Scholars Research Library
|
|
|
- Rolf Skinner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Available online at Annals of Biological Research, 2010, 1 (2) : ( ISSN Antifertility effects of Azadirachta indica (Neem) - A Review Parveen Bansal 1, Renu Bansal 1, Vikas Gupta 2* 1 Baba Farid University of Health Sciences, Faridkot, India 2 National Institute of Ayurvedic Pharmaceutical Research, Patiala, India Abstract Most population studies conclude that today's skyrocketing growth in human population is creating a serious underlying threat to the well being of the world's natural and economic resources. Whether neem, can help to reduce runaway population growth is' uncertain. However, as noted earlier, exploratory research has indicated that certain neem, ingredients have contraceptive properties. Thus it is possible that, given research attention, products from this tree could come into widespread use for the reduction of unwanted pregnancies. This review gives a bird's eye view mainly on the contraceptive therapeutic potential of neem tree so as to promote the research on this magic tree. Keywords: Azadirachta indica, Contraceptive, Spermicidal, Implantation, Male fertility INTRODUCTION Neem, a native of Indian subcontinent is a highly esteemed tree for the people in the region. The plant is considered sacred and is used by the Hindus in several ceremonies, rituals and in worship of the New Year day [1]. It is associated with a rural festival "Ghatasthapana" to avert diseases [2-4]. The Juice of fresh green leaves of Azadirachta indica was believed to suppress" Kam vasna" (desire for sex) so saints and "sanyasees" in shrines and the pupils studying in "Gurukul" consumed it for the same purpose. From an initial caution and scepticism neem, has now been universally accepted as a miracle tree. During last three decades neem has attracted the brains of The scientific community and has attained a place of pride in national and international scenario. Neem has been found to contain a vast array of biologically active compounds, which are chemically diverse and have got an enormous therapeutic potential. Not only this many reviews have been already appeared from time to time on its constituents in general [5-7]. Its chemistry dates back to when influenced by its folk-lore medicinal values the chemists took up the isolation of active principles and Siddiqui [8] was the first to report the isolation of three products namely nimbin, nimbidin and nimbinin from its oil. The National Research Council of USA has given an excellent account of this tree in their 108
2 publication 'Neem' A tree for solving global problems'. The society of pesticide science in India has also given an elaborative account regarding this tree in "Neem Research and Development'. Two other comprehensive compilations on the multifaceted research involving diverse disciplines of science were done by Jacobson and Tiwari [9, 10]. This review has been done to provide an insight into pharmacological work done to substantiate traditional claims to establish its contraceptive potential in modem medicine demonstrated as antimplantation effect, spermicidal effect, oral contraceptive, abortifacient, antispermatogenic effect and antifertility effect. Its contraceptive effect has been tried through oral, vaginal and subcutaneous routes of application. Either oil as such, or oil or leaf extracts have been used. Neem is being projected as a cheap and effective antifertility agent. In 1959 the antifertility property of neem components in rats and human were published [11, 12]. In this study addition of aqueous solution of sodium nimbidinate salt to semen of rat and human being resulted in death of sperm in different percentage and in different time period. Similarly oil proved to be spermicidal against rhesus monkey and human spermatozoa in vitro [13], when used intra vaginally the oil prevented pregnancy in rats (20 µl), rhesus monkeys and women (10ml). The oil did not reveal any side effects on repeated application as confirmed by histopathological studies on reproductive organs or other tissues where as oral dose of as low as 25µl oil demonstrated a complete anti implantation effect in rat [14]. In vitro testing of spermicidal activity of neem oil posed a problem of mixing the oil with water phase i.e. semen. So cyclohexane, which had no effect on spermatozoa motility at 2% concentration, was used to dissolve most of the test neem products. After diluting the mixture with a solution oftween-80 (0.1 %), the spermatozoa movement could be observed under a microscope [15]. Both the precoital and postcoital antifertility effects of vaginal application of neem oil have been subsequently confirmed in rhesus monkeys [16]. According to a report from scientists of Defence Institute of Physiology and Allied Sciences (DIPAS), a neem extract (Nim-76) is believed to be refined to give birth control effect. This study showed that neem oil applied intravaginally before sexual intercourse prevented pregnancy without any adverse effect on vagina, cervix and uterus. Further radio lisotopic studies indicated that neem oil is not absorbed from the vagina [14]. The active components of neem oil have been found to be absorbed through the vaginal mucosa into circulation and exerted antifertility effects in addition to direct spermicidal effect. The spermicidal property in post coital stages is rather undesirable because if used in pregnant women, it may lead to defects in embryonic development. Nim-76 a potent volatile fraction however inhibited spermatozoa motility in vitro in rat and human beings [17, 18]. It was found superior than raw neem oil in that it acts mainly by its spermicidal effect and no alterations in hormone values were observed. Several other studies have also shown that the mechanism 'of action of neem is not hormonal but probably direct spermicidal" [19, 20]. These findings were based on an analysis of the histoarchitecture of the uterus of treated rats and were subsequently confirmed by other workers [21]. Since the effect seems to be non hormonal it would be expected to elicit fewer side effects than the steroidal contraceptives. According to another report [22] neem oil in graded doses of 2, 4, 6 ml per kg. body weight did not inhibit ovulation activity in rabbits. According to other study neem oil constituents based formulation is 100% active to prevent pregnancy and does not produce any side effects [23]. Subcutaneous application of neem oil components like nimbi din or nimbidiol did not show any estrogenic activity [24,25]. In another report neem oil up to 0.3 ml/rat subcutaneously did not possess any estrogenic, antiestrogenic, progestrational or antiprogestational activity [26]. Subcutaneous administration of neem oil has been reported to inhibit pregnancy [27]. Study 109
