ABDUL RAZZAK AL YUSUF. Cross-sectional echocardiography has been demonstrated. to have predictive accuracy superior even to
|
|
|
- Tracey Kelly
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Postgraduate Medical Journal (August 1983) 59, Left ventricular thrombi after acute myocardial infarction SUDHIR K. BHATNAGAR M.R.C.P. Summary Two-dimensional echocardiography was utilized in a prospective study to find the incidence, characteristics and natural history of left ventricular thrombus in 50 consecutive patients with acute myocardial infarction. The overall incidence of thrombosis was 14%; 191% in anterior and 5% in inferior infarction. The thrombus was detected at the apex in 4, along the ventricular septum in 2 and at both these sites in one patient. It was observed 3-10 days after the infarction. Thrombus at the ventricular septum, seen in this study, has not been reported previously in acute myocardial infarction. Development of apical and septal thrombi was significantly associated with akinesis of these sites. Only 2 patients with protruding thrombi had systemic embolism. We conclude that the apex as well as the septum are common sites for thrombosis in patients with severe wall motion abnormalities following acute anterior infarction. Careful observation of these sites during echocardiography may reveal thrombi prone for embolization. KEY WORDS: two-dimensional echocardiography, acute myocardial infarction, ventricular thrombi, arterial embolism. Introduction Left ventricular thrombus is a common complication in congestive cardiomyopathy, ventricular aneurysm and acute myocardial infarction and its features in these conditions have been well described (Ports et al., 1978; Reeder, Tajik and Seward, 1981). Recently, it has been shown that it can be detected noninvasively by platelet imaging (Stratton et al., 198 la), radionucide angiography (Stratton et al., 198 lb) and two-dimensional echocardiography (Ports et al., 1978; Meltzer et al., 1979; De Maria et al., 1979). Address for reprints: Dr Sudhir K. Bhatnagar, P.O. Box 44294, Hawalli, Kuwait, Arabian Gulf. Faculty of Medicine, Kuwait University, Kuwait ABDUL RAZZAK AL YUSUF F.R.C.P. Cross-sectional echocardiography has been demonstrated to have predictive accuracy superior even to contrast left ventriculography and is therefore the preferred technique for the recognition of intraventricular thrombi (Reeder et al., 1981). Information concerning left ventricular thrombus in acute myocardial infarction as compared to other disease states is limited (Asinger et al., 1981a). Therefore, a prospective study of a consecutive group of patients admitted with acute transmural infarction was carried out utilizing two-dimensional echocardiography in order to determine the incidence, characteristics and associations of left ventricular thrombus. Patients and methods Fifty-five consecutive patients admitted to the coronary care unit of Al-Sabah Hospital with acute transmural myocardial infarction for the first time were studied during a 7-month period. There were 52 males and 3 females, aged between years. Myocardial infarction was diagnosed on the basis of typical prolonged cardiac pain, evolution of electrocardiographic changes and serial elevation in cardiac enzymes; total creatine kinase (CK), serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). Patients were not routinely anticoagulated and did not receive any anti-arrhythmic therapy unless necessary. A routine 12-lead electrocardiogram was performed on admission and twice daily for the first 72 hr. The initial echocardiographic study was performed within 36 hr of admission and serially on day 3 and day 10 (day 0 defined as the day of admission) in all patients. Assessment of cardiac failure was made according to the Killip classification (Killip and Kimbell, 1967) on day 0, 3 and 10. Two-dimensional echocardiographic study was performed using a commercially available phased array system (Irex III). A 2 25 mhz, 32 element focussed transducer with a sector scan of 80' was used. Real time images were recorded on half-inch video tane usina a Sony /83/ $ The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine
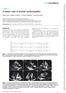
2 496 S. K Bhatnagar and A.R Al Yusuf TABLE 1. Clinical characteristics of patients with acute myocardial infarction Group A (No thrombus) Group B (Thrombus present) Characteristic Anterior infarction Inferior infarction Anterior infarction Inferior infarction Number of patients Age (years) 49±10 52±10 49±16 65 (range) (28-70) (29-67) (29-70) Killip class 1-4±07 11+±03 1-7±05 1 Peak CK(IU/1) 1409± ± ± Peak SGOT(IU/1) 244± ±80 410± Peak LDH(IU/1) 826± ± ± Values are mean ± s.d. The enzyme values are the highest obtained and the Killip class the worst score. Betamax cassette recorder. These images were then available for redisplay and evaluation in real-time, slow motion or single frame format. A systematic examination was made utilizing parasternal long axis view, short axis views at the mitral valve and papillary muscle levels and apical 2 and 4 chamber views (Tajik et al., 1978). Apical views were obtained utilizing shallow depth of field settings of 7T5 or 10 cm, in order to avoid near field artifacts and were most useful in studying the left ventricular apex for wall motion abnormalities and thrombi (Asinger et al., 1981b). Ventricular thrombosis was diagnosed when an echo dense mass in the left ventricle, that had distinct margins clearly delineated from the underlying myocardium and endocardial echo was seen, associated with a wall motion abnormality (Meltzer et al., 1979; Asinger et al., 198 lb). Agreement of 2 independent observers was required for the diagnosis of thrombosis. When the thrombus was noticed, echocardiographic examination was repeated at 3-day intervals during hospitalization and at fortnightly intervals after discharge of the patient. Apical and septal wall motion was analyzed visually utilizing all the echocardiographic views and classified as normal, hypokinetic and akinetic (Asinger et al., 198 la). All patients had at least 3 echocardiograms. Five patients were excluded from the study because of unsatisfactory echocardiograms. The remaining 50 patients were divided into 2 groups, depending on the absence (Group A) or presence (Group B) of ventricular thrombus (Table 1). Statistical methods Values for clinical and enzymatic observations were expressed as mean +-standard deviation. Comparisons in the clinical groups were made by the median values using chi-square test or Mann-Whitney test. The incidence of left ventricular thrombosis in the clinical groups was tested by the 'test of significance between two proportions'. Differences were considered significant if P was <0 05. Results The overall incidence of left ventricular thrombosis was found to be 14% (7 of 50); 19% (6 of 31) in patients with anterior and 5% (1 of 19) in patients with inferior infarction (difference not statistically significant). Clinical characteristics of the patients studied are shown in Table 1. The average worst Killip class did not differ significantly between patients with anterior infarction with or without thrombi. Among the enzymes, only the peak SGOT values were significantly higher in group B patients compared with patients in group A (P<O 05). As there was only one patient with inferior infarction in group B, no comparison was made between this and inferior infarct patients in group A. The features of 7 patients with a definite thrombus (Group B) are shown in Table 2. The thrombus was detected at the left ventricular apex alone in 4 patients (example Fig. 1 and 3), along the ventricular septum in 2 patients (example, Fig. 4) and in one patient a mobile, protruding thrombus, in addition to an apical thrombus, was noticed at the septum near the left ventricular outflow tract (Fig. 2). Contrast left ventriculography confirmed the presence of apical thrombus in one patient (case 1) 150 days later. The thrombus was detected in 6 patients by the third day and, in only one case, it was detected on the tenth day. Two patients died, the thrombus resolved in 3 between days and was still present in the other 2 at day 60 and 150 respectively.
