Symptomatic significance of gastric mucosal changes
|
|
|
- Anissa Barton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gut, 1977, 18, Symptomatic significance of gastric mucosal changes after surgery for peptic ulcer A. M. HOARE, E. L. JONES, J. ALEXANDER-WILLIAMS, AND C. F. HAWKINS From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Queen Elizabeth Medical Centre, Birmingham SUMMARY Eighty-four patients who had undergone different types of operation for duodenal ulcer have been studied by endoscopy and gastric biopsy. Half suffered from dyspepsia and vomiting but the other half had no symptoms and acted as controls. Endoscopic and histological abnormalities were found in both groups of patients. However, certain findings occurred more commonly in those with symptoms; severe and extensive hyperaemia, bile staining of the gastric mucus, and bile reflux seen on endoscopy were all significantly more common in those with symptoms than in those without. Active gastritis in the proximal stomach was also more common in those with symptoms. Gastritis of the stoma and antrum was found in 89 %' of all patients; as it was unconnected with symptoms it can be regarded as a 'normal' finding. The incidences of contact bleeding, erosions, and oedema were not significantly different in the two groups. An abnormal appearance of the gastric mucosa after partial gastrectomy was observed soon after gastroscopes were introduced (Schindler, 1923). Yet the relevance of this is still controversial. Although Cotton et al. (1973) thought that hyperaemia was not significant, others (Keighley et al., 1975; O'Neill et al., 1975) have found it more common in patients with symptoms. There is confusion about the nomenclature of these mucosal changes, some authors have referred to the abnormal endoscopic findings as gastritis (Stempien et al., 1971). We have reserved the term gastritis for atrophy or inflammation seen on histological examination of biopsy specimens. The red mucosa seen endoscopically has been called hyperaemia. Gastritis is seen in histological specimens taken from both symptomatic and asymptomatic patients after gastric operations (Lees and Grandjean, 1958; Benedict, 1960), but is less common in those with recurrent ulcers (Johnston, 1966). Simon et al. (1973) found it was more common after Billroth II than Billroth I resections. It is seen more often after operations for gastric than duodenal ulcer (Wall et al., 1967; Aukee and Krohn, 1972), but this may be due to the higher preoperative incidence of gastritis in those with gastric ulcer. No studies of gastritis and mucosal changes seen Received for publication 2 February 1977 endoscopically have yet been performed comparing patients with symptoms with matched controls. We have therefore performed an endoscopic and histological study of 42 patients with dyspepsia and vomiting after gastric surgery and compared them with a group of matched postoperative patients with no symptoms. Methods PATIENTS Eighty-four patients, who had undergone one operation for proven duodenal ulcer and who had no recurrent ulcer, have been studied. Forty-two of these had no dyspepsia or vomiting. (Thirty-three patients volunteered for endoscopy and nine were investigated for iron deficiency anaemia and were found to have no gastrointestinal cause of blood loss). All the volunteers had undergone a previous endoscopy and informed consent was obtained before the examination. They have been compared with 42 patients drawn from 150 patients referred because of dyspepsia and vomiting after gastric operations. The patients who most closely resembled the control patients were chosen. The two groups were matched for the type of operation, age (within 10 years) and the interval since operation (within two years if the operation was performed less than 10 years ago, or within five years if greater). Oral cholecystograms had been performed on all patients with symptoms 295
2 296 and only those without biliary disease were included. A total of 32 patients had Billroth II partial gastrectomies performed on average 14 years previously (one to 37 years before), 20 had vagotomy and antrectomy all about one year before, 22 had vagotomy and pyloroplasty on average seven years previously (one to 20 years ago), and 10 had proximal gastric vagotomy, all about one year before. The average age was 52 years and 21 were female. TECHNIQUES Endoscopy was performed on all patients by one of us (A.M.H.) using an end-viewing Olympus GIF instrument. Assessment was made of the degree of mucosal hyperaemia, bile reflux, bile staining of the mucus on the gastric mucosa, erosions, contact bleeding, oedema, 'granularity' of the mucosa, and veins visible beneath the mucosa. Each factor was graded as absent, mild, moderate, or severe. Bile reflux in this paper refers to reflux seen during endoscopy, or bile seen in the stomach indicating previous reflux. It was considered severe if there was a continuous flow of bile throughout the examination requiring repeated aspiration, and moderate if the stomach was full of bile but only trivial reflux into the stomach occurred after passing the instrument. An endoscopic score has been compiled including the severity and extent of erythema, the presence of a granular mucosa, bile reflux, and bile staining of the mucosa. Each of these factors was graded zero to three and the score was the sum of these grades. The American Cystoscope Makers spiked forceps were used for taking biopsies. Two were taken from 2-5 and 5 cm from the cardio-oesophageal junction and four from around the stoma or pylorus. In addition, biopsies were obtained 5 and 7 5 cm on the greater curve from the pylorus if partial gastrectomy had not been performed. They were all assessed 'blind' by one of us (E.L.J.) using the criteria of Whitehead et al. (1972). The type of mucosa (pyloric, body, or cardiac), grade of gastritis, activity of gastritis, and presence and type of metaplasia (intestinal or pseudo-pyloric) were established. Gastritis was graded as superficial if the inflammatory and reactive changes affected only the superficial epithelium, gastric pit region, and related lamina propria. It was graded as atrophic gastritis when these changes affected the gland layer. Active gastritis was indicated by invasion of polymorphs into epithelial elements of the gastric mucosa associated with degenerative changes. Except where stated in the text, statistical analysis was performed using the x2 test and Fisher's Exact Test when the expected frequencies were less than five. A. M. Hoare, E. L. Jones, J. Alexander- Williams, and Clifford F. Hawkins Results SYMPTOMS At the time of endoscopy 39 of the 42 symptomatic patients complained of vomiting, which was bilestained in 31. Eighteen patients had epigastric pain which was relieved by alkali in six. The pain occurred after meals in 11 patients, and intermittently in the remainder. Twenty-two patients suffered from epigastric discomfort; this occurred after meals in eight and was relieved by alkali in five. The remainder had intermittent discomfort relieved by vomiting in 11. Two patients had symptoms of vomiting without pain or discomfort. Two patients in the 'asymptomatic' group had epigastric fullness after meals, but none complained of epigastric pain, nausea, or vomiting. ENDOSCOPIC FINDINGS All of the endoscopic findings (Table 1) were seen in both symptomatic and asymptomatic patients apart from a 'granular mucosa' which was present only in six symptomatic patients. Some findings were significantly more common in those with symptoms than those without them: severe and extensive hyperaemia (p < 0 01), severe bile reflux (p < 0025), bile staining (p < 0001), and a granular mucosa (p < O05). Bile staining and a granular mucosa occurred only in patients with severe bile reflux, and Table 1 Endoscopicfindings Asymptomatic Symptomatic (42) (42) Hyperaemia None 4 0 Mild Moderate Severe 9 18 Extent hyperaemia Stomal Mid-stomach Total 6 13 Bile reflux None 6 3 Mild 7 7 Moderate Severe Bile staining Absent Present 3 20 Granularity Absent Present 0 6 Contact bleeding Absent Present Oedema Absent Present 11 4 Erosions Absent Present 9 9 Number of patients in parentheses.
