Early Development ~ 5 ½ Weeks Gestation
|
|
|
- Daniel Job Williams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNDERSTANDING THE CRYPTORCHID This section is designed to make the procedure of castration and crytorchidectomy easier to understand. Some oversimplification of the embryology of the testis and the assumption that readers are familiar with anatomical and developmental terminology is required for brevity. The following is not intended to be a detailed discussion of the embryology of male development in the horse, but a simplified version pointing out some important factors in the surgical anatomy of cryptorchid castrations. Transverse Plane through the Scrotum and Inguinal Canal For more detailed information, please refer to the selected bibliography at the end of this section. Anatomy and Anatomical Terminology The word cryptorchid is used to describe any testis that is not in the scrotum. There are three types of cryptorchids. 1. Inguinal 2. Abdominal 3. Incomplete In the normal juvenile or adult male horse the testis is found in the scrotum. A peritoneal process, the vaginal tunic (or just the tunic ) passes through the inguinal canal and surrounds the blood and nerve supply to the testis, as well as the vas deferens, and Note that the tunic and the peritoneal lining are one continuous structure. surrounds testis and epididymis in the scrotum. (The blood vessels are branches of the testicular artery and vein, which leave the caudal aorta and vena cava in the dorsal lumbar region, near the kidneys.) The inguinal canal in the horse is relatively longer than in other species and runs between a deep and a superficial hole in the body wall. These are called the internal inguinal ring and the external inguinal ring, respectively. The external inguinal ring is larger than the internal inguinal ring and is palpable in the groin region, especially with the horse in dorsal recumbency. The internal inguinal ring is smaller and is not palpable from outside the abdomen. The vaginal ring is the peritoneal lining of the internal inguinal ring. The vaginal process is a conical piece of the peritoneal lining that is attached to the tail of the epididymis by the ligament of the tail of the epididymus and will become the vaginal tunic once the epididymus and testis pass through the inguinal canal and exit the abdomen. Testicular Development and Descent in the Equine Fetus (very simplified!) The left and right testes each differentiate on the dorsal body wall from the corresponding Wolffian or mesonephric duct next to the primordial kidneys (mesonephros) in the first 5 ½ weeks of fetal development. At this time a chord of mesenchyme, called the gubermaculum runs from the caudal pole of the testis and the developing tail of the epididymis to the caudo-ventral body wall. This structure Early Development ~ 5 ½ Weeks Gestation
2 will differentiate into the ligament of the tail of the epididymus, and the vaginal ring itself. These structures are critical in finding and delivering a cryptorchid testis in surgery. Testis at its Largest Testis after Shrinking Between 5 and 8 months of pregnancy the testes lay right next to the developing vaginal ring (to which it is attached by the gubernaculum) and become quite large. In fact, during this period the intra-abdominal fetal testis is as large as that of a full-grown stallion. This increase in size occurs by adding cells inside of the testis and causes the bottom of the organ to approach the internal inguinal ring while the top of the testis remains in contact with the dorsal abdominal wall. Prior to birth, the testes begin to shrink. As they shrink, they pull away from the kidney, while they remain very close to the inguinal canal. Just as they added cells to grow in size, they lose cells to shrink. This process leaves each testis somewhat soft and pliable, which allows it to slip through the internal inguinal ring (vaginal ring) and into the inguinal canal. Normally, the testis slips into the inguinal canal during a brief period prior to parturition when the internal inguinal ring is widest in its development. During this limited amount of time the testis must shrink enough to pass through the ring. If not one could think of it as having lost the chance to enter the canal and is, therefore, trapped in the abdomen. In this case the testis will never leave the abdomen unless it is removed surgically. On the other hand, if the testes are able to slip into the inguinal canal during this time frame (and most of them do) they will eventually migrate subcutaneously to the scrotum (although they may remain in the inguinal canal for some period of time after birth). The vast majority do become scrotal testes, and are removed by routine castration technique. Those that remain in the inguinal canal or do not quite make it to the scrotum will often arrive in the scrotum as the horse matures and the testes enlarge. Horsemen refer to this as the testis descending, or dropping. The colloquial term for a horse with a testis hidden in the inguinal canal or under the skin outside the scrotum is a high flanker. Testis Entering the Canal
3 If the testis does NOT enter the canal (remains in the abdomen), it is most often found just inside the internal inguinal ring. At times the tail of the epididymus enters the inguinal canal unaccompanied by the testis. This is referred to as an incomplete cryptorchid. On very rare occasions a testis will remain in the dorsal or caudal abdomen, anywhere from the origin of the testicular arteries and veins in the lumbar region, along the normal pattern of decent in the fetus, to near the internal inguinal ring. Testis as it Passes through the Canal Normal Testis in the Scrotum Incomplete Cryptorchid in the Scrotum The Incomplete Cryptorchid Testis in the Inguinal Canal The Cryptorchid Testis
4 Inguinal Cryptorchids and High Flankers In younger horses with small testes, the cremaster muscle can pull the testis into the external inguinal ring and hide it inside the inguinal canal. For this reason, some prefer to wait until horses are older than a year for castration. However, horses cannot pull a testis through the internal inguinal canal and into the abdomen. Inguinal and subcutaneous testes are actually easy to find using good anesthesia technique, patient positioning, and anatomical knowledge. The inguinal cryptorchid is the most common presentation and is no more difficult to castrate than a normal testis. Push your hand firmly into the ring. If the testis is in the inguinal canal, it will be expelled superficially and appear as a smooth movable structure under the loose skin between the external inguinal ring and the scrotum. To find an inguinal or subcutaneous testis: 1. Put the horse into dorsal or semi-dorsal recumbency. Find and Palpate the Inguinal Canal 2. Find the easily palpable external inguinal ring in the groin region of the patient. It will be a 3-4 inch slit running in and parallel to the crease between the abdominal wall and the inside of thigh (see figure ). 3. Put firm downward pressure into the inguinal canal. If the testis is in the canal it will slide into the subcutaneous space and be readily palpable. Feeling along a line between the external ring and the scrotum will identify subcutaneous testes, as well. Unlike superficial inguinal lymph nodes and fat, a testis is oblong, smooth, and slippery. 4. If the testis can be manipulated into the scotum, the castration proceeds by the normal protocol. If the testis cannot be moved to the scrotum, an incision is made over the testis (or over the inguinal canal) and the testis is emasculated as it would be in a routine castration. Abdominal Cryptorchids Both the abdominal and incomplete cryptorchid are more difficult cases to handle. Remember: the abdominal cryptorchid testis is ALMOST always found just inside the internal inguinal ring. This is as one would expect from the development and decent of the testis discussed above. Therefore, in the majority of cases the testis can be pulled through the internal inguinal ring and the inguinal canal with a little firm, gentle traction. In the extremely rare instance that the cryptorchid testis is not next to the internal inguinal ring, it may be found at any point along the path followed during normal decent between the lumbar dorsal body wall and the internal inguinal ring. The Surgical Approach to an Abdominal Cryptorchid Testis There area a variety of techniques to finding and removing an abdominal testis in the horse. The following approach has proven effective and safe for field cryptorchid castrations and will be discussed in a series of sequential steps. To be successful, a grasp of the anatomical and developmental aspects of the testis and surrounding structures is essential. Once it has been established that the testis is not in the scrotum, the inguinal canal, or under the skin between these two structures, proceed as follows: 1. Establish that the horse is at an adequate plain of anesthesia to allow it to be placed in dorsal recumbency and that it is adequately relaxed. This may require additional xylazine, ketamine, and valium. Glycerol Guaicolate or Triple Drip may also be used if a catheter is in place. A good experienced field anesthetist should be in charge of anesthesia.
