BASIC KNOWLEDGE ABOUT INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS FOR CLINICIAN
|
|
|
- Lewis Maximilian King
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BASIC KNOWLEDGE ABOUT INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS FOR CLINICIAN When should I suspect infective endocarditis? Antibiotic regimen Patient care after completion of treatment Prophylactic Regimens Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis (PVE) Health Care Associated Endocarditis(HAE) When should I suspect infective endocarditis? 1. Sepsis of unknown origin 2. New valve lesion / regurgitant murmur 3. Arterial Emboli (limb, stroke, kidney) 4. Hematuria, glomerulonephritis 5. Peripheral abscess (spleen, spine, ) 6. Fever plus: Cardiac prostheses New CHF Heart disease (Valve, congenital, pace maker) Skin (Osler, Janeway ) lesions New conduction defects Multifocal/rapid changing pulmonic infiltrations IV drug abuse What should be done once endocarditis is suspected?
2 1. Delay antibiotics until 3 sets (3 aerobic + 3 anaerobic) of blood cultures (BC) are taken, each of the six bottles should contain 8-10 ml of blood (Figure) 2. Order basic lab: CBC, ESR, CRP, Urinalysis, Rheumatoid factor, Urea/creatinine & Liver function tests. 3. Order Echo ASAP. Order TEE from the start if there is: prosthesis, progressive valve insufficiency, suspected valve ring abscess or Staph aureus infection What are the criteria for diagnosis of endocarditis? Major criteria 1. Positive Blood culture for IE At least 2 positive BC drawn 12 h apart; or all of 3 BC for typical microorganisms consistent with IE: Viridans streptococci, Streptococcus bovis, HACEK group, Staphylococcus aureus; or enterococci. Single positive BC for Coxiella burnetii (or C. burnetii anti phase 1 IgG antibody titer >1:800) 2. Positive Echo: vegetation, abscess, or dehiscence of prosthetic valve 3. New valvular regurgitation (worsening of preexisting murmur not enough) Minor criteria 1. Predisposing heart condition, pace maker lead, or IV drug abuse 2. Fever, temperature >38 C for at least 6D 3. Vascular phenomena: arterial emboli, mycotic aneurysm, intracranial hemorrhage, conjunctival hemorrhages, and Janeway s lesions 4. Immune phenomena: glomerulonephritis, Osler s nodes, Roth s spots, and positive rheumatoid factor 5. Microbiological evidence: positive BC but does not meet a major criterion as noted above or positive serology for typical micro-organism. Definitive IE is diagnosed if there are - 2 major criteria; or - 1 major criterion and 3 minor criteria; or - 5 minor criteria Possible IE is diagnosed if there is - 1 major criterion and 1 minor criterion; or - 3 minor criteria Reject the diagnosis of IE if there is - Firm alternative diagnosis explaining the clinical findings - Resolution of IE syndrome with antibiotic therapy for <4 days - No pathological evidence of IE at surgery with antibiotic therapy for <4 days - Does not meet criteria for possible IE as above Causes of negative blood cultures?
3 - Most common: antibiotic use before collecting blood or sending inadequate blood volume for culture. - Other reasons: atypical pathogens (Bartonella, Chlamydia, Coxiella, Brucella, Legionella, fungi & HACEK) - History: contact with Birds (Chlamydia), Cats & Dogs (Bartonella), Goat, row meet & cattle (Coxiella, Brucella) - Guided by the clinical history, order special culture media or serologic tests (see table). What if the Echo is negative despite strong clinical suspicion? If the initial TTE is negative à order TEE. If the initial TEE is negative à repeat TEE after one W Consider differential diagnosis Consider second opinion Antibiotic regimen for culture negative IE (or pending BC results)? Native valves: Ampicillin-sulbactam 12 g/24 h IV in 4 equally divided doses plus Gentamicin 3 mg/kg QD IV/IM in 3 equal doses for 4-6 weeks Prosthetic valve endocarditis: Vancomycin 30 mg/kg per 24 h IV in 2 equally divided doses plus Gentamicin sulfate 3 mg/kg per 24 h IV/IM in 3 equally divided doses + Rifampicin Clinical condition Common organisms Injection drug use Indwelling vascular devices S. aureus Coagulase-negative staph β-hemolytic strept Fungi Gram-negative bacilli Polymicrobial S. aureus Coagulase-negative staph Fungi Aerobic Gramnegative bacilli Corynebacterium Alcoholism, cirrhosis Bartonella Aeromonas Clinical condition Genitourinary disorders, (eg. pregnancy, delivery, and abortion) Chronic skin disorders Poor dental health, dental s Common organisms Enterococcus Group B streptococci Listeria monocytogenes Gram-negative bacilli Neisseria S. aureus β-hemolytic streptococci Viridans streptococci Nutritionally variant streptococci Abiotrophia HACEK organisms Diabetes mellitus S. aureus β-hemolytic strept S. pneumoniae Burn patients S aureus Gram-negative bacilli,
4 Listeria S. pneumoniae β-hemolytic strept Contact with Brucella sp AIDS contaminated milk or Coxiella burnetii infected farm Erysipelothrix sp animals Suggested Organism based on clinical condition including Fungi Dog cat exposure Bartonella Pasteurella Capnocytophaga Salmonella sp S. pneumoniae S. aureus Anticoagulation policy with systemic emboli, prosthetic valves or AF? - In Valve prosthesis, warfarin, a target INR: 2. - Stop all anticoagulation with S aureus prosthetic valve IE complicated by recent CNS emboli for at least the first 2 weeks of antibiotic therapy. When to consider referral to surgery? - Heart failure (NYHA III-IV) not responsive to medical treatment - Acute aortic or mitral insufficiency with signs of ventricular failure - Valve perforation or rupture - Fungal endocarditis - New heart block - Large abscess or extension of abscess despite appropriate antimicrobial therapy - Persistent vegetation after systemic embolization - Anterior mitral leaflet vegetation, particularly with size 10 mm - 1 embolic events during first 2 wk of antimicrobial therapy - Increase in vegetation size despite appropriate antimicrobial therapy Patient care after completion of treatment: 1. Before or at completion of therapy Obtain TTE to establish new baseline Educate patient about signs of endocarditis, need for antibiotic prophylaxis for dental/surgical s Thorough dental evaluation and treatment if not performed earlier in evaluation Prompt removal of IV catheter at completion of antimicrobial therapy Drug rehabilitation referral for patients who use illicit injection drugs 1. Follow-up 2. Obtain at least 3 sets of BC from separate sites for any unexplained fever & before initiation of antibiotic therapy 3. Evaluation of valvular and ventricular function (echocardiography)
5 4. Scrupulous oral hygiene and frequent dental professional office visits Procedures that require endocarditis prophylaxis: 1. Dental s 2. Tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy 3. Bronchoscopy (rigid bronchoscope) 4. Sclerotherapy for esophageal varices 5. Esophageal dilation 6. ERCP 7. Biliary tract surgery 8. Surgical operations that involve intestinal mucos 9. Prostatic surgery 10. Cystoscopy Procedures that don t require endocarditis prophylaxis: 1. Endotracheal intubation 2. Bronchoscopy (flexible bronchoscope) 3. Tympanostomy tube insertion 4. TEE 5. Endoscopy 6. Cardiac catheterization, including PTCA, stents Prophylactic Regimens Prophylactic Regimens for Dental, Oral, Respiratory, or Esophageal Procedures Agent Regimen Situation Standard general prophylaxis Amoxicillin Adults: 2.0 g; children: 50 mg/kg orally 1 h before Unable to take oral medications Ampicillin Adults: 2.0 g IM or IV; children: 50 mg/kg IM or IV within 30 min before Allergic to penicillin Clindamycin or Adults: 600 mg; children: 20 mg/kg orally 1 h before Cephalexin or cefadroxil or Adults: 2.0 g; children; 50 mg/kg orally 1 h before Azithromycin or clarithromycin Adults: 500 mg; children: 15 mg/kg orally 1 h before Allergic to penicillin Clindamycin or Adults: 600 mg; children: 20 mg/kg IV and unable to take oral Cefazolin medications within 30 min before Adults: 1.0 g; children: 25 mg/kg IM or IV within 30 min before Prophylactic Regimens for Genitourinary/GIT s
