D A Elphick, Y R Mahida
|
|
|
- Shavonne Green
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1802 Reent advanes in basi siene PANETH CELLS: THEIR ROLE IN INNATE IMMUNITY AND INFLAMMATORY DISEASE THE See end of artile for authors affiliations Correspondene to: Professor Y R Mahida, Institute of Infetion, Immunity, and Inflammation, C Floor, West Blok, Queen s Medial Centre, Nottingham NG7 2UH, UK; Yash.Mahida@ Nottingham.a.uk I D A Elphik, Y R Mahida Gut 2005; 54: doi: /gut n this artile, we disuss the urrent understanding of how the intestinal muosa may exert ontrol over luminal bateria, and how intestinal inflammation ould ensue when this ontrol is lost. We shall review researh showing how Paneth ells, and evolutionarily onserved innate immune mehanisms, are emerging as key mediators of intestinal muosal defene. SMALL BOWEL CHALLENGE Maintenane of a sterile environment in the small intestinal lumen represents a formidable hallenge for the host. The multitude of villi and rypts reate an expansive epithelial surfae of approximately 400 m 2, allowing effiient nutrient absorption but a wealth of potential entry sites for invading mirobes. To heighten the hallenge, the intestinal muosa omprises a single layer of epithelial ells, unlike the multiple layers found at other muosal surfaes. This aids nutrient absorption and water and eletrolyte transport, yet spreads defensive strategies thinly. The nutrient rih luminal ontent would appear to provide an ideal ulture medium, and there is onstant exposure to a large population of miro-organisms, both ingested along with food and from the adjaent olon with its heavy baterial load. In addition, epithelial ells are replaed every 2 5 days from pluripotential stem ells in the base of the rypts 1 and so ontinuous antimirobial protetion for these stem ells is of paramount importane as damage to or parasitisation of stem ells would have severe onsequenes for the maintenane of the normal digestive epithelium. Against all the odds, mirobial density in the healthy proximal small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, proximal ileum) is low. 2 In ontrast, in the distal ileum and olon, there is extensive resident baterial flora (total,10 14 ) onsisting of,400 different speies of anaerobi and aerobi bateria. 3 Muosal defene mehanisms in the proximal small bowel are able to maintain a ruial barrier to mirobial invasion yet allow effiient nutrient absorption. ADAPTIVE VERSUS INNATE IMMUNITY The immune system has many faets, whih an be grouped into adaptive and innate omponents. 4 Adaptive immunity, whih is only found in vertebrates, is mediated by T and B ells whih display struturally unique reeptors that are generated by gene rearrangement. On binding of reeptor to its speifi antigen, lonal expansion of lymphoytes results to eliit a direted immune response. However, it takes three to five days for a suffiient number of lymphoytes to be produed and to differentiate into effetor ells, whih is more than enough time for most pathogens to invade and damage the host. In ontrast, innate immunity refers to inbuilt mehanisms, many of whih are relatively onserved throughout the animal and plant kingdoms, that respond immediately to a wide variety of miro-organisms and an be seen as a first line of defene to ontrol an invasion before lonal lymphoytes an mount a speifi attak. We shall disuss the role of adaptive and innate immune mehanisms in the defene of the gut s epithelial monolayer. Muosal adaptive immunity The adaptive muosal immune system an prinipally be divided into indutive sites, where antigens from muosal surfaes stimulate naïve T and B lymphoytes, and effetor sites, where antigen sensitised ells extravasate and differentiate. Effetor sites inlude the lamina propria and epithelium where synthesis and seretion of seretory IgA (siga) antibodies ours. Whereas systemi immunity depends on antigeni supply to the lymph nodes and spleen via lymph and peripheral blood, the muosal immune system atively samples antigen from muosal surfaes and is tolerant of innouous substanes and ommensal bateria. Indutive sites for muosal immunity onsist of organised lymphati folliles termed muosa assoiated lymphati tissue, whih may our singly or may ongregate in Peyer s pathes (or the appendix), as well as draining lymph nodes 5 Follile assoiated epithelium, whih overs organised lymphoid tissue in the intestine, ontains speialised M ells that transport luminal antigens into the dome area of the follile where antigen presenting dendriti ells (DC) and lymphoytes oexist. DCs also send Gut: first published as /gut on 11 November Downloaded from on 13 August 2018 by guest. Proteted by opyright.
2 proesses between gut epithelial ells without disturbing tight juntion integrity and sample ommensal and pathogeni gut bateria. 5 When T and B ells are ativated in Peyer s pathes, they express the a4b7 integrin and migrate to the blood. 6 Gut endothelial ells express MADCAM-1, the ligand for a4b7, whih allows Peyer s path derived ells to migrate from the blood to the lamina propria. 6 The lamina propria is filled with plasma ells that serete 2 5 g of siga into the gut lumen daily. 7 Dimeri siga is one of the most important defene fators on muosal surfaes. It is resistant to proteolysis, and its task is to prevent both the adherene of bateria to muosa and their penetration into the internal environment. Muosal innate immunity Innate immune mehanisms proteting the gut muosa omprise mehanial, ellular, and hemial omponents working at three levels: the extra-epithelial, epithelial, the subepithelial levels. The mehanial element is the physial barrier of the epithelium, along with muus oating, enteroyte shedding, and peristalsis. The hemial element inludes pathogen Figure 1 Shemati diagram of Toll-like reeptor (TLR) and nuleotide binding oligomerisation domain (NOD) protein interations with omponents of the baterial ell wall and subsequent nulear fator kb (NFkB) ativation. Lipopolysaharide (LPS), diaminopimelate (DAP), and muramyl dipeptide (MDP) from the peptidoglyan (PGN) baterial ell wall bind to TLR4, NOD1, and NOD2, respetively. Phosphorylation (P) of IkBa leads to release of NFkB whih migrates to the nuleus to promote transription of speifi genes. Table1 Reeptor TLR2 TLR2+TLR 1 TLR2+TLR6 TLR3 TLR4 TLR5 TLR7 TLR8 TLR9 NOD1 NOD2 Host reognition of mirobial omponents Ligand Lipoteihoi aid from Gram positive bateria Triayl lipoproteins Diayl lipoproteins dsrna Lipopolysaharide Flagellin ssrna reognition on endosomes (mouse) ssrna reognition on endosomes (human) CpG (baterial) DNA D-Glu-meso-DAP (diaminopimelate; Gram negative peptidoglyan motif) Muramyl dipeptide from peptidoglyan TLR, Toll-like reeptor; NOD, nuleotide binding oligomerisation domain. reognition moleules, proteins, or peptides that indue mirobial killing and ytokines that orhestrate an immune response. The ellular element inludes epithelial ells, mast ells, dendriti ells, phagoyti ells, suh as marophages and granuloytes, natural killer ells, and d T ells. The extra-epithelial defene barrier inludes antimirobial proteins and peptides, suh as lysozyme and defensins, whih disrupt mirobial ell walls, muus oating that traps bateria to be removed by peristalsis, and ommensal flora that provides resistane to olonisation. Defene at the level of the epithelial ell inludes the mehanial barrier to penetration of the epithelial monolayer and tight juntions, and pattern reognition reeptors (PRRs) whih reognise highly onserved motifs, designated pathogen assoiated moleular patterns (PAMPs), whih are present in large groups of miro-organisms, but not their hosts, and are usually essential for the pathogeniity or survival of the mirobe. Examples of PAMPs are lipopolysaharide or peptidoglyan, whih are both omponents of baterial, but not host, ell walls. Unlike lymphoyte reeptors in adaptive immunity, reeptors for the innate immune system are germline oded and, therefore, are not altered by prior exposure to pathogens. 8 9 Binding to PRRs triggers the seretion of hemokines that lead to the reruitment of ellular omponents of the innate immune response. Toll-like reeptors (TLRs) and nuleotide binding oligomerisation domain (NOD) proteins are two lasses of PRRs in mammals TLRs are transmembrane moleules whih link the extraellular ompartment, where reognition of mirobial pathogens ours, and the intraellular ompartment, where signalling asades leading to ellular responses are initiated (fig 1). NOD proteins are ytosoli and so reognise mirobial omponents after invasion into the ell. Toll-like reeptors The first disovery of Toll related proteins in mammals in 1998 was quikly followed by demonstration that mammalian TLR4 was the long sought after signalling reeptor in a protein omplex responsible for the reognition of lipopolysaharide leading to the ellular responses that result in endotoxi shok In mammals, there are at least 11 members of the TLR family, and TLR1 9 are onserved in humans and mie. 11 Many of the PAMPs reognised by individual TLRs have been eluidated (see table 1). Ligand binding to the extraellular leuine-rih repeat portion of the TLRs sets up an intraellular asade of reruitment of adaptor moleules and ativation of kinases, 1803 Gut: first published as /gut on 11 November Downloaded from on 13 August 2018 by guest. Proteted by opyright.
3 1804 whih ulminates in the phosphorylation of IkBa, the inhibitory moleule for nulear fator kb (NFkB). 10 NFkB enompasses induible transription fators that are important ativators of genes involved in inflammatory and immunologial responses. 14 The ative form of NFkB onsists of heterogenous dimers that share a homologous region responsible for DNA binding, nulear loalisation, and ytoplasmi interation with IkB proteins. The p60:p50 heterodimer is the predominant form of ative NFkB. It is stored in an inative state in the ytoplasm bound to inhibitory proteins of the IkB family (of whih IkBa is the best haraterised). IkB masks the nulear loalisation signal of NFkB, thereby retaining it in the ytoplasm. Following stimulation (by, for example, ativated TLR, NOD protein, or proinflammatory ytokines suh as interleukin 1 or tumour nerosis fator a), IkB is degraded to release ative NFkB, whih migrates to the nuleus to bind to its sequene reognition motif on promoters of target genes, leading to transriptional upregulation of a number of genes involved in inflammatory responses. NOD proteins The NOD proteins, NOD1 and NOD2, have reently been shown to represent an intraellular pathogen sensing system in mammals, both reognising baterial peptidoglyan, although eah responding to distint motifs of this moleule (see table 1). 15 Like TLRs, NOD1 and NOD2 have a C terminal series of leuine rih repeats that failitate PAMP reognition. At the N terminus, NOD1 has one aspase ativating and reruitment domain (CARD) while NOD2 had two suh CARD domains. NOD1 and NOD2 are also designated CARD4 and CARD15, respetively. Like TLRs, ativation of NOD proteins sets up an intraellular asade of events ulminating in NFkB ativation via IkBa phosphorylation Reently, researh on NOD2 has reeived onsiderable attention as a geneti approah has identified NOD2 as the first suseptibility gene for Crohn s disease, as well as for Blau syndrome, a rare autoinflammatory disease affeting the eye and joints Subepithelial omponents, inluding marophages, dendriti ells, and myofibroblasts, reognise pathogens and their omponents that have breahed the epithelial layer. Ativation of ell assoiated reeptors leads to release of ytokines and hemokines to reruit innate immune effetor ells, and antigen presentation to T ells to eliit an adaptive immune response. Key points: innate immune mehanisms Germline oded mehanisms that respond immediately to mirobes and do not require prior exposure to antigen Pattern reognition reeptors (PRRs) inlude Toll-like reeptors (TLRs) and nuleotide binding oligomerisation domain (NOD) proteins PRRs reognise pathogen assoiated moleular patterns (PAMPs) PAMPs are present on mirobes but not hosts PAMP reognition leads to mirobial killing by various means Antimirobial peptides, suh as defensins, are important effetors Antigen presenting ells failitate an adaptive immune response Figure 2 Small intestinal rypt showing Paneth ells with seretory granules, stem ells, enteroytes, muin sereting goblet ells, and an intermediate ell (features of Paneth and goblet ells). Exposure to baterial produts leads to release of antimirobial peptides and proteins from Paneth and intermediate ells. PANETH CELLS Paneth ells were first desribed over a entury ago as granulated ells at the base of the small intestinal rypts of Lieberkühn. 20 While their funtion remained an enigma until reent years, they are now onsidered to be important in innate intestinal defene as regulators of mirobial density in the small intestine and in the protetion of nearby stem ells. There are on average 5 12 Paneth ells in eah small intestinal rypt and, in ontrast with other epithelial ell types, they migrate down from the stem ell zone to the rypt base where they are relatively long lived (20 days ompared with 3 5 days for enteroytes) Stem ells also give rise to three other ell lineages enteroytes, goblet ells, and enteroendorine ells most of whih migrate upwards and populate the villi. Paneth ells are filled with numerous prominent apial ytoplasmi granules whih, on ell stimulation, an be released into the rypt lumen (fig 2). 23 Various histohemial stains, inluding eosin, periodi aid Shiff s stain, and phloxine-tartrazine (fig 3), 24 intensely stain the basi Paneth ell granules whereas more reently preise staining has been ahieved with immunohistohemistry employing antibodies against Paneth ell speifi omponents, inluding lysozyme, 25 defensins (fig 4), 26 and seretory phospholipase A2 (spla2). 27 Sometimes, ells with morphologial features of Paneth ells and goblet ells are observed in the villi and are termed intermediate ells (fig 3). Although the funtion of intermediate ells is not lear, they have been shown to express defensins (figs 3, 4). Paneth ell pattern reognition reeptors Studies in Paneth ell ontaining isolated murine small intestinal rypts have shown seretion of mirobiidal peptides (predominantly ryptdins) following exposure to Gram negative or Gram positive bateria or their produts, lipopolysaharide, lipoteihoi aid, lipid A, and muramyl dipeptide. 29 It is of interest that fungi or protozoa did not stimulate Paneth ell degranulation. Whether the baterial produts interat with Paneth ells diretly or via rypt non-paneth ells remains to be determined. Lipid A is the Gut: first published as /gut on 11 November Downloaded from on 13 August 2018 by guest. Proteted by opyright.