3 Symptomatic significance ofgastric mucosal changes after surgery for peptic ulcer PROXIMAL GASTRIC. VAGOTOMY I I VAGOTOMY AND PYLOROPLASTY VAGOTOMY AND ANTRECTOMY NO SYMPTOMS BILLROTH I PARTIAL GASTRECTOMY I Fig ENDOSCOPIC SCORE 'Endoscopic score' in patients with and without symptoms after four gastric operations the severity and extent of hyperaemia correlated with bile reflux (p < 0002 using Spearman's rank correlation coefficient). The average endoscopic scores of symptomatic patients are higher than those of the patients without symptoms (Fig. 1). Using the Sign test the differences are significant for patients after Billroth II partial gastrectomy (p < 005), vagotomy and antrectomy (p < 002), and vagotomy and pyloroplasty (p < 0-05), and for all patients (p < O0O0O1). HISTOLOGICAL APPEARANCE Atrophic gastritis was recognised in biopsies from the antrum or stoma in 45 patients (54 %). In all patients with atrophic gastritis the intervening lamina propria showed a heavy infiltrate of plasma cells and frequently contained large lymphoid follicles (Fig. 2). In 27 patients atrophic gastritis was seen in biopsies from the antrum or around the stoma but not in those from the proximal stomach. The appearances of biopsies from the antrum or stoma are shown in Table 2. There was no correlation between symptoms and the presence of atrophic gastritis or chronic superficial gastritis. 'Active' gastritis with focal collections of polymorphs within the gland lumen and invasion of the gland epithelium (Fig. 3) was seen in 26 patients. Polymorphs in the gastric pits, mimicking the appearance of crypt abscesses in ulcerative colitis, were also seen in these , I I,,,..."""' % % X.,.,.. -1 I 297 patients (Fig. 4). Active gastritis in the distal stomach was more common in patients with symptoms than those without, but the differences were not statistically significant. Intestinal metaplasia was seen in at least one biopsy In 10 patients with dyspepsia and vomiting and six without such symptoms. The surface mucosa was covered by projecting pseudovilli lined by small intestinal absorptive cells and frequent globlet cells (Fig. 5). The results of histological examination of biopsies taken high on the lesser curve are shown in Table 3. After Billroth II partial gastrectomy and vagotomy and antrectomy atrophic gastritis was commoner in symptomatic patients than in those without symptoms. The differences between the symptomatic and asymptomatic patients are significant when Billroth II partial gastrectomy and vagotomy and antrectomy are considered together (p < 0 05). They are not significant for all operations or any individual operation. Active gastritis in the proximal stomach was found significantly more frequently in those with symptoms than those without (p < 0 01). Active gastritis was found only in those patients with severe bile reflux and an endoscopic 'score' greater than 7. All those with a granular mucosa on endoscopy had active gastritis. After Billroth II partial gastrectomy and vagotomy and antrectomy atrophic gastritis was more often found in those with severe bile reflux, but the correlation is not
4 298 Fig. 2 Gastric stoma. Atrophic gastritis showing loss of tubules, degeneration, and atrophy ofothers associated with a diffuse chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate and lymphoidfollicle. H and E, x 120 Table 2 Gastritis ofstoma or antrum A. M. Hoare, E. L. Jones, J. Alexander- Williams, and Clifford F. Hawkins Gastritis Number Normal Superficial Atrophic Active Billroth II Asymptomatic Symptomatic Vagotomy and antrectomy Asymptomatic Symptomatic Vagotomy and pyloroplasty Asymptomatic Symptomatic Proximal gastric vagotomy Asymptomatic Symptomatic Total Asymptomatic Symptomatic significant. After proximal gastric vagotomy nine patients had a patchy red appearance of the antrum (described as scarlatina by Taor et al., 1975) and all had atrophic gastritis in the antrum. Apart from Fig. 3 Pyloric mucosal glands. Polymorph infiltrate of lamina propria and glands. H and E, x 300 this, there is no relationship between endoscopic and histology findings. Eleven patients had veins visible in the mucosa but only one of these had atrophic gastritis histologically. Neither endoscopic 'score' nor gastritis was related to the patient's age, sex, smoking habits, or alcohol intake. The severity of the endoscopic change and degree of gastritis did not increase with time after the operation. Discussion Assessment of endoscopic changes is subjective, but all gastroscopies in this study were performed by one person. All those who had undergone a vagotomy and antrectomy or proximal vagotomy were assessed without knowledge of the symptoms. This was not so with all the remaining patients but the results for these were the same as for those assessed blind. The high incidence of endoscopic abnormalities was similar to other series after gastric surgery (Hirshchowitz and Luketic, 1971; Cotton et al., 1973). The extent of changes varied with the operation per-
5 Symptomatic significance ofgastric mucosal changes after surgery for peptic ulcer Fig. 4 Gastricpits. Polymorph aggregates in lumen resembling crypt abscesses. H and E, x 300 formed, the most frequent and severe being after Billroth II partial gastrectomy and the least after proximal gastric vagotomy. Severe erythema, which occurred even if the gastric mucosa was normal histologically, was associated with bile reflux and possibly due to it. Other changes related to bile reflux were bile staining of the mucus, a granular mucosa, and active gastritis in the proximal stomach. Although objective methods of measurement of bile reflux have been devised (Capper et al., 1966; Rhodes et al., 1969; Black et al., 1971), none has been assessed in patients who have had gastric surgery. A simple reliable test of bile reflux is needed. Our patients with bile reflux and associated endoscopic changes suffered from symptoms more commonly than those without these findings. There was no statistically significant relationship between the incidence of gastritis and bile reflux, though gastritis was rare in the proximal stomach after proximal gastric vagotomy, which produces little reflux. The failure to correlate bile reflux and gastritis may be due to the crude method of assessing bile reflux endoscopically. Experimental work in animals Fig. 5 Pyloric mucosa. Intestinal metaplasia and pseudo-villi. H and E, x 150 Table 3 High lesser curve gastritis Number Normal Gastritis Superficial Atrophic Active Billroth II Asymptomatic Symptomatic Vagotomy and antrectomy Asymptomatic Symptomatic Vagotomy and pyloroplasty Asymptomatic Symptomatic Proximal gastric vagotomy Asymptomatic Symptomatic Total Asymptomatic Symptomatic has shown that reflux of duodenal contants into the stomach causes gastritis (Du Plessis, 1962; Lawson, 1964, 1972) and this finding has led to bile diversion operations performed in man for dyspepsia and bile vomiting. Results have been classified as universally good in some series (Joseph et al., 1973; Herrington
