Normal and Cryptorchid Castration. Servizio di medicina e chirurgia del cavallo UNITE
|
|
|
- Howard Murphy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Normal and Cryptorchid Castration Servizio di medicina e chirurgia del cavallo UNITE
2 Castration: Surgical Removal of Testes One of the most commonly performed equine surgical procedures Its complications are among the most common causes of malpractice claims against veterinarians Synonyms for castration include: Orchidectomy Orchiectomy Castration Emasculation Gelding Cutting
3 Postoperative Complications of Castration Hemorrhage Swelling Infection Septic Peritonitis Hydrocele Intestinal Evisceration Omentum Eventration (Prolapse) Continued Stallion-like Behavior
4 Testis Anatomy Scrotum skin tunica dartos Tunica vaginalis visceral tunic (tunica vaginalis propria) parietal tunic (tunica vaginalis communis) vaginal process o vaginal sac vaginal ring vaginal cavity Epididymis head (caput) body (corpus) tail (cauda)
5 Testis Anatomy Ligamentous structures proper ligament of testis between the caudal pole of the mature testis and the tail of epididymis ligament of tail of epididymis between the tail of epididymis and parietal tunic of the vaginal process scrotal ligament between the parietal tunic of the vaginal process and the bottom of the scrotum
6 Testis Anatomy Spermatic cord tunica vaginalis ductus deferens testicular artery (a branch of the abdominal aorta) testicular veins (pampiniform plexus) lymphatic vassel testicular plexus (autonomic and visceral sensory nerve)
7 Testis Anatomy Cremaster muscle a slip of the internal abdominal oblique muscle is not included as a component of the cord because it lies external to the parietal tunic lies on the caudolateral surface of the parietal tunic and attaches to this tunic at the caudal pole of the testis contraction of the cremaster muscle retracts the testis
8 Testis Anatomy parietal tunic is not incised but is freed from the scrotal ligament and scrotal fascia parietal tunic and cremaster muscle have been incised and are partially retracted
9 Castration Indications Reduce or prevent sexual behavior and aggressive temperament Sterilize horses unsuitable for contributing to the genetic pool Orchitis, epididymitis, testicular neoplasia, hydrocele, varicocele, testicular damage caused by trauma, torsion of the spermatic cord or inguinal herniation (unilateral or sometimes bilateral)
10 Castration Preoperative consideration Full physical examination Scrotal/inguinal areas should be palpated and inspected for the absence of inguinal herniation and for the presence of both testes Sedation permits safe palpation and occasionally facilitates palpation of an inguinal testis by causing the cremaster muscles to relax
11 Castration Preoperative consideration Tetanus prophylaxis (tetanus toxoid booster or tetanus antitoxin) Antimicrobial use to prevent postoperative infections is questionable and generally based on clinician preference Preoperative and postoperative administration of NSAID may help control pain and swelling
12 Castration Surgical techniques of orchiectomy are OPEN CLOSED HALF- or SEMI- or MODIFIED-CLOSED Castration can be performed (surgeon s preference and experience) In STANDING sedated horses using local anesthesia In RECUMBENT position (lateral or dorsal) with the horse under general anesthesia
13 Castration Approach Scrotal incision Inguinal incision (horse is anesthetized and positioned in dorsal recumbency) Closure of the skin incision Primary intention healing (sutured castration) Secondary intention healing (unsutured castration)
14 Standing Castration with an Open Technique Direct infiltration of local anesthetic into testicular parenchyma Subcutaneous infiltration of local anesthetic along proposed incision line
15 Standing Castration with an Open Technique A) tensing the testicles in the scrotum B) scrotal incision C) completed incision into the parietal vaginal tunic D) testicles prolapsed through the incision of the vaginal tunic
16 Standing Castration with an Open Technique E) peforation of the mesorchium F) emasculation of the musculofibrous portion of the spermatic cord G) emasculation of the vascular spermatic cord
17 Emasculators commonly used for Equine Castrations Left to right: Improved White, Reimer, Serra
18 Recumbent Castration with a Closed Technique through a Scrotal Approach Closed castration is more difficult to accomplish in the standing horse Full exteriorisation of the vaginal process is much eisier when the animal is in recumbency Hind limbs tied in a frog leg position Upper hindlimb pulled foreward and secured with rope
19 Recumbent Castration with a Closed Technique through a Scrotal Approach Two skin incision are made through the scrotal skin and tunica dartos parallel to median raphe Alternatively the bottom of the scrotum is removed by placing traction on the scrotal raphe
20 Recumbent Castration with a Closed Technique through a Scrotal Approach Scrotal fascia is stripped from the parietal tunic using dry swab until the cremaster muscle and parietal tunic are fully esposed The entire spermatic cord is then emasculated close to the superficial inguinal ring In horses with large spermatic cord cremaster muscle can be bluntly dissected from the spermatic and the emasculators applied separately prior to crushing and severing
21 Ligation around Vaginal Tunic The closed technique has no advantage over the open technique in preventing evisceration if a ligature is not applied to the cord proximal to the site of transection
22 Recumbent Castration with a Closed Technique through a Scrotal Approach Proper application of the emasculator with the prominent external assembly nuts facing the testis and the correct perpendicular orientation to the spermatic cord. Stretching of the scrotal skin incisions to promote adequate drainage
23 Zurich technique Used in Europe To ensure adequate scrotal drainage involves suturing a 30-cm-long gauze drain to the stumps of the cords with heavy catgut suture The drain that exits the scrotal wound is removed 2 days after castration by rupturing the catgut suture with a sharp tug on the drain
24 Recumbent Castration with a Half- or Semi- or Modified Closed Technique through a Scrotal Approach A) scrotal incision B) extruted testicle C) incision of the parietal vaginal tunic D) thumb inserted into tunic incision
25 Recumbent Castration with a Half- or Semi- or Modified Closed Technique through a Scrotal Approach E) prolapsed testicle with fingers hooked into the inverted vaginal tunic F) stripping scrotal fascia from the spermatic cord G) extending the incision in the vaginal tunic H) emasculation of spermatic cord
26 Henderson Castration Instrument Instrument can be attached to the spermatic cord proximal to the testis to facilitate twisting and severing of the spermatic cord Initially upon rotation of the drill, the testis is allowed to partially retract into the scrotum
27 Henderson Castration Instrument After revolutions, the cord and attached structures will be severed in a tightly twisted fashion Coiled, sealed segment of spermatic cord attached to testicle
28 Simplified Castration With the Equitwister The Equitwister Testicle wrapped between the tines at the end of the shaft. Light pull on the instrument keeps the cord straight, the cord is then twisted by turning the handle
29 Primary Castration with an Inguinal Approach This technique is frequently used when castrating horses 2 years old or older to avoid evisceration With the horse anesthetized and surgical field draped The testis is pushed craniad from the scrotum so that it lies close to the superficial inguinal ring a 5- to 7-cm cutaneous incision is created over the superficial inguinal ring