6 Situation High-risk patients High-risk patients allergic to ampicillin/amoxicillin Moderate-risk patients Moderate-risk patients allergic to ampicillin/amoxicillin Agents Ampicillin plus gentamicin Vancomycin plus gentamicin Amoxicillin or ampicillin Regimen Adults: ampicillin 2.0 g IM or IV plus gentamicin 1.5 mg/kg (not to exceed 120 mg) within 30 min of starting ; 6 h later, ampicillin 1 g IM/IV or amoxicillin 1 g orally Children: ampicillin 50 mg/kg IM or IV (not to exceed 2.0 g) plus gentamicin 1.5 mg/kg within 30 min of starting the ; 6 h later, ampicillin 25 mg/kg IM/IV or amoxicillin 25 mg/kg orally Adults: vancomycin 1.0 g IV over 1-2 h plus gentamicin 1.5 mg/kg IV/IM (not to exceed 120 mg); complete injection/infusion within 30 min of starting Children: vancomycin 20 mg/kg IV over 1-2 h plus gentamicin 1.5 mg/kg IV/IM; complete injection/infusion within 30 min of starting Adults: amoxicillin 2.0 g orally 1 h before, or ampicillin 2.0 g IM/IV within 30 min of starting Children: amoxicillin 50 mg/kg orally 1 h before, or ampicillin 50 mg/kg IM/IV within 30 min of starting Vancomycin Adults: vancomycin 1.0 g IV over 1-2 h complete infusion within 30 min of starting Children: vancomycin 20 mg/kg IV over 1-2 h; complete infusion within 30 min of starting PROSTHETIC VALVE ENDOCARDITIS
7 Infective endocarditis on top of prosthetic material; mechanical or tissue valves, valve rings, pacemaker or defibrillation leads and synthetic shunts represents approximately 25% of endocarditis cases. The incidence is expected to increase as the number of invasive cardiac s continues to rise. The risk of prosthetic valve endocarditis (PVE) is not uniform. The risk is greatest during the first 6 months after surgery (particularly during the initial 5-6 weeks) and thereafter declines to a lower risk. Patients operated for native valve endocarditis are at special risk for PVE. Mechanical prostheses are more liable to infection than tissue valves, but after 12 months, the risk of infection of Bioprothesis exceeds that of mechanical valves. The risk of infection on a pacemaker/defibrillator lead is higher for repeat s rather than initial implantations. There are two forms of PVE; early and late. The arbitrary cutoff between the two is one year. PVE within 12 months after valve surgery is likely to be derived from events during the surgical admission. On the other hand, late PVE is more likely to be community acquired. This difference explains the causative microbiology in the two situations. In early PVE, the commonest organisms are those originating in the hospital environment: Coagulase negative staphylococci, Staphylococcus aureus, gram negative bacilli and fungi. In late PVE, the predominant pathogens are streptococci, enterococci followed by staphylococci. The mere presence of prosthetic material endangers the integrity of the natural body defenses against microbial invasion. The normal laminar flow is replaced by eddies which favor deposition of fibrin on adjacent endothelial surfaces which may form a nidus for infection. Migration of polymorphs, lymphocytes to the site of infection is markedly hampered by a prosthetic surface. This explains why the pathology of PVE differs from the leaflet-limited form seen in native valves. Infection on mechanical prostheses commonly extends beyond the valve ring to the annulus, periannular tissue as well as the fibrous trigone between the aortic and mitral valves. The consequences are usually drastic with valve dehiscence, severe paravalvular regurgitation, ring abscess, fistulous tracts and conduction disturbances. Because of the aggressive underlying infection, systemic complications are more frequent in PVE than in native valve IE. CHF, cerebrovascular complications, and sepsis may be encountered separately or combined in up to one fourth of patients with PVE. The first manifestation of PVE may be a fatal prosthetic valve dehiscence or obstruction. The clinical picture and the diagnosis of PVE can be deceptive but nevertheless more complicated. A high index of suspicion is necessary. Fever in the perioperative period is commonly ascribed to wound infection, pneumonia or transfusion reactions. Embolization can be attributed to inadequate anticoagulation. Even blood cultures may be rendered non-diagnostic by the frequently prescribed parenteral antibiotics. The dense shadows of metallic leaflets usually mask any vegetation in transthoracic echocardiograms. That s why tranesophageal echocardiography (TEE) is preferred as an initial imaging method in suspected PVE. Even by TEE it may be difficult to discern small vegetations from suture material. Penetration of antimicrobials from the blood stream to the site of infection is also markedly limited by the presence of prosthetic material. The choice of the initial empirical regimen is based on the most commonly cultured organisms in early PVE;
8 staphylococci. The most effective combination for methicillin resistant Staphylococci is Vancomycin, gentamycin and rifampicin. The value of rifampicin is in its unique antistaphylococcal activity on prosthetic surfaces. For methicillin susceptible Staphylococci, vancomycin is replaced by nafcillin or large dose cefazolin. A quinolone may be used as an alternative in gentamycin resistant strains. Surgery stands a very important role in the management of PVE. Some authorities consider the mere presence of prosthetic endocarditis an indication for redo surgery. A homograft represents the best option to replace an infected metallic prosthesis with. In real life, one must balance the risk of a redo valve replacement with extensive debridement as well as the availability of homografts on one hand and the high risk of progressive uncontrollable infection and systemic complications on the other hand. An unstable prosthesis with >40% dehiscence of the circumference is a clear indication of emergency surgery. HEALTH CARE ASSOCIATED ENDOCARDITIS (HAE) This is a relatively new term that has replaced the old one, nosocomial endocarditis. It applies to the following situations: 1. Endocarditis diagnosed > 72 hr from hospital admission, provided there is evidence that endocarditis was not present on admission 2. Endocarditis diagnosed within 60 days ( some may extend this period up to 6 months) from a previous hospital admission 3. Early post operative Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis (PVE) 4. Risk of bacteremia was performed (the risk may be as simple as inserting a cannula or as invasive as cardiac surgery) Patients with HAE share common and serious features: 1. Virulent type of pathogens (Methicillin Resistant Staphylococci, Gram negative bacilli and fungi) 2. Poor prognosis: higher rates of complications and mortality (mortality rates approaching 40 % in our series and some of the European series) 3. Poor response to medical treatment and frequent need for cardiac surgery HAE occurs mainly as a result of a breakdown in the chain of infection control in hospitals. Such a difficult, coasty problem with poor outcome could be prevented by following strict rules of hospital infection control. HAE should be dealt with as preventable rather than a curative disease.
