Performanceofanimplantableautomatic atrial fibrillation detection device: impact of software adjustments and relevance of manual episode analysis
|
|
|
- Cory Higgins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Europace (2011) 13, doi: /europace/euq511 CLINICAL RESEARCH Atrial Fibrillation Performanceofanimplantableautomatic atrial fibrillation detection device: impact of software adjustments and relevance of manual episode analysis Charlotte Eitel, Daniela Husser, Gerhard Hindricks, Manuela Frühauf, Sebastian Hilbert, Arash Arya, Thomas Gaspar, Ulrike Wetzel, Andreas Bollmann, and Christopher Piorkowski* Heart Center, Department of Electrophysiology, University of Leipzig, Strümpellstrasse 39, Leipzig, Germany Received 14 August 2010; accepted after revision 14 December 2010; online publish-ahead-of-print 16 February 2011 Aims Implantable loop recorders (ILRs) with specific atrial fibrillation () detection algorithms (ILR-) have been developed for continuous monitoring. We sought to analyse the clinical value of a new monitoring device and to compare it to serial 7-day Holter.... Methods Sixty-four consecutive patients suffering from paroxysmal were included in this prospective analysis and received and results an ILR-. Manual electrogram analysis was performed for each automatically detected episode and each was categorized into one of three possible diagnoses: no, definite, and possible (non-diagnostic). Analysis was performed separately before and after a software upgrade that was introduced during the course of the study. A subgroup of patients (51 of 64) underwent catheter ablation with subsequent serial 7-day Holter in comparison with the ILR-. A total of 333 interrogations were performed (203 before and 130 after software upgrade). The number of patients with misdetection was significantly reduced from 72 to 44% following the software upgrade (P ¼ 0.001). The number of patients with non-diagnostic interrogations went from 38 to 16% (P ¼ 0.001). Compared with serial 7-day Holter, the ILR- had a tendency to detect a higher number of patients with recurrences (31 vs. 24%; P ¼ 0.125).... Conclusions The rate of detection on ILR- may be higher compared with standard monitoring. However, false-positive recordings hamper the clinical value. Developements in device technology and device handling are necessary to minimize non-diagnostic interrogations Keywords Atrial fibrillation Implantable loop recorder ECG monitoring Introduction Atrial fibrillation () is the most commonly diagnosed arrhythmia, resulting in significant morbidity and cost to the healthcare system. 1 Asymptomatic or silent arrhythmia is a frequent condition in patients suffering from. 1,2 It is observed in a substantial number of patients suffering from cryptogenic stroke. 3 Due to the inability to reliably detect asymptomatic recurrences, These authors contributed equally. *Corresponding author. Tel: ; fax: , piorkowskic@yahoo.de Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. & The Author For permissions please journals.permissions@oup.com. The online version of this article has been published under an open access model. Users are entitled to use, reproduce, disseminate, or display the open access version of this article for non-commercial purposes provided that the original authorship is properly and fully attributed; the Journal, Learned Society and Oxford University Press are attributed as the original place of publication with correct citation details given; if an article is subsequently reproduced or disseminated not in its entirety but only in part or as a derivative work this must be clearly indicated. For commercial re-use, please contact journals.permissions@oup.com.
2 Implantable device for monitoring 481 clinical and scientific uncertainty remains for fundamental treatment decisions such as rate vs. rhythm control or the need for oral anticoagulation. 4 Several methods have been described to improve rhythm monitoring in patients. 3,5 7 In general, these data have shown an increased detection rate with longer monitoring durations. 6,8 However, even with serial 7-day Holter electrocardiograms (ECGs) or daily plus symptom-activated transtelephonic ECG monitoring, it is estimated to detect only 70% of all recurring episodes. 9 To provide continuous rhythm monitoring, implantable leadless loop recorders with specific detection algorithms (ILR-) have been developed. In patients with paroxysmal, the XPECT trial evaluated the detection performance of an ILR- (Reveal XT) against a specialized surface ECG Holter device over a short monitoring period of 46 h. The results of the study indicated a high sensitivity of 96.1% for detecting. However, specificity (85.4%) was limited by falsely stored episodes in 15% of the patients. 10 The purpose of this study was to analyse the performance of the implantable continuous detection device in a clinical setting before and after introduction of a software upgrade with monitoring periods covering several months and to compare it with standard monitoring based on serial 7-day Holter. Methods Patient population and study design Between September 2007 and February 2008, 64 consecutive patients (69% male, mean age years) suffering from paroxysmal were included into this prospective analysis. Thirteen patients (20%) suffered from lone and 45 (70%) from arterial hypertension with a mean left atrial diameter of mm and a left ventricular ejection fraction of %. All of the patients had received an ILR- (Medtronic Reveal XT TM model 9529) during the course of the XPECT study. 10 After termination of the XPECT study, the patients were included into routine clinical follow-up. Our data represent an analysis of the ILR- performance during a longer and clinically relevant monitoring period of an average of 57 days (75% range: days). Due to a high amount of misdetection, mostly caused by oversensing of myopotentials and artefacts, a software update (see below) was introduced in June 2008 during the course of the study. Interrogations were analysed with the use of manual EGM analysis (see below) and results before and after software update were compared. During the course of the study, a subgroup of patients (n ¼ 51, 79%) underwent circumferential pulmonary vein isolation and was followed with serial (post-ablation, after 3 months, after 6 months, after 12 months) 7-day Holter recordings (Lifecard CF, DelmarReynolds Medical Inc, Irvine, CA, USA) in addition to the ILR- interrogations. The physician performing the Holter analysis was blinded with regard to patient name, date of ablation, and the patient s symptom log. Based on the ILR- detection algorithm (see below), recurrence was defined as a documented episode lasting longer than 2 min to allow for comparison between ILR- and 7-day Holter monitoring results. Implant procedure The ILR- was implanted in a left parasternal position. Optimal orientation of the device axis was determined prior to implantation. For that, the vector check tool was used (Medtronic, Minneapolis, MN, USA), which allows testing for the highest R-wave amplitude obtained from a single lead recording in different locations/orientations on the body surface. During implantation, the device was pushed into the subcutaneous tissue without prior pocket preparation, in order to assure close tissue-device contact and to prevent mobility of the device within the pocket. The device was fixated within the pocket. Software and device description The detection algorithm operates through an assessment on the regularity of RR intervals (Lorenz plot) within a 2 min time window. 11 Once is diagnosed, it is stored as a sustained episode within the automatic episode counter, showing date and time of occurrence as well as episode length. After detection, the device is capable of storing 2 min of each episode as electrogram (EGM) with a total storage capacity of 49.5 min. Once storage is exhausted, older EGMs are overwritten with newer ones. However, the automatic episode counter is not overwritten until the next interrogation. The mentioned upgraded software aims at a reduction of noiseinduced false-positive episodes by reducing the noise rejection threshold from 60 to 5 s. In this way, episodes containing.5 s of noise in a 2 min window are not considered for classification. As additional device tools, an external assistant box (Medtronic Reveal XT TM patient assistant model 9539) allows patients to tag and store symptomatic episodes by activating a recording button; furthermore, the patient can check whether EGM storage capacity is exhausted by activating an interrogation button. Nevertheless, this alarm was not activated in our patients. In addition to detection, the device also detects and classifies other types of arrhythmias, e.g. asystole, bradycardia, and tachycardia. However, storage of non- episodes was disabled unless individual patient history warranted detection of other arrhythmias. In these cases, storage of those episodes was permitted; however, only episodes were analysed. Interrogations and follow-up All patients were integrated in the routine follow-up within the pacemaker/implantable cardiac defibrillator clinic with quarterly visits and additional visits upon request. Interrogation of the ILR- is similar to pacemaker interrogations and requires the Medtronic programmer (Medtronic CareLink programmer model 2090, software model SW007). The standard setting for R-wave sensing was 0.05 mv. Depending on the occurrence of under- or oversensing, it was adjusted during follow-up accordingly. From a clinical perspective, each interrogation was classified according to the diagnosis derived from automatic detection and manual analysis of all stored EGMs (Figure 1A and B). Automatically stored episodes were judged by an experienced physician as adequate if there was an irregular RR pattern in the absence of P-waves throughout the EGM recording. With that approach, an interrogation could lead to the diagnosis: (i) no ; (ii) definite ; (iii) possible (non-diagnostic interrogation) (Table 1). The diagnosis of no was made in cases where the automatic counter was zero. Statistics The data were tested for normal (Gaussian) distribution using Kolmogoroff Smirnov test. Normally distributed continuous variables are presented as mean + standard deviation (SD). In case of a non-gaussian distribution, median and quartiles are given. Categorical variables are expressed as number and percentage of patients and interrogations, respectively.
