3D Dynamic Ultrasound In Obstructed Defecation
|
|
|
- Arthur Ward
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 3D Dynamic Ultrasound In Obstructed Defecation By Ramy Salahudin Abdelkader Assist. Lecturer of General Surgery Cairo University Introduction Pelvic floor is complex system, with passive and active components that : provide pelvic support maintain continence coordinate relaxation during urination and defecation Obstructed defecation syndrome : It is best defined as normal desire to defecate but inability to satisfactorily evacuate rectum. It falls under more general term constipation. Constipation is a nationwide health problem that significantly impairs healthrelated quality of life The term constipation is all encompassing and portrays little information about underlying etiology or potential treatment options It is far better to divide patients with constipation into primary and secondary types 1
2 Constipation Primary versus secondary constipation Patient with symptoms of impaired evacuation must be evaluated for 2ry causes for constipation such as : Mechanical causes e.g. Rectal or colon cancer Endocrine or metabolic disorders e.g. Hypothyroidism, diabetes, hypercalcemia Neurologic diseases e.g. Multiple sclerosis, parkinson s disease Medications e.g. Opiates, analgesics, antidepressants History of sexual abuse should be considered in women with anismus Primary constipation due to physiologic dysfunction can be divided into Normal transit constipation Slow transit constipation Pelvic floor disorders Subtypes of primary constipation Normal transit constipation patients have normal transit times through colon but have perception of constipation due to evacuation difficulties or due to hard stool. Slow transit constipation propulsion of intraluminal contents is delayed in portions of colon or throughout entire colon. Pelvic floor disorders Functional disorders Dyssynergic Defecation (Anismus) Structural disorders: Rectocele Rectal intussusception Enterocele Descending Perineum Syndrome 2
3 Rome III criteria for diagnosis of functional constipation Criteria must be present for at least 3 months with symptom onset at least 6 months prior to diagnosis: 1. Must include two or more of following: < 3 bowel movements / week. Straining at 25% of defecations. Lumpy or hard stools at 25% of defecations. Sensation of anorectal obstruction at 25% of defecations. Sensation of incomplete evacuation at 25% of defecations. Manual disimpaction at 25% of defecations. 2. Absence of loose stools without laxatives. 3. Inadequate criteria to diagnose constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-C). Background & Rationale In ODS, clinical history & examination mainstay of diagnosis To be combined with physiological tests and imaging techniques No clear recommended imaging guidelines for assessment of patients withods. Evacuation disorders are caused by morphologic & functional abnormalities dynamic imaging techniques 3
4 Conventional defecography Gold standard examination Pros & Cons Minimally invasive Technically simple Radiation exposure Specific radiology environment Doesn t show anatomical structures involved in defecation Limited ability to detect anterior and middle compartment s abnormalities Need to evaluate pelvic floor as a unit arised due to association of defecatory disorders with POP in females Evaluation extended by opacifying S.bowel, vagina & U.B. Examination complexity Procedural invasiveness Time consuming Poor tolerability Considerable dose of radiation exposure Recently, alternatives to defecography developed e.g. Dynamic MRI Dynamic ultrasonography Relative advantages Showing the entire pelvis Ability to evaluate anal sphincter defects 4
5 Dynamic MRI: Open or closed-configuration unit. Open system is more physiological but not widely available. Avoids exposure to harmful ionizing radiation. Allows excellent visualization of surrounding soft tissues and support structures of pelvic organs The use of MRI is restricted by availability cost supine position (less suitable for identifying abnormalities ) It is not as dynamic as ultrasound imaging. Dynamic US: Advantages Excellent efficiency in assessment of Anal sphincter defects Ano-perineal suppuration Anal canal tumors Interesting results in evaluation of pelvic floor disorders Low cost, availability and simplicity Different approaches are available e.g. Transperineal Transvaginal Transrectal (2D vs 3D endoprobe, injecting water vs gel) Studies using different approaches produced findings consistent with defecography in assess. ODS 5
6 Echodefecography: Murad-Regadas et al. Developed echodefecography, 3D dynamic anorectal ultrasonography technique Using a 360 transducer, automatic scanning and high frequencies for high- resolution images To evaluate evacuation disorders affecting : Posterior compartment (rectocele, intussusception, anismus) Middle compartment (grade II or III sigmoidocele/enterocele) The standardization of the technique, parameters, and values of echodefecography makes the method reproducible Aim of the study compare accuracy of Dynamic Anorectal Endosonography (Echodefecography) with 1. Dynamic MRI defecography 2. Conventional defecography in the diagnosis of pelvic floor disorders. 6
7 Echodefecoraphy Technique Patients are examined in the left lateral position after rectal enema. The endoprobe is inserted into the lower rectum and positioned 6 7 cm from the anal verge. Images are acquired by four automatic scans and analyzed in axial and 3D midline longitudinal (ML) planes Scan 1 Transducer position: 6cm from anal margin. Structures scanned: lower rectum, anorectal junction, anal canal AT REST Aim: 3D examination of anatomical configuration of anal canal for checking muscle injury. 7
8 Scan 2 Transducer position: 6cm from anal margin. Structures scanned: lower rectum, anorectal junction, anal canal AT REST&STRAINING o o o 15s. at rest: lower rectum. 20s. during straining: lower rectum, anorectal junction, upper & proximal mid-anal canal. 15 s. at rest: distal mid & lower anal canal. Aim: Evaluation of PR movement during evacuation normal relaxation or paradoxical contraction(anismus). Scan 3 Transducer position: 7cm from anal margin. Structures scanned: the same as scan 2 but at 7 cm. Aim: Scan is more proximal for dectection of rectal invagination. This is confirmed in next scan. 8
9 Scan 4 Transducer position: 7cm from anal margin. Structures scanned: the same as scan 3 but after injection of ml gel into rectal ampulla. Aim: Demonstrating & quantifying anatomical & functional changes of all structures (anal canal, anorectal junction and pelvic floor) associated with voiding. squatting position is most physiological but inadequate and uncomfortable for exam using a 3D endoprobe left lateral position & inserting endoprobe into rectum didn t prevent patients from evacuating intrarectal gel Sufficient distension of anorectum by max. 180 ml gel induce voiding urge It keeps patient s privacy allows efficient evacuation (unlike evaluation by other modalities which is regarded embarrassing) 9
10 Image Interpretation Anismus: (1)Axial plane: Transducer position at PR level Angle is made by drawing 2 diagonal lines from 3 & 9 o'clock at internal circumference of transducer and converge at 6 o'clock at internal border of PR muscle. Angle is compared at rest & during straining. Normal: The angle is relatively closed due to PR relaxation. Anismus: The angle is wider due to paradoxical contraction of PR. A Patient with anismus (axial): A Resting. B Evacuatory effort Increased angle. B Anismus (2)Sagittal plane: Angle is made by convergence of 1.5cm line parallel to internal border of PR muscle & vertical line perpendicular to axis of anal canal. Angle is compared at rest & during straining Normal: the angle is widened due to PR relaxation. Anismus: The angle is narrowed due to paradoxical contraction of PR. A B Patient with anismus(sagittal): A Resting. B Evacuatory effort Decreased angle. 10
