METHODS AND DEVICES FOR ANAL SPHYNCTER TONOMETRY: CHALLENGES AND SOLUTIONS. Summary
|
|
|
- Chloe Lindsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article METHODS AND DEVICES FOR ANAL SPHYNCTER TONOMETRY: CHALLENGES AND SOLUTIONS Sergey D. Iliev, Pencho T. Tonchev, Dimitar J. Stoykov, 1 Slavcho T. Tomov, Biser K. Borisov2, 3 Dobromir D. Nguen, Alexandra I. Vulcheva3 Surgical Clinic, University Hospital - Pleven 1 Clinic of Oncogynecology, University Hospital - Pleven 2 Clinic of Nephrology and Haemodialysis, University Hospital - Pleven 3 Student, Medical University Pleven Summary Anal tonometry contributes to objective assessment of the functional status of the anal sphincter complex. There are a variety of methods used in measuring the difference in pressures, generated by this complex, as well as various devices. In everyday practice, few health establishments in this country have such devices. We aimed to evaluate the requirements to devices of this kind in view of choosing an appropriate method and a device, so as to invent and put to the test in everyday practice a relevant device. We created a 5-channel anal sphincter tonometer connected to a computer. The software specially developed for the purpose makes it possible to obtain and record real-time results from the tonometry, carried out simultaneously or in sequence at different levels of the anal canal. Keywords: sphinctertonometry, sphincter pressure gauges, anal sphincter, rectoinhibitory reflex, anal sphincter pressure Methods in sphincter tonometry: advantages and disadvantages Anal sphincter tonometry helps to objectively assess the functional status of the anal sphincter complex. In clinical practice, any surgical intervention on the anal canal and the distal part of the colon should be undertaken after a careful preliminary assessment of the sphincter tone. It is important to know what the effect of a surgical operation on anal continence might be. The latter helps to determine the adequacy of any specific method of treatment. Corresponding Author: Sergey D. Iliev Clinic of Surgery UMHAT Dr G.Stranski 5800, Pleven Bulgaria sergeyiliev@gmail.com Received: November 20, 2011 Revision received: December 01, 2011 Accepted: December 22, What is measured and why? Parameters that could be measured by anal tonometry Resting anal pressure The anal pressure at rest (RAP) is responsible for continence of the anal sphincter complex. If the values of RAP decrease below a specific level, anal incontinence of varying degrees may occur. The internal sphincter is in physiological tonic contraction while the external sphincter is in partial contraction even during sleep [1, 2, 3]. Resting anal pressure is mainly determined by the contractions of the external anal sphincter. The muscle is in continuous tone due to phase variations of slow
2 Iliev S. et al. Methods and devices for anal sphyncter tonometry:... waves. They are most commonly observed when the resting pressure is high and they occur at a rate of 6 to 20 per minute with an amplitude of cm Н2О [4, 5]. Extremely slow waves with a high pressure and a rate of 1-3 per minute are registered in 5% of healthy volunteers examined [6]. The value of the anal pressure is formed by the internal sphincter which contributes for 50 to 80 % of it, the external sphincter 25-30% and the hemorrhoid tissue 15-20%. Resting anal pressure is lower in females than in males [7, 8] and decreases with age [8]. Usually, a value of cm Н2О is considered normal. Volitional contraction anal pressure Volitional contraction anal pressure (VCAP) is responsible for controlling the urge to defecate and overcoming the increased intraabdominal pressure. When the values of VCAP lower than a definite threshold, anal incontinence of a varying degree occurs and the urge cannot be controlled. The external sphincter is responsible for volitional contraction pressure which is measured as the difference between resting anal pressure and the maximum value measured in volitional contraction pressure [9]. It is lower in females and decreases with age [7]. The reflex of contraction of the external anal sphincter as a response to increased intraabdominal pressure is tested while coughing during the examination, which should be routinely performed during anal manometry [10]. Cough anal pressure Cough anal pressure (CAP) shows the difference occurring in the rectal pressure caused by increased intraabdominal pressure during coughing and the pressure in the anal canal, determined by the tone of the external sphincter and a transitory volitional contraction of the external sphincter, accompanies the cough reflex. When the values of CAP become lower than the values of pressure in the rectum, varying degrees of anal incontinence may occur. Rectoanal inhibitory reflex Rectoanal inhibitory reflex (RAIR) is the decrease in the values of resting anal pressure by 20%, while the pressure in the rectum increases as a result of distension or contraction [11, 12], generated by the intramural nerve path [13;14] with subsequent return to normal values. The reflex can be examined by balloon dilation of the rectum, during which anal pressure values are recorded. A balloon is attached to the tip of a perfusion catheter and placed in the rectum. The anal pressure is then stabilized and the balloon is filled with ml of air or liquid. This leads to a decrease of the rest anal pressure by 20% with a subsequent return to normal ranges (positive reflex). This reflex is absent in patients with Hirshsprung disease [15]. A significant relaxation of the anal sphincter occurs in cases of increased rectal pressure is found in patients with fecal incontinence and patients with constipation [16]. How is it measured? Advantages and disadvantages of methods. Devices and techniques for sphincter tonometry Laeven was the first to apply anorectal tonometry in assessing the tone of the anal sphincter in Later, Gaston (1948), V. N. Demin (1954), Janchev (1959), A. M. Aminev (1965) and other authors suggested new approaches in sphincter tonometry and improved the technique. In 1960, Hill proposed registering the gradient of pressure in the ano-rectum with placing a hydro-perfusion system. In 1974, Holschneider applied the method for distinguishing different forms of chronic obstipation. Today we have a large variety of methods for recording the pressure gradient, generated by the anal sphincter complex. The pressure can be measured simultaneously or step by step at different levels of the anal canal. This is usually accomplished at intervals of 1cm, although some perfusion systems can make recordings at intervals of 0.75cm. Simultaneous recording of all the values is preferable because it saves time for the sphincter complex to adapt to the catheter and time it takes to measure the normal rest pressure which is about 3 minutes. The use of the pull-through technique requires calibration of the rest pressure on each level of the anal canal. The maximal diameter of the recording device should be less than 5 mm. Catheters with larger diameter increase pressure in the anal canal because of irritation of the anal sphincter complex with a subsequent increase in muscle tone [2, 17, 18]. Perfusion systems Perfusion catheters are set of small tubes with low stretch coefficient and side holes connected to sensor for registering the pressure, perfused with gas-free water at constant rate which may be 0.4 to 0.6 ml/min. Constant perfusion is needed for keeping the side holes open all the time. The pressure in the catheter is the index of resistance 109
3 110 of the liquid flow leaking out of it. Catheters used have 4 or 6 channels. A perfusion catheter can be also applied using a pull-through technique. A possible cause for inaccurate results when using this technique is the likelihood of the liquid to leak out, irritate the anal mucosa, thus causing contraction of the sphincter complex. Advantage: The perfusion systems are considered most accurate. Disadvantages: This is very expensive laboratory equipment, requiring continuous water flow and generating positional differences in values registered. Perfusion systems are not suitable for routine out hospital practice. Balloon systems Balloon systems consist of a balloon filled with liquid or air, attached to a smooth nonexpandable tube that is connected to a sensor to register the gradient of pressure. The balloon systems filled with water yield results comparable to those filled with air [19, 20]. Modern balloon systems use micro balloons with a diameter of 4mm. A stationary pull-through technique can be applied. With this method, no information is obtained about the about variations in radial pressure because the balloon only records the maximal pressure in every zone. Advantage: They are suitable for everyday practice outside the hospital. Disadvantage: they are not as precise as perfusion systems and no information about changes in radial pressure are obtained. Sleeve catheters Catheters of this type have an elastic membrane, fixed on a catheter to form a closed chamber through which water is perfused [21]. The sleeve stretches through the whole anal canal and can measure the pressure on every level. This technique is applied to measure pressure during defecation, while the patient is sitting on a toilet dish thus registering movement of the anus in caudal direction. The use of sleeve catheters is limited only to physiological studies in special laboratories. Advantage: They are highly precise and demonstrate physiological changes during defecation. Disadvantages: This is very expensive laboratory equipment necessitating specific conditions. It is not suitable for routine everyday practice. Straingauge catheters (deformation sensors) The now available strain gauge transducers have resistors that are fixed on a metal diaphragm placed into vacuum. The pressure applied on the diaphragm changes the resistance in the system, and this resistance is converted into units for measuring pressure [22, 23]. The catheters used can consist of one or more transducers, applied with stationary pull-through technique or simultaneous recording device. A stationary system or ambulatory system can be used for obtaining real time values. Advantage: Strain gauge catheters can be used in everyday practice in a setting outside the hospital. Disadvantages: The equipment is rather expensive, the price depending on the number of transducers used. The device is not as precise as perfusion systems. No information can be obtained regarding the changes in radial pressure. Vector manometry The use of a perfusion catheter to record radial pressure makes it possible to generate a 3D graph indicating the tone of the anal sphincter. The catheter has 8 side openings and a stationary pullthrough technique or continuous pull-through technique is used [25]. Vector manometry is useful for determining the origin of the sphincter deficit, regardless of the cause muscular defect or a neurogenic lesion with a non-damaged sphincter ring. Advantage: The device provides a high level of precision and reliability in detecting defects of sphincter lesions, and a 3D presentation of the sphincter dysfunction can be obtained. Disadvantages: The device can be used in a specialized laboratory setting, rather than in everyday practice. The reliability of results obtained is comparable to those obtained using endoanal echography. Ambulatory manometry The systems available for measuring anal tone use stain gauge transducers. They are easy to handle but probes with a sufficient number of transducers are very expensive and ambulatory perfusion systems are necessary. The probe should have three transducers one at the top to measure rectal pressure, and two for anal pressure. The minimum distance between the transducers in a flexible probe is 2 cm. However, if the anal canal is short, it is impossible to use two locations. The application of one anal transducer implies its positioning midway along the anal canal. Advantage: These systems are applicable in everyday practice. Disadvantage: The measurement is not reliably precise.
