Wood Surface Treatments to Prevent Extractive Staining of Paints
|
|
|
- Melvin Little
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Wood Surface Treatments to Prevent Extractive Staining of Paints William C. Feist Abstract A number of water-soluble chemicals including stannous chloride, zinc oxide-ammonia complex, copper chromate, and simple chromium compounds were used to pretreat the surfaces of redwood and western redcedar. Each of these chemical treatments was successful to a degree in preventing the staining, by water-soluble wood extractives, of subsequently applied water-base latex paints. A number of different treating variables were evaluated. CAUTION: Latex or other water-base primers are NOT FOR USE over bare redwood, cedar, or cypress, since these primers will not resist the natural bleeding of water-soluble stains (extractives) in these woods. This warning, or one very similar to it, appears on paint cans and in many descriptive books and pamphlets on painting. The reason for it is that watersoluble extractives from certain wood species can produce an unsightly red-to-brown discoloration on paint coatings, particularly on porous paints, whenever moisture has access to the wood substrate (10). Proposed solutions to the problem of extractive staining have been described in early (9) and recent literature (4,7). The recent studies were on lead-free compounds since Public Law , Lead Paint Poisoning Prevention Act, January 13, 1971, banned the use of lead-containing compounds in those paints with which children could come into contact. The extractive staining of latex paints had generally been controlled by reactive lead silicate pigments. The staining was also controlled by the use of an oleoresinous primer coat (2,10,11). Pretreatment of redwood and cedar surfaces with certain inorganic chemicals, notably copper chromate and related compounds, is effective in fixing complexing the water-soluble extractives in redwood and cedar (and other wood species of high extractives content) and thus minimizing paint staining (1) Recent work describes pretreatments with zinc salt complexes (5,6). The chemical nature of these extractives and some proposed mechanisms of fixation have also recently been reviewed (8). The objective of the present work was to in- vestigate methods of fixing water-soluble wood extractives to prevent them from subsequently discoloring paint, and permit the application of primarily water base latex painting systems directly to wood without special primers. This would greatly simplify the wood painting process and might also enhance the life of the exterior coating as reported previously (1). Wood Samples Samples of redwood (Sequoia sempervirens) and western redcedar (Thuja plicata), measuring 4-1/2 The author is Research Chemist, USDA Forest Serv. Forest Prod. Lab., Madison, Wis. The author thanks P. G. Sotos for preparing samples and performing analyses and E. A. Mraz for suggestions and advice. 50 MAY 1977
2 Table 1. COMPOSITION OF COPPER CHROMATE SOLUTIONS. Components Quantity (g) CuSO 4 5 H 2 O Na 2 Cr 2 O 7 2 H 2 O NH 4 OH (30% NH) H 2 O Molar ratio, Cu/Cr 3/1 1/1 1/3 3/1 1/1 1/3 inches by 3/8 inch by 15 inches longitudinally, were cut from large boards. Each sample was divided into five equal longitudinal parts by urethane varnish stripes. Thus, different concentrations of treating chemical could be examined on the same sample as well as be compared to an untreated wood area. The samples were stored at 30 percent relative humidity (RH and 26.7 C prior to treatment. Chemicals Tested Copper Chromate Earlier work at the Forest Products Laboratory indicated the effectiveness of copper chromate (CuCrO 4 ) compounds in fixing wood extractives (1). This work was continued with an examination of the effect of treating variables on the efficacy of the treatment. Variables investigated included: concentration of chemical, ratio of copper to chromium, effect of time after treatment and before subsequent painting, and effect of heating the surface-treated wood before painting. The chemicals used in this portion of the study are shown in Table 1. Each solution had a total copper and chromium content (referred to hereafter as total metals) of 2.5 percent. Additional dilutions tested were 1.25 and 0.63 percent total metals. Stannous Chloride Oxides of tin are amphoteric and a number of complex ions can be formed in solution by adding acid or alkali (3). Four stannous chloride (SnCl 2 ) solutions were freshly prepared using either hydrochloric acid or odium hydroxide in three of them. Three concentrations of stannous ion (tin metal) were examined 2.5, 1.25, and 0.63 percent. Compositions of the treating solutions are shown in Table 2. A solution containing 5 percent tin was used in a later comparative study (9.5% stannous chloride). Zinc Oxide Zinc oxide (ZnO) complexed with ammonia was evaluated for comparative purposes since it had been reported to prevent staining of paint over wood (5,6). Table 2 COMPOSITION OF STANNOUS CHLORIDE SOLUTIONS. Components Quantity (g) SnCl 2 2H 2 O H 2 O acidic hydrochloric acid (HCl), 20.0 Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) The 4 percent zinc metal solution was prepared by dissolving 10 grams zinc oxide and 12 grams ammonium carbonate in 178 milliliters of 6 percent ammonium hydroxide. Additional dilutions evaluated were 2 and 1 percent zinc metal. Chromate Salts Three chromate compounds were examined in addition to copper chromate. A solution of chromium trioxide (CrO 3, chromic acid) was prepared by dissolving 10 grams of the chemical in 190 milliliters of water to give a solution with 2.5 percent chromium metal. Dilutions of 1.25 and 0.63 percent chromium were examined. The other chromates were ammonium chromate (14.6 g in ml water) and sodium dichromate (14.3 g of sodium dichromate dihydrate in ml water). General Procedure The treating chemical was applied by brush to each wood sample at an approximate rate of 15 grams of solution per 1,000 square centimeters. The end portions of each wood sample were left untreated and the center portions treated with one of each of the three dilutions of chemical. After any conditioning or post treatment, the samples were wiped with a cloth to remove any excess surface chemicals. Then two coats of a standard, laboratory-prepared, white acrylic latex paint were applied with a 5-hour interval between coats. After 24 hours at room temperature, the samples were placed on open-back racks at 26.7 C and 90 percent RH for periods of 1 to 3 months. Three end-matched wood samples were used to study either the effect of heating after treatment, or conditioning time after treatment and before painting. The heat-study boards were treated and wrapped tightly in aluminum foil to prevent drying, and placed in a forced-draft oven at 60 or 80 C for 1 or 2 hours. The samples were unwrapped and allowed to stand at room temperatures for 24 hours before painting. The boards used to study conditioning time were treated and placed in 80 percent RH and 26.7 C for 1, 3, or 7 days before painting. Brightness Measurement The amount of extractive staining through the white latex paint was determined visually by comparing the treated areas to untreated areas and by the use of a tristimulus colorimeter. With the colorimeter, the brightness of the white painted surface was measured using a standard paper test, TAPPI Method T 217, M-48. The method gives a number indicative of the brightness or reflectance of the sample. The standard used was three coats of the acrylic latex paint on an aluminum plate, which gave a brightness value of 90. Chemical Treatments vs. Commercial Primers Several promising chemical pretreatments were compared to three commercial primer paints for effectiveness in preventing extractive staining through a latex paint. Two primers were oil-base alkyd paints recommended for use over new redwood and cedar. The third commercial primer was a latex paint FOREST PRODUCTS JOURNAL Vol. 27, No. 5 51
3 Three end-matched samples were used for each chemical tested and each wood- The wood samples were preconditioned for 7 days at 30, 65, or 90 percent, RH and 26.7 C. The samples were then treated with three concentrations of each of the five chemicals and allowed to stand 24 hours at ambient conditions. Two coats of the standard acrylic latex paint were then applied with 5 hours between coats. After 24 hours of drying at room temperature, the samples were stored on open-back racks at 90 percent RH and 26.7 C. Brightness values were determined at 1, 2, and 3 months. Figure 1. Range of brightness values for latex paints on untreated redwood exposed to 90 percent RH and 26.7 C. not recommended for use over staining-type wood. The chemicals were stannous chloride, chromium trioxide, zinc oxide, acid copper chromate, and ammoniacal copper chromate. The concentration of the stannous chloride was doubled for this experiment (5% metal). The acid and ammoniacal copper chromates were prepared at a Cu/Cr ratio of 1/1. Four redwood and two cedar boards were randomly selected for each chemical or primer. Each sample was divided into five equal longitudinal parts by a urethane varnish stripe for the chemical pretreatments or into two equal parts for the primer application. The chemical pretreatments were brush-applied at three different concentrations. After 24 hours at room temperature, two coats of the standard acrylic latex paint were applied with a 5-hour interval between coats. For the boards with commercial primers, the primer coat was applied on one-half of the board and allowed to dry 24 hours under ambient conditions. One coat of acrylic latex paint was then applied to the unprimed half of the sample. After 5 hours, a second coat of latex paint was applied over the entire sample. In this way, only two total coats of paint were on each sample, the same as for the chemically treated samples. All samples stood for an additional 24 hours, brightness values were measured, and the samples placed at 90 percent RH and 26.7 C on open-back frames. Brightness values were measured at 1, 2, and 3 months. Effect of RH Preconditioning redwood and cedar samples at different RHs may influence the subsequent effectiveness of extractive fixation by chemical