Neonatal Nutrition. Growth Expectations, Parenteral & Enteral Nutrition Considerations. Suzanne Smith, MS, RD, LD Neonatal Dietitian
|
|
|
- Thomasina Malone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 3/2011 Neonatal Nutrition Growth Expectations, Parenteral & Enteral Nutrition Considerations Suzanne Smith, MS, RD, LD Neonatal Dietitian Levine Children s s Hospital ASCOM# Pager ID# 8237
2 Selected Criteria for Preterm Infants at Highest Nutrition Risk in the NICU setting < 1000 grams <30 weeks gestation IUGR / SGA Multiple gestation, (discordance between multiples) >15% weight loss from birth > weeks with continued weight loss / poor weight gain Unable to advance enteral feedings, prolonged need for IV nutrition Conjugated Bilirubin > 2 mg/dl Chronic lung disease NEC Gastrointestinal issues Risk for or development of osteopenia (unable to tolerate fortified human milk or premature formula, serum phosphorus < 4 mg/dl dl,, serum alkaline phosphate > 600 U/L) Groh-Wargo, S. & Sapsford, A. Enteral Nutrition Support of the Preterm Infant in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Nutr Clin Pract 2009;24;363.
3 Classification Definitions Gestation Preterm <37 weeks gestation Term weeks gestation Post term >42 weeks gestation Birth weight Low Birth Weight Very Low Birth Weight Extremely Low Birth Weight Micro-preemies Small for gestation age Small Appropriate Large <2500 grams <1500 grams <1000 grams < 750 grams Weight <10th% Weight > 10th% & < 90th% Weight > 90th% Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
4 Anthropometrics - Weight Weight Reflects the total mass of body compartments, including lean tissue, fat, and extra/intracellular fluid. Initial weight loss of <10% in term infant and <15% in the preterm infant is expected Weight loss is attributed to contraction of body water compartments and catabolism of endogenous stores (glycogen, lipid, lean tissue) before energy and nutrient needs are met Initial weight loss reaches its nadir by ~4-6 6 DOL Birth weight should be regained by weeks of life Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
5 Age Related Changes in Body Composition kg 2.0 kg 3.5 kg 10.5 kg Water Protein Fat Water Protein Fat Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
6 Anthropometrics - Weight Weight gain is based on normal intrauterine growth averages Weight needs to be assessed daily Preterm Infant <2000 grams grams/kg kg/day Infant >2000 grams grams per day Term Infants First 3 months of life grams per day Averaging weight gain over past 7 days [Monday s s weight last Monday s s weight / 7 / today s s wt in kg] Thinking Point Weight gain is not always an accurate measure of growth 2 2 changes in fluid status Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
7 Anthropometrics - Weight Use birth weight for first 7 days of life for ALL calculations Use current or daily weight after DOL 7 If there is a big fluctuation in birth weight vs. current weight, an analysis weight may need to be used Monitor for unusual weights 2 2 fluid, scales, or equipment
8 Anthropometrics - Length Length measurements more accurately reflect lean body mass and is not influenced by fluid status Length is more difficult to accurately measure Preterm Term Based on normal intrauterine growth Incremental gain in crown-heel length cm/week First 3 months of life, infants grow cm/week 0.75cm/week Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
9 Anthropometrics - Head Circumference Head growth correlates well with brain growth during fetal development, infancy, and childhood and with later developmental achievement in preterm infants Pre-term Term Recommended growth cm/week First 3 months of life 0.5 cm/week Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
10 2 types available Growth Charts Intrauterine growth data Postnatal growth data Located in Serner, Neodata,, & Paper Chart Ideal growth chart to use in NICU = Fenton as it is based on fetal growth data Thinking Point Which is more concerning: Symmetric or Asymmetric SGA? Fenton TR. BMC Pediatrics 2003;3:13.
11 Reporting Infant s s Growth During Rounds Sunday evening all growth parameters are obtained Report growth parameters on Monday morning rounds Weight, rate of gain over past 7 days < 2 kg = report weight gain/per kg over the past 7 days If infant is not back to birth weight, express weight loss as a % of birth weight Use Fenton Growth Charts to document growth percentiles Length, rate of growth and percentile HC, rate of growth and percentile
12 Indications for TPN Functional immaturity of GI tract Necrotizing Enterocolitis Congenital GI anomalies Gastroschisis, omphalocele,, bowel obstruction, bowel atresia Malabsorption syndroms SBS, CF, meconium ileus Impaired GI motility Prematurity, ileus from surgery/sepsis, Hirshsprung s disease Impaired GI perfusion that decreases GI motility Congenital heart disease, PDA, hypotension Inadequate enteral nutrient intake Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
13 The Role of TPN in the NICU Initially, the role of TPN is to provide sufficient calories and AA to prevent negative energy and nitrogen balance Minimum intake of 60 non-protein kcal/kg/day and 2.5 g AA/kg/day The rate of catabolism is higher in smaller infants and the need for positive nitrogen balance is more pronounced Secondary, the role of TPN is to provide enough energy to support adequate growth and weight gain Provide non-protein kcal/kg/day and 3.5-4g/kg/day of protein
14 IV Access Peripheral (osmolarity( <1000 mosm/l) Maximum Dextrose 11% >11% associated with incidence of phlebitis and skin sloughing secondary to osmolarity Midline Central Maximum Dextrose 25% - try not to go >D15 UVC PICC / PCVC Maximum Dextrose 25% - try not to go >D15
15 Initial Fluid Status General Guidelines <750 grams ml/kg/day >751 grams 80 ml/kg/day Term Infants 60 ml/kg/day Postnatal fluid restriction during the first 1-31 days is associated with reduced incidence of CLD Increase fluids by ml/kg daily until you reach ~130 ml/kg/d for PN EN fluid goal is ~150ml/kg/d Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
16 Factors that increase IWL Increased Activity RDS Low Relative Humidity High Ambient Temperature Fever ELBW Metabolic Acidosis ( respiratory( loss) Cardiac Disease ( respiratory loss) Skin Breakdown, Injury, or Congenital Defects Phototherapy Radiant Warmers Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
17 Factors that decrease IWL Humidified Incubator Humidified Inspired Gas Double Wall Incubator Topical Agents Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
18 Miscellaneous Fluid Losses Chest Tube Drainage Gastric Suction Vomiting Third Spacing Loss Diarrhea Phototherapy ( stool( water losses) Glycosuria ( urinary water losses) High Renal Solute Load ( urine fluid loss) Infants with abdominal wall defects Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
19 Indications for Fluid Restriction Renal Failure CHF, significant PDA Meningitis Postoperative status - inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion with decreased urine output Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
20 Components of TPN Macronutrients Dextrose Amino Acids Lipids Micronutrients Electrolytes Vitamins & Minerals Trace Elements
21 Dextrose GIR - Glucose Infusion Rate - mg/kg/min [ml/kg/d X dextrose% / 100 X 0.7] Preterm start at mg/kg/min Try not to run GIR <4 mg/kg/min for more than days - brain needs at least a GIR of 4 Advance by 1 mg/kg/min is glucose is stable Maximize GIR at: <10 if infant is <1000 grams mg/kg/min if infant is >1000 grams Glucose >150 = consider GIR Glucose >200 results in osmotic diuresis and E-E disturbances Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
22 Functions of Glucose Glucose functions as an energy source for all cells, and is essential for: CNS Erythrocytes Retinal tissue and renal medulla Brain uses 90% of total glucose consumption Endogenous glucose production may provide only 1/3 of the total glucose needed by preterm infants Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
23 Differential: Hypo- & Hyperglycemia Causes of Hypoglycemia SGA LGA Indomethacin therapy Rapid discontinuation of IV dextrose Extreme Prematurity Gluconeogenesis Glucogenesis Glycogenolysis IDM Inadequate exogenous dextrose delivery Causes of Hyperglycemia Sepsis Extreme prematurity Glyogeneis Glycolysis Surgery / stress Malnutrition Renal disease Excessive dextrose infusion Glucocorticoid therapy Thiazide diuretic therapy Excessive exogenous dextrose delivery Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
