Title. Issue Date American Fisheries Society.
|
|
|
- Dayna Lynch
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Role of Follicle-Stimulating Hormon Inversion of Sevenband Grouper Epin Kline, Richard J.; Khan, Izhar A.; Citation North American Journal of Aquacultu Issue Date URL Right 2008 American Fisheries Society This document is downloaded
2 North American Journal of Aquaculture 70: , 2008 Ó Copyright by the American Fisheries Society 2008 DOI: /A [Article] Role of Follicle-Stimulating Hormone and Androgens on the Sexual Inversion of Sevenband Grouper Epinephelus septemfasciatus RICHARD J. KLINE* AND IZHAR A. KHAN Marine Science Institute, University of Texas at Austin, Port Aransas, Texas 78373, USA KIYOSHI SOYANO AND MEGUMI TAKUSHIMA Institute for East China Sea Research, Nagasaki University, Nagasaki , Japan Abstract. This study was designed to characterize the amount of androgen implant and the time period necessary to cause sexual inversion in sevenband grouper Epinephelus septemfasciatus and to determine whether administration of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) with or without androgens had any effect on the sexual state of this species. Seventy-two fish were treated with 10 lg of recombinant FSH/kg body weight (BW) or saline control in cocoa butter. Two days later, cocoa butter and a-cellulose pellet implants of control, 0.1 mg of low-androgen mixture (LoAN)/kg BW, or 5 mg of high-androgen mixture (HiAN)/kg BW were injected into the same fish. Fish were sampled after 3 and 5 weeks. Gonadosomatic indices (GSIs) at 3 weeks for FSH, HiAN, and FSHþHiAN treatment groups were significantly lower than the control values. At 5 weeks, no significant difference was observed, although the GSIs for HiAN treatment groups were lowest at both sampling points. The highest GSI values recorded were in the FSH-only treatment group at 5 weeks. All the controls remained in the immature female state throughout the study. High-dose androgen levels caused sexual transition of gonadal tissue at 3 weeks with spermatocytes present in all individuals. At 5 weeks, all individuals in the HiAN treatment group had complete inversion to male gonad, and sperm sinus development occurred in four individuals. However, incomplete sexual inversion was observed in the FSHþHiAN treatment groups with some ovarian tissue persisting even at 5 weeks. Exogenous FSH treatment alone appears to stimulate ovarian growth in the postspawning period. The 3-week period of sexual transition in this study is one of the shortest time periods recorded for grouper sexual inversion. This may be due to androgen treatment in the postspawning period, the proposed period of natural sex change in several grouper species. * Corresponding author: rkline@utmsi.utexas.edu Received March 20, 2007; accepted July 18, 2007 Published online March 27, 2008 The mahata or sevenband grouper Epinephelus septemfasciatus is a popular food fish species in the southwest region of Japan. Aquaculture of this species is of great interest owing to the high market value of wild-caught fish, which peaks in winter. In December 2006, the species peaked at 5,000 yen/kg (;US$42.62/ kg), sold as whole fish (Nagasaki Fish Market, unpublished data). The sevenband grouper is a protogynous hermaphrodite that reaches female sexual maturity at age 4 and sexual inversion to male at age 7 8 (K. Soyano, unpublished). The spawning period for the sevenband grouper in Japan begins in the late spring and continues until early summer, and gonads regress in late summer (Shein et al. 2004). Obtaining male broodstock for captive culture is problematic owing to the advanced age at sexual inversion. Furthermore, additional information regarding the reproductive cycle and hormone action on gonads is needed for better reproductive management of this species in aquaculture. Research on the maturation and spawning of this species is under way in Nagasaki, Japan, to develop techniques for sustainable aquaculture. A variety of regulatory factors, such as sex steroids (Higa et al. 2003; Nakamura et al. 2003), enzyme pathway inhibitors (Bhandari et al. 2004; Kroon et al. 2005), and neurohormones (Watanabe et al. 1995; Kramer and Imbriano 1997), have been implicated in the sex change of hermaphroditic species. Owing to the capacity for sex change in many marine teleost species and the long time needed to change to the terminal sex, several studies have applied exogenous hormones to induce precocious sexual inversion in hermaphroditic fish (Hassin et al. 1997; Lee et al. 2000; Yeh et al. 2003a, 2003b). The most commonly used hormones are androgens, especially more potent synthetic forms, such as 17a-methyltestosterone (MT; Yeh et al. 1989; Glamuzina et al. 1998; Mor et al. 2001). Methods of application vary, from addition to the feed (Kuo et al. 1988) to slow-release implants (Yeh et al. 1989). Results of individual studies in groupers vary in the amount of time necessary to induce complete sexual inversion, ranging from several months in the dusky 266
3 HORMONE EFFECTS IN SEVENBAND GROUPER 267 grouper E. marginatus (Glamuzina et al. 1998) to 6 months in the blue-spotted grouper E. fario (Kuo et al. 1988). Previous studies on the orange-spotted grouper E. coioides and potato grouper E. tukula in Taiwan have shown that high-dose androgen implants containing a mixture of testosterone (T) and synthetic androgens at levels between 1 and 10 mg/kg body weight (BW) were the most effective at inducing sex change over several months of treatment (Yeh et al. 2003a, 2003b). However, dosage and time requirements for hormone-induced sexual inversion by means of this method are variable in different species, and similar information is lacking for the sevenband grouper. The gonadotropins (follicle-stimulating hormone [FSH] and luteinizing hormone [LH]) are important pituitary hormones that control development and maturation of gonads in teleost fishes (Miura et al. 1991; Swanson et al. 1991; Khan and Thomas 1999). Luteinizing hormone has been demonstrated to regulate all stages of gametogenesis in both male and female fish and has been shown to bind both LH and FSH receptors in the gonads of coho salmon Oncorhynchus kisutch and African catfish Clarias gariepinus (Miwa et al. 1994; Vischer et al. 2003). On the other hand, FSH has been shown to perform a more limited role in the initial oogenesis and spermatogenesis in gonochoristic models, such as salmon and catfish (Swanson et al. 1991; Vischer et al. 2003). The roles of these two gonadotropins are similar between the sexes in these two species of fish (Planas and Swanson 1995). However, these data are limited to a few families of fish, and data for other families (e.g., sea basses and groupers [family Serranidae] and porgies [family Sparidae]) suggest that a differential role of gonadotropins between the sexes may exist. In the red seabream Pagrus major and black porgy Acanthopagrus schlegeli, some evidence of differential expression of FSH has been shown between the sexes. In the red seabream, a protandrous hermaphrodite, FSH messenger RNA (mrna) levels in males drastically increase during the spawning season, while FSH mrna levels in females remain low throughout all phases of the reproductive cycle (Gen et al. 2003). In the black porgy, which is a protogynous hermaphrodite, higher abundance of FSH receptor transcripts has been observed in testicular tissue than in ovarian tissue (Du et al. 2005), thereby suggesting a differential role for FSH in sexual inversion of hermaphroditic fishes. On the other hand, in the orange-spotted grouper, MT treatment in the feed caused a significant reduction in FSH mrna transcript levels after 20 d, while sexual inversion was occurring (Zhang et al. 2007). Clearly, more information on the role of FSH in relation to sex change is needed. The present study was designed to (1) characterize the amount of androgen implant and the time period necessary to cause sexual inversion in sevenband grouper and (2) to determine whether administration of FSH with or without androgens had any effect on the sexual state of sevenband grouper. Methods Experimental animals. Seventy-eight 5-year-old female sevenband grouper (BW, kg; total length, cm [mean 6 SE]), produced at the Nagasaki Prefectural Institute of Fisheries (Nagasaki, Japan) and housed in a large floating net pen, (5 m 3 ) were used in this study. Six representative fish were sampled before the experiment to verify gonadal stage and approximate weight for treatment dosage. The remaining 72 fish were housed in two smaller net pens (4 m 3 ) during the experiment. The fish were subjected to ambient photoperiod and temperature in the new Nagasaki Port area and fed a mixture of chopped fish and squid to satiation three times each week. Water temperature was recorded daily at the Nagasaki Institute of Fisheries with a digital thermometer. During all phases of the experiment, fish were evenly distributed and sampled from the two net pens. Hormones and chemicals. Androgens (T, MT, and testosterone propionate [TP]), cocoa butter, and a-cellulose were purchased from Sigma Chemical Co. (St. Louis, Missouri). Recombinant FSH from red seabream raised in a baculovirus silkworm expression system was a gift from Koichiro Gen (National Research Institute of Fisheries, Japan). FSH administration. Initially, all fish were captured, anesthetized with 2-phenoxyethanol (0.05%), and weighed to the nearest 10 g. All fish were injected with a transponder tag for subsequent identification. Two groups of 36 fish each were injected with either saline and cocoa butter (control) or 10 lg of FSH and cocoa butter/kg BW (treatment). Selection of this dose was based on the level of maximum effectiveness for red seabream (K. Gen, National Research Institute of Fisheries, unpublished data). Androgen treatments. After 2 d, an androgen treatment was administered to each fish (Table 1). All fish were recaptured, anesthetized with 2-phenoxyethanol (0.05%), identified via transponder tag, and implanted with an a-cellulose cocoa butter implant containing either 0, 0.1 mg low-androgen mixture (LoAN)/kg BW, or 5 mg high-androgen mixture (HiAN)/kg BW of T, MT, and TP at an equal weight ratio following the pellet design of Yeh et al. (1989). These pellets were implanted into each fish intramus-
