J. C. POIRIER. Station de Physiologie de la Reproduction, LN.R.A., Nouzilly Monnaie, France. *
|
|
|
- Nathan Baldwin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The role of testicular fluid on blood plasma levels of FSH and LH in the ram (1) M. R. BLANC J. L. DACHEUX C. CAHOREAU, M. COUROT MarieThérèse HOCHEREAU de REVIERS, A. LACROIX Claudine PISSELET C.PERREAU J. C. POIRIER Station de Physiologie de la Reproduction, LN.R.A., Nouzilly Monnaie, France. * Laboratoire de Physiologie comparée Faculté des Sciences Tours. Summary. The secretion of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) is partly regulated by a nonsteroid factor, inhibin, present in the testicular lymph and rete testis fluid (RTF). We were interested to know whether the RTF excreted into the epididymis has a regulatory role on the secretion of FSH and LH. The remaining rete testis of 6 adult rams hemicastrated 6 to 10 months earlier was cannulated. These rams were castrated either the day after the flow of RTF spontaneously stopped or 15 days after cannulation if the cannula was still functional. Two daily blood samples were taken from 7 days before cannulation to 7 days after castration and circulating levels of FSH, LH and testosterone were measured. Rete testis cannulation did not affect FSH, LH or testosterone plasma levels, although castration induced a sudden decrease in testosterone concentration and a rapid increase in FSH and LH levels. The present results suggest that the inhibin present in the RTF excreted into the epididymis does not play any role in the regulation of FSH and LH secretion. These hormones could be regulated by the inhibin present in the efferent circulation (lymph or blood) from the testis. Introduction. Ovine testicular fluid secreted by the testis into the epididymis has been shown to contain inhibin (Setchell and Sirinathsinghji, 1972 ; Setchell and Jacks, 1974 ; Baker et al., 1976 ; Blanc and Dacheux, 1976 ; Davies et al., 1976 ; Franchimont et al., 1977). Since this substance is known to regulate FSH and LH in the ram (Blanc et al., 1978 ; Cahoreau et al., 1979), we were interested to know whether the RTF has a regulatory role on the level of gonadotrophins in the peripheral blood of the adult ram, or whether, since testicular lymph is known to contain inhibin activity (Eddie et (1) This work was presented at the meeting of the French Society of Physiology nov. 77 (Cahoreau et at., 1977). in Grenobl e
2 LH, For The al., 1977 ; Baker et al., 1978), this role might be relevant to the inhibin secreted by the Sertoli cells into the extratubular compartment of the testis and drained through the lymphatic vessels to the blood stream. Such an hypothesis has been also postulated by Cahoreau et al. (1977) and Walton et al. (1978). In order to investigate this alternative, the remaining testis of adult hemicastrated rams was cannulated to remove RTF and prevent its reabsorption by the epididymis ; concentrations of FSH, LH and testosterone in the peripheral blood have been compared before and during cannulation as well as after castration. The results are discussed in the present report. Material and methods. Animals. This experiment was carried out at the end of the breeding season (November) on 6 adult IledeFrance rams, hemicastrated 6 to 10 months previously. Experimental design. testicular fluid (RTF) which would have been secreted into the epididymis through the ductuli efferentes was collected from a cannula inserted into the rete testis at the top of the testis according to the method of Voglmayr et al. (1966) modified by Edwards et 01. (1976). The animals were castrated in the morning 15 days later or on the day after the flow of RTF spontaneously stopped. The RTF was collected at 4!C on the animal ; its volume and sperm density were checked every 24 hrs. Blood samples were collected twice a day at hr and hr by acute jugular venepuncture from 7 days before insertion of the cannula to 7 days after castration. Blood plasma was immediately separated by centrifugation at g and stored at ― 20 C until assay. Hormone assays. FSH and testosterone were measured in plasma samples by specific radioimmunoassays using the double antibody techniques of Pelletier et at. (1968) for LH, Blanc and Poirier (1979) for FSH and Garnier et al. (1978) for testosterone. Results are expressed as ng of reference preparations of these hormones per ml of blood plasma. As the levels in morning and evening samples did not differ significantly within animals, results are given as mean daily concentrations of hormones in the plasma. Analysis of results. each hormone, the daily individual results of each of the 6 rams have been pooled (mean ± s.e.m.) for comparisons of hormonal levels before and after cannulation as well as before and after castration. Statistical analyses were performed by «t» test of paired data. Results. a) Production of RTF and spermatozoa. Two rams were castrated when the cannula was still operating on day 15 ; in other animals, flow of testicular fluid stopped on day 6 (n 2), day 11 (n 1) and = = day 12 = (n 1). The fluid outflow, overall mean : 1.32! 0.1 ml/h, sperm density : 143! 17 x 10 6 spermatozoa (spz)/ml, and daily collected spz : 5.12! 0.38 x 109,
3 were fairly variable between animals but quite consistent throughout the period of cannulation for each animal except in one ram in which sperm density and daily collected spermatozoa decreased sharply from day 6 onwards. b) Hormonal patterns. As shown in figures la, b, c, removal of whole testicular fluid secreted by the testis into the ductuli efferentes did not change the peripheral blood plasma concentrations of either FSH, LH or testosterone. Means and standard errors of the mean did not differ significantly before and throughout the period of cannulation. The pattern observed for testosterone, with a general trend for the concentration of this steroid to decrease throughout the experiment, was not related to cannulation but was possibly a function of season. In the same rams, removal of the remaining testis resulted in a significant and sharp increase of blood LH and FSH from the day after castration onwards, ending in a 5fold and 9fold increase, respectively, 7 days after orchidectomy, and a small decrease of testosterone : 0.5 versus 1.4 ng/ml after vs before castration (fig.1d, e, f). On the day of castration, the mean LH plasma level was already higher than before castration due to the rapid increase of the hormone concentration as soon as a few hours after castration.