24 Protein Written as gm/kg/day Preterm start at 3.0 gm/kg/day Advance by gm/kg/day Maximum of 4.0 gm/kg/day Protein is essential for: Cell Maturation Remodeling Growth Functional activity of enzymes and transport proteins The average well LBW infant receiving no exogenous protein source loses 1% of endogenous protein stores daily. Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
25 Written in gm/kg/day Preterm start at 1.5 gm/kg/day Advance by gm/kg/day Maximum Lipid 3.0 gm/kg/day Intravenous Lipids Concentrated energy source Essential for normal growth and development, including retinal development and function, brain development, and cell structures and function Essential to prevent fatty acid deficiency Can develop w/in 72 hours of birth gm/kg/d Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
26 Non-Protein Calorie : Nitrogen Ratio NPC:N Ratio = Non-protein calories / nitrogen from PRO Non-Protein Calories = calories from CHO (GIR x 4.9) + calories from Fat (gm/kg Fat x 10) Nitrogen = grams/kg of protein / 6.25 Ratio indicates if you are providing enough calories from non-protein substrates so that the baby does not use the protein for energy - rather endogenous deposition of lean body mass Ratios Optimal > 130 Low < 130 Give more dextrose or lipid High > 200 Give more protein and less dextrose Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
27 Composition of TPN Calculating TPN Calories CHO (50-55%) 55%) Gm/kg CHO X 3.4 or GIR X 4.9 Combine to get total calories from Protein (10-20%) TPN per kg Gm/kg/d of PRO X 4 Fat (30-50%) Gm/kg/d of FAT X 10 Lower energy requirements for PN than EN b/c there are no requirements for digestion of fecal losses due to incomplete absorption ( kcal/kg) Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
28 Electrolytes and Minerals Do not need to add on DOL 1-21 Labs reflect maternal values for the first hours of life Do not want to make drastic changes to electrolytes want to correct gradually without over correction allow for natural diuresis
29 Sodium Normal value meq/l Start at 2 meq/kg/day Goal is 2-52 meq/kg/day based on infant needs Look at fluid status before correcting sodium levels Add once the diuresis phase begins Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
30 Sodium Continued Some clinical conditions affecting exogenous sodium requirements Extreme prematurity = limited renal tubular sodium re-absorption Infants with fractional excretion require more exogenous Na+ Abdominal wall defects = sodium wasting SBS Premature skin Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
31 Potassium Normal value meq/l Start at 1 meq/kg/day Goal is 2-32 meq/kg/day based on infant needs If the level is high, find out if it was a heel stick and if the lab is reporting hemolysis Add once the diuresis phase begins Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
32 Potassium Continued Non-oliguric oliguric hyperkalemia is common Extreme prematurity Bruising Catabolism Metabolic acidosis Potassium intake Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
33 E- Carriers Na K 1) Acetate 2) Phosphorus 3) Chloride
34 Normal values Acetate Bicarb (on renal) pco (on blood gas) Base excess 22 to +2 (on blood gas) Start at 1mEq/kg/day Adjust based on infant needs May need to sacrifice phosphorus to provide acetate Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
35 Chloride Normal value meq/l Necessary to correct other electrolyte imbalances left-over ;; Na and K added to TPN with acetate and phosphate first, then with chloride Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
36 Magnesium Normal value meq/l Dosage: Preterm 0.3 meq/kg/day Term 0.5 meq/kg/day Do NOT add Mg until DOL 4 If mom was treated with Mg, check infant Mg level on DOL 4 to assess level before adding to TPN Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
37 Calcium and Phosphate Calcium Normal <1 week 6-10mg/dL wks 8-11mg/dL8 3mo-1yr 9-12mg/dL 9 Start at 2mEq/kg/day Advance to mEq/kg/day Maintain a :1 1.7:1 ratio with phosphorus Can start on on day 1 w/o PO4 Phosphorus Normal <1wk mg/dL 11.7mg/dL 3-7wk mg/dl 1mo mg/dl Start at 1.3 mmol/kg/day Advance to 1.5-2mmol/kg/day Maintain a 2:1 Calcium:Phos ratio for solubility Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
38 Clinical Case Study Neonate receiving sub-optimal TPN Laboratory Studies Reveal: P04 AlkPhos Ca What do you do?
39 Inversing Ca:PO4 Ratio Neonate receiving sub-optimal TPN with P04, and Ca Rational: Hormonal Control of Calcium 1) PTH 2) Calcitriol [1,25(OH) 2 D 3 ] 3) Calcitonin TPN Prescription: Inverse Ca:PO4 Ratio for hours Vachharajani, A., et. al. (2009) Metabolic Bone Disease of Prematurity. NeoReviews, (10), 8. p
40 Trace Elements Standard Trace Minerals Chromium 0.26mcg/kg Copper 26mcg/kg, Manganese 7.8mcg/kg, Selenium 3.1mcg/kg, Zinc 400 mcg/kg Hepatic Trace Minerals Renal Trace Minerals Tsang, R., DeMarini, S., Rath, L. L. Fluids, electrolytes, vitamins, and trace minerals. In C. Kenner, J. W. Lott (Eds.).Comprehensive neonatal nursing: A physiologic perspective. 3rd ed. St. Louis: Saunders; 2003: Zlotkin, S., Atkinson, S., & Lockitch, G. (1996) Trace elements in nutrition for premature infants. Clinics in Perinatology. 22:
41 Cholestasis Hepatic Trace Minerals (direct bili >2.0mg/dL) Copper is excreted through the liver and infants with limited Cu excretion 2 2 cholestasis or other conditions that reduce bile excretion should not receive full dosing D/C supplemental Manganese Chromium 0.2mcg/kg, Copper 10 mcg/kg, Selenium 2mcg/kg, Zinc 400 mcg/kg Consider reducing lipids to gm/kg Reinshagen et al 2008 >1 gm of lipid during bouts of cholestasis oxidant load and tissue damage. Rao, R. & Georgieff, M. Microminerals. In Tsang, R., Uauy, R., Koletzko, B., & Zlotkin, S. (Eds.) Nutrition of the Perterm Infant: Scientific Basis and Pratical Guidelines. 2nd ed. Cincinnati:Digital Educatioon Publishing, Inc.; 2005: Reinshagen, K. et.al.the chronic liver disease in patients with short bowel syndrome: etiology and treatment. Minerva Pediatr Jun;61(3):
42 Enterohepatic Circulation of Bile Hunt & Groff,1990
43 How does the PN cause liver damage? Enteral lipids Enteral lipids are absorbed by the enterocytes in the form of a micelle and packed into chylomicrons The chylomicrons acquire apolipoproteins from the circulating HDL and then are metabolized by the liver Parenteral lipids The Intravenous lipid (IL) emulsions such as Intra-Lipids mimic the size and structure of chylomicrons but contain only W6 FA and TGs devoid of cholesterol and protein IL depend on apolipoprotein E, lipoprotein lipase and LDL- receptors for clearance IL may be cleared as whole particles not by the liver but by other tissues thereby causing TPN induced steatosis Ching, Gura, Modi,, & Jaksic, Nutrition in Clinical Practice,2007, 22 (6)
44 Renal Insufficiency Renal Trace Minerals (urine output is <1.0mL/kg/hr for >2days and/or with elevated creatinine) Selenium and Chromium is excreted through the kidney and supplementation should be decreases or D/C if renal function is impaired Chromium 0.1mcg/kg, Copper 20mcg/kg, Manganese 1mcg/kg, Selenium 1mcg/kg, Zinc 400 mcg/kg Tsang, R., DeMarini, S., Rath, L. L. Fluids, electrolytes, vitamins, and trace minerals. In C. Kenner, J. W. Lott (Eds.).Comprehensive neonatal nursing: A physiologic perspective. 3rd ed. St. Louis: Saunders; 2003: Zlotkin, S., Atkinson, S., & Lockitch, G. (1996) Trace elements in nutrition for premature infants. Clinics in Perinatology. 22:
45 Carnitine Added to enhance β-oxidation by transporting LCFA groups and acetyl-coa across the mitochondrial membrane Clinical intolerance is 2 : 2 Lack of endogenous carnitine along with altered synthesis and storage Lower levels of lipoprotein lipase Can be synthesized from lysine and methionine in the liver and kidney in term infants Prophylactically add 20 mg/kg when infants are <2000 grams birth weight Add 30-40mg/kg when TG are >200 Shatsky, F., and Borum, P. Should Carnitine Be Added to Parenteral Nutrition Solutions? Nutrition in Clinical Practice. 2000; 15: McDonald, C., MacKay, M., Curtis, J., Mulroy, C., and Jackson, W. Carnitine and Cholestatis: Nutritional Dilemmas for the Parenterally Nourished Newborn. Support Line. 2003; 25 (2):
46 Cysteine Preterm infants lack the ability to synthesize cysteine from methionine Can create a small metabolic acidosis in very small infants - give acetate to buffer Ca/PO4 solubility Helps to incidence of PNALD Always add 40 mg/gm protein Groh-Wargo, Thompson, Cox. (2009) ADA Pocket Guide to Neonatal Nutrition.