5 2. Roll the horse into dorsal recumbency and untie the hind legs. If the rear legs are flexed with a rope it will be much more difficult to visualize the external inguinal ring. The horse can be stabilized by a handler supporting each forelimb at the shoulder. A large pad for the horse s head and some attention to the rockiness of the ground will prevent pressure injuries to the patient. 3. Place bags, towels, or aluminum foil over the horse s hind feet to prevent dirt from dropping into the surgical field. 4. Do a good surgical prep over the entire inguinal area, including the medial sides of the thighs and from the pubis to the end of the sheath. Place a dry towel or cotton in the sheath to keep the penis out of the way and absorb leaked urine. 5. Draping in the triangular pattern shown is highly desirable, as there will be instances when it may be necessary to enter the abdominal cavity. 6. Surgeon and assistant must scrub their hands and wear gloves. Sterile sleeves for the surgeon will also allow entry into the abdomen in the rare instances where that is necessary. 7. The surgeon kneels directly behind the patient with the assistant in front of the leg on the side to be explored. 8. Palpate the external inguinal ring as above, just to be sure that the testis is not inguinal and to identify the incision site. 9. Make an incision directly over the external inguinal ring and parallel to it. The incision should be about 1½ times the length of the palpable slit that is the external ring and should be extended no deeper than the dermis. The remaining dissection to find the external inguinal ring is done bluntly with the fingers. Injury to large vessels in this region will make visualization very difficult. As the external inguinal ring is dissected out, the assistant uses fingers or retractors to open the incision and allow visualization. A large self-retaining retractor can be used, but is less adaptable than an assistant. 10. The loose areolar connective tissue is bluntly dissected until the white, fibrous external inguinal ring is exposed. A white finger-like projection coming up from the interior of the ring indicates an incomplete cryptorchid covered by the vaginal process. If this is the case, the white membrane The Drape The Landmark Vessels Gathering the Vessels The Vaginal Process
6 (vaginal process) is opened with scissors and the epididymis is pulled into the incision and used as a handle to deliver the testis from the abdomen, as described below. 11. More commonly, a group of very thin vessels will be seen going from the surrounding fascia, over the edge of the external inguinal ring and down into the inguinal canal. These vessels may fan out along the entire length of the canal or be in a more discrete bundle. They indicate the tissue that would become the scrotal ligament in a normally descended testis. They should be grasped together, making a bundle. 12. Carefully place traction on the bundled vessels (scrotal ligament) to evert the vagninal process through the internal inguinal ring (vaginal ring) and into the inguinal canal. The vaginal process is conical and the tip can be visualized as a small white structure as it passes out of the external inguinal ring. Palpation with an index finger during traction, will establish that the base of the cone is deep inside the inguinal canal. This structure will be more or less easy to mobilize in different horses. 13. Once the vaginal process is identified, it is opened with scissors or the point of a scalpel. Immediately inside the tip of the vaginal process is the ligament of the tail of the epididymis (remnant of the embryonic gubernaculum). This structure is grasped and used to deliver the epididymus through the inguinal canal and into the incision. Firm pressure is required to do this, but it is important not to break and lose the ligament or the epididymis. 14. Using the epididymal structures as a guide and handle traction in placed on the abdominal testis. The object is to deliver the testis through the smallest hole in the vaginal process and without disrupting the internal inguinal ring. A combination of traction, massage with an index finger, and occasionally stretching the vaginal process will deliver nearly every testis, with some patience. 15. Once the testis appears through the external inguinal ring, its vessels are ligated as one unit with 2 or 3 Vicryl and cut, along with the vas deferens. The cryptorchid testis and the epididymus are removed and the contralateral testis is castrated. 16. If only minor stretching of the vaginal process is required to remove the cryptorchid testis and the internal inguinal ring was not invaded, the incision is left open to heal by second Opening the Vaginal Process Stretching the Incision in the Vaginal Process Delivering the Tail of the Epididymus
7 intention and no further suturing is required. If the testis was larger and more difficult to deliver the inguinal canal can be closed with 2 or 3 Vicryl, by placing one or a few cruciate or simple interrupted stitches across the inguinal canal. 17. Because the inguinal canal in the horse is long and runs up the body wall, the internal inguinal ring cannot be readily identified for suturing. So it is difficult to do a firm closure of the canal if the internal ring has been opened significantly. Further, any suturing in this area should be done with care, due to the large vessels that lay in the fascia around the inguinal canal. If there is concern about the integrity of the closure and possible evisceration, the incision should be tightly packed with a sterile towel and the skin closed in a simple continuous pattern, over the towel. Then in hours the sutures and towel are removed. At this time swelling caused by the towel will have closed the canal and granulation has started. This generally Delivering the Testis requires a second, though brief, anesthesia. 18. IF the vessels indicating the scrotal ligament cannot be identified; IF the landmarks are broken while attempting to exert traction; or IF the testis is too large to be delivered through the internal inguinal ring: a parainguinal incision can be made, allowing the surgeon to enter the abdomen through a very small incision just next to the inguinal canal. 19. To utilize the parainguinal incision the assistant retracts the existing skin incision cranially and medially. In this region the internal abdominal oblique muscle is thin, but strong and fibrous. The surgeon selects a site a few inches medial and parallel to the external inguinal ring. A small stab incision is made just though the external muscle sheath. This is extended into the abdomen by using a blunt instrument, such as a the tip of Mayo scissors. The instrument is opened, stretching the incision so that the surgeon can stick two or three fingers into the abdomen. 20. Since the majority of abdominal testes are just next to the internal inguinal ring, the surgeon sweeps laterally and deep to the body wall incision, to palpate and grasp the testis, epididymis, or vas deferens and deliver the testis from the abdomen. The vessels are ligated and cut as above. Closure of the parainguinal incision with sutures in the internal abdominal oblique is a simple matter and very strong. No towel packing or removal is necessary. The skin incision is left open to heal by second intention. 21. In the rare instances in which the abdominal testis cannot be found via the small parainguinal incision described above, the surgeon simply extends the incision made bluntly in the abdominal wall, and, with a sterile sleeve, can explore the entire abdomen, following the decent of the testis from the dorsal body wall. Again, the incision, just large enough to permit the surgeon s arm is easy to close, once the testis is found and removed. Things Not to Do Start surgery before all anesthetic drugs and surgical supplies are immediately ready Start surgery before the horse is adequately anesthetized Sharply incise structures deep to the skin in the inguinal region. Injury to the large external pudental veins in this region and their branches will result in extreme difficulty in visualizing structures.
