Impact of Fenthion on Ionic Regulation in the Blood of Freshwater Fish, Cyprinus carpio (Linn).
|
|
|
- Lester Armstrong
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IOSR Journal Of Environmental Science, Toxicology And Food Technology (IOSR-JESTFT) e-issn: ,p- ISSN: Volume 8, Issue 1 Ver. I (Jan. 2014), PP Impact of Fenthion on Ionic Regulation in the Blood of Freshwater Fish, Cyprinus carpio (Linn). Leena Muralidharan V.K.K.Menon collegeof com& Sharad Dighe college of science, Bhandup (east), Mumbai 42.,PG Dept of zoology,mumbai University Maharastra,India. Abstract: The blood of fresh water, edible fish, Cyprinus carpio was exposed to sub lethal concentration of fenthion for 24, 48, 72 and 96 h to evaluate alterations in the levels of minerals i.e., sodium, potassium, chloride, calcium and magnesium. The increased mineral sodium and potassium play an important role in neuromuscular excitability, acid-base balance and increased osmotic pressure of the fish. The decreased calcium is of great importance in blood coagulation, muscle contraction and nerve transmission of the fish. The increased magnesium participates in principal metabolic activities, in formation of bones and teeth. Reduction in Chloride ion contents may be due to blockage of chloride ion from gut into serum due to Fenthion stress. Key Words: Cyprinus carpio; calcium, chloride; magnesium;, potassium; sodium I. Introduction Ionic regulation is the capacity of an organism to build up and maintain specific ionic gradients between body fluids and the cell fluids. The regulation of ionic composition of the body fluid is presumed to have adaptive significance for the organism (Burton 1973). Unfortunately, in today s world all the water resources such as lakes, ponds, rivers, sea etc. have become a common damp yard for domestic sewage, exposure for oils, industrial chemicals, pesticides, metals etc. Investigations carried out by [1]-to[22] have shown that pesticide impair osmoregulatory ability in many aquatic forms. The ionic regulation studies contribute valuable information to the role of ions in the blood chemistry of aquatic animals. Thus, the purpose of the present study was to know or study the influence of three sublethal doses of Fenthion for 60 days chronic exposure on blood electrolytes like Na +, K +, Ca ++, Mg ++ and Cl in the fish Cyprinus carpio. II. Materials And Methods: The fishes were brought to the laboratory and were acclimatized following the standard procedure. After acclimatization healthy looking fish were selected and divided into different groups of eight each and were exposed to 0.38, and mg/l Fenthion for a period of 60 days. A control group was also maintained in duplicate for comparison. All the other conditions such as feeding, changing of water, maintaining ph, 02, temp. etc. were retained constant throughout the experimental period. The blood was removed at the end of 60 days test period from exposed and control fish by cutting their tail region. At first the trunk region was blotted with sterile.cloth and the blood was drawn into 2.5 c.c. disposable plastic syringe equipped with Z1 gauge short bevel needle. The collected fresh blood samples were centrifuged at a speed of 1000 R.P.M. for 10 minutes so as to separate blood corpuscles and serum. Clear serum thus obtained was used for further analysis. For determination of Na + and K + a flame photometer model was used as per method described by [23].The calcium content of blood was estimated by Clark-collip method which is modification of Kramer - Tisdals method as described by [23].The magnesium content of the blood was estimated by the method of [24] as described by [23]and[25].Estimation of chloride ion was done by following the method as described by [23]. III. Results And Discussion: The values of blood ions Na +, K +, Ca ++, Mg + and Cl in control and exposed fish are presented in table 1; Fig. 4a. Sodium (Na + ): Sodium is the major and chief cation of blood plasma. The important function of Na + in animal body appears to be in connection with osmoregulation and acid base balance besides catalytic effect on enzyme activity. Elevation in sodium ion level was observed in fish chronically exposed to 0.38 and mg/l of Fenthion while at mg/l Fenthion, not much difference in sodium ion levels was noted as compared to control ones. (Table.1; Fig. 4a.) Very few workers have experimented on ionic changes in blood of fresh water fish exposed to toxic substances. [3] observed elevated sodium level in buffer exposed to Endrin and suggested that this elevation is due to the loss of sodium ion from liver into the serum due to damage caused to liver. According to [4], serum osmolarity of the highest Endrin dosed trout, increased 4.4% over that of exercised control whereas osmolarity of exercised control increased only 2% above that of non exercised control and he 63 Page
2 further suggested that this elevation could be due to alternated cellular biopotentials. Kinter and Janicki 1971) noted elevation of sodium Anguilla prostrate exposed to DDT. According to [15],1[19],[20] ionic regulatory changes and acid base disturbance caused was due to alteration of gill function when rainbow trout Salmo gairdneri was exposed to zinc. [27], reported that ATPase enzyme is believed to constitute the pump responsible for the outward transport of Na + and inward movement of K + across the gill epithelium. According to [28] inhibition of ATPase and inhibition of oxygen uptake in the tissues may lead to disruption of osmoregulation in the fish. Taking the support of these different views given by different workers, it may be suggested that in the present study, the elevation of sodium ion level in serum of exposed Cyprinus carpio could be due to oxygen debt, ATPase enzyme inhibition and histopathological damage to gill and liver tissues. Fig1-6,table5.1 Potassium (K + ): Here, in the present study, potassium content in the experimental blood was elevated as compared to control (Table No..1; Fig. 4a). Potassium is an important constituent of extra cellular fluid having a great influence on muscular activity. According to [12] potassium is the main intra cellular cation involved in physiological functions like acid base balance, osmotic pressure, nerve and muscle functions. It also helps in enzymatic transfer of phosphate from ATP to pyruvic acid and undoubtedly has a role in a number of basic cellular enzymatic functions. According to [29] exposure to sublethal concentrations of DDT and Endrin in fresh water fishes Anguilla vulgans and Mulgil cephalus impaired liver functions and this is evident from transfer of major cations from hepatic tissue to serum. [3] observed elevation in potassium content in buffer exposed to Endrin. [4] experimented on Endrin (0.01 ppb 96 hr] dosed trout and reported that serum potassium level increased while potassium content in liver was lower than control and suggested that elevation of K + in serum was due to transfer of cations from injured hepatic tissue into serum. Hyperkalemia was noted in Cyprinus carpio exposed to Fenthion in the present Study. According to [29], if there is no damage to gut epithelium, potassium which is more concentrated in plasma than in surrounding water would be expected to move from blood into gut resulting in lower potassium level. Since in the present work no such reduction in potassium level in the serum was observed, it can be interpreted that gut epithelium damage caused accumulation of potassium ion in blood resulting in hyperkalemia. Elevated level could also be due to interference of Fenthion in enzyme activity responsible for the active removal and excretion of potassium. Further, the damage caused, to gill and liver tissues observed might also be the reason in active expulsion of potassium ion. (fig1-6&fig4a). Calcium (Ca ++ ): Ionised calcium has important functions in blood coagulation. It regulates water and inorganic ions through cell membrane and contributes in the maintenance of action potential in muscle and nerve cells. [2], reported hypercalcemic condition in Cyprinodont fish exposed to mercury. Although they suggested that liver damage was the most reasonable explanation but also at the same time elaborated that damaged gill epithelium causes increase in permeability, and the damage to intestinal mucosa causes free exchange of ions between gut content and submucosal bed, thus overall causing active expulsion of the electrolytes. In the present context hypercalcemia (table.1) observed in Cyprinus carpio supports the above suggestion (fig1-8). [14] related increase in calcium ion in Aldrin exposed fish with damage caused 'to liver and according to her increase was due to' leakage of ions to serum. [4] reported increase in calcium ion in goldfish exposed to Endrin chronically. According to [11] increased calcium ion in Channa puncfatus exposed to 2, 3-4 triamino azo benzene could be due to transfer of calcium from other tissues to serum. Thus, hypercalcemia observed in present work could be attributed to leakage caused due to histopathological damage of intestine epithelium, liver and gill (fig1-8) Secondly, it can also be due to impairment in active expulsion of electrolytes. Magnesium (Mg ++ ): Magnesium ion activity extends to all major anabolic and catabolic processes involving the main metabolites, It activates large number of enzymes concerned in intermediatery metabolism. Hypermagnssia was observed in the present study in all the exposed fishes Table.1; Fig. 4a. [11] reported similar increase in magnesium ions in 2, 3-4 triamino azobenzene exposed Channa punctatus and suggested that it could be due to leakage of magnesium ions caused by tissue injury. [4] reported elevation in magnesium ions in serum of Endrin exposed goldfish. Excess of magnesium ion in serum can occur when absorption from gut exceeds excretion by kidneys. Hypermagnesia, can also be characterised from the depression of central nervous system, mentioned by Hawk et. al. (1965). According to [29] magnesium is needed for activation of alkaline phosphatase enzyme which if inhibited results in the liberation of free Mg +2 ions into the blood causing increase of magnesium in the blood. Alkaline phosphatase inhibition table2 observed can be related with the, results obtained here. 64 Page
