Crohn's disease of the duodenum
|
|
|
- Terence Barker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Crohn's disease of the duodenum F. WARREN NUGENT,' M. RICHMOND,2 AND S. K. PARK3 Gut, 1977, 18, From the Department of Gastroenterology, Lahey Clinic Foundation, Boston, Massachusetts, USA SUMMARY Crohn's disease of the duodenum is uncommon, occurring in approximately 2% of patients with Crohn's disease. Approximately 165 cases have been reported in small series in the literature. Our report includes 36 patients, most of whom had symptoms of duodenal disease coincident with or after obvious disease elsewhere in the gastrointestinal tract, although occasionally duodenal disease developed first and rarely disease was confined to the duodenum. Upper abdominal pain and symptoms of gastroduodenal obstruction are the commonest patterns of presentation. Significant weight loss is common, and occasionally major upper gastrointestinal bleeding occurs. The commonest pattern of involvement was contiguous disease of the proximal duodenum and distal stomach. Endoscopically, diffuse granularity, nodularity, and ulceration are seen accompanied by lack of distensibility of the involved area. Granulomas are rarely found in endoscopic biopsies. A bypass procedure was carried out on 18 patients, 15 of whom continue to be free of symptoms with an average follow-up of 6-6 years. When symptoms of obstruction dictate, operative bypass is accompanied by favourable long-term results in the large majority of patients. Crohn's disease most commonly involves the terminal ileum or colon but it may occur in any part of the alimentary tract from the mouth to the anus (Bishop et al., 1972; Fedotin et al., 1974). Involvement of the duodenum is uncommon but is being recognised with increasing frequency. In a review of the world literature in 1965, Edwards et al. (1965) revealed that only 48 cases had been reported. Since then, an additional 76 cases have been cited in a review by Paget et al. (1972). Further scattered reports have appeared (Bagby et al., 1972; Farmer et al., 1972; Roseman, 1972; Sanders and Schimmel, 1972; Haggitt and Meissner, 1973; Kim et al., 1973; Thompson et al., 1975) increasing the total number to approximately 165 cases. We have encountered 36 patients with Crohn's disease involving the duodenum over a 20 year period. The clinical, radiological, endoscopic, and pathological features of this uncommon entity and the results of medical and surgical management are reported. Methods PATIENTS All patients with a diagnosis of Crohn's disease of 'Address for reprint requests: Dr Nugent, Lahey Clinic Foundation, 605 Commonwealth Avenue, Boston, Ma 02215, USA. "Present address: Waltham, Massachusetts, USA. "Present address: Daegu, Korea. Received for publication 18 August 1976 the duodenum seen between 1955 and 1974 were included in our review. Diagnosis was established by one of two criteria: the histological finding of noncaseating granulomatous inflammation of the duodenum with or without obvious Crohn's disease elsewhere in the intestinal tract and without evidence of any systemic granulomatous disease, or Crohn's disease of the small or large bowel and a radiologicalfinding of diffuse inflammatory change in the duodenum consistent with Crohn's disease. Clinical features Twenty-five men and 11 women were included in the group of patients studied. Age at onset of Crohn's disease varied from 5 to 59 years (mean, 27 years), and age at onset of duodenal Crohn's disease ratiged from 5 to 67 years (mean, 30 years). Of these patients, in 19 the onset of duodenal disease appeared to coincide with the onset of disease in other parts of the gastrointestinal tract; 11 patients had obvious disease elsewhere of four to 40 years' duration (mean, 10 years) before duodenal disease developed. In six patients disease was initially confined to the duodenum with or without involvement of the gastric antrum. In one of these six patients, terminal ileitis developed four years later. In another, widespread jejunal disease in continuity with disease in the duodenum developed seven years later, and, in a third patient, severe diffuse gastric Crohn's disease requiring total gastrectomy occurred 20 years later. In the other three patients the disease remained confined to the 115
2 116 F. Warren Nugent, M. Richmond, and S. K. Parkduodenum throughout its course, although all three had histological involvement of the gastric antrum. Of the 32 patients who had Crohn's disease elsewhere in their gastrointestinal tract (excluding stomach), one had oesophageal disease, five had disease in the proximal small intestine, 16 had disease in the terminal ileum, seven had colonic disease, and three had widespread disease throughout the small and large intestine. Symptoms The symptoms of Crohn's disease of the duodenum are listed in the Table. Epigastric pain was by far Table Clinical symptoms 36 patients Number Percent Pain Nausea Vomiting Weight loss (> 4-5 kg) Melaena 5 14 Fever 2 6 the commonest symptom; most often it was postprandial and accompanied by nausea and sometimes vomiting. Vomiting usually offered relief of pain. Some patients had pain suggestive of duodenal ulcer pain in that it was relieved by food or antacids, although it was not usually episodic. In the majority of patients, symptoms reflected the obstructive nature of the lesion. Significant weight loss was common. Major upper gastrointestinal bleeding, presenting as haematemesis or melaena, occurred in five patients. Radiology Radiologically, three patterns of disease were noted in the duodenum. The first and commonest was contiguous involvement of the gastric antrum and proximal duodenum. Of the 36 patients, 20 had this pattern of involvement radiologically (seven others had histological evidence of gastroduodenal disease with radiological changes confined to the duodenum). A second pattern, seen in six patients, was involvement of an isolated segment of the descending duodenum. The third pattern was involvement of the distal duodenum. Three patients had this pattern, all of whom had contiguous involvement of at least a short segment of proximal jejunum. The earliest radiological features, regardless of the site of disease, were irregular thickening, oedema, and a cobblestone pattern of the mucosa (Figure, A). As the disease progresses, stenosis becomes a prominent finding (Figure, B). Eventually, stenosis becomes severe and a string sign develops (Figure, C). Fissures and pseudodiverticula were seen occasionally. Reflux of barium into the common bile duct and pancreatic duct occurred in one patient. In patients, with gastroduodenal involvement, progressive stenosis of the pyloric area may produce a pseudo- Billroth I appearance, in which the identity of the pylorus becomes entirely obscured (Figure, D). Endoscopy Endoscopic examination was carried out on 17 patients, and biopsies were obtained. The mucosa of the involved antrum and duodenum had a diffusely granular appearance with some nodularity and varying degrees of superficial ulceration. Linear ulcers were seen at times, and stiffness and lack of distensibility of the involved area were noted. Varying degrees of stenosis were encountered, and, in some, the involved areas were markedly rigid with stricture formation. The endoscope could not always traverse the pyloric canal or duodenum because of the stenosis. Pathological features At the time of operation, the appearance of a thickened, indurated, and oedematous duodenum suggests the diagnosis of Crohn's disease. Enlarged mesenteric lymph nodes and thickening and oedema of the mesentery may be present. When the mucosa is exposed by duodenotomy, it appears oedematous with thickened folds and has a granular surface. Mucosal ulcerations are sometimes obvious and may be superficial or deep (Haggitt and Meissner, 1973). Histologically, there is chronic inflammation and fibrosis involving the entire duodenal wall, and noncaseating granulomas may be present in any layer of the wall or in the regional lymph nodes. The histological changes are identical with those seen in Crohn's disease elsewhere in the gastrointestinal tract. Of our patients 28 had histological diagnoses either at the time of operation or by endoscopic or capsule biopsy. Twelve patients had all histological features of Crohn's disease, including granulomas. In 16 patients, no granulomas were identified, but chronic inflammation and fibrosis of the duodenal wall, consistent with the diagnosis of Crohn's disease, were seen. Granulomas were not demonstrated in any of the 17 patients who had endoscopic biopsies. A gastric specimen from one of the three patients who had a capsule biopsy revealed granulomas. Treatment Of the 36 patients, 20 were operated on for obstruction of the pylorus or duodenum. Of these, 18 patients had a bypass procedure (gastroenterostomy and vagotomy, six; gastroenterostomy, six; Billroth
3 Crohn's disease of the duodenum I7 A Figure A: early radiological changes ofoedema and cobblestone pattern. B: stenosis and deformity of the gastric antrum and proximal duodenum. C: marked stenosis with string sign. D: obliteration of the pylorus: 'pseudo- Billroth 1.' My\:.\N. 117 I4.I *I