8 Attempt to find the landmarks around the inguinal canal without good light. Especially avoid having the sun shining in the surgeon s eyes when working outdoors. A good bright headlamp is a big help. Inadequately dissect the fascia from the external inguinal ring. Visualization of the edges of the ring is essential for success. Make sure you can clearly see the ring and if that requires a longer skin incision, make a longer incision. Break the remnant of the scrotal ligament: it is the major landmark to the vaginal process. Using large curved Carmault forceps seems to be less traumatic than Ochsners or Kellys. Some surgeons use sponge forces. Disrupt the internal inguinal ring. This necessitates suturing the inguinal canal and packing the area with a sterile towel, which must be later removed in a second anesthesia. A Few Last Points: IF the patient s castration history is unclear and there is scar on the scrotum it may better to postpone the surgery until a serum testosterone or estrone sulfate (depending on the age of the horse) can determine if testicular tissue is present. If this is not possible or if the horse is known to be a hemicastrate, exploration of the inguinal canal as described above will either lead to the cryptorchid testis or it will yield the white fibrous stump of the chord from a removed testis, coming from the external ring into the subcutaneous tissues. Since in Quarter Horse and Paint families an abdominal cryptorchid testis is more likely to be on the left side, it is sensible to approach the left inguinal region first. However, if a chord stump is found on the left side then the right inguinal canal is explored to find the testis. Always make sure that you can identify the testis, the head of the epididymis, and the tail of the epididymus before completing a castration. The most common cause of hemicastration (leaving an abdominal testis in the abdomen) is mistaking the tail of the epididymis for a small testis. If you can identify all three structures, you know that you have a complete castration. While with adequate sterile technique primary closure of inguinal incisions is possible, the issues of positioning, anesthesia, follow-up, and unrecognized breaks in asepsis make healing an open incision a good alternative in the field. These incisions, even with blunt dissection, seem to heal as rapidly as standard scrotal castrations. Remember: have a clear plan and everything AT YOUR FINGERTIPS before you consider starting surgery. This is no time to go looking for equipment and always plan for the procedure being difficult! If you find that you are not ready, allow the horse to recover and plan the procedure for another day. Be realistic and prepared to stop the procedure and allow the horse to recover IF: o You cannot find the important landmarks at the external inguinal ring or you cannot deliver the testis through the inguinal canal and do not want to enter the abdomen o Light is poor or it is getting dark o There a serious break in asepsis (ie mud falling into the incision) o Weather has changed: wind, dust, rain o The horse is not well anesthetized. This can often happen if an adequate plan of anesthesia was not attained at the start due to inadequate dosage or because the patient was excessively excited. The novice should not attempt this procedure on untrained horses that require IM or oral detomidine to allow venipuncture. At any point in the progression of the technique as described above, if the surgeon feels that they cannot successfully complete the procedure. It is far better to stop (given that the abdomen is closed) and allow the horse to recover. Castration is an elective procedure that can be rescheduled when conditions are better. While we cannot always predict complications: First, do no harm. Selected Bibliography:
9 1. Schumacher J: in Auer, JA, Equine Surgery, 1st ed, W. B. Saunders Co, Philadelphia, 1992, pg Smith JA. The Development and Descent of the Testis in the Horse. Veterinary Annual, 15 th ed., Grunnell CSG and Hill FWG eds. John Wright and Sons Ltd., Bristol, 1975, pgs Bergin WC, Gier HT, et al, A Developmental Concept of Equine Cryptorchidism. Biology of Reproduction, 3,, 1970, Dyce KM, Sack WO, and Wensing CJG. In Textbook of Veterinary Anatomy (Second ed.), WB Saunders Company, Philadelphia, Wilson DG and Reinertson EL. A Modified Parainguinal Approach for Cryptorchidectomy in Horses An Evaluation in 107 Horses. Veterinary Surgery, 16:1,1987, 1-4.
Proceedings of the 12th International Congress of the World Equine Veterinary Association WEVA
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 12th International Congress of the World Equine Veterinary Association WEVA November 2-5, 2011 Hyderabad, India Reprinted in IVIS with the Permission of WEVA Organizers
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 12th International Congress of the World Equine Veterinary Association WEVA November 2-5, 2011 Hyderabad, India Reprinted in IVIS with the Permission of WEVA Organizers
DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
SURGICAL PROCEDURE DESCRIPTIONS
 SURGICAL PROCEDURE DESCRIPTIONS GONADECTOMY: CASTRATION USING SCROTAL METHOD 1. The animal is anesthetized and placed in dorsal recumbency with the tail toward the surgeon. 2. The abdominal and scrotal
SURGICAL PROCEDURE DESCRIPTIONS GONADECTOMY: CASTRATION USING SCROTAL METHOD 1. The animal is anesthetized and placed in dorsal recumbency with the tail toward the surgeon. 2. The abdominal and scrotal
Normal and Cryptorchid Castration. Servizio di medicina e chirurgia del cavallo UNITE
 Normal and Cryptorchid Castration Servizio di medicina e chirurgia del cavallo UNITE Castration: Surgical Removal of Testes One of the most commonly performed equine surgical procedures Its complications
Normal and Cryptorchid Castration Servizio di medicina e chirurgia del cavallo UNITE Castration: Surgical Removal of Testes One of the most commonly performed equine surgical procedures Its complications
SURGICAL FIELD WORK WITH R-VETS
 REQUIRED PREPARATION SURGICAL FIELD WORK WITH R-VETS We expect all participants of the clinic to have prepared. This includes; 1. Read the chapter on equine castration in Turner and McIlwraith Techniques
REQUIRED PREPARATION SURGICAL FIELD WORK WITH R-VETS We expect all participants of the clinic to have prepared. This includes; 1. Read the chapter on equine castration in Turner and McIlwraith Techniques
the liver and kidney function (both vital when dealing with anaesthetic drugs) and to rule out any unsuspected illnesses.
 Orchiectomy: Castration reduces overpopulation by inhibiting male fertility and decreases male aggressiveness, roaming, and undesirable urination behaviour. It helps prevent androgenrelated diseases, including
Orchiectomy: Castration reduces overpopulation by inhibiting male fertility and decreases male aggressiveness, roaming, and undesirable urination behaviour. It helps prevent androgenrelated diseases, including
Surgical management of the undescended testis is performed
 Undescended Testes/Orchiopexy James C.Y. Dunn, MD, PhD, 1 Akemi L. Kawaguchi, MD, 2 and Eric W. Fonkalsrud, MD 1 Surgical management of the undescended testis is performed to prevent the potential complications
Undescended Testes/Orchiopexy James C.Y. Dunn, MD, PhD, 1 Akemi L. Kawaguchi, MD, 2 and Eric W. Fonkalsrud, MD 1 Surgical management of the undescended testis is performed to prevent the potential complications
حسام أبو عوض. -Dr. Mohammad Muhtasib. 1 P a g e
 5 حسام أبو عوض - -Dr. Mohammad Muhtasib 1 P a g e There are two types of inguinal hernia: direct and indirect. Hernia: protrusion of the small intestine or the greater omentum of the intra-abdominal organs
5 حسام أبو عوض - -Dr. Mohammad Muhtasib 1 P a g e There are two types of inguinal hernia: direct and indirect. Hernia: protrusion of the small intestine or the greater omentum of the intra-abdominal organs
Technique Guide. Bard MK Hernia Repair. Featuring Modified Onflex Mesh SOFT TISSUE REPAIR. Anterior Approach to a Preperitoneal Inguinal Hernia Repair
 Bard MK Hernia Repair Featuring Modified Onflex Mesh Technique Guide Anterior Approach to a Preperitoneal Inguinal Hernia Repair SOFT TISSUE REPAIR Right Procedure. Right Product. Right Outcome. The opinions
Bard MK Hernia Repair Featuring Modified Onflex Mesh Technique Guide Anterior Approach to a Preperitoneal Inguinal Hernia Repair SOFT TISSUE REPAIR Right Procedure. Right Product. Right Outcome. The opinions
How-To Booklet: Pediatric Spay-Neuter. Surgical Techniques Pictorial
 How-To Booklet: Pediatric Spay-Neuter Surgical Techniques Pictorial Brenda Griffin, DVM, MS, DACVIM 1. Approach to Scrotal Neuter for Puppies 2. Cord Tie 3. Figure 8 Knot 4. Ovarian Pedicle Tie 5. Modified
How-To Booklet: Pediatric Spay-Neuter Surgical Techniques Pictorial Brenda Griffin, DVM, MS, DACVIM 1. Approach to Scrotal Neuter for Puppies 2. Cord Tie 3. Figure 8 Knot 4. Ovarian Pedicle Tie 5. Modified
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman
 Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Fetal Pig Dissection:
 Fetal Pig Dissection: REMEMBER: Dissection involves disassembling and observing something to determine its internal structure and develop an understanding of the relationship of those structures to function.
