravelling the myths surrounding chronic kidney disease Practical Evidence for Informed Practice Oct 21 2016 Dr. Scott Klarenbach University of Alberta Slide 1: Option B (Presenter with NO
CSI for CKD Unravelling the myths surrounding chronic kidney disease Practical Evidence for Informed Practice Oct 21 2016 Dr. Scott Klarenbach University of Alberta Slide 1: Option B (Presenter with NO
Medicine Dr. Dana Lecture 1 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
 Medicine Dr. Dana Lecture 1 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Renal function Kidney has many roles: 1. Excretory function 2. Osmolality regulation 3. Acid base balance 4. BP regulation through salt and water balance
Medicine Dr. Dana Lecture 1 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Renal function Kidney has many roles: 1. Excretory function 2. Osmolality regulation 3. Acid base balance 4. BP regulation through salt and water balance
The National Quality Standards for Chronic Kidney Disease
 The National Quality Standards for Chronic Kidney Disease Dr Robert Lewis Chief of Service, Wessex Kidney Centre, Portsmouth Specialist Committee Member Quality Standard for Chronic Kidney Disease, NICE
The National Quality Standards for Chronic Kidney Disease Dr Robert Lewis Chief of Service, Wessex Kidney Centre, Portsmouth Specialist Committee Member Quality Standard for Chronic Kidney Disease, NICE
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education
 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education Year One Developed Summer 2017 Overview Basic A & P of: Urinary system Kidneys Followed by: Introduction to Acute Kidney Injury Urinary System The
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education Year One Developed Summer 2017 Overview Basic A & P of: Urinary system Kidneys Followed by: Introduction to Acute Kidney Injury Urinary System The
Acute Kidney Injury. I. David Weiner, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation University of Florida and NF/SGVHS
 Acute Kidney Injury I. David Weiner, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation University of Florida and NF/SGVHS 374-6102 David.Weiner@medicine.ufl.edu www.renallectures.com Concentration
Acute Kidney Injury I. David Weiner, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation University of Florida and NF/SGVHS 374-6102 David.Weiner@medicine.ufl.edu www.renallectures.com Concentration
Caring for the AKI Survivor: What is Required?
 Caring for the AKI Survivor: What is Required? Ron Wald, MDCM MPH FRCPC Division of Nephrology St. Michael s Hospital and University of Toronto February 28, 2019 A patient in your ICU 65M with DM, HTN,
Caring for the AKI Survivor: What is Required? Ron Wald, MDCM MPH FRCPC Division of Nephrology St. Michael s Hospital and University of Toronto February 28, 2019 A patient in your ICU 65M with DM, HTN,
Chronic Kidney Disease. Paul Cockwell Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham
 Chronic Kidney Disease Paul Cockwell Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham Paradigms for chronic disease 1. Acute and chronic disease is closely linked 2. Stratify risk and tailor interventions around failure
Chronic Kidney Disease Paul Cockwell Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham Paradigms for chronic disease 1. Acute and chronic disease is closely linked 2. Stratify risk and tailor interventions around failure
Acute Kidney Injury in the ED
 + Acute Kidney Injury in the ED + Dr Eric Clark, MD FRCPC University of Ottawa Canada Canadian Association of Emergency Physicians + Outline 1. Diagnostic challenges 2. ED treatment 3. Contrast induced
+ Acute Kidney Injury in the ED + Dr Eric Clark, MD FRCPC University of Ottawa Canada Canadian Association of Emergency Physicians + Outline 1. Diagnostic challenges 2. ED treatment 3. Contrast induced
Update in. Acute Kidney Injury. Mark Devonald Consultant Nephrologist. Nottingham AKI Research Group
 Update in Acute Kidney Injury Mark Devonald Consultant Nephrologist If you stay awake you might hear about Why AKI is important Some cases to illustrate some specific points A couple of updates on AKI
Update in Acute Kidney Injury Mark Devonald Consultant Nephrologist If you stay awake you might hear about Why AKI is important Some cases to illustrate some specific points A couple of updates on AKI
Adding Insult to Injury. Marlies Ostermann Consultant in Nephrology & Critical Care Guy s & St Thomas Hospital, London
 Acute Kidney Injury Adding Insult to Injury Marlies Ostermann Consultant in Nephrology & Critical Care Guy s & St Thomas Hospital, London Content 1. Brief review of AKI and its impact 2. Comments on the
Acute Kidney Injury Adding Insult to Injury Marlies Ostermann Consultant in Nephrology & Critical Care Guy s & St Thomas Hospital, London Content 1. Brief review of AKI and its impact 2. Comments on the
Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach
 Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach Primary Care Update Creighton University School of Medicine. April 27 th, 2018 Disclosure Slide I have no disclosures and have no conflicts with this presentation.
Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach Primary Care Update Creighton University School of Medicine. April 27 th, 2018 Disclosure Slide I have no disclosures and have no conflicts with this presentation.
AKI: un dramma diffuso nei paesi poveri Maurizio Gallieni
 AKI: un dramma diffuso nei paesi poveri Maurizio Gallieni U.O. Nefrologia e Dialisi - Ospedale S. Carlo Borromeo, ASST Santi Paolo e Carlo DIBIC L. Sacco - Università degli Studi di Milano Thousands of
AKI: un dramma diffuso nei paesi poveri Maurizio Gallieni U.O. Nefrologia e Dialisi - Ospedale S. Carlo Borromeo, ASST Santi Paolo e Carlo DIBIC L. Sacco - Università degli Studi di Milano Thousands of
Acute kidney injury. Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals
 Acute kidney injury Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals page 2 of 12 Acute kidney injury You have been given this leaflet because you have had an episode of acute kidney injury (AKI).
Acute kidney injury Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals page 2 of 12 Acute kidney injury You have been given this leaflet because you have had an episode of acute kidney injury (AKI).
Understanding Acute Kidney Injury. Emotional and. practical support
 Understanding Acute Kidney Injury Emotional and practical support This leaflet is for people who have been told that they have had Acute Kidney Injury and it s been designed to answer questions you may
Understanding Acute Kidney Injury Emotional and practical support This leaflet is for people who have been told that they have had Acute Kidney Injury and it s been designed to answer questions you may
National Chronic Kidney Disease Audit
 National Chronic Kidney Disease Audit // National Report: Part 2 December 2017 Commissioned by: Delivered by: // Foreword by Fiona Loud And if, as part of good, patient-centred care, a record of your condition(s),
National Chronic Kidney Disease Audit // National Report: Part 2 December 2017 Commissioned by: Delivered by: // Foreword by Fiona Loud And if, as part of good, patient-centred care, a record of your condition(s),
NICE Clinical Guideline 169 Acute Kidney Injury Local Implementation Gap Analysis
 NICE Clinical Guideline 169 Acute Kidney Injury Local Implementation Gap Analysis Please tick appropriate box in response to questions below and return to Michelle Timoney (michelle.timoney@nhs.net) by
NICE Clinical Guideline 169 Acute Kidney Injury Local Implementation Gap Analysis Please tick appropriate box in response to questions below and return to Michelle Timoney (michelle.timoney@nhs.net) by
Sepsis in primary care. Sarah Bailey, Emma Evans, Nicola Shoebridge, Fiona Wells
 Sepsis in primary care Sarah Bailey, Emma Evans, Nicola Shoebridge, Fiona Wells sepsisnurses@uhcw.nhs.uk Quiz!! OR Hands on your heads Hands on your hips Definition. The Third International Consensus Definition
Sepsis in primary care Sarah Bailey, Emma Evans, Nicola Shoebridge, Fiona Wells sepsisnurses@uhcw.nhs.uk Quiz!! OR Hands on your heads Hands on your hips Definition. The Third International Consensus Definition
Ricky Bell Renal/ICM Registrar
 Ricky Bell Renal/ICM Registrar Objectives When to call renal How to manage the patient with AKI How the manage the patient with CKD (HD/PD) Special AKI situations What do the guidelines say? My referral
Ricky Bell Renal/ICM Registrar Objectives When to call renal How to manage the patient with AKI How the manage the patient with CKD (HD/PD) Special AKI situations What do the guidelines say? My referral
Acute kidney injury. Dr P Sigwadi Paediatric nephrology
 Acute kidney injury Dr P Sigwadi Paediatric nephrology Introduction Is common in critically ill patients e.g. post cardiac surgery Occurs when renal function is diminished to a point where body fluid and
Acute kidney injury Dr P Sigwadi Paediatric nephrology Introduction Is common in critically ill patients e.g. post cardiac surgery Occurs when renal function is diminished to a point where body fluid and
The Oxford AHSN Sepsis Pathway
 From confusion to consensus: The Oxford AHSN Sepsis Pathway Andrew Brent Sepsis Clinical Lead, Oxford AHSN & Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 From: The Third International
From confusion to consensus: The Oxford AHSN Sepsis Pathway Andrew Brent Sepsis Clinical Lead, Oxford AHSN & Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 From: The Third International