4 118 II and vagotomy, three; Billroth II, two; and duodenojejunostomy, one). Of these 18 patients, 15 continue to be free of all significant upper gastrointestinal symptoms one to 19 years later (average, 6-6 years). One patient died six years after operation from extensive Crohn's disease of the stomach, duodenum, small bowel, and colon, all of which were present before duodenal surgery. Two patients have had local extension of disease beyond areas that were involved at the time of operation. In one patient, severe Crohn's disease of all remaining stomach developed, resulting in a linitis plastica type of lesion. Four years after the original subtotal gastrectomy, total gastrectomy with oesophagojejunostomy was required, and the patient remains well 18 months later. Histological examination of the resected stomach revealed diffuse, noncaseating granulomatous disease. This patient has never had Crohn's disease elsewhere in the gastrointestinal tract. In the second patient, widespread local extension into the distal half of the stomach and into the proximal jejunum developed four years after gastroenterostomy and vagotomy, resulting in partial small bowel obstruction. The patient was treated with steroids and has responded well to treatment for the past 18 months. Two patients underwent operations that did not bypass the duodenum. One patient had a pyloroplasty and is free of symptoms 11 years later, and the other patient had a duodenectomy and died in the postoperative period. Of the 16 patients who were treated without operation, 12 have received steroids intermittently. Of the 12 patients, four now have no significant symptoms one, two, six, and six years later, five have moderate symptoms and mild to moderate disability (two, four, six, 14, and 14 years later) and three have died, all with widespread Crohn's disease which had been present from the onset of disease. These patients died three, seven, and 19 years after operation. Four patients were treated conservatively without steroid therapy. Of these patients, two have no significant symptoms (nine and 15 years later), and two have mild to moderate symptoms and disability (one and two years later). Discussion Crohn's disease involving the duodenum is quite rare. The 36 cases that have been presented represent 2% of the total population of the new patients with Crohn's disease we saw during the 20 year period. Others (Van Patter et al., 1954; Jones et al., 1966; Fielding et al., 1970; Legge et al., 1970) have reported the incidence to be from 0-5 % to 4%. Age and sex distribution are not unlike those for Crohn's F. Warren Nugent, M. Richmond, and S. K. Park disease located elsewhere. In most patients, symptoms of duodenal disease develop at the same time as or after the appearance of obvious disease elsewhere in the gastrointestinal tract. A few patients have symptoms of duodenal disease before disease is detected elsewhere, and an occasional patient has disease confined to the duodenum with or without involvement of the distal stomach. Others (Paget et al., 1972; Silva and Thomas, 1972; Wise et al., 1971) have reported disease confined to the duodenum. Concomitant Crohn's disease that occurs elsewhere in the gastrointestinal tract has been reported from all sites, but most of the patients in our series had disease in the small intestine. Clinically, patients present with upper abdominal pain usually localised to the epigastrium and without a specific pattern of radiation. The pain most commonly occurs after eating and is sometimes accompanied by nausea. Symptoms of high intestinal obstruction may or may not be present. In some patients, the pain has characteristics suggestive of duodenal ulcer in that relief is obtained with antacids or food. In some cases it is difficult to differentiate duodenal Crohn's from peptic ulcer. This differential diagnosis must depend upon radiological, endoscopic, and histological findings. Eventually, obstruction of the pylorus or proximal duodenum occurs in the majority of patients with Crohn's disease of the duodenum. Most patients experience significant weight loss. Major upper gastrointestinal bleeding occurred in five of our patients and has occasionally been reported (Paget et al., 1972; Kim et al., 1973). Pancreatitis did not develop in any of our patients, although free reflux of barium into the pancreatic and common bile ducts was seen in one patient. Legge et al. (1971) reported evidence of pancreatitis in four of 11 patients, three of whom had reflux of barium into the pancreatic duct and another had reflux of barium into the biliary tract. Three of these patients had an accompanying rise in the serum amylase level. The similarity of the symptoms of pancreatitis to those of Crohn's disease of the duodenum makes it difficult to detect minor degrees of pancreatitis. Most of our patients had radiological changes involving the proximal duodenum. The pylorus is obviously not a barrier to extension of Crohn's disease; all of our patients with involvement of the proximal duodenum also had involvement of the distal stomach, although this was not always apparent radiologically. A few patients had involvement of an isolated segment of the middle part of the duodenum, and a few had involvement of the distal duodenum with contiguous involvement of the
5 Crohn's disease of the duodenum 119 proximal jejunum. Characteristically, radiological changes included evidence of diffuse inflammatory change, oedema, and ulceration, with eventual stenosis or obstruction (Durrance, 1962; Roberts and Hamilton, 1966; Cohen, 1967; Nelson, 1969; Fielding et al., 1970; Bagby et al., 1972). None of our patients had spontaneous perforation or fistula from the duodenum, and these complications are not reported in the literature; however, an occasional patient has had a fistula after operation on the duodenum (Fielding et al., 1970; Hermos et al., 1970). Relatively little information has been reported in the literature regarding the endoscopic appearance of Crohn's disease of the duodenum. Roseman (1972) reported a single case in which enlarged, rigid prepyloric folds were noted as well as similar large, stiffened folds in the duodenum, but no ulcerations were seen. Biopsy of the duodenal mucosa revealed nonspecific inflammation and a noncaseating granuloma. Danzi et al. (1976) described 14 patients with Crohn's disease of the stomach or duodenum, three with duodenal involvement alone. Endoscopic findings revealed diffuse nodularity and granularity with superficial erosions and ulcerations. Thickening of the antral and duodenal folds was noted with some degree of stenosis. Two of nine endoscopic biopsies demonstrated granulomatous inflammation; the others were nonspecific. In our patients, diffuse granularity, nodularity, and stiffening of the folds were universally seen. The ulcerations present in most instances varied from superficial erosions to larger ulcerations. The wall of the gastric antrum and duodenum demonstrated lack of distensibility with poor contractions and varying degrees of stenosis. At times stenosis prevented passage of the endoscope through the distal antrum, pylorus, or proximal duodenum. Unfortunately, biopsy specimens obtained by endoscopic means are small and are limited to the mucosa. This poses a problem in the histological confirmation of Crohn's disease of the duodenum. We were unable to find granulomas in any of the 17 patients in our series who had endoscopic biopsies. Of the three patients who had capsule biopsies, granulomas were identified in one. Haggitt and Meissner (1973) reported that granulomas are commoner in the mucosa in Crohn's disease of the duodenum than in Crohn's disease lower in the gastrointestinal tract. We have been disappointed, however, by our inability to demonstrate granulomas in endoscopic biopsies in patients who were operated on subsequently and in whom granulomas were present in the deeper layers of the gastric or duodenal wall. Hermos et al. (1970) found granulomas in two patients who had biopsies with a biopsy capsule. Multiple biopsies were performed on both patients, and results were entirely normal in some of these examinations. Mucosal involvement may be patchy, and the finding of nonspecific inflammation without granulomas, or even a normal biopsy, does not exclude the presence of Crohn's disease. Medical treatment should be the treatment of choice for all patients with nonobstructing Crohn's disease of the duodenum and is similar to that of Crohn's disease elsewhere in the gastrointestinal tract (Nugent, 1975). If obstruction develops, bypass surgery is indicated, and our experience and that of others (Fielding et al., 1970; Farmer et al., 1972) suggests that it is accompanied by excellent longterm relief of the duodenal symptoms. As long as the duodenum that is involved is bypassed, the exact type of procedure does not seem important. References Bagby, R. J., Rogers, J. V., Jr, and Hobbs, C. (1972). Crohn's disease of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum: a review with emphasis on the radiographic findings. Southern Medical Journal, 65, Bishop, R. P., Brewster, A. C., and Antonioli, D. A. (1972). Crohn's disease of the mouth. Gastroenterology, 62, Cohen, W. N. (1967). Gastric involvement in Crohn's disease. American Journal of Roentgenology, Radium Therapy, and Nuclear Medicine, 101, Danzi, J. T., Farmer, R. G., Sullivan, B. H., and Rankin, G. B. (1976). Endoscopic features of gastroduodenal Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology, 70, Durrance, F. Y. (1962). Regional enteritis of the duodenum. American Journal of Roentgenology, Radiumn Therapy, and Nuclear Medicine, 88, Edwards, A. M., Michalyshyn, B., Sherbaniuk, R. W., and Costopoulos, L. B. (1965). Regional enteritis of the duodenum: a review and report of five cases. Canadian Medical Association Journal, 93, Farmer, R. G., Hawk, W. A., and Turnbull, R. B., Jr (1972). Crohn's disease of the duodenum (transmural duodenitis): clinical manifestations. Report of 11 cases. Amnerican Journal of Digestive Diseases, 17, Fedotin, M. S., Grimmett, G. M., and Shelburne, J. (1974). Crohn's disease of the mouth. American Journal ofdigestive Diseases, 19, Fielding, J. F., Toye, D. K., Beton, D. C., and Cooke, W. T. (1970). Crohn's disease of the stomach and duodenum. Gut, 11, Haggitt, R. C., and Meissner, W. A. (1973). Crohn's disease of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Amnerican Journal of Clinical Pathology, 59, Hermos, J. A., Cooper, H. L., Kramer, P., and Trier, J. S. (1970). Histological diagnosis by peroral biopsy of Crohn's disease of the proximal intestine. Gastroenterology, 59, Jones, G. W., Jr, Dooley, M. R., and Schoenfield, L. F. (1966). Regional enteritis with involvement of the duodenum. Gastroenterology, 51, Kim, U., Zimmerman, M. J., and Weiss, M. (1973). Massive upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage associated with Crohn's disease of the stomach and duodenum. A case report. American Journal of Gastroenterology, 59, Legge, D. A., Carlson, H. C., and Judd, E. S. (1970).