4 Discussion. The experiment reported here was performed to investigate the physiological importance of inhibin contained in RFT for the regulation of gonadotrophins. The effect of diversion of RTF before being reabsorbed in the epididymis on circulating FSH and LH was thought to highlight the role of the material which normally flows through the epididymis. As did Walton et at. (1978), we carried out the experiment in hemicastrated rams since it is surgically more successful to cannulate the remaining rete testis of such animals instead of both organs of normal rams. Animals were used a long time after hemicastration, when compensatory testicular hypertrophy was completely established (Hochereaude Reviers et al., 1976). This would explain the elevated sperm density in RTF observed in the present experiment (143! 17 x 10 6 spz./ml) which is higher than that reported for entire IledeFrance rams in the breeding season (113 ::i:: 8 x 10 6 spz./ml) (Dacheux et a/., 1977). With a similar flow rate of fluid in both groups of animals, this results in a higher number of spermatozoa collected per testis in hemicastrated as compared to normal rams : 5.1 (present results) versus 3.5 x 109 spz./day (Dacheux et al., 1977). These figures are surprisingly similar to 5.7! 0.5 and 3.9! 0.3 x 109 spz./day calculated from quantitative histological data used to estimate the daily production of round spermatids per testis in the entire and hemicastrated ram during the breeding season (Hochereaude Reviers et al.,1976). This suggests that both techniques, testicular cannulation as well as quantitative histology, are equally reliable when used to estimate daily sperm production in the ram. It also shows that testicular cannulation, when operated properly, does not interfere with testicular sperm production at least during several days after surgery (Voglmayr et al., 1967 ; Walton et al., 1978 : in which the mean daily sperm production of hemicastrated rams, 4.6! 0.34 x 10!, is similar to that observed in the present work ; Cahoreau et 01., 1979). Sperm production of the rams used in this experiment was indicative of active spermatogenesis. Since this process is probably related to the inhibin content of RTF (Voglmayr et al., 1976), it is clear that hemicastrated rams were appropriate to study the effect of removal of testicular fluid on the circulating gonadotrophins. It is evident from our results that cannulation of the rete testis during the breeding season did not change the levels of LH and FSH in the peripheral blood plasma of IledeFrance rams whereas orchidectomy induced an increase of the same parameters. This suggests that RTF may not be the major route of secretion of the inhibin which is biologically active in the regulation of gonadotrophins. Similar results were obtained by Walton et al. (1978) after testicular cannulation of mature Clun Forest rams between July and November, which is earlier in the breeding season than in the present experiment. These authors concluded that «the inhibin in RFT may not contribute significantly to the overall feedback control of FSH in rams during the autumn». These results agree with those of Setchell et al. (1977) and Davies et al. (1978) in the rat where it was shown that ligation of efferent ducts of the testis, which prevents the fluid secreted by the gonad from flowing into the epididymis, was without immediate effect on FSH secretion. FSH began to rise only after a delay when the tubules decreased
5 This in size as a consequence of a disorganization of the germinal epithelium (Setchell et at., 1977), resulting in a decrease in production of inhibin (Voglmayr et al., 1976). Inhibin must enter, at least partly, into the blood and/or the lymphatic flow independently of entering RTF. This argument is supported by the presence of inhibin activity in ovine testicular lymph (Eddie et al., 1977 ; Baker et al., 1978). Thus, in normal animals inhibin would be secreted partly into the lumen ofthe tubules reaching the rete testis and epididymis (Le Lannou and Chambon, 1977) and partly directly from the Sertoli cells into the lymphatic and capillary network through the basement membrane of the seminiferous tubules. This is consistent with the structure of the testis barrier in the tubules as Sertoli cells are present both in the adluminal and external compartments of the tubules (Dym and Fawcett, 1970). Thus, in addition to steroids, only inhibin secreted in the lymph and blood may contribute to the feedback control of FSH and LH. The physiological role of the RTF which flows through the epididymis be carefully studied. Could it be related to the maturation process of sperm the epididymis? This needs further research. Re5u remains to cells in en d6cembre Accepte en fevrier Acknowledgements. study was supported by grants from the Degetation Generale 6 la Recherche Scientifique et Technique (DGRST ) and the Institut National de la Sant6 et de la Recherche M6dicale (INSERM ). The skillful Thanks are due to assistance of the INRA s hospital staff is gratefully acknowledged. Meredith Lemon for discussion in preparation and correction of this manuscript. Résumé. La régulation de la sécrétion des hormones folliculostimulante (FSH) et lutéinisante (LH) est en partie assurée par un facteur non stéroïdien, l inhibine, présent dans la lymphe efférente testiculaire et dans le liquide de «rete testis» (RTF). Aussi étaitil intéressant de savoir si le RTF excrété dans l épididyme avait un rôle régulateur sur la sécrétion de FSH et de LH. Une canulation du «rete testis» a été pratiquée sur 6 béliers adultes hémicastrés depuis 6 à 10 mois. Ces béliers ont été castrés, soit le jour suivant l arrêt spontané de l écoulement du RTF, soit 15 jours après la canulation si celleci était encore fonctionnelle. Des prélèvements sanguins (2 par jour) ont été effectués du 7e jour avant la canulation au 7ejou r après la castration en vue du dosage RIA des hormones circulantes. La canulation du «rete testis» n affecte pas les taux plasmatiques de FSH, LH et testosterone. Par contre, la castration provoque une diminution immédiate de testostérone et une augmentation rapide des concentrations plasmatiques de FSH et de LH. Ces résultats suggèrent que l inhibine présente dans le RTF et excrétée dans l épididyme n intervient pas dans la régulation de la sécrétion de FSH et de LH. Ce rôle régulateur pourrait être assuré par l inhibine présente dans la circulation efférente (lymphatique ou sanguine) du testicule. References BAKER H. W. G., BREMNER W. J., BURGER H. G., de KRETSER D. M., DULMANIS A., EDDIE L. W., HUDSON B., KEOGH E. J., LEE V. W. K., RENNIE G. C., Testicular control of follicle stimulating hormone secretion. Rec. Progr. Horm. Res., 32, BAKER H. W. G., BURGER H. G., de KRETSER D. M., EDDIE L. W., HIGGINSON R. E., HUDSON B., LEE V. W. K., Studies on purification of inhibin from ovine testicular secretions using an «in vitro» bioassay. Int. J. Androl., Suppl. 2, BLANC M. R., CAHOREAU C., COUROT M., DACHEUX J. L., HOCHEREAUde REVIERS M. T.,
6 PISSELET C., Plasma follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) suppression in the cryptochid ram by a nonsteroid factor (inhibin) from ram rete testis fluid. Int. J. Androt., Suppl. 2, BLANC M. R., DACHEUX J. L., Existence of inhibin activity in the ram rete testis fluid : effect of physiological doses on plasma LH and FSH. 1. R. C. S. Med. Sci., 4, 460. BLANC M. R., POIRIER J. C., A new homologous radioimmunoassay for ovine follicle stimulating hormone : development and characterization. Ann. Biol. anim. Bioch. Biophys., 19, CAHOREAU C., LACROIX A., BLANC M. R., COUROT M., DACHEUX J. L., HOCHEREAUde REVIERS M. T., PISSELET C., TERQUI M., Influence des secretions exocrines et endocrines du testicule sur les niveaux plasmatiques de FSH et LH chez le b6lier. J. Physiol., Paris, 73, 94A (abstr.). CAHOREAU C., BLANC M. R., DACHEUX J. L., PISSELET C., COUROT M., Inhibin activity in ram rete testis fluid : depression of plasma follitropin (FSH) and lutropin (LH) in the castrate and cryptorchid ram. J. Reprod. Fert., (in press). DACHEUX J. L., PISSELET C., BLANC M., HOCHEREAUde REVIERS M. T., COUROT M., Variations saisonni6res des secretions exocrines (fluide et spermatozoides) chez le b6lier adulte (IledeFrance). J. Physiol., Paris, 73, 99A (abstr.). DAVIES R. V., MAIN S. J., YOUNG M. G. W. L., SETCHELL B. P., Bioassay of inhibinlike activity in rete testis fluid and its partial purification. J. Endocr., 68, 26P (abstr.). DAVIES R. V., MAIN S. J., SETCHELL B. P., Inhibin : Evidence for its existence, methods of bioassay and nature of the active material. Int. J. Androl., Suppl. 