Animal Reproduction. Hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. # lectures for cumulative test # 01 book 01
|
|
|
- Holly Holmes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) , 05 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings 01-02: Introduction to Animal Reproduction (2) Meetings 03-04: Reproductive Structures and their Functions (2) Meetings 05-07: and its Liposoluble and Watersoluble Hormones (3) Meetings 08-09: The Neuroendocrine Control of Male and Female Puberty Onset (2) Meetings 10-11: REVIEW AND TEST #1 Meetings 12-17: Female and Male Reproduction and Techniques for their Control (6) Meetings 18-19: REVIEW AND TEST #2 Meetings 20-21: Reproductive Behavior and the Spermatozoa in the Female Tract (2) Meetings 22-23: Embryogenesis, Placentation, Parturition and Lactation (3) Meetings 24-25: Puerperium, Lactation and Reproductive Ageing (2) Meeting 26 Reproductive Pathology and Case Studies (1) Meetings 27-28: REVIEW AND TEST #3 AND TEST #4 slides: There are not intended to be the sole source for studying the course material!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Slides are good to review the course material after you have study your course textbook Slides are a good indicator of the relative importance of lecture topics (see slide # per topic) Group slides by titles when using them to review course material. Match lectures and text. Hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis # lectures for cumulative test # 01 book 01 Introduction: rules, regulations, course overview and pre-requisites 02 Introduction: hormones, organs, control, and processes 03 Overview: organization and function of female reproduction 04 Overview: organization and function of male reproduction 05 Embryogenesis / maturation of hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis 06 Liposoluble hormones involved in male and female reproduction 07 Watersoluble hormones involved in male and female reproduction 08 Neuro-endocrine control of the onset of puberty in males and females 09 Neuro-endocrine control of the onset of puberty in males and females 10 REVIEW material from lecture # 01 through lecture # EXAM # 01 - material from lecture # 01 through lecture # 09 Page 1
2 Derivation of the primary embryonic germ layers and of the various organs and systems from these layers. Page 2
3 Head fold of amnium partially covering forebrain Mid-brain Hind-brain Page 3
4 The main embryological events in the development of the reproductive system. Page 4
5 An hypothalamic pituitary unit consists of a vascular link to anterior and a neuronal link to posterior pituitary Hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis Embryonic development of the anterior and posterior lobes of the pituitary gland (vascular vs neuronal). Page 5
6 Lesion 1 From the neural tube to the Rathke s pouch (RP) in controls (A) and in embryos lesioned in the ARNP (B) Page 6
7 The undifferentiated state has a bipotential gonad and both Mullerian (female) and Wolffian (male) systems. Hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis Migration of primordial germ cells from the yolk sac into the gonadal ridge. Page 7
8 Development and regression of the mesonephros with concurrent development of the gonad (dorsal view). Page 8
9 Pathway of events leading to formation of the male and female reproductive system. Page 9
10 The bipotential gonad can give origin to an ovary (cortex, default) or to a testis (medulla). Hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis The female pattern is default unless TDF, a transcription factor of the SRY gene, is present Page 10
11 beware of single bars Complete testicular feminization (XY, AR mutation) and an undervirilized male Hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis The developmental sequence of the testis. Page 11
12 Major steps in the descent of the testes. Hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis (cranial) (caudal) Fusion of paramesonephric ducts with urogenital sinus to form the vagina (left, dorsal view) and the formation of supportive structures of female tract. Page 12
13 (surge center is active in females but inactive in males due to the hypothalamic sex differentiation. Thus, only females have preovulatory LH surges). Q2 A phasic GnRH neuronal subnetwork is involved in the genesis of the preovulatory surge of LH. A tonic subnetwork is involved in the negative feedback on LH. Comments on question #02 Page 13
14 Comments on question #02 Page 14
Animal Reproduction. Overview of Male Reproduction. # lectures for cumulative test # 01 book 01
 Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 04 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 04 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Reproduction. Review for test #3. # lectures for cumulative test # 03 book
 Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 27 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture slides:
Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 27 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture slides:
Animal Reproduction. Reproductive Cyclicity. # lectures for cumulative test # 02 book 12. Reproductive cyclicity: terminology and basic concepts
 Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 14 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 14 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Reproduction. Spermatozoa in female tract. # lectures for cumulative test # 03 book
 Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 21 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 21 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology"
 Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology" Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development: Part A Development of the Pituitary Gland" Infundibulum" Brain" Rathke s Pouch" Stomodeum" Germ Cell Migration"
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology" Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development: Part A Development of the Pituitary Gland" Infundibulum" Brain" Rathke s Pouch" Stomodeum" Germ Cell Migration"
Sex Differentiation. Course Outline. Topic #! Topic lecture! Silverthorn! Membranes (pre-requisite material)!!
