New insights into the significance of protein quality in human diets
|
|
|
- Margery Atkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 New insights into the significance of protein quality in human diets Daniel TOME AgroParisTech -Department of Life Science and Health, INRA - UMR914 Nutrition Physiology and Ingestive Behavior F Paris, France
2 Introduction Protein quality describes the ability of a protein source to achieve defined nutritional and metabolic actions related to protein requirement. Traditionally, protein requirement is determined as the lowest level of dietary protein intake that will balance the losses of nitrogen from the body, and thus maintain the body protein mass in persons at energy balance. During the last decades understanding of protein s actions expanded and new research indicated increasingly complex roles for protein and amino acids in regulation of various other functions
3 Protein and amino acid : metabolism and functions Support protein turnover and homeostasis as substrate or as signal molecules (leucine) participate to energy metabolism either directly or through gluconeogenesis some specific amino acid have a regulatory role as precursor of nitrogenous compounds (cysteine, tryptophane, arginine, ) Body protein Dietary protein breakdown Synthesis Indispensable amino acids Dispensable amino acids Free amino acids De novo synthesis of dispensable amino acid Nitrog en Urea Nitrogenous compounds Carbon radicals Energy CO2+H2O Glucose
4 1- Protein quality and nitrogen balance The current criterion for protein quality evaluation is to meet maintenance needs plus special needs for growth, pregnancy, or lactation. Traditionally, protein requirement is determined as the lowest level of dietary protein intake that will balance the losses of nitrogen from the body, and thus maintain the body protein mass in persons at energy balance. This has been discussed in the context of a protein s ability to provide nitrogen and specific patterns of amino acids to satisfy the requirement for synthesis of protein and its role in maintaining body protein mass. This is currently determined from growth measurement, protein and nitrogen digestibility, nitrogen balance, nitrogen retention or protein turnover at whole body level or in specific protein pools.
5 Protein, amino acid, nitrogen balance and protein requirement + special requirements for growth or pregnancy/lactation Body Proteins Food protein and amino acid intake Amino Acid Fecal, urinary, miscellaneous Nitrogen losses Nitrogen and indispensable amino acids Nitrogen balance Adaptation to nitrogen intake to reach nitrogen balance maintenance requirement
6 Safe protein requirement and current protein quality Providing bioavailable nitrogen and indipensable amino acids to achieve nitrogen balance Requirement for Nitrogen : Meta-analysis of N- balance in adults - mean requirement of 0.66 g protein/kg/d and safe protein requirement of 0.83 g protein /kg/d. Requirement for indispensable amino acid : lysine, sulfur (methionine + cysteine), threonine, tryptophan, branched chain (leucine, isoleucine, valine), aromatic (phenylalanine + tyrosine), histidine
7 Amino acid requirement and reference pattern : Indispensable amino acid composition of a reference protein reaching amino acid requirement at the safe level of protein intake (0,66 g/kg/d in adult)
8 Indispensable amino acids in food proteins and diets compared with the requirement pattern (FAO/WHO/UNU 2007
9 Distribution of lysine in food proteins and diets for adult (as % lysine requirement) Calculated for 0.66 g/kg/d protein intake (= mean protein requirement) and 30 mg/kg/d mean lysine requirement in adult Wheat Maize Rice Cassava Yam Potato Egg Soya Milk Beef Indian diet Western diet (derived from FAO, WHO, 2002)
10 Indispensable amino acid in animal and plant protein compared with the reference protein amino acid pattern AA g/100g Lysine Methionine + Cysteine Reference Animal Cereals Legumes Lysine is limiting in cereals Sulphur amino acid can be limiting in legumes Animal protein have no limiting amino acid
11 In vivo measurement of nitrogen retention : Net postprandial dietary nitrogen utilization (NPPU) of different protein sources in humans Fouillet et al, J. Nutr. 132: 3208S 3218S, 2002 NPPU is assessed after the ingestion of a single 15N-labeled mixed meal and the measurement of the fraction of dietary N transferred to urea. Postprandial dietary N retention is calculated from the amount of dietary N absorbed that is neither recovered in urine nor in the body urea pool 8 h after the meal ingestion.
12 Increasing Habitual Protein Intake Accentuates Differences in Postprandial Dietary Nitrogen Utilization between Protein Sources in Humans. (Morens et al J. Nutr. 133: , 2003). Net postprandial protein utilization (NPPU) of milk (n=12) and soy protein (n=8) by humans as a function of the prevailing protein intake (normal protein, NP or high protein, HP) assessed after ingestion of a 15Nlabeled protein meal. There was a significant influence of diet (P ), protein source (P ) and their interaction (P 0.001) on NPPU, as assessed by a two-way ANOVA. *,**Soy and millk protein groups differ at each protein level, P 0.02 and P , respectively (post-hoc Tukey s test).
13 Changes in Quantity Closely Associated with Quality Context of current protein intake Ł Most nutritionally complete habitual diets include protein intake higher than these needs Ł Adaptation of protein and amino acid metabolism may modify requirement and quality references As protein intake increases, more difficult to generate single reference pattern to predict 4adaptation of amino acids metabolism 4consequent fate of the dietary amino acids 4especially across lifespan and all physiological conditions Protein digestibility and colonic health Ł colonic protein degradation and metabolism could generate toxic components
14 Dietary protein and protein turnover AA support protein turnover and homeostasis as substrate and as signal molecules (BCAA, leucine) differently in the different tissues and organs Control and limiting factors for protein synthesis Ł Indispensable amino acids are the main limiting factors for body protein synthesis Ł The kinetic of amino acid delivery to tissues influences anabolic response and oxidation in splanchnic and peripheral tissues Ł Leucine is considered as an anabolic signal for protein synthesis (in muscle?) Consequences for protein requirement and quality?