pretreatments. This influence was evaluated for five chemicals and three RHs. Results and Discussion Paint, especially porous paints of the latex house paint type, can be severely discolored by the water soluble extractives from the heartwood of redwood and western redcedar whenever water (rain, dew, or vapor) has ready access to the wood substrate. The concentration of the extractives varies within a particular piece of wood as well as from piece to piece, and the uneven staining results in an unsightly appearance. This variability in extractives content and subsequent staining is illustrated (Fig. 1) where the brightness values for the painted, untreated redwood and cedar boards are shown as a function of exposure time to 90 percent RH. This variability made assessment of each individual chemical treatment difficult, especially when comparing treating variables. Using endmatched samples or averaging results over several replicates reduced this problem- In addition, every attempt was made to select uniformly dark boards This study involved a large number of treatment variables and observations of brightness values representing extractive staining. Rather than attempt to cover all the aspects and observations, only the most encouraging results will be summarized here. The brightness values (Table 3) for paint over treated redwood and cedar after 3 months exposure to 90 percent RH, show that stannous chloride, chromium trioxide, zinc oxide-ammonia complex, and copper chromates effectively prevented staining by wood extractives. These treatments compared favorably to the recommended practice for preventing paint staining, namely, use of an oil-base primer under the latex paint topcoat. The copper- or chromium-containing chemicals were all effective even at low concentrations of 0.63 percent metal, but these are colored chemicals and a slight green color would sometimes migrate through the paint. This was most-noticeable at the 25 percent metal concentration. The stannous chloride treatment was an effective treatment, particularly at 5 percent tin concentration, although other experiments indicated that boards with exceptionally high extractives content would sometimes stain unevenly through the paint film. In all the experiments performed, no one chemical treatment was totally effective in fixing extractives and preventing the subsequent staining of paint. Generally, extractive staining was more prevalent in untreated redwood than in untreated cedar boards 52 MAY 1977
4 Table 3. BRIGHTNESS VALUES FOR TREATED AND PAINTED REDWOOD AND CEDAR BOARDS BEFORE AND AFTER 3 MONTHS' EXPOSURE TO 90 PERCENT RH AND 26.7 C. STANDARD PAINT ON ALUMINUM = 90. Redwood 1 Cedar 2 Treatment Before After Before After Stannous chloride 5% tin 2.5% tin 1.25% tin Chromium trioxide 2.5% chromium 1.25% chromium 0.63% chromium Zinc oxide-ammonia 4 % zinc 2 % zinc 1 % zinc Ammoniacal copper chromate 2.5% metals Acid copper chromate 2.5% metals 3 Oil-base Primer-1 Oil-base Primer-2 Latex base Primer 1 Each value ix an average of 4. Each value ix au average of 2. 1 Copper and chromium Most chemical treatments were more effective on cedar than on redwood except for cedar with apparent high extractives content on the wood surface, which caused dark, uneven streaking through the applied paint Figure 2 shows a typical test panel after 3 months exposure to 90 percent RH. The end portions of each board were untreated. The center portions were treated with each of the three chemical concentrations. Each board was either randomly selected or end-matched, depending on the purpose of the experiment. In the panel in Figure 2, the three boards were end-matched to evaluate the effect of preconditioning the boards at three different RHs before chemical treatment. This is discussed later. Development of Staining Staining of paint over redwood or cedar increases with exposure to high humidity. In Figure 3, brightness values for the chemically treated samples are compared with untreated painted wood and oilbase primed, painted wood. The effectiveness of the various chemicals investigated is apparent; staining continues through exposure, although differences between 2 and 3 months are generally less than those between 1 and 2 months. Stannous chloride and chromium trioxide gave slightly better results than did the other chemicals investigated, with the zinc oxideammonium treatment being least effective. The variability in the staining of untreated wood is again obvious (Fig. 3). Reconditioning at Three RHs The end-matched samples of redwood and cedar preconditioned to 30, 60, or 90 percent RH were evaluated after 3 months exposure to 90 percent RH (Table 4). Generally, the chemical treatment was slightly more effective on wood which had been preconditioned at 30 percent RH rather than at 60 or 90 percent; that is, drier wood can be treated more FOREST PRODUCTS JOURNAL Vol. 27, No. 5 53
5 Table 4. BRIGHTNESS VALUES FOR PAINTRD REDWOOD AND CEDAR TREATED AFTER CONDITIONING TO 30, 65. AND 90 PERCENT RH AND SUBSEQUENTLY EXPOSED TO 90 PERCENT RH AND 26.7 C FOR 3 MONTHS. STANDARD PAINT ON ALUMINUM = 90. Treatment Stannous chloride 5% tin 2.5% tin 1.25% tin Chromium trioxide 2.5% chromium 1.25% chromium 0.63% chromium Zinc oxide-ammonia 4% zinc 2% zinc 1% zinc Ammoniacal copper chromate 2.5% metals 1 Acid copper chromate 2.5% metals 1 1 Copper and chromium. Redwood at RH of Cedar at RH of readily. The differences observed were relatively small for redwood and very small for cedar. Concentration effects are also apparent. Other Treatment Variables A variety of treating times, chemical ratios, concentrations, and heat treatments was investigated to determine their effects on extractive fixation and subsequent staining of applied latex paint. The copper chromate chemicals were investigated to the greatest extent. Conditioning time after treatment, ratio of copper to chromium, concentration, heat treatment after chemical treatment, and related variables were examined. In these experiments, little difference was noted through a wide range of variables. The most important factors that affected the results were the variability of the extractives in the wood, and the concentration and nature of chemical. Stannous chloride treatments were performed on redwood and cedar (Table 2) with either hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide added to change the ph and the composition of the stannous ion in solution (complex ion formation). Little difference was observed in the four treatments investigated. Chemical Treatments And Durability All paint panels were installed on a test fence in Madison, Wisconsin. The panels face south and were installed at 90. These panels will remain in test and be inspected annually so that the durability and any staining of the standard paint over the treated wood surfaces can be evaluated. These results will be reported in the future. Conclusions A numher of water-soluble chemicals, ranging from stannous chloride and zinc oxide-ammonia complex to chromate compounds and chromium. trioxide, were evaluated for their ability to fix the water-soluble extractives of redwood and western redcedar. All compounds investigated were successful to a degree in fixing the extractives and minimizing the staining of water-base latex paints applied over the treated wood. No chemical treatment was more effective than the generally recommended practice of priming extractive-rich woods with oil-base primer paints to prevent or control extractive staining. Many treatments were as effective, however, particularly stannous chloride, chromium trioxide, and ammoniacal copper chromate. The compounds containing colored chromium caused some chemical staining through the applied white latex paint. A number of treatment variables were investigated including concentration, temperature, preconditioning to different RHs, conditioning time after treatment, and ratios of chemicals. Only chemical concentration had any marked effect. A 9.5 percent stannous chloride treatment (5% tin) was consistently effective and, because of its colorless solutions, did not develop color in the applied paint. None of the chemical solutions gave completely consistent results. When the treatments were used on very dark redwood or cedar samples, indicative of high concentrations of extractives on the surface, some uneven staining was observed through the white paint even at the highest chemical concentrations examined. Chemical pretreatment of extractive-rich wood surfaces can be an effective tool in preventing the staining of applied water-base latex paints cawed by migration of the water-soluble extractives. Literature Cited
Formulating for Tannin Stain Inhibition
 Formulating for Tannin Stain Inhibition April 23, 2013 Nathan Kofira Tannin staining is the discoloration of a painted surface due to the migration of water soluble Tannins (tannic acids) through the film
Formulating for Tannin Stain Inhibition April 23, 2013 Nathan Kofira Tannin staining is the discoloration of a painted surface due to the migration of water soluble Tannins (tannic acids) through the film
GLUING FIRE-RETARDANT- TREATED DOUGLAS-FIR AND WESTERN HEMLOCK
 U.S. DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE FOREST PRODUCTS LABORATORY In Cooperation with the University of Wisconsin FOREST SERVICE MADISON, WIS. U.S.D.A. FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH NOTE FPL-0160 NOVERMBER 1968 GLUING
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE FOREST PRODUCTS LABORATORY In Cooperation with the University of Wisconsin FOREST SERVICE MADISON, WIS. U.S.D.A. FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH NOTE FPL-0160 NOVERMBER 1968 GLUING
Corrosion Inhibitors. Background & Mechanisms. Applications & Formulating Strategies
 Corrosion Inhibitors for Waterborne Alkyd Technology 28 th Biennial Western Coatings Societies Symposium & Show Las Vegas, Nevada October 2007 Outline: Corrosion Inhibitors Background & Mechanisms Applications
Corrosion Inhibitors for Waterborne Alkyd Technology 28 th Biennial Western Coatings Societies Symposium & Show Las Vegas, Nevada October 2007 Outline: Corrosion Inhibitors Background & Mechanisms Applications
Can wetting and dispersing additives improve the durability of coatings?
