Chromium and zinc contamination of parenteral nutrient solution components commonly used in infants and children
|
|
|
- Mitchell Webster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chromium and zinc contamination of parenteral nutrient solution components commonly used in infants and children EMILY B. HAK, MICHAEL C. STORM, AND RICHARD A. HELMS Abstract: Chromium and zinc contamination of components of parenteral nutrient (PN) solutions used in infants and children was studied. Solutions of amino acids, L- cysteine hydrochloride, dextrose, electrolytes, minerals, vitamins, multiple trace elements, and individual trace elements were obtained. A variety of manufacturers, lots, and expiration dates were represented when possible. The solutions were analyzed for chromium and zinc by flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry. In all amino acid products, chromium concentration was below the limit of detection and zinc concentration ranged from 0.06 to 4.97 mg/ L. In the L-cysteine hydrochloride products, chromium was measurable in only two lots (0.11 and 0.23 mg/l); zinc was measurable in all lots (32 86 mg/l). Sodium and potassium salts of chloride and acetate had chromium concentrations of mg/l and zinc concentrations of mg/ L. Phosphate salts contained chromium mg/l and zinc mg/l. In We recently determined serum and urine levels of chromium and zinc in infants and children receiving parenteral nutrition for longer than three months and measured the amounts of those elements in the parenteral nutrient (PN) solutions. 1,2 We found, as have others, that many PN solutions contained more chromium than was added as traceelement supplementation. 3-5 However, we also unexpectedly found that some dextrose and amino acid solutions, in particular those with added L-cysteine hydrochloride, contained significantly more zinc than was added. 1 The objectives of the study reported here were to measure chromium and zinc in PN solution components, to determine if there is a relationship between the amount of contaminant and the storage time and container size, and to calculate the amount of contaminant chromium and zinc that typically would be provided to an infant by a PN solution. calcium gluconate, zinc concentration was mg/ L. In four lots of multiple trace elements, chromium was % and zinc was % of the labeled amount. A PN solution for a <10-kg infant compounded from the components assayed would provide up to an additional 0.7 µg of chromium per kilogram and 200 µg of zinc per kilogram. Zinc and chromium contaminants were detected in many of the products that are common components of PN solutions for infants and children; the contamination may be sufficient to result in the administration of zinc and chromium in amounts exceeding current recommendations. Index terms: Amino acids; Calcium gluconate; Caloric agents; Chromium; Concentration; Contamination; Cysteine hydrochloride; Dextrose; Elements; Injections; Metals; Minerals; Nutrition; Pediatrics; Phosphates; Potassium chloride; Replacement solutions; Sodium chloride; Toxicity; Vitamins; Zinc Am J Health-Syst Pharm. 1998; 55:150-4 Methods Solutions of amino acids, L-cysteine hydrochloride, dextrose, electrolytes, minerals, vitamins, multiple trace elements, and individual trace elements were obtained from various manufacturers (Table 1). Multiple lots of individual products were included when available. Products that were past their expiration dates were also included. M.V.I. Pediatric was reconstituted in doubledistilled, metal-free water according to the package insert. All other products were sampled directly. Chromium and zinc concentrations were measured with a Perkin-Elmer 3300 flame atomic absorption spectrophotometer equipped with a flow spoiler, an AS 90 autosampler, and an AS 91 controller (Perkin-Elmer, Foster City, CA). Air:acetylene mixtures of 10:3.8 L/min for chromium and 10:2 L/min for zinc were used. Perkin-Elmer Intensitron lamps were used, and settings for initial lamp current, slit, and energy followed the EMILY B. HAK, PHARM.D., BCNSP, is Associate Professor; MICHAEL C. STORM, PH.D., is Associate Professor; and RICHARD A. HELMS, PHARM.D., is Professor, Department of Clinical Pharmacy, The Center for Pediatric Pharmacokinetics and Therapeutics, The University of Tennessee, Memphis. Address reprint requests to Dr. Hak at the Department of Clinical Pharmacy, 26 S. Dunlap Street, Memphis, TN 38163, or to ehak@utmem1.utmem.edu. Supported in part by a State of Tennessee Center of Excellence grant and the Pediatric Pharmacology Research Unit at The University of Tennessee, Memphis. Presented at the Clinical Congress of the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition, San Francisco, CA, January 28, Copyright 1998, American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. All rights reserved /98/ $ Am J Health-Syst Pharm Vol 55 Jan
2 Chromium and zinc contamination Reports Table 1. Chromium and Zinc Concentrations in Parenteral Nutrient Solution Components Tested Solution Source manufacturer s recommendations. Atomic absorption spectrophotometry (AAS)-grade chromium and zinc standards (VWR Scientific, South Plainfield, NJ) and samples were diluted with high-purity, metal-free 0.1 N nitric acid (prepared from ultra-pure nitric acid [Ultrex II, J. T. Baker, Inc., Phillipsburg, NJ, lot J25545]). Standards and samples were prepared in duplicate. The autosampler was set so that measurement of each standard was replicated three times and each sample two times. All analyses for each metal was performed on the same day in February Each sample was diluted to 1:10 with AAS-grade 0.1 N nitric acid and analyzed. Samples that were outside the linear range of the working standards at a 1:10 dilution ( mg/l for chromium and mg/l for zinc) were further diluted to 1:100 and 1:1000 with 0.1 N nitric acid if necessary. The analytical range of the standard curve for each element was linear within the accepted range for both elements (correlation coefficients, for chromium and for zinc). Measurements that were less than 0.02 mg/l were considered below the assay s limit of detection. Results are reported as the mean ± S.D. for duplicate measurements of single samples for the individual lots. Expiration Date Chromium Concentration (mg/l) b Zinc Concentration (mg/l) b FreAmine III 8.5% McGaw J1E /83 < ± 0.05 Aminosyn 10% Abbott DM /95 < ± 0.03 TrophAmine 10% McGaw J5H /96 < ± 0.00 FreAmine III 10% McGaw J5K /97 < ± 0.01 Dextrose 70% McGaw J5K096A /97 < ± 0.01 L-cysteine hydrochloride 50 mg/ml McGaw P0B /92 < ± 3.9 McGaw P1P / ± ± 2.2 American Regent / ± ± 3.2 Abbott R1 10 5/95 < ± 6.4 McGaw P3L /95 < ± 9.9 Abbott R1 10 2/96 < ± 4.2 McGaw P5D /97 < ± 0.9 Potassium chloride 2 meq/ml Abbott DM / ± ± 0.14 Abbott DK 20 7/ ± ± 0.03 Potassium acetate 4 meq/ml Lyphomed / ± ± 0.21 Potassium phosphate 3 mmol P/mL Lyphomed / ± ± 0.12 Abbott DK 50 6/ ± ± 0.14 Sodium acetate 2 meq/ml Abbott DK 100 3/ ± ± 0.07 Sodium chloride 14.6% Abbott DM / ± ± 0.09 Sodium phosphate 3 mmol P/mL Abbott DK 50 12/ ± ± 0.06 Calcium gluconate 10% Lyphomed / ± ± 0.53 Int Med System BB053A / ± ± 0.06 Magnesium sulfate 4 meq/ml Abbott DK 50 11/ ± ± 0.04 Selenium 40 µg/ml SoloPak /96 < ± 0.50 Manganese sulfate 0.1 mg/ml Lyphomed /88 < ± 0.11 M.V.I. Pediatric Rorer F /91 < ± 0.07 Astra N /96 < ± 0.09 P.T.E.-4 Lyphomed / ± ± 24 Multitrace-4 American Regent / ± ± 41 American Regent / ± ± 12 American Regent / ± ± 10 a All containers were made of plastic, except for lot DK of potassium chloride, for which containers were made of glass. b Reported as mean ± S.D. for duplicate determinations of single samples. Lot Volume (ml) a The results were examined for correlations between metal content and product volume (in milliliters) and expiration date by using Cricket Graph III, version (Computer Associates Int., Inc., Islandia, NY). The amounts of chromium and zinc that would be provided as contaminants were calculated for each product. These concentrations were then used to calculate the microgram-per-kilogram doses of contaminant chromium and zinc for the individual components of an infant PN solution providing pediatric amino acids 2.5 g/kg, glucose 85 kcal/kg, sodium 38.5 meq/l, potassium chloride 20 meq/l, phosphorus 1 mmol/kg, calcium gluconate 2.5 meq/kg, magnesium sulfate 0.4 meq/ kg, M.V.I. Pediatric 5 ml, selenium 3 µg/kg, and 40 mg of L-cysteine hydrochloride per gram of amino acids on a daily basis. Results Table 1 lists the concentrations of chromium and zinc that were found in the various PN solution components. Chromium concentration was below the limit of detection in all amino acid products, and zinc was measurable in all amino acid products (range, mg/l). In the L-cysteine hydrochloride products, chro- Vol 55 Jan Am J Health-Syst Pharm 151