Daniel C. DeSimone, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine
 Daniel C. DeSimone, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Faculty photo will be placed here Desimone.Daniel@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Infective Endocarditis Mayo School of Continuous Professional Development
Daniel C. DeSimone, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Faculty photo will be placed here Desimone.Daniel@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Infective Endocarditis Mayo School of Continuous Professional Development
NATIONAL HEART FOUNDATION HOSPITAL & RESEARCH INSTITUTE
 Welcome INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS: WHERE WE ARE AT 2005? DR MD HABIBUR RAHMAN FCPS(Medicine) NATIONAL HEART FOUNDATION HOSPITAL & RESEARCH INSTITUTE DEFINITION OF INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Infective endocarditis
Welcome INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS: WHERE WE ARE AT 2005? DR MD HABIBUR RAHMAN FCPS(Medicine) NATIONAL HEART FOUNDATION HOSPITAL & RESEARCH INSTITUTE DEFINITION OF INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Infective endocarditis
Overview. Clinical Scenario. Endocarditis: Treatment & Prevention. Prophylaxis The Concept. Jeremy D. Young, MD, MPH. Division of Infectious Diseases
 Endocarditis: Treatment & Prevention Jeremy D. Young, MD, MPH Division of Infectious Diseases Clinical Scenario Patient with MVP scheduled to have wisdom teeth extracted. Has systolic murmur with mid-systolic
Endocarditis: Treatment & Prevention Jeremy D. Young, MD, MPH Division of Infectious Diseases Clinical Scenario Patient with MVP scheduled to have wisdom teeth extracted. Has systolic murmur with mid-systolic
Dr Babak Tamizi far MD. Assistant Professor Of Internal Medicine Al-Zahra Hospital Isfahan University Of Medical Sciences
 Dr Babak Tamizi far MD. Assistant Professor Of Internal Medicine Al-Zahra Hospital Isfahan University Of Medical Sciences ١ ٢ ٣ A 57-year-old man presents with new-onset fever, shortness of breath, lower
Dr Babak Tamizi far MD. Assistant Professor Of Internal Medicine Al-Zahra Hospital Isfahan University Of Medical Sciences ١ ٢ ٣ A 57-year-old man presents with new-onset fever, shortness of breath, lower
Endocarditis, including Prophylaxis
 Endocarditis, including Prophylaxis ACOI Board Review 2018 gerald.blackburn@beaumont.org (No Disclosures) Infective Endocarditis Persistant bacteremia (blood cultures drawn >12 hrs apart) w/ organisms
Endocarditis, including Prophylaxis ACOI Board Review 2018 gerald.blackburn@beaumont.org (No Disclosures) Infective Endocarditis Persistant bacteremia (blood cultures drawn >12 hrs apart) w/ organisms
The changing landscape of infective endocarditis (IE)in congenital heart disease (CHD)
 The changing landscape of infective endocarditis (IE)in congenital heart disease (CHD) Rekwan Sittiwangkul,MD Department of Pediatrics. Chiang Mai University Hospital, 24 th March 2018 Infective endocarditis
The changing landscape of infective endocarditis (IE)in congenital heart disease (CHD) Rekwan Sittiwangkul,MD Department of Pediatrics. Chiang Mai University Hospital, 24 th March 2018 Infective endocarditis
Heart on Fire: Infective Endocarditis. Objectives. Disclosure 8/27/2018. Mary McGreal DNP, RN, ANP-c, CCRN
 Heart on Fire: Infective Endocarditis Mary McGreal DNP, RN, ANP-c, CCRN Objectives Discuss the incidence of infective endocarditis? Discuss the pathogenesis of infective endocarditis? Discuss clinical
Heart on Fire: Infective Endocarditis Mary McGreal DNP, RN, ANP-c, CCRN Objectives Discuss the incidence of infective endocarditis? Discuss the pathogenesis of infective endocarditis? Discuss clinical
Challenging clinical situation
 Challenging clinical situation A young patient with prosthetic aortic valve endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France October 25 th 2014 Case report History of the disease Clinical
Challenging clinical situation A young patient with prosthetic aortic valve endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France October 25 th 2014 Case report History of the disease Clinical
Diagnostic strategy. Dr Pilar Tornos Hospital Vall d Hebron Barcelona
 Diagnostic strategy Dr Pilar Tornos Hospital Vall d Hebron Barcelona Faculty disclosure Pilar Tornos I disclose the following financial relationships: Paid speaker for Recordati, Edwards. Diagnosis of
Diagnostic strategy Dr Pilar Tornos Hospital Vall d Hebron Barcelona Faculty disclosure Pilar Tornos I disclose the following financial relationships: Paid speaker for Recordati, Edwards. Diagnosis of
Infective Endocarditis Empirical therapy Antibiotic Guidelines. Contents
 Infective Endocarditis Empirical therapy Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Group Additional author(s): as above Authors Division: Division of Clinical
Infective Endocarditis Empirical therapy Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Group Additional author(s): as above Authors Division: Division of Clinical
Infective endocarditis (IE) By Assis. Prof. Nader Alaridah MD, PhD
 Infective endocarditis (IE) By Assis. Prof. Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Infective endocarditis (IE) is an inflammation of the endocardium.. inner of the heart muscle & the epithelial lining of heart valves.
Infective endocarditis (IE) By Assis. Prof. Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Infective endocarditis (IE) is an inflammation of the endocardium.. inner of the heart muscle & the epithelial lining of heart valves.
Infections Amenable to OPAT. (Nabin Shrestha + Ajay Mathur)
 3 Infections Amenable to OPAT (Nabin Shrestha + Ajay Mathur) Decisions regarding outpatient treatment of infections vary with the institution, the prescribing physician, the individual patient s condition
3 Infections Amenable to OPAT (Nabin Shrestha + Ajay Mathur) Decisions regarding outpatient treatment of infections vary with the institution, the prescribing physician, the individual patient s condition
Michael Stander, Pharm.D.
 Michael Stander, Pharm.D. Endocarditis: Goals Epidemiology Presentation of acute and subacute. Diagnosis: What is Dukes Criteria and how do we approach the diagnosis of endocarditis? Treatment: Understand
Michael Stander, Pharm.D. Endocarditis: Goals Epidemiology Presentation of acute and subacute. Diagnosis: What is Dukes Criteria and how do we approach the diagnosis of endocarditis? Treatment: Understand
Infective Endocarditis
 Infective Endocarditis Infective Endocarditis Historical Perspective.. A concretion larger than a pigeon s egg; contained in the left auricle. Burns, 1809 Osler s Gulstonian lectures provided the 1 st
Infective Endocarditis Infective Endocarditis Historical Perspective.. A concretion larger than a pigeon s egg; contained in the left auricle. Burns, 1809 Osler s Gulstonian lectures provided the 1 st
Infective endocarditis
 Infective endocarditis Today's lecture is about infective endocarditis, the Dr started the lecture by asking what are the most common causative agents of infective endocarditis? 1-Group A streptococci
Infective endocarditis Today's lecture is about infective endocarditis, the Dr started the lecture by asking what are the most common causative agents of infective endocarditis? 1-Group A streptococci
Infective Endocarditis
 Definition Infective Endocarditis Pattaya Riengchan M.D. MAR 16, 2017 Infection of endocardial surface of the heart and implies the physical presence microorganisms in the lesion Heart valves are most
Definition Infective Endocarditis Pattaya Riengchan M.D. MAR 16, 2017 Infection of endocardial surface of the heart and implies the physical presence microorganisms in the lesion Heart valves are most
Microbiological diagnosis of infective endocarditis; what is new?