11 Anorectocele: Sagittal plane: Scan 4 Normal: During straining the posterior vaginal wall displaces the anterior rectal wall, anorectal junction and upper anal canal backwards and downwards. Anorectocele: during straining the anterior rectal wall, anorectal junction and upper anal canal displace the posterior vaginal wall forwards. Distance is measured between 2 parallel lines drawn on the projection of posterior vaginal wall at initial straining and maximal straining (herniation) Size of anorectocele. Echodefecographic classification: grade1: cm. grade2: cm. grade3: >1.3cm. A B C a Normal patient: Line 1: parallel with the vaginal wall at rest. Line 2: parallel with the vaginal wall during straining. Line3: distance between lines 1 and 2 (arrow). b Patient with anorectocele grade III: c Patient with anorectocele grade I, d Patient with anorectocele grade II Line 1: parallel with the vaginal wall during initial straining. Line 2: parallel with the vaginal wall at maximal herniation point. Line 3: distance between lines 1 and 2 (anorectocele size) (arrows). D 11
12 Intussusception: Easily identified when two parallel muscle layers are visualized in the axial and longitudinal planes during straining without intrarectal gel Scan 3. When intrarectal gel is employed the two muscle layers are seen projecting into the rectal lumen Scan 4. Minor intussusception small displacements with practically parallel muscle layers Severe cases muscle layers are further displaced and appear perpendicular to each other. A B Patient with anorectocele grade III (arrowheads) with posterior rectal intussusception (arrows). a Axial image without gel. b Axial image with gel C c Mid sagittal image with gel 12
13 Enterocele The intestinal loops are usually visualized on the projection of the anterior quadrant of the mid to lower rectum close to the bladder and the uterus, even during straining. Enterocele is identified by the presence of intestinal loops on the projection of the lower rectum and upper anal canal at the level of the PR muscle and is easily observed in the axial and longitudinal planes scans 2, 3&4. A Enterocele (arrows) with anorectocele grade II (arrowheads). a Axial image without gel. b Mid sagittal image with gel. B Perineal Descent The transducer is positioned proximally to the PR muscle. The PR muscle is initially scanned at rest (3 s), then during straining. The transducer does not follow the descending muscles of the pelvic floor but remains in the same position until the PR muscle becomes visible distally, then the scan is stopped. Straining time is directly proportional to the distance of perineal descent. The perineal descent length is quantified by measuring the distance between the position of the proximal border of the PR muscle at rest and at the point it is identified again after being displaced due to the evacuatory effort. 13
14 A B a Normal patient, mid sagittal plane. b Patient with perineal descent. Increased distance between both positions of the puborectalis muscle Patients & Methods Prospective randomized controlled study April April patients (10 males and 20 females) Mean age of 39 years (14 76 years) Divided into 2 equal groups: Group A: 11 females & 4 males with a mean age of 41.4 years underwent echodefecography and MR defecography Group B: 9 females & 6 males with a mean age 36.7 years underwent echodefecography and cinedefecography. 14
15 Patients & Methods Inclusion criteria Dyschezia for at least 6months Defined according to Rome III criteria Excessive straining, Lumpy or hard stools Sensation of incomplete evacuation of stools Sensation of anorectal obstruction Manual disimpaction of stool, or vaginal maneuvers to assist defecation Exclusion criteria Any organic pathology of the colon or rectum detected by clinical examination or colonoscopy Pregnancy Anal incontinence Refusal to undergo evaluations, Contraindications to performance of MRI E.G. Prothetic valve Contraindications to performance of EAUS E.G. Anal stenosis Anismus Angle at rest =63.5 ) Axial plane Angle during straining = 72 Angle at rest =90.6 Sagittal plane Angle during straining =
16 Rectocele Grade 1 Size= 0.54 cm Grade 2 Size= 0.87 cm Grade 3 Size= 1.57 cm Intussusception Anterior posterior Circumferential Hemi-circum 16
17 Enterocele Anorectal Descent 17
18 18
19 19
20 Results Group A Echodefecography (EDF) identified Anismus in 6 cases (40%) Rectocele in 9 cases (60%) Intussusception in 10 cases (66.7%) Enterocele in 4 cases (26.7%) Anorectal descent in 10 cases (66.7%) MR defecography (MRD) identified Rectocele in 8 cases (53.3%) Anorectal descent in 14 cases (93.3%) Cystocele in 7 cases (46.7%) Uterocele in 5 cases (33.3%) No anismus, intussusception or enterocele were detected No significant statistical difference between EDF and MRD Rectocele and anorectal descent (P value 0.205, respectively) No statistics were computed in comparing EDF and MRD Anismus, intussusception and enterocele as MRD was constant Results Group B Echodefecography (EDF) identified Anismus in 3 cases (20%) Rectocele in 13 cases (86.7) Intussusception in 12 cases (80%) Enterocele in 2 cases (13.3%) Anorectal descent in 7 cases (46.7%). Cinedefecography (CDF) identified Anismus in 2 cases (13.3%) Rectocele in 14 cases (93.3%) Intussusception in 1 case (6.7%) Anorectal descent in 11 cases (73.3%) No enterocele was detected. No significant statistical difference between EDF & CDF Anismus (P value 0.225) Statistical agreement between EDF & CDF Good rectocele ( value 0.634) Moderate anorectal descent ( value 0.483) Poor intussusception ( value 0.035) No statistics were computed in comparing EDF & CDF enterocele as CDF was constant 20
21 Accuracy of EDF in comparison to MRD Sensitivity Specificity Accuracy Anorectal Descent Rectocele Enterocele Anismus Intussusception Sensitivity Specificity Accuracy Accuracy of EDF in comparison to CDF Sensitivity Specificity Accuracy 20 0 Rectocele Enterocele Anismus Anorectal Descent Intussusception Sensitivity Specificity Accuracy
22 Conclusion Echodefecography has good accuracy of detection of rectocele and anorectal descent when compared with cinedefecography and MR defecography. It identified more cases of anismus, intussusception and enterocele than did the other 2 modalities. It has the advantages of being simple inexpensive, available easy to perform with fast learning curve well tolerated by patients It is better than cinedefecography visualize all anatomic structures involved in defecation avoid exposing patients to harmful radiation. Also, it is superior to MR defecography in detection of anal sphincter complex defects which is important to be assessed before surgical management. Thank you 22
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION 686 DISEASES OF THE COLON &RECTUM VOLUME54: 6 (2011)
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Prospective Multicenter Trial Comparing With in the Assessment of Anorectal Dysfunction in Patients With Obstructed Defecation F. Sergio P. Regadas, Ph.D. 1 Eric M. Haas, M.D. 2 Maher
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Prospective Multicenter Trial Comparing With in the Assessment of Anorectal Dysfunction in Patients With Obstructed Defecation F. Sergio P. Regadas, Ph.D. 1 Eric M. Haas, M.D. 2 Maher
Guide to Pelvic Floor Multicompartment Scanning
 Guide to Pelvic Floor Multicompartment Scanning These guidelines have been prepared by Giulio A. Santoro, MD, PhD, Head Pelvic Floor Unit, Section of Anal Physiology and Ultrasound, Coloproctology Service,
Guide to Pelvic Floor Multicompartment Scanning These guidelines have been prepared by Giulio A. Santoro, MD, PhD, Head Pelvic Floor Unit, Section of Anal Physiology and Ultrasound, Coloproctology Service,
The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons
 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/dcrjournal by BhDMf5ePHKav1zEoum1tQfN4a+kJLhEZgbsIHo4XMi0hCywCX1AWnYQp/IlQrHD3IJrtBKuSsQVRz8fA4yAY0a8W1YLRn6mHykFpaZ5LFvI= on 03/16/2018
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/dcrjournal by BhDMf5ePHKav1zEoum1tQfN4a+kJLhEZgbsIHo4XMi0hCywCX1AWnYQp/IlQrHD3IJrtBKuSsQVRz8fA4yAY0a8W1YLRn6mHykFpaZ5LFvI= on 03/16/2018
Applied Anatomy and Physiology of the Pelvic Floor. Dr David Tarver Consultant Radiologist, Poole
 Applied Anatomy and Physiology of the Pelvic Floor Dr David Tarver Consultant Radiologist, Poole Pelvic Floor 1. Sacrospinous Ligament 2. Levator Ani A Puborectalis B. Pubococcygeus C. Iliococcygeus 3.
