What is sphincter of Oddi dysfunction?
|
|
|
- Diane McLaughlin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Leading article Gut, 1989, 30, What is sphincter of Oddi dysfunction? Summary Ever since its description approximately 100 years ago, the sphincter of Oddi has been surrounded by controversy. First, whether it indeed existed, second, whether it had a significant physiological role in man and more recently whether abnormalities in its function give rise to a clinical syndrome. Data from animal and human studies, using sensitive techniques, have helped define the physiological role of the sphincter of Oddi, and more recent studies are determining the factors which control sphincter of Oddi function. These studies support Oddi's original description that the sphincter has a major role in the control of flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum, and equally importantly helps prevent the reflux of duodenal contents into the biliary and pancreatic ductal systems. The controversy of whether abnormalities in sphincter of Oddi motility result in clinical syndromes has not been totally resolved. Part of the difficulty has been inability to document normal and hence abnormal function of the sphincter. With the emergence of endoscopic biliary manometry as a sensitive and reproducible technique, however, the motility of the human sphincter of Oddi has come under closer scrutiny and allowed definition of possible disorders. We have used the term sphincter of Oddi dysfunction to define manometric abnormalities in patients who present with signs and symptoms consistent with a biliary or pancreatic ductal origin. Based on the manometry, we have subdivided the dysfunction into two groups; a group characterised by a stenotic pattern - that is, raised sphincter basal pressure - and a second group having a dyskinetic pattern - that is, paradoxical response to cholecystokinin injection, rapid contraction frequency, high percentage of retrograde contractions, or short periods of raised basal pressure. It is apparent from the mamometry but also from the clinical data that the patients are a heterogeneous group and thus any therapy would need to be tailored for each patient and abnormality. The most recent therapeutic data suggest that patients with the stenotic pattern on manometry respond to division of the sphincter, however, those patients with the dyskinetic manometric pattern show no significant effect after sphincterotomy. Further prospective trials evaluating therapeutic options are under way and their results are eagerly awaited. Just over 100 years ago Rugero Oddi described the collection of smooth muscle at the lower end of the bile duct which now bears his name.' He postulated that this sphincter played a vital role in the control of flow of bile and pancreatic secretions and that abnormalities in its function would be associated with clinical syndromes. Since then, clinicians have given a 753
2 754 Toouli variety of names to symptomatology said to originate from a malfunctioning sphincter of Oddi. These names include odditis, biliary dyskinesia, postcholecystectomy syndrome and sphincter of Oddi stenosis.213 Precise definition of each of these entities is lacking and the plethora of clinical descriptions only serve to further confuse discussion. In an attempt to develop a terminology which may be reproducible we introduced the term sphincter of Oddi dysfunction to encompass all of the potential motility abnormalities of the sphincter and attempted to define subcategories based on objective manometric findings.4 The nomenclature is also based on the existing understanding of the physiology of the sphincter of Oddi and several hypotheses on potential abnormalities of normal function which may lead to a dysfunctioning sphincter. Normal function Understanding of the normal motility of the sphincter of Oddi has arisen from studies mainly in animals' and to a lesser extent in man.6 Anatomical dissections show that the sphincter of Oddi differs between species and hence its normal physiological function might also be expected to be different between species. The human sphincter of Oddi is 6 to 10 mm in length and is situated almost entirely in the wall of the duodenum traversing an oblique course. Dogs, cats, and pigs have sphincters of smaller dimensions but differ from man in that the bile duct and pancreatic duct enter the duodenum separately. In the Australian possum and American oppossum, the two ducts merge in a similar manner to man, but the sphincter has a long extraduodenal course which extends for up to 20 to 25 mm in length. The extraduodenal position of the sphincter of Oddi in the possum has made this animal suitable for detailed study in order to help understand the mechanisms of controlling flow across the sphincter. Physiological studies in man7 and animals9 10 have shown that the sphincter of Oddi generates a small resistance of approximately 5 mm Hg at the opening of the bile duct and pancreatic duct. Superimposed on this tonal pressure are prominent phasic contractions (100 to 150 mm Hg) which are mainly orientated in an antegrade direction and contract at a frequency of two to six per minute. In possums the phasic contractions propel small volumes of fluid from the bile duct into the duodenum hence bile flows as a result of the phasic contractile activity with small amounts expelled passively between contractions.8 In man, bile flow occurs mainly by a passive mechanism in between the phasic contractions, the contractions only serving to propel a small bolus of fluid and thus clearing the ductal opening." In both species the frequency of contractions varies during fasting and shows an increase just before phase III duodenal activity.` 12 After feeding, the frequency of contractions increases in the possum'2 whilst in man the amplitude of the contractions decreases and the tone is reduced." Both of these responses facilitate increased flow of bile from the bile duct into the duodenum; in the possum active propulsion is enhanced whilst in man passive flow between contractions is facilitated. These differences between the possum and man serve to illustrate species variations but also the complexity of the motility of the sphincter of Oddi. This complex motility is orchestrated by the interplay of neuronal and hormonal mechanisms, the precise details of which have not yet been elucidated.
3 What is sphincter ofoddi dysfunction? Clinical features The diagnosis of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction is most usually considered in patients with persistent or recurrent biliary type symptoms after cholecystectomy.'3 Furthermore, patients with recurrent pancreatitis, where a cause cannot be determined, are also considered to be candidates for sphincter of Oddi dysfunction.`4 The prevalence of the disorder has not been defined. It is not known whether the disorder exists before cholecystectomy, is related to the problem which led to cholecystectomy, or results from changes brought about by cholecystectomy. It is not known whether the disorder is congenital or secondary to changes produced as a result of passage of gall stones or other debris through the sphincter of Oddi. We have interviewed over 100 patients considered to be candidates of postcholecystectomy sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. As a result of these interviews, a clinical pattern has emerged and alerts us to the possibility of the disorder so that the more invasive and objective investigations are performed. The majority of patients are women, between the ages of 30 and 50 years. Symptoms occur approximately five years after cholecystectomy and are similar to those symptoms experienced before cholecystectomy and relieved by the operation. The major symptom is pain, which is usually epigastric radiating to the right upper quadrant and into the back. The pain is often related to a fatty type meal but also occurs spontaneously. In some patients the pain wakes the patient in the early morning hours. Patients fall into two major groups. One group of patients have distinct episodes of pain with intervals of weeks to months between episodes. Another group experience a more regular pain of moderate intensity almost daily, but in addition more, severe episodes of pain occur at intervals of weeks or months. An interesting feature in a subgroup of these patients is a sensitivity to opiate containing medication, particularly codeine, morphine, and Omnopon. Even small doses of codeine such as occurs in certain cough mixtures may initiate a severe episode of pain. In another subgroup, the above features may be accompanied by a rise in serum amylase and a diagnosis of recurrent pancreatitis is made. Inevitably, these patients undergo endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) examination of the bile duct and pancreatic duct to exclude a morphological cause for the symptoms. In some, the endoscopist may note that the pain is reproduced by manipulation of the papilla and by injection of contrast into the bile duct. Objective signs which support a diagnosis of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction include abnormal serum amylase or abnormal serum liver transaminases in association with an episode of pain. Furthermore, ERCP may reveal an abnormally dilated bile duct or pancreatic duct and delay in emptying of contrast from the bile duct into the duodenum. (Fig. 1). The majority of patients, however, will not have any objective signs to support the more subjective symptoms hence the need for development of objective investigations which may assist in the diagnosis of SO dysfunction. Investigations of sphincter of Oddi function ERCP Definition of the anatomy of the bile duct and pancreatic duct is essential as 755