3 Left ventricular thrombi after myocardial infarction 497 TABLE 2. Clinical and echocardiographic features of patients with left ventricular thrombus (Group B) LVT Case Site of infarct LVT site length (cm) Type of LVT Wall motion at LVT site Day appeared Resolution/time taken (days) Anticoagulation* I Anterior (1) Septum 1-5 Pt A 10 Yes/20 (2) Apex 3 M A 10 Yes/180 + t2 Anterior Apex 1 5 Pt A 3 No/- + 3 Anterior Septum 3 M A 3 No/150 t4 Anterior Apex 1 M A 3 No/- + 5 Inferolateral Septum 2 M H 3 Yes/60 6 Anterior Apex 15 M A 3 No/ Anterior Apex 15 M A 3 Yes/25 + ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~-p - -' - Abbreviations: LVT = left ventricular thrombus; M = mural; P = protruding; A = akinesis; H = hypokinesis. *commenced after thrombus detection; tdied; ::Systemic embolism. FIG. 1. Apical two-chamber view (Case 6). Arrows denote thrombus (T) at the apex. LV = Left ventricle; LA = Left Atrium. FIG. 3. Apical view (Case 2). Protruding thrombus (arrows) at the apex. Other abbreviations as in previous figures. T VID.~ ~ ~~~. _ S - ~~ Postgrad Med J: first published as /pgmj on 1 August Downloaded from FiG;. 2. Parasternal long axis view (Case 1). Protruding thrombus (arrow) along the ventricular septum (S) near the LV outflow tract (LVOT) A = Anterior; P = Posterior; other abbreviations as in Fig. 1. Clinical systemic embolism occurred in 2 patients within 10 days of the infarct and only these 2 patients had protruding thrombi. Fici. 4. Parasternal long axis view (Case 3). Mural thrombus (arrows) at the septum (S); Ao = aorta; I = inferior; S = superior; other abbreviations as in previous figures. Echocardiographic wall motion analysis Analysis of apical wall motion at the time of initial study in the 2 groups is shown in Table 3. This remained unchanged in the subsequent studies. The incidence of thrombosis at the apex in patients with on 19 September 2018 by guest. Protected
4 498 S. K. Bhatnagar and A. R. Al Yusuf TABLE 3. Comparison of apical and septal wall motion in patients with and without left-ventricular thrombi Number of patients Group A (No thrombus) Group B (Thrombus +) Anterior infarction Inferior infarction Anterior infarction Inferior infarction Type of wall. motion (Apex) (Septum) (Apex) (Septum) (Apex) (Septum) (Apex) (Septum) Normal Hypokinesis * Akinesis t 2* 0 0 *Septal thrombi, t5 of these had apical thrombus. apical akinesis (both groups combined) was 22% (5 of 23) and the presence of thrombus at this site was significantly associated with apical akinesis by chisquare test (P<0 05). The incidence of thrombosis at the septum in patients with akinesis of this region (both groups combined) was 25% (2 of 8) and its occurrence at this site was also significantly associated with akinetic septum by chi-square test (P<0-01). Discussion The overall incidence of left ventricular thrombosis detected by two-dimensional echocardiography, following acute transmural myocardial infarction in this study was 14%, similar to the incidence in a recent report (Asinger et al., 1981a), although in autopsy studies this has been reported to vary from 38% (Jordan et al., 1952) to 67% (Garvin, 1941). The incidence of thrombosis at the left ventricular apex was 22% in patients with apical akinesis. Our data indicates that akinesis of the ventricular apex predisposes to thrombus formation at this site, a finding that is in agreement with the observation of Asinger et al, (1981a). We also observed a higher incidence of ventricular thrombosis in anterior than in inferior infarction, although this difference did not reach statistical significance. An unusual observation in the present study was the presence of thrombus along the ventricular septum in 3 of the 7 patients. This finding has not been previously described in association with acute myocardial infarction. In previous reports however, septal thrombi have been noticed with cardiomyopathy and left ventricular aneurysm (Reeder et al., 1981). Protruding thrombi with free intracavitary motion of their margins were noted to have a high risk of embolization, as both patients with this type of thrombus were the only patients who had clinical sysemic embolism. This observation confirms other reports (De Maria et al., 1979; Haugland et al., 1981). Whether anticoagulation will prevent embolism in such patients will have to be determined by prospective studies, but presently it appears prudent to anticoagulate such patients. The size of the thrombi in our patients was small, unlike the large mural thrombi that are more common in congestive cardiomyopathy (Reeder et al., 1981). Previous autopsy studies in patients dying of acute infarction have reported a higher incidence of ventricular thrombosis in extensive anterior infarction and in the presence of cardiac failure (Jordan et al., 1952; Garvin, 1941). In the present study, the majority of thrombi were also found in patients with anterior infarction. However, there was no difference in the severity of cardiac failure assessed by the Killip classification, in patients with anterior infarction with or without thrombi. It is interesting to note that thrombi were seen only at the apex and the septum in this series and along the inferior wall in only one other report (Asinger et al., 1981b). Focal stasis of intracavitary blood together with endocardial injury seem to be necessary for the development of thrombus (Jordan et al., 1952) and it is probably due to these factors that thrombus tends to develop at the apex. Although the predisposing factors for the development of septal thrombi in our patients are not clear, it appears from our data that akinesis of this site plays a major role. Our results indicate that although the left ventricular apex is the most common site for thrombosis following acute myocardial infarction, the ventricular septum may also be involved. Whether early short-term anticoagulation following acute infarction in patients with severe wall motion abnormalities can prevent ventricular thrombosis has to be determined by prospective trials. References ASINGER, R.W., MIKELL, F.L., ELSPERGER, J. & HODGES, M. (1981a) Incidence of left-ventricular thrombosis after acute transmural myocardial infarction: serial evaluation by twodimensional echocardiography. New England Journal ofmedicine, 305, 297. ASINGER, R.W., MIKELL, F.L., SHARMA, B. & HoDGES, M. (1981b) Observations on detecting left ventricular thrombus with two
5 dimensional echocardiography: emphasis on avoidance of false positive diagnosis. American Journal of Cardiology, 47, 145. GARVIN, C.F. (1941) Mural thrombi in the heart. American Heart Journal, 21, 713. HAUGLAND, J.M., ASINGER, R.W., MIKELL, F.L., ELSPERGER, K.J. & HODGES, M. (1981) Embolic potential of left ventricular thrombus (LVT) detected by two-dimensional echocardiography (2DE). (abstract) American Journal of Cardiology, 47, 471. JORDAN, R.A., MILLER, R.D., EDWARDS, J.E. & PARKER, R.L. (1952) Thrombo-embolism in acute and in healed myocardial infarction. Circulation, 6, 1. KILLIP, T. III & KIMBELL, J.T. (1967) Treatment of myocardial infarction in a coronary care unit: a two year experience with 250 patients. American Journal of Cardiology, 20, 457. MARIA, A.N. DE, BOMMER, W., NEUMANN, A., GREHL, T., WEIN- ART, L., NARDO, S. DE, AMSTERDAM, E.A. & MASON, D.T. (1979) Left ventricular thrombi identified by cross-sectional echocardiography. Annals of Internal Medicine, 90, 14. MELTZER, R.S., GUTHANER, D., RAKOWSKI, H., Popp, R.L. & MARTIN, R.P. (1979) Diagnosis ofleft ventricular thrombi by twodimensional echocardiography. British Heart Journal, 42, 261. Left ventricular thrombi after myocardial infarction 499 PORTS, T.A., COGAN, J., SCHILLER, N.B. & RAPAPORT, E. (1978) Echocardiography of left ventricular masses. Circulation, 58, 528. REEDER, G.S., TAJIK, A.J. & SEWARD, J.B. (1981) Left ventricular mural thrombus-two dimensional echocardiographic diagnosis. Proceeding, Mayo Clinic, 56, 82. STRATTON, J.R., RITCHIE, J.L., HAMILTON, G.W., HAMMER- MEISTER, K.E. & HARKER, L.A. (1981a) Left ventricular thrombi: in vivo detection by Indium-III platelet imaging and two dimensional echocardiography. American Journal of Cardiology, 47, 874. STRATTON, J.R., RITCHIE, J.L., HAMMERMEISTER, K.E., KENNEDY, J.W. & HAMILTON, G.W. (1981b) Detection of left ventricular thrombi with radionuclide angiography. American Journal of Cardiology, 48, 565. TAJIK, A.J., SEWARD, J.B., HAGLER, D.J., MAIR, D.D. & LIE, J.T. (1978) Two-dimensional real-time ultrasonic imaging of the heart and great vessels: technique, image orientation, structure identification and validation. Proceedings, Mayo Clinic, 53, 271. (Accepted 17 February 1983) Postgrad Med J: first published as /pgmj on 1 August Downloaded from on 19 September 2018 by guest. Protected
Echocardiographic visualization of the anatomic causes of mitral regurgitation
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (May 1982) 58, 257-263 PAPERS Echocardiographic visualization of the anatomic causes of mitral regurgitation resulting from myocardial infarction ROBERT M. DONALDSON M.R.C.P.