Fetal Pig Dissection: REMEMBER: Dissection involves disassembling and observing something to determine its internal structure and develop an understanding of the relationship of those structures to function.
Inguinal and Femoral Hernias. August 10, 2016 Basic Science Lecture Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Health Science Center
 Inguinal and Femoral Hernias August 10, 2016 Basic Science Lecture Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Health Science Center Background Approximately 20 million groin hernias are repaired each
Inguinal and Femoral Hernias August 10, 2016 Basic Science Lecture Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Health Science Center Background Approximately 20 million groin hernias are repaired each
Proceedings of the 9th International Congress of World Equine Veterinary Association
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 9th International Congress of World Equine Veterinary Association Jan. 22-26, 2006 - Marrakech, Morocco Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Conference Organizers
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 9th International Congress of World Equine Veterinary Association Jan. 22-26, 2006 - Marrakech, Morocco Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Conference Organizers
Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb A Patient's Guide to Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb
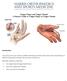 Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb A Patient's Guide to Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb Introduction Trigger finger and trigger thumb are conditions affecting the movement of the tendons as they bend the
Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb A Patient's Guide to Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb Introduction Trigger finger and trigger thumb are conditions affecting the movement of the tendons as they bend the
The Scrotum & Testes Prof. Dr. Imran Qureshi
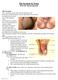 The Scrotum & Testes Prof. Dr. Imran Qureshi The Scrotum It is a cutaneous pouch of the anterior abdominal wall. Most layers of the abdominal wall are represented in its structure. It contains the testes
The Scrotum & Testes Prof. Dr. Imran Qureshi The Scrotum It is a cutaneous pouch of the anterior abdominal wall. Most layers of the abdominal wall are represented in its structure. It contains the testes
"Easy-On" Caponizing Set. Instruction Book. Sears, Roebuck & Co. Chicago, Ill. BLACK LANGSHAN CAPON. Ten Months Old - Weight 11 Pounds.
 BLACK LANGSHAN CAPON Ten Months Old - Weight 11 Pounds Instruction Book "Easy-On" Caponizing Set Copyright 1922 Published for Sears, Roebuck & Co. Chicago, Ill. Dallas, Tex. Philadelphia, Pa. Seattle,
BLACK LANGSHAN CAPON Ten Months Old - Weight 11 Pounds Instruction Book "Easy-On" Caponizing Set Copyright 1922 Published for Sears, Roebuck & Co. Chicago, Ill. Dallas, Tex. Philadelphia, Pa. Seattle,
BP and Heart Rate by Telemetry
 BP and Heart Rate by Telemetry Version: 1 Modified from: Butz et al. Physiol Genomics. 2001 Mar 8;5(2):89-97. Edited by: Dr. Lynette Bower, UC Davis Summary Reagents and Materials Protocol Reagent Preparation
BP and Heart Rate by Telemetry Version: 1 Modified from: Butz et al. Physiol Genomics. 2001 Mar 8;5(2):89-97. Edited by: Dr. Lynette Bower, UC Davis Summary Reagents and Materials Protocol Reagent Preparation
M. Al-Mohtaseb. Tala Saleh. Faisal Nimri
 4 5 M. Al-Mohtaseb Tala Saleh Faisal Nimri Inguinal Hernia - An abdominal hernia is the protrusion of part of the abdominal content beyond the normal confines of the abdominal wall through weak points
4 5 M. Al-Mohtaseb Tala Saleh Faisal Nimri Inguinal Hernia - An abdominal hernia is the protrusion of part of the abdominal content beyond the normal confines of the abdominal wall through weak points
Terminology: castration, orchiectomy, emasculation, gelding, cutting.
 Terminology: castration, orchiectomy, emasculation, gelding, cutting. Equine Castration Overview: - Castration is the surgical removal of the testes. In horses, this is often performed as young colts (1
Terminology: castration, orchiectomy, emasculation, gelding, cutting. Equine Castration Overview: - Castration is the surgical removal of the testes. In horses, this is often performed as young colts (1
Implanting an Adult Rat with the Single-Channel Epoch Transmitter for Recording Electrocardiogram in the Type II electrode configuration.
 Implanting an Adult Rat with the Single-Channel Epoch Transmitter for Recording Electrocardiogram in the Type II electrode configuration. Recommended Surgical Tools A. Scalpel handle B. Scalpel blade (#15)
Implanting an Adult Rat with the Single-Channel Epoch Transmitter for Recording Electrocardiogram in the Type II electrode configuration. Recommended Surgical Tools A. Scalpel handle B. Scalpel blade (#15)
Fetal Pig Dissection Day 2 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 Name: Date: Period: Fetal Pig Dissection Day 2 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Dissection Roles (choose a different role from Day 1): Recorder reads directions out loud to group and records answers
Name: Date: Period: Fetal Pig Dissection Day 2 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Dissection Roles (choose a different role from Day 1): Recorder reads directions out loud to group and records answers
Inguinal Canal. It is an oblique passage through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall. Present in both sexes
 Inguinal canal Inguinal Canal It is an oblique passage through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall Present in both sexes It allows structures to pass to and from the testis to the abdomen in
Inguinal canal Inguinal Canal It is an oblique passage through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall Present in both sexes It allows structures to pass to and from the testis to the abdomen in
Dissection: The Fetal Pig
 Lab Exercise Dissection: The Fetal Pig Objectives - To learn some of anatomical structures of the fetal pig. - To be able to make contrasts and comparisons of structures between different animal phyla
Lab Exercise Dissection: The Fetal Pig Objectives - To learn some of anatomical structures of the fetal pig. - To be able to make contrasts and comparisons of structures between different animal phyla
Reproductive System. Where it all begins
 Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
CHILD HYDROCELE OPERATION. COPYRIGHT M.H.EDWARDS 2005 FILE NAME SW-CHHY OPERATION NO 037 SURGEON... Last updated
 CHILD HYDROCELE OPERATION COPYRIGHT M.H.EDWARDS 2005 FILE NAME SW-CHHY OPERATION NO 037 SURGEON... Last updated 30 12 05 CHILD HYDROCELE OPERATION GRADE 4 (SEVERE) THESE S COVER MALE PATIENT LESS THAN
CHILD HYDROCELE OPERATION COPYRIGHT M.H.EDWARDS 2005 FILE NAME SW-CHHY OPERATION NO 037 SURGEON... Last updated 30 12 05 CHILD HYDROCELE OPERATION GRADE 4 (SEVERE) THESE S COVER MALE PATIENT LESS THAN
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH
 ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
Transfemoral Amputation
 Transfemoral Amputation Pre-Op: 42 year old male who sustained severe injuries in a motorcycle accident. Note: he is a previous renal transplant recipient and is on immunosuppressive treatments. His injuries
Transfemoral Amputation Pre-Op: 42 year old male who sustained severe injuries in a motorcycle accident. Note: he is a previous renal transplant recipient and is on immunosuppressive treatments. His injuries
Aus Artificial Uretheral Sphincter Port System
 NORFOLK VET PRODUCTS the AUS for the long-term relief of incontinence in dogs and cats making life easier for pets Speciality Medical Devices For The Veterinary Community the Aus Artificial Uretheral Sphincter
NORFOLK VET PRODUCTS the AUS for the long-term relief of incontinence in dogs and cats making life easier for pets Speciality Medical Devices For The Veterinary Community the Aus Artificial Uretheral Sphincter
UNDERSTANDING. Permanent Birth Control for Men
 UNDERSTANDING VASECTOMY Permanent Birth Control for Men Is Vasectomy for You? Vasectomy is a simple, safe procedure that makes a man sterile (unable to father a child). It s the most effective birth control
UNDERSTANDING VASECTOMY Permanent Birth Control for Men Is Vasectomy for You? Vasectomy is a simple, safe procedure that makes a man sterile (unable to father a child). It s the most effective birth control
PATCHING AND SECTION OF THE PULMONARY ORIFICE OF THE HEART.*
 Published Online: 1 July, 1914 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20.1.3 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on December 24, 2018 PATCHING AND SECTION OF THE PULMONARY ORIFICE OF THE HEART.* BY THEODORE
Published Online: 1 July, 1914 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20.1.3 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on December 24, 2018 PATCHING AND SECTION OF THE PULMONARY ORIFICE OF THE HEART.* BY THEODORE
What are Varicoceles?