4 Iliev S. et al. Methods and devices for anal sphyncter tonometry:... Requirements to devices in view of needs of everyday practice and related problems The problem remains how to identify a reproducible method for objective quantitative evaluation of sphincter dysfunction. At present, the assessment is based on a digital rectal examination and a subjective interpretation of a semi-quantitative scale. The specialized equipment available on the market is unaffordable and suitable for use in a laboratory setting. We defined the requirements to the device we needed: It should be portable and suitable for use in both laboratory and ambulatory conditions. It should measure the pressure at different levels in the anal canal and the rectum. There should be a balloon to allow using liquid to register the changes in RAIR, Calibration should be possible to standard manometric apparatuses and make the results obtained comparable to values obtained by other devices. It should work with precise sensors for pressure and microprocessor analog-digital converter. The probe of the device should be not more than 10mm in diameter The connection to a laptop computer and power supply should be of 5 volts maximum. The software should register data frequently enough up to three readings per second and present the data graphically in real time. The software should integrate all data required by the protocol of the investigation: personal data, diagnosis, treatment administered. There should be the option to print out the graphs representing the data obtained and the statement of the investigator. The device and the software should be relatively non-expensive and allow to be updated. The software should provide export of data for the purposes of processing. Ambulatory sphincter tonometry device We constructed a device and developed software for anal tonometry which has the advantages and the precision of the devices for laboratory studies and a compact size like that of portable devices. The probe used is a five channel balloon catheter, 7 mm in diameter and 5cm in length, correlating with the sizes of the zone with increased pressure in the anal canal, which is 45sm in length. The pressure gradient is measured in the zone with a length of 4cm for the anal canal, and that of 1cm registers the pressure in the rectum. We also took into consideration the diameter of the probe, recommended in studies less than 10 mm, because a probe of this size does not provoke an increase in the sphincter tone when inserted in the anal canal. The balloons are 0.1mm thin and 1cm long. They are placed along the 5-cm zone, and then filled with distilled water. The first balloon registers the pressure in the rectum and is used for examination of the rectoanal inhibitory reflex. It is connected to a syringe for injecting air or liquid. The second balloon registers the pressure in the anal canal at the level of the deep part of the external anal sphincter and puborectal muscle. The third balloon registers the tone at the level of the medial part of the external anal sphincter. The fourth balloon registers the pressure in the anal canal at the level of the superficial external sphincter. The fifth balloon registers the pressure in the anal canal at the level of the subcutaneous part of the external anal sphincter. The probe is presented schematically in Figure 1. Figure 1. The probe of the sphincter manometer The sphincter manometer registers in real time the pressure in the anal canal in rest, in volitional contraction and while coughing. The software created by us can digitally present the data recorded. The data is recorded every second. Every sensor measures the 111
5 pressure in the anal in a circular zone 1cm in length. Before examination the device is calibrated in a horizontal position, in which the pressure from the five balloons is registered. During examination, the data received is a result of the values acquired during the study minus the values received during calibration. The data has a graphic and numeric expression and can be recorded in cm Н2О or mm Hg. The software allows reading the peak levels and automatically records them in an EXCEL table. First, we examine the sphincter tone at rest, which is a result of the tone of the internal anal sphincter, and partly the tone of the external anal sphincter. While coughing and in volitional contraction, the data obtained objectively reflects the data about the tone of the external anal sphincter at the anatomical levels mentioned above. The following inflation of the rectal balloon with 50 ml of liquid allows the registration of the status of the rectoanal inhibitory reflex (presence or absence). If a 20% increase in the values of the anal pressure at rest is seen after inflation of the rectal balloon with 50ml, with a subsequent return to normal ranges, we assume that the rectoanal inhibitory reflex is positive. If there is no change in the anal tone at rest and after inflating the rectal balloon, the reflex is negative (lack of reflex). A graphic presentation of the recorded values is shown on Figure cm Н2О, a decrease is registered in the pressure of the sphincter complex with more than 20% from the one measured while at rest, with a subsequent return to normal ranges after the rectal balloon is deflated. The values measured in the subcutaneous anal sphincter are shown in black, the ones in the superficial anal sphincter in blue; the ones in the medial anal sphincter in yellow, yellow ; green the ones in the deep anal sphincter in green, and these in the puborectal muscle in red. Figure 3. Graphic presentation of the registered values of anal canal pressure in rest, in volitional contraction and while coughing, and RAIR Figure 2. Graphic presentation of the registered values of anal canal pressure at rest, in volitional contraction and while coughing, and RAIR Examination protocol The examination is performed on a patient who is in supine position on his/her left side, with legs bent at the hip and knee joints. After the probe is inserted into the anus, a period of 5 minutes is required for the sphincter to adapt. After this period, a series of three volitional contractions, each for 5 seconds is conducted. Between each volitional contraction there is a period of 30 seconds. This is followed by a single cough; inflation of the rectal balloon with 50 ml of liquid which stays inflated for 1 minute. This allows us to examine the rectoanal inhibitory reflex. Finally, the balloon is deflated which is followed by one last volitional contraction. On the graph the rectoanal inhibitory reflex is negative. Figure 3 demonstrates a positive rectoanal inhibitory reflex. When the pressure is increased in the rectal ampulla by inflating a balloon with 50 ml of water until a value of 240 Problems with data interpretation. When normal, the anal canal is elastic and can expand when using different catheters for measuring anorectal pressure and the catheters do not change the results from the examination. nd rd In cases of old scars present, or 2 and 3 degree hemorrhoids when probes with a larger diameter