3 Table 2. Amounts of Contaminant Chromium and Zinc Provided to Infant (<10 kg) in Parenteral Nutrient Solution Compounded from Components Assayed Component Amount Chromium (µg/kg/day) Zinc (µg/kg/day) Amino acids 2.5 g/kg < (TrophAmine) Glucose 85 kcal/kg < Sodium 2.5 meq/kg chloride Potassium 2 meq/kg chloride Sodium 1 mmol P/kg phosphate Calcium 2.5 meq/kg gluconate Magnesium 0.4 meq/kg sulfate M.V.I. Pediatric 5 ml < Selenium 3 µg/kg < L-cysteine 40 mg/g < hydrochloride amino acids Total mium was measurable in only two lots from different manufacturers; zinc was measurable in all lots. A PN solution for a <10-kg infant compounded from the components that were assayed, including pediatric amino acids 2.5 g/kg with 40 mg of L-cysteine hydrochloride per gram of amino acids, would provide up to an additional 0.7 µg of chromium per kilogram and 200 µg of zinc per kilogram from contaminants (Table 2). The labeled amount of chromium in P.T.E.-4 was 1 µg/ml and in Multitrace-4 was 4 µg/ml. Both multipletrace-element products were labeled to contain 1 mg of zinc per milliliter. Variation from the labeled amounts was less than 10%, except for P.T.E.-4, whose zinc concentration was 13.5% greater than the labeled amount. Chromium and zinc contamination did not have any obvious correlation with expiration date. For amino acids (expiration dates, May 1983 to August 1997), L-cysteine hydrochloride (February 1992 to April 1997), and multiple-trace-element products (July 1990 to July 1997), there appeared to be no relationship between the expiration date and the chromium or zinc content. The oldest amino acid product evaluated, one lot of Fre- Amine III 8.5%, did contain substantial amounts of zinc. Potassium chloride was the only product evaluated that was available in both glass and plastic containers. The chromium and zinc contents did not differ between the two container types (for glass, chromium 0.02 mg/ml and zinc 0.45 mg/ml; for plastic, chromium 0.02 mg/ml and zinc 0.43 mg/ml). A wide range of glass product volumes ( ml) were examined to look for a correlation of container size with chromium and zinc contamination. Those products that were formulated with chromium or zinc (Multitrace-4 and P.T.E.-4), the very old unit of Fre- Amine III 8.5% (expiration date, May 1983), and all the L-cysteine hydrochloride products (very low ph) were excluded from this correlation analysis. Chromium and zinc concentrations in the remaining products were inversely correlated with glass product size. For chromium, r 2 was 0.58 and the power relationship was chromium concentration = 6.76(size in milliliters) For zinc, r 2 was 0.5 and the power relationship was zinc concentration = 2.12(size in milliliters) Discussion The problem of trace-element contamination has been described for a wide variety of PN products. 2-9 Trace elements may be inherent in raw materials, be introduced into a product during manufacturing or compounding, or result from product interaction with container components over time. Historically, the most significant problem involving trace-element contamination of PN products was aluminum contamination of dialysis solutions. Aluminum deposition in brain and bone tissue of patients undergoing dialysis caused dialysis dementia 6 and osteodystrophy. 7 The occurrence of these conditions has been greatly decreased by improved manufacturing processes that result in less aluminum in PN products. Aluminum toxicity continues to be a concern in children, and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that efforts to reduce the amount of contaminant aluminum in PN products be continued. 10 Chromium contamination of PN products has been recognized for several years and probably results from chromium present in the raw materials. Several investigators have measured the amount of chromium in a variety of PN products, components of PN solutions, and in amino acid and dextrose admixtures and fat emulsion. 3-5 Unlike Ito et al., 4 who found measurable amounts of chromium in amino acid products, we found none. However, our assay was not sensitive enough to detect the small amounts of chromium ( mg/l) previously reported. The amounts of chromium in the different dextrose, electrolyte, and mineral products that were evaluated in our study were greater than previously reported. This suggests that concentrations of contaminant chromium vary widely among lots from a single manufacturer, among manufacturers, and with container size. Contaminant zinc was found to be present in an early crystalline amino acid product (FreAmine II 8.5%) in amounts ranging from to 1.88 mg/l 11 ; however, zinc contamination in components of PN solutions had not been evaluated further until now. We had previously noted that PN solutions that contained L-cysteine hydrochloride had more zinc than was added as trace-element supplementation, 1 and therefore we expected that some L-cysteine products would have measurable amounts of zinc. However, we did not 152 Am J Health-Syst Pharm Vol 55 Jan
4 Chromium and zinc contamination Reports expect that zinc would be present in all L-cysteine products, and we did not expect as much as we found. During manufacturing of rubber, zinc oxide is added to accelerate vulcanization; thus, zinc is present in many rubber stoppers. 12 Zinc is also in the materials used to produce glass bottles. We suspect that contaminant zinc in PN products comes from the leaching of zinc from materials in direct contact with the solution, such as rubber stoppers or glass, rather than from raw material contamination. The amount of zinc in the L-cysteine hydrochloride products was variable and was not correlated with expiration date. Thus, the variability in zinc concentrations in different products likely relates, in part, to storage conditions. Storing L-cysteine hydrochloride, a product with a ph of 1.3, in a container on its side or upside down would result in greater contact between the solution and the stopper and would increase the amount of zinc leached from the stopper. Even though the 1983 amino acid product is not very acidic (ph, ~6.8), the greatest amount of zinc found in an amino acid formulation was in this product; this finding may be related both to the position in which the product was stored and to how long it was stored. The two lots of L-cysteine hydrochloride with the smaller amounts of zinc were from the Abbott universal additive syringe, which has a stopper material different from those of the other L-cysteine containers. The presence of zinc in this product is most likely due to the constant contact of the L-cysteine solution with the stopper material. We postulate that the high zinc concentration in the L-cysteine products is due to the low solution ph, which may facilitate zinc extraction from the stopper. Recommended dosages for trace elements in infants and children receiving PN solutions have been extrapolated from requirements for healthy infants and children, with consideration given to bioavailability. With parenteral nutrition, absorptive mechanisms regulating the amount of trace elements that reach the systemic circulation are bypassed, so it is important to give the appropriate dosages. Current dosage recommendations for zinc are 250 µg/kg/day for term infants less than three months of age and 100 µg/kg/day for term infants more than three months of age. 13 The maximum daily dose of contaminant zinc that would be provided from PN solutions compounded from the components we evaluated is twice the recommended daily dose for a term infant older than three months. The current dosage recommendation for chromium is 0.2 µg/kg/day. 13 The maximum daily dose of contaminant chromium that would be provided from the dextrose and amino acid solutions we studied is three times the recommended daily dose. Small amounts of chromium would also be provided via fat emulsion. 4,5 It is possible that many trace elements are being given in excessive amounts because of contamination of components of PN products. 2,4,5,14 To complicate matters, the amount and type of contamination vary with the product, the lot, and the manufacturer. Patients receiving long-term parenteral nutrition may be exposed to excessive trace elements for extended periods and thus are at increased risk for toxicity. Moukarzel et al. 5 reported that children receiving PN solutions for longer than one year had a decreased glomerular filtration rate that appeared to be related to excessive chromium intake. Others found an inverse relationship between plasma concentrations of chromium and iron that was thought to be due to competition between chromium and iron for transferrin. 15 Thus, routine monitoring of certain trace elements, in particular chromium and perhaps zinc, may be important in patients, notably infants and children, who receive long-term parenteral nutrition. Clinicians should consider instituting practices that minimize trace-element contamination of PN solutions. These include storing containers upright to minimize PN solution contact with stoppers, preferentially using newly manufactured products, and using products from as large a container as is possible and practical. An important potential issue could be trace-element deficiency, should there be changes in manufacturing processes or in containers that essentially eliminate trace-element contamination of products. Conclusion Zinc and chromium contaminants were detected in many of the products that are common components of PN solutions for infants and children; the contamination may be sufficient to result in the administration of zinc and chromium in amounts that exceed current recommendations. References 1. Cochran EB, Mouser J, Helms RA et al. Effects of L-cysteine HCl dose on serum concentration and urinary elimination of zinc in children on home TPN. Pediatr Res. 1994; 35:125A. Abstract. 