Trachoma: global magnitude of a preventable cause of blindness
|
|
|
- Felicia Foster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Chronic Disease and Health Promotion Department, Prevention of Blindness and Deafness, World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland; 2 School of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco, California, USA Correspondence to: Dr S P Mariotti, World Health Organization, 20 avenue appia Geneva, Switzerland; mariottis@who.int Accepted 3 December 2008 Published Online First 19 December 2008 Trachoma: global magnitude of a preventable cause of blindness S P Mariotti, 1 D Pascolini, 1 J Rose-Nussbaumer 2 ABSTRACT Objectives: Trachoma is the leading cause of infectious blindness worldwide. It is known to be highly correlated with poverty, limited access to healthcare services and water. In 2003, the WHO estimated that 84 million people were suffering from active trachoma, and 7.6 million were severely visually impaired or blind as a result of trachoma: this study provides an updated estimate of the global prevalence of trachoma based on the most recent information available. Methods: A literature search of recent published and unpublished surveys in the 57 endemic countries was carried out: the result of surveys that used the WHO trachoma grading system and additional information from regional and country experts served as a basis to determine the prevalence of trachoma in each country. Results: Population-based surveys provided recent information for 42 out of 57 endemic countries million people are estimated to be suffering from active trachoma, and 8.2 million are estimated to have trichiasis. Conclusions: The current estimate of prevalence of trachoma is lower than the previous WHO estimates: this can be explained by the success in implementing control strategy, by more accurate data, as well as by socioeconomic development in endemic countries. Trachoma is the leading cause of infectious blindness worldwide: 1 it is caused by ocular infections with Chlamydia trachomatis that might result in chronic inflammation of the eyelids. These infections occur mainly in children, peaking around age 1 5 and declining thereafter. This chronic inflammation of the eyelids produces scarring of the conjunctiva that can subsequently cause entropion trichiasis, resulting in inturned eyelashes. The inturned eyelashes as well as other alterations of the eye, such as lacrimal function and corneal limbus, harm the cornea causing severe pain, corneal opacity and consequent vision loss. 2 The disease is known to be highly correlated with poverty, lack of personal and community hygiene, limited access to healthcare and water. It is prevalent in Africa, Asia and some parts of Latin America, the Middle East and the Western Pacific. 3 Active trachoma affects mainly women and children, and cicatricial trachoma affects on average women three times more than men likely secondary to their prolonged contact with infected children. 4 5 In 2003, the WHO estimated that 84 million people were suffering from active trachoma, and 7.6 million were severely visually impaired or blind as a result of trachoma. 6 When visual impairment occurs during the productive years of life, it results in economic hardship for families and communities: it has been Global issues estimated that in countries ranked with a low Human Development Index ( en/statistics/) the disease could result in a total of 2.9 billion dollars in lost productivity each year. 7 In 1997, the WHO established the Alliance for Global Elimination of Trachoma (GET) by the year The elimination strategy has been summarised with the acronym SAFE, which stands for Surgery for trichiasis, Antibiotics, Facial cleanliness and Environmental change, such as clean water and latrines This paper provides an updated estimate of the global magnitude of trachoma based on the most recent information available. The knowledge of the prevalence of trachoma at country and global level is essential for the planning and for the implementation of the interventions needed to eliminate this preventable cause of blindness and ultimately for the achievement of the WHO World Health Assembly Resolution for the Global Elimination of Trachoma by 2020 WHA 51:11 (available at en/index.html). METHODS Epidemiological data An extensive literature search was carried out for published and unpublished literature from the year 2000 onwards regarding the prevalence of trachoma in the 57 countries known to be endemic. Published data were searched using Medline with the keywords trachoma prevalence up to 6 July The studies selected were population-based surveys that gave a description of sample design and plan, sample size, response rate and examination methods. Unpublished data were gathered in part during the Eleventh Meeting of the WHO Alliance for the Global Elimination of Trachoma by from the reports and presentations of country experts. Additional data were obtained by contacting experts from countries and regions or researchers in academic institutions. The majority of the surveys used an established WHO protocol for sampling populations to determine prevalence of trachoma (available at english.pdf). All surveys selected assessed trachoma using the simplified WHO trachoma grading system ( en/index2.html): Trachomatous Inflammation Follicular (TF) was defined as the presence of five or more follicles in the upper tarsal conjunctiva; Trachomatous Inflammation Intense (TI) was defined as pronounced inflammatory thickening of the tarsal conjunctiva that obscures more than half of the normal deep tarsal vessels; Trachomatous Br J Ophthalmol 2009;93: doi: /bjo
2 Table 1 Available studies on the prevalence of trachoma: 1996 to 2007 Country Date of survey Location Type of survey Age group Sources Afghanistan 2006 Four provinces Door-to-door assessment All ages Comprehensive Eye Care Program, Ministry of Public Health Afghanistan Australia Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities Screening in schools and in remote communities, clinical assessments All ages Mak DB et al. The Office for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Health, Australian Government Department of Health Brazil Thirteen states School screening 1 9 Trachoma Control Program, Health Surveillance Secretariat, Brazil Ministry of Health Burkina Faso 2005 Bugondè, Diapaga districts Population-based survey 1 9, 15 and older Programme National de Prévention de la Cécité, Ministry of Health, Burkina Faso Cambodia 2000 Six endemic regions Trachoma rapid assessment 0 14, 40 and older National Prevention of Blindness Program, National Program for Eye Health, Ministry of Health, Cambodia Cameroon 2006 Kolofata district, Far North Province Population-based survey 1 10, women over 14 Einterz EM et al 2008 Chad Eight provinces Population-based survey 1 10, women over 14 Dézoumbé D. et al 2007, Programme National de lutte contre la cécité, Ministry of Health, Republic of Chad China Ten provinces Trachoma rapid assessment 1 9, 40 and older National Programme for Prevention of Blindness, Ministry of Health, China Egypt 2001 Menofiya Governorate Population-based survey 2 6, 50 and older Gamal Ezz al Arab et al 2001 Eritrea 2006 Three endemic regions: North Red Population-based survey 1 9, 15 and older Blindness Prevention Program, Ministry of Health of the State of Sea, Debub, Gash Barka Eritrea Ethiopia All regions of the country Population-based survey All ages Berhane Y et al 2006, Federal Ministry of Health of Ethiopia Gambia 2006 North Bank, Lower River Population-based survey 0 9 Prevention of Blindness Program, Ministry of Health, Gambia Ghana Northern Region, Upper West Region Population-based survey 1 10, 40 and older National Eye Care Programme, Ministry of Health, Ghana Guinea Upper and Middle Guinea Population-based survey and assessment 0 10, women over 14, Programme de lutte contre la cécité, Ministry of Health, Guinea Guinea-Bissau 2005 Whole country Population-based survey all ages Prevention of Blindness and Deafness, Ministry of Public Health, Republic of Guinea-Bissau India 2006 Punjab, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Trachoma rapid assessment,10, 15 and older Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health and Uttarakhand, Haryana, Gujarat Family Welfare, India Iran (Islamic Republic of) 2002 Four provinces in the south Trachoma rapid assessment All ages Ministry of Health and Education, Kenya 2004 Five endemic districts in Rift Valley Population-based survey 1 9, 15 and older Karimurio J et al 2006 Province and one in Eastern Province Malawi Salima and Chikwana districts (Central and South Provinces) Trachoma rapid assessment 5 9, and 0 9 National Programme for Prevention of Blindness, Ministry of Health, Malawi Mali 1996 and All endemic regions Population-based survey 0 9, 15 and older Programme national de lutte contre la cécité, Ministry of Health, Mali Mauritania 2004 National survey Population-based survey 1 9, 14 and older Programme national de lutte contre la cécité, Ministry of Health, Mauritania Mexico 2006 Chiapas Surveillance house to house All ages State Institute of Health, Chiapas, Mexico Morocco 2004 Five endemic regions Community-based surveillance All ages Programme national de lutte contre la cécité, Ministry of Health, Kingdom of Morocco Mozambique 2002 Northern Manica Province Population-based survey 1 9, 40 and older National Programme for Prevention of Blindness, Ministry of Health, Mozambique Myanmar 2006 Meiktila District Population-based survey 40 and older, Durkin SR et al 2007 Nepal , 2006 Niger Several districts in the Zinder, Maradi and Diffa regions Several endemic districts Population-based survey and trachoma rapid assessment all ages National Trachoma Program, Ministry of Health and Population, Nepal Population-based survey 1 9, 15 and older Programme national de lutte contre la cécité, Ministry of Public Health, Republic of Niger and Abdou A et al 2007 Nigeria Eight endemic regions Population-based survey 1 9, 15 and older National Programme for Prevention of Blindness, Ministry of Health, Nigeria Continued 564 Br J Ophthalmol 2009;93: doi: /bjo