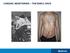
3 482 C. Eitel et al. Figure 1 (A) Device stored electrogram with correctly classified atrial fibrillation. (B) Device stored electrogram with misclassified (red arrows) due to myopotentials (upper panel) and PAC (lower panel). Table 1 Definition of clinical diagnosis of interrogations based on manual electrogram analysis Automatic episode counter no episodes limited episodes multiple episodes (EGM not for all (EGM for all episodes) episodes)... Manual EGM analysis Only SR With With Only SR Diagnosis No No Possible (non-diagnostic) Differences between continuous normally distributed data before and after the software upgrade were tested for statistical significance using the paired t-test. In case of continuous data with a non-gaussian distribution the Wilcoxon test was used. Differences between categorical data before and after the software upgrade as well as the rate of detection on ILR- and on 7-day Holter were tested for statistical significance using the McNemar test. All analyses were performed using SPSS for Windows, Release A P-value of,0.05 was considered statistically significant. Results No complications occurred during or after implantation, no persistent discomfort was reported and no explanations of the device were necessary during follow-up. Among the 64 patients, a total of 333 interrogations were performed. Of those, 203 interrogations occurred before and 130 interrogations occurred after the software upgrade. Results of manual interrogation analysis are displayed separately for interrogations before and after the software upgrade in Figure 2A and B. Details on distribution of interrogations, number of episodes, length of follow-up period, mean R-wave amplitude, length of clinical follow-up, and amount of storage overflow are summarized in Table 2. Non-diagnostic interrogations Interrogations with automatically stored episodes containing only EGMs with sinus rhythm and artefacts leading to
4 Implantable device for monitoring 483 A Interrogations before update in 64 patients n = 203 Automatic episode counter no episodes n = 32 limited episodes, EGM for all episodes n = 70 multiple episodes, EGM not for all episodes n = 101 Manual EGM analysis no artefacts n = 32 (16%) n = 23 (11%), and SR n = 47 (23%), and SR n = 57 (28%) n = 44 (22%) Diagnosis No No Possible B Interrogations after update in 64 patients n = 130 Automatic episode counter no episodes n = 40 limited episodes, EGM for all episodes n = 48 multiple episodes, EGM not for all episodes n = 42 Manual EGM analysis no artefacts n = 40 (31%) n = 24 (19%), and SR n = 24 (19%), and SR n = 29 (22%) n = 13 (10%) Diagnosis No No Possible Figure 2 (A and B) Clinical classification of interrogations before and after software upgrade. misdetection could be found in 22% of interrogations prior and 10% after the software upgrade, respectively (Figure 2A and B). For these interrogations, however, it is unclear whether was present among the remaining automatically stored episodes without available EGM. Causes of atrial fibrillation misdetection Before and after software upgrade, reasons for misdetection were the occurrence of myopotentials/noise in 70/203 interrogations (35%) vs. 28/130 (22%), T-wave oversensing in 3/203 (1.5%) vs. 1/130 (1%), frequent premature ventricular or atrial complexes (PVCs/PACs) in 28/203 (15%) vs. 26/130 (20%), as well as R-wave undersensing in 9/203 (4%) vs. 7/130 (5%), respectively. Individual patient analysis before and after software upgrade The length of follow-up intervals between consecutive interrogations did not vary before and after software upgrade [49 (23; 98) vs. 68 (25; 98) days; P ¼ 0.276]. However, the length of total clinical follow-up before and after software upgrade was significantly longer prior software upgrade ( days prior upgrade vs after upgrade; P, 0.001). Table 2 Characteristics of interrogations before and after software upgrade Before After P-value software software upgrade upgrade... Total number of interrogations, n Number of interrogations ,0.001 per patient a Number of episodes, n b 27 (3; 125) 5 (1; 20),0.001 R-wave amplitude, mv b 0.7 (0.4; 0.8) 0.7 (0.5; 0.9) c Monitoring period, days b 49 (23; 98) 68 (25; 98) d Length of clinical follow-up a ,0.001 e Interrogations with storage overflow, n (%) 101 (50%) 42 (32%) a Data given as mean and standard deviation. b Data given as median and quartiles. c Monitoring interval between two subsequent ILR- interrogations. d Length of clinical follow-up was defined as total monitoring time before and after software upgrade. e Interrogations with storage overflow were defined as interrogations including automatic episodes without available EGM.
5 484 C. Eitel et al. Overall, introduction of the new software upgrade significantly reduced the number of patients with any misdetection of [46/64 (72%) vs. 28/64 (44%); P ¼ 0.001]. This reduction was mainly attributable to a significantly lower number of patients having misdetection due to myopotentials or noise [32/64 (50%) vs. 15/64 (23%); P, 0.001]. On the other hand, the occurrence of R-wave undersensing [6/64 (9%) vs. 5/64 (8%); P ¼ 1.0], T-wave oversensing [3/64 (5%) vs. 1/64 (2%); P ¼ 0.625], misdetection of PVC [3/64 (5%) vs. 1/64 (2%), P ¼ 0.625], and PAC [20/64 (31%) vs. 14/64 (22%), P ¼ 0.238] were not significantly improved with the introduction of the software upgrade. The number of patients with clinically non-diagnostic interrogations was significantly reduced [24/64 (38%) vs. 10/64 (16%); P ¼ 0.001] (Figure 3). A detailed evaluation of the 10 patients with nondiagnostic interrogations despite the software upgrade revealed the following reasons of frequent misdetection: myopotential oversensing (n ¼ 7), frequent PACs (n ¼ 5), R-wave undersensing (n ¼ 3). Simultaneous over- and undersensing occurred in three patients, posing a challenge for the adjustment of R-wave sensing. Atrial fibrillation detection on implantable loop recorder compared with 7-day Holter Out of 64 patients, 51 (80%) underwent circumferential PV isolation. With serial 7-day Holter monitoring, 12 of 51 (24%) patients had documented episodes of recurrences. In all of these patients, was correctly identified by the ILR-. In four additional patients, recurrences were detected by the ILR- which was not seen on 7-day Holter. Therefore, the rate of documented recurrence had a tendency to be higher on ILR-, but failed to reach statistical significance [16/51 (31%) vs. 12/51 (24%); P ¼ 0.125]. Discussion Main findings This is the first study to evaluate the implantable continuous detection device in long-term clinical routine based on a manual Number of patients (%) Patients before software upgrade Patients after software upgrade P<0.001 P=1.0 P<0.001 No Possible nondiagnostic n = Figure 3 Clinical classification of patients before and after the software upgrade. analysis of automatically stored episodes. Compared with highquality standard measures of monitoring such as serial 7-day Holter, the device increased the total number of patients with detection. However, we also found a high rate of false-positive recordings mainly caused by oversensing of myopotentials and noise. Together with an only limited EGM storage capacity that led to non-diagnostic interrogations in 38% of the patients. Following software upgrade, the specificity of the device improved with non-diagnostic interrogations in 16% of the patients. Role of implantable loop recorders in atrial fibrillation detection Implantable loop recorders have become an important diagnostic tool for the patient with unexplained syncope and are well established for this purpose. 12 In how far this monitoring strategy is useful for rhythm follow-up in patients with remains to be evaluated. During an initial validation study, a high sensitivity of 96.1% for detecting was found, while specificity was limited by falsely stored episodes in 15% of the patients. 10 Recently, a second study has compared the detection rate obtained from ILR- against three-monthly 24-h Holter in patients after surgical ablation of over a 1-year follow-up. Exclusive usage of automatically detected episodes obtained with the old detection algorithm prior to the software upgrade together with the lack of any information on manual EGM analysis and the problem of misdetection limits the understanding on the true value of the ILR- for long-term continuous monitoring in this study. 13 Our study is the first one using the ILR- as long-term continuous monitoring device in clinical routine and validating its diagnostic accuracy according to manual analysis of all automatically stored episodes. Some key findings need to be emphasized. The detection rate of the device tended to be higher compared with standard serial 7-day Holter ECG recordings. However, due to oversensing of myopotentials and subsequent misdetection, specificity is lacking. Similar results have been shown for other device-based rhythm monitoring, e.g. pacemaker or implantable defibrillators. In prospective randomized trials, the relative portion of misclassified episodes by an implanted dual-chamber pacemaker is 26%. 14 Oversensing of myopotentials, mostly from the pectoral muscle, was found to be the leading cause for false-positive annotation in our study. In order to minimize myopotential detection, a new and improved software algorithm was released during the course of the study. Our results show that using the updated algorithm the number of patients with non-diagnostic interrogations could be reduced from 38 to 16%. However, considering the invasive nature of the follow-up tool, this rate of non-diagnostic data sets has to be improved. Measurements to reduce non-diagnostic interrogations Besides further software developments, several measures can be discussed to reduce the number of non-diagnostic interrogations. To recognize false-positive episodes, all automatically detected