3 Hypermagnesia can also be due to impaired mechanism of excretion as reported by [12] who further stated that failure in active expulsion of ion results in accumulation of Mg +2 ion in serum blood. In the present work hypermagnesia(table.1)can be related to damage caused to gill epithelium, Liver & kidney tissues, thus causing leakage of Mg +2 ions into the blood circulatory system or it could also be due to inhibition in enzyme activity and impaired excretory mechanism(.fig4,5 &table5.1) Chloride (Cl ): Chloride ion is one of the major anions concerned in osmotic pressure regulation.hypochloremia was observed in the present work (table.1)when Cyprinus carpio was exposed to different doses of Fenthion for 60 days.[4],[10],[30] observed similar decrease in chloride ion in different species of fish exposed to insecticides. [29] reported that the depletion in chloride ion could be due to the damage caused to gut epithelium which prevented the movement of chloride ions from gut into serum in cyprinodont fish exposed to Mercury. In the present study, reduction in Chloride(Table.1&fig4a) ion contents may be due to blockage of chloride ion from gut into serum due to Fenthion stress or it could also be due to leakage of Cl from tissues to surrounding water due to insecticide stress.(fig6&7) IV. Conclusion: A comparison of control with chronically exposed Cyprinus carpio to Fenthion for period of 60 days exhibited elevation in sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium & depletion in chloride ion levels. This could be attributed to ATPase inhibition, damage caused to the important tissues and interference of Fenthion in transport of ions in blood. References: [1] Burton, R.F. (1973). The significance of ionic concentrations in the internal media of animals, Biol. Rev. 48, [2] Baldwin, E. (1949). An introduction to comparative biochemistry. 3rd Ed. Comp. Univ. Press, Lond. 164 pp. [3] Eisler, R. and Edmounds, H. (1966). Effect of Endrin on blood and tissue chemistry of marine fish. Trans Am. Fish Soc. 95, [4] Grant. B.F. and Mehrle, P.M. (1970). Chronic Endrin poisoning in gold fish Carassinus auratus. J. Fish. Res. Board. Can. 27, [5] Davis, P.W., Friedoff, J.M. and weedemeyer, G.A. (1972). Organochlorine insecticide and polychlorinated phenyl (PCB) inhibition of Na ATPase in rainbow trout. Bull. Env. Cont. Toxicol. 8, [6] Desaiah, D. Cutkamp, C.K. Yap, H.H. and Konch. R.B. (1972). Inhibition of oligomycin senstitive and insensitive magnessim adenosine triphoshate activity in fish by polychlorinated biphenyl. Biochem. Pharmacol. 21, [7] Cutkamp, C.K., Yah, H.H., Cheng, Y.Y. and Kouch, R.B. (1972). ATPase activity in fish tissue homogenate and inhibitory effects of DDT and related compound. Chem. Biol. Interaction. 3:4, [8] Kinter,W.B. & Janicki, R.H. (1971). DDT disrupted osmoregulation event in the intestine of the eel Anguilla adapted to sea water. Science, 173, [9] Grant, B.F. and Mehrle, P.M. (1973). Endrin toxicosis in rainbow trout Salmo gairdneri. J.Fish Res. Board. Can. 30, [10] Haux, G. and Larsson, A. (1979). Effects of DDT on blood plasma electrolytes in the Platichthys flasus in hypotonic brackish water. Ambio. 8, [11] Goel, K.A. and Garg_ V. (1980) Triamino ozobenzene induced heamatological biochemical anomalies in fish C. puntatus. Bull. Env.,Conl. Toxic. 25, [12] Larsson, A., Bangston, l3.l. and Haux, C. (1981). Disturbed ion balance in flounder Platichthys falsus exposed to sublethal levels of Cadmium. Aquatic Toxicol. Vol. 1, No.1, [13] Weisbart, F.M. and Feinner,D (1974). Sublethal effect of DDT. on osmotic ionic and ionic regulation by gold fish Caraniuss auratus Can. J. Zool. 52(6), [14] Yagana Bano (1982). Effects of Aldrin on serum and liver constituents of fresh water cat fish Clarius batrachus. Proc. Ind. Acad. Sci. (Animal Sci). Vol. 91, No.1, Jan pp. [15] Spray Dauglas, J. and Chris, M.W. (1985). Can.J.Fish. Aquat. sci. 42(3) (Abstract). [16] Shastry, K.V. AND Dasgupta, A., 1991: Effect of nuvacron on the nutritive value of freshwater teleost fish, Channa punctatus. J. Environ. Biol., 12 (3): [17] Singh, N.N. AND Srivastava, A.K., 1998: Formothion induced biochemical changes inblood and tissues of freshwater catfish, Heteropneustes fossilis. Malys. J.Appl. Biol., 27 (1): [18] Singh, N.N., Srivastava, A.K. and Srivastava, A.K., 1993: Biochemical changes in thefreshwater Indian catfish, Heteropneustes fossilis following exposure to sublethal concentration of aldrin. J. Environ. Biol., 14 (1): [19] Mishra, D., Srivastaa, S., Srivastava, S.K. AND Srivastav,A. K., 2001: Plasma calcium and inorganic phosphate levels of a freshwater catfish, Heteropneustesfossilis in response to cypermethrin treatment. J. Ecophysiol. Occup. Hlth., l: [20] Tseng Y.C, Hwang P.P:2008: Some insights into energy metabolism for ionic regulation in fishes.c.biochem.physio.c.toxicol.pharmacol.,nov 148 (4) [21] HWANG,P.P, LEE.T.H ANDLIN,L.Y 2011: Ionic regulation in fish gills recent progress inthecellularandmolecularmechanisms.am.j.phy.regul.integ.comp.physio.,july301(1) [22] Abdul naveed.,venkateshwarlu.p and Jannaiah.C. (2011):Impact of Triazophos on Ionic Regulation in the Blood of Freshwater Fish, Channa punctatus (Bloch),British Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology 2(3): [23] Hawk, P.B., Oser, B.l.. and Summerson W.H. (1965). Hawk practical physiological chemistry 4th ed. ILL. Oser Mcgraw hill book comp. Inc., N.Y. Toranto, London. [24] Neill. P.W. and Neely, R.A. (1956). As cited by Varley.H. (1963). 409 pp. [25] Varley, H. (1953). Practical clinical Biochemistry. The White Frairs Press Ltd., London. [26] Janicki, R.H. and Kinter, W.B. (1971). Nature, Page
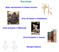
4 [27] Adam, B.L., Zaugg, W.S. and Mc1ain.I,.R. (1973). Temperature effects on trout Salmo gairdneri as measured by gill sodium - Potassium stimulated adenosine triphosphatase. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 44 A [28] Koundiyu, P.K. and Ramamoorthi.R. (1981). Tissue respiration of T.mossambica exposed to sublethal conc, of Sumithion and Sevinin,Current Sci. No. 5, Vol. 50, p. 21. [29] Hilmy, A.H., Shabana, M.B. and Saiyed, M.M. (1982). Ionic regulation of the blood in the cyprinodont Aphanius under the effect of experimental Mercury pollution water. Soil. Pollution. 18, [30] Mishra,,T.S. and Srivastava, A.K. (1983). Malathion induced haematological and biochemical change in the Indian cat fish' Heteropneustus fossils.env. Res. 30, Table:.1 CHANGES IN IONIC CONSTITUENTS IN CYPRINUS CARPIO WHEN EXPOSED TO FENTHION CHRONICALLY FOR A PERIOD OF 60 DAYS. = Standard deviation (5 determir1ations) in %. * = P < 0.05 % = Percent change from control after 60 days exposure to Fenthion. ** = P < Fig1:Gill of fish exposed to 0.38 mg/ml.fenthion for 60 days exposure showing vacuolated, deformed and shortened secondary lamellae (arrow mark) 66 Page
5 Fig2:Gills of fish exposed to0.193 mg/ml fenthion for 60 days showing ruptured secondary lamellae. Fig 3:Gill of fish exposed to 0.96 mg/ml fenthion for 60 days showing disoriented epithelial cells and swollen chloride cells. Fig 4:Liver of fish exposed to mg/ml showing pycnosis and large number of necrotic regions. 67 Page
6 Fig5:Liver of fish exposed to 0.38 mg/ml fenthion showing vacuolated, cloudy swollen, disintegrated and extremely ruptured hepatic cells. Fig6 Intestine of of fish exposed to 0.38mg/l Fenthion showing epithelial cell lesion, shrunken and extremely damaged villi. fig7:intestine of fish exposed to 0.096mg/l Fenthion showing ruptured epithelial cells increase in number of goblet cells. 68 Page
7 fig8: Kidney of fish exposed to0.193 mg/ml fenthion showing extreme degeneration of renal cells. 69 Page
8 70 Page
Journal of Biological and Chemical Research An International Peer Reviewed / Referred Journal of Life Sciences and Chemistry
 Sumithion Intoxication on Serum Inorganic Phosphorous Levels of Mud Eel, Amphipnous cuchia By T.S. Naqvi ISSN 2319-3077 Online/Electronic ISSN 0970-4973 Print Index Copernicus International Value IC Value
Sumithion Intoxication on Serum Inorganic Phosphorous Levels of Mud Eel, Amphipnous cuchia By T.S. Naqvi ISSN 2319-3077 Online/Electronic ISSN 0970-4973 Print Index Copernicus International Value IC Value
Biochemical Profile of Channa gachua (Ham.) Exposed to Sub-lethal Doses of Dichlorvos (DDVP)
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Toxicology Volume 8 Number 1 Biochemical Profile of Channa gachua (Ham.) Exposed to Sub-lethal Doses of Dichlorvos (DDVP) S Mastan, P Ramayya Citation S Mastan, P Ramayya.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Toxicology Volume 8 Number 1 Biochemical Profile of Channa gachua (Ham.) Exposed to Sub-lethal Doses of Dichlorvos (DDVP) S Mastan, P Ramayya Citation S Mastan, P Ramayya.
Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1
 Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1 The body fluids are solutions of inorganic and organic solutes. The concentration balance of the various components is maintained in order for the cell and tissue
Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1 The body fluids are solutions of inorganic and organic solutes. The concentration balance of the various components is maintained in order for the cell and tissue
Transport of Solutes and Water
 Transport of Solutes and Water Across cell membranes 1. Simple and Facilitated diffusion. 2. Active transport. 3. Osmosis. Simple diffusion Simple diffusion - the red particles are moving from an area
Transport of Solutes and Water Across cell membranes 1. Simple and Facilitated diffusion. 2. Active transport. 3. Osmosis. Simple diffusion Simple diffusion - the red particles are moving from an area
Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard. Biology Level 3
 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Biology Level 3 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard 91604 Demonstrate understanding of how an animal maintains a stable internal environment
Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Biology Level 3 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard 91604 Demonstrate understanding of how an animal maintains a stable internal environment
CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Body fluid refers to body water and its dissolved substances. B. Regulatory mechanisms insure homeostasis of body fluids since their malfunction may seriously
CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Body fluid refers to body water and its dissolved substances. B. Regulatory mechanisms insure homeostasis of body fluids since their malfunction may seriously
Biochemical investigations on monocrotophos exposed fish, Channa gachua (Ham.)
 Current World Environment Vol. 1(2), 189-194 (2006) Biochemical investigations on monocrotophos exposed fish, Channa gachua (Ham.) PRAKASH CHANDER KOUL, S.A. MASTAN, S.S. MUDASER ANDRABI, JAVED AHMED GANAIE¹
Current World Environment Vol. 1(2), 189-194 (2006) Biochemical investigations on monocrotophos exposed fish, Channa gachua (Ham.) PRAKASH CHANDER KOUL, S.A. MASTAN, S.S. MUDASER ANDRABI, JAVED AHMED GANAIE¹
PHYSIOLOGY OF LOW TEMPERATURE ACCLIMATION IN TROPICAL POIKILOTHERMS. BY KANDULA PAldPAPATHI RAO
 PHYSIOLOGY OF LOW TEMPERATURE ACCLIMATION IN TROPICAL POIKILOTHERMS I. Ionic Changes in the Blood of the Freshwater Mussel, Lamellfdens marginalis, and the Earthworm, LampRo mauritii BY KANDULA PAldPAPATHI
PHYSIOLOGY OF LOW TEMPERATURE ACCLIMATION IN TROPICAL POIKILOTHERMS I. Ionic Changes in the Blood of the Freshwater Mussel, Lamellfdens marginalis, and the Earthworm, LampRo mauritii BY KANDULA PAldPAPATHI
Osmoregulation regulates solute concentrations and balances the gain and loss of water
 Ch 44 Osmoregulation & Excretion Osmoregulation regulates solute concentrations and balances the gain and loss of water Freshwater animals show adaptations that reduce water uptake and conserve solutes
Ch 44 Osmoregulation & Excretion Osmoregulation regulates solute concentrations and balances the gain and loss of water Freshwater animals show adaptations that reduce water uptake and conserve solutes
Sub-Lethal Effect of Cypermethrin on Ca, Mg and Na /K - ATPase Activity in Fresh Water Teleost, Cyprinus carpio
 World Journal of Zoology 10 (3): 168-174, 2015 ISSN 1817-3098 IDOSI Publications, 2015 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjz.2015.10.3.9581 Sub-Lethal Effect of Cypermethrin on Ca, Mg and Na /K - ATPase Activity in Fresh
World Journal of Zoology 10 (3): 168-174, 2015 ISSN 1817-3098 IDOSI Publications, 2015 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjz.2015.10.3.9581 Sub-Lethal Effect of Cypermethrin on Ca, Mg and Na /K - ATPase Activity in Fresh
BY B. PADMANABHANAIDU AND R. RAMAMURTHY Department of Zoology, Sri Venkateswara University, Tirupati, India. {Received 23 May i960)
 J. Exp. Biol. (1961), 38, 35-41 25 With 3 text-figures Printed in Great Britain THE INFLUENCE OF SEX AND SIZE ON THE OSMOTIC PRESSURE, THE CHLORIDE AND THE FREE AMINO ACIDS OF THE BLOOD OF THE FRESHWATER
J. Exp. Biol. (1961), 38, 35-41 25 With 3 text-figures Printed in Great Britain THE INFLUENCE OF SEX AND SIZE ON THE OSMOTIC PRESSURE, THE CHLORIDE AND THE FREE AMINO ACIDS OF THE BLOOD OF THE FRESHWATER
WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM
 WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM Attila Miseta Tamás Kőszegi Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2016 1 Average daily water intake and output of a normal adult 2 Approximate contributions to plasma osmolality
WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM Attila Miseta Tamás Kőszegi Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2016 1 Average daily water intake and output of a normal adult 2 Approximate contributions to plasma osmolality
Comparative Study of Biochemical Alterations Induced by Carbofuran and Malathion on Channa punctatus (Bloch.)