6 300 A. M. Hoare, E. L. Jones, J. Alexander- Williams, and Clifford F. Hawkitns et al., 1974), but others have had some poor results (Van Heerden et al., 1975). Gastritis of the stoma or antrum was found in 89 % of all patients and was unconnected with symptoms, so can be regarded as a 'normal finding'. Endoscopic changes of gastritis may be obscured by erythema. There is little erythema after proximal gastric vagotomy and then a patchy red or 'scarlatina' appearance in the antrum, described by Taor et al. (1975) indicates atrophic gastritis as it does before an operation. Other mucosal lesions were not associated with the symptoms of dyspepsia or vomiting, but they may be significant for other reasons. Erosions may cause gastrointestinal bleeding, though none of the asymptomatic patients with iron deficiency anaemia had erosions. Oedema can be mistaken for a carcinoma radiologically or even endoscopically; indeed, one of the symptomatic patients with mucosal oedema was originally thought to have a neoplasm. The high incidence of oedema after vagotomy and antrectomy is unexplained. There are no specific endoscopic changes associated with dyspepsia after gastric surgery, but endoscopy and gastric biopsy can be helpful in assessing a patient, who has symptoms after gastric surgery but no recurrent ulcer. Mucosal hyperaemia, granular mucosa, bile-stained mucus, bile reflux seen endoscopically, and active gastritis in biopsies of the proximal stomach are associated with dyspepsia and vomiting, but not inactive gastritis, oedema, contact bleeding, or erosions. We thank the consultants who referred their patients and allowed us to study their asymptomatic patients, and the patients who willingly agreed to endoscopy. We are grateful to Mr K. Matthews and Dr Cross of the Department of Hospital Statistics for their help with the statistics. References Aukee, S., and Krohn, K. (1972). Occurrence and progression of gastritis in patients operated on for peptic ulcer. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, 7, Benedict, E. B. (1960). A gastroscopic biopsy study of fifty post-operative stomachs. Gastroenterology, 38, Black, R. B., Roberts, G., and Rhodes, J. (1971). The effect of healing on bile reflux in gastric ulcer. Gut, 12, Capper, W. M., Airth, G. R., and Kilby, J. 0. (1966). A test for pyloric regurgitation. La'zcet, 2, Cotton, P. B., Rosenberg, M. T., Axon, A. T. R., Davis, M., Pierce, J. W., Price, A. B., Stevenson, G. W., and Waldram, R. (1973). Diagnostic yield of fibre-optic endoscopy in the operated stomach. British Journal of Surgery, 60, Du Plessis, D. J. (1962). Gastric mucosal changes after operations on the stomach. South African Medical Journal, 36, Herrington, J. L., Sawyers, J. L., and Whitehead, W. A. (1974). Surgical management of reflux gastritis. Annals of Surgery, 180, Hirschowitz, B. I., and Luketic, G. C. (1971). Endoscopy in the post-gastrectomy patient. An analysis of 580 patients. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, 18, Johnston, D. H. (1966). A biopsy study of the gastric mucosa in post-operative patients with and without marginal ulcer. American Journal of Gastroenterology, 46, Joseph, W. L., Rivera, R. A., O'Kieffe, D. A., Geelhoed, G. W., and McCune, W. S. (1973). Management of postoperative alkali reflux gastritis. Annals of Surgery, 177, Keighley, M. R. B., Asquith, P., and Alexander-Williams, J. (1975). Duodenogastric reflux: a cause of gastric mucosal hyperaemia and symptoms after operations for peptic ulceration. Gut, 16, Lawson, H. H. (1964). Effect of duodenal contents on the gastric mucosa under experimental conditions. Lancet, 1, Lawson, H. H. (1972). The reversibility of post-gastrectomy alkaline reflux gastritis by a Roux-en-Y loop. British Journal of Surgery, 59, Lees, F., and Grandjean, L. C. (1958). The gastric and jejunal mucosae in healthy patients with partial gastrectomy Archives of Internal Medicine, 101, O'Neill, M., Whelton, M. J., Doyle, C., Shorten, E., and Hennessy, T. (1975). Endoscopic findings in patients after definitive gastric surgery. Irish Medical Journal, 68, Rhodes, J., Barnardo, D. E., Phillips, S. F., Rovelstad, R. A., and Hoffmann, A. F. (1969). Increased reflux of bile into the stomach in patients with gastric ulcer. Gastroenterology, 57, Schindler, R. (1923). Lehrbuch und Atlas der Gastroskopie. Lehmann: Munchen. (Quoted in Schindler, R. (1947). Gastritis, pp Heinemann: London.) Simon, L., Figus, A. I., and Bajtai, A. (1973). Chronic gastritis following resection of the stomach. American Journal of Gastroenterology, 60, Stempien, S. J., Dagradi, A. E., and Tan, D. T. D. (1971). Endoscopic aspects of the gastric mucosa ten years or more after vagotomy-pyloroplasty. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, 18, Taor, R. E., Fox, B., Ware, J., and Johnson, A. G. (1975). Gastritis-Gastroscopic and Microscopic. Endoscopy, 7, Van Heerden, J. A., Phillips, S. F., Adson, M. A., and Mcllrath, D. C. (1975). Post-operative reflux gastritis. American Journal of Surgery, 129, Wall, A. J., Ungar, B., Baird, C. W., Langford, I. M., and Mackay, I. R. (1967). Malnutrition after partial gastrectomy. Influence of site of ulcer and type of anastomosis and role of gastritis. American Journal of Digestive Disease, 12, Whitehead, R., Truelove, S. C., and Gear, M. W. L. (1972). The histological diagnosis of chronic gastritis in fibreoptic gastroscope biopsy specimens. Journal of ClinicalPathology, 25,1-11.
Gastric ulcer and gastritis
 Gastric ulcer and gastritis M. W. L. GEAR1, S. C. TRUELOVE, AND R. WHITEHEAD Gut, 1971, 12, 639-645 From the Nuffield Department of Clinical Medicine and The Department of Morbid Anatomy, Radcliffe Infirmary,
Gastric ulcer and gastritis M. W. L. GEAR1, S. C. TRUELOVE, AND R. WHITEHEAD Gut, 1971, 12, 639-645 From the Nuffield Department of Clinical Medicine and The Department of Morbid Anatomy, Radcliffe Infirmary,
REFLUX ALKALINE GASTRITIS* SYRACUSE, NEW YORK
 VOL. 115, No. 2 REFLUX ALKALINE GASTRITIS* By SEUK KY KIM, M.D.,t LLOYD S. ROGERS, M.D.,t and ROBERT E. HEITZMAN, M.D. SYRACUSE, NEW YORK E ARLY physiologists thought that gastric acid was partly controlled
VOL. 115, No. 2 REFLUX ALKALINE GASTRITIS* By SEUK KY KIM, M.D.,t LLOYD S. ROGERS, M.D.,t and ROBERT E. HEITZMAN, M.D. SYRACUSE, NEW YORK E ARLY physiologists thought that gastric acid was partly controlled
- Helicobacter - THE EASE AND DIFFICULTY OF A NEW DISCOVERY. Robin Warren
 - Helicobacter - THE EASE AND DIFFICULTY OF A NEW DISCOVERY Robin Warren EARLY DAYS First reports 100 years ago considered spirochaetes 1940 Freedburg saw curved organisms in the stomach 1954 Palmer: Freedburg
- Helicobacter - THE EASE AND DIFFICULTY OF A NEW DISCOVERY Robin Warren EARLY DAYS First reports 100 years ago considered spirochaetes 1940 Freedburg saw curved organisms in the stomach 1954 Palmer: Freedburg
A Study of the Correlation between Endoscopic and Histological Diagnoses in Gastroduodenitis
 000-9 70/8 7/80S-0749 THE AMERICAN JOIIRNAE. OF GAsrR()E.NrER 1987 by Am. Coll.ofGastroenterology Vo!.8. No. 8, 1487 Printed in U.S.A. A Study of the Correlation between Endoscopic
000-9 70/8 7/80S-0749 THE AMERICAN JOIIRNAE. OF GAsrR()E.NrER 1987 by Am. Coll.ofGastroenterology Vo!.8. No. 8, 1487 Printed in U.S.A. A Study of the Correlation between Endoscopic
Histological appearances of the gastric mucosa
 Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 179-186 Histological appearances of the gastric mucosa 15-27 years after partial gastrectomy ANN SAVAGE AND S. JONES From the Departments ofpathology and Surgery,
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 179-186 Histological appearances of the gastric mucosa 15-27 years after partial gastrectomy ANN SAVAGE AND S. JONES From the Departments ofpathology and Surgery,
Histological appearances of oesophagus, antrum and duodenum and their correlation with symptoms in patients with a duodenal ulcer
 Gut, 95, 6, 95- Histological appearances of oesophagus, antrum and duodenum and their correlation with symptoms in patients with a duodenal ulcer R J EARLAM, J AMERIGO, T KAKAVOULIS, AND D J POLLOCK Fwm
Gut, 95, 6, 95- Histological appearances of oesophagus, antrum and duodenum and their correlation with symptoms in patients with a duodenal ulcer R J EARLAM, J AMERIGO, T KAKAVOULIS, AND D J POLLOCK Fwm
Helicobacter and gastritis
 1 Helicobacter and gastritis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped gram-negative rod. H. pylori is associated with antral gastritis, duodenal (peptic) ulcer disease, gastric ulcers,
1 Helicobacter and gastritis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped gram-negative rod. H. pylori is associated with antral gastritis, duodenal (peptic) ulcer disease, gastric ulcers,
Gastric mucosa after partial gastrectomy
 Gastric mucosa after partial gastrectomy B. M. PULIMOOD, A. KNUDSEN, AND N. F. COGHILL' From the West Middlesex Hospital, Isleworth, Middlesex Gut, 1976, 17, 463-470 SUMMARY A partial gastrectomy of Billroth
