Study of Extrarenalmanifestions and Clinico-Radiological Correlation in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
|
|
|
- Amos Morrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: , p-issn: Volume 14, Issue 5 Ver. IV (May. 2015), PP Study of Extrarenalmanifestions and Clinico-Radiological Correlation in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease 1 Ramesh Chandra.V, 2 Prasad Gullipalli Assistant professor, Department of Nephrology, Andhra medical College, Visakhapatnam Associate Professor, Department of Nephrology, Andhra medical College, Visakhapatnam Abstract: Objectives:The objective of this study is to know the prevalence of renal and extra renal manifestations of 50 cases of ADPKD attending King George Hospital, Visakhapatnam, AP between August 2008 and May Results: Male to Female ratio is 1.08;1, mean age of patients is 42.1 years(+/-1.4yr). They were diagnosed as having ADPKD during evaluation of pain abdomen / loin pain in 30% of cases, by family screening in 14% of cases, hematuria in 4% of cases, during the evaluation of hypertension in 4% of cases, during evaluation of fever in 12% of cases, vomiting in 6% of cases. At the time of diagnosis of ADPKD, 58% of patients had hypertension,and palpable kidneys in 64% of patients. Mean hemoglobin at diagnosis was 9.59+/-1.39 gm/dl, mean proteinuria was 0.56+/-0.34 gm/day, and mean creatinine was 3.05+/-2.61 mg/dl. These patients had liver cysts in 28% of cases, intracranial aneurysm in 4%, diverticulosis in 6%, splenic cysts in 4%, renal calculi in 16%, cyst infection in 16%, cyst hemorrhage in 8%, cyst malignancy in 2%, pancreatic cysts in 6%, ovarian cysts in 16%, MVP in 6%. These patients had a family history in 56% of cases and family history of cerebrovascular accident in10 % of cases. Keywords:ADPKD, extra renal, liver cysts, aneurysms, cyst hemorrhage. I. Aims And Objectives The present study isconducted to evaluate the prevalence of renal and extrarenal manifestations andto correlate the ultrasonographic findings with clinical features in patients with ADPKD. II. Materials And Methods The present study was conducted in the Department of Nephrology, Andhra Medical College, King George Hospital, Visakhapatnam, South India between February 2011 and march Fifty subjects with ultrasonographically diagnosed ADPKD seen in outpatient department or admitted in the department of Nephrology are included in the study, after taking full informed consent.ultrasonographic diagnostic criteria used are those proposed by Ravine et al Ultrasonographic examination is carried out by a single examiner using Mhz probe.detailed history and physical examination are carried out and recorded in theproforma. During history and from previous medical records a note will be made of all the episodes of renal pain, hematuria, all episodes of upper or lower urinary tract enfections with positive cultures, episodes of renal calculi indicated by either passage of stone, presence of stone on plain kidney, ureter, bladder film or ultrasound, the patient s age when ADPKD was first diagnosed, history of cardiac symptoms or gastrointestinal symptoms, family history of ADPKD or cerebrovascular accidents was recorded. During physical examination presence of any abdominal masses, abdominal hernias and arterial blood pressure is recorded. Any adult patient is considered to be hypertensive if the untreated blood pressure is > 140/90 mm of Hg or if he or she has been previously diagnosed and treated for hypertension. Chronic renal failure was defined as estimated creatinine clearance of < 90 ml / min ( bycockroft and Gault formula ). End stage renal disease is defined as creatinine clearance < 10 ml/min as estimated by Cockroft and Gault formula ( NKF, 2002 ). 10 ml blood is drawn for biochemical tests which are carried out in renal lab, KGH,Visakhapatnam. Biochemical tests include measurement of blood urea, serum creatinine, calcium. Urine examination includes 24 hr urine protein, microscopic examination of urine. Serum creatinine along with age and weight of the patient was used to estimate glomerular filtration rate by using Cockroft and Gault formula. Colonoscopy was performed in those patients who had complaints of bloody diarrhea or haemotochezia associated with fever and pain abdomen. The procedure was done after the acute episode has subsided. 2D ECHO was performed in all subjects to look for valvular lesions, left ventricular hypertrophy, chamber enlargement, left ventricular ejection fraction and wall motion abnormalities. Magnetic Resonance Angiography of brain was done in selected subjects who gave history of cerebrovascular accident either for DOI: / Page
2 himself or in the family. A non contrast CT scan of the abdomen was done in subjects in whom cyst infection, haemorrhage or malignancy either on clinical examination or ultrasound abdomen were seen III. Results Fifty patients of ADPKD were included in the study. 52% of these were males and 48% were females. Mean age of subjects was years and mean age at diagnosis of ADPKD was 40.5 years. Minimum age of the patient when the diagnosis of ADPKD was made was 18yrs and maximum age was 64 yrs. Maximum number of patients were in the age group of yrs. Family history of ADPKD was positive in 56 % of all the subjects and family history of CVA was positive in 10% of subjects. Overall prevalence of hypertension was 58 % among these ADPKD patients. Among males, hypertension was seen in 65.3 % (17/26) and among females in 50% (12/24). Overall prevalence of chronic renal failure among these ADPKD patients was 94%(47/50). Among females prevalence was 96.1% and among males prevalence was 100%. The number of patients in different stages of CKD are- CKD 1 3 subjects, CKD2 12 subjects, CKD 3 13 subjects, CKD 4 6 subjects, CKD 5 16 subjects.twenty percent of patients are in ESRD at presentation and started on maintenance hemodialysis. Mean age of ESRD is 41.7 yrs. Minimum age of ESRD patient was 20 yrs and maximum age was 55yrs. Most common presentation was with hypertension observed in 58 % of patients. Overall, 64 % of patients had palpable kidneys at presentation. Out of 50 patients, 7 cases were detected during family screening and others during evaluation of pain abdomen, mass per abdomen, hypertension, febrile illness or breathlessness. Loin pain was the presenting symptom in 30 % of cases. Thirty percent of patients had azotemic symptoms at presentation(table1). Urinary tract infection was observed in 32 % (16/50) of cases, 10 being male and 6 being female. Haematuria was observed in 12 % (6/50) of cases. Renal calculi were observed in 18 % (9/50) of patients where 10 % of females and 8% of males had evidence of renal stones. Cyst infection was seen in 16% (8/50 ) and cyst malignancy in 2% ( 1/50 ) of this ADPKD population. Cyst haemorrhage was observed in 8% ( 4/50 ) of cases ( table 2 ). Out of the extrarenal manifestations, liver cysts were seen in 28 % ( 14/50 ) of cases. Liver cysts were more common in females (16 %) as compared to males (12 %) ( table 3 ) Pancreatic cysts were observed in 6 % ( 3/50 ) and splenic cysts in 4% ( 2/50 ) of this population. Five patients gave history of cerebrovascular accident in the family and another 7 patients gave a history of severe headache and vomitings. Magnetic Resonance angiography performed in these 12 patients revealed small intracranial aneurysms in the anterior circulation in 2 patients. Although not associated with ADPKD, ovarian cysts were an incidental finding in 16 % of patients. Mitral valve prolapse was detected in 6 % ( 3/50 ) of cases during routine 2D ECHO. Colonoscopy performed for various lower gastrointestinal symptoms revealed colonic diverticulosis in 6 % ( 3/50 ) of patients. Mean hemoglobin was /-1.39 gm/dl and mean serum creatinine was / mg/dl ( Fig 14 ). Sixty four percent of patients had proteinuria out of which 16 % had> 1 gm/day. Mean proteinuria was / gm/dl ( Fig 1). Correlations Kidney size was correlated with various clinical parameters. Depending on kidney size, all the subjects were divided into 6 quartiles.quartile cm, Quartile 2- >13 15 cm, Quartile 3- >15 17 cm, Quartile 4- >17 19 cm, Quartile 5- >19 21 cm, Quartile 6- >21cm. As the size of the kidneys increased, the serum creatinine also increased, which was significant ( p = ) (Fig 2 ). DOI: / Page