47 Heparin & Multivitamin Heparin If a PCVC has been ordered, add to TPN watch osmolarity Automatically calculated by computerized TPN program 1 unit / ml Multivitamin Automatically dosed by computerized TPN program based on infant s s weight MVI includes: Vitamin A, B1, B2, B12, C, D, E, K, biotin, dexpanthemol,, folic acid, niacinaminde
48 TPN Considerations with Clinical Conditions - SBS Protocol posted in office 130 ml/kg/d GIR PRO 4 g/kg/d Lipid g/kg/d Hepatic Trace Elements When Direct Bili is >2 Zantac 2mg/kg/d (debatable) Monitor serum sodium closely 2 2 exogenous requirements Wessel, J. & Kocoshis,S. Nutritional Management of Infants with Short Bowel Syndrome, Sem Perinatology, 2007, 31 (2) 104.
49 Wound Healing Nutrient/Vitamin For Wound Healing Zinc Vitamin C Protein g/kg/d Arginine,, Glutamine up to 1000mg per day 150 mg per day Molnar, Joseph. (2007) Nutrition and Wound Healing. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL.
50 TPN Monitoring Check with Neonatologist.generally: RFP after birth If 50% of TFV is from TPN Q Monday & Thursday (unless something abnormal) RFP TGs (if abnormal) Q 2 weeks LFTs If an infant is on full Enteral Feeds Neonatologist will decide RFP (only if following something abnormal) LFT (only if following ALk phos/direct bili)
51 TFV = PN +EN When to incorporate enteral feeds in total fluid volume Typically EN volume is included in TFV when feeding advancement is written Discontinuing TPN If an infant has access issues, determine the cost:benefit ratio of the line placement Generally discontinue TPN when EN reaches mL/kg/d 120mL/kg/d
52 Restarting TPN (i.e.npo( i.e.npo) ) after Being on EN What do you do with your TPN when an infant is made NPO after being on EN? Generally.prescribe maximized amounts of macro- & micronutrients GIR = PRO= = 4 Lipid = 3 Na = 3 K = 2 Ca/PO4 = 2:1
53 Enteral Nutrition Information Promote BM for all infants unless contraindicated Infants born <1500grams can receive donor milk; must sign consent form Infants start on 20 kcal per ounce of breastmilk. Generally feeds are started Q3 hours NG for preemies not able to po Refer to feeding protocol for volume and advancement
54 Enteral Nutrition Information Fortify feeds of breast milk once infant is taking ml/kg/d 120ml/kg/d fortify breast milk with HMF (in-patient) to 22 kcal/oz - if tolerated after hours increase to 24 kcal/oz using HMF if warrented 22 kcal/oz = 1 pkt HMF + 50 ml of breast milk 24 kcal/oz = 1 pkt HMF + 25 ml of breast milk D/c Recipe / All po feeds / >34 weeks 22 kcal/oz = ½ teaspoon of Enfacare/Neosure powder + 90 ml of BM 24 kcal/oz = 1 teaspoon of Enfacare/Neosure powder + 90 ml of BM
55 How Much How Long How Often Universal recommendations to be made to mothers by staff during lactogenesis Pump dependent mothers should be at 500ml by end of week one. There are 2 weeks of hormonal assistance to establish a mother s s milk supply, so we need to recognize there is a problem prior to this time. Volumes (HOW MUCH) Day ml Q Day Day ml Q Day Time (HOW LONG) minutes per side 2 min past last drop or minutes per side on day 3 Frequency (HOW OFTEN) Every hours
56 Formula Choices Infants <2000 g birth weight Enfamil Premature 24 Special Care 24, 30 Infants >2000g and <36 weeks Enfacare 22 or Neosure 22 Term infants >36 weeks Enfamil or Similac
57 MVI and Vitamin D AAP Recommendation Breast fed infant 400IU Q day Formula fed infant taking <1L formula Q day 400IU Q day Start MVI with iron once infant achieves full feeds <2kg 0.5 ml Q day >2 kg 1 ml Q day Wagner,C., Greer, F., et.al. (2008) Prevention of Rickets and Vitamin D Deficiency in Infants, Children, and Adolescents. Pediatrics, 122 (5),
PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants. Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital
 Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital Objectives Review maintenance fluid & electrolyte requirements in neonates Discuss
Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital Objectives Review maintenance fluid & electrolyte requirements in neonates Discuss
Parenteral Nutrition Recommendations for Pediatric Patients
 Fluid Dextrose Amino acid Lipid Parenteral Nutrition Recommendations for Pediatric Patients (Calculated for normal organ function and normal caloric requirements) PN orders are due by 11 AM daily Newborn
Fluid Dextrose Amino acid Lipid Parenteral Nutrition Recommendations for Pediatric Patients (Calculated for normal organ function and normal caloric requirements) PN orders are due by 11 AM daily Newborn
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES
 INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5-10% Postnatal diuresis is delayed in Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Preterm babies have limited capacity to excrete
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5-10% Postnatal diuresis is delayed in Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Preterm babies have limited capacity to excrete
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY
 INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5 10% in first week of life Preterm neonates have more total body water and may lose 10 15% of their weight in
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5 10% in first week of life Preterm neonates have more total body water and may lose 10 15% of their weight in
Nutrition in the premie World
 SURVIVAL AND GROWTH NUTRITION ESSENTIALS Nutrition in the premie World DR VISH SUBRAMANIAN MD MRCP (UK) FAAP NEONATAL CRITICAL CARE MERCY CHILDRENS HOSPITAL., SPRINGFIELD MO Prematurity Nutritional Requirements
SURVIVAL AND GROWTH NUTRITION ESSENTIALS Nutrition in the premie World DR VISH SUBRAMANIAN MD MRCP (UK) FAAP NEONATAL CRITICAL CARE MERCY CHILDRENS HOSPITAL., SPRINGFIELD MO Prematurity Nutritional Requirements
Nutrition in the NICU ANDI MARKELL RD, LD
 Nutrition in the NICU ANDI MARKELL RD, LD PORTLAND, OREGON ANDI MARKELL NUTRITION CONSULTANT Conflict of Interest I had no conflict of interest until 2015 when I was asked to join the Nutrition Advisory
Nutrition in the NICU ANDI MARKELL RD, LD PORTLAND, OREGON ANDI MARKELL NUTRITION CONSULTANT Conflict of Interest I had no conflict of interest until 2015 when I was asked to join the Nutrition Advisory
Nutrition in the preterm - current menu Dr Heena Hooker Consulting Neonatal Paediatrician Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi
 Nutrition in the preterm - current menu Dr Heena Hooker Consulting Neonatal Paediatrician Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi Outline O Background O Challenges in preterm nutrition O Parenteral Nutrition
Nutrition in the preterm - current menu Dr Heena Hooker Consulting Neonatal Paediatrician Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi Outline O Background O Challenges in preterm nutrition O Parenteral Nutrition
NUTRITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
 NUTRITION AIMS To achieve growth and nutrient accretion similar to intrauterine rates To achieve best possible neurodevelopmental outcome To prevent specific nutritional deficiencies Target population
NUTRITION AIMS To achieve growth and nutrient accretion similar to intrauterine rates To achieve best possible neurodevelopmental outcome To prevent specific nutritional deficiencies Target population
4/15/2014. Nurses Take the Lead to Improve Overall Infant Growth. Improving early nutrition. Problem Identification
 Nurses Take the Lead to Improve Overall Infant Growth Cathy Lee Leon, RN, BSN, MBA, NE-BC California Pacific Medical Center-San Francisco Improving early nutrition Standardized feeding protocol Problem
Nurses Take the Lead to Improve Overall Infant Growth Cathy Lee Leon, RN, BSN, MBA, NE-BC California Pacific Medical Center-San Francisco Improving early nutrition Standardized feeding protocol Problem
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION. Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah
 PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah Johor Bahru Malnutrition INTRODUCTION pathologic state of varying severity with clinical features caused
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah Johor Bahru Malnutrition INTRODUCTION pathologic state of varying severity with clinical features caused
Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention?
 Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? 1 Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention? Key questions to ask with initial consultation Can the gastrointestinal (GI) tract be utilized? Can the GI tract be
Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? 1 Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention? Key questions to ask with initial consultation Can the gastrointestinal (GI) tract be utilized? Can the GI tract be
Aggressive Nutrition in Preterm Infants
 Aggressive Nutrition in Preterm Infants Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential
Aggressive Nutrition in Preterm Infants Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential
Preterm Dietary Supplements
 Preterm Dietary Supplements Dr Umesh Vaidya IAP Neocon, Mumbai 2015 Preterm VLBW Nutrition : Ideal practice Minimal enteral feeds (10 ml / kg / day) Human breast milk Feed advancement @ 20 ml / kg / day
Preterm Dietary Supplements Dr Umesh Vaidya IAP Neocon, Mumbai 2015 Preterm VLBW Nutrition : Ideal practice Minimal enteral feeds (10 ml / kg / day) Human breast milk Feed advancement @ 20 ml / kg / day
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Indication See algorithm. Timing Start TPN as indicated on algorithm 1. There is no need to build up TPN volume. The volume of TPN (including lipids) should equate to the total
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Indication See algorithm. Timing Start TPN as indicated on algorithm 1. There is no need to build up TPN volume. The volume of TPN (including lipids) should equate to the total
Parenteral Nutrition
 Approved by: Parenteral Nutrition Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures Manual :
Approved by: Parenteral Nutrition Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures Manual :
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition. in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT. Dzulfikar DLH. Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit
 The Role of Parenteral Nutrition in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Dzulfikar DLH Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit Department of Child Health, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjajaran, Hasan
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Dzulfikar DLH Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit Department of Child Health, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjajaran, Hasan
Prematurity: Optimizing Growth in the NICU for Later Metabolic Outcomes
 Prematurity: Optimizing Growth in the NICU for Later Metabolic Outcomes Malki Miller MS, RD, CNSC Neonatal Dietitian, Maimonides Infants and Children s Hospital Adjunct Lecturer of Human and Pediatric,
Prematurity: Optimizing Growth in the NICU for Later Metabolic Outcomes Malki Miller MS, RD, CNSC Neonatal Dietitian, Maimonides Infants and Children s Hospital Adjunct Lecturer of Human and Pediatric,
Infant Nutrition & Growth to Optimize Outcome Fauzia Shakeel, MD
 Infant Nutrition & Growth to Optimize Outcome Fauzia Shakeel, MD Neonatologist All Children s Hospital / Johns Hopkins Medicine Affiliate Assistant Professor, University of South Florida September 2014
Infant Nutrition & Growth to Optimize Outcome Fauzia Shakeel, MD Neonatologist All Children s Hospital / Johns Hopkins Medicine Affiliate Assistant Professor, University of South Florida September 2014
11/4/10 SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP SAM: PREVENT MALNUTRITION 200. Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure
 Jae H Kim MD PhD Lisa Stellwagen MD Division of Neonatology UC San Diego, Medical Center SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure Jae H. Kim, MD,
Jae H Kim MD PhD Lisa Stellwagen MD Division of Neonatology UC San Diego, Medical Center SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure Jae H. Kim, MD,
PROTOCOL FOR PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 PROTOCOL FOR PARENTERAL NUTRITION Based on; Roberton s textbook of neonatology. 4 th edition. 2005. Sudha Chaudari and Sandeep Kumar.TPN in neonates. Indian Paediatrics. November 2006 Deepak Chawla, Anu
PROTOCOL FOR PARENTERAL NUTRITION Based on; Roberton s textbook of neonatology. 4 th edition. 2005. Sudha Chaudari and Sandeep Kumar.TPN in neonates. Indian Paediatrics. November 2006 Deepak Chawla, Anu
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes
 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
Post Discharge Nutrition. Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP
 Post Discharge Nutrition Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential conflicts of interest:
Post Discharge Nutrition Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential conflicts of interest:
Principles of nutrition in the preterm infant. Importance of nutrition: Undernutrition is very common in VLBW infants
 Principles of nutrition in the preterm infant Dr. S. Navarro-Psihas Pädiatrie IV, Klinik für Neonatologie Medizinische Universität Innsbruck Importance of nutrition: Undernutrition is very common in VLBW
Principles of nutrition in the preterm infant Dr. S. Navarro-Psihas Pädiatrie IV, Klinik für Neonatologie Medizinische Universität Innsbruck Importance of nutrition: Undernutrition is very common in VLBW
Fluid & Electrolyte Management and Early Nutritional Care of the Extremely Preterm Infant. J.M. Lorenz, M.D. April 2014
 Fluid & Electrolyte Management and Early Nutritional Care of the Extremely Preterm Infant J.M. Lorenz, M.D. April 2014 DISCLOSURES Dr. Lorenz has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict
Fluid & Electrolyte Management and Early Nutritional Care of the Extremely Preterm Infant J.M. Lorenz, M.D. April 2014 DISCLOSURES Dr. Lorenz has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict
Introduce the basics of the newborn resuscitation period Practice calculations for TPN orders Learn how to manage basic ventilator settings
 Introduce the basics of the newborn resuscitation period Practice calculations for TPN orders Learn how to manage basic ventilator settings Complex concepts you may be expected to know Not taught this
Introduce the basics of the newborn resuscitation period Practice calculations for TPN orders Learn how to manage basic ventilator settings Complex concepts you may be expected to know Not taught this
ENTERAL NUTRITION Identifying risk of patients for enteral feeding problems: Low risk: Moderate risk: High risk:
 ENTERAL NUTRITION Statement of best practice Feeding with mother s own breastmilk is protective against sepsis, NEC and death All mothers should be informed about this and strongly encouraged to express
ENTERAL NUTRITION Statement of best practice Feeding with mother s own breastmilk is protective against sepsis, NEC and death All mothers should be informed about this and strongly encouraged to express
Effect of changing lipid formulation in Parenteral Nutrition in the Newborn Experimental Pathology BSc
 Effect of changing lipid formulation in Parenteral Nutrition in the Newborn Experimental Pathology BSc Word count: 6939 0 CONTENTS Abstract...2 Acknowledgements...3 Introduction...4 Materials and Methods...11
Effect of changing lipid formulation in Parenteral Nutrition in the Newborn Experimental Pathology BSc Word count: 6939 0 CONTENTS Abstract...2 Acknowledgements...3 Introduction...4 Materials and Methods...11
HUMAN MILK FOR PRETERM INFANTS: ONE SIZE FITS ALL?