3 indicates that the administration of neem oil may kill the blastocysts kin in the uterus of pregnant rats. Another group of scientists have shown that feeding of neem extracts for shorter duration caused no significant changes in the ovarian or uterine histology however longer treatment did cause arrest of follicular growth and thickening and scattering of stromal and glandular cells [28]. Male rats when tested for fertility after feeding neem oil had been found to result in a significant loss of reproductive function [22]. There were no inhibitions of spermatogenesis in any of the groups demonstrating that probably the drug induced functional sterility without interfering with structural integrity of the testis or the process of spermatogenesis. Another report has given contrast results in which administration of neem bark extract (50% EtOH) or neem seed oil (petroleum ether extract at a dose of 0.5g/kg body weight for 2 months caused arrest of spermatogenesis [29]. An active principle in water extracts of crushed green leaves caused reversible antifertility action without inhibition of spermatogenesis. This active principle was thermo stable [30, 31]. This extract was also found active in mice, rats, rabbits and guinea pigs [32]. When 100 mg of dried leaf powder suspended in 1ml of distilled water per day, was given for a period of 24 days, it was suggestive of reversible antiandrogenic effect on the histological and biochemical parameters of testis of adult albino rats [33, 34]. Upadhyay et al. [35] observed a long-term contraceptive effect of single intra-vas administration of neem oil in male rats. The antifertility effect was observed for 8 months and was found to be an alternative approach to vasectomy. No inflammatory/obstructive changes in epididymis and vas deferens were observed. There was no change in blood testosterone levels. Purified neem seed extract called praneem was reported to cause termination of pregnancy by bleeding and a decrease in progesterone levels in rats, baboons and monkeys [36]. It was also reported to abrogate pregnancy in primates [37]. Indigenously available neem oil in its natural form as tested for its spermicidal activity (in vitro and in vivo). Undiluted neem oil was found to possess strong spermicidal action (within 30s.) against rhesus monkey and human spermatozoa in vitro, whereas 3 mg. of neem leaf extract, when treated with human spermatozoa, kills 100% of sperm within 20 s. The time taken by sperm to travel to the oviduct from the cervix in women is 5-68 min, when all conditions are favorable in the fertile period [38]. Therefore, neem leaf extract is more advantageous than the undiluted neem oil, which takes 30 s to kill the sperm. Praneem polyherbal cream has been developed by garg et al. [39], which has synergistic spermicidal concentration for praneen (25%) reetha saponins (0.05%) and quinine hydrochloride (0.34%) and was found at this concentration to result in 100% immobilization of sperm within 20s [40]. Until now, neem seed extract or oil or oil components were studied as an effective contraceptive that.is hydrophobic in nature. The neem leaf extract, which is hydrophilic in nature, mixes immediately with water as well as body fluids and kills sperm within 20 s, with its use, a more potent vaginal contraceptive may be developed. A novel use of neem (Azadirachta indica) oil, a traditional plant product, for long-term and reversible blocking of fertility after a single intrauterine application is described by Upadhyay et al. [41]. Female Wistar rats of proven fertility were given a single dose (100 µl) of neem oil by intrauterine route; control animal received the same volume of peanut oil. Whereas all control animals became pregnant and delivered normal litters, the rats treated with neem oil remained 110
4 infertile for variable periods ranging form 107 to 180 days even after repeated mating with males of proven fertility. The block in fertility was, however, reversible as half of the animal's regained fertility and delivered normal litters by five months after treatment, without any apparent teratogenic effects. Unilateral administration of neem oil in the uterus blocked pregnancy only on the side of application, whereas the contra lateral uterine horn treated with peanut oil had normally developing foetuses; no sign of implantation or foetal resorption was noted in the neem-oil-treated horn. The ovaries on both side had 4-6 coropora lutea, indicating no effect of treatment on ovarian function. The animal treated with neem oil showed a significant leukocytic infiltration in the uterine epithelium between days 3 and 5 post coitum i.e., during the preimplantation period. Intrauterine application of neem oil appears to induce a preimplantation block in fertility. Neem oil in vitro proved to be a strong spermicidal agent. Rhesus monkey and human spermatozoa became totally immotile within 30 seconds of contact with the undiluted oil. In vivo studies in rats (20) rabbits (8), rhesus monkeys (14), and human volunteers (10) proved that neem oil has also been found to have anti-implantation/ abortifacient effect in rats and rabbits if applied intravaginally on day 2 to day 7 of expected pregnancy [42]. The minimum effective dose is 25 µl for rats. One month after the stoppage of neem oil application there was complete reversibility in fertility in these animals. It has no deleterious effect on the subsequent pregnancies and the offspring. Histopathological studies on rat's vagina, cervix and uterus showed no ill effects of neem oil in these tissues. In contrast, nonyl-phenoxy polyethoxy ethanol, a polyethoxy ethanol, a popular