A study of clinical and etiological profile of infective endocarditis and its correlation with echocardiography in patients of rheumatic heart disease
|
|
|
- Diane Hensley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Sarkar A et al. Int J Adv Med Oct;4(5): pissn eissn Original Research Article DOI: A study of clinical and etiological profile of infective endocarditis and its correlation with echocardiography in patients of rheumatic heart disease Achyut Sarkar 1, Prashant Kumar 1 *, Somnath Mukherjee 1, Anurag Passi 1, Jitendra Kumar Singh 2 1 Department of Cardiology, IPGMER, Kolkata, West Bengal, India 2 Department of Medicine, RIMS, Ranchi, Jharkhand, India Received: 03 September 2017 Accepted: 07 September 2017 *Correspondence: Dr. Prashant Kumar, pkumar_rims@yahoo.com Copyright: the author(s), publisher and licensee Medip Academy. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. ABSTRACT Background: This observational study was to determine the offending microorganisms and clinical profile of infective endocarditis in rheumatic heart disease patients in local population of Jharkhand, the response of disease to medical treatment and to evaluate the prognosis of the cases. Methods: 25 cases of Rheumatic heart disease, fulfilling the diagnostic criteria for infective endocarditis were studied prospectively with baseline investigations, blood culture and echocardiography and were treated with appropriate antibiotics. Results: In this study, the mean age observed was 26 year and male patient to female patient ratio was 3.16:1. Aortic valve was the commonest valve to be involved. Cardiac murmurs were present in all patients, splenomegaly was present in 56% of patients but peripheral signs of infective endocarditis were rare. Blood culture was positive in 28% of cases and staphylococcus aureus was the main organism isolated. 23 cases out of 25 cases studied showed vegetations on echocardiography mostly on aortic or mitral valve. In majority of patients (80%) injection Penicillin G and Gentamicin were started in standard recommended dose first on empirical basis but later on suitable antibiotics were started according to sensitivity pattern. Mortality was significantly high (20%). Conclusions: Fever and constitutional symptoms were the most common presentation. Mild to moderate anemia, leucocytosis, high ESR were very common but, peripheral signs were rarely observed in our study. Staphylococcus was the predominant etiological agent and treatment of endocarditis was more successful when suitable antibiotics were started after culture and sensitivity. Keywords: Echocardiography, Infective endocarditis, Rheumatic heart disease INTRODUCTION Infective endocarditis is a disease caused by microbial infection of the endothelial surface of the heart. Infective endocarditis is often called acute or subacute. Acute infective endocarditis is caused typically by staphylococcus aureus. It presents with marked toxicity and progresses during days to several weeks to valvular destruction and metastatic infection. Subacute infective endocarditis, usually caused by viridians streptococci, enterococci, coagulase negative staphylococci, or gramnegative coccobacilli, evolves during weeks to months International Journal of Advances in Medicine September-October 2017 Vol 4 Issue 5 Page 1323
2 with only modest toxicity and rarely cause metastatic infection. 1 It is a very serious complication of rheumatic valvular heart disease. Several studies from developed countries have shown changing spectrum of infective endocarditis which are attributed to better diagnostic facility, greater longevity of patients with congenital and acquired valvular disease, aggressive surgical approach, emergence of new risk group for infective endocarditis (intravenous drug abuse, prosthetic heart valves, nosocomial bacteremia, degenerative heart disease), declining incidence of rheumatic heart disease. 2,3 Echocardiography has added a great deal to the ability to confirm or reject the diagnosis of infective endocarditis. 4 First of all vegetative lesions can be detected. Echocardiography also plays a major role in the recognition of complication of endocarditis as perivalvular abscesses, aneurysm, fistulas, rupture of valvular leaflets, chordae and papillary muscles or interventricular septum. Very few Indian studies are available regarding infective endocarditis. That too, most of works have been done on pediatric age group. The data from Indian studies differ from that of most of the western countries in several aspects like, population at risk for infective endocarditis, incidence of rheumatic heart disease, availability of transesophageal echocardiography and other diagnostic facility, emergency facility for surgical correction, etc. Therefore, infective endocarditis in India requires further studies. METHODS All patients attending Cardiology, Medicine or Pediatric O.P.D. or Emergency in Rajendra Institute of Medical Sciences, from October 2011 to October 2012, clinically suspected of having infective endocarditis were thoroughly investigated. Those cases of rheumatic heart disease, labeled as having infective endocarditis has been taken for further study. The study was done on 25 selected patients of Rheumatic heart disease, fulfilling the diagnostic criteria for infective endocarditis. Diagnostic criteria proposed by DUKE university was applied for the study. 5 A complete clinical history and physical examination along with special attention to predisposing factors and complication were taken according to the points as per Performa. A complete hemogram, urinalysis especially for microscopic hematuria, chest X-ray and EGG was undertaken routinely. Before initiation of therapy blood cultures were taken. A detailed M mode and 2 D echocardiographic study was performed in all suspected cases, and doubtful cases underwent TEE. Further investigations were done to document and confirm complications wherever it was indicated. Informed consents were taken from all the patients and the ethics committee approval was obtained prior to study initiation. RESULTS Study have selected 25 cases of Rheumatic heart disease, fulfilling the diagnostic criteria for infective endocarditis. Age of the patients studied varied from 10 to 50 years with maximum number of patients were in the age group of years (11 patients = 44%). Male to female patients ratio was 3.16:1. Maximum number of patients had combined mitral and aortic valve lesion (48%). Commonest combined lesions in our patients were mitral and aortic regurgitation (24%).Source of infection was detected in only 5 patients (20%) in our study. Table 1: Relative incidences of different clinical features and complications in patients presenting with infective endocarditis. Symptoms No. of patients Percentage Fever Malaise Weight loss Anorexia Oedema 8 32 Arthralgia 8 32 Myalgia 4 16 Altered sensorium/ neurological deficit 7 28 Oliguria/ anuria 5 20 Breathlessness Signs Fever Altered sensorium 5 20 Pallor Clubbing 9 36 Pedal edema 6 24 Lymphadenopathy 4 16 JVP (raised) Murmurs Splenomegaly Petechiae 1 4 Osler s node - - Janeway lesions - - Splinter hemorrhage - - Roth s spot - - Peripheral emboli 5 20 Fundus exam N - Complications Refractory heart failure 7 28 Cerebro vascular accidents 4 16 Acute renal failure 5 20 Peripheral arterial embolism 5 20 Septicemia 3 12 Upper GI bleeding 1 4 All patients in our study had mild to moderate grade fever (100%). On examination, almost all patients had pallor. 5 International Journal of Advances in Medicine September-October 2017 Vol 4 Issue 5 Page 1324
3 patients were in altered sensorium with or without focal neurological deficit. Cardiac murmur was auscultated in all patients. Eleven patients (44%) were in congestive heart failure. Among peripheral signs of infective endocarditis clubbing was present in nine patients (36%). Other signs like oslers node, Janeway lesion and roth s spots were not seen in any of the patients. One patient had petechial hemorrhage. Among the study group, spleen was enlarged in 14 patients (Table 1). Table 2: Results of different investigations in patients presenting with infective endocarditis. Hb% (mg/dl) No. of patients Percentage Normal > Mild Anaemia Moderate anaemia Severe anaemia < Total leucocyte count <10,000 cells/mm Blood culture positivity Positive (+ve) 7 28 Negative (-ve) Vegetations on echocardiography Aortic RCC NCC 2 8 Both RCC and NCC 2 8 Mitral 7 28 AML 6 24 PML 1 4 Both AML and PML - - Both aortic and mitral 1 4 Haemoglobin level was less than normal in all 25 studied cases (100%), while 3 patients were severely anaemic with haemoglobin level less than 7gm/dl. Thirteen patients of the study group had leukocyte count more than 10,000 cells per cubic millimeter at the time of admission (Table 2). Almost all patients in study group had raised ESR [23 patients (92%)]. Only four patients (16%) showed feature of microscopic haematuria. Blood culture was positive in seven out of