30 Primary Castration with an Inguinal Approach The inguinal fascia overlying the testis is incised to expose the parietal tunic of the testis The parietal tunic is incised longitudinally for 5 cm in an area not covered by the cremaster muscle The ligament of the tail of the epididymis is located with an index finger, and by applying traction on this structure, the testis is pulled from the vaginal cavity
31 Primary Castration with an Inguinal Approach The ligament of the tail of the epididymis is transected The mesorchium and the distal part of the mesofuniculum are bluntly separated from the epididymus and the distal part of the spermatic cord respectively Bleeding vessels are cauterized to prevent hemorrhage into the vaginal cavity
32 Primary Castration with an Inguinal Approach Two ligatures (one transfixing and one modified Miller s knot) of absorbable heavy suture (2 USP) are applied 1 cm apart, as far proximad as possible, to the spermatic cord The vasculature and ductus deferens are severed 2 cm distal to the distal ligature After inspection the stump is replaced into the vaginal cavity
33 Primary Castration with an Inguinal Approach The vaginal tunic is closed in a simple continous pattern using absorbable monofilament 2/0 USP suture The overlying fascia is similarly sutured in one or two layer The same suture material is used for subcuticular suture of the skin in a simple continuous pattern
34 Laparoscopic Castration without Orchidectomy Minimally invasive Excellent visualization of the spermatic cord Visual confirmation that adequate hemostasis of the mesorchium occurs Eliminates the requirement for general anaesthesia and its associated risks Advantage of a more rapid return to function Indications Horse at risk of general anesthesia Large vaginal rings and risk of evisceration Castration of descended testicle after abdominal cryptorchid castration
35 Laparoscopic Castration without Orchidectomy Ligating and transecting the blood supply and ductus deferens of scrotal testes laparoscopically with the horse standing or anesthetized results in avascular necrosis of the testicular parenchyma with the testes in situ
36 Laparoscopic Castration without Orchidectomy 5.6% of inguinally retained testes and 3.4% of normally descended testes failed to become completely necrotic as a result of an alternative blood supply from the cremasteric or external pudendal artery or both
37 Cryptorchidectomy Cryptorchidism ( hidden testis ) refers to the failure of descent of one or both testes from the fetal position in the scrotum The term cryptorchid is used to describe the nondescend testis and by extension affected horses Colloquial terms for the condition include: Rig Ridgling Original Monorchid, Anorchid, Polyorchid, False rig
38 Cryptorchidectomy Retrospective studies of large numbers indicate: retention of the right and left testis occurs nearly equally unilateral retention occurs about nine times more often than does bilateral retention most (about 60%) retained right testes are located inguinally abdominal retention more commonly occurs with the left testis (right testis is smaller than the left during the stage of testicular regression) bilateral abdominal retention of testes is nearly 2.5 times more prevalent than bilateral inguinal retention the occurence of both abdominal and inguinal testes in the same horse is relatively uncommonn
39 Descent of the Testis: Gubernaculum Divided into three parts: Cranial part becomes the proper ligament of the testis Middle part becomes the ligament of the tail of the epididymis Caudal or scrotal part become the scrotal ligament : in abdominally retained testis is referred to as the inguinal extension of the gubernaculum testis
40 Inguinal Canal oblique passage in the abdominal wall spermatic cord, genito-femoral nerve, external pudendal vasculature and the efferent lymphatic vessels internal opening deep inguinal ring is a slit bordered cranially by the caudal edge of the internal abdominal oblique muscle, ventromedially by the rectus abdominis muscle and prepubic tendon and caudally by the inguinal ligament external opening superficial inguinal ring: is a slit in the external abdominal oblique muscle
41 Criptorchidism in Horses: Classification Inguinal retention testis situated external to the superficial inguinal ring testis situated within the inguinal canal Partial or Incomplete Abdominal retention Complete Abdominal retention
42 Inguinal Cryptorchid Testis
43 Partial or Incomplete Abdominal Cryptorchid Testis
44 Complete Abdominal Cryptorchid Testis
45 Descended and retained testes
46 Descended and retained testes
47 Cryptorchidectomy Diagnosis of cryptorchidism: easily if no attempt has been made to castrate the horse external palpation of the scrotum reveals the absence of one or both testes gonadal agenesis is extremely rare if the history that the horse has not been castrated is reliable, the retained testis must be in an ectopic, inguinal, or abdominal position Horse purchased as geldings but displaying stallion-like behavior pose more of a diagnostic challenge
48 Cryptorchidectomy Diagnostic work up of cryptorchidism: Good case history very important Physical examination visual inspection and palpation of the scrotum and the inguinal region rectal examination Ultrasound examination transrectal transcutaneous inguinal Hormonal assays (plasma or serum testosterone and estrone sulfate) Diagnostic laparoscopy
49
50
51 Cryptorchidectomy Surgical approaches Invasive (requires insertion of a entire hand into the abdomen) Abdominal exploration through the inguinal canal Suprapubic paramedian Flank laparotomy Noninvasive (the testis can be removed by introducing only two fingers or less into the abdominal cavity) Inguinal approach with eversion of the vaginal process Parainguinal approach Minimalinvasive Laparoscopic cryptorchidectomy
52 Cryptorchidectomy Selection of the surgical approaches The paramedian and flank approaches allow removal of only an abdominal testis (retraction of an inguinal testis into the abdomen can usually be accomplished only with difficulty) The inguinal approach allows removal of either an abdominal or an inguinal testis Except for the flank and laparoscopic standing approaches the horse must be anesthetized When general anesthesia is not practical an abdominal testis can be removed with the horse standing Castration of partial cryptorchid by the inexperienced surgeon my result in removal of of the tail of the epididymis inadvertently leaving the testis within the abdomen
53 Cryptorchid Castration: Noinvasive Inguinal Approach The horse is anesthetized and positioned in dorsal recumbency The superficial inguinal ring is exposed through an 8- to 15-cm skin incision (depending on the horse s size) made directly over the superficial inguinal ring The inguinal fascia is separated digitally to expose the superficial inguinal ring
54 Cryptorchid Castration: Noinvasive Inguinal Approach An inguinal testis is readily encountered when the superficial inguinal ring is exposed If the testis has already been removed, the stump of the spermatic cord is encountered as it exits the canal An abdominal testis can be retrieved locating the rudimentary common vaginal tunic or vaginal process
55 Nonivasive Inguinal Approach: Partial Abdominal Cryptorchid The vaginal process of the partial abdominal cryptorchid testis lies everted within the inguinal canal and is readily encountered during inguinal exploration