4 268 KLINEETAL. TABLE 1. Experimental protocol (treatment and sampling regime) for the administration of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and androgen at 3- and 5-week sampling periods in sexual inversion study conducted in seven band grouper. Treatments are as follows: FSH ¼ 10 mg recombinant red seabream FSH/kg body weight (BW), LoAN (low-androgen mixture) ¼ 0.1 mg androgen/kg BW, HiAN (high-androgen mixture) ¼ 5 mg androgen/kg BW. Treatment group Number of fish 3 weeks 5 weeks Control 6 6 FSH 6 6 LoAN 6 6 HiAN 6 6 FSH þ LoAN 6 6 FSH þ HiAN 6 6 Total cularly, behind the dorsal fin, and were prepared from the mixture of androgens with cocoa butter and a- cellulose 3:6 weight ratio following the methods of Yeh et al. (1989). The control and treatment groups were evenly distributed between two net pens. Sampling procedures. Fish were sampled equally from the two net pens at 3 weeks (August 2) and 5 weeks (August 15) in the early morning, as shown in Table 1. Between treatment and the first sampling period, one fish died in the LoAN treatment group. All fish were anesthetized with 2-phenoxyethanol (0.05%) and identified via transponder tag. All fish, gonad, and liver weights were recorded to the nearest gram. Hepatosomatic index (HSI) and gonadosomatic index (GSI) were calculated with the following formula: Organ weight 3 100: Body weight organ weight For histological examination, gonadal tissue was sampled at several locations along the gonad and fixed in Bouin s solution for 24 h. The samples were serially dehydrated and embedded in paraffin, and 3 5-lm transverse sections were made of each fixed tissue and stained with Mayer s hematoxylin and eosin. Each slide was examined with a light microscope and scored qualitatively for gonadal sex and stage similar to those in Bhandari et al. (2003) and Yeh et al. (2003a). Representative sections were digitized with a Cool- SNAP-Pro color camera (Media Cybernetics, Silver Spring, Maryland) and QCapture Pro 5.0 software (QImaging, Burnaby, British Columbia). Statistical analyses. Data for HSI and GSI for did not meet the assumptions of normality for parametric tests, even when transformations were applied (Zar 1999). Therefore, differences in both GSI and HSI treatment groups were compared with Kruskal Wallis one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by a post hoc Mann Whitney U-test (Siegel and Castellan 1988). Differences between 3- and 5-week control groups were compared with the Mann Whitney U-test. Significance was determined at P, All data are expressed as mean 6 SE. Results Between the two sampling periods, the water temperature surrounding the floating net pens increased. Between the start of the study and week 3, the temperature remained relatively constant at 288C. Between weeks 3 and 5 of the sampling periods, the temperature increased to more than 308C. Spawning temperature of this species is temperature dependent and ranges from 208C to258c (Shein et al. 2004). Hepatosomatic Index There were no significant differences in HSI between the control and treatment groups at each sampling period. However, HSIs were significantly different in the controls between the two sampling periods. The mean HSI was % and % for the 3- and 5-week sampling periods, respectively. Gonadosomatic Index There was no significant difference in the GSIs of fish between the initial control and 3-week control groups (data not included). The GSIs for the five treatments and controls during the 3- and 5-week sampling periods are displayed in Figure 1. At 3 weeks, the GSIs for the FSH, HiAN, and FSHþHiAN groups were significantly lower than those of the control group. No significant difference was observed between treatment groups; however, the lowest GSI was observed in the HiAN treatment groups (Figure 1, left panel). At 5 weeks, the GSIs of control fish were significantly lower than for the 3-week sampling period. None of the 5-week treatment groups were significantly different from the corresponding control group. However, the lowest GSI was observed in the two HiAN treatment groups (Figure 1, right panel). The GSIs of the FSH treatment group were variable for both sampling periods, although the highest overall GSI values (0.72, 0.33, and 0.27%) were observed in three fish at the 5-week sampling period (Figure 1, left panel). Histological Examination There was no difference in the gonadal histology of the initial control and 3-week control groups (data not included). The 3- and 5-week control groups showed
5 HORMONE EFFECTS IN SEVENBAND GROUPER 269 FIGURE 1. Gonadosomatic indices (GSIs) of sevenband grouper at 3- and 5-week sampling periods. The asterisks indicate significantly lower than control, and the plus signs indicate significantly lower than 3-week control. Treatments are as follows: FSH ¼ 10 lg recombinant red seabream FSH/kg body weight (BW), LoAN ¼ 0.1 mg androgen/kg BW, HiAN ¼ 5 mg androgen/ kg BW. Each bar represents the mean 6 SE of six fish, except for the 3-week LoAN group where n ¼ 5. Abbreviations: CONT ¼ control, FSH ¼ follicle-stimulating hormone, LoAN ¼ low-androgen mixture, HiAN ¼ high-androgen mixture. no evidence of change from the F1 regressing female state. Ovaries consisted of gonia and perinucleolar stage oocytes (Figure 2A, G). The 5-week controls had much more degraded ovaries showing considerable atresia and phagocytosis along with more gonial cell proliferation (Figure 2G). The tissue sections from the FSH treatment groups at 3 and 5 weeks contained all ovarian tissue (Figure 2B, H) however this treatment group showed considerable changes not seen in the controls. At 3 weeks, gonial cell abundance had drastically increased in all fish and had proliferated throughout the ovarian lamellae (Figure 2B). Connective tissue and stromal tissue had also proliferated throughout the ovary. At 5 weeks, increased stromal and gonial cell proliferation was still evident in some samples. In three of six fish (Figure 2H), oocytes were much larger and more developed, some advancing to the early cortical alveoli stage. Little atresia was present in the surrounding oocytes. In comparison to all other experimental groups, these three fish had much larger oocytes and well- formed ovarian lamellae. In the LoAN treatment groups, the majority of the gonad tissue was female with a combination of perinucleolar and atretic oocytes along with gonial cells. At both 3 and 5 weeks, the LoAN treatment groups exhibited numerous small perinucleolar oocytes not seen in the controls (Figure 2C, I, respectively). Occasional spermatogenic tissue was also present in the form of spermatocytes (Figure 2C). Gonad tissue from the FSHþLoAN treatment displayed some similarities with the FSH-only treatment. At 3 weeks, stromal tissue and vascularization were evident (Figure 2D), and at 5 weeks (Figure 2J), two fish had oocytes that were larger and appeared similar to those seen in the FSH-only treatment. However, the abundance of these cells was much reduced in the FSHþLoAN treatment when compared to the FSH-only treatments. Occasional spermatogenic tissue was seen in the form of spermatocytes. The gonadal structure in the 3- and 5-week FSHþLoAN treatment groups was distinctly ovarian, displaying a mixture of atretic and intact perinucleolar oocytes. In comparison to the controls and LoAN treatment groups, there was an increase in gonial cell abundance. The gonadal tissue of fish treated with the HiAN dose had substantially changed at both sampling periods. In all fish from both sampling periods, the majority of the tissue was spermatogenic. At 3 weeks, the majority of the tissue was early stage (M1) testicular tissue demonstrating an abundance of spermatocytes and spermatids (Figure 2E). Any remaining oocytes were atretic, and yellow-brown bodies were present. At 5 weeks, very few atretic oocytes were present, a complete reconfiguration of the gonad occurring. The majority of the cells observed were at the late stages of spermatogenesis and had a preponderance of spermatids and spermatozoa (Figure 2L). In four of six individuals, distinctive sperm sinuses had formed indicating complete sexual transition to male (M2). Ovarian lamellae structure was absent from these samples. Similar effects of reconfiguring the ovary to testis were observed in the FSHþHiAN and HiAN treatments. However, in the FSHþHiAN treatment, more ovarian tissue persisted along the periphery of the lamellae structure at 3 weeks (Figure 2F), and the ovarian lamellae structure persisted at 5 weeks (Figure
6 270 KLINEETAL. FIGURE 2. Representative sections of gonadal tissue from sevenband grouper at 3- and 5-week sampling periods showing (A) control at 3 weeks, (B) follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) treatment group at 3 weeks, (C) low-androgen (LoAN) treatment group: 0 at 3 weeks, (D) FSHþLoAN treatment group at 3 weeks, (E) high-androgen (HiAN) treatment group at 3 weeks, (F) FSHþHiAN treatment group at 3 weeks, (G) control at 5 weeks, (H) FSH treatment group at 5 weeks, (I) LoAN treatment group at 5 weeks, (J) FSHþLoAN treatment group at 5 weeks, (K) HiAN treatment group at 5 weeks, (L) FSHþHiAN treatment group at 5 weeks. Treatments are as follows: FSH ¼ 10 lg recombinant red seabream FSH/kg body weight (BW), LoAN ¼ 0.1 mg androgen/kg BW, HiAN ¼ 5 mg androgen/kg BW. Abbreviations: PO ¼ perinucleolar stage oocyte, St ¼ stromal cells, Go ¼ gonial cell, SPo ¼ small new-growth perinucleolar oocyte, Sc ¼ spermatocyte, Ao ¼ atretic oocyte, Sd ¼ spermatid, Ph ¼ phagocytosis of oocyte, Ca ¼ early cortical alveoli, Ss ¼ sperm sinus with spermatozoa, OL ¼ ovarian lamellae. Bar indicates 100 lm. 2L) where it had not in the HiAN treatment alone. Furthermore, the stage of development of the spermatogenic tissue was not as advanced as in FSHþHiAN treatment alone. At 3 weeks, more gonial cells and spermatocytes were present along with many more oocytes around the periphery in comparison to HiAN treatment. At 5 weeks, more gonial cells and fewer spermatozoa were present in FSHþHiAN treatment compared to HiAN treatment alone. However, in two of six fish in the 5-week FSHþHiAN treatment group, sperm sinus had developed. Discussion This study demonstrates sexual inversion in sevenband grouper to the male M1 stage within 3 weeks of a high-androgen treatment with or without FSH pretreatment. By 5 weeks, most cells reach an advanced stage of spermatogenesis with a complete structural reorga-