6 Implantable device for monitoring 485 episodes need to be confirmed on manual EGM analysis. Therefore, it is necessary to prevent EGM storage overcrowding. That can be achieved with two methods. First, the patient assistant box has the ability to indicate full EGM storage through an alarm signal which should initiate a visit to the device clinic in order to retrieve and analyse all available EGMs. That in return would lead to individualized follow-up intervals. Secondly, remote monitoring techniques like the CareLink network allow patient initiated sending of diagnostic and monitoring information from home. This provides the possibility of regularly relieving the EGM storage and could enhance manual EGM analysis for all automatically stored episodes. Prolongation of the detection period for sustained may be a different way to prevent episodes of misdetection, because false-positive episodes are rather short. Programming options of the ILR- include detection periods for sustained of 6 min and more. Clearly, shorter episodes will then be unrecognized. The clinical and scientific impact of such a change in definition of sustained remains to be evaluated. The impact of the above-discussed measures on the accuracy of the ILR- in the clinical setting of continuous monitoring has to be assessed within further studies. Study limitations This study is an observational study reporting the first experiences with an implantable leadless continuous monitoring device for in a clinical setting. It needs to be emphasized, however, that patients follow-up intervals were routinely integrated into the pacemaker clinic, i.e. follow-up intervals were not individualized for each patient since they were not based on patients self assessment of remaining EGM storage capacity with the patient assistant. The CareLink system facilitating remote device interrogation with the aim of reducing storage overflow was also not available in our patients. Nevertheless, the importance of manual episode analysis and the problem of storage exhaustion due to false-positive episodes first arose from our experience with the device. Variations in length of clinical follow-up and in frequencies of interrogations before and after software upgrade as well as performance of ablation during the course of the study might have impacted the results of the study. Although the number of non-diagnostic interrogations was reduced after software upgrade, the lack of a gold standard for continuous monitoring over such extended follow-up periods prevents a conclusive assessment of diagnostic accuracy with respect to positive and negative predictive values. Therefore, decreasing the number or proportion of stored episodes with noise does not necessarily imply an actual improvement in detection accuracy from the users perspective. Although we could show that this device is valid, its relevance for clinical decision-making in patients with remains to be seen. As this device is mainly used for detection, other atrial and ventricular arrhythmias have not been evaluated in this study. Conclusion The ILR- is a first and promising tool for continuous monitoring. To incorporate this device into routine patient care, developments in device technology and device handling are still necessary to minimize the number of non-diagnostic interrogations. Conflict of interest: none declared. Funding D.H. was supported by the Volkswagen Foundation, Germany, and research grants (HU 1679/1-1, DFG, and NBL Formel.1-109, University Leipzig). Funding to pay the Open Access publication charges for this article was provided by the Heart Center Leipzig. References 1. Israel CW, Gronefeld G, Ehrlich JR, Li YG, Hohnloser SH. Long-term risk of recurrent atrial fibrillation as documented by an implantable monitoring device: implications for optimal patient care. J Am Coll Cardiol 2004;43: Savelieva I, Camm AJ. Clinical relevance of silent atrial fibrillation: prevalence, prognosis, quality of life, and management. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 2000;4: Tayal AH, Tian M, Kelly KM, Jones SC, Wright DG, Singh D et al. Atrial fibrillation detected by mobile cardiac outpatient telemetry in cryptogenic TIA or stroke. Neurology 2008;71: Brignole M, Vardas P, Hoffman E, Huikuri H, Moya A, Ricci R et al. Indications for the use of diagnostic implantable and external ECG loop recorders. Europace 2009;11: Go AS, Hylek EM, Phillips KA, Chang Y, Henault LE, Selby JV et al. Prevalence of diagnosed atrial fibrillation in adults: national implications for rhythm management and stroke prevention: the AnTicoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation (ATRIA) Study. JAMA 2001;285: Hindricks G, Piorkowski C, Tanner H, Kobza R, Gerds-Li JH, Carbucicchio C et al. Perception of atrial fibrillation before and after radiofrequency catheter ablation: relevance of asymptomatic arrhythmia recurrence. Circulation 2005;112: Kottkamp H, Tanner H, Kobza R, Schirdewahn P, Dorszewski A, Gerds-Li JH et al. Time courses and quantitative analysis of atrial fibrillation episode number and duration after circular plus linear left atrial lesions: trigger elimination or substrate modification: early or delayed cure?. J Am Coll Cardiol 2004;44: Dagres N, Kottkamp H, Piorkowski C, Weis S, Arya A, Sommer P et al. Influence of the duration of Holter monitoring on the detection of arrhythmia recurrences after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation Implications for patient follow-up. Int J Cardiol 2010;139: Kirchhof P, Auricchio A, Bax J, Crijns H, Camm J, Diener HC et al. Outcome parameters for trials in atrial fibrillation: recommendations from a consensus conference organized by the German Atrial Fibrillation Competence NETwork and the European Heart Rhythm Association. Europace 2007;9: Hindricks G, Pokushalov E, Urban L, Taborsky M, Kuck KH, Lebedev D et al. Performance of a new implantable cardiac monitor in detecting and quantifying atrial fibrillation results of the XPECT trial. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2010;3: Sarkar S, Ritscher D, Mehra R. A detector for a chronic implantable atrial tachyarrhythmia monitor. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 2008;55: Kusumoto F, Goldschlager N. Implantable cardiac arrhythmia devices Part II: implantable cardioverter defibrillators and implantable loop recorders. Clin Cardiol 2006;29: Hanke T, Charitos EI, Stierle U, Karluss A, Kraatz E, Graf B et al. Twenty-four-hour holter monitor follow-up does not provide accurate heart rhythm status after surgical atrial fibrillation ablation therapy: up to 12 months experience with a novel permanently implantable heart rhythm monitor device. Circulation 2009;15:S Schmidt B, Asbach S, Schweika O, Zehender M, Bode C, Faber TS. Atrial fibrillation reduces the atrial impedance amplitude during cardiac cycle: a novel detection algorithm to improve recognition of atrial fibrillation in pacemaker patients. Europace 2007;9:812 6.
AF monitoring and stroke: XPECT & REVEAL LINQ. Helmut Pürerfellner, Linz, Austria
 AF monitoring and stroke: XPECT & REVEAL LINQ Helmut Pürerfellner, Linz, Austria 2 Medtronic Confidential 3 Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2010;3:141-47 Reveal XT versus LINQ 5 Parameter Reveal XT Reveal
AF monitoring and stroke: XPECT & REVEAL LINQ Helmut Pürerfellner, Linz, Austria 2 Medtronic Confidential 3 Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2010;3:141-47 Reveal XT versus LINQ 5 Parameter Reveal XT Reveal
Implantable Cardiac Monitors for Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Detection: Ready for Routine Use?
 Implantable Cardiac Monitors for Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Detection: Ready for Routine Use? Helmut Pürerfellner, MD, Assoc. Prof. Saint Elisabeth s Sisters Hospital Academic Teaching Center Linz/Austria
Implantable Cardiac Monitors for Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Detection: Ready for Routine Use? Helmut Pürerfellner, MD, Assoc. Prof. Saint Elisabeth s Sisters Hospital Academic Teaching Center Linz/Austria
Arrhythmia/Electrophysiology
 Arrhythmia/Electrophysiology Perception of Atrial Fibrillation Before and After Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation Relevance of Asymptomatic Arrhythmia Recurrence Gerhard Hindricks, MD; Christopher Piorkowski,
Arrhythmia/Electrophysiology Perception of Atrial Fibrillation Before and After Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation Relevance of Asymptomatic Arrhythmia Recurrence Gerhard Hindricks, MD; Christopher Piorkowski,
Automatic Identification of Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Lead Problems Using Intracardiac Electrograms
 Automatic Identification of Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Lead Problems Using Intracardiac Electrograms BD Gunderson, AS Patel, CA Bounds Medtronic, Inc., Minneapolis, USA Abstract Implantable
Automatic Identification of Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Lead Problems Using Intracardiac Electrograms BD Gunderson, AS Patel, CA Bounds Medtronic, Inc., Minneapolis, USA Abstract Implantable
Atrial fibrillation: why it's important to make opportunities diagnosis in single chamber ICD patients
 ADVANCES IN CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS and GREAT INNOVATIONS IN CARDIOLOGY Turin October 13-15, 2016 Atrial fibrillation: why it's important to make opportunities diagnosis in single chamber ICD patients Dott.
ADVANCES IN CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS and GREAT INNOVATIONS IN CARDIOLOGY Turin October 13-15, 2016 Atrial fibrillation: why it's important to make opportunities diagnosis in single chamber ICD patients Dott.