2. Mouser J, Cochran EB, Helms RA et al. Chromium concentrations in children on home TPN and the relationship to intake. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1994; 18(suppl):34S. 3. Anderson RA. Chromium and parenteral nutrition. Nutrition. 1995; 11(suppl): Ito Y, Alcock NW, Shils ME. Chromium content of total parenteral nutrition solutions. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1990; 14: Moukarzel AA, Song MK, Buchman AL et al. Excessive chromium intake in children receiving total parenteral nutrition. Lancet. 1992; 339: Sedman AB, Wilkening GN, Warady BA et al. Encephalopathy in childhood secondary to aluminum toxicity. J Pediatr. 1984; 105: Ott SM, Maloney NA, Klein GL et al. Aluminum is associated with low bone formation in patients receiving chronic parenteral nutrition. Ann Intern Med. 1983; 98: Milliner DS, Shinaberger JH, Shuman P et al. Inadvertent aluminum administration during plasma exchange due to aluminum contamination of albumin-replacement solutions. N Engl J Med. 1985; 312: Koo WWK. Aluminum in parenteral nutrition solution Vol 55 Jan Am J Health-Syst Pharm 153
5 sources and possible alternatives. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1986; 10: Committee on Nutrition. Aluminum toxicity in infants and children. Pediatrics. 1996; 97: Shearer CA, Bozian RC. The availability of trace elements in intravenous hyperalimentation solutions. Drug Intell Clin Pharm. 1977; 11: Smith EJ, Nash RJ. Elastomeric closures for parenterals. In: Avis KE, Lachman L, Lieberman HA, eds. Pharmaceutical dosage forms. Vol. 2. Parenteral medications. New York: Dekker; 1986: Greene HL, Hambidge KM, Schanler R et al. Guidelines for the use of vitamins, trace elements, calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus in infants and children receiving total parenteral nutrition: report of the Subcommittee on Pediatric Parenteral Nutrient Requirements from the Committee on Clinical Practice Issues of the American Society for Clinical Nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr. 1988; 48: Hambidge KM, Sokol RJ, Fidanza SJ et al. Plasma manganese concentrations in infants and children receiving parenteral nutrition. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1989; 13: Bougle D, Bureau F, Deschrevel G et al. Chromium and parenteral nutrition in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1993; 17: Am J Health-Syst Pharm Vol 55 Jan
Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition
 Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition Carol J Rollins, MS, RD, PharmD, BCNSP Coordinator, Nutrition Support Team The University of Arizona Medical Center www.nutritioncare.org Conflict of Interest None
Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition Carol J Rollins, MS, RD, PharmD, BCNSP Coordinator, Nutrition Support Team The University of Arizona Medical Center www.nutritioncare.org Conflict of Interest None
Ensuring Safe Management of Parenteral Nutrition During Drug Shortages: Strategies and Protocols for Enabling Clinician Success
 Ensuring Safe Management of Parenteral Nutrition During Drug Shortages: Strategies and Protocols for Enabling Clinician Success Mandy Corrigan, MPH, RD, CNSC Nutrition Support Clinician mandycorrigan1@gmail.com
Ensuring Safe Management of Parenteral Nutrition During Drug Shortages: Strategies and Protocols for Enabling Clinician Success Mandy Corrigan, MPH, RD, CNSC Nutrition Support Clinician mandycorrigan1@gmail.com
Section 8.4 Special Dilutions
 Section 8.4 Special Dilutions Terminology: Diluent: Pediatric Compound Sterile Preparations (CSPs): Special Dilutions: Calculating Special Dilutions: Ratio-Proportion vs Dimensional Analysis Part A Calculating
Section 8.4 Special Dilutions Terminology: Diluent: Pediatric Compound Sterile Preparations (CSPs): Special Dilutions: Calculating Special Dilutions: Ratio-Proportion vs Dimensional Analysis Part A Calculating
Solubility Study of Zinc and Phosphates in PN and IV Fluid. Rex Speerhas, RPh, BCNSP Nutrition Support Clinical Specialist
 Solubility Study of Zinc and Phosphates in PN and IV Fluid Rex Speerhas, RPh, BCNSP Nutrition Support Clinical Specialist What is that Brown Precipitate? What is that Brown Precipitate? Background Home
Solubility Study of Zinc and Phosphates in PN and IV Fluid Rex Speerhas, RPh, BCNSP Nutrition Support Clinical Specialist What is that Brown Precipitate? What is that Brown Precipitate? Background Home
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 19 October 2011
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 October 2011 PEDIAVEN AP-HP G15, solution for infusion 1000 ml of solution in two chamber bag, B/4 (CIP code: 419
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 October 2011 PEDIAVEN AP-HP G15, solution for infusion 1000 ml of solution in two chamber bag, B/4 (CIP code: 419
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Indication See algorithm. Timing Start TPN as indicated on algorithm 1. There is no need to build up TPN volume. The volume of TPN (including lipids) should equate to the total
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Indication See algorithm. Timing Start TPN as indicated on algorithm 1. There is no need to build up TPN volume. The volume of TPN (including lipids) should equate to the total
The Drug Shortage Crisis
 Objectives: The Drug Shortage Crisis Jay M. Mirtallo, MS, RPh, BCNSP, FASHP Director, MS in Health System Pharmacy Associate Professor of Clinical Pharmacy The Ohio State University, College of Pharmacy
Objectives: The Drug Shortage Crisis Jay M. Mirtallo, MS, RPh, BCNSP, FASHP Director, MS in Health System Pharmacy Associate Professor of Clinical Pharmacy The Ohio State University, College of Pharmacy
Prevention of Transcription Errors with Pediatric TPN Orders Using a Web Interface
 Prevention of Transcription Errors with Pediatric TPN Orders Using a Web Interface Organization Name: University of Maryland Type: Acute Care Hospital Medical Center Contact Person: Belinda Todjo, PharmD
Prevention of Transcription Errors with Pediatric TPN Orders Using a Web Interface Organization Name: University of Maryland Type: Acute Care Hospital Medical Center Contact Person: Belinda Todjo, PharmD
What s In The Bag? 3-in-1 versus 2-in-1 PN
 What s In The Bag? 3-in-1 versus 2-in-1 PN Amber Verdell, PharmD, BCPS, BCNSP Assistant Professor, Pharmacy Practice West Coast University, Los Angeles, CA Disclosures I have no commercial relationships
What s In The Bag? 3-in-1 versus 2-in-1 PN Amber Verdell, PharmD, BCPS, BCNSP Assistant Professor, Pharmacy Practice West Coast University, Los Angeles, CA Disclosures I have no commercial relationships
Module 8: Practice Problems
 Module 8: Practice Problems 1. Convert a blood plasma level range of 5 to 20 µg/ml of tobramycin (Z = 467.52) to µmol/l. 5 µg/ml = 10.7 µmol/l 20 µg/ml = 42.8 µmol/l 2. A preparation contains in each milliliter,
Module 8: Practice Problems 1. Convert a blood plasma level range of 5 to 20 µg/ml of tobramycin (Z = 467.52) to µmol/l. 5 µg/ml = 10.7 µmol/l 20 µg/ml = 42.8 µmol/l 2. A preparation contains in each milliliter,
APPENDIX 1 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SmPC Country: Lebanon Date of approval : 17/08/2011 Procedure : National APPENDIX 1 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1- NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT DECAN, concentrate for solution for infusion 2- QUALITATIVE
SmPC Country: Lebanon Date of approval : 17/08/2011 Procedure : National APPENDIX 1 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1- NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT DECAN, concentrate for solution for infusion 2- QUALITATIVE
Aluminium contamination in products for parenteral nutrition
 Aluminium contamination in products for parenteral nutrition 1. Introduction In the 1970s, aluminium (Al) toxicity was first implicated in the bone disease and neurologic complications seen in patients
Aluminium contamination in products for parenteral nutrition 1. Introduction In the 1970s, aluminium (Al) toxicity was first implicated in the bone disease and neurologic complications seen in patients
Risk Management in Parenteral Nutrition. J. Boullata
 Risk Management in Parenteral Nutrition J. Boullata Objectives Upon completion of this session, the participant will be able to: Describe safety issues with parenteral nutrition (PN) Present the PN-use
Risk Management in Parenteral Nutrition J. Boullata Objectives Upon completion of this session, the participant will be able to: Describe safety issues with parenteral nutrition (PN) Present the PN-use
Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention?
 Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? 1 Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention? Key questions to ask with initial consultation Can the gastrointestinal (GI) tract be utilized? Can the GI tract be
Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? 1 Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention? Key questions to ask with initial consultation Can the gastrointestinal (GI) tract be utilized? Can the GI tract be
Vamin 18 EF QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 Title Page Information Dec. 2000 1 (7) Number Vamin 18 EF 121-01 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Vamin 18 g N/l electrolyte-free infusion fluid, solution 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1000
Title Page Information Dec. 2000 1 (7) Number Vamin 18 EF 121-01 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Vamin 18 g N/l electrolyte-free infusion fluid, solution 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1000
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION - INDIAN CONTEXT. Dr. Sarath Gopalan
 PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION - INDIAN CONTEXT Dr. Sarath Gopalan Senior Consultant in Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, New Delhi PN DELIVERY CENTRAL PERIPHERAL
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION - INDIAN CONTEXT Dr. Sarath Gopalan Senior Consultant in Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, New Delhi PN DELIVERY CENTRAL PERIPHERAL
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS. Synthamin 14, 8.5% Amino Acid Intravenous Infusion
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Synthamin 14, 8.5% Amino Acid Intravenous Infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION L-Leucine Ph. Eur 0.620% w/v L-Isoleucine
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Synthamin 14, 8.5% Amino Acid Intravenous Infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION L-Leucine Ph. Eur 0.620% w/v L-Isoleucine
Module 8: Electrolyte Solutions
 PHARMACEUTICAL CALCULATIONS FALL 207 Contents General Vocab & Definitions... 2 Milliequivalent Calculations... 2 Millimole and Micromole Calculations... 5 Osmolarity... 6 Daily Water Requirement Calculations
PHARMACEUTICAL CALCULATIONS FALL 207 Contents General Vocab & Definitions... 2 Milliequivalent Calculations... 2 Millimole and Micromole Calculations... 5 Osmolarity... 6 Daily Water Requirement Calculations
STANDARD FORMULATED SUPPLEMENTARY SPORTS FOODS
 STANDARD 2.9.4 FORMULATED SUPPLEMENTARY SPORTS FOODS Purpose This Standard defines and regulates the composition and labelling of foods specially formulated to assist sports people in achieving specific
STANDARD 2.9.4 FORMULATED SUPPLEMENTARY SPORTS FOODS Purpose This Standard defines and regulates the composition and labelling of foods specially formulated to assist sports people in achieving specific
Food for special medical purposes. phenylketonuria (PKU) Important notice: Suitable only for individuals with proven phenylketonuria.
 PKU Nutri 1 Energy Food for special medical purposes. For the dietary management of proven phenylketonuria (PKU) in infants from birth to 12 months and as a supplementary feed up to 3 years. An amino acid
PKU Nutri 1 Energy Food for special medical purposes. For the dietary management of proven phenylketonuria (PKU) in infants from birth to 12 months and as a supplementary feed up to 3 years. An amino acid
The nutrient formulas used for parenteral nutrition are
 CASE REPORT Possible Incompatibility between Amino Acids and Copper in Solutions for Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition Maxime Thibault INTRODUCTION The nutrient formulas used for parenteral nutrition are
CASE REPORT Possible Incompatibility between Amino Acids and Copper in Solutions for Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition Maxime Thibault INTRODUCTION The nutrient formulas used for parenteral nutrition are
For more information about Thomson Reuters Micromedex, visit Information valid as of March 17, 2011.
 pentetate calcium trisodium Micromedex drugpoints Summary DrugPoints Summaries provide information on dosage, pharmacokinetics, cautions, interactions, clinical applications, adverse effects, comparative
pentetate calcium trisodium Micromedex drugpoints Summary DrugPoints Summaries provide information on dosage, pharmacokinetics, cautions, interactions, clinical applications, adverse effects, comparative
Aminosteril N-Hepa 8%, solution for infusion. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 Title Page Information Aminosteril N-Hepa 8% November 2001 1 (7) 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Aminosteril N-Hepa 8%, solution for infusion. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1000 ml solution
Title Page Information Aminosteril N-Hepa 8% November 2001 1 (7) 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Aminosteril N-Hepa 8%, solution for infusion. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1000 ml solution
THE AUTHOR OF THIS WHAT S NEW IN NUTRITION? OBJECTIVES & OUTLINE EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE: PARENTERAL NUTRITION (PN)
 WHAT S NEW IN NUTRITION? Alisha Mutch, Pharm.D., BCPS THE AUTHOR OF THIS PRESENTATION HAS NOTHING TO DISCLOSE. OBJECTIVES & OUTLINE MALNUTRITION OBJECTIVES Indicate when parenteral nutrition (PN) is warranted
WHAT S NEW IN NUTRITION? Alisha Mutch, Pharm.D., BCPS THE AUTHOR OF THIS PRESENTATION HAS NOTHING TO DISCLOSE. OBJECTIVES & OUTLINE MALNUTRITION OBJECTIVES Indicate when parenteral nutrition (PN) is warranted
Parenteral Nutrition
 Parenteral Nutrition Standard Operating Procedures Stony Brook University Hospital Pharmacy Department Authors and Contributors: Amanda Waldeck, PharmD, BCPS Nutrition Support Pharmacist Alfredo Viera
Parenteral Nutrition Standard Operating Procedures Stony Brook University Hospital Pharmacy Department Authors and Contributors: Amanda Waldeck, PharmD, BCPS Nutrition Support Pharmacist Alfredo Viera
D.K.M COLLEGE FOR WOMEN (AUTONOMOUS) VELLORE-1 DEPARTMENT OF FOODS AND NUTRITION ESSENTIAL OF MICRO NUTRIENTS
 D.K.M COLLEGE FOR WOMEN (AUTONOMOUS) VELLORE-1 DEPARTMENT OF FOODS AND NUTRITION ESSENTIAL OF MICRO NUTRIENTS Class: II M.Sc Subject Code: 15CPFN3A Unit - I (6 Marks Questions) 1. Write a note on performed
D.K.M COLLEGE FOR WOMEN (AUTONOMOUS) VELLORE-1 DEPARTMENT OF FOODS AND NUTRITION ESSENTIAL OF MICRO NUTRIENTS Class: II M.Sc Subject Code: 15CPFN3A Unit - I (6 Marks Questions) 1. Write a note on performed
ASEPTIC DISPENSING TECHNIQUES/DRUG- NUTRIENT INTERACTIONS
 ASEPTIC DISPENSING TECHNIQUES/DRUG- NUTRIENT INTERACTIONS HARBANS KAUR DHILLON PRESIDENT OF PENSMA KUALA LUMPUR MALAYSIA PENSA 2007 University Malaya Medical Centre Kuala Lumpur ASEPTIC DISPENSING Ppn
ASEPTIC DISPENSING TECHNIQUES/DRUG- NUTRIENT INTERACTIONS HARBANS KAUR DHILLON PRESIDENT OF PENSMA KUALA LUMPUR MALAYSIA PENSA 2007 University Malaya Medical Centre Kuala Lumpur ASEPTIC DISPENSING Ppn
Parenteral Micronutrient Recommendations and Laboratory Monitoring for Infants on Long Term Parenteral Nutrition (PN)
 Parenteral Micronutrient Recommendations and Laboratory Monitoring for nfants on Long Term Parenteral Nutrition (PN) Dosage Micronutrient Preterm Term Trace Elements (mcg/kg/day) (mcg/kg/day) 1 Chromium
Parenteral Micronutrient Recommendations and Laboratory Monitoring for nfants on Long Term Parenteral Nutrition (PN) Dosage Micronutrient Preterm Term Trace Elements (mcg/kg/day) (mcg/kg/day) 1 Chromium
Product Information: PediaSure 1.5 Cal with Fiber
 Product Information: PediaSure 1.5 Cal with Fiber 1 of 5 PEDIASURE 1.5 CAL WITH FIBER is a higher * caloric density product designed to meet the higher energy requirements of pediatric patients who are