7 HORMONE EFFECTS IN SEVENBAND GROUPER 271 nization of the gonad. Similar results have been observed in other species of grouper using this technique (Yeh et al. 1989, 2003a, 2003b). These studies have examined only a small tissue sample collected with a cannula, which cannot provide detailed information regarding changes occurring throughout the gonad. The present study describes more detailed histological examination of the gonadal tissue after FSH and androgen treatments. The a-cellulose androgen mixture is a very potent technique to cause sexual inversion in hermaphroditic species, and fish have been successfully spawned by means of this technique as early as 90 d (Yeh et al. 2003a). In this study, histological observation of gonadal tissue revealed that treatment groups could be easily distinguished from the control groups by the stage of gonadal growth as early as 3 weeks after the treatments. The 3-week time period for complete sexual transition to the M1 stage for fish receiving high-androgen treatment is the one of the shortest time periods recorded in published studies for induced sexual inversion in groupers (Hassin et al. 1997; Glamuzina et al. 1998; Yeh et al. 2003b). This may be due to the timing of androgen treatment relative to the natural reproductive cycle in this species, which in the present study was the postspawning period. This is also the period for natural sexual inversion observed in several grouper species (Sadovy and Shapiro 1987; Bhandari et al. 2003) and, therefore, the fish are probably more receptive to androgen treatment at this stage. The low dose of androgen (0.1 mg/kg) that caused sexual transition in two of seven orange-spotted grouper (Yeh et al. 2003b) was ineffective in causing sexual transition in sevenband grouper. However, the high-dose androgens caused sexual inversion in both species. The only apparent effect of the 0.1 mg/kg androgen implant in sevenband grouper was an increase in the abundance of small perinucleolar stage oocytes, which is consistent with the effects of lower androgen doses (0.001 and 0.01 mg/kg) reported in orange-spotted grouper. It is unclear at this stage whether this effect of low-dose androgens is due to possible conversion of testosterone to estradiol or a direct action of androgens themselves. Interestingly, FSH treatment alone at 3 weeks appears to stimulate reorganization of the gonad and growth of structural components such as stromal and vascular cells in sevenband grouper. At 5 weeks, the higher GSI values and increased oocyte diameters observed in several fish could be the result of additional cell growth (stromal tissue and gonia). This finding appears to be consistent with the data for orange-spotted grouper and red seabream, where MT treatment in the former species and 11-ketotestosterone (11-KT) treatment in the latter species down regulate FSHb mrna expression. It is possible that natural sexual inversion to the male state in sevenband grouper may require a down regulation of FSH by 11-KT production. In this study, exogenous FSH treatment appeared to slow the process of sexual inversion to the male state that was observed with high-androgen treatment alone. The persistence of lamellae structures and oocytes could indicate a prevention of apoptosis in the oocytes in the periphery of the ovarian lamellae. The FSH treatment before androgen implant could have initially driven growth of the gonad in the feminine direction that was then reversed by the subsequent androgen treatment. In other words, FSH may direct the gonad to grow initially, and the fate of the cells (gonial and stromal) is determined by the surrounding steroid environment. To investigate this, future studies could incorporate treatment with androgens followed by FSH to determine whether FSH plays a differential role in gonadal development between the sexes. The increase in water temperature between sampling periods caused increased degradation of the gonad in the control fish. However, the FSH-treated fish and a few of the fish receiving FSH low-androgen treatment had much larger perinucleolar oocytes. Furthermore, both high-androgen treatments appeared more advanced at 5 weeks. This apparent temperature independence is intriguing and should be further investigated. In conclusion, androgen implantation is a powerful tool for use in captive culture of sevenband grouper. This technique appears to work while the gonad is regressing in the postspawning season. Follicle-stimulating hormone appears to stimulate new cell growth in the postspawning period and to direct growth in the ovarian direction, inhibiting to some degree the effects of androgen alone. Acknowledgments We thank the members of the Soyano laboratory at the Center for East China Sea Research, Nagasaki University, for help with the experiments and processing of samples. The recombinant seabream FSH was provided by Koichiro Gen. This research was funded by the East Asia and Pacific Summer Studies Program and the Sid Richardson Memorial Fund. This is contribution 1194 of the University of Texas at Austin Marine Science Institute. References Bhandari, R. K., M. Higa, S. Nakamura, and M. Nakamura Aromatase inhibitor induces complete sex change
8 272 KLINEETAL. in the protogynous honeycomb grouper (Epinephelus merra). Molecular Reproduction and Development 67: Bhandari, R. K., H. Komuro, S. Nakamura, M. Higa, and M. Nakamura Gonadal restructuring and correlative steroid hormone profiles during natural sex change in protogynous honeycomb grouper (Epinephelus merra). Zoological Science 20: Du, J. L., Y. H. Lee, W. S. Yueh, and C. F. Chang Seasonal profiles of brain and pituitary gonadotropinreleasing hormone and plasma luteinizing hormone in relation to sex change of protandrous black porgy, Acanthopagrus schlegeli. Biology of Reproduction 72: Gen, K., S. Yamaguchi, K. Okuzawa, N. Kumakura, H. Tanaka, and H. Kagawa Physiological roles of FSH and LH in red seabream, Pagrus major. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry 28: Glamuzina, B., N. Glavic, B. Skaramuca, and V. Kozul Induced sex reversal of dusky grouper, Epinephelus marginatus (Lowe). Aquaculture Research 29: Hassin, S., D. demonbrison, Y. Hanin, A. Elizur, Y. Zohar, and D. M. Popper Domestication of the white grouper, Epinephelus aeneus. 1. Growth and reproduction. Aquaculture 156: Higa, M., K. Ogasawara, A. Sakaguchi, Y. Nagahama, and M. Nakamura Role of steroid hormones in sex change of protogynous wrasse. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry 28: Khan, I. A., and P. Thomas Ovarian cycle, teleost fish. Pages in E. Knobil and J. D. Neill, editors. Encyclopedia of reproduction, volume 3. Academic Press, San Diego, California. Kramer, C. R., and M. A. Imbriano Neuropeptide Y (NPY) induces gonad reversal in the protogynous bluehead wrasse, Thalassoma bifasciatum (Teleostei: Labridae). Journal of Experimental Zoology 279: Kroon, F. J., P. L. Munday, D. A. Westcott, J. P. A. Hobbs, and N. R. Liley Aromatase pathway mediates sex change in each direction. Proceedings of the Royal Society Biological Sciences Series B 272: Kuo, C. M., Y. Y. Ting, and S. L. Yeh Induced sex reversal and spawning of blue-spotted grouper, Epinephelus fario. Aquaculture 74: Lee, Y. H., F. Y. Lee, W. S. Yueh, P. Tacon, J. L. Du, C. N. Chang, S. R. Jeng, H. Tanaka, and C. F. Chang Profiles of gonadal development, sex steroids, aromatase activity, and gonadotropin II in the controlled sex change of protandrous black porgy, Acanthopagrus schlegeli Bleeker. General and Comparative Endocrinology 119: Miura, T., K. Yamauchi, H. Takahashi, and Y. Nagahama Hormonal induction of all stages of spermatogenesis in vitro in the male Japanese eel (Anguilla japonica). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA 88: Miwa, S., L. G. Yan, and P. Swanson Localization of two gonadotropin receptors in the salmon gonad by in vitro ligand autoradiography. Biology of Reproduction 50: Mor, G., M. Eliza, J. Song, B. Wiita, S. Chen, and F. Naftolin a-Methyl testosterone is a competitive inhibitor of aromatase activity in Jar choriocarcinoma cells and macrophage-like THP-1 cells in culture. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 79: Nakamura, M., R. K. Bhandari, and M. Higa The role estrogens play in sex differentiation and sex changes of fish. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry 28: Planas, J. V., and P. Swanson Maturation-associated changes in the response of the salmon testis to the steroidogenic actions of gonadotropins (GTH-I and GTH-II) in vitro. Biology of Reproduction 52: Sadovy, Y., and D. Y. Shapiro Criteria for the diagnosis of hermaphroditism in fishes. Copeia 1987: Shein, N. L., H. Chuda, T. Arakawa, K. Mizuno, and K. Soyano Ovarian development and final oocyte maturation in cultured sevenband grouper Epinephelus septemfasciatus. Fisheries Science 70: Siegel, S., and N. J. Castellan Nonparametric statistics for the behavioral sciences, 2nd edition. McGraw-Hill, New York. Swanson, P., K. Suzuki, H. Kawauchi, and W. W. Dickhoff Isolation and characterization of two coho salmon gonadotropins, GTH-I and GTH-II. Biology of Reproduction 44: Vischer, H. F., J. C. M. Granneman, M. H. K. Linskens, R. W. Schulz, and J. Bogerd Both recombinant African catfish LH and FSH are able to activate the African catfish FSH receptor. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology 31: Watanabe, W. O., S. C. Ellis, E. P. Ellis, W. D. Head, C. D. Kelley, A. Moriwake, C. S. Lee, and P. K. Bienfang Progress in controlled breeding of Nassau grouper (Epinephelus striatus) broodstock by hormone induction. Aquaculture 138: Yeh, S.-L., C.-M. Kuo, Y.-Y. Ting, and C.-F. Chang. 2003a. Androgens stimulate sex change in protogynous grouper, Epinephelus coioides: spawning performance in sexchanged males. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology 135C: Yeh, S.-L., C.-M. Kuo, Y.-Y. Ting, and C.-F. Chang. 2003b. The effects of exogenous androgens on ovarian development and sex change in female orange-spotted protogynous grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Aquaculture 218: Yeh, S.-L., Y. Y. Ting, and C. M. Kuo Technique of pellet implantation and preparation for induced sex reversal of the groupers Epinephelus salmonoides, Epinephelus fario. Bulletin of the Taiwan Fisheries Research Institute 47: Zar, J. H Biostatistical analysis, 4th edition. Prentice- Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey. Zhang, W. M., Y. Zhang, L. H. Zhang, H. H. Zhao, X. Li, H. Huang, and H. R. Lin The mrna expression of P450 aromatase, gonadotropin b-subunits and FTZ-F1 in the orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) during 17a-methyltestosterone-induced precocious sex change. Molecular Reproduction and Development 74:
Sex Inversion of Sexually Immature Honeycomb Grouper (Epinephelus merra) by Aromatase Inhibitor
 Sex Inversion of Sexually Immature Honeycomb Grouper (Epinephelus merra) by Aromatase Inhibitor Authors: Ramji Kumar Bhandari, Hiroki Komuro, Mikihiko Higa, and Masaru Nakamura Source: Zoological Science,
Sex Inversion of Sexually Immature Honeycomb Grouper (Epinephelus merra) by Aromatase Inhibitor Authors: Ramji Kumar Bhandari, Hiroki Komuro, Mikihiko Higa, and Masaru Nakamura Source: Zoological Science,
The first success of glass eel production in the world: basic biology on fish reproduction advances new applied technology in aquaculture
 Fish Physiol Biochem (2005) 31:193 199 DOI 10.1007/s10695-006-0024-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE The first success of glass eel production in the world: basic biology on fish reproduction advances new applied technology
Fish Physiol Biochem (2005) 31:193 199 DOI 10.1007/s10695-006-0024-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE The first success of glass eel production in the world: basic biology on fish reproduction advances new applied technology
Protogynous Hermaphroditism in the Sand Diver Trichonotus filamentosus
 Œ Ÿ ª ŽYŽŽŒ± ê j. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 57(1), 35-40 (1991) Protogynous Hermaphroditism in the Sand Diver Trichonotus filamentosus Janny Dirk Kusen,*1 Kiyoshi Nakagawa,2 Yutaka Yogo,*3 and Akinobu Nakazono*1
Œ Ÿ ª ŽYŽŽŒ± ê j. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 57(1), 35-40 (1991) Protogynous Hermaphroditism in the Sand Diver Trichonotus filamentosus Janny Dirk Kusen,*1 Kiyoshi Nakagawa,2 Yutaka Yogo,*3 and Akinobu Nakazono*1
GENERAL SUMMARY. Observations
 GENERAL SUMMARY Observations The seasonal variation in the gonadosomatic indices (GSI) of male and female confirmed that the spawning season of Lepidocephalus thermalis was from October to November, coinciding
GENERAL SUMMARY Observations The seasonal variation in the gonadosomatic indices (GSI) of male and female confirmed that the spawning season of Lepidocephalus thermalis was from October to November, coinciding
The effect of aromatase inhibitor, fadrozole, on sgnrha-stimulated LH secretion in goldfish (Carassius auratus) and common carp (Cyprinus carpio)
 Vol. 6, Suppl. 1 195 The effect of aromatase inhibitor, fadrozole, on sgnrha-stimulated LH secretion in goldfish (Carassius auratus) and common carp (Cyprinus carpio) Tomasz Mikolajczyk 1, Jaroslaw Chyb,
Vol. 6, Suppl. 1 195 The effect of aromatase inhibitor, fadrozole, on sgnrha-stimulated LH secretion in goldfish (Carassius auratus) and common carp (Cyprinus carpio) Tomasz Mikolajczyk 1, Jaroslaw Chyb,
WP 3 : REPRODUCTION & GENETICS Matura7on and spawning induc7on of Grey Mullet (Mugil cephalus)
 New species for EU aquaculture WP 3 : REPRODUCTION & GENETICS Matura7on and spawning induc7on of Grey Mullet (Mugil cephalus) Hanna Rosenfeld, Vered Zlatnikov, Chen Bracha, Eldad Toledano, Iris Meiri-Ashkenazi
New species for EU aquaculture WP 3 : REPRODUCTION & GENETICS Matura7on and spawning induc7on of Grey Mullet (Mugil cephalus) Hanna Rosenfeld, Vered Zlatnikov, Chen Bracha, Eldad Toledano, Iris Meiri-Ashkenazi
Corticosteroids affect the testicular androgen production in male common carp, Cyprinus carpio L.
 Chapter 5 Corticosteroids affect the testicular androgen production in male common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. Co-authors: Jan G.D. Lambert, Henk J.Th. Goos submitted inhibits the testicular androgen production
Chapter 5 Corticosteroids affect the testicular androgen production in male common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. Co-authors: Jan G.D. Lambert, Henk J.Th. Goos submitted inhibits the testicular androgen production
Induction of Sex Inversion in Juvenile Grouper, Epinephelus suillus, (Valenciennes) by Injections of 17ƒ -Methyltestosterone
 Japan. J. Ichthyol. 40 (4): 413-420, 1994 Induction Sex Inversion in Juvenile Grouper, Epinephelus suillus, (Valenciennes) by Injections 17ƒ -Methyltestosterone Josefa D. Tan-Fermin, Luis Maria B. Garcia
Japan. J. Ichthyol. 40 (4): 413-420, 1994 Induction Sex Inversion in Juvenile Grouper, Epinephelus suillus, (Valenciennes) by Injections 17ƒ -Methyltestosterone Josefa D. Tan-Fermin, Luis Maria B. Garcia
REPRODUCTIVE ASPECTS OF CULTURED HUMPBACK GROUPER (Cromileptes altivelis) FOR SUPPORTING SEED PRODUCTION
 Reproductive aspects of cultured humpback grouper... (Sari Budi Moria Sembiring) REPRODUCTIVE ASPECTS OF CULTURED HUMPBACK GROUPER (Cromileptes altivelis) FOR SUPPORTING SEED PRODUCTION Sari Budi Moria
Reproductive aspects of cultured humpback grouper... (Sari Budi Moria Sembiring) REPRODUCTIVE ASPECTS OF CULTURED HUMPBACK GROUPER (Cromileptes altivelis) FOR SUPPORTING SEED PRODUCTION Sari Budi Moria
114. Sex Reversal in the Japanese W rasse, By Yo K. OKADA, M.J.A. (Comm. Oct. 12, 1962)
 e 508 [Vol. 38, 114. Sex Reversal in the Japanese W rasse, Halichoeres poecilopterus By Yo K. OKADA, M.J.A. (Comm. Oct. 12, 1962) The Labridae are a group of fish mostly assuming beautiful colouration
e 508 [Vol. 38, 114. Sex Reversal in the Japanese W rasse, Halichoeres poecilopterus By Yo K. OKADA, M.J.A. (Comm. Oct. 12, 1962) The Labridae are a group of fish mostly assuming beautiful colouration
Research Article. Ribera de Cabanes, Castellón, España Corresponding author: Vicente Gracia-López
 Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res., 46(1): 83-90, 2018 DOI: 10.3856/vol46-issue1-fulltext-10 Sex steroids and gonad development of leopard grouper 83 Research Article Reproductive cycle of leopard grouper Mycteroperca
Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res., 46(1): 83-90, 2018 DOI: 10.3856/vol46-issue1-fulltext-10 Sex steroids and gonad development of leopard grouper 83 Research Article Reproductive cycle of leopard grouper Mycteroperca
larvi 2013 Pubertal development of Atlantic Bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus) in captivity Berkovich Nadia 6th fish & shellfish larviculture symposium
 larvi 213 6th fish & shellfish larviculture symposium Pubertal development of Atlantic Bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus) in captivity Berkovich Nadia ghent university, belgium, 2- september 213 The key neuroendocrine
larvi 213 6th fish & shellfish larviculture symposium Pubertal development of Atlantic Bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus) in captivity Berkovich Nadia ghent university, belgium, 2- september 213 The key neuroendocrine
Kazunori Fujii. National Research Institute of Fisheries and Environment of Inland Sea, Fisheries Research Agency
 The Effects of Endocrine Disruptors on Fish Maturation and Reproduction - A Focus on Projects Underway at the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries - Kazunori Fujii National Research Institute
The Effects of Endocrine Disruptors on Fish Maturation and Reproduction - A Focus on Projects Underway at the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries - Kazunori Fujii National Research Institute
Spermatogenesis and sperm characteristics in captive greater amberjack
 Spermatogenesis and sperm characteristics in captive greater amberjack WP3_Reproduction and Genetics_ Greater amberjack Third Annual Coordination Meeting 17-19 January 2017 Barcelona, Spain WP3_Reproduction
Spermatogenesis and sperm characteristics in captive greater amberjack WP3_Reproduction and Genetics_ Greater amberjack Third Annual Coordination Meeting 17-19 January 2017 Barcelona, Spain WP3_Reproduction
Title. CitationGeneral and Comparative Endocrinology, 165(2): Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information. migration in chum salmon
 Title Changes in the plasma levels of insulin-like growth migration in chum salmon Onuma, Takeshi A.; Makino, Keita; Katsumata, Hiroshi Author(s) Fukuwaka, Masa-aki; Azumaya, Tomonori; Swanson, Penn CitationGeneral
Title Changes in the plasma levels of insulin-like growth migration in chum salmon Onuma, Takeshi A.; Makino, Keita; Katsumata, Hiroshi Author(s) Fukuwaka, Masa-aki; Azumaya, Tomonori; Swanson, Penn CitationGeneral
PERIODICITY OF SEX CHANGE AND REPRODUCTION IN THE RED HIND, EPINEPHELUS GUTTA TUS, A PROTOGYNOUS GROUPER
 BULLETIN OF MARINE SCIENCE. 53(3): 1151-1162. 1993 CORAL REEF PAPER PERIODICITY OF SEX CHANGE AND REPRODUCTION IN THE RED HIND, EPINEPHELUS GUTTA TUS, A PROTOGYNOUS GROUPER Douglas Y. Shapiro, Yvonne Sadovy
BULLETIN OF MARINE SCIENCE. 53(3): 1151-1162. 1993 CORAL REEF PAPER PERIODICITY OF SEX CHANGE AND REPRODUCTION IN THE RED HIND, EPINEPHELUS GUTTA TUS, A PROTOGYNOUS GROUPER Douglas Y. Shapiro, Yvonne Sadovy
Neurons and Hormones 3
 Neurons and Hormones 3 Neural Command Centers Behavioral Schedules Daily rhythms: internal and external factors Long-term rhythms: internal and external factors Priorities & the Social Environment Hormones
Neurons and Hormones 3 Neural Command Centers Behavioral Schedules Daily rhythms: internal and external factors Long-term rhythms: internal and external factors Priorities & the Social Environment Hormones
Effect of Gonadotrophins and Gonadotrophin Releasing Hormone (GnRH) on folliculogenesis in the domestic pigeon, Columba livia.