Postgraduate Medical Journal (May 1982) 58, 257-263 PAPERS Echocardiographic visualization of the anatomic causes of mitral regurgitation resulting from myocardial infarction ROBERT M. DONALDSON M.R.C.P.
Embolic potential of left ventricular thrombi detected by two-dimensional echocardiography
 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND NATURAL HISTORY THROMBOEMBOLIC DISEASE Embolic potential of left ventricular thrombi detected by two-dimensional echocardiography J. MARK HAUGLAND, M.D., RICHARD W. ASINGER, M.D., FRANK
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND NATURAL HISTORY THROMBOEMBOLIC DISEASE Embolic potential of left ventricular thrombi detected by two-dimensional echocardiography J. MARK HAUGLAND, M.D., RICHARD W. ASINGER, M.D., FRANK
Left Ventricular Thrombosis, Wall Motion Abnormalities, and Blood Viscosity Changes after First Transmural Anterior Myocardi81lnfarction*
 Left Ventricular Thrombosis, Wall Motion Abnormalities, and Blood Viscosity Changes after First Transmural Anterior Myocardi81lnfarction* Sudhir K. Bhatnagar, M.R.C.P.; Aranka Hudak, M.D.; and Abdul Razzak
Left Ventricular Thrombosis, Wall Motion Abnormalities, and Blood Viscosity Changes after First Transmural Anterior Myocardi81lnfarction* Sudhir K. Bhatnagar, M.R.C.P.; Aranka Hudak, M.D.; and Abdul Razzak
The Natural History of Left Ventricular Thrombus in Myocardial Infarction: A Rationale in Support of Masterly Inactivity
 JACC Vol. 14, No. 4 October 1989:903-l I The Natural History of Left Ventricular Thrombus in Myocardial Infarction: A Rationale in Support of Masterly Inactivity PETROS NIHOYANNOPOULOS, MD, GILLIAN C.
JACC Vol. 14, No. 4 October 1989:903-l I The Natural History of Left Ventricular Thrombus in Myocardial Infarction: A Rationale in Support of Masterly Inactivity PETROS NIHOYANNOPOULOS, MD, GILLIAN C.
LEFT VENTRICULAR THROMBUS IN ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
 LEFT VENTRICULAR THROMBUS IN ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION RATHI N 2, MAHESHWARI N 1, KUMARI D, SACHDEWANI RK, MEMON NA 2, MEMON F 3 ABSTRACT Objective: To determine Left ventricular thrombus (LVT) in acute
LEFT VENTRICULAR THROMBUS IN ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION RATHI N 2, MAHESHWARI N 1, KUMARI D, SACHDEWANI RK, MEMON NA 2, MEMON F 3 ABSTRACT Objective: To determine Left ventricular thrombus (LVT) in acute
Role of Early 2D Echocardiography in Patient with Acute Myocardial Infarction in Correlation with Electrocardiography and Clinical Presentation
 MVP Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol 1(2), 51 55, July 2014 Role of Early 2D Echocardiography in Patient with Acute Myocardial Infarction in Correlation with Electrocardiography and Clinical Presentation
MVP Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol 1(2), 51 55, July 2014 Role of Early 2D Echocardiography in Patient with Acute Myocardial Infarction in Correlation with Electrocardiography and Clinical Presentation
Myocardial Infarction
 Myocardial Infarction MI = heart attack Defined as necrosis of heart muscle resulting from ischemia. A very significant cause of death worldwide. of these deaths, 33% -50% die before they can reach the
Myocardial Infarction MI = heart attack Defined as necrosis of heart muscle resulting from ischemia. A very significant cause of death worldwide. of these deaths, 33% -50% die before they can reach the
Left Ventricular Thrombi Identified by Cross-Sectional Echocardiography
 Left Ventricular Thrombi Identified by Cross-Sectional Echocardiography ANTHONY N. DeMARIA, M.D.; WILLIAM BOMMER, M.D.; ALEXANDER NEUMANN, B.S.; TODD GREHL, M.D.; LYNN WEINART, B.S.; SALLY DeNARDO, M.D.;
Left Ventricular Thrombi Identified by Cross-Sectional Echocardiography ANTHONY N. DeMARIA, M.D.; WILLIAM BOMMER, M.D.; ALEXANDER NEUMANN, B.S.; TODD GREHL, M.D.; LYNN WEINART, B.S.; SALLY DeNARDO, M.D.;
Images in Cardiovascular Medicine
 Images in Cardiovascular Medicine Numerous Small Vegetations Revealing Libman-Sacks Endocarditis in Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome Hideo Yamamoto, MD; Tamaki Iwade, MD; Ryuji Nakano, MD; Masahiro
Images in Cardiovascular Medicine Numerous Small Vegetations Revealing Libman-Sacks Endocarditis in Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome Hideo Yamamoto, MD; Tamaki Iwade, MD; Ryuji Nakano, MD; Masahiro
Myocardial performance index, Tissue Doppler echocardiography
 Value of Measuring Myocardial Performance Index by Tissue Doppler Echocardiography in Normal and Diseased Heart Tarkan TEKTEN, 1 MD, Alper O. ONBASILI, 1 MD, Ceyhun CEYHAN, 1 MD, Selim ÜNAL, 1 MD, and
Value of Measuring Myocardial Performance Index by Tissue Doppler Echocardiography in Normal and Diseased Heart Tarkan TEKTEN, 1 MD, Alper O. ONBASILI, 1 MD, Ceyhun CEYHAN, 1 MD, Selim ÜNAL, 1 MD, and
detection of potentially embolic intracardiac masses
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1981 ;44:803-809 The role of two-dimensional echocardiography in the detection of potentially embolic intracardiac masses in patients with cerebral ischaemia
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1981 ;44:803-809 The role of two-dimensional echocardiography in the detection of potentially embolic intracardiac masses in patients with cerebral ischaemia
NAKAO, RDCS 2. J Cardiol 2002 Dec; 40 6 :
 J Cardiol 2002 Dec; 40 6 : 259 265 T Usefulness of Left Ventricular Opacification With Intravenous Contrast Echocardiography in Patients With Asymptomatic Negative T Waves on Electrocardiography 1 2 2
J Cardiol 2002 Dec; 40 6 : 259 265 T Usefulness of Left Ventricular Opacification With Intravenous Contrast Echocardiography in Patients With Asymptomatic Negative T Waves on Electrocardiography 1 2 2
Radiologic Assessment of Myocardial Viability
 November 2001 Radiologic Assessment of Myocardial Viability Joshua Moss, Harvard Medical School Year III Patient EF 66yo female with a 3-year history of intermittent chest pain previously relieved by sublingual
November 2001 Radiologic Assessment of Myocardial Viability Joshua Moss, Harvard Medical School Year III Patient EF 66yo female with a 3-year history of intermittent chest pain previously relieved by sublingual
HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY (HCM) PRESENTED AS UNSTABLE ANGINA COMPLICATED BY SERIOUS VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS CASE REPORT AND REVIEW LITERATURE
 HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY (HCM) PRESENTED AS UNSTABLE ANGINA COMPLICATED BY SERIOUS VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS CASE REPORT AND REVIEW LITERATURE Lusyun Kumar Yadav * and Jin li Jun Department of Cardiology,
HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY (HCM) PRESENTED AS UNSTABLE ANGINA COMPLICATED BY SERIOUS VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS CASE REPORT AND REVIEW LITERATURE Lusyun Kumar Yadav * and Jin li Jun Department of Cardiology,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Left ventricle pseudoaneurysm as late postoperative complication of a large apical aneurysm
 CASE REPORT Left ventricle pseudoaneurysm as late postoperative complication of a large apical aneurysm Mariana M. Floria 1, 4, Carmen Elena Pleșoianu 2, 4, Michel Buche 3, Baudouin Marchandise 4, Erwin
CASE REPORT Left ventricle pseudoaneurysm as late postoperative complication of a large apical aneurysm Mariana M. Floria 1, 4, Carmen Elena Pleșoianu 2, 4, Michel Buche 3, Baudouin Marchandise 4, Erwin