4 Figure 3 Low (A, B) and high (C, D) power views of phloxine-tartrazine stained setions of uninfeted ontrol (A, C) and T spiralis infeted (B, D) murine small intestine. A few Paneth ells (with predominantly yellow granules) are present at the base of uninfeted rypts. In T spiralis infeted intestine, there is a marked inrease in the number of Paneth ells (with red granules). Moreover, intermediate ells (arrowed) are seen in some villi. Two (A, B) of the figures are reprodued from Kamal and olleagues, 28 with permission from Blakwell Publishing Ltd. Figure 4 (A) Setion of human jejunal muosa showing human defensin 5 immunoreative Paneth ells at the base of rypts. (B) Transmission eletron mirograph of human jejunal rypt showing three Paneth ells with eletron dense granules in the apial ytoplasm. biologially ative omponent of lipopolysaharide, and isolated Paneth ells have been shown to respond equivalently to different forms of lipid A and lipoteihoi aid, implying reognition of ommon omponents of these glyoproteins. 30 Surprisingly, murine Paneth ells do not express mrna transripts for TLR4. Lipopolysaharide and lipid A mediated Paneth ell responses, independent of TLR4, were demonstrated in TLR4 defiient C3H/HeJ mie. 30 Murine Paneth ells do express mrna transripts for TLR 1 3 and TLR 5 9. The funtional ativity of TLR9 has reently been demonstrated by Paneth ell degranulation in response to its ligand, CpG (baterial) DNA. 31 NOD2 protein, whih is an intraellular reeptor for muramyl dipeptide, has reently been shown to be expressed in the ytoplasm of Paneth ells. The potential role of Paneth ells in the pathogenesis of Crohn s disease in patients with NOD2 mutations is disussed below. Paneth ell antimirobial peptides Several proteins and peptides, inluding lysozyme, spla2, and enteri a-defensins, ryptdin related sequene peptides, and angiogenin 4, with well doumented antimirobial ativity, have been loalised to Paneth ell granules. On exposure to viable or heat killed bateria or to mirobial produts, suh as lipopolysaharide or lipoteihoi aid, Paneth ells release their granules resulting in inreased onentrations of antimirobial peptides in the intestinal lumen. 29 This is believed to prevent mirobial invasion into the rypt miroenvironment, providing protetion for the stem ell zone, and also ontribute towards the ontrol of mirobial density in the small intestinal lumen. Lysozyme Lysozyme is an antibaterial protein that is found at signifiant onentrations in many human seretions, 1805 Gut: first published as /gut on 11 November Downloaded from on 13 August 2018 by guest. Proteted by opyright.
5 1806 inluding tears, breast milk, saliva, and gastri and small intestinal seretions. It is expressed in the intestinal trat by gastri and pylori glands, duodenal Brunner s glands, small intestinal Paneth ells, marophages, and granuloytes, but not in the normal olon. 36 Lysozyme is predominantly ative against Gram positive bateria. It leaves glyosidi bonds whih stabilise peptidoglyan, resulting in baterial lysis. Gram negative bateria have an outer membrane whih protets the underlying peptidoglyan ell wall and so are relatively resistant to lysozyme. The likely importane of lysozyme in intestinal innate defene has been suggested by its lak in Paneth ells in newborn infants with nerotising enteroolitis. 37 The lak of lysozyme may render these infants suseptible to baterial transloation and subsequent sepsis syndrome. Seretory phospholipase A2 spla2 is a omponent of Paneth ell granules 27 and is released into the intestinal lumen on stimulation by baterial produts, inluding lipopolysaharide. 38 spla2 purified from murine small intestinal Paneth ells has been shown to have bateriidal ativity against Salmonella typhimurium and Listeria monoytogenes, indiating its role in small intestinal muosal defene. 39 Enteri a-defensins of mie and men Defensins are small (29 45 amino aids in length) ationi peptides that have been divided into two main families, the a- and b-defensins, on the basis of the disulphide bond pairing pattern. The defensins are synthesised as preursor polypeptides that are post-translationally proessed into mature ative peptides. The antimirobial ativity of these peptides is believed to be due to the formation of a membrane spanning pore that eventually leads to lysis of the baterium. In humans, four neutrophil defensins (HNP-1, -2, -3, -4) were identified first, followed by two enteri a-defensins (HD-5, -6), expression of whih is normally restrited to Paneth ells in the small intestine. Enteri a-defensins have been well haraterised in murine Paneth ells and are termed ryptdins ( rypt defensins ). In ontrast with enteri a-defensins, human b-defensin 1 (HBD-1) and other members of the b-defensin family appear to be expressed by most epithelial ells of the small and large intestine. HBD-1 is expressed onstitutively while HBD-2 is indued by stimuli that ativate the transriptional fator NFkB. 41 Defensins may have multiple roles, dependent on onentration. Murine ryptdins reah onentrations of mg/ml in the rypt miroenvironment. 29 These onentrations are at least 1000 times higher than minimal bateriidal onentrations in vitro, indiating the potential for a-defensins to maintain sterility in the rypt and protet the stem ells. It is plausible that lower onentrations of a-defensins that reah the small intestinal lumen have an appreiable effet on resident miroflora. In keeping with this, mie defiient in the proessing enzyme matrilysin that do not express ative ryptdins are suseptible to small intestinal olonisation by non-invasive Esherihia oli speies. 42 Cryptdin 2 and 3 have also been shown to form pores in intestinal epithelial ells and to lead to a hloride seretory response, 43 whih would be expeted to flush the epithelial surfae of bateria. More reently, ryptdin 3 (but not the non-pore forming ryptdin 4) has been reported to indue expression of the potent polymorphonulear hemoattratant interleukin 8 via alium dependent ativation of p38 mitogen ativated protein kinase (MAPK) and NFkB signalling pathways. 44 These studies suggest that in addition to antimirobial ativity, some enteri a-defensins are apable of induing biologial effets in epithelial ells to enhane muosal protetion against luminal miro-organisms. Cryptdin related sequene (CRS) peptides CRS peptides have reently been desribed as a group of highly potent antimirobial peptides in mie. 34 They are a family of ovalently linked dimeri antimirobial moleules, a feature that might ontribute to their diversity and potentiate effiient protetion of the intestinal muosa. They are proessed in a similar way to ryptdins, with highly similar pro-regions of the peptide, with two possible proessing sites for matrilysin (enzyme that proessed ryptdin preursors, see below). CRS peptides have also been shown to bind and redue the immunostimulatory ativity of LPS. 34 Angiogenins Angiogenins have reently been established as a family of endogenous antimirobial proteins. 35 Although impliated in the growth of human tumour ells in mie, human angiogenin has been shown to exhibit mirobiidal ativity against systemi baterial and fungal pathogens. A likely role for this lass of mirobiidal proteins in the defene of the intestinal muosa has been demonstrated by expression of angiogenin 4 by mouse Paneth ells. 35 Baterial produts stimulate the release of the mirobiidal angiogenin 4 from Paneth ell granules into the gut lumen. Paneth ell: baterial interations Paneth ells respond to baterial stimulation by releasing antimirobial peptides/proteins stored within granules into the rypt lumen. Of these antimirobial peptides, a-defensins have been the most thoroughly studied. Mouse a-defensins Enteri a-defensins (ryptdins) from mouse small intestinal Paneth ells were the first non-leuoyte defensins to be identified, 45 and six have now been haraterised and found to exhibit broad spetrum antimirobial ativity. They are ative against E oli, Listeria monoytogenes, Staphyloous aureus, and Giardia lamblia, although individual ryptdins exhibit antimirobial ativity of varying range and poteny. 46 Antibody to ryptdins 1, 2, 3, and 6 has been shown in vitro to neutralise 70% of the bateriidal ativity sereted by mouse rypts, indiating the importane of a-defensins in muosal defene. 29 The mehanisms by whih preursor forms of ryptdins are proessed into mature ative peptides have reently been haraterised. Paneth ell granules in the mouse have been found to ontain matrilysin (MMP-7), a matrix metalloproteinase enzyme whih leaves the propeptide so that Paneth ell degranulation releases ative defensin into the rypt lumen. 42 Prosegment and mature ryptdins have been demonstrated in Paneth ell granules, and analyses suggest that the majority of proryptdin is proessed by MMP-7 within the granules. 29 The in vivo importane of ryptdin ativation has been shown by MMP-7 null mie, whih aumulate proryptdin in their Paneth ell granules and are more suseptible to oral administration of the enteri pathogen Salmonella typhimurium. 42 Gut: first published as /gut on 11 November Downloaded from on 13 August 2018 by guest. Proteted by opyright.
