Clinical Profile & Outcome of Infective Endocarditis patients admitted in tertiary care center in eastern part of Nepal
|
|
|
- Brendan Wilkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 10 Original Article Clinical Profile & Outcome of Infective Endocarditis patients admitted in tertiary care center in eastern part of Nepal Sherpa K, Shah P, Khati Y, Jha SK, Sharma SK, Karki P Department of Internal Medicine, BP Koirala Institute of Health Sciences, Dharan Corresponding to: Dr. Kunjang Sherpa, Abstract Introduction: Data regarding the pattern and outcome of infective endocarditis from developing countries are sparse and there have been few studies in our part of the world understanding the clinical profile and outcome of patients with infective endocarditis. Methods: It was a hospital based descriptive retrospective cross-sectional with the objective on clinical profile and outcome of infective endocarditis patients admitted in tertiary care center in eastern part of Nepal. The study included cases admitted in department of internal medicine ward, BPKIHS with diagnosis of infective endocarditis from year 2008 to Results: A total of 20 patients were diagnosed as case of infective endocarditis during the period from 2008 to 2015 in department of internal medicine. The median age of study group was 31 years (range 14-56). Male to female ratio was 9:1. Among various risk factors, history of Intravenous drug use was the main risk factor present in 50% of patients, followed by definite rheumatic heart disease in 40 % of study population. Fever, Chills and sweats were main symptom present in all patients,anemia in 90 %, heart murmur in 80%, anorexia in 45%, myalgia in 35 %, splenomegaly in 15 %, neurological manifestation, clubbing, Roth's s and embolic phenomenon in 5% of patients. The most common valve involved was tricuspid valve, present in 50 % patient, followed by mitral valve in 35% patient and aortic valve in 15% of patients. Anemia was most common laboratory abnormalities present in 90% of the patients followed by leukocytosis in 80 % of patients, microscopic hematuria and disarranged renal function test was present in 40 % of the patients. Blood culture positivity was seen in 30 % of cases and the pathogen isolated was Staphylococcus aureus. Prior antibiotic treatment was received by 40 % of patients. Acute Renal failure was the main complication appeared which was present in 25 % of patients followed by Neurological manifestations in 5 % and peripheral embolic phenomenon was present 5 % of patients. Conclusion:The spectrum of our infective endocarditis patients differ from those seen in the west in terms of epidemiology, predisposing factors, microbiology, complications, and outcome. Fever, pallor and heart murmur were most common symptoms and acute renal failure was the most common complication. Majority of our patients improve despite having lack of surgical backup. Culture-negative endocarditis continues to have a high prevalence in developing countries like Nepal, largely due to prior antibiotic use before clinical presentation. Introduction Infective endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner tissues of the heart, the endocardium. It is caused by infectious agents, or pathogens, which are usually bacterial but other organisms can also be responsible. Before the age of modern antibiotics it was almost universally fatal 1. Infective endocarditis (IE) remains a serious cardiac problem despite the availability of improved diagnostic and therapeutic facilities. Studies
2 Clinical Profile &... from the west have shown remarkable changes in the spectrum of IE 2,3. The epidemiology, clinical, and microbiologic spectrum of infective endocarditis (IE) is significantly different in the developing countries compared to the western world. These differences can be attributable to multiple factors present in poorer countries including significantly higher incidences of rheumatic heart disease (RHD) and uncorrected congenital heart disease, excessive and improper use of antibiotics, late clinical presentation, and worse outcomes 4,5. Data regarding the pattern and outcome of infective endocarditis from developing countries are sparse and there have been few studies in our part of world understanding the clinical profile and outcome of patients with infective endocarditis. In light of the changing global trends in endocarditis over the last four decades, further insight into the clinical expression of the disease in developing countries is warranted. We therefore, undertook this study to determine the clinical characteristics, and microbiological profile and outcome of patients with Infective endocarditis at tertiary care center in eastern part of Nepal. Methods A hospital based descriptive retrospective crosssectional study was done and included all cases admitted in department of internal medicine ward, BPKIHS with diagnosis of infective endocarditis from year 2008 to Ethical clearance was obtained from the institution ethical committee. Data was collected from the filed cases with diagnosis of infective endocarditis obtained from medical record section from year 2008 to 2015 admitted in department of internal medicine. Appropriate tools and techniques were used to collect data. Information on clinical epidemiological profile, risk factor, involvement of valve and outcome of the patients were collected.data was entered in Microsoft Excel 2010 and converted into SPSS (statistical package for social science) 17.0 version for statistical analysis. For descriptive statistics, percentage, mean, standard deviation and median, was calculated along with graphical and tabular presentation were made. Results A total of 20 patients were diagnosed as case of infective endocarditis during the period of 2008 to 2015 in department of internal medicine. The median age of study group was 31 years (range 14-56). Male to female ratio was 9:1. Among various risk factor, history of Intravenous drug use was the main risk factor present in 50% of patient, 40 % patients has definite RHD, history of the RHD in 20 % patients, with history of previous infective endocarditis in 10 %, Age related valve lesion in 5 % and prosthetic valve replacement in 5% of study population. Among patients diagnosed as RHD only 2 patients were receiving penicillin prophylaxis. Fever, Chills and sweat were main symptom present in all 100% patients followed by anemia in 90 %, heart murmur in 80%, anorexia in 45%, myalgia in 35 %, splenomegaly in 15 %, neurological manifestation in 5%, clubbing in 5 %, Roth's spot in 5 %, embolic phenomenon in 5% of patients. (Table1) The most common valve involved was tricuspid valve present in 50 % patient, followed by mitral valve in 35% patient and aortic valve in 15% of patients. combined mitral and aortic valve was involved in 10 % of cases and 5 % patients had involvement of mitral, aortic and tricuspid valve Anemia was most common laboratory abnormalities present in 90% of the patients followed by leukocytosis in 80 % of patients,microscopic hematuria and disarranged renal function test was present in 40 % of the patients.blood culture positivity was seen in 30 % of cases and the pathogen isolated was Staphylococcus aureus in all cases. Prior antibiotic treatment was received by 40 % of patients. Among the total patients 19 patient improved with treatment, one patient was referred to other centre. Acute Renal failure was the main complication which was present in 25 % of patient followed by Neurological manifestations in 5 % and peripheral embolic phenomenon was present 5 % of patients (Table 2) 11
3 12 Sherpa K, et al., Table 1. clinical profile and risk factors in the study population. Patients characteristics Categories Number of patients Percentage < Age group Gender > Male Female 2 10 Sunsari Address Morang 4 20 Jhapa 3 15 Dhankutta 2 10 Laborer 9 45 Occupation Student 7 35 Farmer 4 20 Risk factor IV drug user history of RHD 4 20 Diagnosed RHD 8 40 History of infective endocarditis 2 10 Age related valve lesion 1 5 Prosthetic valve 1 5 Clinical Features Fever Chills and sweat Anemia Heart murmur Anorexia, weight loss, malaise 9 45 Myalgia, arthralgia 6 30 Splenomegaly 3 15 Neurologic manifestation 1 5 Clubbing 1 5 Roth s Spot 1 5 Embolic Phenemenon 1 5