Algorithms & Information Sheets
 Minor Ailment Scheme Algorithms & Information Sheets Acute Diarrhoea Diarrhoea is an increased frequency, fluidity or volume of the bowel movements with the passage of soft and watery stools as compared
Minor Ailment Scheme Algorithms & Information Sheets Acute Diarrhoea Diarrhoea is an increased frequency, fluidity or volume of the bowel movements with the passage of soft and watery stools as compared
Management of early chronic kidney disease
 Management of early chronic kidney disease GREENLANE SUMMER GP SYMPOSIUM 2018 Jonathan Hsiao Renal and General Physician Introduction A growing public health problem in NZ and throughout the world. Unknown
Management of early chronic kidney disease GREENLANE SUMMER GP SYMPOSIUM 2018 Jonathan Hsiao Renal and General Physician Introduction A growing public health problem in NZ and throughout the world. Unknown
What s new in kidneys a renal update for Anaesthetists
 What s new in kidneys a renal update for Anaesthetists Thursday 11 th December 2014 Roslyn Simms Clinical Lecturer in Nephrology Renal update What s new/update AKI When to start RRT in AKI? Perioperative
What s new in kidneys a renal update for Anaesthetists Thursday 11 th December 2014 Roslyn Simms Clinical Lecturer in Nephrology Renal update What s new/update AKI When to start RRT in AKI? Perioperative
QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS
 KEY MESSAGES 1 SCREENING CRITERIA Screen: Patients with DM and/or hypertension at least yearly. Consider screening patients with: Age >65 years old Family history of stage 5 CKD or hereditary kidney disease
KEY MESSAGES 1 SCREENING CRITERIA Screen: Patients with DM and/or hypertension at least yearly. Consider screening patients with: Age >65 years old Family history of stage 5 CKD or hereditary kidney disease
Community & In-hospital ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY (AKI) Guidelines
 Community & In-hospital ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY (AKI) Guidelines Aug 2017 Page 1 of 18 Contents Page Primary and community care Prevention of acute kidney injury 3 Community AKI guideline 4 AKI Sick Day Guidance
Community & In-hospital ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY (AKI) Guidelines Aug 2017 Page 1 of 18 Contents Page Primary and community care Prevention of acute kidney injury 3 Community AKI guideline 4 AKI Sick Day Guidance
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and egfr: Decision and Dilemma. Dr Bhavna K Pandya Consultant Nephrologist University Hospital Aintree
 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and egfr: Decision and Dilemma Dr Bhavna K Pandya Consultant Nephrologist University Hospital Aintree Topics CKD background egfr background Patient with egfr Referral Guidelines
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and egfr: Decision and Dilemma Dr Bhavna K Pandya Consultant Nephrologist University Hospital Aintree Topics CKD background egfr background Patient with egfr Referral Guidelines
SERVICE SPECIFICATION 6 Conservative Management & End of Life Care
 SERVICE SPECIFICATION 6 Conservative Management & End of Life Care Table of Contents Page 1 Key Messages 2 2 Introduction & Background 2 3 Relevant Guidelines & Standards 2 4 Scope of Service 3 5 Interdependencies
SERVICE SPECIFICATION 6 Conservative Management & End of Life Care Table of Contents Page 1 Key Messages 2 2 Introduction & Background 2 3 Relevant Guidelines & Standards 2 4 Scope of Service 3 5 Interdependencies
Frimley Health Area Prescribing Committee
 Frimley Health Area Prescribing Committee Frimley Health NHS Foundation Trust North East Hampshire and Farnham CCG East Berkshire CCG Surrey Heath CCG Buckinghamshire CCG SHARED CARE Guideline Amber Traffic
Frimley Health Area Prescribing Committee Frimley Health NHS Foundation Trust North East Hampshire and Farnham CCG East Berkshire CCG Surrey Heath CCG Buckinghamshire CCG SHARED CARE Guideline Amber Traffic
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) / Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) To STOP OR Not in Advanced Renal Disease
 Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) / Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) To STOP OR Not in Advanced Renal Disease Investigator Meeting 12 th September 2017 - Sheffield Prof Sunil Bhandari Consultant