3 Table 1 Continued Country Date of survey Location Type of survey Age group Sources Population-based survey 1 5 Khandekar R. et al 2006 Oman 2005 Three regions: Dhakhiliya, North Sharqiya, South Batinah Trachoma rapid assessment 1 10, 40 and older Mathew A et al 2007 Pacific Islands Subregion Kiribati, Nauru, Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, Fiji Door-to-door assessment All ages Prevention and Control of Blindness Programme, Ministry of Health, Government of Pakistan Pakistan 2004 All four provinces and in the Northern Area Senegal Whole country and Thiès Region Population-based survey 1 9, women over 14 Saal MB et al 2003 and Programme National de Lutte contre la Cécité, Ministry of Health, Senegal Population-based survey 1 9, 15 and older Ngondi J et al 2005, 2006 and Prevention of Blindness Administration Federal Ministry of Health, Sudan Sudan 2003, Eastern Equatoria, Upper Nile, Unity, Northern, Kassala and Khartoum States Tanzania (United Repubic of) Fifty districts in endemic regions Population-based survey 1 9, 15 and older National Eye Care Program, Ministry of Health and Social Welfare, United Republic of Tanzania Uganda 2006 Three districts in the Northern and Population-based survey 1 9, 15 and older National Programme for Prevention of Blindness, Ministry of Eastern regions Health, Uganda 1 5, 35 and older National Programme for Prevention of Blindness, Ministry of Health Viet Nam and Khandekar R et al 2006 Viet Nam 2001, 2006 Districts in the northern provinces School-based assessment and populationbased survey Yemen 2004 Nine Governorates and Socotra Island Trachoma rapid assessment 1 9 Al Khatib TK et al 2006 Zambia Gwembe District, Southern Region Exhaustive screening of population in chosen All ages Astle WF et al 2006 villages Trichiasis (TT) was defined as at least one eyelash rubbing on the eyeball. Active trachoma was defined as Trachomatous Inflammation Follicular and/or Trachomatous Inflammation Intense (TF/TI). A database was created to record and analyse country-specific data on prevalence of active trachoma and trichiasis. Populations Estimates of country population were based on the 2004 UN demographic assessment by the United Nations Population Division, 12 urban and rural distribution from the UN World Urbanization Prospect. 13 The population size and structure for districts, provinces or states within countries were based on country census when available or from other public domain sources ( Estimates of prevalence Prevalence of active trachoma was estimated from the available data for children less than 10 years old. The prevalence of active trachoma for all ages was estimated using the model proposed at the WHO 2nd Global Scientific Meeting on Trachoma in that was based on the results from the available data from countries and that has been validated in subsequent studies from Gambia, 11 Ethiopia 14 and Tanzania. 15 The model applies four correction factors to the prevalence of TF/TI,10 years to make projections for all ages (1.0, 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 to prevalence of,10%, 10 19%, 20 29%, (30% respectively).the same model provides three correction factors to estimate the prevalence of trichiasis for all the population 14 years and older: 1.3 to be applied to the prevalence determined for women ages 14 and older; 1.05 to age-specific prevalence determined for both sexes over 30 and 1.1 to age-specific prevalence determined for both sexes over 40. Prevalence was first determined at district level; the results from a single survey within a district were extrapolated to the entire district if it was considered representative and if it was known that the whole district was endemic. Prevalence estimated for one district in a province/state was extrapolated to the whole province/state using analogous criteria. The total number of cases of trachoma in the country was then estimated from the prevalence in districts, provinces or states; information from country experts was essential to identify the endemic areas and thus avoid over- or underestimates. In a few cases, national surveys were available (see table 1). In the case of countries missing data, prevalence was estimated from the information in unpublished reports from Ministries of Health or from proxy countries chosen according to similarity of epidemiology and demographic structure. Based on the prevalence of active trachoma and trichiasis, the Ultimate Intervention Goals (UIG) for Antibiotics and for Surgery were estimated for each country. The UIG-A is the number of people to be treated with antibiotics. In low endemic districts, where the prevalence of active trachoma is less than or equal to 10%, it is the number of cases multiplied by a factor of 3 to include the average number of family members; in high endemic districts, with a prevalence higher than 10%, mass drug treatment is required, and consequently the UIG-A corresponds to the population in the district. The UIG-S ultimate intervention goal for trichiasis surgery is to provide surgical interventions to all current estimated patients. Br J Ophthalmol 2009;93: doi: /bjo
4 Table 2 Country Estimated active trachoma and trachomatous trichiasis in endemic countries in 2007 from available data Country population in 2004 (millions) Population living in endemic areas (millions) Cases of Trachomatous Inflammation Follicular/ Trachomatous Inflammation in endemic areas (thousands) Afghanistan Algeria Australia Benin Botswana Brazil Burkina Faso Central African Republic Cambodia Cameroon Chad China Côte d Ivoire Djibouti Egypt Eritrea Ethiopia Fiji Gambia Ghana Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau India Iran (Islamic Republic of) Iraq Kenya Kiribati Lao People s Democratic Republic Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Malawi Mali Mauritania Mexico Morocco Mozambique Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Niger Nigeria Oman Pakistan Papua New Guinea Senegal Solomon Islands Somalia Sudan Tanzania (United Republic of) Togo Uganda Vanuatu Vietnam Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe All endemic countries Cases of Trachomatous Trichiasis in endemic areas (thousands) Italics indicate countries for which prevalence was estimated on proxy countries or on other assumptions because of the lack of recent population-based data. 566 Br J Ophthalmol 2009;93: doi: /bjo
5 RESULTS For 42 countries out of the 57 known to be endemic for trachoma, there were population-based surveys or assessments consistent with the inclusion criteria for this study. Notably, 32 countries have carried out in the last 5 years national surveys or surveys of entire endemic areas, among them the most populous of the endemic countries, China, India and Nigeria. For 11 of the known endemic countries (Benin, Botswana, Côte d Ivoire, Guatemala, Iraq, Libyan Arab Jamahiriya, Namibia, Papua New Guinea, Somalia, Togo and Zimbabwe) there were no surveys conducted in the last 15 or 20 years; for four countries (Algeria, Central African Republic, Djibouti and Lao People s Democratic Republic) the information was prior to the year In these 15 countries, the estimated population living in endemic areas for trachoma is 58 million, only 22% of the total population. The available studies for 42 countries are shown in table 1 (for the bibliography, see int/blindness/publications/references/en/trachoma_08.pdf). Table 2 shows for the 57 endemic countries the estimated population living in endemic areas, the number of people with active trachoma and trichiasis. Globally, 1.2 billion people live in endemic areas, 40.6 million people are suffering from active trachoma, and 8.2 million have trichiasis; 48.5% of the global burden of active trachoma is concentrated in five countries: Ethiopia, India, Nigeria, Sudan and Guinea. On the other hand, 50% of the global burden of trichiasis is concentrated in only three countries: China, Ethiopia and Sudan. Overall, Africa is the most affected continent; 27.8 million cases of active trachoma (68.5% of all) and 3.8 million cases of trichiasis (46.6% of all) are located in 28 of the 46 countries in the WHO African Region, with an estimated population of 279 million living in endemic areas. The disease is still prevalent in some countries or areas of countries of four other WHO regions: the Eastern-Mediterranean (12 countries, population in endemic areas 144 million), the Western Pacific (11 countries, population in endemic areas 400 million), South-East Asia (three countries, population in endemic areas 362 million) and the Americas (three countries, population in endemic areas 58 million). The European region is the only WHO region to be free of trachoma. According to these estimates, the ultimate intervention goals require antibiotic treatment for some 340 million people and trichiasis surgeries for 8.2. Trichiasis, however, continues to occur in adults exposed to trachoma in the past: the UIG for trichiasis surgery determined in this paper does not make projections on the incident cases and is therefore an underestimate. DISCUSSION Limitations The estimates presented in this paper are based partly on population-based surveys and assessments, and partly on assumptions and projections. Each of these sources can introduce errors on the final estimates due to the following factors: heterogeneity of sampling and examination methods despite the use of the same WHO protocol; use of a model to estimate prevalence of active trachoma and trichiasis for all ages and for both sexes; assumptions on the prevalence and geographical distribution of trachoma to extrapolate data from communities to districts, from districts to provinces/states and from states/provinces to countries; assumptions to extrapolate prevalence from proxy countries to countries missing data. To minimise the bias introduced by the limitations above, studies were chosen only if they were consistent with the selection criteria. The projections for