Product Information: PediaSure 1.5 Cal with Fiber 1 of 5 PEDIASURE 1.5 CAL WITH FIBER is a higher * caloric density product designed to meet the higher energy requirements of pediatric patients who are
Appendix D: Aerobic and Anaerobic Leaching Tests
 Appendix D: Aerobic and Anaerobic Leaching Tests This appendix contains the entire data set for the aerobic and anaerobic testing. Testing was performed for the potential components of the final media
Appendix D: Aerobic and Anaerobic Leaching Tests This appendix contains the entire data set for the aerobic and anaerobic testing. Testing was performed for the potential components of the final media
PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
Product Information: PediaSure Peptide 1.5 Cal
 Product Information: PediaSure Peptide 1.5 Cal 1 of 5 PEDIASURE PEPTIDE 1.5 is a nutritionally complete, peptide-based formula for the nutritional needs of children 1-13 years with malabsorption, maldigestion,
Product Information: PediaSure Peptide 1.5 Cal 1 of 5 PEDIASURE PEPTIDE 1.5 is a nutritionally complete, peptide-based formula for the nutritional needs of children 1-13 years with malabsorption, maldigestion,
DBL MAGNESIUM SULFATE CONCENTRATED INJECTION
 DBL MAGNESIUM SULFATE CONCENTRATED INJECTION NAME OF MEDICINE Magnesium Sulfate BP DESCRIPTION DBL Magnesium Sulfate Concentrated Injection is a clear, colourless, sterile solution. Each ampoule contains
DBL MAGNESIUM SULFATE CONCENTRATED INJECTION NAME OF MEDICINE Magnesium Sulfate BP DESCRIPTION DBL Magnesium Sulfate Concentrated Injection is a clear, colourless, sterile solution. Each ampoule contains
Product Information: Vital AF 1.2 Cal
 Product Information: Vital AF 1.2 Cal 1 of 5 VITAL AF 1.2 CAL is Advanced Formula therapeutic nutrition with ingredients to help manage inflammation and symptoms of GI intolerance. For tube or oral feeding.
Product Information: Vital AF 1.2 Cal 1 of 5 VITAL AF 1.2 CAL is Advanced Formula therapeutic nutrition with ingredients to help manage inflammation and symptoms of GI intolerance. For tube or oral feeding.
48 th Annual Meeting. A Review of Pharmacy Calculations for Pharmacy Technicians. Metric System of Measurement. Disclosure. Common Conversions
 48 th Annual Meeting A Review of Pharmacy Calculations for Pharmacy Technicians Nina Pavuluri, Ph.D. Navigating the Oceans of Opportunity Metric System of Measurement Base Unit Factor Name Symbol 1 (g,
48 th Annual Meeting A Review of Pharmacy Calculations for Pharmacy Technicians Nina Pavuluri, Ph.D. Navigating the Oceans of Opportunity Metric System of Measurement Base Unit Factor Name Symbol 1 (g,
PRODUCT INFORMATION. DESCRIPTION Addaven is a concentrated trace element solution for infusion which is clear and colourless to slightly yellow.
 PRODUCT INFORMATION Addaven NAME OF MEDICINE Addaven is a concentrated trace element solution containing the following simple salts: chromic chloride hexahydrate (CAS No.:10060-12-5), cupric chloride dihydrate
PRODUCT INFORMATION Addaven NAME OF MEDICINE Addaven is a concentrated trace element solution containing the following simple salts: chromic chloride hexahydrate (CAS No.:10060-12-5), cupric chloride dihydrate
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS. Medical conditions that require parenteral nutrition for supply of energy and essential fatty acids.
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Alphalipid 200 mg/ml emulsion for infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1000 ml of the emulsion contain: Soya-bean oil,
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Alphalipid 200 mg/ml emulsion for infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1000 ml of the emulsion contain: Soya-bean oil,
Grinder-Pedersen L, Rasmussen SE, Bugel S, Jorgensen LV, Dragsted LO, Gundersen V, Sandstrom B.
 1. Organic vs. Commercially Grown Fruits and Vegetables. 2. Effect of diets based on foods from conventional versus organic production on intake and excretion of flavonoids and markers of antioxidative
1. Organic vs. Commercially Grown Fruits and Vegetables. 2. Effect of diets based on foods from conventional versus organic production on intake and excretion of flavonoids and markers of antioxidative
AAFCO Check Sample 2015 Minerals Program. A Targeted and Engineered Concentration Program
 AAFC Check Sample 215 Minerals Program A Targeted and Engineered Concentration Program Approach: 16 Target Elements This quarterly program focuses on minerals of health and toxicological importance in
AAFC Check Sample 215 Minerals Program A Targeted and Engineered Concentration Program Approach: 16 Target Elements This quarterly program focuses on minerals of health and toxicological importance in
Package leaflet: Information for the user. Aminoven 5% Solution for infusion Aminoven 10% Solution for infusion Aminoven 15% Solution for infusion
 Package leaflet: Information for the user Aminoven 5% Solution for infusion Aminoven 10% Solution for infusion Aminoven 15% Solution for infusion Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using
Package leaflet: Information for the user Aminoven 5% Solution for infusion Aminoven 10% Solution for infusion Aminoven 15% Solution for infusion Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using
Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick Neonatal Pharmacist
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Designation: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Designation: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick
DISCLOSURE. Learning Objectives. Controversies in Parenteral Nutrition
 Controversies in Parenteral Nutrition Christopher Duggan, MD, MPH Center for Nutrition Center for Advanced Intestinal Rehabilitation (CAIR) Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Boston
Controversies in Parenteral Nutrition Christopher Duggan, MD, MPH Center for Nutrition Center for Advanced Intestinal Rehabilitation (CAIR) Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Boston
Phosphoremia (mmol/l) Calcemia (mmol/l) Postnatal age (days) Postnatal age (days) Urinary Calcium (mg/kg/d) Phosphoremia (mmol/l)
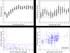 3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
Mineral Nutrients. NOW Guide to Mineral Nutrients
 Mineral Nutrients NOW Guide to Mineral Nutrients The Health Benefits of Mineral Nutrients Mineral nutrients (also called dietary elements and dietary minerals) are inorganic substances that are essential
Mineral Nutrients NOW Guide to Mineral Nutrients The Health Benefits of Mineral Nutrients Mineral nutrients (also called dietary elements and dietary minerals) are inorganic substances that are essential
Product Information: Ketonex -1
 Product Information: 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers with maple syrup urine disease (MSUD). Isoleucine-, leucine- and valine-free. Use under medical supervision. Branched-chain amino acid-free
Product Information: 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers with maple syrup urine disease (MSUD). Isoleucine-, leucine- and valine-free. Use under medical supervision. Branched-chain amino acid-free
Product Information: PediaSure Grow & Gain
 Product Information: PediaSure Grow & Gain 1 of 5 PediaSure Grow & Gain is clinically proven * nutrition to help kids grow, and is a nutritious supplement for kids falling behind on growth. 1,2,3,4,5 May
Product Information: PediaSure Grow & Gain 1 of 5 PediaSure Grow & Gain is clinically proven * nutrition to help kids grow, and is a nutritious supplement for kids falling behind on growth. 1,2,3,4,5 May
CPT David J. Licciardello, DVM Veterinary Advisor
 CPT David J. Licciardello, DVM Veterinary Advisor Carbohydrates Fats (Fatty Acids) Minerals Proteins (Amino Acids) Vitamins Water Referred to as Fiber Made up of the forage portion of a diet In a complete