6 120 F. Warren Nugent, M. Richmond, and S. K. Park Roentgenologic features of regional enteritis of the upper gastrointestinal tract. American Journal of Roentgenology, Radium Therapy, and Nuclear Medicine, 110, Legge, D. A., Hoffman, H. N., and Carlson, H. C. (1971). Pancreatitis as a complication of regional enteritis of the duodenum. Gastroenterology, 61, Nelson, S. W. (1969). Some interesting and unusual manifestations of Crohn's disease ('regional enteritis') of the stomach, duodenum and small intestine. American Journal of Roentgenology, Radium Therapy, and Nuclear Medicine, 107, Nugent, F. W. (1975). Crohn's colitis comes of age. American Journal of Gastroenterology, 63, Paget, E. T., Owens, M. P., Peniston, W. O., and Mathewson, C., Jr (1972). Massive upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage. A manifestation of regional enteritis of the duodenum. Archives of Surgery, 104, Roberts, S. M., and Hamilton, W. W. (1966). Regional enteritis of the duodenum. Radiology, 86, Roseman, D. M. (1972). Crohn's disease of the stomach and duodenum. Report of a case. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, 19, Sanders, M. G., and Schimmel, E. M. (1972). The relationship between granulomatous bowel disease and duodenal ulcer. American Journal of Digestive Diseases, 17, Silva, J. R., and Thomas, J. M. (1972). Isolated regional enteritis of the duodenum. American Journal of Gastroenterology, 57, Thompson, W. M., Cockrill, H., Jr, Rice, R. P. (1975). Regional enteritis of the duodenum. American Journal of Roentgenology, Radium Therapy, and Nuclear Medicine, 123, Van Patter, W. N., Bargen, J. A., Dockerty, M. B., Feldman, W. H., Mayo, C. W., and Waugh, J. M. (1954) Regional enteritis. Gastroenterology, 26, Wise, L., Kyriakos, M., McCown, A., and Ballinger, W. F. (1971). Crohn's disease of the duodenum. A report and analysis of 11 new cases. American Journal of Surgery, 121, Addendum Since this manuscript was originally written, we have seen an additional eight patients with duodenal Crohn's disease. Seven have had endoscopic biopsies, and in four granulomas were demonstrated. Three of these patients have had bypass operations (total of 18), and all three have had complete relief of upper gastrointestinal symptoms (18 of 21 in all). Gut: first published as /gut on 1 February Downloaded from on 6 October 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
ENDOSCOPIC FEATURES OF GASTRODUODENAL CROHN'S DISEASE
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 70:9-13, 1976 Copyright 1976 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 70, No.1 Printed in U.S.A. ENDOSCOPIC FEATURES OF GASTRODUODENAL CROHN'S DISEASE JOSEPH T. DANZI, M.D., RICHARD G. FARMER,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 70:9-13, 1976 Copyright 1976 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 70, No.1 Printed in U.S.A. ENDOSCOPIC FEATURES OF GASTRODUODENAL CROHN'S DISEASE JOSEPH T. DANZI, M.D., RICHARD G. FARMER,
CASE REPORTS CROHN'S DISEASE OF THE STOMACH. In 1932 Crohn et ap described a granulomatous
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 50, No.4 Printed in U.S.A. CASE REPORTS CROHN'S DISEASE O THE STOACH O. ADRIAN JOHNSON,.D., DONALD W. HOSKINS,.D., JEAN TODD,.D., AND
GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 50, No.4 Printed in U.S.A. CASE REPORTS CROHN'S DISEASE O THE STOACH O. ADRIAN JOHNSON,.D., DONALD W. HOSKINS,.D., JEAN TODD,.D., AND
The Role of Ultrasound in the Assessment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 The Role of Ultrasound in the Assessment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Dr. Richard A. Beable Consultant Gastrointestinal Radiologist Queen Alexandra Hospital Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust Topics for Discussion
The Role of Ultrasound in the Assessment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Dr. Richard A. Beable Consultant Gastrointestinal Radiologist Queen Alexandra Hospital Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust Topics for Discussion
IBD. Crohn s. Outline. Ulcerative colitis versus Crohn s disease: is biopsy useful? UC vs. Crohn s? Is it easy? Biopsy settings 21/07/2017 IBD
 Outline Ulcerative colitis versus Crohn s disease: is biopsy useful? Roger Feakins Colorectal biopsies Ileal and upper GI biopsies Special situations New techniques Summary Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
Outline Ulcerative colitis versus Crohn s disease: is biopsy useful? Roger Feakins Colorectal biopsies Ileal and upper GI biopsies Special situations New techniques Summary Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
GRANULOMATOUS COLITIS: SIGNIFICANCE OF INVOLVEMENT OF THE TERMINAL ILEUM
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 64: 1071-1076, 1973 Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64, No.6 Printed in U.S.A. GRANULOMATOUS COLITIS: SIGNIFICANCE OF INVOLVEMENT OF THE TERMINAL ILEUM JAMES A. NELSON,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 64: 1071-1076, 1973 Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64, No.6 Printed in U.S.A. GRANULOMATOUS COLITIS: SIGNIFICANCE OF INVOLVEMENT OF THE TERMINAL ILEUM JAMES A. NELSON,
GASTROENTEROLOGY. Official Publication of the American Gastroenterological Association. CoPYRIGHT 1975 THE WILLIAMS & WILKINS Co.
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Official Publication of the American Gastroenterological Association CoPYRIGHT 1975 THE WILLIAMS & WILKINS Co. Vol68 April 1975 Number 4 ALIMENTARY TRACT CLINICAL PATTERNS IN CROHN'S DISEASE:
GASTROENTEROLOGY Official Publication of the American Gastroenterological Association CoPYRIGHT 1975 THE WILLIAMS & WILKINS Co. Vol68 April 1975 Number 4 ALIMENTARY TRACT CLINICAL PATTERNS IN CROHN'S DISEASE:
Mohamed EL-hemaly Gastro- intestinal surgical center, Mansoura University.