 Can wetting and dispersing additives improve the durability of coatings? János Hajas BYK-Chemie, Wesel, Germany Topics: WETTING AND DISPERSING ADDITIVE, DURABILITY, CORROSION RESISTANCE 1. Abstracts There
Can wetting and dispersing additives improve the durability of coatings? János Hajas BYK-Chemie, Wesel, Germany Topics: WETTING AND DISPERSING ADDITIVE, DURABILITY, CORROSION RESISTANCE 1. Abstracts There
TECHNICAL NOTE SURFACE PREPARATION GUIDE
 TECHNICAL NOTE SURFACE PREPARATION GUIDE For high strength structural bonds, paint, oxide films, oils, dust, mould, release agents and all other surface contaminants must be completely removed. However,
TECHNICAL NOTE SURFACE PREPARATION GUIDE For high strength structural bonds, paint, oxide films, oils, dust, mould, release agents and all other surface contaminants must be completely removed. However,
WEATHERING AND FINISH PERFORMANCE OF ACETYLATED ASPEN FIBERBOARD1 William C. Feist. Roger M. Rowel1. and John A. Youngquist
 WEATHERING AND FINISH PERFORMANCE OF ACETYLATED ASPEN FIBERBOARD1 William C. Feist Supervisory Research Chemist Roger M. Rowel1 Research Chemist and John A. Youngquist Supervisory Research General Engineer
WEATHERING AND FINISH PERFORMANCE OF ACETYLATED ASPEN FIBERBOARD1 William C. Feist Supervisory Research Chemist Roger M. Rowel1 Research Chemist and John A. Youngquist Supervisory Research General Engineer
Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3
 Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3 Objectives: To observe the solubility of alcohols relative to their chemical structure, to perform chemical tests to distinguish primary, secondary and
Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3 Objectives: To observe the solubility of alcohols relative to their chemical structure, to perform chemical tests to distinguish primary, secondary and
Can Wetting and Dispersing Additives Improve the Durability of Coatings? János Hajas. Technical support manager Coating additives
 Lehet-e nedvesitö-és diszpergálószerekkel a festékek tartósságát javítani? Wetting, Dispersion and Stabilization of Titanium Dioxide in Organic Coatings Can Wetting and Dispersing Additives Improve the
Lehet-e nedvesitö-és diszpergálószerekkel a festékek tartósságát javítani? Wetting, Dispersion and Stabilization of Titanium Dioxide in Organic Coatings Can Wetting and Dispersing Additives Improve the
EFFICIENCY OF ANTICORROSIVE PIGMENTS BASED ON METAL PHOSPHATES
 EFFICIENCY OF ANTICORROSIVE PIGMENTS BASED ON METAL PHOSPHATES Ing. David Veselý, Ph.D. University of Pardubice, Institute of Chemistry and Technology of Macromolecular Compounds, Faculty of Chemical Technology,
EFFICIENCY OF ANTICORROSIVE PIGMENTS BASED ON METAL PHOSPHATES Ing. David Veselý, Ph.D. University of Pardubice, Institute of Chemistry and Technology of Macromolecular Compounds, Faculty of Chemical Technology,
E55A GELATIN, GELLING GRADE Gelatina
 00-0PDG.pdf 0 0 0 0 EA GELATIN, GELLING GRADE Gelatina DEFINITION Purified protein obtained from collagen of animals (including fish and poultry) by partial alkaline and/or acid hydrolysis, by enzymatic
00-0PDG.pdf 0 0 0 0 EA GELATIN, GELLING GRADE Gelatina DEFINITION Purified protein obtained from collagen of animals (including fish and poultry) by partial alkaline and/or acid hydrolysis, by enzymatic
Chemistry 212. Experiment 3 ANALYSIS OF A SOLID MIXTURE LEARNING OBJECTIVES. - learn to analyze a solid unknown with volumetric techniques.
 Experiment 3 The objectives of this experiment are to LEARNING OBJECTIVES - learn to analyze a solid unknown with volumetric techniques. - use stoichiometry to determine the percentage of KHP in a solid
Experiment 3 The objectives of this experiment are to LEARNING OBJECTIVES - learn to analyze a solid unknown with volumetric techniques. - use stoichiometry to determine the percentage of KHP in a solid
SSPC GUIDE 12 to ZINC - RICH COATING SYSTEMS
 ADVANCED PROTECTIVE COATING SYSTEM SSPC GUIDE 12 to ZINC - RICH COATING SYSTEMS 1. Scope 1.1 This guide provides general information on the description, selection, and application of zinc-rich coatings
ADVANCED PROTECTIVE COATING SYSTEM SSPC GUIDE 12 to ZINC - RICH COATING SYSTEMS 1. Scope 1.1 This guide provides general information on the description, selection, and application of zinc-rich coatings
GB Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB NATIONAL STANDARD
 Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB5009.5-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Sales@ChineseStandard.net GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 5009.5-2016 National food safety standard
Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB5009.5-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Sales@ChineseStandard.net GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 5009.5-2016 National food safety standard
PUTTING ON PAPER. Dow Paper Coatings
 PUTTING ON PAPER Dow Paper Coatings www.dow.com/papercoatings Dow Paper Coatings offers access to a broad portfolio of technologies and chemistries for coated paperboard, SBS paperboard, coated freesheet,
PUTTING ON PAPER Dow Paper Coatings www.dow.com/papercoatings Dow Paper Coatings offers access to a broad portfolio of technologies and chemistries for coated paperboard, SBS paperboard, coated freesheet,
EUROPEAN QUALIFYING EXAMINATION 2006
 EUROPEAN QUALIFYING EXAMINATION 2006 PAPER A CHEMISTRY This paper comprises: * Letter from the applicant 2006/A(Ch)/e/1-6 * Document 1 2006/A(Ch)/e/7 * Document 2 2006/A(Ch)/e/8-10 2006/A(Ch)/e - 1 - LETTER
EUROPEAN QUALIFYING EXAMINATION 2006 PAPER A CHEMISTRY This paper comprises: * Letter from the applicant 2006/A(Ch)/e/1-6 * Document 1 2006/A(Ch)/e/7 * Document 2 2006/A(Ch)/e/8-10 2006/A(Ch)/e - 1 - LETTER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O156999A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0156999 A1 Biddulph et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) BLACK TRIVALENT CHROMIUM CHROMATE CONVERSION COATING (75)
(19) United States US 2004O156999A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0156999 A1 Biddulph et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) BLACK TRIVALENT CHROMIUM CHROMATE CONVERSION COATING (75)
ZINC RICH PRIMERS FOR CORROSION PROTECTION. J. Peter Ault, P.E., PCS Elzly Technology Corporation Ocean City, NJ
 ZINC RICH PRIMERS FOR CORROSION PROTECTION J. Peter Ault, P.E., PCS Elzly Technology Corporation Ocean City, NJ Abstract: Various types of zinc-rich coatings are available for corrosion protection. The
ZINC RICH PRIMERS FOR CORROSION PROTECTION J. Peter Ault, P.E., PCS Elzly Technology Corporation Ocean City, NJ Abstract: Various types of zinc-rich coatings are available for corrosion protection. The
Using the Si-O strength
 Using the Si-O strength Epoxy-siloxane and acrylic-siloxane systems improve the performance of corrosion protection coatings. Hybrid systems based on polysiloxanes can provide higher anticorrosive performance
Using the Si-O strength Epoxy-siloxane and acrylic-siloxane systems improve the performance of corrosion protection coatings. Hybrid systems based on polysiloxanes can provide higher anticorrosive performance
Sodium Reference Electrode Filling Solution 2M NH 4 Cl Material Safety Data Sheet
 900010 Sodium Reference Electrode Filling Solution 2M NH 4 Cl I. PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION: Sodium Reference Electrode Filling Solution 2M NH 4 Cl 900010 NFPA RATINGS: HEALTH: 1 FLAMMABILITY: 0 REACTIVITY:
900010 Sodium Reference Electrode Filling Solution 2M NH 4 Cl I. PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION: Sodium Reference Electrode Filling Solution 2M NH 4 Cl 900010 NFPA RATINGS: HEALTH: 1 FLAMMABILITY: 0 REACTIVITY:
(Writing model for laboratory note book)
 Paper: Lab 50 Syllabus *************************************************************************** Experiment: Organic Qualitative analysis 1) Detection of elements (Nitrogen, Sulphur and halogens). 2)
Paper: Lab 50 Syllabus *************************************************************************** Experiment: Organic Qualitative analysis 1) Detection of elements (Nitrogen, Sulphur and halogens). 2)
Purity Tests for Modified Starches
 Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016 Purity Tests for Modified Starches This monograph was also published in: Compendium
Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016 Purity Tests for Modified Starches This monograph was also published in: Compendium
Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3
 Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3 bjectives: (A) To observe the solubility of alcohols relative to their chemical structure and (B) chemical tests will be performed to distinguish primary,
Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3 bjectives: (A) To observe the solubility of alcohols relative to their chemical structure and (B) chemical tests will be performed to distinguish primary,
6.02 Uniformity of Dosage Units
 6.02 Uniformity of Dosage Units Change 1. Content Uniformity, 3. Criteria and Table 6.02-2 as follows: 1. Content Uniformity Select not less than 30 units, and proceed as follows for the dosage form designated.