all ages and sex were compared with the results from studies that reported age- and sex-specific data, and were found to be consistent. All extrapolations made for countries or areas within a country were based on information from country experts or academic researchers. Given the heterogeneity of the data and in some cases the non-reporting of the confidence intervals of the studies, it was not possible to determine the extent of uncertainty of the estimates at global level. Estimated prevalence of active trachoma and trichiasis The estimate of 40 million cases of active trachoma presented in this paper is significantly lower than the previous WHO estimate of 84 million made in This difference can be attributed to previous overestimations for China and India, but it is also due to declines in prevalence attributable to stable socio-economic development in some countries (eg, Oman, Iran, Vietnam) and in the success of current interventions in other countries where development is still lagging (eg, Mexico, Morocco, The Gambia, Ghana, Mali, etc). In China and India, reassessment of prevalence was conducted recently. The estimate made in 2004 for China of 26 million cases of active trachoma was based on partial and probably dated figures from the endemic provinces: current estimates are based on population-based assessments conducted in 10 provinces in 2005, Beijing, Sichuan, Yunnan, Qinghai, Chongqing, Shanxi, Zhanjiang, Neimeng, Hainan and Hebei. The standardised prevalence of active trachoma for these provinces was 2.34% in children aged 10 years and younger. In the absence of data suggesting active trachoma or trichiasis in other provinces, the prevalence was applied only to the population in these provinces. The number of 1.3 million cases of active trachoma therefore could be a conservative estimate. In India, the previous estimate for 2004 was based on extensive surveys conducted in 1989 in 15 states and one pilot study conducted in According to the pilot study, there was a 25% reduction in prevalence of trachoma in India since Applied to the prevalence values of 1989, this reduction resulted in an estimated 20 million cases of active trachoma. The current estimate is based on the population-based assessments conducted in 2006 in six states, Punjab, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Haryana and Gujarat, that were identified as possibly the only endemic areas in the country. The assessments showed an average prevalence of active trachoma of 6% in children under 10 years of age resulting in 4.5 million cases when applied to the five endemic states. Trichiasis is perhaps the most important measure of the severity of the disease because of increased risk of visual impairment. The present estimate of 8.2 million cases of trichiasis exceeds the estimated 7.6 million in 2004: this increase is due to a revision of the estimates according to new available data. CONCLUSION Despite the limitations, this study represents an updated global estimate of trachoma. It is clear that trachoma remains an important public health concern with millions still suffering from an eliminable disease. This study also shows that trachoma remains endemic in many parts of Africa and Asia, and still affects many in Latin American and the Middle East, highlighting the needs and gaps in the provision of services. Obtaining the ultimate intervention goals for antibiotic Br J Ophthalmol 2009;93: doi: /bjo
6 treatment and trichiasis surgeries clearly will require calling for action to governments, NGOs, private sectors and all other health professionals. The SAFE integrated approach recommended by WHO to reach elimination of trachoma by the year 2020 must continue to be implemented and expanded, targeting social development along with healthcare interventions. Competing interests: SPM and DP are staff members of the World Health Organization. The authors alone are responsible for the views expressed in this publication, and they do not necessarily represent the decisions, policy or views of the World Health Organization. REFERENCES 1. Resnikoff S, Pascolini D, Etya ale D, et al. Global data on visual impairment in the year Bull World Health Organ 2004;82: Bowman RJ, Jatta B, Cham B, et al. Natural history of trachomatous scarring in The Gambia: results of a 12-year longitudinal follow-up. Ophthalmology 2001;108: Polack S, Brooker S, Kuper H, et al. Mapping the global distribution of trachoma. Bull World Health Organ 2005;83: West S, Nguyen MP, Mkocha H, et al. Gender equity and trichiasis surgery in the Vietnam and Tanzania national trachoma control programmes. Br J Ophthalmol 2004;88: Courtright P, West SK. Contribution of sex-linked biology and gender roles to disparity with trachoma. Emerg Infect Dis 2004;10: WHO Alliance for the Global Elimination of Blinding Trachoma by Report of the 2nd Global Scientific Meeting on Trachoma, Geneva, August Geneva: WHO, 2003 (WHO/PBD/GET.03.1). 7. Frick KD, Basilion EV, Hanson CL, et al. Estimating the burden and economic impact of trachomatous visual loss. Ophthalmic Epidemiol 2003;10: Prevention of Blindness and Deafness. Planning for the global elimination of trachoma (GET). Report of a WHO consultation. Geneva, November Geneva: WHO, 1997 (WHO/PBL/97.60). trachoma/en/get_1996.pdf (accessed 6 Feb 2009). 9. Mariotti SP, Prüss A. The SAFE strategy. Preventing trachoma: a guide for environmental sanitation and improved hygiene. Geneva: WHO, 2001 (WHO/PBD/GET/ 00.7/rev.1). (accessed 6 Feb 2009). 10. Gambir M, Basanez M, Turner F, et al. Trachoma: transmission, infection and control. Lancet Infect Dis 2007;7: WHO Alliance for the Global Elimination of Blinding Trachoma by Report of the 11th meeting of the WHO Alliance for the Global Elimination of Blinding Trachoma, 2 4 April 2007, Cairo. Geneva: WHO, 2007 (WHO/PBD/GET/11). 12. United Nations. World population prospects: the 2004 revision (CD-ROM edn, extended dataset). New York: United Nations, United Nations. World urbanization prospects: the 2003 revision. New York: United Nations, Federal Ministry of Health of Ethiopia. National survey on blindness, low vision and trachoma in Ethiopia. Addis Ababa: Federal Ministry of Health of Ethiopia, Solomon AW, Holland MJ, Alexander NDE, et al. Mass treatment with single-dose azithromycin for trachoma. N Engl J Med 2004;351: Br J Ophthalmol: first published as /bjo on 19 December Downloaded from on 4 October 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright. 568 Br J Ophthalmol 2009;93: doi: /bjo
Annex 2 A. Regional profile: West Africa
 Annex 2 A. Regional profile: West Africa 355 million people at risk for malaria in 215 297 million at high risk A. Parasite prevalence, 215 Funding for malaria increased from US$ 233 million to US$ 262
Annex 2 A. Regional profile: West Africa 355 million people at risk for malaria in 215 297 million at high risk A. Parasite prevalence, 215 Funding for malaria increased from US$ 233 million to US$ 262
Summary of the Seventeenth Meeting of the International Task Force for Disease Eradication (II) October 12, 2010
 Summary of the Seventeenth Meeting of the International Task Force for Disease Eradication (II) October 12, 2010 The Seventeenth Meeting of the International Task Force for Disease Eradication (ITFDE)
Summary of the Seventeenth Meeting of the International Task Force for Disease Eradication (II) October 12, 2010 The Seventeenth Meeting of the International Task Force for Disease Eradication (ITFDE)
What is this document and who is it for?
 Measles and Rubella Initiative s Standard Operating Procedures for Accessing Support for Measles and Rubella Supplementary Immunization Activities During 2016 In the context of measles and rubella elimination
Measles and Rubella Initiative s Standard Operating Procedures for Accessing Support for Measles and Rubella Supplementary Immunization Activities During 2016 In the context of measles and rubella elimination
Global reductions in measles mortality and the risk of measles resurgence
 Global reductions in measles mortality 2000 2008 and the risk of measles resurgence Measles is one of the most contagious human diseases. In 1980 before the use of measles vaccine was widespread, there
Global reductions in measles mortality 2000 2008 and the risk of measles resurgence Measles is one of the most contagious human diseases. In 1980 before the use of measles vaccine was widespread, there
EXPLANATION OF INDICATORS CHOSEN FOR THE 2017 ANNUAL SUN MOVEMENT PROGRESS REPORT
 UNICEF / Zar Mon Annexes EXPLANATION OF INDICATORS CHOSEN FOR THE 2017 ANNUAL SUN MOVEMENT PROGRESS REPORT This report includes nine nutrition statistics, as per the 2017 Global Nutrition Report. These
UNICEF / Zar Mon Annexes EXPLANATION OF INDICATORS CHOSEN FOR THE 2017 ANNUAL SUN MOVEMENT PROGRESS REPORT This report includes nine nutrition statistics, as per the 2017 Global Nutrition Report. These
Main global and regional trends
 I N T R O D U C T I O N Main global and regional trends Promising developments have been seen in recent years in global efforts to address the AS epidemic, including increased access to effective treatment
I N T R O D U C T I O N Main global and regional trends Promising developments have been seen in recent years in global efforts to address the AS epidemic, including increased access to effective treatment
Eligibility List 2018
 The Global Fund s 2017-2022 strategy and allocation-based approach enables strategic investment to accelerate the end of HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria and build resilient and sustainable systems for
The Global Fund s 2017-2022 strategy and allocation-based approach enables strategic investment to accelerate the end of HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria and build resilient and sustainable systems for
GOAL 2: ACHIEVE RUBELLA AND CRS ELIMINATION. (indicator G2.2) Highlights
 GOAL 2: ACHIEVE RUBELLA AND CRS ELIMINATION (indicator G2.2) Highlights As of December 2014, 140 Member States had introduced rubella vaccines; coverage, however, varies from 12% to 94% depending on region.