 Asian J. Exp. Sci., Vol. 22, No. 3, 2008; 439-443 Effect of Gonadotrophins and Gonadotrophin Releasing Hormone (GnRH) on folliculogenesis in the domestic pigeon, Columba livia. V. D. Hegde Department of
Asian J. Exp. Sci., Vol. 22, No. 3, 2008; 439-443 Effect of Gonadotrophins and Gonadotrophin Releasing Hormone (GnRH) on folliculogenesis in the domestic pigeon, Columba livia. V. D. Hegde Department of
Sex Determination and Gonadal Sex Differentiation in Fish
 Sex Determination and Gonadal Sex Differentiation in Fish Yoshitaka Nagahama Okazaki National Research Institutes, Japan This first slide shows the processes of gonadal sex differentiation and gametogenesis
Sex Determination and Gonadal Sex Differentiation in Fish Yoshitaka Nagahama Okazaki National Research Institutes, Japan This first slide shows the processes of gonadal sex differentiation and gametogenesis
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones
 10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
INTRODUCTION. Hyun Kyu Kim 1, Jung-Hyun Kim 1, Hea Ja Baek 2 and Joon Yeong Kwon 1
 Dev. Reprod. Vol. 20, No. 4, 367~377, December, 2016 https://doi.org/10.12717/dr.2016.20.4.367 ISSN 2465-9525 (Print) ISSN 2465-9541 (Online) Gene Expression of Aromatases, Steroid
Dev. Reprod. Vol. 20, No. 4, 367~377, December, 2016 https://doi.org/10.12717/dr.2016.20.4.367 ISSN 2465-9525 (Print) ISSN 2465-9541 (Online) Gene Expression of Aromatases, Steroid
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20977 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Burgerhout, Erik Title: Tools and triggers for eel reproduction Issue Date: 2013-06-18
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20977 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Burgerhout, Erik Title: Tools and triggers for eel reproduction Issue Date: 2013-06-18
Steroidogenic and maturation-inducing potency of native gonadotropic hormones in female chub mackerel, Scomber japonicus
 Ohga et al. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology 2012, 10:71 RESEARCH Open Access Steroidogenic and maturation-inducing potency of native gonadotropic hormones in female chub mackerel, Scomber japonicus
Ohga et al. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology 2012, 10:71 RESEARCH Open Access Steroidogenic and maturation-inducing potency of native gonadotropic hormones in female chub mackerel, Scomber japonicus
The Morphology of Gonadal Tissue and Male Germ Cells in the Protandrous Black Porgy, Acanthopagrus schlegeli
 Zoological Studies 41(2): 216-227 (2002) The Morphology of Gonadal Tissue and Male Germ Cells in the Protandrous Black Porgy, Acanthopagrus schlegeli Jing-Duan Huang, Mong-Fong Lee and Ching-Fong Chang*
Zoological Studies 41(2): 216-227 (2002) The Morphology of Gonadal Tissue and Male Germ Cells in the Protandrous Black Porgy, Acanthopagrus schlegeli Jing-Duan Huang, Mong-Fong Lee and Ching-Fong Chang*
Problems with early sexual maturation in on-growth farms
 Utrecht University PUBERTIMING Photoperiod control of puberty in farmed fish: Development of new techniques and research into underlying physiological mechanisms G.L. Taranger 1, Eva Andersson 1, S.O.
Utrecht University PUBERTIMING Photoperiod control of puberty in farmed fish: Development of new techniques and research into underlying physiological mechanisms G.L. Taranger 1, Eva Andersson 1, S.O.
Germ Cell Transplantation in Fish
 Larvi 2009 Germ Cell Transplantation in Fish Goro Yoshizaki (Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology, SORST/JST) Tuna Mackerel Body weight; 300 kg 300 g Body length; 3 m 30 cm Scombridae family
Larvi 2009 Germ Cell Transplantation in Fish Goro Yoshizaki (Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology, SORST/JST) Tuna Mackerel Body weight; 300 kg 300 g Body length; 3 m 30 cm Scombridae family
Title. CitationAquaculture Europe, 36(2): Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information.
 Title Controlled reproduction in the Japanese eel (Anguill Author(s)Ijiri, Shigeho; Tsukamoto, Katsumi; Chow, Seinen; Ku CitationAquaculture Europe, 36(2): 13-17 Issue Date 2011-06 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/47268
Title Controlled reproduction in the Japanese eel (Anguill Author(s)Ijiri, Shigeho; Tsukamoto, Katsumi; Chow, Seinen; Ku CitationAquaculture Europe, 36(2): 13-17 Issue Date 2011-06 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/47268
BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 54, (1996) Francisco Prat, 2 John P. Sumpter, and Charles R. Tyler
 BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 54, 1375-1382 (1996) Validation of Radioimmunoassays for Two Salmon Gonadotropins (GTH I and GTH II) and Their Plasma Concentrations Throughout the Reproductive Cycle in Male and
BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 54, 1375-1382 (1996) Validation of Radioimmunoassays for Two Salmon Gonadotropins (GTH I and GTH II) and Their Plasma Concentrations Throughout the Reproductive Cycle in Male and
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Effects of Endocrine Disruptors/Modulators on Fishes
 Effects of Endocrine Disruptors/Modulators on Fishes Vicki S. Blazer and Luke Iwanowicz National Fish Health Research Laboratory Leetown Science Center Kearneysville, WV Fish and Endocrine Disruptors/Modulators
Effects of Endocrine Disruptors/Modulators on Fishes Vicki S. Blazer and Luke Iwanowicz National Fish Health Research Laboratory Leetown Science Center Kearneysville, WV Fish and Endocrine Disruptors/Modulators
Pituitary-gonadal Relationship in the Catfish Clarias batrachus (L): A Study Correlating Gonadotrophin-II and Sex Steroid Dynamics
 Pituitary-gonadal Relationship in the Catfish Clarias batrachus (L): A Study Correlating Gonadotrophin-II and Sex Steroid Dynamics Author(s): K. P. Joy, M. S. Singh, B. Senthilkumaran, and H. J Th Goos
Pituitary-gonadal Relationship in the Catfish Clarias batrachus (L): A Study Correlating Gonadotrophin-II and Sex Steroid Dynamics Author(s): K. P. Joy, M. S. Singh, B. Senthilkumaran, and H. J Th Goos
b Station Expérimentale D'Aquaculture, IFREMER, Chemin de Maguelone, Palavas, France
 Please note that this is an author-produced PDF of an article accepted for publication following peer review. The definitive publisher-authenticated version is available on the publisher Web site Aquaculture
Please note that this is an author-produced PDF of an article accepted for publication following peer review. The definitive publisher-authenticated version is available on the publisher Web site Aquaculture
Hormonal treatments to induce spawning
 Hormonal treatments to induce spawning Daniel Żarski Department of Gamete and Embryo Biology Institute of Animal Reproduction and Food Research Polish Academy of Sciences, Olsztyn, POLAND Pikeperch, Sander
Hormonal treatments to induce spawning Daniel Żarski Department of Gamete and Embryo Biology Institute of Animal Reproduction and Food Research Polish Academy of Sciences, Olsztyn, POLAND Pikeperch, Sander
REPRODUCTION & GENETICS. Hormones
 REPRODUCTION & GENETICS Hormones http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=np0wfu_mgzo Objectives 2 Define what hormones are; Compare and contrast the male and female hormones; Explain what each hormone in the mail
REPRODUCTION & GENETICS Hormones http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=np0wfu_mgzo Objectives 2 Define what hormones are; Compare and contrast the male and female hormones; Explain what each hormone in the mail
Masculinization of Flowerhorn by Immersion in Androgens
 Research Article by Immersion in Androgens Somrudee Silarudee * and Pawapol Kongchum Faculty of Animal Sciences and Agricultural Technology, Silpakorn University, Phetchaburi IT Campus, Cha-Am, Phetchaburi,
Research Article by Immersion in Androgens Somrudee Silarudee * and Pawapol Kongchum Faculty of Animal Sciences and Agricultural Technology, Silpakorn University, Phetchaburi IT Campus, Cha-Am, Phetchaburi,
SEANET Research Theme: Aquaculture in a changing ecosystem
 Date Submitted: September 14 th, 2017 Student Name: Michele Condon Year of School: Junior Department of Marine Sciences Email: mcondon@une.edu Faculty Mentor: Dr. Carrie Byron, Adam St. Gelais SEANET Research
Date Submitted: September 14 th, 2017 Student Name: Michele Condon Year of School: Junior Department of Marine Sciences Email: mcondon@une.edu Faculty Mentor: Dr. Carrie Byron, Adam St. Gelais SEANET Research
Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Science, Prince of Songkla University, Hat-Yai, Songkhla 90112, Thailand. b
 doi: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.2006.32.337 ScienceAsia 32 (2006): 337-343 Immunocytochemical Identification of Gonadotropic Cell Types and Changes in Cell Numbers during Annual Reproductive Cycle in
doi: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.2006.32.337 ScienceAsia 32 (2006): 337-343 Immunocytochemical Identification of Gonadotropic Cell Types and Changes in Cell Numbers during Annual Reproductive Cycle in
Reproductive Endocrinology. Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007
 Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
REPRODUCCIÓN. La idea fija. Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
Animal Reproduction Chapter 46. Fission. Budding. Parthenogenesis. Fragmentation 11/27/2017
 Animal Reproduction Chapter 46 Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Sexual reproduction is the creation of an offspring by fusion of a male gamete (sperm) and female gamete
Animal Reproduction Chapter 46 Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Sexual reproduction is the creation of an offspring by fusion of a male gamete (sperm) and female gamete
PHOTOPERIODIC CONTROL OF THE TESTICULAR CYCLE IN THE EASTERN RED-WINGED BLACKBIRD, (AGELAIUS PHOENICEUS PHOENICEUS)
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Bird Control Seminars Proceedings Wildlife Damage Management, Internet Center for September 1970 PHOTOPERIODIC CONTROL OF
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Bird Control Seminars Proceedings Wildlife Damage Management, Internet Center for September 1970 PHOTOPERIODIC CONTROL OF
Annual changes in serum calcium and inorganic phosphate levels and correlation with gonadal status of a freshwater murrel, Channa punctatus (Bloch)
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1998) 31: 169-173 Calcium and phosphate levels in murrel ISSN 1-879X 169 Annual changes in serum calcium and inorganic phosphate levels and correlation
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1998) 31: 169-173 Calcium and phosphate levels in murrel ISSN 1-879X 169 Annual changes in serum calcium and inorganic phosphate levels and correlation
Hormonal Control of Male Sexual Function
 Hormonal Control of Male Sexual Function A majority of the control of sexual functions in the male (and the female) begins with secretions of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) by the hypothalamus.