4 Clinical Profile &... Table- 2 Outcome and Complications in the study population OUTCOME FREQUENCY PERCENTAGE IMPROVED complications Renal failure 5 40 Neurological manifestation Embolic phenomenon Referred 1 5 Discussion The Research was descriptive cross-sectional retrospective study which was intended to study regarding demographic profile, risk factor, sign and symptom, laboratory profile and outcome of patients with infective endocarditis admitted in tertiary care center in eastern part of Nepal.The median age of our study is 31 year and majority of patients in IE group, 70%were below 30 years, this is similar to all previous study from India 10. But this is in contrast to the western studies where majority of patients had presented beyond the fourth decade.this can be due to the fact that RHD continues to be a significant problem in developing world which usually presents at younger age 6. Among these patients 90% were male and 10%were female. The male to female ratio was 9:1. This ratio is much greater than previous study done at our hospital which was 1.2:1 7. The younger age and more prevalence in male patients may be due to increase IV drug abuser and problem of RHD in eastern part of Nepal. According to our study majority of the patient were resident of Sunsari district which comprises 55% of the total patient admitted in ward with the diagnosisof infective endocarditis. Most of the patient from Sunsari were younger age group with history of IV drug abuser.right sided infective endocarditis were more common then left sided infective endocarditis in eastern part of Nepal. The study revealed right sided IE secondary to intravenous drug abuse has showed an alarming increase in eastern part of Nepal as compared to previous study of 9.1 %. 7. Rheumatic heart disease was the another common risk factor for left sided infective endocarditis which was present in 40 % of study population. RHD was also one of the commonest underlying heart disease in our study that is similar to other studies from India 8. Previously it is reported that RHD and congenital heart disease were the most common risk factor and there is left sided endocarditis is more common in developing countries 9 but in our study it is seen that intravenous drug use is the most common risk factor for infective endocarditis and right sided endocarditis are common as there is increasing with use of IV drug abuse in young population eastern part of Nepal. Regarding clinical features, fever, chills and sweating was present in 100% cases which was similar to previous study 7 which was followed by anemia in 90 % cases and 80% had heart murmur.forty five percent of cases had anorexia, weight loss, about 30% had myalgia,arthralgia and splenomegaly was found in 23.1% cases. Rest of symptoms like heart murmur, clubbing, Roth s spot and embolic phenomenon comprises 5% equally. While none of the patient had Osler s node, Janeway lesion, murmur, nail hemorrhage and petechial rashes. The most common valve involved is tricuspid valve present in (n=10) 50 %patient which is quite different from the previous study done in developing countries. The reason is due to the increase in IV drug abuse in eastern part of Nepal. Similarly mitral valve involved seen in (n=7) 35%. Aortic valve involvement was least common (n=3) 15%.There wasone case with prosthetic valve involvement. In our study, blood culture were positive in 30 % of study population and staph. aureus was isolated as causative organism in all positive cases.this is similar to the previous studies in developing countries, which have reported culture positivity in 21-47% episodes. 10,11,12 Blood cultures have been reported to be positive in more than 90.0% patients of IE in western series. 13,14. Prior antibiotic therapy may be the important reason for high culture negativity in our series, since a high proportion of culture negative IE patients had received antibiotic therapy before admission to our hospital. Recent large western series have reported a change in the microbial spectrum. Staphylococcus aureushas been reported as the commonest microorganism with relative decline in streptococcal endocarditis 15. This is attributable to aging population, rising drug abuse, patients with prosthetic valves and increasing frequency of nosocomial and iatrogenic endocarditis. Similarity to the west studies, Staphylococcus was the commonest isolates 30 % in our studycases which may be due to increase IV drug abuser in eastern part of Nepal. Ninty five percent of our cases improved and while 5% cases were referred to other centre. The studies 13
5 14 from industrialized countries have shown a consistent improvement in survival of patients with IE over the past four decades. A similar decrease in mortality is also seen in patients from the Indian subcontinent 9. Acute renal failure, neurological manifestations and embolic phenomenon are the main complication recorded in our study. Among them acute renal failure is the leading complication, which is manifested in 40% cases and neurological manifestation& embolic phenomenon seen in 5% cases equally. The major limitation of study was that it was an retrospective study where only hospital record were used, less sample size and outcome evaluated only during hospital discharge but no follow up data could be done. Despite various limitation of the study, the study reflects the general picture of infective endocarditis at a tertiary hospital in a developing country and it shows the differences in predisposing factors, etiological agents, common clinical symptoms and complications and outcome during hospital stay. Conclusion The spectrum of our infective endocarditis patients differ from those seen in the west in terms of epidemiology, predisposing factors, microbiology, complications, and outcome.it occurs in relatively younger population with Intra venous drug user and rheumatic heart disease being the commonest underlying risk factors for the infective endocarditis in eastern part on Nepal.Fever, pallor and heart murmur were most common symptoms and acute renal failure was the most common complication. Majority of our patients improved despite having lack of surgical backup. Culture-negative endocarditis continues to have a high prevalence in developing countries like Nepal, largely due to prior antibiotic use before clinical presentation. We believe that multidisciplinary team is needed to improve diagnosis and management of infective endocarditis patients and Prevention of IV drug abuse and RHD plays major role in decreasing infective endocarditis patients. Conflict of interest: None declared References Sherpa K, et al., 1. Heiro M, Helenius H, Mäkilä S, infective endocardis in Finish teaching hospital: a study on 326 inside treated during heart :2006 oct 92(10) : Kaye D. Changing pattern of InfectiveEndocarditis. Am J Med. 1985; 78: Netzer ROM, Zollinger E, Seiler C, et al. Infective endocarditis: Clinical spectrum,presentation and outcome, An analysisof 212 cases Heart. 2000; 84: Rizui SF, Khan MA, Kundi A etal. status of rheumatic heart disease in rural Pakistan Heart 2004; 90: Chatterjee A, Das D, Kohli P etal. Awareness of infective endocartitis prophylactic and dental hygine in cardinc patients after phyrium contact. Indian J Paediatric 2004:71: Awadallah SM, Kavey RW, Byrum CJ, et al, The changing pattern of infective endocarditis in childhood. Am J Cardiol 1991; 68: Ghimire M, Karki P, Khanal B, Acharya P, Sharma SK, PahariBishnu clinical profile and microbiological pathogens involved in patients with Infective Endocarditis, Journal of College of Medical Sciences- Nepal 2008; 8:4 8. Chaudhary R, Grover A, Varma J, et al, Active infective endocarditis observedin an Indian hospital Am JCardiol. 1992; 70: Tariq M, Alam M, Munir G, et al, Infective endocarditis: a five-year experienceat a tertiary care hospital in Pakistan. International Journal of InfectiousDiseases.; 2004; 8: Jalal S, Khan KA, Alai MS, Clinical spectrum of infective endocarditis. 15years experience. Indian Heart J. 1998; 50: Datta BN, Khatri HN, Bidwai PS et al Infective endocarditis at autopsy in Northern India- a study of 120 cases. Jrn Heart J. 1982; 23: Khanal B, Harish BN, Sethuraman KR, et al, Infective endocarditis: report of prospective study in an Indian hospital.tropical Doctor. 2002; 32: Sandre RM, Shafiran SD. Infective endocarditis : review of 135 cases over 9years. Clin Infect Dis. 1996; 22: Bayer AS, Ward JI, Ginzton LE, et al, Evaluation of new clinical criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis. Am J Med.; 1994; 96: Van der Meer JT, Thompson J, Valkenburg HA, et al. Epidemiology of bacterialendocarditis in the Netherlands. ArchIntern Med. 1992; 152:
Michael Stander, Pharm.D.