 Mohamed EL-hemaly Gastro- intestinal surgical center, Mansoura University. Chronic transmural inflammatory process of the bowel & affects any part of the gastro -intestinal tract from the mouth to the
Mohamed EL-hemaly Gastro- intestinal surgical center, Mansoura University. Chronic transmural inflammatory process of the bowel & affects any part of the gastro -intestinal tract from the mouth to the
Gastric gland metaplasia in the small and
 Gut, 1977, 18, 214-218 Gastric gland metaplasia in the small and large intestine I. YOKOYAMA, S. KOZUKA, K. ITO, K. KUBOTA, Y. YOKOYAMA, AND T. KONDO From the Second Department of Surgery and the Second
Gut, 1977, 18, 214-218 Gastric gland metaplasia in the small and large intestine I. YOKOYAMA, S. KOZUKA, K. ITO, K. KUBOTA, Y. YOKOYAMA, AND T. KONDO From the Second Department of Surgery and the Second
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction. Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College
 Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
REFLUX ALKALINE GASTRITIS* SYRACUSE, NEW YORK
 VOL. 115, No. 2 REFLUX ALKALINE GASTRITIS* By SEUK KY KIM, M.D.,t LLOYD S. ROGERS, M.D.,t and ROBERT E. HEITZMAN, M.D. SYRACUSE, NEW YORK E ARLY physiologists thought that gastric acid was partly controlled
VOL. 115, No. 2 REFLUX ALKALINE GASTRITIS* By SEUK KY KIM, M.D.,t LLOYD S. ROGERS, M.D.,t and ROBERT E. HEITZMAN, M.D. SYRACUSE, NEW YORK E ARLY physiologists thought that gastric acid was partly controlled
CROHN S DISEASE. The term "inflammatory bowel disease" includes Crohn's disease and the other related condition called ulcerative colitis.
 CROHN S DISEASE What does it consist of? Crohn s disease is an inflammatory process that affects mostly to the intestinal tract, although it can affect any other part of the digestive apparatus from the
CROHN S DISEASE What does it consist of? Crohn s disease is an inflammatory process that affects mostly to the intestinal tract, although it can affect any other part of the digestive apparatus from the
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery
 World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 6, Issue 5 2016 Article 4 Isolated Jejunal Crohn s Disease, A Diagnostic Dilemma Elise Biesboer BS Lacey Stelle MD Michelle M. Olson MD, MACM Paul Tender MD University
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 6, Issue 5 2016 Article 4 Isolated Jejunal Crohn s Disease, A Diagnostic Dilemma Elise Biesboer BS Lacey Stelle MD Michelle M. Olson MD, MACM Paul Tender MD University
OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF ULCER DISEASE
 Página 1 de 8 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Greenfield, Lazar J., Mulholland, Michael W., Oldham, Keith T., Zelenock, Gerald B., Lillemoe, Keith D. Surgery: Scientific Principles & Practice,
Página 1 de 8 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Greenfield, Lazar J., Mulholland, Michael W., Oldham, Keith T., Zelenock, Gerald B., Lillemoe, Keith D. Surgery: Scientific Principles & Practice,
Symptomatic significance of gastric mucosal changes
 Gut, 1977, 18, 295-300 Symptomatic significance of gastric mucosal changes after surgery for peptic ulcer A. M. HOARE, E. L. JONES, J. ALEXANDER-WILLIAMS, AND C. F. HAWKINS From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital,
Gut, 1977, 18, 295-300 Symptomatic significance of gastric mucosal changes after surgery for peptic ulcer A. M. HOARE, E. L. JONES, J. ALEXANDER-WILLIAMS, AND C. F. HAWKINS From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital,
GASTRIC HETEROTOPIA IN THE ILEUM WITH ULCERATION AND CHRONIC BLEEDING
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 66: 113-117, 1974 Copyright 1974 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 66, No.1 Printed in U.S.A. CASE REPORTS GASTRIC HETEROTOPIA IN THE ILEUM WITH ULCERATION AND CHRONIC BLEEDING KARIM
GASTROENTEROLOGY 66: 113-117, 1974 Copyright 1974 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 66, No.1 Printed in U.S.A. CASE REPORTS GASTRIC HETEROTOPIA IN THE ILEUM WITH ULCERATION AND CHRONIC BLEEDING KARIM
Small Intestinal Biopsy in a Patient with Crohn's Disease of the Duodenum
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 76:1009-1014, 1979 Small Intestinal Biopsy in a Patient with Crohn's Disease of the Duodenum The Spectrum of Abnormal Findings in the Absence of Granulomas MICHAEL D. SCHUFFLER and ROBERT
GASTROENTEROLOGY 76:1009-1014, 1979 Small Intestinal Biopsy in a Patient with Crohn's Disease of the Duodenum The Spectrum of Abnormal Findings in the Absence of Granulomas MICHAEL D. SCHUFFLER and ROBERT
INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS
 INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS Lecture 1 and 2 دز اسماعيل داود فرع الطب كلية طب الموصل Radiological tests of structure (imaging) Plain X-ray: May shows soft tissue outlines like liver, spleen,
INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS Lecture 1 and 2 دز اسماعيل داود فرع الطب كلية طب الموصل Radiological tests of structure (imaging) Plain X-ray: May shows soft tissue outlines like liver, spleen,
Gastroenterology Tutorial
 Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
Crohn's disease CAUSES COURSE OF CROHN'S DISEASE TREATMENT. Sulfasalazine
 Crohn's disease Crohn's disease is an inflammatory condition of the digestive tract that affects children and adults. Common features of Crohn's disease include mouth sores, diarrhea, abdominal pain, weight
Crohn's disease Crohn's disease is an inflammatory condition of the digestive tract that affects children and adults. Common features of Crohn's disease include mouth sores, diarrhea, abdominal pain, weight
IBD 101. Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition
 IBD 101 Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Objectives Identify factors involved in the development of inflammatory bowel
IBD 101 Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Objectives Identify factors involved in the development of inflammatory bowel
General Data. Gender : Male Birthday and age : 12/07/24,80 y/o Occupation : 無 Date of Admission :
 General Data Gender : Male Birthday and age : 12/07/24,80 y/o Occupation : 無 Date of Admission : 92-07-09 1 Chief complaint Upper abdominal fullness 30 minutes after having foods with sometimes epigastralgia
General Data Gender : Male Birthday and age : 12/07/24,80 y/o Occupation : 無 Date of Admission : 92-07-09 1 Chief complaint Upper abdominal fullness 30 minutes after having foods with sometimes epigastralgia
Nutritional Management in Enterocutaneous fistula Dr Deepak Govil
 Nutritional Management in Enterocutaneous fistula Dr Deepak Govil MS, PhD (GI Surgery) Senior Consultant Surgical Gastroenterology Indraprastha Apollo Hospital New Delhi What is enterocutaneous fistula
Nutritional Management in Enterocutaneous fistula Dr Deepak Govil MS, PhD (GI Surgery) Senior Consultant Surgical Gastroenterology Indraprastha Apollo Hospital New Delhi What is enterocutaneous fistula
Clinical Management of Obscure- Overt Gastrointestinal Bleeding. Presented by Dr. 張瀚文
 Clinical Management of Obscure- Overt Gastrointestinal Bleeding Presented by Dr. 張瀚文 Definition Obscure: : hard to understand; not clear. Overt: : public; not secret. Occult: : hidden from the knowledge
Clinical Management of Obscure- Overt Gastrointestinal Bleeding Presented by Dr. 張瀚文 Definition Obscure: : hard to understand; not clear. Overt: : public; not secret. Occult: : hidden from the knowledge
SARCINA VENTICULARI IS A POSSIBLE CAUSATIVE MICROORGANISM OTHER THAN H.PYLORI IN GASTRIC OUTLET OBSTRUCTION PATHOGENESIS
 SARCINA VENTICULARI IS A POSSIBLE CAUSATIVE MICROORGANISM OTHER THAN H.PYLORI IN GASTRIC OUTLET OBSTRUCTION PATHOGENESIS 55 years old male, Farm worker, married, from Ibb Heavy Smoker, Khat chewer non-alcohol
SARCINA VENTICULARI IS A POSSIBLE CAUSATIVE MICROORGANISM OTHER THAN H.PYLORI IN GASTRIC OUTLET OBSTRUCTION PATHOGENESIS 55 years old male, Farm worker, married, from Ibb Heavy Smoker, Khat chewer non-alcohol
children Crohn s disease in MR enterography for GI Complications Microscopy Characterization Primary sclerosing cholangitis Anorectal fistulae
 MR enterography for Crohn s disease in children BOAZ KARMAZYN, MD PEDIATRIC RADIOLOGY ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR Characterization Crohn disease Idiopathic chronic transmural IBD Increasing incidence Age 7/100,000
MR enterography for Crohn s disease in children BOAZ KARMAZYN, MD PEDIATRIC RADIOLOGY ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR Characterization Crohn disease Idiopathic chronic transmural IBD Increasing incidence Age 7/100,000
Unusual manifestations of peptic
 Unusual manifestations of peptic ulcer disease William M. Thompson, M.D. George Norton, M.D.* Frederick M. Kelvin, F.R.C.R., M.R.C.P. R. Kristina Gedgaudas, M.D. Robert A. Halvorsen, M.D. Reed P. Rice,
Unusual manifestations of peptic ulcer disease William M. Thompson, M.D. George Norton, M.D.* Frederick M. Kelvin, F.R.C.R., M.R.C.P. R. Kristina Gedgaudas, M.D. Robert A. Halvorsen, M.D. Reed P. Rice,
Surgical Management of IBD. Val Jefford Grand Rounds October 14, 2003
 Surgical Management of IBD Val Jefford Grand Rounds October 14, 2003 Introduction Important Features Clinical Presentation Evaluation Medical Treatment Surgical Treatment Cases Overview Introduction Two
Surgical Management of IBD Val Jefford Grand Rounds October 14, 2003 Introduction Important Features Clinical Presentation Evaluation Medical Treatment Surgical Treatment Cases Overview Introduction Two
The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary systems.