MEDTRONIC CARELINK NETWORK FOR PACEMAKERS. Comparison between the Medtronic CareLink Network for Pacemakers and Transtelephonic Monitoring
 MEDTRONIC CARELINK NETWORK FOR PACEMAKERS Comparison between the Medtronic CareLink Network for Pacemakers and Transtelephonic Monitoring Transtelephonic Monitoring Transmission What can you determine
MEDTRONIC CARELINK NETWORK FOR PACEMAKERS Comparison between the Medtronic CareLink Network for Pacemakers and Transtelephonic Monitoring Transtelephonic Monitoring Transmission What can you determine
EHRA Accreditation Exam - Sample MCQs Cardiac Pacing and ICDs
 EHRA Accreditation Exam - Sample MCQs Cardiac Pacing and ICDs Dear EHRA Member, Dear Colleague, As you know, the EHRA Accreditation Process is becoming increasingly recognised as an important step for
EHRA Accreditation Exam - Sample MCQs Cardiac Pacing and ICDs Dear EHRA Member, Dear Colleague, As you know, the EHRA Accreditation Process is becoming increasingly recognised as an important step for
Post-ablation Management: Drug therapy, Anticoagulation and long-term Monitoring
 Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation: State of the Art Post-ablation Management: Drug therapy, Anticoagulation and long-term Monitoring Dipen Shah Service de Cardiologie Hospital Cantonal de Genève
Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation: State of the Art Post-ablation Management: Drug therapy, Anticoagulation and long-term Monitoring Dipen Shah Service de Cardiologie Hospital Cantonal de Genève
Introduction. CLINICAL RESEARCH Syncope and implantable loop recorders
 Europace (2013) 15, 1215 1222 doi:10.1093/europace/eut036 CLINICAL RESEARCH Syncope and implantable loop recorders Tachycardia detection performance of implantable loop recorders: results from a large
Europace (2013) 15, 1215 1222 doi:10.1093/europace/eut036 CLINICAL RESEARCH Syncope and implantable loop recorders Tachycardia detection performance of implantable loop recorders: results from a large
La strategia diagnostica: il monitoraggio ecg prolungato. Michele Brignole
 La strategia diagnostica: il monitoraggio ecg prolungato Michele Brignole ECG monitoring and syncope In-hospital monitoring Holter Monitoring External loop recorder Remote (at home) telemetry Implantable
La strategia diagnostica: il monitoraggio ecg prolungato Michele Brignole ECG monitoring and syncope In-hospital monitoring Holter Monitoring External loop recorder Remote (at home) telemetry Implantable
Consensus document: Screening and Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation
 Consensus document: Screening and Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation Yong-Seog Oh, M.D.,Ph.D. Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary s Hospital, College of Medicine, The
Consensus document: Screening and Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation Yong-Seog Oh, M.D.,Ph.D. Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary s Hospital, College of Medicine, The
Adapting detection sensitivity based on evidence of irregular sinus arrhythmia to improve atrial fibrillation detection in insertable cardiac monitors
 Europace (2017) 0, 1 8 doi:10.1093/europace/eux272 CLINICAL RESEARCH Adapting detection sensitivity based on evidence of irregular sinus arrhythmia to improve atrial fibrillation detection in insertable
Europace (2017) 0, 1 8 doi:10.1093/europace/eux272 CLINICAL RESEARCH Adapting detection sensitivity based on evidence of irregular sinus arrhythmia to improve atrial fibrillation detection in insertable
Subclinical AF: Implications of device based episodes
 Subclinical AF: Implications of device based episodes Michael R Gold, MD, PhD Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Disclosures: Clinical Trials and Consulting: Medtronic, Boston Scientific
Subclinical AF: Implications of device based episodes Michael R Gold, MD, PhD Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Disclosures: Clinical Trials and Consulting: Medtronic, Boston Scientific
Trigger Activity More Than Three Years After Left Atrial Linear Ablation Without Pulmonary Vein Isolation in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 46, No. 2, 2005 2005 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/05/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.03.063
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 46, No. 2, 2005 2005 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/05/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.03.063
Diagnostic capabilities of the implantable therapeutic systems
 Cardiac pacing 2012 and beyound Monday August 27, 2012 Diagnostic capabilities of the implantable therapeutic systems Pekka Raatikainen Heart Center Co. Tampere University Hospital and University of Tampere
Cardiac pacing 2012 and beyound Monday August 27, 2012 Diagnostic capabilities of the implantable therapeutic systems Pekka Raatikainen Heart Center Co. Tampere University Hospital and University of Tampere
Cardiac Implanted Electronic Devices Pacemakers, Defibrillators, Cardiac Resynchronization Devices, Loop Recorders, etc.
 Cardiac Implanted Electronic Devices Pacemakers, Defibrillators, Cardiac Resynchronization Devices, Loop Recorders, etc. The Miracle of Living February 21, 2018 Matthew Ostrom MD,FACC,FHRS Division of
Cardiac Implanted Electronic Devices Pacemakers, Defibrillators, Cardiac Resynchronization Devices, Loop Recorders, etc. The Miracle of Living February 21, 2018 Matthew Ostrom MD,FACC,FHRS Division of
Real-world performance of an enhanced atrial fibrillation detection algorithm in an insertable cardiac monitor
 Real-world performance of an enhanced atrial fibrillation detection algorithm in an insertable cardiac monitor Suneet Mittal, MD, FHRS, John Rogers, MD, Shantanu Sarkar, PhD, Jodi Koehler, MS, Eduardo
Real-world performance of an enhanced atrial fibrillation detection algorithm in an insertable cardiac monitor Suneet Mittal, MD, FHRS, John Rogers, MD, Shantanu Sarkar, PhD, Jodi Koehler, MS, Eduardo
Ambulatory Cardiac Monitors and Outpatient Telemetry Corporate Medical Policy
 Ambulatory Cardiac Monitors and Outpatient Telemetry Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Ambulatory Event Monitors and Mobile Cardiac Outpatient Telemetry File Code: UM.SPSVC.13 Origination: 10/2015 Last
Ambulatory Cardiac Monitors and Outpatient Telemetry Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Ambulatory Event Monitors and Mobile Cardiac Outpatient Telemetry File Code: UM.SPSVC.13 Origination: 10/2015 Last
Performance of Atrial Fibrillation Detection in a New Single-Chamber ICD
 DEVICES Performance of Atrial Fibrillation Detection in a New Single-Chamber ICD ABHISHEK DESHMUKH, M.D.,* MARK L. BROWN, PH.D., ELISE HIGGINS, B.S., BRIAN SCHOUSEK, B.S., ATHULA ABEYRATNE, PH.D., GIOVANNI
DEVICES Performance of Atrial Fibrillation Detection in a New Single-Chamber ICD ABHISHEK DESHMUKH, M.D.,* MARK L. BROWN, PH.D., ELISE HIGGINS, B.S., BRIAN SCHOUSEK, B.S., ATHULA ABEYRATNE, PH.D., GIOVANNI
Long-Term ECG Monitoring Using an ILR. Evgeny Pokushalov, MD, PhD
 Long-Term ECG Monitoring Using an ILR Evgeny Pokushalov, MD, PhD Long- Term ECG Monitoring Using an ILR Evgeny Pokushalov, MD, PhD, FESC State Research Ins;tute of Circula;on Pathology, Novosibirsk, Russia
Long-Term ECG Monitoring Using an ILR Evgeny Pokushalov, MD, PhD Long- Term ECG Monitoring Using an ILR Evgeny Pokushalov, MD, PhD, FESC State Research Ins;tute of Circula;on Pathology, Novosibirsk, Russia
ECG monitoring after ischemic stroke of TIA of unknown source with an insertable monitor? YES
 ECG monitoring after ischemic stroke of TIA of unknown source with an insertable monitor? YES Isabelle C Van Gelder University Medical Center Groningen The Netherlands ESC stroke council Prague January
ECG monitoring after ischemic stroke of TIA of unknown source with an insertable monitor? YES Isabelle C Van Gelder University Medical Center Groningen The Netherlands ESC stroke council Prague January
Performance of a New Leadless Implantable Cardiac Monitor in Detecting and Quantifying Atrial Fibrillation Results of the XPECT Trial
 Performance of a New Leadless Implantable Cardiac Monitor in Detecting and Quantifying Atrial Fibrillation Results of the XPECT Trial Gerhard Hindricks, MD, PhD; Evgueny Pokushalov, MD; Lubos Urban, MD;
Performance of a New Leadless Implantable Cardiac Monitor in Detecting and Quantifying Atrial Fibrillation Results of the XPECT Trial Gerhard Hindricks, MD, PhD; Evgueny Pokushalov, MD; Lubos Urban, MD;
Efstratios I. Charitos 1, Paul D. Ziegler 2, Ulrich Stierle 1, Hans-Hinrich Sievers 1, Hauke Paarmann 3, Thorsten Hanke 1. What s New?