 HUMAN MILK FOR PRETERM INFANTS: ONE SIZE FITS ALL? Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Professor and Chief Division of Neonatology Vice Chair, Clinical Research Department of Pediatrics Chair, Augusta University
HUMAN MILK FOR PRETERM INFANTS: ONE SIZE FITS ALL? Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Professor and Chief Division of Neonatology Vice Chair, Clinical Research Department of Pediatrics Chair, Augusta University
ENTERAL NEEDS OF PRETERM INFANTS
 ENTERAL NEEDS OF PRETERM INFANTS A Capstone Seminar Paper for NTR 690: Seminar in Nutrition Presented to Dr. Rayane AbuSabha Department of Nutrition Sciences Sage Graduate School In Partial Fulfillment
ENTERAL NEEDS OF PRETERM INFANTS A Capstone Seminar Paper for NTR 690: Seminar in Nutrition Presented to Dr. Rayane AbuSabha Department of Nutrition Sciences Sage Graduate School In Partial Fulfillment
Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition
 Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition Audis Bethea, Pharm.D. Assistant Professor Therapeutics I December 5 & 9, 2003 Parenteral Nutrition Definition process of supplying nutrients via the intravenous route
Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition Audis Bethea, Pharm.D. Assistant Professor Therapeutics I December 5 & 9, 2003 Parenteral Nutrition Definition process of supplying nutrients via the intravenous route
Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick Neonatal Pharmacist
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Designation: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Designation: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick
Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients. Hamdy Amin, Pharm.D., MBA, BCNSP Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
 Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy Amin, Pharm.D., MBA, BCNSP Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Disclosure Information Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy
Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy Amin, Pharm.D., MBA, BCNSP Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Disclosure Information Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy
Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition The Department of Health in England has asked NICE to develop a new guideline on parenteral nutrition in
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition The Department of Health in England has asked NICE to develop a new guideline on parenteral nutrition in
Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter
 Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter for nutrients and wastes Lubricant Insulator and shock
Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter for nutrients and wastes Lubricant Insulator and shock
Satellite Symposium. Sponsored by
 Satellite Symposium Sponsored by Management of fluids and electrolytes in the preterm infant in the first week of life Pam Cairns St Michaels Hospital Bristol Healthy, term, breast fed babies Limited intake
Satellite Symposium Sponsored by Management of fluids and electrolytes in the preterm infant in the first week of life Pam Cairns St Michaels Hospital Bristol Healthy, term, breast fed babies Limited intake
Minimal Enteral Nutrition
 Abstract Minimal Enteral Nutrition Although parenteral nutrition has been used widely in the management of sick very low birth weight infants, a smooth transition to the enteral route is most desirable.
Abstract Minimal Enteral Nutrition Although parenteral nutrition has been used widely in the management of sick very low birth weight infants, a smooth transition to the enteral route is most desirable.
3/26/18. Total Parenteral Nutrition Roundtable Discussion. Disclosure Information. Objectives. Monitoring Parameters & Complications
 Total Parenteral Nutrition Roundtable Discussion Monitoring Parameters & Complications Jessica Pech MSN, APN, CPNP-PC Division of Pediatric Surgery Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago
Total Parenteral Nutrition Roundtable Discussion Monitoring Parameters & Complications Jessica Pech MSN, APN, CPNP-PC Division of Pediatric Surgery Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago
DISCLOSURE. Learning Objectives. Controversies in Parenteral Nutrition
 Controversies in Parenteral Nutrition Christopher Duggan, MD, MPH Center for Nutrition Center for Advanced Intestinal Rehabilitation (CAIR) Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Boston
Controversies in Parenteral Nutrition Christopher Duggan, MD, MPH Center for Nutrition Center for Advanced Intestinal Rehabilitation (CAIR) Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Boston
Dr Shipa Shah, Lorraine Bell Dietician
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Enteral feeding and use of fortification and supplements in the preterm infant Dr Shipa Shah, Lorraine Bell Dietician Neonatalogy
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Enteral feeding and use of fortification and supplements in the preterm infant Dr Shipa Shah, Lorraine Bell Dietician Neonatalogy
Nutrition Support for the ELBW Infant: Implications for More than Just Growth. Josef Neu, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Florida
 Nutrition Support for the ELBW Infant: Implications for More than Just Growth Josef Neu, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Florida AGA 27 week : How do we Nourish this Baby? Parenteral Nutrition:
Nutrition Support for the ELBW Infant: Implications for More than Just Growth Josef Neu, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Florida AGA 27 week : How do we Nourish this Baby? Parenteral Nutrition:
Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition
 Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition Carol J Rollins, MS, RD, PharmD, BCNSP Coordinator, Nutrition Support Team The University of Arizona Medical Center www.nutritioncare.org Conflict of Interest None
Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition Carol J Rollins, MS, RD, PharmD, BCNSP Coordinator, Nutrition Support Team The University of Arizona Medical Center www.nutritioncare.org Conflict of Interest None
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion , version 1.1
 EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion 13.7.2015, version 1.1 III.1. Elements for a Public Summary III.1.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion 13.7.2015, version 1.1 III.1. Elements for a Public Summary III.1.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral
Intensive Care Nutrition. Dr Alan Race BSc(Hons) PhD FRCA
 Intensive Care Nutrition Dr Alan Race BSc(Hons) PhD FRCA Objectives 1. What examiners say 2. Definition 3. Assessment 4. Requirements 5. Types of delivery 6. CALORIES Trial 7. Timing 8. Immunomodulation
Intensive Care Nutrition Dr Alan Race BSc(Hons) PhD FRCA Objectives 1. What examiners say 2. Definition 3. Assessment 4. Requirements 5. Types of delivery 6. CALORIES Trial 7. Timing 8. Immunomodulation
Parenteral Micronutrient Recommendations and Laboratory Monitoring for Infants on Long Term Parenteral Nutrition (PN)
 Parenteral Micronutrient Recommendations and Laboratory Monitoring for nfants on Long Term Parenteral Nutrition (PN) Dosage Micronutrient Preterm Term Trace Elements (mcg/kg/day) (mcg/kg/day) 1 Chromium
Parenteral Micronutrient Recommendations and Laboratory Monitoring for nfants on Long Term Parenteral Nutrition (PN) Dosage Micronutrient Preterm Term Trace Elements (mcg/kg/day) (mcg/kg/day) 1 Chromium
HIJAM-HMF A READY RECKONER HUMAN MILK FORTIFIER 1 gm per Sachet
 HIJAM-HMF A READY RECKONER HUMAN MILK FORTIFIER 1 gm per Sachet To ensure long-term health and development of preterm infants, an early nutritional support is utmost important. Breast milk is undoubtedly
HIJAM-HMF A READY RECKONER HUMAN MILK FORTIFIER 1 gm per Sachet To ensure long-term health and development of preterm infants, an early nutritional support is utmost important. Breast milk is undoubtedly
Phosphoremia (mmol/l) Calcemia (mmol/l) Postnatal age (days) Postnatal age (days) Urinary Calcium (mg/kg/d) Phosphoremia (mmol/l)
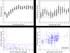 3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 19 October 2011
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 October 2011 PEDIAVEN AP-HP G15, solution for infusion 1000 ml of solution in two chamber bag, B/4 (CIP code: 419
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 October 2011 PEDIAVEN AP-HP G15, solution for infusion 1000 ml of solution in two chamber bag, B/4 (CIP code: 419
Pediatric Nutrition Care as a strategy to prevent hospital malnutrition. Div Pediatric Nutrition and Metabolic Diseases Dept of Child Health
 Pediatric Nutrition Care as a strategy to prevent hospital malnutrition Div Pediatric Nutrition and Metabolic Diseases Dept of Child Health Child is not a miniature adult Specific for child growth and