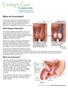 What are Varicoceles? A varicocele is when veins become enlarged inside your scrotum (the pouch of skin that holds your testicles). These veins are called the pampiniform plexus. Ten to 15 of every 100
What are Varicoceles? A varicocele is when veins become enlarged inside your scrotum (the pouch of skin that holds your testicles). These veins are called the pampiniform plexus. Ten to 15 of every 100
Hernia. emoryhealthcare.org
 Hernia Have you noticed a bulge or pain in your abdominal wall or groin? If so you may have a hernia. You may be in the process of confirming this diagnosis with your Primary Care Physician or already
Hernia Have you noticed a bulge or pain in your abdominal wall or groin? If so you may have a hernia. You may be in the process of confirming this diagnosis with your Primary Care Physician or already
Thyroidectomy. Siu Kwan Ng. Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II 47
 06 Thyroidectomy Siu Kwan Ng Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II 47 Thyroidectomy STEP 1. EXPOSING THE THYROID GLAND The collar incision Figure 1 (curvilinear skin crease incision) is made at 1.5-2
06 Thyroidectomy Siu Kwan Ng Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II 47 Thyroidectomy STEP 1. EXPOSING THE THYROID GLAND The collar incision Figure 1 (curvilinear skin crease incision) is made at 1.5-2
Placing PEG and Jejunostomy Tubes in Dogs and Cats
 Placing PEG and Jejunostomy Tubes in Dogs and Cats I. Gastrostomy tube A. Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) tube placement Supplies for PEG tube placement: Supplies and equipment for general anesthesia
Placing PEG and Jejunostomy Tubes in Dogs and Cats I. Gastrostomy tube A. Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) tube placement Supplies for PEG tube placement: Supplies and equipment for general anesthesia
Forelimb Amputation. Indications. Pre operatively 11/12/2008. Technique Preparing for surgery. Bone neoplasia. Severe trauma/paralysis
 Forelimb Amputation January 10, 2007 Amy Bringardner Becky Pentecost Indications Bone neoplasia Osteosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Chondrosarcoma Severe trauma/paralysis Brachial plexus avulsion Infection Congenital
Forelimb Amputation January 10, 2007 Amy Bringardner Becky Pentecost Indications Bone neoplasia Osteosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Chondrosarcoma Severe trauma/paralysis Brachial plexus avulsion Infection Congenital
Chapter 2. Simple Nephrectomy. Please Give Three Tips for Laparoscopic Simple Nephrectomy. Dr. de la Rosette
 Chapter 2 Simple Nephrectomy Please Give Three Tips for Laparoscopic Simple Nephrectomy............. 39 How Does One Find the Renal Hilum during Transperitoneal Laparoscopic Nephrectomy?.................
Chapter 2 Simple Nephrectomy Please Give Three Tips for Laparoscopic Simple Nephrectomy............. 39 How Does One Find the Renal Hilum during Transperitoneal Laparoscopic Nephrectomy?.................
UCSF Pediatric Urology Child and Family Information Material
 UCSF Pediatric Urology Child and Family Information Material ------------------------------------------------------------------------ The Undescended Testicle What is an Undescended Testicle? The undescended
UCSF Pediatric Urology Child and Family Information Material ------------------------------------------------------------------------ The Undescended Testicle What is an Undescended Testicle? The undescended
CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1. Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book)
 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1 Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book) Introduction When you have finished examining the model, you are ready to begin your
CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1 Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book) Introduction When you have finished examining the model, you are ready to begin your
INGUINAL HERNIA REPAIR PROCEDURE GUIDE
 ROOM CONFIGURATION The following figure shows an overhead view of the recommended OR configuration for a da Vinci Inguinal Hernia Repair (Figure 1). NOTE: Configuration of the operating room suite is dependent
ROOM CONFIGURATION The following figure shows an overhead view of the recommended OR configuration for a da Vinci Inguinal Hernia Repair (Figure 1). NOTE: Configuration of the operating room suite is dependent
SOP: Urinary Catheter in Dogs and Cats
 SOP: Urinary Catheter in Dogs and Cats These SOPs were developed by the Office of the University Veterinarian and reviewed by Virginia Tech IACUC to provide a reference and guidance to investigators during
SOP: Urinary Catheter in Dogs and Cats These SOPs were developed by the Office of the University Veterinarian and reviewed by Virginia Tech IACUC to provide a reference and guidance to investigators during
Knee Disarticulation Amputation
 Knee Disarticulation Amputation Pre-Op 64 year old man, previous spinal cord injury, diabetes, renal failure, and a history of spasticity with dynamic knee flexion contracture. He had an open left ankle
Knee Disarticulation Amputation Pre-Op 64 year old man, previous spinal cord injury, diabetes, renal failure, and a history of spasticity with dynamic knee flexion contracture. He had an open left ankle
Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Femoral triangle Is a triangular depressed area located in the upper
Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Femoral triangle Is a triangular depressed area located in the upper
Undescended Testicle
 What is the normal descending testis? The testicle begins to form just before the second fetal month and starts to look like a testicle around the fourth fetal month. By then it has migrated down from
What is the normal descending testis? The testicle begins to form just before the second fetal month and starts to look like a testicle around the fourth fetal month. By then it has migrated down from
The Tell Tale Heart. Introduction to the Heart. Name
 The Tell Tale Heart CIBT Student Laboratory Exercise Name Introduction to the Heart The main function of the heart is to keep blood constantly moving throughout the body. In mammals the heart is a large
The Tell Tale Heart CIBT Student Laboratory Exercise Name Introduction to the Heart The main function of the heart is to keep blood constantly moving throughout the body. In mammals the heart is a large
Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Introduction A. Preparing the Fetal Pig Anterior Posterior Dorsal Ventral length gender mammary papillae
 Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Preserved Fetal Pig Cotton String Dissection tray Dissection pins Disposable Gloves Paper towels Dissection scissors Label pins Lab apron Re-sealable bag Dissection probe
Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Preserved Fetal Pig Cotton String Dissection tray Dissection pins Disposable Gloves Paper towels Dissection scissors Label pins Lab apron Re-sealable bag Dissection probe
LAPAROSCOPIC HERNIA REPAIR
 LAPAROSCOPIC HERNIA REPAIR Treating Your Hernia with Laparoscopy When You Have a Hernia Anyone can have a hernia. This is a weakness or tear in the wall of the abdomen. It often results from years of wear
LAPAROSCOPIC HERNIA REPAIR Treating Your Hernia with Laparoscopy When You Have a Hernia Anyone can have a hernia. This is a weakness or tear in the wall of the abdomen. It often results from years of wear
Castration: Getting the Best Result for Farm and Calf