 Microbiological diagnosis of infective endocarditis; what is new? Dr Amani El Kholy, MD Professor of Clinical Pathology (Microbiology), Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University ESC 2017 1 Objectives Lab Diagnostic
Microbiological diagnosis of infective endocarditis; what is new? Dr Amani El Kholy, MD Professor of Clinical Pathology (Microbiology), Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University ESC 2017 1 Objectives Lab Diagnostic
The microbial diagnosis of infective endocarditis (IE)
 The microbial diagnosis of infective endocarditis (IE) Pierrette Melin Medical Microbiology pm-chulg sbimc 10.05.2007 1 Introduction for diagnosis Review of microbiological investigation of IE and perspectives
The microbial diagnosis of infective endocarditis (IE) Pierrette Melin Medical Microbiology pm-chulg sbimc 10.05.2007 1 Introduction for diagnosis Review of microbiological investigation of IE and perspectives
Infective Endocarditis
 Infective Endocarditis Definition Historical perspective Classification Epidemiological Features Etiology Pathogenesis Clinical presentation Diagnosis Treatment options Prevention Infective endocarditis
Infective Endocarditis Definition Historical perspective Classification Epidemiological Features Etiology Pathogenesis Clinical presentation Diagnosis Treatment options Prevention Infective endocarditis
Infective endocarditis
 Infective endocarditis This is caused by microbial infection of a heart valve (native or prosthetic), the lining of a cardiac chamber or blood vessel, or a congenital anomaly (e.g. septal defect). The
Infective endocarditis This is caused by microbial infection of a heart valve (native or prosthetic), the lining of a cardiac chamber or blood vessel, or a congenital anomaly (e.g. septal defect). The
PRINCIPLES OF ENDOCARDITIS
 015 // Endocarditis CONTENTS 140 Principles of Endocarditis 141 Native Valve Endocarditis 143 Complications of Native Valve Endocarditis 145 Right Heart Endocarditis 145 Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis 146
015 // Endocarditis CONTENTS 140 Principles of Endocarditis 141 Native Valve Endocarditis 143 Complications of Native Valve Endocarditis 145 Right Heart Endocarditis 145 Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis 146
Infective Endocarditis
 Frank Lowy Infective Endocarditis 1. Introduction Infective endocarditis (IE) is an infection of the heart valves. A large number of different bacteria are capable of causing this disease. Depending on
Frank Lowy Infective Endocarditis 1. Introduction Infective endocarditis (IE) is an infection of the heart valves. A large number of different bacteria are capable of causing this disease. Depending on
Update on the prevention, diagnosis and management of Infective Endocarditis (IE)
 Update on the prevention, diagnosis and management of Infective Endocarditis (IE) Dr.Ahmed Yahya Mohammed Alarhabi MD, MsC,FcUSM,FACC,MAHA Consultant Interventional Cardiologist Head of Cardiac Center
Update on the prevention, diagnosis and management of Infective Endocarditis (IE) Dr.Ahmed Yahya Mohammed Alarhabi MD, MsC,FcUSM,FACC,MAHA Consultant Interventional Cardiologist Head of Cardiac Center
Guidelines for The Management of Infective Endocarditis
 Guidelines for The Management of Infective Endocarditis By Dr. Sinan Butrus F.I.C.M.S Clinical Standards & Guidelines Kurdistan Board For Medical Specialties Infective endocarditis IE is an infection of
Guidelines for The Management of Infective Endocarditis By Dr. Sinan Butrus F.I.C.M.S Clinical Standards & Guidelines Kurdistan Board For Medical Specialties Infective endocarditis IE is an infection of
Bacterial Endocarditis
 Objectives Bacterial Endocarditis John C. Rotschafer, Pharm. D. Professor College of Pharmacy University of Minnesota Identify which valves are commonly involved with endocarditis Identify common pathogens
Objectives Bacterial Endocarditis John C. Rotschafer, Pharm. D. Professor College of Pharmacy University of Minnesota Identify which valves are commonly involved with endocarditis Identify common pathogens
April 16, 09:00-09:15 중앙대학교 윤신원
 April 16, 09:00-09:15 중앙대학교 윤신원 When to perform Echocardiography in IE? Vegetations?(pathologic Whatever the level hallmark) of suspicion Intracardiac abscess? Confirm or R/O at the Earliest opportunity.
April 16, 09:00-09:15 중앙대학교 윤신원 When to perform Echocardiography in IE? Vegetations?(pathologic Whatever the level hallmark) of suspicion Intracardiac abscess? Confirm or R/O at the Earliest opportunity.
Infective Endocarditis عبد المهيمن أحمد
 Infective Endocarditis إعداد : عبد المهيمن أحمد أحمد علي Infective endocarditis Inflammation of the heart valve or endocardium of the heart. The agents are usually bacterial, but other organisms can also
Infective Endocarditis إعداد : عبد المهيمن أحمد أحمد علي Infective endocarditis Inflammation of the heart valve or endocardium of the heart. The agents are usually bacterial, but other organisms can also
Infected cardiac-implantable electronic devices: diagnosis, and treatment
 Infected cardiac-implantable electronic devices: diagnosis, and treatment The incidence of infection following implantation of cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) is increasing at a faster rate
Infected cardiac-implantable electronic devices: diagnosis, and treatment The incidence of infection following implantation of cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) is increasing at a faster rate
Echocardiography after stroke - where to look
 Echocardiography after stroke - where to look Vuyisile T. Nkomo, MD,MPH, FACC, FASE Joint Cardiac Imaging Society of South Africa/Mayo Clinic Echocardiography Workshop 2017 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
Echocardiography after stroke - where to look Vuyisile T. Nkomo, MD,MPH, FACC, FASE Joint Cardiac Imaging Society of South Africa/Mayo Clinic Echocardiography Workshop 2017 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both.