Applied Anatomy and Physiology of the Pelvic Floor Dr David Tarver Consultant Radiologist, Poole Pelvic Floor 1. Sacrospinous Ligament 2. Levator Ani A Puborectalis B. Pubococcygeus C. Iliococcygeus 3.
Magnetic resonance follow-up protocol for patients after stapled transanal rectal resection for intussusception and rectocele
 Magnetic resonance follow-up protocol for patients after stapled transanal rectal resection for intussusception and rectocele Poster No.: C-2659 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S.
Magnetic resonance follow-up protocol for patients after stapled transanal rectal resection for intussusception and rectocele Poster No.: C-2659 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S.
The use of conventional defecography in clinical practice
 The use of conventional defecography in clinical practice Poster No.: C-1564 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Šmite, R. Laguns ; Lielvarde/LV, Riga/LV Keywords: Pelvic floor dysfunction,
The use of conventional defecography in clinical practice Poster No.: C-1564 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Šmite, R. Laguns ; Lielvarde/LV, Riga/LV Keywords: Pelvic floor dysfunction,
The use of conventional defecography in clinical practice
 The use of conventional defecography in clinical practice Poster No.: C-1564 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Šmite, R. Laguns ; Lielvarde/LV, Riga/LV Keywords: Pelvic floor dysfunction,
The use of conventional defecography in clinical practice Poster No.: C-1564 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Šmite, R. Laguns ; Lielvarde/LV, Riga/LV Keywords: Pelvic floor dysfunction,
High-field (3T) magnetic resonance defecography with functional assessment of the evacuation phase: A pictorial essay
 High-field (3T) magnetic resonance defecography with functional assessment of the evacuation phase: A pictorial essay Poster No.: C-430 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal and
High-field (3T) magnetic resonance defecography with functional assessment of the evacuation phase: A pictorial essay Poster No.: C-430 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal and
Elderly Man With Chronic Constipation
 Elderly Man With Chronic Constipation Linda Nguyen, MD Director, Neurogastroenterology and Motility Clinical Assistant Professor Stanford University Overview Normal bowel function Defining Constipation:
Elderly Man With Chronic Constipation Linda Nguyen, MD Director, Neurogastroenterology and Motility Clinical Assistant Professor Stanford University Overview Normal bowel function Defining Constipation:
Fecal Incontinence. What is fecal incontinence?
 Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
JNM Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility
 ㅋ JNM Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 17 No. 4 October, 2011 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 http://dx.doi.org/10.5056/jnm.2011.17.4.416 How to Interpret
ㅋ JNM Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 17 No. 4 October, 2011 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 http://dx.doi.org/10.5056/jnm.2011.17.4.416 How to Interpret
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (April 2018) Vol. 71 (3), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (April 2018) Vol. 71 (3), Page 2742-2750 Role of dynamic MRI in assessment of Pelvic Floor Dysfunction in Females Nada Ahmed Hussein, Naglaa Hussein Shebrya, Nermeen
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (April 2018) Vol. 71 (3), Page 2742-2750 Role of dynamic MRI in assessment of Pelvic Floor Dysfunction in Females Nada Ahmed Hussein, Naglaa Hussein Shebrya, Nermeen
Pelvic Floor Ultrasound Imaging. Prof HP Dietz (Sydney) A/Prof KL Shek (Sydney) Dr R Guzman Rojas (Santiago de Chile) Dr Kamil Svabik (Prague)
 Pelvic Floor Ultrasound Imaging Workshop IUGA 2015 Nice Faculty: Prof HP Dietz (Sydney) A/Prof KL Shek (Sydney) Dr R Guzman Rojas (Santiago de Chile) Dr Kamil Svabik (Prague) The use of translabial ultrasound
Pelvic Floor Ultrasound Imaging Workshop IUGA 2015 Nice Faculty: Prof HP Dietz (Sydney) A/Prof KL Shek (Sydney) Dr R Guzman Rojas (Santiago de Chile) Dr Kamil Svabik (Prague) The use of translabial ultrasound
Anorectal Diagnostic Overview
 Anorectal Diagnostic Overview 11-25-09 3.11.2010 2009 2010 Anorectal Manometry Overview Measurement of pressures and the annotation of rectal sensation throughout the rectum and anal canal to determine:
Anorectal Diagnostic Overview 11-25-09 3.11.2010 2009 2010 Anorectal Manometry Overview Measurement of pressures and the annotation of rectal sensation throughout the rectum and anal canal to determine:
Functional disorders of the ano-rectal compartment - the diagnostic role of dynamic MRI
 Functional disorders of the ano-rectal compartment - the diagnostic role of dynamic MRI Award: Magna Cum Laude Poster No.: C-2490 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. P. Caetano, D.
Functional disorders of the ano-rectal compartment - the diagnostic role of dynamic MRI Award: Magna Cum Laude Poster No.: C-2490 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. P. Caetano, D.