2, DYM M., FAWCETT D. W., The bloodtestis barrier in the rat and the physiological compartmentation of the seminiferous epithelium. Biol. Reprod, 3, EDDIE L. W., BAKER H. W. G., HIGGINSON R. E., HUDSON B., KEOGH E. J., de KRETSER D. M., BURGER H. G., An «in vitro» bioassay for inhibin. Endocrinology, 100, Suppl., Abstr. n 268. EDWARDS E. M., DACHEUX J. L., WAITES G. M. H., Effects of achlorohydrin on the metabolism of testicular and epididymal spermatozoa of rams. J. Reprod. Fert., 48, FRANCHIMONT P., CHARI S., HAZEEHAGELSTEIN M. T., DEBRUCHE M. L., DURAISWAMI S., Evidence for the existence of inhibin, In TROEN P., NANKIN H. R., The testis in normal and infertile men. Raven Press, N. Y. GARNIER D. H., COTTA Y., TERQUI M., Androgen radioimmunoassay in the ram : results of direct plasma testosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone measurement and physiological evaluation. Ann. Biol. anim. Bioch. Biophys., 18, HOCHEREAUde REVIERS M. T., LOIR M., PELLETIER J., Seasonal variations in the response of the testis and LH levels to hemicastration of adult rams. J. Reprod. Fert., 46, LE LANNOU D., CHAMBON Y., Presence dans 1 6pididyme d un facteur abaissant fortement le taux sanguin de FSH chez le rat. C. R. Soc. Biol., 171, PELLETIER J., KANN G., DOLAIS J., ROSSELIN G., Dosage radioimmunologique de I hormone lut6inisante plasmatique chez le mouton. Mise au point de la technique de dosage. C. R. Acad. Sci., Paris, S6r. D, 266, SETCHELL B. P., JACKS F., Inhibinlike activity in rete testis fluid. J. Endocr., 62, SETCHELL B. P., MAIN S. J., DAVIES R. V., Effect of ligation of the efferent ducts of the testis on serum gonadotrophins and testosterone in rats. J. Endocr., 72, 13P14P (abstr.). SETCHELL B. P., SIRINATHSINGHJI D. J., Antigonadotrophic activity in rete testis fluid. A possible «inhibin». J. Endocr. 53, LXLXI (abstr.). VOGLMAYR J. K., WAITES G. M. H., SETCHELL B. P., Studies on spermatozoa and fluid collected directly from the testis of the conscious ram. Nature, 210, VOGLMAYR, J. K., SCOTT T. W., SETCHELL B. P., WAITES G. M. H., Metabolism of testicular spermatozoa and characteristics of testicular fluid collected from conscious ram. J. Reprod. Fert., 14, VOGLMAYR J. K., ROBERSON C., BARTKE A., Effects of local testicular heating and rete testis fluid on plasma FSH and testosterone levels in male rats. J. Reprod. Fert., 46, WALTON J. S., EVINS J. D., WAITES G. M. H., Effect of chronic removal of testicular fluid on the release of FSH in hemicastrated rams. J. Endocr., 77,
Histological testicular parameters in bilateral cryptorchid adult rams
 Histological testicular parameters in bilateral cryptorchid adult rams Marie-Thérèse Hochereau-De Reviers, M. R. Blanc, Claire Cahoreau, M. Courot, J. L. Dacheux, Claudine Pisselet To cite this version:
Histological testicular parameters in bilateral cryptorchid adult rams Marie-Thérèse Hochereau-De Reviers, M. R. Blanc, Claire Cahoreau, M. Courot, J. L. Dacheux, Claudine Pisselet To cite this version:
Station de Recherches Avicoles. *Station de Physiologie de la Reproduction LN.R.A., Nouzilly, Monnaie, France.
 Control of Sertoli and germ cell populations and sheep testes in the cock M. de REVIERS, MarieThérèse HOCHEREAUde REVIERS M. R. BLANC J. P. BRILLARD, M. COUROT J. PELLETIER Station de Recherches Avicoles
Control of Sertoli and germ cell populations and sheep testes in the cock M. de REVIERS, MarieThérèse HOCHEREAUde REVIERS M. R. BLANC J. P. BRILLARD, M. COUROT J. PELLETIER Station de Recherches Avicoles
Mechanism of Action of Inhibin
 BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 24, 541-5 5 (1981) Mechanism of Action of Inhibin R. S. SCOTT and H. G. BURGER Medical Research Centre, Prince Henry s Hospital, Melbourne, Victoria 34, A ustralia ABSTRACT Cultured
BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 24, 541-5 5 (1981) Mechanism of Action of Inhibin R. S. SCOTT and H. G. BURGER Medical Research Centre, Prince Henry s Hospital, Melbourne, Victoria 34, A ustralia ABSTRACT Cultured
Sertoli cells and development of seminiferous epithelium. lmpuberal. phase. Hypophysectomy of impuberal lambs results in a decrease in the total
 lmpuberal Prepubertal Adult Sertoli cells and development of seminiferous epithelium MarieThérèse HOCHEREAUde REVIERS Christine PERREAU M. COUROT Claudine PISSELET Station de Physiologie de la Reproduction,
lmpuberal Prepubertal Adult Sertoli cells and development of seminiferous epithelium MarieThérèse HOCHEREAUde REVIERS Christine PERREAU M. COUROT Claudine PISSELET Station de Physiologie de la Reproduction,
Detection of anti-m\l=u"\llerian activity in boar rete testis fluid
 Detection of anti-m\l=u"\llerian activity in boar rete testis fluid Nathalie Josso, J. Y. Picard, J. L. Dacheux and M. Courot Unité de Recherches de Génétique Médicale (INSERM), Hôpital des Enfants-Malades,
Detection of anti-m\l=u"\llerian activity in boar rete testis fluid Nathalie Josso, J. Y. Picard, J. L. Dacheux and M. Courot Unité de Recherches de Génétique Médicale (INSERM), Hôpital des Enfants-Malades,
Many studies have been published concerning the in vitro conversion of testosterone
 Testosterone gradient across the tubular wall F. H. COMHAIRE A. VERMEULEN Section of Endocrinology of the Department of Internal Medicine, State University, Akademisch Ziekenhuis, De Pintelaan, 135 B 9000
Testosterone gradient across the tubular wall F. H. COMHAIRE A. VERMEULEN Section of Endocrinology of the Department of Internal Medicine, State University, Akademisch Ziekenhuis, De Pintelaan, 135 B 9000
Histology of Male Reproductive system (1)
 Histology of Male Reproductive system (1) Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Learning Objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the organization of the testis Define seminiferous
Histology of Male Reproductive system (1) Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Learning Objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the organization of the testis Define seminiferous
Testicular feed back on the hypothalamo-pituitary axis in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri R.)
 Testicular feed back on the hypothalamopituitary axis in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri R.) R. Billard, Pierrette Reinaud To cite this version: R. Billard, Pierrette Reinaud. Testicular feed back on the
Testicular feed back on the hypothalamopituitary axis in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri R.) R. Billard, Pierrette Reinaud To cite this version: R. Billard, Pierrette Reinaud. Testicular feed back on the
androgens (including testosterone) has been demonstrated in Sertoli cells (Grootegoed Effects of FSH and testosterone on Sertoli cells
 Effects of FSH and testosterone on Sertoli cells and spermatocytes from rat testis F. F. G. ROMMERTS J. A. GROOTEGOED, H. J. VAN DER MOLEN Department of Biochemistry (Division of Chemical Endocrinology),
Effects of FSH and testosterone on Sertoli cells and spermatocytes from rat testis F. F. G. ROMMERTS J. A. GROOTEGOED, H. J. VAN DER MOLEN Department of Biochemistry (Division of Chemical Endocrinology),
Effects of induced hypoprolactinaemia in the ram : plasma gonadotrophin levels, LH and FSH receptors and histology of the testis
 Effects of induced hypoprolactinaemia in the ram : plasma gonadotrophin levels, LH and FSH receptors and histology of the testis B. Barenton, M. T. Hochereau-De Reviers, C. Perreau, J.-C. Poirier To cite
Effects of induced hypoprolactinaemia in the ram : plasma gonadotrophin levels, LH and FSH receptors and histology of the testis B. Barenton, M. T. Hochereau-De Reviers, C. Perreau, J.-C. Poirier To cite
Comparative action of cyproterone and cyproterone acetate on pituitary and plasma gonadotropin levels, the male genital
 Comparative action of cyproterone and cyproterone acetate on pituitary and plasma gonadotropin levels, the male genital tract and spermatogenesis in the growing rat Marie-Claude VIGUIER-MARTINEZ,Marie-Thérèse
Comparative action of cyproterone and cyproterone acetate on pituitary and plasma gonadotropin levels, the male genital tract and spermatogenesis in the growing rat Marie-Claude VIGUIER-MARTINEZ,Marie-Thérèse
weights of the testis and the accessory glands (Amatayakul et al.,1971 ; Swerdloff et al., 1971)
 A reinvestigation of hypothalamic-pituitary testicular interactions : simultaneous changes in tissue and plasma levels of gonadotrophins, prolactin, testosterone and hypothalamic LH-RH after bilateral
A reinvestigation of hypothalamic-pituitary testicular interactions : simultaneous changes in tissue and plasma levels of gonadotrophins, prolactin, testosterone and hypothalamic LH-RH after bilateral
Laboratoire d Hormonologie, U.N.C.E.I.A., 13, rue Jouet, Maisons-Alfort, and Institut National Agronomique Paris-Grignon, France.
