Infective endocarditis
|
|
|
- Leona Potter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Infective endocarditis This is caused by microbial infection of a heart valve (native or prosthetic), the lining of a cardiac chamber or blood vessel, or a congenital anomaly (e.g. septal defect). The causative organism is usually a bacterium, but may be a rickettsia, chlamydia or fungus. Pathophysiology Infective endocarditis typically occurs at sites of pre-existing endocardial damage, but infection with particularly virulent or aggressive organisms (e.g. Staphylococcus aureus) can cause endocarditis in a previously normal heart; staphylococcal endocarditis of the tricuspid valve is a common complication of intravenous drug misuse. Many acquired and congenital cardiac lesions are vulnerable to endocarditis, particularly areas of endocardial damage caused by a high-pressure jet of blood, such as ventricular septal defect, mitral regurgitation and aortic regurgitation, many of which are haemodynamically insignificant. In contrast, the risk of endocarditis at the site of haemodynamically important low-pressure lesions, such as a large atrial septal defect, is minimal. Infection tends to occur at sites of endothelial damage because they attract deposits of platelets and fibrin that are vulnerable to colonisation by blood-borne organisms. The avascular valve tissue and presence of fibrin and platelet aggregates help to protect proliferating organisms from host defence mechanisms. When the infection is established, vegetations composed of organisms, fibrin and platelets grow and may become large enough to cause obstruction or embolism. Adjacent tissues are destroyed and abscesses may form. Valve regurgitation may develop or increase if the affected valve is damaged by tissue distortion, cusp perforation or disruption of chordae. Extracardiac manifestations, such as vasculitis and skin lesions, are due to emboli or immune complex deposition. Mycotic aneurysms may develop in arteries at the site of infected emboli. At autopsy, infarction of the spleen and kidneys and, sometimes, an immune glomerulonephritis are found. Microbiology Over three-quarters of cases are caused by streptococci or staphylococci. The viridans group of streptococci (Streptococcus mitis, Strep. sanguis) are commensals in the upper respiratory tract that may enter the blood stream on chewing or teeth- data:text/html;charset=utf-8,%3ch2%20id%3d%2277c45d9bcafc42838aebaa126c81e6e4%22%20style%3d%22margin%3a%201.3em%200px%200.5em%3b%20padding%3a%200px%3b%20border%3a%200px%3b%20font-fa 1/12
2 brushing, or at the time of dental treatment, and are common causes of subacute endocarditis (Box ). Other organisms, including Enterococcus faecalis, E. faecium and Strep. bovis, may enter the blood from the bowel or urinary tract. Strep. milleri and Strep. bovis endocarditis is associated with large-bowel neoplasms Microbiology of infective endocarditis Pathogen Of native valve (n = 280) In IV drug users (n = 87) Staphylococci 124 (44%) 60 (69%) 10 Staph. aureus 106 (38%) 60 (69%) 3 Coagulase-negative 18 (6%) 0 7 Early (n = 15) Of prosthetic valve (67%) (20%) (47%) Streptococci 86 (31%) 7 (8%) 0 25 Oral 59 (21%) 3 (3%) 0 19 Others (nonenterococcal) Late (n = 72) 33 (46%) 15 (21%) 18 (25%) (35%) (26%) 27 (10%) 4 (5%) 0 6 (8%) Enterococcus spp. 21 (8%) 2 (2%) 1 (7%) 5 (7%) HACEK group (see text) 12 (4%) (1%) data:text/html;charset=utf-8,%3ch2%20id%3d%2277c45d9bcafc42838aebaa126c81e6e4%22%20style%3d%22margin%3a%201.3em%200px%200.5em%3b%20padding%3a%200px%3b%20border%3a%200px%3b%20font-fa 2/12
3 Polymicrobial 6 (2%) 8 (9%) 0 1 (1%) Other bacteria 12 (4%) 4 (5%) 0 2 (3%) Fungi 3 (1%) 2 (2%) 0 0 Negative blood culture 16 (6%) 4 (5%) 4 (27%) 5 (7%) Adapted from Moreillon P, Que YA. Lancet 2004; 363: Staph. aureus has now overtaken streptococci as the most common cause of acute endocarditis. It originates from skin infections, abscesses or vascular access sites (e.g. intravenous and central lines), or from intravenous drug use. It is highly virulent and invasive, usually producing florid vegetations, rapid valve destruction and abscess formation. Other causes of acute endocarditis include Strep. pneumoniae and Strep. pyogenes. Post-operative endocarditis after cardiac surgery may affect native or prosthetic heart valves or other prosthetic materials. The most common organism is a coagulase-negative staphylococcus (Staph. epidermidis), a normal skin commensal. There is frequently a history of wound infection with the same organism. Staph. epidermidisoccasionally causes endocarditis in patients who have not had cardiac surgery, and its presence in blood cultures may be erroneously dismissed as contamination. Another coagulase-negative staphylococcus, Staph. lugdenensis,causes a rapidly destructive acute endocarditis that is associated with previously normal valves and multiple emboli. Unless accurately identified, it may also be overlooked as a contaminant. In Q fever endocarditis due to Coxiella burnetii, the patient often has a history of contact with farm animals. The aortic valve is usually affected and there may also be hepatitis, pneumonia and purpura. Life-long anti biotic therapy may be required. Gram-negative bacteria of the so-called HACEK group (Haemophilus spp., Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans,cardiobacterium hominis, Eikenella spp. and Kingella kingae) are slow-growing, fastidious organisms that are only revealed after prolonged culture and may be resistant to penicillin. Brucella is associated with a history of contact with goats or cattle and often affects the aortic valve. data:text/html;charset=utf-8,%3ch2%20id%3d%2277c45d9bcafc42838aebaa126c81e6e4%22%20style%3d%22margin%3a%201.3em%200px%200.5em%3b%20padding%3a%200px%3b%20border%3a%200px%3b%20font-fa 3/12
4 Yeasts and fungi (Candida, Aspergillus) may attack previously normal or prosthetic valves, particularly in immunocompromised patients or those with indwelling intravenous lines. Abscesses and emboli are common, therapy is difficult (surgery is often required) and mortality is high. Concomitant bacterial infection may be present. Incidence The incidence of infective endocarditis in community-based studies ranges from 5 to 15 cases per per annum. More than 50% of patients are over 60 years of age (Box ). In a large British study, the underlying condition was rheumatic heart disease in 24% of patients, congenital heart disease in 19%, and other cardiac abnormalities (e.g. calcified aortic valve, floppy mitral valve) in 25%. The remaining 32% were not thought to have a pre-existing cardiac abnormality Endocarditis in old age Symptoms and signs: may be non-specific, e.g. confusion, weight loss, malaise and weakness, and the diagnosis may not be suspected. Common causative organisms: often enterococci (from the urinary tract) and Strep. bovis (from a colonic source). Morbidity and mortality: much higher. Clinical features Endocarditis can take either an acute or a more insidious subacute form. However, there is considerable overlap because the clinical pattern is influenced not only by the organism, but also by the site of infection, prior antibiotic therapy and the presence of a valve or shunt prosthesis. The subacute form may abruptly develop acute life-threatening complications, such as valve disruption or emboli. Subacute endocarditis This should be suspected when a patient with congenital or valvular heart disease develops a persistent fever, complains of data:text/html;charset=utf-8,%3ch2%20id%3d%2277c45d9bcafc42838aebaa126c81e6e4%22%20style%3d%22margin%3a%201.3em%200px%200.5em%3b%20padding%3a%200px%3b%20border%3a%200px%3b%20font-fa 4/12
5 unusual tiredness, night sweats or weight loss, or develops new signs of valve dysfunction or heart failure. Less often, it presents as an embolic stroke or peripheral arterial embolism. Other features (Fig ) include purpura and petechial haemorrhages in the skin and mucous membranes, and splinter haemorrhages under the fingernails or toe nails. Osler s nodes are painful tender swellings at the fingertips that are probably the product of vasculitis; they are rare. Digital clubbing is a late sign. The spleen is frequently palpable; in Coxiella infections, the spleen and the liver may be considerably enlarged. Microscopic haematuria is common. The finding of any of these features in a patient with persistent fever or malaise is an indication for re-examination to detect hitherto unrecognised heart disease. data:text/html;charset=utf-8,%3ch2%20id%3d%2277c45d9bcafc42838aebaa126c81e6e4%22%20style%3d%22margin%3a%201.3em%200px%200.5em%3b%20padding%3a%200px%3b%20border%3a%200px%3b%20font-fa 5/12