6 Iliev S. et al. Methods and devices for anal sphyncter tonometry:... are used, the values obtained may be higher than normal. The anal pressure increases when the examination is performed in a standing position because of the increased intraabdominal pressure which in turn increases the tone of the external anal sphincter. When examining RAIR in a standup position, it is necessary to inflate the balloons with air because of its low relative weight. The inflation of the rectal balloon with liquid is applied when the examination is performed in supine position of the patient. The decrease in the anal pressure at rest by 20%, followed by return to normal ranges is considered as positive rectoanal inhibitory reflex. When the results from the examination are interpreted, age, previous surgical procedures, presence of illness at the time of the examination, the equipment used and the protocol of the examination are taken into consideration. Figure 4 presents the device itself. Figure 4. Ambulatory sphinctertonometry device developed Discussion The device we propose is easy to handle. Calibration before each time the device is used helps to achieve results that are accurate and comparable to results obtained using similar devices. Calibration takes one minute. Once a week, the device is checked with an external manometer fore accuracy of calibrations and settings of the program with a specially designed set. Every examination takes 3-5 minutes. The results are printed out on the patient examination form. The device has so far been used to examine: Healthy volunteers to serve as a control group. Patients with anal fissure. Patients with anal fistula. Patients with gynaecological diseases. Patients with oncological diseases. A total of 143 males and 164 females were examined. The changes in the values of anal pressure found were determined according to the diseases and the treatment administered. The changes in RAIR were found in patients with cancer of the anorectum, in patients with anal fissure and patients with anal fistula. The results also correlated with the complaints of the patients, the subjective assessment based on digital rectal examination of the tone (R2=0.77) and the evaluation based on the scale of incontinence (R2=0.87). Conclusion Sphincter tonometry on its own is not a gold standard for assessment of the functional status of the anal sphincter complex. It is an addition to the other instrumental methods for diagnostics and complex assessment of the anal function. The device proposed by us is easy to use. It helps to objectively assess the sphincter tone on every anatomic level. It also gives information about the presence or absence of RAIR. Sphincter tonometry is an objective method to help determine the treatment plan and outcome and the degree of anal continence before and after treatment. Reference 1. Frenckner B, von Euler C. Influence of pudental block of the function of the anal sphincters. Gut. 1975;16: G u t i e r r e z J G, O l i a i A, C h e y, W Y. Manometricprofile of the internal anal sphincter in man. Gastroenterology. 1975;68: Lester B, Penninckx F, Kerremans R. The composition of anal basal pressure: An in vivo and in vitro study in man. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1989;4: Hancock B, D, Smith K. The internalsphincterand Lord's procedure for hemorrhoids. Br J Surg. 1975;62: Kerremans R. Morphological and physiological aspects of anal continence and defaecation. Brussels: Editions Arscia; Hancock BD. Measurement of anal pressure and motility. Gut. 1976;17: Loening-Baucke V, Anuras S. Effect of age and sex on anorectalmanometry. Am J Gastroenterol. 113
7 1985;80: Sun WM, Read NW. Anorectal function in normal subjects the effect of gender. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1989;4: Keighley MRB, Henry MM, Bartolo DCC, Mcc Mortensen NJ. Anorectal physiology measurement: report of a working party. Br J Surg. 1989;76(4): Meagher AP, Lubowski DZ, King DW. The cough response of the anal sphincter. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1993;8: Denny-Broun D, Robertson EG. An investigation of the nervous control of defecation. Brain. 1935;58: Naudy B, Planche D, Monges B, Salducci J. Relaxation of the internal anal sphincter elicited by rectal and extra-rectal distension in man. In: Roman C, editor. GastrointestinalMotility. London: MTP Press; p Gowers WR. The autonomic action of the sphincter ani. Proc R SocMed. 1877;26: Lubowsky DZ, Nichollas RJ, Swash M, Jordan MJ. Neural control of internal anal sphincter function. Br J Surg. 1987;74: Lawson JON, Nixon HH. Anal canal pressure in the diagnosis of Hirschsprung's disease. J Pediatr Surg. 1967;2: Kaur G, Gardiner A, Duthie GS. Rectoanal reflex parameters in incontinence and constipation. Dis Colon Rectum. 2002;45: Duthie HL, Watts JM. Contribution of the external anal sphincter to the pressure zone in the anal 114 canal.gut. 1965;6: Gibbons CP, Read NW. Anal hypertonia in fissures: cause or effect? Br J Surg. 1986;73: Miller R, Bartolo DCC, James D, Mortensen NJMcC. Air-filled microballoon manometry for use in anorectal physiology. Br J Surg. 1989;76: Orrom WJ, Wong WD, Rothenberger DA, Jensen LL. Evaluation of an air-filled microballoon and mini transducer in the clinical practice of anorectalmanometry. Dis Colon Rectumet. 1990;33: Dent J. A New technique for continuous sphincter pressure measurement. Gastroenterology. 1976;71: Roberts JP, Williams NS. The role and technique of ambulatory manometry. Bailliere's Clin Gastroenterol. 1992;6: Schouten WR, van Vroonhoven TJ. A simple method of anorectalmanometry. Dis Colon Rectumet. 1983,26: Perry RE, Blatchhford GJ, Christensen MA, Thorson AG, Attwood SEA. Manometric diagnosis of anal sphinter injuries. Am J Surg. 1990;159: Yang YK, Wexner SD. Anal pressure vectography is of no apparent benefit for sphincter evaluation. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1994;9:92-5.
Measurement of anal pressure and motility
 Measurement of anal pressure and motility B. D. HANCOCK' From the University Hospital of South Manchester Gut, 1976, 17, 645-651 SUMMARY A fine open perfused system and a closed balloon system for the
Measurement of anal pressure and motility B. D. HANCOCK' From the University Hospital of South Manchester Gut, 1976, 17, 645-651 SUMMARY A fine open perfused system and a closed balloon system for the
Function of the anal sphincters in patients with
 Function of the anal sphincters in patients with intussusception of the rectum B. FRENCKNER AND T. IHRE Gut, 1976,17, 147-151 From the Department of Clinical Physiology and the Department of Surgery, Serafimer
Function of the anal sphincters in patients with intussusception of the rectum B. FRENCKNER AND T. IHRE Gut, 1976,17, 147-151 From the Department of Clinical Physiology and the Department of Surgery, Serafimer
Viscous Fluid Retention: A New Method for Evaluating Anorectal Function
 Viscous Fluid Retention: A New Method for Evaluating Anorectal Function Michael Srensen, M.D., Tine Tetzschner, M.D., le 0. Rasmussen, M.D., John Christiansen, M.D. From the Department of Surgery D, Glostrup
Viscous Fluid Retention: A New Method for Evaluating Anorectal Function Michael Srensen, M.D., Tine Tetzschner, M.D., le 0. Rasmussen, M.D., John Christiansen, M.D. From the Department of Surgery D, Glostrup
Anorectal Diagnostic Overview
 Anorectal Diagnostic Overview 11-25-09 3.11.2010 2009 2010 Anorectal Manometry Overview Measurement of pressures and the annotation of rectal sensation throughout the rectum and anal canal to determine:
Anorectal Diagnostic Overview 11-25-09 3.11.2010 2009 2010 Anorectal Manometry Overview Measurement of pressures and the annotation of rectal sensation throughout the rectum and anal canal to determine:
MCOMPASS ANAL MANOMETRY AN OVERVIEW
 MCOMPASS ANAL MANOMETRY AN OVERVIEW ANAL MANOMETRY MEASURES PRESSURE ALLOWS INTERPRITATION SENSATION RAIR RECTAL COMPLIANCE MOTIVATION OF THE PATIENT FUNCTION OF THE PUDENDAL NERVE WHEN TO USE ANAL MANOMETRY
MCOMPASS ANAL MANOMETRY AN OVERVIEW ANAL MANOMETRY MEASURES PRESSURE ALLOWS INTERPRITATION SENSATION RAIR RECTAL COMPLIANCE MOTIVATION OF THE PATIENT FUNCTION OF THE PUDENDAL NERVE WHEN TO USE ANAL MANOMETRY
Langley Catheter Protocols
 Langley Catheter Protocols Stericom Ltd Units 1&2 Higham Mead Chesham HP5 2AH England Tel: +44 (0)1494 794315 Fax: +44 (0)1494 772759 info@stericom.com www.stericom.com Instructions for use The 2-balloon
Langley Catheter Protocols Stericom Ltd Units 1&2 Higham Mead Chesham HP5 2AH England Tel: +44 (0)1494 794315 Fax: +44 (0)1494 772759 info@stericom.com www.stericom.com Instructions for use The 2-balloon
Force in the anal canal and anal continence
 Gut, 1967, 8, 354 Force in the anal canal and anal continence C. D. COLLINS, H. L. DUTHIE, T. SHELLEY, AND G. E. WHITTAKER From the University Department of Surgery, Royal Infirmary, Sheffield EDITORIAL
Gut, 1967, 8, 354 Force in the anal canal and anal continence C. D. COLLINS, H. L. DUTHIE, T. SHELLEY, AND G. E. WHITTAKER From the University Department of Surgery, Royal Infirmary, Sheffield EDITORIAL
MCOMPASS ANAL MANOMETRY AN OVERVIEW
 MCOMPASS ANAL MANOMETRY AN OVERVIEW ANAL MANOMETRY MEASURES PRESSURE ALLOWS INTERPRITATION SENSATION RAIR RECTAL COMPLIANCE MOTIVATION OF THE PATIENT FUNCTION OF THE PUDENDAL NERVE WHEN TO USE ANAL MANOMETRY
MCOMPASS ANAL MANOMETRY AN OVERVIEW ANAL MANOMETRY MEASURES PRESSURE ALLOWS INTERPRITATION SENSATION RAIR RECTAL COMPLIANCE MOTIVATION OF THE PATIENT FUNCTION OF THE PUDENDAL NERVE WHEN TO USE ANAL MANOMETRY
Fecal Incontinence. What is fecal incontinence?
 Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
mcompass Interpretation Quick Reference Guide
 mcompass Interpretation Quick Reference Guide This document is designed to give you a starting point for reviewing of the mcompass anorectal manometry results. By no means are these the only questions
mcompass Interpretation Quick Reference Guide This document is designed to give you a starting point for reviewing of the mcompass anorectal manometry results. By no means are these the only questions
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction. Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
Application of Anorectal Dynamics in the Treatment of Colon Disease Packing
 Application of Anorectal Dynamics in the Treatment of Colon Disease Packing Zongyue Gao 1, 2, a, Yuyan Liu 1, 2, b, Chunxia Wan 1, 2, c 3, d* and Xiaoli Zhou 1 Henan Province Hospital of TCM, 450000, Henan,
Application of Anorectal Dynamics in the Treatment of Colon Disease Packing Zongyue Gao 1, 2, a, Yuyan Liu 1, 2, b, Chunxia Wan 1, 2, c 3, d* and Xiaoli Zhou 1 Henan Province Hospital of TCM, 450000, Henan,
Diagnosis of Impaired Defecatory Function with Special Reference to Physiological Tests
 Defecatory Dysfunction Diagnosis of Impaired Defecatory Function with Special Reference to Physiological Tests JMAJ 46(9): 373 377, 2003 Masatoshi OYA, Masashi UENO, and Tetsuichiro MUTO Department of
Defecatory Dysfunction Diagnosis of Impaired Defecatory Function with Special Reference to Physiological Tests JMAJ 46(9): 373 377, 2003 Masatoshi OYA, Masashi UENO, and Tetsuichiro MUTO Department of
Minimum standards of anorectal manometry
 Neurogastroenterol. Mot. (22) 14, 553 559 Minimum standards of anorectal manometry S. S. C. RAO, F. AZPIROZ,* N. DIAMANT, P. ENCK,à G. TOUGAS & A. WALD University of Iowa, Iowa City, USA; *Hospital General
Neurogastroenterol. Mot. (22) 14, 553 559 Minimum standards of anorectal manometry S. S. C. RAO, F. AZPIROZ,* N. DIAMANT, P. ENCK,à G. TOUGAS & A. WALD University of Iowa, Iowa City, USA; *Hospital General
Crucial Role of Rectoanal Inhibitory Reflex in Emptying Function After Anoplasty in Infants with Anorectal Malformations
 Original Article Crucial Role of Rectoanal Inhibitory Reflex in Emptying Function After Anoplasty in Infants with Anorectal Malformations Surasak Sangkhathat, Sakda Patrapinyokul and Noppawan Osatakul,
Original Article Crucial Role of Rectoanal Inhibitory Reflex in Emptying Function After Anoplasty in Infants with Anorectal Malformations Surasak Sangkhathat, Sakda Patrapinyokul and Noppawan Osatakul,
Comparison of Electrotherapy, Rubber Band Ligation and Hemorrhoidectomy in the Treatment of Hemorrhoids: A Clinical and Manometric Study
 Original Article 9 Comparison of Electrotherapy, Rubber Band Ligation and Hemorrhoidectomy in the Treatment of Hemorrhoids: A Clinical and Manometric Study A Izadpanah 1*, SV Hosseini 2, M Mahjoob 1 1.
Original Article 9 Comparison of Electrotherapy, Rubber Band Ligation and Hemorrhoidectomy in the Treatment of Hemorrhoids: A Clinical and Manometric Study A Izadpanah 1*, SV Hosseini 2, M Mahjoob 1 1.
Anorectal manometry results in defecation disorders
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1983, 58, 257-261 Anorectal manometry results in defecation disorders D MOLNAR, L S TAITZ, 0 M URWIN, AND J K H WALES Department of Paediatrics, University of Sheffield,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1983, 58, 257-261 Anorectal manometry results in defecation disorders D MOLNAR, L S TAITZ, 0 M URWIN, AND J K H WALES Department of Paediatrics, University of Sheffield,
Internal sphincter and the nature of haemorrhoids
 Gut, 1977, 18, 651-655 Internal sphincter and the nature of haemorrhoids B. D. HANCOCK From Wythenshawe Hospital, Manchester SUMMARY Internal anal sphincter activity has been studied in 84 patients with
Gut, 1977, 18, 651-655 Internal sphincter and the nature of haemorrhoids B. D. HANCOCK From Wythenshawe Hospital, Manchester SUMMARY Internal anal sphincter activity has been studied in 84 patients with
PREPARING FOR ANORECTOAL MANOMETRY. ManoScan Anorectal Manometry System
 PREPARING FOR ANORECTOAL MANOMETRY ManoScan Anorectal Manometry System WHAT IS ANORECTAL MANOMETRY? Anorectal manometry is a test used to evaluate the function and coordination of the sphincter and pelvic
PREPARING FOR ANORECTOAL MANOMETRY ManoScan Anorectal Manometry System WHAT IS ANORECTAL MANOMETRY? Anorectal manometry is a test used to evaluate the function and coordination of the sphincter and pelvic
Color Atlas of High Resolution Manometry
 Color Atlas of High Resolution Manometry Color Atlas of High Resolution Manometry Edited by Jeffrey Conklin, MD GI Motility Program Mark Pimentel, MD, FRCP(C) Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Edy Soffer, MD
Color Atlas of High Resolution Manometry Color Atlas of High Resolution Manometry Edited by Jeffrey Conklin, MD GI Motility Program Mark Pimentel, MD, FRCP(C) Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Edy Soffer, MD
Influence of pudendal block on the function of
 Gut, 1975, 16, 482-489 Influence of pudendal block on the function of the anal sphincters B. FRENCKNER AND CHR. V. EULER From the Departments ofclinical Physiology and ofanaesthesiology, Serafimer Hospital,
Gut, 1975, 16, 482-489 Influence of pudendal block on the function of the anal sphincters B. FRENCKNER AND CHR. V. EULER From the Departments ofclinical Physiology and ofanaesthesiology, Serafimer Hospital,
JNM Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility
 JNM Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 21 No. 1 January, 2015 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 http://dx.doi.org/10.5056/jnm14025 Original Article Comparison
JNM Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 21 No. 1 January, 2015 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 http://dx.doi.org/10.5056/jnm14025 Original Article Comparison
Saint-Petersburg State Pediatric Medical University, Saint-Petersburg, Russia
 Saint-Petersburg State Pediatric Medical University, Saint-Petersburg, Russia Modern technologies in treatment of fecal incontinence in children Komissarov Igor Alexeevich- Ph.D, M.D, Prof. Kolesnikova
Saint-Petersburg State Pediatric Medical University, Saint-Petersburg, Russia Modern technologies in treatment of fecal incontinence in children Komissarov Igor Alexeevich- Ph.D, M.D, Prof. Kolesnikova
Use of Anorectal Manometry During Rectal Infusion of Saline to Investigate Sphincter Function in Incontinent Patients
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1983;85:105-13 Use of Anorectal Manometry During Rectal Infusion of Saline to Investigate Sphincter Function in Incontinent Patients N. W. READ, W. G. HAYNES, D. C. C. BARTOLO, J. HALL,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1983;85:105-13 Use of Anorectal Manometry During Rectal Infusion of Saline to Investigate Sphincter Function in Incontinent Patients N. W. READ, W. G. HAYNES, D. C. C. BARTOLO, J. HALL,
High Resolution Anorectal Manometry (HRARM) in Healthy Egyptian Population
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 79, No. 2, December: 245-251, 2011 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com High Resolution Anorectal Manometry (HRARM) in Healthy Egyptian Population HALA M.K. IMAM, M.D. and
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 79, No. 2, December: 245-251, 2011 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com High Resolution Anorectal Manometry (HRARM) in Healthy Egyptian Population HALA M.K. IMAM, M.D. and
Endorectal Balloon during Image Guided Radiation Therapy for Prostate Carcinoma Reduces Radiation Proctitis at 2 Years
 Endorectal Balloon during Image Guided Radiation Therapy for Prostate Carcinoma Reduces Radiation Proctitis at 2 Years Poster No.: R-0041 Congress: Type: 2015 ASM Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. Botten,
