The Functional Role of Transperineal Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Females with Urinary Incontinence Compared to Urodynamic Studies
|
|
|
- Matthew Mervin Howard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, March: , The Functional Role of Transperineal Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Females with Urinary Incontinence Compared to Urodynamic Studies MANAL H. WAHBA, M.D.*; RANIA F. ABDELSAYED, M.D.** and AHMED A.S. MAHMOUD, M.D.*** The Department of Radiology, Cairo University*,** and Theodor Bilharz Institute*** Abstract Objective: To prospectively evaluate the role of transperineal ultrasound in the diagnosis of female with urinary incontinence compared to urodymanic studies as the golden standard. Patients and Methods: This study had institutional review board approval, and informed consent was obtained from all participants. This pilot study included twenty female patients, their age ranges from year old (mean age 34.5 years). All patients underwent clinical examination, urodyanmic studies and transperineal ultrasound examination. According to the clinical findings 15 patients were diagnosed as mixed urinary incontinence (Involuntary leakage associated with urgency) and 5 patients as stress urinary incontinence (involuntary leakage on effort, exertion, sneezing or coughing. The transperineal ultrasound was conducted using an (GE. ultrasound machine). A 6.5 MHz end fire vaginal endoprobe was applied to the perineum in the axial and sagittal planes. The patients were examined at rest and during different grades of straining. The ultrasound criteria evaluated by the US include: 1- Bladder neck position 2- Posterior urethro-vesical angle 3- Anterior urethral (rotational) angle 4- Urethral luminal diameter and wall thickness 5- Bladder wall thickness. Results: Out of 20 patients with urinary incontinence; 12 patients (60%) had positive sonographic findings. However 8 patients (40%) were negative on perineal ultrasound. The positive sonsograhic findings were as follow; urethral hypermobility and intrinsic sphincteric deficiency (ISD) were detected in 7 (35%) patients, 3 (15%) patients had only urethral hypermobilty, while ISD was diagnosed in 2 (10%) patients. The ultrasound was 100% in agreement with urodynamics diagnosis in patients with intrinsic sphincter deficiency. 71.5% in patients with both urethral hypermobility and intrinsic sphincter deficiency, while 66.7% in patients with urethral hypermobility only. Conclusion: Transperineal ultrasound is a simple, easily conducted examination that can be used as screening imaging modality in patients with urinary incontinence to diagnose patients who are in need for further assessment. Correspondence to: Dr. Manal H. Wahba, The Department of Radiology, Cairo University Key Words: Transperineal ultrasound Stress incontinence Urodynamic urethral hypermobility Intrinsic sphincteric deficiency Uretherovesical. Introduction URINARY incontinence is a bothersome condition for many women, with an overall prevalence of approximately 40% [1]. Any leakage at least once in the past year, ranges from 2 5 to 5 1 %, Weekly urine leakage was reported in 10% of women in an ethnically diverse urban population [2]. The precise anatomical and physiological mechanisms involved in urinary incontinence are poorly understood. Urinary continence occurs because maximum urethral pressure remains greater than intravesical pressure during bladder filling, and increases in intra-abdominal pressure are transmitted equally to the bladder and proximal urethra. The vesical neck and proximal urethra are normally intra-abdominal structures that lie above a wellsupported pelvic diaphragm and they are positioned in such a way to promote the equal distribution of forces to the bladder and urethra during increases in intraabdominal pressure [3]. Poor anatomical support of the bladder neck, bladder base and proximal urethra, resulting in descent and hypermobility outside the intra-abdominal transmission zone, is considered the pathological basis of stress urinary incontinence [4]. Although it is not a life-threatening disease, it might have a significant influence on the physical, psychological, and social well-being of the affected patients [5]. Stress, urge, and mixed urinary incontinence are the most common subtypes of urinary incontinence [1]. Transperineal ultrasound especially has provided a good visualization of the urinary bladder, 231
2 232 The Functional Role of Transperineal Ultrasound in the Evaluation bladder base, urethrovesical (UV) junction, urethra and the symphysis pubis [6]. It has been used as an alternative to conventional radiological techniques to assess the dynamic changes of the urethrovesical junction and proximal urethra for two decades [7]. It has been shown to detect the overall reduction of urethral muscular wall thickness in urinary incontinence [8]. Videourodynamics consists of the simultaneous registration of pressure in the bladder and rectum, and external sphincter behavior, visualizing the bladder cycle in fluoroscopy. Videourdynamics is considered by most to be the gold standard for evaluating urinary incontinence [5]. Observations of thousands of videourodynamic examinations demonstrated that 76% of those classified as having intrinsic sphincter deficiency were recorded as having consistently low leak point pressures (less than 60cm H 2 O). It has over the last few years evolved as an easily performed and reliable test to determine the ability of the urethra to resist the expulsive force of the bladder generated by increased intra-abdominal pressure. The term valsalva (or abdominal) leak point pressure (VLPP) represents a measure of the intravesical pressure that is required to overcome urethral resistance during a stress manoeuvre such as coughing or straining [9]. It represents the lowest bladder pressure at which urethral leakage occurs during a prompted stress maneuver. As a dynamic test, it is a reflection of the stress competence of the urethra, which ultimately mirrors its ability to resist abdominal pressure as an expulsive force. Detrusor leak point pressure (DLPP) by contrast is the pressure at which detrusor stretch or contraction generates sufficient force to induce involuntary urinary leakage [9,10]. The aim of this study is to prospectively evaluate the role of transperineal ultrasound in the diagnosis of female with urinary incontinence compared to urodymanic studies as the golden standard. Patients and Methods This pilot study included twenty female patients, their age ranges from years old (mean age 34.5 years). All patients underwent clinical examinations, urodynamic studies and transperineal ultrasound examination. According to the clinical findings 15 patients were diagnosed as mixed urinary incontinence (i.e the complaint of involun- tary leakage associated with urgency also with exertion, effort, sneezing or coughing) and 5 patients as stress urinary incontinence. The transperineal ultrasound was conducted (using LOGIQ 7 PRO, GE ) General electric medical system ultrasound machine. A 6.5 MHz end fire vaginal endoprobe applied to the perineum in the axial and sagittal planes. Transperineal US was performed by positioning the transducer tenderly onto the perineum in midsagittal line to visualize pubic symphysis, urethra and bladder, vagina and anal canal. The patients were examined at rest and during different grades of straining. The ultrasound criteria evaluated by the US include: 1- Bladder neck position. 2- Posterior urethro-vesical angle. (PUVA). 3- Anterior urethral (rotational) angle. (AUA). 4- Urethral luminal diameter and wall thickness. 5- Bladder wall thickness. The urodynamic study is a dynamic test, which documents the abdominal pressure required to induce incontinence and performed by inserting urethral & rectal catheters. A transurethral doublelumen catheter is connected to fluid source & the other was used for measuring the intravesical pressure. It should be as small as possible but not so small as too dampen pressure transmission or limit the desired filling rate. The abdominal leak point pressure (ALPP) was measured that represents the lowest bladder pressure at which urethral leakage occurs during a prompted stress maneuver. All cases were performed at Kasr Al-Aini Hospital, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University during Results From the 20 patients with urinary incontinence; 12 patients (60%) had positive sonographic findings. However 8 patients (40%) were negative on perineal ultrasound. The positive sonsographic findings were as follow; urethral hypermobility and intrinsic sphincteric deficiency (ISD) were detected in 7 (35%) patients, 3 (15%) patients had only urethral hypermobility, while ISD was diagnosed in 2 (10%) patients. The patients were classified according to the ultrasonographic findings into three groups, and are presented as in Table (1) as the following:
3 Manal H. Wahba, et al. 233 Table (1): The details of the ultrasonographic findings in each group were summarized. No of cases BN decent Increase of PUVA Rotational angle Urethral thickness & diameter Funeling Group A 3 (15%) 3 (15%) 3 (15%) 1 (5%) Group B 2 (10%) 2 (10%) Group C 7 (35%) 1 (5%) 7 (35%) 7 (35%) 7 (35%) 1 (5%) Group A: Urethral hypermobility which was characterized by: 1- Widening of the PUVA 105 degree (Fig Increased AUA (rotational angle) 110 degree (Fig. 2). 3- Significant downward displacement of the bladder base and proximal uethra. PUVA Rotational angle Fig. (1): Transperineal ultrasound of a female patient complaining of mixed urinary incontinence shows widening of the posterior urethral angle. (PUVA is an angle formed between a line drawn tangent the proximal half of the urethra and a line tan-gent the infero-posterior aspect of the bladder base). And also shows increased in the rotational angle (which refers to the slope of the proximal half of the urethral axis with respect to the x axis of the pubic bone). PUVA Rotational angle Fig. (2): TPUS with urethral hypermobility revealing increased PUVA (112 degrees), widening of the rotational angle (120 degrees), no bladder base descent, normal urethral wall thickness and vascularity with ALPP <60cm H 2 O that is seen in the urodynamic study.