Gastric mucosa after partial gastrectomy B. M. PULIMOOD, A. KNUDSEN, AND N. F. COGHILL' From the West Middlesex Hospital, Isleworth, Middlesex Gut, 1976, 17, 463-470 SUMMARY A partial gastrectomy of Billroth
Gastroenterology Tutorial
 Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
Mucosal changes in gastric ulceration and their response to carbenoxolone sodium
 Gut, 1975, 16, 590-597 Mucosal changes in gastric ulceration and their response to carbenoxolone sodium H. W. STEER' AND D. G. COLIN-JONES2 From Southampton University Medical School SUMMARY The epithelial
Gut, 1975, 16, 590-597 Mucosal changes in gastric ulceration and their response to carbenoxolone sodium H. W. STEER' AND D. G. COLIN-JONES2 From Southampton University Medical School SUMMARY The epithelial
Gastric gland metaplasia in the small and
 Gut, 1977, 18, 214-218 Gastric gland metaplasia in the small and large intestine I. YOKOYAMA, S. KOZUKA, K. ITO, K. KUBOTA, Y. YOKOYAMA, AND T. KONDO From the Second Department of Surgery and the Second
Gut, 1977, 18, 214-218 Gastric gland metaplasia in the small and large intestine I. YOKOYAMA, S. KOZUKA, K. ITO, K. KUBOTA, Y. YOKOYAMA, AND T. KONDO From the Second Department of Surgery and the Second
Crohn's disease of the duodenum
 Crohn's disease of the duodenum F. WARREN NUGENT,' M. RICHMOND,2 AND S. K. PARK3 Gut, 1977, 18, 115-120 From the Department of Gastroenterology, Lahey Clinic Foundation, Boston, Massachusetts, USA SUMMARY
Crohn's disease of the duodenum F. WARREN NUGENT,' M. RICHMOND,2 AND S. K. PARK3 Gut, 1977, 18, 115-120 From the Department of Gastroenterology, Lahey Clinic Foundation, Boston, Massachusetts, USA SUMMARY
Update on the pathological classification of gastritis. Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada
 Update on the pathological classification of gastritis Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS GASTROPATHY 1. Acute 2. Chronic 3. Uncommon
Update on the pathological classification of gastritis Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS GASTROPATHY 1. Acute 2. Chronic 3. Uncommon
Good Hope General Hospital, Sutton Coldfield, Warwickshire. this country with the gastrocamera (Olympus model
 Postgrad. med. J. (September 1969) 45, 577-582. Gastroscopy combined with intragastric photography D. D. GIBBS B.A., D.M., M.R.C.P. Consultant Physician Summary This paper relates experience in the use
Postgrad. med. J. (September 1969) 45, 577-582. Gastroscopy combined with intragastric photography D. D. GIBBS B.A., D.M., M.R.C.P. Consultant Physician Summary This paper relates experience in the use
Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration
 Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual
Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual
Gastric Polyps. Bible class
 Gastric Polyps Bible class 29.08.2018 Starting my training in gastroenterology, some decades ago, my first chief always told me that colonoscopy may seem technically more challenging but gastroscopy has
Gastric Polyps Bible class 29.08.2018 Starting my training in gastroenterology, some decades ago, my first chief always told me that colonoscopy may seem technically more challenging but gastroscopy has
SARCINA VENTICULARI IS A POSSIBLE CAUSATIVE MICROORGANISM OTHER THAN H.PYLORI IN GASTRIC OUTLET OBSTRUCTION PATHOGENESIS
 SARCINA VENTICULARI IS A POSSIBLE CAUSATIVE MICROORGANISM OTHER THAN H.PYLORI IN GASTRIC OUTLET OBSTRUCTION PATHOGENESIS 55 years old male, Farm worker, married, from Ibb Heavy Smoker, Khat chewer non-alcohol
SARCINA VENTICULARI IS A POSSIBLE CAUSATIVE MICROORGANISM OTHER THAN H.PYLORI IN GASTRIC OUTLET OBSTRUCTION PATHOGENESIS 55 years old male, Farm worker, married, from Ibb Heavy Smoker, Khat chewer non-alcohol
KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil D ass Dass, Lecturer 25th July, 2011
 KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil Dass, Lecturer 25 th July, 2011 Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the students t will be able to: Define peptic pp ulcer Describe the etiology and pathology
KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil Dass, Lecturer 25 th July, 2011 Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the students t will be able to: Define peptic pp ulcer Describe the etiology and pathology
A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE EFFECTS OF NONSTEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs) ON THE GASTRIC AND DUODENAL MUCOSA
 A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE EFFECTS OF NONSTEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs) ON THE GASTRIC AND DUODENAL MUCOSA Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 287 To 290 Naheed Moghal, N.A. Jafarey
A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE EFFECTS OF NONSTEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs) ON THE GASTRIC AND DUODENAL MUCOSA Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 287 To 290 Naheed Moghal, N.A. Jafarey
IBD. Crohn s. Outline. Ulcerative colitis versus Crohn s disease: is biopsy useful? UC vs. Crohn s? Is it easy? Biopsy settings 21/07/2017 IBD
 Outline Ulcerative colitis versus Crohn s disease: is biopsy useful? Roger Feakins Colorectal biopsies Ileal and upper GI biopsies Special situations New techniques Summary Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
Outline Ulcerative colitis versus Crohn s disease: is biopsy useful? Roger Feakins Colorectal biopsies Ileal and upper GI biopsies Special situations New techniques Summary Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
PATHOLOGY OF NON NEOPLASTIC LESIONS OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT.
 PATHOLOGY OF NON NEOPLASTIC LESIONS OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. OESOPHAGEAL LESIONS OESOPHAGITIS AND OTHER NON NEOPLASTIC DISORDERS Corrosive Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD), Pills, Acid intake,
PATHOLOGY OF NON NEOPLASTIC LESIONS OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. OESOPHAGEAL LESIONS OESOPHAGITIS AND OTHER NON NEOPLASTIC DISORDERS Corrosive Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD), Pills, Acid intake,
The permeation of gastric epithelial cells by leucocytes
 Gut, 1964, 5, 160 The permeation of gastric epithelial cells by leucocytes D. D. GIBBS From the Department of Medicine, The London Hospital EDITORIAL SYNOPSIS The cytological observations reported here
Gut, 1964, 5, 160 The permeation of gastric epithelial cells by leucocytes D. D. GIBBS From the Department of Medicine, The London Hospital EDITORIAL SYNOPSIS The cytological observations reported here
Proximal Gastric Vagotomy Without Drainage for Treatment of Perforated Duodenal Ulcer
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1982;179-83 Proximal Gastric Vagotomy Without Drainage for Treatment of Perforated Duodenal Ulcer PAUL H. JORDAN, Jr. Surgical Services of the Cora and Webb Mading Department of Surgery,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1982;179-83 Proximal Gastric Vagotomy Without Drainage for Treatment of Perforated Duodenal Ulcer PAUL H. JORDAN, Jr. Surgical Services of the Cora and Webb Mading Department of Surgery,
Helicobacter Pylori Testing HELICOBACTER PYLORI TESTING HS-131. Policy Number: HS-131. Original Effective Date: 9/17/2009
 Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
HDF Case Whipple s disease
 HDF Case 952556 Whipple s disease 63 yo female complaining of a diarrhea for 2 months, weigth loss (12 Kg in 3 months), and joint pains. Duodenal biopsy performed. Scanning view, enlarged intestinal villi,
HDF Case 952556 Whipple s disease 63 yo female complaining of a diarrhea for 2 months, weigth loss (12 Kg in 3 months), and joint pains. Duodenal biopsy performed. Scanning view, enlarged intestinal villi,
OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF ULCER DISEASE
 Página 1 de 8 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Greenfield, Lazar J., Mulholland, Michael W., Oldham, Keith T., Zelenock, Gerald B., Lillemoe, Keith D. Surgery: Scientific Principles & Practice,
