Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Introduction A. Preparing the Fetal Pig Anterior Posterior Dorsal Ventral length gender mammary papillae
|
|
|
- Julie Leonard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
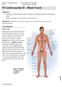
1 Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Preserved Fetal Pig Cotton String Dissection tray Dissection pins Disposable Gloves Paper towels Dissection scissors Label pins Lab apron Re-sealable bag Dissection probe Metric Ruler Introduction Mammals are warm-blooded vertebrates that feed their young milk from mammary glands and have hair or fur on their bodies. The largest single group of mammals is the placental mammals. Placental mammals develop inside their mother, where they are connected to her by a placenta, a large organ filled with blood vessels. These blood vessels allow the mother s blood to supply the fetus with nutrients and oxygen while removing wastes and carbon dioxide. Humans are placental mammals and so are most domesticated animals; such as dogs, cats, horses and cows. The fetal pig is an excellent organism to study because it is relatively small, easy to acquire, and exhibits all mammalian characteristics as well as special fetal structures. A. Preparing the Fetal Pig 1. Obtain disposable gloves, lab apron, dissecting tray and dissecting equipment, and a fetal pig. 2. With safety glasses and gloves on, remove the pig from the pail and lay on a dissecting tray. 3. Review the directional terms for the pig in Figure 1. Note the differences between fourlegged animals and humans. Anterior is toward the head end of the pig. Posterior is toward the tail end of the pig. Dorsal is toward the back surface. Ventral is toward the belly surface. 4. Place your pig ventral surface up on the dissecting tray. 5. Measure the length of your fetal pig (from snout to rump) in cm. 6. Determine the gender of your pig. Males have a urogenital opening (opening for the penis) that is posterior to the umbilical cord. The scrotum (small bulges) is anterior to the anus. Females also have a urogenital opening located anterior to the anus. The opening is enclosed by small folds called labia that form a projection called the genital papilla. 7. Locate the mammary papillae. These are nipples on the abdomen. They are present in both male and female pigs. 8. Label the re-sealable bag with the names of your group members and the gender of your pig. FIGURE 1 Directional Terminology for the Fetal Pig Dorsal Posterior Anterior Ventral
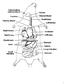
2 B. Preparing for dissection 1. You will be dissecting and observing the internal organ systems by system. Do not remove any organ before you are directed to do so. Take care not to damage any structures when locating and dissecting other structures. Also, remember that no system functions alone. Be aware of how each system relates to others. 2. Secure the pig for dissection using two pieces of cotton string. Tie one piece of string securely around one wrist of your pig. Take the string under the dissecting pan and tie it to the other wrist. Repeat this procedure with the ankles. Tighten the strings to keep the legs apart. 3. Study the diagrams carefully to help you locate all the structures printed in italics. Throughout this investigation italic type will indicate major structures that need to be located and labeled on your diagram and inside the pig. 4. Begin the dissection of the abdominal cavity by making cuts with your scalpel as shown in Figure 2. Cut through the skin and muscle tissue, but be aware of the depth of your scalpel, so as not to injure the underlying organs. Use scissors to cut through the thoracic cavity, gently cut through the bones of the rib cage so as not to damage the heart and lungs. 5. After making these cuts, pin back the flaps of skin and tissue to expose the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 6. Follow the large vein at the base of the umbilical cord. Cut the vein so that the flap of skin with the umbilical cord can be turned back. 7. After each structure has been located and observed, label it in the diagram and use the indicated number to label it inside your pig. FIGURE 2 Directions for making incisions FIGURE 3 Endocrine Organs
3 C. The Endocrine System 1. There are two main endocrine organs in the thoracic cavity, the thyroid gland and the thymus. The thyroid gland is an oval gland lying over the trachea posterior to the larynx. The thymus is a glandular looking with small lobules and is posterior to the larynx on top of the thyroid gland on the trachea, and extending to partially cover the heart. Because the pig is fetal, the thymus gland will be quite large with two definite lobes. 2. There are three main endocrine organs in the abdominal cavity: the pancreas, adrenal glands, and female gonads. Locate the diaphragm that separates the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities. Reflect the stomach and look beneath it for the glandular-looking pancreas. It is located close to the curve in the first part of the small intestine and extends to the left toward the spleen. Label the pancreas when labeling the digestive organs. 3. The bean-shaped adrenal glands are located near the anterior part of the kidneys. Both the kidneys and adrenal glands are located behind the peritoneum. Label the adrenal glands when labeling the kidney 4. Have the instructor check the labeling of the thyroid gland and the thymus. D. The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems 1. Beginning at the top of the stomach, trace the esophagus as it passes through the diaphragm and under the heart. At the anterior end of the esophagus on the ventral side is the trachea. Notice the rings of cartilage that surround the trachea. These rings give the trachea the appearance of a vacuum cleaner hose. Trace the trachea to the point at which it branches to each lung. 2. Continue the dissection of the neck anteriorly to find an enlarged area of cartilage. This is the larynx, often called the voice box. At the beginning of the trachea is the epiglottis, which is a flap that covers the respiratory tract during ingestion. FIGURE 5 Circulatory and Respiratory Organs FIGURE 6 The Heart
