Screen annually for patients with any of the following risk factors:
|
|
|
- Everett Griffith
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CASE DEFINITION Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is either of the following, persisting for at least three months, repeated on at least two occasions: 1. Markers of kidney damage (e.g. proteinuria, haematuria or structural abnormalities on renal imaging) and / or: 2. GFR < 60 ml/min/1.73m 2. Both egfr and ACR are required to determine the stage and risk category of CKD as albuminuria is one of the biggest known risk factors for progression to End Stage Kidney Disease (ESKD). TABLE 1: KDIGO STAGING OF CKD egfr Stage 1 egfr 90 Stage 2 egfr Stage 3 egfr Stage 3b egfr Stage 4 egfr Stage 5 egfr <15 or dialysis NO CKD (unless other markers of kidney damage detected) MODERATE HIGH RISK CKD VERY HIGH MODERATE HIGH RISK CKD VERY HIGH ACR (mg/mmol) Normal Microalbuminuria < Macroalbuminuria >30 HIGH RISK CKD VERY HIGH SCREENING Up to 60% of adults in some Kimberley communities have markers of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD). Increased creatinine occurs late in CKD and implies significant kidney damage. Screen annually for patients with any of the following risk factors: Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander person aged >= 15 years of age; Smoking; Obesity (BMI > 30kg/m 2 ); Family history of CKD; History of cardiovascular disease (e.g. stroke/cva, heart attack/mi, peripheral vascular disease / PVD); Hypertension; Diabetes; Previous acute kidney injury (AKI); Use of nephrotoxic drugs (e.g. NSAIDS). Patients assessed as not having risk factors should be regularly screened for the development of risk factors over time. Screening for CKD requires: Blood pressure (BP) measurement; Blood test for urea, electrolytes and creatinine (UEC); Urine test for albumin:creatinine ratio (ACR): o Dipstick prior to sending and document result; o If leucocytes, blood and/or nitrates consider possible UTI / STI (see Table 2). TABLE 2: OTHER CAUSES OF ABNORMAL KIDNEY SCREENING TESTS AND APPROPRIATE FOLLOW-UP Abnormality Proteinuria with abnormal urine dipstick due to suspected urinary tract infection (UTI) or urethritis from sexually transmissible infection (STI). Proteinuria / raised creatinine after vigorous exercise or heavy protein consumption. Isolated proteinuria in person without other risk factors for CKD aged less than 30 years (i.e. possible orthostatic proteinuria). Increase in creatinine after commencement of ACE-inhibitor / ARB. Management Send urine for MCS and consider UTI treatment in discussion with GP. Follow appropriate STI guidelines for counselling, testing and treating possible STI (See RESOURCES). Repeat ACR with proof of cure of infection in three months or as clinically indicated. Repeat screening when patient has not exercised in the previous 24 hours or fasting sample. Recheck ACR on morning first void urine collected immediately on first standing Creatinine rise to 25% acceptable see management section. Monitor weekly until stable. Considerations in interpreting screening results: Creatinine levels vary with muscle mass: egfr on laboratory reports may under or overestimate renal function in people with extremes of body size, muscular diseases or amputations calculators can be used to factors in body weight (see RESOURCES); Abnormalities persisting less than 3 months indicate acute kidney injury (AKI) which increases the risk of subsequent CKD; Episodes of AKI should be investigated for a cause and documented in the medical record; Newly abnormal egfr should be repeated within a week to identify rapidly declining renal function.
2 ASSESSMENT All patients with confirmed CKD require: BP, BMI, check for peripheral oedema; Renal tract ultrasound; FBP, CRP, iron studies, uric acid, LFT, calcium/ magnesium / phosphate, lipids, PTH (if calcium or phosphate are abnormal); Hepatitis B, hepatitis C, syphilis and HIV serology if not done within the last 12 months, with appropriate counselling as per Kimberley protocols; HbA1c: o If diabetic and not done within the last 3 months; o Otherwise, If not done within the last 12 months. If ACR > 30 and not previously done: Serum protein electrophoresis, urine protein electrophoresis, complements, ANA, ENA; If haematuria and not previously done: ANCA, anti-gbm If haematuria and additional risk factors for malignancy (see Box 1): as above plus cystoscopy and / or urology referral, cytology x 3 (consider that transport delays may affect results). HAEMATURIA is: Microscopic: Hb on dipstick OR RBC detected on urine MCS, on two separate occasions at least a week apart, not associated with infection or menstruation, OR: Macroscopic: Red, brown or dark discoloration of urine observed by patient or staff. Confirm where possible by dipstick or urine MCS. Macroscopic haematuria requires urgent urological follow-up to exclude malignancy, regardless of whether a urine MCS has bacterial growth, as malignancy predisposes to UTI. BOX 1: RISK FACTORS FOR UROLOGICAL MALIGNANCY Age >35 years; Smoking history (risk correlates with the extent of exposure); History of macroscopic haematuria; History of other less common risk factors: chronic cystitis or irritative voiding symptoms; pelvic irradiation, exposure to cyclophosphamide; aristolochic acid; occupationally to chemicals or dyes (benzenes or aromatic amines), such as printers, painters, and chemical plant workers; chronic indwelling foreign body; previous analgesic abuse. Microscopic haematuria is also a sign of glomerulonephritis. Document it s presence on any referrals and investigate appropriately (see baseline assessment). Confirm haematuria when the patient is not menstruating if possible. MANAGEMENT PREVENT PROGRESSION People with moderate or severe CKD (ACR > 30 mg/mmol or egfr <45) are at the highest cardiovascular risk category, regardless of their score on absolute cardiovascular risk tools. Address all identified cardiovascular risk factors. Smoking cessation helps prevent progression to CKD. See SMOKING CESSATION and, HYPERLIPIDAEMIA protocols; Ensure immunisations up to date, HBV immune. Optimise control for patients with diabetes (see DIABETES protocol); Consider nephrotoxicity when prescribing and advise re: OTC medications such as NSAIDS. Appropriate early referral and management improves outcomes. Manage proteinuria or hypertension with ACE/ARB: For patients with proteinuria, ACE-Inhibitors (ACE-I) / Angiotension-II-Receptor Blockers (ARB) reduce overall mortality and progression to ESKD. For all patients with proteinuria (ACR > 30 mg/mmol, or >3 mg/mmol and DM, IHD or HTN): Prescribe an ACE-I OR ARB for all patients without contraindications, titrate to maximum dose tolerated without symptomatic hypotension. Monitor BP, UEC fortnightly during up-titration. Seek advice if: o Potassium 6.0 mmol/l consider drug interactions e.g. spironolactone; o Creatinine rise > 20% - consider bilateral renal artery stenosis. Do not combine ACE and ARB due to risk of acute kidney injury. Once ACE-I or ARB maximised, use other agents as needed to control BP to goal of 130/80 unless other target specified by nephrologist / physician (see HYPERTENSION protocol). For other patients with CKD, use ACE or ARB as the preferred first option for managing hypertension. PREVENT ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY (AKI): In acutely unwell patients with CKD: Check weight, BP, peripheral oedema, monitor UEC regularly;
3 Consider temporarily ceasing ACE-I / ARB / diuretics in especially with hypotension / hypovolaemia (if unsure contact physician / nephrologist for advice); Recheck UEC once acute illness has resolved to determine new baseline and ensure ceased medications are restarted.