15 Muscle protein synthesis is stimulated by amino acid and leucine in adult Synthesis breakdown Effect of balanced amino acid infusion (164 mg/h/kg) on Muscle Protein Synthesis and Breakdown (from Biolo et al, 1997). Correlation between muscle protein synthesis and arterial flux of leucine (higher values are obtained with amino acid iv infusion) (Wolfe, 2000).
16 Consequences of different kinetic and blood amino acid profile induced by whey (W), casein (C) or total milk protein (TMP) (Lacroix et al, 2006) Amino acid delivery, protein anabolic effect, signal AA (BAA, ) Amino acid deamination, urea production, energy metabolism
17 Peripheral and Splanchnic Metabolism of Dietary Nitrogen Are Differently Affected by the Protein Source in Humans (Fouillet el al J. Nutr. 132: , 2002) Milk peripheral soy Splanchnic and peripheral protein synthesis efficiencies (PSE) of dietary N (8 h) after the ingestion of a meal made up of milk protein (n 9) or soy protein ( n 10) in humans. Splanchnic soy Milk Splanchnic and peripheral retention of dietary amino acids, after the ingestion of a meal made up of milk protein (n 9) or soy protein ( n 10) in humans. Milk soy Splanchnic Milk soy Peripheral
18 Body Protein Metabolism with advancing age Efficiency of indispensable AA use may decrease with advancing age Ł Dose-response relationship between IAA concentrations in the blood and muscle protein synthesis Ł Anabolic resistance of protein synthesis in skeletal muscle can be overcome by increased essential amino acids Ł Need for both nutritional support and resistance exercise Specific amino acid pattern of the extra protein involved is unknown Ł Limited studies on relative influence of different protein sources Ł What is the optimal dietary amino acid pattern in terms of specific amino acids, total IAA content, or conditionally indispensable AA? Ł Abundant animal evidence points to potential for leucine
19 2- Amino acid-dependent modulation of energy and glucose metaolism Varying the amount and quality of protein affects energy intake, insulin secretion and action, thereby regulating energy and glucose homeostasis High protein diet is accompanied by increased stimulation of insulin and glucagon, high glycogen turnover, and stimulation of gluconeogenesis A high protein diet improves glucose, insulin secretion, insulin sensitivity, inhibits liver lipogenesis, and stimulates glycolysis in muscle
20 Protein and amino acid metabolism pathways Body protein turnover pathways Tissues and organs : Gut, liver, muscle, skin, kidney, brain,.. Food protein (quantity, quality) Amino Acid urea Carbon radicals CO2+H2O Energy Nitrogenous compounds Glucose, glycogen, fatty acids, triglycerides,... Other amino acid metabolic pathways
21 Protein, satiety and food and energy intake Dietary protein and amino acids generate signals involved in the induction of satiety and in the control of food intake They associate nutrients (amino acids, glucose, ), gut neuropeptides (CCK, PYY, ) and hormones (insulin, ) signals They act in the brain either indirectly through vagus-mediated pathways or directly after their release in the peripheral blood
22 Consequence of a 25 days high milk or whey protein diet on food intake in the rat (Pichonet al, J Nutr2006) 0,4 a Energy intake (1000kJ/d) b b c b,c 0,3 0,2 0,1 0 Milk Milk Whey Milk Whey P14C76L10 P55C35L10 P55C15L30 NP diet HP diets
23 Consequence of a 25 days high milk or whey protein diet on food intake and body weight in the rat (Pichonet al, J Nutr2006) a b Body weight gain (g/d) c b,c b,c a b White adipose tissue (g/100g BW) Milk Milk Whey Milk Whey P14C76L10 P55C35L10 P55C15L30 NP diet HP diets b b NP -Normal Protein diet HP -High protein diet b
24 A high protein diet reduces food intake, body weight and adipose tissue in rats (8 weeks) Food intake kj/d (8 th week) High Carb P14C76L10 HProt P55C35L10 Blouet et al, J. Nutr. 136: , 2006.