Pulmonary arteriovenous fistula
 International Journal of Medical Imaging 2014; 2(2): 34-38 Published online April 10, 2014 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi) doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20140202.16 Pulmonary arteriovenous fistula
International Journal of Medical Imaging 2014; 2(2): 34-38 Published online April 10, 2014 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi) doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20140202.16 Pulmonary arteriovenous fistula
Cardiac ultrasound protocols
 Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
The Normal Echocardiogram
 The Normal Echocardiogram Pravin V. Patil, MD FACC Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Acknowledgments Dr. Susan Wiegers Dr. Martin Keane Temple Cardiac Sonographers Disclosures No relevant
The Normal Echocardiogram Pravin V. Patil, MD FACC Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Acknowledgments Dr. Susan Wiegers Dr. Martin Keane Temple Cardiac Sonographers Disclosures No relevant
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW
 PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION
 LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION Jamilah S AlRahimi Assistant Professor, KSU-HS Consultant Noninvasive Cardiology KFCC, MNGHA-WR Introduction LV function assessment in Heart Failure:
LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION Jamilah S AlRahimi Assistant Professor, KSU-HS Consultant Noninvasive Cardiology KFCC, MNGHA-WR Introduction LV function assessment in Heart Failure:
Top 10 Facts in Contrast Echocardiography. Pamela R. Burgess, BS, RDCS, RDMS, RVT, FASE
 Top 10 Facts in Contrast Echocardiography Pamela R. Burgess, BS, RDCS, RDMS, RVT, FASE Presenter Disclosure The following relationship exist related to this presentation: Pamela R. Burgess, BS, RDCS, RDMS,
Top 10 Facts in Contrast Echocardiography Pamela R. Burgess, BS, RDCS, RDMS, RVT, FASE Presenter Disclosure The following relationship exist related to this presentation: Pamela R. Burgess, BS, RDCS, RDMS,
Acute Myocardial Infarction
 Acute Myocardial Infarction Hafeza Shaikh, DO, FACC, RPVI Lourdes Cardiology Services Asst.Program Director, Cardiology Fellowship Associate Professor, ROWAN-SOM Acute Myocardial Infarction Definition:
Acute Myocardial Infarction Hafeza Shaikh, DO, FACC, RPVI Lourdes Cardiology Services Asst.Program Director, Cardiology Fellowship Associate Professor, ROWAN-SOM Acute Myocardial Infarction Definition:
Segmental Tissue Doppler Image-Derived Tei Index in Patients With Regional Wall Motion Abnormalities
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2010.40.3.114 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2010 The Korean Society of Cardiology Open Access Segmental Tissue Doppler Image-Derived Tei Index
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2010.40.3.114 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2010 The Korean Society of Cardiology Open Access Segmental Tissue Doppler Image-Derived Tei Index
Managing Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy with Imaging. Gisela C. Mueller University of Michigan Department of Radiology
 Managing Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy with Imaging Gisela C. Mueller University of Michigan Department of Radiology Disclosures Gadolinium contrast material for cardiac MRI Acronyms Afib CAD Atrial fibrillation
Managing Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy with Imaging Gisela C. Mueller University of Michigan Department of Radiology Disclosures Gadolinium contrast material for cardiac MRI Acronyms Afib CAD Atrial fibrillation
How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto
 How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto Introduction Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common genetic cardiomyopathy,
How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto Introduction Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common genetic cardiomyopathy,
Comparison of Two-Dimensional Echocardiography and Ultrafast Cardiac Computed Tomography for Evaluating Intracardiac Thrombi in Cerebral Ischemia
 1033 Comparison of Two-Dimensional Echocardiography and Ultrafast Cardiac Computed Tomography for Evaluating Intracardiac Thrombi in Cerebral Ischemia Betsy B. Love, MD, Lynn K. Struck, MD, William Stanford,
1033 Comparison of Two-Dimensional Echocardiography and Ultrafast Cardiac Computed Tomography for Evaluating Intracardiac Thrombi in Cerebral Ischemia Betsy B. Love, MD, Lynn K. Struck, MD, William Stanford,
Ischemic Heart Disease
 Ischemic Heart Disease Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Division of Pathology University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology General Consideration Results from partial
Ischemic Heart Disease Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Division of Pathology University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology General Consideration Results from partial
Accuracy of ECG in assessment of postmyocardial infarction left ventricular function & its comparison with echocardiography
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 10 Ver. V (Oct. 2014), PP 80-84 Accuracy of ECG in assessment of postmyocardial infarction
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 10 Ver. V (Oct. 2014), PP 80-84 Accuracy of ECG in assessment of postmyocardial infarction
Echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular function in patients of acute myocardial infarction
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Anjali VS et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Aug;4(4):926-931 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20173070
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Anjali VS et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Aug;4(4):926-931 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20173070
Case 47 Clinical Presentation
 93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING
 PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus. Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE)
 Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE) Purpose: Rapid Cardiac Echocardiography (RCE) This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE) Purpose: Rapid Cardiac Echocardiography (RCE) This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
Diagnosis of aneurysm of the thoracic aorta. Comparison between two non invasive techniques: two-dimensional echocardiography and computed tomography
 European Heart Journal (1984) 5, 545-555 Diagnosis of aneurysm of the thoracic aorta. Comparison between two non invasive techniques: two-dimensional echocardiography and computed tomography S. ILICETO*,
European Heart Journal (1984) 5, 545-555 Diagnosis of aneurysm of the thoracic aorta. Comparison between two non invasive techniques: two-dimensional echocardiography and computed tomography S. ILICETO*,
Tricuspid Valve Prolapse Diagnosed by Cross-Sectional Echocardiography*
 Tricuspid Valve Prolapse Diagnosed by Cross-Sectional Echocardiography* T.loseph MardeUi, M.D.; Joel Morganroth, M.D., F.C.C.P.;t Chin C. Chen, M.D.; Masahito Naito, M.D.; and JaimeVergel, M.D. Cross-sectional