Pediatric Nutrition Care as a strategy to prevent hospital malnutrition Div Pediatric Nutrition and Metabolic Diseases Dept of Child Health Child is not a miniature adult Specific for child growth and
Melinda Elliott, MD Senior Director, Clinical Education and Professional Development, Prolacta Bioscience Neonatologist, Pediatrix Medical Group of
 Melinda Elliott, MD Senior Director, Clinical Education and Professional Development, Prolacta Bioscience Neonatologist, Pediatrix Medical Group of Maryland Breast Milk is for Babies, Cows Milk is for
Melinda Elliott, MD Senior Director, Clinical Education and Professional Development, Prolacta Bioscience Neonatologist, Pediatrix Medical Group of Maryland Breast Milk is for Babies, Cows Milk is for
NICU Nutrition Pathway
 NICU Nutrition Pathway Safely Infusing NICU TPN Starter and Custom TPN April17 th 2018 Pharmacists: Paul Kasprzak RPH BCPS Kelly Kopec PharmD Major Practice Changes in the Preparation and Administration
NICU Nutrition Pathway Safely Infusing NICU TPN Starter and Custom TPN April17 th 2018 Pharmacists: Paul Kasprzak RPH BCPS Kelly Kopec PharmD Major Practice Changes in the Preparation and Administration
THE AUTHOR OF THIS WHAT S NEW IN NUTRITION? OBJECTIVES & OUTLINE EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE: PARENTERAL NUTRITION (PN)
 WHAT S NEW IN NUTRITION? Alisha Mutch, Pharm.D., BCPS THE AUTHOR OF THIS PRESENTATION HAS NOTHING TO DISCLOSE. OBJECTIVES & OUTLINE MALNUTRITION OBJECTIVES Indicate when parenteral nutrition (PN) is warranted
WHAT S NEW IN NUTRITION? Alisha Mutch, Pharm.D., BCPS THE AUTHOR OF THIS PRESENTATION HAS NOTHING TO DISCLOSE. OBJECTIVES & OUTLINE MALNUTRITION OBJECTIVES Indicate when parenteral nutrition (PN) is warranted
Short Bowel Syndrome: Medical management
 Short Bowel Syndrome: Medical management La Sindrome dell'intestino Corto in età pediatrica Brescia 18 marzo 2011 Jon A.Vanderhoof, M.D. Division of Pediatric GI Harvard Medical School Children s Hospital,
Short Bowel Syndrome: Medical management La Sindrome dell'intestino Corto in età pediatrica Brescia 18 marzo 2011 Jon A.Vanderhoof, M.D. Division of Pediatric GI Harvard Medical School Children s Hospital,
Surgical Nutrition for the Cardiothoracic Patient. Stephanie Kunioki RD, CNSC, LD Memorial Hermann TMC
 Surgical Nutrition for the Cardiothoracic Patient Stephanie Kunioki RD, CNSC, LD Memorial Hermann TMC Financial Disclosures NONE Declared PROPER NUTRITION Surgical Effects on Nutrition Intake & Status
Surgical Nutrition for the Cardiothoracic Patient Stephanie Kunioki RD, CNSC, LD Memorial Hermann TMC Financial Disclosures NONE Declared PROPER NUTRITION Surgical Effects on Nutrition Intake & Status
Neonatal Hypoglycemia. Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010
 Neonatal Hypoglycemia Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010 Definition The S.T.A.B.L.E. Program defines hypoglycemia as: Glucose delivery or availability is inadequate to meet glucose demand (Karlsen,
Neonatal Hypoglycemia Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010 Definition The S.T.A.B.L.E. Program defines hypoglycemia as: Glucose delivery or availability is inadequate to meet glucose demand (Karlsen,
Nutrition. Chapter 45. Reada Almashagba
 Nutrition Chapter 45 1 Nutrition: - Nutrient are organic substances found in food and are required for body function - No one food provide all essential nutrient Major function of nutrition: providing
Nutrition Chapter 45 1 Nutrition: - Nutrient are organic substances found in food and are required for body function - No one food provide all essential nutrient Major function of nutrition: providing
Provincial Clinical Knowledge Topic Parenteral Nutrition, Neonate Inpatient Version 1.1
 Provincial Clinical Knowledge Topic Parenteral Nutrition, Neonate Inpatient Version 1.1 2019, Alberta Health Services, CKCM This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives
Provincial Clinical Knowledge Topic Parenteral Nutrition, Neonate Inpatient Version 1.1 2019, Alberta Health Services, CKCM This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives
CHS 431. Enteral and Parental Nutrition (Practical Part)
 King Saud University College of Applied Medical Sciences Community Health Sciences CHS 431 Enteral and Parental Nutrition (Practical Part) 1 st semester 1432-1433 Student Name: Student Number:.. Total
King Saud University College of Applied Medical Sciences Community Health Sciences CHS 431 Enteral and Parental Nutrition (Practical Part) 1 st semester 1432-1433 Student Name: Student Number:.. Total
Professor Joseph HADDAD Pediatric Department Saint George Univ Hosp Balamand Univ Beirut Lebanon
 Nutrition & Growth in Premature Infant Professor Joseph HADDAD Pediatric Department Saint George Univ Hosp Balamand Univ Beirut Lebanon PART ONE : THE GROWTH OF THE PREMATURE INFANT ARE WE ON THE RIGHT
Nutrition & Growth in Premature Infant Professor Joseph HADDAD Pediatric Department Saint George Univ Hosp Balamand Univ Beirut Lebanon PART ONE : THE GROWTH OF THE PREMATURE INFANT ARE WE ON THE RIGHT
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 + Inflammatory Bowel Disease Christina Kalafsky, Dietetic Intern University of Maryland College Park Children s National Medical Center Case Study January 31, 2014 + Outline n Inflammatory Bowel Disease
+ Inflammatory Bowel Disease Christina Kalafsky, Dietetic Intern University of Maryland College Park Children s National Medical Center Case Study January 31, 2014 + Outline n Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Nutritional Goals and Requirements
 Maria Luisa Forchielli, MD; Sarah J. Miller, PharmD 2 Nutritional Goals and Requirements Introduction Due to nutrition s direct impact on health and disease, nutritional goals and requirements for patients
Maria Luisa Forchielli, MD; Sarah J. Miller, PharmD 2 Nutritional Goals and Requirements Introduction Due to nutrition s direct impact on health and disease, nutritional goals and requirements for patients
Refeeding syndrome a practical approach
 Refeeding syndrome a practical approach PENG pre-bapen Conference Teaching Day Birmingham Monday 20 th November 2017 Rhys White Acting Clinical and Operational Lead Dietitian Guys and St Thomas NHS Foundation
Refeeding syndrome a practical approach PENG pre-bapen Conference Teaching Day Birmingham Monday 20 th November 2017 Rhys White Acting Clinical and Operational Lead Dietitian Guys and St Thomas NHS Foundation
Role of human milk fortifier on weight gain in very low birth weight babies
 International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Verma GK et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2018 Mar;5(2):353-358 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Verma GK et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2018 Mar;5(2):353-358 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
Product Information: Similac Special Care 24
 Product Information: Similac Special Care 24 1 of 5 A 24 Cal/fl oz iron-fortified feeding for growing, low-birth-weight infants and premature infants. Use under medical supervision. OptiGRO is our exclusive
Product Information: Similac Special Care 24 1 of 5 A 24 Cal/fl oz iron-fortified feeding for growing, low-birth-weight infants and premature infants. Use under medical supervision. OptiGRO is our exclusive
Introduction to Clinical Nutrition
 M-III Introduction to Clinical Nutrition Donald F. Kirby, MD Chief, Section of Nutrition Division of Gastroenterology 1 Things We Take for Granted Air to Breathe Death Taxes Another Admission Our Next
M-III Introduction to Clinical Nutrition Donald F. Kirby, MD Chief, Section of Nutrition Division of Gastroenterology 1 Things We Take for Granted Air to Breathe Death Taxes Another Admission Our Next
Methods of Nutrition Support KNH 406
 Methods of Nutrition Support KNH 406 Malnutrition 30 50% of hospitalized patients 95% of nursing home patients Resulting in reduced quality of life & increased health care costs May be remedied by providing
Methods of Nutrition Support KNH 406 Malnutrition 30 50% of hospitalized patients 95% of nursing home patients Resulting in reduced quality of life & increased health care costs May be remedied by providing
Aminosyn 10% (ph 6) Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION Flexible Plastic Container R x only
 Aminosyn 10% (ph 6) Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn 10% (ph 6), Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution
Aminosyn 10% (ph 6) Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn 10% (ph 6), Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution
Neonatal Hypoglycemia
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Neonatal Hypoglycemia. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics.