25 Protein stimulate insulin response Correlationbetweendaily proteinintakeand acute insulinresponseto glucose as an estimateof insulinsecretioncapacity Santosa et al, Diabetologia, 2000
26 Amino acids stimulate liver gluconeogenesis (a) Plasma concentrations of glucose during an infusion of saline (Con) or amino acids (AA+S) together with somatostatin to inhibit an endogenous release of glucoregulatory hormones including insulin (pancreatic clamps) as well as an infusion of amino acids without somatostatin (AA-S). (b) Contributions of gluconeogenesis (GNG) and glycogenolysis (GLY) to the tracer determined rates of endogenous glucose production (EGP) in the presence of the above-described conditions; an infusion of saline (CON) or amino acids together with somatostatin (AA + S) as well as an infusion of amino acids without somatostatin (AA S) M Krebs, EurJ Clin Invest, 2005
27 Increasing protein and lowering carbohydrates decreases de novo fatty acid synthesis (FAS), and enhances adipose tissue lipolysis (LPL) in rats Pichon et al, J Nutr, 2006
28 Consequence of a 25 days high milk or whey protein diet on insulin, glucose and triglycerides in the rat (Pichonet al, J Nutr2006) 125 Glucose (mg/dl) a b Insulin (µui/ml) b,c c b,c ,5 a Triglycerides (mmol/l) 50 0 Milk Milk Whey Milk Whey P14C76L10 P55C35L10 P55C15L30 NP diet HP diets NP -Normal Protein diet HP -High protein diet 1 a,b b 0,5 b b 0 Milk Milk Whey Milk Whey P14C76L10 P55C35L10 P55C15L30 NP diet HP diets
29 High-Protein feeding improves Glycemic Control in Rats fed ad libitum High Carb P14C76L10 HProt P55C35L10 Blouet et al, J. Nutr. 136: , Glucose tolerance (mmol min/l) * Protein improved glucose tolerance in rat fed 7 weeks a HP diet compared to rat fed ad libitum a NP diet or rat fed the NP diet pair-fed to the HP diet (NPr) NP NPr HP NP -Normal Protein diet HP -High protein diet NPr NP restricted (pair-fed HP)
30 A high protein diet improves glucose, insulin, HOMA index (insulin sensitivity), inhibits liver lipogenesis, and stimulates glycolysis in muscle (7-8 weeks) Blouet et al, J. Nutr. 136: , NP P14C76L10 HP P55C35L10 The homeostatic model assessment (HOMA) index was calculated as follows: HOMA = Insulin (pmol/l) x Glucose (mmol/l)/ Lower expression of FAS, the rate-limiting enzyme of hepatic lipogenesis -Lower expression of SREBP-1c, a key mediator of insulin action on FAS expression -Increased expression of HKII, the first enzyme involved in muscle glucose utilization
31 3- Amino acid as precursor of nitrogenous compounds Nitrogenous compounds Neuromediators glutathione Taurine Carnitine Carnosine Nucleic acids Creatine Nitrogen Monoxyde Polyamines Serotonin Epinephrine/Norepinephrine GABA glutamate Cys, gly, glu Cys Lys, Met His, b-ala Asp, Gln Arg, Gly Arg Arg, Orn Trp Tyr Glu Glu
32 Sensitive pathways in amino acid homeostasis µmol/kg/j cystéine glutamate Glycine Flux plamastique Synthèse de gluthation Synthèse de taurine µmol/kg/j Arginine Glycine Méthionine Flux plamastique Synthèse de créatine Synthèse de NO
33 Glutathion synthesis Le glutathion est un tripeptide présent dans les cellules à des concentrations comprises entre 0,5 et 10,0 mm. O SH CH 2 H Le glutathion est synthétisé dans le cytosol à partir du glutamate, de la cystéine et de la glycine. La proportion de cystéine utilisée par la synthèse de GSH est très importante puisqu elle représente entre 30 et 50 % de l utilisation totale de cet acide aminé chez l homme. γ CH 2 CH 2 C H C NH + 3 N H CH C O N CH 2 COO - Chez le volontaire sain qu un apport alimentaire restreint en acides aminés soufrés diminue de manière marquée le taux de synthèse du GSH circulant COO - glutamate cystéine glycine
34 Cystein availability is limiting when glutathion requirement is increased Dietary cystein glycine cystein glutamine Body protein NADP GSSG reductase NADPH GSHred GSSGox Oxidative Stress
35 Whey protein, exercise and stress A pre-exercice a-lactalbumin-enriched whey preparation improves post-exercise liver glutathione with a dosedependent effect of the cysteine content in the rat. Glutathione (µmol/g) CON GLUC TMP a-lac NAC α-lac-enriched Treatment : Rats receive the meal complement They wait for 1 hours They run for 2 hours. Liver glutathione is determined after running Cysteine intake (mg) (Mariotti et al, 2004)
36 Increasing cysteine dietary intake limits the adverse effects of a high-sucrose diet on oxidative stress and glucose homeostasis in rats. (HS 0 ) total milk proteins, singly (HS 1 ) supplemented with 5.5 g/kg N-acetylcysteine (NAC) (HS 2 ) supplemented with16 g/kg N-acetylcysteine (NAC) (HSa) α-lactalbumin-rich whey concentrate Blouet et al, 2007 insulin postprandial AUC values (AUCi, µg.min/l) Blood GSH Ehc Plasma insulin concentrations
37 Conclusion Currently accepted methods for measuring protein quality do not consider the diverse roles of amino acids beyond the first limiting indispensable amino acid for growth or nitrogen balance. Research continues to evolve in assessing protein s role in optimal health in relation with the level of protein in the diet and the specific role of individual amino acids. The evidence available to date suggests that quality is important not only at the lowest level of dietary protein intake that balances the losses of nitrogen from the body but also at higher intakes. The concept of protein quality must expand to incorporate newly emerging actions of protein into the protein quality concept. As a consequence there is need to continue to explore implications for protein and amino acid quality assessment.
38 Protein and Health Protein quality has been first related to the role of dietary protein in order to avoid deficiency Ł By providing nitrogen and indispensable amino acids Ł to achieve nitrogen balance require 0.8 g/kg/d protein of good quality Recent approaches more precisely evaluate protein and amino acid metabolic pathways and their influence on «health markers» ŁImproving body composition, energy homeostasis, glucose homeostasis, insulin sensitivity, lipid metabolism, inflammatoryprocesses, oxidative stress Ł Which quantity and optimal amino acid composition?