4 756 mm Hg..i1001 ejei ' Cephalad SO 0 Middle SO 1001 ',,il_, ~~~~~~~~~~~100- Caudad SO mm Hq 400 Fig. 1 Endoscopic retrogiade cholangiogram on a patient Cephalad SO wit/i postchol cystectomy iecur uient biliaiy type pain 0] associated wit/i raised liver enzymes dur-ing pain episodes. Cholangiogram s/lows a moderately dilated extralhepatic bile 400, duct. At 45 minutes aftei introduction of contrast, tlhere is little.flowfi-om t/e bile ducts. Middle SO 0] Table Control data on biliaty manometry 4001 Mediani Ratnge Common bile duct (mm Hg) Sphincter of Oddi Basal pressure (mm Hg) Wase amplitude (mm Hg) Wave frequency (n/min) Wase direction Antegrade % (0) Simultaneous %i Retrograde %/9 0-5( Time (s) Fig. 2 Triple lumen catheter recordingfrom the sphincter of Oddi, showing a normal tracing. Phasic contractions are superimposed on a modest basal pressure. Caudad SO J Touli Time (s) Fig. 3 Triple lumen catheter recording from the sphincter of Oddi in the patient illustrated in Fig. 1. The catheter is witliddrawn from the bile duct across the sphincter into the duodenum in a stepwise manner indicated by the black marks. The tracing illustrates a high basal pressure recorded on all three lumens. is exclusion of morphological abnormalities which may give rise to the symptoms. A cholangiogram will also determine duct diameter. A corrected diameter in excess of 12 mm is consistent with dilatation and may indicate a relative resistance to flow across the sphincter of Oddi. (Fig. 1). MORPHINE NEOSTIGMINE TEST This investigation was first described for the diagnosis of idiopathic recurrent pancreatitis, however, it has been adapted for screening of patients with suspected sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Its sensitivity and specificity as assessed by results of therapy is very poor. Hence the investigation has not been considered useful in the diagnosis of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Given the fact that the term sphincter of Oddi dysfunction encompasses a variety of possible aetiological conditions,
5 What is sphincter of Oddi dysfunction? however, which include patients with abnormal and normal responses to opiates plus fibrotic and non-fibrotic changes in the sphincter, it is not surprising that this test is not specific for all patients. In the identification and screening of patients with possible sphincter of Oddi dysfunction there is a need for a provocative test, as most patients experience only intermittent episodes of pain. The morphine neostigmine provocative test may identify a subgroup of patients with sphincter of Oddi dysfunction who are abnormally sensitive to opiates. The test is performed by administering morphine (0.12 mg/kg) and neostigmine (0.012 mg/kg) intramuscularly. Blood is taken at hourly intervals for five hours to determine serum liver enzyme concentrations. A positive test comprises reproduction of pain with a rise in liver enzymes (serum alanine transaminase or aspartate transaminase) to greater than double the upper limit of normal.`' DUCTAL DIAMETER AFTER SPECIFIC STIMULATION In the search for provocative non-invasive investigations to screen patients suspected of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction, two investigations using ultrasound techniques have emerged as possible candidates. Evaluation of pancreatic ductal size has been determined after administration of secretin (lu/kg) which produces maximal pancreatic juice flow. In the presence of a normally functioning sphincter of Oddi there is transient increase in pancreatic duct diameter as a result of increased flow. In the presence of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction, a prolonged increase in ductal diameter in excess of 20 minutes after secretin injection is observed.'6 A similar test has recently been reported for the bile duct. The diameter of the bile duct is determined by ultrasound and alterations noted after a fatty meal. Prolonged dilatation of the bile duct after fatty meal stimulation suggests a relative stenosis of the sphincter.'7 Current studies are under way to help define the sensitivity and specificity of the above investigations. It would be expected that in view of the heterogeneity of the possible mechanisms which make up sphincter of Oddi dysfunction that neither of the above investigations will prove to be highly specific and similar to the morphine neostigmine test, help to identify a subgroup of patients. SCINTIGRAPHY Radionuclide methods for assessing bile flow across the sphincter of Oddi potentially should provide the most significant and specific data of functional changes. Quantitative hepatobiliary scintigraphy after sphincter of Oddi provocation by specific stimulants may further enhance its diagnostic value. To date, however, most studies have presented data showing that scintigraphy is useful in the diagnosis of major stenosis but quite insensitive in differentiating patients with intermittent symptoms.'71'9 MANOMETRY Manometric evaluation of sphincter of Oddi function has produced the most recent advance in understanding of the normal function of the sphincter and also has allowed for identification of abnormalities in sphincter of Oddi motility. These manometric abnormalities have provided the basis for description of subgroups of patients with sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Manometry is performed through an endoscopic route by adaptation of 757
6 758 Toouli ERCP techniques,2' at operation by direct cannulation of the bile duct22 and postoperatively in patients with T-tubes in the bile duct.' A miniaturised triple lumen catheter perfused by a minimally compliant pneumohydraulic perfusion system may be positioned across the sphincter so that three lumens record pressure changes. A separate catheter records pressure changes from the duodenum. The sphincter of Oddi is characterised manometrically by regular phasic contractions superimposed on a modest basal tone (Fig 2). Studies in control subjects4 and normal volunteers24 25 have defined the normal manometric profile of the sphincter of Oddi (Table). Manometric abnormalities have been described in patients with clinical features consistent with sphincter of Oddi dysfunction and as a result two major subgroups have been identified based entirely on the manometric results.4 The groups are as follows: Sphincter of Oddi stenosis Manometrically these patients have an abnormally raised basal pressure (>40 mm Hg). (Fig. 3) Emerging evidence suggests that there may be an association between raised basal pressure and duct diameter, plus abnormalities in liver enzymes in relation to episodes of pain. An association is also present with patients who have an abnormal fatty meal sonogram'7 and abnormal secretin stimulated pancreatic duct diameter.'6 The correlation between the various investigations is, however, not tight. Pathological correlation is lacking, however, and it is postulated that a high basal pressure may result from fibrotic stenosis, muscle hypertrophy or mucosal oedema.26 Sphincter of Oddi dyskinesia Manometrically a variety of disorders are included in this group. So far, the following manometric dyskinetic abnormalities have been described;4 paradoxical response to cholecystokinin octapeptide injection, rapid contraction frequency, episodes of raised basal pressure or an excess of retrograde contractions. Patients who respond abnormally to morphine or to a fatty meal stimulus may have these manometric abnormalities. Pathologically there have not been any reproducible abnormalities described. A possible defect in the enteric nervous system, however, may account for the paradoxical response seen after cholecystokinin-octapeptide administration.26 This hypothetical neuronal defect may be similar to that described for achalasia of the oesophagus and awaits future confirmation.27 Treatment of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction As far as is known, sphincter of Oddi dysfunction is not a life threatening disorder. Undoubtedly patients suspected of having this disorder are severely debilitated. The mechanism for production of pain is unknown. It is postulated that the relative obstruction of flow through the sphincter of Oddi results in bile duct or pancreatic duct distension which in turn gives rise to either pain or pain and pancreatitis respectively. The observation of reproduction of the pain by manipulating the papilla of Vater at endoscopy, however, is difficult to reconcile with the above hypothesis. Similarly the lack of duct dilatation in a number of patients suspected to have the disorder does not readily fit in with a hypothesis of sphincter stenosis. Another confounding factor might be the possibility that sphincter of Oddi dysfunc-
7 What is sphincter of Oddi dysfunction? tion is just one of a number of bowel motility disorders which might afflict any one individual and directing therapy at one part of the gastrointestinal tract would not be expected to cure all symptoms. The first line of treatment usually tried in patients with suspected sphincter of Oddi dysfunction is administration of smooth muscle relaxant medications"` such as hyoscine-n-butylbromide, mebeverine HCL, dicyclomine HCL, glyceril trinitrate-sorbide nitrate and nifedipine. Response to these medications is variable and there are no prospective studies showing significant long-standing successful outcomes. Glyceril trinitrate - sorbide nitrate and nifedipine are associated with significant symtomatic side effects which limits their utilisation. The most effective form of therapy is division of the sphincter of Oddi either via endoscopy or transabdominal operation. Logic dictates that if the pain is produced by spasm of the sphincter then division of the sphincter should stop further episodes of pain. If the major problem relates solely to the biliary tract, all that needs to be divided is the choledochal part of the sphincter of Oddi. In those patients who develop recurrent pancreatitis as a result of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction, however, then division of both the choledochal and pancreatic duct components of the sphincter of Oddi should be performed.3"3' A number of studies have evaluated the effect of sphincterotomy on patients with suspected sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. In one study, a group of patients underwent manometry of the sphincter of Oddi. A selected subgroup subsequently had an endoscopic sphincterotomy and their clinical response was evaluated in relation to the manometric findings. There was no significant correlation between manometry and clinical outcome.32 In this study neither the patients nor the clinicians were blinded to the form of treatment. Furthermore, patient selection may have influenced the results as only those patients who had socially debilitating symptoms were offered sphincterotomy. This study does, however, question the results of a separate study which appraised clinical response in a group of patients who were randomly allocated to one of two groups - that is, sphincterotomy or sham sphincterotomy. All of these patients underwent sphincter of Oddi manometry before randomisation but the manometry was not used to determine treatment. On reviewing the manometry and correlating it with the clinical outcome, it was noted that patients with the stenotic pattern - that is, raised sphincter of Oddi basal pressure - were either cured or significantly improved, whilst those patients with the dyskinetic manometric changes showed no change after sphincterotomy.33 Interestingly, all other objective parameters of sphincter stenosis, such as dilated duct or delayed emptying of contrast from the bile duct did not correlate with either the manometry or the clinical outcome. One would expect, however, that division of the sphincter of Oddi should be effective in the treatment of all types of sphincter of Oddi manometric abnormality as effective division should eliminate all forms of dysfunction. The operation of transduodenal sphincteroplasty and pancreatic ductal septectomy has been performed in patients with sphincter of Oddi dysfunction producing recurrent pancreatitis. In these patients results comparable with those reported after endoscopic sphincterotomy for patients with raised basal pressure are reported.3"3' 759