6.02 Uniformity of Dosage Units Change 1. Content Uniformity, 3. Criteria and Table 6.02-2 as follows: 1. Content Uniformity Select not less than 30 units, and proceed as follows for the dosage form designated.
the Effect of Microwave
 Preparation and Surface Activity of the Hydrolyzed Protein Surfactant from Chrome Shavings under the Effect of Microwave Haibin Gu, Pingping Li, Li Wang, Weite Yang, Xianghua Wang, Wuyong Chen National
Preparation and Surface Activity of the Hydrolyzed Protein Surfactant from Chrome Shavings under the Effect of Microwave Haibin Gu, Pingping Li, Li Wang, Weite Yang, Xianghua Wang, Wuyong Chen National
Annex XV Dossier. Sodium dichromate, dihydrate. EC Number: CAS Number:
 Annex XV Dossier Sodium dichromate, dihydrate EC Number: 234-190-3 CAS Number: 7789-12-0 PROPOSAL FOR IDENTIFICATION OF A SUBSTANCE AS A CMR CAT 1 OR 2, PBT, vpvb OR A SUBSTANCE OF AN EQUIVALENT LEVEL
Annex XV Dossier Sodium dichromate, dihydrate EC Number: 234-190-3 CAS Number: 7789-12-0 PROPOSAL FOR IDENTIFICATION OF A SUBSTANCE AS A CMR CAT 1 OR 2, PBT, vpvb OR A SUBSTANCE OF AN EQUIVALENT LEVEL
POLYTONE UA 810. Aldehyde Resin
 An Aldehyde Resin which is yellowing resistant, practically soluble in almost all paint solvents and compatible with almost all coating raw material. Aldehyde Resin POLYOLS & POLYMERS PVT.LTD. C-1/58-59,
An Aldehyde Resin which is yellowing resistant, practically soluble in almost all paint solvents and compatible with almost all coating raw material. Aldehyde Resin POLYOLS & POLYMERS PVT.LTD. C-1/58-59,
nubiola Zn free pigments: How they work Dr. Ricard March Nubiola
 nubiola Zn free pigments: How they work Dr. Ricard March Nubiola Protective Coatings, Düsseldorf, 12/13.9.2013 nubiola Agenda Agenda Historical Evolution of Anticorrosive Pigments Corrosion Protection
nubiola Zn free pigments: How they work Dr. Ricard March Nubiola Protective Coatings, Düsseldorf, 12/13.9.2013 nubiola Agenda Agenda Historical Evolution of Anticorrosive Pigments Corrosion Protection
Change to read: BRIEFING
 BRIEFING Dibasic Calcium Phosphate Dihydrate, USP 29 page 359. The Japanese Pharmacopoeia is the coordinating pharmacopeia for the international harmonization of the compendial standards for the Dibasic
BRIEFING Dibasic Calcium Phosphate Dihydrate, USP 29 page 359. The Japanese Pharmacopoeia is the coordinating pharmacopeia for the international harmonization of the compendial standards for the Dibasic
Ammonia Volatilization from Urea, Mechanisms, Magnitude, and Management
 Ammonia Volatilization from Urea, Mechanisms, Magnitude, and Management David E. Kissel University of Georgia Overview Urea Consumption Definitions UAN Solution Reactions Urea Dissolution and Diffusion
Ammonia Volatilization from Urea, Mechanisms, Magnitude, and Management David E. Kissel University of Georgia Overview Urea Consumption Definitions UAN Solution Reactions Urea Dissolution and Diffusion
USER SPECIFICATIONS FOR QUINTOLUBRIC 888 Series DESCRIPTION OF THE MOST IMPORTANT PROPERTIES AND THE POSSIBLE VARIATIONS AND TOLERANCES
 USER SPECIFICATIONS FOR QUINTOLUBRIC 888 Series OVERVIEW The QUINTOLUBRIC 888 Series of fluids are based on a synthetic organic ester, which is the main base component, plus a number of selected additives
USER SPECIFICATIONS FOR QUINTOLUBRIC 888 Series OVERVIEW The QUINTOLUBRIC 888 Series of fluids are based on a synthetic organic ester, which is the main base component, plus a number of selected additives
Chameleon Technical Data Sheet
 Chameleon Technical Data Sheet 1. Sensitivity Data The sensitivity of the Chameleon sensors was determined by exposing individual cassettes to a challenge agent for varying amounts of time. Observers were
Chameleon Technical Data Sheet 1. Sensitivity Data The sensitivity of the Chameleon sensors was determined by exposing individual cassettes to a challenge agent for varying amounts of time. Observers were
Figure 2. Figure 1. Name: Bio AP Lab Organic Molecules
 Name: Bio AP Lab Organic Molecules BACKGROUND: A cell is a living chemistry laboratory in which most functions take the form of interactions between organic molecules. Most organic molecules found in living
Name: Bio AP Lab Organic Molecules BACKGROUND: A cell is a living chemistry laboratory in which most functions take the form of interactions between organic molecules. Most organic molecules found in living
7.2.7 Analytical Techniques
 7.2.7 Analytical Techniques 55 minutes 59 marks Page 1 of 20 Q1. A company making sweets uses different colour additives in different countries. In some countries the company uses Allura Red to colour
7.2.7 Analytical Techniques 55 minutes 59 marks Page 1 of 20 Q1. A company making sweets uses different colour additives in different countries. In some countries the company uses Allura Red to colour
4. 10/09/14 Ch. 5: Populations /22/14 Ch. 2: Chemistry of Life 55
 Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 1 2. 09/02/14 Ch. 1: The Science of Biology 09/16/14 Ch. 4: Ecosystems and Communities 17 3. 09/23/14 Ch. 3: The Biosphere 26 4. 10/09/14 Ch. 5: Populations 45
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 1 2. 09/02/14 Ch. 1: The Science of Biology 09/16/14 Ch. 4: Ecosystems and Communities 17 3. 09/23/14 Ch. 3: The Biosphere 26 4. 10/09/14 Ch. 5: Populations 45
Black-Magic RT-S20/25 Replenisher Product Code: Revised Date: 01/11/2013
 Black-Magic RT-S20/25 Replenisher Room Temperature Blackening Solution For Iron And Steel Black-Magic RT-S20/25 Replenisher liquid concentrate is used for replenishment and maintenance of both Black-Magic
Black-Magic RT-S20/25 Replenisher Room Temperature Blackening Solution For Iron And Steel Black-Magic RT-S20/25 Replenisher liquid concentrate is used for replenishment and maintenance of both Black-Magic
Protective Equipment: Hazards Identification: ZINC OXIDE POWDER - COA - MSDS.