 Castration: Getting the Best Result for Farm and Calf Richard Laven PhD BVetMed MRCVS Why castrate your calves? Castration of bull calves has significant advantages. Steers are much easier and safer to
Castration: Getting the Best Result for Farm and Calf Richard Laven PhD BVetMed MRCVS Why castrate your calves? Castration of bull calves has significant advantages. Steers are much easier and safer to
Surgical Approach and Occlusion of the Vasa
 From No-Scalpel Vasectomy: An Illustrated Guide for Surgeons, Third Edition 2003 EngenderHealth 5 Surgical Approach and Occlusion of the Vasa A lthough the no-scalpel technique is almost bloodless, an
From No-Scalpel Vasectomy: An Illustrated Guide for Surgeons, Third Edition 2003 EngenderHealth 5 Surgical Approach and Occlusion of the Vasa A lthough the no-scalpel technique is almost bloodless, an
Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference
 www.ivis.org Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference Oct. 17-19, 2008 Barcelona, Spain http://www.sevc.info Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the SEVC www.ivis.org
www.ivis.org Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference Oct. 17-19, 2008 Barcelona, Spain http://www.sevc.info Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the SEVC www.ivis.org
SPINAL IMMOBILIZATION
 Spinal Immobilization Decision Assessment Recent studies have shown an increase in mortality for patients with isolated penetrating trauma who are spinally immobilized. Therefore spinal immobilization
Spinal Immobilization Decision Assessment Recent studies have shown an increase in mortality for patients with isolated penetrating trauma who are spinally immobilized. Therefore spinal immobilization
Definition. A hole in the septum between the right and left atria. Causes oxygen-poor blood and oxygen-rich blood to mix.
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 13d Lab Activity adapted from You Gotta Have Heart: Congenital Heart Defects and Heart Surgery by Rebecca Johns & CDC. Name(s): Period: Date: Common Heart Defects Congenital
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 13d Lab Activity adapted from You Gotta Have Heart: Congenital Heart Defects and Heart Surgery by Rebecca Johns & CDC. Name(s): Period: Date: Common Heart Defects Congenital
Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Inguinal orchidectomy for testicular cancer
 Surgery Illustrated Focus on Details SURGERY ILLUSTRATED SURGICAL ATLASPIZZOCARO and GUARNERI PIZZOCARO and GUARNERI BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Inguinal orchidectomy for
Surgery Illustrated Focus on Details SURGERY ILLUSTRATED SURGICAL ATLASPIZZOCARO and GUARNERI PIZZOCARO and GUARNERI BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Inguinal orchidectomy for
Surgical Atlas The posterior lumbotomy
 Original Article SURGERY ILLUSTRATED PANSADORO Surgical Atlas The posterior lumbotomy VITO PANSADORO Urology, Vincenzo Pansadoro Foundation, Rome, Italy ILLUSTRATIONS by STEPHAN SPITZER, www.spitzer-illustration.com
Original Article SURGERY ILLUSTRATED PANSADORO Surgical Atlas The posterior lumbotomy VITO PANSADORO Urology, Vincenzo Pansadoro Foundation, Rome, Italy ILLUSTRATIONS by STEPHAN SPITZER, www.spitzer-illustration.com
POSTERIOR 1. situated behind: situated at or toward the hind part of the body :
 ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
RECTAL INJURY IN UROLOGIC SURGERY. Inadvertent rectal injury from a urologic procedure is often subtle but has serious postoperative consequences.
 RECTAL INJURY IN 27 UROLOGIC SURGERY Inadvertent rectal injury from a urologic procedure is often subtle but has serious postoperative consequences. With good mechanical bowel preparation plus antibiotic
RECTAL INJURY IN 27 UROLOGIC SURGERY Inadvertent rectal injury from a urologic procedure is often subtle but has serious postoperative consequences. With good mechanical bowel preparation plus antibiotic
COMPLETION PROJECT POSITIONING THE PATIENT IN THE OR Source- Alexander s Care of the Patient in Surgery
 COMPLETION PROJECT POSITIONING THE PATIENT IN THE OR Source- Alexander s Care of the Patient in Surgery Name Date 1. The systems involved with anesthesia, positioning and operative procedures are: a. b.
COMPLETION PROJECT POSITIONING THE PATIENT IN THE OR Source- Alexander s Care of the Patient in Surgery Name Date 1. The systems involved with anesthesia, positioning and operative procedures are: a. b.
7 weeks: 28 mm 8 weeks: 40 mm 15 weeks: 220 mm 17 weeks: 300 mm
 Fetal Pig Dissection Background Pigs are placental mammals and show the distinguishing characteristics of that group. In studying the anatomy of the fetal, or unborn, pig, you will see that its various
Fetal Pig Dissection Background Pigs are placental mammals and show the distinguishing characteristics of that group. In studying the anatomy of the fetal, or unborn, pig, you will see that its various
5 IN THEATRE. The anaesthetic
 5 IN THEATRE The anaesthetic Spinal anaesthesia is the preferred method for all fistula cases (Figure 5.1). Many surgeons give spinal anaesthesia themselves. Bupivacaine 0.5% in glucose (Marcain Heavy)
5 IN THEATRE The anaesthetic Spinal anaesthesia is the preferred method for all fistula cases (Figure 5.1). Many surgeons give spinal anaesthesia themselves. Bupivacaine 0.5% in glucose (Marcain Heavy)
Modified Radical Mastectomy
 Modified Radical Mastectomy Valerie L. Staradub, MD, and Monica Morrow, MD S urgical management options for breast cancer include modified radical mastectomy (MRM), MRM with immediate reconstruction, and
Modified Radical Mastectomy Valerie L. Staradub, MD, and Monica Morrow, MD S urgical management options for breast cancer include modified radical mastectomy (MRM), MRM with immediate reconstruction, and
#5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels
 #5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels Objectives: Identify a list of human arteries and veins using a virtual human dissection and a human model Dissect and identify a list of arteries and veins in the cat
#5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels Objectives: Identify a list of human arteries and veins using a virtual human dissection and a human model Dissect and identify a list of arteries and veins in the cat
Centerline Carpal Tunnel Release
 Centerline Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgical Technique Centerline Carpal Tunnel Release Centerline Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgical Set Up The patient is positioned supine on the operating
Centerline Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgical Technique Centerline Carpal Tunnel Release Centerline Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgical Set Up The patient is positioned supine on the operating
Alexander C Vlantis. Selective Neck Dissection 33
 05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Discectomy. PHYSIO.coza
 A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Discectomy SANDTON MEDICLINIC 011 706 7495 FAIRWAYS LIFE HOSPITAL 011 875 1827 ST STITHIANS 082 378 9642 JEPPE BOYS HIGH SCHOOL 084 816 5457 JOHANNESBURG, SANDTON@PHYSIO.CO.ZA
A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Discectomy SANDTON MEDICLINIC 011 706 7495 FAIRWAYS LIFE HOSPITAL 011 875 1827 ST STITHIANS 082 378 9642 JEPPE BOYS HIGH SCHOOL 084 816 5457 JOHANNESBURG, SANDTON@PHYSIO.CO.ZA
Name Date: Block: Honors Marine Biology Mr. Conlan - Squid Dissection Lab Objective: Can you identify a squid s structures and their functions?