all twenty-five patients (28%) while in 18 patients blood culture was negative despite repeated collection of sample and incubation for seven day (Table 2). Staphylococcus aureus was the commonest organism to be grown and was seen in 3 of 25 patient s blood sample (12%). It was sensitive to vancomycin in all 3 cases. Staphylococcus aureus was sensitive to aminoglycosides in two but resistant in one sample. Staphylococcus aureus was resistant to penicillin G in all 3 patients. In one patient culture showed growth of coagulase negative staphylococci. It was sensitive to ciprofloxacin, Oxacillin and Vancomycin. Streptococcus viridans was grown in 2 patient s blood culture (8%). It was sensitive to penicillin G and aminoglycosides. One patient showed growth of acinobacter. In 23 out of 25 patients vegetations were documented on echocardiography (92%). Most commonly involved valve was aortic (in 15 patients (60%). Mitral valve was involved in 7 patients (28%). Of these most patients have vegetations on AML. In one patient vegetation was present in both mitral and aortic valve. Treatment was started on empirical basis in all patients after sending 3 blood samples for blood culture. Empirically treatment was started with injections of Penicillin G in 12 to 18 million IU in 6 divided doses with injection of gentamicin in 3 to 5mg/kg/day in 3 divided doses in 20 patients (80%). 4 of these patients expired during the course of treatment. 11 patients responded to treatment and become afebrile in 8 days and treatment was given for only 2 weeks. Five of these patients became afebrile after 10 days of treatment and injection penicillin G was continued for additional 2 weeks with total duration of treatment given was 4 weeks (Table 3). Injection ceftriaxone 2gm IV OD was started in 5 patients (20%), One of these patients expired on third day due to poor general condition. Rest of the patients completed the 4 weeks course successfully. Table 3: Treatments of patients presenting with infective endocarditis with different regimens of antibiotics and mortality outcomes in those patients. Regimen with duration Penicillin G (12-18 million IU) IV in 6 divided doses -for 2 weeks Plus Gentamicin - for 2 weeks (1mg/kg IV 8 hours) Penicillin G (12-18 million IU) IV in 6 divided doses - for 4 weeks Plus Gentamicin -for 2 weeks (1mg/kg IV 8 hr) Ceftriaxone (2gm) IV OD -for 4 weeks. No. of patients (%) 15 (60%) 4 5 (20%) Mortality Mortality was significantly high (20%) and the cause of death was attributed to septicemia (8%), refractory heart failure (4%), acute renal failure (4%) and arrhythmia/sudden death (4%). DISCUSSION Most of the western studies where there is upward shift in mean age from 30 to about 50 years in past 3 decades. 6 In India mean age has remained more or less the same with majority of Indian patients still being under 40 years of age. Important factors include low life expectancy and high incidence of rheumatic heart disease. 7 In our study age group varied from 11 to 43 years with maximum number of patients in the age group of 10 to 20 years age International Journal of Advances in Medicine September-October 2017 Vol 4 Issue 5 Page 1325
4 group (11 patients = 44%) and the mean age observed was years. In our study, total number of male patients was 19 and that of female patients was 6. Male to female ratio was 3.16:1. This figure is in accordance with other Indian studies. 7 Lone aortic valve involvement was noted in 32% of cases and combined involvement of both aortic and mitral valve was noted in 48% of cases in present study. Isolated mitral valve lesion was seen in 20% of cases. These findings are in consistent with Indian and western studies. Tricuspid valve involvement is rare as noted by various studies and same is with pulmonary valve. In our study tricuspid valve was involved in 4% of the cases, and that too in association with mitral valve lesion. Isolated tricuspid valve involvement was not observed in our study. In this study, source of infection was detected in only 20% of cases; similar observations were made by others. 8 In our study 11 patients (44%) were already diagnosed case of rheumatic heart disease and only 5 patients (20%) were taking long acting penicillin prophylaxis. This suggests poor compliance among our patients. Fever is one of the cardinal manifestation of infective endocarditis. In our study, all patients had mild to moderate grade fever (100%). Fever varied from 41.2 to 100% in other series. A moderate normocytic normochromic anaemia is a common finding in infective endocarditis. In our study, all patients had pallor (100%). This is in accordance with various Indian studies. However, the incidence of anaemia in western series varied from 34-91%. This high incidence of anaemia among Indians may be explained mainly by poor nutritional status and long duration of illness before presentation. In present study spleen was enlarged in 14 patients (56%). It has been recorded to occur in 36-60% of Indian patients. Among peripheral signs of IE, clubbing was noted in 9 patients (36%). Incidence of clubbing in Indian studies varies from 32-80%. In west presently clubbing is identified in only 10-20% of cases. High incidence of clubbing in Indian studies is because of late presentation of these patients. One patient has petechial haemorrhage (4%) in our study. In spite of thorough search in our cases we failed to identity other signs like splinter hemorrhage Osler s node and Janeway lesions even in single case. Various studies have shown that these are uncommon finding of IE. 9,10 In our study 28% of patients developed congestive heart failure. Incidence of heart failure varied from 21 to 75% in various studies. Indian workers have reported a higher incidence of congestive heart failure in their study. In present study 16% of patients developed hemiplegia/hemiparesis. It commonly results from embolism of middle cerebral artery by friable vegetations. This is in accordance to findings reported in various studies. 11,12 In present study, Haemoglobin was low in all patients 88% of them had mild to moderate anaemia. This finding is in accordance with the finding of various Indian studies. Incidence of leucocytosis varies from 39-58% in various studies. 13 In our study in 52% of patients leucocytosis was seen. Most of them were case of acute IE with history of less than 4 weeks. In present study 92% of patients has raised ESR. In various studies, the percentage of patients showing raised ESR ranges from 72% to 100%. 2 In present study microscopic hematuria was detected in 16% of patients. Similar incidence has been seen in different Indian series. A higher incidence has been reported from the west. In this study blood culture was positive in 28% of cases, in Indian studies blood culture positivity varies from 21% to 97%. While as in western series culture positivity varies from 73 to 97%. In present study staphylococcus aureus was the main organism isolated in 12% of cases. Streptococcus viridans was isolated in 8% cases and coagulase negative staphylococcus and acinobacter were isolated from one cases each (4%). Results in these studies are different from results of various western studies but matching with some of Indian studies. 14 The sensitivity of TTE for the detection of vegetations, even with the use of harmonic imaging and other modern techniques, in patients with NVE is approximately 45% to 65%, whereas that of TEE in these patients is 85% to 95%. The likelihood of a false-negative study can be reduced to 5% to 10% if TEE is repeated. 15 TEE is the preferred approach in patients in whom TTE is technically suboptimal and is the procedure of choice for imaging of the pulmonary valve and patients with suspected PVE. 13,15 In present study vegetations were demonstrated in 92% of cases. In present study vegetations were mainly confined to aortic and mitral valves. Aortic valve was involved in 60% of cases and mitral valve in 28% cases. In one patient, vegetation was seen on both mitral and aortic valve. Similar results have been shown in various. Indian studies. 7,10 However, in western studies mitral valve is more commonly involved as compared to Indian study. This may be because of high incidence of mitral valve prolapse or prosthetic valve as predisposing cardiac lesion in patients with IE. Out of 25 patients 5 patients expired during hospital study in our study (20%). Of these patients culture was positive in four patients and three had staphylococcal infection. This figure of mortality is comparable to other Indian reports of 21-54%. 7,9,10 More recent series suggest that mortality can be reduced to 10-13% by timely surgical interventions. In our study mortality was high with staphylococcal infective endocarditis. The factors contributing to mortality include non-availability of surgical facilities and poor economic status of our patients who could not afford the high cost of cardiac surgery which could be life-saving in patients of refractory heart failure and uncontrolled sepsis. International Journal of Advances in Medicine September-October 2017 Vol 4 Issue 5 Page 1326