6 Inhibition of Paneth ell ryptdin and lysozyme expression has been reported after oral inoulation of mie with wildtype Salmonella typhimurium. 47 Studies using heat killed and mutant S typhimurium showed that diret interations between live wild-type bateria and epithelial ells are required to inhibit ryptdin expression. Moreover, it was demonstrated that the epithelial ell responses are mediated via the p38 MAPK pathway. The effet of S typhimurium on ryptdin and lysozyme expression appears to be pathogen speifi as Listeria monoytogenes, whih also invades murine (and human) small intestine, did not have any effet. Human enteri a-defensins Whereas six enteri a-defensins have been haraterised in mie, only two (HD-5 and HD-6) have been identified in humans. 48 These, like ryptdins, are predominantly expressed in Paneth ells of the small intestine, and HD-5 has been isolated from ileal tissue and haraterised Reombinant HD-5 has been shown to have a wide spetrum of killing ativity, being ative against both Gram positive and Gram negative bateria as well as fungi (Listeria monoytogenes, Esherihia oli, Salmonella typhimurium, and Candida albians) The important ontribution of human a-defensins to enteri muosal immunity has been demonstrated by a reent in vivo study in whih transgeni mie expressing HD-5 in small intestinal Paneth ells profoundly influened muosal protetion against virulent Salmonella typhimurium. 52 This was manifest by a redution in the baterial burden in the intestinal lumen and faees, dereased baterial transloation to the spleen, and higher survival rates after lethal Salmonella hallenge. 52 However, HD-5 transgeni mie did not have a survival advantage when intraperitoneally inoulated with Salmonella, indiating that the effet of HD-5 is mediated in the intestinal lumen. The mehanism of inreased intestinal defene against Salmonella in the HD-5- transgeni mie is not lear, as HD-5 and mouse ryptdins have similar in vitro ativity against this pathogen. In ontrast with mie, human Paneth ell granules ontain only the proform of HD-5 (amino aids 20 94; fig 5), and they do not ontain matrilysin In vitro, pro-hd-5 an be proessed to the mature form (amino aids 63 94) by trypsin, whih together with a 1 -antitrypsin and panreati seretory trypsin inhibitor (Kazal-type trypsin inhibitor) are expressed in Paneth ells Analysis of terminal ileal fluid taken at endosopy has onfirmed that the predominant in vivo form of luminal HD-5 is indeed the mature (amino aids 63 94) peptide predited by in vitro trypsin leavage. 51 Luminal aspirates also yielded a slightly longer HD-5 form (amino aids 56 94). Of note, both of these isoforms are C terminal to an arginine residue, whih is typial of trypsin leavage. It has therefore been proposed that following seretion by Paneth ells, enzymatially ative trypsin proesses pro-hd-5 to the mature form in vivo. 51 Key points: enteri a-defensins However, a further luminal form of HD-5 has been isolated from ileal neobladder urine. 49 In these subjets, after radial ystetomy for transitional ell arinoma of the bladder, an ileal neobladder was fashioned. Enteri defensins were then isolated from urine. The and mature HD-5 forms found in ileal aspirates were also found in neobladder urine, but a longer form, 36 94, was also present. This form has been shortened from pro-hd-5 (20 94) but not at a trypsin leavage site. This same form (36 94) was also found in vitro when isolated small intestinal rypts were stimulated with either the holinergi agonist arbamyl holine or baterial lipopolysaharide. 26 It may therefore be that alternative mehanisms, or additional steps, for the proessing of pro- HD-5 to the mature form exist. Paneth ell: parasite interations Paneth ell granule depletion has been observed in subjets with human immunodefiieny virus related ryptosporidiosis 55 and mie infeted with the nematode Trihinella spiralis 28 but the mehanism remains to be determined. In parasite infeted mie, there is also an inrease in the number of Paneth ells (fig 3), whih is maximal around the time of worm expulsion Transfer experiments in T ell defiient mie suggest that muosal T ells play an important role in induing an inrease in the number of Paneth ells in parasite infeted mie. 28 Expression profiling studies in the small intestine of T spiralis infeted mie have shown that Paneth ell speifi ryptdins are strongly represented. 56 Paneth ells: a link with inflammatory bowel disease Metaplasti Paneth ells in olitis Although in the normal gastrointestinal trat Paneth ells are onfined to the small intestine, they an appear in aberrant sites in various disease states. Expression of small intestinal epithelium elsewhere in the gastrointestinal trat is termed intestinal metaplasia, and the term omplete metaplasia is used if Paneth ells are present. 57 Formation of intestinal metaplasia is usually preeded by hroni inflammation suh as in Barrett s oesophagus or in the stomah following hroni Heliobater pylori infetion. 58 Paneth ell metaplasia ours in hroni inflammatory onditions of the olon, most notably ulerative olitis and oloni Crohn s disease, 26 but also divertiulitis 59 and radiation olitis. 60 Metaplasti Paneth ells seen in inflammatory bowel disease olitis are usually Signal Propeptide Mature peptide MRTIAILAAILLVALQAQA ESLQERADEATTQKQSGEDNQDLAISFAGNGLSALRTSGSQAR ATCYCRTGRCATRESLSGVCEISGRLYRLCCR Figure 5 Amino aid sequene of human defensin (HD)-5. Preursor form of HD-5 (amino aids 20 94) is stored in Paneth ell granules, and has been shown to be proessed to three predominant forms (amino aids 63 94, 56 94, 36 94) during and/or after release into the lumen (see text for details). Two forms exist in humans: HD-5 and HD-6 Sereted into the rypt lumen by Paneth ells Seletively attak mirobial ell membranes Mouse defensin isoforms provide 70% of rypt antimirobial ativity Transgeni mie expressing HD-5 are proteted against orally administered virulent Salmonella typhimurium Gut: first published as /gut on 11 November Downloaded from on 13 August 2018 by guest. Proteted by opyright.
7 1808 seen in the rypt region, and are morphologially idential to small intestinal Paneth ells. 26 Immunohistohemial studies indiate that they express the antimirobial proteins lysozyme, 61 spla2, 62 and a-defensins. 26 It is likely that in the olon affeted by inflammatory bowel disease, metaplasti Paneth ells help protet the damaged oloni epithelium against baterial invasion. NOD2 protein is expressed in Paneth ells NOD2 protein is a ytosoli PRR of the innate immune system that reognises muramyl dipeptide, a onstituent of peptidoglyan whih is present in baterial ell walls. 63 Mutations in the NOD2 gene, on hromosome 16, have been assoiated with Crohn s disease They lead to a defiieny in the gene produt to sense muramyl dipeptide. 64 Three main mutations in this gene aount for 80% of the total mutations assoiated with Crohn s disease, and 25 43% of Cauasian Crohn s patients arry at least one of these mutations. Two of these single nuleotide polymorphisms result in single amino aid hanges (R702W, G908R), and the third a frameshift mutation leading to a trunated protein (1007 fs). All mutations affet the C terminal leuine-rih repeat, or muramyl dipeptide reeptor, domain. Genotype-phenotype orrelations have demonstrated that NOD2 mutations are assoiated with ileal disease, a tendeny to develop stritures, and with a younger age at onset. 67 As the NOD2 gene has reently been shown to be expressed in the ytoplasm of Paneth ells, there is onsiderable urrent interest in a possible link between the presene of defetive NOD2 protein in Paneth ells and the development of small bowel Crohn s disease. It may be that defetive reognition of baterial produts via NOD2 leads to dysregulation of Paneth ell mediated responses against intestinal bateria in Crohn s disease. This redued baterial sensing may lead to an inreased suseptibility of the intestinal muosa to invasion by luminal bateria, and to the development of hroni inflammation. NOD2 protein-antimirobial peptides: is there a link within Paneth ells? Altered expression of antimirobial peptides seondary to expression of the mutant NOD2 gene in Paneth ells ould lead to abnormal olonisation of the small bowel with mirobes, whih may provoke hroni inflammation via adaptive immune mehanisms. There is some reent evidene of a link between the NOD2 gene and expression of a-defensins in Paneth ells. NOD2 defiient (NOD2 2/2 ) mie have been found to show redued Paneth ell expression of transripts of the enteri a-defensins ryptdin 4 and ryptdin 10 sequene and there was further redution in expression of these transripts after intragastri infetion with the Gram positive intraellular baterium Listeria monoytogenes. 68 Interestingly, NOD2 2/2 mie are outwardly healthy and display no overt symptoms or histologial evidene of intestinal inflammation when Key points: NOD2 protein Mutations in NOD2 are assoiated with Crohn s ileitis NOD2 is found in Paneth ells, whih are prominent in the ileum Paneth ells release a-defensins to maintain rypt sterility a-defensin expression may be redued in Crohn s ileitis observed for up to six months However, when hallenged with L monoytogenes via the intragastri route, NOD2 2/2 mie had greater suseptibility to infetion, as shown by signifiantly greater numbers of bateria reovered from the liver and spleen ompared with wild-type ontrols. In ontrast, NOD2 2/2 mie showed no differene to wild-type mie when inoulated with L monoytogenes, either by intravenous or intraperitoneal injetion, indiating that NOD2 may play a key role in mediating protetion of the intestinal muosa against baterial infetion. Expression of enteri a-defensin mrna has reently been shown to be redued in terminal ileal biopsies from patients with Crohn s disease, with redued expression being more pronouned in the presene of NOD2 mutations. 70 Although this result adds further redene to the hypothesis that Crohn s disease may be assoiated with a redution in muosal innate immunity, there is muh yet to be explained. For example, the mehanism by whih NOD2 may regulate expression of Paneth ell a-defensins remains to be determined. A number of reent studies have reported the effet of NOD2 mutations in responses by ells other than Paneth ells but are not onsidered further as they are beyond the sope of this artile. SUMMARY A variety of mehanisms are needed to mediate host protetion against miro-organisms in the intestine prior to indution of highly speifi adaptive immune responses. Reent studies suggest that Paneth ells play an important role in innate host defene via their ability to serete antimirobial peptides and proteins. There is onsiderable urrent interest in host and mirobial fators that may regulate Paneth ell funtion. As they are able to respond to omponents of the ommensal mirobial flora, there is also signifiant urrent interest in the ontribution of these ells to the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease.... Authors affiliations D A Elphik, Y R Mahida, Institute of Infetion, Immunity, and Inflammation and Division of Gastroenterology, University of Nottingham and University Hospital, Nottingham, UK Conflit of interest: None delared. REFERENCES 1 Booth C, Potten CS. Gut instints: thoughts on intestinal epithelial stem ells. J Clin Invest 2000;105: Justesen T, Nielsen OH, Jaobsen IE, et al. The normal ultivable miroflora in upper jejunal fluid in healthy adults. Sand J Gastroenterol 1984;19: Smith G, Gorbah S. Normal alimentary trat flora. In: Blaser M, Smith P, Ravidin J, eds. Infetions of the gastrointestinal trat. New York: Raven Press, 1995: Medzhitov R, Janeway C Jr. Innate immunity. N Engl J Med 2000;343: Brandtzaeg P, Pabst R. Let s go muosal: ommuniation on slippery ground. Trends Immunol 2004;25: Campbell DJ, Kim CH, Buther EC. Chemokines in the systemi organization of immunity. Immunol Rev 2003;195: Fagarasan S, Honjo T. Intestinal IgA synthesis: regulation of front-line body defenes. Nat Rev Immunol 2003;3: Fernie-King B, Seilly DJ, Davies A, et al. Subversion of the innate immune response by miro-organisms. Ann Rheum Dis 2002;61(suppl 2):ii Fearon DT, Loksley RM. The instrutive role of innate immunity in the aquired immune response. Siene 1996;272: Philpott DJ, Girardin SE. The role of Toll-like reeptors and Nod proteins in baterial infetion. Mol Immunol 2004;41: Takeda K, Akira S. Toll-like reeptors in innate immunity. Int Immunol 2005;17:1 14. Gut: first published as /gut on 11 November Downloaded from on 13 August 2018 by guest. Proteted by opyright.