4 234 The Functional Role of Transperineal Ultrasound in the Evaluation Group B: Intrinsic sphincteric deficiency (ISD) which was characterized by: 1- Reduction of the urethral wall thickness (normal mean values 4.3mm±5mm) and its hypovascularity with increased urethral lumen diameter (5mm) (Fig. 3). 2- Opening of the bladder neck (BN) with coughing and straining (funneling). Group C: Characterized by the presence of causes of urethral hypermobility and ISD (Figs. 4,5). Based on urodynamic study of those 20 patients, 6 (30%) were negative and 14 (70%) were positive on urodynamics. Of the 14 positive urodynamics patients, 2 patients had no positive findings on transperineal ultrasound and the other 12 (60%) patients had the following findings as shown in Table (2). The ultrasound was in agreement with urodynamics diagnosis in nine cases (75%) patients. In three cases (25%) patients there was disagreement between urodynamics and ultrasound. From these three patients (two cases) 16% patients were diagnosed by ultrasound as having both urethral hypermobility and ISD, and one case (8%) of urethral hypermobility only, with no agreement to ALPP (>60cm H 2 O) that is seen on urodynamic study. Hence the ultrasound was 100% in agreement with urodynamics diagnosis in patients with intrinsic sphincter deficiency. 71.5% in patients with both urethral hypermobility and intrinsic sphincter deficiency (Fig. 5), while 66.7% in patients with urethral hypermobility only. Urethral luminal diamter and wall thickness Fig. (3): TPUS (sagittal and axial) demonstrates decreased urethral wall thickness (34mm) and increased in urethral diameter (77mm) with normal PUVA and rotational angle in 45Y incontinent women with ISD (group B) seen by U/S and an agreement to ALPP <60cm H 2 O that is seen on urodynamic study. PUVA Rotational angle Fig. (4): Urethral hypermobility and ISD (group C) seen by U/S in (both resting and straining) with an agreement to ALPP <60cm H 2 O on urodynamic study.
5 Manal H. Wahba, et al. 235 (A) (B) (C) (D) Fig. (5): TPUS showing increase in urethral diameter (60mm) A- And decreased urethral wall thickness (35mm) in B- As well as widening of the PUVA (152 degrees) C- And increased rotational movement (118 degrees) in D- US findings consistent with that of urethral hypermobility and ISD with an agreement to ALPP <60cm H 2 O that is seen on urodynamic study. Table (2): Number of patients with positive urodynamic study in the three groups classified according to the ultrasonographic findings. Patients group ALPP <60mm H 2 O Urodynamic examination Detrouser instability Low bladder capacity No finding Group A 2 (10%) 2 (10%) 1 (5%) Group B 2 (10%) 2 (10%) Group C 5 (25%) 3 (15%) 2 (10%) 2 (10%) Discussion Urinary incontinence is a bothersome condition for many women, with an overall prevalence of approximately 40%. Stress, urge, and mixed urinary incontinence are the most common subtypes of urinary incontinence [1]. On clinical examination, bladder neck mobility assessment in the study of patients with urinary incontinence is mandatory. The Q-tip test does not produce reliable results [10]. Significant anatomical changes on cystourethrography in SUI patients were recognized as long as 50 years ago. These changes included loss of the normal PUV angle (90-100º), so that the base of the bladder and the urethra are in line; funneling of the UV junction; and increased downward movement of the bladder base and rotation of the urethra on straining [6]. A video urodynamic study is still an expensive method to use routinely. Magnetic resonance imaging is another viable alternative but has not widely used in the investigation of urinary incontinence. For all these reasons, ultrasonography is the principal modality for studies of the anatomy and functionality of the lower urinary tract in patients with a history of urinary leakage [11] Together with history, clinical examination and urodynamics, it has been shown to improve the accuracy of the diagnosis of the functional and morphological disorder [6].
6 236 The Functional Role of Transperineal Ultrasound in the Evaluation Ultrasonography in the evaluation of urinary incontinence is an easy, inexpensive technique, and it is considered comfortable for most patients. Nowadays, it is becoming more widespread as a complementary examination in diagnostic investigations. In contrast to other radiologic techniques, it is a noninvasive procedure without exposure to X-ray hazards and with similar or even superior outcomes [11] Perineal ultrasound especially has given good visualization of the bladder, bladder base, urethrovesical (UV) junction and the symphysis pubis [5]. In contrast to urodynamic evaluation, this technique enables the lesion causing the incontinence to be seen in real time (Fig. 4). It is possible to see the posterior caudal movement of the urethrovesical junction and therefore to visualize urethral hypermobility [12]. This study shows the main morphological changes in UI with group A (urethral hypermobility) was increased posterior vesicle angle, increased rotational angle and funneling of the bladder neck. This was compatible with Chen et al., 2006 [7] who reported that, serial reports have indicated that the morphological features of UI are change in urethral angles, funneling of the bladder neck, and location of the urethrovesical junction being at the most dependent point of the lower urinary tract also César et al., 2011 [12] found that is possible to see the posterior caudal movement of the urethrovesical junction and therefore to visualize urethral hypermobility. Intrinsic sphincter deficiency results from inadequate coaptation and compression due to loss of muscle strength and volume. In intrinsic sphincter deficiency, there is malfunction of the sphincter itself, which leads to an open vesical neck at rest and a low Valsalva leak point pressure [13]. Urethral hypermobility results from weakening of urethra supporting structures leading to downward displacement and rotation of the urethra. Both conditions lead to stress urinary incontinence, which results in leakage of urine with increase in intraabdominal pressure when the urethra opens concomitantly, such as during a cough, strain, laugh, or exercise. Most patients have elements of both disorders in varying degrees [14]. In our results we found the presence of high association of urinary incontinence with urethral hypermobility associated with intrinsic sphincter deficiency in group C (hypermobility and ISD) which they represented most of the positive ultrasonographic cases in our study. This finding also reported in the study of Arriola et al., [15] as they found a high association of stress urinary incontinence with urethral hypermobility associated with intrinsic sphincter deficiency. We also found that most of our cases who were positive by perineal Ultrasound with a significant urethral hypermobility, this was supported by Lavanga et al., 2000 [16] and Antovska [17] who reported a significant degree of urethral axis rotation in most of the patients group with incontinence compared to healthy individuals. Oliveira et al., [11] reported that, urethral diameter values greater than 6mm highly suggest the presence of ISD, with accuracy evaluated around 84%. This was compatible with this study with accuracy about 82% related to urodynamic study. We found there was no correlation between hypermobility of the bladder neck with findings of leak point pressure that was seen in group A. However, the urethral diameter showed a positive correlation with leak