 Name Date: Block: Honors Marine Biology Mr. Conlan - Squid Dissection Lab Objective: Can you identify a squid s structures and their functions? Helpful Hints Everyone must wear safety goggles during the
Name Date: Block: Honors Marine Biology Mr. Conlan - Squid Dissection Lab Objective: Can you identify a squid s structures and their functions? Helpful Hints Everyone must wear safety goggles during the
Background & Indications Probe Selection
 Teresa S. Wu, MD, FACEP Director, EM Ultrasound Program & Fellowship Co-Director, Simulation Based Training Program & Fellowship Associate Program Director, EM Residency Program Maricopa Medical Center
Teresa S. Wu, MD, FACEP Director, EM Ultrasound Program & Fellowship Co-Director, Simulation Based Training Program & Fellowship Associate Program Director, EM Residency Program Maricopa Medical Center
 Name: Date: Period: The Dissection 1. Place your specimen dorsal side down. Make your incisions following the diagram below. Make sure to make shallow cuts with the scissors. DO NOT CUT TOO DEEP! You will
Name: Date: Period: The Dissection 1. Place your specimen dorsal side down. Make your incisions following the diagram below. Make sure to make shallow cuts with the scissors. DO NOT CUT TOO DEEP! You will
MIAA. Minimally Invasive Anterior Approach Surgical technique
 MIAA Minimally Invasive Anterior Approach Surgical technique Contents Introduction 3 With-Table MIAA technique 4 A1. Patient positioning/draping 4 A2. Skin incision 4 A3. Muscular dissection 4 A4. Muscle
MIAA Minimally Invasive Anterior Approach Surgical technique Contents Introduction 3 With-Table MIAA technique 4 A1. Patient positioning/draping 4 A2. Skin incision 4 A3. Muscular dissection 4 A4. Muscle
DISCHARGE DIAGNOSES: End stage renal disease secondary to rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis.
 DISCHARGE SUMMARY DISCHARGE DIAGNOSES: End stage renal disease secondary to rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis. OPERATIONS/PROCEDURES: Living related renal transplantation. HISTORY: For full details
DISCHARGE SUMMARY DISCHARGE DIAGNOSES: End stage renal disease secondary to rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis. OPERATIONS/PROCEDURES: Living related renal transplantation. HISTORY: For full details
The front of the thigh. Dr.Amjad shatarat
 The front of the thigh Femoral triangle (Scarpa s triangle) Is a triangular depressed area located in the upper part of the medial aspect of the thigh immediately below the inguinal ligament. Superiorly:
The front of the thigh Femoral triangle (Scarpa s triangle) Is a triangular depressed area located in the upper part of the medial aspect of the thigh immediately below the inguinal ligament. Superiorly:
Heart Dissection. 5. Locate the tip of the heart or the apex. Only the left ventricle extends all the way to the apex.
 Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
LAB: Sheep or Pig Heart Dissection
 Biology 12 Name: Circulatory System Per: Date: Observation: External Anatomy LAB: Sheep or Pig Heart Dissection 1. Line a dissecting tray with paper towel for easy clean up as the heart is fatty and will
Biology 12 Name: Circulatory System Per: Date: Observation: External Anatomy LAB: Sheep or Pig Heart Dissection 1. Line a dissecting tray with paper towel for easy clean up as the heart is fatty and will
Name Partner(s) Name. Name your rat. Rat Dissection Lab
 Name Partner(s) Name Name your rat Rat Dissection Lab!!CAUTION!! You must follow all safety instructions as outlined in this lab manual and by your teacher. There are several sharp objects being used during
Name Partner(s) Name Name your rat Rat Dissection Lab!!CAUTION!! You must follow all safety instructions as outlined in this lab manual and by your teacher. There are several sharp objects being used during
Table of Contents: CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Knife Assembly... Page 6 VERSION 2.2
 www.s2ssurgical.com Table of Contents: Preparation... Page 1 Dissection... Page 2 Tunneling... Page 3 Release... Page 4 Closure... Page 6 Knife Assembly... Page 6 CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
www.s2ssurgical.com Table of Contents: Preparation... Page 1 Dissection... Page 2 Tunneling... Page 3 Release... Page 4 Closure... Page 6 Knife Assembly... Page 6 CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
Transfemoral Amputation
 Transfemoral Amputation Preop This 26 year old male sustained a gunshot wound to the left thigh. He was treated emergently with revascularization and fasciotomies. He was transferred to our regional trauma
Transfemoral Amputation Preop This 26 year old male sustained a gunshot wound to the left thigh. He was treated emergently with revascularization and fasciotomies. He was transferred to our regional trauma
SHOULDER INSTABILITY
 SHOULDER INSTABILITY Your shoulder is the most flexible joint in your body, allowing you to throw fastballs, lift a heavy suitcase, scratch your back, and reach in almost any direction. Your shoulder joint
SHOULDER INSTABILITY Your shoulder is the most flexible joint in your body, allowing you to throw fastballs, lift a heavy suitcase, scratch your back, and reach in almost any direction. Your shoulder joint
Human Body Systems. Human Body Project Notes
 Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
A Patient's Guide to Ganglions of the Wrist
 Introduction A ganglion is a small, harmless cyst, or sac of fluid, that sometimes develops in the wrist. Doctors don't know exactly what causes ganglions, but a ganglion that isn't painful and doesn't
Introduction A ganglion is a small, harmless cyst, or sac of fluid, that sometimes develops in the wrist. Doctors don't know exactly what causes ganglions, but a ganglion that isn't painful and doesn't
A Patient s Guide to Arthroscopy of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Arthroscopy of the Hip Introduction A hip arthroscopy is a procedure where a small video camera attached to a fiberoptic lens is inserted into the hip joint to allow a surgeon to see
A Patient s Guide to Arthroscopy of the Hip Introduction A hip arthroscopy is a procedure where a small video camera attached to a fiberoptic lens is inserted into the hip joint to allow a surgeon to see
Colon Cancer Surgery
 Colon Cancer Surgery Introduction Colon cancer is a life-threatening condition that affects thousands of people. Doctors usually recommend surgery for the removal of colon cancer. If your doctor recommends
Colon Cancer Surgery Introduction Colon cancer is a life-threatening condition that affects thousands of people. Doctors usually recommend surgery for the removal of colon cancer. If your doctor recommends
Kidney Disease Treatment Options
 Page 1 Fact sheet The kidneys play a number of important roles in your body such as: extracting excess water to make urine (wee) controlling your blood pressure filtering waste products and toxins from
Page 1 Fact sheet The kidneys play a number of important roles in your body such as: extracting excess water to make urine (wee) controlling your blood pressure filtering waste products and toxins from
Pilates Arc A DETAILED GUIDE FOR PRACTICING PILATES
 Pilates Arc A DETAILED GUIDE FOR PRACTICING PILATES TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Welcome! 2 What is Pilates? 4 Pilates Principles 5 Introduction to the Pilates Arc Pilates Arc Exercises 6 Step Roll Down Series
Pilates Arc A DETAILED GUIDE FOR PRACTICING PILATES TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Welcome! 2 What is Pilates? 4 Pilates Principles 5 Introduction to the Pilates Arc Pilates Arc Exercises 6 Step Roll Down Series