6 F IG Clinical features which may be present in endocarditis. Insets (Petechial rash, nail-fold i Acute endocarditis This presents as a severe febrile illness with prominent and changing heart murmurs and petechiae. Clinical stigmata of chronic endocarditis are usually absent. Embolic events are common, and cardiac or renal failure may develop rapidly. Abscesses may be detected on echocardiography. Partially treated acute endocarditis behaves like subacute endocarditis. Post-operative endocarditis This may present as an unexplained fever in a patient who has had heart valve surgery. The infection usually involves the valve ring and may resemble subacute or acute endocarditis, depending on the virulence of the organism. Morbidity and mortality are high and redo surgery is often required. The range of organisms is similar to that seen in native valve disease, but when endocarditis occurs during the first few weeks after surgery, it is usually due to infection with a coagulase-negative staphylococcus that was introduced during the peri-operative period. A clinical diagnosis of endocarditis can be made on the presence of two major, one major and three minor, or five minor criteria (Box ) Diagnosis of infective endocarditis (modified Duke criteria) Major criteria Positive blood culture data:text/html;charset=utf-8,%3ch2%20id%3d%2277c45d9bcafc42838aebaa126c81e6e4%22%20style%3d%22margin%3a%201.3em%200px%200.5em%3b%20padding%3a%200px%3b%20border%3a%200px%3b%20font-fa 6/12
7 Typical organism from two cultures Persistent positive blood cultures taken > 12 hrs apart Three or more positive cultures taken over > 1 hr Endocardial involvement Positive echocardiographic findings of vegetations New valvular regurgitation Minor criteria Predisposing valvular or cardiac abnormality Intravenous drug misuse Pyrexia 38 C Embolic phenomenon Vasculitic phenomenon Blood cultures suggestive: organism grown but not achieving major criteria Suggestive echocardiographic findings Definite endocarditis = two major, or one major and three minor, or five minor Possible endocarditis = one major and one minor, or three minor Investigations Blood culture is the crucial investigation because it may identify the infection and guide antibiotic therapy. Three to six sets of blood cultures should be taken prior to commencing therapy and should not wait for episodes of pyrexia. The first two specimens will detect bacteraemia in 90% of culture-positive cases. Aseptic technique is essential and the risk of contaminants should be minimised by sampling from different venepuncture sites. An in-dwelling line should not be used to take cultures. Aerobic and anaerobic cultures are required. data:text/html;charset=utf-8,%3ch2%20id%3d%2277c45d9bcafc42838aebaa126c81e6e4%22%20style%3d%22margin%3a%201.3em%200px%200.5em%3b%20padding%3a%200px%3b%20border%3a%200px%3b%20font-fa 7/12
8 Echocardiography is key for detecting and following the progress of vegetations, for assessing valve damage and for detecting abscess formation. Vegetations as small as 2 4 mm can be detected by transthoracic echocardiography, and even smaller ones (1 1.5 mm) can be visualised by transoesophageal echocardiography (TOE), which is particularly valuable for identifying abscess formation and investigating patients with prosthetic heart valves. Vegetations may be difficult to distinguish in the presence of an abnormal valve; the sensitivity of transthoracic echo is approximately 65% but that of TOE is more than 90%. Failure to detect vegetations does not exclude the diagnosis. Elevation of the ESR, a normocytic normochromic anaemia, and leucocytosis are common but not invariable. Measurement of serum CRP is more reliable than the ESR in monitoring progress. Proteinuria may occur and microscopic haematuria is usually present. The ECG may show the development of AV block (due to aortic root abscess formation) and occasionally infarction due to emboli. The chest X-ray may show evidence of cardiac failure and cardiomegaly. Management The case fatality of bacterial endocarditis is approximately 20% and even higher in those with prosthetic valve endocarditis and those infected with antibiotic-resistant organisms. A multidisciplinary approach, with cooperation between the physician, surgeon and microbiologist, increases the chance of a successful outcome. Any source of infection should be removed as soon as possible; for example, a tooth with an apical abscess should be extracted. Empirical treatment depends on the mode of presentation, the suspected organism, and whether the patient has a prosthetic valve or penicillin allergy (Box ). If the presentation is acute, flucloxacillin and gentamicin are recommended, while for a subacute or indolent presentation, benzyl penicillin and gentamicin are preferred. In those with penicillin allergy, a prosthetic valve or suspected meticillin-resistant Staph. aureus (MRSA) infection, triple therapy with vancomycin, gentamicin and oral rifampicin should be considered. Following identification of the causal organism, determination of the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) for the organism is essential to guide antibiotic therapy Antimicrobial treatment of common causative organisms in infective data:text/html;charset=utf-8,%3ch2%20id%3d%2277c45d9bcafc42838aebaa126c81e6e4%22%20style%3d%22margin%3a%201.3em%200px%200.5em%3b%20padding%3a%200px%3b%20border%3a%200px%3b%20font-fa 8/12
9 endocarditis Organism Antimicrobial Dose Native valve Viridans streptococci and Strep. bovis Duration Prosthetic valve MIC 0.1 Benzyl 1.2 g 6 times daily 4 wks 1 6 wks mg/l penicillin IV 1 mg/kg 2 3 times and gentamicin IV daily 2 wks 2 wks MIC > 0.1 to < Benzyl 1.2 g 6 times daily 4 wks 6 wks 0.5 mg/l penicillin IV 1 mg/kg 2 3 times and gentamicin IV daily 2 wks 4 6 wks MIC 0.5 Benzyl 1.2 g 6 times daily 4 wks 6 wks mg/l penicillin IV 1 mg/kg 2 3 times and gentamicin IV daily 4 wks 4 6 wks Enterococci Ampicillin- Ampicillin IV 2 g 6 times daily 4 wks 6 wks sensitive and 1 mg/kg 2 3 times gentamicin IV 2 daily 4 wks 6 wks Ampicillin- Vancomycin 1 g twice daily 4 wk 6 wks resistant IV 1 mg/kg 2 3 times and daily data:text/html;charset=utf-8,%3ch2%20id%3d%2277c45d9bcafc42838aebaa126c81e6e4%22%20style%3d%22margin%3a%201.3em%200px%200.5em%3b%20padding%3a%200px%3b%20border%3a%200px%3b%20font-fa 9/12
10 gentamicin 4 wks 6 wks IV 2 Staphylococci Penicillinsensitive Penicillinresistant Meticillinsensitive Penicillinresistant Meticillinresistant Benzyl penicillin IV Flucloxacillin IV Vancomycin IV and gentamicin IV 1.2 g 6 times daily 4 wks 6 wks 2 g 6 times daily (< 4 wks 6 wks 3 85 kg 6-hourly) 1 g twice daily 4 wks 6 wks 3 1 mg/kg 3 times 4 wks 6 wks 3 daily (MIC = minimum inhibitory concentration) A 2-week treatment regimen may be sufficient for fully sensitive strains of Strep. viridans and Strep. bovis, provided specific conditions are met (Box ). For the empirical treatment of bacterial endocarditis, penicillin plus gentamicin is the regimen of choice for most patients; when staphylococcal infection is suspected, however, vancomycin plus gentamicin is recommended Conditions for the short-course treatment of Strep. viridans/bovis endocarditis Native valve infection data:text/html;charset=utf-8,%3ch2%20id%3d%2277c45d9bcafc42838aebaa126c81e6e4%22%20style%3d%22margin%3a%201.3em%200px%200.5em%3b%20padding%3a%200px%3b%20border%3a%200px%3b%20font-fa 10/12
11 MIC 0.1 mg/l No adverse prognostic factors (e.g. heart failure, aortic regurgitation, conduction defect) No evidence of thromboembolic disease No vegetations > 5 mm diameter Clinical response within 7 days Cardiac surgery (débridement of infected material and valve replacement) is advisable in a substantial proportion of patients, particularly those with Staph. aureus and fungal infections (Box ). Antimicrobial therapy must be started before surgery Indications for cardiac surgery in infective endocarditis Heart failure due to valve damage Failure of antibiotic therapy (persistent/uncontrolled infection) Large vegetations on left-sided heart valves with evidence or high risk of systemic emboli Abscess formation N.B. Patients with prosthetic valve endocarditis or fungal endocarditis often require cardiac surgery. Prevention Until recently, antibiotic prophylaxis was routinely given to people at risk of infective endocarditis undergoing interventional procedures. However, as this has not been proven to be effective and the link between episodes of infective endocarditis and interventional procedures has not been demonstrated, antibiotic prophylaxis is no longer offered routinely for defined interventional procedures. Valve replacement surgery data:text/html;charset=utf-8,%3ch2%20id%3d%2277c45d9bcafc42838aebaa126c81e6e4%22%20style%3d%22margin%3a%201.3em%200px%200.5em%3b%20padding%3a%200px%3b%20border%3a%200px%3b%20font-fa 11/12