Proteins and Amino Acids. Benjamin Caballero, MD, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
AMINO ACID METABOLISM. Sri Widia A Jusman Dept. of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI
 AMINO ACID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Dept. of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Amino acids derived from dietary protein absorbed from intestine through blood taken up by tissues used for biosynthesis
AMINO ACID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Dept. of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Amino acids derived from dietary protein absorbed from intestine through blood taken up by tissues used for biosynthesis
Energy metabolism - the overview
 Energy metabolism - the overview Josef Fontana EC - 40 Overview of the lecture Important terms of the energy metabolism The overview of the energy metabolism The main pathways of the energy metabolism
Energy metabolism - the overview Josef Fontana EC - 40 Overview of the lecture Important terms of the energy metabolism The overview of the energy metabolism The main pathways of the energy metabolism
Optimizing Protein in a Carbohydrate World
 Optimizing Protein in a Carbohydrate World Donald K. Layman, Ph.D. Professor Emeritus Department of Food Science & Human Nutrition University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign The confused consumer 1 Myth:
Optimizing Protein in a Carbohydrate World Donald K. Layman, Ph.D. Professor Emeritus Department of Food Science & Human Nutrition University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign The confused consumer 1 Myth:
Integrative Metabolism: Significance
 Integrative Metabolism: Significance Energy Containing Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Catabolism Energy Depleted End Products H 2 O NH 3 ADP + Pi NAD + NADP + FAD + Pi NADH+H + NADPH+H + FADH2 Cell
Integrative Metabolism: Significance Energy Containing Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Catabolism Energy Depleted End Products H 2 O NH 3 ADP + Pi NAD + NADP + FAD + Pi NADH+H + NADPH+H + FADH2 Cell
Metabolism of amino acids. Vladimíra Kvasnicová
 Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
Page 8/6: The cell. Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products)
 Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Amino Acids: essential nonessential
 Protein: a component of every living cell provides structure and framework in the body plays a role in fluid balance and acid--base balance used to transport substances through the blood provides 4 cal/g
Protein: a component of every living cell provides structure and framework in the body plays a role in fluid balance and acid--base balance used to transport substances through the blood provides 4 cal/g
1. Describe the relationship of dietary protein and the health of major body systems.
 Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Amino acid Catabolism
 Enzymatic digestion of dietary proteins in gastrointestinal-tract. Amino acid Catabolism Amino acids: 1. There are 20 different amino acid, they are monomeric constituents of proteins 2. They act as precursors
Enzymatic digestion of dietary proteins in gastrointestinal-tract. Amino acid Catabolism Amino acids: 1. There are 20 different amino acid, they are monomeric constituents of proteins 2. They act as precursors
AMINO ACIDS NON-ESSENTIAL ESSENTIAL
 Edith Frederika Introduction A major component of food is PROTEIN The protein ingested as part of our diet are not the same protein required by the body Only 40 to 50 gr of protein is required by a normal
Edith Frederika Introduction A major component of food is PROTEIN The protein ingested as part of our diet are not the same protein required by the body Only 40 to 50 gr of protein is required by a normal
EFFECTS OF AMINO ACID SUBSTITUTIONS FOR WHEY PROTEIN CONCENTRATE ON WEANLING PIG PERFORMANCE. Authors: J. Chung, S.D. Carter and J.C.
 EFFECTS OF AMINO ACID SUBSTITUTIONS FOR WHEY PROTEIN CONCENTRATE ON WEANLING PIG PERFORMANCE 1999 Animal Science Research Report Authors: Story in Brief Pages 266-272 J. Chung, S.D. Carter and J.C. Whisenhunt
EFFECTS OF AMINO ACID SUBSTITUTIONS FOR WHEY PROTEIN CONCENTRATE ON WEANLING PIG PERFORMANCE 1999 Animal Science Research Report Authors: Story in Brief Pages 266-272 J. Chung, S.D. Carter and J.C. Whisenhunt
Reactions and amino acids structure & properties
 Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Classification of amino acids: -
 Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
9/6/2011. Amino Acids. C α. Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups
 Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Amino Acids. Amino Acids. Fundamentals. While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an NH. 3 and CO NH 3
 Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Midterm 2. Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98. Standard Deviation: 17.7
 Midterm 2 Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98 Standard Deviation: 17.7 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Review of Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Synthesis of few amino acids Dietary
Midterm 2 Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98 Standard Deviation: 17.7 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Review of Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Synthesis of few amino acids Dietary
Latest developments in policy and research on the DIAASmethod to determine protein quality
 Latest developments in policy and research on the DIAASmethod to determine protein quality Daniel Tomé AgroParisTech, INRA, France and Wageningen University, The Netherlands Event name Introduction The
Latest developments in policy and research on the DIAASmethod to determine protein quality Daniel Tomé AgroParisTech, INRA, France and Wageningen University, The Netherlands Event name Introduction The
Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry
 Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids
 Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Amino Acid Metabolism
 Amino Acid Metabolism Last Week Most of the Animal Kingdom = Lazy - Most higher organisms in the animal kindom don t bother to make all of the amino acids. - Instead, we eat things that make the essential
Amino Acid Metabolism Last Week Most of the Animal Kingdom = Lazy - Most higher organisms in the animal kindom don t bother to make all of the amino acids. - Instead, we eat things that make the essential
Midterm 2 Results. Standard Deviation:
 Midterm 2 Results High: Low: Mean: Standard Deviation: 97.5% 16% 58% 16.3 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Dietary (Exogenous) Proteins Hydrolyzed
Midterm 2 Results High: Low: Mean: Standard Deviation: 97.5% 16% 58% 16.3 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Dietary (Exogenous) Proteins Hydrolyzed
Amino Acids in Dairy Nutrition Where Do They Fit?
 Amino Acids in Dairy Nutrition Where Do They Fit? T. R. Overton and L. E. Chase Department of Animal Science Cornell University As our understanding of the biology underlying specifics of protein nutrition
Amino Acids in Dairy Nutrition Where Do They Fit? T. R. Overton and L. E. Chase Department of Animal Science Cornell University As our understanding of the biology underlying specifics of protein nutrition
Soy Protein. Muscle health benefits: for Sports Nutrition Recovery and during aging. May 9, Mark Cope, PhD
 Soy Protein Muscle health benefits: for Sports Nutrition Recovery and during aging May 9, 2017 Mark Cope, PhD Blending Proteins to Provide Better Muscle Health Importance of Muscle Health The Benefits
Soy Protein Muscle health benefits: for Sports Nutrition Recovery and during aging May 9, 2017 Mark Cope, PhD Blending Proteins to Provide Better Muscle Health Importance of Muscle Health The Benefits
What systems are involved in homeostatic regulation (give an example)?