 Sex Differentiation The goal of these lectures is to discuss how a control system is formed. For this, we will use basic physiology associated with the control of reproduction (from sexual differentiation
Sex Differentiation The goal of these lectures is to discuss how a control system is formed. For this, we will use basic physiology associated with the control of reproduction (from sexual differentiation
Animal Reproduction. Reproductive Cyclicity. # lectures for cumulative test # 02 book 12. Reproductive cyclicity: terminology and basic concepts
 Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 15 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 15 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Mohammad Sha ban. Basheq Jehad. Hamzah Nakhleh
 11 Mohammad Sha ban Basheq Jehad Hamzah Nakhleh Physiology of the reproductive system In physiology, we are concerned with the mechanisms in which the system functions, and how the system responds to different
11 Mohammad Sha ban Basheq Jehad Hamzah Nakhleh Physiology of the reproductive system In physiology, we are concerned with the mechanisms in which the system functions, and how the system responds to different
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology
 Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology Development of the Pituitary Gland Lec 5: Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development Stomodeum Brain Infundibulum Rathke s Pouch Germ Cell Migration
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology Development of the Pituitary Gland Lec 5: Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development Stomodeum Brain Infundibulum Rathke s Pouch Germ Cell Migration
11. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION. Germinal cells, gonocytes. Indifferent stage INDIFFERENT STAGE
 11. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION INDIFFERENT STAGE Early in pregnancy, (within 10-15 % of the pregnancy s expected length) a genital ridge is formed in the sides of the embryonic tissue, ventral to the mesonephros
11. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION INDIFFERENT STAGE Early in pregnancy, (within 10-15 % of the pregnancy s expected length) a genital ridge is formed in the sides of the embryonic tissue, ventral to the mesonephros
under its influence, male development occurs; in its absence, female development is established.
 Sex differentiation is a complex process that involves many genes, including some that are autosomal. The key to sexual dimorphism is the Y chromosome, which contains the testis determining gene called
Sex differentiation is a complex process that involves many genes, including some that are autosomal. The key to sexual dimorphism is the Y chromosome, which contains the testis determining gene called
REPRODUCCIÓN. La idea fija. Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
- production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote
 Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Sex differentiation to puberty. Introduction
 ex to puberty exual in general: chromosomal, gonadal and phenotypic sex, endocrine control of phenotypic, role of testicular hormones in male development, disorders of sexual 30 Hypothalamic sexual : sexual
ex to puberty exual in general: chromosomal, gonadal and phenotypic sex, endocrine control of phenotypic, role of testicular hormones in male development, disorders of sexual 30 Hypothalamic sexual : sexual
Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2
 Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2 ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER. Some critical words are boldfaced. This exam is 7 pages long.
Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2 ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER. Some critical words are boldfaced. This exam is 7 pages long.
W.S. O University of Hong Kong
 W.S. O University of Hong Kong Development of the Genital System 1. Sexual differentiation 2. Differentiation of the gonads a. Germ cells extragonadal in origin b. Genital ridge intermediate mesoderm consisting
W.S. O University of Hong Kong Development of the Genital System 1. Sexual differentiation 2. Differentiation of the gonads a. Germ cells extragonadal in origin b. Genital ridge intermediate mesoderm consisting
1. Be able to characterize the menstrual cycle from the perspective of the ovary a. Follicular phase b. Luteal phase
 Human Sexuality Exam II Review Material Gametogenesis: Oogenesis 1. Be able to characterize the menstrual cycle from the perspective of the ovary a. Follicular phase b. Luteal phase 2. Know the relative
Human Sexuality Exam II Review Material Gametogenesis: Oogenesis 1. Be able to characterize the menstrual cycle from the perspective of the ovary a. Follicular phase b. Luteal phase 2. Know the relative
Neuroendocrinology an integrative approach
 Neuroendocrinology an integrative approach JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (848) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 04 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered:
Neuroendocrinology an integrative approach JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (848) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 04 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered:
BIOL 2402 Reproductive Systems!