12 Diseased heart valves can be replaced with mechanical or biological prostheses. The three most commonly used types of mechanical prosthesis are the ball and cage, tilting single disc and tilting bi-leaflet valves. All generate prosthetic sounds or clicks on auscultation. Pig or allograft valves mounted on a supporting stent are the most commonly used biological valves. They generate normal heart sounds. All prosthetic valves used in the aortic position produce a systolic flow murmur. All mechanical valves require long-term anticoagulation because they can cause systemic thromboembolism or may develop valve thrombosis or obstruction (Box ); the prosthetic clicks may become inaudible if the valve malfunctions. Biological valves have the advantage of not requiring anticoagulants to maintain proper function; however, many patients undergoing valve replacement surgery, especially mitral valve replacement, will have atrial fibrillation that requires anticoagulation anyway. Biological valves are less durable than mechanical valves and may degenerate 7 or more years after implantation, particularly when used in the mitral position. They are more durable in the aortic position and in older patients, so are particularly appropriate for patients over 65 undergoing aortic valve replacement Prosthetic heart valves: optimal anticoagulant control Mechanical valves Target INR Ball and cage (e.g. Starr Edwards) 3.5 Tilting disc (e.g. Bjork Shiley) Bi-leaflet (e.g. St Jude) 3.0 Biological valves with atrial fibrillation 2.5 Symptoms or signs of unexplained heart failure in a patient with a prosthetic heart valve may be due to valve dysfunction, and urgent assessment is required. Biological valve dysfunction is usually associated with the development of a regurgitant murmur. data:text/html;charset=utf-8,%3ch2%20id%3d%2277c45d9bcafc42838aebaa126c81e6e4%22%20style%3d%22margin%3a%201.3em%200px%200.5em%3b%20padding%3a%200px%3b%20border%3a%200px%3b%20font-fa 12/12
NATIONAL HEART FOUNDATION HOSPITAL & RESEARCH INSTITUTE
 Welcome INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS: WHERE WE ARE AT 2005? DR MD HABIBUR RAHMAN FCPS(Medicine) NATIONAL HEART FOUNDATION HOSPITAL & RESEARCH INSTITUTE DEFINITION OF INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Infective endocarditis
Welcome INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS: WHERE WE ARE AT 2005? DR MD HABIBUR RAHMAN FCPS(Medicine) NATIONAL HEART FOUNDATION HOSPITAL & RESEARCH INSTITUTE DEFINITION OF INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Infective endocarditis
Infective endocarditis (IE) By Assis. Prof. Nader Alaridah MD, PhD
 Infective endocarditis (IE) By Assis. Prof. Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Infective endocarditis (IE) is an inflammation of the endocardium.. inner of the heart muscle & the epithelial lining of heart valves.
Infective endocarditis (IE) By Assis. Prof. Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Infective endocarditis (IE) is an inflammation of the endocardium.. inner of the heart muscle & the epithelial lining of heart valves.
Daniel C. DeSimone, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine
 Daniel C. DeSimone, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Faculty photo will be placed here Desimone.Daniel@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Infective Endocarditis Mayo School of Continuous Professional Development
Daniel C. DeSimone, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Faculty photo will be placed here Desimone.Daniel@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Infective Endocarditis Mayo School of Continuous Professional Development
Dr Babak Tamizi far MD. Assistant Professor Of Internal Medicine Al-Zahra Hospital Isfahan University Of Medical Sciences
 Dr Babak Tamizi far MD. Assistant Professor Of Internal Medicine Al-Zahra Hospital Isfahan University Of Medical Sciences ١ ٢ ٣ A 57-year-old man presents with new-onset fever, shortness of breath, lower
Dr Babak Tamizi far MD. Assistant Professor Of Internal Medicine Al-Zahra Hospital Isfahan University Of Medical Sciences ١ ٢ ٣ A 57-year-old man presents with new-onset fever, shortness of breath, lower
Michael Stander, Pharm.D.
 Michael Stander, Pharm.D. Endocarditis: Goals Epidemiology Presentation of acute and subacute. Diagnosis: What is Dukes Criteria and how do we approach the diagnosis of endocarditis? Treatment: Understand
Michael Stander, Pharm.D. Endocarditis: Goals Epidemiology Presentation of acute and subacute. Diagnosis: What is Dukes Criteria and how do we approach the diagnosis of endocarditis? Treatment: Understand
Infective Endocarditis Empirical therapy Antibiotic Guidelines. Contents
 Infective Endocarditis Empirical therapy Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Group Additional author(s): as above Authors Division: Division of Clinical
Infective Endocarditis Empirical therapy Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Group Additional author(s): as above Authors Division: Division of Clinical
Heart on Fire: Infective Endocarditis. Objectives. Disclosure 8/27/2018. Mary McGreal DNP, RN, ANP-c, CCRN
 Heart on Fire: Infective Endocarditis Mary McGreal DNP, RN, ANP-c, CCRN Objectives Discuss the incidence of infective endocarditis? Discuss the pathogenesis of infective endocarditis? Discuss clinical
Heart on Fire: Infective Endocarditis Mary McGreal DNP, RN, ANP-c, CCRN Objectives Discuss the incidence of infective endocarditis? Discuss the pathogenesis of infective endocarditis? Discuss clinical
Endocarditis, including Prophylaxis
 Endocarditis, including Prophylaxis ACOI Board Review 2018 gerald.blackburn@beaumont.org (No Disclosures) Infective Endocarditis Persistant bacteremia (blood cultures drawn >12 hrs apart) w/ organisms
Endocarditis, including Prophylaxis ACOI Board Review 2018 gerald.blackburn@beaumont.org (No Disclosures) Infective Endocarditis Persistant bacteremia (blood cultures drawn >12 hrs apart) w/ organisms
Sepsis and Infective Endocarditis
 Sepsis and Infective Endocarditis Michal Holub Department of Infectious Diseases First Faculty of Medicine Charles University in Prague and University Military Hospital Bacteremia and Sepsis bacteremia
Sepsis and Infective Endocarditis Michal Holub Department of Infectious Diseases First Faculty of Medicine Charles University in Prague and University Military Hospital Bacteremia and Sepsis bacteremia
Infective Endocarditis
 Frank Lowy Infective Endocarditis 1. Introduction Infective endocarditis (IE) is an infection of the heart valves. A large number of different bacteria are capable of causing this disease. Depending on
Frank Lowy Infective Endocarditis 1. Introduction Infective endocarditis (IE) is an infection of the heart valves. A large number of different bacteria are capable of causing this disease. Depending on
Overview. Clinical Scenario. Endocarditis: Treatment & Prevention. Prophylaxis The Concept. Jeremy D. Young, MD, MPH. Division of Infectious Diseases
 Endocarditis: Treatment & Prevention Jeremy D. Young, MD, MPH Division of Infectious Diseases Clinical Scenario Patient with MVP scheduled to have wisdom teeth extracted. Has systolic murmur with mid-systolic
Endocarditis: Treatment & Prevention Jeremy D. Young, MD, MPH Division of Infectious Diseases Clinical Scenario Patient with MVP scheduled to have wisdom teeth extracted. Has systolic murmur with mid-systolic
Infective Endocarditis
 Infective Endocarditis Infective Endocarditis Historical Perspective.. A concretion larger than a pigeon s egg; contained in the left auricle. Burns, 1809 Osler s Gulstonian lectures provided the 1 st
Infective Endocarditis Infective Endocarditis Historical Perspective.. A concretion larger than a pigeon s egg; contained in the left auricle. Burns, 1809 Osler s Gulstonian lectures provided the 1 st
Bacterial Endocarditis
 Objectives Bacterial Endocarditis John C. Rotschafer, Pharm. D. Professor College of Pharmacy University of Minnesota Identify which valves are commonly involved with endocarditis Identify common pathogens
Objectives Bacterial Endocarditis John C. Rotschafer, Pharm. D. Professor College of Pharmacy University of Minnesota Identify which valves are commonly involved with endocarditis Identify common pathogens
Infective Endocarditis
 Infective Endocarditis Definition Historical perspective Classification Epidemiological Features Etiology Pathogenesis Clinical presentation Diagnosis Treatment options Prevention Infective endocarditis