CONSTIPATION. Atan Baas Sinuhaji
 CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
LAPAROSCOPIC REPAIR OF PELVIC FLOOR
 LAPAROSCOPIC REPAIR OF PELVIC FLOOR Dr. R. K. Mishra Elements comprising the Pelvis Bones Ilium, ischium and pubis fusion Ligaments Muscles Obturator internis muscle Arcus tendineus levator ani or white
LAPAROSCOPIC REPAIR OF PELVIC FLOOR Dr. R. K. Mishra Elements comprising the Pelvis Bones Ilium, ischium and pubis fusion Ligaments Muscles Obturator internis muscle Arcus tendineus levator ani or white
Constipation. What is constipation? What is the criteria for having constipation? What are the different types of constipation?
 What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
What the radiologist needs to know!
 What the radiologist needs to know! Clare Molyneux Sam Treadway Sathi Sukumar Wal Baraza Abhiram Sharma Karen Telford University Hospital of South Manchester Manchester UK Introduction Indications Investigations
What the radiologist needs to know! Clare Molyneux Sam Treadway Sathi Sukumar Wal Baraza Abhiram Sharma Karen Telford University Hospital of South Manchester Manchester UK Introduction Indications Investigations
Constipation. (Medical Aspects)
 Constipation (Medical Aspects) By Dr. Ehab Abdel Khalik MD. Anatomy of the anorectum The rectum is 12-15 15 cm. long. It connects with the sigmoid colon by the rectosigmoid junction which is believed to
Constipation (Medical Aspects) By Dr. Ehab Abdel Khalik MD. Anatomy of the anorectum The rectum is 12-15 15 cm. long. It connects with the sigmoid colon by the rectosigmoid junction which is believed to
Pelvic Prolapse. A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction
 Pelvic Prolapse A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction Pelvic Prolapse When an organ becomes displaced, or slips down in the body, it is referred to as a prolapse. Your physician has diagnosed
Pelvic Prolapse A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction Pelvic Prolapse When an organ becomes displaced, or slips down in the body, it is referred to as a prolapse. Your physician has diagnosed
Pelvic Floor Disorders. Amir Darakhshan MD FRCS (Gen Surg) Consultant Colorectal and General Surgeon
 Pelvic Floor Disorders Amir Darakhshan MD FRCS (Gen Surg) Consultant Colorectal and General Surgeon What is Pelvic Floor Disorder Surgical perspective symptoms of RED, FI or prolapse on the background
Pelvic Floor Disorders Amir Darakhshan MD FRCS (Gen Surg) Consultant Colorectal and General Surgeon What is Pelvic Floor Disorder Surgical perspective symptoms of RED, FI or prolapse on the background
Imaging of Pelvic Floor Weakness. Dr Susan Kouloyan-Ilic Radiologist Epworth Medical Imaging The Women s, Melbourne
 Imaging of Pelvic Floor Weakness Dr Susan Kouloyan-Ilic Radiologist Epworth Medical Imaging The Women s, Melbourne Outline Overview and Epidemiology Risk Factors, Causes and Results Review of Relevant
Imaging of Pelvic Floor Weakness Dr Susan Kouloyan-Ilic Radiologist Epworth Medical Imaging The Women s, Melbourne Outline Overview and Epidemiology Risk Factors, Causes and Results Review of Relevant
Ben Herbert Alex Wojtowicz
 Ben Herbert Alex Wojtowicz 54 year old female presenting with: Dragging sensation Urinary incontinence Some faecal incontinence HPC Since May 14 had noticed a mass protruding from the vagina when going
Ben Herbert Alex Wojtowicz 54 year old female presenting with: Dragging sensation Urinary incontinence Some faecal incontinence HPC Since May 14 had noticed a mass protruding from the vagina when going
GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction. Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield
 GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield Aims o o o To give an overview of lower GI investigations To demonstrate
GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield Aims o o o To give an overview of lower GI investigations To demonstrate
Robotic Ventral Rectopexy
 Robotic Ventral Rectopexy What is a robotic ventral rectopexy? The term rectopexy refers to an operation in which the rectum (the part of the bowel nearest the anus) is put back into its normal position
Robotic Ventral Rectopexy What is a robotic ventral rectopexy? The term rectopexy refers to an operation in which the rectum (the part of the bowel nearest the anus) is put back into its normal position
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery
 World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 6, Issue 5 2016 Article 8 Sigmoidocele: A Rare Cause Of Constipation In Males Noor Shah MD Milind Kachare MD Craig Rezac MD Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 6, Issue 5 2016 Article 8 Sigmoidocele: A Rare Cause Of Constipation In Males Noor Shah MD Milind Kachare MD Craig Rezac MD Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical
ACCIDENTAL BOWEL LEAKAGE: A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO EVALUATION. Tristi W. Muir, MD Chair, Department of OB/GYN Houston Methodist Hospital
 ACCIDENTAL BOWEL LEAKAGE: A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO EVALUATION Tristi W. Muir, MD Chair, Department of OB/GYN Houston Methodist Hospital Accidental Bowel Leakage What Gets the Woman into Your Office 67%
ACCIDENTAL BOWEL LEAKAGE: A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO EVALUATION Tristi W. Muir, MD Chair, Department of OB/GYN Houston Methodist Hospital Accidental Bowel Leakage What Gets the Woman into Your Office 67%
Biofeedback for Pelvic Floor Disorders and Incontinence
 The UNC Center for Functional GI & Motility Disorders www.med.unc.edu/ibs Biofeedback for Pelvic Floor Disorders and Incontinence Olafur S. Palsson, Psy.D. Associate Professor of Medicine UNC Center for
The UNC Center for Functional GI & Motility Disorders www.med.unc.edu/ibs Biofeedback for Pelvic Floor Disorders and Incontinence Olafur S. Palsson, Psy.D. Associate Professor of Medicine UNC Center for
Pelvic static MR vs MR-defecography in the study of woman's pelvic floor disorders
 Pelvic static MR vs MR-defecography in the study of woman's pelvic floor disorders Poster No.: B-0043 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: A. ambrosi, G. De Franco, F. Lorusso, M. Cascarano,
Pelvic static MR vs MR-defecography in the study of woman's pelvic floor disorders Poster No.: B-0043 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: A. ambrosi, G. De Franco, F. Lorusso, M. Cascarano,
2. Pelvic Floor Anatomy: The primary supportive structures of the pelvis consist of the pelvic fascia and pelvic floor musculature.
 MR Imaging of the Female Pelvic Floor Katarzyna J. Macura, MD, PhD The Russell H. Morgan Department of Radiology and Radiological Sciences Johns Hopkins University Baltimore, MD 21287 kmacura@jhmi.edu
MR Imaging of the Female Pelvic Floor Katarzyna J. Macura, MD, PhD The Russell H. Morgan Department of Radiology and Radiological Sciences Johns Hopkins University Baltimore, MD 21287 kmacura@jhmi.edu
A Constipation Scoring System to Simplify Evaluation and Management of Constipated Patients
 A Constipation Scoring System to Simplify Evaluation and Management of Constipated Patients Feran Agachan, M.D., Teng Chen, M.D., Johann Pfeifer, M.D., Petachia Reissman, M.D., Steven D. Wexner, M.D.,
A Constipation Scoring System to Simplify Evaluation and Management of Constipated Patients Feran Agachan, M.D., Teng Chen, M.D., Johann Pfeifer, M.D., Petachia Reissman, M.D., Steven D. Wexner, M.D.,
MRI defecography. Anatomic and functional Cine-based evaluation of the pelvic floor dysfunction.