 Dr. Chris Doumen! Female Reproductive Anatomy BIOL 2402 Reproductive Systems! Establishing the Ovarian Cycle During childhood, until puberty Ovaries grow and secrete small amounts of estrogens Estrogen
Dr. Chris Doumen! Female Reproductive Anatomy BIOL 2402 Reproductive Systems! Establishing the Ovarian Cycle During childhood, until puberty Ovaries grow and secrete small amounts of estrogens Estrogen
Development of the urogenital system
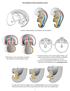 Development of the urogenital system Location of the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros Differentiation of the intermedierm mesoderm into nephrotome and mesonephric tubules Connection between aorta
Development of the urogenital system Location of the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros Differentiation of the intermedierm mesoderm into nephrotome and mesonephric tubules Connection between aorta
Menstrual Cycle. Last example of how a circle works. Course Outline. Topic #! Topic lecture! Silverthorn! Membranes (pre-requisite material)!!
 The goal of these lectures is to discuss how control system is formed and operates. For this, basic physiology associated with the control the menstrual cycle will be used. The sections for this lecture
The goal of these lectures is to discuss how control system is formed and operates. For this, basic physiology associated with the control the menstrual cycle will be used. The sections for this lecture
Urinary system development. Male ( ) and Female ( ) Reproductive Systems Development
 Urinary system development Male ( ) and Female ( ) Reproductive Systems Development Urogenital system develops from mesodermal uro-genital ridge (intermediate mesoderm) development of male and female genital
Urinary system development Male ( ) and Female ( ) Reproductive Systems Development Urogenital system develops from mesodermal uro-genital ridge (intermediate mesoderm) development of male and female genital
Development of the Genital System
 Development of the Genital System Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta The mesonephros develops primitive nephrotomes draining into a mesonephric duct nephrotome mesonephric
Development of the Genital System Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta The mesonephros develops primitive nephrotomes draining into a mesonephric duct nephrotome mesonephric
IN SUMMARY HST 071 NORMAL & ABNORMAL SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION Fetal Sex Differentiation Postnatal Diagnosis and Management of Intersex Abnormalities
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY HST 071 Title: Fetal Sex Differentiation Postnatal Diagnosis
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY HST 071 Title: Fetal Sex Differentiation Postnatal Diagnosis
Chapter 16: Steroid Hormones (Lecture 17)
 Chapter 16: Steroid Hormones (Lecture 17) A) 21 or fewer carbon atoms B) Precursor: 27 carbon cholesterol C) major classes of steroid hormones 1) progestagens a) progesterone- prepares lining of uterus
Chapter 16: Steroid Hormones (Lecture 17) A) 21 or fewer carbon atoms B) Precursor: 27 carbon cholesterol C) major classes of steroid hormones 1) progestagens a) progesterone- prepares lining of uterus
Embryology /organogenesis/ Week 4 Development and teratology of reproductive system.
 Embryology /organogenesis/ Week 4 Development and teratology of reproductive system. Male or female sex is determined by spermatozoon Y in the moment of fertilization SRY gene, on the short arm of the
Embryology /organogenesis/ Week 4 Development and teratology of reproductive system. Male or female sex is determined by spermatozoon Y in the moment of fertilization SRY gene, on the short arm of the
Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326
 Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326 READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER REGARDLESS OF WHAT YOU MARK ON THE
Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326 READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER REGARDLESS OF WHAT YOU MARK ON THE
Reproductive physiology. About this Chapter. Case introduction. The brain directs reproduction 2010/6/29. The Male Reproductive System
 Section Ⅻ Reproductive physiology Ming-jie Wang E-Mail: mjwang@shmu.edu.cn About this Chapter The reproductive organs and how they work the major endocrine functions of sexual glands actions of sex hormones
Section Ⅻ Reproductive physiology Ming-jie Wang E-Mail: mjwang@shmu.edu.cn About this Chapter The reproductive organs and how they work the major endocrine functions of sexual glands actions of sex hormones
Chapter 18 Development. Sexual Differentiation
 Chapter 18 Development Sexual Differentiation There Are Many Levels of Sex Determination Chromosomal Sex Gonadal Sex Internal Sex Organs External Sex Organs Brain Sex Gender Identity Gender Preference
Chapter 18 Development Sexual Differentiation There Are Many Levels of Sex Determination Chromosomal Sex Gonadal Sex Internal Sex Organs External Sex Organs Brain Sex Gender Identity Gender Preference
Reproduction. Introduction
 Reproduction The goal of these lectures is to discuss basic physiology associated with the control of reproduction (from sexual diferentiation to adult reproductive function). 26 The sections for this
Reproduction The goal of these lectures is to discuss basic physiology associated with the control of reproduction (from sexual diferentiation to adult reproductive function). 26 The sections for this
Normal and Abnormal Development of the Genital Tract. Dr.Raghad Abdul-Halim
 Normal and Abnormal Development of the Genital Tract Dr.Raghad Abdul-Halim objectives: Revision of embryology. Clinical presentation, investigations and clinical significance of most common developmental
Normal and Abnormal Development of the Genital Tract Dr.Raghad Abdul-Halim objectives: Revision of embryology. Clinical presentation, investigations and clinical significance of most common developmental
Sexual differentiation is sequential process:
 Genital lsystem J. H. Lue Sexual differentiation is sequential process:.genetic (chromosomal) sex -- determined at fertilization.gonad sex -- is differentiated after 7th week.phenotypic sex -- under normal
Genital lsystem J. H. Lue Sexual differentiation is sequential process:.genetic (chromosomal) sex -- determined at fertilization.gonad sex -- is differentiated after 7th week.phenotypic sex -- under normal
IB 140 Midterm #1 PRACTICE EXAM (lecture topics 1-5)
 IB 140 Midterm #1 PRACTICE EXAM (lecture topics 1-5) For all the questions on this exam, the correct answer is the single best answer that is available in the answer key. 1) Which of the following is NOT
IB 140 Midterm #1 PRACTICE EXAM (lecture topics 1-5) For all the questions on this exam, the correct answer is the single best answer that is available in the answer key. 1) Which of the following is NOT