Endorectal Balloon during Image Guided Radiation Therapy for Prostate Carcinoma Reduces Radiation Proctitis at 2 Years Poster No.: R-0041 Congress: Type: 2015 ASM Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. Botten,
GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction. Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield
 GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield Aims o o o To give an overview of lower GI investigations To demonstrate
GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield Aims o o o To give an overview of lower GI investigations To demonstrate
ACCIDENTAL BOWEL LEAKAGE: A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO EVALUATION. Tristi W. Muir, MD Chair, Department of OB/GYN Houston Methodist Hospital
 ACCIDENTAL BOWEL LEAKAGE: A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO EVALUATION Tristi W. Muir, MD Chair, Department of OB/GYN Houston Methodist Hospital Accidental Bowel Leakage What Gets the Woman into Your Office 67%
ACCIDENTAL BOWEL LEAKAGE: A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO EVALUATION Tristi W. Muir, MD Chair, Department of OB/GYN Houston Methodist Hospital Accidental Bowel Leakage What Gets the Woman into Your Office 67%
Influence of autonomic nerves on the internal anal
 Gut, 1976, 17, 306-312 Influence of autonomic nerves on the internal anal sphincter in man B. FRENCKNER AND T. IHRE From the Departments of Clinical Physiology and Surgery, Serafimer Hospital, S-112 83
Gut, 1976, 17, 306-312 Influence of autonomic nerves on the internal anal sphincter in man B. FRENCKNER AND T. IHRE From the Departments of Clinical Physiology and Surgery, Serafimer Hospital, S-112 83
Anorectal Manometry Overview Quick Reference Guide
 Anorectal Manometry Overview Quick Reference Guide Parkman HP, McCallum RW, Rao SSC Anorectal Manometry. GI Motility Testing: A Laboratory and Office Handbook. 163-178 Alterations of anorectal function
Anorectal Manometry Overview Quick Reference Guide Parkman HP, McCallum RW, Rao SSC Anorectal Manometry. GI Motility Testing: A Laboratory and Office Handbook. 163-178 Alterations of anorectal function
Wider Patient Eligibility for Fecal Management Systems
 1 Wider Patient Eligibility for Fecal Management Systems BACKGROUND Balloon cuff based catheters limits management of patients with poor anal sphinter tone, as it puts them at high risk for device expulsion.
1 Wider Patient Eligibility for Fecal Management Systems BACKGROUND Balloon cuff based catheters limits management of patients with poor anal sphinter tone, as it puts them at high risk for device expulsion.
ANAL SPHINCTER PRESSURE CHARACTERISTICS
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright 1967 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 52, No.3 Printed in U.S.A. ANAL SPHINCTER PRESSURE CHARACTERISTICS LEONARD A. KATZ, M.D., HERBERT J. KAUFMANN, M.D., AND HOWARD M. SPIRO,
GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright 1967 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 52, No.3 Printed in U.S.A. ANAL SPHINCTER PRESSURE CHARACTERISTICS LEONARD A. KATZ, M.D., HERBERT J. KAUFMANN, M.D., AND HOWARD M. SPIRO,
Sphincter exercises for people with bowel control problems. Information for patients. Physiotherapy Department
 Sphincter exercises for people with bowel control problems Information for patients Physiotherapy Department 01625 661481 @EastCheshireNHS Leaflet Ref: 11229 Published: June 18 Review: 31/0/5/2021 Page
Sphincter exercises for people with bowel control problems Information for patients Physiotherapy Department 01625 661481 @EastCheshireNHS Leaflet Ref: 11229 Published: June 18 Review: 31/0/5/2021 Page
CONSTIPATION. Atan Baas Sinuhaji
 CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
reconditioning of the defecation reflex?
 252 Departments of Surgery and Gastroenterology, University of Edinburgh, Western General Hospital, Edinburgh M Papachrysostomou A N Smith Correspondence to: Professor A N Smith, Department of Surgery,
252 Departments of Surgery and Gastroenterology, University of Edinburgh, Western General Hospital, Edinburgh M Papachrysostomou A N Smith Correspondence to: Professor A N Smith, Department of Surgery,
Anorectal physiology test
 Anorectal physiology test We hope this factsheet will help to answer some of your questions about having an anorectal physiology test. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don t hesitate
Anorectal physiology test We hope this factsheet will help to answer some of your questions about having an anorectal physiology test. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don t hesitate
Endorectal Balloon (ERB) Endorectal Balloon (ERB) Instructions for Use
 Endorectal Balloon (ERB) Instructions for Use GRF-0004-00 Rev. 08 Page 1 of 9 Contents Instructions for Use... 3 Indications for Use... 3 Contraindications... 3 Storage... 4 Warnings... 4 Accessories Provided...
Endorectal Balloon (ERB) Instructions for Use GRF-0004-00 Rev. 08 Page 1 of 9 Contents Instructions for Use... 3 Indications for Use... 3 Contraindications... 3 Storage... 4 Warnings... 4 Accessories Provided...
Lower oesophageal sphincter tone in patients with peptic stricture
 Thorax, 1978, 33, 574578 Lower oesophageal sphincter tone in patients with peptic stricture R LOBELLO,1 M STEKELMAN, AND D A W EDWARDS2 From the Surgical Unit, University College Hospital Medical School,
Thorax, 1978, 33, 574578 Lower oesophageal sphincter tone in patients with peptic stricture R LOBELLO,1 M STEKELMAN, AND D A W EDWARDS2 From the Surgical Unit, University College Hospital Medical School,
SACRAL NERVE STIMULATION FOR EXPERIENCE IN CHILDREN
 SACRAL NERVE STIMULATION FOR COLORECTAL DISEASES: EXPERIENCE IN CHILDREN C. LOUIS-BORRIONE - JM. GUYS TIMONE-ENFANTS MARSEILLE SACRAL NEUROMODULATION IN CHILDREN 26 : Humphreys et al - 23 children with
SACRAL NERVE STIMULATION FOR COLORECTAL DISEASES: EXPERIENCE IN CHILDREN C. LOUIS-BORRIONE - JM. GUYS TIMONE-ENFANTS MARSEILLE SACRAL NEUROMODULATION IN CHILDREN 26 : Humphreys et al - 23 children with
Anorectal Physiology: Test and Clinical Application
 eview Journal of the Korean Society of DOI: 10.3393/jksc.2010.26.5.311 pissn 2093-7822 eissn 2093-7830 Department of Surgery, St. Vincent s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine,
eview Journal of the Korean Society of DOI: 10.3393/jksc.2010.26.5.311 pissn 2093-7822 eissn 2093-7830 Department of Surgery, St. Vincent s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine,
ANORECTAL MANOMETRY SYSTEM
 ManoScan AR ANORECTAL MANOMETRY SYSTEM ManoScan High Resolution Manometry Diagnosing with definition ManoScan AR ManoScan AR provides a comprehensive assessment of the pressure activity of the rectum and
ManoScan AR ANORECTAL MANOMETRY SYSTEM ManoScan High Resolution Manometry Diagnosing with definition ManoScan AR ManoScan AR provides a comprehensive assessment of the pressure activity of the rectum and
ManoScan. Catheters and Probes. ManoScan HRM Catheters. ManoShield Disposable Catheter Sheath
 ManoScan Catheters and Probes ManoScan HRM Catheters ManoScan HRM catheters incorporate the very latest advancements in sensing technology. ManoScan HRM catheters work with the ManoShield TM disposable
ManoScan Catheters and Probes ManoScan HRM Catheters ManoScan HRM catheters incorporate the very latest advancements in sensing technology. ManoScan HRM catheters work with the ManoShield TM disposable
Summary and conclusion. Summary And Conclusion
 Summary And Conclusion Summary and conclusion Rectal prolapse remain a disorder for which no single ideal treatment was approved for all cases. Complete rectal prolapse (procidentia) is the circumferential
Summary And Conclusion Summary and conclusion Rectal prolapse remain a disorder for which no single ideal treatment was approved for all cases. Complete rectal prolapse (procidentia) is the circumferential
Gastrointestinal Motility 2: Intestinal and Colonic Motility Jack Grider, Ph.D.