8 760 Touli The selection of patients for appropriate and specific treatment has not been clearly defined."4 Current studies are under way evaluating the effect of treatment based on manometric findings. The results of these prospective randomised double blinded studies are eagerly awaited and it is hoped will assist in defining appropriate therapy for patients with sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. The assistance of the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia and Flinders Medical Centre Research Foundation is gratefully acknowledged. J TOOULI Department of Surgery, Flinders Medical Centre, Bedford Park, South Australia, 5042 References I Oddi R. D'une disposition a sphincter speciale de l'ouverture du canal cholidoque. Arch Ital Biol 1887; 8: Tondelli P, Gyr K. Postsurgical syndromes. Clin Gastroenterol 1983; 12: Nardi GL. Papillitis and stenosis of the sphincter of Oddi. Surg Clinics North Am 1973; 53: Toouli J, Roberts-Thomson I, Dent J, Lee J. Manometric disorders in patients with suspected sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Gastroenterology 1985; 88: Boyden EA. The sphincter of Oddi in man and certain representative mammals. Surgery 1937; 1: Boyden EA. The anatomy of the choledochoduodenal junction in man. Surgery 1957; 104: Toouli J, Geenen JE, Hogan WJ, Dodds WJ, Arndorfer RC. Sphincter of Oddi motor activity: a comparison between patients with common bile stones and controls. Gastroenterology 1982; 82: Toouli J, Dodds WJ, Honda R, et al. Motor function of the opossum sphincter of Oddi. J Clin Invest 1983; 71: Behar J, Biancani P. Effect of cholecystokinin and the octapeptide of cholecystokinin on the feline sphincter of Oddi and gallbladder. Mechanisms of action. J Clin Invest 1980; 66: Berci G, Johnson N. Functional studies of the extrahepatic biliary system in the dog by use of a controlled biliary fistula. Ann Surg 1965; 161: Worthley CS, Baker RA, Saccone GTP, lannos J, McGee M, Toouli J. Interdigestive and post-prandial contractile activity of the human sphincter of Oddi. Aust NZ J Med 1987; 17: Honda R, Toouli J, Dodds WJ, Sarna S, Hogan WJ, Itoh Z. Relationship of sphincter of Oddi spike bursts to gastrointestinal myoeletric activity in conscious opossums. J Clin Invest 1982; 69: Tondelli P, Gyr K, Stalder GA, Allgower M. The biliary tract. Cholecystectomy. Clin Gastroenterol 1979; 8: Toouli J, Roberts-Thomson I, Dent J, Lee J. Sphincter of Oddi manometric disorders in patients with idiopathic recurrent pancreatitis. Br J Surg 1985; 72: Roberts-Thomson I, Toouli J. Abnormal responses to morphine neostigmine in patients with undefined biliary-type pain. Gut 1985; 26: Bolondi L, Gaiani S, Gullo L and Labo G. Secretin administration induces a dilatation of the main pancreatic duct. Dig Dis Sci 1984; 29: Darweesh RMA, Dodds WJ, Hogan WJ, et al. Efficacy of quantitative hepatobiliary scintigraphy and fatty meal sonography for evaluating patients with suspected partial common duct obstruction. Gastroenterology 1988; 94: Roberts-Thomson IC, Toouli J, Blanchett W, Lichtenstein M and Andrews JT. Assessment of bile flow by radioscintigraphy in patients with biliary-type pain after cholecystectomy. Aust NZ J Med 1986; 16:
9 What is sphincter of Oddi dysfunction? Zcman RK, Burrell MI, Dobbins J, et al. Postcholecystectomy syndrome; evaluation using biliary scintigraphy and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Radiology 1985; 156: Lee RG, Gregg JA, Koroshetz AM, et al. Sphincter of Oddi stenosis using hepatobiliary scintigraphy and endoscopic manometry. Radiology 1985; 156: Geenen JE, Hogan WJ, Dodds WJ, Steward ET, Arndorfer RC. Intraluminal prcssurc recording from the human sphincter of Oddi. Gastroenterology 1980; 78: Toouli J. Perendoscopic versus intra-operative sphincter of Oddi manometry. Ital J Gastroenterol 1985; 17: Torsoli A, Corazziari E, Habib FI, et al. Frequencies and cyclical pattern of the human sphincter of Oddi phasic activity. Gut 1986; 27: Gregg JA, Carr-Locke DL. Endoscopic pancreatic and biliary manometry in pancreatic. biliary and papillary disease and after sphincteroplasty. Gut 1984; 25: Funch-Jensen P, Kruse A, Ravnsbaek J. Endoscopic sphincter of Oddi manometry in healthy volunteers. Scand J Gastroenterol 1987; 22: Toouli J, Roberts-Thomson IC, Dent J, Lee J. Sphincter of Oddi (SO) manometric disorders in patients with idiopathic relapsing pancreatitis. Br J Surg 1985; 72: Dodds WJ, Dent J, Hogan WJ, Patel FK, Toouli J, Arndorfcr RC. Paradoxical lower oesophageal sphincter contraction induced by cholecystokinin-octapeptide in patients with achalasia. Gastroenterology 1981; 80: Bar Meir S, Halpern Z, Bardan E. Nitrate therapy in a patient with papillary dysfunction. Am J Gastroenterol 1983; 78: Guclrud M, Mendoza S, Rossiter G, et al. Effect of nifedipine on sphincter of Oddi motor function in humans. Studies in healthy volunteers and patients with biliary dyskinesia [Abstracti. Gastroenterology 1987; 92: Moody FG, Becker JM, Potts JR. Transduodenal sphincteroplasty and transampullary septectomy for post-cholecystectomy pain. Ann Surg 1983; 197: Nardi GL, Michelassi F, Zannini P. Transduodenal sphincteroplasty 5-25 year follow-up of 89 patients. Ann Surg 1983; 198: Roberts-Thomson IC, Toouli J. Is endoscopic sphincterotomy for disabling biliary-type pain after cholecystectomy effective? Gastrointest Endosc 19,85; 31: Geenen JE, Hogan WJ, Dodds WJ, Toouli J, Venu RP. Longterm results of endoscopic sphincterotomy (ES) for treating patients with sphincter of Oddi (SO) dysfunction: A prospective study. Gastroenterology 1987; 92: Steinberg WM. Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction: a clinical controversy. Gastroenterology 1988; 95: Gut: first published as /gut on 1 June Downloaded from on 10 July 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
SPHINCTER OF ODDI DYSFUNCTION (SOD)
 SPHINCTER OF ODDI DYSFUNCTION (SOD) Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction refers to structural or functional disorders involving the biliary sphincter that may result in impedance of bile and pancreatic juice
SPHINCTER OF ODDI DYSFUNCTION (SOD) Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction refers to structural or functional disorders involving the biliary sphincter that may result in impedance of bile and pancreatic juice
Manometry based randomised trial of endoscopic sphincterotomy for sphincter of Oddi dysfunction
 98 GI Surgical Unit, Flinders Medical Centre, Adelaide, Australia J Toouli I C Roberts-Thomson G T P Saccone P Jeans MCox P Anderson C Worthley N Shanks A Craig Department of Gastroenterology, Royal North
98 GI Surgical Unit, Flinders Medical Centre, Adelaide, Australia J Toouli I C Roberts-Thomson G T P Saccone P Jeans MCox P Anderson C Worthley N Shanks A Craig Department of Gastroenterology, Royal North
Scintigraphy versus manometry in patients with suspected biliary sphincter of Oddi dysfunction
 35 BILIARY DISEASE Scintigraphy versus manometry in patients with suspected biliary sphincter of Oddi dysfunction A G Craig, D Peter, GTPSaccone, P Ziesing, A Wycherley, J Toouli... See end of article
35 BILIARY DISEASE Scintigraphy versus manometry in patients with suspected biliary sphincter of Oddi dysfunction A G Craig, D Peter, GTPSaccone, P Ziesing, A Wycherley, J Toouli... See end of article
Abnormal responses to morphine-neostigmine in patients with undefined biliary type pain
 Abnormal responses to morphine-neostigmine in patients with undefined biliary type pain I C ROBERTS-THOMSON AND J TOOULI Gut, 1985, 26, 1367-1372 From the Clinical Research Unit, The Walter and Eliza Hall
Abnormal responses to morphine-neostigmine in patients with undefined biliary type pain I C ROBERTS-THOMSON AND J TOOULI Gut, 1985, 26, 1367-1372 From the Clinical Research Unit, The Walter and Eliza Hall
Case Report (1) Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction. Case Report (3) Case Report (2) Case Report (4) Case Report (5)
 Dr David Westaby Imperial NHS Trust Imperial College Medical School London Case Report (1)! TD 33yr old male! Feb May 2010: Recurrent episodes of abdominal pain! June 2010 Episode severe abdominal pain
Dr David Westaby Imperial NHS Trust Imperial College Medical School London Case Report (1)! TD 33yr old male! Feb May 2010: Recurrent episodes of abdominal pain! June 2010 Episode severe abdominal pain
Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain
 Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain 1 patient with recurrent episodes of pain (not daily), in the epigastrium/right upper quadrant, lasting >30 mins, building to a steady level, interrupting
Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain 1 patient with recurrent episodes of pain (not daily), in the epigastrium/right upper quadrant, lasting >30 mins, building to a steady level, interrupting
Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction Type III, Manometry and Sphincterotomy: Sham Won, Game Over
 Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction Type III, Manometry and Sphincterotomy: Sham Won, Game Over C. Mel Wilcox, M.D., M.S.P.H. Professor of Medicine, Surgery and Pediatrics University of Alabama, Birmingham Basil
Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction Type III, Manometry and Sphincterotomy: Sham Won, Game Over C. Mel Wilcox, M.D., M.S.P.H. Professor of Medicine, Surgery and Pediatrics University of Alabama, Birmingham Basil
Sphincter of Oddi spasm (SOS) is a rare disorder whose diagnosis is a great clinical challenge.