10. Development of genital system. Gonads. Genital ducts. External genitalia.
 10. Development of genital system. Gonads. Genital ducts. External genitalia. Gonads, genital ducts and the external genital organs initially pass through an indifferent period of development, which is
10. Development of genital system. Gonads. Genital ducts. External genitalia. Gonads, genital ducts and the external genital organs initially pass through an indifferent period of development, which is
DEVELOPMENT OF THE ADRENAL GLAND; TESTES AND MESONEPHRIC DUCT. Reading Assignment: The Developing Human, Clinically Oriented Embryology pp
 Developmental Anatomy Steven M. Hill, Ph.D. 9/16/13 DEVELOPMENT OF THE ADRENAL GLAND; TESTES AND MESONEPHRIC DUCT Reading Assignment: The Developing Human, Clinically Oriented Embryology pp. 264-273. Objectives:
Developmental Anatomy Steven M. Hill, Ph.D. 9/16/13 DEVELOPMENT OF THE ADRENAL GLAND; TESTES AND MESONEPHRIC DUCT Reading Assignment: The Developing Human, Clinically Oriented Embryology pp. 264-273. Objectives:
Reproductive Physiology Primordial Germ Cells Yolk Sac Sex Chromosomes Females Males Sex-Linked Traits
 Reproductive Physiology Primordial Germ Cells - from Yolk Sac these migrate to fetus when it is 5 weeks old - these cells give rise to the gonads (ovaries for female, testes for male) first they form the
Reproductive Physiology Primordial Germ Cells - from Yolk Sac these migrate to fetus when it is 5 weeks old - these cells give rise to the gonads (ovaries for female, testes for male) first they form the
Sexual differentiation:
 Abnormal Development of Female Genitalia Dr. Maryam Fetal development of gonads, external genitalia, Mullerian ducts and Wolffian ducts can be disrupted at a variety of points, leading to a wide range
Abnormal Development of Female Genitalia Dr. Maryam Fetal development of gonads, external genitalia, Mullerian ducts and Wolffian ducts can be disrupted at a variety of points, leading to a wide range
Animal Development. Lecture 3. Germ Cells and Sex
 Animal Development Lecture 3 Germ Cells and Sex 1 The ovary of sow. The ovary of mare. The ovary of cow. The ovary of ewe. 2 3 The ovary. A generalized vertebrate ovary. (Wilt and Hake, Ch 2, 2004) 4 The
Animal Development Lecture 3 Germ Cells and Sex 1 The ovary of sow. The ovary of mare. The ovary of cow. The ovary of ewe. 2 3 The ovary. A generalized vertebrate ovary. (Wilt and Hake, Ch 2, 2004) 4 The
Action of reproductive hormones through the life span 9/22/99
 Action of reproductive hormones through the life span Do reproductive hormones affect the life span? One hypothesis about the rate of aging asserts that there is selective pressure for either high rate
Action of reproductive hormones through the life span Do reproductive hormones affect the life span? One hypothesis about the rate of aging asserts that there is selective pressure for either high rate
PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY OF SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION
 PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY OF SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION Prof. Dr med. Jolanta Słowikowska-Hilczer Department of Andrology and Reproductive Endocrinology Medical University of Łódź, Poland Sexual determination
PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY OF SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION Prof. Dr med. Jolanta Słowikowska-Hilczer Department of Andrology and Reproductive Endocrinology Medical University of Łódź, Poland Sexual determination
Lab Exercise Endocrine System
 Lab Exercise Endocrine System Name Date Materials: Human torso model Compound light microscope Prepared slides of the pituitary gland, pineal gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, thymus gland, adrenal
Lab Exercise Endocrine System Name Date Materials: Human torso model Compound light microscope Prepared slides of the pituitary gland, pineal gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, thymus gland, adrenal
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I)
 Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Alterations of Neurologic Function
 Pathophysiology JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 08 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Lectures, tests, grades, office hours, textbook, Material
Pathophysiology JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 08 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Lectures, tests, grades, office hours, textbook, Material
Cell to Cell Communication
 Review #1 08 Review using OPAL figures Review using class web PDF Preview of test #1 Cell to Cell Communication 1 Communication Strategies endocrine neurocrine paracrine autocrine Endocrine System Overview
Review #1 08 Review using OPAL figures Review using class web PDF Preview of test #1 Cell to Cell Communication 1 Communication Strategies endocrine neurocrine paracrine autocrine Endocrine System Overview
MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure.
 Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
FLASH CARDS. Kalat s Book Chapter 11 Alphabetical
 FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 11 Alphabetical alpha-fetoprotein alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-Fetal Protein (AFP) or alpha-1- fetoprotein. During a prenatal sensitive period, estradiol
FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 11 Alphabetical alpha-fetoprotein alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-Fetal Protein (AFP) or alpha-1- fetoprotein. During a prenatal sensitive period, estradiol
2. Which of the following factors does not contribute to ion selectivity?
 General Biology Summer 2014 Exam II Sample Answers 1. Which of the following is TRUE about a neuron at rest? A. The cytosol is positive relative to the outside B. Na+ concentrations are higher inside C.
General Biology Summer 2014 Exam II Sample Answers 1. Which of the following is TRUE about a neuron at rest? A. The cytosol is positive relative to the outside B. Na+ concentrations are higher inside C.
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System
 9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
Development of the female Reproductive System. Dr. Susheela Rani
 Development of the female Reproductive System Dr. Susheela Rani Genital System Gonads Internal genitals External genitals Determining sex chronology of events Genetic sex Determined at fertilization Gonadal
Development of the female Reproductive System Dr. Susheela Rani Genital System Gonads Internal genitals External genitals Determining sex chronology of events Genetic sex Determined at fertilization Gonadal
Cell to Cell Communication
 Review #1 15 Review using OPAL figures Review using class web PDF Preview of test #1 Cell to Cell Communication 1 Communication Strategies endocrine neurocrine paracrine autocrine Endocrine System Overview
Review #1 15 Review using OPAL figures Review using class web PDF Preview of test #1 Cell to Cell Communication 1 Communication Strategies endocrine neurocrine paracrine autocrine Endocrine System Overview
Sexual Development. 6 Stages of Development
 6 Sexual Development 6 Stages of Development Development passes through distinct stages, the first of which is fertilization, when one sperm enters one ovum. To enter an ovum, a sperm must undergo the
6 Sexual Development 6 Stages of Development Development passes through distinct stages, the first of which is fertilization, when one sperm enters one ovum. To enter an ovum, a sperm must undergo the
HORMONES & REPRODUCTION OUTLINE
 1 HORMONES & REPRODUCTION Dr. Steinmetz OUTLINE 2 The Endocrine System Sexual Reproduction Hormonal Role in Sexual Differentiation Gender Differences and Gender Identity Characterizing Complex Behaviors
1 HORMONES & REPRODUCTION Dr. Steinmetz OUTLINE 2 The Endocrine System Sexual Reproduction Hormonal Role in Sexual Differentiation Gender Differences and Gender Identity Characterizing Complex Behaviors
The reproductive system
 The reproductive system THE OVARIAN CYCLE HORMONAL REGULATION OF OOGENSIS AND OVULATION hypothalamic-pituitary-ovary axis Overview of the structures of the endocrine system Principal functions of the
The reproductive system THE OVARIAN CYCLE HORMONAL REGULATION OF OOGENSIS AND OVULATION hypothalamic-pituitary-ovary axis Overview of the structures of the endocrine system Principal functions of the
Urogenital System. PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. 钱晓菁 XIAO-JING QIAN Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College
 Urogenital System 钱晓菁 XIAO-JING QIAN Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College intermediate mesoderm urogenital ridge mesonephric ridge genital ridge I. Urinary System 1. kidney
Urogenital System 钱晓菁 XIAO-JING QIAN Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College intermediate mesoderm urogenital ridge mesonephric ridge genital ridge I. Urinary System 1. kidney
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems. Chapter 39: Biology II
 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
The Biology of Sex: How We Become Male or Female.