 Gastrointestinal Motility 2: Intestinal and Colonic Motility Jack Grider, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Contrast the types of motility in the small intestine. 2. Describe the neural circuits that mediate peristalsis.
Gastrointestinal Motility 2: Intestinal and Colonic Motility Jack Grider, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Contrast the types of motility in the small intestine. 2. Describe the neural circuits that mediate peristalsis.
Increased motor unit fibre density in the external
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1980, 43, 343-347 Increased motor unit fibre density in the external anal sphincter muscle in ano-rectal incontinence: a single fibre EMG study M E NEILL
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1980, 43, 343-347 Increased motor unit fibre density in the external anal sphincter muscle in ano-rectal incontinence: a single fibre EMG study M E NEILL
REF PERINEOMETER (BIOFEEDBACK MONITOR) FOR FECAL INCONTINENCE AND KEGEL EXERCISES SEE INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE INSTRUCTION MANUAL
 REF 18-1005 PERINEOMETER (BIOFEEDBACK MONITOR) FOR FECAL INCONTINENCE AND KEGEL EXERCISES SEE INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE INSTRUCTION MANUAL TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...................... 1 Monitor 5 Device
REF 18-1005 PERINEOMETER (BIOFEEDBACK MONITOR) FOR FECAL INCONTINENCE AND KEGEL EXERCISES SEE INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE INSTRUCTION MANUAL TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...................... 1 Monitor 5 Device
Constipation. Information for adults. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1
 Constipation Information for adults GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Contents Role of the large intestine..3 Mass movements in the large intestine..4
Constipation Information for adults GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Contents Role of the large intestine..3 Mass movements in the large intestine..4
PE R I PR OB E PERINEAL PROBES FOR THE TREATMENT OF INCONTINENCE BY ELECTROSTIMULATION & BIOFEEDBACK
 PE R I PR OB E PERINEAL PROBES FOR THE TREATMENT OF INCONTINENCE BY ELECTROSTIMULATION & BIOFEEDBACK Urinary incontinence is a problem affecting many people, predominantly female for anatomical reasons.
PE R I PR OB E PERINEAL PROBES FOR THE TREATMENT OF INCONTINENCE BY ELECTROSTIMULATION & BIOFEEDBACK Urinary incontinence is a problem affecting many people, predominantly female for anatomical reasons.
Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Voskuijl, W. P. (2005).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Voskuijl, W. P. (2005).
Investigation of anal motor characteristics of the sensorimotor response (SMR) using 3-D anorectal pressure topography
 Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 300: G236 G240, 2011. First published November 25, 2010; doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00348.2010. Investigation of anal motor characteristics of the sensorimotor response (SMR)
Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 300: G236 G240, 2011. First published November 25, 2010; doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00348.2010. Investigation of anal motor characteristics of the sensorimotor response (SMR)
Hemorrhoids. Carlos R. Alvarez-Allende PGY-III Colorectal Surgery
 Hemorrhoids Carlos R. Alvarez-Allende PGY-III Colorectal Surgery Overview Anatomy Classification Etiology Incidence Symptoms Differential Diagnosis Medical Management Surgical Management Anatomy Anal canal
Hemorrhoids Carlos R. Alvarez-Allende PGY-III Colorectal Surgery Overview Anatomy Classification Etiology Incidence Symptoms Differential Diagnosis Medical Management Surgical Management Anatomy Anal canal
Surgical Management for Defecation Dysfunction
 Defecatory Dysfunction Surgical Management for Defecation Dysfunction JMAJ 46(9): 378 383, 2003 Tatsuo TERAMOTO Professor, 1st Department of Surgery, School of Medicine, Toho University Abstract: Typical
Defecatory Dysfunction Surgical Management for Defecation Dysfunction JMAJ 46(9): 378 383, 2003 Tatsuo TERAMOTO Professor, 1st Department of Surgery, School of Medicine, Toho University Abstract: Typical
Lets talk about Faecal incontinence (FI) in Scleroderma
 Lets talk about Faecal incontinence (FI) in Scleroderma Dr. Shamaila Butt Gastroenterology Research Registrar GI Physiology unit University College Hospital London GI manifestations in Scleroderma Oesophagus
Lets talk about Faecal incontinence (FI) in Scleroderma Dr. Shamaila Butt Gastroenterology Research Registrar GI Physiology unit University College Hospital London GI manifestations in Scleroderma Oesophagus
Treatment of functional constipation in children: Evidence-based recommendations from ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN 2014
 Treatment of functional constipation in children: Evidence-based recommendations from ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN 2014 BS. Nguyễn Thị Kim Ngân Khoa Tiêu Hóa BV Nhi Đồng 2 Introduction Constipation is a common
Treatment of functional constipation in children: Evidence-based recommendations from ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN 2014 BS. Nguyễn Thị Kim Ngân Khoa Tiêu Hóa BV Nhi Đồng 2 Introduction Constipation is a common
Progress report. Anal continence. sphincter which is 15 to 5 mm in thickness and surrounds the craniad 2 to
 Gut, 1971, 12, 844-852 Progress report Anal continence Anal continence depends on an adaptable barrier formed at the ano-rectal junction and in the anal canal by a combination of forces. These are due
Gut, 1971, 12, 844-852 Progress report Anal continence Anal continence depends on an adaptable barrier formed at the ano-rectal junction and in the anal canal by a combination of forces. These are due
A Nursing Assessment Tool for Adults With Fecal Incontinence
 Journal of Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing 2000, 279- A Nursing Assessment Tool for Adults With Fecal Incontinence Christine Norton, MA, RN, and Sonya Chelvanayagam, MSc, RN Abstract Fecal incontinence
Journal of Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing 2000, 279- A Nursing Assessment Tool for Adults With Fecal Incontinence Christine Norton, MA, RN, and Sonya Chelvanayagam, MSc, RN Abstract Fecal incontinence
Patient Information Leaflet. Sphincter Exercises for people with Bowel Control Problems
 Patient Information Leaflet Sphincter Exercises for people with Bowel Control Problems Sphincter Exercises for people with Bowel Control Problems Introduction Sphincter exercises can help you to improve
Patient Information Leaflet Sphincter Exercises for people with Bowel Control Problems Sphincter Exercises for people with Bowel Control Problems Introduction Sphincter exercises can help you to improve
Effect of Biofeedback Therapy in Constipation According to Rectal Sensation
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 7, No. 2, March 2013, pp. 157-162 ORiginal Article Effect of Biofeedback Therapy in Constipation According to Rectal Sensation Ji Yong Ahn, Seung-Jae Myung, Kee Wook Jung, Dong-Hoon
Gut and Liver, Vol. 7, No. 2, March 2013, pp. 157-162 ORiginal Article Effect of Biofeedback Therapy in Constipation According to Rectal Sensation Ji Yong Ahn, Seung-Jae Myung, Kee Wook Jung, Dong-Hoon
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Suspected Hirschsprung's Disease in Infants: The Diagnostic Accuracy of Contrast Enema
 HK J Paediatr (new series) 2016;21:74-78 Suspected Hirschsprung's Disease in Infants: The Diagnostic Accuracy of Contrast Enema PMY TANG, MWY LEUNG, NSY CHAO, KKW LIU, TW FAN Abstract Key words Objective:
HK J Paediatr (new series) 2016;21:74-78 Suspected Hirschsprung's Disease in Infants: The Diagnostic Accuracy of Contrast Enema PMY TANG, MWY LEUNG, NSY CHAO, KKW LIU, TW FAN Abstract Key words Objective:
SPHINCTER OF ODDI DYSFUNCTION (SOD)
 SPHINCTER OF ODDI DYSFUNCTION (SOD) Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction refers to structural or functional disorders involving the biliary sphincter that may result in impedance of bile and pancreatic juice
SPHINCTER OF ODDI DYSFUNCTION (SOD) Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction refers to structural or functional disorders involving the biliary sphincter that may result in impedance of bile and pancreatic juice
Physiologic Anatomy and Nervous Connections of the Bladder
 Micturition Objectives: 1. Review the anatomical organization of the urinary system from a physiological point of view. 2. Describe the micturition reflex. 3. Predict the lines of treatment of renal failure.