8 12 Rok FL, Hardiman G, Timans JC, et al. A family of human reeptors struturally related to Drosophila Toll. Pro Natl Aad Si U S A 1998;95: Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, et al. Defetive LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10SCr mie: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Siene 1998;282: Mahida YR, Johal S. NF-kappa B may determine whether epithelial ellmirobial interations in the intestine are hostile or friendly. Clin Exp Immunol 2001;123: Chamaillard M, Girardin SE, Viala J, et al. Nods, Nalps and Naip: intraellular regulators of baterial-indued inflammation. Cell Mirobiol 2003;5: Ogura Y, Inohara N, Benito A, et al. Nod2, a Nod1/Apaf-1 family member that is restrited to monoytes and ativates NF-kappa B. J Biol Chem 2001;276: Hugot JP, Chamaillard M, Zouali H, et al. Assoiation of NOD2 leuine-rih repeat variants with suseptibility to Crohn s disease. Nature 2001;411: Ogura Y, Bonen DK, Inohara N, et al. A frameshift mutation in NOD2 assoiated with suseptibility to Crohn s disease. Nature 2001;411: Mieli-Rihard C, Lesage S, Rybojad M, et al. CARD15 mutations in Blau syndrome. Nat Genet 2001;29: Paneth J. Uber Die Seernierenden Zellen das Dunndarm-Epithels. Arhiv fur mikroskepish anatomie 1888;31: Bry L, Falk P, Huttner K, et al. Paneth ell differentiation in the developing intestine of normal and transgeni mie. Pro Natl Aad Si U S A 1994;91: Cheng H. Origin, differentiation and renewal of the four main epithelial ell types in the mouse small intestine. IV. Paneth ells. Am J Anat 1974;141: Ouellette AJ, Sathell DP, Hsieh MM, et al. Charaterization of luminal Paneth ell alpha-defensins in mouse small intestine: Attenuated antimirobial ativities of peptides with trunated amino termini. J Biol Chem 2000;275: Lendrum A. The phloxine-tartrazine method as a general histologial stain and for the demonstration of inlusion bodies. J Pathol Bateriol 1947;59: Erlandsen SL, Parsons JA, Taylor TD. Ultrastrutural immunoytohemial loalization of lysozyme in the Paneth ells of man. J Histohem Cytohem 1974;22: Cunliffe RN, Rose FR, Keyte J, et al. Human defensin 5 is stored in preursor form in normal Paneth ells and is expressed by some villous epithelial ells and by metaplasti Paneth ells in the olon in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2001;48: Nevalainen TJ, Gronroos JM, Kallajoki M. Expression of group II phospholipase A2 in the human gastrointestinal trat. Lab Invest 1995;72: Kamal M, Wakelin D, Ouellette AJ, et al. Muosal T ells regulate Paneth and intermediate ell numbers in the small intestine of T. spiralis-infeted mie. Clin Exp Immunol 2001;126: Ayabe T, Sathell DP, Wilson CL, et al. Seretion of mirobiidal alphadefensins by intestinal Paneth ells in response to bateria. Nat Immunol 2000;1: Tanabe H, Ayabe T, Bainbridge B, et al. Mouse paneth ell seretory responses to ell surfae glyolipids of virulent and attenuated pathogeni bateria. Infet Immun 2005;73: Rumio C, Besusso D, Palazzo M, et al. Degranulation of paneth ells via tolllike reeptor 9. Am J Pathol 2004;165: Lala S, Ogura Y, Osborne C, et al. Crohn s disease and the NOD2 gene: a role for paneth ells. Gastroenterology 2003;125: Ogura Y, Lala S, Xin W, et al. Expression of NOD2 in Paneth ells: a possible link to Crohn s ileitis. Gut 2003;52: Hornef MW, Putsep K, Karlsson J, et al. Inreased diversity of intestinal antimirobial peptides by ovalent dimer formation. Nat Immunol 2004;5: Hooper LV, Stappenbek TS, Hong CV, et al. Angiogenins: A new lass of mirobiidal proteins involved in innate immunity. Nat Immunol 2003;4: Klokars M, Reitamo S. Tissue distribution of lysozyme in man. J Histohem Cytohem 1975;23: Coutinho HB, Carmona da Mota H, Coutinho VB, et al. Absene of lysozyme (muramidase) in the intestinal Paneth ells of newborn infants with nerotising enteroolitis. J Clin Pathol 1998;51: Harwig SSL, Tan L, Qu XD, et al. Bateriidal properties of murine intestinal phospholipase A2. J Clin Invest 1995;95: Qu XD, Lloyd KC, Walsh JH, et al. Seretion of type II phospholipase A2 and ryptdin by rat small intestinal Paneth ells. Infet Immun 1996;64: Ouellette AJ, Bevins CL. Paneth ell defensins and innate immunity of the small bowel. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2001;7: Cunliffe RN, Mahida YR. Expression and regulation of antimirobial peptides in the gastrointestinal trat. J Leuko Biol 2004;75: Wilson CL, Ouellette AJ, Sathell DP, et al. Regulation of intestinal alphadefensin ativation by the metalloproteinase matrilysin in innate host defense. Siene 1999;286: Lener WI, Cheung G, Strohmeier GR, et al. Indution of epithelial hloride seretion by hannel-forming ryptdins 2 and 3. Pro Natl Aad Si U S A 1997;94: Lin PW, Simon PO Jr, Gewirtz AT, et al. Paneth ell ryptdins at in vitro as apial pararine regulators of the innate inflammatory response. J Biol Chem 2004;279: Ouellette AJ, Greo RM, James M, et al. Developmental regulation of ryptdin, a ortiostatin/defensin preursor mrna in mouse small intestinal rypt epithelium. J Cell Biol 1989;108: Ouellette AJ, Hsieh MM, Nosek MT, et al. Mouse Paneth ell defensins: Primary strutures and antibaterial ativities of numerous ryptdin isoforms. Infet Immun 1994;62: Salzman NH, Chou MM, De Jong H, et al. Enteri Salmonella infetion inhibits paneth ell antimirobial peptide expression. Infet Immun 2003;71: Jones DE, Bevins CL. Paneth ells of the human small intestine express an antimirobial peptide gene. J Biol Chem 1992;267: Porter EM, Poles MA, Lee JS, et al. Isolation of human intestinal defensins from ileal neobladder urine. FEBS Letters 1998;434: Porter EM, Van Dam E, Valore EV, et al. Broad-spetrum antimirobial ativity of human intestinal defensin 5. Infet Immun 1997;65: Ghosh D, Porter E, Shen B, et al. Paneth ell trypsin is the proessing enzyme for human defensin-5. Nat Immunol 2002;3: Salzman NH, Ghosh D, Huttner KM, et al. Protetion against enteri salmonellosis in transgeni mie expressing a human intestinal defensin. Nature 2003;422: Bohe M, Borgstrom A, Lindstrom C, et al. Panreati endoproteases and panreati seretory trypsin inhibitor immunoreativity in human Paneth ells. J Clin Pathol 1986;39: Molmenti EP, Perlmutter DH, Rubin DC. Cell-speifi expression of alpha1- antitrypsin in human intestinal epithelium. J Clin Invest 1993;92: Kelly P, Feakins R, Domizio P, et al. Paneth ell granule depletion in the human small intestine under infetive and nutritional stress. Clin Exp Immunol 2004;135: Knight PA, Pemberton AD, Robertson KA, et al. Expression profiling reveals novel innate and inflammatory responses in the jejunal epithelial ompartment during infetion with Trihinella spiralis. Infet Immun 2004;72: Wong WM, Stamp GWH, Elia G, et al. Proliferative populations in intestinal metaplasia: Evidene of deregulation in Paneth and goblet ells, but not endorine ells. J Pathol 2000;190: Smith VC, Genta RM. Role of Heliobater pylori gastritis in gastri atrophy, intestinal metaplasia, and gastri neoplasia. Miros Res Teh 2000;48: Sandow MJ, Whitehead R. The Paneth ell. Gut 1979;20: Watanabe H. Experimentally indued intestinal metaplasia in Wistar rats by X-ray irradiation. Gastroenterology 1978;75: Klokars M, Reitamo S, Reitamo JJ, et al. Immunohistohemial identifiation of lysozyme in intestinal lesions in ulerative olitis and Crohn s disease. Gut 1977;18: Haapamaki MM, Gronroos JM, Nurmi H, et al. Gene expression of group II phospholipase A2 in intestine in ulerative olitis. Gut 1997;40: Girardin SE, Bonea IG, Viala J, et al. Nod2 is a general sensor of peptidoglyan through muramyl dipeptide (MDP) detetion. J Biol Chem 2003;278: Inohara N, Ogura Y, Fontalba A, et al. Host reognition of baterial muramyl dipeptide mediated through NOD2. Impliations for Crohn s disease. J Biol Chem 2003;278: Cuthbert AP, Fisher SA, Mirza MM, et al. The ontribution of NOD2 gene mutations to the risk and site of disease in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 2002;122: Lesage S, Zouali H, Cezard JP, et al. CARD15/NOD2 mutational analysis and genotype-phenotype orrelation in 612 patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Hum Genet 2002;70: Ahmad T, Armuzzi A, Bune M, et al. The moleular lassifiation of the linial manifestations of Crohn s disease. Gastroenterology 2002;122: Kobayashi KS, Chamaillard M, Ogura Y, et al. Nod2-dependent regulation of innate and adaptive immunity in the intestinal trat. Siene 2005;307: Pauleau AL, Murray PJ. Role of nod2 in the response of marophages to tolllike reeptor agonists. Mol Cell Biol 2003;23: Wehkamp J, Harder J, Weihenthal M, et al. NOD2 (CARD15) mutations in Crohn s disease are assoiated with diminished muosal alpha-defensin expression. Gut 2004;53: Gut: first published as /gut on 11 November Downloaded from on 13 August 2018 by guest. Proteted by opyright.
Recent advances in basic science BACTERIAL INTERACTIONS WITH CELLS OF THE INTESTINAL MUCOSA: TOLL- LIKE RECEPTORS AND NOD2
 1182 Reent advanes in basi siene BACTERIAL INTERACTIONS WITH CELLS OF THE INTESTINAL MUCOSA: TOLL- LIKE RECEPTORS AND NOD2 Published online first 19 April 2005 Correspondene to: Dr E Cario, University
1182 Reent advanes in basi siene BACTERIAL INTERACTIONS WITH CELLS OF THE INTESTINAL MUCOSA: TOLL- LIKE RECEPTORS AND NOD2 Published online first 19 April 2005 Correspondene to: Dr E Cario, University
Defective neutrophil function in low-birth-weight,
 J Clin Pathol 1981 ;34:366-37 Defetive neutrophil funtion in low-birth-weight, premature infants H AL-HADITHY, IE ADDISON, AH GOLDSTONE, JC CAWLEY, AND JC SHAW From the Departments of Haematology and Paediatris,
J Clin Pathol 1981 ;34:366-37 Defetive neutrophil funtion in low-birth-weight, premature infants H AL-HADITHY, IE ADDISON, AH GOLDSTONE, JC CAWLEY, AND JC SHAW From the Departments of Haematology and Paediatris,
Role of the actin cytoskeleton on epithelial Na
 Kidney International, Vol. 48 (1995), pp. 970 984 Role of the atin ytoskeleton on epithelial Na hannel regulation Hoiio F. ANTIELLO Renal Unit, Massahusetts General Hospital and Department of Mediine,
Kidney International, Vol. 48 (1995), pp. 970 984 Role of the atin ytoskeleton on epithelial Na hannel regulation Hoiio F. ANTIELLO Renal Unit, Massahusetts General Hospital and Department of Mediine,
Stefan D Anker, Stephan von Haehling
 464 See end of artile for authors affiliations Correspondene to: Dr Stefan D Anker, National Heart and Lung Institute, Department of Clinial Cardiology, Dovehouse Street, London SW3 6LY, UK; s.anker@imperial.a.uk
464 See end of artile for authors affiliations Correspondene to: Dr Stefan D Anker, National Heart and Lung Institute, Department of Clinial Cardiology, Dovehouse Street, London SW3 6LY, UK; s.anker@imperial.a.uk
describing DNA reassociation* (renaturation/nucleation inhibition/single strand ends)
 Pro. Nat. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 73, No. 2, pp. 415-419, February 1976 Biohemistry Studies on nulei aid reassoiation kinetis: Empirial equations desribing DNA reassoiation* (renaturation/nuleation inhibition/single
Pro. Nat. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 73, No. 2, pp. 415-419, February 1976 Biohemistry Studies on nulei aid reassoiation kinetis: Empirial equations desribing DNA reassoiation* (renaturation/nuleation inhibition/single
Chapter III. Efficacy of promising agents/combinations in preventing vaginal/cervical inflammation caused by infection with T. vaginalis Introduction
 Chapter III Effiay of promising agents/ombinatio in preventing vaginal/ervial inflammation aused by infetion with T. vaginalis Introdution A ontraeptive mirobiide is supposed to be in ontat with the erviovaginal
Chapter III Effiay of promising agents/ombinatio in preventing vaginal/ervial inflammation aused by infetion with T. vaginalis Introdution A ontraeptive mirobiide is supposed to be in ontat with the erviovaginal
TWSpahn,TKucharzik RECENT ADVANCES IN BASIC SCIENCE MODULATING THE INTESTINAL IMMUNE SYSTEM: THE ROLE OF LYMPHOTOXIN AND GALT ORGANS.