 Michael Stander, Pharm.D. Endocarditis: Goals Epidemiology Presentation of acute and subacute. Diagnosis: What is Dukes Criteria and how do we approach the diagnosis of endocarditis? Treatment: Understand
Michael Stander, Pharm.D. Endocarditis: Goals Epidemiology Presentation of acute and subacute. Diagnosis: What is Dukes Criteria and how do we approach the diagnosis of endocarditis? Treatment: Understand
Heart on Fire: Infective Endocarditis. Objectives. Disclosure 8/27/2018. Mary McGreal DNP, RN, ANP-c, CCRN
 Heart on Fire: Infective Endocarditis Mary McGreal DNP, RN, ANP-c, CCRN Objectives Discuss the incidence of infective endocarditis? Discuss the pathogenesis of infective endocarditis? Discuss clinical
Heart on Fire: Infective Endocarditis Mary McGreal DNP, RN, ANP-c, CCRN Objectives Discuss the incidence of infective endocarditis? Discuss the pathogenesis of infective endocarditis? Discuss clinical
Infective Endocarditis عبد المهيمن أحمد
 Infective Endocarditis إعداد : عبد المهيمن أحمد أحمد علي Infective endocarditis Inflammation of the heart valve or endocardium of the heart. The agents are usually bacterial, but other organisms can also
Infective Endocarditis إعداد : عبد المهيمن أحمد أحمد علي Infective endocarditis Inflammation of the heart valve or endocardium of the heart. The agents are usually bacterial, but other organisms can also
Dr Babak Tamizi far MD. Assistant Professor Of Internal Medicine Al-Zahra Hospital Isfahan University Of Medical Sciences
 Dr Babak Tamizi far MD. Assistant Professor Of Internal Medicine Al-Zahra Hospital Isfahan University Of Medical Sciences ١ ٢ ٣ A 57-year-old man presents with new-onset fever, shortness of breath, lower
Dr Babak Tamizi far MD. Assistant Professor Of Internal Medicine Al-Zahra Hospital Isfahan University Of Medical Sciences ١ ٢ ٣ A 57-year-old man presents with new-onset fever, shortness of breath, lower
VALVULAR HEART DISEASE
 VALVULAR HEART DISEASE Stenosis: failure of a valve to open completely, obstructing forward flow. - almost always due to a chronic process (e.g., calcification or valve scarring). Insufficiency : failure
VALVULAR HEART DISEASE Stenosis: failure of a valve to open completely, obstructing forward flow. - almost always due to a chronic process (e.g., calcification or valve scarring). Insufficiency : failure
A study of clinical and etiological profile of infective endocarditis and its correlation with echocardiography in patients of rheumatic heart disease
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Sarkar A et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Oct;4(5):1323-1327 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20174177
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Sarkar A et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Oct;4(5):1323-1327 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20174177
results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both.
 results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both. The outcome of valvular disease depends on : 1-the valve involved 2-the degree of impairment 3-the cause of its development
results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both. The outcome of valvular disease depends on : 1-the valve involved 2-the degree of impairment 3-the cause of its development
Rheumatic Heart Disease Revisited: Patterns of Valvular Involvement from a Consecutive Cohort in Eastern Nepal
 Rheumatic Heart Disease Revisited: Patterns of Valvular Involvement from a Consecutive Cohort in Eastern Nepal Shrestha NR1, Pilgrim T2, Karki P1, Bhandari R1, Basnet S1, Tiwari S1, Urban P3. Dr. Nikesh
Rheumatic Heart Disease Revisited: Patterns of Valvular Involvement from a Consecutive Cohort in Eastern Nepal Shrestha NR1, Pilgrim T2, Karki P1, Bhandari R1, Basnet S1, Tiwari S1, Urban P3. Dr. Nikesh
Daniel C. DeSimone, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine
 Daniel C. DeSimone, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Faculty photo will be placed here Desimone.Daniel@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Infective Endocarditis Mayo School of Continuous Professional Development
Daniel C. DeSimone, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Faculty photo will be placed here Desimone.Daniel@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Infective Endocarditis Mayo School of Continuous Professional Development
Clinical profile and outcome of infective endocarditis at the Aga Khan University Hospital
 ecommons@aku Section of Internal Medicine Department of Medicine January 2009 Clinical profile and outcome of infective endocarditis at the Aga Khan University Hospital M. Tariq Aga Khan University, muhammed.tariq@aku.edu
ecommons@aku Section of Internal Medicine Department of Medicine January 2009 Clinical profile and outcome of infective endocarditis at the Aga Khan University Hospital M. Tariq Aga Khan University, muhammed.tariq@aku.edu
ACCME/Disclosures 4/13/2016 IDPB
 ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
A Study of Infective Endocarditis in Malta
 Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 6(6): 98-104 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjcm doi: 10.11648/j.sjcm.20170606.11 ISSN: 2327-2724 (Print); ISSN: 2327-2732 (Online) A Study of Infective
Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 6(6): 98-104 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjcm doi: 10.11648/j.sjcm.20170606.11 ISSN: 2327-2724 (Print); ISSN: 2327-2732 (Online) A Study of Infective
Infective Endocarditis
 Infective Endocarditis Definition Historical perspective Classification Epidemiological Features Etiology Pathogenesis Clinical presentation Diagnosis Treatment options Prevention Infective endocarditis
Infective Endocarditis Definition Historical perspective Classification Epidemiological Features Etiology Pathogenesis Clinical presentation Diagnosis Treatment options Prevention Infective endocarditis
Infective Endocarditis
 Infective Endocarditis Infective Endocarditis Historical Perspective.. A concretion larger than a pigeon s egg; contained in the left auricle. Burns, 1809 Osler s Gulstonian lectures provided the 1 st
Infective Endocarditis Infective Endocarditis Historical Perspective.. A concretion larger than a pigeon s egg; contained in the left auricle. Burns, 1809 Osler s Gulstonian lectures provided the 1 st
Infective Endocarditis
 Frank Lowy Infective Endocarditis 1. Introduction Infective endocarditis (IE) is an infection of the heart valves. A large number of different bacteria are capable of causing this disease. Depending on
Frank Lowy Infective Endocarditis 1. Introduction Infective endocarditis (IE) is an infection of the heart valves. A large number of different bacteria are capable of causing this disease. Depending on
The spectrum of Acute Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease in children presenting to the Pediatric Unit at Port Moresby General Hospital
 The spectrum of Acute Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease in children presenting to the Pediatric Unit at Port Moresby General Hospital Thyna Orelly DCH AIM To document acute rheumatic fever or
The spectrum of Acute Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease in children presenting to the Pediatric Unit at Port Moresby General Hospital Thyna Orelly DCH AIM To document acute rheumatic fever or
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN CHILDREN
 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN CHILDREN Rohayati Taib RIPAS Hospital, Bundar Seri Begawan, Brunei Darussalam Infective Endocarditis (IE) is a microbial infection of the endocardium. It encompasses both bacterial
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN CHILDREN Rohayati Taib RIPAS Hospital, Bundar Seri Begawan, Brunei Darussalam Infective Endocarditis (IE) is a microbial infection of the endocardium. It encompasses both bacterial
Update on the prevention, diagnosis and management of Infective Endocarditis (IE)
 Update on the prevention, diagnosis and management of Infective Endocarditis (IE) Dr.Ahmed Yahya Mohammed Alarhabi MD, MsC,FcUSM,FACC,MAHA Consultant Interventional Cardiologist Head of Cardiac Center
Update on the prevention, diagnosis and management of Infective Endocarditis (IE) Dr.Ahmed Yahya Mohammed Alarhabi MD, MsC,FcUSM,FACC,MAHA Consultant Interventional Cardiologist Head of Cardiac Center
Clinical Characteristics and In-Hospital Prognosis of Infective Endocarditis in Two Eastern Counties of Taiwan
 Original Article Acta Cardiol Sin 2014;30:151 156 Infective Endocarditis Clinical Characteristics and In-Hospital Prognosis of Infective Endocarditis in Two Eastern Counties of Taiwan Jen-Che Hsieh, 1,4
Original Article Acta Cardiol Sin 2014;30:151 156 Infective Endocarditis Clinical Characteristics and In-Hospital Prognosis of Infective Endocarditis in Two Eastern Counties of Taiwan Jen-Che Hsieh, 1,4
Disclosures. Native Valve Endocarditis and its Complications. Outline. Outline. Basics. Basics 3/23/2017
 Native Valve Endocarditis and its Complications SCVP and Binford Dammin Society of Infectious Disease Pathologists Shared Companion Meeting USCAP 2017 Annual Meeting Disclosures Relevant financial relationships
Native Valve Endocarditis and its Complications SCVP and Binford Dammin Society of Infectious Disease Pathologists Shared Companion Meeting USCAP 2017 Annual Meeting Disclosures Relevant financial relationships
Infective Endocarditis for Primary Care Physicians
 Infective Endocarditis for Primary Care Physicians David N Gilbert, MD Disclosures Consultant to: Merck Pfizer Medicine Company Cempra 1 Introduction There are roughly 30,000 new cases of IE in the US
Infective Endocarditis for Primary Care Physicians David N Gilbert, MD Disclosures Consultant to: Merck Pfizer Medicine Company Cempra 1 Introduction There are roughly 30,000 new cases of IE in the US
INFECTIOUS endocarditis (IE) is a
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis Sensitivity of the Duke vs von Reyn Criteria Maija Heiro, MD; Jukka Nikoskelainen, MD, PhD; Jaakko J. Hartiala, MD, PhD; Markku K. Saraste, MD;
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis Sensitivity of the Duke vs von Reyn Criteria Maija Heiro, MD; Jukka Nikoskelainen, MD, PhD; Jaakko J. Hartiala, MD, PhD; Markku K. Saraste, MD;
Endocarditis, including Prophylaxis
 Endocarditis, including Prophylaxis ACOI Board Review 2018 gerald.blackburn@beaumont.org (No Disclosures) Infective Endocarditis Persistant bacteremia (blood cultures drawn >12 hrs apart) w/ organisms
Endocarditis, including Prophylaxis ACOI Board Review 2018 gerald.blackburn@beaumont.org (No Disclosures) Infective Endocarditis Persistant bacteremia (blood cultures drawn >12 hrs apart) w/ organisms
Infective endocarditis (IE) By Assis. Prof. Nader Alaridah MD, PhD
 Infective endocarditis (IE) By Assis. Prof. Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Infective endocarditis (IE) is an inflammation of the endocardium.. inner of the heart muscle & the epithelial lining of heart valves.