vaginal contraceptive cream, showed signs of severs irritant reaction in these tissues. Radioisotope studies indicated that neem oil was not absorbed from the vagina, it thus out its possible systemic effects. Results of the present study indicated that neem oil is an "ideal" female contraceptive, being easily available, cheap and non-toxic. Another study was carried out to evaluate the effective concentration of aqueous extract of old and tender Azadirachta indica (neem) leaves to immobilize and kill 100% human spermatozoa within 20 s [43]. The results of the 'study revealed that the aqueous extract of old and tender neem leaves is a potent spermicidal, which is demonstrated through docs-dependent study on the effect of motility of spermatozoa and then confirmed by viability test. No morphological changes were found in the sperm head, mid- piece and tail when compared with untreated sperm. Therefore, 100% killing of sperm may by due to blockage of some biochemical pathway like energy utilization, which would require' further investigation. The potency of lyophilized aqueous extract of old and tender leaves remains the same and the effectiveness does not change with storage time to 4 year. According to Dhawan et al. [44] Ethanol/water (1:1) extract of the dried seed, administered orally to female rats at a dose of 100 mg/kg, did not demonstrate any antiimplantation effect. A similar type of study has shown inactivity of the seed oil administered by gastric incubation at a dose of 5.0ml/ animal [45]. Lal et al. [46, 47] has shown just contradictory results by demonstrating activity of essential oil administered orally to the rat a, the dose of 4.0 ml kg on days 1-3. In two different studies antispermatogenic effect of dried leaf extract was screened. Ethanol (80%) extract of the dried leaf, administered intragastrically to male rats at a dose of 100 mg/kg daily for 21 days was inactive for antispermatogenic activity however there was loss of libido in 100% males [48] whereas the dried leaf administered intra gastrically to male rats at a dose of mg/animal daily for 24 days was active [49]. The seed oil has also been shown to effect the sperm/egg interaction at a concentration of 10-25% and thus inhibit fertilization and development of fertilized ova [50]. The dried seed administered intravaginally was active as spermicidal in baboon, monkey and rabbit [51]. 111
5 CONCLUSION Keeping in view the importance of neem tree in national regional land international perspective there is an urgent need to locate collect and study its diversity and develop effect measures to store it for current and future use. At the same time it is also essential to undertake ethno botanical studies to link its various therapeutic uses with ethnic/ folklore remedies to evaluate how different tribes use neem in different areas of its occurrence. There is a dire need to document this folklore traditional knowledge, which is vanishing rapidly due to lack of awareness in these people, also effective measures are required to document available diversity and bring out systematic information for wider dissemination and utilization of world's genetic diversity in neem for exploring its therapeutic potential further. REFERENCES [1] S. Sengupta, Tree symbol worship in India, Indian Floklore Society, Calcutta, [2] D.N. Tewari, Monograph on neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss), International Book Distributors, Dehradun, India, [3] P. Joshi, J. Exon. Tax.Bot., l983, 3, [4] S.K. Jain, Glimpses of Indian Ethnobotany, Oxford and I. B. H. Publications Co, New Delhi, [5] C. Devkumar, S.K. Mukherjee, Res. Bull., 1983, 40, [6] S. Siddiqui, B.S. Siddiqui, S. Faizi, T. Mahmood, Phytochem., 1988, 27, [7] J.D. Kabeh, M.G.D.S.S. Jalingo, Int. J. Agri. Biol., 2007, 9, 3, [8] S. Siddiqui, Curr. Sci., 1942, 11, [9] M. Jacobson, Focus on Photochemical pesticides, 1, The neem tree, CRC press, Inc. Boca Rotan, Florida, USA, 1988; pp [10] D.N. Tewari, Monograph on neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss), International Book Distributors, Dehradun, India, 1992; pp [11] V.N. Sharma, P.K. Saksena, Indian J.Med. Res., 1959, 47, [12] V.N. Sharma, P.K. Saksena, Indian J. Med. Sci., 1959, 13, [13] K.C. Sinha, S.S. Riar, R.S. Tiwari, A.K. Dhawan, J. Bardhan, P. Thomas, A.K. Kain, R.K. Jain, Indian journal Medical Research, 1984, 79, [14] K.C. Sinha, S.S. Riar, J. Bardhan, P. Thomas, A.K. Kain, R.K. Jain, Indian Journal Medical Research, 1984, 80, [15] C. Devakumar, S.S. Riar, G. Iiavazhagan, A.K. Kain, J. Bardhan, P. Thomas, B. Singh, A modified procedure for in vitro spermicidal assay of neem products. Neem Newsletter, 1990, 7, [16] J. Bardhan, S.S. Riar, R.C. Sawhney, A.K. Kain, P. Thomas, G. Iiavazhagan, Ind. J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 1991, 35, [17] S.S. Riar, C. Devakumar, G. Iiavazhagan, J. Bardhan, A.K. Kain, P. Thomas, R. Singh, B. Singh, Contraception, 1990, 42, [18] S.S. Riar, C. Devakumar, R.C. Sawhney, G. Iiavazhagan, J. Bardhan, A.K. Kain, P. Thomas, R. Singh, B. Singh, R. Parshad, Contraception, 1991, 44, [19] M. Mateenuddin, K.K. Kharaitkar, K.N. Mendulkar, N.L. Sadre, Indian Journal Physiology Pharmacology, 1986, 30, [20] A.O. Prakash, R.K. Tewari, R. Mathur, J. Ethnopharmacol., 1988, 23, [21] R. Tewari, S. Pathak, A. Prakash, J.Ethnopharmacol., 1989, 25, [22] A.K. Khare, M.C. Isrivastava, M.K. Sharma, J.P. Tewari, Probe, 1984, 23, 2, [23] A.O. Prakash, R. Mathur, Planta Medica, 1986, 5, [24] S.P. Murthy, M. Sirsi, Ind. J. Physiol Pharmacol., 1958, 2,