#5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels
 Page1 #5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels Objectives: Observe slide of artery and vein cross-section Identify a list of human arteries and veins using a virtual human dissection Dissect and identify a list
Page1 #5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels Objectives: Observe slide of artery and vein cross-section Identify a list of human arteries and veins using a virtual human dissection Dissect and identify a list
Taking Care of Your Back
 Taking Care of Your Back Most people will feel back pain at some point in their lives, but not all back pain is the same for everyone. The good news is, most low back pain improves without any treatment
Taking Care of Your Back Most people will feel back pain at some point in their lives, but not all back pain is the same for everyone. The good news is, most low back pain improves without any treatment
Adductor canal (Subsartorial) or Hunter s canal
 Adductor canal (Subsartorial) or Hunter s canal John Hunter described the exposure and ligation of the femoral artery in this canal for aneurysm of the popliteal artery; this method has the advantage that
Adductor canal (Subsartorial) or Hunter s canal John Hunter described the exposure and ligation of the femoral artery in this canal for aneurysm of the popliteal artery; this method has the advantage that
The Language of Anatomy. (Anatomical Terminology)
 The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
Initial placement 20FR Guidewire PEG kit REORDER NO:
 Initial placement 20FR Guidewire PEG kit REORDER NO: 00710802 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE 1 of 5 These products have been manufactured not to include latex. Intended Use: The Initial placement 20FR Guidewire
Initial placement 20FR Guidewire PEG kit REORDER NO: 00710802 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE 1 of 5 These products have been manufactured not to include latex. Intended Use: The Initial placement 20FR Guidewire
The arteriovenous fistula for haemodialysis
 The arteriovenous fistula for haemodialysis Department of Renal Medicine Patient Information Leaflet Introduction The information contained in this booklet is for: Patients waiting to go on the haemodialysis
The arteriovenous fistula for haemodialysis Department of Renal Medicine Patient Information Leaflet Introduction The information contained in this booklet is for: Patients waiting to go on the haemodialysis
THE TRANSPLANTATION OF THE RECTUS MUSCLE OR ITS
 THE TRANSPLANTATION OF THE RECTUS MUSCLE OR ITS SHEATH FOR THE CURE OF INGUINAL HERNIA WHEN THE CONJOINED TENDON IS OBLITERATED. THE TRANS- PLANTATION OF THE SARTORIUS MUSCLE FOR THE CURE OF RECURRENT
THE TRANSPLANTATION OF THE RECTUS MUSCLE OR ITS SHEATH FOR THE CURE OF INGUINAL HERNIA WHEN THE CONJOINED TENDON IS OBLITERATED. THE TRANS- PLANTATION OF THE SARTORIUS MUSCLE FOR THE CURE OF RECURRENT
Initial placement 24FR Pull PEG kit REORDER NO:
 Initial placement 24FR Pull PEG kit REORDER NO: 00710805 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE 1 of 5 These products have been manufactured not to include latex. Intended Use: The Initial placement 24FR Pull PEG kit is
Initial placement 24FR Pull PEG kit REORDER NO: 00710805 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE 1 of 5 These products have been manufactured not to include latex. Intended Use: The Initial placement 24FR Pull PEG kit is
A Patient s Guide to Dupuytren s Contracture Surgery
 A Patient s Guide to Dupuytren s Contracture Surgery 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not
A Patient s Guide to Dupuytren s Contracture Surgery 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not
Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Binds, support, and strengthen body tissues, protect and insulate internal organ, serve as
 Connective tissue Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Binds, support, and strengthen body tissues, protect and insulate internal organ, serve as major transport system, compartmentalizes
Connective tissue Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Binds, support, and strengthen body tissues, protect and insulate internal organ, serve as major transport system, compartmentalizes
HERNIA SURGERY. Surgery to Repair Your Abdominal Wall
 HERNIA SURGERY Surgery to Repair Your Abdominal Wall Understanding Hernias A hernia (or bulge ) is a weakness or defect in the wall of the abdomen. This weakness may be present at birth. Or, it can be
HERNIA SURGERY Surgery to Repair Your Abdominal Wall Understanding Hernias A hernia (or bulge ) is a weakness or defect in the wall of the abdomen. This weakness may be present at birth. Or, it can be
Back Safety Healthcare #09-066
 Back Safety Healthcare Version #09-066 I. Introduction A. Scope of training This training program applies to healthcare employees whose job requires them to lift patients or other heavy objects. Lifting
Back Safety Healthcare Version #09-066 I. Introduction A. Scope of training This training program applies to healthcare employees whose job requires them to lift patients or other heavy objects. Lifting
US Patent No. 6,309,396B1. G. David Ritland, M.D.
 US Patent No. 6,309,396B1 G. David Ritland, M.D. The Femur Finder is designed to direct the guide wire into the medullary canal. Do not use it to manipulate the fracture fragments, reduce the fracture,
US Patent No. 6,309,396B1 G. David Ritland, M.D. The Femur Finder is designed to direct the guide wire into the medullary canal. Do not use it to manipulate the fracture fragments, reduce the fracture,
Stiff Shoulder Tips for decreasing your pain and increasing movement
 Patient Education Tips for decreasing your pain and increasing movement Your stiff shoulder may be painful and limit your movement. There are many causes of shoulder stiffness. Most times stretching exercises
Patient Education Tips for decreasing your pain and increasing movement Your stiff shoulder may be painful and limit your movement. There are many causes of shoulder stiffness. Most times stretching exercises
THE HUMERUS 20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW
 20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW The marrow canal of the humerus is funnel-shaped. Its successful pinning is influenced by many factors. With a few exceptions, the entire humerus
20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW The marrow canal of the humerus is funnel-shaped. Its successful pinning is influenced by many factors. With a few exceptions, the entire humerus
Anatomy & Physiology Autopsy of a Banana Planes / Anatomical Directions
 Anatomy & Physiology Autopsy of a Banana Planes / Anatomical Directions Purpose: During this lab you will demonstrate your knowledge of directional terms by performing an autopsy on a banana. It is important
Anatomy & Physiology Autopsy of a Banana Planes / Anatomical Directions Purpose: During this lab you will demonstrate your knowledge of directional terms by performing an autopsy on a banana. It is important
Chest Tube Thoracostomy
 Chest Tube Thoracostomy INTRODUCTION A chest tube thoracostomy is commonly done in the ED to evacuate an abnormal accumulation of fluid (blood, empyema) or air from the pleural space under an elective,
Chest Tube Thoracostomy INTRODUCTION A chest tube thoracostomy is commonly done in the ED to evacuate an abnormal accumulation of fluid (blood, empyema) or air from the pleural space under an elective,