 International Research Journal of Biological Sciences ISSN 2278-3202 Comparative Study of Biochemical Alterations Induced by Carbofuran and Malathion on Channa punctatus (Bloch.) Abstract Muddassir Ahmad
International Research Journal of Biological Sciences ISSN 2278-3202 Comparative Study of Biochemical Alterations Induced by Carbofuran and Malathion on Channa punctatus (Bloch.) Abstract Muddassir Ahmad
Osmoregulation and Osmotic Balance
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44808 1 Osmoregulation and Osmotic Balance OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m44808 1 Osmoregulation and Osmotic Balance OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
Chapter 7. Haematology
 Chapter 7 Haematology INTRODUCTION Currently it has been realized that a large variety of insecticides used extensively to control insect pests and to augment agricultural yield eventually reach the aquatic
Chapter 7 Haematology INTRODUCTION Currently it has been realized that a large variety of insecticides used extensively to control insect pests and to augment agricultural yield eventually reach the aquatic
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 27 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Fluid Compartments and Fluid In adults, body fluids make up between 55% and 65% of total body mass. Body
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 27 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Fluid Compartments and Fluid In adults, body fluids make up between 55% and 65% of total body mass. Body
International Journal of Zoological Investigations
 International Journal of Zoological Investigations Vol. 1, No. 1, 72-76 (2015) International Journal of Zoological Investigations ISSN: XX-XXXX Contents available at Journals Home Page: www.ijzi.net Biochemical
International Journal of Zoological Investigations Vol. 1, No. 1, 72-76 (2015) International Journal of Zoological Investigations ISSN: XX-XXXX Contents available at Journals Home Page: www.ijzi.net Biochemical
THE ACTIVITY AND CHARACTERISTICS OF THE Ca 2+ ATPase OF FISH GILLS IN RELATION TO ENVIRONMENTAL CALCIUM CONCENTRATIONS
 p. Biol. (1981), 90, 115-121 1 3 figures Printed in Great Britain THE ACTIVITY AND CHARACTERISTICS OF THE Ca 2+ ATPase OF FISH GILLS IN RELATION TO ENVIRONMENTAL CALCIUM CONCENTRATIONS BY K. L. SHEPHARD
p. Biol. (1981), 90, 115-121 1 3 figures Printed in Great Britain THE ACTIVITY AND CHARACTERISTICS OF THE Ca 2+ ATPase OF FISH GILLS IN RELATION TO ENVIRONMENTAL CALCIUM CONCENTRATIONS BY K. L. SHEPHARD
Effects of sub-lethal concentrations of zinc on histological changes and bioaccumulation of zinc by kidney of fish Channa punctatus (Bloch)
 Journal of Environmental Biology April 2006, 27(2) 211-215 (2006) Triveni Enterprises, Lucknow (India) For personal use only Free paper downloaded from: www.jeb.co.in Commercial distribution of this copy
Journal of Environmental Biology April 2006, 27(2) 211-215 (2006) Triveni Enterprises, Lucknow (India) For personal use only Free paper downloaded from: www.jeb.co.in Commercial distribution of this copy
Animal Form and Function. Exchange surfaces. Animal Form and Function
 Animal Form and Function Surface:Volume ratio decreases with size Today s topics: Review for exam Physical Constraints affect the design of animals Homeostasis Sensors and effectors Exchange surfaces Design
Animal Form and Function Surface:Volume ratio decreases with size Today s topics: Review for exam Physical Constraints affect the design of animals Homeostasis Sensors and effectors Exchange surfaces Design
Assessment of the distribution of AMG positive material in the brain of largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides
 University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange University of Tennessee Honors Thesis Projects University of Tennessee Honors Program 5-2009 Assessment of the distribution
University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange University of Tennessee Honors Thesis Projects University of Tennessee Honors Program 5-2009 Assessment of the distribution
Impact of dye effluent on Enzymological changes in freshwater fish Oreochromis mossambicus
 IOSR Journal of Biotechnology and Biochemistry (IOSR-JBB) ISSN: 2455-264X, Volume 3, Issue 6 (Nov.- Dec. 2017), PP 34-38 www.iosrjournals.org Impact of dye effluent on Enzymological changes in freshwater
IOSR Journal of Biotechnology and Biochemistry (IOSR-JBB) ISSN: 2455-264X, Volume 3, Issue 6 (Nov.- Dec. 2017), PP 34-38 www.iosrjournals.org Impact of dye effluent on Enzymological changes in freshwater
Awesome Osmosis and Osmoregulation. 2. Describe some of the methods of osmoregulation by freshwater and marine organisms.
 Awesome Osmosis and Osmoregulation Purpose: By the end of this lab students should be able to: 1. Understand osmosis and be able explain the differences between isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solutions.
Awesome Osmosis and Osmoregulation Purpose: By the end of this lab students should be able to: 1. Understand osmosis and be able explain the differences between isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solutions.
RESPIRATORY RESPONSE OF ASIAN CATFISH, CLARIAS BATRACHUS, TO FLUORIDE
 119 Respiratory response of catfish to fluoride 119 RESPIRATORY RESPONSE OF ASIAN CATFISH, CLARIAS BATRACHUS, TO FLUORIDE Anand Kumar, Sandeep Bajpai, Nalini Tripathi, Madhu Tripathi a Lucknow (U.P.),
119 Respiratory response of catfish to fluoride 119 RESPIRATORY RESPONSE OF ASIAN CATFISH, CLARIAS BATRACHUS, TO FLUORIDE Anand Kumar, Sandeep Bajpai, Nalini Tripathi, Madhu Tripathi a Lucknow (U.P.),
EFFECTS OF EXPOSURE TO SUB-LETHAL CONCENTRATIONS OF AMMONIA AND HYPOXIA ON THE SWIMMING PERFORMANCE OF BROWN TROUT (SALMO TRUTTA)
 EFFECTS OF EXPOSURE TO SUB-LETHAL CONCENTRATIONS OF AMMONIA AND HYPOXIA ON THE SWIMMING PERFORMANCE OF BROWN TROUT (SALMO TRUTTA) A. Shingles, School of Biosciences, University of Birmingham, Birmingham,
EFFECTS OF EXPOSURE TO SUB-LETHAL CONCENTRATIONS OF AMMONIA AND HYPOXIA ON THE SWIMMING PERFORMANCE OF BROWN TROUT (SALMO TRUTTA) A. Shingles, School of Biosciences, University of Birmingham, Birmingham,
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance
 Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
DR. SHAMSUL AZAHARI ZAINAL BADARI DEPARTMENT OF RESOURCES MANAGEMENT AND CONSUMER STUDIES FACULTY OF HUMAN ECOLOGY UPM
 DR. SHAMSUL AZAHARI ZAINAL BADARI DEPARTMENT OF RESOURCES MANAGEMENT AND CONSUMER STUDIES FACULTY OF HUMAN ECOLOGY UPM Mineral nutrients are inorganic elements found in food which the body cannot synthesis.
DR. SHAMSUL AZAHARI ZAINAL BADARI DEPARTMENT OF RESOURCES MANAGEMENT AND CONSUMER STUDIES FACULTY OF HUMAN ECOLOGY UPM Mineral nutrients are inorganic elements found in food which the body cannot synthesis.