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) / Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) To STOP OR Not in Advanced Renal Disease Investigator Meeting 12 th September 2017 - Sheffield Prof Sunil Bhandari Consultant
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) (Southampton pathway)
 Background information Patient information Key messages for this pathway Definitions and abbreviations used in this pathway Classification of CKD Diagnosis of CKD Summary of referral criteria Screening
Background information Patient information Key messages for this pathway Definitions and abbreviations used in this pathway Classification of CKD Diagnosis of CKD Summary of referral criteria Screening
CKD at the primary and secondary care interface. Paul Cockwell Consultant Nephrologist Clinical Service Lead Renal Medicine, QEHB
 CKD at the primary and secondary care interface Paul Cockwell Consultant Nephrologist Clinical Service Lead Renal Medicine, QEHB The Health improvement Network (THIN): 6.7 million patients from 426 primary
CKD at the primary and secondary care interface Paul Cockwell Consultant Nephrologist Clinical Service Lead Renal Medicine, QEHB The Health improvement Network (THIN): 6.7 million patients from 426 primary
Dr.Nahid Osman Ahmed 1
 1 ILOS By the end of the lecture you should be able to Identify : Functions of the kidney and nephrons Signs and symptoms of AKI Risk factors to AKI Treatment alternatives 2 Acute kidney injury (AKI),
1 ILOS By the end of the lecture you should be able to Identify : Functions of the kidney and nephrons Signs and symptoms of AKI Risk factors to AKI Treatment alternatives 2 Acute kidney injury (AKI),
Wednesday September 20 th CMT Regional Study Day. Dr Colin Mason, Consultant DME, Addenbrooke s Hospital
 Wednesday September 20 th CMT Regional Study Day Dr Colin Mason, Consultant DME, Addenbrooke s Hospital Develop a structured approach to a patient presenting with a fall Risk stratify who can go home and
Wednesday September 20 th CMT Regional Study Day Dr Colin Mason, Consultant DME, Addenbrooke s Hospital Develop a structured approach to a patient presenting with a fall Risk stratify who can go home and
RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University
 RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture each student should be able to: Define acute & chronic kidney disease(ckd)
RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture each student should be able to: Define acute & chronic kidney disease(ckd)
Chronic heart failure: management of chronic heart failure in adults in primary and secondary care (partial update)
 Chronic heart failure: management of chronic heart failure in adults in primary and secondary care (partial update) NICE guideline Apendix C The algorithms Draft for consultation, January 2010 Chronic
Chronic heart failure: management of chronic heart failure in adults in primary and secondary care (partial update) NICE guideline Apendix C The algorithms Draft for consultation, January 2010 Chronic
CKD FOR INTERNISTS. Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College
 CKD FOR INTERNISTS Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College INTRODUCTION In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative(KDOQI)
CKD FOR INTERNISTS Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College INTRODUCTION In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative(KDOQI)
Management of Nephrotic Syndrome
 Management of Nephrotic Syndrome 1. Introduction Incidence 2-4/100,000. Boys > girls 3:2; age of onset 2-6 years 80% of cases in children is due to minimal change (MCD) of which 80% will respond to steroid
Management of Nephrotic Syndrome 1. Introduction Incidence 2-4/100,000. Boys > girls 3:2; age of onset 2-6 years 80% of cases in children is due to minimal change (MCD) of which 80% will respond to steroid
Introduction. 1. Introduction
 1. Introduction Chronic kidney disease (CKD) encompasses a spectrum of different pathophysiologic processes associated with abnormal kidney function, and a progressive decline in glomerular filtration
1. Introduction Chronic kidney disease (CKD) encompasses a spectrum of different pathophysiologic processes associated with abnormal kidney function, and a progressive decline in glomerular filtration