Infective endocarditis (IE) By Assis. Prof. Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Infective endocarditis (IE) is an inflammation of the endocardium.. inner of the heart muscle & the epithelial lining of heart valves.
Épidémiologie des endocardites infectieuses à Staphylococcus aureus (Epidemiology of S. aureus endocarditis)
 Épidémiologie des endocardites infectieuses à Staphylococcus aureus (Epidemiology of S. aureus endocarditis) Lyon, 30 Novembre 2018 Univ.-Prof. Dr. med. Achim J. Kaasch Institut für Medizinische Mikrobiologie
Épidémiologie des endocardites infectieuses à Staphylococcus aureus (Epidemiology of S. aureus endocarditis) Lyon, 30 Novembre 2018 Univ.-Prof. Dr. med. Achim J. Kaasch Institut für Medizinische Mikrobiologie
Pr AMEL OMEZZINE LETAIEF CHU FarhatHached Sousse
 Pr AMEL OMEZZINE LETAIEF CHU FarhatHached Sousse cours de collège infectiologie Sousse le27/02/2013 ENDOCARDITIS There is a change in epidemiology Clinical features of IE remains classical Diagnosis of
Pr AMEL OMEZZINE LETAIEF CHU FarhatHached Sousse cours de collège infectiologie Sousse le27/02/2013 ENDOCARDITIS There is a change in epidemiology Clinical features of IE remains classical Diagnosis of
DESCRIPTIVE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF A GASTROENTERITIS OUT BREAK IN SUNSARI DISTRICT, NEPAL
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Journal of Nepal Medical Association, 2002:41:383-387 DESCRIPTIVE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF A GASTROENTERITIS OUT BREAK IN SUNSARI DISTRICT, NEPAL Sharma A K 1, Jha N 1, Ramachandran V G 1 Shariff
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Journal of Nepal Medical Association, 2002:41:383-387 DESCRIPTIVE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF A GASTROENTERITIS OUT BREAK IN SUNSARI DISTRICT, NEPAL Sharma A K 1, Jha N 1, Ramachandran V G 1 Shariff
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS AMONGST INTRAVENOUS DRUG ABUSERS SEEN AT THE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL, KUALA LUMPUR
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 42 No. 4 December 1987 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS AMONGST INTRAVENOUS DRUG ABUSERS SEEN AT THE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL, KUALA LUMPUR R. JAYAMALAR MBBS, MRCP. "N. PARASAKTHI MBBS, MSc. "S.D.
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 42 No. 4 December 1987 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS AMONGST INTRAVENOUS DRUG ABUSERS SEEN AT THE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL, KUALA LUMPUR R. JAYAMALAR MBBS, MRCP. "N. PARASAKTHI MBBS, MSc. "S.D.
A Study on Demographic & Radiological Profile of Children with Seizure Disorder Admitted in the Pediatric Emergency Ward of a Tertiary Care Centre
 Original Research A Study on Demographic & Radiological Profile of Children with Seizure Disorder Admitted in the Pediatric Emergency Ward of a Tertiary Care Centre Taraknath Ghosh*, Mrinalkanti Ghosh#,
Original Research A Study on Demographic & Radiological Profile of Children with Seizure Disorder Admitted in the Pediatric Emergency Ward of a Tertiary Care Centre Taraknath Ghosh*, Mrinalkanti Ghosh#,
THE INCREASING IMPORTANCE OF HEALTH CARE-ASSOCIATED INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS
 THE INCREASING IMPORTANCE OF HEALTH CARE-ASSOCIATED INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Javier López Díaz Instituto de Ciencias del Corazón (ICICOR) Hospital Clínico de Valladolid, Spain No conflict of interest Page
THE INCREASING IMPORTANCE OF HEALTH CARE-ASSOCIATED INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Javier López Díaz Instituto de Ciencias del Corazón (ICICOR) Hospital Clínico de Valladolid, Spain No conflict of interest Page
Cancer profile in B.P. Koirala institute of health sciences, Dharan, Nepal: A five-year study
 ISSN 2315-6864 Vol. 2(12) pp. 122-127 January 2013 Available online http//www.basicresearchjournals.org Copyright 2013 Basic Research Journal Full Length Research Paper Cancer profile in B.P. Koirala institute
ISSN 2315-6864 Vol. 2(12) pp. 122-127 January 2013 Available online http//www.basicresearchjournals.org Copyright 2013 Basic Research Journal Full Length Research Paper Cancer profile in B.P. Koirala institute
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Toyoda N, Chikwe J, Itagaki S, Gelijns AC, Adams DH, Egorova N. Trends in infective endocarditis in California and New York State, 1998-2013. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.4287
Supplementary Online Content Toyoda N, Chikwe J, Itagaki S, Gelijns AC, Adams DH, Egorova N. Trends in infective endocarditis in California and New York State, 1998-2013. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.4287
The changing landscape of infective endocarditis (IE)in congenital heart disease (CHD)
 The changing landscape of infective endocarditis (IE)in congenital heart disease (CHD) Rekwan Sittiwangkul,MD Department of Pediatrics. Chiang Mai University Hospital, 24 th March 2018 Infective endocarditis
The changing landscape of infective endocarditis (IE)in congenital heart disease (CHD) Rekwan Sittiwangkul,MD Department of Pediatrics. Chiang Mai University Hospital, 24 th March 2018 Infective endocarditis
Prognostic factors in infective endocarditis
 Boston University OpenBU Theses & Dissertations http://open.bu.edu Boston University Theses & Dissertations 2016 Prognostic factors in infective endocarditis Grzybinski, Sarah https://hdl.handle.net/2144/19176
Boston University OpenBU Theses & Dissertations http://open.bu.edu Boston University Theses & Dissertations 2016 Prognostic factors in infective endocarditis Grzybinski, Sarah https://hdl.handle.net/2144/19176
Shabib A. Alhadheri, M.D.