point pressure values of less than 60cm H 2 O seen in group B (ISD) and the same results had been described by Dietz and Clarke, 2001 [18] and also this finding was compatible with Oliveira et al., 2006 whose reported that, the hypermobility of the bladder neck did not correlate with findings of leak point pressure, however, the urethral diameter showed a positive correlation with leak point pressure values of less than 60cm H 2 O. In conclusion, together with history, clinical examination and urodynamics, perineal ultrasound has been shown to improve the accuracy of the diagnosis of the functional and morphological disorder. In our study we found that the main morphological changes seen in UI were increase in the posterior vesicle angle and rotational angle, bladder neck descent, funneling of the bladder neck in group and a reduction of the urethral wall thickness and increased in its luminal diameter. The highest association between a reduction of the urethral wall thickness and increased its luminal diameter seen by perineal ultrasound with decreased in ALPP <60mm H 2 O on urodynamic study was seen in patients group B (ISD). We are aware of the limitation of this study in the form of relatively small number of patients and further future study with large number of patients is recommended. Conclusion: Together with history, clinical examination and urodynamics, transperineal ultrasound has been shown to improve the accuracy of the diagnosis
7 Manal H. Wahba, et al. 237 of the functional and morphological disorder. It is an easy, inexpensive technique, and it is considered comfortable for most patients. In our study we were found that the PU is easy, inexpensive technique, and it is considered comfortable for most patients. Now it becomes more widespread as a complementary examination in diagnostic investigations in UI. The main morphological changes seen was widening of the posterior vesical angle, increased anterior urethrovesical angle, displacement of the bladder neck, funneling of the bladder neck, decreased urethral wall thickness and vascularity and increased urethral luminal diameter. And from our study for those 20 patients, there were 75% patients with MUI and 25% patients with SUI diagnosed clinically. We found the accuracy of PU in the diagnosis of UI was 82%. The highest agreements (100%) between decrease in the urethral wall thickness with it is hypovascularity and increased in the urethral diameter with the decreased in the ALPP (<60mm H 2 O) was seen in group A (ISD) while the lowest agreements (66.7%) was seen in group B (hypermobility only group). References 1- MCNANLEY A.R., DUECY E.E., GUNHILDE M., et al.: Symptom-based, clinical, and urodynamic diagnoses of urinary incontinence: Female Pelvic Med. Reconstr Surg., (16): , BUCKLEY B.S. and LAPITAN M.C.: Prevalence of urinary incontinence in men, women, and children current evidence: Findings of the fourth international consultation on incontinence. AU, epidemiology committee of the fourth international consultation on incontinence, Paris SO Urology, 76 (2): 265, DELANCEY J.O., CARDOZO L. and STASKIN D.: Textbook of female urology and urogynecology. 1 st ed. london: Isis Medical Media., , SENDAG F., VIDINLI H., KAZANDI M., et al.: Role of perineal sonography in the evaluation of patients with stress urinary incontinence. Australian and new zealand Journal of Radiology of Obstetric and Gynecology, 43: 54-57, NOVARA G. and ARTIBANI W.: Imaging for urinary incontinence-a contemporary perspective: Current Opinionin Urology, (16): , VIRTANEN H.S. and KIILHOLMA: Urogynecologic ultrasound is a useful aid in the assessment of female stress urinary incontinence-a prospective study with TVT Procedure: Int. Urogynecol. J., 13: , CHEN H.Y., HUANG Y.L., HUNG Y.C., et al.: Evaluation of stress urinary incontinence by computer-aided vectorbased perineal ultrasound: Acta. Obstetricia et Gynecologica., 85: , PILONI V.L. and SPASSAFUMO L.: Sonography of the female pelvic floor: Pelviperineology, 26: 59-65, ARTIBANI W. and CERRUTO M.A.: The role of imaging in urinary incontinence. BJU Int., 95: , MANIAM P. and GOLDMAN H.B.: Removal of transurethral catheter during urodynamics may unmask stress urinary incontinence. J. Urol., 167: 171, OLIVEIRA F.R., RAMOS J.G. and COSTA S.M.: Translabial ultrasonography in the assessment of urethral diameter and intrinsic urethral sphincter deficiency. American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine, 25: , CÉSAR R.R.L., CÉSAR F.R.L., ROSALES E.A., et al.: Ultrasonography in female non-neurological urinary incontinence evaluation. Rev. Mex. Urol., 71 (6): , MACURA K.J., GENADRY R.R. and BLUEMKE D.A.: MR imaging of the female urethra and supporting ligaments in assessment of urinary incontinence: Spectrum of Abnormalities. Continuing medical education. Radiographics., 26: , SANTIAGU S.K., ARIANAYAGAM M., WANG A., et al.: Urinary incontinence pathophysiology and management outline. Australian Family Physician, 3 7: , ARRIOLA A.P., DALENZ V. S. and SCHANZ P.J.: Study of female urinary incontinence with single channel urodynamics. Comparison of the symptoms on admission. Neurological and Urodinamic Urology, 62 (2): , LAVANGA M., CHIONO L., SCHENONE M., et al.: Translabial ultrasonography in the diagnosis of stress urinary incontinence in women. Arch. Ital. Urol. Andrology, 72: , ANTOVSKA V.S.: Ultrasound characteristics of patients with urinary stress incontinence with or without genital Prolapse. Korean. J. Urol. October., 53 (10): , DIETZ H.P. and CLARKE B.: The urethral pressure profile and ultrasound imaging of the lower urinary tract. Int. Urogynecol J. Pelvic. Floor. Dysfunction, 12: 38-41, 2001.
Iraqi JMS. Perineal Ultrasound for Evaluating Bladder Neck and Urethra in Stress Urinary Incontinence
 Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine ISSN 1681-6579 Email: iraqi_jms_alnahrain @yahoo.com http://www.colmed-nahrain.edu.iq/ Perineal Ultrasound for Evaluating Bladder Neck and Urethra
Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine ISSN 1681-6579 Email: iraqi_jms_alnahrain @yahoo.com http://www.colmed-nahrain.edu.iq/ Perineal Ultrasound for Evaluating Bladder Neck and Urethra
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2010 January 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2009 February ; 20(2): 171 175. doi:10.1007/ s00192-008-0738-0. The Cough Game : Are there
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2009 February ; 20(2): 171 175. doi:10.1007/ s00192-008-0738-0. The Cough Game : Are there
Guide to Pelvic Floor Multicompartment Scanning
 Guide to Pelvic Floor Multicompartment Scanning These guidelines have been prepared by Giulio A. Santoro, MD, PhD, Head Pelvic Floor Unit, Section of Anal Physiology and Ultrasound, Coloproctology Service,
Guide to Pelvic Floor Multicompartment Scanning These guidelines have been prepared by Giulio A. Santoro, MD, PhD, Head Pelvic Floor Unit, Section of Anal Physiology and Ultrasound, Coloproctology Service,
Pathophysiological Rationale for Surgical Treatments of Stress Urinary Incontinence
 Pathophysiological Rationale for Surgical Treatments of Stress Urinary Incontinence Urology Grand Rounds April 6, 2005 Herman Christopher Kwan R4 A familiar case? 62 year old female initial presentation
Pathophysiological Rationale for Surgical Treatments of Stress Urinary Incontinence Urology Grand Rounds April 6, 2005 Herman Christopher Kwan R4 A familiar case? 62 year old female initial presentation
Urodynamics in women. Aims of Urodynamics in women. Why do Urodynamics?