Página 1 de 8 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Greenfield, Lazar J., Mulholland, Michael W., Oldham, Keith T., Zelenock, Gerald B., Lillemoe, Keith D. Surgery: Scientific Principles & Practice,
Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 Final Pathology:
 Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 A 74 year old male with a history of GERD presents complaining of dysphagia. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 A 74 year old male with a history of GERD presents complaining of dysphagia. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy
594 Lewin, Weinstein, and Riddell s Gastrointestinal Pathology and Its Clinical Implications
 594 Lewin, Weinstein, and Riddell s Gastrointestinal Pathology and Its Clinical Implications Figure 13-20. Stages in the natural history of H. pylori. Biopsies from the antrum are on the left and the oxyntic
594 Lewin, Weinstein, and Riddell s Gastrointestinal Pathology and Its Clinical Implications Figure 13-20. Stages in the natural history of H. pylori. Biopsies from the antrum are on the left and the oxyntic
Cholecystectomy and duodenogastric reflux: interacting effects over the gastric mucosa
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3641-z RESEARCH Open Access Cholecystectomy and duodenogastric reflux: interacting effects over the gastric mucosa Erdinc Mercan 1, Ugur Duman 1, Deniz Tihan 1, Evren Dilektasli
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3641-z RESEARCH Open Access Cholecystectomy and duodenogastric reflux: interacting effects over the gastric mucosa Erdinc Mercan 1, Ugur Duman 1, Deniz Tihan 1, Evren Dilektasli
STOMACH and DUODENUM DISEASE
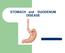 STOMACH and DUODENUM DISEASE STOMACH ANATOMY In the living and upright posture, the stomach is a j-shaped. It has two surfaces, two curvatures and two openings. Esophagus Fundus cardia Pylorus B o d y
STOMACH and DUODENUM DISEASE STOMACH ANATOMY In the living and upright posture, the stomach is a j-shaped. It has two surfaces, two curvatures and two openings. Esophagus Fundus cardia Pylorus B o d y
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for 2005
 The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for 2005 jointly to Barry J. Marshall and J. Robin Warren for their discovery of "the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and its role in gastritis and peptic ulcer
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for 2005 jointly to Barry J. Marshall and J. Robin Warren for their discovery of "the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and its role in gastritis and peptic ulcer
Postgastrectomy and Postvagotomy Syndromes
 H. D. Becker W.F. Caspary Postgastrectomy and Postvagotomy Syndromes With 84 Figures (Mainly in Two Colors) Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York 1980 Professor Dr. med. H. D. Becker KlInik und PolIklImk
H. D. Becker W.F. Caspary Postgastrectomy and Postvagotomy Syndromes With 84 Figures (Mainly in Two Colors) Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York 1980 Professor Dr. med. H. D. Becker KlInik und PolIklImk
A PLACEBO CONTROLLED TRIAL OF BISMUTH SALICYLATE IN HELICOBACTER PYLORI ASSOCIATED GASTRITIS
 A PLACEBO CONTROLLED TRIAL OF BISMUTH SALICYLATE IN HELICOBACTER PYLORI ASSOCIATED GASTRITIS Pages with reference to book, From 154 To 156 Javed Iqbal Kazi, Naeem Aon Jafarey, Syed Mahmood Alam ( Department
A PLACEBO CONTROLLED TRIAL OF BISMUTH SALICYLATE IN HELICOBACTER PYLORI ASSOCIATED GASTRITIS Pages with reference to book, From 154 To 156 Javed Iqbal Kazi, Naeem Aon Jafarey, Syed Mahmood Alam ( Department
Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with Atrophic gastritis in patients with Dyspepsia
 ADVANCES IN BIORESEARCH Adv. Biores., Vol 8 [3] May 2017: 137-141 2017 Society of Education, India Print ISSN 0976-4585; Online ISSN 2277-1573 Journal s URL:http://www.soeagra.com/abr.html CODEN: ABRDC3
ADVANCES IN BIORESEARCH Adv. Biores., Vol 8 [3] May 2017: 137-141 2017 Society of Education, India Print ISSN 0976-4585; Online ISSN 2277-1573 Journal s URL:http://www.soeagra.com/abr.html CODEN: ABRDC3
INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS
 INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS Lecture 1 and 2 دز اسماعيل داود فرع الطب كلية طب الموصل Radiological tests of structure (imaging) Plain X-ray: May shows soft tissue outlines like liver, spleen,
INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS Lecture 1 and 2 دز اسماعيل داود فرع الطب كلية طب الموصل Radiological tests of structure (imaging) Plain X-ray: May shows soft tissue outlines like liver, spleen,
Histopathogenesis of intestinal metaplasia: minute
 J Clin Pathol 1987;40:13-18 Histopathogenesis of intestinal metaplasia: minute lesions of intestinal metaplasia in ulcerated stomachs K MUKAWA, T NAKAMURA, G NAKANO, Y NAGAMACHI From the First Department
J Clin Pathol 1987;40:13-18 Histopathogenesis of intestinal metaplasia: minute lesions of intestinal metaplasia in ulcerated stomachs K MUKAWA, T NAKAMURA, G NAKANO, Y NAGAMACHI From the First Department
Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic Patterns and Histopathological Severity of
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 808505, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/808505 Research Article Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic
Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 808505, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/808505 Research Article Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic
HELICOBACTER THE EASE AND DIFFICULTY OF A NEW DISCOVERY
 HELICOBACTER THE EASE AND DIFFICULTY OF A NEW DISCOVERY Nobel Lecture, December 8, 2005 by J. Robin Warren Perth, WA 6000, Australia. PREFACE This is the story of my discovery of Helicobacter. At various
HELICOBACTER THE EASE AND DIFFICULTY OF A NEW DISCOVERY Nobel Lecture, December 8, 2005 by J. Robin Warren Perth, WA 6000, Australia. PREFACE This is the story of my discovery of Helicobacter. At various
Primary mucinous adenocarcinoma developing in an ileostomy stoma
 Gut, 1988, 29, 1607-1612 Primary mucinous adenocarcinoma developing in an ileostomy stoma P J SMART, S SASTRY, AND S WELLS From the Departments of Histopathology and Surgery, Bolton General Hospital, Fan
Gut, 1988, 29, 1607-1612 Primary mucinous adenocarcinoma developing in an ileostomy stoma P J SMART, S SASTRY, AND S WELLS From the Departments of Histopathology and Surgery, Bolton General Hospital, Fan
Surgery for Complications of Peptic Ulcer Disease (Definitive Treatment)
 Surgery for Complications of Peptic Ulcer Disease (Definitive Treatment) Amid Keshavarzi, MD UCHSC Grand Round 3/20/2006 Department of Surgery Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology Clinical manifestation
Surgery for Complications of Peptic Ulcer Disease (Definitive Treatment) Amid Keshavarzi, MD UCHSC Grand Round 3/20/2006 Department of Surgery Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology Clinical manifestation
Indolent mucoid carcinoma of stomach
 J. clin. Path., 1974, 27, 536-541 Indolent mucoid carcinoma of stomach W. L. BRANDER', P. R. G. NEEDHAM, AND A. D. MORGAN From the Department of Histopathology, Westminster Medical School, London synopsis
J. clin. Path., 1974, 27, 536-541 Indolent mucoid carcinoma of stomach W. L. BRANDER', P. R. G. NEEDHAM, AND A. D. MORGAN From the Department of Histopathology, Westminster Medical School, London synopsis
An assessment of the augmented histamine test
 Gut, 1963, 4, 243 An assessment of the augmented histamine test in the diagnosis of peptic ulcer Correlations between gastric secretion, age and se of patients, and site and nature of the ulcer J. H. BARON1
Gut, 1963, 4, 243 An assessment of the augmented histamine test in the diagnosis of peptic ulcer Correlations between gastric secretion, age and se of patients, and site and nature of the ulcer J. H. BARON1
Case Scenario 1. The patient has now completed his neoadjuvant chemoradiation and has been cleared for surgery.