 The Biology of Sex: How We Become Male or Female. Dr. Tamatha Barbeau, Dept. of Biology Guest Lecture for Gender 200 March 2017 Objectives: 1. Sex vs. Gender defined. 2. Biological sex based on inheritance
The Biology of Sex: How We Become Male or Female. Dr. Tamatha Barbeau, Dept. of Biology Guest Lecture for Gender 200 March 2017 Objectives: 1. Sex vs. Gender defined. 2. Biological sex based on inheritance
VM 744 THERIOGENOLOGY Spring 2013
 VM 744 THERIOGENOLOGY Spring 2013 Credits-3 Coordinator: Patrick M., DVM, PhD, Diplomate ACT Department of Clinical Sciences Office: Equine Reproduction Laboratory Phone: 491-8626 email: pmccue@colostate.edu
VM 744 THERIOGENOLOGY Spring 2013 Credits-3 Coordinator: Patrick M., DVM, PhD, Diplomate ACT Department of Clinical Sciences Office: Equine Reproduction Laboratory Phone: 491-8626 email: pmccue@colostate.edu
4/23/2018. Endocrine System: Overview. Endocrine System: Overview
 Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
Development of the Urinary System
 Development of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Understand the development of the kidney and related organs of the urinary system. Define the pronephrons, mesonephrons and metanephrons. Understand
Development of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Understand the development of the kidney and related organs of the urinary system. Define the pronephrons, mesonephrons and metanephrons. Understand
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Embryology of the Female Reproductive Tract
 Embryology of the Female Reproductive Tract Andrew Healey Contents 1 Introduction... 21 2 Embryology of the Female Genitourinary Tract... 22 2.1 Development of the Gonads... 22 2.2 Relationship Between
Embryology of the Female Reproductive Tract Andrew Healey Contents 1 Introduction... 21 2 Embryology of the Female Genitourinary Tract... 22 2.1 Development of the Gonads... 22 2.2 Relationship Between
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
BIOL 439: Endocrinology
 1 Biol 439-01 (Call # 15034) Michael Chen, Ph.D. Biol Sci 247 (323) 343-2084 MW 4:20-6:00 pm Biol Sci. 120 mchen@calstatela.edu Office hours: TWR: 2:00-4:00 pm BIOL 439: Endocrinology This course provides
1 Biol 439-01 (Call # 15034) Michael Chen, Ph.D. Biol Sci 247 (323) 343-2084 MW 4:20-6:00 pm Biol Sci. 120 mchen@calstatela.edu Office hours: TWR: 2:00-4:00 pm BIOL 439: Endocrinology This course provides
Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary
 Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary Hypothalamus neuron cell bodies produce ADH: supraoptic nuclei Oxytocin: paraventricular nuclei Transported along the hypothalamohypophyseal tract Stored in
Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary Hypothalamus neuron cell bodies produce ADH: supraoptic nuclei Oxytocin: paraventricular nuclei Transported along the hypothalamohypophyseal tract Stored in
Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages )
 Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system? How does the endocrine system maintain homeostasis?
Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system? How does the endocrine system maintain homeostasis?