 Atrial fibrillation density 3 Applied Cardiopulmonary Pathophysiology 7: 3-0, 203 Atrial fibrillation density: A novel measure of atrial fibrillation temporal aggregation for the characterization of atrial
Atrial fibrillation density 3 Applied Cardiopulmonary Pathophysiology 7: 3-0, 203 Atrial fibrillation density: A novel measure of atrial fibrillation temporal aggregation for the characterization of atrial
MEDICAL POLICY Cardiac Event Monitors/ Cardiac Event Detection
 POLICY: PG0039 ORIGINAL EFFECTIVE: 10/01/11 LAST REVIEW: 12/12/17 MEDICAL POLICY Cardiac Event Monitors/ Cardiac Event Detection GUIDELINES This policy does not certify benefits or authorization of benefits,
POLICY: PG0039 ORIGINAL EFFECTIVE: 10/01/11 LAST REVIEW: 12/12/17 MEDICAL POLICY Cardiac Event Monitors/ Cardiac Event Detection GUIDELINES This policy does not certify benefits or authorization of benefits,
Remote Monitoring & the Smart Home of the 21 Century
 Cardiostim EHRA Europace 2016, Nice - June 8-11, 2016 Remote Monitoring & the Smart Home of the 21 Century Antonio Raviele, MD, FESC, FHRS President ALFA -Alliance to Fight Atrial fibrillation- Venezia
Cardiostim EHRA Europace 2016, Nice - June 8-11, 2016 Remote Monitoring & the Smart Home of the 21 Century Antonio Raviele, MD, FESC, FHRS President ALFA -Alliance to Fight Atrial fibrillation- Venezia
AF Today: W. For the majority of patients with atrial. are the Options? Chris Case
 AF Today: W hat are the Options? Management strategies for patients with atrial fibrillation should depend on the individual patient. Treatment with medications seems adequate for most patients with atrial
AF Today: W hat are the Options? Management strategies for patients with atrial fibrillation should depend on the individual patient. Treatment with medications seems adequate for most patients with atrial
Interactive Simulator for Evaluating the Detection Algorithms of Implantable Defibrillators
 22 March 2002 Interactive Simulator for Evaluating the Detection Algorithms of Implantable Defibrillators F. HINTRINGER, O. PACHINGER Division of Cardiology, Department for Internal Medicine, University
22 March 2002 Interactive Simulator for Evaluating the Detection Algorithms of Implantable Defibrillators F. HINTRINGER, O. PACHINGER Division of Cardiology, Department for Internal Medicine, University
2009 CPT Codes for Cardiac Device Monitoring
 2009 CPT Codes for Cardiac Device Monitoring December 2008 Notices Current Procedural Terminology (CPT ) is copyright 2008 American Medical Association. All Rights reserved. No fee schedules, basic units,
2009 CPT Codes for Cardiac Device Monitoring December 2008 Notices Current Procedural Terminology (CPT ) is copyright 2008 American Medical Association. All Rights reserved. No fee schedules, basic units,
November 2016 POWERFULLY SIMPLE CARDIAC MONITORING. SEEQ External Cardiac Monitor (ECM) System. From the leaders who brought you Reveal LINQ ICM
 November 2016 POWERFULLY SIMPLE CARDIAC MONITORING SEEQ External Cardiac Monitor (ECM) System From the leaders who brought you Reveal LINQ ICM TRADITIONAL HOLTER MONITORING TYPICALLY 1-2 DAYS NOT LONG
November 2016 POWERFULLY SIMPLE CARDIAC MONITORING SEEQ External Cardiac Monitor (ECM) System From the leaders who brought you Reveal LINQ ICM TRADITIONAL HOLTER MONITORING TYPICALLY 1-2 DAYS NOT LONG
PERMANENT PACEMAKERS AND IMPLANTABLE DEFIBRILLATORS Considerations for intensivists
 PERMANENT PACEMAKERS AND IMPLANTABLE DEFIBRILLATORS Considerations for intensivists Craig A. McPherson, MD, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Constantine Manthous, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Clinical
PERMANENT PACEMAKERS AND IMPLANTABLE DEFIBRILLATORS Considerations for intensivists Craig A. McPherson, MD, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Constantine Manthous, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Clinical
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: AMBULATORY EVENT MONITORS
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: AMBULATORY EVENT MONITORS PAGE: 1 OF: 8 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: AMBULATORY EVENT MONITORS PAGE: 1 OF: 8 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
A Prospective Study Comparing the Sensed R Wave in Bipolar and Extended Bipolar Configurations: The PropR Study
 A Prospective Study Comparing the Sensed R Wave in Bipolar and Extended Bipolar Configurations: The PropR Study ANEESH V. TOLAT, M.D.,* MELISSA WOICIECHOWSKI, M.S.N.,* ROSEMARIE KAHR, R.C.I.S.,* JOSEPH
A Prospective Study Comparing the Sensed R Wave in Bipolar and Extended Bipolar Configurations: The PropR Study ANEESH V. TOLAT, M.D.,* MELISSA WOICIECHOWSKI, M.S.N.,* ROSEMARIE KAHR, R.C.I.S.,* JOSEPH
Role of Extended External Auto-Triggered Loop Recorder Monitoring for Atrial Fibrillation
 Circulation Journal Official Journal of the Japanese Circulation Society http://www.j-circ.or.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Arrhythmia/Electrophysiology Role of Extended External Auto-Triggered Loop Recorder Monitoring
Circulation Journal Official Journal of the Japanese Circulation Society http://www.j-circ.or.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Arrhythmia/Electrophysiology Role of Extended External Auto-Triggered Loop Recorder Monitoring
as the cause of recurrent syncope 3 allows appropriate management aimed
 Case Report Hellenic J Cardiol 2009; 50: 155-159 The Role of the Implantable Loop Recorder in the Investigation of Recurrent Syncope SKEVOS K. SIDERIS 1, TERESA A. MOUSIAMA 1, PAVLOS N. STOUGIANNOS 1,
Case Report Hellenic J Cardiol 2009; 50: 155-159 The Role of the Implantable Loop Recorder in the Investigation of Recurrent Syncope SKEVOS K. SIDERIS 1, TERESA A. MOUSIAMA 1, PAVLOS N. STOUGIANNOS 1,
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: ambulatory_event_monitors 10/2000 4/2017 4/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service There are a wide
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: ambulatory_event_monitors 10/2000 4/2017 4/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service There are a wide
INTERPRETING THE ECG IN PATIENTS WITH PACEMAKERS
 INTERPRETING THE ECG IN PATIENTS WITH PACEMAKERS BEFORE INTERPRETING THE ECG: Nora Goldschlager, M.D. MACP, FACC, FAHA, FHRS. Cardiology San Francisco General Hospital UCSF Disclosures: None 1 2 QUESTIONS
INTERPRETING THE ECG IN PATIENTS WITH PACEMAKERS BEFORE INTERPRETING THE ECG: Nora Goldschlager, M.D. MACP, FACC, FAHA, FHRS. Cardiology San Francisco General Hospital UCSF Disclosures: None 1 2 QUESTIONS
The Therapeutic Role of the Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia
 The Therapeutic Role of the Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia By Sandeep Joshi, MD and Jonathan S. Steinberg, MD Arrhythmia Service, Division of Cardiology
The Therapeutic Role of the Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia By Sandeep Joshi, MD and Jonathan S. Steinberg, MD Arrhythmia Service, Division of Cardiology
Recurrent Implantable Defibrillator Discharges (ICD) Discharges ICD Storm
 Recurrent Implantable Defibrillator Discharges (ICD) Discharges ICD Storm Guy Amit, MD, MPH Soroka University Medical Center Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Beer-Sheva, Israel Disclosures Consultant:
Recurrent Implantable Defibrillator Discharges (ICD) Discharges ICD Storm Guy Amit, MD, MPH Soroka University Medical Center Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Beer-Sheva, Israel Disclosures Consultant:
Supplemental Material
 Supplemental Material 1 Table S1. Codes for Patient Selection Cohort Codes Primary PM CPT: 33206 or 33207 or 33208 (without 33225) ICD-9 proc: 37.81, 37.82, 37.83 Primary ICD Replacement PM Replacement
Supplemental Material 1 Table S1. Codes for Patient Selection Cohort Codes Primary PM CPT: 33206 or 33207 or 33208 (without 33225) ICD-9 proc: 37.81, 37.82, 37.83 Primary ICD Replacement PM Replacement
Role of Implantable Loop Recorder in the Evaluation of Syncope
 Role of Implantable Loop Recorder in the Evaluation of Syncope June Soo Kim, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Medicine Cardiac & Vascular Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Definition & Mechanism
Role of Implantable Loop Recorder in the Evaluation of Syncope June Soo Kim, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Medicine Cardiac & Vascular Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Definition & Mechanism
Implantable cardioverter defibrillator, Inappropriate shock, Lead failure
 Inappropriate Discharges of Intravenous Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators Owing to Lead Failure Takashi WASHIZUKA, 1 MD, Masaomi CHINUSHI, 1 MD, Ryu KAZAMA, 1 MD, Takashi HIRONO, 1 MD, Hiroshi WATANABE,
Inappropriate Discharges of Intravenous Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators Owing to Lead Failure Takashi WASHIZUKA, 1 MD, Masaomi CHINUSHI, 1 MD, Ryu KAZAMA, 1 MD, Takashi HIRONO, 1 MD, Hiroshi WATANABE,
Implantable loop recorders Michele Brignole Arrhythmologic Center, Lavagna, Italy
 Implantable loop recorders Michele Brignole Arrhythmologic Center, Lavagna, Italy DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST Medtronic, minimal ILR: available devices Reveal DX/XT, Medtronic Confirm, St Jude
Implantable loop recorders Michele Brignole Arrhythmologic Center, Lavagna, Italy DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST Medtronic, minimal ILR: available devices Reveal DX/XT, Medtronic Confirm, St Jude
Κατάλυση παροξυσμικής κολπικής μαρμαρυγής Ποια τεχνολογία και σε ποιους ασθενείς; Χάρης Κοσσυβάκης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ.