Micturition Objectives: 1. Review the anatomical organization of the urinary system from a physiological point of view. 2. Describe the micturition reflex. 3. Predict the lines of treatment of renal failure.
Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Faecal Incontinence
 Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Faecal Incontinence Questions & Answers GLASGOW COLORECTAL CENTRE Ross Hall Hospital 221 Crookston Road Glasgow G52 3NQ e-mail: info@colorectalcentre.co.uk Ph: Main hospital
Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Faecal Incontinence Questions & Answers GLASGOW COLORECTAL CENTRE Ross Hall Hospital 221 Crookston Road Glasgow G52 3NQ e-mail: info@colorectalcentre.co.uk Ph: Main hospital
Original article Pathophysiology and diagnosis of descending perineum syndrome in children
 Original article Pathophysiology and diagnosis of descending perineum syndrome in children MIChAel D. levin State Geriatric Center, Netanya, Israel Abstract: The purpose of this study is to offer a safe,
Original article Pathophysiology and diagnosis of descending perineum syndrome in children MIChAel D. levin State Geriatric Center, Netanya, Israel Abstract: The purpose of this study is to offer a safe,
Anorectal malformations include a wide spectrum of
 JOURNAL OF LAPAROENDOSCOPIC & ADVANCED SURGICAL TECHNIQUES Volume 20, Number 1, 2010 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089=lap.2008.0343 Laparoscopic-Assisted Pull-Through for Congenital Rectal Stenosis
JOURNAL OF LAPAROENDOSCOPIC & ADVANCED SURGICAL TECHNIQUES Volume 20, Number 1, 2010 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089=lap.2008.0343 Laparoscopic-Assisted Pull-Through for Congenital Rectal Stenosis
A Guide to Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders
 A Guide to Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders Albert J. Bredenoord André Smout Jan Tack A Guide to Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders Albert J. Bredenoord Gastroenterology and Hepatology Academic Medical
A Guide to Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders Albert J. Bredenoord André Smout Jan Tack A Guide to Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders Albert J. Bredenoord Gastroenterology and Hepatology Academic Medical
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery
 World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 3, Issue 3 2013 Article 5 Closed Versus Open Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy Technique in Treatment of Anal Fissure Seyed Reza Mousavi Jr Shohada Medical Center,
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 3, Issue 3 2013 Article 5 Closed Versus Open Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy Technique in Treatment of Anal Fissure Seyed Reza Mousavi Jr Shohada Medical Center,
ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Benign Anorectal Disorders
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Benign Anorectal Disorders Arnold Wald, MD, MACG 1, Adil E. Bharucha, MBBS, MD 2, Bard C. Cosman, MD, MPH, FASCRS 3 and William E. Whitehead, PhD, MACG 4 1 Division
ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Benign Anorectal Disorders Arnold Wald, MD, MACG 1, Adil E. Bharucha, MBBS, MD 2, Bard C. Cosman, MD, MPH, FASCRS 3 and William E. Whitehead, PhD, MACG 4 1 Division
Introduction of Rapid barostat bag (RBB) protocol for the assessment of rectal function
 New technology for assessment and treatment of colorectal dysfunction Ascona 23rd of April 2015 Introduction of Rapid barostat bag (RBB) protocol for the assessment of rectal function Matthias Sauter Division
New technology for assessment and treatment of colorectal dysfunction Ascona 23rd of April 2015 Introduction of Rapid barostat bag (RBB) protocol for the assessment of rectal function Matthias Sauter Division
Accidental Bowel Leakage (Fecal Incontinence)
 Accidental Bowel Leakage (Fecal Incontinence) What is Accidental Bowel Leakage (ABL)? Accidental bowel leakage is the inability to control solid or liquid stool. This is the inability to control gas and
Accidental Bowel Leakage (Fecal Incontinence) What is Accidental Bowel Leakage (ABL)? Accidental bowel leakage is the inability to control solid or liquid stool. This is the inability to control gas and
National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Urodynamic Testing National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the urinary tract? The urinary tract
Urodynamic Testing National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the urinary tract? The urinary tract
HIGH RESOLUTION AND HIGH DEFINITION ANORECTAL MANOMETRY: USEFULNESS, LIMITATIONS, WHEN AND WHY. José María Remes Troche.
 HIGH RESOLUTION AND HIGH DEFINITION ANORECTAL MANOMETRY: USEFULNESS, LIMITATIONS, WHEN AND WHY José María Remes Troche. Digestive Phisiology and Motility Lab University of Veracruz, Mexico DISCLOSURE:
HIGH RESOLUTION AND HIGH DEFINITION ANORECTAL MANOMETRY: USEFULNESS, LIMITATIONS, WHEN AND WHY José María Remes Troche. Digestive Phisiology and Motility Lab University of Veracruz, Mexico DISCLOSURE:
11/04/2011 OVERVIEW. Neurogenic Bowel Management. in adults with Spinal Cord Injury (S.C.I.) Sequence of events in normal Defecation
 Neurogenic Bowel Management in adults with Spinal Cord Injury (S.C.I.) Dimitrios D. Ergeletzis MD Physiatrist Director of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Dept.- GIROKOMEION ATHENS, Greece OVERVIEW Anatomy
Neurogenic Bowel Management in adults with Spinal Cord Injury (S.C.I.) Dimitrios D. Ergeletzis MD Physiatrist Director of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Dept.- GIROKOMEION ATHENS, Greece OVERVIEW Anatomy
Biofeedback for Pelvic Floor Disorders and Incontinence
 The UNC Center for Functional GI & Motility Disorders www.med.unc.edu/ibs Biofeedback for Pelvic Floor Disorders and Incontinence Olafur S. Palsson, Psy.D. Associate Professor of Medicine UNC Center for
The UNC Center for Functional GI & Motility Disorders www.med.unc.edu/ibs Biofeedback for Pelvic Floor Disorders and Incontinence Olafur S. Palsson, Psy.D. Associate Professor of Medicine UNC Center for
University of Groningen. Hirschsprung's disease: early diagnosis and long-term outcomes Meinds, Rob
 University of Groningen Hirschsprung's disease: early diagnosis and long-term outcomes Meinds, Rob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Hirschsprung's disease: early diagnosis and long-term outcomes Meinds, Rob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
The World Leader in G.I. Disposable Probes, Supplies and Accessories
 The World Leader in G.I. Disposable Probes, Supplies and Accessories High Definition G.I. Diagnostics comfortable easy smooth flexible Gastroenterology probes from Sandhill Scientific are the perfect choice
The World Leader in G.I. Disposable Probes, Supplies and Accessories High Definition G.I. Diagnostics comfortable easy smooth flexible Gastroenterology probes from Sandhill Scientific are the perfect choice
Ultrastructural changes in internal anal sphincter in neurogenic faecal incontinence
 Gut, 1988, 29, 1692-1698 Ultrastructural changes in internal anal sphincter in neurogenic faecal incontinence M SWASH, A GRAY, D Z LUBOWSKI, AND R J NICHOLLS From the Sir Alan Parks Physiology Department,
Gut, 1988, 29, 1692-1698 Ultrastructural changes in internal anal sphincter in neurogenic faecal incontinence M SWASH, A GRAY, D Z LUBOWSKI, AND R J NICHOLLS From the Sir Alan Parks Physiology Department,
Evaluation of Anorectal and Pelvic Floor Muscle Function
 Chapter Chapter Evaluation of Anorectal and Pelvic Floor Muscle 121 Evaluation of Anorectal and Pelvic Floor Muscle Function Contents.1 Anatomical Background................... 122.2 Functional Parameters
Chapter Chapter Evaluation of Anorectal and Pelvic Floor Muscle 121 Evaluation of Anorectal and Pelvic Floor Muscle Function Contents.1 Anatomical Background................... 122.2 Functional Parameters
Long-Term Bowel Symptoms Following Corrective Surgery
 HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE Samuel Nurko MD MPH Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Children s Hospital Medical Center, Boston Ma Long-Term Bowel Symptoms Following Corrective Surgery
HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE Samuel Nurko MD MPH Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Children s Hospital Medical Center, Boston Ma Long-Term Bowel Symptoms Following Corrective Surgery
Human Anatomy rectum
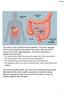 rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
Fecal Incontinence. Inability to retain feces or bowel movements, resulting in involuntary passage of feces or bowel movements
 Fecal Incontinence (Involuntary Passage of Feces or Bowel Movements) Basics OVERVIEW Inability to retain feces or bowel movements, resulting in involuntary passage of feces or bowel movements GENETICS
Fecal Incontinence (Involuntary Passage of Feces or Bowel Movements) Basics OVERVIEW Inability to retain feces or bowel movements, resulting in involuntary passage of feces or bowel movements GENETICS
3D Dynamic Ultrasound In Obstructed Defecation
 3D Dynamic Ultrasound In Obstructed Defecation By Ramy Salahudin Abdelkader Assist. Lecturer of General Surgery Cairo University Introduction Pelvic floor is complex system, with passive and active components
3D Dynamic Ultrasound In Obstructed Defecation By Ramy Salahudin Abdelkader Assist. Lecturer of General Surgery Cairo University Introduction Pelvic floor is complex system, with passive and active components
Magnetic resonance follow-up protocol for patients after stapled transanal rectal resection for intussusception and rectocele
 Magnetic resonance follow-up protocol for patients after stapled transanal rectal resection for intussusception and rectocele Poster No.: C-2659 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S.