Screen annually for patients with any of the following risk factors:
 CASE DEFINITION Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is either of the following, persisting for at least three months, repeated on at least two occasions: 1. Markers of kidney damage (e.g. proteinuria, haematuria
CASE DEFINITION Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is either of the following, persisting for at least three months, repeated on at least two occasions: 1. Markers of kidney damage (e.g. proteinuria, haematuria
National Audit of CKD in Primary Care
 National Audit of CKD in Primary Care David C Wheeler Royal Free Campus University College London d.wheeler@ucl.ac.uk Kidney for General Physicians RCP London 24 th November 2017 Who looks after CKD patients
National Audit of CKD in Primary Care David C Wheeler Royal Free Campus University College London d.wheeler@ucl.ac.uk Kidney for General Physicians RCP London 24 th November 2017 Who looks after CKD patients
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERENCE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERECE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease CKD VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERECE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease CKD VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management
Understanding what the public know about their kidneys and what they do. Findings from Ipsos MORI survey July 2014
 Understanding what the public know about their kidneys and what they do Findings from Ipsos MORI survey July 2014 Publication date 15.01.2015 Understanding what the public know about their kidneys and
Understanding what the public know about their kidneys and what they do Findings from Ipsos MORI survey July 2014 Publication date 15.01.2015 Understanding what the public know about their kidneys and
Suboptimal hydration harms patients.
 Suboptimal hydration harms patients. NHS Fife is committed to improving hydration management. To achieve this we need your help! In 2014 new fluid balance charts were implemented in the Victoria Hospital,
Suboptimal hydration harms patients. NHS Fife is committed to improving hydration management. To achieve this we need your help! In 2014 new fluid balance charts were implemented in the Victoria Hospital,
ENDPOINTS FOR AKI STUDIES
 ENDPOINTS FOR AKI STUDIES Raymond Vanholder, University Hospital, Ghent, Belgium SUMMARY! AKI as an endpoint! Endpoints for studies in AKI 2 AKI AS AN ENDPOINT BEFORE RIFLE THE LIST OF DEFINITIONS WAS
ENDPOINTS FOR AKI STUDIES Raymond Vanholder, University Hospital, Ghent, Belgium SUMMARY! AKI as an endpoint! Endpoints for studies in AKI 2 AKI AS AN ENDPOINT BEFORE RIFLE THE LIST OF DEFINITIONS WAS
Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus
 Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus 1 Contents Executive Summary... 3 How to Screen for Diabetic Nephropathy... 4 What to Measure... 4 Frequency
Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus 1 Contents Executive Summary... 3 How to Screen for Diabetic Nephropathy... 4 What to Measure... 4 Frequency
Ultrasound in Acute Kidney Injury. Pamela Parker Ultrasound Specialty Manager
 Ultrasound in Acute Kidney Injury Pamela Parker Ultrasound Specialty Manager Aims What is Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)? Discuss the implications of AKI for USS Revisit Resistive Index (RIs) Why? The FACTS
Ultrasound in Acute Kidney Injury Pamela Parker Ultrasound Specialty Manager Aims What is Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)? Discuss the implications of AKI for USS Revisit Resistive Index (RIs) Why? The FACTS
MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY, THE ALGORHITHM
 MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY, THE ALGORHITHM Are Particular Anti-hypertensives More Effective or Harmful Than Others in Hypertension in Pregnancy? Existing data is inadequate Methyldopa and
MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY, THE ALGORHITHM Are Particular Anti-hypertensives More Effective or Harmful Than Others in Hypertension in Pregnancy? Existing data is inadequate Methyldopa and
Elevation of Serum Creatinine: When to Screen, When to Refer. Bruce F. Culleton, MD, FRCPC; and Jolanta Karpinski, MD, FRCPC
