Action of various new analgesic drugs on the
|
|
|
- Jeffrey McDonald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gut, 1967, 8, 296 Action of various new analgesic drugs on the human common bile duct D. S. HOPTON AND H. B. TORRANCE From Manchester Royal Infirmary EDITORIAL COMMENT There is experimental evidence from the studies of these authors that phenazocine (Narphen) might be a particularly suitable analgesic for the treatment of biliary pain. The pain of patients suffering from biliary tract disease is usually treated by administering morphine or pethidine, with or without an antispasmodic drug such as aminophylline; but both these analgesics cause spasm of the sphincters controlling the flow of bile into the duodenum. In 1936, Butsch, McGowan, and Walters reported typical biliary colic occurring after giving morphine to patients following cholecystectomy and T-tube drainage of the common duct, and were able to correlate this pain with a rise in common bile duct pressure. Bergh and Layne (190) attributed post-morphine pain to spasm of the sphincter of Oddi. More recently, raised serum amylase and serum lipase levels have been demonstrated in normal subjects after giving morphine and secretin (Myhre, Nesbitt, and Hurly, 199; Burke, Plummer, and Bradford, 1950). Radiographic studies have conclusively shown spasm of the common bile duct sphincter after giving morphine (Caroli, Porcher, Pequignot, and Delattre, 1960). Pethidine can also be shown to cause spasm of the sphincter and raise the bile duct pressure although to a less but still significant extent than morphine (Figs. 1 and 2). The immediate cause of biliary pain is thought to be either increased duct pressure or ischaemia induced by sphincter muscle spasm or a combination of both factors. Often these two conditions will be aggravated by local inflammation or irritation such as that caused by a stone passing down the duct or arrested in the lower portion of the duct. It is clearly illogical to treat biliary pain with drugs which cause sphincter spasm and increased bile duct pressure; but because of the central analgesic and sedative effects of morphine and pethidine it is justified to use these drugswhen no better isavailable. During recent years several powerful new analgesic drugs have been made available, but little work has been reported on their action on the biliary tract. Efron (1958) reported that Avafortan caused no spasm of the biliary sphincter, and recommended this drug for treating pain of common bile duct origin. Unfortunately, the active principle in Avafortan is amidopyrine; on occasion this drug causes agranulocytosis and its use is no longer justified. Boulter (1961) investigated the effect of levorphanol (Dromoran) on the flow rate of saline through the human common bile duct and concluded that this drug caused spasm of the sphincter as marked as that caused by morphine. Robelet, Bizard-Gregoire, and Bizard (1965) reported the effect of dextromoramide (Palfium) on the perfused common bile duct of the guinea-pig. Intravenous injection of this drug stopped the perfusion, indicating spasm of the sphincter. Crema, Benzi, Frigo, and Berte (1965), after perfusion experiments on the bile ducts of dogs and cats, concluded that 'morphine, meperidine, levorphanol, methadone, and dextromoramide injected intravenously were strongly active on the terminal bile duct, reducing flow through it'. This paper reports the effects of pressure in the human common bile duct of five new analgesic drugs administered parenterally. METHOD Investigations were made with the willing cooperation of patients after cholecystectomy and during T-tube drainage of the common bile duct. Pressure changes in the common bile duct were transmitted through a T-tube connected to a saline-filled glass U-tube manometer. Fluctuations in pressure were recorded by an ink-writing pen attached to a float. Zero reference was obtained for each investigation by adjusting the 5 cm. mark of the manometer to the level at which the T-tube entered the skin. This arbitrary reference point was chosen for its convenience in recognition and because the important measurement was of changes in common bile duct pressure rather than absolute values. The apparatus was primed with sterile normal saline at the 296
2 Action of various new analgesic drugs on the human common bile duct beginning of the recording but no attempt was made to perfuse the duct. Any pressure rise was thus dependent on the continued secretion of bile by the liver, and it was assumed that this occurred at a constant rate during the investigation. No investigation was carried out less than 10 days after operation. Fluctuation in the rate of bile secretion was minimized by fasting of the patient although drinks of water were allowed. In most of the patients the common bile duct had been explored by passing a sound downwards through the sphincter into the duodenum. In some of these patients a duodenotomy had then been carried out and the mucosa at the tip of the ampulla of Vater had been incised. In no case, however, was a sphincterotomy performed which would extend as high as the choledochal sphincter. ASSESSMENT OF PRESSURE CHANGES The pressure changes after injecting morphine and FIG. 1. FIG. 2. MORPHINE (10 mg i.m.) pethidine are well recognized and these were used as a basis for comparison of the effects of the new analgesics. Any rise in pressure was classified under one of four headings. MARKED pressure rise, 10 cm. or more, usually occurs after giving morphine. MODERATE pressure rise, 5-10 cm., usually occurs after giving pethidine. MINIMAL pressure rise, less than 5 cm. or a sharp spike on the tracing lasting for less than five minutes, may be due to small positional changes of the patient, or to coughing or straining. NIL; no change in pressure. RESULTS Morphine (10 mg. i.m.) was administered on four occasions and a marked rise in pressure was recorded each time (Fig. 1). Pethidine (100 mg. i.m.) was given on four 15 min Typical tracing showing marked rise in common bile duct pressure after giving morphine, 10 mg. intramuscularly. PETHIDINE (100 i.m.) Tracing ofpressure in common bile duct showing a moderate rise after giving pethidine, 100 mg. intramuscularly. 15 min 297
3 298 Drug Proprietary Name Dromoran Palium Doloxene Operidine Narphen Drug Morphine Pethidine Dromoran Palfium Doloxene Phenoperidine Narphen Approved Name Levorphanol Dextromoramide Dextropropoxyphene Hydrochloride Phenoperidine Phenazocine TABLE II EFFECTS OF FIVE DRUGS ON BILIARY PRESSURE No. of Effect on Pressure in Common Bile Duct Investigations D. S. Hopton and H. B. Torrance TABLE I DETAILS OF THE FIVE DRUGS TESTED Analgesic Strength 2 mg. i.m. comparable with 10 mg. morphine i.m. 5 mg. i.m. comparable with 10 mg. morphine i.m. Comparable with codeine 2 mg. i.m. comparable with 10 mg. morphine i.m. 2 mg. i.m. stronger than 15 mg. morphine i.m. Nil Minimal Moderate Marked (5 cm. or (5-10 cm.) (10cm.) 5 min.) occasions also and a moderate pressure rise was recorded on each occasion (Fig. 2). The five new analgesics which were investigated are listed in Table I, and Table LI summarizes the results. LEVORPHANOL (DROMORAN) This strong analgesic was given as a 2 mg. intramuscular injection. It was administered on three occasions to different patients. On all three occasions, the pressure rose, twice to a marked extent and once to a moderate extent. DEXTROMORAMIDE (PALFIUM) This strong analgesic was given four times by intramuscular injection of FIG S min 3 2 NARPHEN 2 mg i.m. Route of Administration Oral Intramuscular Intravenous mg. On two occasions a moderate rise in pressure occurred and on two occasions a minimal rise in pressure occurred. DEXTROPROPOXYPHENE HYDROCHLORIDE (DOLOXENE) This relatively weak analgesic is marketed in tablet form only in the United Kingdom. However, the manufacturers provided 100 mg. ampoules for intramuscular injection and this drug was administered orally twice and by injection three times. On no occasion was any change in pressure recorded. PHENOPERIDINE (OPERIDINE: DIPHENYL PROPYLAMINE) The degree of analgesia obtained with this drug depends upon the dose. Two mg. intramuscularly produces a strong analgesic effect. Phenoperidine was given intramuscularly nine times in this dosage and 1 mg. was given intravenously twice. On eight occasions, no pressure rise was recorded. Three times, including both those occasions when the drug was given by intravenous injection, a minimal pressure rise occurred. PHENAZOCINE (NARPHEN) This very strong analgesic was given six times as a 2 mg. intramuscular injection. On four occasions, no pressure rise was recorded, but two injections were followed by minimal rises in pressure (Fig. 3). Tracing ofpressure in common bile duct showing a minimal rise afterphenazocine (Narphen), 2 mg. intramuscularly. 9 6