Tricuspid Valve Prolapse Diagnosed by Cross-Sectional Echocardiography* T.loseph MardeUi, M.D.; Joel Morganroth, M.D., F.C.C.P.;t Chin C. Chen, M.D.; Masahito Naito, M.D.; and JaimeVergel, M.D. Cross-sectional
Assessment of Left Ventricular Wall Motion Abnormalities with the Use of Color Kinesis: A Valuable Visual and Training Aid
 Assessment of Left Ventricular Wall Motion Abnormalities with the Use of Color Kinesis: A Valuable Visual and Training Aid Yung-Sang Lau, MBBS, MMed (Int. Med.), Josephine V. Puryear, RDMS, Sandra C. Gan,
Assessment of Left Ventricular Wall Motion Abnormalities with the Use of Color Kinesis: A Valuable Visual and Training Aid Yung-Sang Lau, MBBS, MMed (Int. Med.), Josephine V. Puryear, RDMS, Sandra C. Gan,
Key words: two-dimensional echocardiography, cardiomyopathy, Introduction. Patients and Methods. Clin. Cardiol. 12, (1989)
 Clin. Cardiol. 12, 91-96 (1989) Echocardiographic Findings of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy and Normalization of Parameters of Left Ventricular Function in Patients with Previous Evidence of Dilated and
Clin. Cardiol. 12, 91-96 (1989) Echocardiographic Findings of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy and Normalization of Parameters of Left Ventricular Function in Patients with Previous Evidence of Dilated and
Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital
 Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital VSD is one of the most common congenital cardiac abnormalities in the newborn. It can occur as an isolated finding or in combination
Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital VSD is one of the most common congenital cardiac abnormalities in the newborn. It can occur as an isolated finding or in combination
Predictors of left ventricular thrombus formation and disappearance after anterior wall myocardial infarction
 European Heart Journal (1998) 19,908-916 Predictors of left ventricular thrombus formation and disappearance after anterior wall myocardial infarction A. N. Neskovic, J. Marinkovic, M. Bojic and A. D.
European Heart Journal (1998) 19,908-916 Predictors of left ventricular thrombus formation and disappearance after anterior wall myocardial infarction A. N. Neskovic, J. Marinkovic, M. Bojic and A. D.
Thrombosis and Embolism From Cardiac Chambers and Infected Valves
 768 lacc Vol g, No 6 December 1986.76B-87B Thrombosis and Embolism From Cardiac Chambers and Infected Valves PHILIP C. ADAMS, BA, MRCP,* MARC COHEN, MD, FACC,* JAMES H. CHESEBRO, MD, FACC,t VALENTIN FUSTER,
768 lacc Vol g, No 6 December 1986.76B-87B Thrombosis and Embolism From Cardiac Chambers and Infected Valves PHILIP C. ADAMS, BA, MRCP,* MARC COHEN, MD, FACC,* JAMES H. CHESEBRO, MD, FACC,t VALENTIN FUSTER,
Syed Nauman Ali, Waqas Mazhar, Kashif Ali Hashmi, Shoaib Abid, ABSTRACT
 Pak Heart J ORIGINAL ARTICLE FREQUENCY OF LEFT VENTRICULAR THROMBUS ON PRE-DISCHARGE ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY OF PATIENTS WITH ACUTE ANTERIOR MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION 1 2 3 4 Syed Nauman Ali, Waqas Mazhar, Kashif
Pak Heart J ORIGINAL ARTICLE FREQUENCY OF LEFT VENTRICULAR THROMBUS ON PRE-DISCHARGE ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY OF PATIENTS WITH ACUTE ANTERIOR MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION 1 2 3 4 Syed Nauman Ali, Waqas Mazhar, Kashif
Real-time 3-dimensional echocardiography (RT3D)
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Feasibility of Real-Time 3-Dimensional Treadmill Stress Echocardiography Donna R. Zwas, MD, Shin Takuma, MD, Samantha Mullis-Jansson, MD, Ali Fard, MD, Hina Chaudhry, MD, Henry Wu, MD,
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Feasibility of Real-Time 3-Dimensional Treadmill Stress Echocardiography Donna R. Zwas, MD, Shin Takuma, MD, Samantha Mullis-Jansson, MD, Ali Fard, MD, Hina Chaudhry, MD, Henry Wu, MD,
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
Muscle dynamics in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (1986) 62, 545-551 Muscle dynamics in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Roando F. Alvares and John F. Goodwin Division ofcardiovascular Diseases, Hammersmith Hospital, London W12,
Postgraduate Medical Journal (1986) 62, 545-551 Muscle dynamics in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Roando F. Alvares and John F. Goodwin Division ofcardiovascular Diseases, Hammersmith Hospital, London W12,
pulmonary valve on, 107 pulmonary valve vegetations on, 113
 INDEX Adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy, 176 Amyloidosis, 160-161 echocardiographic abnormalities in, 160 intra-mural tumors similar to, 294 myocardial involvement in, 160-161 two-dimensional echocardiography
INDEX Adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy, 176 Amyloidosis, 160-161 echocardiographic abnormalities in, 160 intra-mural tumors similar to, 294 myocardial involvement in, 160-161 two-dimensional echocardiography
Journal of American Science 2014;10(9) Congenital Heart Disease in Pediatric with Down's Syndrome
 Journal of American Science 2014;10(9) http://www.jofamericanscience.org Congenital Heart Disease in Pediatric with Down's Syndrome Jawaher Khalid Almaimani; Maryam Faisal Zafir; Hanan Yousif Abbas and
Journal of American Science 2014;10(9) http://www.jofamericanscience.org Congenital Heart Disease in Pediatric with Down's Syndrome Jawaher Khalid Almaimani; Maryam Faisal Zafir; Hanan Yousif Abbas and
Severe Mitral Regurgitation May Prevent Mural Thrombus Formation within the Left Ventricle with Systolic Dysfunction
 Severe Mitral Regurgitation May Prevent Mural Thrombus Formation within the Left Ventricle with Systolic Dysfunction Nihal ÖZDEMIR, 1 MD, Cihangir KAYMAZ, 1 MD, Enver DAGLAR, 1 MD, Osman KARAKAYA, 1 MD,
Severe Mitral Regurgitation May Prevent Mural Thrombus Formation within the Left Ventricle with Systolic Dysfunction Nihal ÖZDEMIR, 1 MD, Cihangir KAYMAZ, 1 MD, Enver DAGLAR, 1 MD, Osman KARAKAYA, 1 MD,
12 th Annual West Virginia ACC Meeting April 8, 2017
 12 th Annual West Virginia ACC Meeting April 8, 2017 Rameez Sayyed, M.D., FACC, FSCAI Associate professor of Medicine Program Director for interventional cardiology Marshall University Joan C. Edwards
12 th Annual West Virginia ACC Meeting April 8, 2017 Rameez Sayyed, M.D., FACC, FSCAI Associate professor of Medicine Program Director for interventional cardiology Marshall University Joan C. Edwards
Left ventricular thrombus in acute myocardial infarction
 European Heart Journal (1996) 17, 164-1645 Review Article Left ventricular thrombus in acute myocardial infarction J. M. van Dantzig, B. J. Delemarre, H. Bot and C. A. Visser Academic Medical Center, Department
European Heart Journal (1996) 17, 164-1645 Review Article Left ventricular thrombus in acute myocardial infarction J. M. van Dantzig, B. J. Delemarre, H. Bot and C. A. Visser Academic Medical Center, Department
Abnormal, Autoquant Adenosine Myocardial Perfusion Heart Imaging. ID: GOLD Date: Age: 46 Sex: M John Doe Phone (310)
 Background: Reason: preoperative assessment of CAD, Shortness of Breath Symptom: atypical chest pain Risk factors: hypertension Under influence: a beta blocker Medications: digoxin Height: 66 in. Weight:
Background: Reason: preoperative assessment of CAD, Shortness of Breath Symptom: atypical chest pain Risk factors: hypertension Under influence: a beta blocker Medications: digoxin Height: 66 in. Weight:
1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI).