 MRI defecography. Anatomic and functional Cine-based evaluation of the pelvic floor dysfunction. Poster No.: C-2583 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. A. SAAVEDRA ABRIL, J. Galicia-Alba,
MRI defecography. Anatomic and functional Cine-based evaluation of the pelvic floor dysfunction. Poster No.: C-2583 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. A. SAAVEDRA ABRIL, J. Galicia-Alba,
Diagnosis of Impaired Defecatory Function with Special Reference to Physiological Tests
 Defecatory Dysfunction Diagnosis of Impaired Defecatory Function with Special Reference to Physiological Tests JMAJ 46(9): 373 377, 2003 Masatoshi OYA, Masashi UENO, and Tetsuichiro MUTO Department of
Defecatory Dysfunction Diagnosis of Impaired Defecatory Function with Special Reference to Physiological Tests JMAJ 46(9): 373 377, 2003 Masatoshi OYA, Masashi UENO, and Tetsuichiro MUTO Department of
Pelvic Support Problems
 AP012, April 2010 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright
AP012, April 2010 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright
Defecation proctography and translabial ultrasound in the investigation of defecatory disorders
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2008; 31: 567 571 Published online 11 April 2008 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.5337 Defecation proctography and translabial ultrasound in
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2008; 31: 567 571 Published online 11 April 2008 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.5337 Defecation proctography and translabial ultrasound in
Constipation. Disease Review
 bowel. 1 Constipation is a symptom, not a disease. Almost everyone experiences Disease Review Constipation Introduction: Constipation is exceedingly common and is rarely associated with mortality in developed
bowel. 1 Constipation is a symptom, not a disease. Almost everyone experiences Disease Review Constipation Introduction: Constipation is exceedingly common and is rarely associated with mortality in developed
Constipation. H. David Vargas, MD. Overview
 Constipation H. David Vargas, MD Overview Constipation is a very common complaint affecting upwards of 15% of all Americans. Fortunately, constipation usually is simple to avoid and easy to treat when
Constipation H. David Vargas, MD Overview Constipation is a very common complaint affecting upwards of 15% of all Americans. Fortunately, constipation usually is simple to avoid and easy to treat when
5/29/2015. Objectives. Functions of the PFM. Various phases of PFM. Evaluation of the PFM
 The Physical Therapist s Approach to the Female Pelvic Floor Musculature Examination and Treatment. Presented By: Evelyne Burtis, DPT Objectives Core and pelvic floor muscles (PFM) Functions of the PFM
The Physical Therapist s Approach to the Female Pelvic Floor Musculature Examination and Treatment. Presented By: Evelyne Burtis, DPT Objectives Core and pelvic floor muscles (PFM) Functions of the PFM
Stapled transanal rectal resection for obstructed defaecation syndrome
 Stapled transanal rectal resection for obstructed Issued: June 2010 www.nice.org.uk/ipg351 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce interventional
Stapled transanal rectal resection for obstructed Issued: June 2010 www.nice.org.uk/ipg351 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce interventional
Diagnostic and therapeutic approach to obstructed defecation syndrome W31, 16 October :00-12:00
 Diagnostic and therapeutic approach to obstructed defecation syndrome W31, 16 October 2012 09:00-12:00 Start End Topic Speakers 09:00 09:05 Introduction Giulio Aniello Santoro 09:05 09:20 Anatomy of the
Diagnostic and therapeutic approach to obstructed defecation syndrome W31, 16 October 2012 09:00-12:00 Start End Topic Speakers 09:00 09:05 Introduction Giulio Aniello Santoro 09:05 09:20 Anatomy of the
State of the art: an integrated approach to pelvic floor ultrasonography
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2011; 37: 381 396 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.8816 State of the art: an integrated approach to pelvic floor ultrasonography
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2011; 37: 381 396 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.8816 State of the art: an integrated approach to pelvic floor ultrasonography
MRI defecography: technique, indications and clinical findings not only in obstructed defecation syndrome
 MRI defecography: technique, indications and clinical findings not only in obstructed defecation syndrome Poster No.: C-1061 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Di Piazza, M. Costanzo,
MRI defecography: technique, indications and clinical findings not only in obstructed defecation syndrome Poster No.: C-1061 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Di Piazza, M. Costanzo,
HIGH RESOLUTION AND HIGH DEFINITION ANORECTAL MANOMETRY: USEFULNESS, LIMITATIONS, WHEN AND WHY. José María Remes Troche.
 HIGH RESOLUTION AND HIGH DEFINITION ANORECTAL MANOMETRY: USEFULNESS, LIMITATIONS, WHEN AND WHY José María Remes Troche. Digestive Phisiology and Motility Lab University of Veracruz, Mexico DISCLOSURE:
HIGH RESOLUTION AND HIGH DEFINITION ANORECTAL MANOMETRY: USEFULNESS, LIMITATIONS, WHEN AND WHY José María Remes Troche. Digestive Phisiology and Motility Lab University of Veracruz, Mexico DISCLOSURE:
Pelvic Floor Descent in Females: Comparative Study of Colpocystodefecography and Dynamic Fast MR Imaging
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 9:373 377 (1999) Original Research Pelvic Floor Descent in Females: Comparative Study of Colpocystodefecography and Dynamic Fast MR Imaging D. Vanbeckevoort, MD, 1
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 9:373 377 (1999) Original Research Pelvic Floor Descent in Females: Comparative Study of Colpocystodefecography and Dynamic Fast MR Imaging D. Vanbeckevoort, MD, 1
Look Beyond the Surface and Get the Complete Pelvic Floor Picture
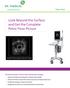 Pelvic Floor Look Beyond the Surface and Get the Complete Pelvic Floor Picture Endovaginal ultrasound. Levator ani defect seen on the right side (arrows). A=anus, B=bladder, LA=levator ani, U=urethra.
Pelvic Floor Look Beyond the Surface and Get the Complete Pelvic Floor Picture Endovaginal ultrasound. Levator ani defect seen on the right side (arrows). A=anus, B=bladder, LA=levator ani, U=urethra.