Hormonal Control of Male Sexual Function A majority of the control of sexual functions in the male (and the female) begins with secretions of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) by the hypothalamus.
SEDAR 2 Data Workshop. 1. Data Collection and Processing of Data for Black Sea Bass Life History Studies
 SEDAR 2 Data Workshop 1. Data Collection and Processing of Data for Black Sea Bass Life History Studies Sampling Since 1979, black sea bass have been sampled with a variety of fishery-independent gear
SEDAR 2 Data Workshop 1. Data Collection and Processing of Data for Black Sea Bass Life History Studies Sampling Since 1979, black sea bass have been sampled with a variety of fishery-independent gear
Spawning advanced and delayed control photoperiod control temperature control
 Spawning advanced and delayed control photoperiod control temperature control Photoperiod control Day Length and Temperature 30 25 Water Temperature (C) 20 15 10 Day Length (h) 5 0 Advancing or delaying
Spawning advanced and delayed control photoperiod control temperature control Photoperiod control Day Length and Temperature 30 25 Water Temperature (C) 20 15 10 Day Length (h) 5 0 Advancing or delaying
Sex change of hatchery produced Amphiprion ocellaris: Influence of mating system removal on gonad maturation and nesting success
 62 J. Mar. Biol. Ass. India, 52 (1) : 62-69, January - June 2010 Rema Madhu et al. Sex change of hatchery produced Amphiprion ocellaris: Influence of mating system removal on gonad maturation and nesting
62 J. Mar. Biol. Ass. India, 52 (1) : 62-69, January - June 2010 Rema Madhu et al. Sex change of hatchery produced Amphiprion ocellaris: Influence of mating system removal on gonad maturation and nesting
The Reproductive Biology of Pagellus bogaraveo, a New Candidate Species for Aquaculture
 42 The Open Marine Biology Journal, 2011, 5, 42-46 Open Access The Reproductive Biology of Pagellus bogaraveo, a New Candidate Species for Aquaculture Valeria Micale *,1, Lucrezia Genovese 1, Maria Cristina
42 The Open Marine Biology Journal, 2011, 5, 42-46 Open Access The Reproductive Biology of Pagellus bogaraveo, a New Candidate Species for Aquaculture Valeria Micale *,1, Lucrezia Genovese 1, Maria Cristina
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction
 Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
Establishing Endocrine and Behavioral Parameters of Reproduction in Captive Pacific Walrus (Odobenus rosmarus divergens)
 Establishing Endocrine and Behavioral Parameters of Reproduction in Captive Pacific Walrus (Odobenus rosmarus divergens) Lisa Triggs University of Washington School of Aquatic and Fishery Sciences Masters
Establishing Endocrine and Behavioral Parameters of Reproduction in Captive Pacific Walrus (Odobenus rosmarus divergens) Lisa Triggs University of Washington School of Aquatic and Fishery Sciences Masters
Managing Precocious Maturation in Chinook Salmon Captive Broodstock
 Managing Precocious Maturation in Chinook Salmon Captive Broodstock Paul Adelizi, Jamie McGrath-Castro and Brian Erlandsen California Department of Fish and Wildlife 2017 Northwest Fish Culture Concepts
Managing Precocious Maturation in Chinook Salmon Captive Broodstock Paul Adelizi, Jamie McGrath-Castro and Brian Erlandsen California Department of Fish and Wildlife 2017 Northwest Fish Culture Concepts
Physiology of Male Reproductive System
 Physiology of Male Reproductive System the anterior pituitary gland serves as the primary control of reproductive function at puberty Ant Pituitary secretes FSH & large amounts of LH (ICSH) FSH & LH cause
Physiology of Male Reproductive System the anterior pituitary gland serves as the primary control of reproductive function at puberty Ant Pituitary secretes FSH & large amounts of LH (ICSH) FSH & LH cause
Seasonal changes in androgen levels in stream- and hatchery-reared Atlantic salmon parr and their relationship to smolting
 Journal of Fish Biology (22) 61, 1294 134 doi:1.16/jfbi.22.2156, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Seasonal changes in androgen levels in stream- and hatchery-reared Atlantic salmon parr
Journal of Fish Biology (22) 61, 1294 134 doi:1.16/jfbi.22.2156, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Seasonal changes in androgen levels in stream- and hatchery-reared Atlantic salmon parr
THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED INJECTIONS OF CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN ON THE TESTES OF THE LEOPARD FROG (RANA PIPIENS SCHREBER)
 THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED INJECTIONS OF CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN ON THE TESTES OF THE LEOPARD FROG (RANA PIPIENS SCHREBER) ROBERT P. McCOURT Department of Zoology and Entomology, The Ohio State University,
THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED INJECTIONS OF CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN ON THE TESTES OF THE LEOPARD FROG (RANA PIPIENS SCHREBER) ROBERT P. McCOURT Department of Zoology and Entomology, The Ohio State University,
Characterization of Luteinizing Hormone and Luteinizing Hormone Receptor and Their Indispensable Role in the Ovulatory Process of the Medaka
 Characterization of Luteinizing Hormone and Luteinizing Hormone Receptor and Their Indispensable Role in the Ovulatory Process of the Medaka Katsueki Ogiwara 1, Chika Fujimori 1, Sanath Rajapakse 2, Takayuki
Characterization of Luteinizing Hormone and Luteinizing Hormone Receptor and Their Indispensable Role in the Ovulatory Process of the Medaka Katsueki Ogiwara 1, Chika Fujimori 1, Sanath Rajapakse 2, Takayuki
Protocol B - Induction of spawning and artificial fertilization [Pratical guide of protocols: broodstock management]
![Protocol B - Induction of spawning and artificial fertilization [Pratical guide of protocols: broodstock management] Protocol B - Induction of spawning and artificial fertilization [Pratical guide of protocols: broodstock management]](/thumbs/77/76138629.jpg) Protocol B - Induction of spawning and artificial fertilization [Pratical guide of protocols: broodstock management] in Felip A. (ed.), Carrillo M. (ed.), Herráez M.P. (ed.), Zanuy S. (ed.), Basurco B.
Protocol B - Induction of spawning and artificial fertilization [Pratical guide of protocols: broodstock management] in Felip A. (ed.), Carrillo M. (ed.), Herráez M.P. (ed.), Zanuy S. (ed.), Basurco B.