5 CONCLUSION Mean age of our patients is still lower than western part of world. Fever and constitutional symptoms are the most common presentation. Mild to moderate anemia, leucocytosis, high ESR are very common. Peripheral signs of infective endocarditis were scanty in this series as - petechial haemorrhage was noted in only 1 patient and Oslers node, splinter hemorrahge, Janeways lesion and Roth s spot were not observed in our study. Staphylococcus was the predominant etiological agent in our study. Treatment of endocarditis was more successful when suitable antibiotics were started after culture and sensitivity rather than the empirical treatment. To conclude, we have reached at a point that infective endocarditis is not so uncommon manifestation seen in the Department of Medicine and Cardiology because of higher incidence of rheumatic heart disease in our society. We must take into account the gravity of the illness and to start an early treatment in order to salvage these cases without which the motility would be higher as discussed. Funding: No funding sources Conflict of interest: None declared Ethical approval: The study was approved by the institutional ethics committee REFERENCES 1. Baddour LM, Wilson WR, Bayer AS. Infective endocarditis: Diagnosis, antimicrobial therapy, and management of complications. A statement for healthcare professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, and the Councils on Clinical Cardiology, Stroke, and Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia, American HeartAssociation. Circulation. 2005;111:e Murdoch DR, Corey GR, Hoen BL. Clinical presentation, etiology, and outcome of infective endocarditis in the 21st century. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169: Finland M, Barnes MW. Changing etiology of Bacterial Endocarditis in the antibacterial era. Ann Int Med. 1970;72: Banchs J, Yusuf SW. Echocardiographic evaluation of cardiac infection. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2012;10:1. 5. Durack DT, Lukes AS, Bright DK. New criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis: Utilization of specific echocardiographic findings. Am J Med. 1994;96: Baddour LM. Twelve-year review of recurrent native-valve infective endocarditis: A disease of the modern antibiotic era. Rev Infect Dis. 1988;10: Chaudhary R. Active infective endocarditis observed in an Indian Hospital Am J Cardiol. 1992;70: Raghu C. Profile of infective endocarditis: trends from a tertiary centre. Indian H.J. 1997;49: Kabde VR, Bidwai PS, Berry JN, Agarwal KC. Clinical and bacteriological studies in infective endocarditis. Indian Heart J. 1970;22: Agarwal RK, Gupta R, Agarwal SC, Dwivedi M. Bacterial endocarditis-its diagnostic problems. J Assoc Physicians India. 1981;29: Thuny F, DiSalvo G, Belliard O. Risk of embolism and death in infective endocarditis: Prognostic value of echocardiography. A prospective multicenter study. Circulation. 2005;112: Dickerman SA, Abrutyn E, Barsic B. The relationship between the initiation of antimicrobial therapy and the incidence of stroke in infective endocarditis: An analysis from the ICE prospective cohort study (ICE-PCS). Am Heart J. 2007;154: Bayer AS, Bolger AF, Taubert KA. Diagnosis and management of infective endocarditis and its complications. Circulation. 1998;98: Lopez J, Fernandez-Hidalgo N, Revilla A. Internal and external validation of a model to predict adverse outcomes in patients with left sided infective endocarditis. Heart. 2011;97: Kini V, Logani S, Ky B. Transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiography for the indication of suspected infective endocarditis: Vegetations, blood cultures and imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiograph. 2010;23:396. Cite this article as: Sarkar A, Kumar P, Mukherjee S, Passi A, Singh JK. A study of clinical and etiological profile of infective endocarditis and its correlation with echocardiography in patients of rheumatic heart disease. Int J Adv Med 2017;4: International Journal of Advances in Medicine September-October 2017 Vol 4 Issue 5 Page 1327
Dr Babak Tamizi far MD. Assistant Professor Of Internal Medicine Al-Zahra Hospital Isfahan University Of Medical Sciences
 Dr Babak Tamizi far MD. Assistant Professor Of Internal Medicine Al-Zahra Hospital Isfahan University Of Medical Sciences ١ ٢ ٣ A 57-year-old man presents with new-onset fever, shortness of breath, lower
Dr Babak Tamizi far MD. Assistant Professor Of Internal Medicine Al-Zahra Hospital Isfahan University Of Medical Sciences ١ ٢ ٣ A 57-year-old man presents with new-onset fever, shortness of breath, lower
Heart on Fire: Infective Endocarditis. Objectives. Disclosure 8/27/2018. Mary McGreal DNP, RN, ANP-c, CCRN
 Heart on Fire: Infective Endocarditis Mary McGreal DNP, RN, ANP-c, CCRN Objectives Discuss the incidence of infective endocarditis? Discuss the pathogenesis of infective endocarditis? Discuss clinical
Heart on Fire: Infective Endocarditis Mary McGreal DNP, RN, ANP-c, CCRN Objectives Discuss the incidence of infective endocarditis? Discuss the pathogenesis of infective endocarditis? Discuss clinical
Challenging clinical situation
 Challenging clinical situation A young patient with prosthetic aortic valve endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France October 25 th 2014 Case report History of the disease Clinical
Challenging clinical situation A young patient with prosthetic aortic valve endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France October 25 th 2014 Case report History of the disease Clinical
Daniel C. DeSimone, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine
 Daniel C. DeSimone, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Faculty photo will be placed here Desimone.Daniel@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Infective Endocarditis Mayo School of Continuous Professional Development
Daniel C. DeSimone, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Faculty photo will be placed here Desimone.Daniel@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Infective Endocarditis Mayo School of Continuous Professional Development
Michael Stander, Pharm.D.
 Michael Stander, Pharm.D. Endocarditis: Goals Epidemiology Presentation of acute and subacute. Diagnosis: What is Dukes Criteria and how do we approach the diagnosis of endocarditis? Treatment: Understand
Michael Stander, Pharm.D. Endocarditis: Goals Epidemiology Presentation of acute and subacute. Diagnosis: What is Dukes Criteria and how do we approach the diagnosis of endocarditis? Treatment: Understand
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS AMONGST INTRAVENOUS DRUG ABUSERS SEEN AT THE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL, KUALA LUMPUR
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 42 No. 4 December 1987 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS AMONGST INTRAVENOUS DRUG ABUSERS SEEN AT THE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL, KUALA LUMPUR R. JAYAMALAR MBBS, MRCP. "N. PARASAKTHI MBBS, MSc. "S.D.
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 42 No. 4 December 1987 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS AMONGST INTRAVENOUS DRUG ABUSERS SEEN AT THE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL, KUALA LUMPUR R. JAYAMALAR MBBS, MRCP. "N. PARASAKTHI MBBS, MSc. "S.D.
NATIONAL HEART FOUNDATION HOSPITAL & RESEARCH INSTITUTE
 Welcome INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS: WHERE WE ARE AT 2005? DR MD HABIBUR RAHMAN FCPS(Medicine) NATIONAL HEART FOUNDATION HOSPITAL & RESEARCH INSTITUTE DEFINITION OF INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Infective endocarditis
Welcome INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS: WHERE WE ARE AT 2005? DR MD HABIBUR RAHMAN FCPS(Medicine) NATIONAL HEART FOUNDATION HOSPITAL & RESEARCH INSTITUTE DEFINITION OF INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Infective endocarditis
Update on the prevention, diagnosis and management of Infective Endocarditis (IE)
 Update on the prevention, diagnosis and management of Infective Endocarditis (IE) Dr.Ahmed Yahya Mohammed Alarhabi MD, MsC,FcUSM,FACC,MAHA Consultant Interventional Cardiologist Head of Cardiac Center
Update on the prevention, diagnosis and management of Infective Endocarditis (IE) Dr.Ahmed Yahya Mohammed Alarhabi MD, MsC,FcUSM,FACC,MAHA Consultant Interventional Cardiologist Head of Cardiac Center
April 16, 09:00-09:15 중앙대학교 윤신원
 April 16, 09:00-09:15 중앙대학교 윤신원 When to perform Echocardiography in IE? Vegetations?(pathologic Whatever the level hallmark) of suspicion Intracardiac abscess? Confirm or R/O at the Earliest opportunity.
April 16, 09:00-09:15 중앙대학교 윤신원 When to perform Echocardiography in IE? Vegetations?(pathologic Whatever the level hallmark) of suspicion Intracardiac abscess? Confirm or R/O at the Earliest opportunity.
