CONGENITAL ABNORMALITIES OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE TRACT
|
|
|
- Ralf Wilfred Powell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CONGENITAL ABNORMALITIES OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE TRACT ANOMALIES OF THE VAGINA, CERVIX, UTERUS, AND ADNEXA INA S. IRABON, MD, FPOGS, FPSRM, FPSGE OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY AND INFERTILITY LAPAROSCOPY AND HYSTEROSCOPY
2 TO DOWNLOAD LECTURE DECK:
3 MAIN REFERENCES Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
4 OUTLINE Review Mullerian embryogenesis Musset s 3 stage process Examination of the newborn s external genitalia Perineal and vaginal defects Abnormalities of the cervix and uterus Abnormalities of the ovary
5 REVIEW OF MULLERIAN EMBRYOGENESIS Paramesonephric ducts = Mullerian ducts Mesonephric ducts = Wolffian ducts
6 REVIEW OF MULLERIAN EMBRYOGENESIS Males: (+) antimullerian hormone Fate of Paramesonephric ducts in males: Most distal appendix of the testes Most proximal prostatic utricle
7 REVIEW OF MULLERIAN EMBRYOGENESIS females: (-) antimullerian hormone
8 REVIEW OF MULLERIAN EMBRYOGENESIS MULLERIAN derivatives? 1. Fallopian tubes 2. Uterus 3. Cervix 4. Upper 1/3 of vagina Ovaries? Lower 2/3 of vagina? Hymen?
9 REVIEW OF MULLERIAN EMBRYOGENESIS Vaginal plate
10 Review of Mullerian embryogenesis Remnants of mesonephric ducts in females: Appendix vesiculosa Epoophoron Paraophoron Gartner duct cysts Paraovarian cysts (cyst of the epoophoron) **Hydatid of Morgagni remnant of Paramesonephric duct
11 MUSSET S 3 STAGE PROCESS The first stage is described as short, taking place at the beginning of the 10 th week. The medial aspects of the more caudal portions of the two ducts fuse, starting in the middle and proceeding simultaneously in both directions. In this way a median septum is formed. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
12 MUSSET S 3 STAGE PROCESS The second stage: 10 th 13th week rapid cell proliferation and the filling in of the triangular space between the two uterine cornua. a thick upper median septum is formed wedge like and gives rise to the usual external contour of the fundus. lower portion of the median septum is resorbed, unifying the cervical canal first and then the upper vagina.` Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
13 MUSSET S 3 STAGE PROCESS The third stage lasts from the 13th 20th week. the degeneration of the upper uterine septum occurs, starting at the isthmic region and proceeding cranially to the top of the fundus. In this way a unified uterine cavity is formed Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
14 EXAMINATION OF THE NEWBORN FOR AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA The first major diagnostic decision of the obstetrician with respect to the newborn is gender assignment. Clitoris: note for any obvious enlargement the opening of the urethra should be identified labia should be gently separated to see if the introitus can be visualized. Observe hymen. Generally, it is partially perforate, revealing the entrance into the vagina. Rectum can be visualized, and it should be tested to be sure that it is perforate Meconium staining is evidence for perforation. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
15 EXAMINATION OF THE NEWBORN FOR AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA Disorders of sexual development (DSD) ambiguous genitalia: 1 in 14,000 Females (individuals with XX karyotypes) with masculinized external genitalia are identified as female pseudohermaphrodites The most common cause is congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
16 EXAMINATION OF THE NEWBORN FOR AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA The timing of antenatal (embryonic) exposure to androgen influences the degree of masculinization The vaginal septum separates from the urogenital sinus at about 12 weeks. Androgen exposure after that point presents primarily with clitoral hypertrophy. The female who has been androgenized may appear similar to the male pseudohermaphrodite suffering from incomplete androgen resistance syndrome... Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
17
18 EXAMINATION OF THE NEWBORN FOR AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA when necessary, perform imaging studies (ultrasound), karyotyping or chromosomal evaluations, serum electrolytes, and steroid hormone levels Until recently, gender was assigned primarily on the principle of phallic adequacy, with neonates with ambiguous phallus being assigned female gender. This principle is now inappropriate and full evaluation with chromosomal studies and appropriately timed corrective measures is now the desired approach. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
19 nvolves checkvic ultrasound serum electronate, an ultragenized tissue al pelvic anatbe performed ctures, includpresence of a genital adrenal e steroid pathproduction of ewborn s genihen possible. e principle of guous phallus rent approach e and to defer r. For the eval- SD, most teruding medical y, gynecology, S Box 11.1 Classification of 46,XX DSD I. Androgen-Induced A. Fetal Source 1. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia a. Virilism only, defective adrenal 21-hydroxylation (CYP21) b. Virilism with salt-losing syndrome, defective adrenal 21-hydroxylation (CYP21) c. Virilism with hypertension, defective adrenal 11β-hydroxylation (CYP11B1) d. Virilism with adrenal insuf ciency, deficient 3β-HSD 2 (HSD3B 2) 2. P450 aromatase (CYP19) deficiency 3. Glucocorticoid receptor gene mutation B. Maternal Source 1. Iatrogenic a. Testosterone and related steroids b. Certain synthetic oral progestagens and rarely diethylstil - bestrol 2. Virilizing ovarian or adrenal tumor 3. Virilizing luteoma of pregnancy 4. Congenital virilizing adrenal hyperplasia in mother * C. Undetermined Source 1. Virilizing luteoma of pregnancy II. Non Androgen-Induced Disturbances in Di f erentiation of Urogenital Structures From Grumbach MM, Hughes IA, Conte FA. Disorders of sex dif erentiation. In: Comprehensive Larsen Gynecology RP, Kronenberg 7 th edition, HM, Melmed 2017 (Lobo S, Polonsky RA, Gershenson KS, eds. DM, Williams Lentz Textbook GM, Valea of FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities Endocrinology. 10th of the ed. Female Philadelphia: Reproductive Saunders; Tract ; pp * In pregnant patient whose disease is poorly controlled or who is noncompliant,
20 1. PERINEAL AND VAGINAL DEFECTS
21 CLITORAL ANOMALIES Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
22 CLITORAL ANOMALIES Bifid Clitoris usually seen in association with extrophy of the bladder. Most female patients with bladder extrophy had associated reproductive tract anomalies.. In such cases, an anterior rotation and a shortening of the vagina with labial fusion are quite common. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
23 Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp LABIAL FUSION Most commonly caused by Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) The most common form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia is caused by an inborn error of metabolism involving deficiency of the enzyme 21-hydroxylase transmitted as an autosomal recessive gene coded on chromosome 6.