 Case Scenario 1 July 10, 2010 A 67-year-old male with squamous cell carcinoma of the mid thoracic esophagus presents for surgical resection. The patient has completed preoperative chemoradiation. This
Case Scenario 1 July 10, 2010 A 67-year-old male with squamous cell carcinoma of the mid thoracic esophagus presents for surgical resection. The patient has completed preoperative chemoradiation. This
Gastrointestinal Tract Cancer
 Gastrointestinal Tract Cancer Tumors of the Stomach Gastric adenocarcinoma Incidence and Epidemiology Incidence mortality rates USA High incidence: Japan, China, Chile, Ireland risk lower socioeconomic
Gastrointestinal Tract Cancer Tumors of the Stomach Gastric adenocarcinoma Incidence and Epidemiology Incidence mortality rates USA High incidence: Japan, China, Chile, Ireland risk lower socioeconomic
Gastrin cells and fasting serum gastrin levels in duodenal ulcer patients A quantitative study based on multiple biopsy specimens
 Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 171-178 Gastrin cells and fasting serum gastrin levels in duodenal ulcer patients A quantitative study based on multiple biopsy specimens JUAN PIRIS AND R. WHITEHEADI
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 171-178 Gastrin cells and fasting serum gastrin levels in duodenal ulcer patients A quantitative study based on multiple biopsy specimens JUAN PIRIS AND R. WHITEHEADI
COMPARISON OF ONCE-A-DAY VERSUS TWICE-A-DAY CLARITHROMYCIN IN TRIPLE THERAPY FOR HELICOBACTER PYLORI ERADICATION
 Phil J Gastroenterol 2006; 2: 25-29 COMPARISON OF ONCE-A-DAY VERSUS TWICE-A-DAY CLARITHROMYCIN IN TRIPLE THERAPY FOR HELICOBACTER PYLORI ERADICATION Marianne P Collado, Ma Fatima P Calida, Peter P Sy,
Phil J Gastroenterol 2006; 2: 25-29 COMPARISON OF ONCE-A-DAY VERSUS TWICE-A-DAY CLARITHROMYCIN IN TRIPLE THERAPY FOR HELICOBACTER PYLORI ERADICATION Marianne P Collado, Ma Fatima P Calida, Peter P Sy,
Gland ducts and multilayered epithelium in mucosal biopsies from gastroesophageal-junction region are useful in characterizing esophageal location
 Diseases of the Esophagus (2005) 18, 87 92 2005 ISDE Blackwell Publishing, Ltd. Original article Gland ducts and multilayered epithelium in mucosal biopsies from gastroesophageal-junction region are useful
Diseases of the Esophagus (2005) 18, 87 92 2005 ISDE Blackwell Publishing, Ltd. Original article Gland ducts and multilayered epithelium in mucosal biopsies from gastroesophageal-junction region are useful
Quiz Adenocarcinoma of the distal stomach has been increasing in the last 20 years. a. True b. False
 Quiz 1 1. Which of the following are risk factors for esophagus cancer. a. Obesity b. Gastroesophageal reflux c. Smoking and Alcohol d. All of the above 2. Adenocarcinoma of the distal stomach has been
Quiz 1 1. Which of the following are risk factors for esophagus cancer. a. Obesity b. Gastroesophageal reflux c. Smoking and Alcohol d. All of the above 2. Adenocarcinoma of the distal stomach has been
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks
 Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
Fibrin thrombi, a cause of clindamycin-associated
 Gut, 1976, 17, 483487 Fibrin thrombi, a cause of clindamycin-associated colitis? W. V. BOGOMOLETZ From the Department of Pathology, Queen Mary's Hospital, London summary Rectal biopsies from five patients
Gut, 1976, 17, 483487 Fibrin thrombi, a cause of clindamycin-associated colitis? W. V. BOGOMOLETZ From the Department of Pathology, Queen Mary's Hospital, London summary Rectal biopsies from five patients
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 4. Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath
 Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 4 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Topics to be covered Peptic ulcer disease Hiatal hernia Gastric neoplasms Peptic ulcer disease (PUD)= chronic gastric ulcer Causes H pylori
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 4 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Topics to be covered Peptic ulcer disease Hiatal hernia Gastric neoplasms Peptic ulcer disease (PUD)= chronic gastric ulcer Causes H pylori
Peptic ulcer disease. Nomin-Erdene. D SOM-531
 Peptic ulcer disease Nomin-Erdene. D SOM-531 Learning objectives Stomach gross anatomy PUD Epidemiology Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Diagnosing Treatment Complicated ulcer disease Surgical procedures
Peptic ulcer disease Nomin-Erdene. D SOM-531 Learning objectives Stomach gross anatomy PUD Epidemiology Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Diagnosing Treatment Complicated ulcer disease Surgical procedures
medically treated patients.7
 J Clin Pathol 1984;37:511-515 Relation between gastric histology and gastric juice ph and nitrite and N-nitroso compound concentrations in the stomach after surgery for duodenal ulcer PCH WATT,* JM SLOAN,*
J Clin Pathol 1984;37:511-515 Relation between gastric histology and gastric juice ph and nitrite and N-nitroso compound concentrations in the stomach after surgery for duodenal ulcer PCH WATT,* JM SLOAN,*
What Every Pathologist Wants the GI Nurse to Know (and how you can help us help you)
 What Every Pathologist Wants the GI Nurse to Know (and how you can help us help you) Jonathan N. Glickman MD PhD Director, GI Pathology, Caris Diagnostics, Newton, MA Associate Professor of Pathology,
What Every Pathologist Wants the GI Nurse to Know (and how you can help us help you) Jonathan N. Glickman MD PhD Director, GI Pathology, Caris Diagnostics, Newton, MA Associate Professor of Pathology,
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ENDOSCOPIC BIOPSIES OF STOMACH
 HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ENDOSCOPIC BIOPSIES OF STOMACH Pages with reference to book, From 177 To 179 Javed Iqbal Kazi, Syed Mahmood Alam ( Departments of Pathology, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre,
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ENDOSCOPIC BIOPSIES OF STOMACH Pages with reference to book, From 177 To 179 Javed Iqbal Kazi, Syed Mahmood Alam ( Departments of Pathology, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre,
Stomach. R.B. Kolachalam, MD
 Stomach R.B. Kolachalam, MD Relevent Anatomy 1.four regions: Cardia, Fundus, Body, and the Pylorus 2. fixed in two locations- at the GEJ and the duodenum Gastric Anatomy body of the stomach: site of mechanical
Stomach R.B. Kolachalam, MD Relevent Anatomy 1.four regions: Cardia, Fundus, Body, and the Pylorus 2. fixed in two locations- at the GEJ and the duodenum Gastric Anatomy body of the stomach: site of mechanical
Gastric emptying following vagotomy and antrectomy and proximal gastric vagotomy
 Gut, 1975, 16, 509-513 Gastric emptying following vagotomy and antrectomy and proximal gastric vagotomy H. KALBASI, F. R. HUDSON, A. HERRING, S. MOSS, H. I. GLASS, AND J. SPENCER From the Departments of
Gut, 1975, 16, 509-513 Gastric emptying following vagotomy and antrectomy and proximal gastric vagotomy H. KALBASI, F. R. HUDSON, A. HERRING, S. MOSS, H. I. GLASS, AND J. SPENCER From the Departments of
Helicobacter pylori Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.4.2099 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Premalignant Gastric Mucosa Using Conventional White Light Source Gastroscopy
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.4.2099 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Premalignant Gastric Mucosa Using Conventional White Light Source Gastroscopy
The clinical significance of radiological changes in duodenal ulcer patients
 Ital J Gastroanter ol 1986; 18: CLINICAL REPORT 8-92 The clinical significance of radiological changes in duodenal ulcer patients RJ EARLAM, RS MURRAY, JC SWANN, EGW SLATER and SJW EVANS 1 The London Hospital,
Ital J Gastroanter ol 1986; 18: CLINICAL REPORT 8-92 The clinical significance of radiological changes in duodenal ulcer patients RJ EARLAM, RS MURRAY, JC SWANN, EGW SLATER and SJW EVANS 1 The London Hospital,
Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting for Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy
 Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting for Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy Authors: Dr Gordon Armstrong, Dr Sue Pritchard 1. General Comments 1.1 Cancer reporting: Biopsies
Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting for Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy Authors: Dr Gordon Armstrong, Dr Sue Pritchard 1. General Comments 1.1 Cancer reporting: Biopsies
OPEN ACCESS TEXTBOOK OF GENERAL SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS TEXTBOOK OF GENERAL SURGERY PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE PC Bornman RS Du Toit EPIDEMIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS The prevalence of duodenal ulcer disease has a variable geographical distribution and differs