4 3. Using Diagrams 5 and 6, locate and label the lungs and the heart, which is enclosed in the pericardium. 4. Have the instructor check the labeling of the respiratory organs and the heart. 5. Remove the pericardium from the heart. Using Figure 6, locate the following structures on the ventral side of the heart; right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle, coronary artery. 6. Turn the heart onto the dorsal side without removing it. Locate the two major veins that bring blood back to the heart; the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava. Locate the right and left pulmonary veins. This is the pair that brings blood back to the heart from the lungs. Both of these empty into the left atrium. 7. Carefully dissect around the heart, picking away the connective tissue between the blood vessels. Locate the pulmonary artery, on the ventral side of the heart, as it leaves the right atrium. The aorta, the largest and most important artery, can be found just beneath the pulmonary artery as it leaves the left ventricle. E. Digestive System 1. Find the large, three-lobed liver at the anterior end of the abdominal cavity. Under the liver is the stomach, a large pouch-like organ with two parts. The large, anterior end is the cardiac stomach and the smaller end is the pyloric stomach. The part where the stomach and the small intestine meet is called the pyloric sphincter. 2. Posterior to the sphincter is the small intestine. Follow it to where it enlarges to become the large intestine or colon. The difference is that the large intestine is slightly larger in diameter and has a small, blind pouch called the caecum. The caecum ends in the appendix in humans and in the pig. FIGURE 4 Digestive Organs 3. Closely observe the membranous, net-like tissue that can be found over the intestines. This is the messentery. The large intestine continues and enlarges, forming the rectum. The point at which the rectum opens to the outside of the body is the anus. Relocate the liver. Lift it up and trace the stomach anteriorly to the esophagus. 4. Observe the dome-shaped muscular wall at the most anterior end of the abdominal cavity just above the liver. This is the diaphragm. 5. Embeddded in the underside of the right central lobe of the liver is the greenish gall bladder. Locate it and then find and trace the bile duct, a small tube-like structures that is attached to the gall bladder. Directly below the gall bladder, on the underside of the stomach you will find a granular-looking organ, the pancreas. Both the gall bladder and pancreas release enzymes through a duct into the small intestine to aid in digestion. Attached to the left edge of the stomach is a reddish smooth organ, this is the spleen.
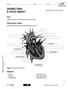
5 6. Have the instructor check the labeling of the digestive organs. 7. Carefully remove the organs of the digestive cavity and measure the entire length of the digestive tract. F. The Urogenital System 1. Since the organs of the digestive system have been removed, the organs of the excretory and reproductive systems will now be exposed. The kidneys are the pair of dark, bean-shaped organs lying on the dorsal wall, behind the peritoneum. The kidneys are supplied with blood by the renal arteries. The renal veins take blood away from the kidneys. They are located just below the renal arteries. Remove these blood vessels very carefully. 2. Coming from the posterior end of the kidney is the ureter. This is the tube that drains urine from the kidney into the urinary bladder for storage. Trace the ureter to the bladder. Cut through the cartilage of the pelvic girdle with scissors. Spread the legs and pelvic girdle as far apart as possible. Locate the urethra, which comes from the urinary bladder to the urogenital opening, through which urine is eliminated from the body. 3. The female gonads, the ovaries and are small, oval organs located posterior to the kidneys. 4. The male gonads, the testes, are located outside of the abdominopelvic cavity in the scrotum. Because these pigs are fetal, the scrotum and testes have not descended much and are merely small bulges. Open the scrotum to view the testes. 5. Have the instructor check the labeling of the urogenital organs. FIGURE 7 Male Urogenital Organs FIGURE 8 Female Urogenital Organs G. Post Dissection 1. Make sure that the instructor has checked all the labeled organs of your pig and that you have correctly labeled all the diagrams.