Infective Endocarditis Definition Historical perspective Classification Epidemiological Features Etiology Pathogenesis Clinical presentation Diagnosis Treatment options Prevention Infective endocarditis
Infective Endocarditis عبد المهيمن أحمد
 Infective Endocarditis إعداد : عبد المهيمن أحمد أحمد علي Infective endocarditis Inflammation of the heart valve or endocardium of the heart. The agents are usually bacterial, but other organisms can also
Infective Endocarditis إعداد : عبد المهيمن أحمد أحمد علي Infective endocarditis Inflammation of the heart valve or endocardium of the heart. The agents are usually bacterial, but other organisms can also
BASIC KNOWLEDGE ABOUT INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS FOR CLINICIAN
 BASIC KNOWLEDGE ABOUT INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS FOR CLINICIAN When should I suspect infective endocarditis? Antibiotic regimen Patient care after completion of treatment Prophylactic Regimens Prosthetic Valve
BASIC KNOWLEDGE ABOUT INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS FOR CLINICIAN When should I suspect infective endocarditis? Antibiotic regimen Patient care after completion of treatment Prophylactic Regimens Prosthetic Valve
Infective endocarditis
 Infective endocarditis Today's lecture is about infective endocarditis, the Dr started the lecture by asking what are the most common causative agents of infective endocarditis? 1-Group A streptococci
Infective endocarditis Today's lecture is about infective endocarditis, the Dr started the lecture by asking what are the most common causative agents of infective endocarditis? 1-Group A streptococci
Microbiological diagnosis of infective endocarditis; what is new?
 Microbiological diagnosis of infective endocarditis; what is new? Dr Amani El Kholy, MD Professor of Clinical Pathology (Microbiology), Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University ESC 2017 1 Objectives Lab Diagnostic
Microbiological diagnosis of infective endocarditis; what is new? Dr Amani El Kholy, MD Professor of Clinical Pathology (Microbiology), Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University ESC 2017 1 Objectives Lab Diagnostic
VALVULAR HEART DISEASE
 VALVULAR HEART DISEASE Stenosis: failure of a valve to open completely, obstructing forward flow. - almost always due to a chronic process (e.g., calcification or valve scarring). Insufficiency : failure
VALVULAR HEART DISEASE Stenosis: failure of a valve to open completely, obstructing forward flow. - almost always due to a chronic process (e.g., calcification or valve scarring). Insufficiency : failure
results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both.
 results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both. The outcome of valvular disease depends on : 1-the valve involved 2-the degree of impairment 3-the cause of its development
results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both. The outcome of valvular disease depends on : 1-the valve involved 2-the degree of impairment 3-the cause of its development
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN CHILDREN
 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN CHILDREN Rohayati Taib RIPAS Hospital, Bundar Seri Begawan, Brunei Darussalam Infective Endocarditis (IE) is a microbial infection of the endocardium. It encompasses both bacterial
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN CHILDREN Rohayati Taib RIPAS Hospital, Bundar Seri Begawan, Brunei Darussalam Infective Endocarditis (IE) is a microbial infection of the endocardium. It encompasses both bacterial
Challenging clinical situation
 Challenging clinical situation A young patient with prosthetic aortic valve endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France October 25 th 2014 Case report History of the disease Clinical
Challenging clinical situation A young patient with prosthetic aortic valve endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France October 25 th 2014 Case report History of the disease Clinical
Heart Valves: Before and after surgery
 Heart Valves: Before and after surgery Tim Sutton, Consultant Cardiologist Middlemore Hospital, Auckland Auckland Heart Group Indications for intervention in Valvular disease To prevent sudden death and
Heart Valves: Before and after surgery Tim Sutton, Consultant Cardiologist Middlemore Hospital, Auckland Auckland Heart Group Indications for intervention in Valvular disease To prevent sudden death and
Diagnostic strategy. Dr Pilar Tornos Hospital Vall d Hebron Barcelona
 Diagnostic strategy Dr Pilar Tornos Hospital Vall d Hebron Barcelona Faculty disclosure Pilar Tornos I disclose the following financial relationships: Paid speaker for Recordati, Edwards. Diagnosis of
Diagnostic strategy Dr Pilar Tornos Hospital Vall d Hebron Barcelona Faculty disclosure Pilar Tornos I disclose the following financial relationships: Paid speaker for Recordati, Edwards. Diagnosis of
PRINCIPLES OF ENDOCARDITIS
 015 // Endocarditis CONTENTS 140 Principles of Endocarditis 141 Native Valve Endocarditis 143 Complications of Native Valve Endocarditis 145 Right Heart Endocarditis 145 Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis 146
015 // Endocarditis CONTENTS 140 Principles of Endocarditis 141 Native Valve Endocarditis 143 Complications of Native Valve Endocarditis 145 Right Heart Endocarditis 145 Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis 146
ACCME/Disclosures 4/13/2016 IDPB
 ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
Infective Endocarditis for Primary Care Physicians
 Infective Endocarditis for Primary Care Physicians David N Gilbert, MD Disclosures Consultant to: Merck Pfizer Medicine Company Cempra 1 Introduction There are roughly 30,000 new cases of IE in the US
Infective Endocarditis for Primary Care Physicians David N Gilbert, MD Disclosures Consultant to: Merck Pfizer Medicine Company Cempra 1 Introduction There are roughly 30,000 new cases of IE in the US
Contents. 1. Introduction. J Antimicrob Chemother 2012; 67: doi: /jac/dkr450 Advance Access publication 14 November 2011
 J Antimicrob Chemother 2012; 67: 269 289 doi:10.1093/jac/dkr450 Advance Access publication 14 November 2011 Guidelines for the diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of endocarditis in adults: a report of
J Antimicrob Chemother 2012; 67: 269 289 doi:10.1093/jac/dkr450 Advance Access publication 14 November 2011 Guidelines for the diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of endocarditis in adults: a report of
Disclosures. Native Valve Endocarditis and its Complications. Outline. Outline. Basics. Basics 3/23/2017
 Native Valve Endocarditis and its Complications SCVP and Binford Dammin Society of Infectious Disease Pathologists Shared Companion Meeting USCAP 2017 Annual Meeting Disclosures Relevant financial relationships
Native Valve Endocarditis and its Complications SCVP and Binford Dammin Society of Infectious Disease Pathologists Shared Companion Meeting USCAP 2017 Annual Meeting Disclosures Relevant financial relationships
Infections Amenable to OPAT. (Nabin Shrestha + Ajay Mathur)
 3 Infections Amenable to OPAT (Nabin Shrestha + Ajay Mathur) Decisions regarding outpatient treatment of infections vary with the institution, the prescribing physician, the individual patient s condition
3 Infections Amenable to OPAT (Nabin Shrestha + Ajay Mathur) Decisions regarding outpatient treatment of infections vary with the institution, the prescribing physician, the individual patient s condition
Infective Endocarditis
 Definition Infective Endocarditis Pattaya Riengchan M.D. MAR 16, 2017 Infection of endocardial surface of the heart and implies the physical presence microorganisms in the lesion Heart valves are most
Definition Infective Endocarditis Pattaya Riengchan M.D. MAR 16, 2017 Infection of endocardial surface of the heart and implies the physical presence microorganisms in the lesion Heart valves are most
Echocardiography after stroke - where to look
 Echocardiography after stroke - where to look Vuyisile T. Nkomo, MD,MPH, FACC, FASE Joint Cardiac Imaging Society of South Africa/Mayo Clinic Echocardiography Workshop 2017 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
Echocardiography after stroke - where to look Vuyisile T. Nkomo, MD,MPH, FACC, FASE Joint Cardiac Imaging Society of South Africa/Mayo Clinic Echocardiography Workshop 2017 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
The changing landscape of infective endocarditis (IE)in congenital heart disease (CHD)