 GASTROINTESTINAL AND HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEMS The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary systems. GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM AND HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM We will examine
GASTROINTESTINAL AND HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEMS The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary systems. GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM AND HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM We will examine
Perforated peptic ulcer
 Perforated peptic ulcer - Despite the widespread use of gastric anti-secretory agents and eradication therapy, the incidence of perforated peptic ulcer has changed little, age limits increase NSAIDs elderly
Perforated peptic ulcer - Despite the widespread use of gastric anti-secretory agents and eradication therapy, the incidence of perforated peptic ulcer has changed little, age limits increase NSAIDs elderly
PYLORIC STENOSIS: AN UNUSUAL COMPLICATION OF ALKALINE CORROSIVE POISONING*
 NOVEMBER, 1968 PYLORIC STENOSIS: AN UNUSUAL COMPLICATION OF ALKALINE CORROSIVE POISONING* By VIVIAN J. HARRIS, M.D.t COLUMBUS, T HE swallowing of an alkaline corrosive, such as sodium hydroxide (lye),
NOVEMBER, 1968 PYLORIC STENOSIS: AN UNUSUAL COMPLICATION OF ALKALINE CORROSIVE POISONING* By VIVIAN J. HARRIS, M.D.t COLUMBUS, T HE swallowing of an alkaline corrosive, such as sodium hydroxide (lye),
Gastrointestinal Disorders. Disorders of the Esophagus 3/7/2013. Congenital Abnormalities. Achalasia. Not an easy repair. Types
 Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
Radiological investigation of the small intestine
 Gut, 1961, 2, 316 Radiological investigation of the small intestine W. G. SCOTT-HARDEN, H. A. R. HAMILTON, AND S. McCALL SMITH From the Cumberland Infirmary, Carlisle SYNOPSIS This paper reports experience
Gut, 1961, 2, 316 Radiological investigation of the small intestine W. G. SCOTT-HARDEN, H. A. R. HAMILTON, AND S. McCALL SMITH From the Cumberland Infirmary, Carlisle SYNOPSIS This paper reports experience
Perforated duodenal ulcer in Reading from 1950 to 1959
 Gut, 1969, 1, 454-459 Perforated duodenal ulcer in Reading from 195 to 1959 PAUL CASSELL From the Royal Berkshire Hospital, Reading During the last 15 years there has been an evolution in the management
Gut, 1969, 1, 454-459 Perforated duodenal ulcer in Reading from 195 to 1959 PAUL CASSELL From the Royal Berkshire Hospital, Reading During the last 15 years there has been an evolution in the management
Surgery for Complications of Peptic Ulcer Disease (Definitive Treatment)
 Surgery for Complications of Peptic Ulcer Disease (Definitive Treatment) Amid Keshavarzi, MD UCHSC Grand Round 3/20/2006 Department of Surgery Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology Clinical manifestation
Surgery for Complications of Peptic Ulcer Disease (Definitive Treatment) Amid Keshavarzi, MD UCHSC Grand Round 3/20/2006 Department of Surgery Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology Clinical manifestation
Endoscopy in IBD. F.Hartmann K.Kasper-Kliniken (St.Marienkrankenhaus) Frankfurt/M.
 F.Hartmann K.Kasper-Kliniken (St.Marienkrankenhaus) Frankfurt/M. F.Hartmann@em.uni-frankfurt.de Indications for endoscopy Diagnosis Management Surveillance Diagnosis Single most valuable tool: ileocolonoscopy
F.Hartmann K.Kasper-Kliniken (St.Marienkrankenhaus) Frankfurt/M. F.Hartmann@em.uni-frankfurt.de Indications for endoscopy Diagnosis Management Surveillance Diagnosis Single most valuable tool: ileocolonoscopy
Gastrointestinal Tract. Anatomy of GI Tract. Anatomy of GI Tract. (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%)
 Gastrointestinal Tract (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy of GI Tract Esophagus bulls-eye or target EG junction seen on sagittal scan posterior to left lobe of liver and anterior to aorta Anatomy
Gastrointestinal Tract (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy of GI Tract Esophagus bulls-eye or target EG junction seen on sagittal scan posterior to left lobe of liver and anterior to aorta Anatomy
Nasogastric tube. Stomach. Pylorus. Duodenum 1. Duodenum 2. Duodenum 3. Duodenum 4
 Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
STOMACH and DUODENUM DISEASE
 STOMACH and DUODENUM DISEASE STOMACH ANATOMY In the living and upright posture, the stomach is a j-shaped. It has two surfaces, two curvatures and two openings. Esophagus Fundus cardia Pylorus B o d y
STOMACH and DUODENUM DISEASE STOMACH ANATOMY In the living and upright posture, the stomach is a j-shaped. It has two surfaces, two curvatures and two openings. Esophagus Fundus cardia Pylorus B o d y
Gastroenterology. Certification Examination Blueprint. Purpose of the exam
 Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil D ass Dass, Lecturer 25th July, 2011
 KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil Dass, Lecturer 25 th July, 2011 Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the students t will be able to: Define peptic pp ulcer Describe the etiology and pathology
KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil Dass, Lecturer 25 th July, 2011 Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the students t will be able to: Define peptic pp ulcer Describe the etiology and pathology
IBD 101. Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition
 IBD 101 Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Objectives Identify factors involved in the development of inflammatory bowel
IBD 101 Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Objectives Identify factors involved in the development of inflammatory bowel
Research Article Endoscopic and Pathologic Changes of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract in Crohn s Disease
 BioMed Research International, Article ID 610767, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/610767 Research Article Endoscopic and Pathologic Changes of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract in Crohn s Disease
BioMed Research International, Article ID 610767, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/610767 Research Article Endoscopic and Pathologic Changes of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract in Crohn s Disease
Ileo-rectal anastomosis for Crohn's disease of
 Ileo-rectal anastomosis for Crohn's disease of the colon W. N. W. BAKER From the Research Department, St Mark's Hospital, London Gut, 1971, 12, 427-431 SUMMARY Twenty-six cases of Crohn's disease of the
Ileo-rectal anastomosis for Crohn's disease of the colon W. N. W. BAKER From the Research Department, St Mark's Hospital, London Gut, 1971, 12, 427-431 SUMMARY Twenty-six cases of Crohn's disease of the
Helicobacter Pylori Testing HELICOBACTER PYLORI TESTING HS-131. Policy Number: HS-131. Original Effective Date: 9/17/2009
 Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
Pancreatic heterotopia as a cause of dyspepsia
 Gut, 1962, 3, 135 Pancreatic heterotopia as a cause of dyspepsia From the R. D. TONKIN, T. E. FIELD, AND P. R. WYKES Westminster Hospital, London, Queen Alexandra Military Hospital, Milbank, London, and
Gut, 1962, 3, 135 Pancreatic heterotopia as a cause of dyspepsia From the R. D. TONKIN, T. E. FIELD, AND P. R. WYKES Westminster Hospital, London, Queen Alexandra Military Hospital, Milbank, London, and
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy
 Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