Accidental Bowel Leakage (Fecal Incontinence)
 Accidental Bowel Leakage (Fecal Incontinence) What is Accidental Bowel Leakage (ABL)? Accidental bowel leakage is the inability to control solid or liquid stool. This is the inability to control gas and
Accidental Bowel Leakage (Fecal Incontinence) What is Accidental Bowel Leakage (ABL)? Accidental bowel leakage is the inability to control solid or liquid stool. This is the inability to control gas and
Function of the anal sphincters in patients with
 Function of the anal sphincters in patients with intussusception of the rectum B. FRENCKNER AND T. IHRE Gut, 1976,17, 147-151 From the Department of Clinical Physiology and the Department of Surgery, Serafimer
Function of the anal sphincters in patients with intussusception of the rectum B. FRENCKNER AND T. IHRE Gut, 1976,17, 147-151 From the Department of Clinical Physiology and the Department of Surgery, Serafimer
Prolapse and Urogynae Incontinence. Lucy Tiffin and Hannah Wheldon-Holmes
 Prolapse and Urogynae Incontinence Lucy Tiffin and Hannah Wheldon-Holmes 66 year old woman with incontinence PC: 7 year Hx of urgency, frequency, nocturia (incl. incontinence at night), and stress incontinence
Prolapse and Urogynae Incontinence Lucy Tiffin and Hannah Wheldon-Holmes 66 year old woman with incontinence PC: 7 year Hx of urgency, frequency, nocturia (incl. incontinence at night), and stress incontinence
Common Gastrointestinal Problems in the Elderly
 Common Gastrointestinal Problems in the Elderly Brian Viviano, D.O. Objectives Understand the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis and management of GI diseases of the elderly. Differentiate
Common Gastrointestinal Problems in the Elderly Brian Viviano, D.O. Objectives Understand the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis and management of GI diseases of the elderly. Differentiate
Defecography: a still needful exam for evaluation of pelvic floor diseases
 Acta Biomed 2016; Vol. 87, Supplement 3: 34-39 Mattioli 1885 Review Defecography: a still needful exam for evaluation of pelvic floor diseases Silvia Eleonora Gazzani 1, Emanuela Angela Marcantoni 1, Giovanni
Acta Biomed 2016; Vol. 87, Supplement 3: 34-39 Mattioli 1885 Review Defecography: a still needful exam for evaluation of pelvic floor diseases Silvia Eleonora Gazzani 1, Emanuela Angela Marcantoni 1, Giovanni
Chapter 2 Overview of Testing of Motility and of the Anorectum
 Chapter 2 Overview of Testing of Motility and of the Anorectum Vanessa C. Costilla and Amy E. Foxx-Orenstein Chapter Objectives At the conclusion of reading this chapter, the reader will be able to: 1.
Chapter 2 Overview of Testing of Motility and of the Anorectum Vanessa C. Costilla and Amy E. Foxx-Orenstein Chapter Objectives At the conclusion of reading this chapter, the reader will be able to: 1.
ig. 2. The organs and their outlet tubes.
 Fig. 1. Birth-related laxity. The diagram shows the baby s head severely stretching ligaments and other tissues in and outside the vagina. This may cause various degrees of looseness, prolapse of the bladder
Fig. 1. Birth-related laxity. The diagram shows the baby s head severely stretching ligaments and other tissues in and outside the vagina. This may cause various degrees of looseness, prolapse of the bladder
Gynecology Dr. Sallama Lecture 3 Genital Prolapse
 Gynecology Dr. Sallama Lecture 3 Genital Prolapse Genital(utero-vaginal )prolapse is extremely common, with an estimated 11% of women undergoing at least one operation for this condition. Definition: A
Gynecology Dr. Sallama Lecture 3 Genital Prolapse Genital(utero-vaginal )prolapse is extremely common, with an estimated 11% of women undergoing at least one operation for this condition. Definition: A
Best Practice Statement on Evaluation of Obstructed Defecation. The symptoms of constipation and obstructed defecation are common in women with
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Best Practice Statement on Evaluation of Obstructed Defecation INTRODUCTION The symptoms of constipation and obstructed defecation are common in women with pelvic floor
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Best Practice Statement on Evaluation of Obstructed Defecation INTRODUCTION The symptoms of constipation and obstructed defecation are common in women with pelvic floor
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction. Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
Disclosure. Acknowledgement. What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Rectal cancer imaging. None
 What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
Constipation an Old Friend. Presented by Dr. Keith Harris
 Constipation an Old Friend Presented by Dr. Keith Harris Irregularity and the Tricks of the Trade." CONSTIPATION What is constipation? INFREQUENT BOWEL MOVEMENTS DIFFICULTY DURING DEFECATION SENSATION
Constipation an Old Friend Presented by Dr. Keith Harris Irregularity and the Tricks of the Trade." CONSTIPATION What is constipation? INFREQUENT BOWEL MOVEMENTS DIFFICULTY DURING DEFECATION SENSATION
John Laughlin 4 th year Cardiff University Medical Student
 John Laughlin 4 th year Cardiff University Medical Student Prolapse/incontinence You need to know: Pelvic floor anatomy in relation to uterovaginal support and continence The classification of uterovaginal
John Laughlin 4 th year Cardiff University Medical Student Prolapse/incontinence You need to know: Pelvic floor anatomy in relation to uterovaginal support and continence The classification of uterovaginal
Accuracy of transvaginal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis and extension of pelvic endometriosis
 Accuracy of transvaginal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis and extension of pelvic endometriosis A.Salem, Kh. Fakhfakh, S. Mehiri, Y. Ben Brahim, F. Ben Amara, H. Rajhi, R. Hamza,
Accuracy of transvaginal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis and extension of pelvic endometriosis A.Salem, Kh. Fakhfakh, S. Mehiri, Y. Ben Brahim, F. Ben Amara, H. Rajhi, R. Hamza,
disease and incontinence
 Operative and diagnostic strategies in pelvic floor disease and incontinence a thesis by Kwong-Wei Emile John Tan Submitted for the degree of DOCTOR OF MEDICINE to Imperial College London 2012 1 Acknowledgements
Operative and diagnostic strategies in pelvic floor disease and incontinence a thesis by Kwong-Wei Emile John Tan Submitted for the degree of DOCTOR OF MEDICINE to Imperial College London 2012 1 Acknowledgements
Definition of Anatomy. Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts.
 Definition of Anatomy Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts. Basic Anatomical Terms Anatomical terms for describing positions: Anatomical position: Supine position:
Definition of Anatomy Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts. Basic Anatomical Terms Anatomical terms for describing positions: Anatomical position: Supine position:
Voiding Diary. Begin recording upon rising in the morning and continue for a full 24 hours.
 Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Perianal Fistulas
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Perianal Fistulas Poster No.: C-0317 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit A. P. Sathe, E. Soh, K. Y. Seto, B. Yeh, D. W. Y. chee, R. Quah,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Perianal Fistulas Poster No.: C-0317 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit A. P. Sathe, E. Soh, K. Y. Seto, B. Yeh, D. W. Y. chee, R. Quah,
Surgical Management for Defecation Dysfunction
 Defecatory Dysfunction Surgical Management for Defecation Dysfunction JMAJ 46(9): 378 383, 2003 Tatsuo TERAMOTO Professor, 1st Department of Surgery, School of Medicine, Toho University Abstract: Typical
Defecatory Dysfunction Surgical Management for Defecation Dysfunction JMAJ 46(9): 378 383, 2003 Tatsuo TERAMOTO Professor, 1st Department of Surgery, School of Medicine, Toho University Abstract: Typical
Langley Catheter Protocols
 Langley Catheter Protocols Stericom Ltd Units 1&2 Higham Mead Chesham HP5 2AH England Tel: +44 (0)1494 794315 Fax: +44 (0)1494 772759 info@stericom.com www.stericom.com Instructions for use The 2-balloon
Langley Catheter Protocols Stericom Ltd Units 1&2 Higham Mead Chesham HP5 2AH England Tel: +44 (0)1494 794315 Fax: +44 (0)1494 772759 info@stericom.com www.stericom.com Instructions for use The 2-balloon
Clinical Policy Bulletin: Defecography
 Defecography Page 1 of 10 Clinical Policy Bulletin: Defecography Revised April 2014 Number: 0718 Policy I. Aetna considers defecography (evacuation proctography) medically necessary in members with constipation
Defecography Page 1 of 10 Clinical Policy Bulletin: Defecography Revised April 2014 Number: 0718 Policy I. Aetna considers defecography (evacuation proctography) medically necessary in members with constipation
Original article Pathophysiology and diagnosis of descending perineum syndrome in children
 Original article Pathophysiology and diagnosis of descending perineum syndrome in children MIChAel D. levin State Geriatric Center, Netanya, Israel Abstract: The purpose of this study is to offer a safe,
Original article Pathophysiology and diagnosis of descending perineum syndrome in children MIChAel D. levin State Geriatric Center, Netanya, Israel Abstract: The purpose of this study is to offer a safe,
Constipation Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.uk
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
Traditional Anterior, Posterior, and Apical Compartment Repairs A Technique Based Review
 Traditional Anterior, Posterior, and Apical Compartment Repairs A Technique Based Review Sandip Vasavada, MD Center for Female Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery The Glickman Urological and Kidney
Traditional Anterior, Posterior, and Apical Compartment Repairs A Technique Based Review Sandip Vasavada, MD Center for Female Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery The Glickman Urological and Kidney
PELVIC FLOOR ULTRASOUND
 PELVIC FLOOR ULTRASOUND How, When, Why Part 1: Phyllis Glanc MD Sunnybrook Health Science Center University of Toronto Phyllis.Glanc@sunnybrook.ca www.phyllisglanc.com (current exact handout) Disclosures
PELVIC FLOOR ULTRASOUND How, When, Why Part 1: Phyllis Glanc MD Sunnybrook Health Science Center University of Toronto Phyllis.Glanc@sunnybrook.ca www.phyllisglanc.com (current exact handout) Disclosures
Urogynaecology & Prolapse. Alexander Denning and Leifa Jennings
 + Urogynaecology & Prolapse Alexander Denning and Leifa Jennings + Contents What even is prolapse / urogynaecology? Pelvic floor anatomy Prolapse Urinary incontinence Prevention The end (woot) + Urogynaecology
+ Urogynaecology & Prolapse Alexander Denning and Leifa Jennings + Contents What even is prolapse / urogynaecology? Pelvic floor anatomy Prolapse Urinary incontinence Prevention The end (woot) + Urogynaecology
Pregnancy related pelvic floor dysfunction- suggested teaching presentation for Midwives
 Pregnancy related pelvic floor dysfunction- suggested teaching presentation for Midwives 1 Aims of this self assessment competency To equip Midwives with the knowledge and skills to teach pelvic floor
Pregnancy related pelvic floor dysfunction- suggested teaching presentation for Midwives 1 Aims of this self assessment competency To equip Midwives with the knowledge and skills to teach pelvic floor
PELVIC FLOOR DYSFUNCTION
 gastrointestinal tract and abdomen PELVIC FLOOR DYSFUNCTION Michael A. Valente, DO, FACS, FASCRS, and Tracy L. Hull, MD, FACS, FASCRS One of the most complex and potentially frustrating groups of patients
gastrointestinal tract and abdomen PELVIC FLOOR DYSFUNCTION Michael A. Valente, DO, FACS, FASCRS, and Tracy L. Hull, MD, FACS, FASCRS One of the most complex and potentially frustrating groups of patients
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: BIOFEEDBACK
 MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 6 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 6 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
Constipation. Information for adults. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1
 Constipation Information for adults GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Contents Role of the large intestine..3 Mass movements in the large intestine..4
Constipation Information for adults GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Contents Role of the large intestine..3 Mass movements in the large intestine..4
Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy
 Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Constipation An Overview. Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment
 CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
The pelvic floor is a system of muscles, ligaments, and tissues that keep your pelvic organs firmly in place.
 The pelvic floor is a system of muscles, ligaments, and tissues that keep your pelvic organs firmly in place. Think of it as the hammock of muscle that holds up your uterus, vagina, bladder, small intestine,
The pelvic floor is a system of muscles, ligaments, and tissues that keep your pelvic organs firmly in place. Think of it as the hammock of muscle that holds up your uterus, vagina, bladder, small intestine,
Colorectal Pathway Board (Clinical Subgroup): Imaging Guidelines September 2015
 Colorectal Pathway Board (Clinical Subgroup): Imaging Guidelines September 2015 1 Contents Page No. 1. Objective 3 2. Imaging Techniques 3 3. Staging of Colorectal Cancer 5 4. Radiological Reporting 6
Colorectal Pathway Board (Clinical Subgroup): Imaging Guidelines September 2015 1 Contents Page No. 1. Objective 3 2. Imaging Techniques 3 3. Staging of Colorectal Cancer 5 4. Radiological Reporting 6
Prediction and prevention of stress urinary incontinence after prolapse surgery van der Ploeg, J.M.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Prediction and prevention of stress urinary incontinence after prolapse surgery van der Ploeg, J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Prediction and prevention of stress urinary incontinence after prolapse surgery van der Ploeg, J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van
Hemorrhoids. Carlos R. Alvarez-Allende PGY-III Colorectal Surgery
 Hemorrhoids Carlos R. Alvarez-Allende PGY-III Colorectal Surgery Overview Anatomy Classification Etiology Incidence Symptoms Differential Diagnosis Medical Management Surgical Management Anatomy Anal canal
Hemorrhoids Carlos R. Alvarez-Allende PGY-III Colorectal Surgery Overview Anatomy Classification Etiology Incidence Symptoms Differential Diagnosis Medical Management Surgical Management Anatomy Anal canal