 The changing landscape of infective endocarditis (IE)in congenital heart disease (CHD) Rekwan Sittiwangkul,MD Department of Pediatrics. Chiang Mai University Hospital, 24 th March 2018 Infective endocarditis
The changing landscape of infective endocarditis (IE)in congenital heart disease (CHD) Rekwan Sittiwangkul,MD Department of Pediatrics. Chiang Mai University Hospital, 24 th March 2018 Infective endocarditis
Endocardite infectieuse
 Endocardite infectieuse 1. Raccourcir le traitement: jusqu où? 2. Proposer un traitement ambulatoire: à partir de quand? Endocardite infectieuse A B 90 P = 0.014 20 P = 0.0005 % infective endocarditis
Endocardite infectieuse 1. Raccourcir le traitement: jusqu où? 2. Proposer un traitement ambulatoire: à partir de quand? Endocardite infectieuse A B 90 P = 0.014 20 P = 0.0005 % infective endocarditis
A Study of Infective Endocarditis in Malta
 Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 6(6): 98-104 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjcm doi: 10.11648/j.sjcm.20170606.11 ISSN: 2327-2724 (Print); ISSN: 2327-2732 (Online) A Study of Infective
Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 6(6): 98-104 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjcm doi: 10.11648/j.sjcm.20170606.11 ISSN: 2327-2724 (Print); ISSN: 2327-2732 (Online) A Study of Infective
April 16, 09:00-09:15 중앙대학교 윤신원
 April 16, 09:00-09:15 중앙대학교 윤신원 When to perform Echocardiography in IE? Vegetations?(pathologic Whatever the level hallmark) of suspicion Intracardiac abscess? Confirm or R/O at the Earliest opportunity.
April 16, 09:00-09:15 중앙대학교 윤신원 When to perform Echocardiography in IE? Vegetations?(pathologic Whatever the level hallmark) of suspicion Intracardiac abscess? Confirm or R/O at the Earliest opportunity.
INFECTIOUS endocarditis (IE) is a
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis Sensitivity of the Duke vs von Reyn Criteria Maija Heiro, MD; Jukka Nikoskelainen, MD, PhD; Jaakko J. Hartiala, MD, PhD; Markku K. Saraste, MD;
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis Sensitivity of the Duke vs von Reyn Criteria Maija Heiro, MD; Jukka Nikoskelainen, MD, PhD; Jaakko J. Hartiala, MD, PhD; Markku K. Saraste, MD;
Update on the prevention, diagnosis and management of Infective Endocarditis (IE)
 Update on the prevention, diagnosis and management of Infective Endocarditis (IE) Dr.Ahmed Yahya Mohammed Alarhabi MD, MsC,FcUSM,FACC,MAHA Consultant Interventional Cardiologist Head of Cardiac Center
Update on the prevention, diagnosis and management of Infective Endocarditis (IE) Dr.Ahmed Yahya Mohammed Alarhabi MD, MsC,FcUSM,FACC,MAHA Consultant Interventional Cardiologist Head of Cardiac Center
Pr AMEL OMEZZINE LETAIEF CHU FarhatHached Sousse
 Pr AMEL OMEZZINE LETAIEF CHU FarhatHached Sousse cours de collège infectiologie Sousse le27/02/2013 ENDOCARDITIS There is a change in epidemiology Clinical features of IE remains classical Diagnosis of
Pr AMEL OMEZZINE LETAIEF CHU FarhatHached Sousse cours de collège infectiologie Sousse le27/02/2013 ENDOCARDITIS There is a change in epidemiology Clinical features of IE remains classical Diagnosis of
Infective Endocarditis
 Chapter 32 Infective Endocarditis Lisa B. Hightow and Meera Kelley The term infective endocarditis (IE) refers to infection of the endocardial surface of the heart and implies a physical presence of microganisms
Chapter 32 Infective Endocarditis Lisa B. Hightow and Meera Kelley The term infective endocarditis (IE) refers to infection of the endocardial surface of the heart and implies a physical presence of microganisms
Prosthetic Valve Infective Endocarditis. Tat Yam Department of Infection Southampton University Hospitals NHS TRust
 Prosthetic Valve Infective Endocarditis Tat Yam Department of Infection Southampton University Hospitals NHS TRust Case History: Episode 1 in MB 73 yr old male, Nigerian PMHx: Hypertension Congestive cardiac
Prosthetic Valve Infective Endocarditis Tat Yam Department of Infection Southampton University Hospitals NHS TRust Case History: Episode 1 in MB 73 yr old male, Nigerian PMHx: Hypertension Congestive cardiac
General management of infective endocarditis
 General management of infective endocarditis Team approach in infective endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 The echolab «Heart Team" Infective Endocarditis
General management of infective endocarditis Team approach in infective endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 The echolab «Heart Team" Infective Endocarditis
Suggested Reading: Pages Donald P. Levine, M.D. Professor of Medicine Page 1 of 8
 Professor of Medicine Page 1 of 8 ENDOCARDITIS I. General A. infectivie endocarditis (IE) 1. definition: infection of the endocardial surface of the heart; implies the physical presence of microorganisms
Professor of Medicine Page 1 of 8 ENDOCARDITIS I. General A. infectivie endocarditis (IE) 1. definition: infection of the endocardial surface of the heart; implies the physical presence of microorganisms
Antibiotic Treatment of Adults With Infective Endocarditis Due to Streptococci, Enterococci, Staphylococci, and HACEK Microorganisms
 Antibiotic Treatment of Adults With Infective Endocarditis Due to Streptococci, Enterococci, Staphylococci, and HACEK Microorganisms Walter R. Wilson, MD; Adolf W. Karchmer, MD; Adnan S. Dajani, MD; Kathryn
Antibiotic Treatment of Adults With Infective Endocarditis Due to Streptococci, Enterococci, Staphylococci, and HACEK Microorganisms Walter R. Wilson, MD; Adolf W. Karchmer, MD; Adnan S. Dajani, MD; Kathryn
An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for infective endocarditis
 REVIEW An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for infective endocarditis Albert W Chan MD FRCPC, Heather J Ross MD FRCPC AW Chan, HJ Ross. An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for
REVIEW An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for infective endocarditis Albert W Chan MD FRCPC, Heather J Ross MD FRCPC AW Chan, HJ Ross. An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for
A study of clinical and etiological profile of infective endocarditis and its correlation with echocardiography in patients of rheumatic heart disease
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Sarkar A et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Oct;4(5):1323-1327 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20174177
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Sarkar A et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Oct;4(5):1323-1327 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20174177
POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00553
 MCC-004 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00553 Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-004 : COMMON CARDIO-VASCULAR DISEASES - II Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note : There will
MCC-004 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00553 Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-004 : COMMON CARDIO-VASCULAR DISEASES - II Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note : There will
Hearts afire: Infective endocarditis
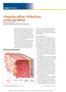 Hearts afire: Infective endocarditis By Kim McCarron, MS, CRNP Clinical Associate Professor Towson University Towson, Md. Editorial Advisory Board Member Nursing made Incredibly Easy! Picturing endocarditis
Hearts afire: Infective endocarditis By Kim McCarron, MS, CRNP Clinical Associate Professor Towson University Towson, Md. Editorial Advisory Board Member Nursing made Incredibly Easy! Picturing endocarditis
Bacterial Endocarditis
 Disclosures Bacterial Endocarditis Henry F. Chambers, MD Allergan research grant Genentech research grant Infective endocarditis: Outline Native valve endocarditis Prosthetic valve endocarditis Cardiac
Disclosures Bacterial Endocarditis Henry F. Chambers, MD Allergan research grant Genentech research grant Infective endocarditis: Outline Native valve endocarditis Prosthetic valve endocarditis Cardiac
New guidelines for the antibiotic treatment of streptococcal, enterococcal and staphylococcal endocarditis. D. C. Shanson
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1998) 42, 292 296 New guidelines for the antibiotic treatment of streptococcal, enterococcal and staphylococcal endocarditis JAC D. C. Shanson Microbiology Department,
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1998) 42, 292 296 New guidelines for the antibiotic treatment of streptococcal, enterococcal and staphylococcal endocarditis JAC D. C. Shanson Microbiology Department,
A Predictable Outcome of a Preventable Disease. Sanjay Kamboj, MD; Shaminder Gupta, MD; Glenn P. Kelley, MD; Fred Helmcke, MD; and Fred A.