 testes LH and testosterone responses to gonadoliberin (LRH) treatment in young bulls prior to and during puberty P. CHANTARAPRATEEP M. THIBIER Laboratoire d Hormonologie, U.N.C.E.I.A., 13, rue Jouet, 94700
testes LH and testosterone responses to gonadoliberin (LRH) treatment in young bulls prior to and during puberty P. CHANTARAPRATEEP M. THIBIER Laboratoire d Hormonologie, U.N.C.E.I.A., 13, rue Jouet, 94700
of Nebraska - Lincoln
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Roman L. Hruska U.S. Meat Animal Research Center U.S. Department of Agriculture: Agricultural Research Service, Lincoln,
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Roman L. Hruska U.S. Meat Animal Research Center U.S. Department of Agriculture: Agricultural Research Service, Lincoln,
photoperiods in Leroy (1970) described seasonal variations in the testicular development of guineafowls
 Testis development and daily sperm output in guinea-fowl raised under constant daily photoperiods J. P. BRILLARD, M. de REVIERS Station de Recherches avicoles, 1.N.R.A. 37380 Monnaie, France. Nouzilly,
Testis development and daily sperm output in guinea-fowl raised under constant daily photoperiods J. P. BRILLARD, M. de REVIERS Station de Recherches avicoles, 1.N.R.A. 37380 Monnaie, France. Nouzilly,
Ram lambs need FSH for normal testicular growth, Sertoli cell numbers and onset of spermatogenesis
 Ram lambs need FSH for normal testicular growth, Sertoli cell numbers and onset of spermatogenesis Robert J. Kilgour, Claudine Pisselet, Maurice P. Dubois, Michel Courot To cite this version: Robert J.
Ram lambs need FSH for normal testicular growth, Sertoli cell numbers and onset of spermatogenesis Robert J. Kilgour, Claudine Pisselet, Maurice P. Dubois, Michel Courot To cite this version: Robert J.
J. Williams, M. De Reviers. To cite this version: HAL Id: hal
 Variations in the plasma levels of luteinizing hormone and androstenedione and their relationship with the adult daily sperm output in cockerels raised under different photoschedules J. Williams, M. De
Variations in the plasma levels of luteinizing hormone and androstenedione and their relationship with the adult daily sperm output in cockerels raised under different photoschedules J. Williams, M. De
Male reproduction. Cross section of Human Testis ผศ.ดร.พญ.ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ภาคว ชาสร รว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล 1. Aims
 Aims Male reproduction Male reproductive structure Spermatogenesis ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ห อง 216 โทร: 7578 Hypothalamo-pituitary-testicular axis Male sex hormone action Male reproductive structure Male reproductive
Aims Male reproduction Male reproductive structure Spermatogenesis ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ห อง 216 โทร: 7578 Hypothalamo-pituitary-testicular axis Male sex hormone action Male reproductive structure Male reproductive
Adapted from Preg. & Part., Senger
 MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY AND SPERMATOGENESIS (Chapter 10) AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) I. MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY (Figure10-1 to 10-3) A. Glands and their respective hormones 1) Hypothalamic hormone:
MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY AND SPERMATOGENESIS (Chapter 10) AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) I. MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY (Figure10-1 to 10-3) A. Glands and their respective hormones 1) Hypothalamic hormone:
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System Constitution of male reproductive system Genital gland ----testis Genital ducts epididymis / ductus deferens / urinary duct Accessory sex glands Penis prostate gland Seminal vesicle
Male Reproductive System Constitution of male reproductive system Genital gland ----testis Genital ducts epididymis / ductus deferens / urinary duct Accessory sex glands Penis prostate gland Seminal vesicle
Original article. Female effect in sheep. I. The effects of sexual receptivity of females and the sexual experience of rams
 Original article Female effect in sheep. I. The effects of sexual receptivity of females and the sexual experience of rams R Gonzalez P Orgeur P Poindron JP Signoret Laboratoire de Comportement Animal,
Original article Female effect in sheep. I. The effects of sexual receptivity of females and the sexual experience of rams R Gonzalez P Orgeur P Poindron JP Signoret Laboratoire de Comportement Animal,
Sperm production, testicular size, serum gonadotropins and testosterone levels in Merino and Corriedale breeds
 Sperm production, testicular size, serum gonadotropins and testosterone levels in Merino and Corriedale breeds D. Fernandez-Abella, D. Becu-Villalobos, I.M. Lacau-Mengido, N. Villegas, O. Bentancur To
Sperm production, testicular size, serum gonadotropins and testosterone levels in Merino and Corriedale breeds D. Fernandez-Abella, D. Becu-Villalobos, I.M. Lacau-Mengido, N. Villegas, O. Bentancur To
Hormones of brain-testicular axis
 (Hormone Function) Hormones of brain-testicular axis anterior pituitary drives changes during puberty controlled by GnRH from hypothalamus begins to secrete FSH, LH LH targets interstitial endocrinocytes
(Hormone Function) Hormones of brain-testicular axis anterior pituitary drives changes during puberty controlled by GnRH from hypothalamus begins to secrete FSH, LH LH targets interstitial endocrinocytes
Influence of dietary intake and weight variation on LH release
 Influence of dietary intake and weight variation on LH release after a gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) injection during the post-partum period of the nursing cow D. GAUTHIER P. MAULÉON Station de
Influence of dietary intake and weight variation on LH release after a gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) injection during the post-partum period of the nursing cow D. GAUTHIER P. MAULÉON Station de
Acquisition of sperm motility and its maintenance during
 Acquisition of sperm motility and its maintenance during storage in the lizard, Lacerta vivipara A. Depeiges and J. L. Dacheux *Biologie Cellulaire et Génétique, Université de Clermont-Ferrand II, BP.
Acquisition of sperm motility and its maintenance during storage in the lizard, Lacerta vivipara A. Depeiges and J. L. Dacheux *Biologie Cellulaire et Génétique, Université de Clermont-Ferrand II, BP.
FSH and LH variations in beef cows during the postpartum period
 FSH and LH variations in beef cows during the postpartum period D. Gauthier, M. R. Blanc, M. Petit, J. Pelletier, G. Trillat To cite this version: D. Gauthier, M. R. Blanc, M. Petit, J. Pelletier, G. Trillat.