24 STEROID PATHWAY IN CAH Others: 11-hydroxylase deficiency 3b-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
25 CONGENITAL ADRENAL HYPERPLASIA Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) may be demonstrated at birth by the presence of ambiguous genitalia in genetic females or present later in childhood. Significant proportions (75%) of newborns with this condition are also at risk for the development of lifethreatening neonatal adrenal crises as a result of sodium loss because of absent aldosterone. In milder disease, delayed diagnosis may result in abnormalities of accelerated bone maturation, leading to short stature.
26 CONGENITAL ADRENAL HYPERPLASIA Treatment of congenital adrenal hyperplasia involves replacement of cortisol. This suppresses ACTH output and therefore decreases the stimulation of the cortisol-producing pathways of the adrenal cortex. For women known to be at risk, those with diagnoses of CAH and those with previously affected children, in-utero therapy may be offered. Dexamethasone given daily after a positive pregnancy test will suppress fetal adrenal glands until the child s gender can be verified with prenatal diagnosis. females with ambiguous genitalia should have psychological support and counseling because of the profound issues raised about identity with this diagnosis.
27 IMPERFORATE HYMEN Hymen Embryology: The hymen represents the junction of the sinovaginal bulbs with the urogenital sinus and is composed of endoderm from the urogenital sinus epithelium. The hymen opens normally during embryonic life to establish a connection between the lumen of the vaginal canal and the vestibule. If this perforation does not take place, the hymen is imperforate. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
28 IMPERFORATE HYMEN It is rare to make the diagnosis of imperforate hymen before puberty, at which point primary amenorrhea is the major symptom. Occasionally in childhood a hydrocolpos or mucocolpos may occur. This is caused by a collection of secretions behind the hymen If discovered, the hymen should be incised to release the buildup. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
29 IMPERFORATE HYMEN Presentation: Primary amenorrhea is the major symptom. At puberty the patient may experience cyclic cramping but no menstrual flow. Hematocolpos/hematometra may occur Menstrual flow may back up through the tubes and form endometrial implants in the peritoneal cavity. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
30 IMPERFORATE HYMEN Presentation: The diagnosis determined by history and by the presence of a bulging membrane at the introitus. Treatment: cruciate incision into the hymen Hemostasis is secured by fine suture, and evolution to normal usually occurs rapidly. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
31 IMPERFORATE HYMEN Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
32 VAGINAL AGENESIS also known as Mullerian agenesis or Mullerian aplasia associated with the Mayer Rokitansky Kuster Hauser (MRKH) syndrome. Congenital absence of vagina and uterus differential diagnosis includes transverse vaginal septum,imperforate hymen, cervical agenesis, and androgen insensitivity syndrome. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
33 VAGINAL AGENESIS Normal pubertal development and primary amenorrhea Physical exam: absence of vaginal opening or presence of short vaginal pouch Rectal exam: inability to palpate uterus Laboratory: reproductive hormones normal; karyotype 46 XX Ultrasound: Absent uterus
34 VAGINAL AGENESIS Up to 50% of women with Mullerian agenesis have concurrent urinary tract anomalies important to investigate urinary tract (request for Kidney-urinary bladder ultrasound or intravenous pyelography) These anomalies include renal agenesis, pelvic kidney, multicystic dysplastic kidney and ureteral duplication. Other associated anomalies: skeletal anomalies, cardiac defects, hearing loss
35 VAGINAL AGENESIS TREATMENT Goal: the creation of a vagina when the patient wishes to become sexually active. Nonsurgical: requires the use of progressive vaginal dilators well-motivated, mature patient over a period of several months. Example: A racing bicycle seat is mounted on a stool and is used to maintain dilator pressure on the introital dimple just posterior to the urethra.. It generally takes 3 to 6 months to develop an adequate neovagina by this technique. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
36 VAGINAL AGENESIS TREATMENT: Surgical reconstruction: Abbe-McIndoe: develop the potential space between the bladder and the rectum and replaced this space with a stent utilizing tissue, most commonly a split-thickness skin graft or synthetic materials Must be done only when the patient will use the vagina frequently. Early and regular postoperative coitus is important for long-term success the timing of the operation to coincide with the opportunity for coitus is important. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
37 VAGINAL AGENESIS TREATMENT Williams procedure: a neovagina is built by utilizing labial skin and results in a vaginal pouch whose axis is directly posterior. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
38 VAGINAL AGENESIS TREATMENT Vecchietti procedure: laparoscopic procedure where sutures are placed in the peritoneal folds between the bladder and rudimentary uterus. The sutures (two) are then fixed to a traction device on the anterior abdominal wall and graduated traction applied for 6 to 8 days. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
39 TRANSVERSE VAGINAL SEPTUM The Mullerian ducts join the sinovaginal bulb at a point known as the Mullerian tubercle. If the area of junction between these structures is not completely canalized transverse vaginal septum will occur This may be partial or complete and generally lies at the junction between the upper third and lower two thirds of the vagina Partial transverse vaginal septa have been reported in diethylstilbestrol (DES)-exposed females. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
40 TRANSVERSE VAGINAL SEPTUM Hematocolpos and hematometrium may occur in a fashion similar to that seen in the imperforate hymen, except that there is no bulging at the introitus Primary amenorrhea with cyclic cramping. Foul-smelling vaginal discharge. If an opening is noted, it may be expanded by manual dilation or simple incision, with suturing of the edges of the vagina on either side. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
41 VAGINAL ADENOSIS In the female who was exposed to DES in utero, the junction between the Mullerian ducts and the sinovaginal bulb may not be sharply demonstrated. If Mullerian elements invade the sinovaginal bulb, remnants may remain as areas of adenosis in the adult vagina. They are generally palpated submucosally, although they may be observable at the surface. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
42 2. ABNORMALITIES IN THE CERVIX AND UTERUS
43 ABNORMALITIES OF THE CERVIX Cervical duplication Septate cervix Cervical agenesis Cervical hypoplasia Hoods/collars/adenosis : DES-related
44 ABNORMALITIES OF THE UTERUS Characterized as lateral fusion defects Occur due to disordered duct fusion and septal resorption
45 ABNORMALITIES OF THE UTERUS
46 ABNORMALITIES OF THE UTERUS Category 1 and 2: anomalies with developmental failure of one or both mullerian ducts Category 3 and 4: anomalies involving a varying degree of failure of midline fusion Category 5 and 6: anomalies with some degree of failure of resorption of the midline septum
47 DIAGNOSIS History Physical examination Imaging: MRI: gold standard in diagnosis 3D ultrasound: cheaper alternative
48 SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
49 ABSENCE OF CERVIX AND UTERUS The cervix and uterus are often not completely absent; the fallopian tubes and possibly some fibrous tissue are usually present. Absence is associated with urinary tract anomalies up to 50% of the time. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
50 A single cervix and a single horn of the uterus with the fallopian tube of the side entering it are seen. The ovary may be present on the opposite side. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp UNICORNUATE UTERUS It is often related to lack of development of the mesonephric system on one side. There is almost always a missing kidney and ureter on the same side.