56 Noninvasive Inguinal Approach: Complete Abdominal Cryptorchid The vaginal process of the complete abdominal cryptorchid lies inverted within the abdominal cavity, along with the epididymis and testis, and difficulty may be encountered in locating and everting it into the canal
57 Cryptorchid Castration: Noinvasive Inguinal Approach An inverted vaginal process can be everted into the inguinal canal by exerting traction on the scrotal ligament (also known as the inguinal extension of the gubernaculum testis) The IEGT is located by examining the margin of the superficial inguinal ring for a fibrous band that descends into the canal An inverted vaginal process can also be everted using a sponge forceps
58 Cryptorchid Castration: Noinvasive Inguinal Approach After the vaginal process is everted and stripped of inguinal fascia, it is incised longitudinally The epididymis contained within is grasped with a hemostat and exteriorized
59 Cryptorchid Castration: Noinvasive Inguinal Approach Applying traction on the proper ligament of the testis, the testis can be pulled through the vaginal ring and exteriorized for removal
60 Cryptorchid Castration: Parainguinal Approach Is preferred over the inguinal approach by some surgeons because the vaginal ring is not disrupted A 4-cm incision is made in the aponeurosis of the external abdominal oblique muscle, 1 to 2 cm medial and parallel to the superficial inguinal ring The aponeurosis of the external abdominal oblique muscle is more easily sutured than the superficial inguinal ring
61 Cryptorchid Castration: Parainguinal Approach The incision is centered over the cranial aspect of the ring Internal abdominal oblique muscle underlying the aponeurosis is spread in the direction of its fibers and the peritoneum is penetrated with a sharp thrust of the index and middle fingers
62 Cryptorchid Castration: Suprapubic Paramedian Approach An 8- to 15-cm longitudinal skin incision is made 5 to 10 cm lateral to the ventral midline The incision begins at the level of the preputial orifice and extends caudally The abdominal tunic and ventral sheath of the rectus abdominis muscle are incised longitudinally, and the underlying fibers of the rectus abdominis muscle are bluntly separated in the same direction The dorsal rectus sheath, retroperitoneal fat and peritoneum are penetrated with a finger then a hand is introduced into the abdomen
63 Cryptorchid Castration: Flank Approach Horse standing or recumbent 10- to 15-cm incision is made through the skin and subcutis in the paralumbar fossa of the affected side The external abdominal oblique muscle is transected in the direction of the skin incision The peritoneum is exposed by splitting the internal abdominal oblique and transversus abdominis muscles in the direction of their fibers The peritoneum and retroperitoneal fat are perforated with a finger to enter the abdomen
64 Laparoscopic Technique of Cryptorchidectomy An abdominal testis can be removed laparoscopically with the horse in standing position in dorsal recumbency in Trendelenburg position No disruption of the internal inguinal/vaginal ring minimizing risk of evisceration Inguinal retained testes should be removed using traditional castration methods to avoid disruption of the vaginal ring Experienced and properly trained surgeon
65 Standing Laparoscopic Cryptorchidectomy The placement and number of the portals in the paralumbar fossa can vary Generally three portals are necessary (three portal technique) One portal is used to insert the laparoscope One portal is used to insert forceps to grasp the testicle One portal is used to insert an instrument to sever the spermatic cord Suture Loop techique, Electrosurgical instrumentation, Ligasure Instrumentation Extracorporeal emasculation (two portal technique or laparoscopic-assisted)
66 Standing Laparoscopic Cryptorchidectomy Typical portal arrangement for laparoscopic cryptorchidectomy in standing sedated horses
67 Standing Laparoscopic Cryptorchidectomy The testicular vessels and ductus deferens of an abdominal testis can be transected intra-abdominally with vessel-sealing devices such as the LigaSure
68 Standing Laparoscopic Cryptorchidectomy Removal of an abdominal testis through a small incision in the paralumbar fossa
69 Laparoscopic Cryptorchidectomy in the Dorsal Recumbent Horse Horse anesthetized, the hindquarters must be elevated to displace the viscera craniad, making positive-pressure ventilation necessary Dorsal recumbent approach works well for cases involving bilateral abdominal retention Hemostasis of the testis can be performed Outside the abdomen (each testis is exteriorized througth the corrisponding instrument portal) Inside the abdomen (only one portal has to be enlarged to remove both testis)
70 Laparoscopic Cryptorchidectomy in the Dorsal Recumbent Horse
71 Laparoscopic Cryptorchidectomy in the Dorsal Recumbent Horse Intraoperative laparoscopic view of the vessel sealing device (LigaSure) applied across the testicular vessels, mesorchium, and vas deferens
72 Grazie per l attenzione! Servizio di medicina e chirurgia del cavallo UNITE
Proceedings of the 12th International Congress of the World Equine Veterinary Association WEVA
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 12th International Congress of the World Equine Veterinary Association WEVA November 2-5, 2011 Hyderabad, India Reprinted in IVIS with the Permission of WEVA Organizers
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 12th International Congress of the World Equine Veterinary Association WEVA November 2-5, 2011 Hyderabad, India Reprinted in IVIS with the Permission of WEVA Organizers
Proceedings of the 9th International Congress of World Equine Veterinary Association
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 9th International Congress of World Equine Veterinary Association Jan. 22-26, 2006 - Marrakech, Morocco Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Conference Organizers
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 9th International Congress of World Equine Veterinary Association Jan. 22-26, 2006 - Marrakech, Morocco Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Conference Organizers
the liver and kidney function (both vital when dealing with anaesthetic drugs) and to rule out any unsuspected illnesses.
 Orchiectomy: Castration reduces overpopulation by inhibiting male fertility and decreases male aggressiveness, roaming, and undesirable urination behaviour. It helps prevent androgenrelated diseases, including
Orchiectomy: Castration reduces overpopulation by inhibiting male fertility and decreases male aggressiveness, roaming, and undesirable urination behaviour. It helps prevent androgenrelated diseases, including
M. Al-Mohtaseb. Tala Saleh. Faisal Nimri
 4 5 M. Al-Mohtaseb Tala Saleh Faisal Nimri Inguinal Hernia - An abdominal hernia is the protrusion of part of the abdominal content beyond the normal confines of the abdominal wall through weak points
4 5 M. Al-Mohtaseb Tala Saleh Faisal Nimri Inguinal Hernia - An abdominal hernia is the protrusion of part of the abdominal content beyond the normal confines of the abdominal wall through weak points
How-To Booklet: Pediatric Spay-Neuter. Surgical Techniques Pictorial
 How-To Booklet: Pediatric Spay-Neuter Surgical Techniques Pictorial Brenda Griffin, DVM, MS, DACVIM 1. Approach to Scrotal Neuter for Puppies 2. Cord Tie 3. Figure 8 Knot 4. Ovarian Pedicle Tie 5. Modified
How-To Booklet: Pediatric Spay-Neuter Surgical Techniques Pictorial Brenda Griffin, DVM, MS, DACVIM 1. Approach to Scrotal Neuter for Puppies 2. Cord Tie 3. Figure 8 Knot 4. Ovarian Pedicle Tie 5. Modified
Terminology: castration, orchiectomy, emasculation, gelding, cutting.