Reproductive cyclicity 19. Introduction. Page 1. repro and its story lines. Male repro: a simpler way of control
 Reproductive cyclicity 19 Male repro: a simpler way of control Menstrual cycles: ovary / uterine anatomy and cell types, follicular phase, ovulation, luteal phase, cyclicity Race events: removal of P4
Reproductive cyclicity 19 Male repro: a simpler way of control Menstrual cycles: ovary / uterine anatomy and cell types, follicular phase, ovulation, luteal phase, cyclicity Race events: removal of P4
Oogenesis. Key Concepts. Female Reproductive Tract
 Oogenesis 1 Key Concepts Female Reproductive Tract Ovary Oogenesis Follicles Ovulation Corpus Luteum Molecular Activity Primordial Germ Cells (PGCs) 2 Female Reproductive Tract Ovary Oviduct Uterus Vagina
Oogenesis 1 Key Concepts Female Reproductive Tract Ovary Oogenesis Follicles Ovulation Corpus Luteum Molecular Activity Primordial Germ Cells (PGCs) 2 Female Reproductive Tract Ovary Oviduct Uterus Vagina
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.45 - ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
!! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid
 Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Bio Section IV Late Development. Development of the Tetrapod Limb. Pattern Formation. Skeletal pattern formation. Gilbert 9e Chapter 13
 Bio 127 - Section IV Late Development Development of the Tetrapod Limb Gilbert 9e Chapter 13 Pattern Formation Limbs show an amazing aspect of development Similarities: Architectural symmetry in all four
Bio 127 - Section IV Late Development Development of the Tetrapod Limb Gilbert 9e Chapter 13 Pattern Formation Limbs show an amazing aspect of development Similarities: Architectural symmetry in all four
REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE
 Reproductive Biotechnologies Andrology I REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE Prof. Alberto Contri REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE SPERMATOGENESIS AND REPRODUCTIVE BEHAVIOR RELATED TO THE ACTIVITY
Reproductive Biotechnologies Andrology I REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE Prof. Alberto Contri REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE SPERMATOGENESIS AND REPRODUCTIVE BEHAVIOR RELATED TO THE ACTIVITY
Sex Determination and Development of Reproductive Organs
 Sex Determination and Development of Reproductive Organs Sex determination The SRY + gene is necessary and probably sufficient for testis development The earliest sexual difference appears in the gonad
Sex Determination and Development of Reproductive Organs Sex determination The SRY + gene is necessary and probably sufficient for testis development The earliest sexual difference appears in the gonad
Male reproduction. Cross section of Human Testis ผศ.ดร.พญ.ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ภาคว ชาสร รว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล 1. Aims
 Aims Male reproduction Male reproductive structure Spermatogenesis ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ห อง 216 โทร: 7578 Hypothalamo-pituitary-testicular axis Male sex hormone action Male reproductive structure Male reproductive
Aims Male reproduction Male reproductive structure Spermatogenesis ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ห อง 216 โทร: 7578 Hypothalamo-pituitary-testicular axis Male sex hormone action Male reproductive structure Male reproductive
Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages )
 Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems 11 What is the function of the parathyroid glands? Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system?
Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems 11 What is the function of the parathyroid glands? Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system?
Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser Syndrome
 Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser Syndrome Item Type text; Electronic Thesis Authors Shy, Hannah Marie Publisher The University of Arizona. Rights Copyright is held by the author. Digital access to this material
Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser Syndrome Item Type text; Electronic Thesis Authors Shy, Hannah Marie Publisher The University of Arizona. Rights Copyright is held by the author. Digital access to this material
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System
 I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
Sexual Reproduction. For most diploid eukaryotes, sexual reproduction is the only mechanism resulting in new members of a species.
 Sex Determination Sexual Reproduction For most diploid eukaryotes, sexual reproduction is the only mechanism resulting in new members of a species. Meiosis in the sexual organs of parents produces haploid
Sex Determination Sexual Reproduction For most diploid eukaryotes, sexual reproduction is the only mechanism resulting in new members of a species. Meiosis in the sexual organs of parents produces haploid
Summary The Endocrine System The Reproductive System Human Endocrine Glands. Endocrine and Reproductive Systems.
 Name Class Date Chapter 39 Summary Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 39 1 The Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands that release secretions
Name Class Date Chapter 39 Summary Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 39 1 The Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands that release secretions
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology
 Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
The Reproductive System
 C h a p t e r 27 The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
C h a p t e r 27 The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Bi-potent Gonads. Sex Determination
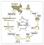 יצירת הגונדות Primordial Germ Cells (PGCs) Somatic cells Genital ridge Bi-potent Gonads Sex Determination Testis and Sperm Ovary and Oocyte Migration of Primordial Germ Cells in the Chick Embryo The