 Urodynamics in women Chendrimada Madhu MD, MA, MRCOG Subspecialty Trainee in Urogynaecology Southmead Hospital 2013 Aims of Urodynamics in women n Confirmation of incontinence and its cause n Definition
Urodynamics in women Chendrimada Madhu MD, MA, MRCOG Subspecialty Trainee in Urogynaecology Southmead Hospital 2013 Aims of Urodynamics in women n Confirmation of incontinence and its cause n Definition
Review Article Pelvic Floor Dysfunction, Body Excreta Incontinence and Continence
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS GYNAECOLOGY Review Article Pelvic Floor Dysfunction, Body Excreta Incontinence and Continence Abdel Karim M El Hemaly 1 * and Laila ASE Mousa 1 1 Professor of Obstetrics and gynaecology,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS GYNAECOLOGY Review Article Pelvic Floor Dysfunction, Body Excreta Incontinence and Continence Abdel Karim M El Hemaly 1 * and Laila ASE Mousa 1 1 Professor of Obstetrics and gynaecology,
Treatment Outcomes of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion
 Are the Treatment Outcomes of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion the Same for Patients with Stress Urinary Incontinence with or without Intrinsic Sphincter Deficiency? A Retrospective Study in Hong Kong
Are the Treatment Outcomes of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion the Same for Patients with Stress Urinary Incontinence with or without Intrinsic Sphincter Deficiency? A Retrospective Study in Hong Kong
Pelvic Floor Ultrasound Imaging. Prof HP Dietz (Sydney) A/Prof KL Shek (Sydney) Dr R Guzman Rojas (Santiago de Chile) Dr Kamil Svabik (Prague)
 Pelvic Floor Ultrasound Imaging Workshop IUGA 2015 Nice Faculty: Prof HP Dietz (Sydney) A/Prof KL Shek (Sydney) Dr R Guzman Rojas (Santiago de Chile) Dr Kamil Svabik (Prague) The use of translabial ultrasound
Pelvic Floor Ultrasound Imaging Workshop IUGA 2015 Nice Faculty: Prof HP Dietz (Sydney) A/Prof KL Shek (Sydney) Dr R Guzman Rojas (Santiago de Chile) Dr Kamil Svabik (Prague) The use of translabial ultrasound
Prediction and prevention of stress urinary incontinence after prolapse surgery van der Ploeg, J.M.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Prediction and prevention of stress urinary incontinence after prolapse surgery van der Ploeg, J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Prediction and prevention of stress urinary incontinence after prolapse surgery van der Ploeg, J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van
Ultrasound imaging of the lower urinary system in women after Burch colposuspension
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001; 17: 58 64 Ultrasound imaging of the lower urinary system in Blackwell Original Paper Science, Ltd women after Burch colposuspension A. MARTAN, J. MASATA, M. HALASKA and
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001; 17: 58 64 Ultrasound imaging of the lower urinary system in Blackwell Original Paper Science, Ltd women after Burch colposuspension A. MARTAN, J. MASATA, M. HALASKA and
Video-urodynamics. P J R Shah Institute of Urology and UCH
 Video-urodynamics P J R Shah Institute of Urology and UCH Bladder Function Storage Capacity and Pressure Emptying Pressure/flow/emptying URODYNAMIC INVESTIGATIONS Free urine flow rate Urethral pressure
Video-urodynamics P J R Shah Institute of Urology and UCH Bladder Function Storage Capacity and Pressure Emptying Pressure/flow/emptying URODYNAMIC INVESTIGATIONS Free urine flow rate Urethral pressure
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics
 International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics COMMITTEE FOR UROGYNAECOLOGY AND PELVIC FLOOR MEMBER: TSUNG-HSIEN (CHARLES) SU, CHAIR (TAIWAN) DAVID RICHMOND, CO-CHAIR (UK) CHITTARANJAN PURANDARE,
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics COMMITTEE FOR UROGYNAECOLOGY AND PELVIC FLOOR MEMBER: TSUNG-HSIEN (CHARLES) SU, CHAIR (TAIWAN) DAVID RICHMOND, CO-CHAIR (UK) CHITTARANJAN PURANDARE,
Ultrasonic Assessment of the Internal Urethral Sphincter in Stress Urinary Incontinence
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics Volume 2 Number 1 Ultrasonic Assessment of the Internal Urethral Sphincter in Stress Urinary Incontinence I Kandil, A El Hemaly, M Radwan Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics Volume 2 Number 1 Ultrasonic Assessment of the Internal Urethral Sphincter in Stress Urinary Incontinence I Kandil, A El Hemaly, M Radwan Citation
Brief involuntary urine loss associated with an increase in abdominal pressure. Pathophysiology of Stress Urinary Incontinence Edward J.
 TREATMENT OF SUI Pathophysiology of Stress Urinary Incontinence Edward J. McGuire, MD Department of Urology, University of Michigan Medical Center, Ann Arbor, MI All cases of stress urinary incontinence
TREATMENT OF SUI Pathophysiology of Stress Urinary Incontinence Edward J. McGuire, MD Department of Urology, University of Michigan Medical Center, Ann Arbor, MI All cases of stress urinary incontinence
Practical urodynamics What PA s need to know. Gary E. Lemack, MD Professor of Urology and Neurology
 Practical urodynamics What PA s need to know Gary E. Lemack, MD Professor of Urology and Neurology Urodynamics essential elements Urethral catheter Fill rate Catheter size Intravesical pressure measurements
Practical urodynamics What PA s need to know Gary E. Lemack, MD Professor of Urology and Neurology Urodynamics essential elements Urethral catheter Fill rate Catheter size Intravesical pressure measurements
URINARY INCONTINENCE. Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
 URINARY INCONTINENCE Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition The involuntary loss of urine May denote a symptom, a sign or a condition Symptom the
URINARY INCONTINENCE Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition The involuntary loss of urine May denote a symptom, a sign or a condition Symptom the
3D Dynamic Ultrasound In Obstructed Defecation
 3D Dynamic Ultrasound In Obstructed Defecation By Ramy Salahudin Abdelkader Assist. Lecturer of General Surgery Cairo University Introduction Pelvic floor is complex system, with passive and active components
3D Dynamic Ultrasound In Obstructed Defecation By Ramy Salahudin Abdelkader Assist. Lecturer of General Surgery Cairo University Introduction Pelvic floor is complex system, with passive and active components
The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence. Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations
 The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations Dr Oseka Onuma Gynaecologist and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgeon 4 Robe Terrace Medindie SA 5081 Urinary incontinence has
The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations Dr Oseka Onuma Gynaecologist and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgeon 4 Robe Terrace Medindie SA 5081 Urinary incontinence has
Association between Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of the Pelvic Floor and de novo Stress Urinary Incontinence after Vaginal Delivery
 Original Article Genitourinary Imaging https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.4.715 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2018;19(4):715-723 Association between Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings
Original Article Genitourinary Imaging https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.4.715 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2018;19(4):715-723 Association between Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings
Management of Female Stress Incontinence
 Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
Imaging of Pelvic Floor Weakness. Dr Susan Kouloyan-Ilic Radiologist Epworth Medical Imaging The Women s, Melbourne
 Imaging of Pelvic Floor Weakness Dr Susan Kouloyan-Ilic Radiologist Epworth Medical Imaging The Women s, Melbourne Outline Overview and Epidemiology Risk Factors, Causes and Results Review of Relevant
Imaging of Pelvic Floor Weakness Dr Susan Kouloyan-Ilic Radiologist Epworth Medical Imaging The Women s, Melbourne Outline Overview and Epidemiology Risk Factors, Causes and Results Review of Relevant
Objectives. Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS
 URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
Ultrasound Characteristics of Patients with Urinary Stress Incontinence with or without Genital Prolapse
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2012.53.10.691 Voiding Dysfunction Ultrasound Characteristics of Patients with Urinary Stress Incontinence with or without Genital Prolapse Vesna S. Antovska
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2012.53.10.691 Voiding Dysfunction Ultrasound Characteristics of Patients with Urinary Stress Incontinence with or without Genital Prolapse Vesna S. Antovska
Differences in Pelvic Floor Morphology Between Continent, Stress Urinary Incontinent, and Mixed Urinary Incontinent Elderly Women: An MRI Study
 Neurourology and Urodynamics 35:515 521 (2016) Differences in Pelvic Floor Morphology Between Continent, Stress Urinary Incontinent, and Mixed Urinary Incontinent Elderly Women: An MRI Study Stephanie
Neurourology and Urodynamics 35:515 521 (2016) Differences in Pelvic Floor Morphology Between Continent, Stress Urinary Incontinent, and Mixed Urinary Incontinent Elderly Women: An MRI Study Stephanie