 Pediatrics in the Red Rocks Sedona, Arizona June 20-22, 2008 Shabib A. Alhadheri, M.D. Pediatric Cardiologist Disclosure I I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial
Pediatrics in the Red Rocks Sedona, Arizona June 20-22, 2008 Shabib A. Alhadheri, M.D. Pediatric Cardiologist Disclosure I I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial
NATIONAL HEART FOUNDATION HOSPITAL & RESEARCH INSTITUTE
 Welcome INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS: WHERE WE ARE AT 2005? DR MD HABIBUR RAHMAN FCPS(Medicine) NATIONAL HEART FOUNDATION HOSPITAL & RESEARCH INSTITUTE DEFINITION OF INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Infective endocarditis
Welcome INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS: WHERE WE ARE AT 2005? DR MD HABIBUR RAHMAN FCPS(Medicine) NATIONAL HEART FOUNDATION HOSPITAL & RESEARCH INSTITUTE DEFINITION OF INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Infective endocarditis
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Dayer MJ, Jones S, Prendergast B, et al. Incidence
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Dayer MJ, Jones S, Prendergast B, et al. Incidence
Infective Endocarditis Empirical therapy Antibiotic Guidelines. Contents
 Infective Endocarditis Empirical therapy Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Group Additional author(s): as above Authors Division: Division of Clinical
Infective Endocarditis Empirical therapy Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Group Additional author(s): as above Authors Division: Division of Clinical
Modifiers of the clinical course of infective endocarditis
 Modifiers of the clinical course of infective endocarditis Ulrika Snygg-Martin M.D., Ph.D. Infectious Diseases Clinic Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg, Sweden Infective endocarditis : modifiers
Modifiers of the clinical course of infective endocarditis Ulrika Snygg-Martin M.D., Ph.D. Infectious Diseases Clinic Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg, Sweden Infective endocarditis : modifiers
PRINCIPLES OF ENDOCARDITIS
 015 // Endocarditis CONTENTS 140 Principles of Endocarditis 141 Native Valve Endocarditis 143 Complications of Native Valve Endocarditis 145 Right Heart Endocarditis 145 Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis 146
015 // Endocarditis CONTENTS 140 Principles of Endocarditis 141 Native Valve Endocarditis 143 Complications of Native Valve Endocarditis 145 Right Heart Endocarditis 145 Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis 146
Spectrum of ear, nose and throat disorders among children reporting to the out-patient department of a tertiary care center, Nepal
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Chaudhari BK et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Sep;4(5):1125-1129 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Chaudhari BK et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Sep;4(5):1125-1129 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
Many Faces of Infective Endocarditis- Radiological Features of Extracardiac Complications.
 Many Faces of Infective Endocarditis- Radiological Features of Extracardiac Complications. Poster No.: C-0923 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Elsayed, M. Chiphang; Wigan/UK Keywords:
Many Faces of Infective Endocarditis- Radiological Features of Extracardiac Complications. Poster No.: C-0923 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Elsayed, M. Chiphang; Wigan/UK Keywords:
Pediatric Open Heart Surgery in Emerging Countries: A 10-year Experience in Mozambique and Cambodia
 Pediatric Open Heart Surgery in Emerging Countries: A 10-year Experience in Mozambique and Cambodia Dr Matthias LACHAUD Cardiopédiatrie, CHU Nantes 22 avril 2015 CONTEXT NGO La Chaine de l Espoir created
Pediatric Open Heart Surgery in Emerging Countries: A 10-year Experience in Mozambique and Cambodia Dr Matthias LACHAUD Cardiopédiatrie, CHU Nantes 22 avril 2015 CONTEXT NGO La Chaine de l Espoir created
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books. International authors and editors. Our authors are among the TOP 1%
 We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
Right-Sided Bacterial Endocarditis
 New Concepts in the Treatment of the Uncontrollable Infection Agustin Arbulu, M.D., Ali Kafi, M.D., Norman W. Thorns, M.D., and Robert F. Wilson, M.D. ABSTRACT Our experience with 25 patients with right-sided
New Concepts in the Treatment of the Uncontrollable Infection Agustin Arbulu, M.D., Ali Kafi, M.D., Norman W. Thorns, M.D., and Robert F. Wilson, M.D. ABSTRACT Our experience with 25 patients with right-sided
MY CONFLICTS OF INTEREST ARE
 MY CONFLICTS OF INTEREST ARE Consulting Spectranetics, St Jude Research Support Spectranetics Advisory Board Spectranetics S L I D E 1 When Devices Go Bad!! S L I D E 2 ICD Erosion Secondary to Pocket
MY CONFLICTS OF INTEREST ARE Consulting Spectranetics, St Jude Research Support Spectranetics Advisory Board Spectranetics S L I D E 1 When Devices Go Bad!! S L I D E 2 ICD Erosion Secondary to Pocket
April 16, 09:00-09:15 중앙대학교 윤신원
 April 16, 09:00-09:15 중앙대학교 윤신원 When to perform Echocardiography in IE? Vegetations?(pathologic Whatever the level hallmark) of suspicion Intracardiac abscess? Confirm or R/O at the Earliest opportunity.
April 16, 09:00-09:15 중앙대학교 윤신원 When to perform Echocardiography in IE? Vegetations?(pathologic Whatever the level hallmark) of suspicion Intracardiac abscess? Confirm or R/O at the Earliest opportunity.
Inflammatory Heart Disease
 Inflammatory Heart Disease Pericarditis inflammation of the pericardium Causes: may result from bacterial, viral or fungal infection can be assoc. w/ systemic diseases such as autoimmune disorders, rheumatic
Inflammatory Heart Disease Pericarditis inflammation of the pericardium Causes: may result from bacterial, viral or fungal infection can be assoc. w/ systemic diseases such as autoimmune disorders, rheumatic
ARTICLE. The Role of Transthoracic Echocardiography in the Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis in Children
 ARTICLE The Role of Transthoracic Echocardiography in the Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis in Children Ashraf M. Aly, MD, PhD; Pippa M. Simpson, PhD; Richard A. Humes, MD Background: Infective endocarditis
ARTICLE The Role of Transthoracic Echocardiography in the Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis in Children Ashraf M. Aly, MD, PhD; Pippa M. Simpson, PhD; Richard A. Humes, MD Background: Infective endocarditis
Endocarditis in the elderly
 Endocarditis in the elderly Gilbert Habib Département de Cardiologie - Timone Marseille Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 Endocarditis in the octogenarian Gilbert Habib Département de Cardiologie - Timone Marseille
Endocarditis in the elderly Gilbert Habib Département de Cardiologie - Timone Marseille Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 Endocarditis in the octogenarian Gilbert Habib Département de Cardiologie - Timone Marseille
An evaluation of the incidence of rheumatic and congenital heart disease among school children in central Nepal
 International Scholars Journals African Journal of Internal Medicine ISSN 2326-7283 Vol. 3 (10), pp. 328-331 November, 2015. Available online at www.internationalscholarsjournals.org International Scholars
International Scholars Journals African Journal of Internal Medicine ISSN 2326-7283 Vol. 3 (10), pp. 328-331 November, 2015. Available online at www.internationalscholarsjournals.org International Scholars
Cardiac Pathology & Rehabilitation
 Cardiac Pathology & Rehabilitation Which of the following best describes the physical activity performed in my leisure time? A. I perform vigorous physical activity 3X/week for 20 minutes each time B.
Cardiac Pathology & Rehabilitation Which of the following best describes the physical activity performed in my leisure time? A. I perform vigorous physical activity 3X/week for 20 minutes each time B.