6 [25] M.P. Suryanarayana, M. Sirsi, Ind. J. Physiol Pharma., 1958, 2, [26] A.O. Prakash, R.K. Tiwari, R. Mathur, J.Ethnopharmacol., 1988, 23, [27] A.O. Prakash, Exploitation of neem oil as an antifertility agent, Intern. Conf. Recent advances in Medicinal Aromatic and Spice Crops, New Delhi, India, [28] A. Mishra, A.O. Prakash, Effect of extract of Azadirachta indica A. juss (seeds) on the vital and reproductive organs to cyclic rats, Intern. Conf. Recent Advances in Medicinal, Aromatic and Spice Crops, New Delhi, India, [29] A. Purohit, V.P. Dixit, Neem Newsletter, 1940, 8, [30] V.Y. Deshpande, K.N. Mendulkar, N.L. Sadre, J. Postgraduate Med., 1980, 26, [31] V.Y. Deshpande, K.N. Mendulkar, N.L. Sadre, Male antifertility activity of Azadirachta indica in mice, Asian Symp. Medicinal plants and Spices, Bangkok, Thailand, [32] N.L. Sadre, V.Y. Deshpande, K.N. Mendulkar, D.H. Nandal, Male antifertility activity of Azadirachta indica in different species, Proc. 2nd Int. Neem conf., 1983; pp [33] A.R. Joshi, R.N. Ahamed, K.M. Pathan, B. Mannivanan, Indian J Exp. Biol., 1996, 34, [34] R.H. Aladdakatti, R.N. Ahmad, M. Ahmad, M.G. Ghosesawar, Basic Clin Pharmacol., 2001, 12, [35] S.N. Upadhyay, S. Dhawan, G.P. Talwar, J Androl., 1993, 14, [36] G.P. Talwar, S. Shah, S. Mukherjee, R. Chabra, Am. J. Reprod. Immunol., 1997, 37, [37] S. Mukherjee, N.K. Lohiya, R. Pal, M.G. Shamla, G.P. Talwar, Contraception, 1990, 53, [38] E. Knobil, J.D. Neill, The Physiology of reproduction, Vol.1, Raven Press, New York, 1994; pp.139. [39] S. Garg, U. Taluja, S.N. Upadhyay, G.P. Talwar, Contraception, 1993, 48, [40] S. Garg, G. Doncel, S. Chabra, S.N. Upadhyay, G.P. Talwar, Contraception, 1994, 50, [41] S.N. Upadhyay, C. Kaushic, G.P. Talwar, Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B, 1990, 242, [42] K.C. Sinha, S.S. Riar, Biological Memoirs., 1985, 110, 1-2, [43] B. Khillare, T.G. Shrivastav, Contraception, 2003, 68, [44] B.N. Dhawan, M.P. Dubey, B.N. Mehrotra, R.P. Rastogi, J.S. Tandon, Indian J. Exp. Biol., 1980, 18, [45] R.K. Tewari, R. Mathur, A.O. Parkash, Icrs J Med Sci., 1986, 14, 10, [46] R. Lal, M. Gandhi, A. Sankranarayanana, V.S. Mathur, P.L. Sharma, Fitoterapia, 1987, 58, 4, [47] R. Lal, A. Sankranarayuanan, V.S. Mathur, P.I. Sharma, Ind. J. Med. Res., 1986, 83, [48] D.N. Choudhary, J.N. Singh, S.K. Verma, B.P. Singh, Indian J Exp. Biol., 1990, 28, 8, [49] P.D. Shaikh, B.M. Mannivanan, K.M. Pathan, M. Kasturi, R.N. Ahamed, Curr. Sci., 1993, 64, 9, [50] S.C. Juneja, R.S. Williams, Life Sci., 1993, 53, 18, [51] G.P. Talwar, S. Garg, Y. Ohar, R. Chabra, A. Ganju, S.N. Upadhyay, Curr Sci., 1995, 68, 4,
SPERMICIDAL ACTIVITY IN VITRO OF BARK EXTRACT OF AZADIRACHTA INDICA IN RATS
 Ancient Science of Life Vol. No XX (&2) July, August, September, October 2000 SPERMICIDAL ACTIVITY IN VITRO OF BARK EXTRACT OF AZADIRACHTA INDICA IN RATS VINITA BHARGAVA and A.O. PRAKASH Laboratory of
Ancient Science of Life Vol. No XX (&2) July, August, September, October 2000 SPERMICIDAL ACTIVITY IN VITRO OF BARK EXTRACT OF AZADIRACHTA INDICA IN RATS VINITA BHARGAVA and A.O. PRAKASH Laboratory of
Neem - natural contraceptive for male and female - an overview
 1 Int. J. Biomol. & Biomed. International Journal of Biomolecules and Biomedicine (IJBB) ISSN: 2221-1063 (Print) 2222-503X (Online) Vol. 1, No.2, p. 1-6, 2011 http://www.innspub.net REVIEW PAPER OPEN ACCESS
1 Int. J. Biomol. & Biomed. International Journal of Biomolecules and Biomedicine (IJBB) ISSN: 2221-1063 (Print) 2222-503X (Online) Vol. 1, No.2, p. 1-6, 2011 http://www.innspub.net REVIEW PAPER OPEN ACCESS
ANTIANDROGENIC PROPERTIES OF NEEM SEED OIL (AZADIRACHTA INDICA) IN MALE RAT AND RABBI
 Ancient Science of Life, Vol No. VII No. 1 July 1987, ANTIANDROGENIC PROPERTIES OF NEEM SEED OIL (AZADIRACHTA INDICA) IN MALE RAT AND RABBI J. D. SHARMA, R. K. JHA, IRA GUPTA, PRABHA JAIN & V.P. DIXIT
Ancient Science of Life, Vol No. VII No. 1 July 1987, ANTIANDROGENIC PROPERTIES OF NEEM SEED OIL (AZADIRACHTA INDICA) IN MALE RAT AND RABBI J. D. SHARMA, R. K. JHA, IRA GUPTA, PRABHA JAIN & V.P. DIXIT
Antidiabetic Activity of Alcoholic Extract of Neem (Azadirachta Indica) Root Bark
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Antidiabetic Activity of Alcoholic Extract of Neem (Azadirachta Indica) Root Bark Prabhakar Patil 1, Sudha Patil 2, Abhay Mane 3, Sushilkumar Verma 4 1 Department of Pharmacology, Navodaya
RESEARCH ARTICLE Antidiabetic Activity of Alcoholic Extract of Neem (Azadirachta Indica) Root Bark Prabhakar Patil 1, Sudha Patil 2, Abhay Mane 3, Sushilkumar Verma 4 1 Department of Pharmacology, Navodaya
Pharmacologyonline 3: (2011) Newsletter Patil et al.
 ANALGESIC ACTIVITY OF ALCOHOLIC EXTRACT OF AZAIRACHTA INDICA (NEEM) ROOT BARK Prabhakar Patil 1*,Sudha Patil 2,Sushilkumar Verma 3,Prabhakar Adake 4 1.Deparment of pharmacology Navodya Medical College
ANALGESIC ACTIVITY OF ALCOHOLIC EXTRACT OF AZAIRACHTA INDICA (NEEM) ROOT BARK Prabhakar Patil 1*,Sudha Patil 2,Sushilkumar Verma 3,Prabhakar Adake 4 1.Deparment of pharmacology Navodya Medical College
SPERMICIDAL ACTIVITY I AQUEOUS EXTRACT OF ABRUS PRECATORIUS (L.) I MALE ALBI O RATS. Rajeshwari Saraswat
 SPERMICIDAL ACTIVITY I AQUEOUS EXTRACT OF ABRUS PRECATORIUS (L.) I MALE ALBI O RATS Department of Chemistry, S..Arts, D.J.M.Commerce & B..S.Science College, Sangamner-422605 Corresponding author: Dr. Department
SPERMICIDAL ACTIVITY I AQUEOUS EXTRACT OF ABRUS PRECATORIUS (L.) I MALE ALBI O RATS Department of Chemistry, S..Arts, D.J.M.Commerce & B..S.Science College, Sangamner-422605 Corresponding author: Dr. Department
WHAT ARE CONTRACEPTIVES?
 CONTRACEPTION WHAT ARE CONTRACEPTIVES? Methods used to prevent fertilization *Also referred to as birth control methods With contraceptives, it is important to look at what works for you and your body.
CONTRACEPTION WHAT ARE CONTRACEPTIVES? Methods used to prevent fertilization *Also referred to as birth control methods With contraceptives, it is important to look at what works for you and your body.
Reversible contraceptive efficacy and safety evaluation of ethanolic extract of Tinospora cordifolia in animal model
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Archives of Applied Science Research, 2011, 3 (5):587-592 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X CODEN (USA) AASRC9 Reversible
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Archives of Applied Science Research, 2011, 3 (5):587-592 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X CODEN (USA) AASRC9 Reversible
Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment
 Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development Section 1 1. Distinguish between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. 2. Which form of reproduction: a.
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development Section 1 1. Distinguish between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. 2. Which form of reproduction: a.