 456 RECENT ADVANCES IN BASIC SCIENCE MODULATING THE INTESTINAL IMMUNE SYSTEM: THE ROLE OF LYMPHOTOXIN AND GALT ORGANS See end of artile for authors affiliations Correspondene to: Dr T Spahn, Department
456 RECENT ADVANCES IN BASIC SCIENCE MODULATING THE INTESTINAL IMMUNE SYSTEM: THE ROLE OF LYMPHOTOXIN AND GALT ORGANS See end of artile for authors affiliations Correspondene to: Dr T Spahn, Department
a-4/b-1 and a-l/b-2 integrins mediate cytokine induced lung leukocyte-epithelial adhesion and injury
 British Journal of Pharmaology (27) 152, 915 929 & 27 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/7 $3. www.brjpharmaol.org RESEARCH PAPER a-4/b-1 and a-l/b-2 integrins mediate ytokine indued lung
British Journal of Pharmaology (27) 152, 915 929 & 27 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/7 $3. www.brjpharmaol.org RESEARCH PAPER a-4/b-1 and a-l/b-2 integrins mediate ytokine indued lung
Prognostic significance of genotyping Helicobacter pylori infection in patients in younger age groups with gastric cancer
 See Editorial, p 167 1 Center for Liver Researh and Diagnostis, Dean College of Medial Sienes, Kanhanbagh, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India; 2 Department of Gastroenterology, Osmania General Hospital,
See Editorial, p 167 1 Center for Liver Researh and Diagnostis, Dean College of Medial Sienes, Kanhanbagh, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India; 2 Department of Gastroenterology, Osmania General Hospital,
peristaltic activity in the colon. surface-acting agents such as bisacodyl and oxyphenisatin (Hardcastle and Mann, 1968).
 Gut, 1970, 11, 41-46 Physial fators in the stimulation of oloni peristalsis J. D. HRDSTLE ND. V. MNN From St Mark's Hospital, London, and The London Hospital SUMMRY The effet of oloni distension and hanges
Gut, 1970, 11, 41-46 Physial fators in the stimulation of oloni peristalsis J. D. HRDSTLE ND. V. MNN From St Mark's Hospital, London, and The London Hospital SUMMRY The effet of oloni distension and hanges
Department of Virology, Wellcome Research Laboratories, Langley Court, Beckenham, Kent BR3 3BS, U.K. and heterologous virus challenge.
 Journal of General Virology (1992), 73, 727-731. Printed in Great Britain 727 Comparison between in vitro neutralization titres and in vivo protetion against homologous and heterologous hallenge indued
Journal of General Virology (1992), 73, 727-731. Printed in Great Britain 727 Comparison between in vitro neutralization titres and in vivo protetion against homologous and heterologous hallenge indued
Dexamethasone modulation of tumour necrosis factor-a (cachectin) release by activated normal human alveolar macrophages
 ur Resplr J 1992, 5, 67-72 Dexamethasone modulation of tumour nerosis fator-a (ahetin) release by ativated normal human alveolar marophages N. Martinet, P. Vaillant, Th. Charles, J. Lambert, Y. Martinet*
ur Resplr J 1992, 5, 67-72 Dexamethasone modulation of tumour nerosis fator-a (ahetin) release by ativated normal human alveolar marophages N. Martinet, P. Vaillant, Th. Charles, J. Lambert, Y. Martinet*
Haemophilus influenzae
 INFCTION AND IMMUNITY, June 1993, p. 2419-2424 19-9567/93/62419-6$2./ Copyright X 1993, Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Vol. 61, No. 6 Inhibition of Human Neutrophil Migration In Vitro by Low- Moleular-Mass
INFCTION AND IMMUNITY, June 1993, p. 2419-2424 19-9567/93/62419-6$2./ Copyright X 1993, Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Vol. 61, No. 6 Inhibition of Human Neutrophil Migration In Vitro by Low- Moleular-Mass
Interrelationships of Chloride, Bicarbonate, Sodium, and Hydrogen Transport in the Human Ileum
 Interrelationships of Chloride, Biarbonate, Sodium, and Hydrogen Transport in the Human Ileum LEsLE A. TURNBERG, FREDERICK A. BIEBERDORF, STEPHEN G. MORAWSKI, and JOHN S. FORDTRAN From the Department of
Interrelationships of Chloride, Biarbonate, Sodium, and Hydrogen Transport in the Human Ileum LEsLE A. TURNBERG, FREDERICK A. BIEBERDORF, STEPHEN G. MORAWSKI, and JOHN S. FORDTRAN From the Department of
Measurement of Dose Rate Dependence of Radiation Induced Damage to the Current Gain in Bipolar Transistors 1
 Measurement of Dose Rate Dependene of Radiation Indued Damage to the Current Gain in Bipolar Transistors 1 D. Dorfan, T. Dubbs, A. A. Grillo, W. Rowe, H. F.-W. Sadrozinski, A. Seiden, E. Spener, S. Stromberg,
Measurement of Dose Rate Dependene of Radiation Indued Damage to the Current Gain in Bipolar Transistors 1 D. Dorfan, T. Dubbs, A. A. Grillo, W. Rowe, H. F.-W. Sadrozinski, A. Seiden, E. Spener, S. Stromberg,
original article Chao-Lien Liu 1, Peiqing Ye 1, Benjamin C Yen 1 and Carol H Miao 1,2
 The Amerian Soiety of Gene & Cell Therapy original artile In Vivo Expansion of Regulatory T ells With IL-2/IL-2 mab Complexes Prevents Anti-fator VIII Immune Responses in Hemophilia A Mie Treated With
The Amerian Soiety of Gene & Cell Therapy original artile In Vivo Expansion of Regulatory T ells With IL-2/IL-2 mab Complexes Prevents Anti-fator VIII Immune Responses in Hemophilia A Mie Treated With
PARKINSON S DISEASE: MODELING THE TREMOR AND OPTIMIZING THE TREATMENT. Keywords: Medical, Optimization, Modelling, Oscillation, Noise characteristics.
 PARKINSON S DISEASE: MODELING THE TREMOR AND OPTIMIZING THE TREATMENT Mohammad Haeri, Yashar Sarbaz and Shahriar Gharibzadeh Advaned Control System Lab, Eletrial Engineering Department, Sharif University
PARKINSON S DISEASE: MODELING THE TREMOR AND OPTIMIZING THE TREATMENT Mohammad Haeri, Yashar Sarbaz and Shahriar Gharibzadeh Advaned Control System Lab, Eletrial Engineering Department, Sharif University
Functional GI disorders: from animal models to drug development
 1 UCLA Center for Neuroviseral Sienes & Women s Health, Departments of Mediine, Physiology and Psyhiatry, David Geffen Shool of Mediine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, USA; 2 UCLA Center for Neuroviseral Sienes
1 UCLA Center for Neuroviseral Sienes & Women s Health, Departments of Mediine, Physiology and Psyhiatry, David Geffen Shool of Mediine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, USA; 2 UCLA Center for Neuroviseral Sienes
Caroline P D Wheeler-Jones
 1366 Take the online multiple hoie questions assoiated with this artile (see page 1374) T Basi siene CELL SIGNALLING IN THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW Caroline P D Wheeler-Jones Heart 2005; 91:1366
1366 Take the online multiple hoie questions assoiated with this artile (see page 1374) T Basi siene CELL SIGNALLING IN THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW Caroline P D Wheeler-Jones Heart 2005; 91:1366
A novel approach to regulate cell membrane permeability for ATP and NADH. formations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae induced by air cold plasma 1
 A novel approah to regulate ell membrane permeability for ATP and NADH formations in Saharomyes erevisiae indued by air old plasma 1 Xiaoyu DONG ( 董晓宇 ), Tingting LIU ( 刘婷婷 ), Yuqin XIONG ( 熊玉琴 ) Shool
A novel approah to regulate ell membrane permeability for ATP and NADH formations in Saharomyes erevisiae indued by air old plasma 1 Xiaoyu DONG ( 董晓宇 ), Tingting LIU ( 刘婷婷 ), Yuqin XIONG ( 熊玉琴 ) Shool
M E Guicciardi, G J Gores
 1024 RECENT ADVANCES IN BASIC SCIENCE APOPTOSIS: A MECHANISM OF ACUTE AND CHRONIC LIVER INJURY See end of artile for authors affiliations Correspondene to: Dr G J Gores, Mayo Clini College of Mediine,
1024 RECENT ADVANCES IN BASIC SCIENCE APOPTOSIS: A MECHANISM OF ACUTE AND CHRONIC LIVER INJURY See end of artile for authors affiliations Correspondene to: Dr G J Gores, Mayo Clini College of Mediine,
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics
 Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
TNFa-induced GM-CSF release from human airway smooth muscle cells depends on activation of an ET-1 autoregulatory positive feedback mechanism
 Additional details of the methods and results, and an additional figure are published online only at http://thorax.bmj. om/ontent/vol64/issue12 1 Department of Pneumology, Clini III for Internal Mediine,
Additional details of the methods and results, and an additional figure are published online only at http://thorax.bmj. om/ontent/vol64/issue12 1 Department of Pneumology, Clini III for Internal Mediine,
polymorphonuclear neutrophil release of granular
 Br. J. Pharma. (1985), 86, 533-537 Phorbol myristate aetate enhanes human polymorphonulear neutrophil release of granular enzymes but inhibits hemokinesis J.R.S. Hoult & Sussan Nourshargh Department of
Br. J. Pharma. (1985), 86, 533-537 Phorbol myristate aetate enhanes human polymorphonulear neutrophil release of granular enzymes but inhibits hemokinesis J.R.S. Hoult & Sussan Nourshargh Department of
Reading a Textbook Chapter
 HENR.546x.APPBpp001-013 7/21/04 9:37 AM Page 1 APPENDIX B Reading a Textbook Chapter Copyright 2005 Pearson Eduation, In. 1 2 Read the following hapter from the ollege textbook Total Fitness: Exerise,
HENR.546x.APPBpp001-013 7/21/04 9:37 AM Page 1 APPENDIX B Reading a Textbook Chapter Copyright 2005 Pearson Eduation, In. 1 2 Read the following hapter from the ollege textbook Total Fitness: Exerise,
and jejunal fluid immunoglobulins in adult coeliac
 Gut, 1974, 15, 371-376 Jejunal muosal immunoglobulin-ontaining ells and jejunal fluid immunoglobulins in adult oelia disease and dermatitis herpetiformis M. LANCASTR-SMITH, PARVN KUMAR, R. MARKS, M. L.