CPT David J. Licciardello, DVM Veterinary Advisor Carbohydrates Fats (Fatty Acids) Minerals Proteins (Amino Acids) Vitamins Water Referred to as Fiber Made up of the forage portion of a diet In a complete
PARENTERAL PREPARATIONS
 PARENTERAL PREPARATIONS INTRODUCTION Parenteral (Gk, para enteron, beside the intestine) dosage forms differ from all other drug dosage forms, because they are injected directly into body tissue through
PARENTERAL PREPARATIONS INTRODUCTION Parenteral (Gk, para enteron, beside the intestine) dosage forms differ from all other drug dosage forms, because they are injected directly into body tissue through
Product Information: Phenex -1
 Product Information: Phenex -1 1 of 5 For nutrition support of infants and toddlers with phenylketonuria (PKU). Phenylalanine-free Use under medical supervision. Phenylalanine-free to allow greater intake
Product Information: Phenex -1 1 of 5 For nutrition support of infants and toddlers with phenylketonuria (PKU). Phenylalanine-free Use under medical supervision. Phenylalanine-free to allow greater intake
Product Category: Pulmocare
 Product Category: Pulmocare Pulmocare Updated 4/8/2014 Product Information: Pulmocare 1 of 5 PULMOCARE is designed for people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis, or respiratory
Product Category: Pulmocare Pulmocare Updated 4/8/2014 Product Information: Pulmocare 1 of 5 PULMOCARE is designed for people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis, or respiratory
Product Information: Pivot 1.5 Cal
 Product Information: Pivot 1.5 Cal 1 of 5 PIVOT 1.5 CAL is a very-high-protein, calorically dense, immune-supporting, hydrolyzed, peptide-based enteral formula for use in metabolically stressed, immunosuppressed
Product Information: Pivot 1.5 Cal 1 of 5 PIVOT 1.5 CAL is a very-high-protein, calorically dense, immune-supporting, hydrolyzed, peptide-based enteral formula for use in metabolically stressed, immunosuppressed
Product Information:
 Product Information: Pro-Phree 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers who require extra calories, minerals, and vitamins and/or protein restriction. Use under medical supervision. Protein-free
Product Information: Pro-Phree 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers who require extra calories, minerals, and vitamins and/or protein restriction. Use under medical supervision. Protein-free
Vanessa Kumpf, PharmD, BCNSP Clinical Pharmacist Center for Human Nutri;on
 Vanessa Kumpf, PharmD, BCNSP Clinical Pharmacist Center for Human Nutri;on Learn what you can do to: Maximize TPN benefits Minimize TPN-related problems Learn how to monitor your therapy Learn how to read
Vanessa Kumpf, PharmD, BCNSP Clinical Pharmacist Center for Human Nutri;on Learn what you can do to: Maximize TPN benefits Minimize TPN-related problems Learn how to monitor your therapy Learn how to read
Product Information: Tyrex -1
 Product Information: Tyrex -1 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers with tyrosinemia types I, II or III. Phenylalanine- and tyrosine-free. Use under medical supervision. Phenylalanine- and tyrosine-free
Product Information: Tyrex -1 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers with tyrosinemia types I, II or III. Phenylalanine- and tyrosine-free. Use under medical supervision. Phenylalanine- and tyrosine-free
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET
 1. PRODUCT NAME ADDAVEN (infusion, solution concentrate) NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each 10 ml ampoule of Addaven contains: Chromic chloride hexahydrate 53.33 µg
1. PRODUCT NAME ADDAVEN (infusion, solution concentrate) NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each 10 ml ampoule of Addaven contains: Chromic chloride hexahydrate 53.33 µg
Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients. Hamdy Amin, Pharm.D., MBA, BCNSP Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
 Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy Amin, Pharm.D., MBA, BCNSP Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Disclosure Information Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy
Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy Amin, Pharm.D., MBA, BCNSP Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Disclosure Information Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy
Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN *
 For the use of a registered medical practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN * DESCRIPTION: NIRMIN * is a clear, colourless injection
For the use of a registered medical practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN * DESCRIPTION: NIRMIN * is a clear, colourless injection
Product Information: Pivot 1.5 Cal
 Product Information: Pivot 1.5 Cal 1 of 5 PIVOT 1.5 CAL is designed for metabolically stressed surgical, trauma, burn, or head and neck cancer patients who could benefit from an immune modulating enteral
Product Information: Pivot 1.5 Cal 1 of 5 PIVOT 1.5 CAL is designed for metabolically stressed surgical, trauma, burn, or head and neck cancer patients who could benefit from an immune modulating enteral
Product Category: Perative
 Product Category: Perative Perative Updated 4/8/2014 Product Information: Perative 1 of 5 PERATIVE is designed for metabolically stressed patients who can benefit from an enteral formula supplemented with
Product Category: Perative Perative Updated 4/8/2014 Product Information: Perative 1 of 5 PERATIVE is designed for metabolically stressed patients who can benefit from an enteral formula supplemented with
Product Information: Propimex -1
 Product Information: Propimex -1 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers with propionic or methylmalonic acidemia. Methionine- and valine-free; low in isoleucine and threonine. Use under medical
Product Information: Propimex -1 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers with propionic or methylmalonic acidemia. Methionine- and valine-free; low in isoleucine and threonine. Use under medical
Product Information: Perative
 Product Information: Perative 1 of 5 PERATIVE is designed for metabolically stressed patients who can benefit from an enteral formula supplemented with arginine. For tube feeding. For supplemental or sole-source
Product Information: Perative 1 of 5 PERATIVE is designed for metabolically stressed patients who can benefit from an enteral formula supplemented with arginine. For tube feeding. For supplemental or sole-source
Growth, Maintenance, Gestation/Lactation
 SENSITIVE-GI TM Sensitive-GI TM Feline formulas contain a limited number of highly digestible ingredients and provide a nutrient profile that is known to benefit gastrointestinal health, appropriately
SENSITIVE-GI TM Sensitive-GI TM Feline formulas contain a limited number of highly digestible ingredients and provide a nutrient profile that is known to benefit gastrointestinal health, appropriately
Product Information: PediaSure Grow & Gain Therapeutic Nutrition
 Product Information: PediaSure Grow & Gain Therapeutic Nutrition Shake 1 of 5 PEDIASURE GROW & GAIN is clinically proven * nutrition to help kids grow and is a nutritious supplement for kids falling behind
Product Information: PediaSure Grow & Gain Therapeutic Nutrition Shake 1 of 5 PEDIASURE GROW & GAIN is clinically proven * nutrition to help kids grow and is a nutritious supplement for kids falling behind
Product Information: Glucerna 1.2 Cal
 Product Information: Glucerna 1.2 Cal 1 of 5 GLUCERNA 1.2 CAL is a calorically dense formula that has CarbSteady, including low glycemic carbohydrates clinically shown to help minimize blood glucose response.