4 TABLE 3: ACE-I AND ANGIOTENSION-II-RECEPTOR BLOCKERS ON THE KSDL ACE- Inhibitors ARB KSDL Quinapril: (5mg, 10mg, 20mg tab) Ramipril: (2.5mg, 5mg, 10mg tab) Irbesartan: (75mg, 150mg, 300mg tab) Supplementary list Enalapril: (5mg, 10mg, 20mg tab) Quinapril / HCT: (20mg / 12.5mg tab) Irbesartan / HCT: (300mg/12.5mg tab) PROMOTE A HEALTHY LIFESTYLE: Achieving a healthy body weight and maintaining a healthy diet helps reduce progression to ESKD. See HEALTHY LIFESTYLE protocol. Additionally, If egfr is < 30 a dietician referral is recommended to manage weight, salt and phosphate intake and fluid. TREAT COMPLICATIONS OF LATE CKD (STAGES 4 5) [Note: Contact renal GP as needed for support with routine pathology]. PTH, phosphate and calcium: Usual pattern is progressively high phosphate and low calcium (Ca++) with compensatory secondary hyperparathyroidism. May require combination of calcitriol (titrated against PTH / serum Ca++) and phosphate binders (titrated against phosphate levels). General guidelines: egfr > 30 with normal Ca++ / phosphate and vitamin D levels < 50 nmol/l: Supplement with cholecalciferol; Acceptable PTH (< 5 times upper limit of normal (ULN)) and normal adj. Ca++ (> 2.1 mmol/l) but high phosphate (> 1.6 mmol/l): Dietary advice +/- phosphate binders (Caltrate / Cal-sup with meals, up to two TDS as needed). Review adherence and correct use. Can add second agent discuss with renal GP; Elevated PTH (>5 times ULN) and / or low adj. Ca++ (< 2.1 mmol/l): Treat high phosphate first, unless symptomatic hypocalcaemia. Start calcitriol 0.25mcg daily, increase fortnightly up to 1mcg daily. Seek advice if adjusted Ca++ rise to >2.4 mmol/l; Monitor serum Ca++ and phosphate fortnightly and PTH monthly whilst changing therapy. Acidosis: If acidosis is persisting (serum bicarbonate < 15 mmol/l) after correction of hypocalcaemia: Start sodium bicarbonate tablets (SodiBic 840mg) 1 BD, up to 2 tablets TDS to a target of 22 mmol/l. Monitor for exacerbation of HTN and heart failure (increased salt load). Anaemia and iron deficiency: Anaemia occurs in late CKD due to both iron deficiency and reduced RBC production, and can be exacerbated by fluid overload. Exclude other causes of anaemia in early CKD, with absolute iron deficiency or in refractory anaemia. General guidelines: TF saturation < 20% and Hb < 110: Treat for iron deficiency, check B12 / folate. Oral iron is poorly absorbed in CKD. Refer for iron infusion if no improvement after one month or as first line in CKD 5; TF saturation > 20% and Hb < 100: May require erythropoietin stimulating agent (ESA) (e.g. Mircera). Discuss with renal GP / nephrologist. Symptoms of ESKD: Should be assessed for regularly: Ask about nausea, vomiting, anorexia, lethargy, SOB, leg swelling, restless leg symptoms and chest pain. Monitor for infections. Patients with CKD are immunosuppressed and vulnerable to infections. Severe infections may occur without prominent fever and dose adjustment of antibiotics may be needed. Contact renal GP, physician or nephrologist for advice as needed. Initiate advanced care planning processes and refer to the pre-dialysis co-ordinator for support in counselling and renal pathway planning. TABLE 4: COMMONLY PRESCRIBED DRUGS WHICH REQUIRE CAUTION IN CKD Drug Metformin Diuretics Colchicine Digoxin Gentamicin Vancomycin ACE-I, ARB NSAIDS Gliclazide Insulin Sitagliptin Risks in CKD / Action required May increase risk of lactic acidosis, particularly when unwell. Withhold if unwell. Dose adjust: egfr 30-45: Max 1g/day; egfr <30: Cease, or discuss with nephrologist / on-call physician. Volume depletion, contributing to AKI. Electrolyte disturbance. Withhold if unwell or dehydrated. Monitor UEC regularly. Accumulation, drug toxicity. Adjust dose according to egfr (see Therapeutic guidelines) + / - monitor levels. May increase risk of AKI during acute illness. Hyperkalaemia. Monitor K+. Withhold if unwell. Cease if egfr < 15 and not required for HTN. Increase risk of AKI. Avoid. Accumulation, Increased hypoglycaemia risk, Dose adjust: egfr 45-60: Reduce dose, egfr < 45: Cease. Accumulation, Increased risk of hypoglycaemia Dose adjust based on BSL monitoring. Accumulation, drug toxicity. Dose adjust: egfr 30-50: 50mg daily, egfr < 30: 25mg daily. WOMEN OF CHILDBEARING AGE Encourage use of reliable contraception, pre-pregnancy counselling and early antenatal care. Stop ACE-I / ARBs as soon as pregnancy planned or suspected. If pregnant, discuss with obstetrician /
5 physician promptly and consider early referral to high risk pregnancy clinic. If breastfeeding, use enalapril as preferred ACE/ARB. REFER / DISCUSS TO NEPHROLOGIST: CALL YOUR LOCAL RENAL HEALTH CENTRE FOR SUPPORT REGARDING THE CARE OF PATIENTS WITH CKD IN THE KIMBERLEY REGION. Persistent haematuria plus proteinuria; Proteinuria > 1g/day (ACR > 70, PCR > 100); ROUTINE SCHEDULE OF CARE FOR STABLE CKD PATIENTS BY RISK CATEGORY* Patients with proteinuria not tolerating ACE/ARB; Patients with very high risk CKD; CKD and difficult to manage HTN on three agents ; Persisting anaemia despite iron therapy; Urgent discussion required: Abnormal egfr / ACR and suspected connective tissue disease (e.g. facial rash, polyarthritis, lethargy, abnormal investigations) ; Heavy proteinuria (ACR>220) and possible nephrotic syndrome (oedema, hypoalbuminaemia, hyperlipidaemia) ; Rapidly declining renal function (egfr decline by 15min/min within 12 months). TO OBSTETRICIAN if planning pregnancy or early pregnancy. TO ALLIED HEALTH as needed, and particularly: Dietician: CKD and high BMI or any BMI and egfr < 30; Diabetes educator: CKD with insulin therapy and / or sub-optimal diabetic control. Kimberley Renal Services TO PRE-DIALYSIS CO-ORDINATOR if egfr<30. TO RENAL GP: CKD patients of any stage. Referral of patients high / very high risk assists with care coordination. CKD STAGES CKD RISK CATEGORY MODERATE RISK: HIGH RISK: VERY HIGH RISK (NOT YET ESKD) CKD STAGE 1 AND 2 egfr > 60 + egfr > 60 + Microalbuminuria Macroalbuminuria CKD STAGE 3 egfr egfr egfr Normal ACR Microalbuminuria + Macroalbuminuria CKD STAGE 3B egfr egfr Normal ACR Microalbuminuria CKD STAGE 4 egfr ESKD CKD STAGE 5 egfr < 15 PATHOLOGY: UEC, ACR, LFT, FBP, CRP, Ca++, Mg++, phosphate 12 monthly. 3 6 monthly. 1 3 monthly. Monthly. HbA1c, lipids 12 monthly, more often for other conditions as needed (e.g. diabetes). PTH Iron studies CLINICAL REVIEW: BP, weight, assess smoking, diet, exercise As needed for the investigation and management of anaemia. Monthly if Hb < 100, otherwise 3 monthly. 12 monthly. 3 6 monthly. 1 3 monthly. Monthly. Symptoms of ESKD 1 3 monthly. Monthly. Every three months. Monthly. Review by renal GP At any stage, on referral from primary provider. Review by nephrologist On referral from primary provider. 3 6 monthly. Each opportunity. Review by pre-dialysis coordinator *Does not apply to patients who are unstable or who have rapidly changing renal function. RESOURCES