Magnetic resonance follow-up protocol for patients after stapled transanal rectal resection for intussusception and rectocele Poster No.: C-2659 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S.
Evaluation of anal canal morphology with MRI in cases with anal fissure
 Evaluation of anal canal morphology with MRI in cases with anal fissure Poster No.: C-1670 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Erden, E. Peker, Z. B#y#kl# Gençtürk, I. Erden; Ankara/TR
Evaluation of anal canal morphology with MRI in cases with anal fissure Poster No.: C-1670 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Erden, E. Peker, Z. B#y#kl# Gençtürk, I. Erden; Ankara/TR
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: BIOFEEDBACK
 MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 6 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 6 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
Bowel dysfunctions following hysterectomy
 Bowel dysfunctions following hysterectomy Marco Scaglia Retrospective studies Retrospective studies 6% of patients developed new symptoms (Carlson 1994) Constipation is more common in women after hysterectomy
Bowel dysfunctions following hysterectomy Marco Scaglia Retrospective studies Retrospective studies 6% of patients developed new symptoms (Carlson 1994) Constipation is more common in women after hysterectomy
The Frequency of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Nutcracker Esophagus and the Effect of Acid-Reduction Therapy on the Motor Abnormality
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.4, December 2000 The Frequency of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Nutcracker Esophagus and the Effect of Acid-Reduction Therapy on the Motor Abnormality Saleh Mohsen
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.4, December 2000 The Frequency of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Nutcracker Esophagus and the Effect of Acid-Reduction Therapy on the Motor Abnormality Saleh Mohsen
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a ... PRESENTATION... Defining and Diagnosing Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 ... PRESENTATION... Defining and Diagnosing Irritable Bowel Syndrome Based on a presentation by Marvin M. Schuster, MD Presentation Summary Approximately 20% of the general population has irritable bowel
... PRESENTATION... Defining and Diagnosing Irritable Bowel Syndrome Based on a presentation by Marvin M. Schuster, MD Presentation Summary Approximately 20% of the general population has irritable bowel
Dyssynergic defecation, also termed anismus, 1 or pelvic floor. Digital Rectal Examination Is a Useful Tool for Identifying Patients With Dyssynergia
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:955 960 Digital Rectal Examination Is a Useful Tool for Identifying Patients With Dyssynergia KASAYA TANTIPHLACHIVA, PRIYANKA RAO, ASHOK ATTALURI, and SATISH
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:955 960 Digital Rectal Examination Is a Useful Tool for Identifying Patients With Dyssynergia KASAYA TANTIPHLACHIVA, PRIYANKA RAO, ASHOK ATTALURI, and SATISH
Duc M. Vo, MD, FACS Northwest Surgical Specialists
 Duc M. Vo, MD, FACS Northwest Surgical Specialists Disclosures none Outline Definition Etiologies Exam findings Additional testing Medical management Surgical options What is fecal incontinence? Recurrent
Duc M. Vo, MD, FACS Northwest Surgical Specialists Disclosures none Outline Definition Etiologies Exam findings Additional testing Medical management Surgical options What is fecal incontinence? Recurrent
A new concept for Biofeedback & Electrostimulation in Uro-Gynaecology using a specially designed probe : PERISIZE
 1 PELVIC FLOOR REHABILITATION A new concept for Biofeedback & Electrostimulation in Uro-Gynaecology using a specially designed probe : PERISIZE First - some reminders about the female pelvic floor The
1 PELVIC FLOOR REHABILITATION A new concept for Biofeedback & Electrostimulation in Uro-Gynaecology using a specially designed probe : PERISIZE First - some reminders about the female pelvic floor The
Bowel and Bladder Management Following Transverse Myeli5s
 Bowel and Bladder Management Following Transverse Myeli5s Janet Dean, MS, RN, CRRN, CRNP Pediatric Nurse Prac55oner Interna5onal Center for Spinal Cord Injury Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilita5on
Bowel and Bladder Management Following Transverse Myeli5s Janet Dean, MS, RN, CRRN, CRNP Pediatric Nurse Prac55oner Interna5onal Center for Spinal Cord Injury Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilita5on
Under Pressure. Dr. Robert Keyes CAEP -- Critical Care May 31, 2015
 Under Pressure Dr. Robert Keyes CAEP -- Critical Care May 31, 2015 Disclosures 1. No disclosures, commercial supports, or conflicts of interest. Learning Objectives 1. To understand the principles of pressure
Under Pressure Dr. Robert Keyes CAEP -- Critical Care May 31, 2015 Disclosures 1. No disclosures, commercial supports, or conflicts of interest. Learning Objectives 1. To understand the principles of pressure
Pelvic floor muscle exercises
 Lifestyle Helpline 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 31 Pelvic floor muscle exercises In this fact sheet: How do pelvic floor muscle exercises help with urinary problems? How do I do the exercises? More
Lifestyle Helpline 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 31 Pelvic floor muscle exercises In this fact sheet: How do pelvic floor muscle exercises help with urinary problems? How do I do the exercises? More
The Praxis FES System and Bladder/Bowel Management in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury
 The Praxis FES System and Bladder/Bowel Management in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury Brian J. Benda 1, Thierry Houdayer 2, Graham Creasey 3, Randal R. Betz 1, Brian T. Smith 1 *, Therese E. Johnston
The Praxis FES System and Bladder/Bowel Management in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury Brian J. Benda 1, Thierry Houdayer 2, Graham Creasey 3, Randal R. Betz 1, Brian T. Smith 1 *, Therese E. Johnston
Local Glyceryl Trinitrate Versus Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy In Management Of Anal Fissure
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 22 Number 2 Local Glyceryl Trinitrate Versus Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy In Management Of Anal Fissure G El-Labban, G El-Gazzaz, E Hokamam Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 22 Number 2 Local Glyceryl Trinitrate Versus Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy In Management Of Anal Fissure G El-Labban, G El-Gazzaz, E Hokamam Citation
Pipeline Technology Conference 2007
 The Complete Solution: Combined Crack and Metal Loss Detection Tool using Phased Array Technology By A. Hugger, J. Franz, H. Charbon, R. Bauernschmitt, M. Tschuch, K.-H. Käshammer, I. Lachtchouk, J. Ehrhardt.
The Complete Solution: Combined Crack and Metal Loss Detection Tool using Phased Array Technology By A. Hugger, J. Franz, H. Charbon, R. Bauernschmitt, M. Tschuch, K.-H. Käshammer, I. Lachtchouk, J. Ehrhardt.
The Use of Glyceryl Tri-Nitrate Ointment in Treatment of Chronic Fissure in Ano
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 28, No. 4, December 2006 The Use of Glyceryl Tri-Nitrate Ointment in Treatment of Chronic Fissure in Ano Suhair Al-Saad, MBChB,FRCS I,CABS,* Hamdi Al- Shenawi, MBBS, FRCS
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 28, No. 4, December 2006 The Use of Glyceryl Tri-Nitrate Ointment in Treatment of Chronic Fissure in Ano Suhair Al-Saad, MBChB,FRCS I,CABS,* Hamdi Al- Shenawi, MBBS, FRCS