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (April 2018) Vol. 71 (3), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (April 2018) Vol. 71 (3), Page 2742-2750 Role of dynamic MRI in assessment of Pelvic Floor Dysfunction in Females Nada Ahmed Hussein, Naglaa Hussein Shebrya, Nermeen
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (April 2018) Vol. 71 (3), Page 2742-2750 Role of dynamic MRI in assessment of Pelvic Floor Dysfunction in Females Nada Ahmed Hussein, Naglaa Hussein Shebrya, Nermeen
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Urodynamics. Technique Development and Preliminary Results
 Neurourology Magnetic Resonance maging Urodynamics nternational Braz J Urol Vol. 32 (3): 336-341, May - June, 2006 Magnetic Resonance maging Urodynamics. Technique Development and Preliminary Results Gustavo
Neurourology Magnetic Resonance maging Urodynamics nternational Braz J Urol Vol. 32 (3): 336-341, May - June, 2006 Magnetic Resonance maging Urodynamics. Technique Development and Preliminary Results Gustavo
REVIEW OF CAUSES, EVALUATION, AND TREATMENTS URINARY INCONTINENCE 101
 REVIEW OF CAUSES, EVALUATION, AND TREATMENTS URINARY INCONTINENCE 101 March 5, 2014 Kevin E Miller, MD Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Kansas School of Medicine- Wichita URINARY INCONTINENCE
REVIEW OF CAUSES, EVALUATION, AND TREATMENTS URINARY INCONTINENCE 101 March 5, 2014 Kevin E Miller, MD Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Kansas School of Medicine- Wichita URINARY INCONTINENCE
Urogynecology in EDS. Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018
 Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence
 Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Judith A. Thompson & Peter B. O Sullivan & N. Kathryn Briffa & Patricia Neumann
 Int Urogynecol J (2007) 18:779 786 DOI 10.1007/s00192-006-0225-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of transperineal and transabdominal ultrasound in the assessment of voluntary pelvic floor muscle contractions
Int Urogynecol J (2007) 18:779 786 DOI 10.1007/s00192-006-0225-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of transperineal and transabdominal ultrasound in the assessment of voluntary pelvic floor muscle contractions
Center for Reconstructive Urethral Surgery Guido Barbagli Center for Reconstructive Urethral Surgery Arezzo - Italy
 Guido Barbagli Arezzo - Italy E-mail: guido@rdn.it Website: www.urethralcenter.it 23 rd ANNUAL EAU CONGRESS Sub-plenary Session on Male urinary incontinence 26 29 March 2008 Milan Italy Incontinence following
Guido Barbagli Arezzo - Italy E-mail: guido@rdn.it Website: www.urethralcenter.it 23 rd ANNUAL EAU CONGRESS Sub-plenary Session on Male urinary incontinence 26 29 March 2008 Milan Italy Incontinence following
Urinary Incontinence. Lora Keeling and Byron Neale
 Urinary Incontinence Lora Keeling and Byron Neale Not life threatening. Introduction But can have a huge impact on quality of life. Two main types of urinary incontinence (UI). Stress UI leakage on effort,
Urinary Incontinence Lora Keeling and Byron Neale Not life threatening. Introduction But can have a huge impact on quality of life. Two main types of urinary incontinence (UI). Stress UI leakage on effort,
Normal micturition involves complex
 NEW TARGET FOR INTERVENTION: THE NEUROUROLOGY CONNECTION * Donald R. Ostergard, MD, FACOG ABSTRACT Urine storage and release are under the control of the parasympathetic, sympathetic, and somatic nervous
NEW TARGET FOR INTERVENTION: THE NEUROUROLOGY CONNECTION * Donald R. Ostergard, MD, FACOG ABSTRACT Urine storage and release are under the control of the parasympathetic, sympathetic, and somatic nervous
Comprehensive 3D Pelvic Floor Ultrasonography with emphasis on endovaginal (EVUS) and endoanal imaging (EAUS) W44, 30 August :00-18:00
 Comprehensive 3D Pelvic Floor Ultrasonography with emphasis on endovaginal (EVUS) and endoanal imaging (EAUS) W44, 30 August 2011 14:00-18:00 Start End Topic Speakers 14:00 14:10 Introduction: Pre-test,
Comprehensive 3D Pelvic Floor Ultrasonography with emphasis on endovaginal (EVUS) and endoanal imaging (EAUS) W44, 30 August 2011 14:00-18:00 Start End Topic Speakers 14:00 14:10 Introduction: Pre-test,
Functional anatomy of the female pelvic floor and lower urinary tract Stefano Floris, MD, PhD Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology
 Functional anatomy of the female pelvic floor and lower urinary tract Stefano Floris, MD, PhD Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Ospedale San Giovanni di Dio, Gorizia, Italy ANATOMY URINARY CONTINENCE
Functional anatomy of the female pelvic floor and lower urinary tract Stefano Floris, MD, PhD Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Ospedale San Giovanni di Dio, Gorizia, Italy ANATOMY URINARY CONTINENCE
The significance of urethral hyperechogenicity in female lower urinary tract symptoms
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004; 24: 67 71 Published online 8 June 2004 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1067 The significance of urethral hyperechogenicity in female
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004; 24: 67 71 Published online 8 June 2004 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1067 The significance of urethral hyperechogenicity in female
Diagnosis of cystocele type by clinical examination and pelvic floor ultrasound
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2012; 39: 710 714 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.10156 Diagnosis of cystocele type by clinical examination and pelvic floor
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2012; 39: 710 714 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.10156 Diagnosis of cystocele type by clinical examination and pelvic floor
Various Types. Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG
 Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
Modern methods of imaging in urogynecology when do we really need them?
 Archives of Perinatal Medicine 23(2), 77 81, 2017 ORIGINAL PAPER Modern methods of imaging in urogynecology when do we really need them? GRZEGORZ SURKONT, EDYTA WLAŹLAK Abstract Imaging is more often used
Archives of Perinatal Medicine 23(2), 77 81, 2017 ORIGINAL PAPER Modern methods of imaging in urogynecology when do we really need them? GRZEGORZ SURKONT, EDYTA WLAŹLAK Abstract Imaging is more often used
Evaluation of Urethrovesical Junction Mobility by Perineal Ultrasonography in Stress Urinary Incontinence
 Evaluation of Urethrovesical Junction Mobility by Perineal Ultrasonography in Stress Urinary Incontinence Pages with reference to book, From 2 To 5 Fuat Demirci, Umur Kuyumcuoglu, Melunet Uludogan, Husnu
Evaluation of Urethrovesical Junction Mobility by Perineal Ultrasonography in Stress Urinary Incontinence Pages with reference to book, From 2 To 5 Fuat Demirci, Umur Kuyumcuoglu, Melunet Uludogan, Husnu
q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 1 WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT YOUR DIAGNOSIS OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE
 493495.q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 1 WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT YOUR DIAGNOSIS OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE 493495.q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 2 What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? Urinary
493495.q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 1 WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT YOUR DIAGNOSIS OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE 493495.q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 2 What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? Urinary
Tape functionality: position, change in shape, and outcome after TVT procedure mid-term results
 Int Urogynecol J (2010) 21:795 800 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1119-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tape functionality: position, change in shape, and outcome after TVT procedure mid-term results Jacek Kociszewski & Oliver
Int Urogynecol J (2010) 21:795 800 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1119-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tape functionality: position, change in shape, and outcome after TVT procedure mid-term results Jacek Kociszewski & Oliver
NEWER DIMENSIONS IN THE EVALUATION OF PELVIC PATHOLOGY BY TRANSPERINEAL ULTRASONOGRAPHY S. C. Sanjay 1, N. Krishnappa 2, Anil Kumar Shukla 3
 NEWER DIMENSIONS IN THE EVALUATION OF PELVIC PATHOLOGY BY TRANSPERINEAL ULTRASONOGRAPHY S. C. Sanjay 1, N. Krishnappa 2, Anil Kumar Shukla 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: S. C. Sanjay, N. Krishnappa, Anil
NEWER DIMENSIONS IN THE EVALUATION OF PELVIC PATHOLOGY BY TRANSPERINEAL ULTRASONOGRAPHY S. C. Sanjay 1, N. Krishnappa 2, Anil Kumar Shukla 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: S. C. Sanjay, N. Krishnappa, Anil
PELVIC FLOOR ULTRASOUND
 PELVIC FLOOR ULTRASOUND How, When, Why Part 1: Phyllis Glanc MD Sunnybrook Health Science Center University of Toronto Phyllis.Glanc@sunnybrook.ca www.phyllisglanc.com (current exact handout) Disclosures
PELVIC FLOOR ULTRASOUND How, When, Why Part 1: Phyllis Glanc MD Sunnybrook Health Science Center University of Toronto Phyllis.Glanc@sunnybrook.ca www.phyllisglanc.com (current exact handout) Disclosures
Leak point pressures: how useful are they?