A Nightmare. R Dulgheru, CHU Liege
 A Nightmare R Dulgheru, CHU Liege Faculty disclosure Raluca Dulgheru I have no financial relationships to disclose. MB, 57 years old male 18/03/2016 to the ER for altered mental status, First weight name
A Nightmare R Dulgheru, CHU Liege Faculty disclosure Raluca Dulgheru I have no financial relationships to disclose. MB, 57 years old male 18/03/2016 to the ER for altered mental status, First weight name
BMJ Open. For peer review only -
 Rheumatic Heart disease: Rationale and Design of a Population-Based Study Protocol of Prevalence and Cardiovascular Outcomes among Schoolchildren in Nepal Journal: BMJ Open Manuscript ID: bmjopen--000
Rheumatic Heart disease: Rationale and Design of a Population-Based Study Protocol of Prevalence and Cardiovascular Outcomes among Schoolchildren in Nepal Journal: BMJ Open Manuscript ID: bmjopen--000
Diagnostic strategy. Dr Pilar Tornos Hospital Vall d Hebron Barcelona
 Diagnostic strategy Dr Pilar Tornos Hospital Vall d Hebron Barcelona Faculty disclosure Pilar Tornos I disclose the following financial relationships: Paid speaker for Recordati, Edwards. Diagnosis of
Diagnostic strategy Dr Pilar Tornos Hospital Vall d Hebron Barcelona Faculty disclosure Pilar Tornos I disclose the following financial relationships: Paid speaker for Recordati, Edwards. Diagnosis of
The changing epidemiology and clinical features of infective endocarditis: A retrospective study of 196 episodes in a teaching hospital in China
 Zhu et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders (2017) 17:113 DOI 10.1186/s12872-017-0548-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The changing epidemiology and clinical features of infective endocarditis: A retrospective
Zhu et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders (2017) 17:113 DOI 10.1186/s12872-017-0548-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The changing epidemiology and clinical features of infective endocarditis: A retrospective
Echocardiographic Diagnosis of Rheumatic Heart Disease
 Echocardiographic Diagnosis of Rheumatic Heart Disease Nigel Wilson Paediatric Cardiologist Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Services Auckland City and Starship Hospitals Auckland, New Zealand Auckland
Echocardiographic Diagnosis of Rheumatic Heart Disease Nigel Wilson Paediatric Cardiologist Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Services Auckland City and Starship Hospitals Auckland, New Zealand Auckland
Challenging clinical situation
 Challenging clinical situation A young patient with prosthetic aortic valve endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France October 25 th 2014 Case report History of the disease Clinical
Challenging clinical situation A young patient with prosthetic aortic valve endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France October 25 th 2014 Case report History of the disease Clinical
Hospital-wide Impact of Mandatory Infectious Disease Consultation on Staphylococcus aureus Septicemia
 Hospital-wide Impact of Mandatory Infectious Disease Consultation on Staphylococcus aureus Septicemia Amanda Guth 1 Amy Slenker MD 1,2 1 Department of Infectious Diseases, Lehigh Valley Health Network
Hospital-wide Impact of Mandatory Infectious Disease Consultation on Staphylococcus aureus Septicemia Amanda Guth 1 Amy Slenker MD 1,2 1 Department of Infectious Diseases, Lehigh Valley Health Network
Acute febrile encephalopathy and its outcome among children in a tertiary care hospital
 International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Deepthi CHA et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2018 Mar;5(2):503-507 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Deepthi CHA et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2018 Mar;5(2):503-507 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
Sepsis and Infective Endocarditis
 Sepsis and Infective Endocarditis Michal Holub Department of Infectious Diseases First Faculty of Medicine Charles University in Prague and University Military Hospital Bacteremia and Sepsis bacteremia
Sepsis and Infective Endocarditis Michal Holub Department of Infectious Diseases First Faculty of Medicine Charles University in Prague and University Military Hospital Bacteremia and Sepsis bacteremia
An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for infective endocarditis
 REVIEW An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for infective endocarditis Albert W Chan MD FRCPC, Heather J Ross MD FRCPC AW Chan, HJ Ross. An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for
REVIEW An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for infective endocarditis Albert W Chan MD FRCPC, Heather J Ross MD FRCPC AW Chan, HJ Ross. An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for
Echocardiography after stroke - where to look
 Echocardiography after stroke - where to look Vuyisile T. Nkomo, MD,MPH, FACC, FASE Joint Cardiac Imaging Society of South Africa/Mayo Clinic Echocardiography Workshop 2017 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
Echocardiography after stroke - where to look Vuyisile T. Nkomo, MD,MPH, FACC, FASE Joint Cardiac Imaging Society of South Africa/Mayo Clinic Echocardiography Workshop 2017 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
CHIA MEDICAL TEAM RESOURCE PROTOCOLS: Rheumatic Heart Disease
 CHIA MEDICAL TEAM RESOURCE PROTOCOLS: Rheumatic Heart Disease It is not very common for children to get an acquired heart disease (meaning that they weren t born with it). In adults, acquired heart disease
CHIA MEDICAL TEAM RESOURCE PROTOCOLS: Rheumatic Heart Disease It is not very common for children to get an acquired heart disease (meaning that they weren t born with it). In adults, acquired heart disease
Infective endocarditis
 Infective endocarditis Today's lecture is about infective endocarditis, the Dr started the lecture by asking what are the most common causative agents of infective endocarditis? 1-Group A streptococci
Infective endocarditis Today's lecture is about infective endocarditis, the Dr started the lecture by asking what are the most common causative agents of infective endocarditis? 1-Group A streptococci
Fever of Unknown Origin in Pediatrics
 Fever of Unknown Origin in Sheldon L. Kaplan, MD Fever of Unknown Origin No standard definition in children Reasonable Definition: Unexplained fever (> 38 C or 100.4 F) persisting for > 2 weeks despite
Fever of Unknown Origin in Sheldon L. Kaplan, MD Fever of Unknown Origin No standard definition in children Reasonable Definition: Unexplained fever (> 38 C or 100.4 F) persisting for > 2 weeks despite
Research Article Seropositivity of Syphilis among Patients Visiting Gynaecology, STI and Dermatology Clinics
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC MICROBIOLOGY Research Article Seropositivity of Syphilis among Patients Visiting Gynaecology, STI and Dermatology Clinics Dhiraj Kumar Chaudhary 1 *, Shah Pradeep Kumar 2 and Khanal
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC MICROBIOLOGY Research Article Seropositivity of Syphilis among Patients Visiting Gynaecology, STI and Dermatology Clinics Dhiraj Kumar Chaudhary 1 *, Shah Pradeep Kumar 2 and Khanal
Hearts afire: Infective endocarditis
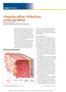 Hearts afire: Infective endocarditis By Kim McCarron, MS, CRNP Clinical Associate Professor Towson University Towson, Md. Editorial Advisory Board Member Nursing made Incredibly Easy! Picturing endocarditis
Hearts afire: Infective endocarditis By Kim McCarron, MS, CRNP Clinical Associate Professor Towson University Towson, Md. Editorial Advisory Board Member Nursing made Incredibly Easy! Picturing endocarditis
DELIVERY PRACTICES AMONG RAJBANSHI
 RESEARCHER I II JULY- DECEMBER 2013 63 DELIVERY PRACTICES AMONG RAJBANSHI Nawa Raj Subba, MPH Ministry of Health and Population khatiwadasom@yahoo.co.in Abstract This is a cross-sectional study with the
RESEARCHER I II JULY- DECEMBER 2013 63 DELIVERY PRACTICES AMONG RAJBANSHI Nawa Raj Subba, MPH Ministry of Health and Population khatiwadasom@yahoo.co.in Abstract This is a cross-sectional study with the
Safety, feasibility and efficacy of outpatient management of moderate pneumonia at Port Moresby General Hospital: a prospective study
 Safety, feasibility and efficacy of outpatient management of moderate pneumonia at Port Moresby General Hospital: a prospective study Dr Rose Morre Master of Medicine research project, 2017 Aim To trial