 ZINC OXIDE POWDER - COA - MSDS http://www.essentialdepot.com/msds/zincoxide.pdf TECHNICAL DATA Representative Physical Properties Mean Surface Particle Diam., μ... 0.12 Specific Surface, m 2 /g... 9.0
ZINC OXIDE POWDER - COA - MSDS http://www.essentialdepot.com/msds/zincoxide.pdf TECHNICAL DATA Representative Physical Properties Mean Surface Particle Diam., μ... 0.12 Specific Surface, m 2 /g... 9.0
Feedstuffs Analysis G-22-1 PROTEIN
 Feedstuffs Analysis G-22-1 PROTEIN PRINCIPLE SCOPE Many modifications of the Kjeldahl method have been accepted for the estimation of protein in organic materials. It comprises sample oxidation and conversion
Feedstuffs Analysis G-22-1 PROTEIN PRINCIPLE SCOPE Many modifications of the Kjeldahl method have been accepted for the estimation of protein in organic materials. It comprises sample oxidation and conversion
Chemical Resistance Guide
 310 CHMICAL RSISTANT Chemical Resistance Guide All test were carried out at 20 C (+/-5), based on specimens having a minimum dry film thickness of 400 microns for 310 Chemical Resistant Coating and having
310 CHMICAL RSISTANT Chemical Resistance Guide All test were carried out at 20 C (+/-5), based on specimens having a minimum dry film thickness of 400 microns for 310 Chemical Resistant Coating and having
Reagent Solutions: Preparation
 Reagent Chemicals Reagent Solutions: Preparation Throughout the Specifications section of this book, the term reagent solution is used to designate solutions described in this section. The tests and limits
Reagent Chemicals Reagent Solutions: Preparation Throughout the Specifications section of this book, the term reagent solution is used to designate solutions described in this section. The tests and limits
Qualitative test of protein-lab2
 1- Qualitative chemical reactions of amino acid protein functional groups: Certain functional groups in proteins can react to produce characteristically colored products. The color intensity of the product
1- Qualitative chemical reactions of amino acid protein functional groups: Certain functional groups in proteins can react to produce characteristically colored products. The color intensity of the product
when material is heated. Store in tightly closed containers to prevent drying or skinning of
 Material Safety Data Sheet 1. PRODUCT AND COMPANY IDENTIFICATION Product Identification Product Name: Elastodeck 350, Elastowall 351, Elastomastic 352, ElastoTone 353, Elastofill 354 Product Use: Elastomeric
Material Safety Data Sheet 1. PRODUCT AND COMPANY IDENTIFICATION Product Identification Product Name: Elastodeck 350, Elastowall 351, Elastomastic 352, ElastoTone 353, Elastofill 354 Product Use: Elastomeric
Mamdouh M. Nassarl and G. D. M. MacKay
 STUDIES ON THE MECHANISM OF FLAME RETARDATION IN WOOD Mamdouh M. Nassarl and G. D. M. MacKay Centre for Energy Studies and Department of Chemical Engineering Technical University of Nova Scotia, P.O. Box
STUDIES ON THE MECHANISM OF FLAME RETARDATION IN WOOD Mamdouh M. Nassarl and G. D. M. MacKay Centre for Energy Studies and Department of Chemical Engineering Technical University of Nova Scotia, P.O. Box
Potions and Poisons B
 Potions and Poisons B Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Rank: Points: Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: This exam consists of 4 sections, (1) multiple
Potions and Poisons B Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Rank: Points: Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: This exam consists of 4 sections, (1) multiple
Name: Per. Date: / 71 points MACROMOLECULE LAB: Testing for the Presence of Macromolecules
 Name: Per. Date: / 71 points MACROMOLECULE LAB: Testing for the Presence of Macromolecules Introduction: There are four broad classes of macromolecules that can be found in living systems. Each type of
Name: Per. Date: / 71 points MACROMOLECULE LAB: Testing for the Presence of Macromolecules Introduction: There are four broad classes of macromolecules that can be found in living systems. Each type of
1.0 Purpose To provide guidelines for preparing reagents used in casework in the Firearm and Tool Mark Section.
 Technical Procedure for Reagent Preparation 1.0 Purpose To provide guidelines for preparing reagents used in casework in the Firearm and Tool Mark Section. 2.0 Scope This procedure applies to all reagents
Technical Procedure for Reagent Preparation 1.0 Purpose To provide guidelines for preparing reagents used in casework in the Firearm and Tool Mark Section. 2.0 Scope This procedure applies to all reagents
Identification of Organic Compounds Lab
 Identification of Organic Compounds Lab Introduction All organic compounds contain the element carbon (C). Organic compounds usually also contain oxygen (O) or hydrogen (H) or both. They may also contain
Identification of Organic Compounds Lab Introduction All organic compounds contain the element carbon (C). Organic compounds usually also contain oxygen (O) or hydrogen (H) or both. They may also contain
Working With MDI and Polymeric MDI: What You Should Know
 Working With MDI and Polymeric MDI: What You Should Know Here are six important points you should know about working with MDI or polymeric MDI The Alliance for the Polyurethanes Industry, prepared this
Working With MDI and Polymeric MDI: What You Should Know Here are six important points you should know about working with MDI or polymeric MDI The Alliance for the Polyurethanes Industry, prepared this
Chemical Pharmaceutical Quality Control. Prof.Dr.Joumaa Al- Zehouri Damascus university Faculty of Pharmacy
 Chemical Pharmaceutical Quality Control Prof.Dr.Joumaa Al- Zehouri Damascus university Faculty of Pharmacy COMPLEXOMETRIC REACTIONS AND TITRATIONS Prof.J.Al-Zehouri 1 ml of 0.1Msodium edetate is equivalent
Chemical Pharmaceutical Quality Control Prof.Dr.Joumaa Al- Zehouri Damascus university Faculty of Pharmacy COMPLEXOMETRIC REACTIONS AND TITRATIONS Prof.J.Al-Zehouri 1 ml of 0.1Msodium edetate is equivalent
QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS OF AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS
 QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS OF AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side chain that varies between different amino acids. Amino acids of
QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS OF AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side chain that varies between different amino acids. Amino acids of
MONOGRAPHS (USP) Saccharin Sodium
 Vol. 31(4) [July Aug. 2005] HARMONIZATION 1225 MONOGRAPHS (USP) BRIEFING Saccharin Sodium, USP 28 page 1745 and page 612 of PF 31(2) [Mar. Apr. 2005]. The United States Pharmacopeia is the coordinating
Vol. 31(4) [July Aug. 2005] HARMONIZATION 1225 MONOGRAPHS (USP) BRIEFING Saccharin Sodium, USP 28 page 1745 and page 612 of PF 31(2) [Mar. Apr. 2005]. The United States Pharmacopeia is the coordinating
SORPTION and SWELLING CHARACTERISTICS of SALT-TREATED WOOD
 U. S. FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH PAPER FPL 60 MAY 1966 U NITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE FOREST SERVICE F OREST PRODUCTS L ABORATORY MADISON. WISCONSIN SORPTION and SWELLING CHARACTERISTICS of SALT-TREATED
U. S. FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH PAPER FPL 60 MAY 1966 U NITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE FOREST SERVICE F OREST PRODUCTS L ABORATORY MADISON. WISCONSIN SORPTION and SWELLING CHARACTERISTICS of SALT-TREATED
Pulpdent Corporation Revision Date: May 7, 2014
 1.0 Commercial Product Name and Supplier 1.1 Commercial product name / designation 1.2 1.2.2 Application / Use SIC 1.2.3 Use Category 1.3 Manufacturer Pulpdent Corporation 80 Oakland Street, P.O. Box 780
1.0 Commercial Product Name and Supplier 1.1 Commercial product name / designation 1.2 1.2.2 Application / Use SIC 1.2.3 Use Category 1.3 Manufacturer Pulpdent Corporation 80 Oakland Street, P.O. Box 780
Instructions for Performing In-Office Lab Tests
 Instructions for Performing In-Office Lab Tests SALIVARY PH- STATIC MEASUREMENT Testing must be done at least 30 minutes from any food or beverage. 1. Simply place a ph testing strip in the patient s mouth
Instructions for Performing In-Office Lab Tests SALIVARY PH- STATIC MEASUREMENT Testing must be done at least 30 minutes from any food or beverage. 1. Simply place a ph testing strip in the patient s mouth
AP Biology Macromolecules
 AP Biology Macromolecules Introduction: There are four broad classes macromolecules that can be found in living systems. Each type macromolecule has a characteristic structure and function in living organisms.