GOAL 2: ACHIEVE RUBELLA AND CRS ELIMINATION (indicator G2.2) Highlights As of December 2014, 140 Member States had introduced rubella vaccines; coverage, however, varies from 12% to 94% depending on region.
Wild Poliovirus*, 03 Aug 2004 to 02 Aug 2005
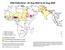 Wild Poliovirus*, 03 Aug 2004 to 02 Aug 2005 Wild virus type 1 Wild virus type 3 Wild virus type 1 & 3 Endemic countries Re-established transmission countries Case or outbreak following importation *Excludes
Wild Poliovirus*, 03 Aug 2004 to 02 Aug 2005 Wild virus type 1 Wild virus type 3 Wild virus type 1 & 3 Endemic countries Re-established transmission countries Case or outbreak following importation *Excludes
Disparities in access: renewed focus on the underserved. Rick Johnston, WHO UNC Water and Health, Chapel Hill 13 October, 2014
 Disparities in access: renewed focus on the underserved Rick Johnston, WHO UNC Water and Health, Chapel Hill 13 October, 2014 Sector proposal for post-2015 targets By 2030: to eliminate open defecation;
Disparities in access: renewed focus on the underserved Rick Johnston, WHO UNC Water and Health, Chapel Hill 13 October, 2014 Sector proposal for post-2015 targets By 2030: to eliminate open defecation;
Funding for AIDS: The World Bank s Role. Yolanda Tayler, WB Bi-regional Workshop for the Procurement of ARVs Phnom Penh, Cambodia
 Funding for AIDS: The World Bank s Role Yolanda Tayler, WB Bi-regional Workshop for the Procurement of ARVs Phnom Penh, Cambodia Outline New resources needs estimates Bridging the gap Global overview of
Funding for AIDS: The World Bank s Role Yolanda Tayler, WB Bi-regional Workshop for the Procurement of ARVs Phnom Penh, Cambodia Outline New resources needs estimates Bridging the gap Global overview of
AIDS in Africa. An Update. Basil Reekie
 AIDS in Africa An Update Basil Reekie Contents General Statistics The trend of HIV in Africa Ugandan experience UNAIDS 2006 Latest African Statistics by Country HIV Intervention Light at the end of the
AIDS in Africa An Update Basil Reekie Contents General Statistics The trend of HIV in Africa Ugandan experience UNAIDS 2006 Latest African Statistics by Country HIV Intervention Light at the end of the
POLIOMYELITIS ERADICATION: PROGRESS REPORT. Information Document CONTENTS BACKGROUND PROGRESS MADE NEXT STEPS... 12
 5 August 9 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-ninth session Kigali, Republic of Rwanda, August 4 September 9 POLIOMYELITIS ERADICATION: PROGRESS REPORT Information Document CONTENTS
5 August 9 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-ninth session Kigali, Republic of Rwanda, August 4 September 9 POLIOMYELITIS ERADICATION: PROGRESS REPORT Information Document CONTENTS
APPENDIX II - TABLE 2.3 ANTI-TOBACCO MASS MEDIA CAMPAIGNS
 WHO REPORT ON THE GLOBAL TOBACCO EPIDEMIC, 2011 APPENDIX II - TABLE 2.3 ANTI-TOBACCO MASS MEDIA CAMPAIGNS (SEE TABLE 4.9) Africa The Americas South-East Asia Europe Eastern Mediterranean Western Pacific
WHO REPORT ON THE GLOBAL TOBACCO EPIDEMIC, 2011 APPENDIX II - TABLE 2.3 ANTI-TOBACCO MASS MEDIA CAMPAIGNS (SEE TABLE 4.9) Africa The Americas South-East Asia Europe Eastern Mediterranean Western Pacific
UNAIDS 2013 AIDS by the numbers
 UNAIDS 2013 AIDS by the numbers 33 % decrease in new HIV infections since 2001 29 % decrease in AIDS-related deaths (adults and children) since 2005 52 % decrease in new HIV infections in children since
UNAIDS 2013 AIDS by the numbers 33 % decrease in new HIV infections since 2001 29 % decrease in AIDS-related deaths (adults and children) since 2005 52 % decrease in new HIV infections in children since
Current State of Global HIV Care Continua. Reuben Granich 1, Somya Gupta 1, Irene Hall 2, John Aberle-Grasse 2, Shannon Hader 2, Jonathan Mermin 2
 Current State of Global HIV Care Continua Reuben Granich 1, Somya Gupta 1, Irene Hall 2, John Aberle-Grasse 2, Shannon Hader 2, Jonathan Mermin 2 1) International Association of Providers of AIDS Care
Current State of Global HIV Care Continua Reuben Granich 1, Somya Gupta 1, Irene Hall 2, John Aberle-Grasse 2, Shannon Hader 2, Jonathan Mermin 2 1) International Association of Providers of AIDS Care
THE CARE WE PROMISE FACTS AND FIGURES 2017
 THE CARE WE PROMISE FACTS AND FIGURES 2017 2 SOS CHILDREN S VILLAGES INTERNATIONAL WHERE WE WORK Facts and Figures 2017 205 58 79 families and transit 31 Foster homes 162 8 3 173 214 2 115 159 136 148
THE CARE WE PROMISE FACTS AND FIGURES 2017 2 SOS CHILDREN S VILLAGES INTERNATIONAL WHERE WE WORK Facts and Figures 2017 205 58 79 families and transit 31 Foster homes 162 8 3 173 214 2 115 159 136 148
World Health organization/ International Society of Hypertension (WH0/ISH) risk prediction charts
 World Health organization/ International Society of Hypertension (WH0/ISH) risk prediction charts (charts in colour) (These charts will be updated in 2014) 2 1. Introduction 2. Instructions on how to use
World Health organization/ International Society of Hypertension (WH0/ISH) risk prediction charts (charts in colour) (These charts will be updated in 2014) 2 1. Introduction 2. Instructions on how to use
Malaria Funding. Richard W. Steketee MACEPA, PATH. April World Malaria Day 2010, Seattle WA
 Malaria Funding Richard W. Steketee MACEPA, PATH April World Malaria Day 2010, Seattle WA Malaria Funding Is there a plan? Is there money? Where does the money come from? Is the money moving efficiently?
Malaria Funding Richard W. Steketee MACEPA, PATH April World Malaria Day 2010, Seattle WA Malaria Funding Is there a plan? Is there money? Where does the money come from? Is the money moving efficiently?