 results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both. The outcome of valvular disease depends on : 1-the valve involved 2-the degree of impairment 3-the cause of its development
results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both. The outcome of valvular disease depends on : 1-the valve involved 2-the degree of impairment 3-the cause of its development
Apport des recommandations européennes
 Apport des recommandations européennes Gilbert Habib Cardiology Department- La Timone Marseille - France Bordeaux le 28 Juin 2011 Infective Endocarditis: a changing disease new high-risk subgroups IVDA
Apport des recommandations européennes Gilbert Habib Cardiology Department- La Timone Marseille - France Bordeaux le 28 Juin 2011 Infective Endocarditis: a changing disease new high-risk subgroups IVDA
VALVULAR HEART DISEASE
 VALVULAR HEART DISEASE Stenosis: failure of a valve to open completely, obstructing forward flow. - almost always due to a chronic process (e.g., calcification or valve scarring). Insufficiency : failure
VALVULAR HEART DISEASE Stenosis: failure of a valve to open completely, obstructing forward flow. - almost always due to a chronic process (e.g., calcification or valve scarring). Insufficiency : failure
Bacterial Endocarditis
 Disclosures Bacterial Endocarditis Henry F. Chambers, MD Allergan research grant Genentech research grant Infective endocarditis: Outline Native valve endocarditis Prosthetic valve endocarditis Cardiac
Disclosures Bacterial Endocarditis Henry F. Chambers, MD Allergan research grant Genentech research grant Infective endocarditis: Outline Native valve endocarditis Prosthetic valve endocarditis Cardiac
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN CHILDREN
 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN CHILDREN Rohayati Taib RIPAS Hospital, Bundar Seri Begawan, Brunei Darussalam Infective Endocarditis (IE) is a microbial infection of the endocardium. It encompasses both bacterial
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN CHILDREN Rohayati Taib RIPAS Hospital, Bundar Seri Begawan, Brunei Darussalam Infective Endocarditis (IE) is a microbial infection of the endocardium. It encompasses both bacterial
VEGETATION NEGATIVE INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS A VIEW POINT... Mumbai Dec 2005 Annual scientific sessions
 VEGETATION NEGATIVE INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS A VIEW POINT... Mumbai Dec 2005 Annual scientific sessions S.Venkatesan,G.Gnanavelu,G.Karthikeyan,V.Jaganathan,R.Alagesan M.Annamalai,S.Shanmugasundaram, S.Geetha,A.Balaguru.G.Anuradha
VEGETATION NEGATIVE INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS A VIEW POINT... Mumbai Dec 2005 Annual scientific sessions S.Venkatesan,G.Gnanavelu,G.Karthikeyan,V.Jaganathan,R.Alagesan M.Annamalai,S.Shanmugasundaram, S.Geetha,A.Balaguru.G.Anuradha
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS. IAP UG Teaching slides
 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IAP UG Teaching slides 2015 16 1 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Infection of the endocardial lining is called infective endocarditis. Involving the endocardium of valves,mural endocardium
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IAP UG Teaching slides 2015 16 1 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Infection of the endocardial lining is called infective endocarditis. Involving the endocardium of valves,mural endocardium
Infective endocarditis (IE) is an
 Jason Andrade, MD, Ellamae Stadnick, MD, Aneez Mohamed, MD Infective endocarditis prophylaxis: An update for clinical practice Antibiotic therapy to prevent endocarditis is now considered un - necessary
Jason Andrade, MD, Ellamae Stadnick, MD, Aneez Mohamed, MD Infective endocarditis prophylaxis: An update for clinical practice Antibiotic therapy to prevent endocarditis is now considered un - necessary
Pr AMEL OMEZZINE LETAIEF CHU FarhatHached Sousse
 Pr AMEL OMEZZINE LETAIEF CHU FarhatHached Sousse cours de collège infectiologie Sousse le27/02/2013 ENDOCARDITIS There is a change in epidemiology Clinical features of IE remains classical Diagnosis of
Pr AMEL OMEZZINE LETAIEF CHU FarhatHached Sousse cours de collège infectiologie Sousse le27/02/2013 ENDOCARDITIS There is a change in epidemiology Clinical features of IE remains classical Diagnosis of
Infective Endocarditis
 Chapter 32 Infective Endocarditis Lisa B. Hightow and Meera Kelley The term infective endocarditis (IE) refers to infection of the endocardial surface of the heart and implies a physical presence of microganisms
Chapter 32 Infective Endocarditis Lisa B. Hightow and Meera Kelley The term infective endocarditis (IE) refers to infection of the endocardial surface of the heart and implies a physical presence of microganisms
, David Stultz, MD.
 http://www.dilbert.com Infective Endocarditis David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 4 December 8, 2004 Handouts available in PDF format at www.drstultz.com Topics to be covered Epidemiology Microbiology
http://www.dilbert.com Infective Endocarditis David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 4 December 8, 2004 Handouts available in PDF format at www.drstultz.com Topics to be covered Epidemiology Microbiology
A CASE OF RIGHT SIDED INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS WITH REACTIVE KNEE ARTHRITIS AND ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY Suresh Babu S 1, A. K. Badrinath 2, K.
 A CASE OF RIGHT SIDED INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS WITH REACTIVE KNEE ARTHRITIS AND ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY Suresh Babu S 1, A. K. Badrinath 2, K. Suresh 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Suresh Babu S, A. K. Badrinath,
A CASE OF RIGHT SIDED INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS WITH REACTIVE KNEE ARTHRITIS AND ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY Suresh Babu S 1, A. K. Badrinath 2, K. Suresh 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Suresh Babu S, A. K. Badrinath,
CDA Position on Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Dental Patients at Risk
 Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Dental Patients at Risk Certain categories of invasive dental treatment are known to produce significant bacteremias. Such bacteremias, although transient, may be detrimental
Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Dental Patients at Risk Certain categories of invasive dental treatment are known to produce significant bacteremias. Such bacteremias, although transient, may be detrimental
A Study of Infective Endocarditis in Malta
 Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 6(6): 98-104 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjcm doi: 10.11648/j.sjcm.20170606.11 ISSN: 2327-2724 (Print); ISSN: 2327-2732 (Online) A Study of Infective
Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 6(6): 98-104 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjcm doi: 10.11648/j.sjcm.20170606.11 ISSN: 2327-2724 (Print); ISSN: 2327-2732 (Online) A Study of Infective
An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for infective endocarditis
 REVIEW An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for infective endocarditis Albert W Chan MD FRCPC, Heather J Ross MD FRCPC AW Chan, HJ Ross. An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for
REVIEW An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for infective endocarditis Albert W Chan MD FRCPC, Heather J Ross MD FRCPC AW Chan, HJ Ross. An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for
MULTIVALVULAR INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS CLINICAL FEATURES, ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC DATA AND OUTCOMES
 Article Original MULTIVALVULAR INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS CLINICAL FEATURES, ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC DATA AND OUTCOMES L. ABID, B. JERBI, I. TRABELSI, A. ZNAZEN*, S. KRICHÈNE, D. ABID, M. AKROUT, S. MALLEK, F. TRIKI,
Article Original MULTIVALVULAR INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS CLINICAL FEATURES, ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC DATA AND OUTCOMES L. ABID, B. JERBI, I. TRABELSI, A. ZNAZEN*, S. KRICHÈNE, D. ABID, M. AKROUT, S. MALLEK, F. TRIKI,
Contents. 1. Introduction. J Antimicrob Chemother 2012; 67: doi: /jac/dkr450 Advance Access publication 14 November 2011
 J Antimicrob Chemother 2012; 67: 269 289 doi:10.1093/jac/dkr450 Advance Access publication 14 November 2011 Guidelines for the diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of endocarditis in adults: a report of
J Antimicrob Chemother 2012; 67: 269 289 doi:10.1093/jac/dkr450 Advance Access publication 14 November 2011 Guidelines for the diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of endocarditis in adults: a report of
SYMPOSIUM 10TH MAY 2007 BELGIUM. Blood culture-negative endocarditis
 SYMPOSIUM 10TH MAY 2007 BELGIUM Blood culture-negative endocarditis Didier RAOULT Didier.raoult@gmail.com Modified Duke criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis (IE) Li JS, et al. Proposed modifications
SYMPOSIUM 10TH MAY 2007 BELGIUM Blood culture-negative endocarditis Didier RAOULT Didier.raoult@gmail.com Modified Duke criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis (IE) Li JS, et al. Proposed modifications
CLINICAL SYNDROMES: COMMUNITY ACQUIRED INFECTIONS
 SECTION 2 CLINICAL SYNDROMES: COMMUNITY ACQUIRED INFECTIONS 118-1 118 Adolf W. Karchmer The prototypic lesion of infective endocarditis, the vegetation (Fig. 118-1), is a mass of platelets, fibrin, microcolonies
SECTION 2 CLINICAL SYNDROMES: COMMUNITY ACQUIRED INFECTIONS 118-1 118 Adolf W. Karchmer The prototypic lesion of infective endocarditis, the vegetation (Fig. 118-1), is a mass of platelets, fibrin, microcolonies
Disclosures. Native Valve Endocarditis and its Complications. Outline. Outline. Basics. Basics 3/23/2017
 Native Valve Endocarditis and its Complications SCVP and Binford Dammin Society of Infectious Disease Pathologists Shared Companion Meeting USCAP 2017 Annual Meeting Disclosures Relevant financial relationships
Native Valve Endocarditis and its Complications SCVP and Binford Dammin Society of Infectious Disease Pathologists Shared Companion Meeting USCAP 2017 Annual Meeting Disclosures Relevant financial relationships
Consensus Statement on Infective Endocarditis / Abridged Version
 CONSENSUS Consensus Statement on Infective Endocarditis / Abridged Version Argentine Society of Cardiology General Directors Secretary (Area of Regulations and Consensuses) Dr. Gustavo Giunta MTSAC 1.
CONSENSUS Consensus Statement on Infective Endocarditis / Abridged Version Argentine Society of Cardiology General Directors Secretary (Area of Regulations and Consensuses) Dr. Gustavo Giunta MTSAC 1.
Sepsis and Infective Endocarditis
 Sepsis and Infective Endocarditis Michal Holub Department of Infectious Diseases First Faculty of Medicine Charles University in Prague and University Military Hospital Bacteremia and Sepsis bacteremia
Sepsis and Infective Endocarditis Michal Holub Department of Infectious Diseases First Faculty of Medicine Charles University in Prague and University Military Hospital Bacteremia and Sepsis bacteremia
A Nightmare. R Dulgheru, CHU Liege
 A Nightmare R Dulgheru, CHU Liege Faculty disclosure Raluca Dulgheru I have no financial relationships to disclose. MB, 57 years old male 18/03/2016 to the ER for altered mental status, First weight name
A Nightmare R Dulgheru, CHU Liege Faculty disclosure Raluca Dulgheru I have no financial relationships to disclose. MB, 57 years old male 18/03/2016 to the ER for altered mental status, First weight name
Infective Endocarditis for Primary Care Physicians
 Infective Endocarditis for Primary Care Physicians David N Gilbert, MD Disclosures Consultant to: Merck Pfizer Medicine Company Cempra 1 Introduction There are roughly 30,000 new cases of IE in the US
Infective Endocarditis for Primary Care Physicians David N Gilbert, MD Disclosures Consultant to: Merck Pfizer Medicine Company Cempra 1 Introduction There are roughly 30,000 new cases of IE in the US
Management of infective endocarditis in children
 Management of infective endocarditis in children Ashutosh Marwah, MD* Savitri Shrivastava, MD DM FAMS FACC* INTRODUCTION Infective endocarditis (IE) continues to remain a serious disease despite advances
Management of infective endocarditis in children Ashutosh Marwah, MD* Savitri Shrivastava, MD DM FAMS FACC* INTRODUCTION Infective endocarditis (IE) continues to remain a serious disease despite advances
Diagnosis and Treatment of Bacterial Endocarditis
 Infectious diseases Board Review Manual Statement of Editorial Purpose The Hospital Physician Infectious Diseases Board Review Manual is a study guide for fellows and practicing physicians preparing for
Infectious diseases Board Review Manual Statement of Editorial Purpose The Hospital Physician Infectious Diseases Board Review Manual is a study guide for fellows and practicing physicians preparing for
Suggested Reading: Pages Donald P. Levine, M.D. Professor of Medicine Page 1 of 8
 Professor of Medicine Page 1 of 8 ENDOCARDITIS I. General A. infectivie endocarditis (IE) 1. definition: infection of the endocardial surface of the heart; implies the physical presence of microorganisms
Professor of Medicine Page 1 of 8 ENDOCARDITIS I. General A. infectivie endocarditis (IE) 1. definition: infection of the endocardial surface of the heart; implies the physical presence of microorganisms
General management of infective endocarditis
 General management of infective endocarditis Team approach in infective endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 The echolab «Heart Team" Infective Endocarditis
General management of infective endocarditis Team approach in infective endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 The echolab «Heart Team" Infective Endocarditis
Endocardite infectieuse
 Endocardite infectieuse 1. Raccourcir le traitement: jusqu où? 2. Proposer un traitement ambulatoire: à partir de quand? Endocardite infectieuse A B 90 P = 0.014 20 P = 0.0005 % infective endocarditis
Endocardite infectieuse 1. Raccourcir le traitement: jusqu où? 2. Proposer un traitement ambulatoire: à partir de quand? Endocardite infectieuse A B 90 P = 0.014 20 P = 0.0005 % infective endocarditis
Infective Endocarditis:
 CME Workshop Infective Endocarditis: Prophylaxis, Diagnosis and Management Presented at a CME program, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba, December 2001. By Davinder S. Jassal, MD; and John M.
CME Workshop Infective Endocarditis: Prophylaxis, Diagnosis and Management Presented at a CME program, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba, December 2001. By Davinder S. Jassal, MD; and John M.
INFECTIOUS endocarditis (IE) is a
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis Sensitivity of the Duke vs von Reyn Criteria Maija Heiro, MD; Jukka Nikoskelainen, MD, PhD; Jaakko J. Hartiala, MD, PhD; Markku K. Saraste, MD;
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis Sensitivity of the Duke vs von Reyn Criteria Maija Heiro, MD; Jukka Nikoskelainen, MD, PhD; Jaakko J. Hartiala, MD, PhD; Markku K. Saraste, MD;
The Challenge of Managing Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia
 The Challenge of Managing Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia M A R G A R E T G R A Y B S P F C S H P C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E M A N A G E R N O R T H / I D P H A R M A C I S T A L B E R T A H E A
The Challenge of Managing Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia M A R G A R E T G R A Y B S P F C S H P C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E M A N A G E R N O R T H / I D P H A R M A C I S T A L B E R T A H E A
109 Infective Endocarditis
 Página 1 de 30 Copyright 2005 McGraw-Hill Kasper, Dennis L., Fauci, Anthony S., Longo, Dan L., Braunwald, Eugene, Hauser, Stephen L., Jameson, J. Larry, Harrison, T. R., Resnick, W. R., Wintrobe, M. M.,
Página 1 de 30 Copyright 2005 McGraw-Hill Kasper, Dennis L., Fauci, Anthony S., Longo, Dan L., Braunwald, Eugene, Hauser, Stephen L., Jameson, J. Larry, Harrison, T. R., Resnick, W. R., Wintrobe, M. M.,
Endocarditis in the elderly
 Endocarditis in the elderly Gilbert Habib Département de Cardiologie - Timone Marseille Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 Endocarditis in the octogenarian Gilbert Habib Département de Cardiologie - Timone Marseille
Endocarditis in the elderly Gilbert Habib Département de Cardiologie - Timone Marseille Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 Endocarditis in the octogenarian Gilbert Habib Département de Cardiologie - Timone Marseille
Hearts afire: Infective endocarditis
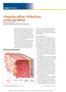 Hearts afire: Infective endocarditis By Kim McCarron, MS, CRNP Clinical Associate Professor Towson University Towson, Md. Editorial Advisory Board Member Nursing made Incredibly Easy! Picturing endocarditis
Hearts afire: Infective endocarditis By Kim McCarron, MS, CRNP Clinical Associate Professor Towson University Towson, Md. Editorial Advisory Board Member Nursing made Incredibly Easy! Picturing endocarditis
Renal Unit. Catheter Related Bacteraemia Guidelines
 Renal Unit Policy Manager Drew Henderson Policy Group Renal Unit Policy Established 21/01/2014 Policy Review Period/Expiry 21/01/2015 Last Updated 21/01/2014 This policy does apply to Medical/Dental Staff
Renal Unit Policy Manager Drew Henderson Policy Group Renal Unit Policy Established 21/01/2014 Policy Review Period/Expiry 21/01/2015 Last Updated 21/01/2014 This policy does apply to Medical/Dental Staff
A Predictable Outcome of a Preventable Disease. Sanjay Kamboj, MD; Shaminder Gupta, MD; Glenn P. Kelley, MD; Fred Helmcke, MD; and Fred A.
 Clinical Case of the Month A Predictable Outcome of a Preventable Disease Sanjay Kamboj, MD; Shaminder Gupta, MD; Glenn P. Kelley, MD; Fred Helmcke, MD; and Fred A. Lopez, MD Infective endocarditis is
Clinical Case of the Month A Predictable Outcome of a Preventable Disease Sanjay Kamboj, MD; Shaminder Gupta, MD; Glenn P. Kelley, MD; Fred Helmcke, MD; and Fred A. Lopez, MD Infective endocarditis is
Echocardiography in Endocarditis
 Echocardiography in Endocarditis Bicol Hospital, Legazpi City, Philippines July 2016 Gregg S. Pressman MD, FACC, FASE Einstein Medical Center Philadelphia, USA Demographics of IE Incidence is 1.4 12.7/100,000
Echocardiography in Endocarditis Bicol Hospital, Legazpi City, Philippines July 2016 Gregg S. Pressman MD, FACC, FASE Einstein Medical Center Philadelphia, USA Demographics of IE Incidence is 1.4 12.7/100,000
Endocarditis and Its Complications: The Role of Echocardiography
 Endocarditis and Its Complications: The Role of Echocardiography Pravin Patil, MD FACC FASE Associate Professor of Medicine Director, Cardiovascular Disease Training Program Lewis Katz School of Medicine
Endocarditis and Its Complications: The Role of Echocardiography Pravin Patil, MD FACC FASE Associate Professor of Medicine Director, Cardiovascular Disease Training Program Lewis Katz School of Medicine
Blood culture 壢新醫院 病理檢驗科 陳啟清技術主任
 Blood culture 壢新醫院 病理檢驗科 陳啟清技術主任 A Positive Blood Culture Clinically Important Organism Failure of host defenses to contain an infection at its primary focus Failure of the physician to effectively eradicate,
Blood culture 壢新醫院 病理檢驗科 陳啟清技術主任 A Positive Blood Culture Clinically Important Organism Failure of host defenses to contain an infection at its primary focus Failure of the physician to effectively eradicate,
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW
 PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
Heart Valves: Before and after surgery
 Heart Valves: Before and after surgery Tim Sutton, Consultant Cardiologist Middlemore Hospital, Auckland Auckland Heart Group Indications for intervention in Valvular disease To prevent sudden death and
Heart Valves: Before and after surgery Tim Sutton, Consultant Cardiologist Middlemore Hospital, Auckland Auckland Heart Group Indications for intervention in Valvular disease To prevent sudden death and
AHA Scientific Statement
 AHA Scientific Statement Infective Endocarditis in Adults: Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications A Scientific Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart
AHA Scientific Statement Infective Endocarditis in Adults: Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications A Scientific Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart
Management of Catheter Related Bloodstream Infection (CRBSI), including Antibiotic Lock Therapy.
 Management of Catheter Related Bloodstream Infection (CRBSI), including Antibiotic Lock Therapy. Written by: Dr K Gajee, Consultant Microbiologist Date: June 2017 Approved by: Drugs & Therapeutics Committee
Management of Catheter Related Bloodstream Infection (CRBSI), including Antibiotic Lock Therapy. Written by: Dr K Gajee, Consultant Microbiologist Date: June 2017 Approved by: Drugs & Therapeutics Committee
POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00553
 MCC-004 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00553 Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-004 : COMMON CARDIO-VASCULAR DISEASES - II Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note : There will
MCC-004 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00553 Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-004 : COMMON CARDIO-VASCULAR DISEASES - II Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note : There will
The EM Educator Series
 The EM Educator Series The EM Educator Series: Why is my patient with gallbladder pathology so sick? Author: Alex Koyfman, MD (@EMHighAK) // Edited by: Brit Long, MD (@long_brit) and Manpreet Singh, MD
The EM Educator Series The EM Educator Series: Why is my patient with gallbladder pathology so sick? Author: Alex Koyfman, MD (@EMHighAK) // Edited by: Brit Long, MD (@long_brit) and Manpreet Singh, MD
ACCME/Disclosures 4/13/2016 IDPB
 ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
, David Stultz, MD.
 http://www.dilbert.com Infective Endocarditis David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 6 August 31, 2005 Topics to be covered Epidemiology Microbiology Clinical presentation Physical Exam Findings Diagnostic
http://www.dilbert.com Infective Endocarditis David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 6 August 31, 2005 Topics to be covered Epidemiology Microbiology Clinical presentation Physical Exam Findings Diagnostic
A study of clinical and etiological profile of infective endocarditis and its correlation with echocardiography in patients of rheumatic heart disease
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Sarkar A et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Oct;4(5):1323-1327 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20174177
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Sarkar A et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Oct;4(5):1323-1327 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20174177
The New England Journal of Medicine. Review Articles
 Review Articles Medical Progress INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN ADULTS ELEFTHERIOS MYLONAKIS, M.D., AND STEPHEN B. CALDERWOOD, M.D. INFECTIVE endocarditis, a microbial infection of the endocardial surface of
Review Articles Medical Progress INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN ADULTS ELEFTHERIOS MYLONAKIS, M.D., AND STEPHEN B. CALDERWOOD, M.D. INFECTIVE endocarditis, a microbial infection of the endocardial surface of
PROSTHETIC VALVE ENDOCARDITIS Dr Bernard Prendergast DM FRCP EUROVALVE CONGRESS MADRID NOVEMBER 2013
 PROSTHETIC VALVE ENDOCARDITIS Dr Bernard Prendergast DM FRCP EUROVALVE CONGRESS MADRID NOVEMBER 2013 Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis A Dangerous Disease Affects 1-6% of prosthetic valves Mechanical and biological
PROSTHETIC VALVE ENDOCARDITIS Dr Bernard Prendergast DM FRCP EUROVALVE CONGRESS MADRID NOVEMBER 2013 Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis A Dangerous Disease Affects 1-6% of prosthetic valves Mechanical and biological
Prosthetic Valve Infective Endocarditis. Tat Yam Department of Infection Southampton University Hospitals NHS TRust
 Prosthetic Valve Infective Endocarditis Tat Yam Department of Infection Southampton University Hospitals NHS TRust Case History: Episode 1 in MB 73 yr old male, Nigerian PMHx: Hypertension Congestive cardiac
Prosthetic Valve Infective Endocarditis Tat Yam Department of Infection Southampton University Hospitals NHS TRust Case History: Episode 1 in MB 73 yr old male, Nigerian PMHx: Hypertension Congestive cardiac
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books. International authors and editors. Our authors are among the TOP 1%
 We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
Antibiotic Treatment of Adults With Infective Endocarditis Due to Streptococci, Enterococci, Staphylococci, and HACEK Microorganisms
 Antibiotic Treatment of Adults With Infective Endocarditis Due to Streptococci, Enterococci, Staphylococci, and HACEK Microorganisms Walter R. Wilson, MD; Adolf W. Karchmer, MD; Adnan S. Dajani, MD; Kathryn
Antibiotic Treatment of Adults With Infective Endocarditis Due to Streptococci, Enterococci, Staphylococci, and HACEK Microorganisms Walter R. Wilson, MD; Adolf W. Karchmer, MD; Adnan S. Dajani, MD; Kathryn
AHA Scientific Statement
 AHA Scientific Statement Infective Endocarditis Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications A Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis,
AHA Scientific Statement Infective Endocarditis Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications A Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis,
Diagnosis and management of bacterial endocarditis in 2003 Blaithnead Murtagh, MD, O.H. Frazier, MD, and George V. Letsou, MD
 Diagnosis and management of bacterial endocarditis in 2003 Blaithnead Murtagh, MD, O.H. Frazier, MD, and George V. Letsou, MD The diagnosis of infective endocarditis has been notoriously difficult. Over
Diagnosis and management of bacterial endocarditis in 2003 Blaithnead Murtagh, MD, O.H. Frazier, MD, and George V. Letsou, MD The diagnosis of infective endocarditis has been notoriously difficult. Over
Prognostic factors in infective endocarditis
 Boston University OpenBU Theses & Dissertations http://open.bu.edu Boston University Theses & Dissertations 2016 Prognostic factors in infective endocarditis Grzybinski, Sarah https://hdl.handle.net/2144/19176
Boston University OpenBU Theses & Dissertations http://open.bu.edu Boston University Theses & Dissertations 2016 Prognostic factors in infective endocarditis Grzybinski, Sarah https://hdl.handle.net/2144/19176
Celia C. Carlos,MD, FPPS, FPIDSP, FPSMID
 Antibiotic Prophylaxis: Use and Abuse Celia C. Carlos,MD, FPPS, FPIDSP, FPSMID Research Institute for Tropical Medicine St. Luke s s Medical Center Our Lady of Lourdes Hospital Antibiotic Prophylaxis Definition
Antibiotic Prophylaxis: Use and Abuse Celia C. Carlos,MD, FPPS, FPIDSP, FPSMID Research Institute for Tropical Medicine St. Luke s s Medical Center Our Lady of Lourdes Hospital Antibiotic Prophylaxis Definition
Getting the Point of Injection Safety
 Getting the Point of Injection Safety Barbara Montana, MD, MPH, FACP Medical Director Communicable Disease Service Outbreak of Enterococcus faecalis endocarditis associated with an oral surgery practice
Getting the Point of Injection Safety Barbara Montana, MD, MPH, FACP Medical Director Communicable Disease Service Outbreak of Enterococcus faecalis endocarditis associated with an oral surgery practice
Infective Endocarditis in Elderly Patients
 AGING AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES Thomas T. Yoshikawa, Section Editor INVITED ARTICLE Infective Endocarditis in Elderly Patients Vinod K. Dhawan Charles R. Drew University of Medicine and Science, Martin Luther
AGING AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES Thomas T. Yoshikawa, Section Editor INVITED ARTICLE Infective Endocarditis in Elderly Patients Vinod K. Dhawan Charles R. Drew University of Medicine and Science, Martin Luther
MICROBIOLOGY - An Overview
 MICROBIOLOGY - An Overview Hieucam Phan, MD Pediatrics St. Luke s Hospital San Francisco, CA Microbiology 6/01 1 Introduction Major Achievements of Medical Sciences in the 20th Century Microbiology DNA
MICROBIOLOGY - An Overview Hieucam Phan, MD Pediatrics St. Luke s Hospital San Francisco, CA Microbiology 6/01 1 Introduction Major Achievements of Medical Sciences in the 20th Century Microbiology DNA
Approach to the Laboratory Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis SWACM 2018
 Approach to the Laboratory Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis SWACM 2018 Rachael Liesman, PhD, D(ABMM) Director, Clinical Microbiology Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Kansas
Approach to the Laboratory Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis SWACM 2018 Rachael Liesman, PhD, D(ABMM) Director, Clinical Microbiology Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Kansas
Case Report Subacute Staphylococcusepidermidis Bacterial Endocarditis Complicated by Mitral-Aortic Intervalvular Fibrosa Pseudoaneurysm
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2012, Article ID 467210, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/467210 Case Report Subacute Staphylococcusepidermidis Bacterial Endocarditis Complicated by Mitral-Aortic Intervalvular
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2012, Article ID 467210, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/467210 Case Report Subacute Staphylococcusepidermidis Bacterial Endocarditis Complicated by Mitral-Aortic Intervalvular
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS AMONGST INTRAVENOUS DRUG ABUSERS SEEN AT THE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL, KUALA LUMPUR
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 42 No. 4 December 1987 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS AMONGST INTRAVENOUS DRUG ABUSERS SEEN AT THE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL, KUALA LUMPUR R. JAYAMALAR MBBS, MRCP. "N. PARASAKTHI MBBS, MSc. "S.D.
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 42 No. 4 December 1987 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS AMONGST INTRAVENOUS DRUG ABUSERS SEEN AT THE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL, KUALA LUMPUR R. JAYAMALAR MBBS, MRCP. "N. PARASAKTHI MBBS, MSc. "S.D.
Microbial Flora of Normal Human Body Dr. Kaya Süer. Near East University Medical Faculty Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology
 Microbial Flora of Normal Human Body Dr. Kaya Süer Near East University Medical Faculty Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology Normal Microbial Flora Skin Conjunctivae Oral Cavity Upper respiratory
Microbial Flora of Normal Human Body Dr. Kaya Süer Near East University Medical Faculty Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology Normal Microbial Flora Skin Conjunctivae Oral Cavity Upper respiratory
Medically Compromised Patients
 Medically Compromised Patients (Part I) Ra ed Salma BDS, MSc, JBOMFS, MFDRCSI All information in this file is updated till April, 2014 Cardiovascular Diseases I. Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD) 1. Angina
Medically Compromised Patients (Part I) Ra ed Salma BDS, MSc, JBOMFS, MFDRCSI All information in this file is updated till April, 2014 Cardiovascular Diseases I. Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD) 1. Angina
POCKET GUIDELINES FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS
 1 ST EDITION CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE PREVENTION, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS POCKET GUIDELINES FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS 1 ST EDITION CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR
1 ST EDITION CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE PREVENTION, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS POCKET GUIDELINES FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS 1 ST EDITION CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR
DICE Session. The endocarditis team. Bernard Iung Bichat Hospital, Paris Diderot University Paris, France
 DICE Session. The endocarditis team Bernard Iung Bichat Hospital, Paris Diderot University Paris, France Faculty disclosure First name - last name I disclose the following financial relationships: Consultant
DICE Session. The endocarditis team Bernard Iung Bichat Hospital, Paris Diderot University Paris, France Faculty disclosure First name - last name I disclose the following financial relationships: Consultant
IE with cerebral hemorrhage
 IE with cerebral hemorrhage Gilbert Habib / Patrizio Lancellotti La Timone Hospital Marseille - France Palermo, 26 April 2018 Case report: aortic bioprosthetic IE History of the disease 75 year-old man
IE with cerebral hemorrhage Gilbert Habib / Patrizio Lancellotti La Timone Hospital Marseille - France Palermo, 26 April 2018 Case report: aortic bioprosthetic IE History of the disease 75 year-old man
Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE) Antibiotic Prophylaxis for. Infective Endocarditis. Version 1.0
 Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE) Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Infective Endocarditis Version 1.0 Date approved: September 2018 Approved by: The Board Review due: August 2019 Policy will be updated
Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE) Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Infective Endocarditis Version 1.0 Date approved: September 2018 Approved by: The Board Review due: August 2019 Policy will be updated