Safety, feasibility and efficacy of outpatient management of moderate pneumonia at Port Moresby General Hospital: a prospective study Dr Rose Morre Master of Medicine research project, 2017 Aim To trial
Surgical Indications of Infective Endocarditis in Children
 2016 Annual Spring Scientific Conference of the KSC April 15-16, 2016 Surgical Indications of Infective Endocarditis in Children Cheul Lee, MD Pediatric and Congenital Cardiac Surgery Seoul St. Mary s
2016 Annual Spring Scientific Conference of the KSC April 15-16, 2016 Surgical Indications of Infective Endocarditis in Children Cheul Lee, MD Pediatric and Congenital Cardiac Surgery Seoul St. Mary s
Renal Unit. Catheter Related Bacteraemia Guidelines
 Renal Unit Policy Manager Drew Henderson Policy Group Renal Unit Policy Established 21/01/2014 Policy Review Period/Expiry 21/01/2015 Last Updated 21/01/2014 This policy does apply to Medical/Dental Staff
Renal Unit Policy Manager Drew Henderson Policy Group Renal Unit Policy Established 21/01/2014 Policy Review Period/Expiry 21/01/2015 Last Updated 21/01/2014 This policy does apply to Medical/Dental Staff
Chiayi, Taiwan. Abstract
 DOI 10.6314/JIMT.201810_29(5).05 2018 29 309-316 Clinical Features and Risks Associated with In-hospital Mortality in Patients with Infective Endocarditis at A Medical Center in Central Taiwan from 2012
DOI 10.6314/JIMT.201810_29(5).05 2018 29 309-316 Clinical Features and Risks Associated with In-hospital Mortality in Patients with Infective Endocarditis at A Medical Center in Central Taiwan from 2012
Endocardite infectieuse
 Endocardite infectieuse 1. Raccourcir le traitement: jusqu où? 2. Proposer un traitement ambulatoire: à partir de quand? Endocardite infectieuse A B 90 P = 0.014 20 P = 0.0005 % infective endocarditis
Endocardite infectieuse 1. Raccourcir le traitement: jusqu où? 2. Proposer un traitement ambulatoire: à partir de quand? Endocardite infectieuse A B 90 P = 0.014 20 P = 0.0005 % infective endocarditis
Endodontic Microbiology
 Endodontic Microbiology The indigenous oral microflora may gain access to the pulp and impair its function along a number of different routes: Direct exposure of the pulp tissue i.e., following caries,
Endodontic Microbiology The indigenous oral microflora may gain access to the pulp and impair its function along a number of different routes: Direct exposure of the pulp tissue i.e., following caries,
Getting the Point of Injection Safety
 Getting the Point of Injection Safety Barbara Montana, MD, MPH, FACP Medical Director Communicable Disease Service Outbreak of Enterococcus faecalis endocarditis associated with an oral surgery practice
Getting the Point of Injection Safety Barbara Montana, MD, MPH, FACP Medical Director Communicable Disease Service Outbreak of Enterococcus faecalis endocarditis associated with an oral surgery practice
Joshua Budhu M.S, Dorian Wood B.S, Marvin Crawford M.D, Khuram Ashraf M.D, Frederick Doamekpor M.D, Olufunke Akinbobuyi M.D
 Accepted Manuscript Aerococcus Viridans Infectious Endocarditis Complicated by Splenic Infarction Joshua Budhu M.S, Dorian Wood B.S, Marvin Crawford M.D, Khuram Ashraf M.D, Frederick Doamekpor M.D, Olufunke
Accepted Manuscript Aerococcus Viridans Infectious Endocarditis Complicated by Splenic Infarction Joshua Budhu M.S, Dorian Wood B.S, Marvin Crawford M.D, Khuram Ashraf M.D, Frederick Doamekpor M.D, Olufunke
Evaluation of Knowledge, Attitude and Practice of Parents of Children with Cardiac Disease about Oral Health
 Original Article Evaluation of Knowledge, Attitude and Practice of Parents of Children with Cardiac Disease about Oral Health M. Fallahinejad Ghajari 1, S. Mojtahedzadeh 2, MJ. Kharazifard 3, B. Mahdavi
Original Article Evaluation of Knowledge, Attitude and Practice of Parents of Children with Cardiac Disease about Oral Health M. Fallahinejad Ghajari 1, S. Mojtahedzadeh 2, MJ. Kharazifard 3, B. Mahdavi
JUSTUS WARREN TASK FORCE MEETING DECEMBER 05, 2012
 SAMUEL TCHWENKO, MD, MPH Epidemiologist, Heart Disease & Stroke Prevention Branch Chronic Disease & Injury Section; Division of Public Health NC Department of Health & Human Services JUSTUS WARREN TASK
SAMUEL TCHWENKO, MD, MPH Epidemiologist, Heart Disease & Stroke Prevention Branch Chronic Disease & Injury Section; Division of Public Health NC Department of Health & Human Services JUSTUS WARREN TASK
Clinical, radiological and bacteriological profile of patients with community acquired pneumonia (CAP)
 Original Research Article Clinical, radiological and bacteriological profile of patients with community acquired pneumonia (CAP) R. S. Pushpa Kumari 1*, V. A. Vipula 2, Sonal Jain 3 1 Professor, Department
Original Research Article Clinical, radiological and bacteriological profile of patients with community acquired pneumonia (CAP) R. S. Pushpa Kumari 1*, V. A. Vipula 2, Sonal Jain 3 1 Professor, Department
THE SPECTRUM OF PAEDIATRIC CARDIAC DISEASE IN VANUATU. Dr Annette Garae (PGDCH)
 THE SPECTRUM OF PAEDIATRIC CARDIAC DISEASE IN VANUATU Dr Annette Garae (PGDCH) Introduction Heart disease in children can be either congenital or acquired. Congenital heart disease (CHD) accounts for nearly
THE SPECTRUM OF PAEDIATRIC CARDIAC DISEASE IN VANUATU Dr Annette Garae (PGDCH) Introduction Heart disease in children can be either congenital or acquired. Congenital heart disease (CHD) accounts for nearly
Prophylaxis against Endocarditis: A Brave New World
 Prophylaxis against Endocarditis: A Brave New World Ann Bolger MD FACC FAHA University of California, San Francisco Nothing to disclose PREVENTION OF INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS: GUIDELINES FROM THE AMERICAN
Prophylaxis against Endocarditis: A Brave New World Ann Bolger MD FACC FAHA University of California, San Francisco Nothing to disclose PREVENTION OF INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS: GUIDELINES FROM THE AMERICAN
General management of infective endocarditis
 General management of infective endocarditis Team approach in infective endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 The echolab «Heart Team" Infective Endocarditis
General management of infective endocarditis Team approach in infective endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 The echolab «Heart Team" Infective Endocarditis
Rheumatic heart disease
 Rheumatic heart disease What will we discuss today? Etiology and epidemiology of rheumatic heart disease Pathogenesis of rheumatic heart disease Morphological changes in rheumatic heart disease Clinical
Rheumatic heart disease What will we discuss today? Etiology and epidemiology of rheumatic heart disease Pathogenesis of rheumatic heart disease Morphological changes in rheumatic heart disease Clinical
Understanding the Parable Of Rheumatic Mitral Valve Repair. Ahmed Abdullah Jamjoom
 Understanding the Parable Of Rheumatic Mitral Valve Repair Ahmed Abdullah Jamjoom Table of Content Introduction Surgical options KFSH&RC Jeddah, Experience Conclusion A sore throat can lead to a broken
Understanding the Parable Of Rheumatic Mitral Valve Repair Ahmed Abdullah Jamjoom Table of Content Introduction Surgical options KFSH&RC Jeddah, Experience Conclusion A sore throat can lead to a broken
Clinico-demographic profile among female with alcohol related problems in the eastern part of Nepal
 Original Article Joshi et.al. among female with alcohol related problems in the eastern part of Nepal RG Joshi 1, P Koirala 2, DR Shakya 3, PM Shyangwa 4 Department of Psychiatry, B.P. Koirala Institute
Original Article Joshi et.al. among female with alcohol related problems in the eastern part of Nepal RG Joshi 1, P Koirala 2, DR Shakya 3, PM Shyangwa 4 Department of Psychiatry, B.P. Koirala Institute
Peripartum management of Rheumatic Heart Disease
 Peripartum management of Rheumatic Heart Disease Dr James Sartain Director of Anaesthesia & Perioperative Medicine Cairns & Hinterland Hospital & Health Service Talk outline Why (still) talk about RHD
Peripartum management of Rheumatic Heart Disease Dr James Sartain Director of Anaesthesia & Perioperative Medicine Cairns & Hinterland Hospital & Health Service Talk outline Why (still) talk about RHD
A Predictable Outcome of a Preventable Disease. Sanjay Kamboj, MD; Shaminder Gupta, MD; Glenn P. Kelley, MD; Fred Helmcke, MD; and Fred A.
