catecholamines (CA) such as noradrenaline
|
|
|
- Dustin Parks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Localization of beta receptors in the anterior segment of the rat eye by a fluorescent analogue of propranolol M. Lahav,* E. Melamed,** Z. Dafna,* and D. Atlas*** A fluorescent analogue of propranolol, 9-AAP, was injected intravenously in order to detect beta-adrenergic receptors in the anterior segment of the albino rat eye. Specific 9-AAP fluorescence was noted along cell membranes of the ciliary epithelium and to a lesser extent in the walls of blood vessels in the ciliary processes and episclera at the limbus. The iris showed maximum 9-AAP binding in the region of the sphincter muscle. These data suggest that 9-AAP may label beta receptors in the anterior segment of the rat eye. Key words: 9-amino-acridin-propranolol, fluorescent betablocker, beta receptors, anterior segment catecholamines (CA) such as noradrenaline have been shown to be present in the iris, ciliary body, and the aqueous drainage channels of various animal species. i It is known that the effect of CA on postsynaptic membranes is mediated in part by betaadrenergic receptors. The latter have been shown to be present in the ciliary body, iris, and possibly in the episcleral drainage channels by indirect physiological and pharmacological methods. 2 " 5 We have recently developed a direct in vivo histochemical method for the detection From the *Ophthalmic Pathology Laboratory and "^Department of Neurology, Hadassah University Hospital and Hebrew University-Hadassah Medical School, and ***Department of Biological Chemistry, Hebrew University, Jerusalem, Israel. This work was supported in part by a grant from the Israel Cancer Association and Herbert Lotman, Philadelphia, Pa. Submitted for publication July 21, Reprint requests: Moshe Lahav, M.D., Ophthalmic Pathology Laboratory, Hadassah Hospital, P.O.B. 499, Jerusalem, Israel. of beta receptors in various tissues by the use of 9-amino-acridin-propranolol (9-AAP). 6 ~ 8 This potent fluorescent beta-adrenergic blocker was used in the present study in an attempt to detect beta-adrenergic receptors in the anterior segment of the rat eye. Methods 9-AAP, a fluorescent analogue of propranolol (N-[-2-hydroxy-3-naphthoxy propyl]-n-[-9-ainino acridin] isopropyl diamine) was used in this study. It has been known to inhibit competitively the /-epinephrine-dependent adenylate cyclase activity in turkey erythrocyte membranes, without affecting the fluoride-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity. In addition, 9-AAP inhibits in a competitive and stereospecific manner the binding of ( I25 I)-hydroxybenzylpindolol to these beta-adrenergic receptors. 9 9-AAP, when injected into rats, has been shown previously to label specifically beta-adrenergic receptors in the rat central nervous system as well as in other organs. 9-AAP in saline, 2.5 mg/100 gm body weight, was injected into the tail vein of 27 albino rats (200 to 220 gm). Controls included (1) five noninjected animals, to rule out autofluorescence, (2) two ani /78/ $00.70/ Assoc. for Res. in Vis. and Ophthal., Inc. 645
2 646 Lahav et al. Invest. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci. July 1978 Fig. 1, Fluorescent photomicrograph of the ciliary body (CB) and limbal regions of rat treated by 9-AAP. Note fluorescence in the episclera! vessels (two arrows) and ciliary body (one arrow). The filtration region (F) is devoid of fluorescence except for a striplike artefact which lies internal to Descemet's membrane. Nonfluorescent cornea (C) and (I) and autofluorescent retinal pigment epithelium (PE) are seen. (Frozen section; xl20.) mals treated by the fluorescent dye 9- amino-acridin alone, and (3) groups of five animals pretreated with one of the following compounds: (±)-propranolol, ( )-propranolol, or (+)-propranolol (5 mg/100 gm in saline by slow intravenous injection). 9-AAP {2.5 mg/100 gm) was administered to each of the pretreated animals 30 min later. All the animals were killed by decapitation under light ether anesthesia 30 min after in jection of 9-AAP. The eyes of all animals were quickly removed and frozen in liquid nitrogen. Later, 10 fx pupil-optic nerve sections were cut on a cryostat at 20. The frozen sections were mounted on glass slides and air-dried. Sodium phosphate buffer 0.08M, ph 7.5, was applied, and coverslips were placed in position. The sections were observed under phase-contrast and transmitted ultraviolet illumination on a Zeiss Universal fluorescent microscope with HBO 200-W superpressure mercury lamp, exciter filter BG-12, and barrier filter 53. Alternate sections were formalin-fixed, stained by hematoxylin and eosin, and observed under the light microscope. Results Accumulations of fluorescent 9-AAP binding sites were seen in the ciliary body, iris, and episcleral tissue at the limbus (Fig. 1). Almost no fluorescence was noted at the ciliary body base in a region corresponding to the ciliary muscle. Few fluorescent dots were present in the stroma of the iris processes, most probably on endothelial cells of the ciliary vessels (Fig. 2, A and B). The ciliary epithelium showed diffuse membrane fluorescence. The resolution of the sections did not permit localization of the fluorescence to one of the two epithelial layers of the ciliary body. However, it was our impression that the fluorescence was more extensive at the outer ciliary epithelial layer, which corresponds to the pigmented ciliary epithelium (Fig. 2, A and B). In the iris, diffuse fluorescence could be seen exclusively in the region of the sphincter muscle (Fig. 3). Fluores-
3 Volume 17 Number 7 Beta receptors of rat anterior segment 647 Fig. 2. A, Ciliary body after injection with 9-AAP. Note diffuse fluorescence of the epithelial cells. Few fluorescent dots which may correspond to regions of stromal blood vessels are seen (arrows). The iris base (I) is devoid of fluorescence. Fluorescent dots are seen in the episclera (ES) as well. (Frozen section; X160.) B, Section through the ciliary body of another animal treated by 9-AAP. The arrows indicate fainter fluorescence on the cell membranes of the inner epithelial layer. The termination of the autofluo re scent pigment epithelial layer is seen (PE). (Frozen section; X120.)
4 648 Lahav et al. Invest. Ophthalmot. Visual Sci. July 1978 Fig. 3. Folded sphincter region of the iris (S) is seen in two focal planes in apposition to Descemet's membrane (D). Note diffuse fluorescence in the sphincter region in contrast to other regions of the iris (I). (Frozen section; xl60.) Fig. 4. Normal ciliary body (CB) and iris (7,) of a rat. {Frozen section; hematoxylin-eosin stain; X16.)