 REVIEW C URRENT OPINION Leak point pressures: how useful are they? Helena Burden, Katherine Warren, and Paul Abrams Purpose of review The present article reviews the literature from the last 12 months
REVIEW C URRENT OPINION Leak point pressures: how useful are they? Helena Burden, Katherine Warren, and Paul Abrams Purpose of review The present article reviews the literature from the last 12 months
What the radiologists should know about US and MR findings of female urinary incontinence surgical tapes.
 What the radiologists should know about US and MR findings of female urinary incontinence surgical tapes. Poster No.: C-0744 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: T. Robba, L. Squintone,
What the radiologists should know about US and MR findings of female urinary incontinence surgical tapes. Poster No.: C-0744 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: T. Robba, L. Squintone,
Dynamic rehabilitative ultrasound for pelvic floor disorders Introduction in techniques and hands-on-workshop
 Dynamic rehabilitative ultrasound for pelvic floor disorders Introduction in techniques and hands-on-workshop Bärbel Junginger, B.Sc. /physiotherapist, manualtherapist (IFOMPT) Kaven Baessler, MD, PhD
Dynamic rehabilitative ultrasound for pelvic floor disorders Introduction in techniques and hands-on-workshop Bärbel Junginger, B.Sc. /physiotherapist, manualtherapist (IFOMPT) Kaven Baessler, MD, PhD
Ralph & Berryl Goldman Fellowship in Neuro urology, voiding dysfunction and bladder reconstruction
 Ralph & Berryl Goldman Fellowship in Neuro urology, voiding dysfunction and bladder reconstruction Length of fellowship: A 1 year Fellowship: This fellowship has been designed for Urology or Gynecology
Ralph & Berryl Goldman Fellowship in Neuro urology, voiding dysfunction and bladder reconstruction Length of fellowship: A 1 year Fellowship: This fellowship has been designed for Urology or Gynecology
Renal Trauma: Management Options
 Renal Trauma: Management Options Immediate surgical repair Nephrectomy Conservative management Alonso RC et al. Kidney in Danger: CT Findings of Blunt and Penetrating Renal Trauma. RadioGraphics 2009;
Renal Trauma: Management Options Immediate surgical repair Nephrectomy Conservative management Alonso RC et al. Kidney in Danger: CT Findings of Blunt and Penetrating Renal Trauma. RadioGraphics 2009;
Operative Approach to Stress Incontinence. Goals of presentation. Preoperative evaluation: Urodynamic Testing? Michelle Y. Morrill, M.D.
 Operative Approach to Stress Incontinence Goals of presentation Michelle Y. Morrill, M.D. Director of Urogynecology The Permanente Medical Group Kaiser, San Francisco Review preoperative care & evaluation
Operative Approach to Stress Incontinence Goals of presentation Michelle Y. Morrill, M.D. Director of Urogynecology The Permanente Medical Group Kaiser, San Francisco Review preoperative care & evaluation
The Urethral Motion Profile Before and After Suburethral Sling Placement
 The Urethral Motion Profile Before and After Suburethral Sling Placement Ka Lai Shek,* Varisara Chantarasorn and Hans Peter Dietz From the Nepean Clinical School, University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia
The Urethral Motion Profile Before and After Suburethral Sling Placement Ka Lai Shek,* Varisara Chantarasorn and Hans Peter Dietz From the Nepean Clinical School, University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia
Pelvic Floor Exercise. Brigi0e Fung Physiotherapist
 Pelvic Floor Exercise Brigi0e Fung Physiotherapist Treatment for urinary incontinence Pelvic floor muscle exercise (Kegel, 1948) Bladder retraining Behaviour modification Treatment for urinary incontinence
Pelvic Floor Exercise Brigi0e Fung Physiotherapist Treatment for urinary incontinence Pelvic floor muscle exercise (Kegel, 1948) Bladder retraining Behaviour modification Treatment for urinary incontinence
Neurogenic bladder. Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder.
 Definition: Neurogenic bladder Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder. Types: Nervous system diseases: Congenital: like myelodysplasia like meningocele.
Definition: Neurogenic bladder Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder. Types: Nervous system diseases: Congenital: like myelodysplasia like meningocele.
Clinical Curriculum: Urogynecology
 Updated July 201 Clinical Curriculum: Urogynecology GOAL: The primary goal of the Urogynecology rotation at the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB) is to train physicians to have a broad knowledge
Updated July 201 Clinical Curriculum: Urogynecology GOAL: The primary goal of the Urogynecology rotation at the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB) is to train physicians to have a broad knowledge
Bill Landry BScPT, BScH, MCPA, CAFCI Family Physiotherapy Centre of London
 Bill Landry BScPT, BScH, MCPA, CAFCI blandry@fpclondon.com Family Physiotherapy Centre of London Objectives To describe the scope of post-prostatectomy incontinence To describe what s been done To provide
Bill Landry BScPT, BScH, MCPA, CAFCI blandry@fpclondon.com Family Physiotherapy Centre of London Objectives To describe the scope of post-prostatectomy incontinence To describe what s been done To provide
Guido Barbagli. Center for Reconstructive ti Urethral lsurgery
 Guido Barbagli Center for Reconstructive ti Urethral lsurgery Arezzo - Italy E-mail: guido@rdn.it Website: www.urethralcenter.it Dedicated to Ruggero Lenzi, teacher and friend. His passing was a great
Guido Barbagli Center for Reconstructive ti Urethral lsurgery Arezzo - Italy E-mail: guido@rdn.it Website: www.urethralcenter.it Dedicated to Ruggero Lenzi, teacher and friend. His passing was a great
The Significance of Beaking Sign on Cystography in Stress Urinary Incontinence 1
 The Significance of Beaking Sign on Cystography in Stress Urinary Incontinence 1 Jae Won Kim, M.D., Jeong Kon Kim, M.D., Seung Soo Lee, M.D., Yu-Ri Kahng, M.D., Myung-Soo Choo, M.D. 2, Kyoung-Sik Cho,
The Significance of Beaking Sign on Cystography in Stress Urinary Incontinence 1 Jae Won Kim, M.D., Jeong Kon Kim, M.D., Seung Soo Lee, M.D., Yu-Ri Kahng, M.D., Myung-Soo Choo, M.D. 2, Kyoung-Sik Cho,
Clinical Study Perineal Ultrasound as a Complement to POP-Q in the Assessment of Cystoceles
 BioMed Research International, Article ID 740925, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/740925 Clinical Study Perineal Ultrasound as a Complement to POP-Q in the Assessment of Cystoceles Laila Najjari,
BioMed Research International, Article ID 740925, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/740925 Clinical Study Perineal Ultrasound as a Complement to POP-Q in the Assessment of Cystoceles Laila Najjari,
What you should know about your diagnosis of incontinence
 What you should know about your diagnosis of incontinence What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? WHAT IS NORMAL URINARY FUNCTION? Urine is a normal waste product of the body that is manufactured by the kidneys
What you should know about your diagnosis of incontinence What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? WHAT IS NORMAL URINARY FUNCTION? Urine is a normal waste product of the body that is manufactured by the kidneys
LAPAROSCOPIC REPAIR OF PELVIC FLOOR
 LAPAROSCOPIC REPAIR OF PELVIC FLOOR Dr. R. K. Mishra Elements comprising the Pelvis Bones Ilium, ischium and pubis fusion Ligaments Muscles Obturator internis muscle Arcus tendineus levator ani or white
LAPAROSCOPIC REPAIR OF PELVIC FLOOR Dr. R. K. Mishra Elements comprising the Pelvis Bones Ilium, ischium and pubis fusion Ligaments Muscles Obturator internis muscle Arcus tendineus levator ani or white
Both the middle and distal sections of the urethra may be regarded as optimal targets for outside in transobturator tape placement
 DOI 10.1007/s00345-014-1261-1 Original Article Both the middle and distal sections of the urethra may be regarded as optimal targets for outside in transobturator tape placement Michał Bogusiewicz Marta
DOI 10.1007/s00345-014-1261-1 Original Article Both the middle and distal sections of the urethra may be regarded as optimal targets for outside in transobturator tape placement Michał Bogusiewicz Marta
Dana Alrafaiah. - Amani Nofal. - Ahmad Alsalman. 1 P a g e
 - 2 - Dana Alrafaiah - Amani Nofal - Ahmad Alsalman 1 P a g e This lecture will discuss five topics as follows: 1- Arrangement of pelvic viscera. 2- Muscles of Pelvis. 3- Blood Supply of pelvis. 4- Nerve
- 2 - Dana Alrafaiah - Amani Nofal - Ahmad Alsalman 1 P a g e This lecture will discuss five topics as follows: 1- Arrangement of pelvic viscera. 2- Muscles of Pelvis. 3- Blood Supply of pelvis. 4- Nerve
Prolapse and Urogynae Incontinence. Lucy Tiffin and Hannah Wheldon-Holmes
 Prolapse and Urogynae Incontinence Lucy Tiffin and Hannah Wheldon-Holmes 66 year old woman with incontinence PC: 7 year Hx of urgency, frequency, nocturia (incl. incontinence at night), and stress incontinence