51 MANAGEMENT OF ABNORMALITIES IN THE CERVIX AND UTERUS For patients with unobstructed abnormalities, therapy may not be needed. septate uteri are often associated with miscarriage problems, and correction may be necessary. Hysteroscopic resection of septum - the treatment of choice Strassman Metroplasty: involves the removal of the septum by a wedge incision and the reunification of the two cavities during laparotomy. laparoscopy allows for differentiation of a septate uterus from a bicornuate or didelphic uterus. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
52 STRASSMAN TECHNIQUE Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
53 3. OVARIAN ABNORMALITIES
54 ACCESSORY OVARY AND SUPERNUMERARY OVARY Accessory ovary - excess ovarian tissue is noted near a normally placed ovary and connected to it. Supernumerary ovary - a third ovary is separated from the normally situated ovaries. Such ovaries may be found in the omentum or retroperitoneally, Patients with supernumerary ovary and accessory ovary had additional congenital defects, most frequently abnormalities of the genitourinary tract. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
55 OVOTESTES Present in individuals with ovaries that have an SRY antigen present. The majority are true hermaphrodites (quite rare). When considerable amounts of testicular tissue are present within the organ, there is a tendency for descent toward the labial scrotal area. Thus, palpation of the gonad in the inguinal canal or within the labial scrotal area is fairly common. Where testicular tissue is present, there is an increased risk for malignant degeneration, and these gonads should be removed after puberty. Comprehensive Gynecology 7 th edition, 2017 (Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA editors); chapter 11, Congenital Abnormalities of the Female Reproductive Tract ; pp
56 OUTLINE Review Mullerian embryogenesis Musset s 3 stage process Examination of the newborn s external genitalia Perineal and vaginal defects Abnormalities of the cervix and uterus Abnormalities of the ovary
57 Thank you! youtube channel: Ina Irabon Doc Ina OB Gyn
Sexual differentiation:
 Abnormal Development of Female Genitalia Dr. Maryam Fetal development of gonads, external genitalia, Mullerian ducts and Wolffian ducts can be disrupted at a variety of points, leading to a wide range
Abnormal Development of Female Genitalia Dr. Maryam Fetal development of gonads, external genitalia, Mullerian ducts and Wolffian ducts can be disrupted at a variety of points, leading to a wide range
Normal and Abnormal Development of the Genital Tract. Dr.Raghad Abdul-Halim
 Normal and Abnormal Development of the Genital Tract Dr.Raghad Abdul-Halim objectives: Revision of embryology. Clinical presentation, investigations and clinical significance of most common developmental
Normal and Abnormal Development of the Genital Tract Dr.Raghad Abdul-Halim objectives: Revision of embryology. Clinical presentation, investigations and clinical significance of most common developmental
1) Intersexuality - Dr. Huda
 1) Intersexuality - Dr. Huda DSD (Disorders of sex development) occur when there is disruption of either: Gonadal differentiation Fetal sex steroid production or action Mullerian abnormalities and Wolffian
1) Intersexuality - Dr. Huda DSD (Disorders of sex development) occur when there is disruption of either: Gonadal differentiation Fetal sex steroid production or action Mullerian abnormalities and Wolffian
DEFINITION: Masculinization of external genitalia in patients with normal 46XX karyotype.
 INTERSEX DISORDERS DEFINITION: Masculinization of external genitalia in patients with normal 46XX karyotype. - Degree of masculinization variable: - mild clitoromegaly - complete fusion of labia folds
INTERSEX DISORDERS DEFINITION: Masculinization of external genitalia in patients with normal 46XX karyotype. - Degree of masculinization variable: - mild clitoromegaly - complete fusion of labia folds
Grand Rounds Mullerian Anomalies. Sara Schaenzer, PGY-3 9/26/18
 Grand Rounds Mullerian Anomalies Sara Schaenzer, PGY-3 9/26/18 Background Congenital uterine anomalies occur in 2-4% of women Three times more common in women with recurrent pregnancy loss True incidence
Grand Rounds Mullerian Anomalies Sara Schaenzer, PGY-3 9/26/18 Background Congenital uterine anomalies occur in 2-4% of women Three times more common in women with recurrent pregnancy loss True incidence
under its influence, male development occurs; in its absence, female development is established.
 Sex differentiation is a complex process that involves many genes, including some that are autosomal. The key to sexual dimorphism is the Y chromosome, which contains the testis determining gene called
Sex differentiation is a complex process that involves many genes, including some that are autosomal. The key to sexual dimorphism is the Y chromosome, which contains the testis determining gene called
PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY OF SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION
 PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY OF SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION Prof. Dr med. Jolanta Słowikowska-Hilczer Department of Andrology and Reproductive Endocrinology Medical University of Łódź, Poland Sexual determination
PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY OF SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION Prof. Dr med. Jolanta Słowikowska-Hilczer Department of Andrology and Reproductive Endocrinology Medical University of Łódź, Poland Sexual determination
Development of the Genital System
 Development of the Genital System Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta The mesonephros develops primitive nephrotomes draining into a mesonephric duct nephrotome mesonephric
Development of the Genital System Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta The mesonephros develops primitive nephrotomes draining into a mesonephric duct nephrotome mesonephric
W.S. O University of Hong Kong
 W.S. O University of Hong Kong Development of the Genital System 1. Sexual differentiation 2. Differentiation of the gonads a. Germ cells extragonadal in origin b. Genital ridge intermediate mesoderm consisting