יצירת הגונדות Primordial Germ Cells (PGCs) Somatic cells Genital ridge Bi-potent Gonads Sex Determination Testis and Sperm Ovary and Oocyte Migration of Primordial Germ Cells in the Chick Embryo The
Male Anatomy. testes, genetically determined in mammals - testis releases hormones that then control the development of secondary sex characteristics
 Male Anatomy Male Anatomy Primary Organ testes, genetically determined in mammals - testis releases hormones that then control the development of secondary sex characteristics 1) Secondary Organs internal
Male Anatomy Male Anatomy Primary Organ testes, genetically determined in mammals - testis releases hormones that then control the development of secondary sex characteristics 1) Secondary Organs internal
The Endocrine System PART A
 9 The Endocrine System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Endocrine System
9 The Endocrine System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Endocrine System
Embryology 3. Spermatogenesis:
 Embryology 3 Spermatogenesis: The 2 testis in males are each divided into lobes and lobules by connective tissue septa forming 250 lobule and in each lobule there are 1 to 4 seminefrous tubule ( so almost
Embryology 3 Spermatogenesis: The 2 testis in males are each divided into lobes and lobules by connective tissue septa forming 250 lobule and in each lobule there are 1 to 4 seminefrous tubule ( so almost
The reproductive lifespan
 The reproductive lifespan Reproductive potential Ovarian cycles Pregnancy Lactation Male Female Puberty Menopause Age Menstruation is an external indicator of ovarian events controlled by the hypothalamicpituitary
The reproductive lifespan Reproductive potential Ovarian cycles Pregnancy Lactation Male Female Puberty Menopause Age Menstruation is an external indicator of ovarian events controlled by the hypothalamicpituitary
Reproductive System. Testes. Accessory reproductive organs. gametogenesis hormones. Reproductive tract & Glands
 Reproductive System Testes gametogenesis hormones Accessory reproductive organs Reproductive tract & Glands transport gametes provide nourishment for gametes Hormonal regulation in men Hypothalamus - puberty
Reproductive System Testes gametogenesis hormones Accessory reproductive organs Reproductive tract & Glands transport gametes provide nourishment for gametes Hormonal regulation in men Hypothalamus - puberty
AnS 214 SI Multiple Choice Set 4 Weeks 10/14-10/23
 AnS 214 SI Multiple Choice Set 4 Weeks 10/14-10/23 The following multiple choice questions pertain to material covered in the last two weeks' lecture sets. Answering the following questions will aid your
AnS 214 SI Multiple Choice Set 4 Weeks 10/14-10/23 The following multiple choice questions pertain to material covered in the last two weeks' lecture sets. Answering the following questions will aid your
Ch 11: Endocrine System
 Ch 11: Endocrine System SLOs Describe the chemical nature of hormones and define the terms proand prepro-hormone. Explain mechanism of action of steroid and thyroid hormones Create chart to distinguish
Ch 11: Endocrine System SLOs Describe the chemical nature of hormones and define the terms proand prepro-hormone. Explain mechanism of action of steroid and thyroid hormones Create chart to distinguish
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE
 Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Bios 90/95. Jennifer Swann, PhD
 Sexual Differentiation Fall 2007 Bios 90/95 Jennifer Swann, PhD Dept Biol Sci, Lehigh University Why have sexes? What determines sex? Environment Genetics Hormones What causes these differences? The true
Sexual Differentiation Fall 2007 Bios 90/95 Jennifer Swann, PhD Dept Biol Sci, Lehigh University Why have sexes? What determines sex? Environment Genetics Hormones What causes these differences? The true
Written re-exam Bachelor in Medicine/MedIS. Exam date: Time: 09:00-11:00. Important information:
 Written re-exam 2016 Course title: Program: Semester: Reproductive endocrinology Bachelor in Medicine/MedIS 4 semester Exam date: 04-08-16 Time: 09:00-11:00 Evaluation form 7-point scale Important information:
Written re-exam 2016 Course title: Program: Semester: Reproductive endocrinology Bachelor in Medicine/MedIS 4 semester Exam date: 04-08-16 Time: 09:00-11:00 Evaluation form 7-point scale Important information:
Lecture 3. Reproductive Endocrinology. (Sep 30, 2008)
 Lecture 3 Reproductive Endocrinology (Sep 30, 2008) Major achievements that speed up the development: 1. The anterior pituitary controls the function of the gonads. 2. Gonads produce steroid hormones that
Lecture 3 Reproductive Endocrinology (Sep 30, 2008) Major achievements that speed up the development: 1. The anterior pituitary controls the function of the gonads. 2. Gonads produce steroid hormones that
M.Sc. (Reproductive Biology & Clinical Embryology)
 M.Sc. (Reproductive Biology & Clinical Embryology) ACADEMIC SCHEDULE Theory (Didactic) Lectures + Seminars + Journal Clubs Semester I & II (2 hours / day) Practicals (Hands-on + Demo) Semester I & II (first
M.Sc. (Reproductive Biology & Clinical Embryology) ACADEMIC SCHEDULE Theory (Didactic) Lectures + Seminars + Journal Clubs Semester I & II (2 hours / day) Practicals (Hands-on + Demo) Semester I & II (first
Biology 30. Morinville Community High School. Unit 2: Endocrine System. Name:
 Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
ENDOCRINE AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS MODULE. Academic Year Study Guide
 ENDOCRINE AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS MODULE Academic Year 2004-2005 Study Guide Objectives of The Endocrine and Reproductive Systems At the end of these systems the students should recognize: 1. The histological
ENDOCRINE AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS MODULE Academic Year 2004-2005 Study Guide Objectives of The Endocrine and Reproductive Systems At the end of these systems the students should recognize: 1. The histological