OPEN ACCESS TEXTBOOK OF GENERAL SURGERY PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE PC Bornman RS Du Toit EPIDEMIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS The prevalence of duodenal ulcer disease has a variable geographical distribution and differs
Hiatus hernia and heartburn
 Hiatus hernia and heartburn E. W. GILLISON,l W. M. CAPPER, G. R. AIRTH, M. J. GIBSON, AND I. BRADFORD From the Department of Gastroenterology, Southmead Hospital, Bristol Gut, 1969, 1, 69-613 SUMMARY The
Hiatus hernia and heartburn E. W. GILLISON,l W. M. CAPPER, G. R. AIRTH, M. J. GIBSON, AND I. BRADFORD From the Department of Gastroenterology, Southmead Hospital, Bristol Gut, 1969, 1, 69-613 SUMMARY The
Chronic gastritis and gastric ulcer
 Gut, 1966, 7, 228 Chronic gastritis and gastric ulcer IAN R. MACKAY' AND I. G. HISLOP2 From the Clinical Research Unit of the Royal Melbourne Hospital and the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical
Gut, 1966, 7, 228 Chronic gastritis and gastric ulcer IAN R. MACKAY' AND I. G. HISLOP2 From the Clinical Research Unit of the Royal Melbourne Hospital and the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical
Gastric epithelium in the duodenum
 Gastric epithelium in the duodenum A. H. JAMES From the Medical Unit, Cardiff Royal Infirmary, Cardiff, Wales Gut, 1964, 5, 285 EDITORIAL SYNOPSIS It has been found that a 'gastric' type of epithelium
Gastric epithelium in the duodenum A. H. JAMES From the Medical Unit, Cardiff Royal Infirmary, Cardiff, Wales Gut, 1964, 5, 285 EDITORIAL SYNOPSIS It has been found that a 'gastric' type of epithelium
Factors relevant to the prognosis of chronic
 Gut, 1975, 16, 714-718 Factors relevant to the prognosis of chronic gastric ulcer D. W. PIPER, MARGARET GREIG, G. A. E. COUPLAND, ELIZABETH HOBBIN, AND JANE SHINNERS From the Departments of Medicine and
Gut, 1975, 16, 714-718 Factors relevant to the prognosis of chronic gastric ulcer D. W. PIPER, MARGARET GREIG, G. A. E. COUPLAND, ELIZABETH HOBBIN, AND JANE SHINNERS From the Departments of Medicine and
Totally laparoscopic distal gastrectomy reconstructed by Rouxen-Y with D2 lymphadenectomy and needle catheter jejunostomy for gastric cancer
 Masters of Gastrointestinal Surgery Totally laparoscopic distal gastrectomy reconstructed by Rouxen-Y with D2 lymphadenectomy and needle catheter jejunostomy for gastric cancer Xin Ye, Jian-Chun Yu, Wei-Ming
Masters of Gastrointestinal Surgery Totally laparoscopic distal gastrectomy reconstructed by Rouxen-Y with D2 lymphadenectomy and needle catheter jejunostomy for gastric cancer Xin Ye, Jian-Chun Yu, Wei-Ming
duodenal ulcer by vagotomy and gastric drainage operation
 Gut, 1961, 2,158 A clinical appraisal of the treatment of chronic duodenal ulcer by vagotomy and gastric drainage operation W. GERALD AUSTEN' AND HAROLD C. EDWARDS From King's College Hospital, London
Gut, 1961, 2,158 A clinical appraisal of the treatment of chronic duodenal ulcer by vagotomy and gastric drainage operation W. GERALD AUSTEN' AND HAROLD C. EDWARDS From King's College Hospital, London
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: helicobacter_pylori_testing 01/01/2019 N/A 01/01/2020 01/01/2019 Policy Effective April 1, 2019 Description
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: helicobacter_pylori_testing 01/01/2019 N/A 01/01/2020 01/01/2019 Policy Effective April 1, 2019 Description
SAM PROVIDER TOOLKIT
 THE AMERICAN BOARD OF PATHOLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Program SAM PROVIDER TOOLKIT Developing Self-Assessment Modules (SAMs) www.abpath.org The American Board of Pathology (ABP) approves educational
THE AMERICAN BOARD OF PATHOLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Program SAM PROVIDER TOOLKIT Developing Self-Assessment Modules (SAMs) www.abpath.org The American Board of Pathology (ABP) approves educational
Case Report Features of the Atrophic Corpus Mucosa in Three Cases of Autoimmune Gastritis Revealed by Magnifying Endoscopy
 Volume 2012, Article ID 368160, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/368160 Case Report Features of the Atrophic Corpus Mucosa in Three Cases of Autoimmune Gastritis Revealed by Magnifying Endoscopy Kazuyoshi Yagi,
Volume 2012, Article ID 368160, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/368160 Case Report Features of the Atrophic Corpus Mucosa in Three Cases of Autoimmune Gastritis Revealed by Magnifying Endoscopy Kazuyoshi Yagi,
Small intestine. Small intestine
 General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease. Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia
 Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
When to Refer for OGD and the Work Up of Upper GI Malignancies
 When to Refer for OGD and the Work Up of Upper GI Malignancies Dr Hong Qiantai Registrar, Department of Surgery GP Forum 27 May 2017 38 year old female, non-smoker, BMI 29 Works as investment banker Presents
When to Refer for OGD and the Work Up of Upper GI Malignancies Dr Hong Qiantai Registrar, Department of Surgery GP Forum 27 May 2017 38 year old female, non-smoker, BMI 29 Works as investment banker Presents
Campylobacter pylor: clinical, histological, and
 J Clin Pathol 1988;41:1316-1321 Campylobacter pylor: clinical, histological, and serological studies C MUSGROVE,* F J BOLTON,t A M KRYPCZYK,* J M TEMPERLEY,4 S A CAIRNS,$ W G OWEN,* D N HUTCHINSONt From
J Clin Pathol 1988;41:1316-1321 Campylobacter pylor: clinical, histological, and serological studies C MUSGROVE,* F J BOLTON,t A M KRYPCZYK,* J M TEMPERLEY,4 S A CAIRNS,$ W G OWEN,* D N HUTCHINSONt From
Persistence of mucosal abnormality in ulcerative colitis
 Gut, 966, 7, 55 Persistence of mucosal abnormality in ulcerative colitis A. P. DICK, L. P. HOLT', AND E. R. DALTON rom Addenbrooke's Hospital, Cambridge, and the Department of Human Ecology, University
Gut, 966, 7, 55 Persistence of mucosal abnormality in ulcerative colitis A. P. DICK, L. P. HOLT', AND E. R. DALTON rom Addenbrooke's Hospital, Cambridge, and the Department of Human Ecology, University
KEYWORDS Dyspepsia, Acid Peptic Disease, Helicobacter Pylori, Urease, Giemsa, Peptic Ulcer, Non-Ulcer Dyspepsia.
 INCIDENCE OF HELICOBACTER PYLORI WITH ACID PEPTIC DISEASE AND MALIGNANT CONDITIONS OF UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN A TERTIARY CENTRE - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Karunamoorthy Rajachidambaram 1, Dinkaran Kaarthesan
INCIDENCE OF HELICOBACTER PYLORI WITH ACID PEPTIC DISEASE AND MALIGNANT CONDITIONS OF UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN A TERTIARY CENTRE - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Karunamoorthy Rajachidambaram 1, Dinkaran Kaarthesan
Use of the Henley loop for postvagotomy diarrhea
 Use of the Henley loop for postvagotomy diarrhea Sharon Grundfest, M.D. Caldwell B. Esselstyn, Jr., M.D. Department of General Surgery D. Roy Ferguson, M.D. Department of Gastroenterology Postvagotomy
Use of the Henley loop for postvagotomy diarrhea Sharon Grundfest, M.D. Caldwell B. Esselstyn, Jr., M.D. Department of General Surgery D. Roy Ferguson, M.D. Department of Gastroenterology Postvagotomy
Postgastrectomy Syndromes
 Postgastrectomy Syndromes Postgastrectomy syndromes are iatrogenic conditions that may arise from partial gastrectomies, independent of whether the gastric surgery was initially performed for peptic ulcer
Postgastrectomy Syndromes Postgastrectomy syndromes are iatrogenic conditions that may arise from partial gastrectomies, independent of whether the gastric surgery was initially performed for peptic ulcer
Rectal biopsy in patients presenting to an infectious disease unit with diarrhoeal disease
 Gut, 1979, 20, 141-148 Rectal biopsy in patients presenting to an infectious disease unit with diarrhoeal disease R. J. DICKINSON, H. M. GILMOUR, AND D. B. L. McCLELLAND' From the Department of Infectious
Gut, 1979, 20, 141-148 Rectal biopsy in patients presenting to an infectious disease unit with diarrhoeal disease R. J. DICKINSON, H. M. GILMOUR, AND D. B. L. McCLELLAND' From the Department of Infectious
SAMs Guidelines DEVELOPING SELF-ASSESSMENT MODULES TEST QUESTIONS. Ver. #
 SAMs Guidelines DEVELOPING SELF-ASSESSMENT MODULES TEST Ver. #5-02.12.17 GUIDELINES FOR DEVELOPING SELF-ASSESSMENT MODULES TEST The USCAP is accredited by the American Board of Pathology (ABP) to offer
SAMs Guidelines DEVELOPING SELF-ASSESSMENT MODULES TEST Ver. #5-02.12.17 GUIDELINES FOR DEVELOPING SELF-ASSESSMENT MODULES TEST The USCAP is accredited by the American Board of Pathology (ABP) to offer
SUMMARY The radiological anatomy of the pyloro-duodenal area after pyloroplasty is. features that indicate a successful operation.