W.S. O University of Hong Kong Development of the Genital System 1. Sexual differentiation 2. Differentiation of the gonads a. Germ cells extragonadal in origin b. Genital ridge intermediate mesoderm consisting
AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA. Dr. HAKIMI, SpAK. Dr. MELDA DELIANA, SpAK
 AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA (DISORDERS OF SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT) Dr. HAKIMI, SpAK Dr. MELDA DELIANA, SpAK Dr. SISKA MAYASARI LUBIS, SpA Pediatric Endocrinology division USU/H. ADAM MALIK HOSPITAL 1 INTRODUCTION Normal
AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA (DISORDERS OF SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT) Dr. HAKIMI, SpAK Dr. MELDA DELIANA, SpAK Dr. SISKA MAYASARI LUBIS, SpA Pediatric Endocrinology division USU/H. ADAM MALIK HOSPITAL 1 INTRODUCTION Normal
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
EMBRYOLOGIC BASIS OF FEMALE CONGENITAL TRACT MALFORMATIONS
 EMBRYOLOGIC BASIS OF FEMALE CONGENITAL TRACT MALFORMATIONS Prof. Pedro Acién, MD, FRCOG Maribel Acién, MD San Juan University Hospital/ Miguel Hernández University Campus of San Juan. Alicante. Spain Instituto
EMBRYOLOGIC BASIS OF FEMALE CONGENITAL TRACT MALFORMATIONS Prof. Pedro Acién, MD, FRCOG Maribel Acién, MD San Juan University Hospital/ Miguel Hernández University Campus of San Juan. Alicante. Spain Instituto
Chapter 18 Development. Sexual Differentiation
 Chapter 18 Development Sexual Differentiation There Are Many Levels of Sex Determination Chromosomal Sex Gonadal Sex Internal Sex Organs External Sex Organs Brain Sex Gender Identity Gender Preference
Chapter 18 Development Sexual Differentiation There Are Many Levels of Sex Determination Chromosomal Sex Gonadal Sex Internal Sex Organs External Sex Organs Brain Sex Gender Identity Gender Preference
Development of the urogenital system
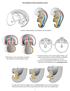 Development of the urogenital system Location of the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros Differentiation of the intermedierm mesoderm into nephrotome and mesonephric tubules Connection between aorta
Development of the urogenital system Location of the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros Differentiation of the intermedierm mesoderm into nephrotome and mesonephric tubules Connection between aorta
Mu llerian Anomalies. Introduction
 CLINICAL OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY Volume 51, Number 1, 214 222 r 2008, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Mu llerian Anomalies LEE P. SHULMAN, MD The Anna Ross Lapham Professor in Obstetrics and Gynecology,
CLINICAL OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY Volume 51, Number 1, 214 222 r 2008, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Mu llerian Anomalies LEE P. SHULMAN, MD The Anna Ross Lapham Professor in Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Urogenital System. PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. 钱晓菁 XIAO-JING QIAN Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College
 Urogenital System 钱晓菁 XIAO-JING QIAN Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College intermediate mesoderm urogenital ridge mesonephric ridge genital ridge I. Urinary System 1. kidney
Urogenital System 钱晓菁 XIAO-JING QIAN Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College intermediate mesoderm urogenital ridge mesonephric ridge genital ridge I. Urinary System 1. kidney
Disordered Sex Differentiation Mixed gonadal dysgenesis Congenital adrenal hyperplasia Mixed gonadal dysgenesis
 Disordered Sex Differentiation DSD has superceded intersex in describing genital anomalies in childhood DSD results from hormonal imbalances due to (i) abnormal genetic status, (ii) enzyme defects, or
Disordered Sex Differentiation DSD has superceded intersex in describing genital anomalies in childhood DSD results from hormonal imbalances due to (i) abnormal genetic status, (ii) enzyme defects, or
FLASH CARDS. Kalat s Book Chapter 11 Alphabetical
 FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 11 Alphabetical alpha-fetoprotein alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-Fetal Protein (AFP) or alpha-1- fetoprotein. During a prenatal sensitive period, estradiol
FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 11 Alphabetical alpha-fetoprotein alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-Fetal Protein (AFP) or alpha-1- fetoprotein. During a prenatal sensitive period, estradiol
Development of the female Reproductive System. Dr. Susheela Rani
 Development of the female Reproductive System Dr. Susheela Rani Genital System Gonads Internal genitals External genitals Determining sex chronology of events Genetic sex Determined at fertilization Gonadal
Development of the female Reproductive System Dr. Susheela Rani Genital System Gonads Internal genitals External genitals Determining sex chronology of events Genetic sex Determined at fertilization Gonadal
Sex Determination and Development of Reproductive Organs
 Sex Determination and Development of Reproductive Organs Sex determination The SRY + gene is necessary and probably sufficient for testis development The earliest sexual difference appears in the gonad
Sex Determination and Development of Reproductive Organs Sex determination The SRY + gene is necessary and probably sufficient for testis development The earliest sexual difference appears in the gonad
A Young Asian Girl with MRKH Type B Syndrome: A Case Report
 A Young Asian Girl with MRKH Type B Syndrome: A Case Report Nidhi Jain 1, Pardaman Singh 2, Deepak Goel 3, Jyotsna kamra 4 1,4 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Maharaja Agarsein Medical College,
A Young Asian Girl with MRKH Type B Syndrome: A Case Report Nidhi Jain 1, Pardaman Singh 2, Deepak Goel 3, Jyotsna kamra 4 1,4 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Maharaja Agarsein Medical College,
Mullerian duct anomalies presenting with primary amenorrhoea
 International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Chandrayan P et al. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Feb;5(2):300-305 www.ijrcog.org pissn 2320-1770 eissn 2320-1789
International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Chandrayan P et al. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Feb;5(2):300-305 www.ijrcog.org pissn 2320-1770 eissn 2320-1789
Let s Talk About Hormones!