 Terminology: castration, orchiectomy, emasculation, gelding, cutting. Equine Castration Overview: - Castration is the surgical removal of the testes. In horses, this is often performed as young colts (1
Terminology: castration, orchiectomy, emasculation, gelding, cutting. Equine Castration Overview: - Castration is the surgical removal of the testes. In horses, this is often performed as young colts (1
SURGICAL PROCEDURE DESCRIPTIONS
 SURGICAL PROCEDURE DESCRIPTIONS GONADECTOMY: CASTRATION USING SCROTAL METHOD 1. The animal is anesthetized and placed in dorsal recumbency with the tail toward the surgeon. 2. The abdominal and scrotal
SURGICAL PROCEDURE DESCRIPTIONS GONADECTOMY: CASTRATION USING SCROTAL METHOD 1. The animal is anesthetized and placed in dorsal recumbency with the tail toward the surgeon. 2. The abdominal and scrotal
حسام أبو عوض. -Dr. Mohammad Muhtasib. 1 P a g e
 5 حسام أبو عوض - -Dr. Mohammad Muhtasib 1 P a g e There are two types of inguinal hernia: direct and indirect. Hernia: protrusion of the small intestine or the greater omentum of the intra-abdominal organs
5 حسام أبو عوض - -Dr. Mohammad Muhtasib 1 P a g e There are two types of inguinal hernia: direct and indirect. Hernia: protrusion of the small intestine or the greater omentum of the intra-abdominal organs
Surgical management of the undescended testis is performed
 Undescended Testes/Orchiopexy James C.Y. Dunn, MD, PhD, 1 Akemi L. Kawaguchi, MD, 2 and Eric W. Fonkalsrud, MD 1 Surgical management of the undescended testis is performed to prevent the potential complications
Undescended Testes/Orchiopexy James C.Y. Dunn, MD, PhD, 1 Akemi L. Kawaguchi, MD, 2 and Eric W. Fonkalsrud, MD 1 Surgical management of the undescended testis is performed to prevent the potential complications
Early Development ~ 5 ½ Weeks Gestation
 UNDERSTANDING THE CRYPTORCHID This section is designed to make the procedure of castration and crytorchidectomy easier to understand. Some oversimplification of the embryology of the testis and the assumption
UNDERSTANDING THE CRYPTORCHID This section is designed to make the procedure of castration and crytorchidectomy easier to understand. Some oversimplification of the embryology of the testis and the assumption
Inguinal Canal. It is an oblique passage through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall. Present in both sexes
 Inguinal canal Inguinal Canal It is an oblique passage through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall Present in both sexes It allows structures to pass to and from the testis to the abdomen in
Inguinal canal Inguinal Canal It is an oblique passage through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall Present in both sexes It allows structures to pass to and from the testis to the abdomen in
ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE
 ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE SCROTUM MICHAEL NOMIKOS M.D. F.E.B.U. UROLOGICAL
ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE SCROTUM MICHAEL NOMIKOS M.D. F.E.B.U. UROLOGICAL
CHILD HYDROCELE OPERATION. COPYRIGHT M.H.EDWARDS 2005 FILE NAME SW-CHHY OPERATION NO 037 SURGEON... Last updated
 CHILD HYDROCELE OPERATION COPYRIGHT M.H.EDWARDS 2005 FILE NAME SW-CHHY OPERATION NO 037 SURGEON... Last updated 30 12 05 CHILD HYDROCELE OPERATION GRADE 4 (SEVERE) THESE S COVER MALE PATIENT LESS THAN
CHILD HYDROCELE OPERATION COPYRIGHT M.H.EDWARDS 2005 FILE NAME SW-CHHY OPERATION NO 037 SURGEON... Last updated 30 12 05 CHILD HYDROCELE OPERATION GRADE 4 (SEVERE) THESE S COVER MALE PATIENT LESS THAN
DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Inguinal orchidectomy for testicular cancer
 Surgery Illustrated Focus on Details SURGERY ILLUSTRATED SURGICAL ATLASPIZZOCARO and GUARNERI PIZZOCARO and GUARNERI BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Inguinal orchidectomy for
Surgery Illustrated Focus on Details SURGERY ILLUSTRATED SURGICAL ATLASPIZZOCARO and GUARNERI PIZZOCARO and GUARNERI BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Inguinal orchidectomy for
GI anatomy Lecture: 2 د. عصام طارق
 GI anatomy Lecture: 2 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To define rectus sheath. To describe anatomy of inguinal canal. To relates types of inguinal hernia to the region. To explore spermatic cord. Rectus Abdominis
GI anatomy Lecture: 2 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To define rectus sheath. To describe anatomy of inguinal canal. To relates types of inguinal hernia to the region. To explore spermatic cord. Rectus Abdominis
Laparoscopic removal of the gonads from male and female horses
 John P. Caron, DVM Michigan State University For more information, please see the companion articles: Equine Laparoscopy: Equipment and Basic Principles (March 2012), Equine Laparoscopy: Abdominal Access
John P. Caron, DVM Michigan State University For more information, please see the companion articles: Equine Laparoscopy: Equipment and Basic Principles (March 2012), Equine Laparoscopy: Abdominal Access
Inguinal and Femoral Hernias. August 10, 2016 Basic Science Lecture Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Health Science Center
 Inguinal and Femoral Hernias August 10, 2016 Basic Science Lecture Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Health Science Center Background Approximately 20 million groin hernias are repaired each
Inguinal and Femoral Hernias August 10, 2016 Basic Science Lecture Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Health Science Center Background Approximately 20 million groin hernias are repaired each
Proceedings of the Society for Theriogenology 2013 Annual Conference
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Society for Theriogenology 2013 Annual Conference Aug. 7-10, 2013 Louisville, KY, USA www.therio.org/ Next SFT Meeting: Aug. 6-9, 2014 Portland, OR, USA Reprinted in the
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Society for Theriogenology 2013 Annual Conference Aug. 7-10, 2013 Louisville, KY, USA www.therio.org/ Next SFT Meeting: Aug. 6-9, 2014 Portland, OR, USA Reprinted in the
Surgical Approach and Occlusion of the Vasa
 From No-Scalpel Vasectomy: An Illustrated Guide for Surgeons, Third Edition 2003 EngenderHealth 5 Surgical Approach and Occlusion of the Vasa A lthough the no-scalpel technique is almost bloodless, an
From No-Scalpel Vasectomy: An Illustrated Guide for Surgeons, Third Edition 2003 EngenderHealth 5 Surgical Approach and Occlusion of the Vasa A lthough the no-scalpel technique is almost bloodless, an
Proceedings of the Society for Theriogenology 2013 Annual Conference
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Society for Theriogenology 2013 Annual Conference Aug. 7-10, 2013 Louisville, KY, USA www.therio.org/ Next SFT Meeting: Aug. 6-9, 2014 Portland, OR, USA Reprinted in the
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Society for Theriogenology 2013 Annual Conference Aug. 7-10, 2013 Louisville, KY, USA www.therio.org/ Next SFT Meeting: Aug. 6-9, 2014 Portland, OR, USA Reprinted in the
Male Reproductive System. Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD
 Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
Technique Guide. Bard MK Hernia Repair. Featuring Modified Onflex Mesh SOFT TISSUE REPAIR. Anterior Approach to a Preperitoneal Inguinal Hernia Repair
 Bard MK Hernia Repair Featuring Modified Onflex Mesh Technique Guide Anterior Approach to a Preperitoneal Inguinal Hernia Repair SOFT TISSUE REPAIR Right Procedure. Right Product. Right Outcome. The opinions
Bard MK Hernia Repair Featuring Modified Onflex Mesh Technique Guide Anterior Approach to a Preperitoneal Inguinal Hernia Repair SOFT TISSUE REPAIR Right Procedure. Right Product. Right Outcome. The opinions
أحمد رواجبة- محمود الحربي- أحمد السالمان-
 -6 أحمد رواجبة- محمود الحربي- أحمد السالمان- 1 P a g e The Male Reproductive System The male genital system structures are divided into: Internal structures: 1- Prostate 3-Ejaculatory ducts External structures:
-6 أحمد رواجبة- محمود الحربي- أحمد السالمان- 1 P a g e The Male Reproductive System The male genital system structures are divided into: Internal structures: 1- Prostate 3-Ejaculatory ducts External structures:
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH
 ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS
 BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
INGUINAL HERNIA REPAIR PROCEDURE GUIDE
 ROOM CONFIGURATION The following figure shows an overhead view of the recommended OR configuration for a da Vinci Inguinal Hernia Repair (Figure 1). NOTE: Configuration of the operating room suite is dependent
ROOM CONFIGURATION The following figure shows an overhead view of the recommended OR configuration for a da Vinci Inguinal Hernia Repair (Figure 1). NOTE: Configuration of the operating room suite is dependent
The Scrotum & Testes Prof. Dr. Imran Qureshi
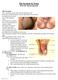 The Scrotum & Testes Prof. Dr. Imran Qureshi The Scrotum It is a cutaneous pouch of the anterior abdominal wall. Most layers of the abdominal wall are represented in its structure. It contains the testes
The Scrotum & Testes Prof. Dr. Imran Qureshi The Scrotum It is a cutaneous pouch of the anterior abdominal wall. Most layers of the abdominal wall are represented in its structure. It contains the testes
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 9; Lecture 2; Wednesday Stuart Sumida. Development and Structure, of the Reproductive System
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 9; Lecture 2; Wednesday Stuart Sumida Development and Structure, of the Reproductive System Don t forget the relationships of the structures of the layers
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 9; Lecture 2; Wednesday Stuart Sumida Development and Structure, of the Reproductive System Don t forget the relationships of the structures of the layers
Scrotum Kacey Morrison Amanda Baxter Sabrina Tucker July 18, 2006 SCROTUM
 Scrotum Kacey Morrison Amanda Baxter Sabrina Tucker July 18, 2006 SCROTUM 1) Other Names: Scrotum None Testicles Testes (Curry Tempkin, p. 236, 2/3/2) Ductus deferens spermatic cord (Tempkin, p. 279, Anatomy
Scrotum Kacey Morrison Amanda Baxter Sabrina Tucker July 18, 2006 SCROTUM 1) Other Names: Scrotum None Testicles Testes (Curry Tempkin, p. 236, 2/3/2) Ductus deferens spermatic cord (Tempkin, p. 279, Anatomy
Abdomen: Introduction. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 Abdomen: Introduction Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Abdominopelvic Cavity Abdominal Cavity Pelvic Cavity Extends from the inferior margin of the thorax to the superior margin of the pelvis and the
Abdomen: Introduction Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Abdominopelvic Cavity Abdominal Cavity Pelvic Cavity Extends from the inferior margin of the thorax to the superior margin of the pelvis and the
Academic Script Surgical Techniques Like Ovariectomy, Orchidectomy, Adrenalectomy, Etc
 Academic Script Surgical Techniques Like Ovariectomy, Orchidectomy, Adrenalectomy, Etc Aim: To Study the Surgical Techniques like Ovariectomy, Orchidectomy, Adrenalectomy, Tubectomy and Vasectomy in Rodents
Academic Script Surgical Techniques Like Ovariectomy, Orchidectomy, Adrenalectomy, Etc Aim: To Study the Surgical Techniques like Ovariectomy, Orchidectomy, Adrenalectomy, Tubectomy and Vasectomy in Rodents
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 17, 2014
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 17, 2014 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 17, 2014 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman
 Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Undescended Testicle
 What is the normal descending testis? The testicle begins to form just before the second fetal month and starts to look like a testicle around the fourth fetal month. By then it has migrated down from
What is the normal descending testis? The testicle begins to form just before the second fetal month and starts to look like a testicle around the fourth fetal month. By then it has migrated down from
Robot Assisted Rectopexy
 1. Abdominal cavity approach 1A Trocars Introduce Introduce five trocars to gain access to the abdominal cavity (in da Vinci Si type; In Xi type the trocar placement may differ slightly). First the camera
1. Abdominal cavity approach 1A Trocars Introduce Introduce five trocars to gain access to the abdominal cavity (in da Vinci Si type; In Xi type the trocar placement may differ slightly). First the camera
Transfemoral Amputation
 Transfemoral Amputation Preop This 26 year old male sustained a gunshot wound to the left thigh. He was treated emergently with revascularization and fasciotomies. He was transferred to our regional trauma
Transfemoral Amputation Preop This 26 year old male sustained a gunshot wound to the left thigh. He was treated emergently with revascularization and fasciotomies. He was transferred to our regional trauma
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen
 Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
This presentation will discuss the anatomy of the anterior abdominal wall as it pertains to gynaecological and obstetric surgery.
 This presentation will discuss the anatomy of the anterior abdominal wall as it pertains to gynaecological and obstetric surgery. 1 The border of the anterior abdominal wall is defined superiorly by the
This presentation will discuss the anatomy of the anterior abdominal wall as it pertains to gynaecological and obstetric surgery. 1 The border of the anterior abdominal wall is defined superiorly by the
Midgut. Over its entire length the midgut is supplied by the superior mesenteric artery
 Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference
 www.ivis.org Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference Oct. 17-19, 2008 Barcelona, Spain http://www.sevc.info Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the SEVC www.ivis.org
www.ivis.org Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference Oct. 17-19, 2008 Barcelona, Spain http://www.sevc.info Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the SEVC www.ivis.org
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 16, 2015
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
Internal abdominal wall and inguinal region. Mathew Wedel, 2015
 Internal abdominal wall and inguinal region Mathew Wedel, 2015 gut tube umbilicus gut tube dorsal mesentery visceral peritoneum gut tube FOREGUT dorsal mesentery parietal peritoneum MIDGUT & HINDGUT gut
Internal abdominal wall and inguinal region Mathew Wedel, 2015 gut tube umbilicus gut tube dorsal mesentery visceral peritoneum gut tube FOREGUT dorsal mesentery parietal peritoneum MIDGUT & HINDGUT gut
Forelimb Amputation. Indications. Pre operatively 11/12/2008. Technique Preparing for surgery. Bone neoplasia. Severe trauma/paralysis
 Forelimb Amputation January 10, 2007 Amy Bringardner Becky Pentecost Indications Bone neoplasia Osteosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Chondrosarcoma Severe trauma/paralysis Brachial plexus avulsion Infection Congenital
Forelimb Amputation January 10, 2007 Amy Bringardner Becky Pentecost Indications Bone neoplasia Osteosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Chondrosarcoma Severe trauma/paralysis Brachial plexus avulsion Infection Congenital
Abdominal Hernia Omar alnoubani MD,MRCS
 Abdominal Hernia Omar alnoubani MD,MRCS Definition of hernia Anatomical landmarks Overview of types of hernia Presentation and Management of common types of hernia What is the definition of a hernia? An
Abdominal Hernia Omar alnoubani MD,MRCS Definition of hernia Anatomical landmarks Overview of types of hernia Presentation and Management of common types of hernia What is the definition of a hernia? An
THE PATIENT S GUIDE TO VARICOCELE
 The Varicocele Decision Varicoceles are a relatively common problem that can hurt a man's fertility. The good news is that this is a fairly simple problem to fix. Dr. Fisch has treated hundreds of men