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
ENERGY FROM INGESTED NUTREINTS MAY BE USED IMMEDIATELY OR STORED
 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 SHORT TERM METABOLISM [METABOLISM] Learning Objectives: Identify primary energy stores of the body Differentiate the metabolic processes of the fed and fasted states Explain
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 SHORT TERM METABOLISM [METABOLISM] Learning Objectives: Identify primary energy stores of the body Differentiate the metabolic processes of the fed and fasted states Explain
Goals. Goals. Maintenance Rations 4/25/2014. Week 4 Lecture 12. Clair Thunes, PhD
 Maintenance Rations Week 4 Lecture 12 Clair Thunes, PhD Animal Science 126 Equine Nutrition Goals Understand that in reality that horses have an amino acid requirement not a CP requirement That there are
Maintenance Rations Week 4 Lecture 12 Clair Thunes, PhD Animal Science 126 Equine Nutrition Goals Understand that in reality that horses have an amino acid requirement not a CP requirement That there are
Amino acid metabolism
 Amino acid metabolism The important reaction commonly employed in the breakdown of an amino acid is always the removal of its -amino group. The product ammonia is excreted after conversion to urea or other
Amino acid metabolism The important reaction commonly employed in the breakdown of an amino acid is always the removal of its -amino group. The product ammonia is excreted after conversion to urea or other
Amino Acids : Towards Precise Nutrition in Monogastric Animals
 [AFMA FORUM 2016 SESSION 4] Amino Acids : Towards Precise Nutrition in Monogastric Animals AFMA 2016 CORRENT AMINO ACIDS 2016 All rights reserved AJINOMOTO EUROLYSINE S.A.S. 1 Dietary crude protein reduction
[AFMA FORUM 2016 SESSION 4] Amino Acids : Towards Precise Nutrition in Monogastric Animals AFMA 2016 CORRENT AMINO ACIDS 2016 All rights reserved AJINOMOTO EUROLYSINE S.A.S. 1 Dietary crude protein reduction
Protein Recommendations: Time for an Update?
 Protein Recommendations: Time for an Update? Rajavel Elango Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Pediatrics, School of Population and Public Health University of British Columbia Scientist Level 1 Nutrition
Protein Recommendations: Time for an Update? Rajavel Elango Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Pediatrics, School of Population and Public Health University of British Columbia Scientist Level 1 Nutrition
UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
Intermediary metabolism. Eva Samcová
 Intermediary metabolism Eva Samcová Metabolic roles of tissues Four major tissues play a dominant role in fuel metabolism : liver, adipose, muscle, and brain. These tissues do not function in isolation.
Intermediary metabolism Eva Samcová Metabolic roles of tissues Four major tissues play a dominant role in fuel metabolism : liver, adipose, muscle, and brain. These tissues do not function in isolation.
Protein & Amino Acid Metabolism
 Pathophysiology 101-823 Unit 4 Metabolism & Metabolic Disease Protein & Amino Acid Metabolism Paul Anderson FALL 2008 Learning Objectives 1. List the metabolic functions of proteins & amino acids. 2. Explain
Pathophysiology 101-823 Unit 4 Metabolism & Metabolic Disease Protein & Amino Acid Metabolism Paul Anderson FALL 2008 Learning Objectives 1. List the metabolic functions of proteins & amino acids. 2. Explain
Proteins are sometimes only produced in one cell type or cell compartment (brain has 15,000 expressed proteins, gut has 2,000).
 Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of
 Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Lecture Notes 2: Protiens
 Lecture Notes 2: Protiens BY/ARSHED ABD ALI SHIHAD Proteins and Amino Acids What Are Proteins? Large molecules Made up of chains of amino acids Are found in every cell in the body Are involved in most
Lecture Notes 2: Protiens BY/ARSHED ABD ALI SHIHAD Proteins and Amino Acids What Are Proteins? Large molecules Made up of chains of amino acids Are found in every cell in the body Are involved in most
EFFECTS OF REPLACING WHEY PROTEIN CONCENTRATE WITH CRYSTALLINE AMINO ACIDS ON WEANLING PIG PERFORMANCE
 EFFECTS OF REPLACING WHEY PROTEIN CONCENTRATE WITH CRYSTALLINE AMINO ACIDS ON WEANLING PIG PERFORMANCE 1999 Animal Science Research Report Authors: Story in Brief Pages 258-265 J. Chung, S.D. Carter,C.V.
EFFECTS OF REPLACING WHEY PROTEIN CONCENTRATE WITH CRYSTALLINE AMINO ACIDS ON WEANLING PIG PERFORMANCE 1999 Animal Science Research Report Authors: Story in Brief Pages 258-265 J. Chung, S.D. Carter,C.V.
Amino acid composition and mineral bioavailability: Important feed quality traits in cereals
 Amino acid composition and mineral bioavailability: Important feed quality traits in cereals Preben Bach Holm University of Aarhus Faculty of Agricultural Sciences Department of Genetics and Biotechnology
Amino acid composition and mineral bioavailability: Important feed quality traits in cereals Preben Bach Holm University of Aarhus Faculty of Agricultural Sciences Department of Genetics and Biotechnology
Amino Acid Oxidation and the Urea Cycle
 Amino Acid Oxidation and the Urea Cycle Amino Acids: Final class of biomolecules whose oxidation contributes significantly to the generation of energy Undergo oxidation in three metabolic circumstances
Amino Acid Oxidation and the Urea Cycle Amino Acids: Final class of biomolecules whose oxidation contributes significantly to the generation of energy Undergo oxidation in three metabolic circumstances
Nitrogen Metabolism. Overview
 Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
What Are Proteins? Lecture 9: Proteins. Proteins: large complex molecules composed of amino acids. Nutrition 150 Shallin Busch, Ph.D.