 Elevation of Serum Creatinine: When to Screen, When to Refer Bruce F. Culleton, MD, FRCPC; and Jolanta Karpinski, MD, FRCPC Presented at the University of Calgary s CME and Professional Development 2006-2007
Elevation of Serum Creatinine: When to Screen, When to Refer Bruce F. Culleton, MD, FRCPC; and Jolanta Karpinski, MD, FRCPC Presented at the University of Calgary s CME and Professional Development 2006-2007
DIABETES MELLITUS. Kidney in systemic diseases. Slower the progression: Pathology: Patients with diabetes mellitus are prone to other renal diseases:
 Kidney in systemic diseases Dr. Badri Paudel The kidneys may be directly involved in a number of multisystem diseases or secondarily affected by diseases of other organs. Involvement may be at a prerenal,
Kidney in systemic diseases Dr. Badri Paudel The kidneys may be directly involved in a number of multisystem diseases or secondarily affected by diseases of other organs. Involvement may be at a prerenal,
Professor Suetonia Palmer
 Professor Suetonia Palmer Department of Medicine Nephrologist Christchurch Hospital Christchurch 14:00-14:55 WS #108: The Kidney Test - When To Test and When to Refer ( and When Not To) 15:05-16:00 WS
Professor Suetonia Palmer Department of Medicine Nephrologist Christchurch Hospital Christchurch 14:00-14:55 WS #108: The Kidney Test - When To Test and When to Refer ( and When Not To) 15:05-16:00 WS
Renal replacement therapy in Pediatric Acute Kidney Injury
 Renal replacement therapy in Pediatric Acute Kidney Injury ASCIM 2014 Dr Adrian Plunkett Consultant Paediatric Intensivist Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK Aims of the presentation Important topic: AKI
Renal replacement therapy in Pediatric Acute Kidney Injury ASCIM 2014 Dr Adrian Plunkett Consultant Paediatric Intensivist Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK Aims of the presentation Important topic: AKI
Shared Care Guideline Metolazone for fluid management in CKD (Adults)
 Shared Care Guideline Metolazone for fluid management in CKD (Adults) It is vital for safe and appropriate patient care that there is a clear understanding of where clinical and prescribing responsibility
Shared Care Guideline Metolazone for fluid management in CKD (Adults) It is vital for safe and appropriate patient care that there is a clear understanding of where clinical and prescribing responsibility
Mr PA. Clinical assessment of hydration. Poor urine output Sunken eyes Moistness of mucosa Cool peripheries Reduction in weight Postural hypotension
 X Anthony Warrens Mr PA 54 years old Previously well Went to Thailand Developed serious diarrhoea and vomiting two days before coming home 24 hours after return, still unwell GP found: urea 24 mmol/l creatinine
X Anthony Warrens Mr PA 54 years old Previously well Went to Thailand Developed serious diarrhoea and vomiting two days before coming home 24 hours after return, still unwell GP found: urea 24 mmol/l creatinine
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Centre for Clinical Practice SCOPE Clinical guideline title: Intravenous fluid therapy in adults in hospital Quality standard title: Intravenous fluid
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Centre for Clinical Practice SCOPE Clinical guideline title: Intravenous fluid therapy in adults in hospital Quality standard title: Intravenous fluid
Invokana (canagliflozin) NEW INDICATION REVIEW
 Invokana (canagliflozin) NEW INDICATION REVIEW Introduction Brand name: Invokana Generic name: Canagliflozin Pharmacological class: Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor Strength and Formulation:
Invokana (canagliflozin) NEW INDICATION REVIEW Introduction Brand name: Invokana Generic name: Canagliflozin Pharmacological class: Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor Strength and Formulation:
Title Protocol for the Management of Urinary Tract Infections for Adult Females and Children in MIUs and WICs
 Document Control Title Protocol for the Management of Urinary Tract Infections for Adult Females and Children in MIUs and WICs Author Author s job title Professional Lead, Minor Injuries Unit Directorate,
Document Control Title Protocol for the Management of Urinary Tract Infections for Adult Females and Children in MIUs and WICs Author Author s job title Professional Lead, Minor Injuries Unit Directorate,
Sepsis in primary care. what is good care?