4 Action of various new analgesic drugs on the human common bile duct 299 DISCUSSION analgesic. If given in slightly larger doses, it will depress respiration to a dangerous extent. Phenazocine (Narphen) is a new potent narcotic analgesic which does not cause a rise in biliary pressure. This drug is less likely to cause respiratory depression, hypotension, or nausea than an equally potent dose of morphine, and tolerance develops more slowly. The effects of the drug are reversed by Nallorphine (Di Pillo, Younger, Scarpa, and Edson, 1960). It has also been demonstrated that phenazocine, unlike morphine, has little or no The structure of the sphincter of Oddi at the lower end of the common bile duct has been fully described by Boyden (1957). He clearly demonstrated that the sphincter of Oddi is a composite structure. The ampullary or papillary sphincter surrounds the tip of the ampulla of Vater and the common bile duct and pancreatic duct each have a separate sphincter. The biliary sphincter consists of two parts, the superior and inferior bile duct or choledochal sphincters, and the flow of bile into the duodenum is mainly controlled by these muscles. The duodenal musculature may also have some constricting action around the ampulla of Vater and certainly raised pressure in the duodenal lumen could cause obstruction to the flow of bile from the common bile duct and thus cause a rise in bile duct pressure (Kock, Kewenter, and Jacobsson, 196). However, the extent to which these separate factors influence the bile duct pressure is still not clear and our investigations did not differentiate between the possible causes of the obstruction to bile flow. It would seem, however, that the most important cause of raised pressure in the bile duct after giving analgesic drugs is contraction of the choledochal sphincter. Both levorphanol (Dromoran) and dextromoramide (Palfium) produced marked or moderate rises in pressure in the common bile duct after doses adequate to give useful analgesia. They show, therefore, no advantage over morphine or pethidine. Dextropropoxyphene hydrochloride (Doloxene) has no apparent effect on common bile duct pressure and so presumably does not cause spasm of the biliary sphincters. It is, however, a comparatively weak analgesic, being more comparable with codeine than with morphine or pethidine (Gruber, 1957). Although it has been passed by the Dunlop Committee for intramuscular injection, it is not generally available in the United Kingdom in this form though it has been extensively used in tablet form. Dextropropoxyphene hydrochloride (Doloxene) is unlikely to be of value in treating the severe pain associated with biliary colic and pancreatitis. We have, however, used it with success on two occasions in patients with chronic abdominal pain apparently due to secondary deposits in the liver arising from cancer of the large bowel. An added advantage is that it does not cause constipation. Phenoperidine (Operidine) caused no rise in biliary pressure after intramuscular injection and only a minimal rise after intravenous injection. This drug is said to be a strong but short-acting broncho-constrictor effect. Our results suggest that phenazocine also differs from morphine in having no effect on the biliary sphincters. Phenazocine is, therefore, on the basis of these investigations more suitable for treating pain of biliary origin than is morphine or pethidine. SUMMARY The effects of levorphanol (Dromoran), dextromoramide (Paffium), dextropropoxyphene hydrochloride (Doloxene), phenoperidine (Operidine), and phenazocine (Narphen) on the pressure in the common bile duct are compared with the pressure rises caused by morphine and pethidine. Phenazocine (Narphen) is said to be a stronger and safer analgesic than morphine and does not cause a rise in biliary pressure. It is suggested that this drug is likely to prove more suitable as an analgesic in biliary pain than either morphine or pethidine. We would like to thank Dr. H. T. Howat for his advice and encouragement in the preparation of this paper. REFERENCES Bergh, G. S., and Layne, J. A. (190). A demonstration of the independent contraction of the sphincter of the common bile duct in human subjects. Amer. J. Physiol., 128, Boulter, P. S. (1961). The effects of analgesics and antispasmodics on flow through the human common bile duct. Guy's Hosp. Rep., 110, Boyden, E. A. (1957). The anatomy of the choledochoduodenal junction in man. Surg. Gynec. Obstet., 10, Burke, J. 0., Plummer, K., and Bradford, S. (1950). Serum amylase response to morphine, mecholyl and secretin as a test of pancreatic function. Gastroenterology, 15, Butsch, W. L., McGowan, J. M., and Walters, W. (1936). Clinical studies on the influence of certain drugs in relation to biliary pain and to the variations in intrabiliary pressure. Surg. Gynec. Obstet., 63, Caroli, J., Porcher, P., Pequignot, G., and Delattre, M. (1960). Contribution ofcineradiography to study of the function of the human biliary tract. Amer. J. dig. Dis., 5, Crema, A., Benzi, G., Frigo, G. M., and Bert6, F. (1965). The responses of the terminal bile duct to morphine and morphine-like drugs. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther., 19, Effron, G. (1958). Analgesia in pancreatitis with special reference to the effect on pressure in the common bile-duct. S. Afr. med. J., 32, Gruber, C. M., Jr. (1957). Codeine phosphate, propoxyphene hydrochloride, and placebo. J. Amer. med. Ass., Kock, N. G., Kewenter J., and Jacobson, B. (196). The influence of the motor activity of the duodenum on the pressure in the common bile duct. Ann. Surg., 160,
5 300 D. S. Hopton and H. B. Torrance Myhre, J., Nesbitt, S., and Hurly, J. T. (199). Response of serum amylase and lipase to pancreatic stimulation as a test of pancreatic function. The mecholyl-secretion and the morphinesecretion tests. Gastroenterology, 13, Di Pillo, F., Younger, M. D., Scarpa, W. J., and Edson, J. N. (1960). Phenazocine: its clinical use as an analgesic. In National Research Council Committee on Drug Addiction and Narcotics. Minutes of Twenty-first Meeting, pp Robelet, A., Bizard-Gregoire, N., and Bizard, J. (1965). The action of dextromoramide on the sphincter of Oddi. In The Biliary System: A Symposium of the N.A.T.O. Advanced Study Institute, edited by W. Taylor, pp Blackwell, Oxford. Gut: first published as /gut on 1 June Downloaded from on 17 August 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
Abnormal responses to morphine-neostigmine in patients with undefined biliary type pain
 Abnormal responses to morphine-neostigmine in patients with undefined biliary type pain I C ROBERTS-THOMSON AND J TOOULI Gut, 1985, 26, 1367-1372 From the Clinical Research Unit, The Walter and Eliza Hall
Abnormal responses to morphine-neostigmine in patients with undefined biliary type pain I C ROBERTS-THOMSON AND J TOOULI Gut, 1985, 26, 1367-1372 From the Clinical Research Unit, The Walter and Eliza Hall
SPHINCTER OF ODDI DYSFUNCTION (SOD)
 SPHINCTER OF ODDI DYSFUNCTION (SOD) Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction refers to structural or functional disorders involving the biliary sphincter that may result in impedance of bile and pancreatic juice
SPHINCTER OF ODDI DYSFUNCTION (SOD) Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction refers to structural or functional disorders involving the biliary sphincter that may result in impedance of bile and pancreatic juice
interstitium at pressures below the maximum secretory pressure of the pancreas. The ink
 Gut, 1970, 11, 69-73 Effect of pressure on the integrity of the duct-acinar system of the pancreas R. C. PIROLA1 AND A. E. DAVIS From the Department of Medicine, Prince Henry Hospital, Sydney, Australia
Gut, 1970, 11, 69-73 Effect of pressure on the integrity of the duct-acinar system of the pancreas R. C. PIROLA1 AND A. E. DAVIS From the Department of Medicine, Prince Henry Hospital, Sydney, Australia
Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction: SOD after EPISOD, Now what do we do?
 Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction: SOD after EPISOD, Now what do we do? Priya A. Jamidar, M.D., FASGE Professor of Medicine, Director of Endoscopy Yale School Y A L E S CH OO L O F MEDIC IN E February in Connecticut
Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction: SOD after EPISOD, Now what do we do? Priya A. Jamidar, M.D., FASGE Professor of Medicine, Director of Endoscopy Yale School Y A L E S CH OO L O F MEDIC IN E February in Connecticut
FIRST AID COVER LIMITED SOP
 FIRST AID COVER LIMITED SOP Drugs IV Naloxone Hydrochloride (N, P) Drugs IM Naloxone Hydrochloride (T) 2A Bridge Approach Tel +44 (0)0775 908 6816 London NW1 8BD Office +44 (0)20 7692 3018 United Kingdom
FIRST AID COVER LIMITED SOP Drugs IV Naloxone Hydrochloride (N, P) Drugs IM Naloxone Hydrochloride (T) 2A Bridge Approach Tel +44 (0)0775 908 6816 London NW1 8BD Office +44 (0)20 7692 3018 United Kingdom
Clinical Anatomy of the Biliary Apparatus: Relations & Variations
 Clinical Anatomy of the Biliary Apparatus: Relations & Variations Handout download: http://www.oucom.ohiou.edu/dbms-witmer/gs-rpac.htm 27 March 2007 Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Professor of Anatomy Department
Clinical Anatomy of the Biliary Apparatus: Relations & Variations Handout download: http://www.oucom.ohiou.edu/dbms-witmer/gs-rpac.htm 27 March 2007 Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Professor of Anatomy Department
THE REGULATION OF THE FLOW OF BILE
 Reprinted from THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSIOLOGY Vol. 74, No. 3, November, ism THE REGULATION OF THE FLOW OF BILE G. E. BURGET From the Department of Physiology, University of Oregon Medical School Received
Reprinted from THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSIOLOGY Vol. 74, No. 3, November, ism THE REGULATION OF THE FLOW OF BILE G. E. BURGET From the Department of Physiology, University of Oregon Medical School Received
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 22 June 2011
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 22 June 2011 SPASFON, film-coated tablets B/30 (CIP code: 309 860-8) SPASFON, suppositories B/10 (CIP code: 309 861-4)
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 22 June 2011 SPASFON, film-coated tablets B/30 (CIP code: 309 860-8) SPASFON, suppositories B/10 (CIP code: 309 861-4)
Reflux of duodenal contents in the pathogenesis of pancreatitis
 Gut, 1964, 5, 260 Reflux of duodenal contents in the pathogenesis of pancreatitis A. D. McCUTCHEON From the Baker Medical Research Institute, Melbourne, Australia1 EDITORIAL SYNOPSIS It is concluded from
Gut, 1964, 5, 260 Reflux of duodenal contents in the pathogenesis of pancreatitis A. D. McCUTCHEON From the Baker Medical Research Institute, Melbourne, Australia1 EDITORIAL SYNOPSIS It is concluded from
Analgesic Drugs PHL-358-PHARMACOLOGY AND THERAPEUTICS-I. Mr.D.Raju,M.pharm, Lecturer
 Analgesic Drugs PHL-358-PHARMACOLOGY AND THERAPEUTICS-I Mr.D.Raju,M.pharm, Lecturer Mechanisms of Pain and Nociception Nociception is the mechanism whereby noxious peripheral stimuli are transmitted to
Analgesic Drugs PHL-358-PHARMACOLOGY AND THERAPEUTICS-I Mr.D.Raju,M.pharm, Lecturer Mechanisms of Pain and Nociception Nociception is the mechanism whereby noxious peripheral stimuli are transmitted to
Biliary tree dilation - and now what?
 Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Package leaflet: Information for the user. Morfin Abcur 10 mg/ml, solution for injection. morphine hydrochloride
 Package leaflet: Information for the user Morfin Abcur 10 mg/ml, solution for injection morphine hydrochloride Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains
Package leaflet: Information for the user Morfin Abcur 10 mg/ml, solution for injection morphine hydrochloride Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains
Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
 Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
Resting patterns of pressure. position of the tubes was ascertained radiologically by
 Guit, 1964, 5, 201 The intraluminal pressure patterns in diverticulosis of the colon Part I Resting patterns of pressure NEIL STAMFORD PAINTER AND S. C. TRUELOVE From the Nuffield Department of Clinical
Guit, 1964, 5, 201 The intraluminal pressure patterns in diverticulosis of the colon Part I Resting patterns of pressure NEIL STAMFORD PAINTER AND S. C. TRUELOVE From the Nuffield Department of Clinical
Pancreas & Biliary System. Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila
 Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Effect of acid infusion into various levels of the intestine on gastric and pancreatic secretion in the cat
 Gut, 1969, 10, 749-753 Effect of acid infusion into various levels of the intestine on gastric and pancreatic secretion in the cat S. J. KONTUREK, J. DUBIEL, AND B. GABRY9 From the Department of Medicine,
Gut, 1969, 10, 749-753 Effect of acid infusion into various levels of the intestine on gastric and pancreatic secretion in the cat S. J. KONTUREK, J. DUBIEL, AND B. GABRY9 From the Department of Medicine,
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Surface Anatomy. Location Shape Weight Role of Five Surfaces Borders Fissures Lobes Peritoneal Lig
 The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
ENDOSCOPIC TREATMENT OF A BILE DUCT
 HPB Surgery, 1990, Vol. 3, pp. 67-71 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 1990 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in the United Kingdom CASE REPORT
HPB Surgery, 1990, Vol. 3, pp. 67-71 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 1990 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in the United Kingdom CASE REPORT
ALVIMOPAN 0.0 OVERVIEW
 ALVIMOPAN 0.0 OVERVIEW A. Alvimopan is a peripherally restricted mu-opioid receptor antagonist. B. DOSING INFORMATION : For the treatment of opioid bowel dysfunction, oral alvimopan doses between 0.5 milligrams
ALVIMOPAN 0.0 OVERVIEW A. Alvimopan is a peripherally restricted mu-opioid receptor antagonist. B. DOSING INFORMATION : For the treatment of opioid bowel dysfunction, oral alvimopan doses between 0.5 milligrams
RE: Shortage of DBL MORPHINE SULFATE 30mg/1mL injection BP ampoule and alternative supply arrangement under Section 19A of the Therapeutic Goods Act
 22 January 2019 RE: Shortage of DBL MORPHINE SULFATE 30mg/1mL injection BP ampoule and alternative supply arrangement under Section 19A of the Therapeutic Goods Act Dear Healthcare Professional, This notification
22 January 2019 RE: Shortage of DBL MORPHINE SULFATE 30mg/1mL injection BP ampoule and alternative supply arrangement under Section 19A of the Therapeutic Goods Act Dear Healthcare Professional, This notification
Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain
 Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain 1 patient with recurrent episodes of pain (not daily), in the epigastrium/right upper quadrant, lasting >30 mins, building to a steady level, interrupting
Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain 1 patient with recurrent episodes of pain (not daily), in the epigastrium/right upper quadrant, lasting >30 mins, building to a steady level, interrupting
Does Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction Even Exist Anymore?
 Does Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction Even Exist Anymore? Grace H. Elta, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine University of Michigan Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction Best studied clinical association: Biliary pain
Does Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction Even Exist Anymore? Grace H. Elta, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine University of Michigan Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction Best studied clinical association: Biliary pain
Drugs Used In Management Of Pain. Dr. Aliah Alshanwani
 Drugs Used In Management Of Pain Dr. Aliah Alshanwani 1 Drugs Used In Management Of Pain A CASE OF OVERDOSE Sigmund Freud, the father of psychoanalysis His cancer of the jaw was causing him increasingly
Drugs Used In Management Of Pain Dr. Aliah Alshanwani 1 Drugs Used In Management Of Pain A CASE OF OVERDOSE Sigmund Freud, the father of psychoanalysis His cancer of the jaw was causing him increasingly
Should Antiemetics be given Prophylactically with Intravenous Opioids while Treating Acute Pain in the Emergency Department?
 Clinical Practice Statement: Should Antiemetics be given Prophylactically with Intravenous Opioids while Treating Acute Pain in the Emergency Department? (6/1/10) Executive Summary The routine administration
Clinical Practice Statement: Should Antiemetics be given Prophylactically with Intravenous Opioids while Treating Acute Pain in the Emergency Department? (6/1/10) Executive Summary The routine administration
in gastric emptying' of the stomach was recorded by an electronic transducer (T1) attached by an air-filled tube to the second limb of
 Gut, 1963, 4, 174 Function of the pylorus and pyloric antrum in gastric emptying' A. K. ARMITAGE AND A. C. B. DEAN From the Department of Surgery, King's College Hospital Medical School, London EDITORIAL
Gut, 1963, 4, 174 Function of the pylorus and pyloric antrum in gastric emptying' A. K. ARMITAGE AND A. C. B. DEAN From the Department of Surgery, King's College Hospital Medical School, London EDITORIAL
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
 Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Medical Imaging and Treatment of the Bile and Pancreatic Ducts CIE-02718 Understanding ERCP Brochure Update_F.indd 1 7/11/18 9:51 A Minimally Invasive
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Medical Imaging and Treatment of the Bile and Pancreatic Ducts CIE-02718 Understanding ERCP Brochure Update_F.indd 1 7/11/18 9:51 A Minimally Invasive
DBL NALOXONE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION USP
 Name of medicine Naloxone hydrochloride Data Sheet New Zealand DBL NALXNE HYDRCHLRIDE INJECTIN USP Presentation DBL Naloxone Hydrochloride Injection USP is a sterile, clear, colourless solution, free from
Name of medicine Naloxone hydrochloride Data Sheet New Zealand DBL NALXNE HYDRCHLRIDE INJECTIN USP Presentation DBL Naloxone Hydrochloride Injection USP is a sterile, clear, colourless solution, free from
ERCP complications and challenges in their diagnosis and management.
 ERCP complications and challenges in their diagnosis and management. Sandie R Thomson Chair of the Division of Gastroenterology, University of Cape Town ERCP Do I have a good Indication? . Algorithm for
ERCP complications and challenges in their diagnosis and management. Sandie R Thomson Chair of the Division of Gastroenterology, University of Cape Town ERCP Do I have a good Indication? . Algorithm for
Dr. Zahiri. In the name of God
 Dr. Zahiri In the name of God small intestine = small bowel is the part of the gastrointestinal tract Boundaries: Pylorus Ileosecal junction Function: digestion and absorption of food It receives bile
Dr. Zahiri In the name of God small intestine = small bowel is the part of the gastrointestinal tract Boundaries: Pylorus Ileosecal junction Function: digestion and absorption of food It receives bile
possibility of a secretion of adrenaline from the suprarenal glands resulting
 355 J Physiol. (I942) IOI, 355-36I 6i2.014.465:577 I74.5 THE EFFECT OF ANAESTHESIA ON THE ADRENALINE CONTENT OF THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS BY P. C. ELMES AND A. A. JEFFERSON From the Department of Pharmacology,
355 J Physiol. (I942) IOI, 355-36I 6i2.014.465:577 I74.5 THE EFFECT OF ANAESTHESIA ON THE ADRENALINE CONTENT OF THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS BY P. C. ELMES AND A. A. JEFFERSON From the Department of Pharmacology,
show-n to give off a branch, and sometimes two or three branches, to
 THE EFFECT OF STIMULATION OF THE VAGI ON THE PYLORIC REGION OF THE STOMACH. BY E. D. McCREA1 AND B. A. McSWINEY. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) THE course taken by the vagus
THE EFFECT OF STIMULATION OF THE VAGI ON THE PYLORIC REGION OF THE STOMACH. BY E. D. McCREA1 AND B. A. McSWINEY. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) THE course taken by the vagus
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to: Given a group of definitions, select the definition of analgesia.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 Narcotic Agents. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1--11-7 LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a group of definitions, select the
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 Narcotic Agents. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1--11-7 LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a group of definitions, select the
Nausicalm solution for injection is a clear colourless solution, presented in 1 ml ampoules.