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Neonatal Hypoglycemia. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics.
Nutrition for the Preterm Infant: Developing a Plan
 Disclosure Nutrition for the Preterm Infant: Developing a Plan Penni Davila Hicks, PhD, RD Medical Science Liaison Abbott Nutrition Columbus, Ohio I am currently an employee of Abbott Nutrition Images
Disclosure Nutrition for the Preterm Infant: Developing a Plan Penni Davila Hicks, PhD, RD Medical Science Liaison Abbott Nutrition Columbus, Ohio I am currently an employee of Abbott Nutrition Images
SAMPLE. Failure to Thrive. Chapter 2. Nutrition Assessment. Mary Sheehan, RD, LD. Sample Client History Terms Related to Failure to Thrive
 Chapter 2 Failure to Thrive Mary Sheehan, RD, LD This chapter provides examples of International Nutrition and Dietetics Terminology (IDNT) terms appropriate for pediatric patients with a medical diagnosis
Chapter 2 Failure to Thrive Mary Sheehan, RD, LD This chapter provides examples of International Nutrition and Dietetics Terminology (IDNT) terms appropriate for pediatric patients with a medical diagnosis
Total Parenteral Nutrition and Enteral Nutrition in the Home. Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 1.02.01 Total Parenteral Nutrition and Enteral Nutrition in the Home Medical Policy Section Durable Medical Equipment Issue Original Policy Date Last Review Status/Date Return to Medical Policy Index
MP 1.02.01 Total Parenteral Nutrition and Enteral Nutrition in the Home Medical Policy Section Durable Medical Equipment Issue Original Policy Date Last Review Status/Date Return to Medical Policy Index
Symposium 3. Pre-term Infant in the First Week of Life
 Symposium 3 Fl id d N t iti S t f th Fluid and Nutrition Support of the Pre-term Infant in the First Week of Life Guidelines for the Provision of Amino Acids in the Preterm Infant During the First Week
Symposium 3 Fl id d N t iti S t f th Fluid and Nutrition Support of the Pre-term Infant in the First Week of Life Guidelines for the Provision of Amino Acids in the Preterm Infant During the First Week
Aminosyn II Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION Flexible Plastic Container R x only
 Aminosyn II Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn II, Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution for intravenous
Aminosyn II Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn II, Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution for intravenous
RD16 Parenteral Nutrition in the NICU 2015 by Jessica McGee, MS, RD, CSP, CNSC, LD
 RD16 Parenteral Nutrition in the NICU 2015 by Jessica McGee, MS, RD, CSP, CNSC, LD Jessica McGee, MS, RD, CSP, LD, CNSC, is a pediatric clinical dietitian and the clinical nutrition manager at Children
RD16 Parenteral Nutrition in the NICU 2015 by Jessica McGee, MS, RD, CSP, CNSC, LD Jessica McGee, MS, RD, CSP, LD, CNSC, is a pediatric clinical dietitian and the clinical nutrition manager at Children
(1 280 ± 286) g; (1 436 ± 201) g
 259 ( 100730) : 34 1 800 g 24 (, 11 ) (, 13 ) 50%, 100 ml / (kg d) FM85, ; (30.6 ± 2.9), (1 280 ± 286) g; (31.6 ± 1.9), (1 436 ± 201) g, 81.6%, 34.1 24.6 d [18.9 vs 17.1 g / (kg d), P = 0.364] (1.16 vs
259 ( 100730) : 34 1 800 g 24 (, 11 ) (, 13 ) 50%, 100 ml / (kg d) FM85, ; (30.6 ± 2.9), (1 280 ± 286) g; (31.6 ± 1.9), (1 436 ± 201) g, 81.6%, 34.1 24.6 d [18.9 vs 17.1 g / (kg d), P = 0.364] (1.16 vs
By; Ashraf El Houfi MD MS (pulmonology) MRCP (UK) FRCP (London) EDIC Consultant ICU Dubai Hospital
 By; Ashraf El Houfi MD MS (pulmonology) MRCP (UK) FRCP (London) EDIC Consultant ICU Dubai Hospital Introduction The significance of nutrition in hospital setting (especially the ICU) cannot be overstated.
By; Ashraf El Houfi MD MS (pulmonology) MRCP (UK) FRCP (London) EDIC Consultant ICU Dubai Hospital Introduction The significance of nutrition in hospital setting (especially the ICU) cannot be overstated.
Product Information: EleCare (for Infants)
 1 of 5 Product Information: 2 of 5 A 20 Cal/fl oz, nutritionally complete amino acid-based formula for infants who cannot tolerate intact or hydrolyzed protein. EleCare is indicated for the dietary management
1 of 5 Product Information: 2 of 5 A 20 Cal/fl oz, nutritionally complete amino acid-based formula for infants who cannot tolerate intact or hydrolyzed protein. EleCare is indicated for the dietary management
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION - INDIAN CONTEXT. Dr. Sarath Gopalan
 PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION - INDIAN CONTEXT Dr. Sarath Gopalan Senior Consultant in Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, New Delhi PN DELIVERY CENTRAL PERIPHERAL
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION - INDIAN CONTEXT Dr. Sarath Gopalan Senior Consultant in Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, New Delhi PN DELIVERY CENTRAL PERIPHERAL
Product Category: EleCare
 EleCare Product Category: EleCare EleCare (for Infants) Updated 4/28/2016 Product Information: EleCare (for Infants) 1 of 4 A 20 Cal/fl oz, nutritionally complete amino acid-based formula for infants who
EleCare Product Category: EleCare EleCare (for Infants) Updated 4/28/2016 Product Information: EleCare (for Infants) 1 of 4 A 20 Cal/fl oz, nutritionally complete amino acid-based formula for infants who
Learning Objectives. At the conclusion of this module, participants should be better able to:
 Learning Objectives At the conclusion of this module, participants should be better able to: Treat asymptomatic neonatal hypoglycemia with buccal dextrose gel Develop patient-specific approaches to intravenous
Learning Objectives At the conclusion of this module, participants should be better able to: Treat asymptomatic neonatal hypoglycemia with buccal dextrose gel Develop patient-specific approaches to intravenous
CPT David J. Licciardello, DVM Veterinary Advisor
 CPT David J. Licciardello, DVM Veterinary Advisor Carbohydrates Fats (Fatty Acids) Minerals Proteins (Amino Acids) Vitamins Water Referred to as Fiber Made up of the forage portion of a diet In a complete
CPT David J. Licciardello, DVM Veterinary Advisor Carbohydrates Fats (Fatty Acids) Minerals Proteins (Amino Acids) Vitamins Water Referred to as Fiber Made up of the forage portion of a diet In a complete
Aminosyn II 8.5% WITH ELECTROLYTES Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION WITH ELECTROLYTES Flexible Plastic Container R x only
 Aminosyn II 8.5% WITH ELECTROLYTES Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION WITH ELECTROLYTES Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn II 8.5% WITH ELECTROLYTES, Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid
Aminosyn II 8.5% WITH ELECTROLYTES Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION WITH ELECTROLYTES Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn II 8.5% WITH ELECTROLYTES, Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid
Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN *
 For the use of a registered medical practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN * DESCRIPTION: NIRMIN * is a clear, colourless injection
For the use of a registered medical practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN * DESCRIPTION: NIRMIN * is a clear, colourless injection
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Digestive System and Body Metabolism 14PART D Metabolism Chemical reactions necessary to maintain
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Digestive System and Body Metabolism 14PART D Metabolism Chemical reactions necessary to maintain
Nutritional assessments and diagnosis of digestive disorders