 Let s Talk About Hormones! This lesson was created by Serena Reves and Nichelle Penney, with materials from the BCTF and The Pride Education Network. Hormones are responsible for the regulation of many
Let s Talk About Hormones! This lesson was created by Serena Reves and Nichelle Penney, with materials from the BCTF and The Pride Education Network. Hormones are responsible for the regulation of many
Pseudohermaphroditism due to Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
 Pseudohermaphroditism due to Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Byoung Uk Park Universidad Francisco Marroquín October 19, 2015 Agenda 1. Case Presentation 2. Image Findings 3. Discussion I. Definition/Incidence
Pseudohermaphroditism due to Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Byoung Uk Park Universidad Francisco Marroquín October 19, 2015 Agenda 1. Case Presentation 2. Image Findings 3. Discussion I. Definition/Incidence
IN SUMMARY HST 071 NORMAL & ABNORMAL SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION Fetal Sex Differentiation Postnatal Diagnosis and Management of Intersex Abnormalities
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY HST 071 Title: Fetal Sex Differentiation Postnatal Diagnosis
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY HST 071 Title: Fetal Sex Differentiation Postnatal Diagnosis
A National Model of Care for Paediatric Healthcare Services in Ireland Chapter 28: Paediatric Gynaecology
 A National Model of Care for Paediatric Healthcare Services in Ireland Chapter 28: Paediatric Gynaecology Clinical Strategy and Programmes Division Table of Contents 28.0 Introduction 2 28.1 Current Service
A National Model of Care for Paediatric Healthcare Services in Ireland Chapter 28: Paediatric Gynaecology Clinical Strategy and Programmes Division Table of Contents 28.0 Introduction 2 28.1 Current Service
Primary Amenorrhea, age 16: Recent Reflections. David A Grainger MD, MPH February 1, 2017
 Primary Amenorrhea, age 16: Recent Reflections David A Grainger MD, MPH February 1, 2017 Primary Amenorrhea No menses by age 13-14 WITHOUT BREAST DEVELOPMENT No menses by age 15-16 WITH BREAST DEVELOPMENT
Primary Amenorrhea, age 16: Recent Reflections David A Grainger MD, MPH February 1, 2017 Primary Amenorrhea No menses by age 13-14 WITHOUT BREAST DEVELOPMENT No menses by age 15-16 WITH BREAST DEVELOPMENT
When testes make no testosterone: Identifying a rare cause of 46, XY female phenotype in adulthood
 When testes make no testosterone: Identifying a rare cause of 46, XY female phenotype in adulthood Gardner DG, Shoback D. Greenspan's Basic & Clinical Endocrinology, 10e; 2017 Sira Korpaisarn, MD Endocrinology
When testes make no testosterone: Identifying a rare cause of 46, XY female phenotype in adulthood Gardner DG, Shoback D. Greenspan's Basic & Clinical Endocrinology, 10e; 2017 Sira Korpaisarn, MD Endocrinology
Vaginal agenesis: A case report*
 Vaginal agenesis: A case report* By Reyalu T. Tan, MD; Sigrid A. Barinaga, MD, FPOGS; and Marie Janice S. Alcantara, MD, FPOGS Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Southern Philippine Medical Center
Vaginal agenesis: A case report* By Reyalu T. Tan, MD; Sigrid A. Barinaga, MD, FPOGS; and Marie Janice S. Alcantara, MD, FPOGS Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Southern Philippine Medical Center
10. Development of genital system. Gonads. Genital ducts. External genitalia.
 10. Development of genital system. Gonads. Genital ducts. External genitalia. Gonads, genital ducts and the external genital organs initially pass through an indifferent period of development, which is
10. Development of genital system. Gonads. Genital ducts. External genitalia. Gonads, genital ducts and the external genital organs initially pass through an indifferent period of development, which is
C. Patrick Shahan, MD University of Tennessee Health Science Center Department of Surgery
 C. Patrick Shahan, MD University of Tennessee Health Science Center Department of Surgery Drop use of hermaphrodite and derivatives 1 in 15,000 live births Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Mixed Gonadal
C. Patrick Shahan, MD University of Tennessee Health Science Center Department of Surgery Drop use of hermaphrodite and derivatives 1 in 15,000 live births Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Mixed Gonadal
SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 1 SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL SEMINAR: SEX HORMONES PART 1 An Overview What are steroid hormones? Steroid
1 SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL SEMINAR: SEX HORMONES PART 1 An Overview What are steroid hormones? Steroid
Intersex Genital Mutilations in ICD-10 Zwischengeschlecht.org / StopIGM.org 2014 (v2.1)
 Intersex Genital Mutilations in ICD-10 Zwischengeschlecht.org / StopIGM.org 2014 (v2.1) ICD-10 Codes and Descriptions: http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en 1. Reference: 17 Most Common
Intersex Genital Mutilations in ICD-10 Zwischengeschlecht.org / StopIGM.org 2014 (v2.1) ICD-10 Codes and Descriptions: http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en 1. Reference: 17 Most Common
Case Based Urology Learning Program
 Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 3 CBULP 2011 019 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 3 CBULP 2011 019 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Approach to Disorders of Sex Development (DSD)
 Approach to Disorders of Sex Development (DSD) Old name: The Approach to Intersex Disorders Dr. Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCP Ass. Professor & Consultant Pediatric Endocrinologist, KAUH, Erfan Hospital & Ibn
Approach to Disorders of Sex Development (DSD) Old name: The Approach to Intersex Disorders Dr. Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCP Ass. Professor & Consultant Pediatric Endocrinologist, KAUH, Erfan Hospital & Ibn
Reconstructive And Conservative Surgery by Tubal Implantation in Mullerian Anomalies A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 6 Ver. III (July. 2016), PP 105-110 www.iosrjournals.org Reconstructive And Conservative Surgery
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 6 Ver. III (July. 2016), PP 105-110 www.iosrjournals.org Reconstructive And Conservative Surgery
Intersex is a group of conditions where there is a discrepancy between the external genitals and the internal genitals (the testes and ovaries).
 Intersex to use the sharing features on this page, please enable JavaScript. Share on facebookshare on IwitterBookmark & SharePrintcr-lnendly version Intersex is a group of conditions where
Intersex to use the sharing features on this page, please enable JavaScript. Share on facebookshare on IwitterBookmark & SharePrintcr-lnendly version Intersex is a group of conditions where
Clinical Standards for Service Planning in PAG
 The British Society for Paediatric & Adolescent Gynaecology. Clinical Standards for Service Planning in PAG Introduction The management of young children and adolescents with gynaecological problems (aged
The British Society for Paediatric & Adolescent Gynaecology. Clinical Standards for Service Planning in PAG Introduction The management of young children and adolescents with gynaecological problems (aged
Uterovaginal Anomalies: Diagnosis and Current Management in Teens
 Uterovaginal Anomalies: Diagnosis and Current Management in Teens Jay Spence, MD, Patricia Gervaize, PhD, and Shilpa Jain, MD Address Division of Reproductive Medicine, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Uterovaginal Anomalies: Diagnosis and Current Management in Teens Jay Spence, MD, Patricia Gervaize, PhD, and Shilpa Jain, MD Address Division of Reproductive Medicine, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Embryology /organogenesis/ Week 4 Development and teratology of reproductive system.
 Embryology /organogenesis/ Week 4 Development and teratology of reproductive system. Male or female sex is determined by spermatozoon Y in the moment of fertilization SRY gene, on the short arm of the
Embryology /organogenesis/ Week 4 Development and teratology of reproductive system. Male or female sex is determined by spermatozoon Y in the moment of fertilization SRY gene, on the short arm of the
CONGENITAL ABNORMALITIES OF GENITAL TRACT - VAGINAL DEFECTS
 CONGENITAL ABNORMALITIES OF GENITAL TRACT - VAGINAL DEFECTS Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 256 To 261 Asif Zia Akhtar ( Department of Obstetric and Gynaecology, Abbasi Shaheed Hospital, Karachi.
CONGENITAL ABNORMALITIES OF GENITAL TRACT - VAGINAL DEFECTS Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 256 To 261 Asif Zia Akhtar ( Department of Obstetric and Gynaecology, Abbasi Shaheed Hospital, Karachi.
11. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION. Germinal cells, gonocytes. Indifferent stage INDIFFERENT STAGE
 11. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION INDIFFERENT STAGE Early in pregnancy, (within 10-15 % of the pregnancy s expected length) a genital ridge is formed in the sides of the embryonic tissue, ventral to the mesonephros
11. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION INDIFFERENT STAGE Early in pregnancy, (within 10-15 % of the pregnancy s expected length) a genital ridge is formed in the sides of the embryonic tissue, ventral to the mesonephros
Goals. Disorders of Sex Development (Intersex): An Overview. Joshua May, MD Pediatric Endocrinology
 Disorders of Sex Development (Intersex): An Overview Joshua May, MD Pediatric Endocrinology Murphy, et al., J Ped Adol Gynecol, 2011 Goals Objectives: Participants will be able to: 1. Apply the medical
Disorders of Sex Development (Intersex): An Overview Joshua May, MD Pediatric Endocrinology Murphy, et al., J Ped Adol Gynecol, 2011 Goals Objectives: Participants will be able to: 1. Apply the medical
Midgut. Over its entire length the midgut is supplied by the superior mesenteric artery
 Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology"
 Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology" Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development: Part A Development of the Pituitary Gland" Infundibulum" Brain" Rathke s Pouch" Stomodeum" Germ Cell Migration"
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology" Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development: Part A Development of the Pituitary Gland" Infundibulum" Brain" Rathke s Pouch" Stomodeum" Germ Cell Migration"
Development of the Urinary System
 Development of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Understand the development of the kidney and related organs of the urinary system. Define the pronephrons, mesonephrons and metanephrons. Understand
Development of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Understand the development of the kidney and related organs of the urinary system. Define the pronephrons, mesonephrons and metanephrons. Understand
Embryology of the Female Reproductive Tract
 Embryology of the Female Reproductive Tract Andrew Healey Contents 1 Introduction... 21 2 Embryology of the Female Genitourinary Tract... 22 2.1 Development of the Gonads... 22 2.2 Relationship Between
Embryology of the Female Reproductive Tract Andrew Healey Contents 1 Introduction... 21 2 Embryology of the Female Genitourinary Tract... 22 2.1 Development of the Gonads... 22 2.2 Relationship Between
Ambiguous genitalia (Disorders of sex development); is any case in which the external genitalia do not appear completely male or completely female.
 Ambiguous genitalia (Disorders of sex development); is any case in which the external genitalia do not appear completely male or completely female. Disorders of sex development (DSD); True hermaphrodite;
Ambiguous genitalia (Disorders of sex development); is any case in which the external genitalia do not appear completely male or completely female. Disorders of sex development (DSD); True hermaphrodite;
Sexual differentiation is sequential process:
 Genital lsystem J. H. Lue Sexual differentiation is sequential process:.genetic (chromosomal) sex -- determined at fertilization.gonad sex -- is differentiated after 7th week.phenotypic sex -- under normal
Genital lsystem J. H. Lue Sexual differentiation is sequential process:.genetic (chromosomal) sex -- determined at fertilization.gonad sex -- is differentiated after 7th week.phenotypic sex -- under normal
AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA & CONGENITAL ADRENALHYPERPLASIA
 AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA & CONGENITAL ADRENALHYPERPLASIA BY Dr Numair Ali sheikh FCPS PGT I Department Of Pediatrics BBH RWP AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA Children born with ambiguous genitalia may be subdivided in to
AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA & CONGENITAL ADRENALHYPERPLASIA BY Dr Numair Ali sheikh FCPS PGT I Department Of Pediatrics BBH RWP AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA Children born with ambiguous genitalia may be subdivided in to
Bios 90/95. Jennifer Swann, PhD
 Sexual Differentiation Fall 2007 Bios 90/95 Jennifer Swann, PhD Dept Biol Sci, Lehigh University Why have sexes? What determines sex? Environment Genetics Hormones What causes these differences? The true
Sexual Differentiation Fall 2007 Bios 90/95 Jennifer Swann, PhD Dept Biol Sci, Lehigh University Why have sexes? What determines sex? Environment Genetics Hormones What causes these differences? The true
Urinary system development. Male ( ) and Female ( ) Reproductive Systems Development
 Urinary system development Male ( ) and Female ( ) Reproductive Systems Development Urogenital system develops from mesodermal uro-genital ridge (intermediate mesoderm) development of male and female genital
Urinary system development Male ( ) and Female ( ) Reproductive Systems Development Urogenital system develops from mesodermal uro-genital ridge (intermediate mesoderm) development of male and female genital
DEVELOPMENT OF THE ADRENAL GLAND; TESTES AND MESONEPHRIC DUCT. Reading Assignment: The Developing Human, Clinically Oriented Embryology pp
 Developmental Anatomy Steven M. Hill, Ph.D. 9/16/13 DEVELOPMENT OF THE ADRENAL GLAND; TESTES AND MESONEPHRIC DUCT Reading Assignment: The Developing Human, Clinically Oriented Embryology pp. 264-273. Objectives:
Developmental Anatomy Steven M. Hill, Ph.D. 9/16/13 DEVELOPMENT OF THE ADRENAL GLAND; TESTES AND MESONEPHRIC DUCT Reading Assignment: The Developing Human, Clinically Oriented Embryology pp. 264-273. Objectives:
DEVELOPMENT (DSD) 1 4 DISORDERS OF SEX
 Wit JM, Ranke MB, Kelnar CJH (eds): ESPE classification of paediatric endocrine diagnosis. 4. Disorders of sex development (DSD). Horm Res 2007;68(suppl 2):21 24 ESPE Code Diagnosis OMIM ICD 10 4 DISORDERS
Wit JM, Ranke MB, Kelnar CJH (eds): ESPE classification of paediatric endocrine diagnosis. 4. Disorders of sex development (DSD). Horm Res 2007;68(suppl 2):21 24 ESPE Code Diagnosis OMIM ICD 10 4 DISORDERS
DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system
 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Essential question What are the structures of the reproductive system? 2 Structures of the
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Essential question What are the structures of the reproductive system? 2 Structures of the
Female Reproductive System
 Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 26 For this lab you
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 26 For this lab you
Congenital Anomalies of the Genital Tract
 Congenital Anomalies of the Genital Tract Prof Keith Edmonds Queen Charlotte s and Chelsea Hospital Imperial College London SSO&G Jonkoping 2015 Should Paediatric and Adolescent Gynaecology be Centralised?