AP Biology Macromolecules Introduction: There are four broad classes macromolecules that can be found in living systems. Each type macromolecule has a characteristic structure and function in living organisms.
Safety Data Sheet. Product Name: DetectX Palladium Screening Fluorescent Detection Kit. Section 1: Identification. Section 2: Hazard(s) Identification
 Safety Data Sheet Revision Date: 17 October 2016 Product Name: DetectX Palladium Screening Fluorescent Detection Kit Section 1: Identification Product Name: DetectX Palladium Screening Fluorescent Detection
Safety Data Sheet Revision Date: 17 October 2016 Product Name: DetectX Palladium Screening Fluorescent Detection Kit Section 1: Identification Product Name: DetectX Palladium Screening Fluorescent Detection
UV + PVD: PERFORMANCE AND DESIGN SOLUTIONS FOR THE AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY. Eileen M. Weber, Red Spot Paint and Varnish, Co., Inc.
 UV + PVD: PERFORMANCE AND DESIGN SOLUTIONS FOR THE AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY Eileen M. Weber, Red Spot Paint and Varnish, Co., Inc. What Is PVD? Physical Vapor Deposition PVD is deposition of a metal onto a
UV + PVD: PERFORMANCE AND DESIGN SOLUTIONS FOR THE AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY Eileen M. Weber, Red Spot Paint and Varnish, Co., Inc. What Is PVD? Physical Vapor Deposition PVD is deposition of a metal onto a
TLC SEPARATION OF AMINO ACIDS
 TLC SEPARATION OF AMINO ACIDS LAB CHROM 7 Adapted from Laboratory Experiments for Organic and Biochemistry. Bettelheim & Landesberg (PA Standards for Sci & Tech 3.1.12.D; 3.4.10.A; 3.7.12.B) INTRODUCTION
TLC SEPARATION OF AMINO ACIDS LAB CHROM 7 Adapted from Laboratory Experiments for Organic and Biochemistry. Bettelheim & Landesberg (PA Standards for Sci & Tech 3.1.12.D; 3.4.10.A; 3.7.12.B) INTRODUCTION
ZINC SILICATES QUALITY ASPECTS APPLICATION
 INTRODUCTION an eight page issue revision of July 2003 Zinc silicates are widely specified as the primer for much of the steel utilised by the petrochemical and offshore industries. They may be used without
INTRODUCTION an eight page issue revision of July 2003 Zinc silicates are widely specified as the primer for much of the steel utilised by the petrochemical and offshore industries. They may be used without
Corrosion Protection of the 21 st Century
 Corrosion Protection of the 21 st Century May 2017 Composition of ZAM Zinc 91% Aluminum 6 % Magnesium 3% Satisfies ASTM A1046 Highly Corrosion Resistant Coated Steel Chemical Treatment Zn-Al 6%-Mg 3% Coating
Corrosion Protection of the 21 st Century May 2017 Composition of ZAM Zinc 91% Aluminum 6 % Magnesium 3% Satisfies ASTM A1046 Highly Corrosion Resistant Coated Steel Chemical Treatment Zn-Al 6%-Mg 3% Coating
Investigation of Cu and Ni Diffusion Amounts for Silicon Substrates
 Investigation of Cu and Ni Diffusion Amounts for Silicon Substrates Sales Engineering dept. Abstract An investigation regarding the Cu and Ni diffusion amounts for silicon substrates was conducted. A Cu
Investigation of Cu and Ni Diffusion Amounts for Silicon Substrates Sales Engineering dept. Abstract An investigation regarding the Cu and Ni diffusion amounts for silicon substrates was conducted. A Cu
EXPERIMENT 8 (Organic Chemistry II) Carboxylic Acids Reactions and Derivatives
 EXPERIMENT 8 (rganic Chemistry II) Carboxylic Acids Reactions and Derivatives Pahlavan/Cherif Materials Medium test tubes (6) Test tube rack Beakers (50, 150, 400 ml) Ice Hot plate Graduated cylinders
EXPERIMENT 8 (rganic Chemistry II) Carboxylic Acids Reactions and Derivatives Pahlavan/Cherif Materials Medium test tubes (6) Test tube rack Beakers (50, 150, 400 ml) Ice Hot plate Graduated cylinders
Lab 05 Introduction Reactions Pre Lab Problems (answer on separate paper)
 Lab 05 Introduction Among the many types of quantitative chemistry techniques, volumetric analysis is a timehonored classical method. The characteristic feature of volumetric analysis is measuring the
Lab 05 Introduction Among the many types of quantitative chemistry techniques, volumetric analysis is a timehonored classical method. The characteristic feature of volumetric analysis is measuring the
EXPERIMENT #5 Water of Hydration
 OBJECTIVES: EXPERIMENT #5 Water of Hydration Observe changes in color and form of a hydrate after heating strongly Accurately weigh reaction mixtures before and after heating Calculate the mass of water
OBJECTIVES: EXPERIMENT #5 Water of Hydration Observe changes in color and form of a hydrate after heating strongly Accurately weigh reaction mixtures before and after heating Calculate the mass of water
Food acidity FIRST LAB
 Food acidity FIRST LAB objective To determine total acidity of milk, juice, vinegar and oil acid value Food acidity Food acids are usually organic acids, with citric, malic, lactic, tartaric, and acetic
Food acidity FIRST LAB objective To determine total acidity of milk, juice, vinegar and oil acid value Food acidity Food acids are usually organic acids, with citric, malic, lactic, tartaric, and acetic
Chemical Effect on Concrete Concrete Treated with Penetron. Acetic Acid to 30% Disintegrates Slowly S/E. Acetone Liquid loss by penetration N/E
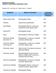 PENETRON SYSTEMS CHEMICAL RESISTANCE/CORROSION CHART Symbols: = No Effect = Slight Effect E = Effected Chemical Effect on Concrete Concrete Treated with Penetron Acetic Acid to 30% Disintegrates Slowly
PENETRON SYSTEMS CHEMICAL RESISTANCE/CORROSION CHART Symbols: = No Effect = Slight Effect E = Effected Chemical Effect on Concrete Concrete Treated with Penetron Acetic Acid to 30% Disintegrates Slowly
The problem with lead paint
 1 The problem with lead paint Outline Background The use of lead in paint Exposure and health impacts Summary 2 Background Lead paints contain lead compounds that are added to give certain properties Wide
1 The problem with lead paint Outline Background The use of lead in paint Exposure and health impacts Summary 2 Background Lead paints contain lead compounds that are added to give certain properties Wide
ESS Method 230.1: Total Phosphorus and Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen, Semi-Automated Method
 ESS Method 230.1: Total Phosphorus and Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen, Semi-Automated Method Environmental Sciences Section Inorganic Chemistry Unit Wisconsin State Lab of Hygiene 465 Henry Mall Madison, WI 53706
ESS Method 230.1: Total Phosphorus and Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen, Semi-Automated Method Environmental Sciences Section Inorganic Chemistry Unit Wisconsin State Lab of Hygiene 465 Henry Mall Madison, WI 53706
For example, monosaccharides such as glucose are polar and soluble in water, whereas lipids are nonpolar and insoluble in water.