 Nausicalm Cyclizine lactate 50 mg/ml solution for injection Presentation Nausicalm solution for injection is a clear colourless solution, presented in 1 ml ampoules. Uses Actions Cyclizine is a piperazine
Nausicalm Cyclizine lactate 50 mg/ml solution for injection Presentation Nausicalm solution for injection is a clear colourless solution, presented in 1 ml ampoules. Uses Actions Cyclizine is a piperazine
Opioid adverse reactions not the usual suspects! DR ANDREW DAVIES
 Opioid adverse reactions not the usual suspects! DR ANDREW DAVIES Overview Introduction Musical hallucinations Charles Bonnet syndrome (Nightmares, vivid dreams) Sleep disordered breathing Sphincter of
Opioid adverse reactions not the usual suspects! DR ANDREW DAVIES Overview Introduction Musical hallucinations Charles Bonnet syndrome (Nightmares, vivid dreams) Sleep disordered breathing Sphincter of
Pancreas and Biliary System
 Pancreas and Biliary System Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Pancreas and Biliary System Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Laparoscopic cholecystectomyy
 Laparoscopic cholecystectomyy What is the gall bladder? The gallbladder is a small pear sized organ that stores bile. Bile is necessary for the digestion of fatty food. The bile duct is a tube that carries
Laparoscopic cholecystectomyy What is the gall bladder? The gallbladder is a small pear sized organ that stores bile. Bile is necessary for the digestion of fatty food. The bile duct is a tube that carries
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017
 ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Meeting nutritional needs of acute care patients Feeding acute pancreatitis patients J. Luttikhold (NL) FEEDING ACUTE PANCREATITIS PATIENTS Joanna Luttikhold, MD PhD Registrar
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Meeting nutritional needs of acute care patients Feeding acute pancreatitis patients J. Luttikhold (NL) FEEDING ACUTE PANCREATITIS PATIENTS Joanna Luttikhold, MD PhD Registrar
ACTION OF SYMPATHOMIMETIC DRUGS ON THE ISOLATED JUNCTION OF THE BILE DUCT AND DUODENUM
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1963), 20, 221-229. ACTION OF SYMPATHOMIMETIC DRUGS ON THE ISOLATED JUNCTION OF THE BILE DUCT AND DUODENUM BY A. CREMA AND F. BERT8 From the Department of Pharmacology, University
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1963), 20, 221-229. ACTION OF SYMPATHOMIMETIC DRUGS ON THE ISOLATED JUNCTION OF THE BILE DUCT AND DUODENUM BY A. CREMA AND F. BERT8 From the Department of Pharmacology, University
PARACOD Tablets (Paracetamol + Codeine phosphate)
 Published on: 22 Sep 2014 PARACOD Tablets (Paracetamol + Codeine phosphate) Composition PARACOD Tablets Each effervescent tablet contains: Paracetamol IP...650 mg Codeine Phosphate IP... 30 mg Dosage Form/s
Published on: 22 Sep 2014 PARACOD Tablets (Paracetamol + Codeine phosphate) Composition PARACOD Tablets Each effervescent tablet contains: Paracetamol IP...650 mg Codeine Phosphate IP... 30 mg Dosage Form/s
PERCUTANEOUS BILIARY DRAINAGE
 PERCUTANEOUS BILIARY DRAINAGE MEDICAL IMAGING INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Introduction This booklet tells you about the procedure known as percutaneous biliary drainage, explains what is involved and what
PERCUTANEOUS BILIARY DRAINAGE MEDICAL IMAGING INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Introduction This booklet tells you about the procedure known as percutaneous biliary drainage, explains what is involved and what
Summary of risk management plan for Dzuveo (Sufentanil (as citrate))
 Part VI: Summary of the risk management plan Summary of risk management plan for Dzuveo (Sufentanil (as citrate)) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Dzuveo. The RMP details important
Part VI: Summary of the risk management plan Summary of risk management plan for Dzuveo (Sufentanil (as citrate)) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Dzuveo. The RMP details important
Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: What s the Verdict in 2014?
 SGNA March 2014 Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: What s the Verdict in 2014? Evan L. Fogel, M.D. Professor of Clinical Medicine ERCP Fellowship Director Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology Indiana University
SGNA March 2014 Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: What s the Verdict in 2014? Evan L. Fogel, M.D. Professor of Clinical Medicine ERCP Fellowship Director Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology Indiana University
Controversies in the management of acute pancreatitis
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (3) Vol., No. 3, Issue 7, 3-7 Controversies in the management of acute pancreatitis Singh DR 1, Mehta A, Dangol UMS 3 1 Lecturer, Medical Officer, 3 Lecturer, Dept.
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (3) Vol., No. 3, Issue 7, 3-7 Controversies in the management of acute pancreatitis Singh DR 1, Mehta A, Dangol UMS 3 1 Lecturer, Medical Officer, 3 Lecturer, Dept.
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 6 April 2011
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 6 April 2011 METEOXANE, capsules B/60 (CIP code: 306 693-3) Applicant: IPRAD Simethicone Hydrated phloroglucinol ATC
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 6 April 2011 METEOXANE, capsules B/60 (CIP code: 306 693-3) Applicant: IPRAD Simethicone Hydrated phloroglucinol ATC
Howida Kamal, Ph.D Ass. Prof. of Pharmaceutics, Cairo University
 Pharmacy Howida Kamal, Ph.D Ass. Prof. of Pharmaceutics, Cairo University Pharmacy Pharmacy Pharmaceutics The science of dosage form design. Pharmacy 1. 2. 3. Dosage forms Information Resources Use of
Pharmacy Howida Kamal, Ph.D Ass. Prof. of Pharmaceutics, Cairo University Pharmacy Pharmacy Pharmaceutics The science of dosage form design. Pharmacy 1. 2. 3. Dosage forms Information Resources Use of
POST-OPERATIVE PANCREATITIS By ARCHIBALD E. CARTER, F.R.C.S.
 248 POST-OPERATIVE PANCREATITIS By ARCHIBALD E. CARTER, F.R.C.S. Fromn\the Department of Surgery, Harvard Medical School, and the Peter B3nt Brigham Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts Introduction Post-operative
248 POST-OPERATIVE PANCREATITIS By ARCHIBALD E. CARTER, F.R.C.S. Fromn\the Department of Surgery, Harvard Medical School, and the Peter B3nt Brigham Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts Introduction Post-operative
SUNY Downstate Medical Center Kings County Hospital
 Management of Choledocholithiasis SUNY Downstate Medical Center Kings County Hospital Department of Surgery Grand Rounds Kiyanda Baldwin October 22, 2009 Case Presentation 43 y/o F c/o jaundice x 3 days
Management of Choledocholithiasis SUNY Downstate Medical Center Kings County Hospital Department of Surgery Grand Rounds Kiyanda Baldwin October 22, 2009 Case Presentation 43 y/o F c/o jaundice x 3 days
patient group direction
 MORPHINE SULPHATE (Oral) v01 1/8 MORPHINE SULPHATE (Oral) PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic)
MORPHINE SULPHATE (Oral) v01 1/8 MORPHINE SULPHATE (Oral) PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic)
Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: Where do we stand in 2015?