Congenital Anomalies of the Genital Tract Prof Keith Edmonds Queen Charlotte s and Chelsea Hospital Imperial College London SSO&G Jonkoping 2015 Should Paediatric and Adolescent Gynaecology be Centralised?
Hearing on SJR13 -- Proposes to amend the Nevada Constitution by repealing the limitation on the recognition of marriage.
 Written statement of Lauren A. Scott- Executive Director Equality Nevada. 1350 Freeport Blvd, #107 Sparks, Nevada 89431 Testimony and Statement for the Record of Hearing on SJR13 -- Proposes to amend the
Written statement of Lauren A. Scott- Executive Director Equality Nevada. 1350 Freeport Blvd, #107 Sparks, Nevada 89431 Testimony and Statement for the Record of Hearing on SJR13 -- Proposes to amend the
Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326
 Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326 READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER REGARDLESS OF WHAT YOU MARK ON THE
Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326 READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER REGARDLESS OF WHAT YOU MARK ON THE
ISSN International Journal of Innovative and Applied Research (2017) Journal home page: RESEARCH ARTICLE
 Journal home page: http://www.journalijiar.com RESEARCH ARTICLE MAYER-ROKITANSKY-KUSTER-HAUSER SYNDROME II (Rare Case). * Dr. Verinder Dhar 1 and Dr. Renu Hashia 2. 1. MD(Medicine), DM(Endo),Medicare Nursing
Journal home page: http://www.journalijiar.com RESEARCH ARTICLE MAYER-ROKITANSKY-KUSTER-HAUSER SYNDROME II (Rare Case). * Dr. Verinder Dhar 1 and Dr. Renu Hashia 2. 1. MD(Medicine), DM(Endo),Medicare Nursing
1. Hypogonadism is usually encountered in the following conditions, except
 1. Hypogonadism is usually encountered in the following conditions, except A. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia B. Noonan Syndrome C. Prader-Willi Syndrome D. Bardet-Biedl Syndrome 2. A 6 year old girl with
1. Hypogonadism is usually encountered in the following conditions, except A. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia B. Noonan Syndrome C. Prader-Willi Syndrome D. Bardet-Biedl Syndrome 2. A 6 year old girl with
Case Report Imperforate Hymen Causing Bilateral Hydroureteronephrosis in an Infant with Bicornuate Uterus
 Case Reports in Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 102683, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/102683 Case Report Imperforate Hymen Causing Bilateral Hydroureteronephrosis in an Infant with Bicornuate Uterus Ayse Secil
Case Reports in Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 102683, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/102683 Case Report Imperforate Hymen Causing Bilateral Hydroureteronephrosis in an Infant with Bicornuate Uterus Ayse Secil
Information leaflet for patients and families. Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH)
 Information leaflet for patients and families Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) What is CAH? CAH is a disorder causing impaired hormone production from the adrenal glands. Hormones are chemical messengers
Information leaflet for patients and families Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) What is CAH? CAH is a disorder causing impaired hormone production from the adrenal glands. Hormones are chemical messengers
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology
 Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology Development of the Pituitary Gland Lec 5: Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development Stomodeum Brain Infundibulum Rathke s Pouch Germ Cell Migration
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology Development of the Pituitary Gland Lec 5: Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development Stomodeum Brain Infundibulum Rathke s Pouch Germ Cell Migration
Disorder name: Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Acronym: CAH
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Draft Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues surrounding
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Draft Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues surrounding
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception
 PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
Animal Reproduction. Hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. # lectures for cumulative test # 01 book 01
 Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 05 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 05 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Hearing on SJR13 -- Proposes to amend the Nevada Constitution by repealing the limitation on the recognition of marriage.
 Written statement of Lauren A. Scott- Executive Director Equality Nevada 1350 Freeport Blvd, #107 Sparks, Nevada 89431 Testimony and Statement for the Record of Hearing on SJR13 -- Proposes to amend the
Written statement of Lauren A. Scott- Executive Director Equality Nevada 1350 Freeport Blvd, #107 Sparks, Nevada 89431 Testimony and Statement for the Record of Hearing on SJR13 -- Proposes to amend the
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 9; Lecture 2; Wednesday Stuart Sumida. Development and Structure, of the Reproductive System
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 9; Lecture 2; Wednesday Stuart Sumida Development and Structure, of the Reproductive System Don t forget the relationships of the structures of the layers
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 9; Lecture 2; Wednesday Stuart Sumida Development and Structure, of the Reproductive System Don t forget the relationships of the structures of the layers
Faculty Nurse Practitioner Case Studies and Quality Assurance Review
 Faculty Nurse Practitioner Case Studies and Quality Assurance Review Satellite Conference and Live Webcast Thursday, July 16, 2009 2:00-3:30 p.m. Central Time Produced by the Alabama Department of Public
Faculty Nurse Practitioner Case Studies and Quality Assurance Review Satellite Conference and Live Webcast Thursday, July 16, 2009 2:00-3:30 p.m. Central Time Produced by the Alabama Department of Public
Management of Reproductive Tract Anomalies
 DOI 10.1007/s13224-017-1001-8 INVITED MINI REVIEW Garima Kachhawa 1 Alka Kriplani 1 Received: 29 March 2017 / Accepted: 21 April 2017 / Published online: 2 May 2017 Ó Federation of Obstetric & Gynecological
DOI 10.1007/s13224-017-1001-8 INVITED MINI REVIEW Garima Kachhawa 1 Alka Kriplani 1 Received: 29 March 2017 / Accepted: 21 April 2017 / Published online: 2 May 2017 Ó Federation of Obstetric & Gynecological
Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
REPRODUCCIÓN. La idea fija. Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
Written re-exam Bachelor in Medicine/MedIS. Exam date: Time: 09:00-11:00. Important information:
 Written re-exam 2016 Course title: Program: Semester: Reproductive endocrinology Bachelor in Medicine/MedIS 4 semester Exam date: 04-08-16 Time: 09:00-11:00 Evaluation form 7-point scale Important information:
Written re-exam 2016 Course title: Program: Semester: Reproductive endocrinology Bachelor in Medicine/MedIS 4 semester Exam date: 04-08-16 Time: 09:00-11:00 Evaluation form 7-point scale Important information:
Testicular feminization. The features of this syndrome in its typical form are these (Fig. 1): (1) Female bodily configuration.