Product Information: Glucerna 1.2 Cal 1 of 5 GLUCERNA 1.2 CAL is a calorically dense formula that has CarbSteady, including low glycemic carbohydrates clinically shown to help minimize blood glucose response.
Electrolytes Solution
 Electrolytes Solution Substances that are not dissociated in solution are called nonelectrolytes, and those with varying degrees of dissociation are called electrolytes. Urea and dextrose are examples
Electrolytes Solution Substances that are not dissociated in solution are called nonelectrolytes, and those with varying degrees of dissociation are called electrolytes. Urea and dextrose are examples
TOXIC AND ESSENTIAL ELEMENTS
 TOXIC AND ESSENTIAL ELEMENTS Assessment of Key Minerals and Harmful Metals Whole Blood, Red Blood Cell and Serum Elements Urine Toxic and Essential Elements Creatinine Clearance Hair Elements Fecal Metals
TOXIC AND ESSENTIAL ELEMENTS Assessment of Key Minerals and Harmful Metals Whole Blood, Red Blood Cell and Serum Elements Urine Toxic and Essential Elements Creatinine Clearance Hair Elements Fecal Metals
CANADA S NEW FOOD LABELLING REGULATIONS
 CANADA S NEW FOOD LABELLING REGULATIONS an ebook from ESHA Research 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 3 The Nutrition Facts Overview... 4 Changes in Daily Value... 4 Formatting... 5 Nutrient Changes...
CANADA S NEW FOOD LABELLING REGULATIONS an ebook from ESHA Research 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 3 The Nutrition Facts Overview... 4 Changes in Daily Value... 4 Formatting... 5 Nutrient Changes...
Short Bowel Syndrome: Medical management
 Short Bowel Syndrome: Medical management La Sindrome dell'intestino Corto in età pediatrica Brescia 18 marzo 2011 Jon A.Vanderhoof, M.D. Division of Pediatric GI Harvard Medical School Children s Hospital,
Short Bowel Syndrome: Medical management La Sindrome dell'intestino Corto in età pediatrica Brescia 18 marzo 2011 Jon A.Vanderhoof, M.D. Division of Pediatric GI Harvard Medical School Children s Hospital,
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION. Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah
 PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah Johor Bahru Malnutrition INTRODUCTION pathologic state of varying severity with clinical features caused
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah Johor Bahru Malnutrition INTRODUCTION pathologic state of varying severity with clinical features caused
Tech Lectures For the Pharmacy Technician
 1 Tech Lectures For the Pharmacy Technician P.O. Box 19357 Denver, CO 80219-0357 303-984-9877 Lecture 14 - Hospital Calculations It is respectfully requested by the Author that no part of this Tech Lecture
1 Tech Lectures For the Pharmacy Technician P.O. Box 19357 Denver, CO 80219-0357 303-984-9877 Lecture 14 - Hospital Calculations It is respectfully requested by the Author that no part of this Tech Lecture
Protein Deposition in Growing and Finishing Pigs
 1 Protein Deposition in Growing and Finishing Pigs DETERMINING WHOLE BODY PROTEIN DEPOSITION RATES IN PIGS. Mark L. Lorschy, Doug A. Gillis, John F. Patience and Kees de Lange. Summary There is controversy
1 Protein Deposition in Growing and Finishing Pigs DETERMINING WHOLE BODY PROTEIN DEPOSITION RATES IN PIGS. Mark L. Lorschy, Doug A. Gillis, John F. Patience and Kees de Lange. Summary There is controversy
Ranchers Choice AN -18%
 Ranchers Choice AN -18% All Purpose For Cattle, Sheep, Horses Guaranteed Analysis CRUDE PROTEIN, not less than... 18.0% CRUDE FAT, not less than... 4.00% CRUDE FIBER, not more than... 1.00% CALCIUM (Ca),
Ranchers Choice AN -18% All Purpose For Cattle, Sheep, Horses Guaranteed Analysis CRUDE PROTEIN, not less than... 18.0% CRUDE FAT, not less than... 4.00% CRUDE FIBER, not more than... 1.00% CALCIUM (Ca),
Product Information: Similac Advance
 Product Information: Similac Advance 1 of 5 A 19 Cal/fl oz, nutritionally complete, milk-based, iron-fortified infant formula for use as a supplement or alternative to breastfeeding. OptiGRO is our exclusive
Product Information: Similac Advance 1 of 5 A 19 Cal/fl oz, nutritionally complete, milk-based, iron-fortified infant formula for use as a supplement or alternative to breastfeeding. OptiGRO is our exclusive
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes
 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
Application Note novaa 800 D. Determination of Macro and Trace Minerals as well as Toxic Trace Metals in Powdered Milk. Challenge.
 Application Note novaa 800 D Determination of Macro and Trace Minerals as well as Toxic Trace Metals in Powdered Milk Introduction The popularity of milk and dairy products is growing worldwide, resulting
Application Note novaa 800 D Determination of Macro and Trace Minerals as well as Toxic Trace Metals in Powdered Milk Introduction The popularity of milk and dairy products is growing worldwide, resulting
Food Nutrient Workshop. Medical Education Director
 Food Nutrient Workshop By: Heather Schofield, B.Sc., DHMHS Medical Education Director Vitamin and Mineral Absorption Segmental absorptive functions of the GI tract: Mouth Esophagus Stomach - glucose -
Food Nutrient Workshop By: Heather Schofield, B.Sc., DHMHS Medical Education Director Vitamin and Mineral Absorption Segmental absorptive functions of the GI tract: Mouth Esophagus Stomach - glucose -
PRODUCT INFORMATION. NAME OF MEDICINE VAMIN 14, VAMIN 14 Electrolyte Free and VAMIN 18 Electrolyte Free
 PRODUCT INFORMATION NAME OF MEDICINE VAMIN 14, VAMIN 14 Electrolyte Free and VAMIN 18 Electrolyte Free DESCRIPTION Table 1 Vamin 14 Vamin 14 Vamin 18 Electrolyte free Electrolyte free g/l % of total amino
PRODUCT INFORMATION NAME OF MEDICINE VAMIN 14, VAMIN 14 Electrolyte Free and VAMIN 18 Electrolyte Free DESCRIPTION Table 1 Vamin 14 Vamin 14 Vamin 18 Electrolyte free Electrolyte free g/l % of total amino
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Addaven concentrate for solution for infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Addaven contains: 1 ml 1 ampoule (10 ml) Chromic
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Addaven concentrate for solution for infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Addaven contains: 1 ml 1 ampoule (10 ml) Chromic
PROJECT WOMEN S ANAEMIA. by My HealthWorks. Associate Member. 125A, 2nd Floor, Shahpur Jat, New Delhi ,
 PROJECT WOMEN S ANAEMIA by My HealthWorks Associate Member 125A, 2nd Floor, Shahpur Jat, New Delhi-110049, Whatsapp: 8076964582, Phone No: 011-26496673-(74) info@myhealthworks.in INTRODUCTION Anaemia is
PROJECT WOMEN S ANAEMIA by My HealthWorks Associate Member 125A, 2nd Floor, Shahpur Jat, New Delhi-110049, Whatsapp: 8076964582, Phone No: 011-26496673-(74) info@myhealthworks.in INTRODUCTION Anaemia is
Product Category: Promote
 Product Category: Promote Promote Promote with Fiber Updated 4/28/2016 Very-High-Protein Nutrition Product Information: Promote 1 of 5 Very-High-Protein Nutrition PROMOTE is a complete, balanced, very-high-protein
Product Category: Promote Promote Promote with Fiber Updated 4/28/2016 Very-High-Protein Nutrition Product Information: Promote 1 of 5 Very-High-Protein Nutrition PROMOTE is a complete, balanced, very-high-protein
Product Information: Perative
 Product Information: Perative 1 of 5 PERATIVE is designed for metabolically stressed patients who can benefit from an enteral formula supplemented with arginine. For tube feeding. For supplemental or sole-source
Product Information: Perative 1 of 5 PERATIVE is designed for metabolically stressed patients who can benefit from an enteral formula supplemented with arginine. For tube feeding. For supplemental or sole-source
Mineral Supplementation of Grazing Beef Cows in Florida
 Mineral Supplementation of Grazing Beef Cows in Florida University of Florida 2010 Beef Cattle Shortcourse John Arthington Professor and Center Director University of Florida IFAS Range Cattle Research
Mineral Supplementation of Grazing Beef Cows in Florida University of Florida 2010 Beef Cattle Shortcourse John Arthington Professor and Center Director University of Florida IFAS Range Cattle Research
Aminosyn -PF 7% Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION - PEDIATRIC FORMULA Flexible Plastic Container R x only
 Aminosyn -PF 7% Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION - PEDIATRIC FORMULA Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn -PF 7%, Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid injection pediatric formula) is a