 IU GI Motility Conference August 5, 2015 Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: Where do we stand in 2015? Evan L. Fogel, M.D. Professor of Medicine ERCP Fellowship Director Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology
IU GI Motility Conference August 5, 2015 Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: Where do we stand in 2015? Evan L. Fogel, M.D. Professor of Medicine ERCP Fellowship Director Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology
Analgesics ROBERT G. TWYCROSS M.A., D.M., F.R.C.P. much in their favour, although nefopam does not fit
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (December 1984) 60, 876-880 Analgesics ROBERT G. TWYCROSS M.A., D.M., F.R.C.P. Sir Michael Sobell House, The Churchill Hospital, Headington, Oxford Introduction There is no
Postgraduate Medical Journal (December 1984) 60, 876-880 Analgesics ROBERT G. TWYCROSS M.A., D.M., F.R.C.P. Sir Michael Sobell House, The Churchill Hospital, Headington, Oxford Introduction There is no
Cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder) Patient Information
 Cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder) Patient Information Author ID: MP Leaflet Number: Surg 060 Name of Leaflet: Cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder) Version: 1 Date Produced: October 2017
Cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder) Patient Information Author ID: MP Leaflet Number: Surg 060 Name of Leaflet: Cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder) Version: 1 Date Produced: October 2017
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Opioid (Narcotic) Analgesics and Antagonists. Lesson 6.1. Lesson 6.1. Opioid (Narcotic) Analgesics and Antagonists
 Slide 1 Opioid (Narcotic) Analgesics and Antagonists Chapter 6 1 Slide 2 Lesson 6.1 Opioid (Narcotic) Analgesics and Antagonists 1. Explain the classification, mechanism of action, and pharmacokinetics
Slide 1 Opioid (Narcotic) Analgesics and Antagonists Chapter 6 1 Slide 2 Lesson 6.1 Opioid (Narcotic) Analgesics and Antagonists 1. Explain the classification, mechanism of action, and pharmacokinetics
Viberzi. Viberzi (eluxadoline) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subsection: Gastrointestinal Agents Original Policy Date: July 24, 2015 Subject: Viberzi Page: 1 of 5 Last
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subsection: Gastrointestinal Agents Original Policy Date: July 24, 2015 Subject: Viberzi Page: 1 of 5 Last
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 8/27/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 35 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 8/27/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 35 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Prom the Department of Pharmacology, McGill University, Montreal, Canada
 365 J. Physiol. (I95I) II3, 365-37I EFFECTS OF NORADRENALINE ON CORONARY FLOW AND HEART CONTRACTION, AS RECORDED CONCURRENTLY IN THE ISOLATED RABBIT HEART BY F. C. LU* AND K. I. MELVILLE Prom the Department
365 J. Physiol. (I95I) II3, 365-37I EFFECTS OF NORADRENALINE ON CORONARY FLOW AND HEART CONTRACTION, AS RECORDED CONCURRENTLY IN THE ISOLATED RABBIT HEART BY F. C. LU* AND K. I. MELVILLE Prom the Department
Facts About BELBUCA (buprenorphine) Buccal Film
 Facts About BELBUCA (buprenorphine) Buccal Film Indication BELBUCA is a recent FDA-approved medication for the treatment of chronic pain severe enough to require daily, around-the-clock, long-term opioid
Facts About BELBUCA (buprenorphine) Buccal Film Indication BELBUCA is a recent FDA-approved medication for the treatment of chronic pain severe enough to require daily, around-the-clock, long-term opioid
The effect of metoclopramide on gastroduodenal
 Gut, 1971, 12, 158-163 The effect of metoclopramide on gastroduodenal and gallbladder contractions A. G. JOHNSON From the Department of Surgery, Charing Cross Hospital Medical School, London SUMMARY The
Gut, 1971, 12, 158-163 The effect of metoclopramide on gastroduodenal and gallbladder contractions A. G. JOHNSON From the Department of Surgery, Charing Cross Hospital Medical School, London SUMMARY The
QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL PHYSIOLOGY
 612.337:612.013.88 "e ra4 78D QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL PHYSIOLOGY AND COGNATE MEDICAL SCIENCES FACTORS INFLUENCING THE MOTILITY OF THE PERFUSED HORSE INTESTINE. By FRANK ALEXANDER. From the Department
612.337:612.013.88 "e ra4 78D QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL PHYSIOLOGY AND COGNATE MEDICAL SCIENCES FACTORS INFLUENCING THE MOTILITY OF THE PERFUSED HORSE INTESTINE. By FRANK ALEXANDER. From the Department
Diseases of exocrine pancreas
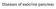 Diseases of exocrine pancreas The exocrine pancreas constitutes 80% to 85% of the organ and is composed of acinar cells that secrete enzymes needed for digestion. the accessory duct of Santorini, the main
Diseases of exocrine pancreas The exocrine pancreas constitutes 80% to 85% of the organ and is composed of acinar cells that secrete enzymes needed for digestion. the accessory duct of Santorini, the main
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Morfin Abcur, 10 mg/ml, solution for injection 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 ml contains 10 mg morphine hydrochloride
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Morfin Abcur, 10 mg/ml, solution for injection 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 ml contains 10 mg morphine hydrochloride
Package leaflet: Information for the patient. Morphine Unimedic 1 mg/ml solution for injection morphine hydrochloride trihydrate
 Package leaflet: Information for the patient Morphine Unimedic 1 mg/ml solution for injection morphine hydrochloride trihydrate Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because
Package leaflet: Information for the patient Morphine Unimedic 1 mg/ml solution for injection morphine hydrochloride trihydrate Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because
SERUM AMYLASE AND SERUM LIPASE LEVELS IN MAN
 Gut, 1960, 1, 125. SERUM AMYLASE AND SERUM LIPASE LEVELS IN MAN AFTER ADMINISTRATION OF SECRETIN AND PANCREOZYMIN BY P. BURTON, ELIZABETH M. HAMMOND, A. A. HARPER, HENRY T. HOWAT, J. E. SCOIT, and H. VARLEY
Gut, 1960, 1, 125. SERUM AMYLASE AND SERUM LIPASE LEVELS IN MAN AFTER ADMINISTRATION OF SECRETIN AND PANCREOZYMIN BY P. BURTON, ELIZABETH M. HAMMOND, A. A. HARPER, HENRY T. HOWAT, J. E. SCOIT, and H. VARLEY
Hepatocellular Dysfunction
 www.nuclearmd.com A Normal HIDA Scan Dynamic or Static images of the abdomen are acquired after the IV administration 6-8 mci of Tc99m disofenin or mebrofenin, for one hour. Patients have to be NPO for
www.nuclearmd.com A Normal HIDA Scan Dynamic or Static images of the abdomen are acquired after the IV administration 6-8 mci of Tc99m disofenin or mebrofenin, for one hour. Patients have to be NPO for
Why would fatty foods aggravate the patient s RUQ pain? What effect does cholecystokinin (CCK) have on gastric emptying?