3 The larger the kidneys, the higher was the proteinuria which was significant( p = ). Fig 3 showing significant correlation between kidney size and proteinuria ( p = ) Chi square test showed significant corrlation between kidney size and hypertension ( p = ).( Fig 4 ) Fig 4 Chi square test showing significant correlation between kidney size and hypertension ( p = ) DOI: / Page
4 Fig 5 Kruskal Wallis test showing significant correlation between kidney size and proteinuria Chi square test also showed significant correlation between kidney size and requirement of dialysis ( p = ) ( Fig 10 ) Fig 6:chi Square Test Showing Correlation Betweenkidney Size And Requirement Of Dialysis ( P = ) However, there was no correlation between kidney size and serum albumin. Also, kidney size does not correlate with hemoglobin. Fig 7 Box and Whisker Plot showing no correlation between kidney size and serum albumin ( p = 0.75 ) DOI: / Page
5 Fig 8 Box and Whisker plot showing no correlation between kidney size and hemoglobin ( p = ) Fig 9 Histogram showing mean haemoglobin ( 9.59+/ gm/dl ) Fig 10 - Histogram showing mean serum creatinine at presentation DOI: / Page
6 IV. Discussion ADPKD is a common genetic disorder, most common and serious sequalae of this disease is ESRD. The various renal and extrarenal manifestations of the disease have been extensively studied. Present study has analysed the clinical profile of fifty ADPKD patients and tried to establish correlation of various clinical parameters with radiologically estimated pole to pole kidney size. In the present study, male to female ratio was 1;1, in previous studies it was 1;2. Mean age of diagnosis in this study was slightly higher (40.5 % ) than previous studies (35.1 % ). Hypertension was prevalent in 58 % of this cohort of ADPKD patients, slightly less compared to previous studies which had a prevalence of 63 to 80 %. In this study, the prevalence of hypertension was 33 % in patients with CKD stage 1, 65 % in CKD stage 3, and 66 % in CKD 4. In this study, the most common mode of diagnosis was during evaluation of abdominal pain / loin pain. Most common clinical feature was hypertension. Most common renal complication was urinary tract infection ( 32 % ), which correlated with previous studies, In this study urinary tract infection was more common in males in contrast to previous study which showed UTI to be more common in females. Haematuria, gross and microscopic have been described to be present in 50 % of patients, it is the presenting symptom in 35 % of ADPKD patients. In the present study, gross haematuria was seen in 12 % and microscopic hematuria in 6 % of patients. Gross hematuria was equally common in males and females, whereas, microscopic hematuria more common in females. Risk factors earlier described for gross hematuria are hypertension and increased renal size. Nephrolithiasis was described in 20 % of patients with ADPKD. In the present study, prevalence of nephrolihiasis was 18 % and more common in males. Proteinuria has been observed in one third of ADPKD patients, and is almost always mild. In this population, proteinuria was found to be more prevalent ( 64 % ), and only 16 % of these had proteinuria of > 1gm / day. Proteinuria was greater in males and in those with larger kidneys. Cyst malignancy was detected by CT abdomen in one patient, who later on succumbed to severe renal failure.among extrarenal manifestations of the disease, liver is the most common organ to be affected by cysts. Approximately 50 % of patients without azotemia have hepatic cysts and prevalence increase with age. Prevalence of hepatic cysts in the present study was 28 %, slightly less than previous studies. In the present study, liver cysts were more common in females ( 16 % ), and in patients with ESRD. All patients with liver cysts had no symptoms of liver disease and tests for liver function were normal. Pancreatic and splenic cysts were seen in 16.7 % and 6.7 % respectively in previous studies. In the present study, the corresponding values were 6 % and 4 %. Family history of cerebrovasular accident was seen in 10 % patients. MR angiography of brain revealed intracranial aneurysms in 4 % of cases which correlates with previous studies. In a Brazilian study, intracranial aneurysms were seen in 3 out of 92 ADPKD patients. Previous studies showed colonic diverticula in 3.3 % of cases. In the present study colonic diverticula were seen in 6 % of patients. Routine 2 D ECHO in all the fifty ADPKD patients revealed Mitral Valve Prolapse in 6 % of cases. One case was associated with mild Mitral insufficiency, the same patient had congestive heart failure but not due to valvular lesion. Earlier studies have described that 45 % of patients of ADPKD will reach ESRD by the age of 60 yr 7, 92. However considerable variability in the age of ESRD have been described which may occur from first year of life, to over age 80. Renal disease has been shown to have less aggressive course in females than males 7,17 and hypertension is a major factor associated with more aggressive course of renal disease 7. Other factors described to be independently related to earlier onset of renal insufficiency in both sexes are presence of gross and microscopic hematuria and occurrence of more severe proteinuria 7. Prevalence of chronic renal failure in the present study was 94 % and 21 % of these patients had ESRD. The prevalence of renal insufficiency was more in males. Kidney Size And Progression Of Renal Disease :Renal enlargement is a hallmark of ADPKD. Evidence indicates that progressive increase in renal size in ADPKD is primarily due to accumulation of fluid within cysts leading to increase in cyst size. Increase in cyst volume is responsible for ultimate decline in glomerular filtration rate, that is the feature of ADPKD. The average age of diagnosis of ADPKD is 27 yrs and hypertension is 31yrs, before loss of renal functon. Once renal dysfunction occurs, a universal rapid decline in renal function (approx 5.9 ml/min/yr) occurs. Food and Drug Administration acceptable outcome measures of progressive renal disease include frequency or time to ESRD, doubling of serum creatinine, or death. All of these outcome measures are ineffective with little or no role in ADPKD due to long presymptomatic phase and late age of onset of renal dysfunction in this disorder. Currently changes in serum creatinine are monitored to determine the extent of disease progression and to assess prognosis. However, serum creatinine donot typically rise in patients with ADPKD until 4 th to 5 th decade of life, when massive enlargement has occurred. Franz and Reubi developed a model of curvilinear relationship between kidney size and function, indicating that significant renal enlargement DOI: / Page