Global summary of the AIDS epidemic, December 2007
 Global summary of the AIDS epidemic, December 27 Number of people living with HIV in 27 Total Adults Women Children under 15 years 33.2 million [3.6 36.1 million] 3.8 million [28.2 33.6 million] 15.4 million
Global summary of the AIDS epidemic, December 27 Number of people living with HIV in 27 Total Adults Women Children under 15 years 33.2 million [3.6 36.1 million] 3.8 million [28.2 33.6 million] 15.4 million
Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved ISBN
 UNAIDS DATA TABLES 2011 Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved ISBN 978-92-9173-945-5 UNAIDS / JC2225E The designations employed and the presentation of
UNAIDS DATA TABLES 2011 Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved ISBN 978-92-9173-945-5 UNAIDS / JC2225E The designations employed and the presentation of
Fertility and Family Planning in Africa: Call for Greater Equity Consciousness
 Fertility and Family Planning in Africa: Call for Greater Equity Consciousness Eliya Msiyaphazi Zulu President, Union for African Population Studies Director of Research, African Population & Health Research
Fertility and Family Planning in Africa: Call for Greater Equity Consciousness Eliya Msiyaphazi Zulu President, Union for African Population Studies Director of Research, African Population & Health Research
Scaling Up Nutrition Action for Africa
 Scaling Up Nutrition Action for Africa Where are we and what challenges are need to be addressed to accelerate malnutrition? Lawrence Haddad Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition Why should African political
Scaling Up Nutrition Action for Africa Where are we and what challenges are need to be addressed to accelerate malnutrition? Lawrence Haddad Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition Why should African political
COLD CHAIN EQUIPMENT OPTIMISATION PLATFORM (CCEOP)
 COLD CHAIN EQUIPMENT OPTIMISATION PLATFORM (CCEOP) Sushila Maharjan Senior Manager, Innovative Finance International Conference on Sustainable Cooling World Bank Washington DC - 29 November 2018 Reach
COLD CHAIN EQUIPMENT OPTIMISATION PLATFORM (CCEOP) Sushila Maharjan Senior Manager, Innovative Finance International Conference on Sustainable Cooling World Bank Washington DC - 29 November 2018 Reach
Global Fund Results Fact Sheet Mid-2011
 Global Fund Results Fact Sheet Mid-2011 This fact sheet outlines some of the common questions and answers regarding results reported by Global Fund-supported programs, including the principles and approach
Global Fund Results Fact Sheet Mid-2011 This fact sheet outlines some of the common questions and answers regarding results reported by Global Fund-supported programs, including the principles and approach
Financing malaria control
 Chapter 6. Financing malaria control The three major sources of funds for malaria control pro - grammes are national government spending, external assistance from donors and household or private out-of-pocket
Chapter 6. Financing malaria control The three major sources of funds for malaria control pro - grammes are national government spending, external assistance from donors and household or private out-of-pocket
Landscape Analysis on Countries' Readiness to Accelerate Action to Reduce Maternal and Child Undernutrition
 35 th Session of the UN Standing Committee on Nutrition (SCN) Hanoi, 3 6 March 2008 Landscape Analysis on Countries' Readiness to Accelerate Action to Reduce Maternal and Child Undernutrition Jorgen Schlundt
35 th Session of the UN Standing Committee on Nutrition (SCN) Hanoi, 3 6 March 2008 Landscape Analysis on Countries' Readiness to Accelerate Action to Reduce Maternal and Child Undernutrition Jorgen Schlundt
Summary of the Seventh Meeting of the ITFDE (II) January 19, 2005
 Summary of the Seventh Meeting of the ITFDE (II) January 19, 2005 The Seventh Meeting of the International Task Force for Disease Eradication (ITFDE) was convened at The Carter Center from 9:00am to 3:30pm
Summary of the Seventh Meeting of the ITFDE (II) January 19, 2005 The Seventh Meeting of the International Task Force for Disease Eradication (ITFDE) was convened at The Carter Center from 9:00am to 3:30pm
GABON. Neglected tropical disease treatment report profile for mass treatment of NTDs
 GABON Neglected tropical disease treatment report 2017 1 2017 profile for mass treatment of NTDs NEGLECTED TROPICAL DISEASES Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a group of preventable and treatable
GABON Neglected tropical disease treatment report 2017 1 2017 profile for mass treatment of NTDs NEGLECTED TROPICAL DISEASES Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a group of preventable and treatable
O c t o b e r 1 0,
 STUDENT VOICES FROM THE FIELD: WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION GENEVA, SWITZERLAND O c t o b e r 1 0, 2 0 1 6 M o l l y P e z z u l o University at Albany School of Public Health MPH Epidemiology Candidate 17
STUDENT VOICES FROM THE FIELD: WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION GENEVA, SWITZERLAND O c t o b e r 1 0, 2 0 1 6 M o l l y P e z z u l o University at Albany School of Public Health MPH Epidemiology Candidate 17
Comparative Analyses of Adolescent Nutrition Indicators
 Comparative Analyses of Adolescent Nutrition Indicators Rukundo K. Benedict, PhD The DHS Program Stakeholders Consultation on Adolescent Girls Nutrition: Evidence, Guidance, and Gaps October 30 31, 2017
Comparative Analyses of Adolescent Nutrition Indicators Rukundo K. Benedict, PhD The DHS Program Stakeholders Consultation on Adolescent Girls Nutrition: Evidence, Guidance, and Gaps October 30 31, 2017
Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine: Current Supply & Demand Outlook. UNICEF Supply Division
 Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine: Current Supply & Demand Outlook UNICEF Supply Division Update: October 2013 0 Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) Supply & Demand Outlook October 2013 Update Key updates
Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine: Current Supply & Demand Outlook UNICEF Supply Division Update: October 2013 0 Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) Supply & Demand Outlook October 2013 Update Key updates
NTDs Slated for Elimination and Eradication
 NTDs Slated for Elimination and Eradication Institute of Medicine Forum on Microbial Threats The Causes and Impacts of Neglected Tropical and Zoonotic Diseases September 21-22, 2010 Washington, DC Donald
NTDs Slated for Elimination and Eradication Institute of Medicine Forum on Microbial Threats The Causes and Impacts of Neglected Tropical and Zoonotic Diseases September 21-22, 2010 Washington, DC Donald
מדינת ישראל. Tourist Visa Table
 Updated 23/05/2017 מדינת ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. Exe = exempted Req = required Press the first
Updated 23/05/2017 מדינת ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. Exe = exempted Req = required Press the first
ANNEX 3: Country progress indicators
 : progress indicators 541 : COUNTRY PROGRESS INDICATORS 2006 REPORT ON THE GLOBAL AIDS EPIDEMIC Annex 3 : COUNTRY PROGRESS INDICATORS As of March 2006, 115 countries had reported indicators on progress
: progress indicators 541 : COUNTRY PROGRESS INDICATORS 2006 REPORT ON THE GLOBAL AIDS EPIDEMIC Annex 3 : COUNTRY PROGRESS INDICATORS As of March 2006, 115 countries had reported indicators on progress
PROGRESS REPORT ON THE ROAD MAP FOR ACCELERATING THE ATTAINMENT OF THE MILLENNIUM DEVELOPMENT GOALS RELATED TO MATERNAL AND NEWBORN HEALTH IN AFRICA
 5 July 2011 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-first session Yamoussoukro, Côte d Ivoire, 29 August 2 September 2011 Provisional agenda item 17.1 PROGRESS REPORT ON THE ROAD MAP FOR
5 July 2011 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-first session Yamoussoukro, Côte d Ivoire, 29 August 2 September 2011 Provisional agenda item 17.1 PROGRESS REPORT ON THE ROAD MAP FOR
מדינת ישראל. Tourist Visa Table. Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents.
 Updated 25/05/2015 ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. (C) Bearers of official passports requiring tourist
Updated 25/05/2015 ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. (C) Bearers of official passports requiring tourist
Prioritizing Emergency Polio Eradication Activities
 Prioritizing Emergency Polio Eradication Activities Managing the Financing Gap the other half of the Emergency Hamid Jafari GPEI Financing 2012-13: Budget = $2.23 b - Confirmed contributions = $1.14 b
Prioritizing Emergency Polio Eradication Activities Managing the Financing Gap the other half of the Emergency Hamid Jafari GPEI Financing 2012-13: Budget = $2.23 b - Confirmed contributions = $1.14 b
Full list of payments made to projects in 2017
 DfID SAFE Ethiopia Non-SSI IP 3,724,841.06 DfID SAFE Chad Non-SSI IP 1,893,149.00 QEDJT Kenya Implementing Partner Non SSI 1,261,816.00 Inegrated Neglected Tropical Diseases Control 1,171,233.68 DfID SAFE
DfID SAFE Ethiopia Non-SSI IP 3,724,841.06 DfID SAFE Chad Non-SSI IP 1,893,149.00 QEDJT Kenya Implementing Partner Non SSI 1,261,816.00 Inegrated Neglected Tropical Diseases Control 1,171,233.68 DfID SAFE
UPDATE UNAIDS 2016 DATE 2016
 GLOBAL AIDS UP GLOBAL AIDS UPDATE UNAIDS 2016 DATE 2016 ENORMOUS GAINS, PERSISTENT CHALLENGES The world has committed to ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030. How to reach this bold target within the Sustainable
GLOBAL AIDS UP GLOBAL AIDS UPDATE UNAIDS 2016 DATE 2016 ENORMOUS GAINS, PERSISTENT CHALLENGES The world has committed to ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030. How to reach this bold target within the Sustainable
Recipients of development assistance for health
 Chapter 2 Recipients of development assistance for health Both low- and middle-income countries are eligible for development assistance for health (DAH). In addition to income, burden of disease, which
Chapter 2 Recipients of development assistance for health Both low- and middle-income countries are eligible for development assistance for health (DAH). In addition to income, burden of disease, which
Age-Sex Structure for Selected African countries in the early 2000s
 Age-Sex Structure for Selected African countries in the early 2000s Abstract This paper uses data from the recent United Nations population projections to examine the changing age-sex structure in selected
Age-Sex Structure for Selected African countries in the early 2000s Abstract This paper uses data from the recent United Nations population projections to examine the changing age-sex structure in selected
Update on Progress and Challenges in Achieving Measles and Rubella Targets
 Update on Progress and Challenges in Achieving Measles and Rubella Targets SAGE Meeting 6 November 2013 P. Strebel, WHO/IVB/EPI Overview Global progress Regional updates Summary 2 Measles and Rubella Targets
Update on Progress and Challenges in Achieving Measles and Rubella Targets SAGE Meeting 6 November 2013 P. Strebel, WHO/IVB/EPI Overview Global progress Regional updates Summary 2 Measles and Rubella Targets
NO CHILD SHOULD DIE OF DIABETES
 NO CHILD SHOULD DIE OF DIABETES THE PROBLEM There is an estimated 1 million youth under the age of 25 with diabetes in the world. In high income countries, children with diabetes have full access to the
NO CHILD SHOULD DIE OF DIABETES THE PROBLEM There is an estimated 1 million youth under the age of 25 with diabetes in the world. In high income countries, children with diabetes have full access to the
Closing the loop: translating evidence into enhanced strategies to reduce maternal mortality
 Closing the loop: translating evidence into enhanced strategies to reduce maternal mortality Washington DC March 12th 2008 Professor Wendy J Graham Opinion-based decisionmaking Evidence-based decision-making
Closing the loop: translating evidence into enhanced strategies to reduce maternal mortality Washington DC March 12th 2008 Professor Wendy J Graham Opinion-based decisionmaking Evidence-based decision-making
Tipping the dependency
 BREAKING NEWS Meeting the investment challenge Tipping the dependency balance Domestic investments exceed international investments total reaching US$ 8.6 billion. 40 countries fund more than 70% of their
BREAKING NEWS Meeting the investment challenge Tipping the dependency balance Domestic investments exceed international investments total reaching US$ 8.6 billion. 40 countries fund more than 70% of their
Aboubacar Kampo Chief of Health UNICEF Nigeria
 Aboubacar Kampo Chief of Health UNICEF Nigeria Many thanks to UNICEF colleagues in Supply Division-Copenhagen and NY for contributing to this presentation Thirty-five countries are responsible for 98%
Aboubacar Kampo Chief of Health UNICEF Nigeria Many thanks to UNICEF colleagues in Supply Division-Copenhagen and NY for contributing to this presentation Thirty-five countries are responsible for 98%
Progress Towards the Child Mortality MDG in Urban Sub-Saharan Africa. Nyovani Janet Madise University of Southampton
 Progress Towards the Child Mortality MDG in Urban Sub-Saharan Africa Nyovani Janet Madise University of Southampton United Nations Expert group Meeting on Population Distribution, Urbanization, Internal
Progress Towards the Child Mortality MDG in Urban Sub-Saharan Africa Nyovani Janet Madise University of Southampton United Nations Expert group Meeting on Population Distribution, Urbanization, Internal
BCG. and your baby. Immunisation. Protecting babies against TB. the safest way to protect your child
 BCG and your baby Protecting babies against TB Immunisation the safest way to protect your child This leaflet is about the BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guerin) vaccination that is being offered to protect your
BCG and your baby Protecting babies against TB Immunisation the safest way to protect your child This leaflet is about the BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guerin) vaccination that is being offered to protect your
Global Fund ARV Fact Sheet 1 st June, 2009
 Global Fund ARV Fact Sheet 1 st June, 2009 This fact sheet outlines the principles and approach in determining the number of people on antiretroviral drugs (ARVs) for HIV/AIDS treatment, with a breakdown
Global Fund ARV Fact Sheet 1 st June, 2009 This fact sheet outlines the principles and approach in determining the number of people on antiretroviral drugs (ARVs) for HIV/AIDS treatment, with a breakdown
FEMALE GENITAL MUTILATION/CUTTING: What might the future hold?