(Received 5th July 1968)
 EFFECT OF AN INTRA-UTERINE DEVICE ON CONCEPTION AND OVULATION IN THE RHESUS MONKEY W. A. KELLY, J. H. MARSTON and P. ECKSTEIN Department of Anatomy, Medical School, Birmingham 15 (Received 5th July 1968)
EFFECT OF AN INTRA-UTERINE DEVICE ON CONCEPTION AND OVULATION IN THE RHESUS MONKEY W. A. KELLY, J. H. MARSTON and P. ECKSTEIN Department of Anatomy, Medical School, Birmingham 15 (Received 5th July 1968)
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Web Activity: Simulation Structures of the Female Reproductive System
 differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya
 Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
C ONSIDERABLE ATTENTION has been given to the antifertility effects of
 Effects of Clomiphene at Different Stages of Pregnancy in the Rat Implications Regarding Possible Action Mechanisms 0. W. DAVIDSON, M.D.,"' K. WADA, M.D.,t and S. J. SEGAL, Ph.D. C ONSIDERABLE ATTENTION
Effects of Clomiphene at Different Stages of Pregnancy in the Rat Implications Regarding Possible Action Mechanisms 0. W. DAVIDSON, M.D.,"' K. WADA, M.D.,t and S. J. SEGAL, Ph.D. C ONSIDERABLE ATTENTION
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
IN VITRO FERTILIZATION OF RABBIT EGGS IN OVIDUCT SECRETIONS FROM DIFFERENT DAYS BEFORE AND AFTER OVULATION*
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright~ 1975 The American Fertility Society Vol. 26, No.7, July 1975 Printed in U.SA. IN VITRO FERTILIZATION OF RABBIT EGGS IN OVIDUCT SECRETIONS FROM DIFFERENT DAYS BEFORE AND
FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright~ 1975 The American Fertility Society Vol. 26, No.7, July 1975 Printed in U.SA. IN VITRO FERTILIZATION OF RABBIT EGGS IN OVIDUCT SECRETIONS FROM DIFFERENT DAYS BEFORE AND
SPERMICIDAL ACTIVITY I AQUEOUS EXTRACT OF BUTEA MO OSPERMA (L.) I MALE ALBI O RATS
 SPERMICIDAL ACTIVITY I AQUEOUS EXTRACT OF BUTEA MO OSPERMA (L.) I MALE ALBI O RATS Rajeshwari Saraswat 1*, Raghunath Pokharkar 2 & Surendra Saraswat 3 1&2 Department of Chemistry, S..Arts, D.J.M.Commerce
SPERMICIDAL ACTIVITY I AQUEOUS EXTRACT OF BUTEA MO OSPERMA (L.) I MALE ALBI O RATS Rajeshwari Saraswat 1*, Raghunath Pokharkar 2 & Surendra Saraswat 3 1&2 Department of Chemistry, S..Arts, D.J.M.Commerce
Fertility and early embryonic development. Chris Willoughby, Huntingdon Life Sciences 11 October 2012
 Fertility and early embryonic development Chris Willoughby, Huntingdon Life Sciences 11 October 2012 Outline 2 What sort of compounds may affect fertility? What areas of reproduction are we assessing in
Fertility and early embryonic development Chris Willoughby, Huntingdon Life Sciences 11 October 2012 Outline 2 What sort of compounds may affect fertility? What areas of reproduction are we assessing in
Biology of fertility control. Higher Human Biology
 Biology of fertility control Higher Human Biology Learning Intention Compare fertile periods in females and males What is infertility? Infertility is the inability of a sexually active, non-contracepting
Biology of fertility control Higher Human Biology Learning Intention Compare fertile periods in females and males What is infertility? Infertility is the inability of a sexually active, non-contracepting
HISTOLOGY OF GONADS IN TILAPIA ZILLII (GERVAIS) FED NEEM (AZADIRACHTA INDICA) LEAF MEAL DIETS
 8 th International Symposium on Tilapia in Aquaculture 2008 1129 HISTOLOGY OF GONADS IN TILAPIA ZILLII (GERVAIS) FED NEEM (AZADIRACHTA INDICA) LEAF MEAL DIETS TEMITOPE JEGEDE 1 AND OYEDAPO FAGBENRO 2 1.
8 th International Symposium on Tilapia in Aquaculture 2008 1129 HISTOLOGY OF GONADS IN TILAPIA ZILLII (GERVAIS) FED NEEM (AZADIRACHTA INDICA) LEAF MEAL DIETS TEMITOPE JEGEDE 1 AND OYEDAPO FAGBENRO 2 1.
Contraceptives. Kim Dawson October 2010
 Contraceptives Kim Dawson October 2010 Objectives: You will learn about: The about the different methods of birth control. How to use each method of birth control. Emergency contraception What are they?
Contraceptives Kim Dawson October 2010 Objectives: You will learn about: The about the different methods of birth control. How to use each method of birth control. Emergency contraception What are they?
Antifertility potential of Neem flower extract on adult female Sprague-Dawley rats
 Antifertility potential of Neem flower extract on adult female Sprague-Dawley rats Gbotolorun S.C., Osinubi A.A., Noronha C.C., Okanlawon A.O. Department of Anatomy, College of Medicine, University of
Antifertility potential of Neem flower extract on adult female Sprague-Dawley rats Gbotolorun S.C., Osinubi A.A., Noronha C.C., Okanlawon A.O. Department of Anatomy, College of Medicine, University of
Effects of Crude Extract of Neem (Azadirachta indica) in Bone Marrow Cells of Mice
 _??_ 1995 The Japan Mendel Society Cytologia 60: 189-193, 1995 Genotoxic Effects of Crude Extract of Neem (Azadirachta indica) in Bone Marrow Cells of Mice K. S. Awasthy1, O. P. Chaurasia and S. P. Sinha
_??_ 1995 The Japan Mendel Society Cytologia 60: 189-193, 1995 Genotoxic Effects of Crude Extract of Neem (Azadirachta indica) in Bone Marrow Cells of Mice K. S. Awasthy1, O. P. Chaurasia and S. P. Sinha
100% Highly effective No cost No side effects
 effective? Advantages Disadvantages How do I get Cost Abstinence For some it can mean no sexual contact. For others it is no sexual intercourse or vaginal penetration. A permanent surgical procedure available
effective? Advantages Disadvantages How do I get Cost Abstinence For some it can mean no sexual contact. For others it is no sexual intercourse or vaginal penetration. A permanent surgical procedure available
Human Reproduction. Human Reproductive System. Scrotum. Male Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System Human Reproduction Chapter 41 Contraceptives Scrotum Testes Epididymus Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Bulbourethral Gland Penis Scrotum Sac of smooth muscle tissue
Human Reproductive System Human Reproduction Chapter 41 Contraceptives Scrotum Testes Epididymus Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Bulbourethral Gland Penis Scrotum Sac of smooth muscle tissue
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal
 What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
Antifertility Effects of Aqueous Leaf Stalk Extract of Piper betel on Seminal LDH Isozymes in Mice
 Human Journals Research Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Aarti Verma et al. Antifertility Effects of Aqueous Leaf Stalk Extract of Piper betel on Seminal LDH Isozymes in
Human Journals Research Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Aarti Verma et al. Antifertility Effects of Aqueous Leaf Stalk Extract of Piper betel on Seminal LDH Isozymes in
LIFE SCIENCES Grade 12 REPRODUCTION 30 JUNE 2014
 REPRODUCTION 30 JUNE 2014 Checklist Make sure you Can describe different reproductive strategies of vertebrates Are able to identify the structure and function of the male and female reproductive organs
REPRODUCTION 30 JUNE 2014 Checklist Make sure you Can describe different reproductive strategies of vertebrates Are able to identify the structure and function of the male and female reproductive organs
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I)
 Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Intrauterine Insemination - FAQs Q. How Does Pregnancy Occur?