Prolapse and Urogynae Incontinence Lucy Tiffin and Hannah Wheldon-Holmes 66 year old woman with incontinence PC: 7 year Hx of urgency, frequency, nocturia (incl. incontinence at night), and stress incontinence
Long-Term Outcome of the Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Female Urinary Incontinence: A 6-Year Follow-Up
 www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2010.51.6.409 Voiding Dysfunction Long-Term Outcome of the Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Female Urinary Incontinence: A 6-Year Follow-Up Jun Hyung Lee, Min Chul
www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2010.51.6.409 Voiding Dysfunction Long-Term Outcome of the Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Female Urinary Incontinence: A 6-Year Follow-Up Jun Hyung Lee, Min Chul
Parameters of two-dimensional perineal ultrasonography for evaluation of urinary incontinence after Radical Prostatectomy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 40 (5): 596-604, September - October, 2014 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.05.03 Parameters of two-dimensional perineal ultrasonography for evaluation of urinary incontinence after
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 40 (5): 596-604, September - October, 2014 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.05.03 Parameters of two-dimensional perineal ultrasonography for evaluation of urinary incontinence after
Introital ultrasound in the diagnosis of lower urinary tract symptoms following anti-incontinence surgery using a synthetic midurethral tape
 International Urogynecology Journal https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-018-3837-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introital ultrasound in the diagnosis of lower urinary tract symptoms following anti-incontinence surgery
International Urogynecology Journal https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-018-3837-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introital ultrasound in the diagnosis of lower urinary tract symptoms following anti-incontinence surgery
Special Thank You NO DISCLOSURES. Objectives. Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Role of Ultrasound Text
 Special Thank You Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Role of Ultrasound Phyllis Glanc Sunnybrook Health Sciences Center Department Medical Imaging Associate Professor, University of Toronto phyllis.glanc@sunnybrook.ca
Special Thank You Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Role of Ultrasound Phyllis Glanc Sunnybrook Health Sciences Center Department Medical Imaging Associate Professor, University of Toronto phyllis.glanc@sunnybrook.ca
Resolution of urge urinary incontinence with midurethral sling surgery in patients with mixed incontinence and low-pressure urethra
 Gynecol Surg (2012) 9:427 432 DOI 10.1007/s10397-012-0735-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Resolution of urge urinary incontinence with midurethral sling surgery in patients with mixed incontinence and low-pressure
Gynecol Surg (2012) 9:427 432 DOI 10.1007/s10397-012-0735-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Resolution of urge urinary incontinence with midurethral sling surgery in patients with mixed incontinence and low-pressure
PREVENTING URINARY INCONTINENCE through PELVIC FLOOR REHABILITATION in DISABLED ELDERLY
 PREVENTING URINARY INCONTINENCE through PELVIC FLOOR REHABILITATION in DISABLED ELDERLY Paolo DI BENEDETTO Lecturer, Tor Vergata University, Rome, Italy Former Director of Rehabilitation Department Institute
PREVENTING URINARY INCONTINENCE through PELVIC FLOOR REHABILITATION in DISABLED ELDERLY Paolo DI BENEDETTO Lecturer, Tor Vergata University, Rome, Italy Former Director of Rehabilitation Department Institute
IUGA : Introduction: Pre-test, Course objectives, clinical (Max 1000 words) and rationale for pelvic floor imaging S.
 IUGA WS 7 Workshop Outline Chairman: S. Abbas Shobeiri, MD (USA) IUGA Title of workshop Comprehensive 3D Pelvic Floor Ultrasonography with emphasis on endovaginal (EVUS) and endoanal imaging IU(EA (EAUS)
IUGA WS 7 Workshop Outline Chairman: S. Abbas Shobeiri, MD (USA) IUGA Title of workshop Comprehensive 3D Pelvic Floor Ultrasonography with emphasis on endovaginal (EVUS) and endoanal imaging IU(EA (EAUS)
Tools for Evaluation. Urodynamics Case Studies. Case 1. Evaluation. Case 1. Bladder Diary SUI 19/01/2018
 Urodynamics Case Studies Christopher K. Payne, MD Vista Urology & Pelvic Pain Partners Emeritus Professor of Urology, Stanford University Tools for Evaluation Ears, Eyes, and Brain Bladder diary Stress
Urodynamics Case Studies Christopher K. Payne, MD Vista Urology & Pelvic Pain Partners Emeritus Professor of Urology, Stanford University Tools for Evaluation Ears, Eyes, and Brain Bladder diary Stress
High-field (3T) magnetic resonance defecography with functional assessment of the evacuation phase: A pictorial essay
 High-field (3T) magnetic resonance defecography with functional assessment of the evacuation phase: A pictorial essay Poster No.: C-430 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal and
High-field (3T) magnetic resonance defecography with functional assessment of the evacuation phase: A pictorial essay Poster No.: C-430 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal and
A PATIENT GUIDE TO Understanding Stress Urinary Incontinence
 A PATIENT GUIDE TO Understanding Stress Urinary Incontinence Q: What is SUI? A: Stress urinary incontinence is defined as the involuntary leakage of urine. The problem afflicts approximately 18 million
A PATIENT GUIDE TO Understanding Stress Urinary Incontinence Q: What is SUI? A: Stress urinary incontinence is defined as the involuntary leakage of urine. The problem afflicts approximately 18 million
This information is intended as an overview only
 This information is intended as an overview only Please refer to the INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE included with this device for indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and other important information
This information is intended as an overview only Please refer to the INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE included with this device for indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and other important information
Bladder neck mobility in continent nulliparous women
 British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology March 2001, Vol. 108, pp. 320±324 Bladder neck mobility in continent nulliparous women Ursula M. Peschers a, *, Gabi Fanger b, Gabriel N. Schaer c, David B.
British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology March 2001, Vol. 108, pp. 320±324 Bladder neck mobility in continent nulliparous women Ursula M. Peschers a, *, Gabi Fanger b, Gabriel N. Schaer c, David B.
Clinical Study Cough Test during Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Preventing Postoperative Urinary Retention
 Advances in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 797854, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/797854 Clinical Study Cough Test during Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Preventing Postoperative Urinary
Advances in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 797854, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/797854 Clinical Study Cough Test during Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Preventing Postoperative Urinary
University of Alberta Reconstructive Urology Fellowship
 FACULTY OF MEDICINE AND DENTISTRY DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY DIVISION OF UROLOGY Keith Rourke, MD, FRCSC Reconstructive Urology Professor Chair of Academic Urology Reconstructive Urology Fellowship Director
FACULTY OF MEDICINE AND DENTISTRY DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY DIVISION OF UROLOGY Keith Rourke, MD, FRCSC Reconstructive Urology Professor Chair of Academic Urology Reconstructive Urology Fellowship Director
Levator Plate Upward Lift on Dynamic Sonography and Levator Muscle Strength
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Levator Plate Upward Lift on Dynamic Sonography and Levator Muscle Strength Ghazaleh Rostaminia, MD, Jennifer Peck, PhD, Lieschen Quiroz, MD, S. Abbas Shobeiri, MD Received December 4,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Levator Plate Upward Lift on Dynamic Sonography and Levator Muscle Strength Ghazaleh Rostaminia, MD, Jennifer Peck, PhD, Lieschen Quiroz, MD, S. Abbas Shobeiri, MD Received December 4,
Abstract. Introduction
 Original article doi:10.1111/codi.12740 Assessment of pubovisceral muscle defects and levator hiatal dimensions in women with faecal incontinence after vaginal delivery: is there a correlation with severity
Original article doi:10.1111/codi.12740 Assessment of pubovisceral muscle defects and levator hiatal dimensions in women with faecal incontinence after vaginal delivery: is there a correlation with severity
How can we measure bladder volumes in women with advanced pelvic organ prolapse?