 FEMALE GENITAL MUTILATION/CUTTING: What might the future hold? UNICEF/NYHQ213-42/Asselin The mutilation or cutting of female genitals, also known as FGM/C, has been practised for centuries among population
FEMALE GENITAL MUTILATION/CUTTING: What might the future hold? UNICEF/NYHQ213-42/Asselin The mutilation or cutting of female genitals, also known as FGM/C, has been practised for centuries among population
IX. IMPROVING MATERNAL HEALTH: THE NEED TO FOCUS ON REACHING THE POOR. Eduard Bos The World Bank
 IX. IMPROVING MATERNAL HEALTH: THE NEED TO FOCUS ON REACHING THE POOR Eduard Bos The World Bank A. INTRODUCTION This paper discusses the relevance of the ICPD Programme of Action for the attainment of
IX. IMPROVING MATERNAL HEALTH: THE NEED TO FOCUS ON REACHING THE POOR Eduard Bos The World Bank A. INTRODUCTION This paper discusses the relevance of the ICPD Programme of Action for the attainment of
POLIO ERADICATION IN THE AFRICAN REGION: PROGRESS REPORT. Information document EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 7 July 2006 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-sixth session Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 28 August 1 September 2006 Provisional agenda item 10.1 POLIO ERADICATION IN THE AFRICAN REGION: PROGRESS
7 July 2006 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-sixth session Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 28 August 1 September 2006 Provisional agenda item 10.1 POLIO ERADICATION IN THE AFRICAN REGION: PROGRESS
Sexual and reproductive health care: A comparison of providers and delivery points between the African Region and other regions
 Core competencies in primary care: Supplement 2 Sexual and reproductive health care: A comparison of providers and delivery points between the African Region and other regions The Core competencies in
Core competencies in primary care: Supplement 2 Sexual and reproductive health care: A comparison of providers and delivery points between the African Region and other regions The Core competencies in
Expert Group Meeting on Strategies for Creating Urban Youth Employment: Solutions for Urban Youth in Africa
 Expert Group Meeting on Strategies for Creating Urban Youth Employment: Solutions for Urban Youth in Africa Measurement/indicators of youth employment Gora Mboup Global Urban Observatory (GUO) UN-HABITAT
Expert Group Meeting on Strategies for Creating Urban Youth Employment: Solutions for Urban Youth in Africa Measurement/indicators of youth employment Gora Mboup Global Urban Observatory (GUO) UN-HABITAT
Addressing climate change driven health challenges in Africa
 Addressing climate change driven health challenges in Africa Ednah N Ototo, Parasitologist, Climate Change and Health Kenyatta University, Kenya Kenya Medical Research Institute Outline The impact of climate
Addressing climate change driven health challenges in Africa Ednah N Ototo, Parasitologist, Climate Change and Health Kenyatta University, Kenya Kenya Medical Research Institute Outline The impact of climate
PROGRESS REPORT ON CHILD SURVIVAL: A STRATEGY FOR THE AFRICAN REGION. Information Document CONTENTS
 29 June 2009 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-ninth session Kigali, Republic of Rwanda, 31 August 4 September 2009 Provisional agenda item 9.2 PROGRESS REPORT ON CHILD SURVIVAL: A
29 June 2009 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-ninth session Kigali, Republic of Rwanda, 31 August 4 September 2009 Provisional agenda item 9.2 PROGRESS REPORT ON CHILD SURVIVAL: A
Impact Dashboard - August 2014
 Impact Dashboard - By, PSI and its network members averted an estimated 29.7 million DALYs globally. PSI has met 53.3% of the strategic plan (SP) target to avert 198.7 million DALYs, and 53.0% of the SP
Impact Dashboard - By, PSI and its network members averted an estimated 29.7 million DALYs globally. PSI has met 53.3% of the strategic plan (SP) target to avert 198.7 million DALYs, and 53.0% of the SP
Social economic development in the prevention of global blindness
 Br J Ophthalmol 2;85:653 657 653 Tufts University, School of Medicine, Boston, MA, USA VHHo University of California at Davis, School of Medicine, Sacramento, CA, USA I R Schwab Correspondence to: Ivan
Br J Ophthalmol 2;85:653 657 653 Tufts University, School of Medicine, Boston, MA, USA VHHo University of California at Davis, School of Medicine, Sacramento, CA, USA I R Schwab Correspondence to: Ivan
ADMINISTRATIVE AND FINANCIAL MATTERS. Note by the Executive Secretary * CONTENTS. Explanatory notes Tables. 1. Core budget
 UNITED NATIONS Distr. GENERAL 13 October 1997 ENGLISH ONLY SUBSIDIARY BODY FOR IMPLEMENTATION Seventh session Bonn, 20-29 October 1997 Item 9 of the provisional agenda ADMINISTRATIVE AND FINANCIAL MATTERS
UNITED NATIONS Distr. GENERAL 13 October 1997 ENGLISH ONLY SUBSIDIARY BODY FOR IMPLEMENTATION Seventh session Bonn, 20-29 October 1997 Item 9 of the provisional agenda ADMINISTRATIVE AND FINANCIAL MATTERS
Global Polio Eradication Initiative
 Global Polio Eradication Initiative Financial resource requirements 2005 to 2008 as of April 2005 WHO Partners in the Global Polio Eradication Initiative World Health Organization 2005 All rights reserved.
Global Polio Eradication Initiative Financial resource requirements 2005 to 2008 as of April 2005 WHO Partners in the Global Polio Eradication Initiative World Health Organization 2005 All rights reserved.