 Gut, 1970, 11, 358-362 D. K. M. TOYE, J. F. K. HUTTON, AND J. ALEXANDER WILLIAMS From the General Hospital, Birmingham SUMMARY The radiological anatomy of the pyloro-duodenal area after pyloroplasty is
Gut, 1970, 11, 358-362 D. K. M. TOYE, J. F. K. HUTTON, AND J. ALEXANDER WILLIAMS From the General Hospital, Birmingham SUMMARY The radiological anatomy of the pyloro-duodenal area after pyloroplasty is
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy
 Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
Management of dyspepsia and of Helicobacter pylori infection
 Management of dyspepsia and of Helicobacter pylori infection The University of Nottingham John Atherton Wolfson Digestive Diseases Centre University of Nottingham, UK Community management of dyspepsia
Management of dyspepsia and of Helicobacter pylori infection The University of Nottingham John Atherton Wolfson Digestive Diseases Centre University of Nottingham, UK Community management of dyspepsia
A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY, HEMATOXYLIN & EOSIN AND GEIMSA STAIN FOR HELICOBACTER PYLORI DETECTION IN CHRONIC GASTRITIS
 Original Research Article Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY, HEMATOXYLIN & EOSIN AND GEIMSA STAIN FOR HELICOBACTER
Original Research Article Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY, HEMATOXYLIN & EOSIN AND GEIMSA STAIN FOR HELICOBACTER
Serotonin- and Somatostatin-Positive Goblet Cell Carcinoid of the Duodenum
 2012 66 4 351 356 Serotonin- and Somatostatin-Positive Goblet Cell Carcinoid of the Duodenum a b* c c c a a b d a c b d 352 Ohara et al. received remedies at another hospital. Hematemesis then recurred
2012 66 4 351 356 Serotonin- and Somatostatin-Positive Goblet Cell Carcinoid of the Duodenum a b* c c c a a b d a c b d 352 Ohara et al. received remedies at another hospital. Hematemesis then recurred
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus
 Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus
 Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus Br J Surg 38 oct. 1950 Definition of Barrett's esophagus A change in the esophageal epithelium of any length that can be recognized
Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus Br J Surg 38 oct. 1950 Definition of Barrett's esophagus A change in the esophageal epithelium of any length that can be recognized
Correlation Between Endoscopic and Histological Findings in Different Gastroduodenal Lesion and its Association with Helicobacter Pylori
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation Between Endoscopic and Histological Findings in Different Gastroduodenal Lesion and its Association with Helicobacter Pylori *A. Sultana 1, SM Badruddoza 2, F Rahman 3 1 Dr.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation Between Endoscopic and Histological Findings in Different Gastroduodenal Lesion and its Association with Helicobacter Pylori *A. Sultana 1, SM Badruddoza 2, F Rahman 3 1 Dr.
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B
 Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
Common Inflammatory Gastrointestinal Disorders: Endoscopic and Pathologic Correlations
 Common Inflammatory Gastrointestinal Disorders: Endoscopic and Pathologic Correlations Nicole C. Panarelli, M.D. Attending Pathologist Montefiore Medical Center Associate Professor of Pathology - Albert
Common Inflammatory Gastrointestinal Disorders: Endoscopic and Pathologic Correlations Nicole C. Panarelli, M.D. Attending Pathologist Montefiore Medical Center Associate Professor of Pathology - Albert
Clinical outcome of proximal versus total gastrectomy for proximal gastric cancer Shiraishi N, Adachi Y, Kitano S, Kakisako K, Inomata M, Yasuda K
 Clinical outcome of proximal versus total gastrectomy for proximal gastric cancer Shiraishi N, Adachi Y, Kitano S, Kakisako K, Inomata M, Yasuda K Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic
Clinical outcome of proximal versus total gastrectomy for proximal gastric cancer Shiraishi N, Adachi Y, Kitano S, Kakisako K, Inomata M, Yasuda K Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic
Perforated duodenal ulcer in Reading from 1950 to 1959
 Gut, 1969, 1, 454-459 Perforated duodenal ulcer in Reading from 195 to 1959 PAUL CASSELL From the Royal Berkshire Hospital, Reading During the last 15 years there has been an evolution in the management
Gut, 1969, 1, 454-459 Perforated duodenal ulcer in Reading from 195 to 1959 PAUL CASSELL From the Royal Berkshire Hospital, Reading During the last 15 years there has been an evolution in the management
A 35 yr old man presents with a month history of burning epigastric pain that occurs between meals------
 A 35 yr old man presents with a month history of burning epigastric pain that occurs between meals------ The pain can be relieved by food or antiacids------ He denies taking aspirin or NSAID------ Lab
A 35 yr old man presents with a month history of burning epigastric pain that occurs between meals------ The pain can be relieved by food or antiacids------ He denies taking aspirin or NSAID------ Lab
Vagotomy for gastric ulcer
 Gut, 1970, 11, 540-545 Progress report Vagotomy for gastric ulcer In all aspects of the surgical treatment of peptic ulcer the trend, in the past decade, has been to substitute vagotomy and a drainage
Gut, 1970, 11, 540-545 Progress report Vagotomy for gastric ulcer In all aspects of the surgical treatment of peptic ulcer the trend, in the past decade, has been to substitute vagotomy and a drainage
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Clinicopathological Study on Gastri Murata, Ikuo; Oda, Hidetoshi; Muta, Nakamuta, Kohji; Tsuruta, Hideo; Oh Makiyama, Kazuya; Hara, Kohei Citation Acta
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Clinicopathological Study on Gastri Murata, Ikuo; Oda, Hidetoshi; Muta, Nakamuta, Kohji; Tsuruta, Hideo; Oh Makiyama, Kazuya; Hara, Kohei Citation Acta
A Practical Approach to Small Bowel Biopsies: All that flattens is not sprue
 A Practical Approach to Small Bowel Biopsies: All that flattens is not sprue UCSF Liver and Gastrointestinal Pathology Update Sept. 4, 2009 How to Go Wrong When Evaluating Small Bowel Biopsies, Based on
A Practical Approach to Small Bowel Biopsies: All that flattens is not sprue UCSF Liver and Gastrointestinal Pathology Update Sept. 4, 2009 How to Go Wrong When Evaluating Small Bowel Biopsies, Based on
Gastritis duodenitis, and circulating levels of gastrin in duodenal ulcer before and after vagotomy
 Gut, 1976, 17, 719-728 Gastritis duodenitis, and circulating levels of gastrin in duodenal ulcer before and after vagotomy D. D. MIKL, K. B. TAYLOR, S. C. TRULOV, AND R. WHITHAD From the Nuffield Department
Gut, 1976, 17, 719-728 Gastritis duodenitis, and circulating levels of gastrin in duodenal ulcer before and after vagotomy D. D. MIKL, K. B. TAYLOR, S. C. TRULOV, AND R. WHITHAD From the Nuffield Department