FSH and LH variations in beef cows during the postpartum period D. Gauthier, M. R. Blanc, M. Petit, J. Pelletier, G. Trillat To cite this version: D. Gauthier, M. R. Blanc, M. Petit, J. Pelletier, G. Trillat.
ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE
 ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE SCROTUM MICHAEL NOMIKOS M.D. F.E.B.U. UROLOGICAL
ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE SCROTUM MICHAEL NOMIKOS M.D. F.E.B.U. UROLOGICAL
Hormonal and follicular relationships in ewes of high and low ovulation rates
 Hormonal and follicular relationships in ewes of high and low ovulation rates L. P. Cahill, J. Saumande, J. P. Ravault, M. Blanc, J. Thimonier, J. C. Mariana and P. Maul\l=e'\on LN.RA.-Station de Physiologie
Hormonal and follicular relationships in ewes of high and low ovulation rates L. P. Cahill, J. Saumande, J. P. Ravault, M. Blanc, J. Thimonier, J. C. Mariana and P. Maul\l=e'\on LN.RA.-Station de Physiologie
temperature by Weil et al. (1975). The annual reproduction cycle in adult carp in Poland : ovarian
 The annual reproduction cycle in adult carp in Poland : ovarian state and serum gonadotropin level K. BIENIARZ P. EPLER B. BRETON Luong Noc THUY Institute of Applied Zoology, Academy of Agriculture, 30-059
The annual reproduction cycle in adult carp in Poland : ovarian state and serum gonadotropin level K. BIENIARZ P. EPLER B. BRETON Luong Noc THUY Institute of Applied Zoology, Academy of Agriculture, 30-059
Efferent Ducts and Epididymis
 increase) the secretion of each of the androgen regulated proteins. Regulation of spermatogenesis is therefore an extremely complex cascade of cell-cell interactions with the Leydig cells supporting germ
increase) the secretion of each of the androgen regulated proteins. Regulation of spermatogenesis is therefore an extremely complex cascade of cell-cell interactions with the Leydig cells supporting germ
Although it has been known for some time that the first growing follicles in the
 Evolution of ovarian follicular population and serum gonadotrophins in the prepubertal period of two strains of rats Marie-Madeleine de REVIERS P. MAULÉON Station de Physiologie de la Reproduction, 1.
Evolution of ovarian follicular population and serum gonadotrophins in the prepubertal period of two strains of rats Marie-Madeleine de REVIERS P. MAULÉON Station de Physiologie de la Reproduction, 1.
Morphological evidence (Fawcett, 1975), phosphate buffer at ph!7.4 before being incubated in the colloidal iron solution.
 The appearance of new electrical properties in the plasma membrane of ram spermatids J. L. COURTENS Station de Physiologie de la Reproduction, INRA, Nouzilly, 37380 Monnaie, France. Summary. The«en bloc»
The appearance of new electrical properties in the plasma membrane of ram spermatids J. L. COURTENS Station de Physiologie de la Reproduction, INRA, Nouzilly, 37380 Monnaie, France. Summary. The«en bloc»
The antisteroid action of the pineal gland
 The antisteroid action of the pineal gland Elena Damian To cite this version: Elena Damian. The antisteroid action of the pineal gland. Annales de biologie animale, biochimie, biophysique, 1979, 19 (4B),
The antisteroid action of the pineal gland Elena Damian To cite this version: Elena Damian. The antisteroid action of the pineal gland. Annales de biologie animale, biochimie, biophysique, 1979, 19 (4B),
Relationship between testicular blood flow, testosterone
 Relationship between testicular blood flow, testosterone secretion and spermatogenic activity in young and adult wild red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) M. Joffre Laboratoire de Physiologie Comparée, Faculté des
Relationship between testicular blood flow, testosterone secretion and spermatogenic activity in young and adult wild red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) M. Joffre Laboratoire de Physiologie Comparée, Faculté des
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System organs that function in: gamete and hormone production not all in abdominal cavity paired testicles = controlled by LH & FSH duct systems accessory glands Testis: Gross Histology
Male Reproductive System organs that function in: gamete and hormone production not all in abdominal cavity paired testicles = controlled by LH & FSH duct systems accessory glands Testis: Gross Histology
dexamethasone\p=n-\gnrhcombined treatment and their relationship to semen output in bulls
 Plasma LH and testosterone responses to synthetic gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) or dexamethasone\p=n-\gnrhcombined treatment and their relationship to semen output in bulls G. Abdel Malak and
Plasma LH and testosterone responses to synthetic gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) or dexamethasone\p=n-\gnrhcombined treatment and their relationship to semen output in bulls G. Abdel Malak and
Production of seminiferous and interstitial fluid in the growing rat after unilateral testicular irradiation
 Production of seminiferous and interstitial fluid in the growing rat after unilateral testicular irradiation P. Laporte, O. Le Floch To cite this version: P. Laporte, O. Le Floch. Production of seminiferous
Production of seminiferous and interstitial fluid in the growing rat after unilateral testicular irradiation P. Laporte, O. Le Floch To cite this version: P. Laporte, O. Le Floch. Production of seminiferous
REPRODUCCIÓN. La idea fija. Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
Basic histology 5/4/2015
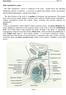 Male reproductive system The male reproductive system is composed of the testes, genital ducts (the adjoining epididymis, and the vas deferens, a accessory sex glands (the seminal vesicles, the prostrate
Male reproductive system The male reproductive system is composed of the testes, genital ducts (the adjoining epididymis, and the vas deferens, a accessory sex glands (the seminal vesicles, the prostrate
Pathology of Male Reproductive System 1
 Pathology of Male Reproductive System 1 Professor dr Ali Hassan Altimimi Professor of Pathology& Histology MSc, PHD, MD(UK) MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The internal male genitalia consist of the testes with
Pathology of Male Reproductive System 1 Professor dr Ali Hassan Altimimi Professor of Pathology& Histology MSc, PHD, MD(UK) MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The internal male genitalia consist of the testes with
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
Testicular interstitial fluid as a monitor for changes in the intratesticular environment in the rat
 Testicular interstitial fluid as a monitor for changes in the intratesticular environment in the rat R. M. Sharpe and Irene Cooper M.R.C. Reproductive Biology Unit, Centre for Reproductive Biology, 37
Testicular interstitial fluid as a monitor for changes in the intratesticular environment in the rat R. M. Sharpe and Irene Cooper M.R.C. Reproductive Biology Unit, Centre for Reproductive Biology, 37
Production of Fertile Sperm. Animal Science 434. Hormonal Regulation of the Testis. hormonal regulation of the testis
 roduction of Fertile Sperm hormonal regulation of the testis nimal Science 434 Lecture 12: Spermatogenesis mitotic division of spermatogonia meiotic divisions of spermatocytes morphologic transformation
roduction of Fertile Sperm hormonal regulation of the testis nimal Science 434 Lecture 12: Spermatogenesis mitotic division of spermatogonia meiotic divisions of spermatocytes morphologic transformation
Morphogenesis of postacrosomal cytoplasm in the spermatid
 Immediately Morphogenesis of postacrosomal cytoplasm in the spermatid head. Experimental study of hypophysectomized and testosteroneinjected rams J. L. COURTENS Station de Physiologie de la Reproduction,
Immediately Morphogenesis of postacrosomal cytoplasm in the spermatid head. Experimental study of hypophysectomized and testosteroneinjected rams J. L. COURTENS Station de Physiologie de la Reproduction,
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
Medical School Histology Basics Male Reproductive System. VIBS 289 lab
 Medical School Histology Basics Male Reproductive System VIBS 289 lab Larry Johnson Texas A&M University OBJECTIVE To conduct a histologic examination of the testis (which produce spermatozoa), excretory
Medical School Histology Basics Male Reproductive System VIBS 289 lab Larry Johnson Texas A&M University OBJECTIVE To conduct a histologic examination of the testis (which produce spermatozoa), excretory
Total follicular populations in ewes of high and low ovulation rates
 Total follicular populations in ewes of high and low ovulation rates L. P. Cahill, J. C. Mariana and P. Maul\l=e'\on I.N.RA. Station de Physiologie de la Reproduction, 37380 Nouzilly, France Summary. The
Total follicular populations in ewes of high and low ovulation rates L. P. Cahill, J. C. Mariana and P. Maul\l=e'\on I.N.RA. Station de Physiologie de la Reproduction, 37380 Nouzilly, France Summary. The
Histological studies suggested that the lumina of the seminiferous tubules and
 The movement of fluid in the seminiferous tubules and rete testis B. P. SETCHELL, R. V. DAVIES R. T. GLADWELL, B. T. HINTON, S. J. MAIN, Lynn PILSWORTH, G. M. H. WAITES Department of Biochemistry, A. R.