Trends in leprosy case detection worldwide since 1985
 Lepr Rev (2004) 75, 19±33 Trends in leprosy case detection worldwide since 1985 ABRAHAM MEIMA, JAN H. RICHARDUS & J. DIK F. HABBEMA Department of Public Health, Erasmus MC, University Medical Center Rotterdam,
Lepr Rev (2004) 75, 19±33 Trends in leprosy case detection worldwide since 1985 ABRAHAM MEIMA, JAN H. RICHARDUS & J. DIK F. HABBEMA Department of Public Health, Erasmus MC, University Medical Center Rotterdam,
Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved
 UNAIDS DATA TABLES 2011 Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved UNAIDS / JC2225E The designations employed and the presentation of the material in this publication
UNAIDS DATA TABLES 2011 Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved UNAIDS / JC2225E The designations employed and the presentation of the material in this publication
Seizures of ATS (excluding ecstasy ), 2010
 Seizures of ATS (excluding ecstasy ), 2010 (countries and territories reporting seizures* of more than 10 kg) 9 5.1 8.7 12.9 Ghana Armenia 0.7 9.9 1 2.1 Syrian Arab Republic Korea (Republic of) Iraq Islamic
Seizures of ATS (excluding ecstasy ), 2010 (countries and territories reporting seizures* of more than 10 kg) 9 5.1 8.7 12.9 Ghana Armenia 0.7 9.9 1 2.1 Syrian Arab Republic Korea (Republic of) Iraq Islamic
Expert Group Meeting on the Regional Report for the African Gender and Development Index
 Expert Group Meeting on the Regional Report for the African Gender and Development Index 9-10 October 2017 United Nations Conference Centre, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia Aide Memoire July 2017 I. Background and
Expert Group Meeting on the Regional Report for the African Gender and Development Index 9-10 October 2017 United Nations Conference Centre, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia Aide Memoire July 2017 I. Background and
Hearing loss in persons 65 years and older based on WHO global estimates on prevalence of hearing loss
 Hearing loss in persons 65 years and older based on WHO global estimates on prevalence of hearing loss Mortality and Burden of Diseases and Prevention of Blindness and Deafness WHO, 2012 In 2012, WHO released
Hearing loss in persons 65 years and older based on WHO global estimates on prevalence of hearing loss Mortality and Burden of Diseases and Prevention of Blindness and Deafness WHO, 2012 In 2012, WHO released
HIV and Harm Reduction in Prisons
 HIV and Harm Reduction in Prisons School of Public Health and Community Medicine Professor Kate Dolan Program of International Research and Training National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre UNSW, Sydney,
HIV and Harm Reduction in Prisons School of Public Health and Community Medicine Professor Kate Dolan Program of International Research and Training National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre UNSW, Sydney,
Maternal Deaths Disproportionately High in Developing Countries
 EMBARGOED until Monday, 20 October, 6am GMT HQ/2003/24 20 October 2003 CF/DOC/PR/2003-82 Maternal Deaths Disproportionately High in Developing Countries African women are 175 times more likely to die in
EMBARGOED until Monday, 20 October, 6am GMT HQ/2003/24 20 October 2003 CF/DOC/PR/2003-82 Maternal Deaths Disproportionately High in Developing Countries African women are 175 times more likely to die in
Impact Dashboard - October 2014
 Impact Dashboard - 2014 By 2014, PSI and its network members averted an estimated 44.2 million DALYs globally. PSI has met 60.6% of the strategic plan (SP) target to avert 198.7 million DALYs, and 56.4%
Impact Dashboard - 2014 By 2014, PSI and its network members averted an estimated 44.2 million DALYs globally. PSI has met 60.6% of the strategic plan (SP) target to avert 198.7 million DALYs, and 56.4%
Comments on this bulletin are welcome. Please to Dr. Mary Agócs
 Global Invasive Bacterial Vaccine Preventable Diseases (IB-VPD) Information and Surveillance Bulletin Reporting Period: January through December 2010 Volume 4: October 2011 The World Health Organization
Global Invasive Bacterial Vaccine Preventable Diseases (IB-VPD) Information and Surveillance Bulletin Reporting Period: January through December 2010 Volume 4: October 2011 The World Health Organization
Excellence and Originality from Necessity: Palliative Care in Africa. Dr Emmanuel Luyirika Executive Director, African Palliative Care Association
 Excellence and Originality from Necessity: Palliative Care in Africa Dr Emmanuel Luyirika Executive Director, African Palliative Care Association Summary of the presentation 1. Introduction 2. Background
Excellence and Originality from Necessity: Palliative Care in Africa Dr Emmanuel Luyirika Executive Director, African Palliative Care Association Summary of the presentation 1. Introduction 2. Background
Analysis of Immunization Financing Indicators from the WHO-UNICEF Joint Reporting Form (JRF),
 Analysis of Immunization Financing Indicators from the WHO-UNICEF Joint Reporting Form (JRF), 2008-2010 Claudio Politi and Oumar Sagna Department of Immunization Vaccines and Biologicals, World Health
Analysis of Immunization Financing Indicators from the WHO-UNICEF Joint Reporting Form (JRF), 2008-2010 Claudio Politi and Oumar Sagna Department of Immunization Vaccines and Biologicals, World Health
Undiscovered progress in. in maternal mortality.
 CHAPTER 1 Undiscovered progress in maternal mortality During the early 1980s, a half-million women died every year during pregnancy, childbirth, or the postpartum period a stunning figure in a world that
CHAPTER 1 Undiscovered progress in maternal mortality During the early 1980s, a half-million women died every year during pregnancy, childbirth, or the postpartum period a stunning figure in a world that
WHO report highlights violence against women as a global health problem of epidemic proportions
 News release WHO/16 20 June 2013 EMBARGO: PLEASE DO NOT DISTRIBUTE OR PUBLISH BEFORE THURSDAY 20 JUNE 2013 AT 15H00 GENEVA TIME, 14H00 LONDON TIME, 13H00 GMT, AND 09H00 EST WHO report highlights violence
News release WHO/16 20 June 2013 EMBARGO: PLEASE DO NOT DISTRIBUTE OR PUBLISH BEFORE THURSDAY 20 JUNE 2013 AT 15H00 GENEVA TIME, 14H00 LONDON TIME, 13H00 GMT, AND 09H00 EST WHO report highlights violence
Regional Consultation on Nutrition and HIV/AIDS in French Speaking Countries in Africa Region
 Regional Consultation on Nutrition and HIV/AIDS in French Speaking Countries in Africa Region Evidence, lessons and recommendations for action Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso 17-20 November 2008 CONCEPT PAPER
Regional Consultation on Nutrition and HIV/AIDS in French Speaking Countries in Africa Region Evidence, lessons and recommendations for action Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso 17-20 November 2008 CONCEPT PAPER
Global Measles and Rubella Update. April 2018
 Global Measles and Rubella Update April 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct
Global Measles and Rubella Update April 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct
Foot-and-Mouth Disease Situation Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Monthly Report
 Foot-and-Mouth Disease Situation Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Monthly Report October 2013 I N F O R M A T I O N S O U R C E S U S E D: Databases: OIE WAHID World Animal Health
Foot-and-Mouth Disease Situation Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Monthly Report October 2013 I N F O R M A T I O N S O U R C E S U S E D: Databases: OIE WAHID World Animal Health
The Promise of Introducing Rubella Containing Vaccines on the Impact of Rubella and Measles Control
 The Promise of Introducing Rubella Containing Vaccines on the Impact of Rubella and Measles Control GAVI Partners Forum 4 6 December 2012, Dar es Salaam, Tanzania Maya van den Ent, MPH, UNICEF Peter Strebel,
The Promise of Introducing Rubella Containing Vaccines on the Impact of Rubella and Measles Control GAVI Partners Forum 4 6 December 2012, Dar es Salaam, Tanzania Maya van den Ent, MPH, UNICEF Peter Strebel,
Donor Support for Contraceptives and Condoms for STI/HIV Prevention
 Donor Support for Contraceptives and Condoms for STI/HIV Prevention 2001 Donor Support for Contraceptives and Condoms for STI/HIV Prevention 2001 Table of Contents List of Abbreviations and Acronyms List
Donor Support for Contraceptives and Condoms for STI/HIV Prevention 2001 Donor Support for Contraceptives and Condoms for STI/HIV Prevention 2001 Table of Contents List of Abbreviations and Acronyms List
Global malaria mortality between 1980 and 2010: a systematic analysis
 Global malaria mortality between 1980 and 2010: a systematic analysis Christopher J L Murray, Lisa C Rosenfeld, Stephen S Lim, Kathryn G Andrews, Kyle J Foreman, Diana Haring, Nancy Fullman, Mohsen Naghavi,
Global malaria mortality between 1980 and 2010: a systematic analysis Christopher J L Murray, Lisa C Rosenfeld, Stephen S Lim, Kathryn G Andrews, Kyle J Foreman, Diana Haring, Nancy Fullman, Mohsen Naghavi,
Using routine data to estimate numbers of women with female genital mutilation / cutting in European countries