6 2. Remove all the pins and place the fetal pig, the cotton string and all portions removed into the re-sealable bag. 3. Place the re-sealable bag in the container indicated by the instructor. 4. Thoroughly wash and dry all dissection equipment. 5. Clean your table with disinfectant and wash your hands thoroughly before leaving the lab Student Student Fetal Pig Dissection 1. The fetal pig assigned to you measures cm ( mm) in length. 2. What is the sex of your dissection pig? 3. How many papillae are there on your pig? 4. What is the function of the papillae? 5. To where does the large vein at the base of the umbilical cord go? 6. What is the function of the thyroid gland? 7. What is the function of the cartilage rings in the trachea? 8. What could happen if the epiglottis failed to cover the respiratory tract during ingestion? 9. To what system does the diaphragm belong? 10. What are the four chambers of the heart? 11. What is the function of the coronary artery? 12. What structure connects the stomach to the mouth? 13. What is the function of the stomach? 14. To what other system, besides the digestive system, does the pancreas belong? 15. What is the function of the mesentery? 16. At what structure does the digestive tract open to the outside? 17. The digestive tract of the fetal pig assigned to you measures cm ( m) in length. 18. What are the functions of the kidneys? 19. What is the function of the urinary bladder? 20. What is the function of the testes /ovaries? Place the numbered pins according to the body parts below. Shaded Boxes for Teacher Use Only # Body Parts Labeled Correctly Pts. Possible Pts. Earned 1 Thymus 4 2 Thyroid 4 3 Heart 4 4 Lung 4 5 Larynx 4 6 Diaphragm 4 7 Liver 4 8 Gall Bladder 4 9 Stomach 4 10 Spleen 4 11 Pancreas 4
7 12 Small Intestine 4 13 Large Intestine 4 14 Kidney 4 15 Adrenal glands 4 16 Urinary Bladder 4 17 Urethra Male Testes / Female Ovaries 4 Label the diagrams below Internal Organs The Heart L 16 1 A K 15 2 B J C I 14 3 D H E A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. G F
8
7 weeks: 28 mm 8 weeks: 40 mm 15 weeks: 220 mm 17 weeks: 300 mm
 Fetal Pig Dissection Background Pigs are placental mammals and show the distinguishing characteristics of that group. In studying the anatomy of the fetal, or unborn, pig, you will see that its various
Fetal Pig Dissection Background Pigs are placental mammals and show the distinguishing characteristics of that group. In studying the anatomy of the fetal, or unborn, pig, you will see that its various
Name: Fetal Pig Dissection Internal Anatomy
 In this lab exercise you will open the thoracic cavities and abdominal pelvic of a fetal pig and identify its major organs. Remember you are dissecting not butchering. The goal is for you to identify all
In this lab exercise you will open the thoracic cavities and abdominal pelvic of a fetal pig and identify its major organs. Remember you are dissecting not butchering. The goal is for you to identify all
OVARIES URETER FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS
 URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
Fetal Pig Dissection. preserved fetal pig dissecting tray and paper towels length of string plastic storage bag and twist tie
 Name Date Class LAB PROGRAM INQUIRY SKILLS B29 Fetal Pig Dissection Skills Objectives using dissection instruments and techniques Describe the appearance of various organs found in a fetal pig. Name the
Name Date Class LAB PROGRAM INQUIRY SKILLS B29 Fetal Pig Dissection Skills Objectives using dissection instruments and techniques Describe the appearance of various organs found in a fetal pig. Name the
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content
 Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Fetal Pig Dissection Day 2 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 Name: Date: Period: Fetal Pig Dissection Day 2 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Dissection Roles (choose a different role from Day 1): Recorder reads directions out loud to group and records answers
Name: Date: Period: Fetal Pig Dissection Day 2 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Dissection Roles (choose a different role from Day 1): Recorder reads directions out loud to group and records answers
Fetal Pig Dissection: External Anatomy
 Name Fetal Pig Dissection: External Anatomy External Anatomy 1. Determine the sex of your pig by looking for the urogenital opening. On females, this opening is located near the anus. On males, the opening
Name Fetal Pig Dissection: External Anatomy External Anatomy 1. Determine the sex of your pig by looking for the urogenital opening. On females, this opening is located near the anus. On males, the opening
Mammalian Dissection: Fetal Pig 11/06
 Mammalian Dissection: Fetal Pig 11/06 Integrated Science 4 Name Per. Introduction Organisms are classified based on similarities and differences to: 1) make sense of the millions of organisms on record,
Mammalian Dissection: Fetal Pig 11/06 Integrated Science 4 Name Per. Introduction Organisms are classified based on similarities and differences to: 1) make sense of the millions of organisms on record,
Fetal Pig Dissection:
 Fetal Pig Dissection: REMEMBER: Dissection involves disassembling and observing something to determine its internal structure and develop an understanding of the relationship of those structures to function.
Fetal Pig Dissection: REMEMBER: Dissection involves disassembling and observing something to determine its internal structure and develop an understanding of the relationship of those structures to function.
BIOLOGY 30S: Fetal Pig Dissection Worksheet
 BIOLOGY 30S: Fetal Pig Dissection Worksheet Name: Part A: External Anatomy & Oral Cavity 1. How long (metric) is your fetal pig? 2. What is the age of your fetal pig? 3. What sense organs are located on
BIOLOGY 30S: Fetal Pig Dissection Worksheet Name: Part A: External Anatomy & Oral Cavity 1. How long (metric) is your fetal pig? 2. What is the age of your fetal pig? 3. What sense organs are located on
Fetal Pig Dissection Packet
 Fetal Pig Dissection Packet Name Period * Each person will turn in his/her own packet You may use the Virtual Fetal Pig Dissection website from Whitman College as a visual reference for all stages of dissection.
Fetal Pig Dissection Packet Name Period * Each person will turn in his/her own packet You may use the Virtual Fetal Pig Dissection website from Whitman College as a visual reference for all stages of dissection.
#8 - Ventral Body Cavity Organs
 #8 - Objectives: Use a cat dissection to study the organs of the ventral body cavity; Use virtual human dissection software and a human model to observe the organs of the Respiratory, Digestive, Urinary,
#8 - Objectives: Use a cat dissection to study the organs of the ventral body cavity; Use virtual human dissection software and a human model to observe the organs of the Respiratory, Digestive, Urinary,
Fetal Pig Dissection Packet (2019)
 Name Period [Each person will turn in his/her own packet] [ Final Score out of 166 points: ] You may use the Virtual Fetal Pig Dissection website from Whitman College as a visual reference for all stages
Name Period [Each person will turn in his/her own packet] [ Final Score out of 166 points: ] You may use the Virtual Fetal Pig Dissection website from Whitman College as a visual reference for all stages
Mammalian Dissection: Fetal Pig Integrated Science 4 Honors
 Mammalian Dissection: Fetal Pig Integrated Science 4 Honors Name Per. Introduction Organisms are classified based on similarities and differences to: 1) make sense of the millions of organisms on record,
Mammalian Dissection: Fetal Pig Integrated Science 4 Honors Name Per. Introduction Organisms are classified based on similarities and differences to: 1) make sense of the millions of organisms on record,
Fetal Pig Dissection Labs Dr. J. Lim
 Fetal Pig Dissection Labs Dr. J. Lim Objective: In this exercise you will examine the organization of the many body systems studied this semester in the context of a single specimen, the fetal pig. Be
Fetal Pig Dissection Labs Dr. J. Lim Objective: In this exercise you will examine the organization of the many body systems studied this semester in the context of a single specimen, the fetal pig. Be
MATERIALS: preserved fetal pig, dissecting pan, dissecting kit, dissecting pins, string, plastic bag, metric ruler, paper towels
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 12 ROCKRIDGE Fetal Pig Dissection NAME: BLOCK: DATE: Partner: BACKGROUND: Mammals are vertebrates having hair on their body and mammary glands to nourish their young. The majority
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 12 ROCKRIDGE Fetal Pig Dissection NAME: BLOCK: DATE: Partner: BACKGROUND: Mammals are vertebrates having hair on their body and mammary glands to nourish their young. The majority
Vertebrate Anatomy Study Guide
 Vertebrate Anatomy Study Guide 1. Anatomical terms: dorsal, ventral, anterior, posterior 2. Body sections: head, neck, thorax, abdomen, tail 3. Body Cavities: oral, thoracic, abdominal, cranial 4. Know
Vertebrate Anatomy Study Guide 1. Anatomical terms: dorsal, ventral, anterior, posterior 2. Body sections: head, neck, thorax, abdomen, tail 3. Body Cavities: oral, thoracic, abdominal, cranial 4. Know
Step 1: Salivary Structures
 (Slide1) Step 1: Salivary Structures Remove the skin, fat and connective fascia to view the salivary glands and ducts. The submaxillary salivary gland is just behind the masseter muscle and pretty easy
(Slide1) Step 1: Salivary Structures Remove the skin, fat and connective fascia to view the salivary glands and ducts. The submaxillary salivary gland is just behind the masseter muscle and pretty easy
#5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels
 #5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels Objectives: Identify a list of human arteries and veins using a virtual human dissection and a human model Dissect and identify a list of arteries and veins in the cat
#5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels Objectives: Identify a list of human arteries and veins using a virtual human dissection and a human model Dissect and identify a list of arteries and veins in the cat
SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX
 SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX 9 In the pig s digestive tract, food flows in only one direction from mouth to anus.this allows for greatly specialized sections that can act independently of each other.
SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX 9 In the pig s digestive tract, food flows in only one direction from mouth to anus.this allows for greatly specialized sections that can act independently of each other.
DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
Student Guide to the Frog Dissection
 Student Guide to the Frog Dissection Dissection Instructions 1. Place the frog in the dissecting pan ventral side up. 2. Use scissors to life the abdominal muscles away from the body cavity. Cut along
Student Guide to the Frog Dissection Dissection Instructions 1. Place the frog in the dissecting pan ventral side up. 2. Use scissors to life the abdominal muscles away from the body cavity. Cut along
Dissection: The Fetal Pig
 Lab Exercise Dissection: The Fetal Pig Objectives - To learn some of anatomical structures of the fetal pig. - To be able to make contrasts and comparisons of structures between different animal phyla
Lab Exercise Dissection: The Fetal Pig Objectives - To learn some of anatomical structures of the fetal pig. - To be able to make contrasts and comparisons of structures between different animal phyla
Fetal Pigs and You BIO 171 WEEK 10
 Fetal Pigs and You BIO 171 WEEK 10 The Domestic Pig: Sus scrofa Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia - Skin covered in hair or fur; Milk-producing glands (mammary glands) in the female to
Fetal Pigs and You BIO 171 WEEK 10 The Domestic Pig: Sus scrofa Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia - Skin covered in hair or fur; Milk-producing glands (mammary glands) in the female to
Fetal Pig Dissection Guide
 Fetal Pig Dissection Guide Day 1 - External Anatomy 1. Obtain a fetal pig and rinse off the excess preservative by holding it under running water. Lay the pig on its side in the dissecting pan and locate
Fetal Pig Dissection Guide Day 1 - External Anatomy 1. Obtain a fetal pig and rinse off the excess preservative by holding it under running water. Lay the pig on its side in the dissecting pan and locate
Fetal Pig Dissection Guide
 Fetal Pig Dissection Guide Background: Mammals are vertebrates having hair on their body and mammary glands to nourish their young. The majority are placental mammals in which the developing young, or
Fetal Pig Dissection Guide Background: Mammals are vertebrates having hair on their body and mammary glands to nourish their young. The majority are placental mammals in which the developing young, or
The$Pig$ $ Dissection$Manual$ (you%only%get%one,%don t%lose%it!)%! DIGENIS!CLASSES!!2016!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Name:!!!!! Block:!!
 The$Pig$ $ Dissection$Manual$ (you%only%get%one,%don t%lose%it)% DIGENISCLASSES2016 Name: Block: Fetal Pig Lab Check off each organ/structure as you locate it on your pig. Answer questions where indicated.