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 215; 46: 233 238 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 1.12/uog.14678 How can we measure bladder volumes in women with advanced pelvic organ
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 215; 46: 233 238 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 1.12/uog.14678 How can we measure bladder volumes in women with advanced pelvic organ
Bard: Continence Therapy. Stress Urinary Incontinence. Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle.
 Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem and one that can be resolved by working
Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem and one that can be resolved by working
Medical Review Criteria Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence
 Medical Review Criteria Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Effective Date: December 21, 2016 Subject: Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Background: Urinary incontinence (the involuntary
Medical Review Criteria Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Effective Date: December 21, 2016 Subject: Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Background: Urinary incontinence (the involuntary
Pathogenesis of urethral funneling in women with stress urinary incontinence assessed by introital ultrasound
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 26: 287 292 Published online 5 August 2005 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1977 Pathogenesis of urethral funneling in women with stress
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 26: 287 292 Published online 5 August 2005 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1977 Pathogenesis of urethral funneling in women with stress
KEYWORDS: cystocele; laparoscopic Burch colposuspension; ultrasound cystourethrography; urodynamic stress incontinence; voiding function
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 25: 289 295 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1838 Dynamic morphological changes in the anterior vaginal wall before
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 25: 289 295 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1838 Dynamic morphological changes in the anterior vaginal wall before
Value of UVJ-M in the diagnosis of SUI in late pregnancy and postpartum
 1772 Value of UVJ-M in the diagnosis of SUI in late pregnancy and postpartum GUIXIN ZHANG 1, WEI JIANG 1, QUANWEI GUO 2 and QUANRONG GUO 3 Departments of 1 Obstetrics and Gynecology, 2 Ultrasonography,
1772 Value of UVJ-M in the diagnosis of SUI in late pregnancy and postpartum GUIXIN ZHANG 1, WEI JIANG 1, QUANWEI GUO 2 and QUANRONG GUO 3 Departments of 1 Obstetrics and Gynecology, 2 Ultrasonography,
Original Article Efficacy of 3D ultrasound on diagnosis of women pelvic flour dysfunction
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(8):16523-16528 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0028796 Original Article Efficacy of 3D ultrasound on diagnosis of women pelvic flour dysfunction Aifang Chen 1*, Yingzi Zhang
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(8):16523-16528 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0028796 Original Article Efficacy of 3D ultrasound on diagnosis of women pelvic flour dysfunction Aifang Chen 1*, Yingzi Zhang
Urogynaecology. Colm McAlinden
 Urogynaecology Colm McAlinden Definitions Urinary incontinence compliant of any involuntary leakage of urine with many different causes Two main types: Stress Urge Definitions Nocturia: More than a single
Urogynaecology Colm McAlinden Definitions Urinary incontinence compliant of any involuntary leakage of urine with many different causes Two main types: Stress Urge Definitions Nocturia: More than a single
Urodynamic findings in women with insensible incontinence
 bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2013) 20, 429 433 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.03146.x Original Article: Clinical Investigation Urodynamic findings in women with insensible Benjamin M Brucker,
bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2013) 20, 429 433 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.03146.x Original Article: Clinical Investigation Urodynamic findings in women with insensible Benjamin M Brucker,
PRE-OPERATIVE URODYNAMIC
 PRE-OPERATIVE URODYNAMIC STUDIES: IS THERE VALUE IN PREDICTING POST-OPERATIVE STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN UNDERGOING PROLAPSE SURGERY? Dr K Janse van Rensburg Dr JA van Rensburg INTRODUCTION POP
PRE-OPERATIVE URODYNAMIC STUDIES: IS THERE VALUE IN PREDICTING POST-OPERATIVE STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN UNDERGOING PROLAPSE SURGERY? Dr K Janse van Rensburg Dr JA van Rensburg INTRODUCTION POP
Learning process for performing and analyzing 3D/4D transperineal ultrasound imaging and interobserver reliability study
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 41: 312 317 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.11192 Learning process for performing and analyzing 3D/4D transperineal ultrasound
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 41: 312 317 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.11192 Learning process for performing and analyzing 3D/4D transperineal ultrasound
Training a Wayward Bladder
 D. James Ballard, PT, DPT, GCS The University of Utah, Dept. of Physical Therapy Training a Wayward Bladder Agenda 1. Discuss urinary incontinence 2. Review pelvic floor and lower urinary tract functional
D. James Ballard, PT, DPT, GCS The University of Utah, Dept. of Physical Therapy Training a Wayward Bladder Agenda 1. Discuss urinary incontinence 2. Review pelvic floor and lower urinary tract functional
Urodynamic Tests. Department of Gynaecology. Patient Information
 Urodynamic Tests Department of Gynaecology Patient Information What are urodynamic tests? Urodynamic tests assess the dynamic function of the lower urinary tract. The tests assess 3 functions; The ability
Urodynamic Tests Department of Gynaecology Patient Information What are urodynamic tests? Urodynamic tests assess the dynamic function of the lower urinary tract. The tests assess 3 functions; The ability
Look Beyond the Surface and Get the Complete Pelvic Floor Picture
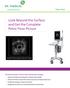 Pelvic Floor Look Beyond the Surface and Get the Complete Pelvic Floor Picture Endovaginal ultrasound. Levator ani defect seen on the right side (arrows). A=anus, B=bladder, LA=levator ani, U=urethra.
Pelvic Floor Look Beyond the Surface and Get the Complete Pelvic Floor Picture Endovaginal ultrasound. Levator ani defect seen on the right side (arrows). A=anus, B=bladder, LA=levator ani, U=urethra.
Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery
 Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery APPLICATION FOR NEW FELLOWSHIP Name of Institution: McGill University Location: Royal Victoria Hospital (Glen Site), St Mary s Hospital Centre Type of Fellowship:
Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery APPLICATION FOR NEW FELLOWSHIP Name of Institution: McGill University Location: Royal Victoria Hospital (Glen Site), St Mary s Hospital Centre Type of Fellowship:
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline
 Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Decidable (Y or N) Inclusion
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Decidable (Y or N) Inclusion
IUGA Fellowship 2013 Final Report
 IUGA Fellowship 2013 Final Report Award Recipient: Andrea C. Santiago, M.D. (Philippines) Dates of Fellowship: June 1, 2013- May 31, 2014 Host Site: University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center Host:
IUGA Fellowship 2013 Final Report Award Recipient: Andrea C. Santiago, M.D. (Philippines) Dates of Fellowship: June 1, 2013- May 31, 2014 Host Site: University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center Host:
ATLAS OF URODYNAMICS. Bladder. Pure. Pves. Pabd. Pdet EMG. Bladder. volume. Cough Strain IDC. Filling. Pure. Pves. Pabd. Pdet EMG
 2 Normal Micturition The micturition cycle (urine storage and voiding) is a nearly subconscious process that is under complete voluntary control. Bladder filling is accomplished without sensation and without
2 Normal Micturition The micturition cycle (urine storage and voiding) is a nearly subconscious process that is under complete voluntary control. Bladder filling is accomplished without sensation and without
Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh Repair: A Prospective Study of 105 Cases
 International Journal of Clinical Urology 2018; 2(1): 20-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcu doi: 10.11648/j.ijcu.20180201.14 Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh
International Journal of Clinical Urology 2018; 2(1): 20-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcu doi: 10.11648/j.ijcu.20180201.14 Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Int Urogynecol J. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2012 December 06.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Int Urogynecol J. 2011 December ; 22(12): 1491 1495. doi:10.1007/s00192-011-1458-4. URETHRAL CLOSURE PRESSURES AMONG PRIMIPAROUS WOMEN
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Int Urogynecol J. 2011 December ; 22(12): 1491 1495. doi:10.1007/s00192-011-1458-4. URETHRAL CLOSURE PRESSURES AMONG PRIMIPAROUS WOMEN