FLASH CARDS. Kalat s Book Chapter 11 Alphabetical
 FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 11 Alphabetical alpha-fetoprotein alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-Fetal Protein (AFP) or alpha-1- fetoprotein. During a prenatal sensitive period, estradiol
FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 11 Alphabetical alpha-fetoprotein alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-Fetal Protein (AFP) or alpha-1- fetoprotein. During a prenatal sensitive period, estradiol
Adapted from Preg. & Part., Senger
 MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY AND SPERMATOGENESIS (Chapter 10) AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) I. MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY (Figure10-1 to 10-3) A. Glands and their respective hormones 1) Hypothalamic hormone:
MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY AND SPERMATOGENESIS (Chapter 10) AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) I. MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY (Figure10-1 to 10-3) A. Glands and their respective hormones 1) Hypothalamic hormone:
Induction of Ovulation by Hormone Treatment in Ussurian Bullhead Leiocassis ussuriensis
 Dev. Reprod. Vol. 16, No. 4, 271 277 (2012) http://dx.doi.org/10.12717/dr.2012.16.4.271 271 Induction of Ovulation by Hormone Treatment in Ussurian Bullhead Leiocassis ussuriensis Sang Gu Lim, Young Soo
Dev. Reprod. Vol. 16, No. 4, 271 277 (2012) http://dx.doi.org/10.12717/dr.2012.16.4.271 271 Induction of Ovulation by Hormone Treatment in Ussurian Bullhead Leiocassis ussuriensis Sang Gu Lim, Young Soo
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
of unknown sub-species with varying genetic make-up. The easiest morphological tool that can be used in differentiating both
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON THE BREEDING PERFORMANCE OF BIDORSALIS HETEROBRANCHUS AND HETEROBRANCHUS LONGIFILIS, USING THREE DOSES OF OVAPRIM Nwadukwe, F.O. Department of Animal and Environmental Biology, Delta
A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON THE BREEDING PERFORMANCE OF BIDORSALIS HETEROBRANCHUS AND HETEROBRANCHUS LONGIFILIS, USING THREE DOSES OF OVAPRIM Nwadukwe, F.O. Department of Animal and Environmental Biology, Delta
Determination of the Ovarian Stages in Wild Persian Sturgeon, Acipenser persicus
 Agriculture Technology and Biological Sciences Determination of the Ovarian Stages in Wild Persian Sturgeon, Acipenser persicus Mahboubeh HOSSENZADE *, Mohammad Reza IMANPOOR, Seyed Mostafa AGHILINEJAD
Agriculture Technology and Biological Sciences Determination of the Ovarian Stages in Wild Persian Sturgeon, Acipenser persicus Mahboubeh HOSSENZADE *, Mohammad Reza IMANPOOR, Seyed Mostafa AGHILINEJAD
Hormones of brain-testicular axis
 (Hormone Function) Hormones of brain-testicular axis anterior pituitary drives changes during puberty controlled by GnRH from hypothalamus begins to secrete FSH, LH LH targets interstitial endocrinocytes
(Hormone Function) Hormones of brain-testicular axis anterior pituitary drives changes during puberty controlled by GnRH from hypothalamus begins to secrete FSH, LH LH targets interstitial endocrinocytes
Masculinization of Blue Hap (Sciaenochromis ahli) Treated with 17α-methyltestosterone
 J. Agr. Sci. Tech. () Vol. 3: 3 Masculinization of Blue Hap (Sciaenochromis ahli) Treated with αmethyltestosterone Downloaded from jast.modares.ac.ir at :5 IRDT on Thursday September 3th A. R. Abed Elmdoust,
J. Agr. Sci. Tech. () Vol. 3: 3 Masculinization of Blue Hap (Sciaenochromis ahli) Treated with αmethyltestosterone Downloaded from jast.modares.ac.ir at :5 IRDT on Thursday September 3th A. R. Abed Elmdoust,
Analysis of Spermatogenesis Using an Eel Model
 Aqua-BioScience Monographs, Vol. 4, No. 4, pp. 105 129 (2011) www.terrapub.co.jp/onlinemonographs/absm/ Analysis of Spermatogenesis Using an Eel Model Chiemi Miura and Takeshi Miura* Research Group for
Aqua-BioScience Monographs, Vol. 4, No. 4, pp. 105 129 (2011) www.terrapub.co.jp/onlinemonographs/absm/ Analysis of Spermatogenesis Using an Eel Model Chiemi Miura and Takeshi Miura* Research Group for
and Spermatogenesis in E. tauvina.
 Chapter IV. Hermaphroditism, Sex inversion, Male Reproductive system and Spermatogenesis in E. tauvina. 4.1. Introduction A hermaphroditic individual is one, which bears recognizable male and female tissues.
Chapter IV. Hermaphroditism, Sex inversion, Male Reproductive system and Spermatogenesis in E. tauvina. 4.1. Introduction A hermaphroditic individual is one, which bears recognizable male and female tissues.
Index. urologic.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acquired hypogonadism, prevalence of, 165 167 primary, 165 secondary, 167 Adipose tissue, as an organ, 240 241 Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acquired hypogonadism, prevalence of, 165 167 primary, 165 secondary, 167 Adipose tissue, as an organ, 240 241 Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital,
Intersex in Bass Emerging Contaminant Issues
 Intersex in Bass Emerging Contaminant Issues Vicki S. Blazer U.S Geological Survey National Fish Health Research Laboratory Leetown Science Center, Kearneysville, WV Sampling With WV DNR u Spring Summer
Intersex in Bass Emerging Contaminant Issues Vicki S. Blazer U.S Geological Survey National Fish Health Research Laboratory Leetown Science Center, Kearneysville, WV Sampling With WV DNR u Spring Summer
Reproductive Hormones
 Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
Evaluating minijack rates in spring Chinook Salmon CONFIRMING THAT SPRING PLASMA 11-KETOTESTOSTERONE LEVEL ACCURATELY PREDICTS FALL MATURATION STATUS
 Evaluating minijack rates in spring Chinook Salmon CONFIRMING THAT SPRING PLASMA 11-KETOTESTOSTERONE LEVEL ACCURATELY PREDICTS FALL MATURATION STATUS Background information What are minijacks and why do
Evaluating minijack rates in spring Chinook Salmon CONFIRMING THAT SPRING PLASMA 11-KETOTESTOSTERONE LEVEL ACCURATELY PREDICTS FALL MATURATION STATUS Background information What are minijacks and why do
Analysis of the Sex-determining Region of the Y Chromosome (SRY) in a Case of 46, XX True Hermaphrodite
 Clin Pediatr Endocrinol 1994; 3(2): 91-95 Copyright (C) 1994 by The Japanese Society for Pediatric Endocrinology Analysis of the Sex-determining Region of the Y Chromosome (SRY) in a Case of 46, XX True
Clin Pediatr Endocrinol 1994; 3(2): 91-95 Copyright (C) 1994 by The Japanese Society for Pediatric Endocrinology Analysis of the Sex-determining Region of the Y Chromosome (SRY) in a Case of 46, XX True
Assessment of High Rates of Precocious Male Maturation in a Spring Chinook Salmon Supplementation Hatchery Program Annual Report
 Assessment of High Rates of Precocious Male Maturation in a Spring Chinook Salmon Supplementation Hatchery Program Annual Report 22-23 DOE/BP-9556-1 August 23 Field37: This Document should be cited as
Assessment of High Rates of Precocious Male Maturation in a Spring Chinook Salmon Supplementation Hatchery Program Annual Report 22-23 DOE/BP-9556-1 August 23 Field37: This Document should be cited as
Course: Animal Production. Instructor: Ms. Hutchinson. Objectives: After completing this unit of instruction, students will be able to:
 Course: Animal Production Unit Title: Hormones TEKS: 130.3 (C)(6)(A) Instructor: Ms. Hutchinson Objectives: After completing this unit of instruction, students will be able to: A. Define what hormones
Course: Animal Production Unit Title: Hormones TEKS: 130.3 (C)(6)(A) Instructor: Ms. Hutchinson Objectives: After completing this unit of instruction, students will be able to: A. Define what hormones
J Chyb 1,2, T Mikolajczyk 2 and B Breton 1
 87 Post-ovulatory secretion of pituitary gonadotropins GtH I and GtH II in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): regulation by steroids and possible role of non-steroidal gonadal factors J Chyb 1,2,
87 Post-ovulatory secretion of pituitary gonadotropins GtH I and GtH II in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): regulation by steroids and possible role of non-steroidal gonadal factors J Chyb 1,2,
Spermatogenesis. What is it and what does it look like? How do hormones regulate spermatogenesis?