The$Pig$ $ Dissection$Manual$ (you%only%get%one,%don t%lose%it)% DIGENISCLASSES2016 Name: Block: Fetal Pig Lab Check off each organ/structure as you locate it on your pig. Answer questions where indicated.
Frog Dissection. Name: Block:
 Name: Block: Frog Dissection Background: As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid and fertilized in
Name: Block: Frog Dissection Background: As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid and fertilized in
EXERCISE Organ Systems Overview
 Solutions Manual Human Anatomy & Physiology Laboratory Manual, Fetal Pig Version 12th Edition Marieb Smith Instructor guide for for Human Anatomy & Physiology Laboratory Manual, Fetal Pig Version 12th
Solutions Manual Human Anatomy & Physiology Laboratory Manual, Fetal Pig Version 12th Edition Marieb Smith Instructor guide for for Human Anatomy & Physiology Laboratory Manual, Fetal Pig Version 12th
Crayfish Dissection. Objectives: Describe the appearance of various organs found in a crayfish. Name the organs that make up systems of the crayfish.
 Crayfish Dissection Objectives: Describe the appearance of various organs found in a crayfish. Name the organs that make up systems of the crayfish. Background: Like all crustaceans, a crayfish has a fairly
Crayfish Dissection Objectives: Describe the appearance of various organs found in a crayfish. Name the organs that make up systems of the crayfish. Background: Like all crustaceans, a crayfish has a fairly
Organ Systems Overview
 Laboratory Manual for Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Marieb SOLUTIONS MANUAL Exercise 2 5 Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/laboratory-manual-for-anatomy-and-physiology-6th-edition-marieb-solutionsmanual/
Laboratory Manual for Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Marieb SOLUTIONS MANUAL Exercise 2 5 Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/laboratory-manual-for-anatomy-and-physiology-6th-edition-marieb-solutionsmanual/
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System
 Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Fetal Pig Dissection
 Fetal Pig Dissection The fetal pig is a mammal like us so it has many structures that are similar to ours. The anatomy class will analyze the structure and function of the external and internal parts of
Fetal Pig Dissection The fetal pig is a mammal like us so it has many structures that are similar to ours. The anatomy class will analyze the structure and function of the external and internal parts of
Name Date Per. HANDOUT Frog Dissection Lab
 Name Date Per UNIT 6 HANDOUT Frog Dissection Lab Purpose: To observe the anatomy of an amphibian To discover characteristics of complex vertebrates To compare anatomy of the frog to that of other organisms
Name Date Per UNIT 6 HANDOUT Frog Dissection Lab Purpose: To observe the anatomy of an amphibian To discover characteristics of complex vertebrates To compare anatomy of the frog to that of other organisms
Dissection on Demand: Fetal Pig
 TEACHER GUIDE Dissection on Demand: Fetal Pig 60-Minute Health & Life Science Lesson Interactive Video Conferencing Grades: 6-12 Dissection on Demand: Fetal Pig Description Observe the dissection of a
TEACHER GUIDE Dissection on Demand: Fetal Pig 60-Minute Health & Life Science Lesson Interactive Video Conferencing Grades: 6-12 Dissection on Demand: Fetal Pig Description Observe the dissection of a
Pig Dissection for Dummies
 Pig Dissection for Dummies External Anatomy 1. Say hello to your pig. To determine the sex of your pig so that you can give him/her an appropriate name, look for a little hole DIRECTLY posterior (toward
Pig Dissection for Dummies External Anatomy 1. Say hello to your pig. To determine the sex of your pig so that you can give him/her an appropriate name, look for a little hole DIRECTLY posterior (toward
In this lab, you will observe the external structures of a crayfish and dissect it to study its internal structures and systems.
 Crayfish Dissection Objectives: Describe the appearance of various organs found in a crayfish. Name the organs that make up systems of the crayfish. Materials: safety goggles, gloves, magnifying glass,
Crayfish Dissection Objectives: Describe the appearance of various organs found in a crayfish. Name the organs that make up systems of the crayfish. Materials: safety goggles, gloves, magnifying glass,
Carolina Biological Supply Company. Rats! Inquiry-Based Dissection with Carolina s Perfect Solution Specimens
 Carolina Biological Supply Company Rats! Inquiry-Based Dissection with Carolina s Perfect Solution Specimens Objectives Introduce basic mammalian anatomy using the rat Perform a rat dissection focusing
Carolina Biological Supply Company Rats! Inquiry-Based Dissection with Carolina s Perfect Solution Specimens Objectives Introduce basic mammalian anatomy using the rat Perform a rat dissection focusing
LAB: Sheep or Pig Heart Dissection
 Biology 12 Name: Circulatory System Per: Date: Observation: External Anatomy LAB: Sheep or Pig Heart Dissection 1. Line a dissecting tray with paper towel for easy clean up as the heart is fatty and will
Biology 12 Name: Circulatory System Per: Date: Observation: External Anatomy LAB: Sheep or Pig Heart Dissection 1. Line a dissecting tray with paper towel for easy clean up as the heart is fatty and will
Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection 1 hour; human torso model ½ hour).
 Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition Marieb SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/human-anatomy-laboratory-manual-with-catdissections-8th-edition-marieb-solutions-manual/
Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition Marieb SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/human-anatomy-laboratory-manual-with-catdissections-8th-edition-marieb-solutions-manual/
#5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels
 Page1 #5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels Objectives: Observe slide of artery and vein cross-section Identify a list of human arteries and veins using a virtual human dissection Dissect and identify a list
Page1 #5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels Objectives: Observe slide of artery and vein cross-section Identify a list of human arteries and veins using a virtual human dissection Dissect and identify a list
Crayfish Observation and Dissection
 Name Period Date Crayfish Observation and Dissection Purpose: In this lab, you will observe the external structures of a crayfish and dissect it to study its internal structures and systems. Materials:
Name Period Date Crayfish Observation and Dissection Purpose: In this lab, you will observe the external structures of a crayfish and dissect it to study its internal structures and systems. Materials:
FROG DISSECTION GUIDE
 FROG DISSECTION GUIDE I. Introduction Frogs belong to the class amphibian. Although many differences exist between humans and frogs, the basic body plans are similar. Humans and frogs both belong to the
FROG DISSECTION GUIDE I. Introduction Frogs belong to the class amphibian. Although many differences exist between humans and frogs, the basic body plans are similar. Humans and frogs both belong to the
Name Partner(s) Name. Name your rat. Rat Dissection Lab
 Name Partner(s) Name Name your rat Rat Dissection Lab!!CAUTION!! You must follow all safety instructions as outlined in this lab manual and by your teacher. There are several sharp objects being used during
Name Partner(s) Name Name your rat Rat Dissection Lab!!CAUTION!! You must follow all safety instructions as outlined in this lab manual and by your teacher. There are several sharp objects being used during
PIG DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ~Date PIG DIGESTIVE SYSTEM It is not easy to study the digestive organs of a human. However, anatomy of the human digestive system can be studied by examining the digestive system of a pig, an animal similar
~Date PIG DIGESTIVE SYSTEM It is not easy to study the digestive organs of a human. However, anatomy of the human digestive system can be studied by examining the digestive system of a pig, an animal similar
Biology Overview Dissection Assignment
 Biology Overview Dissection Assignment What is this assignment about? After learning several major systems of the human body, this overview dissection assignment is for you to review all of those major
Biology Overview Dissection Assignment What is this assignment about? After learning several major systems of the human body, this overview dissection assignment is for you to review all of those major
NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE. X Biology II
 Unit 2-5, Animal Biology & Organ Systems, FETAL PIG DISSECTION MANUAL X Biology II, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE X Biology II
Unit 2-5, Animal Biology & Organ Systems, FETAL PIG DISSECTION MANUAL X Biology II, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE X Biology II
d) the pulmonary vein b) the superior vena cava e) the inferior vena cava c) the pulmonary artery The large vessels of a sheep s heart
 CHAPTER 8 Investigation 8.A: Identifying Structures of the Circulatory System Question: What features of a mammalian heart can you identify in a real or virtual heart? What route does blood take through
CHAPTER 8 Investigation 8.A: Identifying Structures of the Circulatory System Question: What features of a mammalian heart can you identify in a real or virtual heart? What route does blood take through
Human Body Systems. Human Body Project Notes
 Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Frog Dissection SNC2P Grade 10 Science Applied Biology Tissues, Organs and Systems of Living Things
 Frog Dissection SNC2P Grade 10 Science Applied Biology Tissues, Organs and Systems of Living Things Purpose To identify and examine the external and internal structures of the frog and compare them with
Frog Dissection SNC2P Grade 10 Science Applied Biology Tissues, Organs and Systems of Living Things Purpose To identify and examine the external and internal structures of the frog and compare them with
Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT
 Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
PROCEDURE A EXTERNAL ANATOMY
 Fetal Pig Dissection OBJECTIVES Know the external anatomy of the fetal pig. Dissect the digestive, respiratory, circulatory, excretory, and reproductive systems of the fetal pig. Identify and know the
Fetal Pig Dissection OBJECTIVES Know the external anatomy of the fetal pig. Dissect the digestive, respiratory, circulatory, excretory, and reproductive systems of the fetal pig. Identify and know the
Homework Packet. The branch of biological science that studies and describes how body parts. The study of the shape and structure of body parts
 Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
This booklet belongs to: Spring Page 1 of 10
 This booklet belongs to: Spring 2013 Page 1 of 10 Frog Dissection Background Amphibians are studied in science for a variety of reasons. Amphibians are unique in many ways because their anatomy allows
This booklet belongs to: Spring 2013 Page 1 of 10 Frog Dissection Background Amphibians are studied in science for a variety of reasons. Amphibians are unique in many ways because their anatomy allows
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
This booklet belongs to: Spring Page 1 of 10
 This booklet belongs to: Spring 2017 Page 1 of 10 Frog Dissection Background Amphibians are studied in science for a variety of reasons. Amphibians are unique in many ways because their anatomy allows
This booklet belongs to: Spring 2017 Page 1 of 10 Frog Dissection Background Amphibians are studied in science for a variety of reasons. Amphibians are unique in many ways because their anatomy allows
"...AND THIS LITTLE PIG..."
 London and District Science Olympics Annual Competition "...AND THIS LITTLE PIG..." Senior Biology "...AND THIS LITTLE PIG..." RULES Biology Grades 9-12 Changes to the rules are marked by a vertical line
London and District Science Olympics Annual Competition "...AND THIS LITTLE PIG..." Senior Biology "...AND THIS LITTLE PIG..." RULES Biology Grades 9-12 Changes to the rules are marked by a vertical line
Fig. A.1. Frontal. plane. Transverse. plane. Sagittal plane. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART
 LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART Because mammals are warm-blooded and generally very active animals, they require high metabolic rates. One major requirement of a high metabolism is
LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART Because mammals are warm-blooded and generally very active animals, they require high metabolic rates. One major requirement of a high metabolism is
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide
 Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
MINK DISSECTION LAB DAY 1 NECK
 MINK DISSECTION LAB PURPOSE: This lab dissection is designed to give you first hand experience with the organs (or their mink counterparts) that we have learned about all year long. After seeing the organs,
MINK DISSECTION LAB PURPOSE: This lab dissection is designed to give you first hand experience with the organs (or their mink counterparts) that we have learned about all year long. After seeing the organs,
3. There are three pairs of salivary glands that have three important functions. These are: a)
 Reference: 1. Use the human systems in your textbook.. 2. Pig instruction packet. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1. What is the process of digestion? 2. List three major glands involved in this process? 3. There are
Reference: 1. Use the human systems in your textbook.. 2. Pig instruction packet. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1. What is the process of digestion? 2. List three major glands involved in this process? 3. There are
Fetal Pig Dissection. Introduction:
 Fetal Pig Dissection Introduction: Today, we begin a new chapter in our study of biology. In the first half of the year we looked at how the smallest units of life work, reproduce and pass on their genes.
Fetal Pig Dissection Introduction: Today, we begin a new chapter in our study of biology. In the first half of the year we looked at how the smallest units of life work, reproduce and pass on their genes.
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology
 Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al
 ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
STREAM. Human Body Project Pages Website QR Code body project/
 STREAM Human Body Project Pages 1 16 Website QR Code https://sites.google.com/a/wyckoffschools.org/human body project/ Project Checklist Did you include Head a brain that can open to show the inside as
STREAM Human Body Project Pages 1 16 Website QR Code https://sites.google.com/a/wyckoffschools.org/human body project/ Project Checklist Did you include Head a brain that can open to show the inside as
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
Dissection on Demand: Fetal Pig
 TEACHER GUIDE DISSECTION ON DEMAND: FETAL PIG 60 Minute Health and Life Science Lesson Science-to-Go! Program Grades: 6-12 Dissection on Demand: Fetal Pig Description Students will perform a dissection
TEACHER GUIDE DISSECTION ON DEMAND: FETAL PIG 60 Minute Health and Life Science Lesson Science-to-Go! Program Grades: 6-12 Dissection on Demand: Fetal Pig Description Students will perform a dissection
Fetal Pig Dissection Honors Biology
 Fetal Pig Dissection Honors Biology Introduction In this lab, you will study the external and internal anatomy of a fetal pig, relate its structures to those of other mammals, and determine differences
Fetal Pig Dissection Honors Biology Introduction In this lab, you will study the external and internal anatomy of a fetal pig, relate its structures to those of other mammals, and determine differences
Frog Dissection-Skin Vista Murrieta High School-- Biomedical Science. Mr. Diaz
 Frog Dissection-Skin Vista Murrieta High School-- Biomedical Science Mr. Diaz Background: Please read entire lab As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but
Frog Dissection-Skin Vista Murrieta High School-- Biomedical Science Mr. Diaz Background: Please read entire lab As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but
Violation of these rules, failure to participate, or unsafe behavior will result in the loss of participation points. THERE WILL BE NO WARNINGS!
 BIOLOGY II MINK DISSECTION ACTIVITY #1 NAME DATE HOUR MINK DISSECTION PART 1: CLASSROOM RULES 1. No food or drink in the lab. 2. Follow directions the first time they are given. 3. No unauthorized dissections.
BIOLOGY II MINK DISSECTION ACTIVITY #1 NAME DATE HOUR MINK DISSECTION PART 1: CLASSROOM RULES 1. No food or drink in the lab. 2. Follow directions the first time they are given. 3. No unauthorized dissections.
THESE ARE THE IMPORTANT CONCEPTUAL UNDERSTANDINGS I NEED TO MASTER FOR THIS UNIT: RESULTS/SCORES FROM LEARNING ASSESSMENTS
 MAP MASTERY Unit 7: Anatomy and Physiology THESE ARE THE IMPORTANT CONCEPTUAL UNDERSTANDINGS I NEED TO MASTER FOR THIS UNIT: A. Demonstrates an understanding of the of the circulatory system. Identify
MAP MASTERY Unit 7: Anatomy and Physiology THESE ARE THE IMPORTANT CONCEPTUAL UNDERSTANDINGS I NEED TO MASTER FOR THIS UNIT: A. Demonstrates an understanding of the of the circulatory system. Identify
Rat Dissection External Anatomy
 1 Rat Dissection External Anatomy 1. Note the hairy coat that covers the rat and the sensory hairs (whiskers) located on the rat's face, called vibrissae. 2. The mouth has a large cleft in the upper lip
1 Rat Dissection External Anatomy 1. Note the hairy coat that covers the rat and the sensory hairs (whiskers) located on the rat's face, called vibrissae. 2. The mouth has a large cleft in the upper lip
Comparing Vertebrates: Fetal Pig and Bullfrog Honors Integrated Science 4
 Comparing Vertebrates: Fetal Pig and Bullfrog Honors Integrated Science 4 Name Per. Introduction Organisms are classified based on similarities and differences to: 1) make sense of the millions of organisms
Comparing Vertebrates: Fetal Pig and Bullfrog Honors Integrated Science 4 Name Per. Introduction Organisms are classified based on similarities and differences to: 1) make sense of the millions of organisms
Introduction in human anatomy
 Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Pharynx. crop. intestine
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system provides nutrients to the body (hearts) Pharynx esophagus gizzard crop intestine stages of digestion: Ingestion: taking in of nutrients Digestion: the breaking
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system provides nutrients to the body (hearts) Pharynx esophagus gizzard crop intestine stages of digestion: Ingestion: taking in of nutrients Digestion: the breaking
Observing the Structure of a Squid
 Name Class Date Chapter 27 Worms and Mollusks Observing the Structure of a Squid Introduction You are probably familiar with clams, snails, slugs, squids, and octupuses, and you probably have noticed how
Name Class Date Chapter 27 Worms and Mollusks Observing the Structure of a Squid Introduction You are probably familiar with clams, snails, slugs, squids, and octupuses, and you probably have noticed how
NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE. X Biology II
 Unit 2-5, Animal Biology & Organ Systems, FETAL PIG DISSECTION MANUAL X Biology II, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE X Biology II
Unit 2-5, Animal Biology & Organ Systems, FETAL PIG DISSECTION MANUAL X Biology II, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE X Biology II
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART BLOOD
 ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
Fetal Pig Dissection Lab
 Fetal Pig Dissection Lab Introduction: In this lab you will be examining many characteristics of an unborn mammal--the fetal pig. Dissection will help you to get a 3-dimensional picture of how all the
Fetal Pig Dissection Lab Introduction: In this lab you will be examining many characteristics of an unborn mammal--the fetal pig. Dissection will help you to get a 3-dimensional picture of how all the
Human Body. The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related.
 Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. Cells: the smallest unit of life.
 Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N
 Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
Heart Dissection. 5. Locate the tip of the heart or the apex. Only the left ventricle extends all the way to the apex.
 Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES
 Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Station # Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 415-421 in your textbook for a general discussion
Name Class Date Station # Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 415-421 in your textbook for a general discussion
Cat Dissection. Muscular Labs
 Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Forensic Dissection An Autopsy
 Forensic Dissection An Autopsy Objectives: Conduct an external investigation of a fetal pig following an autopsy protocol. Conduct an internal investigation of a fetal pig following an autopsy protocol.
Forensic Dissection An Autopsy Objectives: Conduct an external investigation of a fetal pig following an autopsy protocol. Conduct an internal investigation of a fetal pig following an autopsy protocol.
Microscopic Anatomy Cytology study of the cell Histology study of tissues
 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
#4 Cardiovascular I The Heart
 Page1 #4 Cardiovascular I The Heart Objectives: Identify a list of human heart structures using a virtual human dissection Dissect a sheep heart to identify external and internal structures Identify a
Page1 #4 Cardiovascular I The Heart Objectives: Identify a list of human heart structures using a virtual human dissection Dissect a sheep heart to identify external and internal structures Identify a
Nervous System. Skeletal System. Muscular System. Reproductive System. Circulatory System. Endocrine System. Respiratory System. Integumentary System
 The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) (Lysosomes) Main Organs: Main Organs: SKIN HAIR NAILS KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA
 URINARY System Name: (Lysosomes) KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA LUNGS SKIN EXCRETORY System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) SKIN HAIR NAILS Skin is the largest Organ. The excretory system collects and
URINARY System Name: (Lysosomes) KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA LUNGS SKIN EXCRETORY System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) SKIN HAIR NAILS Skin is the largest Organ. The excretory system collects and
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body
 Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Bio 5/6
 Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
DISSECTING A PIG S HEART
 DISSECTING A PIG S HEART LAB 59 OBSERVATION STUDENT BOOK Chapter 6, page 185 Goal Locate and observe structures of a mammal s heart. Observation criteria Identify the structures of the heart indicated
DISSECTING A PIG S HEART LAB 59 OBSERVATION STUDENT BOOK Chapter 6, page 185 Goal Locate and observe structures of a mammal s heart. Observation criteria Identify the structures of the heart indicated
Lab Schedule for Rest of Semester
 Laboratory 9 Cat Dissection II Respiratory Urinary/Reproductive Systems Lab Schedule for Rest of Semester Cat dissection labs Dissection II (today) Respiratory (Ex. 57 in Hole) Human Reproductive Systems
Laboratory 9 Cat Dissection II Respiratory Urinary/Reproductive Systems Lab Schedule for Rest of Semester Cat dissection labs Dissection II (today) Respiratory (Ex. 57 in Hole) Human Reproductive Systems
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole
 CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II
 Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
7/4/2018. Key Objectives. A and P 2401 Lecture 2 TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS. Negative Feedback Examples. Review of Homeostasis
 Key Objectives Review of Homeostasis Negative Feedback Mechanisms Positive Feedback Mechanisms Body Systems and Function A and P 2401 Lecture 2 HOMEOSTASIS TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS The
Key Objectives Review of Homeostasis Negative Feedback Mechanisms Positive Feedback Mechanisms Body Systems and Function A and P 2401 Lecture 2 HOMEOSTASIS TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS The