 Published on: 8 Apr 2013 Intrauterine Insemination - FAQs Q. How Does Pregnancy Occur? A. The female reproductive system involves the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix and vagina. The female hormones,
Published on: 8 Apr 2013 Intrauterine Insemination - FAQs Q. How Does Pregnancy Occur? A. The female reproductive system involves the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix and vagina. The female hormones,
Sperm production. Sperm production. Meiosis. Mitosis. The cells of Leydig in testes secrete
 Sperm production Ductus deferens Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Sperm production Ductus deferens Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Sperm production. Sperm production. Controlling sperm production. Meiosis. Mitosis. The cells of Leydig in testes secrete
 Ductus deferens Sperm production Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Ductus deferens Sperm production Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Contraception Effective Methods of Birth Control
 Contraception Effective Methods of Birth Control Abstinence Means choosing NOT to have sex It is the ONLY method that is 100% effective It is your right to be in control of your body and say NO What are
Contraception Effective Methods of Birth Control Abstinence Means choosing NOT to have sex It is the ONLY method that is 100% effective It is your right to be in control of your body and say NO What are
Asian Journal of Pharmacy and Life Science ISSN Vol. 1 (4), Oct-Dec, 2011
 Studies on antifertility effect of rhizome of curcuma longa linn. Amit kumar ghosh* (1), Anup kumar das (1), Kajal kumar patra (3), 1. Department of Pharmacology, R.G.Kar Medical College, Kolkata, India
Studies on antifertility effect of rhizome of curcuma longa linn. Amit kumar ghosh* (1), Anup kumar das (1), Kajal kumar patra (3), 1. Department of Pharmacology, R.G.Kar Medical College, Kolkata, India
ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY OF HELICTERES ISORA ROOT
 ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY OF HELICTERES ISORA ROOT Sama Venkatesh *1, G.Dayananda Reddy 1, B.Madhava Reddy 1, M.Lakshman 2. 1 Department of Pharmacognosy, G.Pulla Reddy College of Pharmacy, Mehdipatnam, Hyderabad
ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY OF HELICTERES ISORA ROOT Sama Venkatesh *1, G.Dayananda Reddy 1, B.Madhava Reddy 1, M.Lakshman 2. 1 Department of Pharmacognosy, G.Pulla Reddy College of Pharmacy, Mehdipatnam, Hyderabad
REPRODUCCIÓN. La idea fija. Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Animal Reproductive Systems. Chapter 42
 Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
6.6 Hormones, homeostasis and reproduction
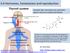 6.6 Hormones, homeostasis and reproduction Essential idea: Hormones are used when signals need to be widely distributed. Thyroxin is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland. It's key role is in controlling
6.6 Hormones, homeostasis and reproduction Essential idea: Hormones are used when signals need to be widely distributed. Thyroxin is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland. It's key role is in controlling
1.Abstinence no sex (Abstinence only education has been proven ineffective in preventing unwanted pregnancies)
 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Contraception 2. STDs 1. Ovary Transplants 2. Freezing Eggs 3. Choosing Gender 4. The Male Pill, parts 1&2 5. Male Birth Control: RISUG 6. Birth Control. 1.Abstinence
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Contraception 2. STDs 1. Ovary Transplants 2. Freezing Eggs 3. Choosing Gender 4. The Male Pill, parts 1&2 5. Male Birth Control: RISUG 6. Birth Control. 1.Abstinence
Reproductive System. Testes. Accessory reproductive organs. gametogenesis hormones. Reproductive tract & Glands
 Reproductive System Testes gametogenesis hormones Accessory reproductive organs Reproductive tract & Glands transport gametes provide nourishment for gametes Hormonal regulation in men Hypothalamus - puberty
Reproductive System Testes gametogenesis hormones Accessory reproductive organs Reproductive tract & Glands transport gametes provide nourishment for gametes Hormonal regulation in men Hypothalamus - puberty
Chris Davies & Greg Handley
 Chris Davies & Greg Handley Contents Definition Epidemiology Aetiology Conditions for pregnancy Female Infertility Male Infertility Shared infertility Treatment Definition Failure of a couple to conceive
Chris Davies & Greg Handley Contents Definition Epidemiology Aetiology Conditions for pregnancy Female Infertility Male Infertility Shared infertility Treatment Definition Failure of a couple to conceive
List of Equipment, Tools, Supplies, and Facilities:
 Unit B: Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6: Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the
Unit B: Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6: Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction
 Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
Family Planning and Infertility
 Family Planning and Infertility Chapter 20 Objectives Discuss types of reversible contraception Natural methods Mechanical barrier methods Hormonal contraceptives Discuss types of permanent contraception
Family Planning and Infertility Chapter 20 Objectives Discuss types of reversible contraception Natural methods Mechanical barrier methods Hormonal contraceptives Discuss types of permanent contraception
Bio 3201 Unit 2 REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT. Cell Division MITOSIS (P )
 Bio 3201 Unit 2 REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT 31 Hours Cell Division MITOSIS (P. 460-469) 1. Describe mitosis in detail; Specifically describe, in detail, the events of interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis
Bio 3201 Unit 2 REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT 31 Hours Cell Division MITOSIS (P. 460-469) 1. Describe mitosis in detail; Specifically describe, in detail, the events of interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis
ANTIBACTERIAL EFFECTS OF CRUDE EXTRACT OF Azadirachta indica AGAINST Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 2, No 5, 2013, 989 993 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) ANTIBACTERIAL EFFECTS OF CRUDE EXTRACT OF Azadirachta indica AGAINST Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 2, No 5, 2013, 989 993 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) ANTIBACTERIAL EFFECTS OF CRUDE EXTRACT OF Azadirachta indica AGAINST Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus
The use of laser to improve semen quality and reproduction performance of sows. Dr. Ivan Sheyko, Bielorussia ; ;
 use of laser to improve semen quality and reproduction performance of sows. Dr. Ivan Sheyko, Bielorussia ; ; In Belarus pig breeding is based on commercial technologies providing for artificial insemination.
use of laser to improve semen quality and reproduction performance of sows. Dr. Ivan Sheyko, Bielorussia ; ; In Belarus pig breeding is based on commercial technologies providing for artificial insemination.