Gut, 1974, 15, 371-376 Jejunal muosal immunoglobulin-ontaining ells and jejunal fluid immunoglobulins in adult oelia disease and dermatitis herpetiformis M. LANCASTR-SMITH, PARVN KUMAR, R. MARKS, M. L.
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE
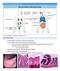 LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
Revision 2: an immunohistochemical approach and evaluation of solid pseudopapillary tumour of the pancreas
 Department of Pathology, University Health Network/ University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada Correspondene to: Professor R Chetty, Department of Pathology, University Health Network, The Toronto General
Department of Pathology, University Health Network/ University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada Correspondene to: Professor R Chetty, Department of Pathology, University Health Network, The Toronto General
Role of MMPs in orchestrating inflammatory response in human monocytes via a TREM-1-PI3K-NF- B pathway
 Artile Role of MMPs in orhestrating inflammatory response in human monoytes via a TREM--PIK-NF- pathway Vanesa Gómez-Piña,, Eriel Martínez,, Irene Fernández-Ruíz, arlos del Fresno, Alessandra Soares-Shanoski,,
Artile Role of MMPs in orhestrating inflammatory response in human monoytes via a TREM--PIK-NF- pathway Vanesa Gómez-Piña,, Eriel Martínez,, Irene Fernández-Ruíz, arlos del Fresno, Alessandra Soares-Shanoski,,
Crosstalk between B lymphocytes, microbiota and the intestinal epithelium governs immunity versus metabolism in the gut
 a r t i l e s Crosstalk between B lymphoytes, mirobiota and the intestinal epithelium governs immunity versus metabolism in the gut Natalia Shulzhenko,0,, Andrey Morgun,0,, William Hsiao 2, Mihele Battle,
a r t i l e s Crosstalk between B lymphoytes, mirobiota and the intestinal epithelium governs immunity versus metabolism in the gut Natalia Shulzhenko,0,, Andrey Morgun,0,, William Hsiao 2, Mihele Battle,
Granulocytosis and Lymphocytopenia in the Blood as Indicators for Drug Adverse Reaction during Calcitonin
 Ata Media et Biologia Vol. 44, No.4, 209-213, 1996 Granuloytosis and Lymphoytopenia in the Blood as Indiators for Drug Adverse Reation during Calitonin Therapy in Patients with Osteoporosis after Gastretomy
Ata Media et Biologia Vol. 44, No.4, 209-213, 1996 Granuloytosis and Lymphoytopenia in the Blood as Indiators for Drug Adverse Reation during Calitonin Therapy in Patients with Osteoporosis after Gastretomy
UThalheimer,CKTriantos,DNSamonakis,DPatch, A K Burroughs
 556 Reent advanes in linial pratie INFECTION, COAGULATION, AND VARICEAL BLEEDING IN CIRRHOSIS See end of artile for authors affiliations Correspondene to: Professor A K Burroughs, Liver Transplantation
556 Reent advanes in linial pratie INFECTION, COAGULATION, AND VARICEAL BLEEDING IN CIRRHOSIS See end of artile for authors affiliations Correspondene to: Professor A K Burroughs, Liver Transplantation
Systematic Review of Trends in Fish Tissue Mercury Concentrations
 Systemati Review of Trends in Fish Tissue Merury Conentrations Tom Grieb 1, Roxanne Karimi 2, Niholas Fisher 2, Leonard Levin 3 (1) Tetra Teh, In., Lafayette, CA, USA; (2) State University of New York,
Systemati Review of Trends in Fish Tissue Merury Conentrations Tom Grieb 1, Roxanne Karimi 2, Niholas Fisher 2, Leonard Levin 3 (1) Tetra Teh, In., Lafayette, CA, USA; (2) State University of New York,
Coupled feedback loops maintain synaptic long-term. potentiation: A computational model of PKMzeta
 1 Draft version 28, 2018-04-30. This paper has not been peer reviewed. Please do not opy or ite without author's permission. Coupled feedbak loops maintain synapti long-term potentiation: omputational
1 Draft version 28, 2018-04-30. This paper has not been peer reviewed. Please do not opy or ite without author's permission. Coupled feedbak loops maintain synapti long-term potentiation: omputational
Methylglyoxal impairs insulin signalling and insulin action on glucose-induced insulin secretion in the pancreatic beta cell line INS-1E
 Diabetologia () 5:9 95 DOI.7/s5--8-8 ARTICLE Methylglyoxal impairs insulin signalling and insulin ation on gluose-indued insulin seretion in the panreati beta ell line INS-E F. Fiory & A. Lombardi & C.
Diabetologia () 5:9 95 DOI.7/s5--8-8 ARTICLE Methylglyoxal impairs insulin signalling and insulin ation on gluose-indued insulin seretion in the panreati beta ell line INS-E F. Fiory & A. Lombardi & C.
Sequence Analysis using Logic Regression
 Geneti Epidemiology (Suppl ): S66 S6 (00) Sequene Analysis using Logi Regression Charles Kooperberg Ingo Ruzinski, Mihael L. LeBlan, and Li Hsu Division of Publi Health Sienes, Fred Huthinson Caner Researh
Geneti Epidemiology (Suppl ): S66 S6 (00) Sequene Analysis using Logi Regression Charles Kooperberg Ingo Ruzinski, Mihael L. LeBlan, and Li Hsu Division of Publi Health Sienes, Fred Huthinson Caner Researh
Innate Immunity. Chapter 3. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Reversal of ammonia coma in rats by L-dopa: a peripheral effect
 Gut, 1979, 2, 28-32 Reversal of ammonia oma in rats by L-dopa: a peripheral effet L. ZV1, W. M. DOZAK, AND R. F. DRR From the Department of Mediine, Hennepin ounty Medial enter and Minneapolis Veterans
Gut, 1979, 2, 28-32 Reversal of ammonia oma in rats by L-dopa: a peripheral effet L. ZV1, W. M. DOZAK, AND R. F. DRR From the Department of Mediine, Hennepin ounty Medial enter and Minneapolis Veterans
Study of Necrosis in the Liver of Formaldehyde and Benzo(α)Pyrene Exposured-Mice
 THE JOURNAL OF TROPICAL LIFE SCIENCE OPEN ACCESS Freely available online VOL. 3, NO. 1, pp. 58 62, January, 2013 Study of Nerosis in the Liver of Formaldehyde and Benzo(α)Pyrene Exposured-Mie Ahmad Soni,
THE JOURNAL OF TROPICAL LIFE SCIENCE OPEN ACCESS Freely available online VOL. 3, NO. 1, pp. 58 62, January, 2013 Study of Nerosis in the Liver of Formaldehyde and Benzo(α)Pyrene Exposured-Mie Ahmad Soni,
Cysticfibrosis. Abnormalities of airway epithelial function and the implications of the discovery of the cystic fibrosis gene
 124 Cystifibrosis - 4 Thorax 1991;46:124-130 Series editor: D JShale University Department of Pharmaology, Cambridge CB2 1QJ A W Cuthbert Reprint requests to: Professor Cuthbert Abnormalities of airway
124 Cystifibrosis - 4 Thorax 1991;46:124-130 Series editor: D JShale University Department of Pharmaology, Cambridge CB2 1QJ A W Cuthbert Reprint requests to: Professor Cuthbert Abnormalities of airway
Mucosal reactive oxygen metabolite production in duodenal ulcer disease
 Gut 1992; 33:1467-1472 Gastrointestinal Siene Researh Unit, Department of Histopathology, and Inflammation Researh Group, The London Hospital Medial College, London G R Davies N J Simmonds T R J Stevens
Gut 1992; 33:1467-1472 Gastrointestinal Siene Researh Unit, Department of Histopathology, and Inflammation Researh Group, The London Hospital Medial College, London G R Davies N J Simmonds T R J Stevens
constituent amino acids in man'
 Gut, 197, 11, 25-254 Intestinal absorption of arnosine and its onstituent amino aids in man' A. M. ASATOOR, J. K. BANDOH2, A. F. LANT, M. D. MILN, AND F. NAVAB From the Medial Unit of the Westminster Hospital,
Gut, 197, 11, 25-254 Intestinal absorption of arnosine and its onstituent amino aids in man' A. M. ASATOOR, J. K. BANDOH2, A. F. LANT, M. D. MILN, AND F. NAVAB From the Medial Unit of the Westminster Hospital,
Effect of Curing Conditions on Hydration Reaction and Compressive Strength Development of Fly Ash-Cement Pastes
 Effet of Curing Conditions on Hydration Reation and Development of Fly Ash-Cement Pastes Warangkana Saengsoy Candidate for the degree of Dotor of Philosophy Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Toyoharu Nawa Division
Effet of Curing Conditions on Hydration Reation and Development of Fly Ash-Cement Pastes Warangkana Saengsoy Candidate for the degree of Dotor of Philosophy Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Toyoharu Nawa Division
RADIATION DOSIMETRY INTRODUCTION NEW MODALITIES
 RADIATION DOSIMETRY M. Ragheb 1/17/2006 INTRODUCTION Radiation dosimetry depends on the aumulated knowledge in nulear siene in general and in nulear and radio hemistry in partiular. The latter is onerned
RADIATION DOSIMETRY M. Ragheb 1/17/2006 INTRODUCTION Radiation dosimetry depends on the aumulated knowledge in nulear siene in general and in nulear and radio hemistry in partiular. The latter is onerned
Comparative Activity of Amoxycillin and Ampicillin in an Experimental Bacterial Infection in Mice
 ANTMCROBAL AGNTS AND CHMOTHRAPY, Sept. 1973, p. 285-293 Copyright i 1973 Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Vol. 4, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Comparative Ativity of Amoxyillin and Ampiillin in an xperimental
ANTMCROBAL AGNTS AND CHMOTHRAPY, Sept. 1973, p. 285-293 Copyright i 1973 Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Vol. 4, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Comparative Ativity of Amoxyillin and Ampiillin in an xperimental
Unit 02 - The Inside Story about Nutrition and Health. True / False
 True / False 1. Geneti traits exert the strongest overall influene on health and longevity. False 2. The bodies of modern humans adapted to exist on a diet of wild game, fish, fruits, nuts, seeds, roots,
True / False 1. Geneti traits exert the strongest overall influene on health and longevity. False 2. The bodies of modern humans adapted to exist on a diet of wild game, fish, fruits, nuts, seeds, roots,
between normal children and children with primary
 Arhives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 224-228 odium transport in erythroytes: differenes between normal hildren and hildren with primary and seondary hypertension M UCHIYAMA, V HAH, C E DAMAN WILLEM,
Arhives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 224-228 odium transport in erythroytes: differenes between normal hildren and hildren with primary and seondary hypertension M UCHIYAMA, V HAH, C E DAMAN WILLEM,
Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses
 MICR2209 Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses Dr Allison Imrie 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which constitute the humoral immune response, and examine the antibody
MICR2209 Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses Dr Allison Imrie 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which constitute the humoral immune response, and examine the antibody
Innate Immunity & Inflammation
 Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Keywords: congested heart failure,cardiomyopathy-targeted areas, Beck Depression Inventory, psychological distress. INTRODUCTION:
 International Journal of Medial Siene and Eduation An offiial Publiation of Assoiation for Sientifi and Medial Eduation (ASME) Original Researh Artile ASSOCIATION BETWEEN QUALITY OF LIFE AND ANXIETY, DEPRESSION,
International Journal of Medial Siene and Eduation An offiial Publiation of Assoiation for Sientifi and Medial Eduation (ASME) Original Researh Artile ASSOCIATION BETWEEN QUALITY OF LIFE AND ANXIETY, DEPRESSION,
Case Report Duplication Cyst in the Third Part of the Duodenum Presenting with Gastric Outlet Obstruction and Severe Weight Loss
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 015, Artile ID 749085, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/015/749085 Case Report Dupliation Cyst in the Third Part of the Duodenum Presenting with Gastri Outlet Obstrution
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 015, Artile ID 749085, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/015/749085 Case Report Dupliation Cyst in the Third Part of the Duodenum Presenting with Gastri Outlet Obstrution
persistence of Clostridium difficile during vancomycin
 Giat 1983. 24 26212 Relapse of antibioti assoiated olitis: endogenous persistene of lostridium diffiile during vanomyin therapy B A J WALTERS. R ROBERTS. R STAFFORD AND E SENEVIRATNE From tlie Departmtietnt
Giat 1983. 24 26212 Relapse of antibioti assoiated olitis: endogenous persistene of lostridium diffiile during vanomyin therapy B A J WALTERS. R ROBERTS. R STAFFORD AND E SENEVIRATNE From tlie Departmtietnt
cholerae Non-Ol and Comparison with a Protease of V. cholerae 01
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Sept. 1989, p. 2799-283 Vol. 57, No. 9 19-9567/89/92799-4$2./ Copyright C) 1989, Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Purifiation and Charaterization of a Protease Produed by Vibrio holerae
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Sept. 1989, p. 2799-283 Vol. 57, No. 9 19-9567/89/92799-4$2./ Copyright C) 1989, Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Purifiation and Charaterization of a Protease Produed by Vibrio holerae
clinical conditions using a tape recorder system
 Thorax (1964), 19, 125 Objetive assessment of ough suppressants under linial onditions using a tape reorder system C. R. WOOLF AND A. ROSENBERG From the Respiratory Unit, Sunnybrook Hospital (Department
Thorax (1964), 19, 125 Objetive assessment of ough suppressants under linial onditions using a tape reorder system C. R. WOOLF AND A. ROSENBERG From the Respiratory Unit, Sunnybrook Hospital (Department
Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of TGF-β-activated Smad2
 Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of -ativated Roger S. Lo* and Joan Massagué* *Cell Biology Program, Howard Hughes Medial Institute, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Caner Center, New York, New York 10021, USA
Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of -ativated Roger S. Lo* and Joan Massagué* *Cell Biology Program, Howard Hughes Medial Institute, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Caner Center, New York, New York 10021, USA
Mechanism of Action of Phenethyl Alcohol: Breakdown of the Cellular Permeability Barrier
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Feb., 1967, p. 56-566 Vol. 93, No. 2 Copyright @ 1967 Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Printed In U.S.A. Mehanism of Ation of Phenethyl Alohol: Breakdown of the Cellular Permeability
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Feb., 1967, p. 56-566 Vol. 93, No. 2 Copyright @ 1967 Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Printed In U.S.A. Mehanism of Ation of Phenethyl Alohol: Breakdown of the Cellular Permeability
Supplementary Information Computational Methods
 Supplementary Information Computational Methods Data preproessing In this setion we desribe the preproessing steps taken to establish the data matrix of hepatoyte single ell gene expression data (Table
Supplementary Information Computational Methods Data preproessing In this setion we desribe the preproessing steps taken to establish the data matrix of hepatoyte single ell gene expression data (Table
Dietary management of gastrointestinal (GI) disease
 J Vet Intern Med 2011;25:230 235 Effet of Diets Differing in Fat Content on Chroni Diarrhea in Cats D.P. Laflamme, H. Xu, and G.M. Long Bakground: Fat-restrited diets have been advoated for dogs with diarrhea
J Vet Intern Med 2011;25:230 235 Effet of Diets Differing in Fat Content on Chroni Diarrhea in Cats D.P. Laflamme, H. Xu, and G.M. Long Bakground: Fat-restrited diets have been advoated for dogs with diarrhea
Opening and Closing Transitions for BK Channels Often Occur in Two
 72 Biophysial Journal Volume 65 August 1993 72-714 Opening and Closing Transitions for BK Channels Often Our in Two Steps via Sojourns through a Brief ifetime Subondutane State William B. Ferguson, Owen
72 Biophysial Journal Volume 65 August 1993 72-714 Opening and Closing Transitions for BK Channels Often Our in Two Steps via Sojourns through a Brief ifetime Subondutane State William B. Ferguson, Owen
Proliferation of Legionella pneumophila as an Intracellular Parasite
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1984, p. 467-471 0099-2240/84/030467-05$02.00/0 Copyright C) 1984, Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Vol. 47, No. 3 Proliferation of Legionella pneumophila as
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1984, p. 467-471 0099-2240/84/030467-05$02.00/0 Copyright C) 1984, Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Vol. 47, No. 3 Proliferation of Legionella pneumophila as
MODELING THE AIRWAY SURFACE LIQUID REGULATION IN HUMAN LUNGS. Peiying Zuo
 MODELING THE AIRWAY SURFACE LIQUID REGULATION IN HUMAN LUNGS Peiying Zuo A dissertation submitted to the faulty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment of the requirements
MODELING THE AIRWAY SURFACE LIQUID REGULATION IN HUMAN LUNGS Peiying Zuo A dissertation submitted to the faulty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment of the requirements
Cytomegalovirus and tumor stress-surveillance by human γδ T cell receptor binding to Endothelial Protein C Receptor
 Cytomegalovirus and tumor stress-surveillane y human γδ T ell reeptor inding to Endothelial Protein C Reeptor Carrie R. Willox, Vinent Pitard, Sonia Netzer, Lionel Couzi, Mahoo Salim, Toias Silerzahn,
Cytomegalovirus and tumor stress-surveillane y human γδ T ell reeptor inding to Endothelial Protein C Reeptor Carrie R. Willox, Vinent Pitard, Sonia Netzer, Lionel Couzi, Mahoo Salim, Toias Silerzahn,
DEPOSITION AND CLEARANCE OF FINE PARTICLES IN THE HUMAN RESPIRATORY TRACT
 PII: S0003^t878(96)00171-8 Ann. oup. Hyg., Vol. 41, Supplement 1, pp. 503-508, 1997 1997 British Oupational Hygiene Soiety Published by Elsevier Siene Ltd. All rights reserved Printed in Great Britain
PII: S0003^t878(96)00171-8 Ann. oup. Hyg., Vol. 41, Supplement 1, pp. 503-508, 1997 1997 British Oupational Hygiene Soiety Published by Elsevier Siene Ltd. All rights reserved Printed in Great Britain
Miles Fisher. Coronary disease DIABETES AND ATHEROGENESIS RESISTANCE AND THE METABOLIC SYNDROME
 336 Correspondene to: Dr Miles Fisher, Wards 4 & 5, Glasgow Royal Infirmary, Glasgow, G4 0SF, UK; miles.fisher@northglasgow. sot.nhs.uk Coronary disease DIABETES AND ATHEROGENESIS INSULIN T Miles Fisher
336 Correspondene to: Dr Miles Fisher, Wards 4 & 5, Glasgow Royal Infirmary, Glasgow, G4 0SF, UK; miles.fisher@northglasgow. sot.nhs.uk Coronary disease DIABETES AND ATHEROGENESIS INSULIN T Miles Fisher
Histometry of lymphoid infiltrate in the thyroid of primary thyrotoxicosis patients
 J. /in. Path., 1976, 29, 398*402 Histometry of lymphoid infiltrate in the thyroid of primary thyrotoxiosis patients Relation of extent of thyroiditis to preoperative drug treatment and postoperative hypothyroidism
J. /in. Path., 1976, 29, 398*402 Histometry of lymphoid infiltrate in the thyroid of primary thyrotoxiosis patients Relation of extent of thyroiditis to preoperative drug treatment and postoperative hypothyroidism
Evidence of hydrogen ion secretion from the human gall bladder in vitro
 554 Department of Mediine, Royal Infirmary of dinburgh, and Department of Pathology, University of dinburgh, Sotland J N Plevris P Hayes I A D Bouhier Department of Pathology D J Harrison orrespondene
554 Department of Mediine, Royal Infirmary of dinburgh, and Department of Pathology, University of dinburgh, Sotland J N Plevris P Hayes I A D Bouhier Department of Pathology D J Harrison orrespondene
Learned spatiotemporal sequence recognition and prediction in primary visual cortex
 Supplementary Materials for Learned spatiotemporal sequene reognition and predition in primary visual ortex Jeffrey P. Gavornik and Mark F. Bear Howard Hughes Medial Institute Piower Institute for Learning
Supplementary Materials for Learned spatiotemporal sequene reognition and predition in primary visual ortex Jeffrey P. Gavornik and Mark F. Bear Howard Hughes Medial Institute Piower Institute for Learning
In the last decade there has been a growing interest in the relationships between infection,
 ii40 * Thorax 2002;57(Suppl II):ii40 ii46 PRO AND ANTI: THE BIOTICS OF ALLERGIC DISEASE HYGIENE J Crane Wellington Asthma Researh Group, Shool of Mediine and Health Sienes, Wellington, New Zealand; rane@wnmeds.a.nz
ii40 * Thorax 2002;57(Suppl II):ii40 ii46 PRO AND ANTI: THE BIOTICS OF ALLERGIC DISEASE HYGIENE J Crane Wellington Asthma Researh Group, Shool of Mediine and Health Sienes, Wellington, New Zealand; rane@wnmeds.a.nz
STRUCTURAL AND HORMONAL ALTERATIONS IN THE GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT OF PARENTERALLY FED RATS
 GASTRONTROLOGY 68:1177-1183, 1975 Copyright 1975 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 68, No.5, Part 1 Printed in U.S.A. STRUCTURAL AND HORMONAL ALTRATIONS IN TH GASTROINTSTINAL TRACT OF PARNTRALLY FD RATS
GASTRONTROLOGY 68:1177-1183, 1975 Copyright 1975 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 68, No.5, Part 1 Printed in U.S.A. STRUCTURAL AND HORMONAL ALTRATIONS IN TH GASTROINTSTINAL TRACT OF PARNTRALLY FD RATS
collagen-induced arthritis
 Pro. Natl. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 92, pp. 517-521, January 1995 Medial Sienes Leukotriene B4 plays a ritial role in the progression of ollagen-indued arthritis R. J. GRIFFITHS*, E. R. PETrIPHER, K. KOCH, C.
Pro. Natl. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 92, pp. 517-521, January 1995 Medial Sienes Leukotriene B4 plays a ritial role in the progression of ollagen-indued arthritis R. J. GRIFFITHS*, E. R. PETrIPHER, K. KOCH, C.