Clinical Profile & Outcome of Infective Endocarditis patients admitted in tertiary care center in eastern part of Nepal
 10 Original Article Clinical Profile & Outcome of Infective Endocarditis patients admitted in tertiary care center in eastern part of Nepal Sherpa K, Shah P, Khati Y, Jha SK, Sharma SK, Karki P Department
10 Original Article Clinical Profile & Outcome of Infective Endocarditis patients admitted in tertiary care center in eastern part of Nepal Sherpa K, Shah P, Khati Y, Jha SK, Sharma SK, Karki P Department
Infective Endocarditis
 Frank Lowy Infective Endocarditis 1. Introduction Infective endocarditis (IE) is an infection of the heart valves. A large number of different bacteria are capable of causing this disease. Depending on
Frank Lowy Infective Endocarditis 1. Introduction Infective endocarditis (IE) is an infection of the heart valves. A large number of different bacteria are capable of causing this disease. Depending on
Joshua Budhu M.S, Dorian Wood B.S, Marvin Crawford M.D, Khuram Ashraf M.D, Frederick Doamekpor M.D, Olufunke Akinbobuyi M.D
 Accepted Manuscript Aerococcus Viridans Infectious Endocarditis Complicated by Splenic Infarction Joshua Budhu M.S, Dorian Wood B.S, Marvin Crawford M.D, Khuram Ashraf M.D, Frederick Doamekpor M.D, Olufunke
Accepted Manuscript Aerococcus Viridans Infectious Endocarditis Complicated by Splenic Infarction Joshua Budhu M.S, Dorian Wood B.S, Marvin Crawford M.D, Khuram Ashraf M.D, Frederick Doamekpor M.D, Olufunke
General management of infective endocarditis
 General management of infective endocarditis Team approach in infective endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 The echolab «Heart Team" Infective Endocarditis
General management of infective endocarditis Team approach in infective endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 The echolab «Heart Team" Infective Endocarditis
Diagnostic strategy. Dr Pilar Tornos Hospital Vall d Hebron Barcelona
 Diagnostic strategy Dr Pilar Tornos Hospital Vall d Hebron Barcelona Faculty disclosure Pilar Tornos I disclose the following financial relationships: Paid speaker for Recordati, Edwards. Diagnosis of
Diagnostic strategy Dr Pilar Tornos Hospital Vall d Hebron Barcelona Faculty disclosure Pilar Tornos I disclose the following financial relationships: Paid speaker for Recordati, Edwards. Diagnosis of
Endocardite infectieuse
 Endocardite infectieuse 1. Raccourcir le traitement: jusqu où? 2. Proposer un traitement ambulatoire: à partir de quand? Endocardite infectieuse A B 90 P = 0.014 20 P = 0.0005 % infective endocarditis
Endocardite infectieuse 1. Raccourcir le traitement: jusqu où? 2. Proposer un traitement ambulatoire: à partir de quand? Endocardite infectieuse A B 90 P = 0.014 20 P = 0.0005 % infective endocarditis
Infective Endocarditis Empirical therapy Antibiotic Guidelines. Contents
 Infective Endocarditis Empirical therapy Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Group Additional author(s): as above Authors Division: Division of Clinical
Infective Endocarditis Empirical therapy Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Group Additional author(s): as above Authors Division: Division of Clinical
Infective Endocarditis
 Infective Endocarditis Infective Endocarditis Historical Perspective.. A concretion larger than a pigeon s egg; contained in the left auricle. Burns, 1809 Osler s Gulstonian lectures provided the 1 st
Infective Endocarditis Infective Endocarditis Historical Perspective.. A concretion larger than a pigeon s egg; contained in the left auricle. Burns, 1809 Osler s Gulstonian lectures provided the 1 st
Infective endocarditis
 Infective endocarditis This is caused by microbial infection of a heart valve (native or prosthetic), the lining of a cardiac chamber or blood vessel, or a congenital anomaly (e.g. septal defect). The
Infective endocarditis This is caused by microbial infection of a heart valve (native or prosthetic), the lining of a cardiac chamber or blood vessel, or a congenital anomaly (e.g. septal defect). The
Infective Endocarditis عبد المهيمن أحمد
 Infective Endocarditis إعداد : عبد المهيمن أحمد أحمد علي Infective endocarditis Inflammation of the heart valve or endocardium of the heart. The agents are usually bacterial, but other organisms can also
Infective Endocarditis إعداد : عبد المهيمن أحمد أحمد علي Infective endocarditis Inflammation of the heart valve or endocardium of the heart. The agents are usually bacterial, but other organisms can also
VALVULAR HEART DISEASE
 VALVULAR HEART DISEASE Stenosis: failure of a valve to open completely, obstructing forward flow. - almost always due to a chronic process (e.g., calcification or valve scarring). Insufficiency : failure
VALVULAR HEART DISEASE Stenosis: failure of a valve to open completely, obstructing forward flow. - almost always due to a chronic process (e.g., calcification or valve scarring). Insufficiency : failure
Bacterial Endocarditis
 Objectives Bacterial Endocarditis John C. Rotschafer, Pharm. D. Professor College of Pharmacy University of Minnesota Identify which valves are commonly involved with endocarditis Identify common pathogens
Objectives Bacterial Endocarditis John C. Rotschafer, Pharm. D. Professor College of Pharmacy University of Minnesota Identify which valves are commonly involved with endocarditis Identify common pathogens
A Predictable Outcome of a Preventable Disease. Sanjay Kamboj, MD; Shaminder Gupta, MD; Glenn P. Kelley, MD; Fred Helmcke, MD; and Fred A.
 Clinical Case of the Month A Predictable Outcome of a Preventable Disease Sanjay Kamboj, MD; Shaminder Gupta, MD; Glenn P. Kelley, MD; Fred Helmcke, MD; and Fred A. Lopez, MD Infective endocarditis is
Clinical Case of the Month A Predictable Outcome of a Preventable Disease Sanjay Kamboj, MD; Shaminder Gupta, MD; Glenn P. Kelley, MD; Fred Helmcke, MD; and Fred A. Lopez, MD Infective endocarditis is
The changing landscape of infective endocarditis (IE)in congenital heart disease (CHD)
 The changing landscape of infective endocarditis (IE)in congenital heart disease (CHD) Rekwan Sittiwangkul,MD Department of Pediatrics. Chiang Mai University Hospital, 24 th March 2018 Infective endocarditis
The changing landscape of infective endocarditis (IE)in congenital heart disease (CHD) Rekwan Sittiwangkul,MD Department of Pediatrics. Chiang Mai University Hospital, 24 th March 2018 Infective endocarditis
Disclosures. Native Valve Endocarditis and its Complications. Outline. Outline. Basics. Basics 3/23/2017
 Native Valve Endocarditis and its Complications SCVP and Binford Dammin Society of Infectious Disease Pathologists Shared Companion Meeting USCAP 2017 Annual Meeting Disclosures Relevant financial relationships
Native Valve Endocarditis and its Complications SCVP and Binford Dammin Society of Infectious Disease Pathologists Shared Companion Meeting USCAP 2017 Annual Meeting Disclosures Relevant financial relationships
Pr AMEL OMEZZINE LETAIEF CHU FarhatHached Sousse
 Pr AMEL OMEZZINE LETAIEF CHU FarhatHached Sousse cours de collège infectiologie Sousse le27/02/2013 ENDOCARDITIS There is a change in epidemiology Clinical features of IE remains classical Diagnosis of
Pr AMEL OMEZZINE LETAIEF CHU FarhatHached Sousse cours de collège infectiologie Sousse le27/02/2013 ENDOCARDITIS There is a change in epidemiology Clinical features of IE remains classical Diagnosis of
Endocarditis in the elderly
 Endocarditis in the elderly Gilbert Habib Département de Cardiologie - Timone Marseille Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 Endocarditis in the octogenarian Gilbert Habib Département de Cardiologie - Timone Marseille
Endocarditis in the elderly Gilbert Habib Département de Cardiologie - Timone Marseille Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 Endocarditis in the octogenarian Gilbert Habib Département de Cardiologie - Timone Marseille
INFECTIOUS endocarditis (IE) is a
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis Sensitivity of the Duke vs von Reyn Criteria Maija Heiro, MD; Jukka Nikoskelainen, MD, PhD; Jaakko J. Hartiala, MD, PhD; Markku K. Saraste, MD;
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis Sensitivity of the Duke vs von Reyn Criteria Maija Heiro, MD; Jukka Nikoskelainen, MD, PhD; Jaakko J. Hartiala, MD, PhD; Markku K. Saraste, MD;
Infective Endocarditis
 Infective Endocarditis Definition Historical perspective Classification Epidemiological Features Etiology Pathogenesis Clinical presentation Diagnosis Treatment options Prevention Infective endocarditis
Infective Endocarditis Definition Historical perspective Classification Epidemiological Features Etiology Pathogenesis Clinical presentation Diagnosis Treatment options Prevention Infective endocarditis
Infective endocarditis (IE) By Assis. Prof. Nader Alaridah MD, PhD
 Infective endocarditis (IE) By Assis. Prof. Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Infective endocarditis (IE) is an inflammation of the endocardium.. inner of the heart muscle & the epithelial lining of heart valves.