 Biology 4A Laboratory Biologically Important Molecules Objectives Perform tests to detect the presence of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids Recognize the importance of a control in a biochemical
Biology 4A Laboratory Biologically Important Molecules Objectives Perform tests to detect the presence of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids Recognize the importance of a control in a biochemical
People who have a zinc deficiency can take hydrated zinc sulfate (ZnSO 4.xH 2O) as a dietary supplement.
 Q1.Zinc forms many different salts including zinc sulfate, zinc chloride and zinc fluoride. (a) People who have a zinc deficiency can take hydrated zinc sulfate (ZnSO 4.xH 2O) as a dietary supplement.
Q1.Zinc forms many different salts including zinc sulfate, zinc chloride and zinc fluoride. (a) People who have a zinc deficiency can take hydrated zinc sulfate (ZnSO 4.xH 2O) as a dietary supplement.
ANTICORROSIVES. Time for ultimate Corrosion Protection. Anticorrosives from A - Z
 Time for ultimate Corrosion Protection Anticorrosives from A Z Corrosion The degradation of metal by chemical or electrochemical means resulting from exposure to weathering, moisture, chemicals or other
Time for ultimate Corrosion Protection Anticorrosives from A Z Corrosion The degradation of metal by chemical or electrochemical means resulting from exposure to weathering, moisture, chemicals or other
ON THE DETERMINATION OF UROBILIN IN URINE.
 ON THE DETERMINATION OF UROBILIN IN URINE. PRELIMINARY REPORT. RY S. MARCUSSEN AND SVEND HANSEN. (From the Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen,.) (Received for publication, September 20,
ON THE DETERMINATION OF UROBILIN IN URINE. PRELIMINARY REPORT. RY S. MARCUSSEN AND SVEND HANSEN. (From the Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen,.) (Received for publication, September 20,
Carbohydrates. Objectives. Background. Experiment 6
 1 of 6 3/15/2011 7:27 PM Experiment 6 Carbohydrates Objectives During this experiment you will look at some of the physical and chemical properties of carbohydrates. Many of the carbohydrates, especially
1 of 6 3/15/2011 7:27 PM Experiment 6 Carbohydrates Objectives During this experiment you will look at some of the physical and chemical properties of carbohydrates. Many of the carbohydrates, especially
Anticorrosives from the experts HEUCOPHOS & HEUCOSIL & HEUCORIN
 Anticorrosives from the experts HEUCOPHOS & HEUCOSIL & HEUCORIN The degradation of metal by chemical or electrochemical means resulting from exposure to weathering, moisture, chemicals or other agents
Anticorrosives from the experts HEUCOPHOS & HEUCOSIL & HEUCORIN The degradation of metal by chemical or electrochemical means resulting from exposure to weathering, moisture, chemicals or other agents
Lab: Organic Compounds
 Lab: Organic Compounds Name(s) Date Period Benchmark: SC.912.L.18.1: Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of biological macromolecules. Background:
Lab: Organic Compounds Name(s) Date Period Benchmark: SC.912.L.18.1: Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of biological macromolecules. Background:
Allylic alcohols improve acrylic polyols
 Allylic alcohols improve acrylic polyols Efforts to reduce the VOC content of two-component urethane coatings have focused primarily on lowering the molecular weight of the polyols. Unfortunately, the
Allylic alcohols improve acrylic polyols Efforts to reduce the VOC content of two-component urethane coatings have focused primarily on lowering the molecular weight of the polyols. Unfortunately, the
LAB Catalase in Liver HONORS BIOLOGY, NNHS
 Name Date Block LAB Catalase in Liver HONORS BIOLOGY, NNHS OBJECTIVES: 1. To observe the effect of catalase on the chemical breakdown of hydrogen peroxide. 2. To observe the effects of temperature and
Name Date Block LAB Catalase in Liver HONORS BIOLOGY, NNHS OBJECTIVES: 1. To observe the effect of catalase on the chemical breakdown of hydrogen peroxide. 2. To observe the effects of temperature and
SOUTH AFRICAN NATIONAL STANDARD
 ISBN 978-0-626-31165-0 SOUTH AFRICAN NATIONAL STANDARD Water Sulfide content Published by SABS Standards Division 1 Dr Lategan Road Groenkloof Private Bag X191 Pretoria 0001 Tel: +27 12 428 7911 Fax: +27
ISBN 978-0-626-31165-0 SOUTH AFRICAN NATIONAL STANDARD Water Sulfide content Published by SABS Standards Division 1 Dr Lategan Road Groenkloof Private Bag X191 Pretoria 0001 Tel: +27 12 428 7911 Fax: +27
IODOMETRIC TITRATION
 IODOMETRIC TITRATION Oxidizing agents In most iodometric titrations, when an excess of iodide ion is present, the tri-iodide ion is formed: I + I - I 3 - Since iodine is readily soluble in a solution of
IODOMETRIC TITRATION Oxidizing agents In most iodometric titrations, when an excess of iodide ion is present, the tri-iodide ion is formed: I + I - I 3 - Since iodine is readily soluble in a solution of
Sheets. Premier Red Aluminum Oxide Dri-Lube Resin Paper Open. Carbo Gold Aluminum Oxide Dri-Lube Paper Open. Aluminum Oxide Waterproof Paper
 Premier Red Aluminum Oxide Dri-Lube Resin Paper Open P-graded, heat-treated, aluminum oxide Consistent finish without a deep abrasive scratch Ultra fine grit P1000, P1200, P1500 Substantially better cut
Premier Red Aluminum Oxide Dri-Lube Resin Paper Open P-graded, heat-treated, aluminum oxide Consistent finish without a deep abrasive scratch Ultra fine grit P1000, P1200, P1500 Substantially better cut
Information Reviewed and Reaffirmed September No. 40. (' %)Zik5.5 4G A WATER-RESISTANT ANIMAL GLUE
 (' %)Zik5.5 4t4 4G A WATER-RESISTANT ANIMAL GLUE Information Reviewed and Reaffirmed September 1955 No. 40 FOREST PRODUCTS LABORATORY MADISON 5, WISCONSIN UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE FOREST
(' %)Zik5.5 4t4 4G A WATER-RESISTANT ANIMAL GLUE Information Reviewed and Reaffirmed September 1955 No. 40 FOREST PRODUCTS LABORATORY MADISON 5, WISCONSIN UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE FOREST
3. PRELIMINARY PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING
 93 3. PRELIMINARY PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING 3.1 INTRODUCTION All the drugs- Ayurvedic, Unani and Herbal extracts were subjected to preliminary phytochemical screening to test the presence of alkaloids, carbohydrates
93 3. PRELIMINARY PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING 3.1 INTRODUCTION All the drugs- Ayurvedic, Unani and Herbal extracts were subjected to preliminary phytochemical screening to test the presence of alkaloids, carbohydrates
(LM pages 91 98) Time Estimate for Entire Lab: 2.5 to 3.0 hours. Special Requirements
 Laboratory 7 Chemical Aspects of Digestion (LM pages 91 98) Time Estimate for Entire Lab: 2.5 to 3.0 hours Special Requirements Incubation. Students should start these sections at the beginning of the
Laboratory 7 Chemical Aspects of Digestion (LM pages 91 98) Time Estimate for Entire Lab: 2.5 to 3.0 hours Special Requirements Incubation. Students should start these sections at the beginning of the
Nitrate and Nitrite Key Words: 1. Introduction 1.1. Nature, Mechanism of Action, and Biological Effects (Fig. 1)
 7 Nitrate and Nitrite Key Words: Nitrate; nitrite; methemoglobin; blood pressure; asphyxia; spinach; spongy cadmium column; zinc metal; sodium nitrate; sodium nitrite; ammonia buffer solution; Jones reductor.
7 Nitrate and Nitrite Key Words: Nitrate; nitrite; methemoglobin; blood pressure; asphyxia; spinach; spongy cadmium column; zinc metal; sodium nitrate; sodium nitrite; ammonia buffer solution; Jones reductor.