Regulation of spike timing in visual cortical circuits
 Regulation of spike timing in visual ortial iruits Paul Tiesinga*, Jean-Mar Fellous and Terrene J. Sejnowski Abstrat A train of ation potentials (a spike train) an arry information in both the average
Regulation of spike timing in visual ortial iruits Paul Tiesinga*, Jean-Mar Fellous and Terrene J. Sejnowski Abstrat A train of ation potentials (a spike train) an arry information in both the average
Evaluation of a prototype for a reference platelet
 932 Royal Postgraduate Medial Shool, Duane Road, London W12 ONN S M Lewis Western Infirmary, Glasgow R M Rowan Toa Medial Eletronis, Kobe, Japan F Kubota Correspondene to: Dr S M Lewis Aepted for publiation
932 Royal Postgraduate Medial Shool, Duane Road, London W12 ONN S M Lewis Western Infirmary, Glasgow R M Rowan Toa Medial Eletronis, Kobe, Japan F Kubota Correspondene to: Dr S M Lewis Aepted for publiation
Iraqi Journal of Veterinary Sciences, Vol. 21, No.1, 2007 (15-27)
 [ Iraqi Journal of Veterinary Sienes, Vol. 21, No.1, 2007 (15-27) IMMUNE RESPONSE IN Rattus rattus norvegius RATS AGAINST INFECTION WITH GIARDIASIS BY THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE EXTRACTED FROM Esherihia oli
[ Iraqi Journal of Veterinary Sienes, Vol. 21, No.1, 2007 (15-27) IMMUNE RESPONSE IN Rattus rattus norvegius RATS AGAINST INFECTION WITH GIARDIASIS BY THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE EXTRACTED FROM Esherihia oli
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine
 Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Thomas Kahan, Lennart Bergfeldt
 250 Cardiomyopathy LEFT VENTRICULAR HYPERTROPHY IN HYPERTENSION: ITS ARRHYTHMOGENIC POTENTIAL DEVELOPMENT See end of artile for authors affiliations Correspondene to: Professor Lennart Bergfeldt, Department
250 Cardiomyopathy LEFT VENTRICULAR HYPERTROPHY IN HYPERTENSION: ITS ARRHYTHMOGENIC POTENTIAL DEVELOPMENT See end of artile for authors affiliations Correspondene to: Professor Lennart Bergfeldt, Department
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for real-time quantitative RT-PCR assay. Nucleotide sequence
 Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for real-time quantitative RT-PCR assay Name FoxO1 forward FoxO1 reverse GK forward GK reverse INS-1 forward INS-1 reverse INS-2 forward INS-2 reverse Glut2 forward Glut2
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for real-time quantitative RT-PCR assay Name FoxO1 forward FoxO1 reverse GK forward GK reverse INS-1 forward INS-1 reverse INS-2 forward INS-2 reverse Glut2 forward Glut2
Partial inactivation of Ankrd26 causes diabetes with enhanced insulin responsiveness of adipose tissue in mice
 Diabetologia (11) :911 9 DOI.7/s-11-3-9 ARTICLE Partial inativation of Ankrd auses diabetes with enhaned insulin responsiveness of adipose tissue in mie G. A. Raiti & T. K. Bera & O. Gavrilova & I. Pastan
Diabetologia (11) :911 9 DOI.7/s-11-3-9 ARTICLE Partial inativation of Ankrd auses diabetes with enhaned insulin responsiveness of adipose tissue in mie G. A. Raiti & T. K. Bera & O. Gavrilova & I. Pastan
Enhanced Bactericidal Action of Lysozyme to Escherichia coli by Inserting a Hydrophobic Pentapeptide into Its C Terminus*
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 0 1994 by The Amerian Soiety for Biohemistry and Moleular Biology, In. Vol. 269, No. 7, Issue of February 18, pp. 5053-5063,1994 Printed in U. S. A. Enhaned Bateriidal
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 0 1994 by The Amerian Soiety for Biohemistry and Moleular Biology, In. Vol. 269, No. 7, Issue of February 18, pp. 5053-5063,1994 Printed in U. S. A. Enhaned Bateriidal
Expression and Significance of p53, Rb, p21/waf-1, p16/ink-4a, and PTEN Tumor Suppressors in Canine Melanoma
 Vet Pathol 39:458 472 (2002) Expression and Signifiane of p53, Rb, p21/waf-1, p16/ink-4a, and PTEN Tumor Suppressors in Canine Melanoma A. KOENIG, S. R. BIANCO, S. FOSMIRE, J. WOJCIESZYN, AND J. F. MODIANO
Vet Pathol 39:458 472 (2002) Expression and Signifiane of p53, Rb, p21/waf-1, p16/ink-4a, and PTEN Tumor Suppressors in Canine Melanoma A. KOENIG, S. R. BIANCO, S. FOSMIRE, J. WOJCIESZYN, AND J. F. MODIANO
Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology. Robin Lorenz
 Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology Robin Lorenz rlorenz@uab.edu Why do we Need to Understand How the Mucosal Immune System Works? The mucosa is the major
Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology Robin Lorenz rlorenz@uab.edu Why do we Need to Understand How the Mucosal Immune System Works? The mucosa is the major
Voltage-Dependent Gating Underlies Loss of ENaC Function in Pseudohypoaldosteronism Type 1
 193 iophysial Journal Volume pril 211 193 1939 Voltage-Dependent Gating Underlies Loss of ENa Funtion in Pseudohypoaldosteronism Type 1 Volodymyr Kuher, Nina oiko, Oleh Pohynyuk, and James D. Stokand *
193 iophysial Journal Volume pril 211 193 1939 Voltage-Dependent Gating Underlies Loss of ENa Funtion in Pseudohypoaldosteronism Type 1 Volodymyr Kuher, Nina oiko, Oleh Pohynyuk, and James D. Stokand *
The effects of bilingualism on stuttering during late childhood
 Additional information is published online only at http:// ad.bmj.om/ontent/vol93/ issue11 1 Division of Psyhology and Language Sienes, University College London, London, UK; 2 Department of Language and
Additional information is published online only at http:// ad.bmj.om/ontent/vol93/ issue11 1 Division of Psyhology and Language Sienes, University College London, London, UK; 2 Department of Language and
Relative sizes of infectious agents
 Relative sizes of infectious agents Bacteria Protozoa Viruses RBC 0.005 0.01 0.03 01 03 05 1 3 5 10 30 50 100 300 Size in microns ( µm ) - log scale Immunity to Infection Principle 1 Every clinical infection
Relative sizes of infectious agents Bacteria Protozoa Viruses RBC 0.005 0.01 0.03 01 03 05 1 3 5 10 30 50 100 300 Size in microns ( µm ) - log scale Immunity to Infection Principle 1 Every clinical infection
Bombesin stimulates insulin secretion by a pancreatic islet cell line
 Pro. Natl. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 81, pp. 1822-1826, Marh 1984 Medial Sienes Bombesin stimulates insulin seretion by a panreati islet ell line (gastrin-releasing peptide/somatostatin/gluagon/hit-t15 ells) SHERIDAN
Pro. Natl. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 81, pp. 1822-1826, Marh 1984 Medial Sienes Bombesin stimulates insulin seretion by a panreati islet ell line (gastrin-releasing peptide/somatostatin/gluagon/hit-t15 ells) SHERIDAN
Original Articles. Experimental disciform edema and necrotizing keratitis in the rabbit. Joseph F. Metcalf, James I. McNeill, and Herbert E.
 Original Artiles Experimental disiform edema and nerotizing keratitis in the rabbit Joseph F. Metalf, James I. MNeill, and Herbert E. Kaufman The development of experimental disiform edema and nerotizing
Original Artiles Experimental disiform edema and nerotizing keratitis in the rabbit Joseph F. Metalf, James I. MNeill, and Herbert E. Kaufman The development of experimental disiform edema and nerotizing
Interaction of Lipopolysaccharides of Helicobacter pylori with
 NFETON AND MMUNTY, Sept. 1994, p. 364-3648 19-9567/94/$4.+ opyright 1994, Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Vol. 62, No. 9 nteration of Lipopolysaharides of Heliobater pylori with Basement Membrane Protein
NFETON AND MMUNTY, Sept. 1994, p. 364-3648 19-9567/94/$4.+ opyright 1994, Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Vol. 62, No. 9 nteration of Lipopolysaharides of Heliobater pylori with Basement Membrane Protein
Salmonella abortus-ovis Infection in Mice
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, May 983, p. 60-607 009-9567/83/05060-07$02.00/0 Copyright 983, Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Vol. 40, No. 2 Immunogeniity of a Low-Virulene Vainal Strain Against Salmonella abortus-ovis
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, May 983, p. 60-607 009-9567/83/05060-07$02.00/0 Copyright 983, Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Vol. 40, No. 2 Immunogeniity of a Low-Virulene Vainal Strain Against Salmonella abortus-ovis
Onset, timing, and exposure therapy of stress disorders: mechanistic insight from a mathematical model of oscillating neuroendocrine dynamics
 Kim et al. RESEARCH arxiv:63.2773v [q-bio.nc] 9 Mar 26 Onset, timing, and exposure therapy of stress disorders: mehanisti insight from a mathematial model of osillating neuroendorine dynamis Lae Kim, Maria
Kim et al. RESEARCH arxiv:63.2773v [q-bio.nc] 9 Mar 26 Onset, timing, and exposure therapy of stress disorders: mehanisti insight from a mathematial model of osillating neuroendorine dynamis Lae Kim, Maria
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2017, 9(10): Research Article
 Available online www.jopr.om Journal of Chemial and Pharmaeutial Researh, 2017, 9(10):95-105 Researh Artile ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Antidiarrhoeal, Antibaterial Ativities and Growth Stimulatory
Available online www.jopr.om Journal of Chemial and Pharmaeutial Researh, 2017, 9(10):95-105 Researh Artile ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Antidiarrhoeal, Antibaterial Ativities and Growth Stimulatory
Intestinal permeability in Crohn's disease
 Arhives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 321-325 Intestinal permeability in Crohn's disease M S MURPHY,* E J EASTHAM,* R NELSON,* A D J PEARSON,* AND M F LAKERt Departments of *Child Health and tclinial
Arhives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 321-325 Intestinal permeability in Crohn's disease M S MURPHY,* E J EASTHAM,* R NELSON,* A D J PEARSON,* AND M F LAKERt Departments of *Child Health and tclinial
Normal Human Blood Glucose and Insulin Levels
 Presented at the COMSOL Conferene 2010 Boston Normal Human Blood Gluose and Insulin Levels In healthy humans, blood gluose levels have to be maintained in a relatively narrow range (3.5 7.0 mm, 60 130
Presented at the COMSOL Conferene 2010 Boston Normal Human Blood Gluose and Insulin Levels In healthy humans, blood gluose levels have to be maintained in a relatively narrow range (3.5 7.0 mm, 60 130
What causes the spacing effect? Some effects ofrepetition, duration, and spacing on memory for pictures
 Memory & Cognition 1975, Vol. 3 (3), 287 294 What auses the spaing effet? Some effets ofrepetition, duration, and spaing on memory for pitures DOUGLAS 1. HNTZMAN, JEFFERY J. SUMMERS, and RCHARD A. BLOCK
Memory & Cognition 1975, Vol. 3 (3), 287 294 What auses the spaing effet? Some effets ofrepetition, duration, and spaing on memory for pitures DOUGLAS 1. HNTZMAN, JEFFERY J. SUMMERS, and RCHARD A. BLOCK
3/10/14. Ultrastructural organization. Gram Stain. Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation. Gram negative.
 Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
PBS Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs , 27-30
 PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
Supplementary Figure 1. Verification of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative
 Supplementary Figure 1. Verifiation of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative neutral red-stained oronal setion from a mouse with a guide annula targeting the IPN. The guide annula sar is irled
Supplementary Figure 1. Verifiation of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative neutral red-stained oronal setion from a mouse with a guide annula targeting the IPN. The guide annula sar is irled