6 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Management in GP, Kidney Health Australia: Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment Guidelines, Kidney Health Australia: KRS Contact list: See or call to request a copy Creatinine clearance calculators: Other chronic disease and STI protocols for the Kimberley region:
QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS
 KEY MESSAGES 1 SCREENING CRITERIA Screen: Patients with DM and/or hypertension at least yearly. Consider screening patients with: Age >65 years old Family history of stage 5 CKD or hereditary kidney disease
KEY MESSAGES 1 SCREENING CRITERIA Screen: Patients with DM and/or hypertension at least yearly. Consider screening patients with: Age >65 years old Family history of stage 5 CKD or hereditary kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease screening and assessment
 Care map information Information resources for patients and carers Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders DEFINITION OF CKD egfr
Care map information Information resources for patients and carers Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders DEFINITION OF CKD egfr
Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus
 Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus 1 Contents Executive Summary... 3 How to Screen for Diabetic Nephropathy... 4 What to Measure... 4 Frequency
Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus 1 Contents Executive Summary... 3 How to Screen for Diabetic Nephropathy... 4 What to Measure... 4 Frequency
Professor Suetonia Palmer
 Professor Suetonia Palmer Department of Medicine Nephrologist Christchurch Hospital Christchurch 14:00-14:55 WS #108: The Kidney Test - When To Test and When to Refer ( and When Not To) 15:05-16:00 WS
Professor Suetonia Palmer Department of Medicine Nephrologist Christchurch Hospital Christchurch 14:00-14:55 WS #108: The Kidney Test - When To Test and When to Refer ( and When Not To) 15:05-16:00 WS
Irish Practice Nurses Association Annual Conference Tullamore Court Hotel OCTOBER 6 th 2012
 Irish Practice Nurses Association Annual Conference Tullamore Court Hotel OCTOBER 6 th 2012 Susan McKenna Renal Clinical Nurse Specialist Cavan General Hospital Renal patient population ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
Irish Practice Nurses Association Annual Conference Tullamore Court Hotel OCTOBER 6 th 2012 Susan McKenna Renal Clinical Nurse Specialist Cavan General Hospital Renal patient population ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
 Early Treatment is the Key Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stage Description GFR (ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) >90 1 Kidney damage with normal or GFR 2 Mild decrease in GFR 60-89 3 Moderate decrease in GFR
Early Treatment is the Key Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stage Description GFR (ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) >90 1 Kidney damage with normal or GFR 2 Mild decrease in GFR 60-89 3 Moderate decrease in GFR
Chronic Kidney Disease
 Chronic Kidney Disease Presence of kidney damage or decreased kidney function for three or more months, - necessary to distinguish CKD from acute kidney disease. Ascertained either by kidney biopsy or
Chronic Kidney Disease Presence of kidney damage or decreased kidney function for three or more months, - necessary to distinguish CKD from acute kidney disease. Ascertained either by kidney biopsy or
Office Management of Reduced GFR Practical advice for the management of CKD
 Office Management of Reduced GFR Practical advice for the management of CKD CKD Online Education CME for Primary Care April 27, 2016 Monica Beaulieu, MD FRCPC MHA CHAIR PROVINCIAL KIDNEY CARE COMMITTEE
Office Management of Reduced GFR Practical advice for the management of CKD CKD Online Education CME for Primary Care April 27, 2016 Monica Beaulieu, MD FRCPC MHA CHAIR PROVINCIAL KIDNEY CARE COMMITTEE
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and egfr: Decision and Dilemma. Dr Bhavna K Pandya Consultant Nephrologist University Hospital Aintree
 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and egfr: Decision and Dilemma Dr Bhavna K Pandya Consultant Nephrologist University Hospital Aintree Topics CKD background egfr background Patient with egfr Referral Guidelines
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and egfr: Decision and Dilemma Dr Bhavna K Pandya Consultant Nephrologist University Hospital Aintree Topics CKD background egfr background Patient with egfr Referral Guidelines
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERENCE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERECE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease CKD VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERECE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease CKD VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management
Nephrology. 3 rd Year Revision Session 06/05/17 Cathal Hannan
 Nephrology 3 rd Year Revision Session 06/05/17 Cathal Hannan Aims Acute Kidney Injury-recognition and management Sample OSCE Station Clinically relevant renal physiology Aetiology of Chronic Kidney Disease
Nephrology 3 rd Year Revision Session 06/05/17 Cathal Hannan Aims Acute Kidney Injury-recognition and management Sample OSCE Station Clinically relevant renal physiology Aetiology of Chronic Kidney Disease
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGNOSIS
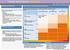 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS GFR categories, description and range WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD CLASSIFICATION OF CKD USING egfr AND ACR CATEGORIES Offer testing for CKD using egfr, creatinine and ACR
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS GFR categories, description and range WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD CLASSIFICATION OF CKD USING egfr AND ACR CATEGORIES Offer testing for CKD using egfr, creatinine and ACR
Key Clinical Tips KIDNEY HEALTH AUSTRALIA
 Key Clinical Tips A measured or estimated GFR < 60 ml/min/1.73 m 2 is associated with increased risks of adverse renal, cardiovascular and other clinical outcomes, irrespective of age. For people with
Key Clinical Tips A measured or estimated GFR < 60 ml/min/1.73 m 2 is associated with increased risks of adverse renal, cardiovascular and other clinical outcomes, irrespective of age. For people with
Management of early chronic kidney disease
 Management of early chronic kidney disease GREENLANE SUMMER GP SYMPOSIUM 2018 Jonathan Hsiao Renal and General Physician Introduction A growing public health problem in NZ and throughout the world. Unknown
Management of early chronic kidney disease GREENLANE SUMMER GP SYMPOSIUM 2018 Jonathan Hsiao Renal and General Physician Introduction A growing public health problem in NZ and throughout the world. Unknown
Type 2 Diabetes. Stopping Smoking. Consider referral to smoking cessation. Consider referring for weight management advice.