 Sepsis in primary care @SepsisUK what is good care? Emmanuel Nsutebu Consultant Infectious Disease Physician & Clinical lead for sepsis Tropical and Infectious Disease Unit Royal Liverpool Hospital Do
Sepsis in primary care @SepsisUK what is good care? Emmanuel Nsutebu Consultant Infectious Disease Physician & Clinical lead for sepsis Tropical and Infectious Disease Unit Royal Liverpool Hospital Do
Management of New-Onset Proteinuria in the Ambulatory Care Setting. Akinlolu Ojo, MD, PhD, MBA
 Management of New-Onset Proteinuria in the Ambulatory Care Setting Akinlolu Ojo, MD, PhD, MBA Urine dipstick results Negative Trace between 15 and 30 mg/dl 1+ between 30 and 100 mg/dl 2+ between 100 and
Management of New-Onset Proteinuria in the Ambulatory Care Setting Akinlolu Ojo, MD, PhD, MBA Urine dipstick results Negative Trace between 15 and 30 mg/dl 1+ between 30 and 100 mg/dl 2+ between 100 and
Outcomes of diabetes care in England and Wales. A summary of findings from the National Diabetes Audit : Complications and Mortality reports
 Outcomes of diabetes care in England and Wales A summary of findings from the National Diabetes Audit 2015 16: Complications and Mortality reports About this report This report is for people with diabetes
Outcomes of diabetes care in England and Wales A summary of findings from the National Diabetes Audit 2015 16: Complications and Mortality reports About this report This report is for people with diabetes
NORTHERN IRELAND GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
 NORTHERN IRELAND GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Practical points for use of estimated GFR + quality outcome framework indicators Developed by GAIN and the Northern Ireland Nephrology
NORTHERN IRELAND GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Practical points for use of estimated GFR + quality outcome framework indicators Developed by GAIN and the Northern Ireland Nephrology
JNC Evidence-Based Guidelines for the Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults
 JNC 8 2014 Evidence-Based Guidelines for the Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults Table of Contents Why Do We Treat Hypertension? Blood Pressure Treatment Goals Initial Therapy Strength of Recommendation
JNC 8 2014 Evidence-Based Guidelines for the Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults Table of Contents Why Do We Treat Hypertension? Blood Pressure Treatment Goals Initial Therapy Strength of Recommendation
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGNOSIS
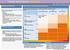 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS GFR categories, description and range WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD CLASSIFICATION OF CKD USING egfr AND ACR CATEGORIES Offer testing for CKD using egfr, creatinine and ACR
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS GFR categories, description and range WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD CLASSIFICATION OF CKD USING egfr AND ACR CATEGORIES Offer testing for CKD using egfr, creatinine and ACR
Irish Practice Nurses Association Annual Conference Tullamore Court Hotel OCTOBER 6 th 2012
 Irish Practice Nurses Association Annual Conference Tullamore Court Hotel OCTOBER 6 th 2012 Susan McKenna Renal Clinical Nurse Specialist Cavan General Hospital Renal patient population ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
Irish Practice Nurses Association Annual Conference Tullamore Court Hotel OCTOBER 6 th 2012 Susan McKenna Renal Clinical Nurse Specialist Cavan General Hospital Renal patient population ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
Acute Kidney Injury; get the basics right first!
 Acute Kidney Injury; get the basics right first! Dr Christopher Wong, Consultant Nephrologist and General Physician, University Hospital Aintree (UHA), Liverpool, UK Acute kidney injury (AKI) Why a new
Acute Kidney Injury; get the basics right first! Dr Christopher Wong, Consultant Nephrologist and General Physician, University Hospital Aintree (UHA), Liverpool, UK Acute kidney injury (AKI) Why a new
The evidence base for interventions to slow the progression of chronic kidney disease: Medical interventions. Jonathan Evans Paediatric Nephrologist
 The evidence base for interventions to slow the progression of chronic kidney disease: Medical interventions Jonathan Evans Paediatric Nephrologist CKD in adults Often unrecognised Preventable Major cardiovascular