 Κατάλυση παροξυσμικής κολπικής μαρμαρυγής Ποια τεχνολογία και σε ποιους ασθενείς; Χάρης Κοσσυβάκης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ» Rhythm control antiarrhythmic drugs vs catheter ablation Summary
Κατάλυση παροξυσμικής κολπικής μαρμαρυγής Ποια τεχνολογία και σε ποιους ασθενείς; Χάρης Κοσσυβάκης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ» Rhythm control antiarrhythmic drugs vs catheter ablation Summary
Cryptogenic Stroke: The role of silent Atrial Fibrillation
 Cryptogenic Stroke: The role of silent Atrial Fibrillation PD Dr. med. Martin A. Ritter Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster Germany ritterm@uni-muenster.de 1 Turin, 25.10.2014 Agenda 1. What is a
Cryptogenic Stroke: The role of silent Atrial Fibrillation PD Dr. med. Martin A. Ritter Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster Germany ritterm@uni-muenster.de 1 Turin, 25.10.2014 Agenda 1. What is a
Introduction to a new "X out of Y" Mode-Switching Algorithm in Inos² CLS and Logos Dual-Chamber Pacemakers
 April 1999 117 Introduction to a new "X out of Y" Mode-Switching Algorithm in Inos² CLS and Logos Dual-Chamber Pacemakers C. W. ISRAEL Department of Cardiology, St.-Josef-Hospital, Ruhr-University, Bochum,
April 1999 117 Introduction to a new "X out of Y" Mode-Switching Algorithm in Inos² CLS and Logos Dual-Chamber Pacemakers C. W. ISRAEL Department of Cardiology, St.-Josef-Hospital, Ruhr-University, Bochum,
Μηνύματα από τις σπουδαιότερες μελέτες στην ηλεκτροφυσιολογία το διάστημα
 Μηνύματα από τις σπουδαιότερες μελέτες στην ηλεκτροφυσιολογία το διάστημα 2015-2016 Δημήτριος M. Κωνσταντίνου Ειδικός Καρδιολόγος, MD, MSc, PhD, CCDS Πανεπιστημιακός Υπότροφος Dr. Konstantinou has received
Μηνύματα από τις σπουδαιότερες μελέτες στην ηλεκτροφυσιολογία το διάστημα 2015-2016 Δημήτριος M. Κωνσταντίνου Ειδικός Καρδιολόγος, MD, MSc, PhD, CCDS Πανεπιστημιακός Υπότροφος Dr. Konstantinou has received
Improving Patient Outcomes with a Syncope Center. Suneet Mittal, MD
 Improving Patient Outcomes with a Syncope Center Suneet Mittal, MD Improving Patient Outcomes with a Syncope Center: Early Risk Stratification of Patients who Require Device Therapy Suneet Mittal, MD Director,
Improving Patient Outcomes with a Syncope Center Suneet Mittal, MD Improving Patient Outcomes with a Syncope Center: Early Risk Stratification of Patients who Require Device Therapy Suneet Mittal, MD Director,
University of Groningen. Ablation of atrial fibrillation de Maat, Gijs Eduard
 University of Groningen Ablation of atrial fibrillation de Maat, Gijs Eduard IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen Ablation of atrial fibrillation de Maat, Gijs Eduard IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
Continuous ECG telemonitoring with implantable devices: the expected clinical benefits
 Continuous ECG telemonitoring with implantable devices: the expected clinical benefits C. W. Israel, M.D. Dept. of Cardiology Evangelical Hospital Bielefeld Germany Carsten.Israel@evkb.de Declaration of
Continuous ECG telemonitoring with implantable devices: the expected clinical benefits C. W. Israel, M.D. Dept. of Cardiology Evangelical Hospital Bielefeld Germany Carsten.Israel@evkb.de Declaration of
Inappropriate electrical shocks: Tackling the beast
 ESC Paris 2011 Inappropriate electrical shocks: Tackling the beast Gerhard Hindricks University of Leipzig Heart Center Dept. of Electrophysiology ESC Paris 2011 Inappropriate electrical shocks: Tackling
ESC Paris 2011 Inappropriate electrical shocks: Tackling the beast Gerhard Hindricks University of Leipzig Heart Center Dept. of Electrophysiology ESC Paris 2011 Inappropriate electrical shocks: Tackling
Interventional solutions for atrial fibrillation in patients with heart failure
 Interventional solutions for atrial fibrillation in patients with heart failure Advances in Cardiovascular Arrhythmias Great Innovations in Cardiology Matteo Anselmino, MD PhD Division of Cardiology Department
Interventional solutions for atrial fibrillation in patients with heart failure Advances in Cardiovascular Arrhythmias Great Innovations in Cardiology Matteo Anselmino, MD PhD Division of Cardiology Department
Wide QRS Tachycardia in a Dual Chamber Pacemaker Patient: What is the Mechanism?
 CASE REPORTS Arrhythmia 2015;16(3):173-177 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.18501/arrhythmia.2015.029 Wide QRS Tachycardia in a Dual Chamber Pacemaker Patient: What is the Mechanism? Eun-Sun Jin, MD, PhD Cardiovascular
CASE REPORTS Arrhythmia 2015;16(3):173-177 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.18501/arrhythmia.2015.029 Wide QRS Tachycardia in a Dual Chamber Pacemaker Patient: What is the Mechanism? Eun-Sun Jin, MD, PhD Cardiovascular
Device Interrogation- Pacemakers, ICD and Loop Recorders. Dulce Obias-Manno, RN, MHSA, CCDS,CEPS, FHRS Device Clinic Coordinator, MHVI
 Device Interrogation- Pacemakers, ICD and Loop Recorders Dulce Obias-Manno, RN, MHSA, CCDS,CEPS, FHRS Device Clinic Coordinator, MHVI Disclosures Consultant: Medtronic Speaker s Bureau: St. Jude Medical
Device Interrogation- Pacemakers, ICD and Loop Recorders Dulce Obias-Manno, RN, MHSA, CCDS,CEPS, FHRS Device Clinic Coordinator, MHVI Disclosures Consultant: Medtronic Speaker s Bureau: St. Jude Medical
Atrial Fibrillation Ablation: in Whom and How
 Update on Consensus Statement on Management of Atrial Fibrillation: EHRA 2012 Atrial Fibrillation Ablation: in Whom and How Update of HRS/EHRA AF/ECAS Ablation Document 2012 Anne M Gillis MD FHRS Professor
Update on Consensus Statement on Management of Atrial Fibrillation: EHRA 2012 Atrial Fibrillation Ablation: in Whom and How Update of HRS/EHRA AF/ECAS Ablation Document 2012 Anne M Gillis MD FHRS Professor
Diagnosing atrial fibrillation using implantable devices
 Diagnosing atrial fibrillation using implantable devices Axel Brandes, MD, FESC Associate Professor of Electrophysiology and Cardiac Arrhythmias Dept. of Cardiology, Odense University Hospital, DK HRC
Diagnosing atrial fibrillation using implantable devices Axel Brandes, MD, FESC Associate Professor of Electrophysiology and Cardiac Arrhythmias Dept. of Cardiology, Odense University Hospital, DK HRC
Medicare Advantage Medical Policy
 Medicare Advantage Medical Policy Current Policy Effective Date: 1/1/18 Title: Ambulatory Event Monitors and Mobile Cardiac Outpatient Telemetry Description/Background Indications for Ambulatory Cardiac
Medicare Advantage Medical Policy Current Policy Effective Date: 1/1/18 Title: Ambulatory Event Monitors and Mobile Cardiac Outpatient Telemetry Description/Background Indications for Ambulatory Cardiac
Cardiac Rhythm Management Coder 2018
 Cardiac Rhythm Management Coder 2018 An easy-to-use tool for coding and reimbursement compliance Prepared and Published By: MedLearn Publishing, A Division of MedLearn Media, Inc. 445 Minnesota Street,
Cardiac Rhythm Management Coder 2018 An easy-to-use tool for coding and reimbursement compliance Prepared and Published By: MedLearn Publishing, A Division of MedLearn Media, Inc. 445 Minnesota Street,
National Horizon Scanning Centre. Dronedarone (Multaq) for atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter. December 2007
 Dronedarone (Multaq) for atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter December 2007 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not
Dronedarone (Multaq) for atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter December 2007 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not
POWERFUL CARDIAC MONITORING
 POWERFUL CARDIAC MONITORING Indications, Guidelines, Clinical Evidence, and Coding Overview for Diagnosing Suspected Arrhythmias and Monitoring Known A-Fib Reveal LINQ Insertable Cardiac Monitoring System
POWERFUL CARDIAC MONITORING Indications, Guidelines, Clinical Evidence, and Coding Overview for Diagnosing Suspected Arrhythmias and Monitoring Known A-Fib Reveal LINQ Insertable Cardiac Monitoring System
INSERTABLE CARDIAC MONITORS FROM ATRIAL FIBRILLATION TO SYNCOPE:
 INSERTABLE CARDIAC MONITORS FROM ATRIAL FIBRILLATION TO SYNCOPE: Established and emerging clinical evidence demonstrates the utility of insertable cardiac monitors (ICMs) in diagnosing a variety of suspected
INSERTABLE CARDIAC MONITORS FROM ATRIAL FIBRILLATION TO SYNCOPE: Established and emerging clinical evidence demonstrates the utility of insertable cardiac monitors (ICMs) in diagnosing a variety of suspected
Shock Reduction Strategies Michael Geist E. Wolfson MC
 Shock Reduction Strategies Michael Geist E. Wolfson MC Shock Therapy Thanks, I needed that! Why Do We Need To Reduce Shocks Long-term outcome after ICD and CRT implantation and influence of remote device
Shock Reduction Strategies Michael Geist E. Wolfson MC Shock Therapy Thanks, I needed that! Why Do We Need To Reduce Shocks Long-term outcome after ICD and CRT implantation and influence of remote device
CURRICULUM GOALS AND OBJECTIVES CLINICAL CARDIOVASCULAR ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM. University of Florida Gainesville, Florida
 CURRICULUM GOALS AND OBJECTIVES CLINICAL CARDIOVASCULAR ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM University of Florida Gainesville, Florida 1. Mission Statement To achieve excellence in the training of fourth
CURRICULUM GOALS AND OBJECTIVES CLINICAL CARDIOVASCULAR ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM University of Florida Gainesville, Florida 1. Mission Statement To achieve excellence in the training of fourth
Teaching Rounds in Cardiac Electrophysiology
 Teaching Rounds in Cardiac Electrophysiology Sustained Multiple Railroad Tracks on Implantable Cardiac Defibrillator Interval Plots Mechanisms and Management Alex Y. Tan, MD; Kenneth A. Ellenbogen, MD;
Teaching Rounds in Cardiac Electrophysiology Sustained Multiple Railroad Tracks on Implantable Cardiac Defibrillator Interval Plots Mechanisms and Management Alex Y. Tan, MD; Kenneth A. Ellenbogen, MD;
Χρήση έξυπνων τεχνολογιών στην ανίχνευση κολπικής μαρμαρυγής Use of smart technology in atrial fibrillation detection
 Χρήση έξυπνων τεχνολογιών στην ανίχνευση κολπικής μαρμαρυγής Use of smart technology in atrial fibrillation detection Χάρης Κοσσυβάκης Επιμελητής A Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ» Risk of Stroke
Χρήση έξυπνων τεχνολογιών στην ανίχνευση κολπικής μαρμαρυγής Use of smart technology in atrial fibrillation detection Χάρης Κοσσυβάκης Επιμελητής A Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ» Risk of Stroke
Cardiac Rhythm Management Coder 2017
 Cardiac Rhythm Management Coder 2017 An easy-to-use tool for coding and reimbursement compliance Prepared and Published By: MedLearn Publishing, A Division of Panacea Healthcare Solutions, Inc. 287 East
Cardiac Rhythm Management Coder 2017 An easy-to-use tool for coding and reimbursement compliance Prepared and Published By: MedLearn Publishing, A Division of Panacea Healthcare Solutions, Inc. 287 East
Recent observations have focused attention on the PVs as a source of ectopic activity i determining i AF
 Atrial Fibrillation in 2010 Panos Vardas Professor of Cardiology President of EHRA Atrial Fibrillation Pathophysiology of AF Triggers Recent observations have focused attention on the PVs as a source of
Atrial Fibrillation in 2010 Panos Vardas Professor of Cardiology President of EHRA Atrial Fibrillation Pathophysiology of AF Triggers Recent observations have focused attention on the PVs as a source of
Why to monitor AF ablation success?