Aminosyn -PF 7% Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION - PEDIATRIC FORMULA Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn -PF 7%, Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid injection pediatric formula) is a
ANNEX. to the COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) /
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, XXX SANTE/12273/2015 ANNEX (POOL/E4/2015/12273/12273-EN ANNEX.doc) D043783/01 [ ](2016) XXX draft ANNEX 1 ANNEX to the COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) / amending Regulation (EU)
EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, XXX SANTE/12273/2015 ANNEX (POOL/E4/2015/12273/12273-EN ANNEX.doc) D043783/01 [ ](2016) XXX draft ANNEX 1 ANNEX to the COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) / amending Regulation (EU)
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition. in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT. Dzulfikar DLH. Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit
 The Role of Parenteral Nutrition in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Dzulfikar DLH Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit Department of Child Health, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjajaran, Hasan
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Dzulfikar DLH Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit Department of Child Health, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjajaran, Hasan
Aminosyn 10% (ph 6) Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION Flexible Plastic Container R x only
 Aminosyn 10% (ph 6) Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn 10% (ph 6), Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution
Aminosyn 10% (ph 6) Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn 10% (ph 6), Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution
Multi Analyte Custom Grade Solution
 1.0 ACCREDITATION / REGISTRATION INORGANIC VENTURES is accredited to ISO Guide 34, "General Requirements for the Competence of Reference Material Producers" and ISO/IEC 17025, "General Requirements for
1.0 ACCREDITATION / REGISTRATION INORGANIC VENTURES is accredited to ISO Guide 34, "General Requirements for the Competence of Reference Material Producers" and ISO/IEC 17025, "General Requirements for
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT DUPHALYTE Solution for injection 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Active substances: Composition per ml VITAMINS
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT DUPHALYTE Solution for injection 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Active substances: Composition per ml VITAMINS
Long term monitoring. Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian St Mark s Hospital
 Long term monitoring Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian St Mark s Hospital Patient 23 year old lady 1/4/14 Colectomy for UC 3-7/4/14 Ischaemic bowel 4 laparotomies Jejunostomy at 35 cm 23/5/14 Weight
Long term monitoring Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian St Mark s Hospital Patient 23 year old lady 1/4/14 Colectomy for UC 3-7/4/14 Ischaemic bowel 4 laparotomies Jejunostomy at 35 cm 23/5/14 Weight
» Monohydrate Citric Acid contains one molecule of water of hydration. It contains not less than 99.5 percent and not more than 100.
 BRIEFING Citric Acid, Monohydrate. The European Pharmacopoeia is the coordinating pharmacopeia for the international harmonization of the compendial standards for the Citric Acid, Monohydrate monograph,
BRIEFING Citric Acid, Monohydrate. The European Pharmacopoeia is the coordinating pharmacopeia for the international harmonization of the compendial standards for the Citric Acid, Monohydrate monograph,
Product Information: PediaSure (Institutional)
 Product Information: PediaSure (Institutional) 1 of 5 PediaSure is a source of complete, balanced nutrition especially designed for children 1 to 13 years of age. May be used as the sole source of nutrition
Product Information: PediaSure (Institutional) 1 of 5 PediaSure is a source of complete, balanced nutrition especially designed for children 1 to 13 years of age. May be used as the sole source of nutrition
Product Category: Vital
 Vital Product Category: Vital Vital AF 1.2 Cal Vital High Protein Vital 1.0 Cal Vital 1.5 Cal Updated 4/28/2016 Vital AF 1.2 Cal Therapeutic Nutrition Product Information: Vital AF 1.2 Cal 1 of 5 Vital
Vital Product Category: Vital Vital AF 1.2 Cal Vital High Protein Vital 1.0 Cal Vital 1.5 Cal Updated 4/28/2016 Vital AF 1.2 Cal Therapeutic Nutrition Product Information: Vital AF 1.2 Cal 1 of 5 Vital
2. PRESCRIPTION STATUS/RESTRICTION OF SALES TO PHARMACIES ONLY 3. COMPOSITION OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
 Title Page Product Information May 2000 1 (6) Product Nephrotect 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Nephrotect 2. PRESCRIPTION STATUS/RESTRICTION OF SALES TO PHARMACIES ONLY For sale in pharmacies only 3.
Title Page Product Information May 2000 1 (6) Product Nephrotect 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Nephrotect 2. PRESCRIPTION STATUS/RESTRICTION OF SALES TO PHARMACIES ONLY For sale in pharmacies only 3.
Product Category: Pivot 1.5 Cal
 Product Category: Pivot 1.5 Cal Pivot 1.5 Cal Updated 4/8/2014 Product Information: Pivot 1.5 Cal 1 of 6 PIVOT 1.5 CAL is designed for metabolically stressed surgical, trauma, burn, and head and neck cancer
Product Category: Pivot 1.5 Cal Pivot 1.5 Cal Updated 4/8/2014 Product Information: Pivot 1.5 Cal 1 of 6 PIVOT 1.5 CAL is designed for metabolically stressed surgical, trauma, burn, and head and neck cancer
***II POSITION OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT
 EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT 1999 2004 Consolidated legislative document 13 March 2002 2000/0080(COD) PE2 ***II POSITION OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT adopted at second reading on 13 March 2002 with a view to the
EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT 1999 2004 Consolidated legislative document 13 March 2002 2000/0080(COD) PE2 ***II POSITION OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT adopted at second reading on 13 March 2002 with a view to the
6 ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS PART II VITAMINS MINERALS WATER
 6 ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS PART II VITAMINS MINERALS WATER VITAMINS What Are They? Tasteless organic compounds that you need in small amounts for growth, reproduction, and overall good health. The DO NOT provide
6 ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS PART II VITAMINS MINERALS WATER VITAMINS What Are They? Tasteless organic compounds that you need in small amounts for growth, reproduction, and overall good health. The DO NOT provide
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. SODIPHOS 22mEq / 10ml Concentrate for solution for infusion. Disodium phosphate dihydrate
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER SODIPHOS 22mEq / 10ml Concentrate for solution for infusion Disodium phosphate dihydrate Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER SODIPHOS 22mEq / 10ml Concentrate for solution for infusion Disodium phosphate dihydrate Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
LifePak Health Benefits. LifePak is optimum supplementation for:
 LifePak What is LifePak? Our comprehensive nutritional wellness program delivering the optimum amounts of all essential and generally beneficial nutrients for long-term health and well-being. LifePak Health
LifePak What is LifePak? Our comprehensive nutritional wellness program delivering the optimum amounts of all essential and generally beneficial nutrients for long-term health and well-being. LifePak Health
Introduction to Clinical Nutrition
 M-III Introduction to Clinical Nutrition Donald F. Kirby, MD Chief, Section of Nutrition Division of Gastroenterology 1 Things We Take for Granted Air to Breathe Death Taxes Another Admission Our Next
M-III Introduction to Clinical Nutrition Donald F. Kirby, MD Chief, Section of Nutrition Division of Gastroenterology 1 Things We Take for Granted Air to Breathe Death Taxes Another Admission Our Next
Aminosyn II Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION Flexible Plastic Container R x only
 Aminosyn II Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn II, Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution for intravenous
Aminosyn II Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn II, Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution for intravenous