 IJNM, 19(3): 75-80, 2004 Diagnosis of Sphincter of Oddi Spasm with Quantitative Cholescintigraphy Gerbail T. Krishnamurthy and Shakuntala Krishnamurthy Department of Nuclear Medicine Tuality Community
IJNM, 19(3): 75-80, 2004 Diagnosis of Sphincter of Oddi Spasm with Quantitative Cholescintigraphy Gerbail T. Krishnamurthy and Shakuntala Krishnamurthy Department of Nuclear Medicine Tuality Community
Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction: SOD after EPISOD, Now what do we do?
 Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction: SOD after EPISOD, Now what do we do? Priya A. Jamidar, M.D., FASGE Professor of Medicine, Director of Endoscopy Yale School Y A L E S CH OO L O F MEDIC IN E February in Connecticut
Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction: SOD after EPISOD, Now what do we do? Priya A. Jamidar, M.D., FASGE Professor of Medicine, Director of Endoscopy Yale School Y A L E S CH OO L O F MEDIC IN E February in Connecticut
Duration of Pain Is Correlated With Elevation in Liver Function Tests in Patients With Symptomatic Choledocholithiasis
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:1077 1082 Duration of Pain Is Correlated With Elevation in Liver Function Tests in Patients With Symptomatic Choledocholithiasis ALA I. SHARARA, NABIL M.
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:1077 1082 Duration of Pain Is Correlated With Elevation in Liver Function Tests in Patients With Symptomatic Choledocholithiasis ALA I. SHARARA, NABIL M.
Change in Bile Duct Pressure Responses After Cholecystectomy: Loss of Gallbladder as a Pressure Reservoir
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1984;87;1154-9 Change in Bile Duct Pressure Responses After Cholecystectomy: Loss of Gallbladder as a Pressure Reservoir MASAO TANAKA, SEIYO IKEDA, and FUMIO NAKAYAMA Department of Surgery
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1984;87;1154-9 Change in Bile Duct Pressure Responses After Cholecystectomy: Loss of Gallbladder as a Pressure Reservoir MASAO TANAKA, SEIYO IKEDA, and FUMIO NAKAYAMA Department of Surgery
The biliary tract transports, stores, and regulates. Functional Gallbladder and Sphincter of Oddi Disorders
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2006;130:1498 1509 Functional Gallbladder and Sphincter of Oddi Disorders JOSE BEHAR,* ENRICO CORAZZIARI, MOISES GUELRUD, WALTER HOGAN, STUART SHERMAN, and JAMES TOOULI # *Rhode Island
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2006;130:1498 1509 Functional Gallbladder and Sphincter of Oddi Disorders JOSE BEHAR,* ENRICO CORAZZIARI, MOISES GUELRUD, WALTER HOGAN, STUART SHERMAN, and JAMES TOOULI # *Rhode Island
Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
 Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is an imaging. technique that is able to non-invasively assess bile and pancreatic ducts,
 SECRETIN AUGMENTED MRCP Riccardo MANFREDI, MD, MBA, FESGAR Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is an imaging technique that is able to non-invasively assess bile and pancreatic ducts, in
SECRETIN AUGMENTED MRCP Riccardo MANFREDI, MD, MBA, FESGAR Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is an imaging technique that is able to non-invasively assess bile and pancreatic ducts, in
Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: What s the Verdict in 2014?
 SGNA March 2014 Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: What s the Verdict in 2014? Evan L. Fogel, M.D. Professor of Clinical Medicine ERCP Fellowship Director Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology Indiana University
SGNA March 2014 Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: What s the Verdict in 2014? Evan L. Fogel, M.D. Professor of Clinical Medicine ERCP Fellowship Director Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology Indiana University
Does Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction Even Exist Anymore?
 Does Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction Even Exist Anymore? Grace H. Elta, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine University of Michigan Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction Best studied clinical association: Biliary pain
Does Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction Even Exist Anymore? Grace H. Elta, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine University of Michigan Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction Best studied clinical association: Biliary pain
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 8/27/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 35 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 8/27/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 35 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: Where do we stand in 2015?
 IU GI Motility Conference August 5, 2015 Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: Where do we stand in 2015? Evan L. Fogel, M.D. Professor of Medicine ERCP Fellowship Director Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology
IU GI Motility Conference August 5, 2015 Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: Where do we stand in 2015? Evan L. Fogel, M.D. Professor of Medicine ERCP Fellowship Director Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology
Biliary tree dilation - and now what?
 Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Relationship of Sphincter of Oddi Spike Bursts
 Relationship of Sphincter of Oddi Spike Bursts to Gastrointestinal Myoelectric Activity in Conscious Opossums RYUICHI HONDA, JAMES TooULI, WYLIE J. DODDS, SUSHIL SARNA, WALTER J. HOGAN, and ZEN ITOH, Departments
Relationship of Sphincter of Oddi Spike Bursts to Gastrointestinal Myoelectric Activity in Conscious Opossums RYUICHI HONDA, JAMES TooULI, WYLIE J. DODDS, SUSHIL SARNA, WALTER J. HOGAN, and ZEN ITOH, Departments
Correspondence should be addressed to Hong Zhu; and Xiaoxing Chen; chen
 Hindawi Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2017, Article ID 9031438, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9031438 Research Article Manometric Measurement of the Sphincter of Oddi in Patients
Hindawi Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2017, Article ID 9031438, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9031438 Research Article Manometric Measurement of the Sphincter of Oddi in Patients
Action of various new analgesic drugs on the
 Gut, 1967, 8, 296 Action of various new analgesic drugs on the human common bile duct D. S. HOPTON AND H. B. TORRANCE From Manchester Royal Infirmary EDITORIAL COMMENT There is experimental evidence from
Gut, 1967, 8, 296 Action of various new analgesic drugs on the human common bile duct D. S. HOPTON AND H. B. TORRANCE From Manchester Royal Infirmary EDITORIAL COMMENT There is experimental evidence from
Key words: acetylcholine, capsaicin, presynaptic cholinergic neurons, postsynaptic cholinergic neurong truncal vagotomy
 Key words: acetylcholine, capsaicin, presynaptic cholinergic neurons, postsynaptic cholinergic neurong truncal vagotomy Fig. 2 Effects of hexamethonium (Co) on CCK8 infusion (2.5-80ng/kglmin)-induced gallbladder
Key words: acetylcholine, capsaicin, presynaptic cholinergic neurons, postsynaptic cholinergic neurong truncal vagotomy Fig. 2 Effects of hexamethonium (Co) on CCK8 infusion (2.5-80ng/kglmin)-induced gallbladder
SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction)
 SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction) SOD refers to the mechanical malfunctioning of the Sphincter of Oddi, which is the valve muscle that regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction) SOD refers to the mechanical malfunctioning of the Sphincter of Oddi, which is the valve muscle that regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
PREVALENCE OF SUBCLINICAL HYPOTHYROIDISM IN COMMON BILE DUCT STONE PATIENTS
 1 Original Article PREVALENCE OF SUBCLINICAL HYPOTHYROIDISM IN COMMON BILE DUCT STONE PATIENTS Ashok Kumar 1, Prem Chand 2, Vandana Singla 3, Vivek Pahuja 4, Associate Professor Surgery, Department of
1 Original Article PREVALENCE OF SUBCLINICAL HYPOTHYROIDISM IN COMMON BILE DUCT STONE PATIENTS Ashok Kumar 1, Prem Chand 2, Vandana Singla 3, Vivek Pahuja 4, Associate Professor Surgery, Department of
A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree
 A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree Thomas Hocker, HMS IV BIDMC Core Radiology Case Presentation September 17, 2007 Review of Normal Pancreaticobiliary Tract Anatomy
A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree Thomas Hocker, HMS IV BIDMC Core Radiology Case Presentation September 17, 2007 Review of Normal Pancreaticobiliary Tract Anatomy
Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, ,
 IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
Recurrent common bile duct stones as a late complication of endoscopic sphincterotomy
 Nzenza et al. BMC Gastroenterology (2018) 18:39 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-018-0765-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Recurrent common bile duct stones as a late complication of endoscopic sphincterotomy
Nzenza et al. BMC Gastroenterology (2018) 18:39 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-018-0765-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Recurrent common bile duct stones as a late complication of endoscopic sphincterotomy
Controversies in the management of acute pancreatitis
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (3) Vol., No. 3, Issue 7, 3-7 Controversies in the management of acute pancreatitis Singh DR 1, Mehta A, Dangol UMS 3 1 Lecturer, Medical Officer, 3 Lecturer, Dept.
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (3) Vol., No. 3, Issue 7, 3-7 Controversies in the management of acute pancreatitis Singh DR 1, Mehta A, Dangol UMS 3 1 Lecturer, Medical Officer, 3 Lecturer, Dept.
Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 6.01.30 Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Medical Policy Section Radiology Is12:2013sue 3:2005 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
MP 6.01.30 Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Medical Policy Section Radiology Is12:2013sue 3:2005 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) in a District General Hospital
 Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) in a District General Hospital Poster No.: C-1790 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit J. A. Maguire 1, H. Kasem 2, M. Akhtar 2, M. Strauss
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) in a District General Hospital Poster No.: C-1790 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit J. A. Maguire 1, H. Kasem 2, M. Akhtar 2, M. Strauss
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma
 Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma Authors: R. Revert Espí, Y. Fernandez Nuñez, I. Carbonell, D. P. Gómez valencia,
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma Authors: R. Revert Espí, Y. Fernandez Nuñez, I. Carbonell, D. P. Gómez valencia,
The effect of metoclopramide on gastroduodenal
 Gut, 1971, 12, 158-163 The effect of metoclopramide on gastroduodenal and gallbladder contractions A. G. JOHNSON From the Department of Surgery, Charing Cross Hospital Medical School, London SUMMARY The
Gut, 1971, 12, 158-163 The effect of metoclopramide on gastroduodenal and gallbladder contractions A. G. JOHNSON From the Department of Surgery, Charing Cross Hospital Medical School, London SUMMARY The
Management of the Mucin Filled Bile Duct. A Complication of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor of the Pancreas
 CASE REPORT Management of the Mucin Filled Bile Duct. A Complication of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor of the Pancreas Anand Patel, Louis Lambiase, Antonio Decarli, Ali Fazel Division of Gastroenterology
CASE REPORT Management of the Mucin Filled Bile Duct. A Complication of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor of the Pancreas Anand Patel, Louis Lambiase, Antonio Decarli, Ali Fazel Division of Gastroenterology
Sex-related differences in predicting choledocholithiasis using current American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy risk criteria
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2018) 31, 1-6 Sex-related differences in predicting choledocholithiasis using current American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy risk criteria Ankit Chhoda
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2018) 31, 1-6 Sex-related differences in predicting choledocholithiasis using current American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy risk criteria Ankit Chhoda
The Use of Pancreatoscopy in the Diagnosis of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor Lesions of the Pancreas
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:S53 S57 The Use of Pancreatoscopy in the Diagnosis of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor Lesions of the Pancreas KENJIRO YASUDA, MUNEHIRO SAKATA, MOOSE
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:S53 S57 The Use of Pancreatoscopy in the Diagnosis of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor Lesions of the Pancreas KENJIRO YASUDA, MUNEHIRO SAKATA, MOOSE
Contrast Material and Gallbladder Kinetics: Implications for Same Day Sonography After Intravenous Pyelography or CT Scanning
 Contrast Material and Gallbladder Kinetics: Implications for Same Day Sonography After Intravenous Pyelography or CT Scanning Omar Khan, MD, PhD, Rene Naipaul, RDMS, Rajendra Singh Rampaul, MB, BS, Vinesh
Contrast Material and Gallbladder Kinetics: Implications for Same Day Sonography After Intravenous Pyelography or CT Scanning Omar Khan, MD, PhD, Rene Naipaul, RDMS, Rajendra Singh Rampaul, MB, BS, Vinesh
Why would fatty foods aggravate the patient s RUQ pain? What effect does cholecystokinin (CCK) have on gastric emptying?
 CASE 28 A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with the acute onset of abdominal pain. Her pain is located to the right upper quadrant (RUQ) and radiates to the right shoulder. She reports
CASE 28 A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with the acute onset of abdominal pain. Her pain is located to the right upper quadrant (RUQ) and radiates to the right shoulder. She reports
Opioid adverse reactions not the usual suspects! DR ANDREW DAVIES
 Opioid adverse reactions not the usual suspects! DR ANDREW DAVIES Overview Introduction Musical hallucinations Charles Bonnet syndrome (Nightmares, vivid dreams) Sleep disordered breathing Sphincter of
Opioid adverse reactions not the usual suspects! DR ANDREW DAVIES Overview Introduction Musical hallucinations Charles Bonnet syndrome (Nightmares, vivid dreams) Sleep disordered breathing Sphincter of
University of Buea. Faculty of Health Sciences. Programme in Medicine
 Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
127 Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3
 CHAPTER 8 Summary Summary 127 In Chapter 1, a general introduction on the principles and applications of intraluminal impedance monitoring in esophageal disorders is provided. Intra-esophageal impedance
CHAPTER 8 Summary Summary 127 In Chapter 1, a general introduction on the principles and applications of intraluminal impedance monitoring in esophageal disorders is provided. Intra-esophageal impedance
The campaign on laboratory: focus on Gallstone Disease and ERCP
 The campaign on laboratory: focus on Gallstone Disease and ERCP Mauro Giuliani, MD, Specialist in Visceral Surgery, Vice Head Physician, Surgical Ward, Ospedale Regionale di Locarno Alberto Fasoli, MD,
The campaign on laboratory: focus on Gallstone Disease and ERCP Mauro Giuliani, MD, Specialist in Visceral Surgery, Vice Head Physician, Surgical Ward, Ospedale Regionale di Locarno Alberto Fasoli, MD,
REOPERATION AFTER CHOLECYSTECTOMY. THE ROLE OF THE CYSTIC DUCT STUMP
 HPB Surgery, 1991, Vol. 4, pp. 129-135 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 1991 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in the United Kingdom REOPERATION
HPB Surgery, 1991, Vol. 4, pp. 129-135 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 1991 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in the United Kingdom REOPERATION
Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction
 Curr Gastroenterol Rep (2010) 12:130 134 DOI 10.1007/s11894-010-0096-1 Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction John Baillie Published online: 10 March 2010 # Springer Science+Business Media, LLC 2010 Abstract Sphincter
Curr Gastroenterol Rep (2010) 12:130 134 DOI 10.1007/s11894-010-0096-1 Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction John Baillie Published online: 10 March 2010 # Springer Science+Business Media, LLC 2010 Abstract Sphincter
Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation
 Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation Poster No.: C-2617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational
Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation Poster No.: C-2617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
 Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Medical Imaging and Treatment of the Bile and Pancreatic Ducts CIE-02718 Understanding ERCP Brochure Update_F.indd 1 7/11/18 9:51 A Minimally Invasive
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Medical Imaging and Treatment of the Bile and Pancreatic Ducts CIE-02718 Understanding ERCP Brochure Update_F.indd 1 7/11/18 9:51 A Minimally Invasive
THE FELLOWSHIP COUNCIL ADVANCED GI SURGERY CURRICULUM FOR FLEXIBLE ENDOSCOPY
 THE FELLOWSHIP COUNCIL ADVANCED GI SURGERY CURRICULUM FOR FLEXIBLE ENDOSCOPY 1. Introduction While general and thoracic surgical training now require basic skills in flexible GI endoscopy, advanced training
THE FELLOWSHIP COUNCIL ADVANCED GI SURGERY CURRICULUM FOR FLEXIBLE ENDOSCOPY 1. Introduction While general and thoracic surgical training now require basic skills in flexible GI endoscopy, advanced training
ENDOSCOPIC TREATMENT OF A BILE DUCT
 HPB Surgery, 1990, Vol. 3, pp. 67-71 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 1990 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in the United Kingdom CASE REPORT
HPB Surgery, 1990, Vol. 3, pp. 67-71 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 1990 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in the United Kingdom CASE REPORT