 What Are Proteins? Lecture 9: Proteins Nutrition 150 Shallin Busch, Ph.D. Proteins: large complex molecules composed of amino acids. Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen Primary source of nitrogen
What Are Proteins? Lecture 9: Proteins Nutrition 150 Shallin Busch, Ph.D. Proteins: large complex molecules composed of amino acids. Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen Primary source of nitrogen
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Evolution Name: Period Date :
 LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
PROTEIN. By: Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology UPM
 PROTEIN By: Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology UPM OBJECTIVES OF THE LECTURE By the end of this lecture, student can: Define
PROTEIN By: Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology UPM OBJECTIVES OF THE LECTURE By the end of this lecture, student can: Define
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A
 Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Should I Eat More Protein?
 Should I Eat More Protein? The undeniable fact that muscles are very rich in protein has led to a huge dietary protein supplement industry. A quick Internet search gave 74,023 pages with stuff about this.
Should I Eat More Protein? The undeniable fact that muscles are very rich in protein has led to a huge dietary protein supplement industry. A quick Internet search gave 74,023 pages with stuff about this.
The role of proteins and amino acids in food intake and satiety
 The role of proteins and amino acids in food intake and satiety Daniel TOME AGROPARISTECH Departement of Life Sciences and Health INRA, UMR914 Nutrition physiology and ingestive behavior, Paris, France
The role of proteins and amino acids in food intake and satiety Daniel TOME AGROPARISTECH Departement of Life Sciences and Health INRA, UMR914 Nutrition physiology and ingestive behavior, Paris, France
ENDURANCE SPORTS NUTRITION
 ENDURANCE SPORTS NUTRITION Complex carbohydrates with low glycemic index Simple carbohydrates with high glycemic index + complex carbs + proteins + electrolytes Simple carbs + complex carbs + proteins
ENDURANCE SPORTS NUTRITION Complex carbohydrates with low glycemic index Simple carbohydrates with high glycemic index + complex carbs + proteins + electrolytes Simple carbs + complex carbs + proteins
Biomolecules: amino acids
 Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids. Table of a-amino Acids Found in Proteins
 Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية
 قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Dr.Diala
 number 32 Done by Mousa Salah Corrected by Bahaa Najjar Doctor Dr.Diala 1 P a g e In the last lecture we talked about the common processes between all amino acids which are: transamination, deamination,
number 32 Done by Mousa Salah Corrected by Bahaa Najjar Doctor Dr.Diala 1 P a g e In the last lecture we talked about the common processes between all amino acids which are: transamination, deamination,
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1. Body weight and fat mass of AdicerKO mice.
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1. Body weight and fat mass of AdicerKO mice. Twelve week old mice were subjected to ad libitum (AL) or dietary restriction (DR) regimens for three months. (A) Body
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1. Body weight and fat mass of AdicerKO mice. Twelve week old mice were subjected to ad libitum (AL) or dietary restriction (DR) regimens for three months. (A) Body
Outline. Ø Standard Recommendations. Ø Minimum / Optimal / Maximum CONFUSION? Ø Quality Ø Impact of Shifting from Animal to Plant-Based Proteins
 Protein 101 Outline Ø Standard Recommendations Ø Minimum / Optimal / Maximum CONFUSION? Ø Quality Ø Impact of Shifting from Animal to Plant-Based Proteins Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI) Dietary Guidelines
Protein 101 Outline Ø Standard Recommendations Ø Minimum / Optimal / Maximum CONFUSION? Ø Quality Ø Impact of Shifting from Animal to Plant-Based Proteins Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI) Dietary Guidelines
The molecule that serves as the major source of readily available body fuel is: a. fat. b. glucose. c. acetyl CoA. d. cellulose.
 The molecule that serves as the major source of readily available body fuel is: a. fat. b. glucose. c. acetyl CoA. d. cellulose. Dietary fats are important because: a. they keep blood pressure normal.
The molecule that serves as the major source of readily available body fuel is: a. fat. b. glucose. c. acetyl CoA. d. cellulose. Dietary fats are important because: a. they keep blood pressure normal.
Preface to the Second Edition... xv Preface to the First Edition... xvii Author... xix. Introduction
 Contents Preface to the Second Edition... xv Preface to the First Edition... xvii Author... xix Part I The Theory Chapter 1 Proteins and Amino Acids... 3 Introduction... 3 Amino Acids... 4 Peptide Linkage...
Contents Preface to the Second Edition... xv Preface to the First Edition... xvii Author... xix Part I The Theory Chapter 1 Proteins and Amino Acids... 3 Introduction... 3 Amino Acids... 4 Peptide Linkage...
Laura Hernandez, MBA RD LD Registered Dietitian KC Bariatric Shawnee, KS
 Laura Hernandez, MBA RD LD Registered Dietitian KC Bariatric Shawnee, KS Protein: What Is It? The word protein is derived from the Greek word prōteios which means primary or of prime importance. Proteins
Laura Hernandez, MBA RD LD Registered Dietitian KC Bariatric Shawnee, KS Protein: What Is It? The word protein is derived from the Greek word prōteios which means primary or of prime importance. Proteins
Nitrogen Metabolism. Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18
 Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
0010 Amino Acids 40 Profile - Plasma
 Accession #: Order #: G1234567 Date Collected: Date Received: 01/22/2013 Reference #: Patient: Date of Birth: 02/05/1962 Date of Report: Telephone: 7704464583 Ordering Physician: 1234 Main St. Anywhere,
Accession #: Order #: G1234567 Date Collected: Date Received: 01/22/2013 Reference #: Patient: Date of Birth: 02/05/1962 Date of Report: Telephone: 7704464583 Ordering Physician: 1234 Main St. Anywhere,
CS612 - Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Lynne A. Wolfe, MS, ACNP, PNP, BC Department of Genetics Yale School of Medicine
 Lynne A. Wolfe, MS, ACNP, PNP, BC Department of Genetics Yale School of Medicine Harvey Levy, MD Mark Korson, MD Piero Rinaldo, MD, PhD Larry Sweetman, PhD K. Michael Gibson, PhD Charlie Roe, MD Jerry
Lynne A. Wolfe, MS, ACNP, PNP, BC Department of Genetics Yale School of Medicine Harvey Levy, MD Mark Korson, MD Piero Rinaldo, MD, PhD Larry Sweetman, PhD K. Michael Gibson, PhD Charlie Roe, MD Jerry
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
9/16/15. Properties of Water. Benefits of Water. More properties of water
 Properties of Water Solid/Liquid Density Water is densest at 4⁰C Ice floats Allows life under the ice Hydrogen bond Ice Hydrogen bonds are stable Liquid water Hydrogen bonds break and re-form Benefits
Properties of Water Solid/Liquid Density Water is densest at 4⁰C Ice floats Allows life under the ice Hydrogen bond Ice Hydrogen bonds are stable Liquid water Hydrogen bonds break and re-form Benefits
Lecture 5: Cell Metabolism. Biology 219 Dr. Adam Ross
 Lecture 5: Cell Metabolism Biology 219 Dr. Adam Ross Cellular Respiration Set of reactions that take place during the conversion of nutrients into ATP Intricate regulatory relationship between several
Lecture 5: Cell Metabolism Biology 219 Dr. Adam Ross Cellular Respiration Set of reactions that take place during the conversion of nutrients into ATP Intricate regulatory relationship between several
SCBC203 Amino Acid Metabolism
 Breakdown of proteins Route I: Dietary protein breakdown SCBC203 Amino Acid Metabolism Dr Sarawut Jitrapakdee Professor of Biochemistry Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science Mahidol University
Breakdown of proteins Route I: Dietary protein breakdown SCBC203 Amino Acid Metabolism Dr Sarawut Jitrapakdee Professor of Biochemistry Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science Mahidol University
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, Name: (print)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Molecular Biology. general transfer: occurs normally in cells. special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions.
 Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
AMINO ACID METABOLISM
 AMINO ACID METABOLISM Synthesis of Urea in Liver The series of reactions that form urea is known as the Urea Cycle or the Krebs-Henseleit Cycle. The urea cycle operates only to eliminate excess nitrogen.
AMINO ACID METABOLISM Synthesis of Urea in Liver The series of reactions that form urea is known as the Urea Cycle or the Krebs-Henseleit Cycle. The urea cycle operates only to eliminate excess nitrogen.
Optimizing Physical Performance: The Science of Supplementation
 Optimizing Physical Performance: The Science of Supplementation There are many different supplements marketed as performance enhancers in the world of sports nutrition. With athletes trying to find an
Optimizing Physical Performance: The Science of Supplementation There are many different supplements marketed as performance enhancers in the world of sports nutrition. With athletes trying to find an
Biochemistry - I. Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I
 Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I Hello, welcome to the course Biochemistry 1 conducted by me Dr. S Dasgupta,
Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I Hello, welcome to the course Biochemistry 1 conducted by me Dr. S Dasgupta,
CHM333 LECTURE 6: 1/25/12 SPRING 2012 Professor Christine Hrycyna AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID:
 AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
Chemistry 121 Winter 17
 Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Metabolism of amino acids I. Josef Fontana
 Metabolism of amino acids I Josef Fontana EC Overview of the lecture Introduction to protein and amino acids metabolism Metabolic pathways of amino acids Transamination Conversion glutamate - glutamine
Metabolism of amino acids I Josef Fontana EC Overview of the lecture Introduction to protein and amino acids metabolism Metabolic pathways of amino acids Transamination Conversion glutamate - glutamine
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an
 Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
Nitrogen Metabolism. Overview
 Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
ANSC 619 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIES. Muscle as Food
 I. Protein in the diet A. Function ANSC 619 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIES Muscle as Food 1. To provide amino acids, not protein. Muscle as Food 2. To prevent protein breakdown, diet must
I. Protein in the diet A. Function ANSC 619 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIES Muscle as Food 1. To provide amino acids, not protein. Muscle as Food 2. To prevent protein breakdown, diet must
LESSON 2.4 WORKBOOK. Part two: Glucose homeostasis in the blood Un-Storing energy
 DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Fasting A state of abstinence from all food or drinks that provide calories. For a complete list of defined terms, see the Glossary. LESSON 2.4 WORKBOOK Part two: Glucose homeostasis
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Fasting A state of abstinence from all food or drinks that provide calories. For a complete list of defined terms, see the Glossary. LESSON 2.4 WORKBOOK Part two: Glucose homeostasis
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy
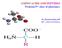 AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]
![Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]](/thumbs/84/90818314.jpg) Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules. Biological Macromolecules. Lipids
 Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules
 Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
Adverse Effects of Amino Acids
 Adverse Effects of Amino Acids AA is assumed that any surplus ingested by animals is disposed of without adverse effects. The ruminant has endowed a detoxification mechanisms by microbial metabolism of
Adverse Effects of Amino Acids AA is assumed that any surplus ingested by animals is disposed of without adverse effects. The ruminant has endowed a detoxification mechanisms by microbial metabolism of
UCLA Nutrition Bytes. Title. Permalink. Journal ISSN. Author. Publication Date
 UCLA Nutrition Bytes Title Whey Protein- The Role of Protein Supplementation in Resistance Training Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/07p2v5wd Journal Nutrition Bytes, 10(2) ISSN 1548-601X Author
UCLA Nutrition Bytes Title Whey Protein- The Role of Protein Supplementation in Resistance Training Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/07p2v5wd Journal Nutrition Bytes, 10(2) ISSN 1548-601X Author
Properties of amino acids in proteins
 Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
0010 Amino Acid Analysis - 40 Plasma
 770.446.5483 770.441.2237 This report contains reference range adjustments from routine revalidation procedures. It also contains the following three upgrades: 1) The amino acids have been reorganized
770.446.5483 770.441.2237 This report contains reference range adjustments from routine revalidation procedures. It also contains the following three upgrades: 1) The amino acids have been reorganized
Hormonal regulation of. Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara
 Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
ProHydrolase Clinical Phase II Study. Deaton, J.; Dawson, H.; Davidson, J.
 Clinical Phase II Study Deaton, J.; Dawson, H.; Davidson, J. Clinical Phase II Study University of Wisconsin - La Crosse Office of Research and Sponsored Programs, Morris Hall 7 State St La Crosse, WI
Clinical Phase II Study Deaton, J.; Dawson, H.; Davidson, J. Clinical Phase II Study University of Wisconsin - La Crosse Office of Research and Sponsored Programs, Morris Hall 7 State St La Crosse, WI
(30 pts.) 16. (24 pts.) 17. (20 pts.) 18. (16 pts.) 19. (5 pts.) 20. (5 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
Protein Supplementation Risk v. Reward
 Protein Supplementation Risk v. Reward Developed by: Fabio Comana, MA., MS. NASM CPT, CES & PES; NSCA CSCS; ACSM EP-C; ACE CPT & HC; CISSN Engage.. Ignite.. Empower.. Introduction Skeletal Muscle: MPS
Protein Supplementation Risk v. Reward Developed by: Fabio Comana, MA., MS. NASM CPT, CES & PES; NSCA CSCS; ACSM EP-C; ACE CPT & HC; CISSN Engage.. Ignite.. Empower.. Introduction Skeletal Muscle: MPS
The Science of Protein. The Continued Exploration of the Impact of High-Quality Protein on Optimal Health
 The Science of Protein The Continued Exploration of the Impact of High-Quality Protein on Optimal Health 1 The Following Will Be Discussed 1. What is Protein? 2. Evolution of Protein Research 3. Protein
The Science of Protein The Continued Exploration of the Impact of High-Quality Protein on Optimal Health 1 The Following Will Be Discussed 1. What is Protein? 2. Evolution of Protein Research 3. Protein
Biol 219 Lec 7 Fall 2016
 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Energy to form ATP Cellular Respiration and Metabolism Glucose ATP Pyruvate Lactate Acetyl CoA NAD + Introducing The Players primary substrate for cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Energy to form ATP Cellular Respiration and Metabolism Glucose ATP Pyruvate Lactate Acetyl CoA NAD + Introducing The Players primary substrate for cellular respiration
Protein: Amino Acids. Chapter 6
 Protein: Amino Acids Chapter 6 Chemist s View of Protein Amino Acid Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen Each amino acid has an amino group, an acid group, a hydrogen atom, and a side group. It
Protein: Amino Acids Chapter 6 Chemist s View of Protein Amino Acid Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen Each amino acid has an amino group, an acid group, a hydrogen atom, and a side group. It
Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #1, 100 points (7 pages)
 Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #1, 100 points (7 pages) READ THIS: Take a numbered test and sit in the seat with that number on it. Remove the numbered sticker from the desk, and stick it on the
Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #1, 100 points (7 pages) READ THIS: Take a numbered test and sit in the seat with that number on it. Remove the numbered sticker from the desk, and stick it on the
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Metabolic integration and Regulation
 Metabolic integration and Regulation 109700: Graduate Biochemistry Trimester 2/2016 Assistant Prof. Dr. Panida Khunkaewla kpanida@sut.ac.th School of Chemistry Suranaree University of Technology 1 Overview
Metabolic integration and Regulation 109700: Graduate Biochemistry Trimester 2/2016 Assistant Prof. Dr. Panida Khunkaewla kpanida@sut.ac.th School of Chemistry Suranaree University of Technology 1 Overview
Definitions and Biochemical Pathways History (Literature Review) Use of Lipids to Build Proteins: Lab Mice & Polar Bears
 Definitions and Biochemical Pathways History (Literature Review) Use of Lipids to Build Proteins: Lab Mice & Polar Bears Use of Carbohydrates to Build Proteins: Tilapia Role of Gut Microbiome: Tilapia
Definitions and Biochemical Pathways History (Literature Review) Use of Lipids to Build Proteins: Lab Mice & Polar Bears Use of Carbohydrates to Build Proteins: Tilapia Role of Gut Microbiome: Tilapia
AMINO ACID METABOLISM
 AMINO ACID METABOLISM PHL-285 Biochemistry-2 Mahmoud N. Nagi, Ph.D. Professor of Biochemistry Overview of amino acid metabolism. Classification of amino acids. Biosynthesis of nonessential amino acids.
AMINO ACID METABOLISM PHL-285 Biochemistry-2 Mahmoud N. Nagi, Ph.D. Professor of Biochemistry Overview of amino acid metabolism. Classification of amino acids. Biosynthesis of nonessential amino acids.
Quantity Per Serving. 27 grams
 Whey Protein Isolate Nutrient Details Certain nutrients are included or omitted in our Regular Whey Isolate formula for specific reasons backed by scientific research and development Nutrient Type Protein
Whey Protein Isolate Nutrient Details Certain nutrients are included or omitted in our Regular Whey Isolate formula for specific reasons backed by scientific research and development Nutrient Type Protein