 1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI). 5- cardiogenic shock (massive MIs >40% of the left ventricle)
1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI). 5- cardiogenic shock (massive MIs >40% of the left ventricle)
Complications of Myocardial Infarction
 Complications of Myocardial Infarction Sunil Mankad, MD, FACC, FCCP, FASE Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Director, Transesophageal Echocardiography Associate Director,
Complications of Myocardial Infarction Sunil Mankad, MD, FACC, FCCP, FASE Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Director, Transesophageal Echocardiography Associate Director,
WHI Form Report of Cardiovascular Outcome Ver (For items 1-11, each question specifies mark one or mark all that apply.
 WHI Form - Report of Cardiovascular Outcome Ver. 6. COMMENTS To be completed by Physician Adjudicator Date Completed: - - (M/D/Y) Adjudicator Code: OMB# 095-044 Exp: 4/06 -Affix label here- Clinical Center/ID:
WHI Form - Report of Cardiovascular Outcome Ver. 6. COMMENTS To be completed by Physician Adjudicator Date Completed: - - (M/D/Y) Adjudicator Code: OMB# 095-044 Exp: 4/06 -Affix label here- Clinical Center/ID:
Myocardial contusion injury (MCI) may occur as a rare
 Cardiovascular Images Myocardial Contusion in an 8-Year-Old Boy A Kick to the Heart Danielle M. Moyé, MD; Adrian K. Dyer, MD; Poonam P. Thankavel, MD Myocardial contusion injury (MCI) may occur as a rare
Cardiovascular Images Myocardial Contusion in an 8-Year-Old Boy A Kick to the Heart Danielle M. Moyé, MD; Adrian K. Dyer, MD; Poonam P. Thankavel, MD Myocardial contusion injury (MCI) may occur as a rare
Impaired Regional Myocardial Function Detection Using the Standard Inter-Segmental Integration SINE Wave Curve On Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Original Article Impaired Regional Myocardial Function Detection Using the Standard Inter-Segmental Integration Ngam-Maung B, RT email : chaothawee@yahoo.com Busakol Ngam-Maung, RT 1 Lertlak Chaothawee,
Original Article Impaired Regional Myocardial Function Detection Using the Standard Inter-Segmental Integration Ngam-Maung B, RT email : chaothawee@yahoo.com Busakol Ngam-Maung, RT 1 Lertlak Chaothawee,
Intro to Bedside Ultrasound. Cardiac Ultrasound
 Intro to Bedside Ultrasound Cardiac Ultrasound TEACHERS University of California-Irvine School of Medicine Nathan Molina nathan.d.molina@gmail.com Trevor Plescia taplescia90@gmail.com Jack Silva jpsilva42@gmail.com
Intro to Bedside Ultrasound Cardiac Ultrasound TEACHERS University of California-Irvine School of Medicine Nathan Molina nathan.d.molina@gmail.com Trevor Plescia taplescia90@gmail.com Jack Silva jpsilva42@gmail.com
Case Report DOUGLAS H. KING, MD, JAMES C. HUHTA, MD, HOWARD P. GUTGESELL, MD, FACC, DAVID A. OTT, MD*
 lacc Vol. 4, No.2 August 198'
lacc Vol. 4, No.2 August 198'
British Society of Echocardiography
 British Society of Echocardiography Affiliated to the British Cardiac Society A Minimum Dataset for a Standard Adult Transthoracic Echocardiogram From the British Society of Echocardiography Education
British Society of Echocardiography Affiliated to the British Cardiac Society A Minimum Dataset for a Standard Adult Transthoracic Echocardiogram From the British Society of Echocardiography Education
Nancy Goldman Cutler, MD Beaumont Children s Hospital Royal Oak, Mi
 Nancy Goldman Cutler, MD Beaumont Children s Hospital Royal Oak, Mi Identify increased LV wall thickness (WT) Understand increased WT in athletes Understand hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) Enhance understanding
Nancy Goldman Cutler, MD Beaumont Children s Hospital Royal Oak, Mi Identify increased LV wall thickness (WT) Understand increased WT in athletes Understand hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) Enhance understanding
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS
 Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract'
 Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract' ROBERT WALMSLEY British Heart Journal, 1979, 41, 263-267 From the Department of Anatomy and Experimental Pathology, The University, St Andrews, Scotland SUMMARY
Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract' ROBERT WALMSLEY British Heart Journal, 1979, 41, 263-267 From the Department of Anatomy and Experimental Pathology, The University, St Andrews, Scotland SUMMARY
Advanced Multi-Layer Speckle Strain Permits Transmural Myocardial Function Analysis in Health and Disease:
 Advanced Multi-Layer Speckle Strain Permits Transmural Myocardial Function Analysis in Health and Disease: Clinical Case Examples Jeffrey C. Hill, BS, RDCS Echocardiography Laboratory, University of Massachusetts
Advanced Multi-Layer Speckle Strain Permits Transmural Myocardial Function Analysis in Health and Disease: Clinical Case Examples Jeffrey C. Hill, BS, RDCS Echocardiography Laboratory, University of Massachusetts
Echocardiographic Evaluation of the Cardiomyopathies. Stephanie Coulter, MD, FACC, FASE April, 2016
 Echocardiographic Evaluation of the Cardiomyopathies Stephanie Coulter, MD, FACC, FASE April, 2016 Cardiomyopathies (CMP) primary disease intrinsic to cardiac muscle Dilated CMP Hypertrophic CMP Infiltrative
Echocardiographic Evaluation of the Cardiomyopathies Stephanie Coulter, MD, FACC, FASE April, 2016 Cardiomyopathies (CMP) primary disease intrinsic to cardiac muscle Dilated CMP Hypertrophic CMP Infiltrative
Two-dimensional echocardiography with a wide angle (600) sector scanner'
 Two-dimensional echocardiography with a wide angle (600) sector scanner' British Heart Journal, 1977, 39, 1071-1075 A. B. HOUSTON, N. L. GREGORY, A. SHAW, D. J. WHEATLEY2, AND E. N. COLEMAN From the Department
Two-dimensional echocardiography with a wide angle (600) sector scanner' British Heart Journal, 1977, 39, 1071-1075 A. B. HOUSTON, N. L. GREGORY, A. SHAW, D. J. WHEATLEY2, AND E. N. COLEMAN From the Department
Hemodynamic Assessment. Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics
 Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
Atrial Septal Defects
 Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
BEDSIDE ASSESSMENT OF PATIENTS WITH STEMI
 BEDSIDE ASSESSMENT OF PATIENTS WITH STEMI Prof. Maria Dorobantu, PhD, FESC, FACC Emergency Hospital of Bucharest, Romania Presenter Disclosures There are no conflicts/ grants/ disclosures for this presentation.