The Varicocele Decision Varicoceles are a relatively common problem that can hurt a man's fertility. The good news is that this is a fairly simple problem to fix. Dr. Fisch has treated hundreds of men
The Acute Scrotum: Sonographic Findings
 The Acute Scrotum: Sonographic Findings 가천의대길병원방사선과 양달모 Gachon Medical School Introduction Many diseases presenting as acute scrotal pain DDx is important for determining the appropriate treatment US with
The Acute Scrotum: Sonographic Findings 가천의대길병원방사선과 양달모 Gachon Medical School Introduction Many diseases presenting as acute scrotal pain DDx is important for determining the appropriate treatment US with
Systematic Anatomy. Shanghai Medical College,Fudan University. Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 )
 Systematic Anatomy Department of Anatomy,Histology & Embryology Shanghai Medical College,Fudan University Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@yahoo.com.cn Office: Building 9,Room308, 54237151-9308
Systematic Anatomy Department of Anatomy,Histology & Embryology Shanghai Medical College,Fudan University Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@yahoo.com.cn Office: Building 9,Room308, 54237151-9308
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
EndoBlade Soft Tissue Release System
 Surgical Technique Endoscopic Gastroc Recession Endoscopic Plantar Fascia Release EndoBlade Soft Tissue Release System Endoscopic Gastroc Recession Arthrex has developed a comprehensive, completely disposable
Surgical Technique Endoscopic Gastroc Recession Endoscopic Plantar Fascia Release EndoBlade Soft Tissue Release System Endoscopic Gastroc Recession Arthrex has developed a comprehensive, completely disposable
Placing PEG and Jejunostomy Tubes in Dogs and Cats
 Placing PEG and Jejunostomy Tubes in Dogs and Cats I. Gastrostomy tube A. Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) tube placement Supplies for PEG tube placement: Supplies and equipment for general anesthesia
Placing PEG and Jejunostomy Tubes in Dogs and Cats I. Gastrostomy tube A. Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) tube placement Supplies for PEG tube placement: Supplies and equipment for general anesthesia
Yes, cranially with ovarian, caudally with vaginal. Yes, with uterine artery (collateral circulation between abdominal +pelvic source)
 Blood supply to internal female genitalia: uterine Internal iliac Sup. large branch: uterus, inf. Small branch: cervix+ sup. Vagina Yes, cranially with ovarian, caudally with vaginal Medially in base of
Blood supply to internal female genitalia: uterine Internal iliac Sup. large branch: uterus, inf. Small branch: cervix+ sup. Vagina Yes, cranially with ovarian, caudally with vaginal Medially in base of
2. List the 8 pelvic spaces: list one procedure or dissection which involves entering that space.
 Name: Anatomy Quiz: Pre / Post 1. In making a pfannensteil incision you would traverse through the following layers: a) Skin, Camper s fascia, Scarpa s fascia, external oblique aponeurosis, internal oblique
Name: Anatomy Quiz: Pre / Post 1. In making a pfannensteil incision you would traverse through the following layers: a) Skin, Camper s fascia, Scarpa s fascia, external oblique aponeurosis, internal oblique
Transfemoral Amputation
 Transfemoral Amputation Pre-Op: 42 year old male who sustained severe injuries in a motorcycle accident. Note: he is a previous renal transplant recipient and is on immunosuppressive treatments. His injuries
Transfemoral Amputation Pre-Op: 42 year old male who sustained severe injuries in a motorcycle accident. Note: he is a previous renal transplant recipient and is on immunosuppressive treatments. His injuries
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 1 done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 1 done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer What is the importance of plexuses? plexuses provides us the advantage of a phenomenon called convergence
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 1 done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer What is the importance of plexuses? plexuses provides us the advantage of a phenomenon called convergence
Inguinal Hernia and Hydrocele
 CHAPTER Inguinal Hernia and Hydrocele Juda Z. Jona Incidence Hernias and hydroceles are among the most common pediatric surgical problems. The incidence of indirect inguinal hernia in the term neonate
CHAPTER Inguinal Hernia and Hydrocele Juda Z. Jona Incidence Hernias and hydroceles are among the most common pediatric surgical problems. The incidence of indirect inguinal hernia in the term neonate
UCSF Pediatric Urology Child and Family Information Material
 UCSF Pediatric Urology Child and Family Information Material ------------------------------------------------------------------------ The Undescended Testicle What is an Undescended Testicle? The undescended
UCSF Pediatric Urology Child and Family Information Material ------------------------------------------------------------------------ The Undescended Testicle What is an Undescended Testicle? The undescended
SURGICAL FIELD WORK WITH R-VETS
 REQUIRED PREPARATION SURGICAL FIELD WORK WITH R-VETS We expect all participants of the clinic to have prepared. This includes; 1. Read the chapter on equine castration in Turner and McIlwraith Techniques
REQUIRED PREPARATION SURGICAL FIELD WORK WITH R-VETS We expect all participants of the clinic to have prepared. This includes; 1. Read the chapter on equine castration in Turner and McIlwraith Techniques
Borders of the Abdomen
 Abdominal wall Borders of the Abdomen Abdomen is the region of the trunk that lies between the diaphragm above and the inlet of the pelvis below Borders Superior: Costal cartilages 7-12. Xiphoid process:
Abdominal wall Borders of the Abdomen Abdomen is the region of the trunk that lies between the diaphragm above and the inlet of the pelvis below Borders Superior: Costal cartilages 7-12. Xiphoid process:
Anatomy of the Body for Piercers
 Nipples are devoid of Raised structures on the areolae are Montgomery glands or tubercles, or areolar glands Normal variation Provide lubrication during breastfeeding Best to avoid piercing them Hair follicles
Nipples are devoid of Raised structures on the areolae are Montgomery glands or tubercles, or areolar glands Normal variation Provide lubrication during breastfeeding Best to avoid piercing them Hair follicles
Cover Page. The following handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation:
 Cover Page The following handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation: http://hdl.handle.net/1887/6119 Author: Spruit, E.N. Title: Increasing the efficiency of laparoscopic surgical
Cover Page The following handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation: http://hdl.handle.net/1887/6119 Author: Spruit, E.N. Title: Increasing the efficiency of laparoscopic surgical
COMPLICATIONS OF HERNIA REPAIR
 COMPLICATIONS OF HERNIA REPAIR Stanley Rogers, MD Associate Clinical Professor of Surgery University of Califronia, San Francisco Paré was respected as a hernia specialist, and was known to have elevated
COMPLICATIONS OF HERNIA REPAIR Stanley Rogers, MD Associate Clinical Professor of Surgery University of Califronia, San Francisco Paré was respected as a hernia specialist, and was known to have elevated
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen
 Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
NBME Anatomy Review. Sylvia Nelsen, Ph.D. March 19, 2015
 NBME Anatomy Review Sylvia Nelsen, Ph.D. March 19, 2015 UPPER & LOWER LIMBS 1. What is the most likely diagnosis in this case? A. Rotator cuff tendinitis: pain w/o weakness B. Adhesive capsulitis: absolute
NBME Anatomy Review Sylvia Nelsen, Ph.D. March 19, 2015 UPPER & LOWER LIMBS 1. What is the most likely diagnosis in this case? A. Rotator cuff tendinitis: pain w/o weakness B. Adhesive capsulitis: absolute
Abdominal muscles. Subinguinal hiatus and ingiunal canal. Femoral and adductor canals. Neurovascular system of the lower limb. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D.