Infective endocarditis (IE) By Assis. Prof. Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Infective endocarditis (IE) is an inflammation of the endocardium.. inner of the heart muscle & the epithelial lining of heart valves.
A Study of Infective Endocarditis in Malta
 Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 6(6): 98-104 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjcm doi: 10.11648/j.sjcm.20170606.11 ISSN: 2327-2724 (Print); ISSN: 2327-2732 (Online) A Study of Infective
Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 6(6): 98-104 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjcm doi: 10.11648/j.sjcm.20170606.11 ISSN: 2327-2724 (Print); ISSN: 2327-2732 (Online) A Study of Infective
PRINCIPLES OF ENDOCARDITIS
 015 // Endocarditis CONTENTS 140 Principles of Endocarditis 141 Native Valve Endocarditis 143 Complications of Native Valve Endocarditis 145 Right Heart Endocarditis 145 Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis 146
015 // Endocarditis CONTENTS 140 Principles of Endocarditis 141 Native Valve Endocarditis 143 Complications of Native Valve Endocarditis 145 Right Heart Endocarditis 145 Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis 146
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN CHILDREN
 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN CHILDREN Rohayati Taib RIPAS Hospital, Bundar Seri Begawan, Brunei Darussalam Infective Endocarditis (IE) is a microbial infection of the endocardium. It encompasses both bacterial
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN CHILDREN Rohayati Taib RIPAS Hospital, Bundar Seri Begawan, Brunei Darussalam Infective Endocarditis (IE) is a microbial infection of the endocardium. It encompasses both bacterial
Echocardiography after stroke - where to look
 Echocardiography after stroke - where to look Vuyisile T. Nkomo, MD,MPH, FACC, FASE Joint Cardiac Imaging Society of South Africa/Mayo Clinic Echocardiography Workshop 2017 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
Echocardiography after stroke - where to look Vuyisile T. Nkomo, MD,MPH, FACC, FASE Joint Cardiac Imaging Society of South Africa/Mayo Clinic Echocardiography Workshop 2017 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
ACCME/Disclosures 4/13/2016 IDPB
 ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
IE with cerebral hemorrhage
 IE with cerebral hemorrhage Gilbert Habib / Patrizio Lancellotti La Timone Hospital Marseille - France Palermo, 26 April 2018 Case report: aortic bioprosthetic IE History of the disease 75 year-old man
IE with cerebral hemorrhage Gilbert Habib / Patrizio Lancellotti La Timone Hospital Marseille - France Palermo, 26 April 2018 Case report: aortic bioprosthetic IE History of the disease 75 year-old man
results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both.
 results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both. The outcome of valvular disease depends on : 1-the valve involved 2-the degree of impairment 3-the cause of its development
results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both. The outcome of valvular disease depends on : 1-the valve involved 2-the degree of impairment 3-the cause of its development
, David Stultz, MD.
 http://www.dilbert.com Infective Endocarditis David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 4 December 8, 2004 Handouts available in PDF format at www.drstultz.com Topics to be covered Epidemiology Microbiology
http://www.dilbert.com Infective Endocarditis David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 4 December 8, 2004 Handouts available in PDF format at www.drstultz.com Topics to be covered Epidemiology Microbiology
Clinical Characteristics and In-Hospital Prognosis of Infective Endocarditis in Two Eastern Counties of Taiwan
 Original Article Acta Cardiol Sin 2014;30:151 156 Infective Endocarditis Clinical Characteristics and In-Hospital Prognosis of Infective Endocarditis in Two Eastern Counties of Taiwan Jen-Che Hsieh, 1,4
Original Article Acta Cardiol Sin 2014;30:151 156 Infective Endocarditis Clinical Characteristics and In-Hospital Prognosis of Infective Endocarditis in Two Eastern Counties of Taiwan Jen-Che Hsieh, 1,4
Infective Endocarditis
 Chapter 32 Infective Endocarditis Lisa B. Hightow and Meera Kelley The term infective endocarditis (IE) refers to infection of the endocardial surface of the heart and implies a physical presence of microganisms
Chapter 32 Infective Endocarditis Lisa B. Hightow and Meera Kelley The term infective endocarditis (IE) refers to infection of the endocardial surface of the heart and implies a physical presence of microganisms
Infective Endocarditis for Primary Care Physicians
 Infective Endocarditis for Primary Care Physicians David N Gilbert, MD Disclosures Consultant to: Merck Pfizer Medicine Company Cempra 1 Introduction There are roughly 30,000 new cases of IE in the US
Infective Endocarditis for Primary Care Physicians David N Gilbert, MD Disclosures Consultant to: Merck Pfizer Medicine Company Cempra 1 Introduction There are roughly 30,000 new cases of IE in the US
Infections Amenable to OPAT. (Nabin Shrestha + Ajay Mathur)
 3 Infections Amenable to OPAT (Nabin Shrestha + Ajay Mathur) Decisions regarding outpatient treatment of infections vary with the institution, the prescribing physician, the individual patient s condition
3 Infections Amenable to OPAT (Nabin Shrestha + Ajay Mathur) Decisions regarding outpatient treatment of infections vary with the institution, the prescribing physician, the individual patient s condition
A CASE OF RIGHT SIDED INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS WITH REACTIVE KNEE ARTHRITIS AND ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY Suresh Babu S 1, A. K. Badrinath 2, K.
 A CASE OF RIGHT SIDED INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS WITH REACTIVE KNEE ARTHRITIS AND ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY Suresh Babu S 1, A. K. Badrinath 2, K. Suresh 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Suresh Babu S, A. K. Badrinath,
A CASE OF RIGHT SIDED INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS WITH REACTIVE KNEE ARTHRITIS AND ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY Suresh Babu S 1, A. K. Badrinath 2, K. Suresh 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Suresh Babu S, A. K. Badrinath,
, David Stultz, MD.
 http://www.dilbert.com Infective Endocarditis David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 6 August 31, 2005 Topics to be covered Epidemiology Microbiology Clinical presentation Physical Exam Findings Diagnostic
http://www.dilbert.com Infective Endocarditis David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 6 August 31, 2005 Topics to be covered Epidemiology Microbiology Clinical presentation Physical Exam Findings Diagnostic
Modifiers of the clinical course of infective endocarditis
 Modifiers of the clinical course of infective endocarditis Ulrika Snygg-Martin M.D., Ph.D. Infectious Diseases Clinic Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg, Sweden Infective endocarditis : modifiers
Modifiers of the clinical course of infective endocarditis Ulrika Snygg-Martin M.D., Ph.D. Infectious Diseases Clinic Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg, Sweden Infective endocarditis : modifiers
MULTIVALVULAR INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS CLINICAL FEATURES, ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC DATA AND OUTCOMES
 Article Original MULTIVALVULAR INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS CLINICAL FEATURES, ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC DATA AND OUTCOMES L. ABID, B. JERBI, I. TRABELSI, A. ZNAZEN*, S. KRICHÈNE, D. ABID, M. AKROUT, S. MALLEK, F. TRIKI,
Article Original MULTIVALVULAR INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS CLINICAL FEATURES, ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC DATA AND OUTCOMES L. ABID, B. JERBI, I. TRABELSI, A. ZNAZEN*, S. KRICHÈNE, D. ABID, M. AKROUT, S. MALLEK, F. TRIKI,
Case-based session. Infective Endocarditis. Applying the new guidelines. A case of large vegetation with neurological complication.