 Type 2 Diabetes Stopping Smoking Consider referral to smoking cessation BMI > 25 kg m² Set a weight loss target of a 5-10% reduction Consider referring for weight management advice Control BP to
Type 2 Diabetes Stopping Smoking Consider referral to smoking cessation BMI > 25 kg m² Set a weight loss target of a 5-10% reduction Consider referring for weight management advice Control BP to
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGNOSIS
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD Offer testing for CKD using egfr, serum creatinine and urinary ACR to people with any of the following risk factors: diabetes hypertension acute
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD Offer testing for CKD using egfr, serum creatinine and urinary ACR to people with any of the following risk factors: diabetes hypertension acute
ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY A PRIMER FOR PRIMARY CARE PHYSICIANS. Myriam Farah, MD, FRCPC
 ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY A PRIMER FOR PRIMARY CARE PHYSICIANS Myriam Farah, MD, FRCPC Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Nephrology, University of British Columbia November 2016 1. How to recognize acute
ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY A PRIMER FOR PRIMARY CARE PHYSICIANS Myriam Farah, MD, FRCPC Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Nephrology, University of British Columbia November 2016 1. How to recognize acute
Chronic Kidney Disease
 Chronic Kidney Disease Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Contact Name and Job Title (author) Directorate & Speciality Guideline for the Identification
Chronic Kidney Disease Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Contact Name and Job Title (author) Directorate & Speciality Guideline for the Identification
Diabetes in Renal Patients. Contents. Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetes in Renal Patients Contents Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy What effect does CKD have on a patient s diabetic control? Diabetic Drugs in CKD and Dialysis Patients Hyper and Hypoglycaemia in
Diabetes in Renal Patients Contents Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy What effect does CKD have on a patient s diabetic control? Diabetic Drugs in CKD and Dialysis Patients Hyper and Hypoglycaemia in
The future is here. It s just not widely distributed yet. William Gibson
 The future is here. It s just not widely distributed yet. William Gibson CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE MANAGEMENT A NEW PARADIGM Aaron Cass, MD, FRCPC Nephrologist, Fraser Health January 22, 2014 Where Are We
The future is here. It s just not widely distributed yet. William Gibson CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE MANAGEMENT A NEW PARADIGM Aaron Cass, MD, FRCPC Nephrologist, Fraser Health January 22, 2014 Where Are We
Applying clinical guidelines treating and managing CKD
 Applying clinical guidelines treating and managing CKD Develop patient treatment plan according to level of severity. Source: Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012
Applying clinical guidelines treating and managing CKD Develop patient treatment plan according to level of severity. Source: Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012
CKD & HT. Anne-Marie Angus
 CKD & HT Anne-Marie Angus Hypertension definitions Persisting BP >140/90 and HBPM >135/85 Stage 1 >140/90 (HBPM >135/85) Stage 2 >160/100 (HBPM >150/90) Severe >180/100 White coat HT Why treat? A major
CKD & HT Anne-Marie Angus Hypertension definitions Persisting BP >140/90 and HBPM >135/85 Stage 1 >140/90 (HBPM >135/85) Stage 2 >160/100 (HBPM >150/90) Severe >180/100 White coat HT Why treat? A major
CKDinform: A PCP s Guide to CKD Detection and Delaying Progression
 CKDinform: A PCP s Guide to CKD Detection and Delaying Progression Learning Objectives Describe suitable screening tools, such as GFR and ACR, for proper utilization in clinical practice related to the
CKDinform: A PCP s Guide to CKD Detection and Delaying Progression Learning Objectives Describe suitable screening tools, such as GFR and ACR, for proper utilization in clinical practice related to the
Chronic kidney disease management primary care
 Care map information Information resources for patients and carers Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders DEFINITION OF CKD egfr
Care map information Information resources for patients and carers Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders DEFINITION OF CKD egfr
CKD FOR INTERNISTS. Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College
 CKD FOR INTERNISTS Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College INTRODUCTION In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative(KDOQI)
CKD FOR INTERNISTS Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College INTRODUCTION In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative(KDOQI)
Hypertension diagnosis (see detail document) Diabetic. Target less than 130/80mmHg
 Hypertension diagnosis (see detail document) Non-diabetic Diabetic Very elderly (older than 80 years) Target less than 140/90mmHg Target less than 130/80mmHg Consider SBP target less than 150mmHg Non-diabetic
Hypertension diagnosis (see detail document) Non-diabetic Diabetic Very elderly (older than 80 years) Target less than 140/90mmHg Target less than 130/80mmHg Consider SBP target less than 150mmHg Non-diabetic
Younger adults with a family history of premature artherosclerotic disease should have their cardiovascular risk factors measured.
 Appendix 2A - Guidance on Management of Hypertension Measurement of blood pressure All adults from 40 years should have blood pressure measured as part of opportunistic cardiovascular risk assessment.
Appendix 2A - Guidance on Management of Hypertension Measurement of blood pressure All adults from 40 years should have blood pressure measured as part of opportunistic cardiovascular risk assessment.
Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care
 Clinical Stream Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care Dr Gerald Waters Dr Gerald Waters Renal Physician Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic Kidney Disease Normal functions of Kidneys Management of CKD Drugs
Clinical Stream Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care Dr Gerald Waters Dr Gerald Waters Renal Physician Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic Kidney Disease Normal functions of Kidneys Management of CKD Drugs
Dr A Pokrajac MD MSc MRCP Consultant
 Dr A Pokrajac MD MSc MRCP Consultant Onset at 5-15 years of T1DM Can be present at diagnosis of T2DM Detect in regular MA/Cr screening (2X first urine sample, no UTI, no other causes) Contributing Factors
Dr A Pokrajac MD MSc MRCP Consultant Onset at 5-15 years of T1DM Can be present at diagnosis of T2DM Detect in regular MA/Cr screening (2X first urine sample, no UTI, no other causes) Contributing Factors
keyword: diuretics Drug monitoring Monitoring diuretics in primary care 2 March 2009 best tests
 www.bpac.org.nz keyword: diuretics Drug monitoring Monitoring diuretics in primary care 2 March 2009 best tests Why do we monitor patients taking diuretics and what do we monitor? Monitoring a person on
www.bpac.org.nz keyword: diuretics Drug monitoring Monitoring diuretics in primary care 2 March 2009 best tests Why do we monitor patients taking diuretics and what do we monitor? Monitoring a person on
Bulletin Independent prescribing information for NHS Wales
 Bulletin Independent prescribing information for NHS Wales October 2017 Chronic kidney disease Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a long-term irreversible deterioration in the function of the kidneys, often
Bulletin Independent prescribing information for NHS Wales October 2017 Chronic kidney disease Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a long-term irreversible deterioration in the function of the kidneys, often
5.2 Key priorities for implementation
 5.2 Key priorities for implementation From the full set of recommendations, the GDG selected ten key priorities for implementation. The criteria used for selecting these recommendations are listed in detail