The movement of fluid in the seminiferous tubules and rete testis B. P. SETCHELL, R. V. DAVIES R. T. GLADWELL, B. T. HINTON, S. J. MAIN, Lynn PILSWORTH, G. M. H. WAITES Department of Biochemistry, A. R.
FIGURE The tunica albuginea is a connective tissue capsule forming the outer part of each testis.
 Testicular Histology (see p. 1034 in text) FIGURE 28.3 1. The tunica albuginea is a connective tissue capsule forming the outer part of each testis. 2. Septa are extensions of the tunica albuginea that
Testicular Histology (see p. 1034 in text) FIGURE 28.3 1. The tunica albuginea is a connective tissue capsule forming the outer part of each testis. 2. Septa are extensions of the tunica albuginea that
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
THE EFFECTS OF LIGATION OF CAUDA EPIDIDYMIDIS ON THE DOG TESTIS
 Copyright 1974 The American Fertility Society FERTILITY AND STERILITY Vol. 25, No.3, March, 1974 Printed in U.S.A. THE EFFECTS OF LIGATION OF CAUDA EPIDIDYMIDIS ON THE DOG TESTIS A. M. VARE, M.B.B.S.,
Copyright 1974 The American Fertility Society FERTILITY AND STERILITY Vol. 25, No.3, March, 1974 Printed in U.S.A. THE EFFECTS OF LIGATION OF CAUDA EPIDIDYMIDIS ON THE DOG TESTIS A. M. VARE, M.B.B.S.,
rapid measurement of MAO in that organ. Urry et al. (1975 a) studied the effect
 Distribution of oxidases in the testis of buffalo, goat and ram : an histochemical study G. S. BILASPURI S. S. GURAYA Department of Zoo%gy Punjab Agricultural University Ludhiana, Punjab, India Summary.
Distribution of oxidases in the testis of buffalo, goat and ram : an histochemical study G. S. BILASPURI S. S. GURAYA Department of Zoo%gy Punjab Agricultural University Ludhiana, Punjab, India Summary.
Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries. Accessory reproductive organs: ducts, glands, and external genitalia
 Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Validation of coupled bioassay for inhibin by pituitary cell culture assay
 J. Biosci., Vol. 14, No. 2, June 1989, pp. 79 90. Printed in India. Validation of coupled bioassay for inhibin by pituitary cell culture assay SUSHMA R. DHINGRA, S. DURAISWAMI, NARENDER KUMAR* and LAKSHMI
J. Biosci., Vol. 14, No. 2, June 1989, pp. 79 90. Printed in India. Validation of coupled bioassay for inhibin by pituitary cell culture assay SUSHMA R. DHINGRA, S. DURAISWAMI, NARENDER KUMAR* and LAKSHMI
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I)
 Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Feulgen-DNA changes in the germ (Microtus agrestis) during their development
 Feulgen-DNA changes in the germ (Microtus agrestis) during their development J. R. CLARKE C. ESNAULT J.-C. NICOLLE cells of the male vole Laboratoire de Physiologie de la Reproduction, LN.R.A. Nouzilly,
Feulgen-DNA changes in the germ (Microtus agrestis) during their development J. R. CLARKE C. ESNAULT J.-C. NICOLLE cells of the male vole Laboratoire de Physiologie de la Reproduction, LN.R.A. Nouzilly,
Reproductive System Purpose General Structures Male Structures Functions Female Anatomy Structures Functions Clinical Applications
 The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
Male Anatomy. testes, genetically determined in mammals - testis releases hormones that then control the development of secondary sex characteristics
 Male Anatomy Male Anatomy Primary Organ testes, genetically determined in mammals - testis releases hormones that then control the development of secondary sex characteristics 1) Secondary Organs internal
Male Anatomy Male Anatomy Primary Organ testes, genetically determined in mammals - testis releases hormones that then control the development of secondary sex characteristics 1) Secondary Organs internal
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones
 10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
(Capra hircus) Original article. JA Delgadillo. Effect of short photoperiodic cycles on male genital. tract and testicular parameters in male goats
 .! -------------.._n - Original article Effect of short photoperiodic cycles on male genital tract and testicular parameters in male goats (Capra hircus) JA Delgadillo MT Hochereau-de Reviers A Daveau
.! -------------.._n - Original article Effect of short photoperiodic cycles on male genital tract and testicular parameters in male goats (Capra hircus) JA Delgadillo MT Hochereau-de Reviers A Daveau
Age Related Effects on Androgen Binding Protein (ABP) in Sheep Testis and Epididymis')
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ANDROLOGY 2 (1979) 49-61 "Laboratoire de Biochimie, CHU Cite de Nacre, 14040 - Caen - France, 'F:'Laboratoire de Physiologic de la Reproduction, INRA, 57980 - Nouzilly - France
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ANDROLOGY 2 (1979) 49-61 "Laboratoire de Biochimie, CHU Cite de Nacre, 14040 - Caen - France, 'F:'Laboratoire de Physiologic de la Reproduction, INRA, 57980 - Nouzilly - France
Changes in FSH and the pulsatile secretion of LH during the delay in oestrus induced by treatment of ewes
 Changes in FSH and the pulsatile secretion of LH during the delay in oestrus induced by treatment of ewes with bovine follicular fluid A. S. McNeilly M.R.C. Reproductive Biology Unit, University of Edinburgh
Changes in FSH and the pulsatile secretion of LH during the delay in oestrus induced by treatment of ewes with bovine follicular fluid A. S. McNeilly M.R.C. Reproductive Biology Unit, University of Edinburgh
The Male Reproductive System
 The Male Reproductive System YONG-MEI CHEN ( 陈咏梅 ) Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College Tel:69156461 E-mail address: pumc_he@126.com Content Spermatogenesis Spermiogenesis
The Male Reproductive System YONG-MEI CHEN ( 陈咏梅 ) Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College Tel:69156461 E-mail address: pumc_he@126.com Content Spermatogenesis Spermiogenesis
THE EFFECT OF THE RATIO OF DILUTION OF RAM SEMEN IN DIFFERENT DILUENTS ON THE CONCEPTION RATE (1)
 THE EFFECT OF THE RATIO OF DILUTION OF RAM SEMEN IN DIFFERENT DILUENTS ON THE CONCEPTION RATE (1) D. Amir, H. Schindler, E. Eyal, A. R. Lehrer, Ora Kempenich-Pinto To cite this version: D. Amir, H. Schindler,
THE EFFECT OF THE RATIO OF DILUTION OF RAM SEMEN IN DIFFERENT DILUENTS ON THE CONCEPTION RATE (1) D. Amir, H. Schindler, E. Eyal, A. R. Lehrer, Ora Kempenich-Pinto To cite this version: D. Amir, H. Schindler,
Reproductive FSH. Analyte Information
 Reproductive FSH Analyte Information 1 Follicle-stimulating hormone Introduction Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH, also known as follitropin) is a glycoprotein hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary
Reproductive FSH Analyte Information 1 Follicle-stimulating hormone Introduction Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH, also known as follitropin) is a glycoprotein hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary
Quantitative studies on spermatogenesis in buffalo (Bubalus bubalis)
 Quantitative studies on spermatogenesis in buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) G. S. Bilaspuri, S. S. Guraya To cite this version: G. S. Bilaspuri, S. S. Guraya. Quantitative studies on spermatogenesis in buffalo
Quantitative studies on spermatogenesis in buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) G. S. Bilaspuri, S. S. Guraya To cite this version: G. S. Bilaspuri, S. S. Guraya. Quantitative studies on spermatogenesis in buffalo
12/3/12. Managing Bull Development to Optimize Fertility Rearing bulls for fertility
 Managing Bull Development to Optimize Fertility Rearing bulls for fertility Effect of post weaning nutrition (after normal calf hood nutrition) - testis size - age at puberty - semen quality Effect of
Managing Bull Development to Optimize Fertility Rearing bulls for fertility Effect of post weaning nutrition (after normal calf hood nutrition) - testis size - age at puberty - semen quality Effect of
DISORDERS OF MALE GENITALS
 Wit JM, Ranke MB, Kelnar CJH (eds): ESPE classification of paediatric endocrine diagnosis. 9. Testicular disorders/disorders of male genitals. Horm Res 2007;68(suppl 2):63 66 ESPE Code Diagnosis OMIM ICD10
Wit JM, Ranke MB, Kelnar CJH (eds): ESPE classification of paediatric endocrine diagnosis. 9. Testicular disorders/disorders of male genitals. Horm Res 2007;68(suppl 2):63 66 ESPE Code Diagnosis OMIM ICD10
Anti-M\l=u"\llerianhormone (AMH) secretion in prepubertal and adult rams
 AntiM\lu"\llerianhormone (AMH) secretion in prepubertal and adult rams O. Cazorla, M. Seck, C. Pisselet, C. Perreau, J. Saumande, J. Fontaine M. de Reviers and M. T. Hochereaude Reviers Université de Tours,
AntiM\lu"\llerianhormone (AMH) secretion in prepubertal and adult rams O. Cazorla, M. Seck, C. Pisselet, C. Perreau, J. Saumande, J. Fontaine M. de Reviers and M. T. Hochereaude Reviers Université de Tours,
Cell Divisions. The autosomes represent the whole body. * Male Sex Chromosomes: XY * Female Sex Chromosomes: XX
 Cell Divisions Each Cell (including gonads) has 46 chromosomes (23 pairs of chromosomes: 22 pairs of autosomes, 1 pair of sex chromosomes) which are located in the nucleus). The autosomes represent the
Cell Divisions Each Cell (including gonads) has 46 chromosomes (23 pairs of chromosomes: 22 pairs of autosomes, 1 pair of sex chromosomes) which are located in the nucleus). The autosomes represent the
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE
 Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
The effect of thyroid activity on adult rat spermatogenesis
 The effect of thyroid activity on adult rat spermatogenesis Ai, J. 1* ; Zarifkar, A. 2 ; Takhshid, M. A. 3 ; Alavi, J. 1 and Moradzadeh, M. 2 1 Department of Anatomical Sciences, School of Medicine, University
The effect of thyroid activity on adult rat spermatogenesis Ai, J. 1* ; Zarifkar, A. 2 ; Takhshid, M. A. 3 ; Alavi, J. 1 and Moradzadeh, M. 2 1 Department of Anatomical Sciences, School of Medicine, University
Male Reproductive System
 21-1 21-2 Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Genital Tract In males the testes, held outside the body in the scrotum (optimum temp of about 35 0 C), produce sperm. Sperm mature in coiled tubes
21-1 21-2 Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Genital Tract In males the testes, held outside the body in the scrotum (optimum temp of about 35 0 C), produce sperm. Sperm mature in coiled tubes
Long term follow-up study of 60 cases
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNALOFANDROLOGY 8 (1985) 177-185 Department of Endocrinology', Clinical Research Unit for the Male2, NataonalResearch Institute for Family Planning, Beijing and Depaltment of Urology3,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNALOFANDROLOGY 8 (1985) 177-185 Department of Endocrinology', Clinical Research Unit for the Male2, NataonalResearch Institute for Family Planning, Beijing and Depaltment of Urology3,
BIOL 2402 Reproductive Systems
 Collin College Dr. Chris Doumen BIOL 2402 Reproductive Systems 1 Reproductive System Most systems between males and females in the human body are similar in structure. The exception of course are the organs
Collin College Dr. Chris Doumen BIOL 2402 Reproductive Systems 1 Reproductive System Most systems between males and females in the human body are similar in structure. The exception of course are the organs
J. Williams. To cite this version: HAL Id: hal
 Plasma levels of progesterone in the domestic hen related to the maturation of ovarian follicles, and changes in the secretion of progesterone by granulosa cells cultured for 24 hours (*) J. Williams To
Plasma levels of progesterone in the domestic hen related to the maturation of ovarian follicles, and changes in the secretion of progesterone by granulosa cells cultured for 24 hours (*) J. Williams To
Oocyte maturation within stimulated immature bovine
 Oocyte maturation within stimulated immature bovine follicles in vivo W. D. FOOTE C. D. MILLS, D. A. PHELPS F. D. TIBBITTS Max C. Fleischmann College of Agriculture, University of Nevada, Reno, Nevada
Oocyte maturation within stimulated immature bovine follicles in vivo W. D. FOOTE C. D. MILLS, D. A. PHELPS F. D. TIBBITTS Max C. Fleischmann College of Agriculture, University of Nevada, Reno, Nevada
Reproductive Endocrinology. Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007
 Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Article Effect of deprivation of endogenous follicle stimulating hormone on rat epididymis: a histological evaluation
 RBMOnline - Vol 17 No 3. 2008 331-337 Reproductive BioMedicine Online; www.rbmonline.com/article/2999 on web 11 July 2008 Article Effect of deprivation of endogenous follicle stimulating hormone on rat
RBMOnline - Vol 17 No 3. 2008 331-337 Reproductive BioMedicine Online; www.rbmonline.com/article/2999 on web 11 July 2008 Article Effect of deprivation of endogenous follicle stimulating hormone on rat
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
Effect of cadmium chloride on the serum levels of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH) and androgens in the adult male rat
 Proc. Indian Acad. Sci., Vol. 87 B, (Experimental Biology-3), No.7, July 1978, pp. 161-167, @ printed in India Effect of cadmium chloride on the serum levels of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing
Proc. Indian Acad. Sci., Vol. 87 B, (Experimental Biology-3), No.7, July 1978, pp. 161-167, @ printed in India Effect of cadmium chloride on the serum levels of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing
Hormonal Control of Male Sexual Function
 Hormonal Control of Male Sexual Function A majority of the control of sexual functions in the male (and the female) begins with secretions of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) by the hypothalamus.
Hormonal Control of Male Sexual Function A majority of the control of sexual functions in the male (and the female) begins with secretions of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) by the hypothalamus.
Evidence for a major role of inhibin in the feedback control of FSH in the male rat
 Evidence for a major role of inhibin in the feedback control of FSH in the male rat G. F. Weinbauer, J. M. S. Bartlett, U. Fingscheidt, C. G. Tsonis, D. M. de Kretser and E. Nieschlag fmflx Planck Clinical
Evidence for a major role of inhibin in the feedback control of FSH in the male rat G. F. Weinbauer, J. M. S. Bartlett, U. Fingscheidt, C. G. Tsonis, D. M. de Kretser and E. Nieschlag fmflx Planck Clinical
Modulation by photoperiod of gonadotrophin secretion in intact and castrated Djungarian hamsters
 Modulation by photoperiod of gonadotrophin secretion in intact and castrated Djungarian hamsters S. M. Simpson, B. K. Follett and D. H. Ellis A.R.C. Research Group on Photoperiodism & Reproduction, Department
Modulation by photoperiod of gonadotrophin secretion in intact and castrated Djungarian hamsters S. M. Simpson, B. K. Follett and D. H. Ellis A.R.C. Research Group on Photoperiodism & Reproduction, Department
CHANGES IN THE ACTIVITY OF AN ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE IN PREPUBERAL MOUSE OVARIES
 CHANGES IN THE ACTIVITY OF AN ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE IN PREPUBERAL MOUSE OVARIES T.A. Bramley, Jane Sage, Joyce Kent, Margaret Ryle To cite this version: T.A. Bramley, Jane Sage, Joyce Kent, Margaret Ryle.
CHANGES IN THE ACTIVITY OF AN ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE IN PREPUBERAL MOUSE OVARIES T.A. Bramley, Jane Sage, Joyce Kent, Margaret Ryle To cite this version: T.A. Bramley, Jane Sage, Joyce Kent, Margaret Ryle.
Reproductive Hormones
 Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Slide #101 (1096). Testis, rat. sustentacular ( Sertoli ) cells Nuclei of Sustentacular cells Leydig cells Spermatogonia Spermatocytes Spermatids pale
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Slide #101 (1096). Testis, rat. sustentacular ( Sertoli ) cells Nuclei of Sustentacular cells Leydig cells Spermatogonia Spermatocytes Spermatids pale
Reproduction. Liang Huawei( 梁华为 )
 Reproduction Liang Huawei( 梁华为 ) E-mail: liang.huawei@yahoo.com.cn Reproduction Reproduction is the biological process by which new individual organisms are produced. An individual does not need the system
Reproduction Liang Huawei( 梁华为 ) E-mail: liang.huawei@yahoo.com.cn Reproduction Reproduction is the biological process by which new individual organisms are produced. An individual does not need the system
Male Reproductive Physiology
 Male Reproductive Physiology Overview Anatomy Function Endocrine and spermatogenesis Testis epididymus,vas deferens,seminal vesicles and prostate Hypothalamic pituitary testicular axis Hormones of the
Male Reproductive Physiology Overview Anatomy Function Endocrine and spermatogenesis Testis epididymus,vas deferens,seminal vesicles and prostate Hypothalamic pituitary testicular axis Hormones of the
The Effects of Selective Withdrawal of FSH or LH. on Spermatogenesis in the Immature Rat
 BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 14,489-494(1976) The Effects of Selective Withdrawal of FSH or LH on Spermatogenesis in the Immature Rat H. G. MADHWA RAJ and MARTIN DYM Departments of Obstetrics and Gynaecology
BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 14,489-494(1976) The Effects of Selective Withdrawal of FSH or LH on Spermatogenesis in the Immature Rat H. G. MADHWA RAJ and MARTIN DYM Departments of Obstetrics and Gynaecology
A.J. TILBROOK, 2 ' 3 D.M. DE KRETSER, 4 and I.J. CLARKE 5 ABSTRACT
 BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 49, 779-788 (1993) Human Recombinant Inhibin A Suppresses Plasma Follicle-Stimulating Hormone to Intact Levels But Has No Effect on Luteinizing Hormone in Castrated Rams' A.J. TILBROOK,
BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 49, 779-788 (1993) Human Recombinant Inhibin A Suppresses Plasma Follicle-Stimulating Hormone to Intact Levels But Has No Effect on Luteinizing Hormone in Castrated Rams' A.J. TILBROOK,
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 1 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM SCPA 602 Anatomical Basis for Pathological Study Updated: 20.09.2018 Lect. Nisamanee Charoenchon, PhD nisamanee.cha@mahidol.ac.th Department of Pathobiology, Mahidol University
1 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM SCPA 602 Anatomical Basis for Pathological Study Updated: 20.09.2018 Lect. Nisamanee Charoenchon, PhD nisamanee.cha@mahidol.ac.th Department of Pathobiology, Mahidol University
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Male Reproductive System Anatomy and Physiology
 1 Male Reproductive System Anatomy and Physiology 1 Anatomy and Physiology of Male Gametogenesis Alex Varghese, Fnu Deepinder, Angali Chandra, Ang Wen Jeat, Furquan Pathan, Ashok Agarwal ABSTRACT Basic
1 Male Reproductive System Anatomy and Physiology 1 Anatomy and Physiology of Male Gametogenesis Alex Varghese, Fnu Deepinder, Angali Chandra, Ang Wen Jeat, Furquan Pathan, Ashok Agarwal ABSTRACT Basic
JANINE L. BROWN,* KRISTINE D. DAHL,t AND PRABIR K. CHAKRABORTY*
 Journal of Anthology, Vol. 12, No. 4, July/August 1991 Copyright #{176} American Society of Andrology Effects of Follicular Fluid Administration on Serum Bioactive and Immunoreactive FSH Concentrations
Journal of Anthology, Vol. 12, No. 4, July/August 1991 Copyright #{176} American Society of Andrology Effects of Follicular Fluid Administration on Serum Bioactive and Immunoreactive FSH Concentrations
Male Reproductive System. Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD
 Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
IMMUNODETECTION OF A HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN-LIKE SUBSTANCE IN HUMAN SPERM
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright' 1977 The American Fertility Society Vol. 28, No. 11, November 1977 Printed in U.S.A. IMMUNODETECTION OF A HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN-LIKE SUBSTANCE IN HUMAN SPERM RICARDO
FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright' 1977 The American Fertility Society Vol. 28, No. 11, November 1977 Printed in U.S.A. IMMUNODETECTION OF A HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN-LIKE SUBSTANCE IN HUMAN SPERM RICARDO
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization
 Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Photoperiodic and melatonin treatments for the control of seasonal reproduction in sheep and goats
 Photoperiodic and melatonin treatments for the control of seasonal reproduction in sheep and goats P. Chemineau, J. Pelletier, Y. Guérin, G. Colas, J. P. Ravault, G. Touré, G. Almeida, J. Thimonier, R.
Photoperiodic and melatonin treatments for the control of seasonal reproduction in sheep and goats P. Chemineau, J. Pelletier, Y. Guérin, G. Colas, J. P. Ravault, G. Touré, G. Almeida, J. Thimonier, R.
