Type A Aortic Dissection Presenting as Acute Ischemic Stroke Caution for Thrombolytic Therapy: A Case Report and Literatures Review
|
|
|
- Louise Tate
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Case Report Type A Aortic Dissection Presenting as Acute Ischemic Stroke Caution for Thrombolytic Therapy: A Case Report and Literatures Review Tawai Ngernsritrakul MD*, Pornchai Sathirapanya MD* * Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University, Hat Yai, Songkhla The authors reported a patient who had type A aortic dissection presenting with sudden onset of right hemiplegia and depressed consciousness. CT scan of brain showed acute cerebral infarction of left corona radiata, posterior limb of left internal capsule combined with left hemispheric brain swelling. An old cerebral infarction at the posterior limb of right internal capsule was also noted. Clinical signs of aortic regurgitation and difference in blood pressures and amplitude of pulses on both arms were associated. Initial chest x-ray revealed widening of the mediastinum. CT scan of chest revealed dissecting aorta extending from the ascending aorta to the mid of the descending aorta. Surgical correction of the aorta was refused and the patient was treated medically with partial neurological deficit. No additional cardiovascular events occurred. Keywords: Aortic dissection, Ischemic stroke, Thrombolytic therapy J Med Assoc Thai 2008; 91 (8): Full text. e-journal: Cerebral infarction due to acute aortic dissection is a rare clinical experience. However, this emergency condition needs accurate diagnosis and prompt management since it has high fatality. Concern for this hidden life threatening cardiovascular disease in patients presenting with acute ischemic stroke is warranted to avoid the unexpected catastrophic outcome from thrombolytic therapy. Case Report A 49-year-old fisherman, with a history of sudden onset of right hemiplegia and depressed consciousness while fishing in the sea, was taken to the emergency department of our center two days later. On the initial evaluation his blood pressure were 90/60 mmhg on the right arm and 120/50 mmhg on the left arm. Pulse rate was regular with 74 beats/min but decreased in amplitude on his right arm. Collapsing pulse was detected in all extremities. On the cardiac Correspondence to: Sathirapanya P, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University, Hat Yai, Songkhla 90110, Thailand. Phone: , Fax: sporncha@medicine.psu.ac.th examination, there was no apical shifting, no ventricular heaving, and no thrill. Normal rhythm of the first and second heart sounds was audible. The diastolic blowing murmur of grade II was heard in the left upper parasternal border. On the neurological examination, he was drowsy and did not respond to commands properly. The pupils were 3 mm in diameter and normally reacted to the light bilaterally. Both eyes were deviated to the left side on primary eyes position, but correctable by tilting the head in the horizontal plane. Right hemiplegia was found. Hyporeflexia and absence of ankle clonus but presence of Babinski s signs were evidenced on the affected side. There was no meningeal irritation signs elicited. Normal carotid pulsation and no carotid bruit were detected. Laboratory studies revealed normal routine blood tests including anti- HIV, serology for syphilis and coagulogram. An electrocardiogram demonstrated normal sinus rhythm with ST segments elevation in II, III and avf were evidenced. No PR interval depression was detected. The initial chest x-ray revealed widening of mediastinum without abnormal lung infiltration (Fig. 1) J Med Assoc Thai Vol. 91 No
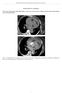
2 Fig. 1 Fig. 2 Chest x-ray showed widening mediastinum CT scan of the brain revealed acute cerebral infarction at the left corona radiate (A and D), internal capsule (B and C) (horizontal arrow) and frontal lobe (C) (vertical arrow) and old cerebral infarction at posterior limb of right internal capsule (B and D) (curved arrow) An emergency CT scan of the brain revealed a hypodensity lesion at the left corona radiata, left thalamus, left temporal, and left frontal area with prominent brain swelling on the left hemisphere indicating acute cerebral infarction along the left middle cerebral artery territory. An old cerebral infarction at the posterior limb of right internal capsule was also detected (Fig. 2). Immediately, an emergency CT scan of the chest was requested after aortic dissection was suspected and it revealed an intimal flap extending from the ascending aorta, the aortic arch to the descending aorta, and ended at the thoraco-abdominal junction. However, the suprarenal abdominal aorta was intact. The dissection extended upwards to involve the innominate artery, left common carotid artery, and left subclavian artery (Fig. 3). The emergency surgical repair of the aorta was planned immediately but it had to be postponed due to his markedly impaired consciousness and high fever of which aspiration pneumonia was suspected. He received broad-spectrum antibiotics and best supportive treatment in the intensive care unit with partial recovery of his alertness in the next several days. The surgical correction was refused by his relatives and the patient was discharged home. He has been cared regularly for one year in the out-patient department and has some hemiparesis left (motor power of grade 3/5) with partial dependence. No additional cardiovascular disorders were reported. Discussion Neurological disorders as the initial manifestation of type A aortic dissection have been reported in 29% in one recent case series, with a high number of ischemic stroke (16%) (1). From a literature review, there were some clinical clues for detection of aortic dissection: 1) History of concomitant chest pain. 2) Loss of carotid pulse without audible carotid bruit. 3) Loss or decreased intensity of peripheral pulse. 4) Signs of cardiac temponade. 5) Unstable vital signs. 6) Diastolic blowing murmur. 7) Signs of dissection of the descending aorta such as paraparesis, mesenteric infarction, and anuria. 8) Widening mediastinum from the chest x-ray. 9) Transient or persistent ST elevation especially in the right coronary artery territory because the common site of aortic dissection that arises at the lateral wall of ascending aorta and the retrograde dissection commonly affects the origin right coronary artery. A comprehensive review of all the reported cases of aortic dissection presenting with ischemic J Med Assoc Thai Vol. 91 No
3 Fig. 3 The contrast enhanced CT scan of the chest demonstrates the aortic dissection. Intimal flap causing double lumens of aorta arises from lateral wall of ascending aorta above the aortic root, approximately at the level of bifurcation of pulmonary artery (A), extend to arch of aorta (B), to descending aorta (C) and terminates at thoraco-abdominal junction-the most distal end of the dissection (D). The dissection also extends upwards to involve Innominate artery (curved arrow) and left common carotid artery. (straight arrow) (E), and finally both common carotid arteries (F) stroke with Pubmed database is shown in Table 1. They presented with sudden either focal or diffuse neurological disorders and ascending aorta was the common site of dissection in all cases. However, only half of them reported chest or back pain suggestive of aortic dissection. A study has shown that only two-thirds of patients of type A aortic dissection experienced pain, and most of those without neurological presentation reported pain (94%) (1). Among these clinical clues, Von Kodolitsch et al (8) reviewed the likelihood ratio of each sign, symp- tom, and basic investigation associated with aortic dissection. The study revealed the most helpful clue was pulse deficit (positive LR 47; 95% CI ), followed by focal neurological deficit (positive LR 33.0; 95% CI ), tear and ribbing pain (positive LR 10.8; 95% CI ), migrating pain (positive LR % CI ), left ventricular hypertrophy (positive LR 3.2; 95% CI ), sudden chest pain (positive LR 2.6; 95% CI ), enlarged aorta or widening mediastinum (positive LR 2.0; 95% CI ), and history of hypertension (positive LR 1.8; 95% CI ). Since the consciousness of the reported case was significantly depressed, the symptom of chest or back pain was unable to be obtained for the initial evaluation. The critical clinical clues for achieving the diagnosis of the fatal condition in the presented case were the difference in the blood pressures and the amplitude of radial pulses between both upper