5.2 Key priorities for implementation From the full set of recommendations, the GDG selected ten key priorities for implementation. The criteria used for selecting these recommendations are listed in detail
Identifying and Managing Chronic Kidney Disease: A Practical Approach
 Identifying and Managing Chronic Kidney Disease: A Practical Approach S. Neil Finkle, MD, FRCPC Associate Professor Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Dalhousie University Program Director,
Identifying and Managing Chronic Kidney Disease: A Practical Approach S. Neil Finkle, MD, FRCPC Associate Professor Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Dalhousie University Program Director,
CKD and risk management : NICE guideline
 CKD and risk management : NICE guideline 2008-2014 Shahed Ahmed Consultant Nephrologist shahed.ahmed@rlbuht.nhs.uk Key points : Changing parameters of CKD and NICE guidance CKD and age related change of
CKD and risk management : NICE guideline 2008-2014 Shahed Ahmed Consultant Nephrologist shahed.ahmed@rlbuht.nhs.uk Key points : Changing parameters of CKD and NICE guidance CKD and age related change of
NORTHERN IRELAND GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
 NORTHERN IRELAND GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Practical points for use of estimated GFR + quality outcome framework indicators Developed by GAIN and the Northern Ireland Nephrology
NORTHERN IRELAND GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Practical points for use of estimated GFR + quality outcome framework indicators Developed by GAIN and the Northern Ireland Nephrology
CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE: WHAT THE PRIMARY CARE CAN OFFER. The annual conference of the Lebanese Society of Family Medicine October 2017 Dr Hiba AZAR
 CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE: WHAT THE PRIMARY CARE CAN OFFER The annual conference of the Lebanese Society of Family Medicine October 2017 Dr Hiba AZAR OUTLINE: A journey through CKD Screening for CKD: The why,
CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE: WHAT THE PRIMARY CARE CAN OFFER The annual conference of the Lebanese Society of Family Medicine October 2017 Dr Hiba AZAR OUTLINE: A journey through CKD Screening for CKD: The why,
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education
 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education Year Three Developed Summer 2017 Objectives Understand Acute Kidney Injury and its relevance to patient care. Brief revision of the Anatomy and physiology
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education Year Three Developed Summer 2017 Objectives Understand Acute Kidney Injury and its relevance to patient care. Brief revision of the Anatomy and physiology
The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009
 The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009 Teresa Northcutt, RN BSN Primaris Program Manager, Prevention - CKD MO-09-01-CKD This material was prepared by Primaris,
The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009 Teresa Northcutt, RN BSN Primaris Program Manager, Prevention - CKD MO-09-01-CKD This material was prepared by Primaris,
Doncaster & Bassetlaw. AKI guidelines for primary care
 Doncaster & Bassetlaw AKI guidelines for primary care Contents: FLOW DIAGRAM: MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH AKI DETECTED IN PRIMARY CARE... 2 FLOW DIAGRAM: MANAGEMENT OF HYPERKALAEMIA.... 3 FLOW DIAGRAM:
Doncaster & Bassetlaw AKI guidelines for primary care Contents: FLOW DIAGRAM: MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH AKI DETECTED IN PRIMARY CARE... 2 FLOW DIAGRAM: MANAGEMENT OF HYPERKALAEMIA.... 3 FLOW DIAGRAM:
Dept of Diabetes Main Desk
 Dept of Diabetes Main Desk 01202 448060 Glucose management in Type 2 Diabetes in Adults The natural history of type 2 diabetes is for HbA1c to deteriorate with time. A stepwise approach to treatment is
Dept of Diabetes Main Desk 01202 448060 Glucose management in Type 2 Diabetes in Adults The natural history of type 2 diabetes is for HbA1c to deteriorate with time. A stepwise approach to treatment is
Management of Nephrotic Syndrome
 Management of Nephrotic Syndrome 1. Introduction Incidence 2-4/100,000. Boys > girls 3:2; age of onset 2-6 years 80% of cases in children is due to minimal change (MCD) of which 80% will respond to steroid
Management of Nephrotic Syndrome 1. Introduction Incidence 2-4/100,000. Boys > girls 3:2; age of onset 2-6 years 80% of cases in children is due to minimal change (MCD) of which 80% will respond to steroid
Elevation of Serum Creatinine: When to Screen, When to Refer. Bruce F. Culleton, MD, FRCPC; and Jolanta Karpinski, MD, FRCPC
 Elevation of Serum Creatinine: When to Screen, When to Refer Bruce F. Culleton, MD, FRCPC; and Jolanta Karpinski, MD, FRCPC Presented at the University of Calgary s CME and Professional Development 2006-2007
Elevation of Serum Creatinine: When to Screen, When to Refer Bruce F. Culleton, MD, FRCPC; and Jolanta Karpinski, MD, FRCPC Presented at the University of Calgary s CME and Professional Development 2006-2007
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) (Southampton pathway)
 Background information Patient information Key messages for this pathway Definitions and abbreviations used in this pathway Classification of CKD Diagnosis of CKD Summary of referral criteria Screening
Background information Patient information Key messages for this pathway Definitions and abbreviations used in this pathway Classification of CKD Diagnosis of CKD Summary of referral criteria Screening
Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males
 Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males Clinical presentation For patients in care homes see UTI in adults where IV Antibiotics in the community may be appropriate (under development) History and
Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males Clinical presentation For patients in care homes see UTI in adults where IV Antibiotics in the community may be appropriate (under development) History and
Summary of recommendations
 Summary of recommendations Measuring blood pressure (BP) Use the recommended technique at every BP reading to ensure accurate measurements and avoid common errs. Pay particular attention to the following:
Summary of recommendations Measuring blood pressure (BP) Use the recommended technique at every BP reading to ensure accurate measurements and avoid common errs. Pay particular attention to the following:
Supplement: Summary of Recommendation Statements CHAPTER 1: DEFINITION AND CLASSIFICATION OF CKD
 Supplement: Summary of Recommendation Statements CHAPTER 1: DEFINITION AND CLASSIFICATION OF CKD 1.1 DEFINITION OF CKD 1.1.1: CKD is defined as abnormalities of kidney structure or function, present for
Supplement: Summary of Recommendation Statements CHAPTER 1: DEFINITION AND CLASSIFICATION OF CKD 1.1 DEFINITION OF CKD 1.1.1: CKD is defined as abnormalities of kidney structure or function, present for
Primary Care Approach to Management of CKD
 Primary Care Approach to Management of CKD This PowerPoint was developed through a collaboration between the National Kidney Foundation and ASCP. Copyright 2018 National Kidney Foundation and ASCP Low
Primary Care Approach to Management of CKD This PowerPoint was developed through a collaboration between the National Kidney Foundation and ASCP. Copyright 2018 National Kidney Foundation and ASCP Low
Identification, management and referral of adults with chronic kidney disease: concise guidelines
 Identification, management and referral of adults with chronic kidney disease: concise guidelines Abstract Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is often thought to be a relatively rare condition requiring specialist
Identification, management and referral of adults with chronic kidney disease: concise guidelines Abstract Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is often thought to be a relatively rare condition requiring specialist
CKD IN THE CLINIC. Session Content. Recommendations for commonly used medications in CKD. CKD screening and referral
 CKD IN THE CLINIC Family Physician Refresher Course Lisa M. Antes, MD April 19, 2017 No disclosures Session Content 1. 2. Recommendations for commonly used medications in CKD Basic principles /patient
CKD IN THE CLINIC Family Physician Refresher Course Lisa M. Antes, MD April 19, 2017 No disclosures Session Content 1. 2. Recommendations for commonly used medications in CKD Basic principles /patient
PRE-DIALYSIS CARE IN CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE PATIENTS DR O. A ADEJUMO MBBS, FWACP, FMCP
 PRE-DIALYSIS CARE IN CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE PATIENTS DR O. A ADEJUMO MBBS, FWACP, FMCP OUTLINE INTRODUCTION BURDEN OF CKD DEFINITION OF PRE-DIALYSIS CARE (PDC) GOALS OF PDC IN CKD COMPONENTS OF PDC ADVANTAGES
PRE-DIALYSIS CARE IN CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE PATIENTS DR O. A ADEJUMO MBBS, FWACP, FMCP OUTLINE INTRODUCTION BURDEN OF CKD DEFINITION OF PRE-DIALYSIS CARE (PDC) GOALS OF PDC IN CKD COMPONENTS OF PDC ADVANTAGES
Diabetes Renal Disease Management. Dr Paul Laboi Dr Vijay Jayagopal York Hospital
 Diabetes Renal Disease Management Dr Paul Laboi Dr Vijay Jayagopal York Hospital 0 Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is a clinical syndrome characterised by the following: Persistent albuminuria
Diabetes Renal Disease Management Dr Paul Laboi Dr Vijay Jayagopal York Hospital 0 Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is a clinical syndrome characterised by the following: Persistent albuminuria
Diabetic Kidney Disease in the Primary Care Clinic
 Diabetic Kidney Disease in the Primary Care Clinic Jess Wheeler, DO Nephrology 2015 Outline: 1. CKD/DKD is a growing problem 2. Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) 3. Diagnosis of Diabetic Kidney
Diabetic Kidney Disease in the Primary Care Clinic Jess Wheeler, DO Nephrology 2015 Outline: 1. CKD/DKD is a growing problem 2. Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) 3. Diagnosis of Diabetic Kidney
Diabetes and Hypertension
 Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Primary Care Physicians and Clinicians. XXX on behalf of the Upper Midwest Fistula First Coalition. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Resources
 August 10, 2007 To: From: RE: Primary Care Physicians and Clinicians XXX on behalf of the Upper Midwest Fistula First Coalition Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Resources Caring for patients with chronic kidney
August 10, 2007 To: From: RE: Primary Care Physicians and Clinicians XXX on behalf of the Upper Midwest Fistula First Coalition Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Resources Caring for patients with chronic kidney
CKD at the primary and secondary care interface. Paul Cockwell Consultant Nephrologist Clinical Service Lead Renal Medicine, QEHB
 CKD at the primary and secondary care interface Paul Cockwell Consultant Nephrologist Clinical Service Lead Renal Medicine, QEHB The Health improvement Network (THIN): 6.7 million patients from 426 primary
CKD at the primary and secondary care interface Paul Cockwell Consultant Nephrologist Clinical Service Lead Renal Medicine, QEHB The Health improvement Network (THIN): 6.7 million patients from 426 primary
Chronic Kidney Disease: Optimal and Coordinated Management
 Chronic Kidney Disease: Optimal and Coordinated Management Michael Copland, MD, FRCPC Presented at University of British Columbia s 42nd Annual Post Graduate Review in Family Medicine Conference, Vancouver,
Chronic Kidney Disease: Optimal and Coordinated Management Michael Copland, MD, FRCPC Presented at University of British Columbia s 42nd Annual Post Graduate Review in Family Medicine Conference, Vancouver,
Guidelines to assist General Practitioners in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes. April 2010
 Guidelines to assist General Practitioners in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes April 2010 Foreword The guidelines were devised by the Diabetes Day Centre in Beaumont Hospital in consultation with a number
Guidelines to assist General Practitioners in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes April 2010 Foreword The guidelines were devised by the Diabetes Day Centre in Beaumont Hospital in consultation with a number
Childhood nephrotic syndrome practice guidelines
 Childhood nephrotic syndrome practice guidelines Dr Shuman Haq Consultant Paediatric Nephrologist Southampton Children s Hospital Definitions Nephrotic syndrome Proteinuria Urine protein : creatinine >200
Childhood nephrotic syndrome practice guidelines Dr Shuman Haq Consultant Paediatric Nephrologist Southampton Children s Hospital Definitions Nephrotic syndrome Proteinuria Urine protein : creatinine >200
Kidney damage with normal or increased GFR Kidney damage with mild reduction in GFR
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Contents Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease Dosing adjustments Hyperphosphataemia management Secondary hyperparathyroidism Anaemias Hyperkalaemia Acidosis Hypertension STAGES OF CHRONIC
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Contents Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease Dosing adjustments Hyperphosphataemia management Secondary hyperparathyroidism Anaemias Hyperkalaemia Acidosis Hypertension STAGES OF CHRONIC
Case #1. Current Management Strategies in Chronic Kidney Disease. Serum creatinine cont. Pitfalls of Serum Cr
 Current Management Strategies in Chronic Kidney Disease Grace Lin, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine, University of California San Francisco Case #1 50 y.o. 70 kg man with long-standing hypertension is
Current Management Strategies in Chronic Kidney Disease Grace Lin, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine, University of California San Francisco Case #1 50 y.o. 70 kg man with long-standing hypertension is
Diabetes and Kidney Disease. Kris Bentley Renal Nurse practitioner 2018
 Diabetes and Kidney Disease Kris Bentley Renal Nurse practitioner 2018 Aims Develop an understanding of Chronic Kidney Disease Understand how diabetes impacts on your kidneys Be able to recognise the risk
Diabetes and Kidney Disease Kris Bentley Renal Nurse practitioner 2018 Aims Develop an understanding of Chronic Kidney Disease Understand how diabetes impacts on your kidneys Be able to recognise the risk
patient group direction
 NITROFURANTOIN v01 1/12 NITROFURANTOIN PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic) Emergency Care Practitioner
NITROFURANTOIN v01 1/12 NITROFURANTOIN PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic) Emergency Care Practitioner
H(a)ematuria. FX Keeley Consultant Urologist Bristol Urological Institute
 H(a)ematuria FX Keeley Consultant Urologist Bristol Urological Institute From Philadelphia to Bristol, England Southmead Hospital, 1916 Southmead Hospital, 2013 Southmead Hospital, 2014 H(a)ematuria Blood
H(a)ematuria FX Keeley Consultant Urologist Bristol Urological Institute From Philadelphia to Bristol, England Southmead Hospital, 1916 Southmead Hospital, 2013 Southmead Hospital, 2014 H(a)ematuria Blood
Patient details GP details Specialist details Name GP Name Dr Specialist Name Dr R. Horton
 Rationale for Initiation, Continuation and Discontinuation (RICaD) Sacubitril/Valsartan (Entresto) For the treatment of symptomatic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (NICE TA388) This document
Rationale for Initiation, Continuation and Discontinuation (RICaD) Sacubitril/Valsartan (Entresto) For the treatment of symptomatic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (NICE TA388) This document
Treatment monitoring protocol for Dimethyl fumarate therapy in active Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis
 Treatment monitoring protocol for Dimethyl fumarate therapy in active Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis This protocol provides monitoring guidance for adult patients requiring Dimethyl fumarate therapy
Treatment monitoring protocol for Dimethyl fumarate therapy in active Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis This protocol provides monitoring guidance for adult patients requiring Dimethyl fumarate therapy
Diabetes Mellitus. Eiman Ali Basheir. Mob: /1/2019
 Diabetes Mellitus Eiman Ali Basheir Mob: 091520385 27/1/2019 Learning Outcomes Discuss the WHO criteria for Diabetes Mellitus diagnosis Describe the steps taken to confirm diagnosis Interpret GTT. Discuss