 Nutritional assessments and diagnosis of digestive disorders AASER ABDELAZIM Assistant professor of Medical Biochemistry Zagazig University, Egypt University of Bisha, KSA aaserabdelazim@yahoo.com 7 Mal
Nutritional assessments and diagnosis of digestive disorders AASER ABDELAZIM Assistant professor of Medical Biochemistry Zagazig University, Egypt University of Bisha, KSA aaserabdelazim@yahoo.com 7 Mal
GESKES/ SSNC Individualized Nutritional Support in the Case of Postnatal Growth Restriction
 Case Presentation for the Course in Clinical Nutrition GESKES/ SSNC Individualized Nutritional Support in the Case of Postnatal Growth Restriction Dr. med. Chantal Cripe-Mamie Division of Neonatology Department
Case Presentation for the Course in Clinical Nutrition GESKES/ SSNC Individualized Nutritional Support in the Case of Postnatal Growth Restriction Dr. med. Chantal Cripe-Mamie Division of Neonatology Department
QI: Exclusive Human Milk Diet for Preterm Infants
 QI: Exclusive Human Milk Diet for Preterm Infants Amy B. Hair, MD Assistant s Professor of Program Director of Neonatal Nutrition Program Director of NICU Intestinal Rehab Team Section of Neonatology Department
QI: Exclusive Human Milk Diet for Preterm Infants Amy B. Hair, MD Assistant s Professor of Program Director of Neonatal Nutrition Program Director of NICU Intestinal Rehab Team Section of Neonatology Department
Acute management of severe malnutrition. Dr Simon Gabe St Mark s Hospital, London
 Acute management of severe malnutrition Dr Simon Gabe St Mark s Hospital, London Malnutrition definition A state resulting from lack of uptake or intake of nutrition leading to altered body composition
Acute management of severe malnutrition Dr Simon Gabe St Mark s Hospital, London Malnutrition definition A state resulting from lack of uptake or intake of nutrition leading to altered body composition
Definition. Failure to Thrive. No clear consensus Growth below the 3 rd or 5 th percentile Decreased growth crossing 2 major growth percentiles
 Failure to Thrive Karen Swarts, MD 6/4/2004 Definition No clear consensus Growth below the 3 rd or 5 th percentile Decreased growth crossing 2 major growth percentiles 1 Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics,
Failure to Thrive Karen Swarts, MD 6/4/2004 Definition No clear consensus Growth below the 3 rd or 5 th percentile Decreased growth crossing 2 major growth percentiles 1 Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics,
ENTERAL NUTRITION IN THE CRITICALLY ILL
 ENTERAL NUTRITION IN THE CRITICALLY ILL 1 Ebb phase Flow phase acute response (catabolic) adoptive response (anabolic) 2 3 Metabolic Response to Stress (catabolic phase) Glucose and Protein Metabolism
ENTERAL NUTRITION IN THE CRITICALLY ILL 1 Ebb phase Flow phase acute response (catabolic) adoptive response (anabolic) 2 3 Metabolic Response to Stress (catabolic phase) Glucose and Protein Metabolism
Neonatal Nutrition Management Guidelines
 Neonatal Nutrition Management Guidelines Nutrition Committee March 2018 Overall Aim 2 Provision of appropriate nutrition to neonates in a timely and safe manner to facilitate adequate growth and development
Neonatal Nutrition Management Guidelines Nutrition Committee March 2018 Overall Aim 2 Provision of appropriate nutrition to neonates in a timely and safe manner to facilitate adequate growth and development
Breast Milk. Composition of Breast Milk
 Breast Milk Composition of Breast Milk Knowledge of the biological composition and constituents of breast milk are critical to the dietitian, because they form the rationale for effective practice in both
Breast Milk Composition of Breast Milk Knowledge of the biological composition and constituents of breast milk are critical to the dietitian, because they form the rationale for effective practice in both
Nutritional Demands of Disease and Trauma
 al Demands of Disease and Trauma Lecture 89 Medical School al Requirements Based on needs to support optimal physiological function Are changed by disease or injury metabolism is altered to prevent further
al Demands of Disease and Trauma Lecture 89 Medical School al Requirements Based on needs to support optimal physiological function Are changed by disease or injury metabolism is altered to prevent further
Nutrition Services at a glance
 Nutrition Services at a glance Ragini Raghuveer, MS, RD, LD/N Systems Clinical Nutrition Manager Linette De Armas, RD, LD/N Clinical Dietitian Melissa Lorenzo, RD, LD/N Clinical Dietitian 1 Learning Objectives
Nutrition Services at a glance Ragini Raghuveer, MS, RD, LD/N Systems Clinical Nutrition Manager Linette De Armas, RD, LD/N Clinical Dietitian Melissa Lorenzo, RD, LD/N Clinical Dietitian 1 Learning Objectives
Nutrition Management in GI Diseases
 Nutrition Management in GI Diseases Aryono Hendarto MD Nutrition & Metabolic Diseases Division Department of Child Health Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital University of Indonesia 1 Patient s Care 1. Drugs 2.
Nutrition Management in GI Diseases Aryono Hendarto MD Nutrition & Metabolic Diseases Division Department of Child Health Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital University of Indonesia 1 Patient s Care 1. Drugs 2.
HOW TO DO EARLY NUTRITION in VLBW INFANTS. David H Adamkin M.D. University of Louisville USA
 HOW TO DO EARLY NUTRITION in VLBW INFANTS David H Adamkin M.D. University of Louisville USA NUTRITIONAL CHALLENGES in EARLY NUTRITION Strategies to Prevent Postnatal Growth Failure Early Total Parenteral
HOW TO DO EARLY NUTRITION in VLBW INFANTS David H Adamkin M.D. University of Louisville USA NUTRITIONAL CHALLENGES in EARLY NUTRITION Strategies to Prevent Postnatal Growth Failure Early Total Parenteral
PROJECT WOMEN S ANAEMIA. by My HealthWorks. Associate Member. 125A, 2nd Floor, Shahpur Jat, New Delhi ,
 PROJECT WOMEN S ANAEMIA by My HealthWorks Associate Member 125A, 2nd Floor, Shahpur Jat, New Delhi-110049, Whatsapp: 8076964582, Phone No: 011-26496673-(74) info@myhealthworks.in INTRODUCTION Anaemia is
PROJECT WOMEN S ANAEMIA by My HealthWorks Associate Member 125A, 2nd Floor, Shahpur Jat, New Delhi-110049, Whatsapp: 8076964582, Phone No: 011-26496673-(74) info@myhealthworks.in INTRODUCTION Anaemia is
Nutrition Intervention After Gastric Bypass Revision
 Nutrition Intervention After Gastric Bypass Revision With an Anastomotic Leak Ali Fox- Montana Dietetic Intern Objectives 1. Describe the etiology of anastomotic leak post Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (G.B.)
Nutrition Intervention After Gastric Bypass Revision With an Anastomotic Leak Ali Fox- Montana Dietetic Intern Objectives 1. Describe the etiology of anastomotic leak post Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (G.B.)
RD s In Practice: Advancing Pediatric Nutrition
 RD s In Practice: Advancing Pediatric Nutrition A Strong Beginning Mindy Morris, DNP, NNP-BC, CNS Extremely Low Birth Weight Program Coordinator Objectives Understand the challenges associated with the
RD s In Practice: Advancing Pediatric Nutrition A Strong Beginning Mindy Morris, DNP, NNP-BC, CNS Extremely Low Birth Weight Program Coordinator Objectives Understand the challenges associated with the
8/20/12. Discuss the importance of thermoregulation in the neonate.
 Sharon Rush MSN NNP-BC Discuss the importance of thermoregulation in the neonate. To maintain correct body temperature range in order to: Reduce oxygen consumption Reduce calorie expenditure Maximize metabolic
Sharon Rush MSN NNP-BC Discuss the importance of thermoregulation in the neonate. To maintain correct body temperature range in order to: Reduce oxygen consumption Reduce calorie expenditure Maximize metabolic