7 takes place before loss of kidney function in ADPKD. Kidney function does not decline in individuals with ADPKD until kidney size is atleast 5 times normal. In the present study, cheap and widely available investigation ultrasonography was used to measure pole to pole length of the kidney. Because of the high interobserver variability in measurement of kidney size, a single observer performed all the scans. Larger kidneys correlated with higher proteinuria, hypertension and higher creatinine. This study could not do any correlation between kidney size and serum albumin and hemoglobin. V. Conclusions ESRD is the most serious complication of ADPKD. recent data suggests, the most objective test to assess disease progression is estimation of kidney size. Although MRI Iis the best method to assess the renal volume accurately but it is expensive and time consuming. Ultrasonography is the viable option for MRI. Due it s non invasiveness it can be repeated any number of times to monitor the size of kidneys and other extrarenal manifestations and complications hence it is used.increased renal size predicts more proteinuria, loss of renal function, hypertension, and progression to ESRD. So, it is reasonable to justify kidney size as a marker of disease severity. Ability to monitor the disease progression accurately will improve the ability to demonstrate efficacy of potential therapies and will also allow to target treatment at those patients who are most at risk. And once effective therapies for ADPKD are developed, these are likely to be effective early in the course of disease and then screening patients at risk of ADPKD may become more prudent Bibliography [1]. Iglesias C G, Torres VE etal, Epidemiology of Adult Polycystic Kidney Disease, Minnesota, AJKD, 1983, 2, [2]. Renal Data System, USRDS, Annual Data Report, 1999, Bethesda, National Institute of Health, [3]. Hugher J, Ward CJ, Peral B etal, The PKD 1 gene encodes a novel protein with multiple cell recognition domains, Nature Genet, ; , [4]. International Polycystic Kidney Disease Consortium ; Polycystic Kidney Disease ; the complete structure of the PKD 1 gene and its protein, Cell, 1995 ; , [5]. Pei Y, Paterson AD, Wang KR et al ; Bilineal disease abd trans-heterozygotes in ADPKD; Am J Hum Genet, 2001; 68 ; [6]. Hateboer N, vdijk MA, Bogdanova N et al ; Comparision of phenotype of PKD types 1 and 2,Lancet, 1999, 353 ; , [7]. Rossetti S, Burton S, et al, JASN 2002, 13, [8]. Geberth S, etal, JASN, 1995; 6 ; , [9]. Zeir M et al : NDT, 1995; 10 ; [10]. Watrick TJ et al ; Cell, 1996 ; 87 ; , [11]. Hugher J, Ward CJ, Peral B etal, The PKD 1 gene encodes a novel protein with multiple cell recognition domains, Nature Genet, ; , [12]. Hayashi TM, Reynolds T, Wu DM et al;charetarization of exon structure of the PKD 2 gene ; Genomics 1997 ; [13]. Yamaguchi T, Wallace DP, et al ; Calcium restriction allows c AMP activation of the B Ref / ERK pathway, J Biochem, 2004; 279; , [14]. Ravine D, Gibson RN, Walker RG,etal ; Evaluation of ultrasonographic dignstic criteria for AKPKD 1, Lancet 1994; 343; ; [15]. Nicolan C, Tossa K, Balenas C, et al ; ADPKD 1and 2; assesment of US sensitivity for diagnosis; Radiology 1999; 213 ; [16]. Grantham JJ, Torres VE, Chapman AB et al, Volume progression in Polycystic Kidney Disease, NEJM 2006 ; 354 ; [17]. Torres VE, ; Water for ADPKD? Probably, Yes,; JASN, 2006 ; 17 ; [18]. Duncan KA, Cuppage FE, Grantham JJ ; Urinary lipid bodies in Polycystic Kidney Disease ; AJKD, 1985;5;49 53, [19]. Schrier RW, Kellcher CL, Mc Fann KK; Charectarstics ofhypertension in young adults with ADPKD compared with the general US population.; Am J Hypertens 2004 ; 17 ; [20]. Gabow P, Johnson AM, et al ; Risk factors for development of hepatic cysts in ADPKD ; Hepatology ; 1990 ; , [21]. Watson M, Macnicol AM, Alan PL ; Effect of ACE inhibition in ADPKD ; KI ; 1992 ; 41 ; [22]. Bajwa ZH, Gupta S; Warfield CA, Pain management in Polycystic Kidney Disease, KI, 2001 ; 60 ; [23]. Torres VE, Ericson SB, Smith LH, et al ; The association of Nephrolithiasis and ADPKD, AJKD, 1988; 11 ; [24]. Klahr S, Breyer JA, Beik, et al ; Dietary protein restriction, blood pressure contral, and progression of kidney disease MDRD study group ; JASN, 1995 ; 5; , [25]. Gabow, PA, Chapman AB, Johnson AM, et al ; Renal structure and Hypertension in ADPKD ; KI, 1990, 38 ; [26]. Drenth JP, te Morsch RH, Smink Ret al ; Germline mutations in PRKCSH are associated with ADPLD ; Nat Genet 2003 ; 33 ; , [27]. Bae KT, Zhu F, Chapman AB, et al ; MRI evaluation of hepatic cysts in early AKPKD, CJASN 2006, 1 ; 64 69, [28]. Griffin MD, Torres VE, Grande TP, Kumar R, Vascular expression of polycystin, JASN, 1997; 8; , [29]. Torres V, Rastoqi S, King BF et al; Hepatic venous outflow obstruction in ADPKD, JASN, 1994; 5; [30]. Blacker-Rovers CP ; de Bevaux RG et al; Diagnosis of renal and hepatic cyst infection by 18 FDG PET in ADPKD ; AJKD 2003; 41; E [31]. Inagawa T ; Trends in incidence and case fatality rates of aneurysmal Sub arachnoid haemorrhage in Izumo city ; Japan, Stroke, 2001, 32; [32]. Leier CV, Baker PB, Kilman JVV et al ; Cardiovascular abnormalities associated with ADPKD, Ann Intern Med 1984 ; 100 ; , [33]. Pirson Y, Torres VE ; Management of cerebral aneurysms in ADPKD ; unruptured asymptomatic intracranial aneurysms, JASN, 2002 ; 13 ; , [34]. Gibbs GF ; Qian et al ; Follow up of Intracranial aneurysm in ADPKD, KI, 2004 ; 65 ; , [35]. Torres VE, Wang S, Somlos etal ; Effective treatment of orthologous model of ADPKD, Nat Med 2004 ; 10 ; , DOI: / Page
8 [36]. Wang X, Harris PC et al ; Effectiveness of vasopressin V2 receptor antagonists OPC and OPC on PCKD development in the PCK rat ; JASN, 2005; 16 ; [37]. Nagao S, Nishi K, Katsuyama M et al ; Increased water intake decreases progression of PCKD in pck rat, JASN, 2006; 17; , [38]. Masyuk TV, Torres VE et al ; Octreotide inhibits hepatic cystogenesis in vitro and in vivo ; a new therapeutic approach for treatment of PCKD, Gastroenterology, 2006 ; 132 ; , [39]. Tao Y, Kim J, Schrier RW, et al, Rapamycin markedly slows disease progression in a rat model of PCKD, JASN, 2005; 16 ; 46 51, [40]. Walz G; Therapeutic approach in ADPKD ; is there light at the end of the tunnel?, NDT 2006 ; 21 ; , Table 1 Loin pain 30% Azotemia 30% Edema 42% Hypertension 58% Urinary symptoms 34% Table 2 UTI 32% Cyst infection 16% Cyst malignancy 2% Cyst hemorrhage 8% Renal calculi 18% Table 3 Liver cysts 28% Intracranial aneurysms 4% Diverticulosis 6% Spleenic cysts 4% Pancreatic cysts 6% Ovarian cysts 16% Mitral valve prolapse 6% DOI: / Page
Nephrology Grand Rounds. Vasishta Tatapudi, MD January 24 th, 2013
 Nephrology Grand Rounds Vasishta Tatapudi, MD January 24 th, 2013 Case Summary Chief complaint: A twenty-six year old African American female veteran presented to ER with left flank pain for two days.
Nephrology Grand Rounds Vasishta Tatapudi, MD January 24 th, 2013 Case Summary Chief complaint: A twenty-six year old African American female veteran presented to ER with left flank pain for two days.
New Treatments for ADPKD how close are we?
 New Treatments for ADPKD how close are we? Leicester General Hospital 28 Jan 2012 Professor Albert Ong a.ong@sheffield.ac.uk The cystic degeneration of the kidneys, once it reaches the point where it can
New Treatments for ADPKD how close are we? Leicester General Hospital 28 Jan 2012 Professor Albert Ong a.ong@sheffield.ac.uk The cystic degeneration of the kidneys, once it reaches the point where it can
Shuma Hirashio 1,2, Shigehiro Doi 1 and Takao Masaki 1*
 Hirashio et al. Renal Replacement Therapy (2018) 4:24 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41100-018-0164-9 CASE REPORT Open Access Magnetic resonance imaging is effective for evaluating the therapeutic effect of
Hirashio et al. Renal Replacement Therapy (2018) 4:24 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41100-018-0164-9 CASE REPORT Open Access Magnetic resonance imaging is effective for evaluating the therapeutic effect of
Renal and extrarenal manifestations of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2006) 39: 533-538 Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ISSN 0100-879X 533 Renal and extrarenal manifestations of autosomal dominant polycystic
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2006) 39: 533-538 Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ISSN 0100-879X 533 Renal and extrarenal manifestations of autosomal dominant polycystic
KDIGO Controversies Conference on Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD)
 KDIGO Controversies Conference on Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) January 16 19, 2014 Edinburgh, United Kingdom Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) is an international
KDIGO Controversies Conference on Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) January 16 19, 2014 Edinburgh, United Kingdom Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) is an international
Analysis of Causes of Mortality in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: A Single Center Study
 Saudi J Kidney Dis Transplant 2009;20(5):806-810 2009 Saudi Center for Organ Transplantation Saudi Journal of Kidney Diseases and Transplantation Original Article Analysis of Causes of Mortality in Patients
Saudi J Kidney Dis Transplant 2009;20(5):806-810 2009 Saudi Center for Organ Transplantation Saudi Journal of Kidney Diseases and Transplantation Original Article Analysis of Causes of Mortality in Patients
Obstructive Nephropathy
 Obstructive Nephropathy Liza A. Lucero RN, FNP-C, MSN Renal Medicine Associates Conflicts No conflict of interests Obstructive Nephropathy Objectives Definition of Obstructive Nephropathy Causes Clinical
Obstructive Nephropathy Liza A. Lucero RN, FNP-C, MSN Renal Medicine Associates Conflicts No conflict of interests Obstructive Nephropathy Objectives Definition of Obstructive Nephropathy Causes Clinical
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Dr. Sameena Iqbal Nephrologist CIUSSS West Island
 Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Dr. Sameena Iqbal Nephrologist CIUSSS West Island Disclosure Honorarium for Consulting on the Reprise trial from Otsuka Mayo clinic preceptorship for PKD with
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Dr. Sameena Iqbal Nephrologist CIUSSS West Island Disclosure Honorarium for Consulting on the Reprise trial from Otsuka Mayo clinic preceptorship for PKD with
QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS
 KEY MESSAGES 1 SCREENING CRITERIA Screen: Patients with DM and/or hypertension at least yearly. Consider screening patients with: Age >65 years old Family history of stage 5 CKD or hereditary kidney disease
KEY MESSAGES 1 SCREENING CRITERIA Screen: Patients with DM and/or hypertension at least yearly. Consider screening patients with: Age >65 years old Family history of stage 5 CKD or hereditary kidney disease
Liver Disease in ADPKD
 Liver Disease in ADPKD The information contained in this presentation is the property of the PKD Foundation and to be used for individual informational purposes only. No part of this presentation is to
Liver Disease in ADPKD The information contained in this presentation is the property of the PKD Foundation and to be used for individual informational purposes only. No part of this presentation is to
Ascites, a New Cause for Bilateral Hydronephrosis: Case Report
 Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 1035 1039 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2009.112 Ascites, a New Cause for Bilateral Hydronephrosis: Case Report D. Jain*, S. Dorairajan, and
Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 1035 1039 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2009.112 Ascites, a New Cause for Bilateral Hydronephrosis: Case Report D. Jain*, S. Dorairajan, and
Grayscale ultrasound characteristics of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease severity an adult and pediatric cohort study
 Original paper Cite as: Strzelczyk M, Podgórski M, Afshari S, Tkaczyk M, Pawlak-Bratkowska M, Grzelak P: Grayscale ultrasound characteristics of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease severity an
Original paper Cite as: Strzelczyk M, Podgórski M, Afshari S, Tkaczyk M, Pawlak-Bratkowska M, Grzelak P: Grayscale ultrasound characteristics of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease severity an
Cystic Renal Disease, for USMLE Step One. Howard J. Sachs, MD
 Cystic Renal Disease, for USMLE Step One Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com The Major Players Medullary Sponge Kidney (MSK) Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) Autosomal Recessive: Childhood Autosomal
Cystic Renal Disease, for USMLE Step One Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com The Major Players Medullary Sponge Kidney (MSK) Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) Autosomal Recessive: Childhood Autosomal
Nephrology Case Presentation for PCKD. Douglas A. Stahura 24 January 2002 With update 2018
 Nephrology Case Presentation for PCKD Douglas A. Stahura 24 January 2002 With update 2018 Case Presentation l 48 y/o WM presents with back pain Sharp, over L side/ribs Intermittent but severe 8/10 No radiation
Nephrology Case Presentation for PCKD Douglas A. Stahura 24 January 2002 With update 2018 Case Presentation l 48 y/o WM presents with back pain Sharp, over L side/ribs Intermittent but severe 8/10 No radiation
Tubulointerstitial Renal Disease. Anna Vinnikova, MD Division of Nephrology
 Tubulointerstitial Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, MD Division of Nephrology Part I: Cystic Renal Disease www.pathguy.com Simple cysts Simple cysts May be multiple Usually 1 5cm, may be bigger Translucent,
Tubulointerstitial Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, MD Division of Nephrology Part I: Cystic Renal Disease www.pathguy.com Simple cysts Simple cysts May be multiple Usually 1 5cm, may be bigger Translucent,
Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology
 Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology I. David Weiner, M.D. C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of Florida College
Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology I. David Weiner, M.D. C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of Florida College
Objectives. Pre-dialysis CKD: The Problem. Pre-dialysis CKD: The Problem. Objectives
 The Role of the Primary Physician and the Nephrologist in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease () By Brian Young, M.D. Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
The Role of the Primary Physician and the Nephrologist in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease () By Brian Young, M.D. Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (AD-
 A Pilot Clinical Study to Evaluate Changes in Urine Osmolality and Urine camp in Response to Acute and Chronic Water Loading in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Irina Barash,* Manish P. Ponda,*
A Pilot Clinical Study to Evaluate Changes in Urine Osmolality and Urine camp in Response to Acute and Chronic Water Loading in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Irina Barash,* Manish P. Ponda,*
Management of New-Onset Proteinuria in the Ambulatory Care Setting. Akinlolu Ojo, MD, PhD, MBA
 Management of New-Onset Proteinuria in the Ambulatory Care Setting Akinlolu Ojo, MD, PhD, MBA Urine dipstick results Negative Trace between 15 and 30 mg/dl 1+ between 30 and 100 mg/dl 2+ between 100 and
Management of New-Onset Proteinuria in the Ambulatory Care Setting Akinlolu Ojo, MD, PhD, MBA Urine dipstick results Negative Trace between 15 and 30 mg/dl 1+ between 30 and 100 mg/dl 2+ between 100 and
The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009
 The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009 Teresa Northcutt, RN BSN Primaris Program Manager, Prevention - CKD MO-09-01-CKD This material was prepared by Primaris,
The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009 Teresa Northcutt, RN BSN Primaris Program Manager, Prevention - CKD MO-09-01-CKD This material was prepared by Primaris,
POLYCYSTIC KIDNEY DISEASE
 PKD YOUR GUIDE TO LIVING WITH POLYCYSTIC KIDNEY DISEASE www.endpkd.ca ABOUT PKD WHAT IS POLYCYSTIC KIDNEY DISEASE? Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a group of genetic diseases that cause fl uid-filled
PKD YOUR GUIDE TO LIVING WITH POLYCYSTIC KIDNEY DISEASE www.endpkd.ca ABOUT PKD WHAT IS POLYCYSTIC KIDNEY DISEASE? Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a group of genetic diseases that cause fl uid-filled
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin
 CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
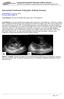 Case Studies [1] July 01, 2014 By Amar Udare, MBBS [2] Case History: 45-year-old female with vague pain in the abdomen. Case History: A 45-year-old female presented with vague pain in the abdomen. A USG
Case Studies [1] July 01, 2014 By Amar Udare, MBBS [2] Case History: 45-year-old female with vague pain in the abdomen. Case History: A 45-year-old female presented with vague pain in the abdomen. A USG
clinical investigation see commentary on page 14
 clinical investigation http://www.kidney-international.org 21 International Society of Nephrology see commentary on page 14 A comparison of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging shows that kidney length
clinical investigation http://www.kidney-international.org 21 International Society of Nephrology see commentary on page 14 A comparison of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging shows that kidney length
Tolvaptan bei ADPKD: Kritische Beurteilung der Studien
 Tolvaptan bei ADPKD: Kritische Beurteilung der Studien Johannes Mann & Stewart Lambie * KfH Nierenzentrum München Schwabing, Klinik für Nieren- & Hochdruckkrankheiten, Friedrich Alexander Univ. Erlangen-Nürnberg
Tolvaptan bei ADPKD: Kritische Beurteilung der Studien Johannes Mann & Stewart Lambie * KfH Nierenzentrum München Schwabing, Klinik für Nieren- & Hochdruckkrankheiten, Friedrich Alexander Univ. Erlangen-Nürnberg
Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease in infancy and childhood: Progression and outcome 1
 Kidney International, Vol. 68 (25), pp. 2218 2224 CLINICAL NEPHROLOGY EPIDEMIOLOGY CLINICAL TRIALS Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease in infancy and childhood: Progression and outcome 1 ABDOLLAH
Kidney International, Vol. 68 (25), pp. 2218 2224 CLINICAL NEPHROLOGY EPIDEMIOLOGY CLINICAL TRIALS Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease in infancy and childhood: Progression and outcome 1 ABDOLLAH
The role of Imaging (scans of the kidneys) in the management of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
 The role of Imaging (scans of the kidneys) in the management of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Dr Roslyn Simms NIHR Clinical Lecturer in Nephrology Saturday 17 th September 2016 Role of Imaging
The role of Imaging (scans of the kidneys) in the management of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Dr Roslyn Simms NIHR Clinical Lecturer in Nephrology Saturday 17 th September 2016 Role of Imaging
Fellow Seminar. Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease F2 吳逸文醫師, 25/08/2004
 Fellow Seminar Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease F2 吳逸文醫師, 25/08/2004 Familial Nephronophthisis ARPKD Polycystic Kidney Disease ADPKD @ Genetics @ Cell biology and pathogenesis @ Clinical picture
Fellow Seminar Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease F2 吳逸文醫師, 25/08/2004 Familial Nephronophthisis ARPKD Polycystic Kidney Disease ADPKD @ Genetics @ Cell biology and pathogenesis @ Clinical picture
Outline. Outline. Introduction CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW 8/11/2011
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
Family History of Renal Disease Severity Predicts the Mutated Gene in ADPKD
 Family History of Renal Disease Severity Predicts the Mutated Gene in ADPKD Moumita Barua,* Onur Cil,* Andrew D. Paterson, Kairon Wang,* Ning He,* Elizabeth Dicks, Patrick Parfrey, and York Pei* *Division
Family History of Renal Disease Severity Predicts the Mutated Gene in ADPKD Moumita Barua,* Onur Cil,* Andrew D. Paterson, Kairon Wang,* Ning He,* Elizabeth Dicks, Patrick Parfrey, and York Pei* *Division
ADPedKD: detailed description of data which will be collected in this registry
 ADPedKD: detailed description of data which will be collected in this registry I. Basic data 1. Patient ID: will be given automatically 2. Personal information - Date of informed consent: DD/MM/YYYY -
ADPedKD: detailed description of data which will be collected in this registry I. Basic data 1. Patient ID: will be given automatically 2. Personal information - Date of informed consent: DD/MM/YYYY -
Predicting and changing the future for people with CKD
 Predicting and changing the future for people with CKD I. David Weiner, M.D. Co-holder, C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University
Predicting and changing the future for people with CKD I. David Weiner, M.D. Co-holder, C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University
Acknowledgements. National Kidney Foundation of Connecticut Mark Perazella. Co-PI Slowing the progression of chronic kidney disease to ESRD
 A Practical Approach to Chronic Kidney Disease Management for the Primary Care Practioner: A web-site sponsored by the National Kidney Foundation of Connecticut Robert Reilly, M.D. Acknowledgements National
A Practical Approach to Chronic Kidney Disease Management for the Primary Care Practioner: A web-site sponsored by the National Kidney Foundation of Connecticut Robert Reilly, M.D. Acknowledgements National
ADPKD, what have the last 10 years taught us? Arlene B. Chapman MD Professor of Medicine Director, Section of Nephrology University of Chicago
 2016 ADPKD, what have the last 10 years taught us? Arlene B. Chapman MD Professor of Medicine Director, Section of Nephrology University of Chicago 2016 Can we TRUMP the cysts? Disclosures Consultant for
2016 ADPKD, what have the last 10 years taught us? Arlene B. Chapman MD Professor of Medicine Director, Section of Nephrology University of Chicago 2016 Can we TRUMP the cysts? Disclosures Consultant for
Volume Progression in Polycystic Kidney Disease
 The new england journal of medicine original article Volume Progression in Polycystic Kidney Disease Jared J. Grantham, M.D., Vicente E. Torres, M.D., Arlene B. Chapman, M.D., Lisa M. Guay-Woodford, M.D.,
The new england journal of medicine original article Volume Progression in Polycystic Kidney Disease Jared J. Grantham, M.D., Vicente E. Torres, M.D., Arlene B. Chapman, M.D., Lisa M. Guay-Woodford, M.D.,
Dialysis: the long case
 Dialysis: the long case Prof Mark Brown St George Public Hospital, Kogarah The case SD 1. What significant things have been omitted from the history? 2. Physical findings 70 RTA; mitral regurg murmur;
Dialysis: the long case Prof Mark Brown St George Public Hospital, Kogarah The case SD 1. What significant things have been omitted from the history? 2. Physical findings 70 RTA; mitral regurg murmur;
Chronic renal disease in the elderly: are all pigs to be considered equal?
 Chronic renal disease in the elderly: are all pigs to be considered equal? W. Van Biesen, Ghent University Hospital Elwood et al, cjasn, 2013 Elderly and CKD: a thematic synthesis Overview CKD in the
Chronic renal disease in the elderly: are all pigs to be considered equal? W. Van Biesen, Ghent University Hospital Elwood et al, cjasn, 2013 Elderly and CKD: a thematic synthesis Overview CKD in the
Renal Cystic Disease. Dr H Bierman
 Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)
 CJASN epress. Published on November 29, 2010 as doi: 10.2215/CJN.03780410 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Kidney and Cyst Volume in Children with ADPKD Melissa A. Cadnapaphornchai,* Amirali Masoumi, John
CJASN epress. Published on November 29, 2010 as doi: 10.2215/CJN.03780410 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Kidney and Cyst Volume in Children with ADPKD Melissa A. Cadnapaphornchai,* Amirali Masoumi, John
Chronic Kidney Disease. Dr Mohan B. Biyani A. Professor of Medicine University of Ottawa/Ottawa Hospital
 Chronic Kidney Disease Dr Mohan B. Biyani A. Professor of Medicine University of Ottawa/Ottawa Hospital Health Seminar Series Date 12 May 2013 Objectives Normal functioning of Kidneys. Risk factors to
Chronic Kidney Disease Dr Mohan B. Biyani A. Professor of Medicine University of Ottawa/Ottawa Hospital Health Seminar Series Date 12 May 2013 Objectives Normal functioning of Kidneys. Risk factors to
Outline. Outline CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW 7/23/2013. Question 1: Which of these patients has CKD?
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Kidney and Cyst Volume in Children with ADPKD
 Article Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Kidney and Cyst Volume in Children with ADPKD Melissa A. Cadnapaphornchai,* Amirali Masoumi, John D. Strain, Kim McFann, and Robert W. Schrier Summary Background and
Article Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Kidney and Cyst Volume in Children with ADPKD Melissa A. Cadnapaphornchai,* Amirali Masoumi, John D. Strain, Kim McFann, and Robert W. Schrier Summary Background and
Primary Care Physicians and Clinicians. XXX on behalf of the Upper Midwest Fistula First Coalition. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Resources
 August 10, 2007 To: From: RE: Primary Care Physicians and Clinicians XXX on behalf of the Upper Midwest Fistula First Coalition Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Resources Caring for patients with chronic kidney
August 10, 2007 To: From: RE: Primary Care Physicians and Clinicians XXX on behalf of the Upper Midwest Fistula First Coalition Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Resources Caring for patients with chronic kidney
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease
 Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease Introduction The examination of care in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a significant challenge, as most large datasets
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease Introduction The examination of care in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a significant challenge, as most large datasets
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function
 Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
Blood Pressure and Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP) Levels in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease.
 Blood Pressure and Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP) Levels in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Rafie Shakir Al-Khafaji* Ali Hmood Al-Saadi** Haider Kamil Zaidan** * Faculty of
Blood Pressure and Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP) Levels in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Rafie Shakir Al-Khafaji* Ali Hmood Al-Saadi** Haider Kamil Zaidan** * Faculty of
TREAT THE KIDNEY TO SAVE THE HEART. Leanna Tyshler, MD Chronic Kidney Disease Medical Advisor Northwest Kidney Centers February 2 nd, 2009
 TREAT THE KIDNEY TO SAVE THE HEART Leanna Tyshler, MD Chronic Kidney Disease Medical Advisor Northwest Kidney Centers February 2 nd, 2009 1 ESRD Prevalent Rates in 1996 per million population December
TREAT THE KIDNEY TO SAVE THE HEART Leanna Tyshler, MD Chronic Kidney Disease Medical Advisor Northwest Kidney Centers February 2 nd, 2009 1 ESRD Prevalent Rates in 1996 per million population December
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM
 USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD Over half of patients from the Medicare 5 percent sample have either a diagnosis of chronic kidney disease
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD Over half of patients from the Medicare 5 percent sample have either a diagnosis of chronic kidney disease
Fluid Resuscitation in Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
 Fluid Resuscitation in Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Robert W. Schrier, MD University of Colorado School of Medicine Denver, Colorado USA Prevalence of acute renal failure in Intensive
Fluid Resuscitation in Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Robert W. Schrier, MD University of Colorado School of Medicine Denver, Colorado USA Prevalence of acute renal failure in Intensive
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Smith D, Chudgar A, Daly B, Cooper M. Evaluation of potential renal transplant recipients with computed tomography angiography. Arch Intern Med. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.2012.1466.
Supplementary Online Content Smith D, Chudgar A, Daly B, Cooper M. Evaluation of potential renal transplant recipients with computed tomography angiography. Arch Intern Med. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.2012.1466.
Outline. Introduction. Outline CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW 6/26/2012
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
 GENETIC TESTING AND MOLECULAR BIOMARKERS Volume 20, Number 12, 2016 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 741 746 DOI: 10.1089/gtmb.2016.0050 Attitudes in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
GENETIC TESTING AND MOLECULAR BIOMARKERS Volume 20, Number 12, 2016 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 741 746 DOI: 10.1089/gtmb.2016.0050 Attitudes in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
Elevation of Serum Creatinine: When to Screen, When to Refer. Bruce F. Culleton, MD, FRCPC; and Jolanta Karpinski, MD, FRCPC
 Elevation of Serum Creatinine: When to Screen, When to Refer Bruce F. Culleton, MD, FRCPC; and Jolanta Karpinski, MD, FRCPC Presented at the University of Calgary s CME and Professional Development 2006-2007
Elevation of Serum Creatinine: When to Screen, When to Refer Bruce F. Culleton, MD, FRCPC; and Jolanta Karpinski, MD, FRCPC Presented at the University of Calgary s CME and Professional Development 2006-2007
Lab Values Explained. working at full strength. Other possible causes of an elevated BUN include dehydration and heart failure.
 Patient Education Lab Values Explained Common Tests to Help Diagnose Kidney Disease Lab work, urine samples and other tests may be given as you undergo diagnosis and treatment for renal failure. The test
Patient Education Lab Values Explained Common Tests to Help Diagnose Kidney Disease Lab work, urine samples and other tests may be given as you undergo diagnosis and treatment for renal failure. The test
Long-term outcomes in nondiabetic chronic kidney disease
 original article http://www.kidney-international.org & 28 International Society of Nephrology Long-term outcomes in nondiabetic chronic kidney disease V Menon 1, X Wang 2, MJ Sarnak 1, LH Hunsicker 3,
original article http://www.kidney-international.org & 28 International Society of Nephrology Long-term outcomes in nondiabetic chronic kidney disease V Menon 1, X Wang 2, MJ Sarnak 1, LH Hunsicker 3,
on PKD Originally Created by Patricia Gabow, MD Jared J. Grantham, MD University of Kansas Medical Center
 Q & on PKD A Originally Created by Patricia Gabow, MD Jared J. Grantham, MD University of Kansas Medical Center Reviewed and Updated (2002) by Arlene Chapman, MD Robin Post, RN Joan Allen, RD Emory University
Q & on PKD A Originally Created by Patricia Gabow, MD Jared J. Grantham, MD University of Kansas Medical Center Reviewed and Updated (2002) by Arlene Chapman, MD Robin Post, RN Joan Allen, RD Emory University
CKD FOR INTERNISTS. Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College
 CKD FOR INTERNISTS Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College INTRODUCTION In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative(KDOQI)
CKD FOR INTERNISTS Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College INTRODUCTION In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative(KDOQI)
Case 2 Dwayne A. Williams CASE 2
 CASE 2 A 40- year- old male with no past medical history presents with bilateral flank pain and dark colored urine for 5 days. During family history taking, he states his father died from kidney failure
CASE 2 A 40- year- old male with no past medical history presents with bilateral flank pain and dark colored urine for 5 days. During family history taking, he states his father died from kidney failure
KDIGO LESSONS LEARNED FROM NEPHROLOGY TRIALS WITH RESPECT TO HEART FAILURE
 LESSONS LEARNED FROM NEPHROLOGY TRIALS WITH RESPECT TO HEART FAILURE Dr. Christopher T Chan Director Division of Nephrology University Health Network Professor of Medicine University of Toronto Disclosure
LESSONS LEARNED FROM NEPHROLOGY TRIALS WITH RESPECT TO HEART FAILURE Dr. Christopher T Chan Director Division of Nephrology University Health Network Professor of Medicine University of Toronto Disclosure
Research Archive. DOI:
 Research Archive Citation for published version: Oscar Swift, Enric Vilar, Belinda Rahman, Lucy Side, and Daniel P. Gale, Attitudes in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Toward
Research Archive Citation for published version: Oscar Swift, Enric Vilar, Belinda Rahman, Lucy Side, and Daniel P. Gale, Attitudes in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Toward
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Polycystic Kidney Disease, Autosomal Dominant OMIM number for disease 173900 Disease
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Polycystic Kidney Disease, Autosomal Dominant OMIM number for disease 173900 Disease
Outline. Outline CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW. Question 1: Which of these patients has CKD?
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
No effect of enalapril on progression in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2003) 18: 2314 2320 DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfg417 Original Article No effect of enalapril on progression in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease Marjan A. van Dijk 1, Martijn
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2003) 18: 2314 2320 DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfg417 Original Article No effect of enalapril on progression in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease Marjan A. van Dijk 1, Martijn
Progress on Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
 . 2009 May;2(2):27-44 Review AJNT Progress on Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Elwaleed Elhassan, Amirali Masoumi and Robert W Schrier * Division of Renal Diseases and Hypertension, School
. 2009 May;2(2):27-44 Review AJNT Progress on Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Elwaleed Elhassan, Amirali Masoumi and Robert W Schrier * Division of Renal Diseases and Hypertension, School
SURGERY, TRANSPLANTATION AND POLYCYSTIC DISEASE. Mr Nick Inston PhD FRCS Consultant Transplant Surgeon Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham
 SURGERY, TRANSPLANTATION AND POLYCYSTIC DISEASE Mr Nick Inston PhD FRCS Consultant Transplant Surgeon Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham What are polycystic kidneys and livers?! Cystic degenerative condition!
SURGERY, TRANSPLANTATION AND POLYCYSTIC DISEASE Mr Nick Inston PhD FRCS Consultant Transplant Surgeon Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham What are polycystic kidneys and livers?! Cystic degenerative condition!
NATIONAL KIDNEY MONTH
 NATIONAL KIDNEY MONTH According to the WebMD website, kidneys have several specific roles: Maintain your body s balance of water and concentration of minerals, such as sodium, potassium, magnesium and
NATIONAL KIDNEY MONTH According to the WebMD website, kidneys have several specific roles: Maintain your body s balance of water and concentration of minerals, such as sodium, potassium, magnesium and
PREVALENCE AND CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF CYSTIC KIDNEY DISEASES AT LAGOS STATE UNIVERSITY TEACHING HOSPITAL
 Tropical Journal of Nephrology Vol.9 Nos. &2, June and December, 204 3 34 Original article PREVALENCE AND CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF CYSTIC KIDNEY DISEASES AT LAGOS STATE UNIVERSITY TEACHING HOSPITAL Awoonidanla
Tropical Journal of Nephrology Vol.9 Nos. &2, June and December, 204 3 34 Original article PREVALENCE AND CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF CYSTIC KIDNEY DISEASES AT LAGOS STATE UNIVERSITY TEACHING HOSPITAL Awoonidanla
THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS
 THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS JACK WATERMAN DO FACOI 2013 NEPHROLOGY SIR RICHARD BRIGHT TERMINOLOGY RENAL INSUFFICIENCY CKD (CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE) ESRD (ENDSTAGE RENAL DISEASE) GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS JACK WATERMAN DO FACOI 2013 NEPHROLOGY SIR RICHARD BRIGHT TERMINOLOGY RENAL INSUFFICIENCY CKD (CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE) ESRD (ENDSTAGE RENAL DISEASE) GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging
 Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
CKD IN THE CLINIC. Session Content. Recommendations for commonly used medications in CKD. CKD screening and referral
 CKD IN THE CLINIC Family Physician Refresher Course Lisa M. Antes, MD April 19, 2017 No disclosures Session Content 1. 2. Recommendations for commonly used medications in CKD Basic principles /patient
CKD IN THE CLINIC Family Physician Refresher Course Lisa M. Antes, MD April 19, 2017 No disclosures Session Content 1. 2. Recommendations for commonly used medications in CKD Basic principles /patient
Research Introduction
 Research Introduction 9.17.13 Altered metabolism in polycystic kidney disease Telomerase activity in polycystic kidney disease cells Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD is the most common
Research Introduction 9.17.13 Altered metabolism in polycystic kidney disease Telomerase activity in polycystic kidney disease cells Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD is the most common
Screening for chronic kidney disease racial implications. Not everybody that pees has healthy kidneys!
 Screening for chronic kidney disease racial implications Not everybody that pees has healthy kidneys! Screening for chronic kidney disease racial implications 1) Definition of CKD 2) Why should we screen
Screening for chronic kidney disease racial implications Not everybody that pees has healthy kidneys! Screening for chronic kidney disease racial implications 1) Definition of CKD 2) Why should we screen
Total Kidney Volume (TKV) in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease as model for biomarker qualification
 Total Kidney Volume (TKV) in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease as model for biomarker qualification Roslyn Simms NIHR Clinical Lecturer in Nephrology NIHR Clinical Trials Fellow Monday 23 rd
Total Kidney Volume (TKV) in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease as model for biomarker qualification Roslyn Simms NIHR Clinical Lecturer in Nephrology NIHR Clinical Trials Fellow Monday 23 rd
Acute Kidney Injury. I. David Weiner, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation University of Florida and NF/SGVHS
 Acute Kidney Injury I. David Weiner, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation University of Florida and NF/SGVHS 374-6102 David.Weiner@medicine.ufl.edu www.renallectures.com Concentration
Acute Kidney Injury I. David Weiner, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation University of Florida and NF/SGVHS 374-6102 David.Weiner@medicine.ufl.edu www.renallectures.com Concentration
Dr.Nahid Osman Ahmed 1
 1 ILOS By the end of the lecture you should be able to Identify : Functions of the kidney and nephrons Signs and symptoms of AKI Risk factors to AKI Treatment alternatives 2 Acute kidney injury (AKI),
1 ILOS By the end of the lecture you should be able to Identify : Functions of the kidney and nephrons Signs and symptoms of AKI Risk factors to AKI Treatment alternatives 2 Acute kidney injury (AKI),
Renal and ureteral involvement in Erdheim-Chester disease: analysis of a single centre cohort
 Renal and ureteral involvement in Erdheim-Chester disease: analysis of a single centre cohort Gaia Manari, Davide Gianfreda, Andrea Posteraro, Alessandro A. Palumbo and Augusto Vaglio Nephrology Unit and
Renal and ureteral involvement in Erdheim-Chester disease: analysis of a single centre cohort Gaia Manari, Davide Gianfreda, Andrea Posteraro, Alessandro A. Palumbo and Augusto Vaglio Nephrology Unit and
Difference in practical dialysis therapy between East Asia and US/EU
 Difference in practical dialysis therapy between East Asia and US/EU Jer-Ming Chang. M.D., Ph.D. 1 Professor, Attending physician, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital; 2 Secretary General, Taiwan Society
Difference in practical dialysis therapy between East Asia and US/EU Jer-Ming Chang. M.D., Ph.D. 1 Professor, Attending physician, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital; 2 Secretary General, Taiwan Society
Tolvaptan: a Possible Treatment for Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Fall 9-20-2013 Tolvaptan: a Possible Treatment for Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Fall 9-20-2013 Tolvaptan: a Possible Treatment for Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney
A Comparison Of Diagnostic Accuracy Of Cystatin C With Creatinine In The Sample Of Patient Of T2 DM With Diabetic Nephropathy
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. V (July. 2017), PP 53-57 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparison Of Diagnostic Accuracy Of
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. V (July. 2017), PP 53-57 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparison Of Diagnostic Accuracy Of
A Study on Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate As A Predictor of Renal Dysfunction Among Adult Hiv Patients on Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 10 Ver. IX (Oct. 2017), PP 28-34 www.iosrjournals.org A Study on Estimated Glomerular Filtration
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 10 Ver. IX (Oct. 2017), PP 28-34 www.iosrjournals.org A Study on Estimated Glomerular Filtration
Management of Cerebral Aneurysms in Polycystic Kidney Disease. Dr H Stockley Consultant Neuroradiologist Greater Manchester Neuroscience Centre
 Management of Cerebral Aneurysms in Polycystic Kidney Disease Dr H Stockley Consultant Neuroradiologist Greater Manchester Neuroscience Centre What is a cerebral aneurysm? Developmental degenerative arterial
Management of Cerebral Aneurysms in Polycystic Kidney Disease Dr H Stockley Consultant Neuroradiologist Greater Manchester Neuroscience Centre What is a cerebral aneurysm? Developmental degenerative arterial
3 generations of ADPKD. 1 long-awaited treatment.