limbs, aortic regurgitation murmur and widening mediastinum in the initial chest radiological study. Computer tomographic scan of chest and transesophageal echocardiography are the very sensitive diagnostic studies for the disorder, however, they are time consuming that would reduce the opportunity of thrombolytic therapy. The simplicity and widely available chest x-ray, though up to 20% may be negative in aortic dissection (9), makes it valuable as a part of the initial assessment of acute stroke sufferers. Emergency surgical treatment is indicated in type A aortic dissection with favorable outcome in experienced surgical and postoperative care teams. The autopsy series before the era of modern treatment estimated that 40-50% of patients with dissection of proximal aorta died within 48 hours and one-year mortality rate was around 90% (10). Since new treatment regimens have been developed and the patients are immediately operated on, the 30-day survival rate has increased to 80-85% and 10-year survival rate has risen to 55% (11). Surgical correction was refused in the presented case and the patient was treated medically with some improvement in neurological deficit and without additional cardiovascular event reported at one year after the onset. Unlike one of our reviewed cases (case 3), the medical treatment failed and the patient died shortly after it was started. This may partly be due to the origin of the dissection in the reported case which did not involve the root of ascending aorta, in which its complication from hemopericardium or hemothorax usually causes a high mortality rate. The caution for this life threatening cardiovascular condition should be of concern and it should 1304 J Med Assoc Thai Vol. 91 No
4 Table 1. Summary of reported cases of aortic dissection presented with neurological deficits from the literature review Age (year) 64 (2) 64 (3) 72 (4) 44 (5) 49 (6) 85 (7) 49* Sex Female Male Female Male Male Female Male Presentation Sudden severe Sudden severe Alteration of Lt hemiparesis Chest pain and Lt Recurrent episode of Alteration of back pain chest pain consciousness hemiparesis aphasia and right-sided consciousness and Alteration of Wernicke aphasia intermittently weakness with Rt. hemiplegia consciousness spontaneous resolution Associated Absent of right Absent of right Diminish radial Not mention Right bundle branch Hypotension Difference in BP symptoms, radial pulse radial pulse pulse bilaterally block, and poor R and radial pulses signs and Acute aortic wave progression between both arms investigation regurgitation in V3-6, and ST Aortic regurgitation Cardiac segment depression murmur temponade in the II, III, and avf Affected Ascending aorta Ascending aorta Ascending aorta Ascending aorta Ascending aorta Ascending to Ascending to vessel Right and left include aortic Right and left Descending aorta Descending aorta at descending aorta descending aorta common cartotid root common cartotid Common iliac the level of superior artery artery artery mesenteric artery Left subclavian Right subclavian artery artery Treatment Surgery Surgery Medical Surgery Percutaneous Surgery Medical management management cardiopulmonary Support Outcome Survived with Expire on Expire 1 day Survive with Expire after 2 days Expire at the day 4 th Survive with partial left hemeplegia postoperative after admission left hemiparesis of admission postoperative deficit at one year day 7 th * The present case report J Med Assoc Thai Vol. 91 No
5 be included as a differential diagnosis in the management of acute ischemic stroke patients before the infusion of thrombolytic agent is started. Our reported case was presented at the time that exceeded the golden period of the thrombolytic treatment; hence, it was not initiated for him. However, for the stroke patients who have impaired consciousness and the thrombolytic therapy is clinically indicated, a thorough cardiovascular examination is warranted. Conclusion This cause of ischemic stroke in clinical practices remains uncommon. However, careful and complete cardiovascular examination combined with routine chest x-ray has to be included in the protocols of acute stroke treatment and this fatal condition has to be suspected when thrombolytic therapy for ischemic stroke is planned. The concomitant abnormalities in cardiovascular examinations and chest radiographic study in acute stroke should raise suspicion of this condition. To avoid the unexpected catastrophic outcome of thrombolytic treatment for acute ischemic stroke, none of these clinical evidences can be overlooked. References 1. Gaul C, Dietrich W, Friedrich I, Sirch J, Erbguth FJ. Neurological symptoms in type A aortic dissections. Stroke 2007; 38: Shimazaki Y, Minowa T, Watanabe T, Koshika M, Toyama H, Inui K. Acute aortic dissection with new massive cerebral infarction - a successful repair with ligature of the right common carotid artery. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2004; 10: Wright V, Horvath R, Baird AE. Aortic dissection presenting as acute ischemic stroke. Neurology 2003; 61: Flemming KD, Brown RD Jr. Acute cerebral infarction caused by aortic dissection: caution in the thrombolytic era. Stroke 1999; 30: Chua CH, Lien LM, Lin CH, Hung CR. Emergency surgical intervention in a patient with delayed diagnosis of aortic dissection presenting with acute ischemic stroke and undergoing thrombolytic therapy. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2005; 130: Kawano H, Tomichi Y, Fukae S, Koide Y, Toda G, Yano K. Aortic dissection associated with acute myocardial infarction and stroke found at autopsy. Intern Med 2006; 45: Zaidat OO, Ubogu EE, Lerner AJ. Recurrent transient ischemic attacks as the initial presenting manifestation of type A aortic dissection. Ann Vasc Surg 2002; 16: von Kodolitsch Y, Loose R, Ostermeyer J, Aydin A, Koschyk DH, Haverich A, et al. Proximal aortic dissection late after aortic valve surgery: 119 cases of a distinct clinical entity. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2000; 48: Earnest F, Muhm JR, Sheedy PF. Roentgenographic findings in thoracic aortic dissection. Mayo Clin Proc 1979; 54: Hirst AE Jr, Johns VJ Jr, Kime SW Jr. Dissecting aneurysm of the aorta: a review of 505 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 1958; 37: Burt CW. Summary statistics for acute cardiac ischemia and chest pain visits to United States EDs, Am J Emerg Med 1999; 17: J Med Assoc Thai Vol. 91 No
6 ภาวะผน งหลอดเล อดแดงเอออร ต าปร แยกต วชน ด เอ นำเสนอด วยอาการของสมองขาดเล อด เฉ ยบพล น ข อพ งระว งเม อจะให การร กษาด วยสารละลายล มเล อด: รายงานผ ป วย 1 ราย และ ทบทวนวรรณกรรม ถวาย เง นศร ตระก ล, พรช ย สถ รป ญญา รายงานผ ป วยหน งรายท ม ภาวะผน งหลอดเล อดแดงเอออร ต าปร แยกต วชน ด เอ ถ กนำมาด วยอาการ อ อนแรงแขนขาซ กขวาเฉ ยบพล น และระด บความร ส กต วลดลง ภาพถ ายเอกซเรย คอมพ วเตอร สมอง พบภาวะ เน อสมองตายเฉ ยบพล นท โคโรน าเรด อาต า ขาหล งของอ นเทอรน ลแคปซ ลด านซ าย ร วมก บภาวะสมองบวมซ กซ าย นอกจากน ย งพบภาวะเน อสมองตายเร อร งท ขาหล งของอ นเทอรน ลแคปซ ลด านขวา จากการตรวจร างกายพบ หล กฐานของล นเอออร ต กร ว ความแตกต างของระด บความด นโลห ตและแรงด นของช พจรบนแขนท งสองข าง ภาพถ ายเอกซเรย ปอดพบว าม เมด แอสต น มกว างมากข น ภาพถ ายเอกซเรย คอมพ วเตอร ทรวงอก พบรอยปร แยกของ หลอดเล อดแดงเอออร ต า ต งแต ส วนท เป นขาข นไปจนถ งก งกลางของส วนท เป นขาลง เน องจากการร กษาทางศ ลยกรรม ถ กปฏ เสธ ผ ป วยจ งได ร บการร กษาทางอาย รกรรม โดยม ความผ ดปกต ทางระบบประสาทเหล ออย หลงเหล ออย บางส วน แต ไม ม ความผ ดปกต ทางหลอดเล อดและห วใจเพ มเต มจากน น J Med Assoc Thai Vol. 91 No
AORTIC DISSECTION. DISSECTING ANEURYSMS OF THE AORTA or CLASSIFICATION
 DISSECTING ANEURYSMS OF THE AORTA or AORTIC DISSECTION CLASSIFICATION DeBakey classified aortic dissections into types I, II, and III :- Type I dissection the tear site originates in the ascending aorta,
DISSECTING ANEURYSMS OF THE AORTA or AORTIC DISSECTION CLASSIFICATION DeBakey classified aortic dissections into types I, II, and III :- Type I dissection the tear site originates in the ascending aorta,
Case 9799 Stanford type A aortic dissection: US and CT findings
 Case 9799 Stanford type A aortic dissection: US and CT findings Accogli S, Aringhieri G, Scalise P, Angelini G, Pancrazi F, Bemi P, Bartolozzi C Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, University
Case 9799 Stanford type A aortic dissection: US and CT findings Accogli S, Aringhieri G, Scalise P, Angelini G, Pancrazi F, Bemi P, Bartolozzi C Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, University
Supplementary material 1. Definitions of study endpoints (extracted from the Endpoint Validation Committee Charter) 1.
 Rationale, design, and baseline characteristics of the SIGNIFY trial: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ivabradine in patients with stable coronary artery disease without clinical
Rationale, design, and baseline characteristics of the SIGNIFY trial: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ivabradine in patients with stable coronary artery disease without clinical
AORTIC DISSECTIONS Current Management. TOMAS D. MARTIN, MD, LAT Professor, TCV Surgery Director UF Health Aortic Disease Center University of Florida
 AORTIC DISSECTIONS Current Management TOMAS D. MARTIN, MD, LAT Professor, TCV Surgery Director UF Health Aortic Disease Center University of Florida DISCLOSURES Terumo Medtronic Cook Edwards Cryolife AORTIC
AORTIC DISSECTIONS Current Management TOMAS D. MARTIN, MD, LAT Professor, TCV Surgery Director UF Health Aortic Disease Center University of Florida DISCLOSURES Terumo Medtronic Cook Edwards Cryolife AORTIC
Optimal repair of acute aortic dissection
 Optimal repair of acute aortic dissection Dept. of Vascular Surgery, The 2nd Xiang-Yale Hospital, Central-South University, China Hunan Major Vessels Diseases Clinical Center Chang Shu Email:changshu01@yahoo.com
Optimal repair of acute aortic dissection Dept. of Vascular Surgery, The 2nd Xiang-Yale Hospital, Central-South University, China Hunan Major Vessels Diseases Clinical Center Chang Shu Email:changshu01@yahoo.com
THORACIC AORTIC DISSECTION
 The Essence of Aortic Dissection THORACIC AORTIC DISSECTION Aortic dissection can be classified as acute if it s onset has been less than 14 days or chronic if its onset has been more than 14 days. Mortality
The Essence of Aortic Dissection THORACIC AORTIC DISSECTION Aortic dissection can be classified as acute if it s onset has been less than 14 days or chronic if its onset has been more than 14 days. Mortality
ISPUB.COM. A pulled muscle," - Aortic Dissection. A Bhagra, N Anand, M Fernanda Bellolio INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 9 Number 1 A pulled muscle," - Aortic Dissection A Bhagra, N Anand, M Fernanda Bellolio Citation A Bhagra, N Anand, M Fernanda Bellolio. A pulled muscle,"
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 9 Number 1 A pulled muscle," - Aortic Dissection A Bhagra, N Anand, M Fernanda Bellolio Citation A Bhagra, N Anand, M Fernanda Bellolio. A pulled muscle,"
Subclavian artery Stenting
 Subclavian artery Stenting Etiology Atherosclerosis Takayasu s arteritis Fibromuscular dysplasia Giant Cell Arteritis Radiation-induced Vascular Injury Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Neurofibromatosis Incidence
Subclavian artery Stenting Etiology Atherosclerosis Takayasu s arteritis Fibromuscular dysplasia Giant Cell Arteritis Radiation-induced Vascular Injury Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Neurofibromatosis Incidence
WHI Form Report of Cardiovascular Outcome Ver (For items 1-11, each question specifies mark one or mark all that apply.
 WHI Form - Report of Cardiovascular Outcome Ver. 6. COMMENTS To be completed by Physician Adjudicator Date Completed: - - (M/D/Y) Adjudicator Code: OMB# 095-044 Exp: 4/06 -Affix label here- Clinical Center/ID:
WHI Form - Report of Cardiovascular Outcome Ver. 6. COMMENTS To be completed by Physician Adjudicator Date Completed: - - (M/D/Y) Adjudicator Code: OMB# 095-044 Exp: 4/06 -Affix label here- Clinical Center/ID:
HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM
 REVIEW DATE REVIEWER'S ID HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM : DISCHARGE DATE: RECORDS FROM: Hospitalization ER Please check all that may apply: Myocardial Infarction Pages 2, 3,
REVIEW DATE REVIEWER'S ID HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM : DISCHARGE DATE: RECORDS FROM: Hospitalization ER Please check all that may apply: Myocardial Infarction Pages 2, 3,
Uptofate Study Summary
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Uptofate Study Summary Acyanotic Atrial septal defect Ventricular septal defect Patent foramen ovale Patent ductus arteriosus Aortic coartation Pulmonary stenosis Cyanotic Tetralogy
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Uptofate Study Summary Acyanotic Atrial septal defect Ventricular septal defect Patent foramen ovale Patent ductus arteriosus Aortic coartation Pulmonary stenosis Cyanotic Tetralogy
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies
 Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
/ / / / / / Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA. Participant ID: Hospital Code: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
 Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Kang D-H, Kim Y-J, Kim S-H, et al. Early surgery versus conventional
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Kang D-H, Kim Y-J, Kim S-H, et al. Early surgery versus conventional
Update on Acute Aortic Syndrome
 SUNDAY Update on Acute Aortic Syndrome Diana Litmanovich, MD Learning objectives To be familiar with the definition, natural history, and imaging findings of acute aortic syndrome, including: I. Aortic
SUNDAY Update on Acute Aortic Syndrome Diana Litmanovich, MD Learning objectives To be familiar with the definition, natural history, and imaging findings of acute aortic syndrome, including: I. Aortic
Clotted false lumen: reappraisal of indications for
 Thorax, 1981, 36, 194-199 Clotted false lumen: reappraisal of indications for medical management of acute aortic dissection C J SANDERSON, STUART RICH, POLLY A BEERE, C E ANAGNOSTOPOULOS, JAMES M LEVETT,
Thorax, 1981, 36, 194-199 Clotted false lumen: reappraisal of indications for medical management of acute aortic dissection C J SANDERSON, STUART RICH, POLLY A BEERE, C E ANAGNOSTOPOULOS, JAMES M LEVETT,
Other 12-Lead ECG Findings
 Other 12-Lead ECG Findings Left Atrial Enlargement Left atrial enlargement is illustrated by increased P wave duration in lead II, top ECG, and by the prominent negative P terminal force in lead V1, bottom
Other 12-Lead ECG Findings Left Atrial Enlargement Left atrial enlargement is illustrated by increased P wave duration in lead II, top ECG, and by the prominent negative P terminal force in lead V1, bottom
Multimodality Imaging of the Thoracic Aorta
 Multimodality Imaging of the Thoracic Aorta Steven Goldstein MD, FACC Director Noninvasive Cardiology MedStar Heart and Vascular Institute Washington Hospital Center Saturday, October 8, 2016 DISCLOSURE