5 Volume 17 Number 7 Beta receptors of rat anterior segment 649 Fig. 5. Ciliary body (CB) and iris (I) of a rat pretreated by {±)-propranolol. Except for mild haze over the ciliary body, no specific 9-AAP fluorescence is seen. (Frozen section; x40.) cence was noted in the walls of blood vessels in the episcleral tissue over the ciliary body (Figs. 1 and 2, A). The filtration area was devoid of fluorescence in most of the sections. Autofluorescent cells were rarely seen in untreated control animals. When present, they could be differentiated from the 9-AAP labeled fluorescent cells, by their orange fluorescence. Fluorescence was practically absent in sections from control animals treated by 9-amino-acridin alone or pretreated with (±)-propranolol and ( )- propranolol (Fig. 5). In sections from control animals pretreated with (+)-propranolol, the distribution pattern of fluorescence was similar to that observed in animals which were treated by 9-AAP alone, though reduced in intensity. Discussion The binding of 9-AAP to beta-receptor sites in the rat eye seems to be a specific one for several reasons. This substance exhibits marked affinity for beta-ad re nergic receptors when studied in vitro in a beta-receptordependent adenylate cyclase system. Similarly, it inhibits in a competitive manner the binding of ( 125 I)-hydroxybenzylpindolol to these beta receptors. 9 In addition, the appearance of the fluorescence in vivo can be blocked in a stereospecific fashion by prior injection of the biologically active beta antagonists (±) or ( )-propranolol but not with (+)-. 6 Furthermore, the binding of 9-AAP in other organs such as the cerebellum, cerebral cortex, heart, and kidney is distinctly localized to areas where the presence of beta receptors was indicated by other indirect methods. 6 " 8 Studies in experimental animals which used histochemical fluorescence techniques demonstrated extensive networks of presynaptic noradrenaline-containing fibers in the episcleral tissue, trabecular meshwork, ciliary body vessels, and iris. l0 ~ 15 In addition, electron microscopic studies have shown dense-cored vesicles in synaptic terminals within these regions. 16 " 22 In the present study, 9-AAP binding sites were observed in the ciliary epithelium, iris sphincter, episcleral vessels, and some of the ciliary vessels of the rat. We suggest that the latter may
6 650 Lahav et al. Invest. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci. July 1978 correspond to beta receptor sites in the anterior segment of the rat eye. In the iris, most of the adrenergic fibers are seen in the dilator area; however, these are present as well in the region of the sphincter muscle. 10 " 12 Complementary betareceptor sites were identified in this region and are probably related to the inhibitory effect of beta-active substances on this muscle. 2 In the ciliary body few adrenergic fibers were reported to be present in the muscle fibers. 10 " 13 Most of the adrenergic fibers are present as adrenergic sheaths around blood vessels. Adrenergic varicosities were observed in the blood vessels of the ciliary processes and under the ciliary epithelium. These fibers were never noted to cross the epithelial basement membrane. 10 " 15 The presynaptic distribution of CA within the ciliary body of various species parallels the distribution of postsynaptic beta-receptor sites labeled by 9-AAP. These were seen along the cell membranes of the ciliary epithelium and to some extent in the blood vessels of the ciliary processes but were almost nonexistent in the ciliary muscle. Therefore the findings in the present study seem to be complementary to the information which is available concerning the distribution of CA in the anterior segment of the eye. Extensive pharmacological and physiological experiments indicate that adrenergic drugs have a complex effect on the eye, with considerable species variations. It is generally agreed, however, that both alpha and beta receptors are involved in the regulation of the intraocular pressure. For instance, the net effect of epinephrine, a substance with both alpha and beta activities, is reduction of the intraocular pressure. 23 The mechanism of its action probably varies with the species of mammals which were investigated. Adrenergic agonists may act on various sites in the anterior segment of the eye, such as on the ciliary vessels, the secretory ciliary epithelium, the trabecular meshwork, and the aqueous drainage channels. 24 " 30 In the rat, 9-AAP binding sites were observed on the ciliary epithelium, the episcleral vessels, and probably on blood vessels of the ciliary processes. We could not, however, identify fluorescent sites in the filtration area. Although pharmacological studies on the rat are not available, the localization of 9-AAP bind - ing sites in these regions seems to support previous results in other species, which claim that beta-adrenergic agonists act mainly on the secretion of aqueous humor and to a lesser extent on the outflow mechanism. 22 ' 24 ~ 28 The distribution of beta receptors in at least three locations in the anterior segment of the rat's eye may provide a partial explanation for the multifaceted effects of beta agonists and beta antagonists 31 " 33 on the intraocular pressure. Further use of 9-AAP in other species may yield additional information on the CA-beta receptor system in the eye. Mr. A. Itzhak provided helpful technical assistance. REFERENCES 1. Laties, A. M.: Specific neurohistology comes of age. A look back and a look forward, INVEST. OPHTHAL- MOL. 11:555, Van Alphen, G. W. H. M., Kern, R., and Robinette, S. L.: Adrenergic receptors of the intraocular muscles, Arch. Ophthalmol. 74:253, Sears, M. L.: The mechanisms of action of adrenergic drugs in glaucoma, INVEST. OPHTHAMOL. 5:115, Langham, M. E., and Diggs, E.: Beta adrenergic responses in the eyes of rabbits, primates and man, Exp. Eye Res. 19:281, Langham, M. E., and Krieglstein, G. K.: The biphasic intraocular pressure response of rabbits to epinephrine, INVEST. OPHTHALMOL. 15:119, Melamed, E., Lahav, M., and Atlas, D.: Direct localization of beta adrenoceptors in the rat cerebellum by a new fluorescent analogue of propranolol, Nature 261:420, Atlas, D., Melamed, E., and Lahav, M.: j8-adrenergic receptors in rat kidney: direct localization by a fluorescent 0-blocker, Lab. Invest. 36:365, Melamed, E., Lahav, M., and Atlas, D.: Beta adrenergic receptors in rat myocardium: direct detection by a new fluorescent beta-blocker, Experientia 32:1387, Atlas, D., and Levitzki, A.: Probing of betaadrenergic receptors by novel fluorescent beta adrenergic blockers, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74:5290, Ehinger, B.: Distribution of adrenergic nerves in the eye and some related structures in the cat, Acta Physiol. Scand. 66:123, Ehinger, B.: Adrenergic nerves to the eye and to
7 Volume 17 Number 7 Beta receptors of rat anterior segment 651 related structures in man and in the cynomolgus monkey (Macaco, irus), INVEST. OPHTHALMOL. 5:42, Ehinger, B.: Ocular adrenergic neurons in the flying fox Pteropus giganteus Briinn (Megachiroptera), Z. Zellforsch. 139:171, Ehinger, B.: Adrenergic nerves in the avian eye and ciliary ganglion, Z. Zellforsch. 82:577, Laties, A., and Jacobowitz, D.: A histochemical study of the adrenergic and cholinergic innervation of the anterior segment of the rabbit eye, INVEST. OPHTHALMOL. 3:592, Laties, A., and Jacobowitz, D.: A comparative study of the autonomic innervation of the eye in monkey, cat and rabbit, Anat. Rec. 156:383, Nishida, S., and Sears, M. L.: Dual innervation of the iris sphincter muscle of the albino guinea pig, Exp. Eye Res. 8:467, Nishida, S., Trotter, J., and Sears, M. L.: Innervation of the chamber angle of the guinea pig eye, Exp. Eye Res. 8:143, Richardson, K. C.: The fine structure of the autonomic nerves after vital staining with methylene blue, Anat. Rec. 164:359, Ehinger, B., Falck, B., and Sporrong, B.: Possible axo-axonal synapses between peripheral adrenergic and cholinergic nerve terminals, Z. Zellforsch. 