japonica,' rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri,' European flounder, Platichthys
 FRANKLIN H. EPSTEIN Department of Internal Medicine, ANDRZEJ MANITIUS** Yale University School of Medicine, EDWARD WEINSTEIN * * * New Haven, Conn. 06510 and Bingham Laboratory, Department ADRIAN I. KATZt
FRANKLIN H. EPSTEIN Department of Internal Medicine, ANDRZEJ MANITIUS** Yale University School of Medicine, EDWARD WEINSTEIN * * * New Haven, Conn. 06510 and Bingham Laboratory, Department ADRIAN I. KATZt
Excretion. Consumption = Growth + (Metabolism + SDA) + F(egestion) + U (excretion) Energetics Processes. Hormonal Control
 Excretion Consumption = Growth + (Metabolism + SDA) + F(egestion) + U (excretion) Energetics Processes Hormonal Control Ingestion Storage Lipid Carbohydrate Mobilization Lipid Carbohydrate Protein Adsorption
Excretion Consumption = Growth + (Metabolism + SDA) + F(egestion) + U (excretion) Energetics Processes Hormonal Control Ingestion Storage Lipid Carbohydrate Mobilization Lipid Carbohydrate Protein Adsorption
Chapter 44. Osmoregulation and Excretion
 Chapter 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion Overview: A Balancing Act Physiological systems of animals operate in a fluid environment Relative concentrations of water and solutes must be maintained within
Chapter 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion Overview: A Balancing Act Physiological systems of animals operate in a fluid environment Relative concentrations of water and solutes must be maintained within
Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Balance
 25 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Balance Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Note to the Instructor: For the third edition of Visual Anatomy & Physiology, we have updated our PowerPoints to fully
25 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Balance Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Note to the Instructor: For the third edition of Visual Anatomy & Physiology, we have updated our PowerPoints to fully
INFLUENCE OF MILD HYPERCAPNIA ON THE EFFECTS OF ENVIRONMENTAL ACIDIFICATION ON RAINBOW TROUT (SALMO GAIRDNERI)
 J. exp. Bid. (1979). 83. 345-349 With 1 figure Printed in Great Britain INFLUENCE OF MILD HYPERCAPNIA ON THE EFFECTS OF ENVIRONMENTAL ACIDIFICATION ON RAINBOW TROUT (SALMO GAIRDNERI) BY C. M. NEVILLE Department
J. exp. Bid. (1979). 83. 345-349 With 1 figure Printed in Great Britain INFLUENCE OF MILD HYPERCAPNIA ON THE EFFECTS OF ENVIRONMENTAL ACIDIFICATION ON RAINBOW TROUT (SALMO GAIRDNERI) BY C. M. NEVILLE Department
Histological Alterations in The Liver Architecture of Freshwater Fish, Rasbora Daniconius, Exposed to Sodium Fluoride
 Histological Alterations in The Liver Architecture of Freshwater Fish, K. B. SANGVE Department of Zoology, Brijlal Biyani Science College, Amravati. (M.S.) 444606 Corresponding author: kiran.sangve@gmail.com
Histological Alterations in The Liver Architecture of Freshwater Fish, K. B. SANGVE Department of Zoology, Brijlal Biyani Science College, Amravati. (M.S.) 444606 Corresponding author: kiran.sangve@gmail.com
H 2 O, Electrolytes and Acid-Base Balance
 H 2 O, Electrolytes and Acid-Base Balance Body Fluids Intracellular Fluid Compartment All fluid inside the cells 40% of body weight Extracellular Fluid Compartment All fluid outside of cells 20% of body
H 2 O, Electrolytes and Acid-Base Balance Body Fluids Intracellular Fluid Compartment All fluid inside the cells 40% of body weight Extracellular Fluid Compartment All fluid outside of cells 20% of body
LEATHER DYE POLLUTION AND ITS IMPACT ON WATER FAUNA. Sheikh Afaq Gowhar College of Public Health and Health informatics, University of Ha il KSA
 LEATHER DYE POLLUTION AND ITS IMPACT ON WATER FAUNA Sheikh Afaq Gowhar College of Public Health and Health informatics, University of Ha il KSA ABSTRACT: Effect of two leather dyes Bismarck brown and acid
LEATHER DYE POLLUTION AND ITS IMPACT ON WATER FAUNA Sheikh Afaq Gowhar College of Public Health and Health informatics, University of Ha il KSA ABSTRACT: Effect of two leather dyes Bismarck brown and acid
Elemental analysis in clinical practice
 Elemental analysis in clinical practice Nicholas J Miller FRCPath, Laboratory Director, Biolab Medical Unit, ThermoFisher summer symposium 7 th June 2011, QEII Conference Centre Nutritional Elements Macro
Elemental analysis in clinical practice Nicholas J Miller FRCPath, Laboratory Director, Biolab Medical Unit, ThermoFisher summer symposium 7 th June 2011, QEII Conference Centre Nutritional Elements Macro
Effects of Sub-Lethal Concentrations of Diazinon on Total Protein and Transaminase Activities in Clarias gariepinus
 Current Research Journal of Biological Sciences 2(6): 390-395, 2010 ISSN: 2041-0778 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2010 Submitted date: September 06, 2010 Accepted date: October 09, 2010 Published date:
Current Research Journal of Biological Sciences 2(6): 390-395, 2010 ISSN: 2041-0778 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2010 Submitted date: September 06, 2010 Accepted date: October 09, 2010 Published date:
Satyendra Singh* and A. K. Srivastava. Department of Zoology, DAV College Kanpur , UP, India
 J. Ecophysiol. Occup. Hlth. 15 (3 & 4), 2015, 89 93 2015 The Academy of Environmental Biology, India DOI : 10.15512/joeoh/2015/v15i3-4/121589 Variations in Hepatosomatic Index (HSI) and Gonadosomatic Index
J. Ecophysiol. Occup. Hlth. 15 (3 & 4), 2015, 89 93 2015 The Academy of Environmental Biology, India DOI : 10.15512/joeoh/2015/v15i3-4/121589 Variations in Hepatosomatic Index (HSI) and Gonadosomatic Index
THE TOXICITY OF THE DOUBLE CHLORIDES OF MERCURY AND SODIUM
 325 THE TOXICITY OF THE DOUBLE CHLORIDES OF MERCURY AND SODIUM I. EXPERIMENTS WITH THE MINNOW PHOXINUS PHOXINUS (L.) BY J. R. ERICHSEN JONES Department of Zoology, University College of Wales, Aberystwyth
325 THE TOXICITY OF THE DOUBLE CHLORIDES OF MERCURY AND SODIUM I. EXPERIMENTS WITH THE MINNOW PHOXINUS PHOXINUS (L.) BY J. R. ERICHSEN JONES Department of Zoology, University College of Wales, Aberystwyth
MERCURY INTOXICATION IN GRASS CARP (CTENOPHARYNGODON IDELLA)
 33 MERCURY INTOXICATION IN GRASS CARP (CTENOPHARYNGODON IDELLA) M. S. Khan, S. A. Khan, Z. I. Chaudhary, M. N. Khan, 1 A. Aslam, K. Ashraf 2, R. M. Ayyub and M. F. Rai. Department of Pathology, 1 Department
33 MERCURY INTOXICATION IN GRASS CARP (CTENOPHARYNGODON IDELLA) M. S. Khan, S. A. Khan, Z. I. Chaudhary, M. N. Khan, 1 A. Aslam, K. Ashraf 2, R. M. Ayyub and M. F. Rai. Department of Pathology, 1 Department
Sensitivity of some freshwater fishes for water pollutants
 Proceedings of International Symposium on Environmental Pollution Control and Waste Management 7- January 02, Tunis (EPCOWM 02), p.38-42. Sensitivity of some freshwater fishes for water pollutants Abbas
Proceedings of International Symposium on Environmental Pollution Control and Waste Management 7- January 02, Tunis (EPCOWM 02), p.38-42. Sensitivity of some freshwater fishes for water pollutants Abbas
Osmoregulation & Excretion, Part 1 Lecture 16 Winter 2014
 Osmoregulation & Excretion, Part 1 Lecture 16 Winter 2014 Homeostasis & Osmoregulation 1 Homeostasis The maintenance of a relatively constant chemical and physical environment within an organism Osmoregulation
Osmoregulation & Excretion, Part 1 Lecture 16 Winter 2014 Homeostasis & Osmoregulation 1 Homeostasis The maintenance of a relatively constant chemical and physical environment within an organism Osmoregulation
SHORT-TERM PCB (AROCLOR 1254) TOXICITY ON FEW PHOSPHATASES IN MICE BRAIN
 Dose-Response, 11:1 8, 2013 Formerly Nonlinearity in Biology, Toxicology, and Medicine Copyright 2013 University of Massachusetts ISSN: 1559-3258 DOI: 10.2203/dose-response.10-037.Kundu SHORT-TERM PCB
Dose-Response, 11:1 8, 2013 Formerly Nonlinearity in Biology, Toxicology, and Medicine Copyright 2013 University of Massachusetts ISSN: 1559-3258 DOI: 10.2203/dose-response.10-037.Kundu SHORT-TERM PCB
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Patho Instructor Notes Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Patho Instructor Notes Revised: 11/2013 Cells form 4 basic tissue groups: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Patho Instructor Notes Revised: 11/2013 Cells form 4 basic tissue groups: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective
Annual changes in serum calcium and inorganic phosphate levels and correlation with gonadal status of a freshwater murrel, Channa punctatus (Bloch)
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1998) 31: 169-173 Calcium and phosphate levels in murrel ISSN 1-879X 169 Annual changes in serum calcium and inorganic phosphate levels and correlation
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1998) 31: 169-173 Calcium and phosphate levels in murrel ISSN 1-879X 169 Annual changes in serum calcium and inorganic phosphate levels and correlation
Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE
 Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE I. RELATED TOPICS Integumentary system Cerebrospinal fluid Aqueous humor Digestive juices Feces Capillary dynamics Lymph circulation Edema Osmosis
Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE I. RELATED TOPICS Integumentary system Cerebrospinal fluid Aqueous humor Digestive juices Feces Capillary dynamics Lymph circulation Edema Osmosis
1. Introduction. 2. Materials and Methods
 American Journal of Life Sciences 2015; 3(1): 17-21 Published online January 28, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajls) doi: 10.11648/j.ajls.20150301.14 ISSN: 2328-5702 (Print); ISSN: 2328-5737
American Journal of Life Sciences 2015; 3(1): 17-21 Published online January 28, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajls) doi: 10.11648/j.ajls.20150301.14 ISSN: 2328-5702 (Print); ISSN: 2328-5737
Biology 2201 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Biology 2201 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life 2.2 Cell Membrane Structure Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different conditions
Biology 2201 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life 2.2 Cell Membrane Structure Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different conditions
THE PHYSIOLOGY OF THE ANTENNAL GLAND OF CARCINUS MAENAS (L.)