 Why to monitor AF ablation success? Why to monitor AF ablation success? CASTLE-AF Primary Endpoint All-cause mortality Worsening heart failure admissions Secondary Endpoints All-cause mortality Worsening
Why to monitor AF ablation success? Why to monitor AF ablation success? CASTLE-AF Primary Endpoint All-cause mortality Worsening heart failure admissions Secondary Endpoints All-cause mortality Worsening
CARDIOINSIGHT TM NONINVASIVE 3D MAPPING SYSTEM CLINICAL EVIDENCE SUMMARY
 CARDIOINSIGHT TM NONINVASIVE 3D MAPPING SYSTEM CLINICAL EVIDENCE SUMMARY April 2017 SUPPORTING EVIDENCE RHYTHM AF VT PUBLICATIONS Driver Domains in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation (Haissaiguerre, et al)
CARDIOINSIGHT TM NONINVASIVE 3D MAPPING SYSTEM CLINICAL EVIDENCE SUMMARY April 2017 SUPPORTING EVIDENCE RHYTHM AF VT PUBLICATIONS Driver Domains in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation (Haissaiguerre, et al)
Dual-Chamber Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator
 February 1998 9 Dual-Chamber Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator A.SH. REVISHVILI A.N. Bakoulev Research Center for Cardiovascular Surgery, Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Moscow, Russia Summary
February 1998 9 Dual-Chamber Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator A.SH. REVISHVILI A.N. Bakoulev Research Center for Cardiovascular Surgery, Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Moscow, Russia Summary
UTILITY OF THE IMPLANTABLE LOOP RECORDER
 UTILITY OF THE IMPLANTABLE LOOP RECORDER John Andriulli, DO Associate Professor of Medicine Director, Arrhythmia Device Program Cooper Medical School of Rowan University Contemporary Practices in Cardiology
UTILITY OF THE IMPLANTABLE LOOP RECORDER John Andriulli, DO Associate Professor of Medicine Director, Arrhythmia Device Program Cooper Medical School of Rowan University Contemporary Practices in Cardiology
Θα πρέπει να αναζηηείηαι η παροσζία ζιωπηλής κολπικής μαρμαρσγή ζε αζθενείς με κρσπηογενές εγκεθαλικό επειζόδιο; Ποιά είναι η καλύηερη μέθοδος;
 Θα πρέπει να αναζηηείηαι η παροσζία ζιωπηλής κολπικής μαρμαρσγή ζε αζθενείς με κρσπηογενές εγκεθαλικό επειζόδιο; Ποιά είναι η καλύηερη μέθοδος; Νικόλαος Φραγκάκης Λέκηορας Καρδιολογίας, FESC Ιπποκράηειο
Θα πρέπει να αναζηηείηαι η παροσζία ζιωπηλής κολπικής μαρμαρσγή ζε αζθενείς με κρσπηογενές εγκεθαλικό επειζόδιο; Ποιά είναι η καλύηερη μέθοδος; Νικόλαος Φραγκάκης Λέκηορας Καρδιολογίας, FESC Ιπποκράηειο
Thromboembolism During Sinus Rhythm in Patients with a History of Atrial Fibrillation
 48 th Annual New York Cardiovascular Symposium Thromboembolism During Sinus Rhythm in Patients with a History of Atrial Fibrillation Is Left Atrial Appendage Dysfunction Sufficient to Generate Clots? December
48 th Annual New York Cardiovascular Symposium Thromboembolism During Sinus Rhythm in Patients with a History of Atrial Fibrillation Is Left Atrial Appendage Dysfunction Sufficient to Generate Clots? December
Raphael Rosso MD, Yuval Levi Med. Eng., Sami Viskin MD Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center
 Radiofrequency Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation: Comparison of Success Rate of Circular Ablation vs Point-by-Point Ablation with Contact Force Assessment in Paroxysmal and Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
Radiofrequency Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation: Comparison of Success Rate of Circular Ablation vs Point-by-Point Ablation with Contact Force Assessment in Paroxysmal and Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
Clinical Results with the Dual-Chamber Cardioverter Defibrillator Phylax AV - Efficacy of the SMART I Discrimination Algorithm
 April 2000 107 Clinical Results with the Dual-Chamber Cardioverter Defibrillator Phylax AV - Efficacy of the SMART I Discrimination Algorithm B. MERKELY Semmelweis University, Dept. of Cardiovascular Surgery,
April 2000 107 Clinical Results with the Dual-Chamber Cardioverter Defibrillator Phylax AV - Efficacy of the SMART I Discrimination Algorithm B. MERKELY Semmelweis University, Dept. of Cardiovascular Surgery,
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Ambulatory Event Monitors and Mobile Cardiac Outpatient Telemetry Page 1 of 33 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Ambulatory Event Monitors and Mobile
Ambulatory Event Monitors and Mobile Cardiac Outpatient Telemetry Page 1 of 33 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Ambulatory Event Monitors and Mobile
Value of the implantable loop recorder for the management of patients with unexplained syncope
 Europace (2004) 6, 70e76 Value of the implantable loop recorder for the management of patients with unexplained syncope Lucas Boersma a, ), Lluís Mont b, Alessandro Sionis b, Emilio García b, Josep Brugada
Europace (2004) 6, 70e76 Value of the implantable loop recorder for the management of patients with unexplained syncope Lucas Boersma a, ), Lluís Mont b, Alessandro Sionis b, Emilio García b, Josep Brugada
Rebuttal. Jerónimo Farré MD 2010
 Rebuttal 1.We do not know what are the types of AF in which ablation is worthless or most effective 2.Waiting implies to consider the ablation at an older age and when the duration of the history of AF
Rebuttal 1.We do not know what are the types of AF in which ablation is worthless or most effective 2.Waiting implies to consider the ablation at an older age and when the duration of the history of AF
PVI and What Else for Persistent AF Lessons Learned from STAR AF 2 CCCEP 2015 October 31, New York
 PVI and What Else for Persistent AF Lessons Learned from STAR AF 2 CCCEP 2015 October 31, New York Atul Verma, MD FRCPC FHRS Director, Arrhythmia Services Southlake Regional Health Centre Faculty of Medicine
PVI and What Else for Persistent AF Lessons Learned from STAR AF 2 CCCEP 2015 October 31, New York Atul Verma, MD FRCPC FHRS Director, Arrhythmia Services Southlake Regional Health Centre Faculty of Medicine
How often should we monitor for reliable detection of atrial fibrillation recurrence? Efficiency considerations and implications for study design
 How often should we monitor for reliable detection of atrial fibrillation recurrence? Efficiency considerations and implications for study design Article (Published Version) Charitos, Efstratios I, Ziegler,
How often should we monitor for reliable detection of atrial fibrillation recurrence? Efficiency considerations and implications for study design Article (Published Version) Charitos, Efstratios I, Ziegler,
עדכונים באלקטרופיזיולוגיה Electrophysiology Unit Soroka University Medical Center Faculty of Health Sciences Ben-Gurion University of the Negev
 עדכונים באלקטרופיזיולוגיה 2014 Electrophysiology Unit Soroka University Medical Center Faculty of Health Sciences Ben-Gurion University of the Negev 1 מבנה הצגת היחידה פעילות ביחידה סקירה על הטיפול באלקטרופיזיולוגיה
עדכונים באלקטרופיזיולוגיה 2014 Electrophysiology Unit Soroka University Medical Center Faculty of Health Sciences Ben-Gurion University of the Negev 1 מבנה הצגת היחידה פעילות ביחידה סקירה על הטיפול באלקטרופיזיולוגיה
CARDIAC MONITORING THE EARLY DAYS
 CARDIAC MONITORING THE EARLY DAYS CARDIAC MONITORING - TODAY SEEQ Mobile cardiac telemetry system for short-term monitoring up to 30 days Reveal LINQ Insertable cardiac monitoring system for long-term
CARDIAC MONITORING THE EARLY DAYS CARDIAC MONITORING - TODAY SEEQ Mobile cardiac telemetry system for short-term monitoring up to 30 days Reveal LINQ Insertable cardiac monitoring system for long-term
Programming of Bradycardic Parameters. C. W. Israel, M.D. Dept. of Cardiology Evangelical Hospital Bielefeld Germany
 Programming of Bradycardic Parameters C. W. Israel, M.D. Dept. of Cardiology Evangelical Hospital Bielefeld Germany Carsten.Israel@evkb.de Programming of ICD Brady Parameters Conflict of Interest Biotronik
Programming of Bradycardic Parameters C. W. Israel, M.D. Dept. of Cardiology Evangelical Hospital Bielefeld Germany Carsten.Israel@evkb.de Programming of ICD Brady Parameters Conflict of Interest Biotronik
POWERFULLY SIMPLE CARDIAC MONITORING
 POWERFULLY SIMPLE CARDIAC MONITORING SEEQ Mobile Cardiac Telemetry (MCT) System From the leaders who brought you Reveal LINQ ICM MEDTRONIC CARDIAC DIAGNOSTIC & MONITORING SYSTEMS TRANSFORM Transform your
POWERFULLY SIMPLE CARDIAC MONITORING SEEQ Mobile Cardiac Telemetry (MCT) System From the leaders who brought you Reveal LINQ ICM MEDTRONIC CARDIAC DIAGNOSTIC & MONITORING SYSTEMS TRANSFORM Transform your
Zio System Publications. Peer-reviewed publications demonstrating the clinical validity and utility of the Zio system
 Zio System Publications Peer-reviewed publications demonstrating the clinical validity and utility of the Zio system Contents Electrocardiographic Responses to Deer Hunting in Men and Women. Wilderness
Zio System Publications Peer-reviewed publications demonstrating the clinical validity and utility of the Zio system Contents Electrocardiographic Responses to Deer Hunting in Men and Women. Wilderness
» A new drug s trial
 » A new drug s trial A placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel arm Trial to assess the efficacy of dronedarone 400 mg bid for the prevention of cardiovascular Hospitalization or death from any cause
» A new drug s trial A placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel arm Trial to assess the efficacy of dronedarone 400 mg bid for the prevention of cardiovascular Hospitalization or death from any cause
ECTOPIC BEATS: HOW MANY COUNT?