107:508, Feeney, L.: Ultrastructure of the nerves in the human trabecular region, INVEST. OPHTHALMOL. 1:462, Geltzer, A. I.: Autonomic innervation of the cat iris, Arch. Ophthalmol. 81:69, Malmfors, T., and Sachs, C: Direct demonstration of the systems of terminals belonging to an individual adrenergic neurons and their distribution in the rat iris, Acta Physiol. Scand. 64:377, Weekers, R., Delmarcelle, Y., and Gustin, J.: Treatment of ocular hypertension by adrenalin and diverse sympathomimetic amines, Am. J. Ophthalmol. 40:666, Sears, M. L., and Ba'ra'ny, E. H.: Outflow resistance and adrenergic mechanisms, Arch. Ophthalmol. 64:839, Eakins, K. E.: The effect of intravitreal injections of norepinephrine, epinephrine and isoproterenol on the intraocular pressure and aqueous humor dynamics of rabbit eyes, J. Pharmacol. 140:79, Langham, M. E., and Rosenthal, R. A.: Role of cervical sympathetic nerve in regulating intraocular pressure and circulation, Am. J. Physiol. 210:786, Langham, M. E., Kitazawa, Y., and Hart, R. W.: Adrenergic responses in the human eye, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 179:47, Gaasterland, D., Kupfer, G., Ross, K., and Gabelmick, H. L.: Studies of aqueous humor dynamics in man. III. Measurements in young normal subjects using norepinephrine and isoproterenol, INVEST. OPHTHALMOL. 12:267, Bill, A.: Blood circulation and fluid dynamics in the eye, Physiol. Rev. 55:383, Macri, F. J., and Ceravio, S. J.: A possible vascular mechanism of aqueous humor formation by ouabain and acetazolamide, Exp. Eye Res. 20:563, Vale, J., Gibbs, C. C., and Phillips, C. I.: Topical propranolol and ocular tension in the human, Br. J. Ophthalmol. 56:770, Vale, J., and Phillips, C. I.: Practolol (Eraldin) eyedrops as an ocular hypotensive agent, Br. J. Ophthalmol. 57:210, Katz, I. M., Hubbard, VV. A., Geston, A. J., and Gould, A. L.: Intraocular pressure decrease in normal volunteers following timolol ophthalmic solution, INVEST. OPHTHALMOL. 15:489, Information for authors Most of the provisions of the Copyright Act of 1976 became effective on January 1, Therefore all manuscripts must be accompanied by the following statement, signed by each author: "The undersigned author(s) transfers all copyright ownership of the manuscript entitled (title of article) to The Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology, Inc., in the event the work is published. The author(s) warrant that the article is original, is not under consideration by another journal, and has not been previously published." Authors will be consulted, when possible, regarding republication of their material.
The identification of adrenergic and cholinergic nerve endings in the trabecular meshwork. Tsunetami Nomura and George K. Smelser
 The identification of adrenergic and cholinergic nerve endings in the trabecular meshwork Tsunetami Nomura and George K. Smelser There are nerves and nerve endings in the trabecular meshwork, but their
The identification of adrenergic and cholinergic nerve endings in the trabecular meshwork Tsunetami Nomura and George K. Smelser There are nerves and nerve endings in the trabecular meshwork, but their
The influence of light and dark on the catecholamine content of the retina and choroid. Charles W. Nichols, David Jacobowitz, and Marianne Hottenstein
 The influence of light and dark on the catecholamine content of the retina and choroid Charles W. Nichols, David Jacobowitz, and Marianne Hottenstein Recent histochemical studies with the use of a fluorescence
The influence of light and dark on the catecholamine content of the retina and choroid Charles W. Nichols, David Jacobowitz, and Marianne Hottenstein Recent histochemical studies with the use of a fluorescence
A. Incorrect! Acetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor given orally or by intravenous injection.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 20: Drugs that Treat Glaucoma Question No. 1 of 10 1. is a topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Question #01 (A) Acetazolamide (B) Clonidine (C) Dorzolamide (D) Apraclonidine
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 20: Drugs that Treat Glaucoma Question No. 1 of 10 1. is a topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Question #01 (A) Acetazolamide (B) Clonidine (C) Dorzolamide (D) Apraclonidine
Effects of selective beta!- and beta 2 -adrenoreceptor agonists and antagonists on intraocular pressure in the cat
 Effects of selective beta!- and beta 2 -adrenoreceptor agonists and antagonists on intraocular pressure in the cat Brenda K. Colasanti and Robert R. Trotter Ocular tension of cats was measured after topical
Effects of selective beta!- and beta 2 -adrenoreceptor agonists and antagonists on intraocular pressure in the cat Brenda K. Colasanti and Robert R. Trotter Ocular tension of cats was measured after topical
AQUEOUS VEINS IN RABBITS*
 Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 119. AQUEOUS VEINS IN RABBITS* BY D. P. GREAVES AND E. S. PERKINS Institute of Ophthalmology, London Director of Research, Sir Stewart Duke-Elder IN the course of investigations
Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 119. AQUEOUS VEINS IN RABBITS* BY D. P. GREAVES AND E. S. PERKINS Institute of Ophthalmology, London Director of Research, Sir Stewart Duke-Elder IN the course of investigations
The biphasic intraocular pressure response of rabbits to epinephrine
 The biphasic intraocular pressure response of rabbits to epinephrine Maurice E. Langham and Gunter K. Krieglstein A study has been made of the pupillary and intraocular pressure responses of conscious
The biphasic intraocular pressure response of rabbits to epinephrine Maurice E. Langham and Gunter K. Krieglstein A study has been made of the pupillary and intraocular pressure responses of conscious
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION
 ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
Adrenergic fibres in the human intestine
 Gut, 1968, 9, 678-682 Adrenergic fibres in the human intestine L. CAPURSO,1 C. A. FRIEDMANN, AND A. G. PARKS From the Research Department, St Mark's Hospital, London, and the London Hospital, Whitechapel,
Gut, 1968, 9, 678-682 Adrenergic fibres in the human intestine L. CAPURSO,1 C. A. FRIEDMANN, AND A. G. PARKS From the Research Department, St Mark's Hospital, London, and the London Hospital, Whitechapel,
XUE HUI Department of Histology& Embryology, Basic Medicine College of Jilin University
 SENSE ORGAN XUE HUI Department of Histology& Embryology, Basic Medicine College of Jilin University EYE fibrous globe lens photosensitive cells a system of cells and nerves concentric layers the sclera
SENSE ORGAN XUE HUI Department of Histology& Embryology, Basic Medicine College of Jilin University EYE fibrous globe lens photosensitive cells a system of cells and nerves concentric layers the sclera
02/03/2014. Average Length: 23mm (Infant ~16mm) Approximately the size of a quarter Volume: ~5mL
 Identify the anatomy of the eye. Explain the basic physiology of the parts of the eye. Briefly discuss various surgeries related to different parts of the anatomy. Average Length: 23mm (Infant ~16mm) Approximately
Identify the anatomy of the eye. Explain the basic physiology of the parts of the eye. Briefly discuss various surgeries related to different parts of the anatomy. Average Length: 23mm (Infant ~16mm) Approximately
VI.2.2 Summary of treatment benefits
 EU-Risk Management Plan for Bimatoprost V01 aetiology), both OAG and ACG can be secondary conditions. Secondary glaucoma refers to any case in which another disorder (e.g. injury, inflammation, vascular
EU-Risk Management Plan for Bimatoprost V01 aetiology), both OAG and ACG can be secondary conditions. Secondary glaucoma refers to any case in which another disorder (e.g. injury, inflammation, vascular
Ganglionic Blockers. Ganglion- blocking agents competitively block the action of
 Ganglionic Blockers Ganglion- blocking agents competitively block the action of acetylcholine and similar agonists at nicotinic (Nn) receptors of both parasympathetic and sympathetic autonomic ganglia.
Ganglionic Blockers Ganglion- blocking agents competitively block the action of acetylcholine and similar agonists at nicotinic (Nn) receptors of both parasympathetic and sympathetic autonomic ganglia.
Aqueous Humor Messengers in the Transient Decrease of Intraocular Pressure After Ganglionectomy
 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 33, No. 11, October 1992 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Aqueous Humor Messengers in the Transient Decrease of Intraocular
Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 33, No. 11, October 1992 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Aqueous Humor Messengers in the Transient Decrease of Intraocular
Medical School Histology Basics. VIBS 289 lab. Eye
 Medical School Histology Basics VIBS 289 lab Eye Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Aqueous humor OUTLINE OVERVIEW CELLULAR STRUCTURES THROUGH WHICH LIGHT PASSES A. CORNEA B. LENS C. RETINA STRUCTURES
Medical School Histology Basics VIBS 289 lab Eye Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Aqueous humor OUTLINE OVERVIEW CELLULAR STRUCTURES THROUGH WHICH LIGHT PASSES A. CORNEA B. LENS C. RETINA STRUCTURES
In vitro determination of the ability of drugs to bind to adrenergic receptors. Arthur H. Neufeld and Ellen D. Page
 In vitro determination of the ability of drugs to bind to adrenergic receptors Arthur H. Neufeld and Ellen D. Page Alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors were studied by measuring the binding of s H-dihydroergocryptine
In vitro determination of the ability of drugs to bind to adrenergic receptors Arthur H. Neufeld and Ellen D. Page Alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors were studied by measuring the binding of s H-dihydroergocryptine
THE EYE: RETINA AND GLOBE
 Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas February 24, 2011, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15. Your histology and gross anatomy books should be useful. Reading: Histology of the Eye from any histology book
Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas February 24, 2011, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15. Your histology and gross anatomy books should be useful. Reading: Histology of the Eye from any histology book
The effect of topical /-epinephrine on regional ocular blood flow in monkeys
 The effect of topical /-epinephrine on regional ocular blood flow in monkeys Albert Aim A 25 ixl volume of a 1-% \-epinephrine borate solution applied on the cornea of one eye in 12 monkeys reduced blood
The effect of topical /-epinephrine on regional ocular blood flow in monkeys Albert Aim A 25 ixl volume of a 1-% \-epinephrine borate solution applied on the cornea of one eye in 12 monkeys reduced blood
Histology of the Eye
 Histology of the Eye Objectives By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: The general structure of the eye. The microscopic structure of:»cornea.»retina. EYE BULB Three coats
Histology of the Eye Objectives By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: The general structure of the eye. The microscopic structure of:»cornea.»retina. EYE BULB Three coats
A,kCetazolamide lowers intraocular pressure
 Ocular and systemic effects of acetazolamide in nephrectomized rabbits Zvi Friedman,* Theodore Krupin, and Bernard Becker The effects of acetazolamide on intraocular pressure (IOP) were studied on rabbits
Ocular and systemic effects of acetazolamide in nephrectomized rabbits Zvi Friedman,* Theodore Krupin, and Bernard Becker The effects of acetazolamide on intraocular pressure (IOP) were studied on rabbits
Influences on the density of /3-adrenergic receptors in the cornea and iris-ciliary body of the rabbit
 Influences on the density of /3-adrenergic receptors in the cornea and iris-ciliary body of the rabbit Arthur H. Neufeld, Kathleen A. Zatvistowski, Ellen D. Page, and B. Britt Bromberg By measurement of
Influences on the density of /3-adrenergic receptors in the cornea and iris-ciliary body of the rabbit Arthur H. Neufeld, Kathleen A. Zatvistowski, Ellen D. Page, and B. Britt Bromberg By measurement of
The effect of dopamine on the intraocular pressure and pupil of the rabbit eye
 The effect of dopamine on the intraocular pressure and pupil of the rabbit eye Richard P. Shannon,* Alden Mead, and Marvin L. Sears The presence of a dopamine-specific receptor that can influence intraocular
The effect of dopamine on the intraocular pressure and pupil of the rabbit eye Richard P. Shannon,* Alden Mead, and Marvin L. Sears The presence of a dopamine-specific receptor that can influence intraocular
Vision I. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Vision I Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Eye Cornea Sclera Conjunctiva 2 Eye The conjunctiva lines the inner surface of the eyelids and outer surface of the sclera. 3
Vision I Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Eye Cornea Sclera Conjunctiva 2 Eye The conjunctiva lines the inner surface of the eyelids and outer surface of the sclera. 3
Cholinergic Inhibitory Response in the Bovine Iris Dilator Muscle
 Cholinergic Inhibitory Response in the Bovine Iris Dilator Muscle Ryo Suzuki,* Takuro Oso,f and Shunsaku Kobayashi* Isometric tension changes of the bovine iris dilator muscle were investigated in vitro.
Cholinergic Inhibitory Response in the Bovine Iris Dilator Muscle Ryo Suzuki,* Takuro Oso,f and Shunsaku Kobayashi* Isometric tension changes of the bovine iris dilator muscle were investigated in vitro.