The evidence base for interventions to slow the progression of chronic kidney disease: Medical interventions Jonathan Evans Paediatric Nephrologist CKD in adults Often unrecognised Preventable Major cardiovascular
The changing face of
 The changing face of sepsis. @SepsisUK Dr Ron Daniels B.E.M. CEO, UK Sepsis Trust CEO, Global Sepsis Alliance Special Adviser (maternal sepsis) to WHO Breast cancer Cognitive impairment Mild 3.8 7.1
The changing face of sepsis. @SepsisUK Dr Ron Daniels B.E.M. CEO, UK Sepsis Trust CEO, Global Sepsis Alliance Special Adviser (maternal sepsis) to WHO Breast cancer Cognitive impairment Mild 3.8 7.1
CKD & HT. Anne-Marie Angus
 CKD & HT Anne-Marie Angus Hypertension definitions Persisting BP >140/90 and HBPM >135/85 Stage 1 >140/90 (HBPM >135/85) Stage 2 >160/100 (HBPM >150/90) Severe >180/100 White coat HT Why treat? A major
CKD & HT Anne-Marie Angus Hypertension definitions Persisting BP >140/90 and HBPM >135/85 Stage 1 >140/90 (HBPM >135/85) Stage 2 >160/100 (HBPM >150/90) Severe >180/100 White coat HT Why treat? A major
Cheshire & Mersey AKI Network Manual. 2 nd Edition, April 2016
 Cheshire & Mersey AKI Network Manual 2 nd Edition, April 2016 Page 1 of 20 Introduction 3 Prevention of acute kidney injury 4 PRIMARY & COMMUNITY CARE Primary Care AKI Management guideline 5 AKI Sick Day
Cheshire & Mersey AKI Network Manual 2 nd Edition, April 2016 Page 1 of 20 Introduction 3 Prevention of acute kidney injury 4 PRIMARY & COMMUNITY CARE Primary Care AKI Management guideline 5 AKI Sick Day
Definition : Stages : ( RIFLE vs. AKIN ) Causes and classification : Pre-renal Renal Post- renal Clinical manifestations and Complication Management
 AKI Definition : Stages : ( RIFLE vs. AKIN ) Causes and classification : Pre-renal Renal Post- renal Clinical manifestations and Complication Management and indications for RRT Etiology prerenal causes
AKI Definition : Stages : ( RIFLE vs. AKIN ) Causes and classification : Pre-renal Renal Post- renal Clinical manifestations and Complication Management and indications for RRT Etiology prerenal causes
Managing Patients with CKD in Primary Care: A Shared Care Pathway. 5 th April 2018
 Managing Patients with CKD in Primary Care: A Shared Care Pathway 5 th April 2018 Learning Objectives 1) What health risks does CKD represent? 2) Why change how we manage CKD in NWL? 1) How do we improve
Managing Patients with CKD in Primary Care: A Shared Care Pathway 5 th April 2018 Learning Objectives 1) What health risks does CKD represent? 2) Why change how we manage CKD in NWL? 1) How do we improve
Henoch Schonlein Purpura
 CHILDREN S SERVICES Henoch Schonlein Purpura Definition A vasculitic syndrome of small vessels classically characterised by a purpuric rash, abdominal pain, arthritis, and nephritis. Platelet count and
CHILDREN S SERVICES Henoch Schonlein Purpura Definition A vasculitic syndrome of small vessels classically characterised by a purpuric rash, abdominal pain, arthritis, and nephritis. Platelet count and
Acute Kidney Injury. Eleanor Haskey BSc(hons) RVN VTS(ECC) VPAC A1
 Acute Kidney Injury Eleanor Haskey BSc(hons) RVN VTS(ECC) VPAC A1 Anatomy and Physiology The role of the kidneys is to filter the blood through the glomerulus to form filtrate. The filtrate is then reabsorbed
Acute Kidney Injury Eleanor Haskey BSc(hons) RVN VTS(ECC) VPAC A1 Anatomy and Physiology The role of the kidneys is to filter the blood through the glomerulus to form filtrate. The filtrate is then reabsorbed
A Care Pathway exists for the management of neutropenic fever. Copies of the care pathway document are available in EAU, A&E, Deanesly and CHU.
 Subject: Neutropenic Fever Guideline for Junior Doctors Date of Implementation: January 2010 Date of Review: January 2012 Director Responsible for Implementation and Review: Policy location: Consultant
Subject: Neutropenic Fever Guideline for Junior Doctors Date of Implementation: January 2010 Date of Review: January 2012 Director Responsible for Implementation and Review: Policy location: Consultant
Younger adults with a family history of premature artherosclerotic disease should have their cardiovascular risk factors measured.
 Appendix 2A - Guidance on Management of Hypertension Measurement of blood pressure All adults from 40 years should have blood pressure measured as part of opportunistic cardiovascular risk assessment.
Appendix 2A - Guidance on Management of Hypertension Measurement of blood pressure All adults from 40 years should have blood pressure measured as part of opportunistic cardiovascular risk assessment.