 CASE 28 A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with the acute onset of abdominal pain. Her pain is located to the right upper quadrant (RUQ) and radiates to the right shoulder. She reports
CASE 28 A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with the acute onset of abdominal pain. Her pain is located to the right upper quadrant (RUQ) and radiates to the right shoulder. She reports
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine. ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama
 Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction)
 SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction) SOD refers to the mechanical malfunctioning of the Sphincter of Oddi, which is the valve muscle that regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction) SOD refers to the mechanical malfunctioning of the Sphincter of Oddi, which is the valve muscle that regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
Liver Scan Biliary with Ejection Fraction Measurement
 APPROVED BY: Director of Radiology Page 1 of 5 Liver Scan Biliary with Ejection Fraction Primary Indications: In patients with chronic abdominal pain, hepatobiliary imaging with gallbladder ejection fraction
APPROVED BY: Director of Radiology Page 1 of 5 Liver Scan Biliary with Ejection Fraction Primary Indications: In patients with chronic abdominal pain, hepatobiliary imaging with gallbladder ejection fraction
3/26/14. Opiates PSY B396 ALCOHOL, ALCOHOLISM, & DRUG ABUSE. Early History Cont d. Early History. Opiate Use in the 19th century. Technology Advances
 Opiates PSY B396 ALCOHOL, ALCOHOLISM, & DRUG ABUSE Chapter 10 Opiates The most dramatic example of the doubleedged sword character of drugs Most potent painkillers Prototype addictive drug: Heroin Early
Opiates PSY B396 ALCOHOL, ALCOHOLISM, & DRUG ABUSE Chapter 10 Opiates The most dramatic example of the doubleedged sword character of drugs Most potent painkillers Prototype addictive drug: Heroin Early
Syringe driver in Palliative Care
 Syringe driver in Palliative Care Introduction: Syringe drivers are portable, battery operated devices widely used in palliative care to deliver medication as a continuous subcutaneous infusion over 24
Syringe driver in Palliative Care Introduction: Syringe drivers are portable, battery operated devices widely used in palliative care to deliver medication as a continuous subcutaneous infusion over 24
DIGESTIVE. CHAPTER 17 Lecture: Part 1 Part 2 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. SMALL INTESTINE DUODENUM > JEJUNUM
BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. SMALL INTESTINE DUODENUM > JEJUNUM
BILIARY TRACT & PANCREAS, PART II
 CME Pretest BILIARY TRACT & PANCREAS, PART II VOLUME 41 1 2015 A pretest is mandatory to earn CME credit on the posttest. The pretest should be completed BEFORE reading the overview. Both tests must be
CME Pretest BILIARY TRACT & PANCREAS, PART II VOLUME 41 1 2015 A pretest is mandatory to earn CME credit on the posttest. The pretest should be completed BEFORE reading the overview. Both tests must be
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 15a Lab Activity
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 15a Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: The Digestive System Digestion is an important process that involves breaking down food and drink into small molecules that can
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 15a Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: The Digestive System Digestion is an important process that involves breaking down food and drink into small molecules that can
Principles of ERCP: papilla cannulation, indications/contraindications and risks. Dr. med. Henrik Csaba Horváth PhD
 Principles of ERCP: papilla cannulation, indications/contraindications and risks Dr. med. Henrik Csaba Horváth PhD Evolution of ERCP 1968. 1970s ECPG Endoscopic CholangioPancreatoGraphy Japan 1974 Biliary
Principles of ERCP: papilla cannulation, indications/contraindications and risks Dr. med. Henrik Csaba Horváth PhD Evolution of ERCP 1968. 1970s ECPG Endoscopic CholangioPancreatoGraphy Japan 1974 Biliary
Development of the Liver and Pancreas
 Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with
![Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with](/thumbs/91/106294335.jpg) 381 6I2.I34:6I2.893 THE CONSTRICTOR RESPONSE OF THE INFERIOR VENA CAVA TO STIMULATION OF THE SPLANCHNIC NERVE BY K. J. FRANKLIN AND A. D. McLACHLIN (From the University Department of Pharmacology, Oxford)
381 6I2.I34:6I2.893 THE CONSTRICTOR RESPONSE OF THE INFERIOR VENA CAVA TO STIMULATION OF THE SPLANCHNIC NERVE BY K. J. FRANKLIN AND A. D. McLACHLIN (From the University Department of Pharmacology, Oxford)
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion. 7/16/2015 MDufilho 1
 Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
Xifaxan, Lotronex and Viberzi Prior Authorization and Quantity Limit Program Summary
 Xifaxan, Lotronex and Viberzi Prior Authorization and Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1,2 Lotronex (alosetron) a Indication For women with severe diarrheapredominant irritable
Xifaxan, Lotronex and Viberzi Prior Authorization and Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1,2 Lotronex (alosetron) a Indication For women with severe diarrheapredominant irritable
In The Name of God. Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis.
 In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY, KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY, KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
Information for Consent Cholecystectomy (Laparoscopic/Open) 膽囊切除術 ( 腹腔鏡 / 開放性 )
 Version 1.0 Page 1 of 3 Information for Consent Cholecystectomy (Laparoscopic/Open) 膽囊切除術 ( 腹腔鏡 / 開放性 ) Introduction Gallbladder is a sac connected to the biliary tree. It serves the function of concentration
Version 1.0 Page 1 of 3 Information for Consent Cholecystectomy (Laparoscopic/Open) 膽囊切除術 ( 腹腔鏡 / 開放性 ) Introduction Gallbladder is a sac connected to the biliary tree. It serves the function of concentration
A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree
 A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree Thomas Hocker, HMS IV BIDMC Core Radiology Case Presentation September 17, 2007 Review of Normal Pancreaticobiliary Tract Anatomy
A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree Thomas Hocker, HMS IV BIDMC Core Radiology Case Presentation September 17, 2007 Review of Normal Pancreaticobiliary Tract Anatomy
Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction
 Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction Ann S. Fulcher, MD Medical College of Virginia Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, Virginia Objectives To
Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction Ann S. Fulcher, MD Medical College of Virginia Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, Virginia Objectives To
UNDERSTANDING CYSTIC FIBROSIS
 UNDERSTANDING CYSTIC FIBROSIS INTRODUCTION Cystic fibrosis is a chronic disease that affects the respiratory and gastrointestinal systems. People with cystic fibrosis have a genetic defect of the lungs
UNDERSTANDING CYSTIC FIBROSIS INTRODUCTION Cystic fibrosis is a chronic disease that affects the respiratory and gastrointestinal systems. People with cystic fibrosis have a genetic defect of the lungs
Manometry based randomised trial of endoscopic sphincterotomy for sphincter of Oddi dysfunction
 98 GI Surgical Unit, Flinders Medical Centre, Adelaide, Australia J Toouli I C Roberts-Thomson G T P Saccone P Jeans MCox P Anderson C Worthley N Shanks A Craig Department of Gastroenterology, Royal North
98 GI Surgical Unit, Flinders Medical Centre, Adelaide, Australia J Toouli I C Roberts-Thomson G T P Saccone P Jeans MCox P Anderson C Worthley N Shanks A Craig Department of Gastroenterology, Royal North
Analgesics OPIOID ANALGESICS
 Analgesics Opioid (Narcotic analgesics) Non-opioid (Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs) OPIOID ANALGESICS Morphine is the most important alkaloid of opium the dried juice obtained from the capsules of
Analgesics Opioid (Narcotic analgesics) Non-opioid (Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs) OPIOID ANALGESICS Morphine is the most important alkaloid of opium the dried juice obtained from the capsules of
ANNEX III LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET
 ANNEX III LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET 1 A. LABELLING 2 PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGE AND THE IMMEDIATE PACKAGE Outer carton Multi-pack 1. NAME OF THE VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT Tralieve
ANNEX III LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET 1 A. LABELLING 2 PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGE AND THE IMMEDIATE PACKAGE Outer carton Multi-pack 1. NAME OF THE VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT Tralieve
Abuse Potential of Morphine/ Dextromethorphan Combinations
 S26 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management Vol. 19 No. 1(Suppl.) January 2000 Proceedings Supplement NMDA-Receptor Antagonists: Evolving Role in Analgesia Abuse Potential of Morphine/ Dextromethorphan
S26 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management Vol. 19 No. 1(Suppl.) January 2000 Proceedings Supplement NMDA-Receptor Antagonists: Evolving Role in Analgesia Abuse Potential of Morphine/ Dextromethorphan
BILE FORMATION, ENTEROHEPATIC CIRCULATION & BILE SALTS
 1 BILE FORMATION, ENTEROHEPATIC CIRCULATION & BILE SALTS Color index Important Further explanation 2 Mind map...3 Functions of bile & stages of bile secretion... 4 Characteristics & composition of bile...5
1 BILE FORMATION, ENTEROHEPATIC CIRCULATION & BILE SALTS Color index Important Further explanation 2 Mind map...3 Functions of bile & stages of bile secretion... 4 Characteristics & composition of bile...5
it by the sympathetic nerve.