 Clinical Case of the Month A Predictable Outcome of a Preventable Disease Sanjay Kamboj, MD; Shaminder Gupta, MD; Glenn P. Kelley, MD; Fred Helmcke, MD; and Fred A. Lopez, MD Infective endocarditis is
Clinical Case of the Month A Predictable Outcome of a Preventable Disease Sanjay Kamboj, MD; Shaminder Gupta, MD; Glenn P. Kelley, MD; Fred Helmcke, MD; and Fred A. Lopez, MD Infective endocarditis is
Infective Endocarditis:
 CME Workshop Infective Endocarditis: Prophylaxis, Diagnosis and Management Presented at a CME program, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba, December 2001. By Davinder S. Jassal, MD; and John M.
CME Workshop Infective Endocarditis: Prophylaxis, Diagnosis and Management Presented at a CME program, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba, December 2001. By Davinder S. Jassal, MD; and John M.
Apport des recommandations européennes
 Apport des recommandations européennes Gilbert Habib Cardiology Department- La Timone Marseille - France Bordeaux le 28 Juin 2011 Infective Endocarditis: a changing disease new high-risk subgroups IVDA
Apport des recommandations européennes Gilbert Habib Cardiology Department- La Timone Marseille - France Bordeaux le 28 Juin 2011 Infective Endocarditis: a changing disease new high-risk subgroups IVDA
MULTIVALVULAR INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS CLINICAL FEATURES, ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC DATA AND OUTCOMES
 Article Original MULTIVALVULAR INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS CLINICAL FEATURES, ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC DATA AND OUTCOMES L. ABID, B. JERBI, I. TRABELSI, A. ZNAZEN*, S. KRICHÈNE, D. ABID, M. AKROUT, S. MALLEK, F. TRIKI,
Article Original MULTIVALVULAR INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS CLINICAL FEATURES, ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC DATA AND OUTCOMES L. ABID, B. JERBI, I. TRABELSI, A. ZNAZEN*, S. KRICHÈNE, D. ABID, M. AKROUT, S. MALLEK, F. TRIKI,
Diagnosis and Treatment of Bacterial Endocarditis
 Infectious diseases Board Review Manual Statement of Editorial Purpose The Hospital Physician Infectious Diseases Board Review Manual is a study guide for fellows and practicing physicians preparing for
Infectious diseases Board Review Manual Statement of Editorial Purpose The Hospital Physician Infectious Diseases Board Review Manual is a study guide for fellows and practicing physicians preparing for
Management of infective endocarditis in children
 Management of infective endocarditis in children Ashutosh Marwah, MD* Savitri Shrivastava, MD DM FAMS FACC* INTRODUCTION Infective endocarditis (IE) continues to remain a serious disease despite advances
Management of infective endocarditis in children Ashutosh Marwah, MD* Savitri Shrivastava, MD DM FAMS FACC* INTRODUCTION Infective endocarditis (IE) continues to remain a serious disease despite advances
VEGETATION NEGATIVE INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS A VIEW POINT... Mumbai Dec 2005 Annual scientific sessions
 VEGETATION NEGATIVE INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS A VIEW POINT... Mumbai Dec 2005 Annual scientific sessions S.Venkatesan,G.Gnanavelu,G.Karthikeyan,V.Jaganathan,R.Alagesan M.Annamalai,S.Shanmugasundaram, S.Geetha,A.Balaguru.G.Anuradha
VEGETATION NEGATIVE INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS A VIEW POINT... Mumbai Dec 2005 Annual scientific sessions S.Venkatesan,G.Gnanavelu,G.Karthikeyan,V.Jaganathan,R.Alagesan M.Annamalai,S.Shanmugasundaram, S.Geetha,A.Balaguru.G.Anuradha
The New England Journal of Medicine. Review Articles
 Review Articles Medical Progress INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN ADULTS ELEFTHERIOS MYLONAKIS, M.D., AND STEPHEN B. CALDERWOOD, M.D. INFECTIVE endocarditis, a microbial infection of the endocardial surface of
Review Articles Medical Progress INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN ADULTS ELEFTHERIOS MYLONAKIS, M.D., AND STEPHEN B. CALDERWOOD, M.D. INFECTIVE endocarditis, a microbial infection of the endocardial surface of
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS AMONGST INTRAVENOUS DRUG ABUSERS SEEN AT THE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL, KUALA LUMPUR
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 42 No. 4 December 1987 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS AMONGST INTRAVENOUS DRUG ABUSERS SEEN AT THE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL, KUALA LUMPUR R. JAYAMALAR MBBS, MRCP. "N. PARASAKTHI MBBS, MSc. "S.D.
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 42 No. 4 December 1987 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS AMONGST INTRAVENOUS DRUG ABUSERS SEEN AT THE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL, KUALA LUMPUR R. JAYAMALAR MBBS, MRCP. "N. PARASAKTHI MBBS, MSc. "S.D.
, David Stultz, MD.