Multimodality Imaging of the Thoracic Aorta Steven Goldstein MD, FACC Director Noninvasive Cardiology MedStar Heart and Vascular Institute Washington Hospital Center Saturday, October 8, 2016 DISCLOSURE
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial
 An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
ESM 1. Survey questionnaire sent to French GPs. Correct answers are in bold. Part 2: Clinical cases: (Good answer are in bold) Clinical Case 1:
 ESM 1. Survey questionnaire sent to French GPs. Correct answers are in bold. Part 2: Clinical cases: (Good answer are in bold) Clinical Case 1: to your office at 2 pm for a feeling of weakness and numbness
ESM 1. Survey questionnaire sent to French GPs. Correct answers are in bold. Part 2: Clinical cases: (Good answer are in bold) Clinical Case 1: to your office at 2 pm for a feeling of weakness and numbness
Growth Rate of Aortic Diameter in Post Treatment of Aortic Dissection
 Growth Rate of Aortic Diameter in Post Treatment of Aortic Dissection Jitladda Wasinrat MD*, Methininat Lertkowit MD*, Thanongchai Siriapisith MD* * Division of Diagnostic Radiology, Department of Radiology,
Growth Rate of Aortic Diameter in Post Treatment of Aortic Dissection Jitladda Wasinrat MD*, Methininat Lertkowit MD*, Thanongchai Siriapisith MD* * Division of Diagnostic Radiology, Department of Radiology,
B myonephropathic metabolic syndrome MNMS 33 CT DeBakey IIIb MNMS
 13 603 607 2004 B B myonephropathic metabolic syndrome MNMS33 CT DeBakey IIIb MNMS 20 A MNMSMNMS 13 603 607 2004 MNMS B malperfusion myonephropathic metabolic syndrome MNMS MNMS Haimovici 1 3 MNMS B MNMS
13 603 607 2004 B B myonephropathic metabolic syndrome MNMS33 CT DeBakey IIIb MNMS 20 A MNMSMNMS 13 603 607 2004 MNMS B malperfusion myonephropathic metabolic syndrome MNMS MNMS Haimovici 1 3 MNMS B MNMS
Follow-up of Aortic Dissection: How, How Often, Which Consequences Euro Echo 2011
 Follow-up of Aortic Dissection: How, How Often, Which Consequences Euro Echo 2011 Susan E. Wiegers, MD, FASE Director of Clinical Echocardiography Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania Disclosure
Follow-up of Aortic Dissection: How, How Often, Which Consequences Euro Echo 2011 Susan E. Wiegers, MD, FASE Director of Clinical Echocardiography Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania Disclosure
A Case of Acute Type B Aortic Dissection: Limited Role of Laboratory Testing for the Diagnosis of Mesenteric Ischemia
 Case Report A Case of Acute Type B Aortic Dissection: Limited Role of Laboratory Testing for the Diagnosis of Mesenteric Ischemia Koichi Akutsu, MD, 1 Hitoshi Matsuda, MD, 2 Hiroaki Sasaki, MD, 2 Kenji
Case Report A Case of Acute Type B Aortic Dissection: Limited Role of Laboratory Testing for the Diagnosis of Mesenteric Ischemia Koichi Akutsu, MD, 1 Hitoshi Matsuda, MD, 2 Hiroaki Sasaki, MD, 2 Kenji
Disclosures: Acute Aortic Syndrome. A. Michael Borkon, M.D. Director of CV Surgery Mid America Heart Institute Saint Luke s Hospital Kansas City, MO
 Acute Aortic Syndrome Disclosures: A. Michael Borkon, M.D. Director of CV Surgery Mid America Heart Institute Saint Luke s Hospital Kansas City, MO No financial relationships to disclose 1 Acute Aortic
Acute Aortic Syndrome Disclosures: A. Michael Borkon, M.D. Director of CV Surgery Mid America Heart Institute Saint Luke s Hospital Kansas City, MO No financial relationships to disclose 1 Acute Aortic
Introduction. Acta Medica Mediterranea, 2014, 30: 85
 Acta Medica Mediterranea, 2014, 30: 85 ATYPICAL PRESENTATIONS OF AORTIC DISSECTIONS: A CASE SERIES HUSEYIN CEBICCI*, OMER SALT**, SUKRU GURBUZ*, TANER SAHIN*, MUSTAFA OGUZ CUMAOGLU*, SERHAT KOYUNCU* *Kayseri
Acta Medica Mediterranea, 2014, 30: 85 ATYPICAL PRESENTATIONS OF AORTIC DISSECTIONS: A CASE SERIES HUSEYIN CEBICCI*, OMER SALT**, SUKRU GURBUZ*, TANER SAHIN*, MUSTAFA OGUZ CUMAOGLU*, SERHAT KOYUNCU* *Kayseri
Open fenestration for complicated acute aortic B dissection
 Art of Operative Techniques Open fenestration for complicated acute aortic B dissection Santi Trimarchi 1, Sara Segreti 1, Viviana Grassi 1, Chiara Lomazzi 1, Marta Cova 1, Gabriele Piffaretti 2, Vincenzo
Art of Operative Techniques Open fenestration for complicated acute aortic B dissection Santi Trimarchi 1, Sara Segreti 1, Viviana Grassi 1, Chiara Lomazzi 1, Marta Cova 1, Gabriele Piffaretti 2, Vincenzo
Occlusion of All Four Extracranial Vessels With Minimal Clinical Symptomatology. Case Report
 Occlusion of All Four Extracranial Vessels With Minimal Clinical Symptomatology. Case Report BY JIRI J. VITEK, M.D., JAMES H. HALSEY, JR., M.D., AND HOLT A. McDOWELL, M.D. Abstract: Occlusion of All Four
Occlusion of All Four Extracranial Vessels With Minimal Clinical Symptomatology. Case Report BY JIRI J. VITEK, M.D., JAMES H. HALSEY, JR., M.D., AND HOLT A. McDOWELL, M.D. Abstract: Occlusion of All Four
Aortic CT: Intramural Hematoma. Leslie E. Quint, M.D.
 Aortic CT: Intramural Hematoma Leslie E. Quint, M.D. 43 M Mid back pain X several months What type of aortic disease? A. Aneurysm with intraluminal thrombus B. Chronic dissection with thrombosed false
Aortic CT: Intramural Hematoma Leslie E. Quint, M.D. 43 M Mid back pain X several months What type of aortic disease? A. Aneurysm with intraluminal thrombus B. Chronic dissection with thrombosed false
[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]
![[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD] [(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]](/thumbs/89/98619893.jpg) 2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
Acute Aortic Syndromes
 Acute Aortic Syndromes Carole J. Dennie, MD Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Background Non-Traumatic Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Carole Dennie MD FRCPC Associate Professor of Radiology and Cardiology
Acute Aortic Syndromes Carole J. Dennie, MD Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Background Non-Traumatic Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Carole Dennie MD FRCPC Associate Professor of Radiology and Cardiology
Echocardiographic Evaluation of the Aorta
 Echocardiographic Evaluation of the Aorta William F. Armstrong M.D. Director Echocardiography Laboratory Professor of Medicine University of Michigan The Aorta: What to Evaluate Dimensions / shape Atherosclerotic
Echocardiographic Evaluation of the Aorta William F. Armstrong M.D. Director Echocardiography Laboratory Professor of Medicine University of Michigan The Aorta: What to Evaluate Dimensions / shape Atherosclerotic
CT of Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Stuart S. Sagel, M.D.