 Case-based session. Infective Endocarditis. Applying the new guidelines. A case of large vegetation with neurological complication. María Nazarena Pizzi Hospital Universitari Vall d Hebron Barcelona. I
Case-based session. Infective Endocarditis. Applying the new guidelines. A case of large vegetation with neurological complication. María Nazarena Pizzi Hospital Universitari Vall d Hebron Barcelona. I
BASIC KNOWLEDGE ABOUT INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS FOR CLINICIAN
 BASIC KNOWLEDGE ABOUT INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS FOR CLINICIAN When should I suspect infective endocarditis? Antibiotic regimen Patient care after completion of treatment Prophylactic Regimens Prosthetic Valve
BASIC KNOWLEDGE ABOUT INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS FOR CLINICIAN When should I suspect infective endocarditis? Antibiotic regimen Patient care after completion of treatment Prophylactic Regimens Prosthetic Valve
An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for infective endocarditis
 REVIEW An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for infective endocarditis Albert W Chan MD FRCPC, Heather J Ross MD FRCPC AW Chan, HJ Ross. An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for
REVIEW An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for infective endocarditis Albert W Chan MD FRCPC, Heather J Ross MD FRCPC AW Chan, HJ Ross. An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for
Indications chirurgicales dans l endocardite infectieuse
 Indications chirurgicales dans l endocardite infectieuse Bruno Hoen ICE AEPEI Agenda Indications of surgery in IE: current guidelines Impact of early valve surgery (EVS) on the prognosis of IE: is the
Indications chirurgicales dans l endocardite infectieuse Bruno Hoen ICE AEPEI Agenda Indications of surgery in IE: current guidelines Impact of early valve surgery (EVS) on the prognosis of IE: is the
Chiayi, Taiwan. Abstract
 DOI 10.6314/JIMT.201810_29(5).05 2018 29 309-316 Clinical Features and Risks Associated with In-hospital Mortality in Patients with Infective Endocarditis at A Medical Center in Central Taiwan from 2012
DOI 10.6314/JIMT.201810_29(5).05 2018 29 309-316 Clinical Features and Risks Associated with In-hospital Mortality in Patients with Infective Endocarditis at A Medical Center in Central Taiwan from 2012
Diagnosis and management of bacterial endocarditis in 2003 Blaithnead Murtagh, MD, O.H. Frazier, MD, and George V. Letsou, MD
 Diagnosis and management of bacterial endocarditis in 2003 Blaithnead Murtagh, MD, O.H. Frazier, MD, and George V. Letsou, MD The diagnosis of infective endocarditis has been notoriously difficult. Over
Diagnosis and management of bacterial endocarditis in 2003 Blaithnead Murtagh, MD, O.H. Frazier, MD, and George V. Letsou, MD The diagnosis of infective endocarditis has been notoriously difficult. Over
A Nightmare. R Dulgheru, CHU Liege
 A Nightmare R Dulgheru, CHU Liege Faculty disclosure Raluca Dulgheru I have no financial relationships to disclose. MB, 57 years old male 18/03/2016 to the ER for altered mental status, First weight name
A Nightmare R Dulgheru, CHU Liege Faculty disclosure Raluca Dulgheru I have no financial relationships to disclose. MB, 57 years old male 18/03/2016 to the ER for altered mental status, First weight name
Endocarditis, including Prophylaxis
 Endocarditis, including Prophylaxis ACOI Board Review 2018 gerald.blackburn@beaumont.org (No Disclosures) Infective Endocarditis Persistant bacteremia (blood cultures drawn >12 hrs apart) w/ organisms
Endocarditis, including Prophylaxis ACOI Board Review 2018 gerald.blackburn@beaumont.org (No Disclosures) Infective Endocarditis Persistant bacteremia (blood cultures drawn >12 hrs apart) w/ organisms
Contents. 1. Introduction. J Antimicrob Chemother 2012; 67: doi: /jac/dkr450 Advance Access publication 14 November 2011
 J Antimicrob Chemother 2012; 67: 269 289 doi:10.1093/jac/dkr450 Advance Access publication 14 November 2011 Guidelines for the diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of endocarditis in adults: a report of
J Antimicrob Chemother 2012; 67: 269 289 doi:10.1093/jac/dkr450 Advance Access publication 14 November 2011 Guidelines for the diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of endocarditis in adults: a report of
Infective Endocarditis
 Definition Infective Endocarditis Pattaya Riengchan M.D. MAR 16, 2017 Infection of endocardial surface of the heart and implies the physical presence microorganisms in the lesion Heart valves are most
Definition Infective Endocarditis Pattaya Riengchan M.D. MAR 16, 2017 Infection of endocardial surface of the heart and implies the physical presence microorganisms in the lesion Heart valves are most
Apport des recommandations européennes
 Apport des recommandations européennes Gilbert Habib Cardiology Department- La Timone Marseille - France Bordeaux le 28 Juin 2011 Infective Endocarditis: a changing disease new high-risk subgroups IVDA
Apport des recommandations européennes Gilbert Habib Cardiology Department- La Timone Marseille - France Bordeaux le 28 Juin 2011 Infective Endocarditis: a changing disease new high-risk subgroups IVDA
Infective Endocarditis:
 CME Workshop Infective Endocarditis: Prophylaxis, Diagnosis and Management Presented at a CME program, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba, December 2001. By Davinder S. Jassal, MD; and John M.
CME Workshop Infective Endocarditis: Prophylaxis, Diagnosis and Management Presented at a CME program, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba, December 2001. By Davinder S. Jassal, MD; and John M.
Prognostic factors in infective endocarditis
 Boston University OpenBU Theses & Dissertations http://open.bu.edu Boston University Theses & Dissertations 2016 Prognostic factors in infective endocarditis Grzybinski, Sarah https://hdl.handle.net/2144/19176
Boston University OpenBU Theses & Dissertations http://open.bu.edu Boston University Theses & Dissertations 2016 Prognostic factors in infective endocarditis Grzybinski, Sarah https://hdl.handle.net/2144/19176
Getting the Point of Injection Safety
 Getting the Point of Injection Safety Barbara Montana, MD, MPH, FACP Medical Director Communicable Disease Service Outbreak of Enterococcus faecalis endocarditis associated with an oral surgery practice
Getting the Point of Injection Safety Barbara Montana, MD, MPH, FACP Medical Director Communicable Disease Service Outbreak of Enterococcus faecalis endocarditis associated with an oral surgery practice
Guidelines for The Management of Infective Endocarditis
 Guidelines for The Management of Infective Endocarditis By Dr. Sinan Butrus F.I.C.M.S Clinical Standards & Guidelines Kurdistan Board For Medical Specialties Infective endocarditis IE is an infection of
Guidelines for The Management of Infective Endocarditis By Dr. Sinan Butrus F.I.C.M.S Clinical Standards & Guidelines Kurdistan Board For Medical Specialties Infective endocarditis IE is an infection of
Overview. Clinical Scenario. Endocarditis: Treatment & Prevention. Prophylaxis The Concept. Jeremy D. Young, MD, MPH. Division of Infectious Diseases
 Endocarditis: Treatment & Prevention Jeremy D. Young, MD, MPH Division of Infectious Diseases Clinical Scenario Patient with MVP scheduled to have wisdom teeth extracted. Has systolic murmur with mid-systolic
Endocarditis: Treatment & Prevention Jeremy D. Young, MD, MPH Division of Infectious Diseases Clinical Scenario Patient with MVP scheduled to have wisdom teeth extracted. Has systolic murmur with mid-systolic
Hearts afire: Infective endocarditis
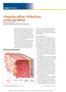 Hearts afire: Infective endocarditis By Kim McCarron, MS, CRNP Clinical Associate Professor Towson University Towson, Md. Editorial Advisory Board Member Nursing made Incredibly Easy! Picturing endocarditis
Hearts afire: Infective endocarditis By Kim McCarron, MS, CRNP Clinical Associate Professor Towson University Towson, Md. Editorial Advisory Board Member Nursing made Incredibly Easy! Picturing endocarditis
Sepsis and Infective Endocarditis
 Sepsis and Infective Endocarditis Michal Holub Department of Infectious Diseases First Faculty of Medicine Charles University in Prague and University Military Hospital Bacteremia and Sepsis bacteremia
Sepsis and Infective Endocarditis Michal Holub Department of Infectious Diseases First Faculty of Medicine Charles University in Prague and University Military Hospital Bacteremia and Sepsis bacteremia
Infected cardiac-implantable electronic devices: diagnosis, and treatment
 Infected cardiac-implantable electronic devices: diagnosis, and treatment The incidence of infection following implantation of cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) is increasing at a faster rate
Infected cardiac-implantable electronic devices: diagnosis, and treatment The incidence of infection following implantation of cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) is increasing at a faster rate
Right-Sided Bacterial Endocarditis
 New Concepts in the Treatment of the Uncontrollable Infection Agustin Arbulu, M.D., Ali Kafi, M.D., Norman W. Thorns, M.D., and Robert F. Wilson, M.D. ABSTRACT Our experience with 25 patients with right-sided
New Concepts in the Treatment of the Uncontrollable Infection Agustin Arbulu, M.D., Ali Kafi, M.D., Norman W. Thorns, M.D., and Robert F. Wilson, M.D. ABSTRACT Our experience with 25 patients with right-sided
AHA Scientific Statement
 AHA Scientific Statement Infective Endocarditis in Adults: Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications A Scientific Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart
AHA Scientific Statement Infective Endocarditis in Adults: Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications A Scientific Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart
Bacteriological outcome of combination versus single-agent treatment for staphylococcal endocarditis
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2003) 52, 820 825 DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkg440 Advance Access publication 30 September 2003 Bacteriological outcome of versus single-agent treatment for staphylococcal
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2003) 52, 820 825 DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkg440 Advance Access publication 30 September 2003 Bacteriological outcome of versus single-agent treatment for staphylococcal
You Won t Believe What I Saw on. Disclosures. Goals. Dimensions 2013 October 18 th Michael Pfeiffer, MD. No Financial Disclosures
 You Won t Believe What I Saw on that ECHO! Dimensions 2013 October 18 th Michael Pfeiffer, MD Disclosures No Financial Disclosures Goals Review unusual and unique echocardiographic images. Briefly present
You Won t Believe What I Saw on that ECHO! Dimensions 2013 October 18 th Michael Pfeiffer, MD Disclosures No Financial Disclosures Goals Review unusual and unique echocardiographic images. Briefly present
Management of infective endocarditis in children
 Management of infective endocarditis in children Ashutosh Marwah, MD* Savitri Shrivastava, MD DM FAMS FACC* INTRODUCTION Infective endocarditis (IE) continues to remain a serious disease despite advances
Management of infective endocarditis in children Ashutosh Marwah, MD* Savitri Shrivastava, MD DM FAMS FACC* INTRODUCTION Infective endocarditis (IE) continues to remain a serious disease despite advances
Endocarditis and Its Complications: The Role of Echocardiography
 Endocarditis and Its Complications: The Role of Echocardiography Pravin Patil, MD FACC FASE Associate Professor of Medicine Director, Cardiovascular Disease Training Program Lewis Katz School of Medicine
Endocarditis and Its Complications: The Role of Echocardiography Pravin Patil, MD FACC FASE Associate Professor of Medicine Director, Cardiovascular Disease Training Program Lewis Katz School of Medicine
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books. International authors and editors. Our authors are among the TOP 1%
 We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Kang D-H, Kim Y-J, Kim S-H, et al. Early surgery versus conventional
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Kang D-H, Kim Y-J, Kim S-H, et al. Early surgery versus conventional
Infective endocarditis
 Infective endocarditis Today's lecture is about infective endocarditis, the Dr started the lecture by asking what are the most common causative agents of infective endocarditis? 1-Group A streptococci
Infective endocarditis Today's lecture is about infective endocarditis, the Dr started the lecture by asking what are the most common causative agents of infective endocarditis? 1-Group A streptococci
Diagnosis and Treatment of Bacterial Endocarditis
 Infectious diseases Board Review Manual Statement of Editorial Purpose The Hospital Physician Infectious Diseases Board Review Manual is a study guide for fellows and practicing physicians preparing for
Infectious diseases Board Review Manual Statement of Editorial Purpose The Hospital Physician Infectious Diseases Board Review Manual is a study guide for fellows and practicing physicians preparing for
The changing epidemiology and clinical features of infective endocarditis: A retrospective study of 196 episodes in a teaching hospital in China
 Zhu et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders (2017) 17:113 DOI 10.1186/s12872-017-0548-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The changing epidemiology and clinical features of infective endocarditis: A retrospective
Zhu et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders (2017) 17:113 DOI 10.1186/s12872-017-0548-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The changing epidemiology and clinical features of infective endocarditis: A retrospective
Case Report Subacute Staphylococcusepidermidis Bacterial Endocarditis Complicated by Mitral-Aortic Intervalvular Fibrosa Pseudoaneurysm
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2012, Article ID 467210, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/467210 Case Report Subacute Staphylococcusepidermidis Bacterial Endocarditis Complicated by Mitral-Aortic Intervalvular
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2012, Article ID 467210, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/467210 Case Report Subacute Staphylococcusepidermidis Bacterial Endocarditis Complicated by Mitral-Aortic Intervalvular
Suggested Reading: Pages Donald P. Levine, M.D. Professor of Medicine Page 1 of 8
 Professor of Medicine Page 1 of 8 ENDOCARDITIS I. General A. infectivie endocarditis (IE) 1. definition: infection of the endocardial surface of the heart; implies the physical presence of microorganisms
Professor of Medicine Page 1 of 8 ENDOCARDITIS I. General A. infectivie endocarditis (IE) 1. definition: infection of the endocardial surface of the heart; implies the physical presence of microorganisms
Surgical Indications of Infective Endocarditis in Children
 2016 Annual Spring Scientific Conference of the KSC April 15-16, 2016 Surgical Indications of Infective Endocarditis in Children Cheul Lee, MD Pediatric and Congenital Cardiac Surgery Seoul St. Mary s
2016 Annual Spring Scientific Conference of the KSC April 15-16, 2016 Surgical Indications of Infective Endocarditis in Children Cheul Lee, MD Pediatric and Congenital Cardiac Surgery Seoul St. Mary s
CLINICAL SYNDROMES: COMMUNITY ACQUIRED INFECTIONS
 SECTION 2 CLINICAL SYNDROMES: COMMUNITY ACQUIRED INFECTIONS 118-1 118 Adolf W. Karchmer The prototypic lesion of infective endocarditis, the vegetation (Fig. 118-1), is a mass of platelets, fibrin, microcolonies
SECTION 2 CLINICAL SYNDROMES: COMMUNITY ACQUIRED INFECTIONS 118-1 118 Adolf W. Karchmer The prototypic lesion of infective endocarditis, the vegetation (Fig. 118-1), is a mass of platelets, fibrin, microcolonies
Case Report Daptomycin Failure for Treatment of Pulmonary Septic Emboli in Native Tricuspid and Mitral Valve
 Case Reports in Infectious Diseases Volume 2013, Article ID 653582, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/653582 Case Report Daptomycin Failure for Treatment of Pulmonary Septic Emboli in Native Tricuspid
Case Reports in Infectious Diseases Volume 2013, Article ID 653582, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/653582 Case Report Daptomycin Failure for Treatment of Pulmonary Septic Emboli in Native Tricuspid
Case Studies in Complex Endocarditis
 Case Studies in Complex Endocarditis Vera H. Rigolin, MD Professor of Medicine Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Medical Director, Echocardiography Laboratory Northwestern Memorial Hospital
Case Studies in Complex Endocarditis Vera H. Rigolin, MD Professor of Medicine Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Medical Director, Echocardiography Laboratory Northwestern Memorial Hospital
109 Infective Endocarditis
 Página 1 de 30 Copyright 2005 McGraw-Hill Kasper, Dennis L., Fauci, Anthony S., Longo, Dan L., Braunwald, Eugene, Hauser, Stephen L., Jameson, J. Larry, Harrison, T. R., Resnick, W. R., Wintrobe, M. M.,
Página 1 de 30 Copyright 2005 McGraw-Hill Kasper, Dennis L., Fauci, Anthony S., Longo, Dan L., Braunwald, Eugene, Hauser, Stephen L., Jameson, J. Larry, Harrison, T. R., Resnick, W. R., Wintrobe, M. M.,
Valve Endocarditis Indications and Timing of Surgery
 Valve Endocarditis Indications and Timing of Surgery Michele Di Mauro, MD, PhD Cardiac Surgeon and Cardiologist Heart Department,SS Annunziata H, Chieti, Italy What do the guidelines say? Heart Failure