 http://www.dilbert.com Infective Endocarditis David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 4 December 8, 2004 Handouts available in PDF format at www.drstultz.com Topics to be covered Epidemiology Microbiology
http://www.dilbert.com Infective Endocarditis David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 4 December 8, 2004 Handouts available in PDF format at www.drstultz.com Topics to be covered Epidemiology Microbiology
WRITTEN BY: Thaer Al-qatish & Sarah Awaisheh
 WRITTEN BY: Thaer Al-qatish & Sarah Awaisheh Not all informations in the slides are included in this sheet so please study the slides. 3 kinds of Intracardiac infections: -endocarditis(inflammation of
WRITTEN BY: Thaer Al-qatish & Sarah Awaisheh Not all informations in the slides are included in this sheet so please study the slides. 3 kinds of Intracardiac infections: -endocarditis(inflammation of
CHIA MEDICAL TEAM RESOURCE PROTOCOLS: Rheumatic Heart Disease
 CHIA MEDICAL TEAM RESOURCE PROTOCOLS: Rheumatic Heart Disease It is not very common for children to get an acquired heart disease (meaning that they weren t born with it). In adults, acquired heart disease
CHIA MEDICAL TEAM RESOURCE PROTOCOLS: Rheumatic Heart Disease It is not very common for children to get an acquired heart disease (meaning that they weren t born with it). In adults, acquired heart disease
Guidelines for The Management of Infective Endocarditis
 Guidelines for The Management of Infective Endocarditis By Dr. Sinan Butrus F.I.C.M.S Clinical Standards & Guidelines Kurdistan Board For Medical Specialties Infective endocarditis IE is an infection of
Guidelines for The Management of Infective Endocarditis By Dr. Sinan Butrus F.I.C.M.S Clinical Standards & Guidelines Kurdistan Board For Medical Specialties Infective endocarditis IE is an infection of
Diagnosis and management of bacterial endocarditis in 2003 Blaithnead Murtagh, MD, O.H. Frazier, MD, and George V. Letsou, MD
 Diagnosis and management of bacterial endocarditis in 2003 Blaithnead Murtagh, MD, O.H. Frazier, MD, and George V. Letsou, MD The diagnosis of infective endocarditis has been notoriously difficult. Over
Diagnosis and management of bacterial endocarditis in 2003 Blaithnead Murtagh, MD, O.H. Frazier, MD, and George V. Letsou, MD The diagnosis of infective endocarditis has been notoriously difficult. Over
The microbial diagnosis of infective endocarditis (IE)
 The microbial diagnosis of infective endocarditis (IE) Pierrette Melin Medical Microbiology pm-chulg sbimc 10.05.2007 1 Introduction for diagnosis Review of microbiological investigation of IE and perspectives
The microbial diagnosis of infective endocarditis (IE) Pierrette Melin Medical Microbiology pm-chulg sbimc 10.05.2007 1 Introduction for diagnosis Review of microbiological investigation of IE and perspectives
Getting the Point of Injection Safety
 Getting the Point of Injection Safety Barbara Montana, MD, MPH, FACP Medical Director Communicable Disease Service Outbreak of Enterococcus faecalis endocarditis associated with an oral surgery practice
Getting the Point of Injection Safety Barbara Montana, MD, MPH, FACP Medical Director Communicable Disease Service Outbreak of Enterococcus faecalis endocarditis associated with an oral surgery practice
Renal Unit. Catheter Related Bacteraemia Guidelines
 Renal Unit Policy Manager Drew Henderson Policy Group Renal Unit Policy Established 21/01/2014 Policy Review Period/Expiry 21/01/2015 Last Updated 21/01/2014 This policy does apply to Medical/Dental Staff
Renal Unit Policy Manager Drew Henderson Policy Group Renal Unit Policy Established 21/01/2014 Policy Review Period/Expiry 21/01/2015 Last Updated 21/01/2014 This policy does apply to Medical/Dental Staff
A Nightmare. R Dulgheru, CHU Liege
 A Nightmare R Dulgheru, CHU Liege Faculty disclosure Raluca Dulgheru I have no financial relationships to disclose. MB, 57 years old male 18/03/2016 to the ER for altered mental status, First weight name
A Nightmare R Dulgheru, CHU Liege Faculty disclosure Raluca Dulgheru I have no financial relationships to disclose. MB, 57 years old male 18/03/2016 to the ER for altered mental status, First weight name
CLINICAL SYNDROMES: COMMUNITY ACQUIRED INFECTIONS
 SECTION 2 CLINICAL SYNDROMES: COMMUNITY ACQUIRED INFECTIONS 118-1 118 Adolf W. Karchmer The prototypic lesion of infective endocarditis, the vegetation (Fig. 118-1), is a mass of platelets, fibrin, microcolonies
SECTION 2 CLINICAL SYNDROMES: COMMUNITY ACQUIRED INFECTIONS 118-1 118 Adolf W. Karchmer The prototypic lesion of infective endocarditis, the vegetation (Fig. 118-1), is a mass of platelets, fibrin, microcolonies
Prognostic factors in infective endocarditis
 Boston University OpenBU Theses & Dissertations http://open.bu.edu Boston University Theses & Dissertations 2016 Prognostic factors in infective endocarditis Grzybinski, Sarah https://hdl.handle.net/2144/19176
Boston University OpenBU Theses & Dissertations http://open.bu.edu Boston University Theses & Dissertations 2016 Prognostic factors in infective endocarditis Grzybinski, Sarah https://hdl.handle.net/2144/19176
The Streptococci. Diverse collection of cocci. Gram-positive Chains or pairs significant pathogens
 The Streptococci Diverse collection of cocci. Gram-positive Chains or pairs significant pathogens Strong fermenters Facultative anaerobes Non-motile Catalase Negative 1 Classification 1 2 Classification
The Streptococci Diverse collection of cocci. Gram-positive Chains or pairs significant pathogens Strong fermenters Facultative anaerobes Non-motile Catalase Negative 1 Classification 1 2 Classification
Case Studies in Complex Endocarditis
 Case Studies in Complex Endocarditis Vera H. Rigolin, MD Professor of Medicine Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Medical Director, Echocardiography Laboratory Northwestern Memorial Hospital
Case Studies in Complex Endocarditis Vera H. Rigolin, MD Professor of Medicine Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Medical Director, Echocardiography Laboratory Northwestern Memorial Hospital
Infected cardiac-implantable electronic devices: diagnosis, and treatment
 Infected cardiac-implantable electronic devices: diagnosis, and treatment The incidence of infection following implantation of cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) is increasing at a faster rate
Infected cardiac-implantable electronic devices: diagnosis, and treatment The incidence of infection following implantation of cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) is increasing at a faster rate
Infective Endocarditis
 بسم رلا هللا Infective Endocarditis In the beginning,we need to identify a term often used in the clinical as a differential diagnosis( DDx) which is Fever of unknown origin FUO, where the pt complains
بسم رلا هللا Infective Endocarditis In the beginning,we need to identify a term often used in the clinical as a differential diagnosis( DDx) which is Fever of unknown origin FUO, where the pt complains
PROSTHETIC VALVE ENDOCARDITIS Dr Bernard Prendergast DM FRCP EUROVALVE CONGRESS MADRID NOVEMBER 2013
 PROSTHETIC VALVE ENDOCARDITIS Dr Bernard Prendergast DM FRCP EUROVALVE CONGRESS MADRID NOVEMBER 2013 Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis A Dangerous Disease Affects 1-6% of prosthetic valves Mechanical and biological
PROSTHETIC VALVE ENDOCARDITIS Dr Bernard Prendergast DM FRCP EUROVALVE CONGRESS MADRID NOVEMBER 2013 Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis A Dangerous Disease Affects 1-6% of prosthetic valves Mechanical and biological
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW
 PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
Approach to the Laboratory Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis SWACM 2018
 Approach to the Laboratory Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis SWACM 2018 Rachael Liesman, PhD, D(ABMM) Director, Clinical Microbiology Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Kansas
Approach to the Laboratory Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis SWACM 2018 Rachael Liesman, PhD, D(ABMM) Director, Clinical Microbiology Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Kansas
Endocarditis in the elderly
 Endocarditis in the elderly Gilbert Habib Département de Cardiologie - Timone Marseille Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 Endocarditis in the octogenarian Gilbert Habib Département de Cardiologie - Timone Marseille
Endocarditis in the elderly Gilbert Habib Département de Cardiologie - Timone Marseille Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 Endocarditis in the octogenarian Gilbert Habib Département de Cardiologie - Timone Marseille
The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors:
 Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
Urine bench. John Ferguson Sept 2013
 Urine bench John Ferguson Sept 2013 Overview Specimen collection- separate presentation Urinalysis: protein, blood, white cells, nitrite Microscopy- crystals and casts- separate presentations quantitative
Urine bench John Ferguson Sept 2013 Overview Specimen collection- separate presentation Urinalysis: protein, blood, white cells, nitrite Microscopy- crystals and casts- separate presentations quantitative
A CASE OF RIGHT SIDED INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS WITH REACTIVE KNEE ARTHRITIS AND ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY Suresh Babu S 1, A. K. Badrinath 2, K.