UNDERSTANDING IBS AND CC Implications for diagnosis and management
 UNDERSTANDING IBS AND CC Implications for diagnosis and management J. TACK, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Gastroenterology University Hospitals, K.U. Leuven Leuven, Belgium TYPES OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS
UNDERSTANDING IBS AND CC Implications for diagnosis and management J. TACK, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Gastroenterology University Hospitals, K.U. Leuven Leuven, Belgium TYPES OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS
Controlled randomised trial of visual biofeedback
 Gut 1995; 37: 95-99 Service de Medecine C, CHG de F6camp, 764 F6camp, France D Koutsomanis St Mark's Hospital, London EC1V 2PS J E Lennard-Jones A J Roy M A Kamm Correspondence to: Professor J E Lennard-Jones,
Gut 1995; 37: 95-99 Service de Medecine C, CHG de F6camp, 764 F6camp, France D Koutsomanis St Mark's Hospital, London EC1V 2PS J E Lennard-Jones A J Roy M A Kamm Correspondence to: Professor J E Lennard-Jones,
Pelvic Organ Prolapse. Natural Solutions
 Pelvic Organ Prolapse Natural Solutions Bringing your body back to its natural state There is a very common problem affecting millions of women. Many women are too embarrassed to talk to their physicians
Pelvic Organ Prolapse Natural Solutions Bringing your body back to its natural state There is a very common problem affecting millions of women. Many women are too embarrassed to talk to their physicians
Summary and conclusion. Summary And Conclusion
 Summary And Conclusion Summary and conclusion Rectal prolapse remain a disorder for which no single ideal treatment was approved for all cases. Complete rectal prolapse (procidentia) is the circumferential
Summary And Conclusion Summary and conclusion Rectal prolapse remain a disorder for which no single ideal treatment was approved for all cases. Complete rectal prolapse (procidentia) is the circumferential
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery
 World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 6, Issue 1 Article 3 Starr Surgery In ODS: A Case Series Of 500 ODS Patients Operated At India s Largest Proctology Clinic Ashwin Dhanarajji Porwal Paresh Manilal
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 6, Issue 1 Article 3 Starr Surgery In ODS: A Case Series Of 500 ODS Patients Operated At India s Largest Proctology Clinic Ashwin Dhanarajji Porwal Paresh Manilal
FEMALE PELVIS Normal Tissue RTOG Consensus Contouring Guidelines
 FEMALE PELVIS Normal Tissue RTOG Consensus Contouring Guidelines Hiram A. Gay, M.D., H. Joseph Barthold, M.D., Elizabeth O Meara, C.M.D., Walter R. Bosch, Ph.D., Issam El Naqa, Ph.D., Rawan Al-Lozi, Seth
FEMALE PELVIS Normal Tissue RTOG Consensus Contouring Guidelines Hiram A. Gay, M.D., H. Joseph Barthold, M.D., Elizabeth O Meara, C.M.D., Walter R. Bosch, Ph.D., Issam El Naqa, Ph.D., Rawan Al-Lozi, Seth
Review Article Pelvic Floor Dysfunction, Body Excreta Incontinence and Continence
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS GYNAECOLOGY Review Article Pelvic Floor Dysfunction, Body Excreta Incontinence and Continence Abdel Karim M El Hemaly 1 * and Laila ASE Mousa 1 1 Professor of Obstetrics and gynaecology,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS GYNAECOLOGY Review Article Pelvic Floor Dysfunction, Body Excreta Incontinence and Continence Abdel Karim M El Hemaly 1 * and Laila ASE Mousa 1 1 Professor of Obstetrics and gynaecology,
Ultrasound - Prostate
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Prostate Ultrasound of the prostate uses sound waves to produce pictures of a man s prostate gland and to help diagnose symptoms such as difficulty urinating or an elevated
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Prostate Ultrasound of the prostate uses sound waves to produce pictures of a man s prostate gland and to help diagnose symptoms such as difficulty urinating or an elevated
Sacral, ilioinguinal, and vasal nerve stimulation for treatment of pelvic, sacral, inguinal and testicular Pain.
 Chapter 14 Sacral, ilioinguinal, and vasal nerve stimulation for treatment of pelvic, sacral, inguinal and testicular Pain. Introduction Sacral nerve root stimulation has been recognized as a treatment
Chapter 14 Sacral, ilioinguinal, and vasal nerve stimulation for treatment of pelvic, sacral, inguinal and testicular Pain. Introduction Sacral nerve root stimulation has been recognized as a treatment
Understanding Pelvic Organ Prolapse. Stephanie Pickett, MD, MS Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery
 Understanding Pelvic Organ Prolapse Stephanie Pickett, MD, MS Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery Disclosures None I am the daughter of a physician assistant. Objectives List types of pelvic
Understanding Pelvic Organ Prolapse Stephanie Pickett, MD, MS Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery Disclosures None I am the daughter of a physician assistant. Objectives List types of pelvic
 INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
Application of Anorectal Dynamics in the Treatment of Colon Disease Packing
 Application of Anorectal Dynamics in the Treatment of Colon Disease Packing Zongyue Gao 1, 2, a, Yuyan Liu 1, 2, b, Chunxia Wan 1, 2, c 3, d* and Xiaoli Zhou 1 Henan Province Hospital of TCM, 450000, Henan,
Application of Anorectal Dynamics in the Treatment of Colon Disease Packing Zongyue Gao 1, 2, a, Yuyan Liu 1, 2, b, Chunxia Wan 1, 2, c 3, d* and Xiaoli Zhou 1 Henan Province Hospital of TCM, 450000, Henan,
Populations Interventions Comparators Outcomes Individuals: With fecal incontinence
 Protocol Biofeedback as a Treatment of Fecal Incontinence or Constipation (20164) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/13 Next Review Date: 03/19 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 09/07, 09/08, 09/09,
Protocol Biofeedback as a Treatment of Fecal Incontinence or Constipation (20164) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/13 Next Review Date: 03/19 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 09/07, 09/08, 09/09,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Associated with
 Table1: Rome III and Rome IV diagnostic criteria for IBS, functional constipation and functional dyspepsia. Rome III diagnostic criteria 1,2 Rome IV diagnostic criteria 3,4 Diagnostic criteria for IBS
Table1: Rome III and Rome IV diagnostic criteria for IBS, functional constipation and functional dyspepsia. Rome III diagnostic criteria 1,2 Rome IV diagnostic criteria 3,4 Diagnostic criteria for IBS
Clinical Curriculum: Urogynecology
 Updated July 201 Clinical Curriculum: Urogynecology GOAL: The primary goal of the Urogynecology rotation at the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB) is to train physicians to have a broad knowledge
Updated July 201 Clinical Curriculum: Urogynecology GOAL: The primary goal of the Urogynecology rotation at the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB) is to train physicians to have a broad knowledge
Biofeedback provides long term benefit for patients with intractable, slow and normal transit constipation
 Gut 1998;42:517 521 517 St Mark s Hospital, London, UK E Chiotakakou-Faliakou M A Kamm AJRoy J B Storrie I C Turner Correspondence to: Dr M A Kamm, St Mark s Hospital, Northwick Park, Watford Road, Harrow,
Gut 1998;42:517 521 517 St Mark s Hospital, London, UK E Chiotakakou-Faliakou M A Kamm AJRoy J B Storrie I C Turner Correspondence to: Dr M A Kamm, St Mark s Hospital, Northwick Park, Watford Road, Harrow,