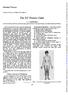 Personal Practice Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1970, 45, 595. The XY Female Child C. J. DEWHURST From the Institute of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Queen Charlotte's Maternity Hospital, and Chelsea
Personal Practice Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1970, 45, 595. The XY Female Child C. J. DEWHURST From the Institute of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Queen Charlotte's Maternity Hospital, and Chelsea
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive system
 Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Ch 20: Reproduction. Keypoints: Human Chromosomes Gametogenesis Fertilization Early development Parturition
 Ch 20: Reproduction Keypoints: Human Chromosomes Gametogenesis Fertilization Early development Parturition SLOs Contrast mitosis/meiosis, haploid/diploid, autosomes/sex chromosomes. Outline the hormonal
Ch 20: Reproduction Keypoints: Human Chromosomes Gametogenesis Fertilization Early development Parturition SLOs Contrast mitosis/meiosis, haploid/diploid, autosomes/sex chromosomes. Outline the hormonal
Development of the Urinary System. 3 Distinct Embryonic Kidney Structures
 Development of the Urinary System Excretory portion of urinary system derived from intermediate mesoderm Week 4: 1 st nephrons/renal corpuscles form Nephrotomes form and develop hollow lumens to form nephric
Development of the Urinary System Excretory portion of urinary system derived from intermediate mesoderm Week 4: 1 st nephrons/renal corpuscles form Nephrotomes form and develop hollow lumens to form nephric
Clinical evaluation of infertility
 Clinical evaluation of infertility DR. FARIBA KHANIPOUYANI OBSTETRICIAN & GYNECOLOGIST PRENATOLOGIST Definition: inability to achieve conception despite one year of frequent unprotected intercourse. Male
Clinical evaluation of infertility DR. FARIBA KHANIPOUYANI OBSTETRICIAN & GYNECOLOGIST PRENATOLOGIST Definition: inability to achieve conception despite one year of frequent unprotected intercourse. Male
Vaginoplasty using amnion graft along with a fourchette flap
 J Obstet Gynecol India Vol. 59, No. 4 : July/August 2009 pg 344-348 Original Article Vaginoplasty using amnion graft along with a fourchette flap Manhas Kamlesh 1, Manhas Amit 2 1 Prof & Head, 2 Resident,
J Obstet Gynecol India Vol. 59, No. 4 : July/August 2009 pg 344-348 Original Article Vaginoplasty using amnion graft along with a fourchette flap Manhas Kamlesh 1, Manhas Amit 2 1 Prof & Head, 2 Resident,
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Unit 7B STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the female reproductive tract. 2. Learn the functions of the female reproductive tract. 3.
Unit 7B STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the female reproductive tract. 2. Learn the functions of the female reproductive tract. 3.
The Female Reproductive System
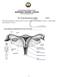 The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
Introduction to GYN Specialties
 Outline Introduction to GYN Specialties Gynecologic Oncology* Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery* Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility* Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology** Family
Outline Introduction to GYN Specialties Gynecologic Oncology* Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery* Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility* Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology** Family
Laparoscopic Morcellation of Didelphic Uterus With Cervical and Renal Aplasia
 CASE REPORT Laparoscopic Morcellation of Didelphic Uterus With Cervical and Renal Aplasia Albert Altchek, MD, Michael Brodman, MD, Peter Schlosshauer, MD, Liane Deligdisch, MD ABSTRACT This is a case report
CASE REPORT Laparoscopic Morcellation of Didelphic Uterus With Cervical and Renal Aplasia Albert Altchek, MD, Michael Brodman, MD, Peter Schlosshauer, MD, Liane Deligdisch, MD ABSTRACT This is a case report
CHAPTER 13 Gynaecological Procedures
 CHAPTER 13 Propunere noua clasificare proceduri folosind codificarea ICD-10-AM versiunea 3, 30 martie 2004 Gynaecological Procedures BLOCK 1240 Application, insertion or removal procedures on ovary 35518-00
CHAPTER 13 Propunere noua clasificare proceduri folosind codificarea ICD-10-AM versiunea 3, 30 martie 2004 Gynaecological Procedures BLOCK 1240 Application, insertion or removal procedures on ovary 35518-00
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system
 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Scrub In The external area between the vulva and the anus is the : a. Cervix b. Endometrium c. Perineum d. Vagina What structure connects the testes
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Scrub In The external area between the vulva and the anus is the : a. Cervix b. Endometrium c. Perineum d. Vagina What structure connects the testes
Ambiguous Genitalia: Etiology, Treatment, and Nursing Implications Leslie A. Parker, RNC, MSN, ARNP
 Ambiguous Genitalia: Etiology, Treatment, and Nursing Implications Leslie A. Parker, RNC, MSN, ARNP = The infant presenting with ambiguous genitalia is a challenge to both the medical and nursing staff.
Ambiguous Genitalia: Etiology, Treatment, and Nursing Implications Leslie A. Parker, RNC, MSN, ARNP = The infant presenting with ambiguous genitalia is a challenge to both the medical and nursing staff.
Module Title: GENITO-URINARY TRACT Date: May 2013 Module Rationale and Competencies
 Module Title: Date: May 2013 Module Rationale and Competencies A paediatric surgeon is required to have a thorough understanding of normal anatomy and physiology, pathophysiology, investigations, differential
Module Title: Date: May 2013 Module Rationale and Competencies A paediatric surgeon is required to have a thorough understanding of normal anatomy and physiology, pathophysiology, investigations, differential
Analysis of Mullerian developmental defects in a tertiary care hospital: a four year experience
 International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Patel SN et al. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Jun;4(3):570-574 www.ijrcog.org pissn 2320-1770 eissn 2320-1789
International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Patel SN et al. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Jun;4(3):570-574 www.ijrcog.org pissn 2320-1770 eissn 2320-1789
Action of reproductive hormones through the life span 9/22/99
 Action of reproductive hormones through the life span Do reproductive hormones affect the life span? One hypothesis about the rate of aging asserts that there is selective pressure for either high rate
Action of reproductive hormones through the life span Do reproductive hormones affect the life span? One hypothesis about the rate of aging asserts that there is selective pressure for either high rate
Reproductive System. Where it all begins
 Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I)
 Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Ahmed Nazer, 1 Ahmed Abu-Zaid, 2 Osama AlOmar, 1 Hany Salem, 1 Ayman Azzam, 3 and Ismail A. Al-Badawi Case Report. 1.
 Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume 2013, Article ID 450165, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/450165 Case Report Bilateral Ectopic Hypoplastic Uteri Attached to Bilateral Pelvic Sidewalls
Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume 2013, Article ID 450165, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/450165 Case Report Bilateral Ectopic Hypoplastic Uteri Attached to Bilateral Pelvic Sidewalls
Development of the urinary system
 Development of the urinary system WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. 3 sets of kidneys developing in succession (temporally and spatially) : Pronephros ] Mesonephros ]- Intermediate
Development of the urinary system WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. 3 sets of kidneys developing in succession (temporally and spatially) : Pronephros ] Mesonephros ]- Intermediate
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