BEDSIDE ASSESSMENT OF PATIENTS WITH STEMI Prof. Maria Dorobantu, PhD, FESC, FACC Emergency Hospital of Bucharest, Romania Presenter Disclosures There are no conflicts/ grants/ disclosures for this presentation.
Cardiac hypertrophy and how it may break an athlete s heart e the Cypriot case
 Eur J Echocardiography (2005) 6, 301e307 Cardiac hypertrophy and how it may break an athlete s heart e the Cypriot case C.E. Chee a,1, C.P. Anastassiades a,1, A.G. Antonopoulos b, A.A. Petsas b, L.C. Anastassiades
Eur J Echocardiography (2005) 6, 301e307 Cardiac hypertrophy and how it may break an athlete s heart e the Cypriot case C.E. Chee a,1, C.P. Anastassiades a,1, A.G. Antonopoulos b, A.A. Petsas b, L.C. Anastassiades
Transposition of the Great Arteries Preoperative Diagnostic Considerations. John Simpson Evelina Children s Hospital London, UK
 Transposition of the Great Arteries Preoperative Diagnostic Considerations John Simpson Evelina Children s Hospital London, UK Areas to be covered Definitions Scope of occurrence of transposition of the
Transposition of the Great Arteries Preoperative Diagnostic Considerations John Simpson Evelina Children s Hospital London, UK Areas to be covered Definitions Scope of occurrence of transposition of the
Case Report. Case Report. Ana Lúcia Martins Arruda, Altamiro Ozório, Eloisa Mattos, José Lázaro de Andrade, Thomas Porter, Wilson Mathias Jr
 Case Report Hypoperfusion of the Left Ventricle in the Absence of Changes in Segmental Contractility as Observed through Echocardiography by Using Microbubbles During Dobutamine Infusion Ana Lúcia Martins
Case Report Hypoperfusion of the Left Ventricle in the Absence of Changes in Segmental Contractility as Observed through Echocardiography by Using Microbubbles During Dobutamine Infusion Ana Lúcia Martins
Research Article Performance of a Simplified Wall Motion Score Index Method for Noncardiologists to Assess Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Emergency Medicine olume 2012, Article ID 309470, pages doi:.402/2012/309470 Research Article Performance of a Simplified Wall Motion Score Index Method for
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Emergency Medicine olume 2012, Article ID 309470, pages doi:.402/2012/309470 Research Article Performance of a Simplified Wall Motion Score Index Method for
Diagnosis of Recent Myocardial Infarction With Quantitative Backscatter Imaging: Preliminary Studies
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Diagnosis of Recent Myocardial Infarction With Quantitative Backscatter Imaging: Preliminary Studies Byron F. Vandenberg, MD,a John E. Stuhlmuller, MD,b Linda Rath, Richard E. Kerber,
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Diagnosis of Recent Myocardial Infarction With Quantitative Backscatter Imaging: Preliminary Studies Byron F. Vandenberg, MD,a John E. Stuhlmuller, MD,b Linda Rath, Richard E. Kerber,
Correlation Between Regional Wall Motion Abnormalities via 2-Dimensional Echocardiography, and Coronary Angiographic Findings
 THE ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY, IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL AND CORONARY JOURNAL ANGIOGRAPHIC FINDINGS VOL.11, SUPPLEMENT,2012 Correlation Between Regional Wall Motion Abnormalities via 2-Dimensional Echocardiography,
THE ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY, IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL AND CORONARY JOURNAL ANGIOGRAPHIC FINDINGS VOL.11, SUPPLEMENT,2012 Correlation Between Regional Wall Motion Abnormalities via 2-Dimensional Echocardiography,
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Echocardiographic Cardiovascular Risk Stratification: Beyond Ejection Fraction
 Echocardiographic Cardiovascular Risk Stratification: Beyond Ejection Fraction October 4, 2014 James S. Lee, M.D., F.A.C.C. Associates in Cardiology, P.A. Silver Spring, M.D. Disclosures Financial none
Echocardiographic Cardiovascular Risk Stratification: Beyond Ejection Fraction October 4, 2014 James S. Lee, M.D., F.A.C.C. Associates in Cardiology, P.A. Silver Spring, M.D. Disclosures Financial none
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1
 Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease
 Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease L. Youngmin Eun, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine The potential advantage of ultrasound
Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease L. Youngmin Eun, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine The potential advantage of ultrasound
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY DATA REPORT FORM
 Patient ID Patient Study ID AVM - - Date of form completion / / 20 Initials of person completing the form mm dd yyyy Study period Preoperative Postoperative Operative 6-month f/u 1-year f/u 2-year f/u
Patient ID Patient Study ID AVM - - Date of form completion / / 20 Initials of person completing the form mm dd yyyy Study period Preoperative Postoperative Operative 6-month f/u 1-year f/u 2-year f/u
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT. Impact of Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Left Ventricular Mass and. Diastolic Function
 ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT Impact of Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Left Ventricular Mass and Diastolic Function Mitra Niroumand Raffael Kuperstein Zion Sasson Patrick J. Hanly St. Michael s Hospital University
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT Impact of Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Left Ventricular Mass and Diastolic Function Mitra Niroumand Raffael Kuperstein Zion Sasson Patrick J. Hanly St. Michael s Hospital University
A classic case of amyloid cardiomyopathy
 Images in... A classic case of amyloid cardiomyopathy Hayan Jouni, 1 William G Morice, 2 S Vincent Rajkumar, 3 Joerg Herrmann 4 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Images in... A classic case of amyloid cardiomyopathy Hayan Jouni, 1 William G Morice, 2 S Vincent Rajkumar, 3 Joerg Herrmann 4 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Pulmonary wedge injections yielding left-sided echocardiographic contrast *
 Br HeartJt 1980; 44: 390-4 Pulmonary wedge injections yielding left-sided echocardiographic contrast * RICHARD S MELTZER, PATRICK W SERRUYS, JACKIE McGHIE, NELLIE VERBAAN, JOS ROELANDT From the Thoraxcentre,
Br HeartJt 1980; 44: 390-4 Pulmonary wedge injections yielding left-sided echocardiographic contrast * RICHARD S MELTZER, PATRICK W SERRUYS, JACKIE McGHIE, NELLIE VERBAAN, JOS ROELANDT From the Thoraxcentre,
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Mitral Annulus Excursion in Normal Horses
 Echocardiographic Evaluation of Mitral Annulus Excursion in Normal Horses Carlos Lightowler, DVM a Giuseppe Piccione, DVM b Maria Laura Cattaneo, DSS c Elisabetta Giudice, DVM, PhD d a Departamento de
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Mitral Annulus Excursion in Normal Horses Carlos Lightowler, DVM a Giuseppe Piccione, DVM b Maria Laura Cattaneo, DSS c Elisabetta Giudice, DVM, PhD d a Departamento de
Questions on Chamber Quantitation
 Questions on Chamber Quantitation @RobertoMLang Which of the following statements is true? 1. The aortic annulus should be measured in midsystole. 2. The aortic annulus should be measured in enddiastole.