Valve Endocarditis Indications and Timing of Surgery Michele Di Mauro, MD, PhD Cardiac Surgeon and Cardiologist Heart Department,SS Annunziata H, Chieti, Italy What do the guidelines say? Heart Failure
THE INCREASING IMPORTANCE OF HEALTH CARE-ASSOCIATED INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS
 THE INCREASING IMPORTANCE OF HEALTH CARE-ASSOCIATED INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Javier López Díaz Instituto de Ciencias del Corazón (ICICOR) Hospital Clínico de Valladolid, Spain No conflict of interest Page
THE INCREASING IMPORTANCE OF HEALTH CARE-ASSOCIATED INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Javier López Díaz Instituto de Ciencias del Corazón (ICICOR) Hospital Clínico de Valladolid, Spain No conflict of interest Page
POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00553
 MCC-004 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00553 Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-004 : COMMON CARDIO-VASCULAR DISEASES - II Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note : There will
MCC-004 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00553 Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-004 : COMMON CARDIO-VASCULAR DISEASES - II Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note : There will
New guidelines for the antibiotic treatment of streptococcal, enterococcal and staphylococcal endocarditis. D. C. Shanson
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1998) 42, 292 296 New guidelines for the antibiotic treatment of streptococcal, enterococcal and staphylococcal endocarditis JAC D. C. Shanson Microbiology Department,
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1998) 42, 292 296 New guidelines for the antibiotic treatment of streptococcal, enterococcal and staphylococcal endocarditis JAC D. C. Shanson Microbiology Department,
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Dayer MJ, Jones S, Prendergast B, et al. Incidence
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Dayer MJ, Jones S, Prendergast B, et al. Incidence
DICE Session. The endocarditis team. Bernard Iung Bichat Hospital, Paris Diderot University Paris, France
 DICE Session. The endocarditis team Bernard Iung Bichat Hospital, Paris Diderot University Paris, France Faculty disclosure First name - last name I disclose the following financial relationships: Consultant
DICE Session. The endocarditis team Bernard Iung Bichat Hospital, Paris Diderot University Paris, France Faculty disclosure First name - last name I disclose the following financial relationships: Consultant
PROSTHETIC VALVE ENDOCARDITIS Dr Bernard Prendergast DM FRCP EUROVALVE CONGRESS MADRID NOVEMBER 2013
 PROSTHETIC VALVE ENDOCARDITIS Dr Bernard Prendergast DM FRCP EUROVALVE CONGRESS MADRID NOVEMBER 2013 Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis A Dangerous Disease Affects 1-6% of prosthetic valves Mechanical and biological
PROSTHETIC VALVE ENDOCARDITIS Dr Bernard Prendergast DM FRCP EUROVALVE CONGRESS MADRID NOVEMBER 2013 Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis A Dangerous Disease Affects 1-6% of prosthetic valves Mechanical and biological
Outcome of Infective Endocarditis: Improved Results Over 18 Years ( )
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Outcome of Infective Endocarditis: Improved Results Over 18 Years (1990 2007) Pachirat O 1, Limwattananon S 2, Tantisirin C 3 and Tatsanavivat P 1 1 Cardiovascular Unit, Srinagarind Hospital,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Outcome of Infective Endocarditis: Improved Results Over 18 Years (1990 2007) Pachirat O 1, Limwattananon S 2, Tantisirin C 3 and Tatsanavivat P 1 1 Cardiovascular Unit, Srinagarind Hospital,
Infective Endocarditis in Elderly Patients
 AGING AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES Thomas T. Yoshikawa, Section Editor INVITED ARTICLE Infective Endocarditis in Elderly Patients Vinod K. Dhawan Charles R. Drew University of Medicine and Science, Martin Luther
AGING AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES Thomas T. Yoshikawa, Section Editor INVITED ARTICLE Infective Endocarditis in Elderly Patients Vinod K. Dhawan Charles R. Drew University of Medicine and Science, Martin Luther
10/16/2014. CCRN Review - Cardiovascular. CCRN Review - Cardiovascular. CCRN Review - Cardiovascular
 Hypertrophic (IHSS) Diagnosis Chest x ray cardiomegaly Electrocardiography LV hypertrophy, ST segment T was changes, Q waves in inferior & precordial leads Atrial & ventricular dysrhythmias Hypertrophic
Hypertrophic (IHSS) Diagnosis Chest x ray cardiomegaly Electrocardiography LV hypertrophy, ST segment T was changes, Q waves in inferior & precordial leads Atrial & ventricular dysrhythmias Hypertrophic
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Native and prosthetic valve infective endocarditis: clinicopathologic correlation and review of the literature
 Malaysian J Pathol 2014; 36(2) : 71 81 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Native and prosthetic valve infective endocarditis: clinicopathologic correlation and review of the literature Adriana LUK, Minhui L KIM,* Heather
Malaysian J Pathol 2014; 36(2) : 71 81 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Native and prosthetic valve infective endocarditis: clinicopathologic correlation and review of the literature Adriana LUK, Minhui L KIM,* Heather
E chocardiography is a valuable tool in the diagnostic
 1020 CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE Repeated echocardiographic examinations of patients with suspected infective endocarditis M L C Vieira, M Grinberg, P M A Pomerantzeff, J L Andrade, A J Mansur... See end of
1020 CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE Repeated echocardiographic examinations of patients with suspected infective endocarditis M L C Vieira, M Grinberg, P M A Pomerantzeff, J L Andrade, A J Mansur... See end of
VEGETATION NEGATIVE INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS A VIEW POINT... Mumbai Dec 2005 Annual scientific sessions
 VEGETATION NEGATIVE INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS A VIEW POINT... Mumbai Dec 2005 Annual scientific sessions S.Venkatesan,G.Gnanavelu,G.Karthikeyan,V.Jaganathan,R.Alagesan M.Annamalai,S.Shanmugasundaram, S.Geetha,A.Balaguru.G.Anuradha
VEGETATION NEGATIVE INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS A VIEW POINT... Mumbai Dec 2005 Annual scientific sessions S.Venkatesan,G.Gnanavelu,G.Karthikeyan,V.Jaganathan,R.Alagesan M.Annamalai,S.Shanmugasundaram, S.Geetha,A.Balaguru.G.Anuradha
Consensus Statement on Infective Endocarditis / Abridged Version
 CONSENSUS Consensus Statement on Infective Endocarditis / Abridged Version Argentine Society of Cardiology General Directors Secretary (Area of Regulations and Consensuses) Dr. Gustavo Giunta MTSAC 1.
CONSENSUS Consensus Statement on Infective Endocarditis / Abridged Version Argentine Society of Cardiology General Directors Secretary (Area of Regulations and Consensuses) Dr. Gustavo Giunta MTSAC 1.
ARTICLE. The Role of Transthoracic Echocardiography in the Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis in Children
 ARTICLE The Role of Transthoracic Echocardiography in the Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis in Children Ashraf M. Aly, MD, PhD; Pippa M. Simpson, PhD; Richard A. Humes, MD Background: Infective endocarditis
ARTICLE The Role of Transthoracic Echocardiography in the Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis in Children Ashraf M. Aly, MD, PhD; Pippa M. Simpson, PhD; Richard A. Humes, MD Background: Infective endocarditis
Valve Disease Board Review Questions
 Valve Disease Board Review Questions Dennis A. Tighe, MD, FASE University of Massachusetts Medical School Worcester, MA Case 1 History A 61 year-old man Presents to hospital with worsening shortness of
Valve Disease Board Review Questions Dennis A. Tighe, MD, FASE University of Massachusetts Medical School Worcester, MA Case 1 History A 61 year-old man Presents to hospital with worsening shortness of
Cardiology III 1/22/2019. Disclosures - none. But first. Objectives. Ischemia EKG s. And second
 Disclosures - none Cardiology III Matthew K Hysell, MD Spectrum Health Lakeland St Joseph, MI 1 2 Objectives Review specific high-yield EKG patterns Ischemia Ischemia mimics Electrolytes Review Cardiac/CV
Disclosures - none Cardiology III Matthew K Hysell, MD Spectrum Health Lakeland St Joseph, MI 1 2 Objectives Review specific high-yield EKG patterns Ischemia Ischemia mimics Electrolytes Review Cardiac/CV
AHA Scientific Statement
 AHA Scientific Statement Infective Endocarditis Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications A Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis,
AHA Scientific Statement Infective Endocarditis Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications A Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis,