 CT of Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Stuart S. Sagel, M.D. Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms Atherosclerotic Dissection Penetrating ulcer Mycotic Inflammatory (vasculitis) Traumatic Aortic Imaging Options Catheter
CT of Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Stuart S. Sagel, M.D. Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms Atherosclerotic Dissection Penetrating ulcer Mycotic Inflammatory (vasculitis) Traumatic Aortic Imaging Options Catheter
Animesh Rathore, MD 4/21/17. Penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers of aorta
 Animesh Rathore, MD 4/21/17 Penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers of aorta Disclosures No financial disclosures Thank You Dr. Panneton for giving this lecture for me. I am stuck at Norfolk with an emergency
Animesh Rathore, MD 4/21/17 Penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers of aorta Disclosures No financial disclosures Thank You Dr. Panneton for giving this lecture for me. I am stuck at Norfolk with an emergency
(For items 1-12, each question specifies mark one or mark all that apply.)
 Form 121 - Report of Cardiovascular Outcome Ver. 9.2 COMMENTS -Affix label here- Member ID: - - To be completed by Physician Adjudicator Date Completed: - - (M/D/Y) Adjudicator Code: - Central Case No.:
Form 121 - Report of Cardiovascular Outcome Ver. 9.2 COMMENTS -Affix label here- Member ID: - - To be completed by Physician Adjudicator Date Completed: - - (M/D/Y) Adjudicator Code: - Central Case No.:
 CLINICAL FEATURES THAT SUPPORT ATHEROSCLEROTIC STROKE 1. cerebral cortical impairment (aphasia, neglect, restricted motor involvement, etc.) or brain stem or cerebellar dysfunction 2. lacunar clinical
CLINICAL FEATURES THAT SUPPORT ATHEROSCLEROTIC STROKE 1. cerebral cortical impairment (aphasia, neglect, restricted motor involvement, etc.) or brain stem or cerebellar dysfunction 2. lacunar clinical
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING
 ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
ECG Workshop. Nezar Amir
 ECG Workshop Nezar Amir Myocardial Ischemia ECG Infarct ECG in STEMI is dynamic & evolving Common causes of ST shift Infarct Localisation Left main artery occlusion: o diffuse ST-depression with ST elevation
ECG Workshop Nezar Amir Myocardial Ischemia ECG Infarct ECG in STEMI is dynamic & evolving Common causes of ST shift Infarct Localisation Left main artery occlusion: o diffuse ST-depression with ST elevation
Coronary Arteriovenous Malformation presenting as Acute Myocardial Infarction. Choon Ta NG, Aaron WONG, Foong-Koon CHEAH, Chi Keong CHING
 Coronary Arteriovenous Malformation presenting as Acute Myocardial Infarction Choon Ta NG, Aaron WONG, Foong-Koon CHEAH, Chi Keong CHING The patient 49 year old Male presented with Chest tightness x 1
Coronary Arteriovenous Malformation presenting as Acute Myocardial Infarction Choon Ta NG, Aaron WONG, Foong-Koon CHEAH, Chi Keong CHING The patient 49 year old Male presented with Chest tightness x 1
Case 1 Organ Set 3. Case 1 (for Organ Sets 1 3) 10/2/2015 CARIOVASCULAR II LABORATORY
 MHD I CRIOVSCULR II LORTORY 0/5/5 Case Organ Set Organ Set 2 Organ Set 3 Case (for Organ Sets 3) 72 year old man with a history of diabetes mellitus type 2, HTN, and hyperlipidemia presents with progressive
MHD I CRIOVSCULR II LORTORY 0/5/5 Case Organ Set Organ Set 2 Organ Set 3 Case (for Organ Sets 3) 72 year old man with a history of diabetes mellitus type 2, HTN, and hyperlipidemia presents with progressive
Case Acute ascending thoracic aortic rupture due to penetrating atherosclerotic ulcer
 Case 12305 Acute ascending thoracic aortic rupture due to penetrating atherosclerotic ulcer Lopes Dias J, Costa NV, Leal C, Alves P, Bilhim T Section: Chest Imaging Published: 2014, Dec. 19 Patient: 68
Case 12305 Acute ascending thoracic aortic rupture due to penetrating atherosclerotic ulcer Lopes Dias J, Costa NV, Leal C, Alves P, Bilhim T Section: Chest Imaging Published: 2014, Dec. 19 Patient: 68
Thoracic aortic trauma A.T.O.ABDOOL-CARRIM ACADEMIC HEAD VASCULAR SURGERY DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY UNIVERSITY OF WITWATERSRAND
 Thoracic aortic trauma A.T.O.ABDOOL-CARRIM ACADEMIC HEAD VASCULAR SURGERY DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY UNIVERSITY OF WITWATERSRAND Thoracic Aortic Trauma In USA and CANADA 7500-8000 die of blunt thoracic aortic
Thoracic aortic trauma A.T.O.ABDOOL-CARRIM ACADEMIC HEAD VASCULAR SURGERY DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY UNIVERSITY OF WITWATERSRAND Thoracic Aortic Trauma In USA and CANADA 7500-8000 die of blunt thoracic aortic
Acute dissections of the descending thoracic aorta (Debakey
 Endovascular Treatment of Acute Descending Thoracic Aortic Dissections Nimesh D. Desai, MD, PhD, and Joseph E. Bavaria, MD Acute dissections of the descending thoracic aorta (Debakey type III or Stanford
Endovascular Treatment of Acute Descending Thoracic Aortic Dissections Nimesh D. Desai, MD, PhD, and Joseph E. Bavaria, MD Acute dissections of the descending thoracic aorta (Debakey type III or Stanford
12 Lead ECG Interpretation
 12 Lead ECG Interpretation Julie Zimmerman, MSN, RN, CNS, CCRN Significant increase in mortality for every 15 minutes of delay! N Engl J Med 2007;357:1631-1638 Who should get a 12-lead ECG? Also include
12 Lead ECG Interpretation Julie Zimmerman, MSN, RN, CNS, CCRN Significant increase in mortality for every 15 minutes of delay! N Engl J Med 2007;357:1631-1638 Who should get a 12-lead ECG? Also include
Vascular Emergencies. Scott M Surowiec, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery Upstate Vascular and Crouse Hospital September 29, 2015
 Vascular Emergencies Scott M Surowiec, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery Upstate Vascular and Crouse Hospital September 29, 2015 Introduction Main vascular emergencies include Ruptured Abdominal Aortic
Vascular Emergencies Scott M Surowiec, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery Upstate Vascular and Crouse Hospital September 29, 2015 Introduction Main vascular emergencies include Ruptured Abdominal Aortic
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
11.1 The Aortic Arch General Anatomy of the Ascending Aorta and the Aortic Arch Surgical Anatomy of the Aorta
 456 11 Surgical Anatomy of the Aorta 11.1 The Aortic Arch 11.1.1 General Anatomy of the Ascending Aorta and the Aortic Arch Surgery of the is one of the most challenging areas of cardiac and vascular surgery,
456 11 Surgical Anatomy of the Aorta 11.1 The Aortic Arch 11.1.1 General Anatomy of the Ascending Aorta and the Aortic Arch Surgery of the is one of the most challenging areas of cardiac and vascular surgery,
Chairman and O. Wayne Isom Professor Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery Weill Cornell Medicine
 Leonard N. Girardi, M.D. Chairman and O. Wayne Isom Professor Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery Weill Cornell Medicine New York, New York Houston Aortic Symposium Houston, Texas February 23, 2017 weill.cornell.edu
Leonard N. Girardi, M.D. Chairman and O. Wayne Isom Professor Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery Weill Cornell Medicine New York, New York Houston Aortic Symposium Houston, Texas February 23, 2017 weill.cornell.edu
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTL MTERIL Marie erna, Martin Kocher, Rohit Philip Thomas. cute aorta, overview of acute T findings and endovascular treatment options (doi: 10.5507/bp.2016.060) Fig. 1. : Non-enhanced T, hemopericardium
SUPPLEMENTL MTERIL Marie erna, Martin Kocher, Rohit Philip Thomas. cute aorta, overview of acute T findings and endovascular treatment options (doi: 10.5507/bp.2016.060) Fig. 1. : Non-enhanced T, hemopericardium
Lab CT scan. Murad Kharabsheh Yaman Alali
 Lab CT scan Murad Kharabsheh Yaman Alali Some rules to read The CT Scan : 1. Remember that it s a transverse section across the body and we are looking at the inferior part of the section (not the superior),
Lab CT scan Murad Kharabsheh Yaman Alali Some rules to read The CT Scan : 1. Remember that it s a transverse section across the body and we are looking at the inferior part of the section (not the superior),
How to manage the left subclavian and left vertebral artery during TEVAR
 How to manage the left subclavian and left vertebral artery during TEVAR Jürg Schmidli Chief of Vascular Surgery Inselspital Hamburg 2017 Dept Cardiovascular Surgery, Bern, Switzerland Disclosure No Disclosures
How to manage the left subclavian and left vertebral artery during TEVAR Jürg Schmidli Chief of Vascular Surgery Inselspital Hamburg 2017 Dept Cardiovascular Surgery, Bern, Switzerland Disclosure No Disclosures
EVAR and TEVAR: Extending Their Use for Rupture and Traumatic Injury. Conflict of Interest. Hypotensive shock 5/5/2014. none
 EVAR and TEVAR: Extending Their Use for Rupture and Traumatic Injury Bruce H. Gray, DO MSVM FSCAI Professor of Surgery/Vascular Medicine USC SOM-Greenville Greenville, South Carolina none Conflict of Interest
EVAR and TEVAR: Extending Their Use for Rupture and Traumatic Injury Bruce H. Gray, DO MSVM FSCAI Professor of Surgery/Vascular Medicine USC SOM-Greenville Greenville, South Carolina none Conflict of Interest
CT Imaging of Blunt and Penetrating Vascular Trauma DENNIS FOLEY MEDICAL COLLEGE WISCONSIN
 CT Imaging of Blunt and Penetrating Vascular Trauma DENNIS FOLEY MEDICAL COLLEGE WISCONSIN THORACO ABDOMINAL TRAUMA 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 5 cc/sec 30 secs 1.25 mm/ 55 mm Z1.375 2.5 mm/ 55 mm Z 1.375 Grade
CT Imaging of Blunt and Penetrating Vascular Trauma DENNIS FOLEY MEDICAL COLLEGE WISCONSIN THORACO ABDOMINAL TRAUMA 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 5 cc/sec 30 secs 1.25 mm/ 55 mm Z1.375 2.5 mm/ 55 mm Z 1.375 Grade
Haemodynamically unstable patient with chest trauma
 HR J Clinical Case - Test Yourself Interventional Haemodynamically unstable patient with chest trauma Dimitrios Tomais, Theodoros Kratimenos, Dimosthenis Farsaris Interventional Radiology Unit, Radiology
HR J Clinical Case - Test Yourself Interventional Haemodynamically unstable patient with chest trauma Dimitrios Tomais, Theodoros Kratimenos, Dimosthenis Farsaris Interventional Radiology Unit, Radiology
cardiac imaging planes planning basic cardiac & aortic views for MR
 cardiac imaging planes planning basic cardiac & aortic views for MR Dianna M. E. Bardo, M. D. Assistant Professor of Radiology & Cardiovascular Medicine Director of Cardiac Imaging cardiac imaging planes
cardiac imaging planes planning basic cardiac & aortic views for MR Dianna M. E. Bardo, M. D. Assistant Professor of Radiology & Cardiovascular Medicine Director of Cardiac Imaging cardiac imaging planes
Case Report 1. CTA head. (c) Tele3D Advantage, LLC
 Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Unusual Causes of Aortic Regurgitation. Case 1
 Unusual Causes of Aortic Regurgitation Judy Hung, MD Cardiology Division Massachusetts General Hospital Boston, MA No Disclosures Case 1 54 year old female with h/o cerebral aneurysm and vascular malformation
Unusual Causes of Aortic Regurgitation Judy Hung, MD Cardiology Division Massachusetts General Hospital Boston, MA No Disclosures Case 1 54 year old female with h/o cerebral aneurysm and vascular malformation
Coral Reef Aorta- Treatment Options?
 Chronic mesenteric ischemia (CMI) Coral Reef Aorta- Treatment Options? Bala Ramanan Vascular Fellow, UCSF CMI is a life-threatening problem that can result in death from inanition or bowel infarction Incidence
Chronic mesenteric ischemia (CMI) Coral Reef Aorta- Treatment Options? Bala Ramanan Vascular Fellow, UCSF CMI is a life-threatening problem that can result in death from inanition or bowel infarction Incidence
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition
 Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
C1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Cardiovascular Disorders
 C1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Cardiovascular Disorders GENERAL ISSUES REGARDING MEDICAL FITNESS-FOR-DUTY 1. These medical standards apply to Union Pacific Railroad (UPRR) employees
C1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Cardiovascular Disorders GENERAL ISSUES REGARDING MEDICAL FITNESS-FOR-DUTY 1. These medical standards apply to Union Pacific Railroad (UPRR) employees
2. The heart sounds are produced by a summed series of mechanical events, as follows:
 Heart Sounds. Phonocardiography 1 Objectives 1. Phonocardiography - Definition 2. What produces the heart sounds 3. Where to listen for the heart sounds 4. How to record a phonocardiogram 5. Normal heart
Heart Sounds. Phonocardiography 1 Objectives 1. Phonocardiography - Definition 2. What produces the heart sounds 3. Where to listen for the heart sounds 4. How to record a phonocardiogram 5. Normal heart
Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right ventricular sinusoids
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 1990 Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 1990 Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right
An Approach to the Patient with Syncope. Guy Amit MD, MPH Soroka University Medical Center Beer-Sheva
 An Approach to the Patient with Syncope Guy Amit MD, MPH Soroka University Medical Center Beer-Sheva Case presentation A 23 y.o. man presented with 2 episodes of syncope One during exercise,one at rest
An Approach to the Patient with Syncope Guy Amit MD, MPH Soroka University Medical Center Beer-Sheva Case presentation A 23 y.o. man presented with 2 episodes of syncope One during exercise,one at rest
Pseudo Heart Disease: 1/5 Norman Bethune Faculty of Medicine, Jilin University, China
 http://www.medicine-on-line.com Pseudo Heart Disease: 1/5 Case 060: Pseudo Heart Disease Author: Affiliation: Zhang Shu Norman Bethune Faculty of Medicine, Jilin University, China A 17 year-old girl presented
http://www.medicine-on-line.com Pseudo Heart Disease: 1/5 Case 060: Pseudo Heart Disease Author: Affiliation: Zhang Shu Norman Bethune Faculty of Medicine, Jilin University, China A 17 year-old girl presented
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW
 PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
The Electrocardiogram part II. Dr. Adelina Vlad, MD PhD
 The Electrocardiogram part II Dr. Adelina Vlad, MD PhD Basic Interpretation of the ECG 1) Evaluate calibration 2) Calculate rate 3) Determine rhythm 4) Determine QRS axis 5) Measure intervals 6) Analyze
The Electrocardiogram part II Dr. Adelina Vlad, MD PhD Basic Interpretation of the ECG 1) Evaluate calibration 2) Calculate rate 3) Determine rhythm 4) Determine QRS axis 5) Measure intervals 6) Analyze
Acute stroke. Ischaemic stroke. Characteristics. Temporal classification. Clinical features. Interpretation of Emergency Head CT
 Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
Early outcomes of acute retrograde dissection in the aortic arch and the ascending aorta data from IRAD
 Early outcomes of acute retrograde dissection in the aortic arch and the ascending aorta data from IRAD Foeke JH Nauta, MD, PhD Resident Cardiothoracic Surgery, Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam Disclosure
Early outcomes of acute retrograde dissection in the aortic arch and the ascending aorta data from IRAD Foeke JH Nauta, MD, PhD Resident Cardiothoracic Surgery, Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam Disclosure
(i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at
 1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
TEVAR FOR! THORACIC AORTIC TRAUMA"
 10th HKL Vascular Surgery Conference and Workshop" TEVAR FOR! THORACIC AORTIC TRAUMA" Dr Hanif Hussein" Vascular and General Surgeon" Department of Surgery" Hospital Kuala Lumpur" Source: MIROS! Thoracic
10th HKL Vascular Surgery Conference and Workshop" TEVAR FOR! THORACIC AORTIC TRAUMA" Dr Hanif Hussein" Vascular and General Surgeon" Department of Surgery" Hospital Kuala Lumpur" Source: MIROS! Thoracic
Neurological Complications of TEVAR. Frank J Criado, MD. Union Memorial-MedStar Health Baltimore, MD USA
 ISES Online Neurological Complications of Frank J Criado, MD TEVAR Union Memorial-MedStar Health Baltimore, MD USA frank.criado@medstar.net Paraplegia Incidence is 0-4% after surgical Rx of TAAs confined
ISES Online Neurological Complications of Frank J Criado, MD TEVAR Union Memorial-MedStar Health Baltimore, MD USA frank.criado@medstar.net Paraplegia Incidence is 0-4% after surgical Rx of TAAs confined
Stroke/TIA. Tom Bedwell
 Stroke/TIA Tom Bedwell tab1g11@soton.ac.uk The Plan Definitions Anatomy Recap Aetiology Pathology Syndromes Brocas / Wernickes Investigations Management Prevention & Prognosis TIAs Key Definitions Transient
Stroke/TIA Tom Bedwell tab1g11@soton.ac.uk The Plan Definitions Anatomy Recap Aetiology Pathology Syndromes Brocas / Wernickes Investigations Management Prevention & Prognosis TIAs Key Definitions Transient
Case 47 Clinical Presentation
 93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Intractable Vomiting: A Dissection in Disguise
 Intractable Vomiting: A Dissection in Disguise Jordan Hunter, OMSIII Scott Kirby, D.O. Charles Finch, D.O., FACOEP Jhunter85@midwestern.edu; skirby76@yahoo.com; cfinch@midwestern.edu Abstract Aortic dissection
Intractable Vomiting: A Dissection in Disguise Jordan Hunter, OMSIII Scott Kirby, D.O. Charles Finch, D.O., FACOEP Jhunter85@midwestern.edu; skirby76@yahoo.com; cfinch@midwestern.edu Abstract Aortic dissection
Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD
 Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Causes of Cardiac Arrythmias Abnormal rhythmicity of the pacemaker Shift of pacemaker from sinus node Blocks at different
Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Causes of Cardiac Arrythmias Abnormal rhythmicity of the pacemaker Shift of pacemaker from sinus node Blocks at different
HISTORY. Question: How do you interpret the patient s history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: 45-year-old man.
 HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
THE FRAMINGHAM STUDY Protocol for data set vr_soe_2009_m_0522 CRITERIA FOR EVENTS. 1. Cardiovascular Disease
 THE FRAMINGHAM STUDY Protocol for data set vr_soe_2009_m_0522 CRITERIA FOR EVENTS 1. Cardiovascular Disease Cardiovascular disease is considered to have developed if there was a definite manifestation
THE FRAMINGHAM STUDY Protocol for data set vr_soe_2009_m_0522 CRITERIA FOR EVENTS 1. Cardiovascular Disease Cardiovascular disease is considered to have developed if there was a definite manifestation
Tortuosity of the Descending Thoracic Aorta Simulating Dissection on Transesophageal Echocardiography
 CASE REPORTS Tortuosity of the Descending Thoracic Aorta Simulating Dissection on Transesophageal Echocardiography Edward S. Katz, MD, Robert M. Applebaum, MD, James P. Earls, MD, Glenn Krinsky, MD, Jeffrey
CASE REPORTS Tortuosity of the Descending Thoracic Aorta Simulating Dissection on Transesophageal Echocardiography Edward S. Katz, MD, Robert M. Applebaum, MD, James P. Earls, MD, Glenn Krinsky, MD, Jeffrey
THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES
 1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
A walk through a STEMI
 A walk through a STEMI M.M. s Story Kim Robison Ashley Corcoran Situation M.M. is an 82 year old male brought in by private vehicle on 10/22/17 to the Emergency Department Pt. c/o left arm numbness, pain
A walk through a STEMI M.M. s Story Kim Robison Ashley Corcoran Situation M.M. is an 82 year old male brought in by private vehicle on 10/22/17 to the Emergency Department Pt. c/o left arm numbness, pain
CT angiography in type I acute aortic dissection complicated with malperfusion - a visual review of obstruciton patterns
 CT angiography in type I acute aortic dissection complicated with malperfusion - a visual review of obstruciton patterns Eneva M. St. Ekaterna University Hospital Report objectives 1. Review malperfusion
CT angiography in type I acute aortic dissection complicated with malperfusion - a visual review of obstruciton patterns Eneva M. St. Ekaterna University Hospital Report objectives 1. Review malperfusion
Asymptomatic Radiology / Clinical data Report / Cohort bias Referral bias. UCSF Vascular Symposium April 7-9, Acute Aortic Dissection
 Aortic Dissection: Natural History What is the Natural History of Aortic Dissection? UCSF Vascular Symposium April 7-9, 2011 Asymptomatic Radiology / Clinical data Report / Cohort bias Referral bias Stephen
Aortic Dissection: Natural History What is the Natural History of Aortic Dissection? UCSF Vascular Symposium April 7-9, 2011 Asymptomatic Radiology / Clinical data Report / Cohort bias Referral bias Stephen
The Fundamentals of 12 Lead EKG. ECG Recording. J Point. Reviewing the Cardiac Conductive System. Dr. E. Joe Sasin, MD Rusty Powers, NRP
 The Fundamentals of 12 Lead EKG Dr. E. Joe Sasin, MD Rusty Powers, NRP SA Node Intranodal Pathways AV Junction AV Fibers Bundle of His Septum Bundle Branches Purkinje System Reviewing the Cardiac Conductive
The Fundamentals of 12 Lead EKG Dr. E. Joe Sasin, MD Rusty Powers, NRP SA Node Intranodal Pathways AV Junction AV Fibers Bundle of His Septum Bundle Branches Purkinje System Reviewing the Cardiac Conductive
Cardiac Emergencies. Jim Bennett Paramedic and Clinical Education Coordinator American Medical Response Spokane, Washington
 Cardiac Emergencies Jim Bennett Paramedic and Clinical Education Coordinator American Medical Response Spokane, Washington The Heart -------Aorta Pulmonary Veins---- Superior Vena Cava------ Right Atrium-----
Cardiac Emergencies Jim Bennett Paramedic and Clinical Education Coordinator American Medical Response Spokane, Washington The Heart -------Aorta Pulmonary Veins---- Superior Vena Cava------ Right Atrium-----
Dissection of descending aorta treated by stent-graft implantation in a patient with Marfan syndrome
 Case Report 1 Dissection of descending aorta treated by stent-graft implantation in a patient with Marfan syndrome Marat. ripov, Ildar Z. bdyldaev, Semen D. Chevgun, ektur S. Daniyarov, Dinara. Toktosunova,
Case Report 1 Dissection of descending aorta treated by stent-graft implantation in a patient with Marfan syndrome Marat. ripov, Ildar Z. bdyldaev, Semen D. Chevgun, ektur S. Daniyarov, Dinara. Toktosunova,
Devendra V. Kulkarni, Rahul G. Hegde, Ankit Balani, and Anagha R. Joshi. 2. Case Report. 1. Introduction
 Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 614647, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/614647 Case Report A Rare Case of Pulmonary Atresia with Ventricular Septal Defect with a Right Sided Aortic Arch and
Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 614647, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/614647 Case Report A Rare Case of Pulmonary Atresia with Ventricular Septal Defect with a Right Sided Aortic Arch and
Multimodality Imaging of Anomalous Left Coronary Artery from the Pulmonary
 1 IMAGES IN CARDIOVASCULAR ULTRASOUND 2 3 4 Multimodality Imaging of Anomalous Left Coronary Artery from the Pulmonary Artery 5 6 7 Byung Gyu Kim, MD 1, Sung Woo Cho, MD 1, Dae Hyun Hwang, MD 2 and Jong
1 IMAGES IN CARDIOVASCULAR ULTRASOUND 2 3 4 Multimodality Imaging of Anomalous Left Coronary Artery from the Pulmonary Artery 5 6 7 Byung Gyu Kim, MD 1, Sung Woo Cho, MD 1, Dae Hyun Hwang, MD 2 and Jong
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
A Case Of Marfan Syndrome With Ascending And Arch Of Aorta Aneurysm Presenting With Type A- Dissection Of Aorta.
 A Case Of Marfan Syndrome With Ascending And Arch Of Aorta Aneurysm Presenting With Type A- Dissection Of Aorta. Dr E Srikanth, Dr Ravi Srinivas MD.DM, Dr O Adikesava Naidu MD.DM, FACC,FESC. Dr Y V Subba
A Case Of Marfan Syndrome With Ascending And Arch Of Aorta Aneurysm Presenting With Type A- Dissection Of Aorta. Dr E Srikanth, Dr Ravi Srinivas MD.DM, Dr O Adikesava Naidu MD.DM, FACC,FESC. Dr Y V Subba
Total Endovascular Repair Type A Dissection. Eric Herget Interventional Radiology
 Total Endovascular Repair Type A Dissection Eric Herget Interventional Radiology 65 year old male Acute Type A Dissection Severe Aortic Regurgitation No co-morbidities Management? Part II Evolving Global
Total Endovascular Repair Type A Dissection Eric Herget Interventional Radiology 65 year old male Acute Type A Dissection Severe Aortic Regurgitation No co-morbidities Management? Part II Evolving Global
Endovascular therapy for Ischemic versus Nonischemic complicated acute type B aortic dissection (catbad).
 Endovascular therapy for Ischemic versus Nonischemic complicated acute type B aortic dissection (catbad). AS. Eleshra, MD 1, T. Kölbel, MD, PhD 1, F. Rohlffs, MD 1, N. Tsilimparis, MD, PhD 1,2 Ahmed Eleshra
Endovascular therapy for Ischemic versus Nonischemic complicated acute type B aortic dissection (catbad). AS. Eleshra, MD 1, T. Kölbel, MD, PhD 1, F. Rohlffs, MD 1, N. Tsilimparis, MD, PhD 1,2 Ahmed Eleshra
Undergraduate Teaching
 Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
Endovascular Management of Thoracic Aortic Pathology Stéphan Haulon, J Sobocinski, B Maurel, T Martin-Gonzalez, R Spear, A Hertault, R Azzaoui
 Endovascular Management of Thoracic Aortic Pathology Stéphan Haulon, J Sobocinski, B Maurel, T Martin-Gonzalez, R Spear, A Hertault, R Azzaoui Aortic Center, Lille University Hospital, France Disclosures
Endovascular Management of Thoracic Aortic Pathology Stéphan Haulon, J Sobocinski, B Maurel, T Martin-Gonzalez, R Spear, A Hertault, R Azzaoui Aortic Center, Lille University Hospital, France Disclosures
HISTORY. Question: What type of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance.
 HISTORY 15-year-old male. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance. PRESENT ILLNESS: A heart murmur was noted in childhood, but subsequent medical care was sporadic. Easy fatigability and slight
HISTORY 15-year-old male. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance. PRESENT ILLNESS: A heart murmur was noted in childhood, but subsequent medical care was sporadic. Easy fatigability and slight
Debate in Management of native COA; Balloon Versus Surgery
 Debate in Management of native COA; Balloon Versus Surgery Dr. Amira Esmat, El Tantawy, MD Professor of Pediatrics Consultant Pediatric Cardiac Interventionist Faculty of Medicine Cairo University 23/2/2017
Debate in Management of native COA; Balloon Versus Surgery Dr. Amira Esmat, El Tantawy, MD Professor of Pediatrics Consultant Pediatric Cardiac Interventionist Faculty of Medicine Cairo University 23/2/2017
Experience of endovascular procedures on abdominal and thoracic aorta in CA region
 Experience of endovascular procedures on abdominal and thoracic aorta in CA region May 14-15, 2015, Dubai Dr. Viktor Zemlyanskiy National Research Center of Emergency Care Astana, Kazakhstan Region Characteristics
Experience of endovascular procedures on abdominal and thoracic aorta in CA region May 14-15, 2015, Dubai Dr. Viktor Zemlyanskiy National Research Center of Emergency Care Astana, Kazakhstan Region Characteristics
Aggressive Resection/Reconstruction of the Aortic Arch in Type A Dissection: Con
 Aggressive Resection/Reconstruction of the Aortic Arch in Type A Dissection: Con Thomas G. Gleason, M.D. Ronald V. Pellegrini Professor and Chief Division of Cardiac Surgery University of Pittsburgh Presenter
Aggressive Resection/Reconstruction of the Aortic Arch in Type A Dissection: Con Thomas G. Gleason, M.D. Ronald V. Pellegrini Professor and Chief Division of Cardiac Surgery University of Pittsburgh Presenter