Autonomic Nervous System
 ANS..??? Autonomic Nervous System Nervous system CNS PNS Autonomic Somatic Symp Parasymp Enteric SOMATIC AUTONOMIC Organ supplied Skeletal muscle Other organs Distal most synapse Nerve fibre Peripheral
ANS..??? Autonomic Nervous System Nervous system CNS PNS Autonomic Somatic Symp Parasymp Enteric SOMATIC AUTONOMIC Organ supplied Skeletal muscle Other organs Distal most synapse Nerve fibre Peripheral
The Orbit. The Orbit OCULAR ANATOMY AND DISSECTION 9/25/2014. The eye is a 23 mm organ...how difficult can this be? Openings in the orbit
 The eye is a 23 mm organ...how difficult can this be? OCULAR ANATOMY AND DISSECTION JEFFREY M. GAMBLE, OD COLUMBIA EYE CONSULTANTS OPTOMETRY & UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY CLINICAL
The eye is a 23 mm organ...how difficult can this be? OCULAR ANATOMY AND DISSECTION JEFFREY M. GAMBLE, OD COLUMBIA EYE CONSULTANTS OPTOMETRY & UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY CLINICAL
Introduction to Autonomic
 Part 2 Autonomic Pharmacology 3 Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology FUNCTIONS OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM The autonomic nervous system (Figure 3 1) is composed of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
Part 2 Autonomic Pharmacology 3 Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology FUNCTIONS OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM The autonomic nervous system (Figure 3 1) is composed of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
Cervical sympathetic stimulation in monkeys and the effects on outflow facility and intraocular volume
 Cervical sympathetic stimulation in monkeys and the effects on outflow facility and intraocular volume A study in the East African vervet (Cercopithecus aethiops) William J. Casey The effects of cervical
Cervical sympathetic stimulation in monkeys and the effects on outflow facility and intraocular volume A study in the East African vervet (Cercopithecus aethiops) William J. Casey The effects of cervical
Eye Fluids. Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud
 Eye Fluids 1 Reference Books: Text Book of Medical physiology (Guyton and Hall) Eleventh edition 2 Fluid System of the Eye (Intraocular Fluid) The eye is filled with intraocular fluid, which maintains
Eye Fluids 1 Reference Books: Text Book of Medical physiology (Guyton and Hall) Eleventh edition 2 Fluid System of the Eye (Intraocular Fluid) The eye is filled with intraocular fluid, which maintains
Human ciliary process adrenergic receptor: pharmacological characterization. James A. Nathanson
 Human ciliary process adrenergic receptor: pharmacological characterization James A. Nathanson To better understand the nature of interaction of various amines with adrenergic receptors in the human ciliary
Human ciliary process adrenergic receptor: pharmacological characterization James A. Nathanson To better understand the nature of interaction of various amines with adrenergic receptors in the human ciliary
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS):
 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): ANS is the major involuntary, unconscious, automatic portion of the nervous system. involuntary voluntary The motor (efferent)portion of the ANS is the major pathway for
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): ANS is the major involuntary, unconscious, automatic portion of the nervous system. involuntary voluntary The motor (efferent)portion of the ANS is the major pathway for
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 11 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Autonomic Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 533 through 552 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words! Work
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 11 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Autonomic Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 533 through 552 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words! Work
ADRENERGIC RESPONSES IN THE HUMAN EYE. MAURICE E. LANGHAM,2 YOSHIAKI KITAZAWA3 aim ROBERT W. HART4
 THE JOVENAL or Pacox.ooy Ax Expzznizwr.x THEP.APBTYrICE Copyright 1971 by The Williame & Wilkina Co. vol. 179, No. 1 Pfsntedin U.S.A. ADRENERGIC RESPONSES IN THE HUMAN EYE MAURICE E. LANGHAM,2 YOSHIAKI
THE JOVENAL or Pacox.ooy Ax Expzznizwr.x THEP.APBTYrICE Copyright 1971 by The Williame & Wilkina Co. vol. 179, No. 1 Pfsntedin U.S.A. ADRENERGIC RESPONSES IN THE HUMAN EYE MAURICE E. LANGHAM,2 YOSHIAKI
Sympathetic Innervation of the Juxtaglomerular Cells of the Kidney
 Sympathetic Innervation of the Juxtaglomerular Cells of the Kidney By Jan Wagermark, M.D., Urban Ungerstedt, M.D., and Arne Ljungqvist, M.D., Ph.D. ABSTRACT Combination of a histochemical fluorescence
Sympathetic Innervation of the Juxtaglomerular Cells of the Kidney By Jan Wagermark, M.D., Urban Ungerstedt, M.D., and Arne Ljungqvist, M.D., Ph.D. ABSTRACT Combination of a histochemical fluorescence
Lujain Hamdan. Ayman Musleh & Yahya Salem. Mohammed khatatbeh
 12 Lujain Hamdan Ayman Musleh & Yahya Salem Mohammed khatatbeh the last lecture, we have studied the differences between the two divisions of the ANS: sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways which work
12 Lujain Hamdan Ayman Musleh & Yahya Salem Mohammed khatatbeh the last lecture, we have studied the differences between the two divisions of the ANS: sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways which work
Ocular hypotensive effect of atenolol (Tenormin, I.c.i.)
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 975) 59, 296 Ocular hypotensive effect of atenolol (Tenormin, I.c.i.) A new beta-adrenergic blocker MARGARET J. ELLIOT, PATRICIA M. CULLEN, AND CALBERT I. PHILLIPS From the Department
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 975) 59, 296 Ocular hypotensive effect of atenolol (Tenormin, I.c.i.) A new beta-adrenergic blocker MARGARET J. ELLIOT, PATRICIA M. CULLEN, AND CALBERT I. PHILLIPS From the Department
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline
 Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Autonomic Nervous System. Introduction
 Autonomic Nervous System Introduction 1 The nervous system is divided into: 1- the central nervous system (CNS; the brain and spinal cord) 2- the peripheral nervous system (PNS; neuronal tissues outside
Autonomic Nervous System Introduction 1 The nervous system is divided into: 1- the central nervous system (CNS; the brain and spinal cord) 2- the peripheral nervous system (PNS; neuronal tissues outside
Neuropsychiatry Block
 Neuropsychiatry Block Physiology of the Autonomic Nervous System By Laiche Djouhri, PhD Dept. of Physiology Email: ldjouhri@ksu.edu.sa Ext:71044 References The Autonomic Nervous System and the Adrenal
Neuropsychiatry Block Physiology of the Autonomic Nervous System By Laiche Djouhri, PhD Dept. of Physiology Email: ldjouhri@ksu.edu.sa Ext:71044 References The Autonomic Nervous System and the Adrenal
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Keri Muma Bio 6 Organization of the Nervous System Efferent Division Somatic Nervous System Voluntary control Effector = skeletal muscles Muscles must be excited by a motor neuron
Autonomic Nervous System Keri Muma Bio 6 Organization of the Nervous System Efferent Division Somatic Nervous System Voluntary control Effector = skeletal muscles Muscles must be excited by a motor neuron
Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition
 Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition Chapter 3 Pharmacology of the Autonomic Nervous System Multimedia Directory Slide 19 Slide 37 Slide 38 Slide 39 Slide 40 Slide 41 Slide 42 Slide 43
Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition Chapter 3 Pharmacology of the Autonomic Nervous System Multimedia Directory Slide 19 Slide 37 Slide 38 Slide 39 Slide 40 Slide 41 Slide 42 Slide 43
SAFE, PERMANENT EYE-COLOR CHANGE
 SAFE, PERMANENT EYE-COLOR CHANGE Prepared by Gregg Homer JSD (PhD) February 1, 2012 THE PIGMENTARY GLAUCOMA ISSUE Glaucoma Defined Glaucoma is currently defined as a disturbance of the structural or functional
SAFE, PERMANENT EYE-COLOR CHANGE Prepared by Gregg Homer JSD (PhD) February 1, 2012 THE PIGMENTARY GLAUCOMA ISSUE Glaucoma Defined Glaucoma is currently defined as a disturbance of the structural or functional
GLAUCOMA. An Overview
 GLAUCOMA An Overview Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com --()-- IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your
GLAUCOMA An Overview Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com --()-- IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your
Efficacy of latanoprost in management of chronic angle closure glaucoma. Kumar S 1, Malik A 2 Singh M 3, Sood S 4. Abstract
 Original article Efficacy of latanoprost in management of chronic angle closure glaucoma Kumar S 1, Malik A 2 Singh M 3, Sood S 4 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 4 Professor, Department of
Original article Efficacy of latanoprost in management of chronic angle closure glaucoma Kumar S 1, Malik A 2 Singh M 3, Sood S 4 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 4 Professor, Department of
Transient Intraocular Pressure Elevation after Trabeculotomy and its Occurrence with Phacoemulsification and Intraocular Lens Implantation
 Transient Intraocular Pressure Elevation after Trabeculotomy and its Occurrence with Phacoemulsification and Intraocular Lens Implantation Masaru Inatani*, Hidenobu Tanihara, Takahito Muto*, Megumi Honjo*,
Transient Intraocular Pressure Elevation after Trabeculotomy and its Occurrence with Phacoemulsification and Intraocular Lens Implantation Masaru Inatani*, Hidenobu Tanihara, Takahito Muto*, Megumi Honjo*,
Report. Superior Cervical Ganglionectomy in Monkeys: Surgical Technique
 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 33, No. 1, January 1992 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Report Superior Cervical Ganglionectomy in Monkeys: Surgical Technique
Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 33, No. 1, January 1992 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Report Superior Cervical Ganglionectomy in Monkeys: Surgical Technique
Ch 9. The Autonomic Nervous System
 Ch 9 The Autonomic Nervous System SLOs Review the organization of the ANS Describe how neural regulation of smooth and cardiac muscles differs from that of skeletal muscles Describe the structure and innervation
Ch 9 The Autonomic Nervous System SLOs Review the organization of the ANS Describe how neural regulation of smooth and cardiac muscles differs from that of skeletal muscles Describe the structure and innervation
Blood-aqueous barrier can be circumvented by lowering intraocular pressure (Schlemm canal/electron microscopy/aqueous humor)
 Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 73, No. 2, pp. 638-642, February 1976 Medical Sciences Blood-aqueous barrier can be circumvented by lowering intraocular pressure (Schlemm canal/electron microscopy/aqueous
Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 73, No. 2, pp. 638-642, February 1976 Medical Sciences Blood-aqueous barrier can be circumvented by lowering intraocular pressure (Schlemm canal/electron microscopy/aqueous
Intro to Glaucoma/2006
 Intro to Glaucoma/2006 Managing Patients with Glaucoma is Exciting Interesting Challenging But can often be frustrating! Clinical Challenges To identify patients with risk factors for possible glaucoma.