Oesophageal Disorders
 Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
ACUTE CHOLANGITIS AS a result of an occluded
 Digestive Endoscopy 2017; 29 (Suppl. 2): 88 93 doi: 10.1111/den.12836 Current status of biliary drainage strategy for acute cholangitis Endoscopic treatment for acute cholangitis with common bile duct
Digestive Endoscopy 2017; 29 (Suppl. 2): 88 93 doi: 10.1111/den.12836 Current status of biliary drainage strategy for acute cholangitis Endoscopic treatment for acute cholangitis with common bile duct
THE CURRENT PLACE OF SHOCK-WAVE LITHOTRIPSY FOR BILE DUCT STONES. Department of Surgery AUSTRALIA
 HPB INTERNATIONAL 217 assessment of a predictive scoring system, both in patients treated by modern techniques and in a less highly selected group of patients, and the authors indicate that such studies
HPB INTERNATIONAL 217 assessment of a predictive scoring system, both in patients treated by modern techniques and in a less highly selected group of patients, and the authors indicate that such studies
Title: The endoscopic ultrasound-assisted Rendez-Vous technique for treatment of recurrent pancreatitis due to pancreas divisum and ansa pancreatica
 Title: The endoscopic ultrasound-assisted Rendez-Vous technique for treatment of recurrent pancreatitis due to pancreas divisum and ansa pancreatica Authors: Sergio López-Durán, Celia Zaera, Juan Ángel
Title: The endoscopic ultrasound-assisted Rendez-Vous technique for treatment of recurrent pancreatitis due to pancreas divisum and ansa pancreatica Authors: Sergio López-Durán, Celia Zaera, Juan Ángel
Variations of the Union between the Terminal Bile Duct and the Pancreatic Duct in Patients with Pancreaticobiliary Maljunction
 Yamanashi Med. J. 18(4), 67~ 75, 2003 Review Variations of the Union between the Terminal Bile Duct and the Pancreatic Duct in Patients with Pancreaticobiliary Maljunction Hideki FUJII 1) 1) Department
Yamanashi Med. J. 18(4), 67~ 75, 2003 Review Variations of the Union between the Terminal Bile Duct and the Pancreatic Duct in Patients with Pancreaticobiliary Maljunction Hideki FUJII 1) 1) Department
Gastrointestinal Motility 2: Intestinal and Colonic Motility Jack Grider, Ph.D.
 Gastrointestinal Motility 2: Intestinal and Colonic Motility Jack Grider, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Contrast the types of motility in the small intestine. 2. Describe the neural circuits that mediate peristalsis.
Gastrointestinal Motility 2: Intestinal and Colonic Motility Jack Grider, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Contrast the types of motility in the small intestine. 2. Describe the neural circuits that mediate peristalsis.
Endoscopic Sphincterotomy and Risk of Malignancy in the Bile Ducts, Liver, and Pancreas
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2008;6:1049 1053 Endoscopic Sphincterotomy and Risk of Malignancy in the Bile Ducts, Liver, and Pancreas CECILIA STRÖMBERG,* JUHUA LUO, LARS ENOCHSSON,* URBAN ARNELO,*
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2008;6:1049 1053 Endoscopic Sphincterotomy and Risk of Malignancy in the Bile Ducts, Liver, and Pancreas CECILIA STRÖMBERG,* JUHUA LUO, LARS ENOCHSSON,* URBAN ARNELO,*
Endoscopic Management of the Iatrogenic CBD Injury
 The Liver Week 2014, Jeju, Korea Endoscopic Management of the Iatrogenic CBD Injury Jong Ho Moon, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine Soon Chun Hyang University School of Medicine Bucheon/Seoul, KOREA
The Liver Week 2014, Jeju, Korea Endoscopic Management of the Iatrogenic CBD Injury Jong Ho Moon, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine Soon Chun Hyang University School of Medicine Bucheon/Seoul, KOREA
Chronic Pancreatitis: When to Scope? Gregory A. Cote, MD, MS Assistant Professor of Medicine Indiana University School of Medicine
 Chronic Pancreatitis: When to Scope? Gregory A. Cote, MD, MS Assistant Professor of Medicine Indiana University School of Medicine Endoscopy & Chronic Pancreatitis Diagnosis EUS ERCP Exocrine Function
Chronic Pancreatitis: When to Scope? Gregory A. Cote, MD, MS Assistant Professor of Medicine Indiana University School of Medicine Endoscopy & Chronic Pancreatitis Diagnosis EUS ERCP Exocrine Function
Gallstones Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. Gutscharity.org.uk
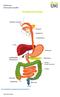 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about gallstones Gall is an old-fashioned word for bile, a liquid made in the liver and stored in the gall bladder
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about gallstones Gall is an old-fashioned word for bile, a liquid made in the liver and stored in the gall bladder
The Frequency of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Nutcracker Esophagus and the Effect of Acid-Reduction Therapy on the Motor Abnormality
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.4, December 2000 The Frequency of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Nutcracker Esophagus and the Effect of Acid-Reduction Therapy on the Motor Abnormality Saleh Mohsen
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.4, December 2000 The Frequency of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Nutcracker Esophagus and the Effect of Acid-Reduction Therapy on the Motor Abnormality Saleh Mohsen
Management of Pancreatic Fistulae
 Management of Pancreatic Fistulae Jose Ramos University of the Witwatersrand Donald Gordon Medical Centre Fistula definition A Fistula is a permanent abnormal passageway between two organs (epithelial
Management of Pancreatic Fistulae Jose Ramos University of the Witwatersrand Donald Gordon Medical Centre Fistula definition A Fistula is a permanent abnormal passageway between two organs (epithelial
Acute Pancreatitis. Case: NG. Idiopathic Pancreatitis is Common. Investigation and Management of Idiopathic Acute Recurrent Pancreatitis (IARP)
 BRIGHAM AND WOMENS HOSPITAL Investigation and Management of (IARP) Acute Pancreatitis j Darwin L. Conwell MD, MS Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Case: NG 54 year old female
BRIGHAM AND WOMENS HOSPITAL Investigation and Management of (IARP) Acute Pancreatitis j Darwin L. Conwell MD, MS Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Case: NG 54 year old female
Journal of Interventional Gastroenterology A Combination of Snare Polypectomy and APC Therapy for Prolapsing Common Bile Duct Adenoma
 Journal of Interventional Gastroenterology A Combination of Snare Polypectomy and APC Therapy for Prolapsing Common Bile Duct Adenoma --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number: Full Title: Article Type: Section/Category:
Journal of Interventional Gastroenterology A Combination of Snare Polypectomy and APC Therapy for Prolapsing Common Bile Duct Adenoma --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number: Full Title: Article Type: Section/Category:
Endoscopic Papillary Balloon Dilation with Large Balloon after Limited Sphincterotomy for Retrieval of Choledocholithiasis
 Yonsei Medical Journal Vol. 47, No. 6, pp. 805-810, 2006 Endoscopic Papillary Balloon Dilation with Large Balloon after Limited Sphincterotomy for Retrieval of Choledocholithiasis Seungmin Bang, Myoung
Yonsei Medical Journal Vol. 47, No. 6, pp. 805-810, 2006 Endoscopic Papillary Balloon Dilation with Large Balloon after Limited Sphincterotomy for Retrieval of Choledocholithiasis Seungmin Bang, Myoung
CPT COD1NG UPDATES Gastroenterology CPT Advisors
 2014 CPT COD1NG UPDATES Gastroenterology CPT Advisors Joel V. Brill, MD, AGA CPT Advisor Daniel C. DeMarco, MD, ACG CPT Advisor Glenn D. Littenberg, MD, ASGE CPT Advisor The American College of Gastroenterology
2014 CPT COD1NG UPDATES Gastroenterology CPT Advisors Joel V. Brill, MD, AGA CPT Advisor Daniel C. DeMarco, MD, ACG CPT Advisor Glenn D. Littenberg, MD, ASGE CPT Advisor The American College of Gastroenterology
Biliary Dyspepsia: Functional Gallbladder and Sphincter of Oddi Disorders
 Chapter 7 Biliary Dyspepsia: Functional Gallbladder and Sphincter of Oddi Disorders Meena Mathivanan, Liisa Meddings and Eldon A. Shaffer Additional information is available at the end of the chapter http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/56779
Chapter 7 Biliary Dyspepsia: Functional Gallbladder and Sphincter of Oddi Disorders Meena Mathivanan, Liisa Meddings and Eldon A. Shaffer Additional information is available at the end of the chapter http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/56779
Primary and secondary esophageal contractions in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (6) 39: 27-31 ISSN -879X 27 Primary and secondary esophageal contractions in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease C.G. Aben-Athar and R.O.
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (6) 39: 27-31 ISSN -879X 27 Primary and secondary esophageal contractions in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease C.G. Aben-Athar and R.O.
oesophageal sphincter pressure in man
 Gut, 1987, 28, 1564-1568 Effect of the diaphragmatic contraction on lower oesophageal sphincter pressure in man R K MITTAL, D F ROCHESTER, AND R W McCALLUM From the Department of Internal Medicine, University
Gut, 1987, 28, 1564-1568 Effect of the diaphragmatic contraction on lower oesophageal sphincter pressure in man R K MITTAL, D F ROCHESTER, AND R W McCALLUM From the Department of Internal Medicine, University
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy
 Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
Unresolved Issues about Post-ERCP Pancreatitis: An Overview
 Unresolved Issues about Post-ERCP Pancreatitis: An Overview Pier Alberto Testoni Division of Gastroenterology and Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, University Vita-Salute San Raffaele, IRCCS San Raffaele Hospital.
Unresolved Issues about Post-ERCP Pancreatitis: An Overview Pier Alberto Testoni Division of Gastroenterology and Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, University Vita-Salute San Raffaele, IRCCS San Raffaele Hospital.
Abstract. Abnormal peristaltic waves like aperistalsis of the esophageal body, high amplitude and broader waves,
 Original Article Esophageal Motility Disorders in Diabetics Waquaruddin Ahmed, Ejaz Ahmed Vohra Department of Medicine, Dr. Ziauddin Medical University, Karachi. Abstract Objective: To see the presence
Original Article Esophageal Motility Disorders in Diabetics Waquaruddin Ahmed, Ejaz Ahmed Vohra Department of Medicine, Dr. Ziauddin Medical University, Karachi. Abstract Objective: To see the presence
Principles of ERCP: papilla cannulation, indications/contraindications and risks. Dr. med. Henrik Csaba Horváth PhD
 Principles of ERCP: papilla cannulation, indications/contraindications and risks Dr. med. Henrik Csaba Horváth PhD Evolution of ERCP 1968. 1970s ECPG Endoscopic CholangioPancreatoGraphy Japan 1974 Biliary
Principles of ERCP: papilla cannulation, indications/contraindications and risks Dr. med. Henrik Csaba Horváth PhD Evolution of ERCP 1968. 1970s ECPG Endoscopic CholangioPancreatoGraphy Japan 1974 Biliary
Periampullary cyst: a surgically remediable cause of pancreatitis
 Gut, 1987, 28, 358-362 Case report Periampullary cyst: a surgically remediable cause of pancreatitis I KALVARIA, P C BORNMAN, A H GIRDWOOD, AND I N MARKS From the Gastrointestinal Clinic, Groote Schuur
Gut, 1987, 28, 358-362 Case report Periampullary cyst: a surgically remediable cause of pancreatitis I KALVARIA, P C BORNMAN, A H GIRDWOOD, AND I N MARKS From the Gastrointestinal Clinic, Groote Schuur
What can you expect after your ERCP?
 ERCP Explained and respond to bed rest, pain relief and fasting to rest the gut with the patient needing to stay in hospital for only a few days. Some patients develop severe pancreatitis and may require
ERCP Explained and respond to bed rest, pain relief and fasting to rest the gut with the patient needing to stay in hospital for only a few days. Some patients develop severe pancreatitis and may require
Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology
 Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology This curriculum is intended for clinicians who perform endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) in gastroenterology. It includes standards for theoretical
Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology This curriculum is intended for clinicians who perform endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) in gastroenterology. It includes standards for theoretical
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Esophageal Manometry: Assessment of Interpreter Consistency
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:218 224 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Esophageal Manometry: Assessment of Interpreter Consistency DEVJIT S. NAYAR, FARAH KHANDWALA, EDGAR ACHKAR, STEVEN S. SHAY, JOEL
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:218 224 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Esophageal Manometry: Assessment of Interpreter Consistency DEVJIT S. NAYAR, FARAH KHANDWALA, EDGAR ACHKAR, STEVEN S. SHAY, JOEL
stents she/he is providing appropriate or inappropriate care?
 Pancreatic Stents Are They Now State of the Art Care? To Help Limit Post ERCP Pancreatitis Glen A. Lehman, M.D. Professor of Medicine and Radiology Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology Indiana University
Pancreatic Stents Are They Now State of the Art Care? To Help Limit Post ERCP Pancreatitis Glen A. Lehman, M.D. Professor of Medicine and Radiology Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology Indiana University
Presence of choledocholithiasis in patients undergoing cholecystectomy for mild biliary pancreatitis
 Original Article Presence of choledocholithiasis in patients undergoing cholecystectomy for mild biliary pancreatitis Pradhan S 1, Shah S 2, Maharjan S 2, Shah JN 3 1 2 2 3 Professor, Patan hospital Correspondence:
Original Article Presence of choledocholithiasis in patients undergoing cholecystectomy for mild biliary pancreatitis Pradhan S 1, Shah S 2, Maharjan S 2, Shah JN 3 1 2 2 3 Professor, Patan hospital Correspondence:
What part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract is composed of striated muscle and smooth muscle?
 CASE 29 A 34-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with the complaint of increased difficulty swallowing both solid and liquid foods. He notices that he sometimes has more difficulty when
CASE 29 A 34-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with the complaint of increased difficulty swallowing both solid and liquid foods. He notices that he sometimes has more difficulty when
Diagnosis of chronic Pancreatitis. Christoph Beglinger, University Hospital Basel, Switzerland
 Diagnosis of chronic Pancreatitis Christoph Beglinger, University Hospital Basel, Switzerland Pancreatitis Pancreas Pancreas - an organ that makes bicarbonate to neutralize gastric acid, enzymes to digest
Diagnosis of chronic Pancreatitis Christoph Beglinger, University Hospital Basel, Switzerland Pancreatitis Pancreas Pancreas - an organ that makes bicarbonate to neutralize gastric acid, enzymes to digest
FUNCTIONAL DISORDERS ROME IV CRITERIA AND DIAGNOSTIC QUESTIONNAIRE DDW 2016,REVIEW. Presented by; Marjan Mokhtare Gastroenterologist, IUMS
 FUNCTIONAL DISORDERS ROME IV CRITERIA AND DIAGNOSTIC QUESTIONNAIRE DDW 2016,REVIEW Presented by; Marjan Mokhtare Gastroenterologist, IUMS Functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs), the most common
FUNCTIONAL DISORDERS ROME IV CRITERIA AND DIAGNOSTIC QUESTIONNAIRE DDW 2016,REVIEW Presented by; Marjan Mokhtare Gastroenterologist, IUMS Functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs), the most common
Esophageal Manometry. John M. Wo, M.D. October 1, 2009
 Esophageal Manometry John M. Wo, M.D. October 1, 2009 Esophageal Manometry Anatomy and physiology of the esophagus Conventional esophageal manometry High resolution esophageal manometry (Pressure Topography)
Esophageal Manometry John M. Wo, M.D. October 1, 2009 Esophageal Manometry Anatomy and physiology of the esophagus Conventional esophageal manometry High resolution esophageal manometry (Pressure Topography)
Radiology. Gastrointestinal. Transient Intraluminal Diverticulum of the Esophagus: A Significant Flow Artifact. Farooq P. Agha
 Gastrointest Radiol 9:9%103 (1984) Gastrointestinal Radiology 9 Springer-Verlag 1984 Transient Intraluminal Diverticulum of the Esophagus: A Significant Flow Artifact Farooq P. Agha Department of Radiology,
Gastrointest Radiol 9:9%103 (1984) Gastrointestinal Radiology 9 Springer-Verlag 1984 Transient Intraluminal Diverticulum of the Esophagus: A Significant Flow Artifact Farooq P. Agha Department of Radiology,
The Pancreas. Basic Anatomy. Endocrine pancreas. Exocrine pancreas. Pancreas vasculature. Islets of Langerhans. Acinar cells Ductal System
 SGNA: Back to Basics Rogelio G. Silva, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Advocate Christ Medical Center GI
SGNA: Back to Basics Rogelio G. Silva, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Advocate Christ Medical Center GI
Making ERCP Easy: Tips From A Master
 Making ERCP Easy: Tips From A Master Raj J. Shah, M.D., FASGE Associate Professor of Medicine University of Colorado School of Medicine Co-Director, Endoscopy Director, Pancreaticobiliary Endoscopy Services
Making ERCP Easy: Tips From A Master Raj J. Shah, M.D., FASGE Associate Professor of Medicine University of Colorado School of Medicine Co-Director, Endoscopy Director, Pancreaticobiliary Endoscopy Services
Setting The study setting was hospital. The economic analysis was carried out in California, USA.
 Preoperative versus postoperative endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in mild to moderate gallstone pancreatitis: a prospective randomized trial Chang L, Lo S, Stabile B E, Lewis R J, Toosie
Preoperative versus postoperative endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in mild to moderate gallstone pancreatitis: a prospective randomized trial Chang L, Lo S, Stabile B E, Lewis R J, Toosie
Cause of Acute Pancreatitis in A Case
 2008 19 531-535 Pancreas Divisum An Infrequent Cause of Acute Pancreatitis in A Case Cheuk-Kay Sun 1, Jui-Hao Chen 1, Kuo-Ching Yang 1, and Chin-Chu Wu 2 1 Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal
2008 19 531-535 Pancreas Divisum An Infrequent Cause of Acute Pancreatitis in A Case Cheuk-Kay Sun 1, Jui-Hao Chen 1, Kuo-Ching Yang 1, and Chin-Chu Wu 2 1 Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal
Mirizzi syndrome with an unusual type of biliobiliary fistula a case report
 Kawaguchi et al. Surgical Case Reports (2015) 1:51 DOI 10.1186/s40792-015-0052-2 CASE REPORT Mirizzi syndrome with an unusual type of biliobiliary fistula a case report Tsutomu Kawaguchi 1,2*, Tadao Itoh
Kawaguchi et al. Surgical Case Reports (2015) 1:51 DOI 10.1186/s40792-015-0052-2 CASE REPORT Mirizzi syndrome with an unusual type of biliobiliary fistula a case report Tsutomu Kawaguchi 1,2*, Tadao Itoh
Positive correlation between symptoms and circulating
 Gut, 1985, 26, 1059-1064 Positive correlation between symptoms and circulating motilin, pancreatic polypeptide and gastrin concentrations in functional bowel disorders D M PRESTON, T E ADRIAN, N D CHRISTOFIDES,
Gut, 1985, 26, 1059-1064 Positive correlation between symptoms and circulating motilin, pancreatic polypeptide and gastrin concentrations in functional bowel disorders D M PRESTON, T E ADRIAN, N D CHRISTOFIDES,
The Biliary System. Contrast medium: Biloptin Telepaque Cholebrin Solu-Biloptin
 The Biliary System Oral Cholecystography (OC) 1. To demonstrate suspected pathology in the gall-bladder. 2. The cystic duct and common bile duct may also be seen. 1. Severe hepatorenal disease 2. Acute
The Biliary System Oral Cholecystography (OC) 1. To demonstrate suspected pathology in the gall-bladder. 2. The cystic duct and common bile duct may also be seen. 1. Severe hepatorenal disease 2. Acute
Case Rep Gastroenterol 2010;4:71 78 DOI: /
 71 Gallstone Ileus, Bouveret s Syndrome and Choledocholithiasis in a Patient with Billroth II Gastrectomy A Case Report of Combined Endoscopic and Surgical Therapy R. Fejes G. Kurucsai A. Székely F. Luka
71 Gallstone Ileus, Bouveret s Syndrome and Choledocholithiasis in a Patient with Billroth II Gastrectomy A Case Report of Combined Endoscopic and Surgical Therapy R. Fejes G. Kurucsai A. Székely F. Luka
Hepatocellular Dysfunction
 www.nuclearmd.com A Normal HIDA Scan Dynamic or Static images of the abdomen are acquired after the IV administration 6-8 mci of Tc99m disofenin or mebrofenin, for one hour. Patients have to be NPO for
www.nuclearmd.com A Normal HIDA Scan Dynamic or Static images of the abdomen are acquired after the IV administration 6-8 mci of Tc99m disofenin or mebrofenin, for one hour. Patients have to be NPO for
Metoclopramide in gastrooesophageal reflux
 Metoclopramide in gastrooesophageal reflux C. STANCIU AND JOHN R. BENNETT From the Gastrointestinal Unit, Hull Royal Infirmary Gut, 1973, 14, 275-279 SUMMARY In 3 patients with gastrooesophageal reflux,
Metoclopramide in gastrooesophageal reflux C. STANCIU AND JOHN R. BENNETT From the Gastrointestinal Unit, Hull Royal Infirmary Gut, 1973, 14, 275-279 SUMMARY In 3 patients with gastrooesophageal reflux,
A Guide to Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders
 A Guide to Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders Albert J. Bredenoord André Smout Jan Tack A Guide to Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders Albert J. Bredenoord Gastroenterology and Hepatology Academic Medical
A Guide to Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders Albert J. Bredenoord André Smout Jan Tack A Guide to Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders Albert J. Bredenoord Gastroenterology and Hepatology Academic Medical
The role of ERCP in chronic pancreatitis
 The role of ERCP in chronic pancreatitis Marianna Arvanitakis Erasme University Hospital, ULB, Brussels, Belgium 10 th Nottingham Endoscopy Masterclass SPEAKER DECLARATIONS This presenter has the following
The role of ERCP in chronic pancreatitis Marianna Arvanitakis Erasme University Hospital, ULB, Brussels, Belgium 10 th Nottingham Endoscopy Masterclass SPEAKER DECLARATIONS This presenter has the following
Percutaneous Removal of Biliary Stone from Anomalous Right Hepatic Duct
 Percutaneous Removal of Biliary Stone from Anomalous Right Hepatic Duct Pages with reference to book, From 94 To 96 Tanveer ul Haq, Mohammed Younus Sheikh, Changes Khan Jadun, M.N. Ahmad, Yousuf H. Husen
Percutaneous Removal of Biliary Stone from Anomalous Right Hepatic Duct Pages with reference to book, From 94 To 96 Tanveer ul Haq, Mohammed Younus Sheikh, Changes Khan Jadun, M.N. Ahmad, Yousuf H. Husen
Achalasia is a rare disease with an annual incidence estimated REVIEWS. Erroneous Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Achalasia
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2011;9:1020 1024 REVIEWS Erroneous Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Achalasia BOUDEWIJN F. KESSING, ALBERT J. BREDENOORD, and ANDRÉ J. P. M. SMOUT
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2011;9:1020 1024 REVIEWS Erroneous Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Achalasia BOUDEWIJN F. KESSING, ALBERT J. BREDENOORD, and ANDRÉ J. P. M. SMOUT
sigmoid for diverticular disease
 Gut, 1970, 11, 121-125 Rectal and colonic studies after resection of the sigmoid for diverticular disease T. G. PARKS From the Department of Surgery, Queen's University of Belfast, and St. Mark's Hospital,
Gut, 1970, 11, 121-125 Rectal and colonic studies after resection of the sigmoid for diverticular disease T. G. PARKS From the Department of Surgery, Queen's University of Belfast, and St. Mark's Hospital,
A LEADER IN ADVANCED ENDOSCOPY AND HEPATOBILIARY SURGERY
 A LEADER IN ADVANCED ENDOSCOPY AND HEPATOBILIARY SURGERY St. Peter s Hospital Advanced Endoscopy & Hepatobiliary Center Welcome The St. Peter s Hospital Advanced Endoscopy & Hepatobiliary Center is a leader
A LEADER IN ADVANCED ENDOSCOPY AND HEPATOBILIARY SURGERY St. Peter s Hospital Advanced Endoscopy & Hepatobiliary Center Welcome The St. Peter s Hospital Advanced Endoscopy & Hepatobiliary Center is a leader