Treating Crohn s and Colitis in the ASC
 Treating Crohn s and Colitis in the ASC Kimberly M Persley, MD Texas Digestive Disease consultants TASC Meeting Outline IBD 101 Diagnosis Treatment Burden of Disease Role of ASC Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Treating Crohn s and Colitis in the ASC Kimberly M Persley, MD Texas Digestive Disease consultants TASC Meeting Outline IBD 101 Diagnosis Treatment Burden of Disease Role of ASC Inflammatory Bowel Disease
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE. Jean-Paul Achkar, MD Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Cleveland Clinic
 INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Jean-Paul Achkar, MD Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Cleveland Clinic WHAT IS INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE (IBD)? Chronic inflammation of the intestinal tract Two related
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Jean-Paul Achkar, MD Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Cleveland Clinic WHAT IS INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE (IBD)? Chronic inflammation of the intestinal tract Two related
Ileo-caecal tuberculosis
 Gut, 1964, 5, 524 Ileo-caecal tuberculosis J. S. HOWELL1 AND P. J. KNAPTON2 Fr-om the Birmingham United Hospitals and the Department of Pathology, University of Birmingham EDITORIAL SYNOPSIS Seven patients
Gut, 1964, 5, 524 Ileo-caecal tuberculosis J. S. HOWELL1 AND P. J. KNAPTON2 Fr-om the Birmingham United Hospitals and the Department of Pathology, University of Birmingham EDITORIAL SYNOPSIS Seven patients
OPEN ACCESS TEXTBOOK OF GENERAL SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS TEXTBOOK OF GENERAL SURGERY PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE PC Bornman RS Du Toit EPIDEMIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS The prevalence of duodenal ulcer disease has a variable geographical distribution and differs
OPEN ACCESS TEXTBOOK OF GENERAL SURGERY PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE PC Bornman RS Du Toit EPIDEMIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS The prevalence of duodenal ulcer disease has a variable geographical distribution and differs
What do we need for diagnosis of IBD
 What do we need for diagnosis of IBD Kaichun Wu Dept. of Gastroenterology, Xijing Hospital Fourth Military Medical University Xi an an,, China In China UC 11.6/10 5,CD 1.4/10 5 Major cause of chronic diarrhea
What do we need for diagnosis of IBD Kaichun Wu Dept. of Gastroenterology, Xijing Hospital Fourth Military Medical University Xi an an,, China In China UC 11.6/10 5,CD 1.4/10 5 Major cause of chronic diarrhea
Role of Malabsorptive Endoscopic Procedures in Obesity Treatment
 FOCUSED REVIEW SERIES: Roles of Bariatric Endoscopy in Obesity Treatment Clin Endosc 2017;50:26-30 https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2017.004 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Role of Malabsorptive
FOCUSED REVIEW SERIES: Roles of Bariatric Endoscopy in Obesity Treatment Clin Endosc 2017;50:26-30 https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2017.004 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Role of Malabsorptive
Capsule Endoscopy: Is it Really Helpful in the Diagnosis of Small Bowel Diseases? Kashif Malik, Muhammad Joher Amin, Syed Waqar Hassan Shah
 Original Article Capsule Endoscopy: Is it Really Helpful in the Diagnosis of Small Bowel Diseases? Kashif Malik, Muhammad Joher Amin, Syed Waqar Hassan Shah ABSTRACT Objective: To determine the diagnostic
Original Article Capsule Endoscopy: Is it Really Helpful in the Diagnosis of Small Bowel Diseases? Kashif Malik, Muhammad Joher Amin, Syed Waqar Hassan Shah ABSTRACT Objective: To determine the diagnostic
GIANT DUODENAL DIVERTICULA*
 JUNE, 1974 GIANT DUODENAL DIVERTICULA* By JACK R. MILLARD, M.D., FRED M. H. ZITER, JR., M.D., and WILLIAM P. SLOVER, M.D. HARTFORD, D UODENAL diverticula are common incidental findings on barium examinations
JUNE, 1974 GIANT DUODENAL DIVERTICULA* By JACK R. MILLARD, M.D., FRED M. H. ZITER, JR., M.D., and WILLIAM P. SLOVER, M.D. HARTFORD, D UODENAL diverticula are common incidental findings on barium examinations
GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Gastroenterology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback from physicians that MOC assessments
GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Gastroenterology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback from physicians that MOC assessments
References. GI Biopsies. What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD
 What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD jcrawford1@nshs.edu Executive Director and Senior Vice President for Laboratory Services North
What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD jcrawford1@nshs.edu Executive Director and Senior Vice President for Laboratory Services North
Inflammatory Bowel Disease When is diarrhea not just diarrhea?
 Inflammatory Bowel Disease When is diarrhea not just diarrhea? Jackie Kazik, MA, PA C CME Resources CAPA Annual Conference, 2011 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Objectives Discuss what is known about the pathophysiology
Inflammatory Bowel Disease When is diarrhea not just diarrhea? Jackie Kazik, MA, PA C CME Resources CAPA Annual Conference, 2011 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Objectives Discuss what is known about the pathophysiology
Certain genes passed on from parent to child increase the risk of developing Crohn's disease, if the right trigger occurs.
 Topic Page: Crohn's disease Definition: Crohn's disease from Benders' Dictionary of Nutrition and Food Technology Chronic inflammatory disease of the bowel, commonly the terminal ileum, of unknown aetiology,
Topic Page: Crohn's disease Definition: Crohn's disease from Benders' Dictionary of Nutrition and Food Technology Chronic inflammatory disease of the bowel, commonly the terminal ileum, of unknown aetiology,
Crohn's disease of the colon and its distinction from diverticulitis
 Crohn's disease of the colon and its distinction from diverticulitis G. T. SCHMIDT, J. E. LENNARD-JONES, B. C. MORSON, AND A. C. YOUNG From St. Mark's Hospital, London Crohn's disease may affect segments
Crohn's disease of the colon and its distinction from diverticulitis G. T. SCHMIDT, J. E. LENNARD-JONES, B. C. MORSON, AND A. C. YOUNG From St. Mark's Hospital, London Crohn's disease may affect segments
Tuberculous Duodenal Stenosis: Report of Two Cases
 444 Tuberculous Duodenal Stenosis: Report of Two Cases O. Benzekri a S. El Mouhadi b M. Chourak a S. Boussetta a M. El Absi a M. Echarab a M. Elouanani a M. Amraoui a A. Errougani a F.H. El Alami a R.
444 Tuberculous Duodenal Stenosis: Report of Two Cases O. Benzekri a S. El Mouhadi b M. Chourak a S. Boussetta a M. El Absi a M. Echarab a M. Elouanani a M. Amraoui a A. Errougani a F.H. El Alami a R.
Case Report An Uncommon Cause of a Small-Bowel Obstruction
 Hindawi Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 1628215, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1628215 Case Report An Uncommon Cause of a Small-Bowel Obstruction Ali Zakaria, Bayan
Hindawi Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 1628215, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1628215 Case Report An Uncommon Cause of a Small-Bowel Obstruction Ali Zakaria, Bayan
Our evidence. Your expertise. SmartPill : The data you need to evaluate motility disorders.