 A CASE OF RIGHT SIDED INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS WITH REACTIVE KNEE ARTHRITIS AND ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY Suresh Babu S 1, A. K. Badrinath 2, K. Suresh 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Suresh Babu S, A. K. Badrinath,
A CASE OF RIGHT SIDED INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS WITH REACTIVE KNEE ARTHRITIS AND ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY Suresh Babu S 1, A. K. Badrinath 2, K. Suresh 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Suresh Babu S, A. K. Badrinath,
109 Infective Endocarditis
 Página 1 de 30 Copyright 2005 McGraw-Hill Kasper, Dennis L., Fauci, Anthony S., Longo, Dan L., Braunwald, Eugene, Hauser, Stephen L., Jameson, J. Larry, Harrison, T. R., Resnick, W. R., Wintrobe, M. M.,
Página 1 de 30 Copyright 2005 McGraw-Hill Kasper, Dennis L., Fauci, Anthony S., Longo, Dan L., Braunwald, Eugene, Hauser, Stephen L., Jameson, J. Larry, Harrison, T. R., Resnick, W. R., Wintrobe, M. M.,
Clinical Indications for Echocardiography
 Clinical Indications for Echocardiography Echocardiography is widely utilised and potential applications are increasing with advances in technology. The aim of this document is two-fold: 1) To define clinical
Clinical Indications for Echocardiography Echocardiography is widely utilised and potential applications are increasing with advances in technology. The aim of this document is two-fold: 1) To define clinical
Clinical evaluation of a fluorescent antibody test for
 J Clin Pathol 1985;38:92-98 Clinical evaluation of a fluorescent antibody test for the serological diagnosis of streptococcal endocarditis DC SHANSON, NICOLA KIRK, R HUMPHREY From the Departments of Clinical
J Clin Pathol 1985;38:92-98 Clinical evaluation of a fluorescent antibody test for the serological diagnosis of streptococcal endocarditis DC SHANSON, NICOLA KIRK, R HUMPHREY From the Departments of Clinical
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS. IAP UG Teaching slides
 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IAP UG Teaching slides 2015 16 1 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Infection of the endocardial lining is called infective endocarditis. Involving the endocardium of valves,mural endocardium
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IAP UG Teaching slides 2015 16 1 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Infection of the endocardial lining is called infective endocarditis. Involving the endocardium of valves,mural endocardium
MANAGEMENT OF HAEMODIALYSIS CATHETER RELATED BLOOD STREAM INFECTION
 MANAGEMENT OF HAEMODIALYSIS CATHETER RELATED BLOOD STREAM INFECTION RRCV CMG Renal and Transplant Service 1. Introduction Catheter related blood stream infection (CR-BSI) is a common complication in patients
MANAGEMENT OF HAEMODIALYSIS CATHETER RELATED BLOOD STREAM INFECTION RRCV CMG Renal and Transplant Service 1. Introduction Catheter related blood stream infection (CR-BSI) is a common complication in patients
, David Stultz, MD.
 http://www.dilbert.com Infective Endocarditis David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 6 August 31, 2005 Topics to be covered Epidemiology Microbiology Clinical presentation Physical Exam Findings Diagnostic
http://www.dilbert.com Infective Endocarditis David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 6 August 31, 2005 Topics to be covered Epidemiology Microbiology Clinical presentation Physical Exam Findings Diagnostic
Right-Sided Bacterial Endocarditis
 New Concepts in the Treatment of the Uncontrollable Infection Agustin Arbulu, M.D., Ali Kafi, M.D., Norman W. Thorns, M.D., and Robert F. Wilson, M.D. ABSTRACT Our experience with 25 patients with right-sided
New Concepts in the Treatment of the Uncontrollable Infection Agustin Arbulu, M.D., Ali Kafi, M.D., Norman W. Thorns, M.D., and Robert F. Wilson, M.D. ABSTRACT Our experience with 25 patients with right-sided
SYMPOSIUM 10TH MAY 2007 BELGIUM. Blood culture-negative endocarditis
 SYMPOSIUM 10TH MAY 2007 BELGIUM Blood culture-negative endocarditis Didier RAOULT Didier.raoult@gmail.com Modified Duke criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis (IE) Li JS, et al. Proposed modifications
SYMPOSIUM 10TH MAY 2007 BELGIUM Blood culture-negative endocarditis Didier RAOULT Didier.raoult@gmail.com Modified Duke criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis (IE) Li JS, et al. Proposed modifications
IE with cerebral hemorrhage
 IE with cerebral hemorrhage Gilbert Habib / Patrizio Lancellotti La Timone Hospital Marseille - France Palermo, 26 April 2018 Case report: aortic bioprosthetic IE History of the disease 75 year-old man
IE with cerebral hemorrhage Gilbert Habib / Patrizio Lancellotti La Timone Hospital Marseille - France Palermo, 26 April 2018 Case report: aortic bioprosthetic IE History of the disease 75 year-old man
TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery. George L. Hicks, Jr., MD
 TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, 2018 Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery George L. Hicks, Jr., MD Aortic Valve Pathology and Treatment Valvular Aortic Stenosis in Adults Average Course (Post mortem data)
TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, 2018 Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery George L. Hicks, Jr., MD Aortic Valve Pathology and Treatment Valvular Aortic Stenosis in Adults Average Course (Post mortem data)
Infective endocarditis (IE) is an
 Jason Andrade, MD, Ellamae Stadnick, MD, Aneez Mohamed, MD Infective endocarditis prophylaxis: An update for clinical practice Antibiotic therapy to prevent endocarditis is now considered un - necessary
Jason Andrade, MD, Ellamae Stadnick, MD, Aneez Mohamed, MD Infective endocarditis prophylaxis: An update for clinical practice Antibiotic therapy to prevent endocarditis is now considered un - necessary
Primary foci of hematogenous periprosthetic joint infections
 Primary foci of hematogenous periprosthetic joint infections Dr. Anastasia Rakow Dr. Nora Renz Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin C.S., w. 73 y.o. 07/2015: presentation with painful knee prosthesis, back
Primary foci of hematogenous periprosthetic joint infections Dr. Anastasia Rakow Dr. Nora Renz Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin C.S., w. 73 y.o. 07/2015: presentation with painful knee prosthesis, back
Endocarditis and Its Complications: The Role of Echocardiography
 Endocarditis and Its Complications: The Role of Echocardiography Pravin Patil, MD FACC FASE Associate Professor of Medicine Director, Cardiovascular Disease Training Program Lewis Katz School of Medicine
Endocarditis and Its Complications: The Role of Echocardiography Pravin Patil, MD FACC FASE Associate Professor of Medicine Director, Cardiovascular Disease Training Program Lewis Katz School of Medicine
DICE Session. The endocarditis team. Bernard Iung Bichat Hospital, Paris Diderot University Paris, France
 DICE Session. The endocarditis team Bernard Iung Bichat Hospital, Paris Diderot University Paris, France Faculty disclosure First name - last name I disclose the following financial relationships: Consultant
DICE Session. The endocarditis team Bernard Iung Bichat Hospital, Paris Diderot University Paris, France Faculty disclosure First name - last name I disclose the following financial relationships: Consultant
Echocardiography in Endocarditis
 Echocardiography in Endocarditis Bicol Hospital, Legazpi City, Philippines July 2016 Gregg S. Pressman MD, FACC, FASE Einstein Medical Center Philadelphia, USA Demographics of IE Incidence is 1.4 12.7/100,000
Echocardiography in Endocarditis Bicol Hospital, Legazpi City, Philippines July 2016 Gregg S. Pressman MD, FACC, FASE Einstein Medical Center Philadelphia, USA Demographics of IE Incidence is 1.4 12.7/100,000
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Kang D-H, Kim Y-J, Kim S-H, et al. Early surgery versus conventional
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Kang D-H, Kim Y-J, Kim S-H, et al. Early surgery versus conventional
Blood culture 壢新醫院 病理檢驗科 陳啟清技術主任
 Blood culture 壢新醫院 病理檢驗科 陳啟清技術主任 A Positive Blood Culture Clinically Important Organism Failure of host defenses to contain an infection at its primary focus Failure of the physician to effectively eradicate,
Blood culture 壢新醫院 病理檢驗科 陳啟清技術主任 A Positive Blood Culture Clinically Important Organism Failure of host defenses to contain an infection at its primary focus Failure of the physician to effectively eradicate,
Many Faces of Infective Endocarditis- Radiological Features of Extracardiac Complications.
 Many Faces of Infective Endocarditis- Radiological Features of Extracardiac Complications. Poster No.: C-0923 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Elsayed, M. Chiphang; Wigan/UK Keywords:
Many Faces of Infective Endocarditis- Radiological Features of Extracardiac Complications. Poster No.: C-0923 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Elsayed, M. Chiphang; Wigan/UK Keywords:
