Journal of Medical Science & Technology
|
|
|
- June Lane
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review Article Journal of Medical Science & Technology Malakoplakia of testis and epididymis: A Review of the Literature Anthony Kodzo-Grey Venyo 1 * Open Access 1 North Manchester General Hospital, Department of Urology, Delaunays Road, Manchester, United Kingdom. Abstract Malakoplakia of the testis / epididymis is uncommon therefore most clinicians globally would be unfamiliar with the disease. Malakoplakia is an extremely rare chronic inflammatory disease which usually affects the genitourinary tract and it is often associated with Escherichia coli infection. Malakoplakia characterized by the observation of Von Hansemann cells and intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies called Michaelis-Gutmann Bodies (M-G bodies). The testes are affected in 12% of cases of malakoplakia and isolated malakoplakia of the epididymis is even rarer. To the knowledge of the author, less than 50 cases of malakoplakia of the testis and less than 15 cases of malakoplakia of the epididymis have been reported so far world-wide. Malakoplakia of the testis / epididymis may present with pain in the testicular area, fever, chills and or a hemi-scrotal mass. Malakoplakia of testis / epididymis is usually seen in middle aged men and they tend to appear clinically as epididymo-orchitis or testicular enlargement with fibrous consistency and some soft areas. Ultrasound scan findings of the testis are non-specific revealing hypo-echogenic or hyper-echogenicity with increased vascularity on Doppler scanning. A number of cases of malakoplakia of the testis and epididymis are associated with immunosuppression, renal transplantation and diabetes. Treatment of malakoplakia includes medical and surgical treatment. The quinolones and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole have been most commonly used. Orchidectomy has been the only way to differentiate malakoplakia from other malignant and infective processes. If a patient with malakoplakia of testis is immunosuppressed then a period of withdrawal may perhaps be beneficial to speed up the recovery process. With the knowledge that malakoplakia of the testis is more common in middle aged men and the fact that testicular tumours are uncommon in the middle aged group perhaps ultrasound guided biopsy of a hypo-echoic or hyperechogenic testicular lesion with increased vascularity could be undertaken to establish the diagnosis if there is evidence of coliform urinary tract infection and a clinical diagnosis of epididymoorchitis has been made but the lesion has not resolved. In that case perhaps prolonged antibiotic treatment with quinolones may help the lesion to resolve and thus avoiding orchidectomy. Malakoplakia involving the testis and or epididymis is an uncommon chronic inflammatory condition which clinicians should consider in the differential diagnosis of testicular swellings. The disease tends to be associated with gram negative infections especially coliform infections. Key Words: Malakoplakia of testis; Malakoplakia of epididymis; Michaelis-Gutmann Bodies; coliforms; epididymoorchitis; quinolones; orchidectomy; ultrasound-guided biopsy. *Corresponding Author: Dr Anthony Kodzo-Grey Venyo. MB ChB FRCS(Ed) FRCSI FGCS Urol LLM, North Manchester General Hospital, Department of Urology, Manchester, United Kingdom, akodzogrey@yahoo.co.uk Received: September 20, 2014, Accepted: November 20, Published: January 20, 2015.This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Introduction Malakoplakia of the testis and Malakoplakia of the epididymis are so rare that most clinicians throughout the world would not have encountered the disease. The ensuing paper contains a review of the literature on malakoplakia of the testis and malakoplakia of the epididymis. The paper is divided into two parts (A) which contains an overview and (B) miscellaneous narrations and discussion from some reported cases. Page62
2 Methods Partially digested bacteria accumulate in Various internet data bases were used to monocytes or macrophages and this lead to the search for case reports, case series, review papers and deposition of calcium and iron on residual other documentations on malakoplakia of testis and bacterial glycolipid. malakoplakia of the epididymis in order to obtain The presence of the resulting basophilic inclusion information on the presentation, epidemiology, structure, the Michaelis-Gutmann body, is pathophysiology, investigation and management of regarded pathognomonic for malakoplakia. the disease. The key words that were used were: Studies had indicated that a decreased Malakoplakia of testis and Malakoplakia of intracellular cyclic guanosine monophosphate epididymis. In all 13 references were identified to be (cgmp) level may interfere with adequate suitable to document literature on the disease. microtubular function and lysosomal activity Results / Literature Review which lead to an incomplete elimination of bacteria from macrophages and monocytes. (A)General Comment Malakoplakia of testis (MOT) may affect the testis alone or it may affect both the testis and epididymis [1]. Quite often in malakoplakia of testis culture grows presence of coliforms [1]. Definition and back ground: Kiel and James [2] defined malakoplakia as an inflammatory condition which presents as a plaque or a nodule which usually affects the genitourinary tract system but malakoplakia may rarely affect the skin. Kiel et al. [2] also stated that malakoplakia was first described in the early 1900s as yellow soft plaques which were seen on the mucosa of the urinary bladder. The microscopic feature of malakoplakia is characterized by the presence of foamy histiocytes with distinctive basophilic inclusions, which are called Michaelis- Gutmann bodies. Cutaneous malakoplasia is rarely seen but it presents in patients who have been immunocompromised and they have defects in macrophage function. Malakoplakia lesions, are yellow-to-pink papules, nevertheless, they can present as nodules or ulcerations. Malakoplakias quite often are diagnosed following histological examination of biopsy specimens. Culture of malakoplakia lesions can yield bacteria of which Escherichia coli is the most common organism cultured. Malakoplakia may also rarely affect the testis and the epididymis. Pathophysiology Kiel and James [2] stated that: It has been understood that malakoplakia emanates from inadequate killing of bacteria by macrophages or monocytes which exhibit defective phagolysosomal activity. Epidemiology Kiel and James [2] stated that: The total number of patients with malakoplakia is less than 500 in the United States of America. Majority of patients who have malakoplakia have genitourinary tract disease, even though malakoplakia involving the gastrointestinal tract and other visceral organs has been described. International frequency of malakoplakia is the same as in the United States of America. Malakoplakia most frequently occurs in patients who have been immunocompromised. Quite often malakoplakia is resistant to treatment. Mortality in patients afflicted by malakoplakia is most commonly a result of an underlying disease. Significant morbidity in malakplakia is related to the chronicity of the condition, which can resist local and systemic therapy. Drainage of sinuses, persistence of disfiguring cutaneous lesions, and the involvement of visceral organs would constitute significant morbidity in patients who have malakoplaka. Presentation Patients with malakoplakia of testis and or epididymis may present with fever, chills, and testicular pain. The patients may also present with a testicular mass. Patients with malakoplakia of testis / epididymis have a history of renal transplantation, diabetes, multiple urinary tract infections and immunosuppression. Malakoplakia of testis tends to occur in middle aged men and in most cases it involves one testis. Page63
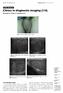
3 Clinical examination findings: Some of the clinical Differential diagnosis: The differential diagnosis of examination findings in malakoplakia of testis / malakoplakia of testis include: Granulomatous epididymis include: a scrotal mass: tenderness over orchitis and Leydig cell tumour. [1] the epididymis and or testis which may make the clinician to establish a provisional diagnosis of epididymoorchitis. Laboratory findings: There may be coliform urinary tract infection associated with malakoplakia of testis. Radiology / Ultra-sound scan: The ultrasound scan appearances of malakoplakia of the testis / epididymis are non-specific. Ultra-sound scan of testis that had been afflicted by malakoplakia may reveal a hypo-echoic mass which is not diagnostic. At times ultrasound scan may reveal a hyper-echogenic mass in the testis. Diagnosis of malakoplakia of the testis can only be confirmed by histological examination of testicular biopsy specimen or orchidectomy specimen. Ultra-sound scan of testes and scrotal contents in malakoplakia of epididymis may reveal a mass in the inferior scrotum which may not be clearly separated from the testis. The mass may be iso-echoic to hypo-echoic with increased vascularity on Doppler scan evaluation in comparison with normal testicular parenchyma. Macroscopic appearance: In malakoplakia of testis gross examination tends to reveal a tan-yellow-brown enlarged testis [1]. Malakoplakia of testis tends to be associated with abscesses and thrombosed vessels. [1] Microscopic features: (see figures 1, 2 and 3) Microscopic examination of the testis with malakoplakia shows testicular atrophy, sheets of histiocytes with Michaelis-Gutmann bodies which is the name given to intracellular and extracellular round structures containing iron and calcium. There is usually evidence of destroyed tubular architecture in the testis. Electron microscopy features: Electron microscopic examination of the testis, affected by malakoplakia reveals bacteria within phagolysomes of histiocytes [1] Diagnosis: Diagnosis of malakoplakia of testis or epididymis can be established by histological examination of biopsy specimens from the mass or excised specimens. It is characterized by the presence of Von Hansemann and intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies called Michaelis-Gutmann bodies [3]. Treatment: Treatment of malakoplakia may be medical or a combination of medical and surgical treatments. Antibiotics that are intracellular bactericidal agents are usually used. (B) Miscellaneous narrations and discussions from some reported cases. Siders et al. [4] reported a 74-year-old man who presented with an acute onset of fever, chills and testicular pain. He was noted to be a diabetic who had undergone renal transplantation 11 years earlier. He had had multiple urinary tract infections associated with immunosuppression. On examination a 3-cm scrotal mass was palpable and a provisional diagnosis of epididymo-orchitis was made, even though the nature of the mass was not clear. He had ultra-sound scan of scrotum which revealed a 2.2 cm x 2.4 cm x 2.5 cm mass on the left side in the inferior scrotum (see figure 1). The mass was not clearly separated from the testis and was iso-echoic to hypo-echoic with increased vascularity on Doppler ultrasound evaluation in comparison with normal testicular parenchyma (see figure 2). The initial ultrasound scan findings were non-specific; nevertheless, based upon the acute onset of symptoms an inflammatory process with bilateral reactive secondary hydrocele was suggested. He had a follow-up ultrasound scan after he had had antibiotic treatment and clinical improvement which revealed a 2.5 cm mass in the left scrotum with echogenicity and hyper-vascularity similar to the previous scan (see figure 3). He was observed and examined regularly for six weeks but the mass remained unchanged. In view of his history of immunosuppression and the fact that the mass had remained the same it was felt malignancy had to be excluded. He underwent a radical orchidectomy with high ligation of the cord structures. Macroscopic examination of the specimen revealed a nodular mass at the junction of the spermatic cord and epididymis with obliteration of the tail of the epididymis. The mass was adherent to the tunica albuginea with indentation of the underlying testis. Histological examination of the specimen revealed typical findings consistent with a diagnosis of malakoplakia without involvement of testis or tunica. Figure 1: This figure shows a haematoxylin and eosin stained section of malakoplakia of testis. Comments: Testicular involvement is seen in 10% - 12% of cases of malakoplakia of genitourinary tract. Tubular architecture is completely destroyed and germ cells are replaced by histiocytes with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm. Several such tubules are seen here. The interstitium contains a lympho-plasmacytic Page64
4 infiltrate. The figure was reproduced with permission from Web Pathology.com Figure 2: This figure shows a haematoxylin and eosin stained section of malakoplakia of testis. Comments: The differential diagnosis of malakoplakia involving testis includes Leydig cell tumour and idiopathic granulomatous orchitis. This figure was reproduced from webpathology.com website with permission from Web Pathology.com analgesia and anti-inflammatory treatment. His clinical condition did not improve after 5 days. His urine culture grew Escherichia coli. He underwent scrotal exploration which revealed that the tunica albuginea was thickened and showed haemorrhagic areas. Thick, purulent fluid within the left testis with yellowish plaques was found (see figure 4). A left orchidectomy was undertaken and histological examination of the excised testis showed eosinophilc cytoplasm. The histocytes exhibited intracytoplasmic Michaelis-Gutmann bodies and PAS stain also confirmed Michaelis-Gutmann bodies. A diagnosis of malakoplakia of testis was confirmed by the histological examination. The purulent fluid on culturing grew Klebsiella pneumonia which was sensitive to Quinolines. He was treated with ciprofloxacin for 3 months and he remained asymptomatic with a follow-up of one year at the time of publication of the paper. Figure 3: Epididymal mass shows numerous histiocytes and Michaelis-Gutmann bodies (arrow) (Haematoxylin and Eosin x 400). This figure was reproduced from Kang Y J, Kim S W, Lee Y S, Kim K H. Malakoplakia of epididymis. Korean Journal of Urology 2013 Apr; 54(4): with permission from the journal, given under the open access article distributed under the terms of the creative commons attribution Non-Commercial Licence ( which permits unrestricted and non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Dubhashi et al. [3] reported a 24-year-old man who presented with pain in his left hemiscrotum of three weeks duration. He did not have any urinary tract symptoms. His clinical examination revealed a swelling in his left hemi-scrotum with an erythematous overlying skin. The swelling on palpation, felt firm associated with local rise in temperature. He did not have any lymph node enlargement. An initial diagnosis of pyocele was made. His urinalysis revealed a few pus cells. He had ultrasound scan of the scrotum which showed an enlarged testis with hypo-echoic echo-texture with highly increased vascularity on Doppler scanning. The ultrasound scan also showed a 9 mm size hypo to iso-echoic wedge shaped lesion at its anterior aspect with no vascularity which was suggestive of haematoma. A diagnosis of left orchitis with small intra-testicular haematoma was made. He was given The first case of malakoplakia of testis was reported in 1958 by Haukohi and Chincinian. [5] A number of postulates exist regarding the aetiology of malakoplakia. McClure [6] suggested that malakoplakia may be an expression of microtubular / microfilamental dysfunction. Alvares Bandres et al. [7] stated that: Page65
5 Various postulates exist with regard to the aetiology of malakoplakia, with three factors playing a major role including: altered phagocytic function of macrophages, gramnegative infection, and an abnormal immune response. Ineffective phagocytosis occurs as a result of defect in the lysosome response of macrophages to bacterial infections which are usually caused by Escherichia coli. There appears to be an imbalance between cyclic adenosine monophosphate (camp) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cgmp), which causes inadequate lysosomic degradation in monocytes. Other disease conditions may co-exist with malakoplakia and some of these include cancer, diabetes, tuberculosis and alcoholic-liver disease. Malakoplakia is an uncommon chronic granulomatous condition of a benign nature which preferentially tends to occur in the genitourinary tract. Testes are affected in 12% of cases of malakoplakia and the first case of malakoplakia of the testis was reported in 1958 and since then by the time of the report of their case of malakoplakia of testis in cases of malakoplakia of the testis had been reported worldwide prior to their publication. Figure 4: Ultrasonography showed a mass lesion of mixed echotexture in epididymal tail. This figure was reproduced from Kang Y J, Kim S W, Lee Y S, Kim K H. Malakoplakia of epididymis. Korean Journal of Urology 2013 Apr; 54(4): with permission from the journal given under the open access article distributed under the terms of the creative commons attribution Non-Commercial Licence ( which permits unrestricted and non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Alvarez Badres et al. [7] reported a case of testicular and epididymal malakoplakia in a 68-yearold man diagnosed with complicated epididymoorchitis who underwent orchidectomy to rule out a malignant tumour. Histopathological examination of the specimen showed a chronic inflammatory infiltrate with histiocytes with eosinophilic cytoplasm containing Michaelis- Gutmann bodies diagnostic of malakoplakia. In 1980, McClure made the ensuing statements [8]: The association between coliform urinary tract infection and malakoplakia of the testis could be explained by the fact that infection of the testis may be acquired via retro-grade spread from the urinary tract and malakoplakia of the testis is intra-tubular initially. Macroscopically, malakoplakia lesions are yellowish soft plaques or nodules; and upon microscopic examination of the lesions tend to reveal Von Hansemann cells which are intensely PAS-posiive structures; Michaelis-Gutmann bodies are pathognomonic of malakoplakia. Escherichia coli was cultured in four out of six cases in whom testicular tissue was cultured for micro-organisms, Klebsiella pneumonia and Proteus were cultured in the other cases. Minor and Lindgren [9] reported an increased frequency of malakoplakia in immunocompromised patients in up to 40% of cases. Christensen et al. [10] stated that treatment of malakoplakia with antibiotics that concentrate in macrophages (e.g. quinolone, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole) is associated with a high cure rate. Kiel and James [2] stated that: Antibiotic treatment which is directed against Escherichia coli in combination with surgery provides the best chance of cure. Bethanecol, a choline agonist, had been used in combination with antibiotics and surgery to treat malakoplakia. Bethanecol may correct the decreased cgmp levels which are understood to interfere with complete bacterial killing. Ascorbic acid had been used to increase the cgmp and cyclic adenosine monophosphate (camp) levels in monocytes, which may represent an effective strategy for treatment. An insufficient number of patients had been treated with ascorbic acid to determine its overall effect. Discontinuation of immunosuppressive drug therapy is usually needed to effectively treat malakoplakia. Page66
6 Malakoplakia of the epididymis without of malakoplakia. His post-operative recovery was involvement of the testis was first reported by Green unremarkable and he had remained well for up to 8 in [11] Siders et al. [4] stated that: months when his case was published. Malakoplakia of the epididymis most often appears as an extension from an adjacent involved testis. By the time of publication of their paper in 2005, malakoplakia confined to the epididymis had been reported 10 times previously. The pathologic and imaging features of malakoplakia are the result of macrophage failure with incomplete digestion of bacteria and granulomatous inflammation. Microscopic examination of malakoplakia shows giant histiocytes with basophilic inclusions known as Michaelis-Gutmann bodies, which are formed from incomplete phagocytosis of bacteria and these inclusions act as foreign bodies and contribute to chronic inflammation and calcifications. Grove et al. [12] suggested that endarteritis and vascular thrombosis are involved in the disease process and manifestations. Imaging findings in malakoplakia are nonspecific and they can range from hypo-echo genicity to hyper-echogenicity often with increased vascularity. Hyper-echoic foci which represent calcifications from chronic infections may also be seen. Guccion et al. [13] in 1978 reported a case of malakoplakia localized to the epididymis. They stated that ultra-structural study had revealed the presence of bacterial bodies in phagolysosomes of malakoplastic macrophages. Kang et al. [14] reported a 61-year-old man who presented with a painful mass in his left epididymis of several months duration. He did not have any fever or a history of trauma. His haematological blood parameters were normal and his urinalysis was normal. His urine culture did not grow any organism. He had ultra-sound scan of the left epididymis which showed a mass lesion of mixed echo-texture in the left epididymal tail (see figure 4). He underwent epididymectomy. Histological examination of the specimen showed an epididymal mass which comprised of sheets of histiocytes with histiocytes with granular eosinophilic cytoplasm (see figure 3) admixed with neutrophils, lymphocytes, and plasma cells. Many of the histiocytes contained small round to oval targetoid structures which were morphologically consistent with Michaelis-Gutmann bodies. The hisological findings were characteristic Summary Malakoplakia is a rare benign chronic inflammatory process which manifests with granulomatous changes and quite often it involves the urogenital system. Malakoplakia of the testis and or epididymis is very rare and may present with testicular pain / lump, fever and chills and these symptoms mimic the presentation of other testicular diseases like epididymo-orchitis and testicular tumour. A number of cases of malakoplakia of testis / epididymis may be associated with renal transplantation, immunosuppression, diabetes, or tuberculosis. Quite often malakoplakis of testis is diagnosed based upon histological examination of the testis following orchidectomy which has been performed as a result of persistent symptoms and persistent testicular mass following a period of antibiotic treatment to exclude malignancy. Ultrasound scan findings in malakoplakia of testis and epididymis are non-specific and they range from hypo-echoic lesions with increased vascularity to hyper-echoic lesions with increased vascularity. A number of cases of malakoplakia of the testis / epididymis are associated with positive urine culture evidence of urinary tract infection of which coliforms are the most common. If there is evidence of urinary tract infection and ultrasound scan evidence of hypoechogenicity/hyper-echogenicity with increased vascularity and the symptoms and testicular mass have not resolved following a period of antibiotic therapy ultrasound guided biopsy of the testicular / epididymal lesion would yield specimens for histological confirmation of malakoplakia. Presence of Michaelis-Gutmann bodies in the histological specimen of the testis and or epididymis is diagnostic of malakoplakia. Malakoplakia of testis / epididymis may be treated by a combination of medical / antibiotic treatment (Quinolones, trimethoprim - sulfamethiazole) and surgery. Malakoplakia of testis / epididymis may be initially misdiagnosed as epididymoorchitis or testicular tumour. Page67
7 If a patient diagnosed with malakoplakia is on immunosuppression then a period of cessation of the immunosuppressant may be beneficial to the recovery of the patient. Conclusions Malakoplakia involving the testis and or epididymis is an uncommon chronic inflammatory condition which clinicians should consider in the differential diagnosis of testicular swellings. Malakoplakia of the testis and or epididymis tend to be associated with gram negative infections especially coliform infections. Conflict of Interest: None Acknowledgements: Acknowledgement to: WebPathology.com for granting copyright permission to the author to reproduce images from their web site. Korean Journal of Urology for granting permission for figures from the journal to be reproduced under the open access article distributed under the terms of the creative commons attribution Non-Commercial Licence ( which permits unrestricted and noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. References 1. Williamson S. Testis and epididymis Nonneoplastic testicular lesions Malakoplakia PathologyOutlines.com 2013 April 21 URL: akia.html 2. Kiel R J, James W D. Malakoplakia Medscape 2012 Jun 19; URL: overview 3. Dubhashi S P, Kumar H, Kulkarni V, Suleman A M. Malakoplakia of the testis. Surgical Science 2014; 5(5): Article ID: 46324,3 pages DOI: /ss Siders B, Win T, Abaza R. Sonographic Evaluation of Epididymal Malakoplakia. Journal Ultrasound Med 2005; 24: Haukohi R S, Chinchinian H. Malakoplakia of Testicle Report of a Case. American Journal of Clinical Pathology 1958; 29: McClure J. Malakoplakia of the Gastrointestinal Tract Postgraduate Medical Journal 1981; 57: Alvares Bandres S, Guarch Troyas R M, Cebrián Lostal J L, Ripa Saldias L, de Pablo Cárdenas A, Jiménez Parra J D. Malakoplakia of the testis: a new case report and a literature review. Actas urologicas Espanolas 2009 Oct; 33(9): doi: 10.16/S (09) McClure J. Malakoplakia of the Testis and its Relationship to Granulomastous Orchitis Journal of Clinical Pathology 1980; 33: Minor L, Lindgren B W. Malakoplakia of the Bladder in a 16-Year-Old Girl. Journal of Urology 2003; 170: Christensen M, Knuhtsen S, Kundsen E. Colonic malakoplakia treated with sulfamethizole and trimethoprim. Ugeskr Laeger Feb 14; 173(7): Green W O. Malakoplakia of the epididymis (without testicular involvement): the first reported case. Arch Pathol 1968; 86: Grove J D C, Harden P, Clark P B. Malakoplakia of epididymis associated with testicular infarction. Br J Urol 1993; 72: Guccion J G, Thorgeirsson U P, Smith B H. Malakoplakia of epididymis. Urology 1978 Dec; 12(6): Kang Y J, Kim S W, Lee Y S, Kim K H. Malakoplakia of epididymis. Korean Journal of Urology 2013 Apr; 54(4): Page68
COLOR DOPPLER ULTRASOUND IN EVALUATION OF SCROTAL LESIONS
 COLOR DOPPLER ULTRASOUND IN EVALUATION OF SCROTAL LESIONS Desai Sanjay D Associate Professor, Department of Radiology, RCSM Govt. Medical College, Kolhapur. ABSTRACT: Color Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive,
COLOR DOPPLER ULTRASOUND IN EVALUATION OF SCROTAL LESIONS Desai Sanjay D Associate Professor, Department of Radiology, RCSM Govt. Medical College, Kolhapur. ABSTRACT: Color Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive,
COLONIC ADENOCARCINOMA WITH MALAKOPLAKIA OF COLON: A CASE REPORT Chitrawati Bal Gargade 1, Abhay Yashwant Desai 2
 COLONIC ADENOCARCINOMA WITH MALAKOPLAKIA OF COLON: A CASE REPORT Chitrawati Bal Gargade 1, Abhay Yashwant Desai 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Chitrawati Bal Gargade, Abhay Yashwant Desai. Colonic Adenocarcinoma
COLONIC ADENOCARCINOMA WITH MALAKOPLAKIA OF COLON: A CASE REPORT Chitrawati Bal Gargade 1, Abhay Yashwant Desai 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Chitrawati Bal Gargade, Abhay Yashwant Desai. Colonic Adenocarcinoma
The Acute Scrotum: Sonographic Findings
 The Acute Scrotum: Sonographic Findings 가천의대길병원방사선과 양달모 Gachon Medical School Introduction Many diseases presenting as acute scrotal pain DDx is important for determining the appropriate treatment US with
The Acute Scrotum: Sonographic Findings 가천의대길병원방사선과 양달모 Gachon Medical School Introduction Many diseases presenting as acute scrotal pain DDx is important for determining the appropriate treatment US with
INFECTIOUS SCROTAL CONDITIONS
 ATHENS 4-6 October 2018 European Society of Urogenital Radiology INFECTIOUS SCROTAL CONDITIONS Mustafa SECIL, MD Professor of Radiology, Dokuz Eylul University Faculty of Medicine Department of Radiology
ATHENS 4-6 October 2018 European Society of Urogenital Radiology INFECTIOUS SCROTAL CONDITIONS Mustafa SECIL, MD Professor of Radiology, Dokuz Eylul University Faculty of Medicine Department of Radiology
Exercise. Discharge Summary
 Exercise Discharge Summary A 32-year-old Brazilian male presented with a 6 month history of right-sided scrotal swelling. Backache was present for 2 months and a history of right epididymitis was present
Exercise Discharge Summary A 32-year-old Brazilian male presented with a 6 month history of right-sided scrotal swelling. Backache was present for 2 months and a history of right epididymitis was present
Acute scrotum. Acute Epididymo-orchitis. Phyllis Yan, APDR (QEH)
 Acute scrotum Acute Epididymo-orchitis Phyllis Yan, APDR (QEH) Conditions leading to acute pain Torsion Acute Epididymitis / Epididymoorchitis Scrotal trauma Inguinal hernias Testicular tumors Epididymitis/epididymo
Acute scrotum Acute Epididymo-orchitis Phyllis Yan, APDR (QEH) Conditions leading to acute pain Torsion Acute Epididymitis / Epididymoorchitis Scrotal trauma Inguinal hernias Testicular tumors Epididymitis/epididymo
Testicular Infarction and Rupture After Blunt Trauma Use of Diagnostic Ultrasound
 Short Review TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2004) 4, 437 441 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2004.101 Testicular Infarction and Rupture After Blunt Trauma Use of Diagnostic Ultrasound Alistair Pace 1, * and
Short Review TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2004) 4, 437 441 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2004.101 Testicular Infarction and Rupture After Blunt Trauma Use of Diagnostic Ultrasound Alistair Pace 1, * and
Painless palpable scrotal mass
 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Urogenital Painless palpable scrotal mass Charis Anastasiadis, Georgia Kyriakopoulou, Charikleia Triantopoulou Radiology Department, Konstantopoulio General Hospital of Nea
Clinical Case - Test Yourself Urogenital Painless palpable scrotal mass Charis Anastasiadis, Georgia Kyriakopoulou, Charikleia Triantopoulou Radiology Department, Konstantopoulio General Hospital of Nea
The Sonographic Pattern of Diseases Presenting with Scrotal Pain at Mulago Hospital, Kampala, Uganda
 http://www.bioline.org.br/js 68 The Sonographic Pattern of Diseases Presenting with Scrotal Pain at Mulago Hospital, Kampala, Uganda J. Opio 1, R.K. Byanyima 2, E. Kiguli-Malwadde 2, S. Kaggwa 3, M. Kawooya
http://www.bioline.org.br/js 68 The Sonographic Pattern of Diseases Presenting with Scrotal Pain at Mulago Hospital, Kampala, Uganda J. Opio 1, R.K. Byanyima 2, E. Kiguli-Malwadde 2, S. Kaggwa 3, M. Kawooya
Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary Pathology Report Final Diagnosis: Oncology Consult
 Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 31-year-old Brazilian male presented with a 6 month history of right-sided scrotal swelling. Backache was present for 2 months and a history of right epididymitis was
Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 31-year-old Brazilian male presented with a 6 month history of right-sided scrotal swelling. Backache was present for 2 months and a history of right epididymitis was
*OPERATIVE PROCEDURE. Serum tumour markers within normal limits S1.04 PRINCIPAL CLINICIAN
 Neoplasia of the Testis - Orchidectomy Histopathology Reporting Proforma Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Indigenous
Neoplasia of the Testis - Orchidectomy Histopathology Reporting Proforma Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Indigenous
Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary Pathology Report Final Diagnosis: Oncology Consult
 Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 31-year-old Brazilian male presented with a 6 month history of right-sided scrotal swelling. Backache was present for 2 months and a history of right epididymitis was
Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 31-year-old Brazilian male presented with a 6 month history of right-sided scrotal swelling. Backache was present for 2 months and a history of right epididymitis was
Intraparenchymatous adenomatoid tumor dependent on the rete testis: A case report and review of literature
 Intraparenchymatous adenomatoid tumor dependent on the rete testis: A case report and review of literature A. Jiménez Pacheco, J. L. Martínez Torres, F. Valle Díaz de la Guardia, M. A. Arrabal Polo, and
Intraparenchymatous adenomatoid tumor dependent on the rete testis: A case report and review of literature A. Jiménez Pacheco, J. L. Martínez Torres, F. Valle Díaz de la Guardia, M. A. Arrabal Polo, and
Global Testicular Infarction in the Presence of Epididymitis
 CASE SERIES Global Testicular Infarction in the Presence of Epididymitis Clinical Features, Appearances on Grayscale, Color Doppler, and Contrast-Enhanced Sonography, and Histologic Correlation Gibran
CASE SERIES Global Testicular Infarction in the Presence of Epididymitis Clinical Features, Appearances on Grayscale, Color Doppler, and Contrast-Enhanced Sonography, and Histologic Correlation Gibran
Testicular ultrasound in acute scrotal pain - beyond testicular torsion
 Testicular ultrasound in acute scrotal pain - beyond testicular torsion Poster No.: C-1284 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Rolla, M. Nogueira, M. J. Aguiar, D. S. Garrido, J. A.
Testicular ultrasound in acute scrotal pain - beyond testicular torsion Poster No.: C-1284 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Rolla, M. Nogueira, M. J. Aguiar, D. S. Garrido, J. A.