 J. Exp. Biol. (1969), 51, 41-45 Printed in Great Britain THE PHYSIOLOGY OF THE ANTENNAL GLAND OF CARCINUS MAENAS (L.) V. SOME NITROGENOUS CONSTITUENTS IN THE BLOOD AND URINE BY R. BINNS Dept. of Zoology,
J. Exp. Biol. (1969), 51, 41-45 Printed in Great Britain THE PHYSIOLOGY OF THE ANTENNAL GLAND OF CARCINUS MAENAS (L.) V. SOME NITROGENOUS CONSTITUENTS IN THE BLOOD AND URINE BY R. BINNS Dept. of Zoology,
STUDY ON RAINBOW TROUT NODULAR GILL DISEASE DETECTED IN POLAND
 Bull Vet Inst Pulawy 51, 547-551, 2007 STUDY ON RAINBOW TROUT NODULAR GILL DISEASE DETECTED IN POLAND JERZY ANTYCHOWICZ Department of Fish Diseases, National Veterinary Research Institute, 24-100 Pulawy,
Bull Vet Inst Pulawy 51, 547-551, 2007 STUDY ON RAINBOW TROUT NODULAR GILL DISEASE DETECTED IN POLAND JERZY ANTYCHOWICZ Department of Fish Diseases, National Veterinary Research Institute, 24-100 Pulawy,
THERMOREGULATION AND OSMOREGULATION. Shelby Cotta and Maddy Davis Period 5, AP Biology 4/2/2015
 THERMOREGULATION AND OSMOREGULATION Shelby Cotta and Maddy Davis Period 5, AP Biology 4/2/2015 Thermoregulation- 40.3 Thermoregulation is the process which allows an animal to maintain its internal temperature
THERMOREGULATION AND OSMOREGULATION Shelby Cotta and Maddy Davis Period 5, AP Biology 4/2/2015 Thermoregulation- 40.3 Thermoregulation is the process which allows an animal to maintain its internal temperature
II. Active Transport (move molecules against conc. gradient - cell must expend energy) (uses carrier proteins)
 Chapter 5 - Homeostasis and Transport I. Passive Transport (no energy from cell required) A. Diffusion 1. movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration a.
Chapter 5 - Homeostasis and Transport I. Passive Transport (no energy from cell required) A. Diffusion 1. movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration a.
J. Environ. Res. Develop. Journal of Environmental Research And Development Vol. 8 No. 2, October-December 2013
 ASCORBATE EFFECT ON THE LEAD CHLORIDE INDU- CED ALTERATIONS IN THE PROTEIN CONTENTS OF FRESH WATER FISH, Channa orientalis (Schneider) Borane V. R.*, Shinde B.R. 1 and Zambare S.P. 2 1. Department of Zoology,
ASCORBATE EFFECT ON THE LEAD CHLORIDE INDU- CED ALTERATIONS IN THE PROTEIN CONTENTS OF FRESH WATER FISH, Channa orientalis (Schneider) Borane V. R.*, Shinde B.R. 1 and Zambare S.P. 2 1. Department of Zoology,
Osmoregulation means the maintenance of the homeostasis of internal environment.
 Osmoregulation by Birds Eldon J. Braun Department of Physiology University of Arizona Bill Schmoker Maintenance of the Internal Environment Osmoregulation means the maintenance of the homeostasis of internal
Osmoregulation by Birds Eldon J. Braun Department of Physiology University of Arizona Bill Schmoker Maintenance of the Internal Environment Osmoregulation means the maintenance of the homeostasis of internal
Basic mechanisms of Kidney function
 Excretion Basic mechanisms of Kidney function Urine formation in Amphibians Urine formation in Mammals Urine formation in Insects Nitrogen balance Kidneys The most fundamental function of kidneys) is to
Excretion Basic mechanisms of Kidney function Urine formation in Amphibians Urine formation in Mammals Urine formation in Insects Nitrogen balance Kidneys The most fundamental function of kidneys) is to
of fresh Abstract and Methods Material Author s Address brought selected water 1976). In fresh exposed frequently quickly this area were
 Conservation Journal 14(1&2) 87-91, 213 ISSN 972-399 (Print) 2278-5124 (Online) Abstracted and Indexed Effect of cold stress on biochemical constituents Anand S. Joshi and Resham Bhalla of fresh water
Conservation Journal 14(1&2) 87-91, 213 ISSN 972-399 (Print) 2278-5124 (Online) Abstracted and Indexed Effect of cold stress on biochemical constituents Anand S. Joshi and Resham Bhalla of fresh water
Cell structure and function flash cards
 Process Cell structure and function flash cards involved in aerobic respiration releasing ATP / energy has a double membrane folded into cristae (to make large SA) mostly occurs in mitochondria; needing
Process Cell structure and function flash cards involved in aerobic respiration releasing ATP / energy has a double membrane folded into cristae (to make large SA) mostly occurs in mitochondria; needing
AP Biology. Homeostasis. Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment. Homeostasis
 Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment omeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: regulate their internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to the
Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment omeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: regulate their internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to the
Principles of Fluid Balance
 Principles of Fluid Balance I. The Cellular Environment: Fluids and Electrolytes A. Water 1. Total body water (TBW) = 60% of total body weight 2. Fluid Compartments in the Body a. Intracellular Compartment
Principles of Fluid Balance I. The Cellular Environment: Fluids and Electrolytes A. Water 1. Total body water (TBW) = 60% of total body weight 2. Fluid Compartments in the Body a. Intracellular Compartment
Physiology. Proper-es of The Body Fluid. Dr. Deniz Balcı.
 Physiology Proper-es of The Body Fluid Dr. Deniz Balcı deniz.balci@neu.edu.tr Outline 1 Volumes & Compartments of Body Fluids 2 Composi-on of Body Fluids 3 Fluid Movement between Compartments Reading Assignment
Physiology Proper-es of The Body Fluid Dr. Deniz Balcı deniz.balci@neu.edu.tr Outline 1 Volumes & Compartments of Body Fluids 2 Composi-on of Body Fluids 3 Fluid Movement between Compartments Reading Assignment
Osmoregulation by Birds. Eldon J. Braun Department of Physiology University of Arizona
 Osmoregulation by Birds Eldon J. Braun Department of Physiology University of Arizona Maintenance of the Internal Environment Osmoregulation means the maintenance of the homeostasis of internal environment.
Osmoregulation by Birds Eldon J. Braun Department of Physiology University of Arizona Maintenance of the Internal Environment Osmoregulation means the maintenance of the homeostasis of internal environment.
Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury.
 Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury. Professor Dr. M. Tariq Javed Dept. of Pathology Faculty of Vet. Science The University Of Agriculture Faisalabad Cell Injury When the cell is exposed
Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury. Professor Dr. M. Tariq Javed Dept. of Pathology Faculty of Vet. Science The University Of Agriculture Faisalabad Cell Injury When the cell is exposed
Edward V. Krizhanovsky, Ph.D., Kamila B. Tursunova
 REPORT ON RESEARCH OF BAE SYNERGY LIQUID PREPARATION INFLUENCE ON MINERAL METABOLISM Edward V. Krizhanovsky, Ph.D., Kamila B. Tursunova Bioenergy Technologies Institute, Sveaborgskaia, 12, Saint- Petersburg,
REPORT ON RESEARCH OF BAE SYNERGY LIQUID PREPARATION INFLUENCE ON MINERAL METABOLISM Edward V. Krizhanovsky, Ph.D., Kamila B. Tursunova Bioenergy Technologies Institute, Sveaborgskaia, 12, Saint- Petersburg,
COMPARISON OF SERUM ZINC AND SERUM POTASSIUM CONCENTRATION IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE PATIENTS
 COMPARISON OF SERUM ZINC AND SERUM POTASSIUM CONCENTRATION IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE PATIENTS *Punam Yadav Department of Chemistry, M. S. College, Saharanpur U.P. *Author for Correspondence ABSTRACT Abnormal
COMPARISON OF SERUM ZINC AND SERUM POTASSIUM CONCENTRATION IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE PATIENTS *Punam Yadav Department of Chemistry, M. S. College, Saharanpur U.P. *Author for Correspondence ABSTRACT Abnormal
Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment. AP Biology
 Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment Homeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: regulate their internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to the
Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment Homeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: regulate their internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to the
Chapter 20 8/23/2016. Fluids and Electrolytes. Fluid (Water) Fluid (Water) (Cont.) Functions
 Chapter 20 Fluids and Electrolytes All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Fluid (Water) Functions Provides an extracellular transportation
Chapter 20 Fluids and Electrolytes All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Fluid (Water) Functions Provides an extracellular transportation
Part 1 The Cell and the Cellular Environment
 1 Chapter 3 Anatomy and Physiology Part 1 The Cell and the Cellular Environment 2 The Human Cell The is the fundamental unit of the human body. Cells contain all the necessary for life functions. 3 Cell
1 Chapter 3 Anatomy and Physiology Part 1 The Cell and the Cellular Environment 2 The Human Cell The is the fundamental unit of the human body. Cells contain all the necessary for life functions. 3 Cell
ZINC INTOXICATION IN SOME FRESHWATER FISHES. I. VARIATIONS IN TISSUE ENERGY RESERVE. by S.A. SHAFFI 1
 Annls Limnol. 16 (1) 1980 : 91-97. ZINC INTOXICATION IN SOME FRESHWATER FISHES. I. VARIATIONS IN TISSUE ENERGY RESERVE by S.A. SHAFFI 1 The effect of Zinc sulphate intoxication on tissue glycogen content
Annls Limnol. 16 (1) 1980 : 91-97. ZINC INTOXICATION IN SOME FRESHWATER FISHES. I. VARIATIONS IN TISSUE ENERGY RESERVE by S.A. SHAFFI 1 The effect of Zinc sulphate intoxication on tissue glycogen content
Standard 2 Exam Biology. 2. This macromolecule is responsible for short term energy storage and structural support in plants
 1. This macromolecule is responsible for structural support, movement, enzymatic activity, cell communication, and is made of amino acids. a. Lipids b. Carbohydrates c. Proteins d. Nucleic Acids e. ATP
1. This macromolecule is responsible for structural support, movement, enzymatic activity, cell communication, and is made of amino acids. a. Lipids b. Carbohydrates c. Proteins d. Nucleic Acids e. ATP
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System. Chapter 50
 Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
EFFECT OF TRIAZOPHOS ON PROTEIN CONTENT IN THE FRESH WATER FISH CYPRINUS CARPIO (LINN.) AFTER ACUTE AND CHRONIC EXPOSURE
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 3, 2016, 1751 1757 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) EFFECT OF TRIAZOPHOS ON PROTEIN CONTENT IN THE FRESH WATER FISH CYPRINUS CARPIO
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 3, 2016, 1751 1757 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) EFFECT OF TRIAZOPHOS ON PROTEIN CONTENT IN THE FRESH WATER FISH CYPRINUS CARPIO
THE EFFECTS OF ION CHANGES ON THE CONTRACTION OF THE RAT UTERUS STIMULATED BY OXYTOCIN
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1961), 16, 45-49. THE EFFECTS OF ION CHANGES ON THE CONTRACTION OF THE RAT UTERUS STIMULATED BY OXYTOCIN BY P. J. BENTLEY AND ELEANOR McEWEN From the Department of Physiology, The
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1961), 16, 45-49. THE EFFECTS OF ION CHANGES ON THE CONTRACTION OF THE RAT UTERUS STIMULATED BY OXYTOCIN BY P. J. BENTLEY AND ELEANOR McEWEN From the Department of Physiology, The
EFFECT OF CYPERMETHRIN ON LIPID LEVEL OF FRESHWATER CRAB P. JACQUEMONTII HEPATOPANCREAS AND MUSCLE
 EFFECT OF CYPERMETHRIN ON LIPID LEVEL OF FRESHWATER CRAB P. JACQUEMONTII HEPATOPANCREAS AND MUSCLE Parate S K Department of Zoology, B. B. Arts, N. B. Commerce and B.P. Science College Digras, Dist. Yavatmal-445203
EFFECT OF CYPERMETHRIN ON LIPID LEVEL OF FRESHWATER CRAB P. JACQUEMONTII HEPATOPANCREAS AND MUSCLE Parate S K Department of Zoology, B. B. Arts, N. B. Commerce and B.P. Science College Digras, Dist. Yavatmal-445203
Fluids and electrolytes
 Body Water Content Fluids and electrolytes Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60% water; healthy females
Body Water Content Fluids and electrolytes Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60% water; healthy females
Impact of Cypermethrin and Ekalux on respiratory and some biochemical activities of a fresh water fish Tilapia mossambica
 Impact of Cypermethrin and Ekalux on respiratory and some biochemical activities of a fresh water fish Tilapia mossambica S. Logaswamy and K. M. Remia* P.G and Research Department of Zoology, Kongunadu
Impact of Cypermethrin and Ekalux on respiratory and some biochemical activities of a fresh water fish Tilapia mossambica S. Logaswamy and K. M. Remia* P.G and Research Department of Zoology, Kongunadu
Plasma Membrane Function
 Plasma Membrane Function Cells have to maintain homeostasis, they do this by controlling what moves across their membranes Structure Double Layer of phospholipids Head (polar) hydrophiliclikes water -
Plasma Membrane Function Cells have to maintain homeostasis, they do this by controlling what moves across their membranes Structure Double Layer of phospholipids Head (polar) hydrophiliclikes water -
ATP: The energy currency of the cell. The ATP Cycle:
 ATP: The energy currency of the cell The ATP Cycle: Changing the rate of catabolic and anabolic reactions- How do you control these chemical reactions? Enzymes and Activation Energy Enzymes as biological
ATP: The energy currency of the cell The ATP Cycle: Changing the rate of catabolic and anabolic reactions- How do you control these chemical reactions? Enzymes and Activation Energy Enzymes as biological
Ions are loss in the urine and by diffusion in the gills
 Water and Salt Physiology ADAPTATIONS: Active ion transport uptake across gill epithelium of a freshwater fish Ions are loss in the urine and by diffusion in the gills Na and CL are gain by two independent
Water and Salt Physiology ADAPTATIONS: Active ion transport uptake across gill epithelium of a freshwater fish Ions are loss in the urine and by diffusion in the gills Na and CL are gain by two independent
Studies on the Effect of Electroplating Effluent on Biochemical Components of Fish Cyprinus carpio
 World Journal of Fish and Marine Sciences 7 (6): 472-478, 2015 ISSN 2078-4589 IDOSI Publications, 2015 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjfms.2015.7.6.101164 Studies on the Effect of Electroplating Effluent on Biochemical
World Journal of Fish and Marine Sciences 7 (6): 472-478, 2015 ISSN 2078-4589 IDOSI Publications, 2015 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjfms.2015.7.6.101164 Studies on the Effect of Electroplating Effluent on Biochemical
Methyl Mercury Induced Changes in the Serum Proteins of Bluegills Lepomis Macrochirus (Teleostei)
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 83, Issue 3 (June, 1983) 1983-06 Methyl Mercury Induced Changes in
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 83, Issue 3 (June, 1983) 1983-06 Methyl Mercury Induced Changes in
OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION
 1 2 3 4 5 6 OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION OSMOREGULATION Process by which animals control their solute concentrations and balance water gain and loss Freshwater animals show adaptations that reduce water
1 2 3 4 5 6 OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION OSMOREGULATION Process by which animals control their solute concentrations and balance water gain and loss Freshwater animals show adaptations that reduce water
Effect of Environmental acidic ph on Oxygen Consumption in Different stages of Fish, Cyprinus carpio(l)
 IOSR Journal of Environmental Science, Toxicology and Food Technology (IOSR-JESTFT) e-issn: 2319-2402,p- ISSN: 2319-2399.Volume 8, Issue 8 Ver. I (Aug. 2014), PP 17-21 Effect of Environmental acidic ph
IOSR Journal of Environmental Science, Toxicology and Food Technology (IOSR-JESTFT) e-issn: 2319-2402,p- ISSN: 2319-2399.Volume 8, Issue 8 Ver. I (Aug. 2014), PP 17-21 Effect of Environmental acidic ph
Body Water Content Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are
 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance Body Water Content Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60%
Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance Body Water Content Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60%
Hypertonic intravenous fluid therapy administration in acutely sick cattle
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Hypertonic intravenous fluid therapy administration in acutely sick cattle Author : ADAM MARTIN Categories : Vets Date : April
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Hypertonic intravenous fluid therapy administration in acutely sick cattle Author : ADAM MARTIN Categories : Vets Date : April
estimates were made of the normal rate of increase in plasma urea over periods in skin and in plasma, hypertonic sodium chloride solution was
 482 J. Physiol. (I95I) II5, 482-487 THE STTE OF BODY WTER IN THE CT BY M. GRCE EGGLETON From the Department of Physiology, University College, London (Received 5 July 1951) In the course of an investigation
482 J. Physiol. (I95I) II5, 482-487 THE STTE OF BODY WTER IN THE CT BY M. GRCE EGGLETON From the Department of Physiology, University College, London (Received 5 July 1951) In the course of an investigation
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
 Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
FORMATHION INDUCED HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE LIVER OF Clarius batrachus
 FORMATHION INDUCED HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE LIVER OF Clarius batrachus SHIKHA SHRIVASTAVA Department of Zoology, Govt. P.G. College, Korba (INDIA) Received August 7, 2006 Accepted February 12,
FORMATHION INDUCED HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE LIVER OF Clarius batrachus SHIKHA SHRIVASTAVA Department of Zoology, Govt. P.G. College, Korba (INDIA) Received August 7, 2006 Accepted February 12,
THE WATER AND ELECTROLYTE EXCHANGE OF NEREIS DIVERSICOLOR (MULLER)
 34 THE WATER AND ELECTROLYTE EXCHANGE OF NEREIS DIVERSICOLOR (MULLER) BY W. G. ELLIS Zoology Department, University College of North Wales, Bangor {Received g December 1936) (With Nine Text-figures) IT
34 THE WATER AND ELECTROLYTE EXCHANGE OF NEREIS DIVERSICOLOR (MULLER) BY W. G. ELLIS Zoology Department, University College of North Wales, Bangor {Received g December 1936) (With Nine Text-figures) IT
OSMO_LUS Osmoregulation in Salmon Lice
 OSMO_LUS Osmoregulation in Salmon Lice Anna Z Komisarczuk 17.10.2017 Content 1. Aim 2. Background: 1. Osmoregulation 2. Osmoregulation in salmon louse 3. Fresh water effects on salmon louse: 1. Survival
OSMO_LUS Osmoregulation in Salmon Lice Anna Z Komisarczuk 17.10.2017 Content 1. Aim 2. Background: 1. Osmoregulation 2. Osmoregulation in salmon louse 3. Fresh water effects on salmon louse: 1. Survival
A Study on the effect of electroplating effluent on biochemical changes in the fresh water fish, Oreochromis mossambicus.
 IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn:2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 12, Issue 6 Ver. V (Nov. Dec. 2017), PP 37-41 www.iosrjournals.org A Study on the effect of electroplating
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn:2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 12, Issue 6 Ver. V (Nov. Dec. 2017), PP 37-41 www.iosrjournals.org A Study on the effect of electroplating
FLUORIDE-INDUCED BIOCHEMICAL CHANGES IN FRESH WATER CATFISH (CLARIAS BATRACHUS, LINN.)
 37 37 FLUORIDE-INDUCED BIOCHEMICAL CHANGES IN FRESH WATER CATFISH (CLARIAS BATRACHUS, LINN.) Anand Kumar, Nalini Tripathi, MadhuTripathi a Lucknow, India SUMMARY: The toxicity of fluoride (F) to 16-cm
37 37 FLUORIDE-INDUCED BIOCHEMICAL CHANGES IN FRESH WATER CATFISH (CLARIAS BATRACHUS, LINN.) Anand Kumar, Nalini Tripathi, MadhuTripathi a Lucknow, India SUMMARY: The toxicity of fluoride (F) to 16-cm
BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation
 Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation 1 Body Water Content On average, we are 50-60 % water For a 70 kg male = 40 liters water This water is divided into
Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation 1 Body Water Content On average, we are 50-60 % water For a 70 kg male = 40 liters water This water is divided into
Sub-lethal Effect of Pesticides on the Distribution of Glutaminases in the Brain of Labeo rohita (Ham.)
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Toxicology Volume 7 Number 2 Sub-lethal Effect of Pesticides on the Distribution of Glutaminases in the Brain of Labeo rohita (Ham.) S Mastan, S Shaffi Citation S Mastan,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Toxicology Volume 7 Number 2 Sub-lethal Effect of Pesticides on the Distribution of Glutaminases in the Brain of Labeo rohita (Ham.) S Mastan, S Shaffi Citation S Mastan,
NORMOSOL -R MULTIPLE ELECTROLYTES INJECTION TYPE 1, USP For Replacing Acute Losses of Extracellular Fluid Flexible Plastic Container
 NORMOSOL -R MULTIPLE ELECTROLYTES INJECTION TYPE 1, USP For Replacing Acute Losses of Extracellular Fluid Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Normosol-R is a sterile, nonpyrogenic isotonic
NORMOSOL -R MULTIPLE ELECTROLYTES INJECTION TYPE 1, USP For Replacing Acute Losses of Extracellular Fluid Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Normosol-R is a sterile, nonpyrogenic isotonic
THE EFFECTS OF HYPOPHYSECTOMY, PROLACTIN THERAPY AND ENVIRONMENTAL CALCIUM ON ELECTROLYTE BALANCE OF THE BROWN TROUT SALMO TRUTTA, L.
 J. exp. Biol. (1976), 64, 331-331 221 With a figures Printed in Great Britain THE EFFECTS OF HYPOPHYSECTOMY, PROLACTIN THERAPY AND ENVIRONMENTAL CALCIUM ON ELECTROLYTE BALANCE OF THE BROWN TROUT SALMO
J. exp. Biol. (1976), 64, 331-331 221 With a figures Printed in Great Britain THE EFFECTS OF HYPOPHYSECTOMY, PROLACTIN THERAPY AND ENVIRONMENTAL CALCIUM ON ELECTROLYTE BALANCE OF THE BROWN TROUT SALMO
Toxicology An Introduction. John Duffus The Edinburgh Centre for Toxicology
 Toxicology An Introduction John Duffus The Edinburgh Centre for Toxicology General considerations Toxicology is the science which lets us know how substances can harm life by physico-chemical reactions
Toxicology An Introduction John Duffus The Edinburgh Centre for Toxicology General considerations Toxicology is the science which lets us know how substances can harm life by physico-chemical reactions
Seasonal, size and comparative study of plasma proteins of four airbreathing freshwater fishes
 Prec. Indian Acad. Sci., Vol. 85 B, No. 6, 1977, pp. 384-390. Seasonal, size and comparative study of plasma proteins of four airbreathing freshwater fishes NEENA SIDDIQU1 Department of Zoology, Aligarh
Prec. Indian Acad. Sci., Vol. 85 B, No. 6, 1977, pp. 384-390. Seasonal, size and comparative study of plasma proteins of four airbreathing freshwater fishes NEENA SIDDIQU1 Department of Zoology, Aligarh
Cell Boundaries Section 7-3
 Cell Boundaries Section 7-3 The most important parts of a cell are its borders, which separate the cell from its surroundings. The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds all cells. The
Cell Boundaries Section 7-3 The most important parts of a cell are its borders, which separate the cell from its surroundings. The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds all cells. The
Transport across the cell membrane
 Transport across the cell membrane Learning objectives Body compartments ECF and ICF Constituents Lipid Bilayer: Barrier to water and water-soluble substances ions glucose H 2 O urea CO 2 O 2 N 2 halothane
Transport across the cell membrane Learning objectives Body compartments ECF and ICF Constituents Lipid Bilayer: Barrier to water and water-soluble substances ions glucose H 2 O urea CO 2 O 2 N 2 halothane
Lecture 19, 04 Nov 2003 Chapter 13, Respiration, Gas Exchange, Acid-Base Balance. Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall 2003
 1 Lecture 19, 04 Nov 003 Chapter 13, Respiration, Gas Exchange, Acid-Base Balance Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall 003 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Bret Pasch Vertebrate Physiology
1 Lecture 19, 04 Nov 003 Chapter 13, Respiration, Gas Exchange, Acid-Base Balance Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall 003 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Bret Pasch Vertebrate Physiology