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom
 1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
to ensure the. Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion of.
 The Reproductive System Fill-In Notes Purpose of life: to ensure the. Stages of Human Development Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion
The Reproductive System Fill-In Notes Purpose of life: to ensure the. Stages of Human Development Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF, ISSN: Vol.8, No.2, pp , 2015
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF, ISSN: 0974-4304 Vol.8, No.2, pp 273-279, 2015 Effect of Melia azedarach Linn. Seed Extract on Estrous Cycle and Reproductive Performance
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF, ISSN: 0974-4304 Vol.8, No.2, pp 273-279, 2015 Effect of Melia azedarach Linn. Seed Extract on Estrous Cycle and Reproductive Performance
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
ANTIPYRETIC ACTIVITY OF TBR-002, A HERBAL FORMULATION
 Ancient Science of Life, Vol No. XV No.1 July 1995, ANTIPYRETIC ACTIVITY OF TBR-002, A HERBAL FORMULATION A. SUBRAMANIAM, P.PUSHPANGADAN, S.RAJASEKHARAN AND P.G LATHA Division of Ethnopharmacology and
Ancient Science of Life, Vol No. XV No.1 July 1995, ANTIPYRETIC ACTIVITY OF TBR-002, A HERBAL FORMULATION A. SUBRAMANIAM, P.PUSHPANGADAN, S.RAJASEKHARAN AND P.G LATHA Division of Ethnopharmacology and
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
What to do about infertility?
 What to do about infertility? Dr. M.A. Fischer Section Head, Division of Urology, Department of Surgery Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Hamilton Health Sciences, Hamilton,
What to do about infertility? Dr. M.A. Fischer Section Head, Division of Urology, Department of Surgery Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Hamilton Health Sciences, Hamilton,
Small Ruminant Reproductive Management Workshop
 Small Ruminant Reproductive Management Workshop Animal Nutrition and Physiology Center, North Dakota State University Sponsors: American Sheep and Goat Center, North Dakota State University, University
Small Ruminant Reproductive Management Workshop Animal Nutrition and Physiology Center, North Dakota State University Sponsors: American Sheep and Goat Center, North Dakota State University, University
Urinary System Chapter 16
 Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones
 10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
In Vitro Antioxidant Activity and Phytochemical Screening of Pholidota articulata
 Human Journals Research Article November 2016 Vol.:5, Issue:1 All rights are reserved by Darshan Singh et al. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity and Phytochemical Screening of Pholidota articulata Keywords:
Human Journals Research Article November 2016 Vol.:5, Issue:1 All rights are reserved by Darshan Singh et al. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity and Phytochemical Screening of Pholidota articulata Keywords:
Unit 6 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Reproductive System Test Bank
 Unit 6 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Reproductive System Test Bank Objective 6.01 Describe the basic functions of the reproductive system. 1. Which of the following is a function of the reproductive system? a. Production
Unit 6 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Reproductive System Test Bank Objective 6.01 Describe the basic functions of the reproductive system. 1. Which of the following is a function of the reproductive system? a. Production
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
EFFECTS OF ORAL ADMINISTRATION OF MORINGA OLEIFERA SEED ON BLOOD CHEMISTRY AND REPRODUCTIVE PERFORMANCE OF FEMALE RABBITS
 Int. J. Agric.Sc & Vet.Med. 2014 Musa Azara S I et al., 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2320-3730 www.ijasvm.com Vol. 2, No. 1, February 2014 2014 www.ijasvm.com. All Rights Reserved EFFECTS OF ORAL ADMINISTRATION
Int. J. Agric.Sc & Vet.Med. 2014 Musa Azara S I et al., 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2320-3730 www.ijasvm.com Vol. 2, No. 1, February 2014 2014 www.ijasvm.com. All Rights Reserved EFFECTS OF ORAL ADMINISTRATION
Infertility: failure to conceive within one year of unprotected regular sexual intercourse. Primary secondary
 Subfertility Infertility: failure to conceive within one year of unprotected regular sexual intercourse. Primary secondary Infertility affects about 15 % of couples. age of the female. Other factors that
Subfertility Infertility: failure to conceive within one year of unprotected regular sexual intercourse. Primary secondary Infertility affects about 15 % of couples. age of the female. Other factors that
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes
 Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
The following lesson on contraception (birth control) is not intended to infer that you will be sexually active as a teen. This is information that
 The following lesson on contraception (birth control) is not intended to infer that you will be sexually active as a teen. This is information that may be used in the future Abstinence Choosing not to
The following lesson on contraception (birth control) is not intended to infer that you will be sexually active as a teen. This is information that may be used in the future Abstinence Choosing not to
17. Preventing pregnancy
 17. Preventing pregnancy Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Define contraception. List ways young people can prevent pregnancy. Background notes What is contraception?
17. Preventing pregnancy Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Define contraception. List ways young people can prevent pregnancy. Background notes What is contraception?
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
THE EFFECTS OF LIGATION OF CAUDA EPIDIDYMIDIS ON THE DOG TESTIS
 Copyright 1974 The American Fertility Society FERTILITY AND STERILITY Vol. 25, No.3, March, 1974 Printed in U.S.A. THE EFFECTS OF LIGATION OF CAUDA EPIDIDYMIDIS ON THE DOG TESTIS A. M. VARE, M.B.B.S.,
Copyright 1974 The American Fertility Society FERTILITY AND STERILITY Vol. 25, No.3, March, 1974 Printed in U.S.A. THE EFFECTS OF LIGATION OF CAUDA EPIDIDYMIDIS ON THE DOG TESTIS A. M. VARE, M.B.B.S.,
Reproductive Systems. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Male reproduction. Cross section of Human Testis ผศ.ดร.พญ.ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ภาคว ชาสร รว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล 1. Aims
 Aims Male reproduction Male reproductive structure Spermatogenesis ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ห อง 216 โทร: 7578 Hypothalamo-pituitary-testicular axis Male sex hormone action Male reproductive structure Male reproductive
Aims Male reproduction Male reproductive structure Spermatogenesis ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ห อง 216 โทร: 7578 Hypothalamo-pituitary-testicular axis Male sex hormone action Male reproductive structure Male reproductive
In vitro antimicrobial activity of leaves and bark extracts of Ficus religiosa (Linn.)
 INDIAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL & BIOLOGICAL RESEARCH (IJPBR). Vol. 1 (1), March., 13 In vitro antimicrobial activity of leaves and bark extracts of Ficus religiosa (Linn.) G.Ramakrishnaiah * 1, T. Hariprasad
INDIAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL & BIOLOGICAL RESEARCH (IJPBR). Vol. 1 (1), March., 13 In vitro antimicrobial activity of leaves and bark extracts of Ficus religiosa (Linn.) G.Ramakrishnaiah * 1, T. Hariprasad
THE EFFECT OF COPPER IMPLANTS IN THE REMINAL VESICLES ON FERTILITY OF THE RAT, RABBIT, AND HAMSTER*
 FERTILITY A(\O Sn:HILIT'l Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 24, :-';0. 1..January 1973 Printed in U.S.A. THE EFFECT OF COPPER IMPLANTS IN THE REMINAL VESICLES ON FERTILITY OF THE RAT, RABBIT,
FERTILITY A(\O Sn:HILIT'l Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 24, :-';0. 1..January 1973 Printed in U.S.A. THE EFFECT OF COPPER IMPLANTS IN THE REMINAL VESICLES ON FERTILITY OF THE RAT, RABBIT,
In vitro study of antibacterial activity of Carissa carandas leaf extracts
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 2012, 2 (1):36-40 ISSN : 2249-7412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY In vitro study of antibacterial activity of Carissa
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 2012, 2 (1):36-40 ISSN : 2249-7412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY In vitro study of antibacterial activity of Carissa
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
THE EFFECT OF OESTRIN ON THE TESTIS OF THE ADULT MOUSE
 389 THE EFFECT OF OESTRIN ON THE TESTIS OF THE ADULT MOUSE BY MARJORIE ALLANSON. (Harold Row Research Scholar, King's College, London.) (Received 5th March, 1931.) (With One Plate.) I. INTRODUCTION. THE
389 THE EFFECT OF OESTRIN ON THE TESTIS OF THE ADULT MOUSE BY MARJORIE ALLANSON. (Harold Row Research Scholar, King's College, London.) (Received 5th March, 1931.) (With One Plate.) I. INTRODUCTION. THE
Unit 9 CONTRACEPTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 Unit 9 CONTRACEPTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Become aware of the magnitude of teen age sexual activity and pregnancy and some of the social and economic effects. 2. Learn about the various means of contraception,
Unit 9 CONTRACEPTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Become aware of the magnitude of teen age sexual activity and pregnancy and some of the social and economic effects. 2. Learn about the various means of contraception,
Spermicidal activity of the hexane extract of Piper longum: An in vitro study
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Spermicidal activity of the hexane extract of Piper longum: An in vitro study Abu Hasnath Md Golam Sarwar a, b, Ranjeet Kumar Nirala a, b, Mohammed Arif a, Beena Khillare b, Sonu
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Spermicidal activity of the hexane extract of Piper longum: An in vitro study Abu Hasnath Md Golam Sarwar a, b, Ranjeet Kumar Nirala a, b, Mohammed Arif a, Beena Khillare b, Sonu
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE
 Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Neem( Azadirachta Indica)
 Neem( Azadirachta Indica) Botanical name: Azadirachta Indica Family: Meliaceae, The mahogany tree family Names of Neem in Different Languages English: Neem, Indian Lilac, Margosa Tree, Nim, Crackjack,
Neem( Azadirachta Indica) Botanical name: Azadirachta Indica Family: Meliaceae, The mahogany tree family Names of Neem in Different Languages English: Neem, Indian Lilac, Margosa Tree, Nim, Crackjack,
FERTILITY & TCM. On line course provided by. Taught by Clara Cohen
 FERTILITY & TCM On line course provided by Taught by Clara Cohen FERTILITY & TCM FERTILITY AND TCM THE PRACTITIONER S ROLE CAUSES OF INFERTILITY RISK FACTORS OBJECTIVES UNDERSTANDING TESTS Conception in
FERTILITY & TCM On line course provided by Taught by Clara Cohen FERTILITY & TCM FERTILITY AND TCM THE PRACTITIONER S ROLE CAUSES OF INFERTILITY RISK FACTORS OBJECTIVES UNDERSTANDING TESTS Conception in
DATE: NAME: CLASS: Chapter 14 Test
 Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction
 Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
TOPICAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ACTIVITY OF PINDA THAILAM, A HERBAL GEL FORMULATION
 Ancient Science of Life Vol : XXVI (1) July, August, September 2004 TOPICAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ACTIVITY OF PINDA THAILAM, A HERBAL GEL FORMULATION K.Periyanayagam, T. Venkatarathnakumar, A. Nagaveni, V.G.Subitha,
Ancient Science of Life Vol : XXVI (1) July, August, September 2004 TOPICAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ACTIVITY OF PINDA THAILAM, A HERBAL GEL FORMULATION K.Periyanayagam, T. Venkatarathnakumar, A. Nagaveni, V.G.Subitha,
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Chapter 14 The Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
AP Biology Ch ANIMAL REPRODUCTION. Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below.
 AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
Outline OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
 UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
Reproductive Endocrinology. Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007
 Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Reproductive physiology. About this Chapter. Case introduction. The brain directs reproduction 2010/6/29. The Male Reproductive System
 Section Ⅻ Reproductive physiology Ming-jie Wang E-Mail: mjwang@shmu.edu.cn About this Chapter The reproductive organs and how they work the major endocrine functions of sexual glands actions of sex hormones
Section Ⅻ Reproductive physiology Ming-jie Wang E-Mail: mjwang@shmu.edu.cn About this Chapter The reproductive organs and how they work the major endocrine functions of sexual glands actions of sex hormones
Structure and physiology of mammalian vas deferens in relation to fertility regulation
 J. Biosci., Vol. 7, Number 2, March 1985, pp. 215 221. Printed in India. Structure and physiology of mammalian vas deferens in relation to fertility regulation N. J. CHINOY Department of Zoology, University
J. Biosci., Vol. 7, Number 2, March 1985, pp. 215 221. Printed in India. Structure and physiology of mammalian vas deferens in relation to fertility regulation N. J. CHINOY Department of Zoology, University
Reproductive System:
 Reproductive System: Purpose: The reproductive system combines genetic information from both parents (in most animals) to produce new life forms. This system produces sex cells (gametes), delivers them,
Reproductive System: Purpose: The reproductive system combines genetic information from both parents (in most animals) to produce new life forms. This system produces sex cells (gametes), delivers them,