 Abdominal muscles. Subinguinal hiatus and ingiunal canal. Femoral and adductor canals. Neurovascular system of the lower limb. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D. External oblique muscle Origin: outer surface of the
Abdominal muscles. Subinguinal hiatus and ingiunal canal. Femoral and adductor canals. Neurovascular system of the lower limb. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D. External oblique muscle Origin: outer surface of the
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL. PHD THESIS UNDESCENDED TESTICLE IN CHILD CLINICAL AND THERAPEUTIC ASPECTS - Abstract -
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL PHD THESIS UNDESCENDED TESTICLE IN CHILD CLINICAL AND THERAPEUTIC ASPECTS - Abstract - SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: Prof. Dr. Ion GEORGESCU PHD
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL PHD THESIS UNDESCENDED TESTICLE IN CHILD CLINICAL AND THERAPEUTIC ASPECTS - Abstract - SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: Prof. Dr. Ion GEORGESCU PHD
Neuticles Testicular Implantation For Pets (US Patent # )
 Natural Vs Altered An Option When Neutering Neuticles Testicular Implantation For Pets (US Patent # 58-681-40) Toll Free 888.638.8425 (816) 690-8337 (Outside US & Canada) Email: Neuticles@aol.com www.neuticles.com
Natural Vs Altered An Option When Neutering Neuticles Testicular Implantation For Pets (US Patent # 58-681-40) Toll Free 888.638.8425 (816) 690-8337 (Outside US & Canada) Email: Neuticles@aol.com www.neuticles.com
Prevention of Surgical Injuries in Gynecology
 in Gynecology John K. Chan, M.D. Division of Gynecologic Oncology Overview Review anatomy, etiology, intraoperative, postoperative management, prevention of injuries to: 1. Urinary tract 2. Gastrointestinal
in Gynecology John K. Chan, M.D. Division of Gynecologic Oncology Overview Review anatomy, etiology, intraoperative, postoperative management, prevention of injuries to: 1. Urinary tract 2. Gastrointestinal
Lecture 01 Internal surface of anterolateral abdominal wall. BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai
 Lecture 01 Internal surface of anterolateral abdominal wall BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 21.12.2017 Internal surface of the anterolateral abdominal wall The internal ( posterior ) surface of the anterolateral
Lecture 01 Internal surface of anterolateral abdominal wall BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 21.12.2017 Internal surface of the anterolateral abdominal wall The internal ( posterior ) surface of the anterolateral
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 9 Urinary Tract and Perineum Key Points 2 9.1 Urinary Bladder & Urinary Retention Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 9 Urinary Tract and Perineum Key Points 2 9.1 Urinary Bladder & Urinary Retention Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
The Anterolateral Abdominal Wall By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 1 P age The Anterolateral Abdominal Wall By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Introduction The abdomen is the region of the trunk located between the thorax and the pelvis. It includes the anterolateral
1 P age The Anterolateral Abdominal Wall By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Introduction The abdomen is the region of the trunk located between the thorax and the pelvis. It includes the anterolateral
Ultrapro Hernia System Bi Layer Dr Cosmas Gora T SpB-KBD. dffdfdfxxgfxgfxgffxgxgxg
 Bi Layer Dr Cosmas Gora T SpB-KBD dffdfdfxxgfxgfxgffxgxgxg Why UHS? Lightweight Mesh Covering entire myopectineal orifices with underlay mesh in preperitoneal space (posterior repair) Covering the inguinal
Bi Layer Dr Cosmas Gora T SpB-KBD dffdfdfxxgfxgfxgffxgxgxg Why UHS? Lightweight Mesh Covering entire myopectineal orifices with underlay mesh in preperitoneal space (posterior repair) Covering the inguinal
Scrotal pain and Swelling
 Scrotal pain and Swelling Color index : Important Further explanation Done By: Nada Alamri Editing link Acute Scrotal Pain DDx: 1) Testicular torsion : Twisting and strangulation of the testicle on the
Scrotal pain and Swelling Color index : Important Further explanation Done By: Nada Alamri Editing link Acute Scrotal Pain DDx: 1) Testicular torsion : Twisting and strangulation of the testicle on the
Modified Radical Mastectomy
 Modified Radical Mastectomy Valerie L. Staradub, MD, and Monica Morrow, MD S urgical management options for breast cancer include modified radical mastectomy (MRM), MRM with immediate reconstruction, and
Modified Radical Mastectomy Valerie L. Staradub, MD, and Monica Morrow, MD S urgical management options for breast cancer include modified radical mastectomy (MRM), MRM with immediate reconstruction, and
Laparoscopic total mesorectal excision (TME) with electric hook for rectal cancer
 Technical Note Page 1 of 8 Laparoscopic total mesorectal excision (TME) with electric hook for rectal cancer Gong Chen, Rong-Xin Zhang, Zhi-Tao Xiao Department of Colorectal Surgery, Sun Yat-sen University
Technical Note Page 1 of 8 Laparoscopic total mesorectal excision (TME) with electric hook for rectal cancer Gong Chen, Rong-Xin Zhang, Zhi-Tao Xiao Department of Colorectal Surgery, Sun Yat-sen University
Lecture Contents. Hernia
 Lecture Contents Definitions Managment of Hernia Composition of Hernia Hernia Etiology Signs and Symptoms Types Classification of Abdominal Hernia External Internal Common - inguinal - Femoral - Umbilical
Lecture Contents Definitions Managment of Hernia Composition of Hernia Hernia Etiology Signs and Symptoms Types Classification of Abdominal Hernia External Internal Common - inguinal - Femoral - Umbilical
Appendectomy. Speaker:Barysheva V.O.,401 gr Leader:Peshikov O.V.