 Using routine data to estimate numbers of women with female genital mutilation / cutting in European countries Alison Macfarlane Division of Midwifery and Radiography, City University London Efua Dorkenoo
Using routine data to estimate numbers of women with female genital mutilation / cutting in European countries Alison Macfarlane Division of Midwifery and Radiography, City University London Efua Dorkenoo
SGCEP SCIE 1121 Environmental Science Spring 2012 Section Steve Thompson:
 SGCEP SCIE 1121 Environmental Science Spring 2012 Section 20531 Steve Thompson: steventhompson@sgc.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net/ 1 First, a brief diversion... Into... how to do better on the next exam,
SGCEP SCIE 1121 Environmental Science Spring 2012 Section 20531 Steve Thompson: steventhompson@sgc.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net/ 1 First, a brief diversion... Into... how to do better on the next exam,
Children in Africa. Key statistics on child survival, protection and development
 Children in Key statistics on child survival, protection and development Key Statistics In, mortality rates among children under five decreased by 48 per cent between 199 and 13, but still half of the
Children in Key statistics on child survival, protection and development Key Statistics In, mortality rates among children under five decreased by 48 per cent between 199 and 13, but still half of the
This portion to be completed by the student Return by July 1 Please use ballpoint pen
 This portion to be completed by the student Return by July 1 Please use ballpoint pen Start term: Fall Exploration Spring Summer Year: Class year: Freshman Sophomore Junior Senior Transfer Full name: Preferred:
This portion to be completed by the student Return by July 1 Please use ballpoint pen Start term: Fall Exploration Spring Summer Year: Class year: Freshman Sophomore Junior Senior Transfer Full name: Preferred:
Rotavirus Vaccine: Supply & Demand Update. UNICEF Supply Division
 Rotavirus Vaccine: & Demand Update UNICEF Division July 0 Rotavirus Vaccine (RV): & Demand Update July This update provides new information on countries and their scheduled RV introductions, forecasted
Rotavirus Vaccine: & Demand Update UNICEF Division July 0 Rotavirus Vaccine (RV): & Demand Update July This update provides new information on countries and their scheduled RV introductions, forecasted
HIBA ABDALRAHIM Capsca Focal Point Public Health Authority
 HIBA ABDALRAHIM Capsca Focal Point Public Health Authority Introduction Definition Symptom Transmission Global situation Local situation Control Content Introduction Yellow fever (YF) is a mosquito-borne
HIBA ABDALRAHIM Capsca Focal Point Public Health Authority Introduction Definition Symptom Transmission Global situation Local situation Control Content Introduction Yellow fever (YF) is a mosquito-borne
JOINT TB AND HIV PROGRAMMING
 JOINT TB AND HIV PROGRAMMING Haileyesus Getahun, WHO. On behalf of the Global Fund Interagency TB and HIV Working Group (Global Fund, PEPFAR, Stop TB Partnership, UNAIDS, WHO) I was admitted in a hospital
JOINT TB AND HIV PROGRAMMING Haileyesus Getahun, WHO. On behalf of the Global Fund Interagency TB and HIV Working Group (Global Fund, PEPFAR, Stop TB Partnership, UNAIDS, WHO) I was admitted in a hospital
World Health Organization Department of Communicable Disease Surveillance and Response
 WHO/CDS/CSR/ISR/2000.1 WHO Report on Global Surveillance of Epidemic-prone Infectious Diseases World Health Organization Department of Communicable Disease Surveillance and Response This document has been
WHO/CDS/CSR/ISR/2000.1 WHO Report on Global Surveillance of Epidemic-prone Infectious Diseases World Health Organization Department of Communicable Disease Surveillance and Response This document has been
1. Consent for Treatment This form must be completed in order to receive healthcare services in the campus clinic.
 HEALTH & WELLNESS SERVICES INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING THE REQUIRED MEDICAL FORMS FOR: U.S. CITIZENS 18 YEARS OF AGE OR OLDER AT THE TIME THE FORMS ARE COMPLETED. THIS REQUIREMENT MUST BE COMPLETED WHETHER:
HEALTH & WELLNESS SERVICES INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING THE REQUIRED MEDICAL FORMS FOR: U.S. CITIZENS 18 YEARS OF AGE OR OLDER AT THE TIME THE FORMS ARE COMPLETED. THIS REQUIREMENT MUST BE COMPLETED WHETHER:
CDC ASSESSMENT OF RISKS TO THE GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE (GPEI) STRATEGIC PLAN
 CDC ASSESSMENT OF RISKS TO THE GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE (GPEI) STRATEGIC PLAN 2010-2012 14 Sept-10 2010 First and Second Quarters (January June) Geographic distribution of wild poliovirus (WPV)
CDC ASSESSMENT OF RISKS TO THE GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE (GPEI) STRATEGIC PLAN 2010-2012 14 Sept-10 2010 First and Second Quarters (January June) Geographic distribution of wild poliovirus (WPV)
Module 2. NTD Strategies
 (MMDP) Trichiasis Caused by infection with a bacterium, Chlamydia trachomatis. Starts in childhood, with repeated episodes of infection. Repeated infections inflammation and scarring of the conjunctiva
(MMDP) Trichiasis Caused by infection with a bacterium, Chlamydia trachomatis. Starts in childhood, with repeated episodes of infection. Repeated infections inflammation and scarring of the conjunctiva
Lessons learned from the IeDEA West Africa Collaboration
 Lessons learned from the IeDEA West Africa Collaboration François DABIS with the contribution of Didier Koumavi EKOUEVI INSERM U-897, Bordeaux, France, Programme PACCI, ANRS site, Abidjan, Côte d Ivoire
Lessons learned from the IeDEA West Africa Collaboration François DABIS with the contribution of Didier Koumavi EKOUEVI INSERM U-897, Bordeaux, France, Programme PACCI, ANRS site, Abidjan, Côte d Ivoire
Mathematical modelling approach to estimating TB burden in children Pete Dodd (University of Sheffield) & James Seddon (Imperial College London)
 Mathematical modelling approach to estimating TB burden in children Pete Dodd (University of Sheffield) & (Imperial College London) Wednesday, 1 April 215 Health Economics & Decision Science School of
Mathematical modelling approach to estimating TB burden in children Pete Dodd (University of Sheffield) & (Imperial College London) Wednesday, 1 April 215 Health Economics & Decision Science School of
D TA companion & Scorecard. to the UNICEF Gender Action Plan. May 2016
 D TA companion & Scorecard to the UNICEF Gender Action Plan May 216 Selected indicators from the UNICEF Strategic Plan 214 217 Prepared by Data, Research and Policy United Nations Children s Fund 3 United
D TA companion & Scorecard to the UNICEF Gender Action Plan May 216 Selected indicators from the UNICEF Strategic Plan 214 217 Prepared by Data, Research and Policy United Nations Children s Fund 3 United
511,000 (57% new cases) ~50,000 ~30,000
 Latest global TB estimates - 2007 (Updated Mar 2009) All forms of TB Greatest number of cases in Asia; greatest rates per capita in Africa Multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) Estimated number of cases 9.27
Latest global TB estimates - 2007 (Updated Mar 2009) All forms of TB Greatest number of cases in Asia; greatest rates per capita in Africa Multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) Estimated number of cases 9.27
WHO Global Task Force on TB Impact Measurement An overview
 WHO Global Task Force on TB Impact Measurement An overview Katherine Floyd (WHO/GTB/TME) 3 rd meeting of the TB estimates subgroup Glion-sur-Montreux, 31March 2 April 2015 GLOBAL TB PROGRAMME 1. Broad
WHO Global Task Force on TB Impact Measurement An overview Katherine Floyd (WHO/GTB/TME) 3 rd meeting of the TB estimates subgroup Glion-sur-Montreux, 31March 2 April 2015 GLOBAL TB PROGRAMME 1. Broad
Sourcing of ARVs & HIV diagnostics. Procurement for Impact P4i
 Sourcing of ARVs & HIV diagnostics Procurement for Impact P4i AMDS ANNUAL STAKEHOLDERS AND PARTNERS MEETING 29 September 2014 Global Fund: Procurement for Impact: P4i Our objective was straightforward:
Sourcing of ARVs & HIV diagnostics Procurement for Impact P4i AMDS ANNUAL STAKEHOLDERS AND PARTNERS MEETING 29 September 2014 Global Fund: Procurement for Impact: P4i Our objective was straightforward:
Access to reproductive health care global significance and conceptual challenges
 08_XXX_MM1 Access to reproductive health care global significance and conceptual challenges Dr Lale Say World Health Organization Department of Reproductive Health and Research From Research to Practice:
08_XXX_MM1 Access to reproductive health care global significance and conceptual challenges Dr Lale Say World Health Organization Department of Reproductive Health and Research From Research to Practice:
MEASLES ELIMINATION BY 2020: A STRATEGY FOR THE AFRICAN REGION. Report of the Secretariat. Executive Summary
 16 June 2011 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-first session Yamoussoukro, Côte d Ivoire, 29 August 2 September 2011 Provisional agenda item 13 MEASLES ELIMINATION BY 2020: A STRATEGY
16 June 2011 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-first session Yamoussoukro, Côte d Ivoire, 29 August 2 September 2011 Provisional agenda item 13 MEASLES ELIMINATION BY 2020: A STRATEGY