Diabetes Mellitus Eiman Ali Basheir Mob: 091520385 27/1/2019 Learning Outcomes Discuss the WHO criteria for Diabetes Mellitus diagnosis Describe the steps taken to confirm diagnosis Interpret GTT. Discuss
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines. AKI guidelines for primary care
 Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines AKI guidelines for primary care Contents: Flow Diagram: Recommended response time to AKI warning stage test results for adults in primary care 2 Table
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines AKI guidelines for primary care Contents: Flow Diagram: Recommended response time to AKI warning stage test results for adults in primary care 2 Table
Section Questions Answers
 Section Questions Answers Guide to CKD Screening and Evaluation -Alec Otteman, MD Delaying Progression - Paul Drawz, MD, MHS, MS 1. Modifiable risk factors for CKD include: a. Diabetes b. Hypertension
Section Questions Answers Guide to CKD Screening and Evaluation -Alec Otteman, MD Delaying Progression - Paul Drawz, MD, MHS, MS 1. Modifiable risk factors for CKD include: a. Diabetes b. Hypertension
Family Medicine Counseling (Additional topics)
 Family Medicine Counseling (Additional topics) Doa'a Samarah Al Zoubi Hope/2010 batch 1. ACEI 2. Diabetic with microalbuminuria 3. Osteoporosis 4. Anti-thyroid drugs and ablation. 1. ACEI counseling: -
Family Medicine Counseling (Additional topics) Doa'a Samarah Al Zoubi Hope/2010 batch 1. ACEI 2. Diabetic with microalbuminuria 3. Osteoporosis 4. Anti-thyroid drugs and ablation. 1. ACEI counseling: -
Tread Carefully Because you Tread on my Nephrons. Prescribing Hints in Renal Disease
 Tread Carefully Because you Tread on my Nephrons Prescribing Hints in Renal Disease David WP Lappin,, MB PhD FRCPI Clinical Lecturer in Medicine and Consultant Nephrologist and General Physician, Merlin
Tread Carefully Because you Tread on my Nephrons Prescribing Hints in Renal Disease David WP Lappin,, MB PhD FRCPI Clinical Lecturer in Medicine and Consultant Nephrologist and General Physician, Merlin
CHEMOTHERAPY PROTOCOL FOR ADMINISTRATION OF VENETOCLAX
 CHEMOTHERAPY PROTOCOL FOR ADMINISTRATION OF VENETOCLAX Therapeutic Indications: Venetoclax monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) in the presence of 17p deletion
CHEMOTHERAPY PROTOCOL FOR ADMINISTRATION OF VENETOCLAX Therapeutic Indications: Venetoclax monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) in the presence of 17p deletion
Shared Care Guideline Metolazone for fluid management in CKD (Adults)
 Shared Care Guideline Metolazone for fluid management in CKD (Adults) It is vital for safe and appropriate patient care that there is a clear understanding of where clinical and prescribing responsibility
Shared Care Guideline Metolazone for fluid management in CKD (Adults) It is vital for safe and appropriate patient care that there is a clear understanding of where clinical and prescribing responsibility
Faculty/Presenter Disclosure
 CSI for CKD Unravelling the myths surrounding chronic kidney disease Practical Evidence for Informed Practice Oct 21 2016 Dr. Scott Klarenbach University of Alberta Slide 1: Option B (Presenter with NO
CSI for CKD Unravelling the myths surrounding chronic kidney disease Practical Evidence for Informed Practice Oct 21 2016 Dr. Scott Klarenbach University of Alberta Slide 1: Option B (Presenter with NO
6/10/2014. Chronic Kidney Disease - General management and standard of care. Management of CKD according to stage (KDOQI 2002)
 Chronic Kidney Disease - General management and standard of care Dr Nathalie Demoulin, Prof Michel Jadoul Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc Université Catholique de Louvain What should and can be done
Chronic Kidney Disease - General management and standard of care Dr Nathalie Demoulin, Prof Michel Jadoul Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc Université Catholique de Louvain What should and can be done
ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour
 ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour Dr Indranil Dasgupta Rationale No national practical
ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour Dr Indranil Dasgupta Rationale No national practical
Western Locality Shared care Information ~ Penicillamine, Rheumatology April 2013
 Western Locality Shared care Information ~ Penicillamine, Rheumatology April 2013 Penicillamine Treatment of: Rheumatoid arthritis Specialist: Please complete the Shared Care letter sending a request to
Western Locality Shared care Information ~ Penicillamine, Rheumatology April 2013 Penicillamine Treatment of: Rheumatoid arthritis Specialist: Please complete the Shared Care letter sending a request to
Connecting Chronic Kidney Disease: the link with Diabetes
 Connecting Chronic Kidney Disease: the link with Diabetes Primary Care Education Workshop This module was conceived and developed by PEAK* 1 Presented by: V0617 Collaborators *This Education was conceived
Connecting Chronic Kidney Disease: the link with Diabetes Primary Care Education Workshop This module was conceived and developed by PEAK* 1 Presented by: V0617 Collaborators *This Education was conceived
CLINICAL GUIDELINE. Document No:CG38 *All Sites Management of adult patients referred to South Tees University Hospitals for hypertension.
 GUIDELINE CLINICAL GUIDELINE Document No:CG38 *All Sites Management of adult patients referred to South Tees University Hospitals for hypertension. TITLE Management of adult patients referred to South
GUIDELINE CLINICAL GUIDELINE Document No:CG38 *All Sites Management of adult patients referred to South Tees University Hospitals for hypertension. TITLE Management of adult patients referred to South
Outpatient Management of Chronic Kidney Disease for the Internist
 Outpatient Management of Chronic Kidney Disease for the Internist Annual Meeting of Maryland Chapter of the American College of Physicians February 3, 2018 MARY (TESSIE) BEHRENS, MD, FACP, FASN, FNKF MID-ATLANTIC
Outpatient Management of Chronic Kidney Disease for the Internist Annual Meeting of Maryland Chapter of the American College of Physicians February 3, 2018 MARY (TESSIE) BEHRENS, MD, FACP, FASN, FNKF MID-ATLANTIC
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
Managing Patients with CKD in Primary Care: A Shared Care Pathway. 5 th April 2018
 Managing Patients with CKD in Primary Care: A Shared Care Pathway 5 th April 2018 Learning Objectives 1) What health risks does CKD represent? 2) Why change how we manage CKD in NWL? 1) How do we improve
Managing Patients with CKD in Primary Care: A Shared Care Pathway 5 th April 2018 Learning Objectives 1) What health risks does CKD represent? 2) Why change how we manage CKD in NWL? 1) How do we improve
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) In Primary Care Supporting early detection and consistent management
 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) In Primary Care Supporting early detection and consistent management Responding to AKI Warning Stage Test Results for Adults in Primary Care: Best Practice Guidance AKI in Primary
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) In Primary Care Supporting early detection and consistent management Responding to AKI Warning Stage Test Results for Adults in Primary Care: Best Practice Guidance AKI in Primary
The evidence base for interventions to slow the progression of chronic kidney disease: Medical interventions. Jonathan Evans Paediatric Nephrologist
 The evidence base for interventions to slow the progression of chronic kidney disease: Medical interventions Jonathan Evans Paediatric Nephrologist CKD in adults Often unrecognised Preventable Major cardiovascular
The evidence base for interventions to slow the progression of chronic kidney disease: Medical interventions Jonathan Evans Paediatric Nephrologist CKD in adults Often unrecognised Preventable Major cardiovascular
Transforming Diabetes Care
 Transforming Diabetes Care Diabetic Kidney Disease: Prevention, Detection and Treatment Alexis Chettiar, ACNP-BC, PhD(c) 1 Polling Question - 1 What is your role as a healthcare provider? a) Dietitian
Transforming Diabetes Care Diabetic Kidney Disease: Prevention, Detection and Treatment Alexis Chettiar, ACNP-BC, PhD(c) 1 Polling Question - 1 What is your role as a healthcare provider? a) Dietitian
Have you seen a patient like Elaine *?
 (linagliptin) 5mg tablets Have you seen a patient like Elaine *? *Hypothetical patient profile Elaine * : 60 years old Housewife *Hypothetical patient profile ELAINE*: T2D Patient with early signs of kidney
(linagliptin) 5mg tablets Have you seen a patient like Elaine *? *Hypothetical patient profile Elaine * : 60 years old Housewife *Hypothetical patient profile ELAINE*: T2D Patient with early signs of kidney
CONCORD INTERNAL MEDICINE CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE PROTOCOL. Revised May 30, 2012
 CONCORD INTERNAL MEDICINE CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE PROTOCOL Douglas G. Kelling, Jr., MD C. Gismondi-Eagan, MD, FACP George C. Monroe III, MD Revised May 30, 2012 The information contained in this protocol
CONCORD INTERNAL MEDICINE CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE PROTOCOL Douglas G. Kelling, Jr., MD C. Gismondi-Eagan, MD, FACP George C. Monroe III, MD Revised May 30, 2012 The information contained in this protocol
Essential Shared Care Agreement: Lithium
 Ref No. E042 Essential Shared Care Agreement: Lithium Please complete the following details: Patient s name, address, date of birth Treatment (indication, dose regimen, brand name) Monitoring (proposed
Ref No. E042 Essential Shared Care Agreement: Lithium Please complete the following details: Patient s name, address, date of birth Treatment (indication, dose regimen, brand name) Monitoring (proposed
Dana Lecture 2 Chronic Kidney Disease
 Medicine Dr. Dana Lecture 2 Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic Kidney Disease Assessment of renal function Classification of CKD Why Chronic renal failure tends to progress Risk factors for progression Management
Medicine Dr. Dana Lecture 2 Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic Kidney Disease Assessment of renal function Classification of CKD Why Chronic renal failure tends to progress Risk factors for progression Management
Hypertension Clinical case scenarios for primary care
 Hypertension Clinical case scenarios for primary care Implementing NICE guidance August 2011 NICE clinical guideline 127 What this presentation covers Five clinical case scenarios, including: presentation
Hypertension Clinical case scenarios for primary care Implementing NICE guidance August 2011 NICE clinical guideline 127 What this presentation covers Five clinical case scenarios, including: presentation
TREATMENTS FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES. Susan Henry Diabetes Specialist Nurse
 TREATMENTS FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES Susan Henry Diabetes Specialist Nurse How can we improve outcomes in Type 2 diabetes? Earlier diagnosis Better patient education Stress central role of lifestyle management
TREATMENTS FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES Susan Henry Diabetes Specialist Nurse How can we improve outcomes in Type 2 diabetes? Earlier diagnosis Better patient education Stress central role of lifestyle management
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005 1 Any adult in the health care system 2 Obtain blood pressure (BP) (Reliable,
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005 1 Any adult in the health care system 2 Obtain blood pressure (BP) (Reliable,
Hot Topics in Diabetic Kidney Disease a primary care perspective
 Hot Topics in Diabetic Kidney Disease a primary care perspective DR SARAH DAVIES GP PARTNER WITH SPECIAL INTEREST IN DIABETES, CARDIFF DUK CLINICAL CHAMPION NB MEDICAL HOT TOPICS PRESENTER AND DIABETES
Hot Topics in Diabetic Kidney Disease a primary care perspective DR SARAH DAVIES GP PARTNER WITH SPECIAL INTEREST IN DIABETES, CARDIFF DUK CLINICAL CHAMPION NB MEDICAL HOT TOPICS PRESENTER AND DIABETES
I hope the shared cared protocol will help with your care of this renal transplant patient. We are happy to discuss any issues with you.
 Paediatric Nephrology Phone (64) 9-3078900 Fax (64) 9-3078938 renalnurse@adhb.govt.nz wwong@adhb.govt.nz tonyak@adhb.govt.nz stackm@adhb.govt.nz chanelp@adhb.govt.nz Dear Colleague, Thank you for resuming
Paediatric Nephrology Phone (64) 9-3078900 Fax (64) 9-3078938 renalnurse@adhb.govt.nz wwong@adhb.govt.nz tonyak@adhb.govt.nz stackm@adhb.govt.nz chanelp@adhb.govt.nz Dear Colleague, Thank you for resuming
Nice CKD Clinical Guidelines 2014 The challenges and benefits they may bring toprimary care
 Nice CKD Clinical Guidelines 2014 The challenges and benefits they may bring toprimary care Paula D Souza Senior CKD Nurse Specialist Royal Devon and Exeter Healthcare Trust Introduction Background What
Nice CKD Clinical Guidelines 2014 The challenges and benefits they may bring toprimary care Paula D Souza Senior CKD Nurse Specialist Royal Devon and Exeter Healthcare Trust Introduction Background What
Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease
 Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease Definition of Metabolic Syndrome National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III Abdominal obesity, defined as a waist circumference
Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease Definition of Metabolic Syndrome National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III Abdominal obesity, defined as a waist circumference
What should you do next? Presenter Disclosure Information. Learning Objectives. Case: George
 2:45 3:45pm Optimizing the Management of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease SPEAKER Jay B. Wish, MD, FACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation:
2:45 3:45pm Optimizing the Management of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease SPEAKER Jay B. Wish, MD, FACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation:
Chronic kidney disease in cats
 Chronic kidney disease in cats What is chronic kidney disease (CKD)? Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the name now used to refer to cats with kidney failure (or chronic kidney failure). CKD is one of the
Chronic kidney disease in cats What is chronic kidney disease (CKD)? Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the name now used to refer to cats with kidney failure (or chronic kidney failure). CKD is one of the
OUTLINE INTRODUCTION EPIDEMIOLOGY CLASSIFICATION DIAGNOSIS AETIOLOGY MANAGEMENT FINANCIAL BURDEN OF ESRD SCREENIG GUIDELINE CONCLUSION
 Dr O. A ADEJUMO OUTLINE INTRODUCTION EPIDEMIOLOGY CLASSIFICATION DIAGNOSIS AETIOLOGY MANAGEMENT FINANCIAL BURDEN OF ESRD SCREENIG GUIDELINE CONCLUSION Introduction Chronic Kidney Disease is defined as
Dr O. A ADEJUMO OUTLINE INTRODUCTION EPIDEMIOLOGY CLASSIFICATION DIAGNOSIS AETIOLOGY MANAGEMENT FINANCIAL BURDEN OF ESRD SCREENIG GUIDELINE CONCLUSION Introduction Chronic Kidney Disease is defined as
Management of New-Onset Proteinuria in the Ambulatory Care Setting. Akinlolu Ojo, MD, PhD, MBA
 Management of New-Onset Proteinuria in the Ambulatory Care Setting Akinlolu Ojo, MD, PhD, MBA Urine dipstick results Negative Trace between 15 and 30 mg/dl 1+ between 30 and 100 mg/dl 2+ between 100 and
Management of New-Onset Proteinuria in the Ambulatory Care Setting Akinlolu Ojo, MD, PhD, MBA Urine dipstick results Negative Trace between 15 and 30 mg/dl 1+ between 30 and 100 mg/dl 2+ between 100 and
CKD FOR PRIMARY CARE MINNESOTA ACADEMY OF PHYSICIANS 2017 HEATHER ANN MUSTER, MD MS
 CKD FOR PRIMARY CARE MINNESOTA ACADEMY OF PHYSICIANS 2017 HEATHER ANN MUSTER, MD MS PLoS One. 2014 Nov 26;9(11):e110535. Of the 445 PCPs who enrolled at least 10 patients, 19 (4.3%) had >50% likelihood
CKD FOR PRIMARY CARE MINNESOTA ACADEMY OF PHYSICIANS 2017 HEATHER ANN MUSTER, MD MS PLoS One. 2014 Nov 26;9(11):e110535. Of the 445 PCPs who enrolled at least 10 patients, 19 (4.3%) had >50% likelihood