 Clinical Case of the Month A Predictable Outcome of a Preventable Disease Sanjay Kamboj, MD; Shaminder Gupta, MD; Glenn P. Kelley, MD; Fred Helmcke, MD; and Fred A. Lopez, MD Infective endocarditis is
Clinical Case of the Month A Predictable Outcome of a Preventable Disease Sanjay Kamboj, MD; Shaminder Gupta, MD; Glenn P. Kelley, MD; Fred Helmcke, MD; and Fred A. Lopez, MD Infective endocarditis is
Epidemiological and bacteriological profile of burn patients at Nepal Medical College Teaching Hospital
 Original Article Nepal Med Coll J 2008; 10(4): 233-237 Epidemiological and bacteriological profile of burn patients at Nepal Medical College Teaching Hospital PR Chalise, S Shrestha, K Sherpa, U Nepal,
Original Article Nepal Med Coll J 2008; 10(4): 233-237 Epidemiological and bacteriological profile of burn patients at Nepal Medical College Teaching Hospital PR Chalise, S Shrestha, K Sherpa, U Nepal,
POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00553
 MCC-004 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00553 Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-004 : COMMON CARDIO-VASCULAR DISEASES - II Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note : There will
MCC-004 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00553 Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-004 : COMMON CARDIO-VASCULAR DISEASES - II Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note : There will
, David Stultz, MD.
 http://www.dilbert.com Infective Endocarditis David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 4 December 8, 2004 Handouts available in PDF format at www.drstultz.com Topics to be covered Epidemiology Microbiology
http://www.dilbert.com Infective Endocarditis David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 4 December 8, 2004 Handouts available in PDF format at www.drstultz.com Topics to be covered Epidemiology Microbiology
2:1 Block with Wenckebach Mechanism in Children Due to Different Etiologies F Laloğlu 1, N Ceviz 1, H Keskin 2, H Olgun 1 ABSTRACT
 2:1 Block with Wenckebach Mechanism in Children Due to Different Etiologies F Laloğlu 1, N Ceviz 1, H Keskin 2, H Olgun 1 ABSTRACT Objective: In children 2:1 Atrioventricular Block (AVB) with Wenckebach
2:1 Block with Wenckebach Mechanism in Children Due to Different Etiologies F Laloğlu 1, N Ceviz 1, H Keskin 2, H Olgun 1 ABSTRACT Objective: In children 2:1 Atrioventricular Block (AVB) with Wenckebach
Surgical Outcomes of Infective Endocarditis among Intravenous Drug Abusers: Results from Two Large Academic Centers
 Surgical Outcomes of Infective Endocarditis among Intravenous Drug Abusers: Results from Two Large Academic Centers Joon Bum Kim 1,3, Julius I. Ejiofor 2, Maroun Yammine 2, Sandra B. Nelson 1, Arthur Y.
Surgical Outcomes of Infective Endocarditis among Intravenous Drug Abusers: Results from Two Large Academic Centers Joon Bum Kim 1,3, Julius I. Ejiofor 2, Maroun Yammine 2, Sandra B. Nelson 1, Arthur Y.
Infective Endocarditis
 Definition Infective Endocarditis Pattaya Riengchan M.D. MAR 16, 2017 Infection of endocardial surface of the heart and implies the physical presence microorganisms in the lesion Heart valves are most
Definition Infective Endocarditis Pattaya Riengchan M.D. MAR 16, 2017 Infection of endocardial surface of the heart and implies the physical presence microorganisms in the lesion Heart valves are most
What s new in Infectious Diseases. Petronella Adomako, MD Infectious Disease Specialist Mckay-Dee Hospital
 What s new in Infectious Diseases Petronella Adomako, MD Infectious Disease Specialist Mckay-Dee Hospital None Disclosures Objectives New information in infectious diseases. New diseases and outbreaks.
What s new in Infectious Diseases Petronella Adomako, MD Infectious Disease Specialist Mckay-Dee Hospital None Disclosures Objectives New information in infectious diseases. New diseases and outbreaks.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. A STUDY ON CLINICAL, LABORATORY PROFILE AND OUTCOME OF DENGUE FEVER Vanamali D.R 1, L. Venugopal 2, P. Yeshwanth 3, Dilip Rampure 4
 A STUDY ON CLINICAL, LABORATORY PROFILE AND OUTCOME OF DENGUE FEVER Vanamali D.R 1, L. Venugopal 2, P. Yeshwanth 3, Dilip Rampure 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Vanamali D.R, L. Venugopal, P. Yeshwanth, DilipRampure.
A STUDY ON CLINICAL, LABORATORY PROFILE AND OUTCOME OF DENGUE FEVER Vanamali D.R 1, L. Venugopal 2, P. Yeshwanth 3, Dilip Rampure 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Vanamali D.R, L. Venugopal, P. Yeshwanth, DilipRampure.
DOPPLER ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IMAGING AS A USEFUL TOOL IN DETECTING RHEUMATIC SILENT CARDITIS Bindu A 1, Santhosh Jose 2, Soumya Jose 3
 DOPPLER ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IMAGING AS A USEFUL TOOL IN DETECTING RHEUMATIC SILENT CARDITIS Bindu A 1, Santhosh Jose 2, Soumya Jose 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Bindu A, Santhosh Jose, Soumya Jose. Doppler
DOPPLER ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IMAGING AS A USEFUL TOOL IN DETECTING RHEUMATIC SILENT CARDITIS Bindu A 1, Santhosh Jose 2, Soumya Jose 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Bindu A, Santhosh Jose, Soumya Jose. Doppler
Disease Spectrum and Mortality in Hospitalized Children of Southern Iran
 Short Communication Iran J Pediatr Dec 2007; Vol 17 ( No 3), Pp:359-363 Disease Spectrum and Mortality in Hospitalized Children of Southern Iran Khadijehsadat Najib 1, MD; Ebrahim Fallahzadeh *2, MD; Mohammad
Short Communication Iran J Pediatr Dec 2007; Vol 17 ( No 3), Pp:359-363 Disease Spectrum and Mortality in Hospitalized Children of Southern Iran Khadijehsadat Najib 1, MD; Ebrahim Fallahzadeh *2, MD; Mohammad
ECU, Center for Health Services Research and Development, 2001
 Map 1.1 Progress Towards Heart Disease Mortality Objective Northampton Gates Currituck Camden Pasquotank Halifax Hertford Perquimans Nash Bertie Chowan Edgecombe Martin Washington Tyrrell Dare Wilson Johnston
Map 1.1 Progress Towards Heart Disease Mortality Objective Northampton Gates Currituck Camden Pasquotank Halifax Hertford Perquimans Nash Bertie Chowan Edgecombe Martin Washington Tyrrell Dare Wilson Johnston
MI Acute occlusion of the proximal left anterior descending (LAD) artery is the cause of 40% to 50% of all MIs. *
 MI *33% -50% die before hospital lethal arrhythmia Sudden Cardiac Death. * Arrhythmias are caused by electrical abnormalities of the ischemic myocardium and conduction system. *Acute occlusion of the proximal
MI *33% -50% die before hospital lethal arrhythmia Sudden Cardiac Death. * Arrhythmias are caused by electrical abnormalities of the ischemic myocardium and conduction system. *Acute occlusion of the proximal