 ECTOPIC BEATS: HOW MANY COUNT? Rupert FG Simpson, 1 Jessica Langtree, 2 *Andrew RJ Mitchell 2 1. King s College Hospital, London, UK 2. Jersey General Hospital, Jersey, UK *Correspondence to mail@jerseycardiologist.com
ECTOPIC BEATS: HOW MANY COUNT? Rupert FG Simpson, 1 Jessica Langtree, 2 *Andrew RJ Mitchell 2 1. King s College Hospital, London, UK 2. Jersey General Hospital, Jersey, UK *Correspondence to mail@jerseycardiologist.com
Outcomes of AF Ablation
 2017 춘계심혈관통합학술대회 AF Summit: Atrial Fibrillation Apr.21(Fri) 14:40-16:10 Rm.300B 15:00-15:10 Outcomes of AF Ablation Gi-Byoung Nam MD Asan Medical Center, UUCM 2017 Annual Spring Scientific Conference of
2017 춘계심혈관통합학술대회 AF Summit: Atrial Fibrillation Apr.21(Fri) 14:40-16:10 Rm.300B 15:00-15:10 Outcomes of AF Ablation Gi-Byoung Nam MD Asan Medical Center, UUCM 2017 Annual Spring Scientific Conference of
AF and arrhythmia management. Dr Rhys Beynon Consultant Cardiologist and Electrophysiologist University Hospital of North Staffordshire
 AF and arrhythmia management Dr Rhys Beynon Consultant Cardiologist and Electrophysiologist University Hospital of North Staffordshire Atrial fibrillation Paroxysmal AF recurrent AF (>2 episodes) that
AF and arrhythmia management Dr Rhys Beynon Consultant Cardiologist and Electrophysiologist University Hospital of North Staffordshire Atrial fibrillation Paroxysmal AF recurrent AF (>2 episodes) that
CLINICAL MEDICAL POLICY
 Policy Name: Policy Number: Responsible Department(s): CLINICAL MEDICAL POLICY Single-use Ambulatory Electrocardiographic Monitors (e.g., Zio Patch) MP-076-MD-DE Medical Management Provider Notice Date:
Policy Name: Policy Number: Responsible Department(s): CLINICAL MEDICAL POLICY Single-use Ambulatory Electrocardiographic Monitors (e.g., Zio Patch) MP-076-MD-DE Medical Management Provider Notice Date:
Seek and Ye Shall Find: Surprising Findings When Using the ILR-LINQ
 Seek and Ye Shall Find: Surprising Findings When Using the ILR-LINQ Suneet Mittal, MD, FACC, FHRS Director, Electrophysiology Laboratory Valley Health System www.arrhythmia.org; @drsuneet October 31, 2015
Seek and Ye Shall Find: Surprising Findings When Using the ILR-LINQ Suneet Mittal, MD, FACC, FHRS Director, Electrophysiology Laboratory Valley Health System www.arrhythmia.org; @drsuneet October 31, 2015
Waterproof quality IP X4
 Actual size Thanks to its high level of miniaturisation, the R.Test Evolution 3 is compact and lightweight (45 g. batteries included), for total discretion. Its exceptional design ensures high patient
Actual size Thanks to its high level of miniaturisation, the R.Test Evolution 3 is compact and lightweight (45 g. batteries included), for total discretion. Its exceptional design ensures high patient
POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER CODING INFORMATION REFERENCES POLICY HISTORY
 Original Issue Date (Created): 7/1/2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 2/28/2018 Effective Date: 10/1/2018 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS
Original Issue Date (Created): 7/1/2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 2/28/2018 Effective Date: 10/1/2018 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS
Ablation for atrial fibrillation during mitral valve surgery: 1-year results through continuous subcutaneous monitoring
 Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery 15 (2012) 37 41 doi:10.1093/icvts/ivs053 Advance Access publication 18 April 2012 ORIGINAL ARTICLE - ADULT CARDIAC Ablation for atrial fibrillation during
Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery 15 (2012) 37 41 doi:10.1093/icvts/ivs053 Advance Access publication 18 April 2012 ORIGINAL ARTICLE - ADULT CARDIAC Ablation for atrial fibrillation during
Biatrial Stimulation and the Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation
 374 September 2001 Biatrial Stimulation and the Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation L. MELCZER Heart Institute, Faculty of Medicine, University of Pécs, Pécs, Hungary I. LORINCZ 1 st Internal Department,
374 September 2001 Biatrial Stimulation and the Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation L. MELCZER Heart Institute, Faculty of Medicine, University of Pécs, Pécs, Hungary I. LORINCZ 1 st Internal Department,
AF ABLATION Concepts and Techniques
 AF ABLATION Concepts and Techniques Antony F Chu, M.D. Director of Complex Ablation Arrhythmia Services Section Division of Cardiology at the Rhode Island and Miriam Hospital HIGHLIGHTS The main indications
AF ABLATION Concepts and Techniques Antony F Chu, M.D. Director of Complex Ablation Arrhythmia Services Section Division of Cardiology at the Rhode Island and Miriam Hospital HIGHLIGHTS The main indications
Cardiac Event Monitors
 Last Review Date: July 14, 2017 Number: MG.MM.DM.18aCv2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Last Review Date: July 14, 2017 Number: MG.MM.DM.18aCv2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
What s new in my specialty?
 What s new in my specialty? Jon Melman, MD Heart Rhythm Specialists McKay-Dee Hospital some would say some would say my specialty 1 some would say my specialty First pacemaker 1958 some would say my specialty
What s new in my specialty? Jon Melman, MD Heart Rhythm Specialists McKay-Dee Hospital some would say some would say my specialty 1 some would say my specialty First pacemaker 1958 some would say my specialty
Mission Statement for our Arrhythmia Care
 Mission Statement for our Arrhythmia Care We are dedicated to provide a compassionate and an outstanding care for patients with cardiac arrhythmias. We will be utilizing the cutting edge and the most advanced
Mission Statement for our Arrhythmia Care We are dedicated to provide a compassionate and an outstanding care for patients with cardiac arrhythmias. We will be utilizing the cutting edge and the most advanced
Topic: Outpatient Cardiac Telemetry Date of Origin: April Section: Medicine Last Reviewed Date: December 2014
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Outpatient Cardiac Telemetry Date of Origin: April 2010 Section: Medicine Last Reviewed Date: December 2014 Policy No: 135 Effective Date: February 1, 2014 IMPORTANT REMINDER
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Outpatient Cardiac Telemetry Date of Origin: April 2010 Section: Medicine Last Reviewed Date: December 2014 Policy No: 135 Effective Date: February 1, 2014 IMPORTANT REMINDER
Ambulatory Event Monitors and Mobile Cardiac Outpatient Telemetry Section 2.0 Medicine Subsection 2.02 Cardiology
 2.02.08 Ambulatory Event Monitors and Mobile Cardiac Outpatient Telemetry Section 2.0 Medicine Subsection 2.02 Cardiology Effective Date December 31, 2014 Original Policy Date April 5, 2007 Next Review
2.02.08 Ambulatory Event Monitors and Mobile Cardiac Outpatient Telemetry Section 2.0 Medicine Subsection 2.02 Cardiology Effective Date December 31, 2014 Original Policy Date April 5, 2007 Next Review