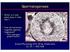 Spermatogenesis What is it and what does it look like? How do hormones regulate spermatogenesis? FSH, androgens, growth factors Animal Physiology (Hill, Wise, Anderson): Ch. 15 435-438 1 Spermatogenesis:
Spermatogenesis What is it and what does it look like? How do hormones regulate spermatogenesis? FSH, androgens, growth factors Animal Physiology (Hill, Wise, Anderson): Ch. 15 435-438 1 Spermatogenesis:
Sperm Production and Cryopreservation in Muskellunge after Carp Pituitary Extract and Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Injection
 The Progressive Fish Culturist, Vol. 58, No. 1, 1996, pp.32-37. American Fisheries Society ISSN: 1548-8640 DOI: 10.1577/1548-8640(1996)0582.3.CO;2 http://afs.allenpress.com/archive/1548-8640/58/1/pdf/i1548-8640-58-1-32.pdf
The Progressive Fish Culturist, Vol. 58, No. 1, 1996, pp.32-37. American Fisheries Society ISSN: 1548-8640 DOI: 10.1577/1548-8640(1996)0582.3.CO;2 http://afs.allenpress.com/archive/1548-8640/58/1/pdf/i1548-8640-58-1-32.pdf
EFFECT OF HCG IMPLANTS ON CHANGE IN TESTOSTERONE AND ESTRADIOL LEVEL IN BLOOD SERUM OF MURREL, CHANNA STRIATUS
 EFFECT OF HCG IMPLANTS ON CHANGE IN TESTOSTERONE AND ESTRADIOL LEVEL IN BLOOD SERUM OF MURREL, CHANNA STRIATUS Selvaraj, S 1., T. Francis 2, M. Venkatasamy and S. Santhoshkumar Department of Fisheries
EFFECT OF HCG IMPLANTS ON CHANGE IN TESTOSTERONE AND ESTRADIOL LEVEL IN BLOOD SERUM OF MURREL, CHANNA STRIATUS Selvaraj, S 1., T. Francis 2, M. Venkatasamy and S. Santhoshkumar Department of Fisheries
Received 8 April 2004; revised 21 September 2004; accepted 22 September 2004 Available online 23 November 2004
 GENERAL AND COMPARATIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY General and Comparative Endocrinology 140 (2005) 61 73 www.elsevier.com/locate/ygcen Cloning of FSHb, LHb, and glycoprotein a subunits from the Russian Sturgeon (Acipenser
GENERAL AND COMPARATIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY General and Comparative Endocrinology 140 (2005) 61 73 www.elsevier.com/locate/ygcen Cloning of FSHb, LHb, and glycoprotein a subunits from the Russian Sturgeon (Acipenser
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Broodstock development and breeding of marine finfishes
 Broodstock development and breeding of marine finfishes Broodstock development and breeding of marine finfishes G. Gopakumar, A.K. Abdul Nazar and R. Jayakumar Mandapam Regional Centre of CMFRI Mandapam
Broodstock development and breeding of marine finfishes Broodstock development and breeding of marine finfishes G. Gopakumar, A.K. Abdul Nazar and R. Jayakumar Mandapam Regional Centre of CMFRI Mandapam
Masculinization of Blue Hap (Sciaenochromis ahli) Treated with 17α-methyltestosterone
 J. Agr. Sci. Tech. () Vol. 3: 3 Masculinization of Blue Hap (Sciaenochromis ahli) Treated with αmethyltestosterone A. R. Abed Elmdoust, H. Farahmand *, Gh. Rafiee, B. Majazi Amiri, and A. R. Mirvaghefi
J. Agr. Sci. Tech. () Vol. 3: 3 Masculinization of Blue Hap (Sciaenochromis ahli) Treated with αmethyltestosterone A. R. Abed Elmdoust, H. Farahmand *, Gh. Rafiee, B. Majazi Amiri, and A. R. Mirvaghefi
although its mechanism is not clear (Fontaine, 1976). Very intense activity of the
 Effects of triiodothyronine and of some gonadotropic and steroid hormones on the maturation of carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) oocytes in vitro P. EPLER, K. BIENIARZ Academy of Agriculture, Department of lchthyobio%gy
Effects of triiodothyronine and of some gonadotropic and steroid hormones on the maturation of carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) oocytes in vitro P. EPLER, K. BIENIARZ Academy of Agriculture, Department of lchthyobio%gy
Supplementary Explanation for Scientific Research Whaling
 Supplementary Explanation for Scientific Research Whaling May 2008 SLIDE 1 - The Position of the Japanese Government on Whaling There are more than 80 species of cetaceans in the world. While some species
Supplementary Explanation for Scientific Research Whaling May 2008 SLIDE 1 - The Position of the Japanese Government on Whaling There are more than 80 species of cetaceans in the world. While some species
ABSTRACT. STRIPED BASS (Morone saxatilis) Ulrike Klenke, Doctor of Philosophy, Center of Marine Biotechnology,
 ABSTRACT Title of Dissertation: GONADAL AND STEROID FEEDBACK REGULATION OF THE HYPOTHALAMUS-PITUITARY AXIS IN STRIPED BASS (Morone saxatilis) Ulrike Klenke, Doctor of Philosophy, 2006 Dissertation directed
ABSTRACT Title of Dissertation: GONADAL AND STEROID FEEDBACK REGULATION OF THE HYPOTHALAMUS-PITUITARY AXIS IN STRIPED BASS (Morone saxatilis) Ulrike Klenke, Doctor of Philosophy, 2006 Dissertation directed
THE INFLUENCE OF LIGHT AND TEMPERATURE ON BODY FAT AND REPRODUCTIVE CONDITIONS OF RAN A PIPIENS 12
 THE INFLUENCE OF LIGHT AND TEMPERATURE ON BODY FAT AND REPRODUCTIVE CONDITIONS OF RAN A PIPIENS 12 FRED J. BRENNER AND PATRICIA E. BRENNER Biology Department, Thiel College, Greenville, Pennsylvania ABSTRACT
THE INFLUENCE OF LIGHT AND TEMPERATURE ON BODY FAT AND REPRODUCTIVE CONDITIONS OF RAN A PIPIENS 12 FRED J. BRENNER AND PATRICIA E. BRENNER Biology Department, Thiel College, Greenville, Pennsylvania ABSTRACT
SEASONAL OVARY DEVELOPMENT AND EFFECTS OF VITAMIN E ON EGG PERFORMANCES IN RABBIT FISH (Siganus guttatus)
 SEASONAL OVARY DEVELOPMENT AND EFFECTS OF VITAMIN E ON EGG PERFORMANCES IN RABBIT FISH (Siganus guttatus) ABSTRACT Pham Quoc Hung 1, Phan Van Ut 1, Nguyen Van An 2, Le Minh Thong 3, Ngo Van Luong 3 Received:
SEASONAL OVARY DEVELOPMENT AND EFFECTS OF VITAMIN E ON EGG PERFORMANCES IN RABBIT FISH (Siganus guttatus) ABSTRACT Pham Quoc Hung 1, Phan Van Ut 1, Nguyen Van An 2, Le Minh Thong 3, Ngo Van Luong 3 Received:
Embryology 3. Spermatogenesis:
 Embryology 3 Spermatogenesis: The 2 testis in males are each divided into lobes and lobules by connective tissue septa forming 250 lobule and in each lobule there are 1 to 4 seminefrous tubule ( so almost
Embryology 3 Spermatogenesis: The 2 testis in males are each divided into lobes and lobules by connective tissue septa forming 250 lobule and in each lobule there are 1 to 4 seminefrous tubule ( so almost
SEASONAL CHANGES IN HISTOLOGYOF THE THYROID GLAND CALOTIS VERSICOLOR
 SEASONAL CHANGES IN HISTOLOGYOF THE THYROID GLAND CALOTIS VERSICOLOR M. D. Kulkarni And A. H. Shinde Department of Zoology Yashwantrao Chavan Arts & Science College, Mangrulpir Dist. Washim. (Received
SEASONAL CHANGES IN HISTOLOGYOF THE THYROID GLAND CALOTIS VERSICOLOR M. D. Kulkarni And A. H. Shinde Department of Zoology Yashwantrao Chavan Arts & Science College, Mangrulpir Dist. Washim. (Received
Model Answer. M.Sc. Zoology (First Semester) Examination Paper LZT 103 (Endocrinology)
 Model Answer M.Sc. Zoology (First Semester) Examination-2013 Paper LZT 103 (Endocrinology) Section A 1. (i) d (ii) b (iii) b (iv) c (v) c (vi) a (vii) c (viii) a (ix) d (x) b Section B Q.2 Answer Hormonal
Model Answer M.Sc. Zoology (First Semester) Examination-2013 Paper LZT 103 (Endocrinology) Section A 1. (i) d (ii) b (iii) b (iv) c (v) c (vi) a (vii) c (viii) a (ix) d (x) b Section B Q.2 Answer Hormonal
PRELIMINARY STUDY ON THE EFFICIENCY OF SEVERAL OVULATION INDUCING HORMONES ON PIKEPERCH (SANDER LUCIOPERCA)
 Lucrări ştiinţifice Zootehnie şi Biotehnologii, vol. 42 (2) (2009), Timişoara. PRELIMINARY STUDY ON THE EFFICIENCY OF SEVERAL OVULATION INDUCING HORMONES ON PIKEPERCH (SANDER LUCIOPERCA) STUDIU PRELIMINAR
Lucrări ştiinţifice Zootehnie şi Biotehnologii, vol. 42 (2) (2009), Timişoara. PRELIMINARY STUDY ON THE EFFICIENCY OF SEVERAL OVULATION INDUCING HORMONES ON PIKEPERCH (SANDER LUCIOPERCA) STUDIU PRELIMINAR
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System
 9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION. Along with growth and spawning season, year at sexual maturity counts as another
 CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 Year at Sexual Maturity in Rainbow Trout Along with growth and spawning season, year at sexual maturity counts as another important trait in farming rainbow trout. Year at sexual
CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 Year at Sexual Maturity in Rainbow Trout Along with growth and spawning season, year at sexual maturity counts as another important trait in farming rainbow trout. Year at sexual
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
Histology of Male Reproductive system (1)
 Histology of Male Reproductive system (1) Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Learning Objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the organization of the testis Define seminiferous
Histology of Male Reproductive system (1) Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Learning Objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the organization of the testis Define seminiferous
gonad phosvitin levels in relation to the seasonal reproductive cycles of female brown trout
 Wild Plasma gonadotropin, estradiol, and vitellogenin and gonad phosvitin levels in relation to the seasonal reproductive cycles of female brown trout L. W. CRIM, D. R. IDLER Marine Sciences Research Laboratory,
Wild Plasma gonadotropin, estradiol, and vitellogenin and gonad phosvitin levels in relation to the seasonal reproductive cycles of female brown trout L. W. CRIM, D. R. IDLER Marine Sciences Research Laboratory,
Tampan, Pekanbaru, Riau 28293, Indonesia. Abstract
 International Journal of Applied Environmental Sciences ISSN 973-677 Volume 11, Number 5 (216), pp. 1173-1181 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com The Improvement of Ovulation Stimulation
International Journal of Applied Environmental Sciences ISSN 973-677 Volume 11, Number 5 (216), pp. 1173-1181 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com The Improvement of Ovulation Stimulation
Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction
 Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The human male and female reproductive cycles are controlled by the interaction of hormones from the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary with
Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The human male and female reproductive cycles are controlled by the interaction of hormones from the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary with
Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development Section 1 1. Distinguish between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. 2. Which form of reproduction: a.
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development Section 1 1. Distinguish between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. 2. Which form of reproduction: a.