Questions on Chamber Quantitation @RobertoMLang Which of the following statements is true? 1. The aortic annulus should be measured in midsystole. 2. The aortic annulus should be measured in enddiastole.
Reversal of cardiac abnormalities in a young man with idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome using a tyrosine kinase inhibitor
 Eur J Echocardiography (2004) 5, 386e390 CASE REPORTS Reversal of cardiac abnormalities in a young man with idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome using a tyrosine kinase inhibitor Luigi Ascione a, ), Mario
Eur J Echocardiography (2004) 5, 386e390 CASE REPORTS Reversal of cardiac abnormalities in a young man with idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome using a tyrosine kinase inhibitor Luigi Ascione a, ), Mario
Cardiovascular Images
 Cardiovascular Images Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosed From Right Heart Changes Seen After Exercise Stress Echocardiography Brian C. Case, MD; Micheas Zemedkun, MD; Amarin Sangkharat, MD; Allen J. Taylor,
Cardiovascular Images Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosed From Right Heart Changes Seen After Exercise Stress Echocardiography Brian C. Case, MD; Micheas Zemedkun, MD; Amarin Sangkharat, MD; Allen J. Taylor,
Echo in CAD: Wall Motion Assessment
 Echo in CAD: Wall Motion Assessment Joe M. Moody, Jr, MD UTHSCSA and STVHCS October 2007 Relevant References ACC/AHA/ASE 2003 Guideline Update for the Clinical Application of Echocardiography Bayes de
Echo in CAD: Wall Motion Assessment Joe M. Moody, Jr, MD UTHSCSA and STVHCS October 2007 Relevant References ACC/AHA/ASE 2003 Guideline Update for the Clinical Application of Echocardiography Bayes de
Normal TTE Examination, Doppler Echocardiography and Normal Antegrade Flow Patterns
 Normal TTE Examination, Doppler Echocardiography and Normal Antegrade Flow Patterns Pravin Patil, MD FACC FASE Associate Professor of Medicine Director, Cardiovascular Disease Training Program Lewis Katz
Normal TTE Examination, Doppler Echocardiography and Normal Antegrade Flow Patterns Pravin Patil, MD FACC FASE Associate Professor of Medicine Director, Cardiovascular Disease Training Program Lewis Katz
Radiology of the respiratory/cardiac diseases (part 2)
 Cardiology Cycle - Lecture 6 436 Teams Radiology of the respiratory/cardiac diseases (part 2) Objectives Done By Team Leaders: Khalid Alshehri Hanin Bashaikh Team Members: Leena Alwakeel Aroob Alhuthail
Cardiology Cycle - Lecture 6 436 Teams Radiology of the respiratory/cardiac diseases (part 2) Objectives Done By Team Leaders: Khalid Alshehri Hanin Bashaikh Team Members: Leena Alwakeel Aroob Alhuthail
Diagnosis of Device Thrombosis
 Diagnosis of Device Thrombosis Andrew Civitello MD, FACC Medical Director, Heart Transplant Program Director, Fellowship Co-Director, Baylor St. Luke's Medical Center / Texas Heart Institute Trends in
Diagnosis of Device Thrombosis Andrew Civitello MD, FACC Medical Director, Heart Transplant Program Director, Fellowship Co-Director, Baylor St. Luke's Medical Center / Texas Heart Institute Trends in
ACUTE CENTRAL PERIFERALEMBOLISM
 EAE TEACHING COURSE 2010 Belgrade, Serbia October 22-23, 2010 ACUTE CENTRAL and PERIFERALEMBOLISM Maria João Andrade Lisbon, PT BACKGROUND Stroke is a leading cause of mortality and long-term disability
EAE TEACHING COURSE 2010 Belgrade, Serbia October 22-23, 2010 ACUTE CENTRAL and PERIFERALEMBOLISM Maria João Andrade Lisbon, PT BACKGROUND Stroke is a leading cause of mortality and long-term disability
Tako-Tsubo Cardiomyopathy by Transient Dynamic Left Midventricular Obstruction
 CSE REPORT DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.1.37 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Tako-Tsubo Cardiomyopathy by Transient Dynamic Left Midventricular
CSE REPORT DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.1.37 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Tako-Tsubo Cardiomyopathy by Transient Dynamic Left Midventricular
Two Cardiology Zebras ERIC MARTIN MD
 Two Cardiology Zebras ERIC MARTIN MD Disclosures Bayer Gilead Sciences NIH Vascular Dynamics, In. Employer Iowa Heart Center/Mercy Des Moines Zebra # 1 History CC: 52-year-old man seen in consultation
Two Cardiology Zebras ERIC MARTIN MD Disclosures Bayer Gilead Sciences NIH Vascular Dynamics, In. Employer Iowa Heart Center/Mercy Des Moines Zebra # 1 History CC: 52-year-old man seen in consultation
Alcohol Septal Ablation for Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy. CardioVascular Research Foundation
 Alcohol Septal Ablation for Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy Alcohol Septal Ablation (ASA) Nonsurgical technique for septal myocardial reduction Dramatic hemodynamic improvement Technically easy
Alcohol Septal Ablation for Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy Alcohol Septal Ablation (ASA) Nonsurgical technique for septal myocardial reduction Dramatic hemodynamic improvement Technically easy
Two-Dimensional Echocardiographic Diagnosis of Intracardiac Masses in Infancy
 JACC Vol. 3, No.3 827 PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Two-Dimensional Echocardiographic Diagnosis of Intracardiac Masses in Infancy GERALD R. MARX, MD,* FREDERICK Z. BIERMAN, MD, FACC, EDWARD MATTHEWS, MD, ROBERTA
JACC Vol. 3, No.3 827 PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Two-Dimensional Echocardiographic Diagnosis of Intracardiac Masses in Infancy GERALD R. MARX, MD,* FREDERICK Z. BIERMAN, MD, FACC, EDWARD MATTHEWS, MD, ROBERTA
Isolated right ventricular ballooning syndrome: a new variant of transient cardiomyopathy
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2011 Isolated right ventricular ballooning syndrome: a new variant of transient
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2011 Isolated right ventricular ballooning syndrome: a new variant of transient
Kawasaki disease: echocardiographic features in 91
 1142 Archives ofdisease in Childhood 1990; 65: 1142-1146 Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London WC1N 3JH Department of Paediatric Cardiology A Suzuki V Gooch S G Haworth Department of
1142 Archives ofdisease in Childhood 1990; 65: 1142-1146 Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London WC1N 3JH Department of Paediatric Cardiology A Suzuki V Gooch S G Haworth Department of
Assessment of LV systolic function
 Tutorial 5 - Assessment of LV systolic function Assessment of LV systolic function A knowledge of the LV systolic function is crucial in the undertanding of and management of unstable hemodynamics or a
Tutorial 5 - Assessment of LV systolic function Assessment of LV systolic function A knowledge of the LV systolic function is crucial in the undertanding of and management of unstable hemodynamics or a
Inspiratory Right Ventricular Outflow Obstruction in a Patient with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
 Case Reports Inspiratory Right Ventricular Outflow Obstruction in a Patient with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Kazufumi TSUCHIHASHI, M.D., Akihito TSUCHIDA, M.D., Nobuichi HIKITA, M.D., Shuji YONEKURA, M.D.,
Case Reports Inspiratory Right Ventricular Outflow Obstruction in a Patient with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Kazufumi TSUCHIHASHI, M.D., Akihito TSUCHIDA, M.D., Nobuichi HIKITA, M.D., Shuji YONEKURA, M.D.,
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