 Our evidence. Your expertise. SmartPill : The data you need to evaluate motility disorders. SmartPill benefits your practice: Convenient performed right in your office Test standardization Provides direct
Our evidence. Your expertise. SmartPill : The data you need to evaluate motility disorders. SmartPill benefits your practice: Convenient performed right in your office Test standardization Provides direct
SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction)
 SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction) SOD refers to the mechanical malfunctioning of the Sphincter of Oddi, which is the valve muscle that regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction) SOD refers to the mechanical malfunctioning of the Sphincter of Oddi, which is the valve muscle that regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
abdominal pain? A clinical and radiologic long term
 Gut, 1984, 25, 341-346 Are superficial lesions of the distal part of the ileum early indicators of Crohn's disease in adult patients with abdominal pain? A clinical and radiologic long term investigation
Gut, 1984, 25, 341-346 Are superficial lesions of the distal part of the ileum early indicators of Crohn's disease in adult patients with abdominal pain? A clinical and radiologic long term investigation
Postgastrectomy Syndromes
 Postgastrectomy Syndromes Postgastrectomy syndromes are iatrogenic conditions that may arise from partial gastrectomies, independent of whether the gastric surgery was initially performed for peptic ulcer
Postgastrectomy Syndromes Postgastrectomy syndromes are iatrogenic conditions that may arise from partial gastrectomies, independent of whether the gastric surgery was initially performed for peptic ulcer
Case Rep Gastroenterol 2010;4:71 78 DOI: /
 71 Gallstone Ileus, Bouveret s Syndrome and Choledocholithiasis in a Patient with Billroth II Gastrectomy A Case Report of Combined Endoscopic and Surgical Therapy R. Fejes G. Kurucsai A. Székely F. Luka
71 Gallstone Ileus, Bouveret s Syndrome and Choledocholithiasis in a Patient with Billroth II Gastrectomy A Case Report of Combined Endoscopic and Surgical Therapy R. Fejes G. Kurucsai A. Székely F. Luka
Hiatus hernia and heartburn
 Hiatus hernia and heartburn E. W. GILLISON,l W. M. CAPPER, G. R. AIRTH, M. J. GIBSON, AND I. BRADFORD From the Department of Gastroenterology, Southmead Hospital, Bristol Gut, 1969, 1, 69-613 SUMMARY The
Hiatus hernia and heartburn E. W. GILLISON,l W. M. CAPPER, G. R. AIRTH, M. J. GIBSON, AND I. BRADFORD From the Department of Gastroenterology, Southmead Hospital, Bristol Gut, 1969, 1, 69-613 SUMMARY The
Case Scenario 1. Discharge Summary
 Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 69-year-old woman was on vacation and noted that she was becoming jaundiced. Two months prior to leaving on that trip, she had had a workup that included an abdominal
Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 69-year-old woman was on vacation and noted that she was becoming jaundiced. Two months prior to leaving on that trip, she had had a workup that included an abdominal
Crohn's Disease. What causes Crohn s disease? What are the symptoms?
 Crohn's Disease Crohn s disease is an ongoing disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, also referred to as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Crohn s disease can affect any area of the GI
Crohn's Disease Crohn s disease is an ongoing disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, also referred to as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Crohn s disease can affect any area of the GI
Patho Basic Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Jürg Vosbeck Pathology
 Patho Basic Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Jürg Vosbeck Pathology General Group of chronic relapsing diseases with chronic bloody or watery diarrhea Usually ulcerative colitis (UC) or Crohn s disease
Patho Basic Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Jürg Vosbeck Pathology General Group of chronic relapsing diseases with chronic bloody or watery diarrhea Usually ulcerative colitis (UC) or Crohn s disease
Crohn's disease: natural history and treatment J. E. LENNARD-JONES. College and St Mark's Hospitals, London
 Postgrad. med. J. (September 1968) 44, 674-678. University Crohn's disease: natural history and treatment J. E. LENNARD-JONES AN EXrENSIVE literature is now available on the pathological anatomy and its
Postgrad. med. J. (September 1968) 44, 674-678. University Crohn's disease: natural history and treatment J. E. LENNARD-JONES AN EXrENSIVE literature is now available on the pathological anatomy and its
Chapter 32 Gastroenterology General Pathophysiology General Risk Factors for GI emergencies: Excessive Consumption Excessive Smoking Increased
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 32 Gastroenterology General Pathophysiology General Risk Factors for GI emergencies: Excessive Consumption Excessive Smoking Increased Ingestion of Caustic Substances Poor Bowel Habits
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 32 Gastroenterology General Pathophysiology General Risk Factors for GI emergencies: Excessive Consumption Excessive Smoking Increased Ingestion of Caustic Substances Poor Bowel Habits
Safe Answers For The American Board of Surgery Certifying Exam & Recertifying Exam
 Safe Answers For The American Board of Surgery Certifying Exam & Recertifying Exam By Sarmad Aji, MD., FACS. A comprehensive review of the most commonly asked questions on the American Board of Surgery
Safe Answers For The American Board of Surgery Certifying Exam & Recertifying Exam By Sarmad Aji, MD., FACS. A comprehensive review of the most commonly asked questions on the American Board of Surgery
Birthday: 1952/07/31 Date of admission:1999/12/30 Age:48 y/o Past medication:esrd under regular HD for 5+ years; denied DM and HTN
 Birthday: 1952/07/31 Date of admission:1999/12/30 Age:48 y/o Past medication:esrd under regular HD for 5+ years; denied DM and HTN Chief Complaint : 1)intermittent LLQ cramping pain for 2 months 2) LGI
Birthday: 1952/07/31 Date of admission:1999/12/30 Age:48 y/o Past medication:esrd under regular HD for 5+ years; denied DM and HTN Chief Complaint : 1)intermittent LLQ cramping pain for 2 months 2) LGI
CT EVALUATION OF GASTRIC LESIONS:
 CT EVALUATION OF GASTRIC LESIONS: Pictural essay Hasni Bouraoui I, Kahloun A, Jemni H, Elouni F, Moulahi H, Daadoucha A, Ben Ali A, Sriha B, Tlili Graies K Departments of Radiology, Gastro enterology,
CT EVALUATION OF GASTRIC LESIONS: Pictural essay Hasni Bouraoui I, Kahloun A, Jemni H, Elouni F, Moulahi H, Daadoucha A, Ben Ali A, Sriha B, Tlili Graies K Departments of Radiology, Gastro enterology,
ISPUB.COM. Quick Review: Crohn's Disease. T Fujii, B Phillips DEFINITION ETIOLOGY
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gastroenterology Volume 2 Number 1 Quick Review: Crohn's Disease T Fujii, B Phillips Citation T Fujii, B Phillips. Quick Review: Crohn's Disease. The Internet Journal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gastroenterology Volume 2 Number 1 Quick Review: Crohn's Disease T Fujii, B Phillips Citation T Fujii, B Phillips. Quick Review: Crohn's Disease. The Internet Journal
Clinical Study Small Bowel Tumors: Clinical Presentation, Prognosis, and Outcomein33PatientsinaTertiaryCareCenter
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Oncology Volume 2008, Article ID 212067, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2008/212067 Clinical Study Small Bowel Tumors: Clinical Presentation, Prognosis, and Outcomein33PatientsinaTertiaryCareCenter
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Oncology Volume 2008, Article ID 212067, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2008/212067 Clinical Study Small Bowel Tumors: Clinical Presentation, Prognosis, and Outcomein33PatientsinaTertiaryCareCenter
Gastric Carcinoma in Patients with Crohn Disease: Report of Four Cases
 311 0361-803X/91/1 572-0311 C American Roentgen Ray Society Seth N. GIick1 Received January 1 7, 1991 ; accepted after re vision March 1 2, 1991. 1 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Hahnemann University
311 0361-803X/91/1 572-0311 C American Roentgen Ray Society Seth N. GIick1 Received January 1 7, 1991 ; accepted after re vision March 1 2, 1991. 1 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Hahnemann University
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery
 World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 3, Issue 2 2013 Article 12 Conservative Management of Perforated Duodenal Diverticulitis Rocio Gonzalez Lopez Maria Isabel Pérez Moreiras Eva Iglesias Porto Carlos
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 3, Issue 2 2013 Article 12 Conservative Management of Perforated Duodenal Diverticulitis Rocio Gonzalez Lopez Maria Isabel Pérez Moreiras Eva Iglesias Porto Carlos