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations
 Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Bilateral Segmental Testicular Infarction
 Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2007) 7, 779 783 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2007.146 Bilateral Segmental Testicular Infarction Aaron Bayne 1, Brad Koslin 2, and Siamak Daneshmand
Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2007) 7, 779 783 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2007.146 Bilateral Segmental Testicular Infarction Aaron Bayne 1, Brad Koslin 2, and Siamak Daneshmand
preceded by pyogenic epididymoorchitis
 J. clin. Path., 1970, 23, 668-675 Infected infarcts of the testis: A study of 18 cases preceded by pyogenic epididymoorchitis D. O'B. HOURIHANE From the Central Histopathology Laboratory of the Federated
J. clin. Path., 1970, 23, 668-675 Infected infarcts of the testis: A study of 18 cases preceded by pyogenic epididymoorchitis D. O'B. HOURIHANE From the Central Histopathology Laboratory of the Federated
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Vikram Dogra, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Urology & BME Department of Imaging Sciences University Of Rochester Medical Center
 Ultrasound of the Scrotum Vikram Dogra, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Urology & BME Department of Imaging Sciences University Of Rochester Medical Center Etiologies of Acute Scrotal Pain Epididymitis/Orchitis
Ultrasound of the Scrotum Vikram Dogra, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Urology & BME Department of Imaging Sciences University Of Rochester Medical Center Etiologies of Acute Scrotal Pain Epididymitis/Orchitis
Guidelines for the Management of Acute Scrotal Pain in Children (V 1.0)
 Guidelines for the Management of Acute Scrotal Pain in Children (V 1.0) Clinical Director Signed Name... Mr C. Hendrickse.. Date 14/10/2011.. Meta Data Guideline Title: Guidelines for the Management of
Guidelines for the Management of Acute Scrotal Pain in Children (V 1.0) Clinical Director Signed Name... Mr C. Hendrickse.. Date 14/10/2011.. Meta Data Guideline Title: Guidelines for the Management of
Differential Diagnosis of Focal Epididymal Lesions With Gray Scale Sonographic, Color Doppler Sonographic, and Clinical Features
 Article Differential Diagnosis of Focal Epididymal Lesions With Gray Scale Sonographic, Color Doppler Sonographic, and Clinical Features Dal Mo Yang, MD, Sun Ho Kim, MD, Ha Na Kim, MD, Jee Hee Kang, MD,
Article Differential Diagnosis of Focal Epididymal Lesions With Gray Scale Sonographic, Color Doppler Sonographic, and Clinical Features Dal Mo Yang, MD, Sun Ho Kim, MD, Ha Na Kim, MD, Jee Hee Kang, MD,
Department of Medical Imaging, The Ottawa Hospital. Satheesh Krishna Sabarish Narayanasamy Wael Shabana Adnan Sheikh
 Department of Medical Imaging, The Ottawa Hospital. Satheesh Krishna Sabarish Narayanasamy Wael Shabana Adnan Sheikh Nothing to disclose Common and unusual presentations and manifestations of testicular
Department of Medical Imaging, The Ottawa Hospital. Satheesh Krishna Sabarish Narayanasamy Wael Shabana Adnan Sheikh Nothing to disclose Common and unusual presentations and manifestations of testicular
ADVERSE EFFECTS OF VASECTOMY: SPERM GRANULOMA OF EPIDIDYMIDES V. P. DIXIT
 ADVERSE EFFECTS OF VASECTOMY: SPERM GRANULOMA OF EPIDIDYMIDES V. P. DIXIT Reproduct ion Physiology Section, Department of Zoology, University of Rajasthan, Jaipur-302004 Summary: Rats and mice were vasectomized
ADVERSE EFFECTS OF VASECTOMY: SPERM GRANULOMA OF EPIDIDYMIDES V. P. DIXIT Reproduct ion Physiology Section, Department of Zoology, University of Rajasthan, Jaipur-302004 Summary: Rats and mice were vasectomized
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology
 Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Gary Faerber, M.D., 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Gary Faerber, M.D., 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
What s Your Diagnosis?
 What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: 5 year old MC Belgian Malinois Presenting Complaint: Perineal hernia as well as not eating or defecating History: The patient presented to the KSU VHC on 7/28/2018 for
What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: 5 year old MC Belgian Malinois Presenting Complaint: Perineal hernia as well as not eating or defecating History: The patient presented to the KSU VHC on 7/28/2018 for
Miss Rashmi Singh Consultant urological Surgeon. Men s Health Seminar Parkside Hospital November 2016
 Miss Rashmi Singh Consultant urological Surgeon Men s Health Seminar Parkside Hospital November 2016 Hernia Hydrocele Varicocele Infections Epididymal cyst Testicular Ca Miscellaneous Phimosis Paraphimosis
Miss Rashmi Singh Consultant urological Surgeon Men s Health Seminar Parkside Hospital November 2016 Hernia Hydrocele Varicocele Infections Epididymal cyst Testicular Ca Miscellaneous Phimosis Paraphimosis
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
TitleUltrasonic evaluation of scrotal sw. Author(s) MISAKI, Toshimitsu; HISAZUMI, Haruo. Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1985), 31(7):
 TitleUltrasonic evaluation of scrotal sw Author(s) MISAKI, Toshimitsu; HISAZUMI, Haruo Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1985), 31(7): 1151-1158 Issue Date 1985-07 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/118548 Right Type Departmental
TitleUltrasonic evaluation of scrotal sw Author(s) MISAKI, Toshimitsu; HISAZUMI, Haruo Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1985), 31(7): 1151-1158 Issue Date 1985-07 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/118548 Right Type Departmental
Role of Colour Doppler Ultrasonography in evaluation of scrotal pain and swelling
 Original Research Article Role of Colour Doppler Ultrasonography in evaluation of scrotal pain and swelling Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College, Rajnandgaon Chattisghar,
Original Research Article Role of Colour Doppler Ultrasonography in evaluation of scrotal pain and swelling Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College, Rajnandgaon Chattisghar,
D. KOJIĆ, 1 VINKA VUKOTIĆ, 1 I. BORIČIĆ, 2 U. BABIĆ, 1 SONJA KAPETANOVIĆ, 3 and T. STAVRIĆ 4
 Arch. Biol. Sci., Belgrade, 66 (3), 1041-1045, 2014 DOI:10.2298/ABS1403041K Evaluation of Indolent EPIDIDYMAL Mass Adenomatoid Tumor of the Epididymis D. KOJIĆ, 1 VINKA VUKOTIĆ, 1 I. BORIČIĆ, 2 U. BABIĆ,
Arch. Biol. Sci., Belgrade, 66 (3), 1041-1045, 2014 DOI:10.2298/ABS1403041K Evaluation of Indolent EPIDIDYMAL Mass Adenomatoid Tumor of the Epididymis D. KOJIĆ, 1 VINKA VUKOTIĆ, 1 I. BORIČIĆ, 2 U. BABIĆ,
Case Report Primary Malignancy in a Supernumerary Testicle Presenting as a Large Pelvic Mass
 Hindawi Volume 2017, Article ID 4529853, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4529853 Case Report Primary Malignancy in a Supernumerary Testicle Presenting as a Large Pelvic Mass Justin Noroozian, 1 Daniel
Hindawi Volume 2017, Article ID 4529853, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4529853 Case Report Primary Malignancy in a Supernumerary Testicle Presenting as a Large Pelvic Mass Justin Noroozian, 1 Daniel
BENIGN & MALIGNANT TESTIS DISEASES. Gary J. Faerber, M.D. Associate Professor, Dept of Urology March 2009 OBJECTIVES
 BENIGN & MALIGNANT TESTIS DISEASES Gary J. Faerber, M.D. Associate Professor, Dept of Urology March 2009 OBJECTIVES 1. Become familiar with the scrotal contents and their anatomical relationship with each
BENIGN & MALIGNANT TESTIS DISEASES Gary J. Faerber, M.D. Associate Professor, Dept of Urology March 2009 OBJECTIVES 1. Become familiar with the scrotal contents and their anatomical relationship with each
Case Report No significant risk of secondary prostatic cancer in a patient with prostatic malakoplakia after a four-year follow-up
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(8):4153-4157 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0073257 Case Report No significant risk of secondary prostatic cancer in a patient with prostatic malakoplakia after a four-year
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(8):4153-4157 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0073257 Case Report No significant risk of secondary prostatic cancer in a patient with prostatic malakoplakia after a four-year
Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents
 Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Bilateral meconium hydrocele An uncommon case
 Bilateral meconium hydrocele An uncommon case Didem Turcan 1, Evrim Yılmaz 1, Deniz Arık 1, Baran Tokar 2 1 Department of Pathology, 2 Department of Pediatric Surgery, Introduction Meconium hydrocele is
Bilateral meconium hydrocele An uncommon case Didem Turcan 1, Evrim Yılmaz 1, Deniz Arık 1, Baran Tokar 2 1 Department of Pathology, 2 Department of Pediatric Surgery, Introduction Meconium hydrocele is
Role of ultrasound and color Doppler in the evaluation of acute scrotal pain
 Bang Med J Khulna 2017; 50 : 26-30 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Abstract Role of ultrasound and color Doppler in the evaluation of acute scrotal pain G Salahuddin 1, SMZ Nayeem 2, SM Hossain 3, S Parvin 4, MM Hossain
Bang Med J Khulna 2017; 50 : 26-30 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Abstract Role of ultrasound and color Doppler in the evaluation of acute scrotal pain G Salahuddin 1, SMZ Nayeem 2, SM Hossain 3, S Parvin 4, MM Hossain
The role of ultrasonography with colour Doppler in the acute scrotum
 The role of ultrasonography with colour Doppler in the acute scrotum Poster No.: C-1509 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. S. R. O. Faustino, A. L. Amado Costa, J. J. B. Leitão, I.
The role of ultrasonography with colour Doppler in the acute scrotum Poster No.: C-1509 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. S. R. O. Faustino, A. L. Amado Costa, J. J. B. Leitão, I.
VI E Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (114)
 264 Medical Education Singapore Med.1 2007, 48 (3) : VI E Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (114) Muttarak M, Thinyu S, Lojanapiwat B Fig. I Clinical photograph of the scrotum. T t o T Fig. 2a Longitudinal
264 Medical Education Singapore Med.1 2007, 48 (3) : VI E Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (114) Muttarak M, Thinyu S, Lojanapiwat B Fig. I Clinical photograph of the scrotum. T t o T Fig. 2a Longitudinal
Wedge Biopsy for Diffuse Lung Diseases
 Chapter VI Wedge Biopsy for Diffuse Lung Diseases Wedge biopsy via thoracoscopic biopsy or open lung biopsy is occasionally performed to obtain tissue for the diagnosis of a diffuse lung disease. A wedge
Chapter VI Wedge Biopsy for Diffuse Lung Diseases Wedge biopsy via thoracoscopic biopsy or open lung biopsy is occasionally performed to obtain tissue for the diagnosis of a diffuse lung disease. A wedge
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi
 number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
Giant Ulcerative Lactating Nodule of Ectopic Breast Mimicking Malignancy.
 57 Giant Ulcerative Lactating Nodule of Ectopic Breast Mimicking Malignancy. I. Roy 1 FRCS(C), E Othieno 2 MMed (Path), R Ssentongo 3 FCS (ECSA) 1 Department of Pathology, St. Raphael of St. Francis Hospital,
57 Giant Ulcerative Lactating Nodule of Ectopic Breast Mimicking Malignancy. I. Roy 1 FRCS(C), E Othieno 2 MMed (Path), R Ssentongo 3 FCS (ECSA) 1 Department of Pathology, St. Raphael of St. Francis Hospital,
Bilateral Epididymal Cyst in 65 Years Old Man A Case Report Thorat Nilesh Suresh 1 *, Raut Subhash Y 2 and Kedar Nita M 3
 Int J Ayu Pharm Chem CASE STUDY www.ijapc.com e-issn 2350-0204 Bilateral Epididymal Cyst in 65 Years Old Man A Case Report Thorat Nilesh Suresh 1 *, Raut Subhash Y 2 and Kedar Nita M 3 1-3 Shalyatantra
Int J Ayu Pharm Chem CASE STUDY www.ijapc.com e-issn 2350-0204 Bilateral Epididymal Cyst in 65 Years Old Man A Case Report Thorat Nilesh Suresh 1 *, Raut Subhash Y 2 and Kedar Nita M 3 1-3 Shalyatantra
Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes
 CHAPTER e40 Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes Carol A. Langford Anthony S. Fauci Diagnosis of the vasculitic syndromes is usually based upon characteristic histologic or arteriographic findings in a patient
CHAPTER e40 Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes Carol A. Langford Anthony S. Fauci Diagnosis of the vasculitic syndromes is usually based upon characteristic histologic or arteriographic findings in a patient
HISTOPATHOLOGY. Shannon Martinson
 HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Role of ultrasound and colour doppler in assessment of adult scrotal pathologies
 Original Research Article Role of ultrasound and colour doppler in assessment of adult scrotal pathologies Ajay Vare 1, Dayanand Kawade 2*, Varsha Rote Kakinalkar 3, Prashant Titare 4, Samruddhi Sonawane
Original Research Article Role of ultrasound and colour doppler in assessment of adult scrotal pathologies Ajay Vare 1, Dayanand Kawade 2*, Varsha Rote Kakinalkar 3, Prashant Titare 4, Samruddhi Sonawane
Scrotum Kacey Morrison Amanda Baxter Sabrina Tucker July 18, 2006 SCROTUM
 Scrotum Kacey Morrison Amanda Baxter Sabrina Tucker July 18, 2006 SCROTUM 1) Other Names: Scrotum None Testicles Testes (Curry Tempkin, p. 236, 2/3/2) Ductus deferens spermatic cord (Tempkin, p. 279, Anatomy
Scrotum Kacey Morrison Amanda Baxter Sabrina Tucker July 18, 2006 SCROTUM 1) Other Names: Scrotum None Testicles Testes (Curry Tempkin, p. 236, 2/3/2) Ductus deferens spermatic cord (Tempkin, p. 279, Anatomy
Scrotal pain and Swelling
 Scrotal pain and Swelling Color index : Important Further explanation Done By: Nada Alamri Editing link Acute Scrotal Pain DDx: 1) Testicular torsion : Twisting and strangulation of the testicle on the
Scrotal pain and Swelling Color index : Important Further explanation Done By: Nada Alamri Editing link Acute Scrotal Pain DDx: 1) Testicular torsion : Twisting and strangulation of the testicle on the
Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males
 Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males Clinical presentation For patients in care homes see UTI in adults where IV Antibiotics in the community may be appropriate (under development) History and
Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males Clinical presentation For patients in care homes see UTI in adults where IV Antibiotics in the community may be appropriate (under development) History and
Cellular Pathology. Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018
 Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
A RARE CASE OF FIBROUS PSEUDO TUMOR
 IJCRR Vol 06 issue 14 Section: Healthcare Category: Case Report Received on: 14/05/14 Revised on: 09/06/14 Accepted on: 10/07/14 Sudha V., Ganthimathy Sekhar, Karunakumar, Jayaganesh, Vimal Chander R.
IJCRR Vol 06 issue 14 Section: Healthcare Category: Case Report Received on: 14/05/14 Revised on: 09/06/14 Accepted on: 10/07/14 Sudha V., Ganthimathy Sekhar, Karunakumar, Jayaganesh, Vimal Chander R.
Figure 2: Lymph node Cortical follicular (F) and paracortical (PC) atrophy, with narrowing of the cortex relative to the medulla (M).
 Figure 1: Lymph node Follicular hyperplasia, with expansion of the follicular germinal centres (F) by large blast cells. Paracortical hyperplasia, with expansion of the paracortex (PC) by small lymphocytes.
Figure 1: Lymph node Follicular hyperplasia, with expansion of the follicular germinal centres (F) by large blast cells. Paracortical hyperplasia, with expansion of the paracortex (PC) by small lymphocytes.
Menigitidis. Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline
 Menigitidis Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea Division of Pathology School of Medicine & Health Sciences Review Normal Microanatomy Image Ref: www.histology-world.com
Menigitidis Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea Division of Pathology School of Medicine & Health Sciences Review Normal Microanatomy Image Ref: www.histology-world.com
Sonography of the Scrotum: Case-Based Review
 AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Sonography of the Scrotum: Case-Based Review Joseph W. Stengel 1,2 and Erick M. Remer 1 ABSTRACT Objective We discuss five scenarios in which sonography
AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Sonography of the Scrotum: Case-Based Review Joseph W. Stengel 1,2 and Erick M. Remer 1 ABSTRACT Objective We discuss five scenarios in which sonography
Imaging Guided Biopsy. Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc Lecturer,Reporting Sonographer
 Imaging Guided Biopsy Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc Lecturer,Reporting Sonographer Objective By the End of this lessons you should : Define what biopsy Justify Aim to perform biopsy
Imaging Guided Biopsy Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc Lecturer,Reporting Sonographer Objective By the End of this lessons you should : Define what biopsy Justify Aim to perform biopsy
6 UROLOGICAL CANCERS. 6.1 Key Points
 6 UROLOGICAL CANCERS 6.1 Key Points Prostate Cancer Commonest cancer in males in Scotland Approximately 99% of cases occur in men aged > 50 years About 40% of cases present in men aged < 70 years when
6 UROLOGICAL CANCERS 6.1 Key Points Prostate Cancer Commonest cancer in males in Scotland Approximately 99% of cases occur in men aged > 50 years About 40% of cases present in men aged < 70 years when
Note: The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
Role of high frequency ultrasound and color Doppler examination in scrotal lesions
 Original article: Role of high frequency ultrasound and color Doppler examination in scrotal lesions 1Sanjeev Sharma, 2 Monika Jindal, 3 Sakshi Sharma, 4 Rekha Goyal, 5 Subhash Goyal 1Assistant Professor
Original article: Role of high frequency ultrasound and color Doppler examination in scrotal lesions 1Sanjeev Sharma, 2 Monika Jindal, 3 Sakshi Sharma, 4 Rekha Goyal, 5 Subhash Goyal 1Assistant Professor
General Surgery Curriculum Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, General Surgeons Australia & New Zealand Association of General Surgeons
 General Surgery Curriculum Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, General Surgeons Australia & New Zealand Association of General Surgeons MODULE TITLE: ABDOMINAL WALL, RETROPERITONEUM, UROGENITAL 5-May-2013
General Surgery Curriculum Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, General Surgeons Australia & New Zealand Association of General Surgeons MODULE TITLE: ABDOMINAL WALL, RETROPERITONEUM, UROGENITAL 5-May-2013
Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Inguinal orchidectomy for testicular cancer
 Surgery Illustrated Focus on Details SURGERY ILLUSTRATED SURGICAL ATLASPIZZOCARO and GUARNERI PIZZOCARO and GUARNERI BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Inguinal orchidectomy for
Surgery Illustrated Focus on Details SURGERY ILLUSTRATED SURGICAL ATLASPIZZOCARO and GUARNERI PIZZOCARO and GUARNERI BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Inguinal orchidectomy for
Case 5385 Tubular ectasia of the rete testis: a benign testicular entity diagnosed on imaging
 Case 5385 Tubular ectasia of the rete testis: a benign testicular entity diagnosed on imaging A. C. Tsili 1, C. Tsampoulas 1, D. Giannakis 2, A. Chaidou 1, N. Sofikitis 2, S. C. Efremidis 1 1 Department
Case 5385 Tubular ectasia of the rete testis: a benign testicular entity diagnosed on imaging A. C. Tsili 1, C. Tsampoulas 1, D. Giannakis 2, A. Chaidou 1, N. Sofikitis 2, S. C. Efremidis 1 1 Department
Scrotum infection types
 P ford residence southampton, ny Scrotum infection types A hydrocele is a sac. The two types of. The most common side effects of needle aspiration are temporary pain in your scrotum and risk of infection.
P ford residence southampton, ny Scrotum infection types A hydrocele is a sac. The two types of. The most common side effects of needle aspiration are temporary pain in your scrotum and risk of infection.
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis. Dr: Salah Ahmed
 Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, Tuen Mun Hospital, Hong Kong; 2 Department of Pathology, Tuen Mun Hospital, Hong Kong.
 JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2016;6(2):254-258 Malakoplakia of the Urinary Tract: A Benign Disease with a Possible Malignant Outcome Wong SHL 1, Yeung VHW 1, Lee WK 2, Lee YK 1, Chan MTY 1, Cheng CH 1, Chu
JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2016;6(2):254-258 Malakoplakia of the Urinary Tract: A Benign Disease with a Possible Malignant Outcome Wong SHL 1, Yeung VHW 1, Lee WK 2, Lee YK 1, Chan MTY 1, Cheng CH 1, Chu
Reticuloendothelial System (RES) & Spleen Dr. Nervana Bayoumy
 Haematology Lectures Reticuloendothelial System (RES) & Spleen Dr. Nervana Bayoumy 1 Objectives 1. Define the term Reticuloendothelial system (RES). 2. Describe the cellular components of RES. 3. Describe
Haematology Lectures Reticuloendothelial System (RES) & Spleen Dr. Nervana Bayoumy 1 Objectives 1. Define the term Reticuloendothelial system (RES). 2. Describe the cellular components of RES. 3. Describe
A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY OF TUBERCULOUS EPIDIDYMO-ORCHITIS IN THAILAND
 Tuberculous Epididymo-Orchitis in Thailand A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY OF TUBERCULOUS EPIDIDYMO-ORCHITIS IN THAILAND Ulan Suankwan 1, Noppadol Larbcharoensub 1, Wit Viseshsindh 2, Cholatip Wiratkapun 3 and
Tuberculous Epididymo-Orchitis in Thailand A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY OF TUBERCULOUS EPIDIDYMO-ORCHITIS IN THAILAND Ulan Suankwan 1, Noppadol Larbcharoensub 1, Wit Viseshsindh 2, Cholatip Wiratkapun 3 and
Cell injury, adaptation and death. Unite one Second Lab.
 Cell injury, adaptation and death Unite one Second Lab. The two lung abscesses seen here are examples of liquefactive necrosis in which there is a liquid center in an area of tissue injury. One abscess
Cell injury, adaptation and death Unite one Second Lab. The two lung abscesses seen here are examples of liquefactive necrosis in which there is a liquid center in an area of tissue injury. One abscess
Malakoplakia in a healthy young female patient
 CASE REPORT Korean J Intern Med 2013;28:475-480 http://dx.doi.org/10.3904/kjim.2013.28.4.475 Malakoplakia in a healthy young female patient Kyung Hee Hyun 1, Hyun Deok Shin 1, and Dong Hoon Kim 2 Departments
CASE REPORT Korean J Intern Med 2013;28:475-480 http://dx.doi.org/10.3904/kjim.2013.28.4.475 Malakoplakia in a healthy young female patient Kyung Hee Hyun 1, Hyun Deok Shin 1, and Dong Hoon Kim 2 Departments
manifestations are uncommon. Initial descriptions of the disease (Rosai and Dorfman, 1969) specifically
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (July 1980) 56, 521-525 Diffuse cutaneous involvement and sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy A. A. WOODCOCK B.Sc., M.B., Ch.B., M.R.C.P. Summary Severe skin involvement
Postgraduate Medical Journal (July 1980) 56, 521-525 Diffuse cutaneous involvement and sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy A. A. WOODCOCK B.Sc., M.B., Ch.B., M.R.C.P. Summary Severe skin involvement
HDF Case Whipple s disease
 HDF Case 952556 Whipple s disease 63 yo female complaining of a diarrhea for 2 months, weigth loss (12 Kg in 3 months), and joint pains. Duodenal biopsy performed. Scanning view, enlarged intestinal villi,
HDF Case 952556 Whipple s disease 63 yo female complaining of a diarrhea for 2 months, weigth loss (12 Kg in 3 months), and joint pains. Duodenal biopsy performed. Scanning view, enlarged intestinal villi,
Acute Groin Pain Following Trauma
 Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Department of Family Medicine Acute Groin Pain Following Trauma Victoria Chen MD Lehigh Valley Health Network, victoria.chen@lvhn.org Follow this and additional
Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Department of Family Medicine Acute Groin Pain Following Trauma Victoria Chen MD Lehigh Valley Health Network, victoria.chen@lvhn.org Follow this and additional
Chapter 17. The Lymphatic System and Immunity. Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Hths 2231 Laboratory 14 Alterations in the Reproductive System and STDs
 Complete activities 1-3. Activity #1: Click on the STD fact-sheet link under activity 1 to complete the information on the STD tables. Write the information on the lab worksheet. Activity #2: Complete
Complete activities 1-3. Activity #1: Click on the STD fact-sheet link under activity 1 to complete the information on the STD tables. Write the information on the lab worksheet. Activity #2: Complete
Doppler ultrasound of the abdomen and pelvis, and color Doppler
 - - - - - - - - - - - - - Testicular tumors are rare in children. They account for only 1% of all pediatric solid tumors and 3% of all testicular tumors [1,2]. The annual incidence of testicular tumors
- - - - - - - - - - - - - Testicular tumors are rare in children. They account for only 1% of all pediatric solid tumors and 3% of all testicular tumors [1,2]. The annual incidence of testicular tumors
Diagnosis and Management of the Acute Scrotum. AUA update series 2016 volume 35. By Anas Hindawi,Urology Resident Moderated by Dr.
 Diagnosis and Management of the Acute Scrotum AUA update series 2016 volume 35 By Anas Hindawi,Urology Resident Moderated by Dr. Khalid Al Sayyid Introduction The acute onset of pain,tenderness or swelling
Diagnosis and Management of the Acute Scrotum AUA update series 2016 volume 35 By Anas Hindawi,Urology Resident Moderated by Dr. Khalid Al Sayyid Introduction The acute onset of pain,tenderness or swelling
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY
 CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of INFECTIOUS DISEASES MICROSCOPY Rengin Ahıskalı Macroscopy samples are shown in the macroscopy presentations of the first two courses.
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of INFECTIOUS DISEASES MICROSCOPY Rengin Ahıskalı Macroscopy samples are shown in the macroscopy presentations of the first two courses.
Bladder Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT. Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT)
 Bladder Case 1 February 17, 2007 Specimen (s) received: Bladder Tumor Pre-operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Post operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of
Bladder Case 1 February 17, 2007 Specimen (s) received: Bladder Tumor Pre-operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Post operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of
CPC 4 Breast Cancer. Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast.
 CPC 4 Breast Cancer Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast. 1. What are the most likely diagnoses of this lump? Fibroadenoma
CPC 4 Breast Cancer Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast. 1. What are the most likely diagnoses of this lump? Fibroadenoma
Testicular fibrous hamartoma: A case report
 Ped Urol Case Rep 2015; 2(5):5-9 DOI: 10.14534/PUCR.2015512749 Ped Urol Case Rep PEDIATRIC UROLOGY CASE REPORTS ISSN: 2148 2969 Journal homepage: http://www.pediatricurologycasereports.com Testicular fibrous
Ped Urol Case Rep 2015; 2(5):5-9 DOI: 10.14534/PUCR.2015512749 Ped Urol Case Rep PEDIATRIC UROLOGY CASE REPORTS ISSN: 2148 2969 Journal homepage: http://www.pediatricurologycasereports.com Testicular fibrous
Abscess. A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body.
 Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
Scrotal Swellings. Dr John Nash GPwSI Urology
 Scrotal Swellings Dr John Nash GPwSI Urology Mode of Presentation Acute Pain Elective Non-acute Pain Acute Painful Presentation Testicular Torsion Torsion of Testicular Appendage ( Hydatid of Morgagni)
Scrotal Swellings Dr John Nash GPwSI Urology Mode of Presentation Acute Pain Elective Non-acute Pain Acute Painful Presentation Testicular Torsion Torsion of Testicular Appendage ( Hydatid of Morgagni)
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Heyam Awad
 number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
 TitleBenign cystic lesion of the tunica Author(s) Tanaka, Kazushi; Kamidono, Sadao; Y Keiichi Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (2004), 50(1): 45-48 Issue Date 2004-01 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/113289 Right Type Departmental
TitleBenign cystic lesion of the tunica Author(s) Tanaka, Kazushi; Kamidono, Sadao; Y Keiichi Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (2004), 50(1): 45-48 Issue Date 2004-01 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/113289 Right Type Departmental
Case Report Seminoma Presenting as Renal Mass, Inferior Vena Caval Thrombus, and Regressed Testicular Mass
 Case Reports in Urology Volume 2015, Article ID 835962, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/835962 Case Report Seminoma Presenting as Renal Mass, Inferior Vena Caval Thrombus, and Regressed Testicular
Case Reports in Urology Volume 2015, Article ID 835962, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/835962 Case Report Seminoma Presenting as Renal Mass, Inferior Vena Caval Thrombus, and Regressed Testicular
New lung lesion in a 55 year-old male treated with chemoradiation for non-small cell lung carcinoma
 July 2016 New lung lesion in a 55 year-old male treated with chemoradiation for non-small cell lung carcinoma Contributed by: Laurel Rose, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Medicine,
July 2016 New lung lesion in a 55 year-old male treated with chemoradiation for non-small cell lung carcinoma Contributed by: Laurel Rose, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Medicine,
International Journal of Case Studies in Clinical Research
 Case Report International Journal of Case Studies in Clinical Research Open Access Acute Vasitis Presenting as an Inguinoscrotal Swelling: A Diagnostic Dilemma 1 Akanji Akinwunmi O, 2 Akinola Oluwaseun
Case Report International Journal of Case Studies in Clinical Research Open Access Acute Vasitis Presenting as an Inguinoscrotal Swelling: A Diagnostic Dilemma 1 Akanji Akinwunmi O, 2 Akinola Oluwaseun
Case Report Multiple Giant Cell Tumors of Tendon Sheath Found within a Single Digit of a 9-Year-Old
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1834740, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1834740 Case Report Multiple Giant Cell Tumors of Tendon Sheath Found within a Single Digit of a 9-Year-Old
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1834740, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1834740 Case Report Multiple Giant Cell Tumors of Tendon Sheath Found within a Single Digit of a 9-Year-Old
Sonography of the scrotum: still the best!
 Sonography of the scrotum: still the best! Poster No.: C-1110 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. Mnari, A. Zrig, M. Maatouk, B. Hmida, R. Salem, W. HarzallahHizem, M. Golli; Monastir/TN
Sonography of the scrotum: still the best! Poster No.: C-1110 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. Mnari, A. Zrig, M. Maatouk, B. Hmida, R. Salem, W. HarzallahHizem, M. Golli; Monastir/TN
Ultrasound of malignant testicular lesions. Arne Hørlyck Department of Radiology Aarhus University Hospital, Skejby
 Ultrasound of malignant testicular lesions Arne Hørlyck Department of Radiology Aarhus University Hospital, Skejby Testis Ultrasound is fantastic!! Scrotum Extratesticular mass: Benign Intratesticular
Ultrasound of malignant testicular lesions Arne Hørlyck Department of Radiology Aarhus University Hospital, Skejby Testis Ultrasound is fantastic!! Scrotum Extratesticular mass: Benign Intratesticular
MALE GENITAL SURGICAL PROCEDURES
 Male Genital Surgical ProceduresDecember 22, 2015 (effective March 1, 201) PENIS Slit of prepuce (complete care) S5 - newborn... 14.35 S58 - infant... 21.50 S59 - adult or child... 30.25 EXCISION Circumcision
Male Genital Surgical ProceduresDecember 22, 2015 (effective March 1, 201) PENIS Slit of prepuce (complete care) S5 - newborn... 14.35 S58 - infant... 21.50 S59 - adult or child... 30.25 EXCISION Circumcision
Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1989), 35(11):
 TitleOsteoma of the testis with its hist Author(s) SASAKI, Koichi; KINOSHITA, Yuzo; HA FUKUNAGA, Noboru Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1989), 35(11): 1965-1968 Issue Date 1989-11 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/116733
TitleOsteoma of the testis with its hist Author(s) SASAKI, Koichi; KINOSHITA, Yuzo; HA FUKUNAGA, Noboru Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1989), 35(11): 1965-1968 Issue Date 1989-11 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/116733
Cardiff MRCS OSCE Courses Testicular Cancer
 Testicular Cancer Scenario: A 40-year-old male presents to the surgical out-patient clinic with a 6-8 week history of a painless lump in his left scrotum. He however complains of a dull ache in the scrotum
Testicular Cancer Scenario: A 40-year-old male presents to the surgical out-patient clinic with a 6-8 week history of a painless lump in his left scrotum. He however complains of a dull ache in the scrotum
Histopathology: chronic inflammation
 Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
THE EFFECTS OF LIGATION OF CAUDA EPIDIDYMIDIS ON THE DOG TESTIS
 Copyright 1974 The American Fertility Society FERTILITY AND STERILITY Vol. 25, No.3, March, 1974 Printed in U.S.A. THE EFFECTS OF LIGATION OF CAUDA EPIDIDYMIDIS ON THE DOG TESTIS A. M. VARE, M.B.B.S.,
Copyright 1974 The American Fertility Society FERTILITY AND STERILITY Vol. 25, No.3, March, 1974 Printed in U.S.A. THE EFFECTS OF LIGATION OF CAUDA EPIDIDYMIDIS ON THE DOG TESTIS A. M. VARE, M.B.B.S.,
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT
 HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
Dr Prashant Jain. Sr. Consultant, Pediatric surgery BLK Superspeciality Hospital
 Dr Prashant Jain Sr. Consultant, Pediatric surgery BLK Superspeciality Hospital Acute Scrotum Presentation 0 Pain in scrotal area 0 Scrotal swelling 0 Scrotal redness take him to nearby emergency... Acute
Dr Prashant Jain Sr. Consultant, Pediatric surgery BLK Superspeciality Hospital Acute Scrotum Presentation 0 Pain in scrotal area 0 Scrotal swelling 0 Scrotal redness take him to nearby emergency... Acute
Evaluation of Testicular Disease using Ultrasound
 Evaluation of Testicular Disease using Ultrasound Abdullah Hamdan 1, Alsafi Abdulla 2, Mohamed Yousef 3 1 Radiologic Technology Department, College of Applied Medical Science, Qassim University, Buraduh,
Evaluation of Testicular Disease using Ultrasound Abdullah Hamdan 1, Alsafi Abdulla 2, Mohamed Yousef 3 1 Radiologic Technology Department, College of Applied Medical Science, Qassim University, Buraduh,
Lymphatic System. Where s your immunity idol?
 Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