Intro to Glaucoma/2006 Managing Patients with Glaucoma is Exciting Interesting Challenging But can often be frustrating! Clinical Challenges To identify patients with risk factors for possible glaucoma.
Changes in outflow facility and content of norepinephrine in iris and ciliary processes of albino rabbits after cervical ganglionectomy
 Changes in outflow facility and content of norepinephrine in iris and ciliary processes of albino rabbits after cervical ganglionectomy M. Sears, K. Mizuno, C. Cintron, A. Alter, and T. Sherk Changes in
Changes in outflow facility and content of norepinephrine in iris and ciliary processes of albino rabbits after cervical ganglionectomy M. Sears, K. Mizuno, C. Cintron, A. Alter, and T. Sherk Changes in
The continuous and quantitative observation of permeability changes of the blood-aqueous barrier in allergic inflammation of the eye
 The continuous and quantitative observation of permeability changes of the blood-aqueous barrier in allergic inflammation of the eye Mariko Okada and Kohkichi Shimada Permeability changes of the blood-aqueous
The continuous and quantitative observation of permeability changes of the blood-aqueous barrier in allergic inflammation of the eye Mariko Okada and Kohkichi Shimada Permeability changes of the blood-aqueous
Glaucoma Clinical Update. Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012
 Glaucoma Clinical Update Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Objectives Understand the different categories of glaucoma Recognize the symptoms and signs of open angle and angle-closure
Glaucoma Clinical Update Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Objectives Understand the different categories of glaucoma Recognize the symptoms and signs of open angle and angle-closure
The Nervous System and Metabolism
 = P1: JZP 8 The Nervous System and Metabolism Dendrites Cell body Axon (may be sheathed in myelin) Nucleus Axonal terminals (synapses) Figure 8.1 Basic structure of a nerve cell (neuron). CH 3_ CH 3 CH
= P1: JZP 8 The Nervous System and Metabolism Dendrites Cell body Axon (may be sheathed in myelin) Nucleus Axonal terminals (synapses) Figure 8.1 Basic structure of a nerve cell (neuron). CH 3_ CH 3 CH
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
STUDIES ON THE ANTIGENIC STRUCTURE OF THE EYE USING THE FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1957) 41, 338. STUDIES ON THE ANTIGENIC STRUCTURE OF THE EYE USING THE FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY TECHNIQUE* BY D. ST. C. ROBERTS From the Nuffield Laboratory of Ophthalmology, University
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1957) 41, 338. STUDIES ON THE ANTIGENIC STRUCTURE OF THE EYE USING THE FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY TECHNIQUE* BY D. ST. C. ROBERTS From the Nuffield Laboratory of Ophthalmology, University
Action of drugs on denervated myoepithelial cells of salivary glands
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 73-79. Action of drugs on denervated myoepithelial cells of salivary glands N. EMMELIN AND A. THULIN Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden Summary 1. The pressure
Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 73-79. Action of drugs on denervated myoepithelial cells of salivary glands N. EMMELIN AND A. THULIN Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden Summary 1. The pressure
Pheochromocytoma: Effects of Catecholamines
 36 PHYSIOLOGY CASES AND PROBLEMS Case 8 Pheochromocytoma: Effects of Catecholamines Helen Ames is a 51-year-old homemaker who experienced what she thought were severe menopausal symptoms. These awful "attacks"
36 PHYSIOLOGY CASES AND PROBLEMS Case 8 Pheochromocytoma: Effects of Catecholamines Helen Ames is a 51-year-old homemaker who experienced what she thought were severe menopausal symptoms. These awful "attacks"
Chapter 7. Objectives
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS
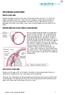 THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Anatomy of Autonomic Motor Pathways Preganglionic neuron
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Anatomy of Autonomic Motor Pathways Preganglionic neuron
A comparison of the sensitivities of innervated and denervated rat vasa deferentia to agonist drugs
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 39, 748-754. A comparison of the sensitivities of innervated and denervated rat vasa deferentia to agonist drugs A. T. BIRMINGHAM*, G. PATRSON AND J. W6JCICKIt Department of Pharmacology,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 39, 748-754. A comparison of the sensitivities of innervated and denervated rat vasa deferentia to agonist drugs A. T. BIRMINGHAM*, G. PATRSON AND J. W6JCICKIt Department of Pharmacology,
n Corneal epithelium is derived from surface ectoderm n Composed of stratified squamous epith. n 5% of total corneal thickness (50-90micro m thick)
 Cornea overview Dr. Sarita Tuladhar MD, Ophthalmology Gandaki Medical College Embryology CORNEA: n Corneal epithelium is derived from surface ectoderm n Corneal stroma, descement memb, bowman s layer,
Cornea overview Dr. Sarita Tuladhar MD, Ophthalmology Gandaki Medical College Embryology CORNEA: n Corneal epithelium is derived from surface ectoderm n Corneal stroma, descement memb, bowman s layer,
LEUKAEMIA*t INFILTRATION OF THE IRIS IN CHRONIC LYMPHATIC. pattemn * Received for pubiication November io, i967.