 3 generations of ADPKD. 1 long-awaited treatment. HOPE is finally here now that treatment is available for people with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). JYNARQUE is proven to slow kidney
3 generations of ADPKD. 1 long-awaited treatment. HOPE is finally here now that treatment is available for people with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). JYNARQUE is proven to slow kidney
Updates in Chronic Kidney Disease Management. Delphine S. Tuot, MDCM, MAS Associate Professor of Medicine UCSF-ZSFG
 Updates in Chronic Kidney Disease Management Delphine S. Tuot, MDCM, MAS Associate Professor of Medicine UCSF-ZSFG No disclosures Research Funding: NIH, Blue Shield of California Foundation Objectives
Updates in Chronic Kidney Disease Management Delphine S. Tuot, MDCM, MAS Associate Professor of Medicine UCSF-ZSFG No disclosures Research Funding: NIH, Blue Shield of California Foundation Objectives
Outline. Outline 10/14/2014 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW. Question 1: Which of these patients has CKD?
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
Predictors of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Progression
 Predictors of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Progression Robert W. Schrier,* Godela Brosnahan,* Melissa A. Cadnapaphornchai,* Michel Chonchol,* Keith Friend, Berenice Gitomer,* and Sandro
Predictors of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Progression Robert W. Schrier,* Godela Brosnahan,* Melissa A. Cadnapaphornchai,* Michel Chonchol,* Keith Friend, Berenice Gitomer,* and Sandro
Vascular calcification in stage 5 Chronic Kidney Disease patients on dialysis
 Vascular calcification in stage 5 Chronic Kidney Disease patients on dialysis Seoung Woo Lee Div. Of Nephrology and Hypertension, Dept. of Internal Medicine, Inha Unv. College of Medicine, Inchon, Korea
Vascular calcification in stage 5 Chronic Kidney Disease patients on dialysis Seoung Woo Lee Div. Of Nephrology and Hypertension, Dept. of Internal Medicine, Inha Unv. College of Medicine, Inchon, Korea
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY. THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel
 PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
1. Albuminuria an early sign of glomerular damage and renal disease. albuminuria
 1. Albuminuria an early sign of glomerular damage and renal disease albuminuria Cardio-renal continuum REGRESS Target organ damage Asymptomatic CKD New risk factors Atherosclerosis Target organ damage
1. Albuminuria an early sign of glomerular damage and renal disease albuminuria Cardio-renal continuum REGRESS Target organ damage Asymptomatic CKD New risk factors Atherosclerosis Target organ damage
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
 I want to know more about... Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease together the answer This booklet is about autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). It is intended as a general guide
I want to know more about... Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease together the answer This booklet is about autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). It is intended as a general guide
Patient Description and Diagnosis: Sarah Jones is a 50-year-old female, 5 4, 131
 Julia Kaesberg Counseling Session KNH 413 February 27 th, 2014 Patient Description and Diagnosis: Sarah Jones is a 50-year-old female, 5 4, 131 pounds and her usual body weight is 125 pounds. Her %UBW
Julia Kaesberg Counseling Session KNH 413 February 27 th, 2014 Patient Description and Diagnosis: Sarah Jones is a 50-year-old female, 5 4, 131 pounds and her usual body weight is 125 pounds. Her %UBW
Impact of APD on Sleep
 Impact of APD on Sleep Sydney C.W. Tang The University of Hong Kong, Queen Mary Hospital, Hong Kong, China APD Symposium: Peritoneal Dialysis Update 26 Mar 2017, Hong Kong Sleep apnea in ESRD General population:
Impact of APD on Sleep Sydney C.W. Tang The University of Hong Kong, Queen Mary Hospital, Hong Kong, China APD Symposium: Peritoneal Dialysis Update 26 Mar 2017, Hong Kong Sleep apnea in ESRD General population:
Nephrolithiasis Associated with Renal Insufficiency: Factors Predicting Outcome
 JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 17, Number 10, December 2003 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Nephrolithiasis Associated with Renal Insufficiency: Factors Predicting Outcome RAJESH KUKREJA, M.S., DNB, MIHIR DESAI,
JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 17, Number 10, December 2003 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Nephrolithiasis Associated with Renal Insufficiency: Factors Predicting Outcome RAJESH KUKREJA, M.S., DNB, MIHIR DESAI,
Cardiovascular Diseases in CKD
 1 Cardiovascular Diseases in CKD Hung-Chun Chen, MD, PhD. Kaohsiung Medical University Taiwan Society of Nephrology 1 2 High Prevalence of CVD in CKD & ESRD Foley RN et al, AJKD 1998; 32(suppl 3):S112-9
1 Cardiovascular Diseases in CKD Hung-Chun Chen, MD, PhD. Kaohsiung Medical University Taiwan Society of Nephrology 1 2 High Prevalence of CVD in CKD & ESRD Foley RN et al, AJKD 1998; 32(suppl 3):S112-9
Tolvaptan for treating autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
 in collaboration with: ERRATUM TO Tolvaptan for treating autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease 1. The word ********* has been marked as commercial in confidence. a. Section 1.4 (page 13): Hence,
in collaboration with: ERRATUM TO Tolvaptan for treating autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease 1. The word ********* has been marked as commercial in confidence. a. Section 1.4 (page 13): Hence,
Dr P Sigwadi 30 May 2012
 Dr P Sigwadi 30 May 2012 Introduction Haematuria Positive blood on urine dipstick 5 red blood cells/ microliter of urine Prevalence Gross haematuria ( macroscopic) 0.13 % Microscopic- 1.5% Haematuria +
Dr P Sigwadi 30 May 2012 Introduction Haematuria Positive blood on urine dipstick 5 red blood cells/ microliter of urine Prevalence Gross haematuria ( macroscopic) 0.13 % Microscopic- 1.5% Haematuria +
The Use of Lanreotide in Polycystic Kidney Disease: A Single-Centre Experience
 Published online: February 5, 2014 1664 5510/14/0041 0018$39.50/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
Published online: February 5, 2014 1664 5510/14/0041 0018$39.50/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
SUISSE ADPKD Cohort Treatment and Outcomes with Tolvaptan, first in class Vasopressin V2 Antagonist. Hirslanden, 22 March 2018 Stefan Russmann
 SUISSE ADPKD Cohort Treatment and Outcomes with Tolvaptan, first in class Vasopressin V2 Antagonist Hirslanden, 22 March 2018 Stefan Russmann 4 th of July 2004 Database development with outcomes and safety
SUISSE ADPKD Cohort Treatment and Outcomes with Tolvaptan, first in class Vasopressin V2 Antagonist Hirslanden, 22 March 2018 Stefan Russmann 4 th of July 2004 Database development with outcomes and safety
Prostate Gland Volume and Its Relationship to Complications of Benign Prostatic Enlargement
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 6 Ver. II (Jun. 2015), PP 33-37 www.iosrjournals.org Prostate Gland Volume and Its Relationship
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 6 Ver. II (Jun. 2015), PP 33-37 www.iosrjournals.org Prostate Gland Volume and Its Relationship
CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE: WHAT THE PRIMARY CARE CAN OFFER. The annual conference of the Lebanese Society of Family Medicine October 2017 Dr Hiba AZAR
 CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE: WHAT THE PRIMARY CARE CAN OFFER The annual conference of the Lebanese Society of Family Medicine October 2017 Dr Hiba AZAR OUTLINE: A journey through CKD Screening for CKD: The why,
CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE: WHAT THE PRIMARY CARE CAN OFFER The annual conference of the Lebanese Society of Family Medicine October 2017 Dr Hiba AZAR OUTLINE: A journey through CKD Screening for CKD: The why,

 www.usrds.org www.usrds.org 1 1,749 + (2,032) 1,563 to
www.usrds.org www.usrds.org 1 1,749 + (2,032) 1,563 to