 Appendectomy Speaker:Barysheva V.O.,401 gr Leader:Peshikov O.V. Appendectomy Indications for operation : Acute appendicitis Chronic appendicitis Tumors of appendix Appendicitis Inflammation of appendix
Appendectomy Speaker:Barysheva V.O.,401 gr Leader:Peshikov O.V. Appendectomy Indications for operation : Acute appendicitis Chronic appendicitis Tumors of appendix Appendicitis Inflammation of appendix
Review Article The Onstep Method for Inguinal Hernia Repair: Operative Technique and Technical Tips
 Surgery Research and Practice Volume 2016, Article ID 6935167, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6935167 Review Article The Onstep Method for Inguinal Hernia Repair: Operative Technique and Technical
Surgery Research and Practice Volume 2016, Article ID 6935167, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6935167 Review Article The Onstep Method for Inguinal Hernia Repair: Operative Technique and Technical
All Men are created. (more or less) Rod Moser, PA, PhD Sutter Roseville Pediatrics Founding President, CAPA
 Rod Moser, PA, PhD Sutter Roseville Pediatrics Founding President, CAPA Balls Stones Family Jewels Meatballs Reece's Pieces Nuts Coconuts Weights Walnuts Gonads / Nads Dumbbells Truffles The sperm factory
Rod Moser, PA, PhD Sutter Roseville Pediatrics Founding President, CAPA Balls Stones Family Jewels Meatballs Reece's Pieces Nuts Coconuts Weights Walnuts Gonads / Nads Dumbbells Truffles The sperm factory
Reproductive System. Where it all begins
 Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
Gross Anatomy ABDOMEN/SESSION 1 Dr. Firas M. Ghazi
 Anterior Abdominal Wall Structure, muscles and surface anatomy Curricular Objectives By the end of this session students are expected to: Practical 1. Identify the hip and distinguish the three bones forming
Anterior Abdominal Wall Structure, muscles and surface anatomy Curricular Objectives By the end of this session students are expected to: Practical 1. Identify the hip and distinguish the three bones forming
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman
 The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Professor of Anatomy &embryology Male genital system Learning Objectives 1. Identify External
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Professor of Anatomy &embryology Male genital system Learning Objectives 1. Identify External
Rama Nada. - Ensherah Mokheemer. - Ahmed salman. 1 P a g e
 - 5 - Rama Nada - Ensherah Mokheemer - Ahmed salman 1 P a g e We will continue talking about the urinary bladder The ligaments of the bladder: 1-Median umbilical ligament: Continuous with apex of the bladder
- 5 - Rama Nada - Ensherah Mokheemer - Ahmed salman 1 P a g e We will continue talking about the urinary bladder The ligaments of the bladder: 1-Median umbilical ligament: Continuous with apex of the bladder
University Park, Pennsylvania 16802, U.S.A
 A MODIFIED TECHNIQUE FOR CANNULATING THE RETE TESTIS OF THE BULL J. K. VOGLMAYR, J. F. KAVANAUGH, L. C. GRIEL, Jr and R. P. AMANN Dairy Breeding Research Center, Department of Dairy Science, and Department
A MODIFIED TECHNIQUE FOR CANNULATING THE RETE TESTIS OF THE BULL J. K. VOGLMAYR, J. F. KAVANAUGH, L. C. GRIEL, Jr and R. P. AMANN Dairy Breeding Research Center, Department of Dairy Science, and Department
THE INS AND OUTS OF HERNIAS WHERE TO START? WHAT IS A HERNIA? CLINICAL INDICATIONS THE INGUINAL CANAL THE CLINICAL QUESTION 18/09/2018
 THE INS AND OUTS OF HERNIAS Cassandra Harrison BA/BSc, MMRU, AMS WHERE TO START? The Clinical Question Essential anatomy Inguinal hernia Scanning technique Variations WHAT IS A HERNIA? CLINICAL INDICATIONS
THE INS AND OUTS OF HERNIAS Cassandra Harrison BA/BSc, MMRU, AMS WHERE TO START? The Clinical Question Essential anatomy Inguinal hernia Scanning technique Variations WHAT IS A HERNIA? CLINICAL INDICATIONS
SOP: Urinary Catheter in Dogs and Cats
 SOP: Urinary Catheter in Dogs and Cats These SOPs were developed by the Office of the University Veterinarian and reviewed by Virginia Tech IACUC to provide a reference and guidance to investigators during
SOP: Urinary Catheter in Dogs and Cats These SOPs were developed by the Office of the University Veterinarian and reviewed by Virginia Tech IACUC to provide a reference and guidance to investigators during
THE TRANSPLANTATION OF THE RECTUS MUSCLE OR ITS
 THE TRANSPLANTATION OF THE RECTUS MUSCLE OR ITS SHEATH FOR THE CURE OF INGUINAL HERNIA WHEN THE CONJOINED TENDON IS OBLITERATED. THE TRANS- PLANTATION OF THE SARTORIUS MUSCLE FOR THE CURE OF RECURRENT
THE TRANSPLANTATION OF THE RECTUS MUSCLE OR ITS SHEATH FOR THE CURE OF INGUINAL HERNIA WHEN THE CONJOINED TENDON IS OBLITERATED. THE TRANS- PLANTATION OF THE SARTORIUS MUSCLE FOR THE CURE OF RECURRENT
10. Development of genital system. Gonads. Genital ducts. External genitalia.
 10. Development of genital system. Gonads. Genital ducts. External genitalia. Gonads, genital ducts and the external genital organs initially pass through an indifferent period of development, which is
10. Development of genital system. Gonads. Genital ducts. External genitalia. Gonads, genital ducts and the external genital organs initially pass through an indifferent period of development, which is
What are Varicoceles?
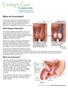 What are Varicoceles? A varicocele is when veins become enlarged inside your scrotum (the pouch of skin that holds your testicles). These veins are called the pampiniform plexus. Ten to 15 of every 100
What are Varicoceles? A varicocele is when veins become enlarged inside your scrotum (the pouch of skin that holds your testicles). These veins are called the pampiniform plexus. Ten to 15 of every 100
Vikram Dogra, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Urology & BME Department of Imaging Sciences University Of Rochester Medical Center
 Ultrasound of the Scrotum Vikram Dogra, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Urology & BME Department of Imaging Sciences University Of Rochester Medical Center Etiologies of Acute Scrotal Pain Epididymitis/Orchitis
Ultrasound of the Scrotum Vikram Dogra, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Urology & BME Department of Imaging Sciences University Of Rochester Medical Center Etiologies of Acute Scrotal Pain Epididymitis/Orchitis
Fascial Turn-Down Flap Repair of Chronic Achilles Tendon Rupture
 19 Fascial Turn-Down Flap Repair of Chronic Achilles Tendon Rupture S. Ghosh, P. Laing, and Nicola Maffulli Introduction Fascial turn-down flaps can be used for an anatomic repair of chronic Achilles tendon
19 Fascial Turn-Down Flap Repair of Chronic Achilles Tendon Rupture S. Ghosh, P. Laing, and Nicola Maffulli Introduction Fascial turn-down flaps can be used for an anatomic repair of chronic Achilles tendon
Chapter 8: The abdomen and perineum
 Chapter 8: The abdomen and perineum The abdomen is that part of the trunk between the diaphragm and pelvis. For descriptive purposes the anterior abdominal wall is divided into nine regions by two horizontal
Chapter 8: The abdomen and perineum The abdomen is that part of the trunk between the diaphragm and pelvis. For descriptive purposes the anterior abdominal wall is divided into nine regions by two horizontal
Inguinal Hernia. Dr. Budi Irwan, SpB-KBD. Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine University of North Sumatera Adam Malik National Hospital
 Inguinal Hernia Dr. Budi Irwan, SpB-KBD Division of Digestive Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine University of North Sumatera Adam Malik National Hospital Definition Abnormal protrusion
Inguinal Hernia Dr. Budi Irwan, SpB-KBD Division of Digestive Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine University of North Sumatera Adam Malik National Hospital Definition Abnormal protrusion
Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries. Accessory reproductive organs: ducts, glands, and external genitalia
 Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Table of Contents: CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Knife Assembly... Page 6 VERSION 2.2
 www.s2ssurgical.com Table of Contents: Preparation... Page 1 Dissection... Page 2 Tunneling... Page 3 Release... Page 4 Closure... Page 6 Knife Assembly... Page 6 CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
www.s2ssurgical.com Table of Contents: Preparation... Page 1 Dissection... Page 2 Tunneling... Page 3 Release... Page 4 Closure... Page 6 Knife Assembly... Page 6 CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
THE HUMERUS 20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW
 20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW The marrow canal of the humerus is funnel-shaped. Its successful pinning is influenced by many factors. With a few exceptions, the entire humerus
20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW The marrow canal of the humerus is funnel-shaped. Its successful pinning is influenced by many factors. With a few exceptions, the entire humerus
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception
 PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