 OBSERVATIONS ON AUGMENTED SALIVARY SECRETION. BY G. V. ANREP. * (From the Institute of Physiology, University College, London.) IN 1889 Langley described a peculiar effect of stimulation of the cerebral
OBSERVATIONS ON AUGMENTED SALIVARY SECRETION. BY G. V. ANREP. * (From the Institute of Physiology, University College, London.) IN 1889 Langley described a peculiar effect of stimulation of the cerebral
Endoscopic Papillary Balloon Dilation with Large Balloon after Limited Sphincterotomy for Retrieval of Choledocholithiasis
 Yonsei Medical Journal Vol. 47, No. 6, pp. 805-810, 2006 Endoscopic Papillary Balloon Dilation with Large Balloon after Limited Sphincterotomy for Retrieval of Choledocholithiasis Seungmin Bang, Myoung
Yonsei Medical Journal Vol. 47, No. 6, pp. 805-810, 2006 Endoscopic Papillary Balloon Dilation with Large Balloon after Limited Sphincterotomy for Retrieval of Choledocholithiasis Seungmin Bang, Myoung
PART 1.B SPC, LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET
 TRAMADOG, solution for injection Decentralised Procedure D195 February 2018 V3 Tramadol HCl 50 mg/ml Part 1.B SPC, Labelling and Package Leaflet PART 1.B SPC, LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET 1B- 1 ANNEX
TRAMADOG, solution for injection Decentralised Procedure D195 February 2018 V3 Tramadol HCl 50 mg/ml Part 1.B SPC, Labelling and Package Leaflet PART 1.B SPC, LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET 1B- 1 ANNEX
ACTIVITY USING RATS A METHOD FOR THE EVALUATION OF ANALGESIC. subject and a variety of stimuli employed. In the examination of new compounds
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1946), 1, 255. A METHOD FOR THE EVALUATION OF ANALGESIC ACTIVITY USING RATS BY 0. L. DAVIES, J. RAVENT6S, AND A. L. WALPOLE From Imperial Chemical Industries, Ltd., Biological Laboratories,
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1946), 1, 255. A METHOD FOR THE EVALUATION OF ANALGESIC ACTIVITY USING RATS BY 0. L. DAVIES, J. RAVENT6S, AND A. L. WALPOLE From Imperial Chemical Industries, Ltd., Biological Laboratories,
AQUEOUS VEINS IN RABBITS*
 Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 119. AQUEOUS VEINS IN RABBITS* BY D. P. GREAVES AND E. S. PERKINS Institute of Ophthalmology, London Director of Research, Sir Stewart Duke-Elder IN the course of investigations
Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 119. AQUEOUS VEINS IN RABBITS* BY D. P. GREAVES AND E. S. PERKINS Institute of Ophthalmology, London Director of Research, Sir Stewart Duke-Elder IN the course of investigations
Viberzi. Viberzi (eluxadoline) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subsection: Gastrointestinal Agents Original Policy Date: July 24, 2015 Subject: Viberzi Page: 1 of 5 Last
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subsection: Gastrointestinal Agents Original Policy Date: July 24, 2015 Subject: Viberzi Page: 1 of 5 Last
disease or in clients who consume alcohol on a regular basis. bilirubin
 NON-OPIOID Acetaminophen(Tylenol) Therapeutic class: Analgesic, antipyretic Aspirin (ASA, Acetylsalicylic Acid) Analgesic, NSAID, antipyretic Non-Opioid Analgesics COMMON USES WHAT I NEED TO KNOW AS A
NON-OPIOID Acetaminophen(Tylenol) Therapeutic class: Analgesic, antipyretic Aspirin (ASA, Acetylsalicylic Acid) Analgesic, NSAID, antipyretic Non-Opioid Analgesics COMMON USES WHAT I NEED TO KNOW AS A
striking difference between these two animals in respect of the sympathetic
 THE PART PLAYED BY THE DUCTS IN THE PANCREATIC SECRETION. BY L. K. KOROVITSKY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Odessa.) THE first object of this work was to compare the secretory innervation
THE PART PLAYED BY THE DUCTS IN THE PANCREATIC SECRETION. BY L. K. KOROVITSKY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Odessa.) THE first object of this work was to compare the secretory innervation
PAIN RELIEF AFTER SURGERY
 PAIN RELIEF AFTER SURGERY Postoperative pain can last for days, weeks or even months. The amount of pain you experience depends on the type of operation and varies widely between patients, even for the
PAIN RELIEF AFTER SURGERY Postoperative pain can last for days, weeks or even months. The amount of pain you experience depends on the type of operation and varies widely between patients, even for the
Chronic Pancreatitis (1 of 4) i
 Chronic Pancreatitis (1 of 4) i If you need this information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact the Customer Care Team on 0800 374 208 email: customercare@ salisbury.nhs.uk.
Chronic Pancreatitis (1 of 4) i If you need this information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact the Customer Care Team on 0800 374 208 email: customercare@ salisbury.nhs.uk.