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 781 INFILTRATION OF THE IRIS IN CHRONIC LYMPHATIC LEUKAEMIA*t BY BRIAN MARTIN The General Infirmary, Leeds OCULAR involvement is common in the leukaemias though the anterior
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 781 INFILTRATION OF THE IRIS IN CHRONIC LYMPHATIC LEUKAEMIA*t BY BRIAN MARTIN The General Infirmary, Leeds OCULAR involvement is common in the leukaemias though the anterior
Answer ALL questions. For each question, there is ONE correct answer. Use the answer grid provided for ALL your answers.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Pharmacy Main Series UG Examination 2017-18 NEUROPHARMACOLOGY PHAP4008Y Time allowed: 2 hours Part ONE Answer ALL questions. For each question, there is ONE correct
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Pharmacy Main Series UG Examination 2017-18 NEUROPHARMACOLOGY PHAP4008Y Time allowed: 2 hours Part ONE Answer ALL questions. For each question, there is ONE correct
Hypertensive Retinopathy
 Ophthalmologica 1989;198:173-177 1989 S. Karger AG. Basel 0030-3755/89/1984-0173 S 2.75/0 Hypertensive Retinopathy Introduction Sohan Singh Hayreh DeparimenI of Ophthalmology. University of Iowa Hospitals
Ophthalmologica 1989;198:173-177 1989 S. Karger AG. Basel 0030-3755/89/1984-0173 S 2.75/0 Hypertensive Retinopathy Introduction Sohan Singh Hayreh DeparimenI of Ophthalmology. University of Iowa Hospitals
3/16/2018. Ultrasound Biomicroscopy in Glaucoma By Ahmed Salah Abdel Rehim. Prof. of Ophthalmology Al-Azhar University
 Ultrasound Biomicroscopy in Glaucoma By Ahmed Salah Abdel Rehim Prof. of Ophthalmology Al-Azhar University 1 Ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM) is a recent technique to visualize anterior segment with the
Ultrasound Biomicroscopy in Glaucoma By Ahmed Salah Abdel Rehim Prof. of Ophthalmology Al-Azhar University 1 Ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM) is a recent technique to visualize anterior segment with the
of Ciliary body, Iris and Irido-corneal angle in Adult Marwari Goat (Capra hircus) R. K. Barhaiyaa *, Malsawmkima, D. M. Bhayani and Y. L.
 DHR International Journal Of Biomedical and Life Sciences (DHR-IJBLS) ISSN 2278-8301, Vol.5(3), 2014 Available online http://www.doublehelixresearch.com/dhrijbls Double Helix Research Original Article
DHR International Journal Of Biomedical and Life Sciences (DHR-IJBLS) ISSN 2278-8301, Vol.5(3), 2014 Available online http://www.doublehelixresearch.com/dhrijbls Double Helix Research Original Article
General organization of central and peripheral components of the nervous system
 General organization of central and peripheral components of the nervous system Today we are focusing on the ANS Part of ANS?? Life depends on the innervation of the viscera... all the rest is biological
General organization of central and peripheral components of the nervous system Today we are focusing on the ANS Part of ANS?? Life depends on the innervation of the viscera... all the rest is biological
Diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma
 Brit. 1. Ophthal. (I 971) 55, 6oo Diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma GWYN MORGAN Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London The term "diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma"
Brit. 1. Ophthal. (I 971) 55, 6oo Diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma GWYN MORGAN Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London The term "diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma"
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements is correct about the component of the autonomic nervous system identified
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements is correct about the component of the autonomic nervous system identified
H. istochemical 1 " 0 and chemical 7 ' 8 evidence
 Dopamine: A retinal neurotransmitter II. Autoradiographic localization of H3-dopamine in the retina Steven G. Kramer, Albert M. Potts, and Yvonne Mangnall Retinal uptake of tritiated dopamine was induced
Dopamine: A retinal neurotransmitter II. Autoradiographic localization of H3-dopamine in the retina Steven G. Kramer, Albert M. Potts, and Yvonne Mangnall Retinal uptake of tritiated dopamine was induced
Chapter 7. The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
The Systemic Effect Of Topical Timolol On Some Cardiovascular Parameters In Owerri Municipality
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 The Systemic Effect Of Topical Timolol On Some Cardiovascular Parameters In Owerri Municipality G Oze, M Emegwamuo, P Eleanya, H
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 The Systemic Effect Of Topical Timolol On Some Cardiovascular Parameters In Owerri Municipality G Oze, M Emegwamuo, P Eleanya, H
Chapter 17. Nervous System Nervous systems receive sensory input, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands. !
 Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY, SYNAPTIC PHARMACOLOGY AND ENDOCRINOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Pharmacy Main series UG Examination 2017-18 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY, SYNAPTIC PHARMACOLOGY AND ENDOCRINOLOGY PHA-5004Y Time allowed: 2 hours Part ONE Answer ALL questions. For
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Pharmacy Main series UG Examination 2017-18 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY, SYNAPTIC PHARMACOLOGY AND ENDOCRINOLOGY PHA-5004Y Time allowed: 2 hours Part ONE Answer ALL questions. For
Building a Major Ophthalmic Pharmaceutical Company. Aerie Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Company Overview June 2-3, 2015
 Building a Major Ophthalmic Pharmaceutical Company Aerie Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Company Overview June 2-3, 2015 1 Important Information Any discussion of the potential use or expected success of our product
Building a Major Ophthalmic Pharmaceutical Company Aerie Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Company Overview June 2-3, 2015 1 Important Information Any discussion of the potential use or expected success of our product
Isoproferenol Stimulates Aqueous Flow in Humans With Horner's Syndrome
 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 29, No. 4, April 1988 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Isoproferenol Stimulates Aqueous Flow in Humans With Horner's Syndrome
Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 29, No. 4, April 1988 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Isoproferenol Stimulates Aqueous Flow in Humans With Horner's Syndrome
PITTMed Cardiology. Pharmacology Modules. Learning Objectives. Site Contents. Fall 2018
 PITTMed Cardiology Fall 2018 Site Contents Pharmacology Modules Please complete the following modules during the first week of class: Adrenergics Cholinergics Adrenergic Drugs in Cardiology Hypercalcemia
PITTMed Cardiology Fall 2018 Site Contents Pharmacology Modules Please complete the following modules during the first week of class: Adrenergics Cholinergics Adrenergic Drugs in Cardiology Hypercalcemia
A LITTLE ANATOMY. three layers of eye: 1. outer: corneosclera. 2. middle - uvea. anterior - iris,ciliary body. posterior - choroid
 GLAUCOMA A LITTLE ANATOMY three layers of eye: 1. outer: corneosclera 2. middle - uvea anterior - iris,ciliary body posterior - choroid connection at the pars plana between post and ant uvea 3. retina
GLAUCOMA A LITTLE ANATOMY three layers of eye: 1. outer: corneosclera 2. middle - uvea anterior - iris,ciliary body posterior - choroid connection at the pars plana between post and ant uvea 3. retina
Autonomic Division of NS
 Autonomic Division of NS Compare and contrast the structures of the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions, including functions and neurotransmitters. Show the levels of integration in the ANS,
Autonomic Division of NS Compare and contrast the structures of the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions, including functions and neurotransmitters. Show the levels of integration in the ANS,
BIOLOGY 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM PRACTICE
 1 Name: BIOLOGY 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM PRACTICE Date: 1) Identify structures X, Y and Z and give one function of each. 2) Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z?
1 Name: BIOLOGY 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM PRACTICE Date: 1) Identify structures X, Y and Z and give one function of each. 2) Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z?
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Goals. Glaucoma PARA PEARL TO DO. Vision Loss with Glaucoma
 Glaucoma Janet R. Fett, OD Drs. Kincaid, Fett and Tharp So Sioux City, NE eyewear21@hotmail.com Goals Understand Glaucoma Disease process Understand how your data (objective and subjective) assists in
Glaucoma Janet R. Fett, OD Drs. Kincaid, Fett and Tharp So Sioux City, NE eyewear21@hotmail.com Goals Understand Glaucoma Disease process Understand how your data (objective and subjective) assists in
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Viscocanalostomy and Canaloplasty File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: viscocanalostomy_and_canaloplasty 11/2011 6/2017 6/2018 6/2017 Description
Corporate Medical Policy Viscocanalostomy and Canaloplasty File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: viscocanalostomy_and_canaloplasty 11/2011 6/2017 6/2018 6/2017 Description
Systemic Pharmacology Lecture 7: Neuropharmacology
 Systemic Pharmacology Lecture 7: Neuropharmacology Drugs act on Sympathetic NS (adrenergic system) Adrenergic Drugs (Sympathomimetics), adrenergic agonists, or alpha- and beta-adrenergic agonists Antiadrenergic
Systemic Pharmacology Lecture 7: Neuropharmacology Drugs act on Sympathetic NS (adrenergic system) Adrenergic Drugs (Sympathomimetics), adrenergic agonists, or alpha- and beta-adrenergic agonists Antiadrenergic
I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors. Chapter 9. Autonomic Motor Nerves. Autonomic Neurons. Autonomic Ganglia. Autonomic Neurons 9/19/11
 Chapter 9 I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Autonomic
Chapter 9 I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Autonomic
Written by Administrator Wednesday, 13 January :27 - Last Updated Thursday, 21 January :34
 angle closure glaucoma A type of glaucoma caused by a sudden and severe rise in eye pressure. Occurs when the pupil enlarges too much or too quickly, and the outer edge of the iris blocks the eye s drainage
angle closure glaucoma A type of glaucoma caused by a sudden and severe rise in eye pressure. Occurs when the pupil enlarges too much or too quickly, and the outer edge of the iris blocks the eye s drainage
1. At the venous end of a capillary, is the dominant force determining water movement. a. Pcap b. cap c. PIF d. IF e. [Na+]
![1. At the venous end of a capillary, is the dominant force determining water movement. a. Pcap b. cap c. PIF d. IF e. [Na+] 1. At the venous end of a capillary, is the dominant force determining water movement. a. Pcap b. cap c. PIF d. IF e. [Na+]](/thumbs/95/122587355.jpg) P531: Exam 1 Sample Question Set #3 The first 9 questions are the relevant questions from the beginning of lecture each day. The remaining 16 questions cover material from the last week of lectures. 1.
P531: Exam 1 Sample Question Set #3 The first 9 questions are the relevant questions from the beginning of lecture each day. The remaining 16 questions cover material from the last week of lectures. 1.
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD How is the organization of the autonomic nervous system different from that of the somatic nervous system? Peripheral Nervous System Divisions Somatic Nervous
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD How is the organization of the autonomic nervous system different from that of the somatic nervous system? Peripheral Nervous System Divisions Somatic Nervous
Biochemistry of the Eye
 Biochemistry of the Eye Elaine R. Berman Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical School Jerusalem, Israel Plenum Press New York and London Contents 1. Selected Topics in Biochemistry Relevant to the Eye 1.1.
Biochemistry of the Eye Elaine R. Berman Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical School Jerusalem, Israel Plenum Press New York and London Contents 1. Selected Topics in Biochemistry Relevant to the Eye 1.1.
Autonomic Nervous System. Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry
 Autonomic Nervous System Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Peripheral Nervous System A. Sensory Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous System 1. Sympathetic Nervous
Autonomic Nervous System Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Peripheral Nervous System A. Sensory Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous System 1. Sympathetic Nervous
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS
 THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA? People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA? People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
The Autonomic Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology
 The Autonomic Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology 1 After studying the endocrine system you should be able to: 1. Describe the organization of the nervous system. 2. Compare and contrast
The Autonomic Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology 1 After studying the endocrine system you should be able to: 1. Describe the organization of the nervous system. 2. Compare and contrast
Glaucoma Glaucoma is a complication which has only recently been confirmed as a feature of
 1.2.4 OPHTHALMOLOGICAL ABNORMALITIES Ocular abnormalities are well documented in patients with NPS 6 62 81 95. 1.2.4.1 Glaucoma Glaucoma is a complication which has only recently been confirmed as a feature
1.2.4 OPHTHALMOLOGICAL ABNORMALITIES Ocular abnormalities are well documented in patients with NPS 6 62 81 95. 1.2.4.1 Glaucoma Glaucoma is a complication which has only recently been confirmed as a feature
Relationship between limbal incisions. angle. and the structures of the anterior chamber
 Brit. _7. Ophthal. (I 973) 57, 722 Relationship between limbal incisions and the structures of the anterior chamber angle MOHAMED I. AYOUB AND AHMED H. SAID Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine,
Brit. _7. Ophthal. (I 973) 57, 722 Relationship between limbal incisions and the structures of the anterior chamber angle MOHAMED I. AYOUB AND AHMED H. SAID Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine,
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Pearson Education, Inc.
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
Glaucoma. How is Glaucoma Diagnosed? Glaucoma Testing
 Glaucoma How is Glaucoma Diagnosed? Glaucoma Testing There is no single test for glaucoma. The diagnosis is made by evaluating the patient from a number of perspectives, using specialized instruments.
Glaucoma How is Glaucoma Diagnosed? Glaucoma Testing There is no single test for glaucoma. The diagnosis is made by evaluating the patient from a number of perspectives, using specialized instruments.
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Anterior Segment of the Eye File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: optical_coherence_tomography_(oct)_anterior_segment_of_the_eye
Corporate Medical Policy Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Anterior Segment of the Eye File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: optical_coherence_tomography_(oct)_anterior_segment_of_the_eye
Deficiencies of Vitamins E and A in the Rat: Lipofuscin Accumulation in the Choroid
 Deficiencies of Vitamins E and A in the Rat: Lipofuscin Accumulation in the Choroid Roland K. Herrmann,* W. Gerald Robison, Jr.,* and John G. Dieri-)- The effects of vitamin E and A deficiencies on the
Deficiencies of Vitamins E and A in the Rat: Lipofuscin Accumulation in the Choroid Roland K. Herrmann,* W. Gerald Robison, Jr.,* and John G. Dieri-)- The effects of vitamin E and A deficiencies on the
The 7 th lecture. Anatomy and Physiology For the. 1 st Class. By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza
 The 7 th lecture In Anatomy and Physiology For the 1 st Class By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza Nervous System (part I) The Nerve Tissue and the Nervous System The Tissues of the Body There are 4 types of tissues
The 7 th lecture In Anatomy and Physiology For the 1 st Class By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza Nervous System (part I) The Nerve Tissue and the Nervous System The Tissues of the Body There are 4 types of tissues