By incision of the pyloric muscle and plastic reconstruction
 Pyloroplasty Jon Arne Söreide, MD, PhD, FACS and Kjetil Söreide, MD By incision of the pyloric muscle and plastic reconstruction of the pyloric channel, pyloroplasty facilitates gastric emptying when the
Pyloroplasty Jon Arne Söreide, MD, PhD, FACS and Kjetil Söreide, MD By incision of the pyloric muscle and plastic reconstruction of the pyloric channel, pyloroplasty facilitates gastric emptying when the
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) 01.06.2016 EoE: immune-mediated disorder food or environmental antigens => Th2 inflammatory response. Key cytokines: IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 stimulate the production of eotaxin-3
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) 01.06.2016 EoE: immune-mediated disorder food or environmental antigens => Th2 inflammatory response. Key cytokines: IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 stimulate the production of eotaxin-3
THE mainstay of the radiographic study of the upper gastrointestinal tract has
 BARIUM-SPRAY EXAMINATION OF THE STOMACH- PRELIMINARY REPORT OF A NEW ROENTGENOGRAPHIC TECHNIC EDWARD BUONOCORE, M.D., and THOMAS F. MEANEY, M.D. Department of Hospital Radiology THE mainstay of the radiographic
BARIUM-SPRAY EXAMINATION OF THE STOMACH- PRELIMINARY REPORT OF A NEW ROENTGENOGRAPHIC TECHNIC EDWARD BUONOCORE, M.D., and THOMAS F. MEANEY, M.D. Department of Hospital Radiology THE mainstay of the radiographic
Owen Dickinson. Consultant in Endoscopy & Interventional Radiology. Upper GI Stenting. Rotherham Foundation Trust
 Owen Dickinson Consultant in Endoscopy & Interventional Radiology Upper GI Stenting Rotherham Foundation Trust Owen Dickinson Consultant in Endoscopy & Interventional Radiology Rotherham Foundation Trust
Owen Dickinson Consultant in Endoscopy & Interventional Radiology Upper GI Stenting Rotherham Foundation Trust Owen Dickinson Consultant in Endoscopy & Interventional Radiology Rotherham Foundation Trust
Billing Guideline. Subject: Colorectal Cancer Screening Exams (Invasive Procedures) Effective Date: 1/1/14 Last revision effective 4/16
 Billing Guideline Subject: Colorectal Cancer Screening Exams (Invasive Procedures) Effective Date: 1/1/14 Last revision effective 4/16 Florida Hospital Care Advantage plans include full coverage of in-network
Billing Guideline Subject: Colorectal Cancer Screening Exams (Invasive Procedures) Effective Date: 1/1/14 Last revision effective 4/16 Florida Hospital Care Advantage plans include full coverage of in-network
Chapter 9. An Unusual Case of Gastric Outlet Obstruction in a Ghanaian Woman. 2 Top 25 Clinical Case Reports
 Chapter 9 An Unusual Case of Gastric Outlet Obstruction in a Ghanaian Woman Joachim Amoako, Henry Obaka, Nelson Affram, Wordui Theodore and Faizal Z Asumda* Department of Surgery, Korle Bu Teaching Hospital,
Chapter 9 An Unusual Case of Gastric Outlet Obstruction in a Ghanaian Woman Joachim Amoako, Henry Obaka, Nelson Affram, Wordui Theodore and Faizal Z Asumda* Department of Surgery, Korle Bu Teaching Hospital,
LOOKING FOR AIR IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, IL
 SIGNIFICANCE OF EXTRALUMINAL ABDOMINAL GAS: LOOKING FOR AIR IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, IL SCBT/MR 2012 October 26,
SIGNIFICANCE OF EXTRALUMINAL ABDOMINAL GAS: LOOKING FOR AIR IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, IL SCBT/MR 2012 October 26,
Clinical Manifestations of Gastrointestinal Disorders. Awni Taleb Abu sneineh
 Clinical Manifestations of Gastrointestinal Disorders Awni Taleb Abu sneineh Major areas of Interest in GIT Esophageal disorders Peptic ulcer disease Inflamatory bowel disease Malignancy Liver disease
Clinical Manifestations of Gastrointestinal Disorders Awni Taleb Abu sneineh Major areas of Interest in GIT Esophageal disorders Peptic ulcer disease Inflamatory bowel disease Malignancy Liver disease
Serotonin- and Somatostatin-Positive Goblet Cell Carcinoid of the Duodenum
 2012 66 4 351 356 Serotonin- and Somatostatin-Positive Goblet Cell Carcinoid of the Duodenum a b* c c c a a b d a c b d 352 Ohara et al. received remedies at another hospital. Hematemesis then recurred
2012 66 4 351 356 Serotonin- and Somatostatin-Positive Goblet Cell Carcinoid of the Duodenum a b* c c c a a b d a c b d 352 Ohara et al. received remedies at another hospital. Hematemesis then recurred
Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 Final Pathology:
 Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 A 74 year old male with a history of GERD presents complaining of dysphagia. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 A 74 year old male with a history of GERD presents complaining of dysphagia. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Evidence Process for Abdominal Pain Guideline Research 11/16/2017. Guideline Review using ADAPTE method and AGREE II instrument 11/16/2017
 Evidence Process for Abdominal Pain Guideline Research Guideline Review using ADAPTE method and AGREE II instrument Approximately 139 Potentially relevant guidelines identified in various resources* 59
Evidence Process for Abdominal Pain Guideline Research Guideline Review using ADAPTE method and AGREE II instrument Approximately 139 Potentially relevant guidelines identified in various resources* 59
Guided by Dr. Michal Amitai Head of Abdominal Imaging Department of Diagnostic Imaging Sheba Medical Center Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv
 Guided by Dr. Michal Amitai Head of Abdominal Imaging Department of Diagnostic Imaging Sheba Medical Center Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University 1 SHARE study My year Collaboration between gastroenterology
Guided by Dr. Michal Amitai Head of Abdominal Imaging Department of Diagnostic Imaging Sheba Medical Center Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University 1 SHARE study My year Collaboration between gastroenterology
(a) (b) Plate 16.1 Esophageal tear after passage of the echoendoscope.
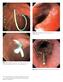 Plate 16.1 Esophageal tear after passage of the echoendoscope. Plate 11.1 Prophylactic pancreatic duct stents. 3-Fr, 4-cm long single-pigtail stent. 5-Fr, 3-cm long flanged stent. Plate 16.2 Esophageal
Plate 16.1 Esophageal tear after passage of the echoendoscope. Plate 11.1 Prophylactic pancreatic duct stents. 3-Fr, 4-cm long single-pigtail stent. 5-Fr, 3-cm long flanged stent. Plate 16.2 Esophageal
Ulcerative Colitis. ulcerative colitis usually only affects the colon.
 Ulcerative Colitis Introduction Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease. It is one of the 2 most common inflammatory bowel diseases. The other one is Crohn s disease. Ulcerative colitis and
Ulcerative Colitis Introduction Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease. It is one of the 2 most common inflammatory bowel diseases. The other one is Crohn s disease. Ulcerative colitis and
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System
 Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Peptic ulcer disease. Nomin-Erdene. D SOM-531
 Peptic ulcer disease Nomin-Erdene. D SOM-531 Learning objectives Stomach gross anatomy PUD Epidemiology Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Diagnosing Treatment Complicated ulcer disease Surgical procedures
Peptic ulcer disease Nomin-Erdene. D SOM-531 Learning objectives Stomach gross anatomy PUD Epidemiology Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Diagnosing Treatment Complicated ulcer disease Surgical procedures
Histology of Crohn's syndrome
 Gut, 1964, 5, 510 Histology of Crohn's syndrome From the Institute of Pathology, W. JONES WILLIAMS Welsh National School of Medicine, Cardiff EDITORIAL SYNOPSIS Three types of inflammatory reactions are
Gut, 1964, 5, 510 Histology of Crohn's syndrome From the Institute of Pathology, W. JONES WILLIAMS Welsh National School of Medicine, Cardiff EDITORIAL SYNOPSIS Three types of inflammatory reactions are
NON INVASIVE MONITORING OF MUCOSAL HEALING IN IBD. THE ROLE OF BOWEL ULTRASOUND. Fabrizio Parente
 NON INVASIVE MONITORING OF MUCOSAL HEALING IN IBD. THE ROLE OF BOWEL ULTRASOUND Fabrizio Parente Gastrointestinal Unit, A.Manzoni Hospital, Lecco & L.Sacco School of Medicine,University of Milan - Italy
NON INVASIVE MONITORING OF MUCOSAL HEALING IN IBD. THE ROLE OF BOWEL ULTRASOUND Fabrizio Parente Gastrointestinal Unit, A.Manzoni Hospital, Lecco & L.Sacco School of Medicine,University of Milan - Italy
Laparoscopy-assisted D2 radical distal subtotal gastrectomy
 Masters of Gastrointestinal Surgery Laparoscopy-assisted D2 radical distal subtotal gastrectomy Xiaogeng Chen, Weihua Li, Jinsi Wang, Changshun Yang Department of Tumor Surgery, Fujian Provincial Hospital,
Masters of Gastrointestinal Surgery Laparoscopy-assisted D2 radical distal subtotal gastrectomy Xiaogeng Chen, Weihua Li, Jinsi Wang, Changshun Yang Department of Tumor Surgery, Fujian Provincial Hospital,