1101 S Winchester Blvd., Ste. G 173 San Jose, CA (408) (408) fax Page 1 of 2
 San Jose Office September 28, 2018 Report 18-262-0106 Zanker Landscape Mateirals 675 Los Esteros Road San Jose, CA 95134 Attn: Beto Ochoa RE: ZB-PPM Reaction at 7.5 is slightly alkaline and with lime absent
San Jose Office September 28, 2018 Report 18-262-0106 Zanker Landscape Mateirals 675 Los Esteros Road San Jose, CA 95134 Attn: Beto Ochoa RE: ZB-PPM Reaction at 7.5 is slightly alkaline and with lime absent
Standard Operating Procedure for Total and Dissolved Phosphorous (Lachat Method)
 Standard Operating Procedure for Total and Dissolved Phosphorous (Lachat Method) Grace Analytical Lab 536 South Clark Street 10th Floor Chicago, IL 60605 June 13, 1994 Revision 1 Standard Operating Procedure
Standard Operating Procedure for Total and Dissolved Phosphorous (Lachat Method) Grace Analytical Lab 536 South Clark Street 10th Floor Chicago, IL 60605 June 13, 1994 Revision 1 Standard Operating Procedure
NPK Fertilizer SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS) OSHA Haz Com Standard 29 CFR Prepared to GHS Rev03.
 SECTION 1: Identification 1.1. Product identifier Product Form : Solid Granule Product Name: : 10-10-20 1.2. Recommended use / restrictions of use : Agricultural fertilizer. No restrictions. 1.3. Details
SECTION 1: Identification 1.1. Product identifier Product Form : Solid Granule Product Name: : 10-10-20 1.2. Recommended use / restrictions of use : Agricultural fertilizer. No restrictions. 1.3. Details
Analysis. Methods of. of Soils, Plants, Waters, Fertilisers & Organic Manures. Edited by HLS Tandon
 Methods of Analysis of Soils, Plants, Waters, Fertilisers & Organic Manures Edited by HLS Tandon Fertiliser Development and Consultation Organisation 204204A Bhanot Corner, 12 Pamposh Enclave New Delhi
Methods of Analysis of Soils, Plants, Waters, Fertilisers & Organic Manures Edited by HLS Tandon Fertiliser Development and Consultation Organisation 204204A Bhanot Corner, 12 Pamposh Enclave New Delhi
HAZARDOUS INGREDIENTS/IDENTITY INFORMATION
 MSDS: Material Safety Data Sheet Hands-On Labs, Inc. 3880 S. Windermere Englewood, CO 80110 Phone 303-679-6252 or 866-206-0773 fax 270-738-0979 Chemistry LabPaqs This list includes all the chemicals used
MSDS: Material Safety Data Sheet Hands-On Labs, Inc. 3880 S. Windermere Englewood, CO 80110 Phone 303-679-6252 or 866-206-0773 fax 270-738-0979 Chemistry LabPaqs This list includes all the chemicals used
Acrylic thinner, standard, fast, slow and extra slow
 Two-component acrylic filler PLAST 775 PLAST 825 EXTRA 755 EXTRA 745 RELATED PRODUCTS P1 white acrylic filler P3 grey acrylic filler P5 black acrylic filler Hardener Acrylic thinner, standard, fast, slow
Two-component acrylic filler PLAST 775 PLAST 825 EXTRA 755 EXTRA 745 RELATED PRODUCTS P1 white acrylic filler P3 grey acrylic filler P5 black acrylic filler Hardener Acrylic thinner, standard, fast, slow
Challenges with Chelated &/or Complexed Minerals (Chelated and Soluble Methods of Analysis Used in FL)
 Challenges with Chelated &/or Complexed Minerals (Chelated and Soluble Methods of Analysis Used in FL) Patty Lucas AAPFCO Laboratory Services Committee Meeting Friday, August 7, 2015 Fertilizer Sample
Challenges with Chelated &/or Complexed Minerals (Chelated and Soluble Methods of Analysis Used in FL) Patty Lucas AAPFCO Laboratory Services Committee Meeting Friday, August 7, 2015 Fertilizer Sample
چهارمین کنگره مهندسی نفت ایران. Lab Investigation of Inorganic Scale Removal Using Chelating Agents and Hydrochloric Acid Solutions.
 Lab Investigation of Inorganic Scale Removal Using Chelating Agents and Hydrochloric Acid Solutions Abstract One of the most important damages to the oil and gas reservoirs, are inorganic scales resulted
Lab Investigation of Inorganic Scale Removal Using Chelating Agents and Hydrochloric Acid Solutions Abstract One of the most important damages to the oil and gas reservoirs, are inorganic scales resulted
Enzymes - Exercise 3 - Rockville
 Enzymes - Exercise 3 - Rockville Objectives -Understand the function of an enzyme. -Know what the substrate, enzyme, and the product of the reaction for this lab. -Understand how at various environments
Enzymes - Exercise 3 - Rockville Objectives -Understand the function of an enzyme. -Know what the substrate, enzyme, and the product of the reaction for this lab. -Understand how at various environments
Aim: To study the effect of ph on the action of salivary amylase. NCERT
 Exercise 28 Aim: To study the effect of ph on the action of salivary amylase. Principle: Optimal activity for most of the enzymes is generally observed between ph 5.0 and 9.0. However, a few enzymes, e.g.,
Exercise 28 Aim: To study the effect of ph on the action of salivary amylase. Principle: Optimal activity for most of the enzymes is generally observed between ph 5.0 and 9.0. However, a few enzymes, e.g.,
Comparison of Performance Criteria for Evaluating Stake Test Data
 Comparison of Performance Criteria for Evaluating Stake Test Data Stan Lebow Grant Kirker Patricia Lebow USDA, Forest Service, Forest Products Laboratory Madison, Wisconsin ABSTRACT Stake tests are a critical
Comparison of Performance Criteria for Evaluating Stake Test Data Stan Lebow Grant Kirker Patricia Lebow USDA, Forest Service, Forest Products Laboratory Madison, Wisconsin ABSTRACT Stake tests are a critical
Acid & Blocked Acid Catalysts
 & & Blocked Catalysts & ACID & BLOCKED ACID CATALYSTS Why Use Catalysts? Today s need for high solids and waterborne coatings requires greater use of high reactivity, low viscosity resins and crosslinkers.
& & Blocked Catalysts & ACID & BLOCKED ACID CATALYSTS Why Use Catalysts? Today s need for high solids and waterborne coatings requires greater use of high reactivity, low viscosity resins and crosslinkers.
Reagent Set DAS ELISA, Alkaline phosphatase label SRA 22001, SRA 23203, SRA 27703, SRA & SRA ToRSV, ArMV, GFLV, AnFBV and PDV
 List of contents Lot number Reagent Set Item 96 wells 500 wells 1000 wells 5000 wells Capture antibody 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525 ml 2.525 ml Alkaline phosphatase enzyme conjugate 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525
List of contents Lot number Reagent Set Item 96 wells 500 wells 1000 wells 5000 wells Capture antibody 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525 ml 2.525 ml Alkaline phosphatase enzyme conjugate 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525
Class 10 Science - Sample Paper Set I
 Time allowed: 3 hours; Maximum marks: 90 General Instructions: a) All Questions are compulsory b) The Question Paper consists of 42 Questions divided in to four sections A, B, C and D c) Section- A comprises
Time allowed: 3 hours; Maximum marks: 90 General Instructions: a) All Questions are compulsory b) The Question Paper consists of 42 Questions divided in to four sections A, B, C and D c) Section- A comprises
CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE. Cellulosum microcristallinum. Cellulose, microcrystalline EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 7.0
 Cellulose, microcrystalline EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 7.0 Phthaloyl groups (C 8 H 5 O 3 ; M r 149.1): typically 30.0 per cent to 36.0 per cent (anhydrous and acid-free substance). Dissolve 1.000 g in 50 ml
Cellulose, microcrystalline EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 7.0 Phthaloyl groups (C 8 H 5 O 3 ; M r 149.1): typically 30.0 per cent to 36.0 per cent (anhydrous and acid-free substance). Dissolve 1.000 g in 50 ml
Lab 2. The Chemistry of Life
 Lab 2 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast organic and inorganic molecules Relate hydrogen bonding to macromolecules found in living things Compare and contrast the four major organic macromolecules:
Lab 2 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast organic and inorganic molecules Relate hydrogen bonding to macromolecules found in living things Compare and contrast the four major organic macromolecules:
