C HAPTER 8 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER CONTENTS MEDIA LIBRARY MEDIA LIBRARY 289 LECTURE NOTES WORKSHEETS 307 QUIZZES 313 ANSWER KEYS 327
|
|
|
- Dana Harrington
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C HAPTER 8 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER CONTENTS MEDIA LIBRARY 289 LECTURE NOTES Objective 1: Combining forms and suffixes 290 Objective 2: Spell and pronounce 291 Objective 3: Organs 292 Objective 4: Accessory organs 295 Objective 5: Teeth 296 Objective 6: Word building 296 Objective 7: Vocabulary 298 Objective 8: Pathology 300 Objective 9: Diagnostic procedures 302 Objective 10: Therapeutic procedures 303 Objective 11: Pharmacology 304 Objective 12: Abbreviations 305 WORKSHEETS 307 QUIZZES 313 ANSWER KEYS 327 MEDIA LIBRARY Student DVD-ROM Twelve different interactive learning games Flash card generator Audio Glossary Professional Profile video Dental Care Body Rhythms Terminology Translator Companion Website Multiple Choice, True/False, and Fill-in-the-Blank practice questions Labeling exercises Case study Additional Professional Profile information New York Times link for research into specific pathologies Web Destination activities Audio Glossary Link to VangoNotes Link to drug updates IRDVD Animations 3D interactive animation of digestive system anatomy Nasogastric intubation Drag-and-drop labeling activity for Digestive system anatomy
2 Videos Orthodontics Gastroesophageal reflux disease Sigmoidoscopy Registered dietician Digital library of all figures from text chapter, labeled and unlabeled Test bank with 200 objective questions per chapter plus two short answer questions 20 classroom response questions PowerPoint presentation for classroom or online utilization OBJECTIVE 1 Identify and define the combining forms and suffixes introduced in this chapter. Text page: 242; PowerPoint slides: 7 12 LECTURE NOTES Combining Forms an/o append/o appendic/o bar/o bucc/o cec/o chol/e cholangi/o cholecyst/o choledoch/o col/o colon/o dent/o duoden/o enter/o esophag/o gastr/o gingiv/o gloss/o hepat/o ile/o jejun/o labi/o lapar/o lingu/o lith/o odont/o or/o palat/o pancreat/o pharyng/o anus appendix appendix weight cheek cecum bile, gall bile duct gallbladder common bile duct colon colon tooth duodenum small intestine esophagus stomach gums tongue liver ileum jejunum lip abdomen tongue stone tooth mouth palate pancreas throat, pharynx TEACHING STRATEGIES Encourage/remind students to add new word parts to their flash cards. Medical Terminology Bee Create PowerPoint flash cards of new combining forms and suffixes presented in this chapter; have all students stand and then define word part; if student is correct, he or she remains standing; if student is wrong, he or she sits down; continue until only one student is standing. LEARNING ACTIVITIES Worksheet 8A New Combining Form and Suffix Handout Worksheet 8B Medical Term Analysis Quiz 8A May be used as a worksheet Text Practice Exercises Student DVD-ROM Learning games Make flash cards CW Practice questions ASSESSMENTS Quiz 8A New Word Parts Quiz Test Bank Fill-in-the-Blank questions 290 Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
3 proct/o pylor/o rect/o sialaden/o sigmoid/o Suffixes -emesis -lithiasis -orexia -pepsia -phagia -prandial -tripsy anus and rectum pylorus rectum salivary gland sigmoid colon vomit condition of stones appetite digestion eat, swallow pertaining to a meal surgical crushing OBJECTIVE 2 Correctly spell and pronounce medical terms and major anatomical structures relating to the digestive system. LECTURE NOTES Pronunciation for medical terms in this chapter can be found: In parentheses following key terms In the Audio Glossary on Student DVD-ROM In the Audio Glossary at Companion Website TEACHING STRATEGIES Emphasize to students: Importance of correctly spelling terms. How sounding out terms can assist in learning how to spell the terms. Say each new term in class and have students repeat it. Pop Questions Use Clicker questions as either a pretest or posttest quiz to gauge student comprehension of spelling strategies. LEARNING ACTIVITIES Worksheet 8B Medical Term Analysis Terminology Checklist Can be used to practice pronunciation using the Audio Glossary as a reference Text Practice Exercises Flash cards Look at the definition and write out/pronounce terms Student DVD-ROM Audio Glossary Spelling Challenge game Crossword and Word Search puzzles 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 291
4 ASSESSMENTS Quiz 8B Spelling Quiz Suggested terms: 1. gastrointestinal 2. periodontal 3. oropharynx 4. peristalsis 5. sphincters 6. sialadenitis 7. anorexia 8. cachexia 9. hematochezia 10. diverticulosis 11. dysentery 12. intussusception 13. volvulus 14. polyposis 15. cholelithiasis 16. cholangiography 17. paracentesis 18. hemorrhoidectomy 19. choledocholithotripsy 20. fistulectomy Test Bank questions OBJECTIVE 3 Locate and describe the major organs of the digestive system and their functions. Text pages: ; PowerPoint slides: 13 24; LECTURE NOTES Also known as gastrointestinal (GI) system; includes approximately 30 feet of continuous muscular tube, called gut, alimentary canal, or gastrointestinal tract; stretches between mouth and anus; organs in system are different sections of tube Beginning at mouth and continuing to anus, organs are oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestines, and colon Accessory organs of digestion organs that participate in digestion process, but not part of continuous alimentary canal; connected to gut by duct; liver, pancreas, gallbladder, and salivary glands Three main functions: digesting food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste Digestion physical and chemical breakdown of large food particles into simple nutrient molecules like glucose, triglycerides, and amino acids Absorption simple nutrient molecules are absorbed from intestines and circulated throughout body by cardiovascular system; used for growth and repair of organs and tissues Elimination food that cannot be digested or absorbed by body is eliminated from gastrointestinal system as solid waste TEACHING STRATEGIES Visual Aids Use full-size anatomical charts and models to illustrate digestive system organs IRDVD See PowerPoint presentation on the Instructor s Resource DVD for a 3D animation of digestive system organs. See PowerPoint presentation on the Instructor s Resource DVD for a drag-anddrop digestive system anatomy activity; display on screen and have students discuss and place labels during class. Pop Questions Use Clicker questions as either a pretest or posttest quiz to gauge student comprehension during lecture. LEARNING ACTIVITIES Worksheet 8C Chapter Review 292 Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
5 Oral Cavity Digestion begins when food enters mouth and is mechanically broken up by chewing movements of teeth Muscular tongue moves food within mouth and mixes it with saliva; see. Figure 8.1 Saliva contains digestive enzymes to break down carbohydrates and slippery lubricants to make food easier to swallow Taste buds, on surface of tongue, can distinguish bitter, sweet, sour, and salty flavors in food Roof of oral cavity is known as palate and is subdivided into hard palate, bony anterior portion, and soft palate, flexible posterior portion Hanging down from posterior edge of soft palate is uvula; serves two important functions; first, it has role in speech production; second, it is location of gag reflex; this reflex is stimulated when food enters throat without swallowing (for example, laughing with food in your mouth); important because swallowing also results in epiglottis covering larynx to prevent food from entering lungs (see. Figure 8.2) Cheeks form lateral walls, and lips are anterior opening Entire oral cavity is lined with mucous membrane; portion of this mucous membrane forms gums, or gingiva, which combine with connective tissue to cover jaw bone and seal off teeth in their bony sockets Text Labeling exercises 8.A & 8.B1 Practice Exercises Student DVD-ROM Labeling exercise Learning games CW Labeling exercise Practice questions Quiz 8C May be used as a worksheet ASSESSMENTS Quiz 8C Labeling Diagram Test Bank questions Pharynx When food swallowed, it enters oropharynx and then laryngopharynx See. Figure 8.2) Air is also traveling through these portions of pharynx Epiglottis is cartilaginous flap that folds down to cover larynx and trachea so that food is prevented from entering respiratory tract and instead continues into esophagus Esophagus Muscular tube about 10 inches long in adults Food entering esophagus is carried through thoracic cavity and diaphragm and into abdominal cavity where it enters stomach See. Figure 8.5 Food is propelled along esophagus by wave-like muscular contractions called peristalsis; peristalsis works to push food through entire gastrointestinal tract Stomach J-shaped muscular organ that acts as bag or sac to collect and churn food with digestive juices Composed of three parts: fundus or upper region, body or main portion, and antrum or lower region See. Figure 8.5 Folds in lining of stomach are called rugae; when stomach fills with food, rugae stretch out and disappear Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is secreted by glands in mucous membrane lining of stomach; food mixes with hydrochloric acid and other gastric juices to form liquid mixture called chyme, which then passes through remaining portion of digestive system 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 293
6 Entry into and exit from stomach is controlled by muscular valves called sphincters; these valves open and close to ensure food can only move forward down gut tube; cardiac sphincter, named for its proximity to heart, is located between esophagus and fundus; also called lower esophageal sphincter (LES), it keeps food from flowing backward into esophagus; antrum tapers off into pyloric sphincter, which regulates passage of food into small intestine; small amount of chyme is allowed to enter small intestine with each opening of sphincter for two important reasons; first, small intestine is much narrower than stomach and cannot hold as much as stomach can; second, chyme is highly acidic and must be thoroughly neutralized as it leaves stomach Small Intestine Also called small bowel Major site of digestion and absorption of nutrients from food Located between pyloric sphincter and colon; see. Figure 8.6 Has three sections: duodenum, jejunum, and ileum 1. Duodenum extends from pyloric sphincter to jejunum; is about 10 to 12 inches long; digestion is completed in duodenum after liquid chyme from stomach is mixed with digestive juices from pancreas and gallbladder 2. Jejunum middle portion; extends from duodenum to ileum and is about 8 feet long 3. Ileum last portion of small intestine and extends from jejunum to colon; 12 feet in length; connects to colon with a sphincter called ileocecal valve Colon Fluid that remains after complete digestion and absorption of nutrients in small intestine enters colon or large intestine; see. Figure 8.7; most of this fluid is water, which is reabsorbed into body; material that remains after absorption is solid waste called feces (or stool); evacuated in bowel movements (BM) Approximately 5 feet long and extends from ileocecal valve of small intestine to anus Cecum pouch or sac-like area in first two to three inches at beginning of colon Vermiform appendix small worm-shaped outgrowth at end of cecum Remaining colon consists of ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, and sigmoid colon; ascending colon on right side extends from cecum to lower border of liver; transverse colon begins where ascending colon leaves off and moves horizontally across upper abdomen toward spleen; descending colon then travels down left side of body to where sigmoid colon begins; sigmoid colon curves in S-shape back to midline of body and ends at rectum Rectum where feces is stored; leads into anus, which contains anal sphincter; sphincter consists of rings of voluntary and involuntary muscles to control evacuation of feces or defecation 294 Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
7 OBJECTIVE 4 Describe the function of the accessory organs of the digestive system. Text pages: ; PowerPoint slides: LECTURE NOTES Accessory organs of digestive system are salivary glands, liver, pancreas, and gallbladder Function by producing digestive fluids and enzymes necessary for chemical breakdown of food Each is attached to gut tube by duct Salivary Glands In oral cavity Produce saliva; watery and slick fluid allows food to be swallowed with less danger of choking; mixed with food in mouth forms bolus (chewed food that is ready to swallow); also contains digestive enzyme amylase that begins digestion of carbohydrates Three pairs of salivary glands: 1. Parotid glands in front of ears 2. Submandibular glands in floor of mouth 3. Sublingual glands in floor of mouth See. Figure 8.8 Liver Large organ located in right upper quadrant of abdomen Has several functions, including processing nutrients absorbed by intestines, detoxifying harmful substances in body, and producing bile; bile is important for digestion of fats and lipids because it breaks up large fat globules into much smaller droplets, making them easier to digest in watery environment inside intestines; process is called emulsification See. Figure 8.9 Gallbladder Bile produced by liver stored in gallbladder (GB) As liver produces bile, it travels down hepatic duct and up cystic duct into gallbladder (see. Figure 8.9) In response to fat in chyme, muscular wall of gallbladder contracts and sends bile back down cystic duct and into common bile duct (CBD), which carries bile to duodenum where it is able to emulsify fat in chyme Pancreas Connected to duodenum by pancreatic duct, see. Figure 8.9 Produces two important secretions for digestion buffers and pancreatic enzymes Buffers neutralize acidic chyme that has just left stomach Pancreatic enzymes chemically digest carbohydrates, fats, and proteins Also endocrine gland that produces hormones insulin and glucagon; plays role in regulating level of glucose in blood and is discussed in further detail in Chapter 11 TEACHING STRATEGIES Visual Aids Use full-size anatomical charts and models to illustrate accessory organs of the digestive system. IRDVD See PowerPoint presentation on the Instructor s Resource DVD for a drag-anddrop digestive system anatomy activity; display on screen and have students discuss and place labels during class. See PowerPoint presentation on the Instructor s Resource DVD for a 3D animation of digestive system organs. Pop Questions Use Clicker questions as either a pretest or posttest quiz to gauge student comprehension during lecture. LEARNING ACTIVITIES Worksheet 8C Chapter Review Text Labeling Exercise 8.B2 Practice Exercises Student DVD-ROM Labeling exercise Learning games CW Labeling exercise Practice questions Quiz 8D May be used as a worksheet ASSESSMENTS Quiz 8D Labeling Diagram Test Bank questions 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 295
8 OBJECTIVE 5 Identify the shape and function of each type of tooth. Text pages: ; PowerPoint slides: LECTURE NOTES Teeth are important part of first stage of digestion Teeth in front of mouth bite, tear, or cut food into small pieces; include incisors and cuspids or canines; see. Figure 8.3 Posterior teeth grind and crush food into even finer pieces; include bicuspids, or pre-molars, and molars Tooth subdivided into crown and root; crown is part of tooth visible above gum line; root is below gum line; root anchored in bony socket of jaw by cementum and tiny periodontal ligaments Crown of tooth is covered by layer of enamel, hardest substance in body; under enamel layer is dentin, substance that makes up main bulk of tooth; hollow interior of tooth is called pulp cavity in crown and root canal in root; these cavities contain soft tissue made up of blood vessels, nerves, and lymph vessels; see. Figure 8.4 Humans have two sets of teeth; first set, often referred to as baby teeth, are deciduous teeth; 20 teeth in this set; erupt through gums between ages of 6 and 28 months; at approximately 6 years of age, these teeth begin to fall out and are replaced by 32 permanent teeth; replacement process continues until about 18 to 20 years of age TEACHING STRATEGIES Visual Aids Use full-size anatomical charts and models to illustrate accessory organs of the digestive system. Pop Questions Use Clicker questions as either a pretest or posttest quiz to gauge student comprehension during lecture. Guest Speaker Invite a dentist or dental hygienist to speak to the class about tooth structure and dental procedures; professionals may be able to bring dental X-rays to share with the class LEARNING ACTIVITIES Worksheet 8C Chapter Review Text Practice Exercises Student DVD-ROM Learning games CW Practice questions ASSESSMENTS Quiz 8G Chapter Review Test Bank questions OBJECTIVE 6 Build and define digestive system medical terms from word parts. Text pages: ; PowerPoint slides: LECTURE NOTES Combining Form an/o Medical Term anal Definition pertaining to anus append/o appendectomy removal of appendix appendic/o appendicitis inflammation of appendix bucc/o buccal pertaining to cheeks buccolabial pertaining to cheeks and lips cholecyst/o cholecystectomy removal of gallbladder TEACHING STRATEGIES Reinforce how many digestive system terms can be constructed from word parts. Read aloud chapter terms that are made up of word parts; have students identify parts and define terms, either aloud or individually on paper. 296 Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
9 cholecystogram record of gallbladder cholecystic pertaining to gallbladder cholecystalgia gallbladder pain col/o colectomy removal of colon colostomy create an opening in colon colorectal pertaining to colon and rectum colon/o colonoscope instrument to view colon colonic pertaining to colon dent/o dental pertaining to teeth dentalgia tooth pain duoden/o duodenal pertaining to duodenum enter/o enteric pertaining to small intestine enteritis small intestine inflammation esophag/o esophageal pertaining to esophagus esophagectasis dilated esophagus gastr/o gastralgia stomach pain gastric pertaining to stomach gastroenteritis inflammation of stomach and small intestine gastroenterologist specialist in stomach and small intestine gastromalacia softening of stomach nasogastric pertaining to nose and stomach gastrostomy create an opening in stomach gastroscope instrument to view inside stomach gastritis stomach inflammation gastrectomy removal of stomach gingiv/o gingival pertaining to gums gingivitis inflammation of gums gloss/o glossal pertaining to tongue hypoglossal pertaining to under tongue hepat/o hepatitis inflammation of liver hepatoma liver tumor hepatic pertaining to liver ile/o ileal pertaining to ileum ileostomy create an opening in ileum jejun/o jejunal pertaining to jejunum lapar/o laparotomy incision into abdomen laparoscope instrument to view inside the abdomen lingu/o sublingual pertaining to under tongue odont/o orthodontic pertaining to straight teeth periodontic pertaining to around teeth or/o oral pertaining to mouth palat/o palatoplasty surgical repair of palate pancreat/o pancreatitis inflammation of pancreas pancreatic pertaining to pancreas pharyng/o pharyngeal pertaining to throat pharyngoplegia paralysis of throat pharyngoplasty surgical repair of throat proct/o proctoptosis drooping rectum and anus proctologist specialist in rectum and anus Write sentences on the board using common words; have students substitute correct medical terms. Pop Questions Use Clicker questions as either a pretest or posttest quiz to gauge student comprehension during lecture. LEARNING ACTIVITIES Worksheet 8A New Combining Forms and Suffixes Handout Worksheet 8B Medical Term Analysis Worksheet 8C Chapter Review Quiz 8E May be used as a worksheet Text Practice Exercises Terminology Checklist Student DVD-ROM Learning games Flash cards CW Practice questions ASSESSMENTS Quiz 8E Word Building Quiz Quiz 8G Chapter Review Test Bank questions 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 297
10 proctopexy surgical fixation of rectum and anus pylor/o pyloric pertaining to pylorus rect/o rectal pertaining to rectum sialaden/o sialadenitis inflammation of salivary gland sigmoid/o sigmoidoscope instrument to view inside sigmoid colon sigmoidal pertaining to sigmoid colon Suffix -emesis Medical Term hematemesis Definition vomiting blood hyperemesis excessive vomiting -orexia anorexia absence of appetite dysorexia abnormal appetite -pepsia bradypepsia slow digestion dyspepsia difficult digestion -phagia aphagia unable to swallow/eat dysphagia difficulty swallowing/eating polyphagia many (excessive) eating -prandial postprandial after a meal OBJECTIVE 7 Identify and define digestive system vocabulary terms. Text pages: ; PowerPoint slides: LECTURE NOTES Term anorexia ascites bowel incontinence bridge cachexia constipation crown dental caries Definition general term meaning loss of appetite that may accompany other conditions; sometimes used to refer to anorexia nervosa, which is personality disorder involving refusal to eat collection or accumulation of fluid in peritoneal cavity inability to control defecation dental appliance attached to adjacent teeth for support to replace missing teeth loss of weight and generalized wasting that occurs during chronic disease experiencing difficulty in defecation or infrequent defecation artificial covering for tooth created to replace original crown gradual decay and disintegration of teeth caused by bacteria; may lead to abscessed teeth; commonly called a tooth cavity TEACHING STRATEGIES Write sentences on the board using common words; have students substitute correct medical terms. Jeopardy Game Have students create questions for terms in this section for a Jeopardy game to be played in class may be combined with Pathology, Diagnostic, and Therapeutic terms. IRDVD See PowerPoint presentation on the Instructor s Resource DVD for a video on the topic of orthodontics. Pop Questions Use Clicker questions as either a pretest or posttest quiz to gauge student comprehension during lecture. LEARNING ACTIVITIES Worksheet 8C Chapter Review 298 Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
11 dentistry denture diarrhea emesis gastroenterology hematochezia implant internal medicine jaundice melena nausea obesity orthodontics periodontics polyp proctology pyrosis regurgitation branch of healthcare involved with prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of conditions involving teeth, jaw, and mouth; dentistry is practiced by dentist or oral surgeon partial or complete set of artificial teeth that are set in plastic materials; acts as substitute for natural teeth and related structures passing of frequent, watery bowel movements; usually accompanies gastrointestinal (GI) disorders vomiting branch of medicine involved in diagnosis and treatment of diseases and disorders of digestive system; physician is gastroenterologist passing bright red blood in stools prosthetic device placed in jaw to which tooth or denture may be anchored branch of medicine involving diagnosis and treatment of diseases and conditions of internal organs such as digestive system; physician is an internist yellow cast to skin, mucous membranes, and whites of eyes caused by deposit of bile pigment from too much bilirubin in blood; bilirubin is waste product produced when worn-out red blood cells are broken down; may be symptom of disorder such as gallstones blocking common bile duct or carcinoma of the liver passage of dark tarry stools; color is result of digestive enzymes working on blood in gastrointestinal tract urge to vomit body weight above healthy level; person 100 pounds overweight has morbid obesity branch of dentistry concerned with correction of problems with tooth alignment; specialist is orthodontist branch of dentistry concerned with treating conditions involving gums and tissues surrounding teeth; specialist is periodontist small tumor with pedicle or stem attachment; commonly found on mucous membranes such as lining of colon or nasal cavity; colon polyps may be pre-cancerous branch of medicine involved in diagnosis and treatment of diseases and disorders of anus and rectum; physician is proctologist pain and burning sensation usually caused by stomach acid splashing up into esophagus; commonly called heartburn return of fluids and solids from stomach into mouth Text Practice Exercises Terminology Checklist Medical Record Analysis Chart Note Transcription Student DVD-ROM Learning games Flash cards CW Practice questions Case Study ASSESSMENTS Quiz 8G Chapter Review Test Bank questions 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 299
12 OBJECTIVE 8 Identify and define selected digestive system pathology terms. Text pages: ; PowerPoint slides: LECTURE NOTES Term Oral Cavity aphthous ulcers cleft lip cleft palate herpes labialis periodontal disease Esophagus esophageal varices gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Stomach gastric carcinoma hiatal hernia peptic ulcer disease (PUD) Small Intestine and Colon anal fistula colorectal carcinoma Crohn s disease Definition painful ulcers in mouth of unknown cause; commonly called canker sores congenital anomaly in which upper lip and jaw bone fail to fuse in midline leaving open gap; often seen along with cleft palate; corrected with surgery congenital anomaly in which roof of mouth has split or fissure; corrected with surgery infection of lip by herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1); also called fever blisters or cold sores disease of supporting structures of teeth, including gums and bones; the most common cause of tooth loss enlarged and swollen varicose veins in lower end of esophagus; if rupture, serious hemorrhage results; often related to liver disease acid from stomach flows backward up into esophagus causing inflammation and pain cancerous tumor in stomach protrusion of stomach through diaphragm and extending into thoracic cavity; gastroesophageal reflux disease is a common symptom; also called a diaphragmatocele ulcer occurring in lower portion of esophagus, stomach, and/or duodenum; caused by acid of gastric juices; initial damage to protective lining of stomach may be caused by Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) bacterial infection; if ulcer extends all way through wall of stomach, it is called perforated ulcer, which requires immediate surgery to repair abnormal tube-like passage from surface around anal opening directly into rectum cancerous tumor along length of colon and rectum form of chronic inflammatory bowel disease affecting primarily ileum and/or colon; also called regional ileitis; autoimmune condition affects all layers of bowel wall and results in scarring and thickening of gut wall TEACHING STRATEGIES Select two students to do 5-minute presentations of their Internet research in class. Write sentences on the board using common words; have students substitute correct medical terms. Jeopardy Game Have students create questions for terms in this section for a Jeopardy game to be played in class may be combined with Vocabulary, Diagnostic, and Therapeutic terms. IRDVD See PowerPoint presentation on the Instructor s Resource DVD for a video on the topic of gastrointestinal reflux disease. Pop Questions Use Clicker questions as either a pretest or posttest quiz to gauge student comprehension during lecture. LEARNING ACTIVITIES Internet Research Have students select a specific pathology and use Internet resources to research its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatments. Worksheet 8C Chapter Review Text Practice Exercises Terminology Checklist Medical Record Analysis Chart Note Transcription Student DVD-ROM Learning games Flash cards CW Practice questions Case Study Web Destination activities on peptic ulcer and gallstones New York Times link for research into specific pathologies ASSESSMENTS Quiz 8G Chapter Review Test Bank questions 300 Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
13 diverticulitis diverticulosis dysentery hemorrhoids ileus inguinal hernia intussusception irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) polyposis ulcerative colitis volvulus Accessory Organs cholecystitis cholelithiasis cirrhosis hepatitis inflammation of diverticulum (an outpouching off the gut), especially in the colon; inflammation often results when food becomes trapped within pouch condition of having diverticula (outpouches off the gut); may lead to diverticulitis if one becomes inflamed disease characterized by diarrhea, often with mucus and blood, severe abdominal pain, fever, and dehydration; caused by ingesting food or water contaminated by chemicals, bacteria, protozoans, or parasites varicose veins in rectum severe abdominal pain, inability to pass stools, vomiting, and abdominal distension as a result of intestinal blockage; may require surgery to reverse blockage hernia or protrusion of loop of small intestine into inguinal (groin) region through weak spot in abdominal muscle wall that develops into hole; may become incarcerated or strangulated if muscle tightens down around loop of intestines and cuts off blood flow result of intestine slipping or telescoping into another section of intestine just below it; more common in children disturbance in functions of intestine from unknown causes; symptoms include abdominal discomfort and alteration in bowel activity; also called spastic colon or functional bowel syndrome small tumors that contain pedicle or stemlike attachment in mucous membranes of colon; may be pre-cancerous chronic inflammatory condition that produces numerous ulcers that form on mucous membrane lining of colon; cause is unknown; also known as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) condition in which bowel twists upon itself and causes an obstruction; painful and requires immediate surgery inflammation of gallbladder; most commonly caused by gallstones in gallbladder or common bile duct that block flow of bile presence of gallstones; may or may not cause symptoms such as cholecystalgia chronic disease of liver associated with failure of liver to function properly inflammation of liver, usually due to viral infection; different viruses are transmitted by different routes, such as sexual contact or from exposure to blood or fecal-contaminated water or food 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 301
14 OBJECTIVE 9 Identify and define selected digestive system diagnostic procedures. Text pages: ; PowerPoint slides: LECTURE NOTES Term Clinical Laboratory Tests alanine transaminase (ALT) aspartate transaminase (AST) fecal occult blood test (FOBT) ova and parasites (O&P) serum bilirubin stool culture Diagnostic Imaging bite-wing X-ray intravenous cholecystography lower gastrointestinal series (lower GI series) percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography (PTC) upper gastrointestinal (UGI) series Endoscopic Procedures colonoscopy Definition enzyme normally present in blood; blood levels are increased in persons with liver disease enzyme normally present in blood; blood levels are increased in persons with liver disease laboratory test on feces to determine if microscopic amounts of blood are present; also called hemoccult or stool guaiac laboratory examination of feces with microscope for presence of parasites or their eggs blood test to determine amount of waste product bilirubin in bloodstream; elevated levels indicate liver disease laboratory test of feces to determine if any pathogenic bacteria are present X-ray taken with part of film holder held between teeth and parallel to teeth dye administered intravenously to patient that allows for X-ray visualization of gallbladder and bile ducts X-ray image of colon and rectum is taken after administration of barium (a radiopaque dye) by enema; also called barium enema (BE) procedure in which contrast medium is injected directly into liver to visualize bile ducts; used to detect obstructions administering of barium contrast material orally and then taking X-ray to visualize esophagus, stomach, and duodenum; also called barium swallow flexible fiberscope called colonoscope is passed through anus, rectum, and colon; used to examine upper portion of colon; polyps and small growths can be removed during this procedure TEACHING STRATEGIES Write sentences on the board using common words; have students substitute correct medical terms. Obtain copies of actual upper and lower GI series or photos taken during a colonoscopy. IRDVD See PowerPoint presentation on the Instructor s Resource DVD for a video on the topic of sigmoidoscopy. Jeopardy Game Have students create questions for terms in this section for a Jeopardy game to be played in class may be combined with Vocabulary, Pathology, and Therapeutic terms. Pop Questions Use Clicker questions as either a pretest or posttest quiz to gauge student comprehension during lecture. LEARNING ACTIVITIES Worksheet 8C Chapter Review Text Practice Exercises Terminology Checklist Medical Record Analysis Chart Note Transcription Student DVD-ROM Learning games Flash cards CW Practice questions Case Study New York Times link for research into specific diagnostic procedures ASSESSMENTS Quiz 8G Chapter Review Test Bank questions 302 Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
15 endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) gastroscopy laparoscopy sigmoidoscopy Additional Diagnostic Procedures paracentesis procedure using endoscope to visually examine hepatic duct, common bile duct, and pancreatic duct; retrograde means to go in backwards direction; endoscope is inserted through anus and worked backwards to area where pancreatic and common bile ducts empty into duodenum use of flexible fiber-optic endoscope to visually examine esophagus, stomach, and beginning of duodenum procedure in which flexible gastroscope is passed through mouth and down esophagus; used to visualize inside stomach; to diagnose peptic ulcers and gastric carcinoma laparoscope is passed into abdominal wall through small incision; abdominal cavity is visually examined for tumors and other conditions; also called peritoneoscopy procedure using flexible sigmoidoscope to visually examine sigmoid colon; used to diagnose cancer and polyps insertion of needle into abdominal cavity to withdraw fluid; tests to diagnose diseases may be conducted on fluid OBJECTIVE 10 Identify and define selected digestive system therapeutic procedures. Text pages: ; PowerPoint slides: LECTURE NOTES Term Dental Procedures extraction root canal Medical Procedures gavage lavage Definition removing or pulling teeth dental treatment involving pulp cavity of root of tooth; procedure used to save tooth that is badly infected or abscessed using nasogastric (NG) tube to place liquid nourishment directly into stomach using nasogastric (NG) tube to wash out stomach; for example, after ingestion of dangerous substances TEACHING STRATEGIES Write sentences on the board using common words; have students substitute correct medical terms. Jeopardy Game Have students create questions for terms in this section for a Jeopardy game to be played in class may be combined with Vocabulary, Pathology, and Diagnostic terms. IRDVD See PowerPoint presentation on the Instructor s Resource DVD for an animation on the topic of nasogastric intubation Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 303
16 nasogastric intubation (NG tube) total parenteral nutrition (TPN) Surgical Procedures anastomosis bariatric surgery choledocholithotripsy colostomy diverticulectomy exploratory laparotomy fistulectomy gastric stapling hemorrhoidectomy hernioplasty laparoscopic cholecystectomy liver transplant flexible catheter is inserted into nose and down esophagus to stomach; may be used for feeding or to suction out stomach fluids providing 100 percent of patient s nutrition intravenously; used when patient is unable to eat to surgically create connection between two organs or vessels; for example, joining together two cut ends of intestines after section is removed group of surgical procedures such as stomach stapling and restrictive banding to reduce size of stomach; treatment for morbid (extreme) obesity crushing of gallstone in common bile duct surgical creation of opening of some portion of colon through abdominal wall to outside surface; fecal material (stool) drains into bag worn on abdomen surgical removal of diverticulum abdominal operation for purpose of examining abdominal organs and tissues for signs of disease or other abnormalities removal of fistula procedure that closes off large section of stomach with rows of staples; results in smaller stomach to assist very obese patients to lose weight surgical removal of hemorrhoids from anorectal area surgical repair of hernia; also called herniorrhaphy surgical removal of gallbladder through very small abdominal incision with assistance of laparoscope transplant of liver from donor See PowerPoint presentation on the Instructor s Resource DVD for video on the topic of registered dieticians. Pop Questions Use Clicker questions as either a pretest or posttest quiz to gauge student comprehension during lecture. Guest Speaker Invite a registered dietician to speak to class about total parenteral nutrition. LEARNING ACTIVITIES Worksheet 8C Chapter Review Text Practice Exercises Terminology Checklist Medical Record Analysis Chart Note Transcription Student DVD-ROM Learning games Flash cards CW Practice questions Case Study New York Times link for research into specific treatment procedures ASSESSMENTS Quiz 8G Chapter Review Test Bank questions OBJECTIVE 11 Identify and define selected medications relating to the digestive system. Text page: 264; PowerPoint slides: LECTURE NOTES Classification Action anorexiant treats obesity by suppressing appetite Generic and Brand Names phendimetrazine, Adipost, Obezine; phentermine, Zantryl, Adipex antacid neutralizes stomach acids calcium carbonate, Tums; aluminum hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide, Maalox, Mylanta TEACHING STRATEGIES Pop Questions Use Clicker questions as either a pretest or posttest quiz to gauge student comprehension during lecture. 304 Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
17 antidiarrheal controls diarrhea loperamide, Imodium; diphenoxylate, Lomotil; kaolin/pectin, Kaopectate antiemetic treats nausea, vomiting, and motion sickness prochlorperazine, Compazine; promethazine, Phenergan emetic induces vomiting ipecac syrup H 2 -receptor antagonists laxative proton pump inhibitors treats peptic ulcers and gastroesophageal reflux disease; when stimulated, H 2 - receptors increase production of stomach acid; using antagonist to block these receptors results in low acid level in stomach treats constipation by stimulating bowel movement used to treat peptic ulcers and gastroesophageal reflux disease; blocks stomach s ability to secrete acid ranitidine, Zantac; cimetidine, Tagamet; famotidine, Pepcid senosides, Senokot; psyllium, Metamucil esomeprazole, Nexium; omeprazole, Prilosec LEARNING ACTIVITIES Have students use a PDR and/or the Internet to look up additional information regarding these medications, such as dosage, side effects, and contraindications. Worksheet 8C Chapter Review Text Practice Exercises Terminology Checklist Student DVD-ROM Learning games Flash cards CW Practice questions ASSESSMENTS Quiz 8G Chapter Review Test Bank questions OBJECTIVE 12 Define selected abbreviations associated with the digestive system. Text page: 264; PowerPoint slides: LECTURE NOTES ac before meals ALT alanine transaminase AST aspartate transaminase Ba barium BE barium enema BM bowel movement BS bowel sounds CBD common bile duct EGD esophagogastroduodenoscopy ERCP endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography FOBT fecal occult blood test GB gallbladder GERD gastroesophageal reflux disease GI gastrointestinal HAV hepatitis A virus HBV hepatitis B virus HCl hydrochloric acid HCV hepatitis C virus TEACHING STRATEGIES Emphasize importance of learning abbreviations and their full meanings; point out how some abbreviations, such as GERD, FOBT, NG, and NPO are typically used rather than full terms. Encourage students to add abbreviations to their flash cards. Write sentences on the board using common words; have students substitute correct abbreviations. Memory Game Have students assist in creating a memory game to be played in class. Pop Questions Use Clicker questions as either a pretest or posttest quiz to gauge student comprehension during lecture Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 305
18 HDV hepatitis D virus HEV hepatitis E virus HSV-1 herpes simplex virus type 1 IBD inflammatory bowel disease IBS irritable bowel syndrome IVC intravenous cholangiography NG nasogastric (tube) NPO nothing by mouth n&v nausea and vomiting O&P ova and parasites pc after meals PO by mouth pp postprandial PTC percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography PUD peptic ulcer disease TPN total parenteral nutrition UGI upper gastrointestinal series LEARNING ACTIVITIES Worksheet 8C Chapter Review Quiz 8F May be used as a worksheet Text Practice Exercises Student DVD-ROM Learning games Flash cards CW Practice questions ASSESSMENTS Quiz 8F Abbreviations Quiz Quiz 8G Chapter Review Test Bank questions 306 Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
19 Worksheet 8A New Combining Form and Suffix Handout Directions: For each combining form below, write out its meaning and then locate a new term from the chapter that uses the combining form or suffix. Combining Forms Meaning Chapter Term Meaning 1. an/o 2. append/o 3. appendic/o 4. bar/o 5. bucc/o 6. cec/o 7. chol/e 8. cholangi/o 9. cholecyst/o 10. choledoch/o 11. col/o 12. colon/o 13. dent/o 14. duoden/o 15. enter/o 16. esophag/o 17. gastr/o 18. gingiv/o 19. gloss/o 20. hepat/o 21. ile/o 22. jejun/o 23. labi/o (Continued ) 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 307
20 Combining Forms Meaning Chapter Term Meaning 24. lapar/o 25. lingu/o 26. lith/o 27. odont/o 28. or/o 29. palat/o 30. pancreat/o 31. pharyng/o 32. proct/o 33. pylor/o 34. rect/o 35. sialaden/o 36. sigmoid/o Suffixes 37. emesis 38. lithiasis 39. orexia 40. pepsia 41. phagia 42. prandial 43. tripsy 308 Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
21 Worksheet 8B Medical Term Analysis Directions: Below are terms built from word parts used in this chapter that are not analyzed in the Word Building Table. Many are built from word parts you have learned in previous chapters. Analyze each term presented below and list and define the word parts used to build each term. Medical Term Word Part Analysis 1. proctology 2. gastroesophageal 3. carcinoma 4. colitis 5. cholecystitis 6. cholelithiasis 7. cholecystography 8. intravenous 9. transhepatic 10. cholangiography 11. colonoscopy (Continued ) 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 309
22 12. cholangiopancreatography 13. esophagogastroduodenoscopy 14. gastroscopy 15. laparoscopy 16. sigmoidoscopy 17. choledocholithotripsy 310 Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
23 Worksheet 8C Chapter Review Anatomy and Physiology 1. The accessory organs of the digestive system are the,,,. 2. is the watery, slippery secretion in the oral cavity that contains the digestive enzyme,. 3. The of a tooth is above the gum line and the of the tooth is below the gum line. 4. The hardest substance in the body is. 5. The prevents food from entering the trachea. 6. The stomach secretes. 7. are rings of muscles that control entry into or exit from an organ. 8. The three sections of the small intestine are the,, and. 9. The appendix is attached to the of the colon. 10. The liver secretes to emulsify fats. Word Building Directions: Build a term that means: 1. inflammation of appendix 2. removal of gallbladder 3. create opening in colon 4. specialist in stomach and small intestine _ 5. instrument to view inside sigmoid colon 6. incision into abdomen 7. pertaining to straight teeth _ (Continued ) 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 311
24 8. surgical repair of palate 9. vomiting blood 10. slow digestion _ Matching 1. ascites 2. cachexia 3. crown 4. caries 5. emesis 6. hematochezia 7. jaundice 8. melena 9. polyp 10. pyrosis 11. aphthous ulcer 12. herpes labialis 13. hemorrhoids 14. fistula 15. hiatal hernia 16. intussusception 17. volvulus 18. cholelithiasis 19. ALT 20. lavage 21. bariatric surgery 22. antiemetic 23. FOBT 24. paracentesis 25. PTC a. tooth cavity b. gallstones c. yellow tint to the skin d. varicose veins in rectum e. test for microscopic blood in stools f. heartburn g. withdrawing fluid from abdominal cavity h. accumulation of fluid in peritoneal cavity i. washing out the stomach j. intestine twisted on itself k. dark, tarry stools l. diaphragmatocele m. X-ray to visualize bile ducts n. bright red blood in the stools o. treatment for morbid obesity p. a diagnostic blood test q. loss of weight and generalized wasting r. abnormal tube-like passageway s. canker sore t. small tumor on a stem or pedicle u. artificial covering for tooth v. treats nausea w. telescoping stretch of intestine x. fever blister y. vomiting 312 Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
25 Name Date Score Quiz 8A New Word Parts Quiz Directions: Define the combining form or suffix in the spaces provided. 1. bar/o 2. append/o 3. cholecyst/o 4. cec/o 5. dent/o 6. chol/e 7. hepat/o 8. lingu/o 9. gastr/o 10. proct/o 11. pharyng/o 12. cholangi/o 13. sialaden/o 14. or/o 15. odont/o _ 16. choledoch/o 17. gingiv/o _ 18. gloss/o 19. colon/o 20. enter/o 21. labi/o 22. tripsy 23. -pepsia 24. -prandial _ 25. -phagia 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 313
26
27 Name Date Score Quiz 8B Spelling Quiz Directions: Write each term as your instructor pronounces it Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 315
28
29 M08_C08.qxp 3/20/08 11:24 AM Page 317 Name Date Score Quiz 8C Labeling Diagram Directions: Label the organs of the digestive system. 1. _ 2. _ 5. _ 6. _ 7. _ 3. _ 8. _ 4. _ 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 317
30
31 Name Date Score Directions: Label the organs of the digestive system. Quiz 8D Labeling Diagram Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 319
32
33 Name Date Score Quiz 8E Word Building Quiz Directions: Build a single medical term for each phrase below. 1. pertaining to the anus 2. pertaining to the cheeks 3. pertaining to the gallbladder 4. pertaining to the colon 5. pertaining to teeth 6. pertaining to the duodenum 7. pertaining to the small intestine 8. pertaining to the esophagus _ 9. pertaining to the stomach 10. pertaining to the gums 11. pertaining to the liver 12. pertaining to the ileum 13. pertaining to the jejunum 14. pertaining to under the tongue 15. pertaining to the mouth 16. pertaining to the pancreas 17. pertaining to the throat 18. pertaining to the pylorus 19. pertaining to the rectum 20. abnormal appetite 21. excessive vomiting 22. slow digestion _ 23. unable to eat/swallow 24. after a meal 25. removal of the appendix 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 321
34
35 Name Date Score Quiz 8F Abbreviation Quiz Directions: Write the medical term for which each abbreviation stands. 1. ac _ 2. Ba _ 3. BS _ 4. CBD 5. ERCP 6. FOBT 7. GB 8. GERD 9. GI _ 10. HCl 11. IBD 12. IVC 13. NG 14. NPO 15. n&v 16. O&P 17. pc _ 18. pp _ 19. TPN 20. PUD 21. UGI 22. PO 23. AST 24. BE 25. HAV 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 323
36
37 Name Date Score Quiz 8G Chapter Review PART I: Multiple Choice Directions: Circle the correct answer. 1. What is the medical term for the return of fluids and solids from the stomach into the mouth? a. dyspepsia b. regurgitation c. dysphagia d. aphagia 2. A protrusion of the stomach through the diaphragm and into the thoracic cavity is a(n) a. inguinal hernia. b. hiatal hernia. c. abdominal hernia. d. disk hernia. 3. The organ that produces bile is the a. gallbladder. b. pancreas. c. liver. d. small intestine. 4. The pathological condition characterized by twisting of the intestine on itself is called a. polyp. b. intussusception. c. volvulus. d. Crohn s disease. 5. The term for chronic disease of the liver with gradual destruction of its cells is a. adhesion. b. cirrhosis. c. peptic ulcer. d. volvulus. 6. The term for a series of X-rays taken of the stomach and duodenum after barium has been swallowed is a. lower GI. b. upper GI. c. anastomosis. d. retrograde cholangiography. 7. What is the medical term for tooth decay? a. ascites b. fistula c. gingivitis d. caries 8. Which surgical term listed below means to create a passageway between two organs? a. gastrectomy b. anastomosis c. lithotripsy d. laparotomy 9. Which treatment listed below involves using a nasogastric tube to place a nutritional liquid into the stomach? a. lavage b. anastomosis c. gavage d. fistulectomy 10. Which of the following conditions is the presence of outpouches off the gut? a. diverticulosis b. polyposis c. diaphragmatocele d. ileus (Continued ) 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 325
38 PART II: Matching Directions: Match the term with its definition. 1. chyme 2. cuspid 3. constipation 4. jaundice 5. periodontics 6. cleft palate 7. Crohn s disease 8. bite-wing 9. extraction 10. proton pump inhibitor a. difficulty with defecation b. treats gum conditions c. an autoimmune condition d. an X-ray of the teeth e. liquefied food leaving the stomach f. to surgically pull teeth g. a symptom of liver disease h. treats peptic ulcers i. a biting tooth j. a congenital condition PART III: Abbreviations Directions: Write the full meaning of the following abbreviations. 1. PUD 2. IBS 3. NPO 4. n&v 5. EGD 326 Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
39 Chapter 8 Answer Keys Worksheet 8A Answer Key 1. anus 2. appendix 3. appendix 4. weight 5. cheek 6. cecum 7. gall, bile 8. bile duct 9. gallbladder 10. common bile duct 11. colon 12. colon 13. tooth 14. duodenum 15. small intestine 16. esophagus 17. stomach 18. gums 19. tongue 20. liver 21. ileum 22. jejunum 23. lip 24. abdomen 25. tongue 26. stone 27. tooth 28. mouth 29. palate 30. pancreas 31. throat, pharynx 32. anus and rectum 33. pylorus 34. rectum 35. salivary gland 36. sigmoid colon Suffixes 37. vomit 38. condition of stones 39. appetite 40. digestion 41. eat, swallow 42. pertaining to a meal 43. surgical crushing Worksheet 8B Answer Key 1. proct/o = anus and rectum; -ology = study of 2. gastr/o = stomach; esophag/o = esophagus; -eal = pertaining to 3. carcin/o = cancer; -oma = tumor 4. col/o = colon; -itis = inflammation 5. cholecyst/o = gallbladder; -itis = inflammation 6. chol/e = gall, bile; -lithiasis = condition of stones 7. cholecyst/o = gallbladder; -graphy = process of recording 8. intra- = within; ven/o = vein; -ous = pertaining to 9. trans- = across; hepat/o = liver; -ic = pertaining to 10. cholangi/o = bile duct; -graphy = process of recording 11. colon/o = colon; -scopy = process of viewing 12. cholangi/o = bile duct; pancreat/o = pancreas; -graphy = process of recording 13. esophag/o = esophagus; gastr/o = stomach duoden/o = duodenum; -scopy = process of viewing 14. gastr/o = stomach; -scopy = process of viewing 15. lapar/o = abdomen; -scopy = process of viewing 16. sigmoid/o = sigmoid colon; -scopy = process of viewing 17. choledoch/o = common bile duct; lith/o = stone; -tripsy = surgical crushing 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 8/DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 327
saliva, salivary glands
 Section IX Digestive System The digestive system refers to the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract. It consists of organs and glands that break down food products to be used by the body as a source
Section IX Digestive System The digestive system refers to the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract. It consists of organs and glands that break down food products to be used by the body as a source
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Combining Forms Append/o appendix Hepat/o liver Appendic/o appendix Lingu/o tongue Col/o colon Myc/o fungus Dent/o teeth Odont/o teeth Enter/o intestine Or/o mouth Esophag/o esophagus
The Digestive System Combining Forms Append/o appendix Hepat/o liver Appendic/o appendix Lingu/o tongue Col/o colon Myc/o fungus Dent/o teeth Odont/o teeth Enter/o intestine Or/o mouth Esophag/o esophagus
Digestive System. Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition)
 Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
The Digestive System. Chapter 25
 The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Digestive System Lecture Notes Read Ch 14; review questions start on page 477 S/A # 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 16, 17, 19, 20, 21, 22, 26, 35
 The PRINCIPLE structure of the digestive system is the Alimentary Canal (Gastrointestinal Tract) = hollow tube much like a hallway in a home. I. Functions of the Digestive System a. Ingestion: Putting
The PRINCIPLE structure of the digestive system is the Alimentary Canal (Gastrointestinal Tract) = hollow tube much like a hallway in a home. I. Functions of the Digestive System a. Ingestion: Putting
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Overview of Digestive System. Histological Organization. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
ESSENTIAL QUESTION. What are the structures of the digestive system? THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the structures of the digestive system? THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM DIGESTIVE SYSTEM, AKA. ALIMENTARY CANAL digestive tract or gastrointestinal tract (GI Tract). A 30 ft. tube from
ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the structures of the digestive system? THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM DIGESTIVE SYSTEM, AKA. ALIMENTARY CANAL digestive tract or gastrointestinal tract (GI Tract). A 30 ft. tube from
The Digestive System. Chapter
 The Digestive System Chapter 15.1 Functions: mechanical and chemical breakdown of food *absorption of nutrients Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs Wall of the Alimentary Canal 15.2 Characteristics
The Digestive System Chapter 15.1 Functions: mechanical and chemical breakdown of food *absorption of nutrients Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs Wall of the Alimentary Canal 15.2 Characteristics
3/16/2016. Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids
 Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids Food being broken down into small molecules Takes place in the alimentary canal Complete digestive system 4 layers of tissue (in book) Lumen 1) MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL--
Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids Food being broken down into small molecules Takes place in the alimentary canal Complete digestive system 4 layers of tissue (in book) Lumen 1) MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL--
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. - Mucosa
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. 3 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Culture Advantage. Anatomy and Medical Terminology for Interpreters
 Culture Advantage Anatomy and Medical Terminology for Interpreters Marlene V. Obermeyer, MA, RN marlene@culture-advantage.com absorption acute aerophagia allergy anastamosis Anal atresia or anorectal atresia
Culture Advantage Anatomy and Medical Terminology for Interpreters Marlene V. Obermeyer, MA, RN marlene@culture-advantage.com absorption acute aerophagia allergy anastamosis Anal atresia or anorectal atresia
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
The Language Of Medicine
 The Language Of Medicine 11 th edition Davi Ellen Chabner Copyright 2017, 2014, 2011, 2007 Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 1 Chapter 6 Additional Suffixes and Digestive System Terminology Copyright
The Language Of Medicine 11 th edition Davi Ellen Chabner Copyright 2017, 2014, 2011, 2007 Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 1 Chapter 6 Additional Suffixes and Digestive System Terminology Copyright
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
The Language Of Medicine
 The Language Of Medicine 10 th edition Davi-Ellen Chabner Copyright 2014, 2011, 2007 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 1 Chapter 5 Digestive System Copyright 2014, 2011, 2007 by Saunders, an imprint
The Language Of Medicine 10 th edition Davi-Ellen Chabner Copyright 2014, 2011, 2007 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 1 Chapter 5 Digestive System Copyright 2014, 2011, 2007 by Saunders, an imprint
Glencoe Health. Lesson 3 The Digestive System
 Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
The Digestive System. Parts and Functions
 The Digestive System Parts and Functions Mechanical Digestion A process of digestion in which food is cut, torn, mashed, and churned into smaller bits. This process starts in the mouth and ends in the
The Digestive System Parts and Functions Mechanical Digestion A process of digestion in which food is cut, torn, mashed, and churned into smaller bits. This process starts in the mouth and ends in the
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 1. The Teeth 5/18/2015
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
Learning Targets. The Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract. Also known as the alimentary canal. Hollow series of organs that food passes through
 Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Nutrition and the Digestive System
 C H A P T E R 16 Nutrition and the Digestive System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List and describe the five basic activities of the digestive process. 2. List the four
C H A P T E R 16 Nutrition and the Digestive System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List and describe the five basic activities of the digestive process. 2. List the four
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES. tube along with several
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
The Human Body: Digestive System
 Directions: Fill in the blanks. 1. Digestive System Is a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus Carries out digestion which is the process of breaking down food
Directions: Fill in the blanks. 1. Digestive System Is a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus Carries out digestion which is the process of breaking down food
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE Remember the structures of the digestive system 1
 BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs 6/1/2015. The Wall of the Digestive Tract
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Digestive System and Body Metabolism 14PART C Accessory Digestive Organs Teeth Salivary glands
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Digestive System and Body Metabolism 14PART C Accessory Digestive Organs Teeth Salivary glands
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
Chabner: The Language of Medicine, 11 th Edition
 Answers to Pronunciation of Terms 5-1 Chabner: The Language of Medicine, 11 th Edition Answers to Pronunciation of Terms Chapter 5: Digestive System Vocabulary and Terminology absorption achlorhydria amino
Answers to Pronunciation of Terms 5-1 Chabner: The Language of Medicine, 11 th Edition Answers to Pronunciation of Terms Chapter 5: Digestive System Vocabulary and Terminology absorption achlorhydria amino
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 The Human Digestive System. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-16. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 6-1. Define the human digestive
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 The Human Digestive System. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-16. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 6-1. Define the human digestive
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion. 7/16/2015 MDufilho 1
 Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
Lesson 1. Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
Chapter 26 The Digestive System
 Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
TEST 5. Module 9 & 10
 TEST 5 Module 9 & 10 Questions from the GVLS website 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels 4. Circulation 5. Blood Pressure 6. Respiratory system 7. Lungs 8. Oxygen 9. Carbon Dioxide 10. The heart is made
TEST 5 Module 9 & 10 Questions from the GVLS website 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels 4. Circulation 5. Blood Pressure 6. Respiratory system 7. Lungs 8. Oxygen 9. Carbon Dioxide 10. The heart is made
Digestive System Notes. Biology - Mrs. Kaye
 Digestive System Notes Biology - Mrs. Kaye Digestion There are two kinds of digestion: Mechanical digestion - the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces to increase surface area for more enzyme
Digestive System Notes Biology - Mrs. Kaye Digestion There are two kinds of digestion: Mechanical digestion - the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces to increase surface area for more enzyme
Digestive System. Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy
 Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 14 PART C The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
14 PART C The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
An overview of the digestive system. mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus
 An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
Purpose To reduce the size of large pieces of food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the blood stream and eventually into cells.
 Purpose To reduce the size of large pieces of food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the blood stream and eventually into cells. Cells are then able to maintain homeostasis 6 main components
Purpose To reduce the size of large pieces of food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the blood stream and eventually into cells. Cells are then able to maintain homeostasis 6 main components
Ingestion Digestion- Absorption- Elimination
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
Digestive System. In one end and out the other.
 Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
* Produces various chemicals to break. down the food. * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes
 * * Produces various chemicals to break down the food * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes * *Mouth *Pharynx *Oesophagus *Stomach *Small and large intestines * *Changes the physical
* * Produces various chemicals to break down the food * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes * *Mouth *Pharynx *Oesophagus *Stomach *Small and large intestines * *Changes the physical
Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes
 Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes In a nutshell... The body uses a variety of small molecules (amino acids, fatty acids, glucose) for its metabolic needs. Food is mechanically and chemically
Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes In a nutshell... The body uses a variety of small molecules (amino acids, fatty acids, glucose) for its metabolic needs. Food is mechanically and chemically
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen Surface Landmarks Xiphoid process T9/T10 Inferior costal margin L2/L3 Iliac Crest L4 level ASIS L5/S1 level Pubic symphysis level of greater trochanter
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen Surface Landmarks Xiphoid process T9/T10 Inferior costal margin L2/L3 Iliac Crest L4 level ASIS L5/S1 level Pubic symphysis level of greater trochanter
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
HEALTHY AND ACTIVE LIVING (FOOD/NUTRITION COMPONENT) Date: April 30 th, 2015 Course: PPL10
 HEALTHY AND ACTIVE LIVING (FOOD/NUTRITION COMPONENT) Date: April 30 th, 2015 Course: PPL10 The remaining semester The remaining semester June 25 th, Final Exam Day (Thursday) What we will cover Food/Nutrition:
HEALTHY AND ACTIVE LIVING (FOOD/NUTRITION COMPONENT) Date: April 30 th, 2015 Course: PPL10 The remaining semester The remaining semester June 25 th, Final Exam Day (Thursday) What we will cover Food/Nutrition:
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS. Mar 16 10:34 PM
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
1 ANIMALS Digestive System Oral Cavity and Esophagus.notebook January 06, 2016
 The Human Digestive System 1 The Human Digestive System 2 You are a tube inside a tube 3 The Digestive System The Four Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion the taking in or eating of food 2. Digestion
The Human Digestive System 1 The Human Digestive System 2 You are a tube inside a tube 3 The Digestive System The Four Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion the taking in or eating of food 2. Digestion
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
POGIL Activity on The Digestive System (Let s go Down the Hatch! )
 POGIL Activity on The Digestive System (Let s go Down the Hatch! ) Life is organized in the following levels: Chemical Level, Cellular Level, Tissue Level, Organ Level, Organ System Level, and finally,
POGIL Activity on The Digestive System (Let s go Down the Hatch! ) Life is organized in the following levels: Chemical Level, Cellular Level, Tissue Level, Organ Level, Organ System Level, and finally,
Digestive System Anatomy
 Digestive System Anatomy The Process of Digestion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j84pqg 8nf0M Parts of the Digestive System The digestive system begins at the mouth, where food enters the body. The mouth
Digestive System Anatomy The Process of Digestion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j84pqg 8nf0M Parts of the Digestive System The digestive system begins at the mouth, where food enters the body. The mouth
a. parotid b. sublingual c. submandibular
 Bozeman Science/ Nature The Digestive System Watch the videos, and answer the questions below. Please write your answers in complete sentences, and explain all concepts thoroughly. 1. What are the four
Bozeman Science/ Nature The Digestive System Watch the videos, and answer the questions below. Please write your answers in complete sentences, and explain all concepts thoroughly. 1. What are the four
Exercise. Digestive System. Digestive system function. 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc.
 Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that
 PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body
 Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
(A) Diarrhea. (B) Stomach cramps. (C) Dehydration due to excess fluid loss. (D) A, B, and C are correct. (E) Only answer B is correct.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
Chapter 9 Digestive System. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 9 Digestive System Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Points to ponder What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where
Chapter 9 Digestive System Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Points to ponder What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where
PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 26 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM D igestion is the process of breaking down complex nutrients into simpler units suitable for absorption. It involves two major processes: mechanical
Student Name CHAPTER 26 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM D igestion is the process of breaking down complex nutrients into simpler units suitable for absorption. It involves two major processes: mechanical
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010
 DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers
 Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Website: websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition
 Website: websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition 2 1 Lecture 3 1. Introduction 2. Digestive System 3. Nutrition Basics 3 Introduction Some Ecology 4 2 Mr. Sun 5 Nuclear Fusion 6 3
Website: websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition 2 1 Lecture 3 1. Introduction 2. Digestive System 3. Nutrition Basics 3 Introduction Some Ecology 4 2 Mr. Sun 5 Nuclear Fusion 6 3
Objective 4- Digestion
 Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Chapter 16. Lecture and Animation Outline
 Chapter 16 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Chapter 16 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION
 ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
Module 2 Heartburn Glossary
 Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Digestion, Absorption, and Transport
 Digestion Digestion, Absorption, and Transport Chapter 3 Breaking down foods into nutrients Prepare for absorption Challenges of digestion Accessing Nutrients digestion Getting nutrients through the body
Digestion Digestion, Absorption, and Transport Chapter 3 Breaking down foods into nutrients Prepare for absorption Challenges of digestion Accessing Nutrients digestion Getting nutrients through the body
Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition Lecture 3 1. Introduction 2. Digestive System 3. Nutrition Basics
 Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition 1 Lecture 3 1. Introduction 2. Digestive System 3. Nutrition Basics 2 1 Introduction Some Ecology 3 Mr. Sun 4 2 Nuclear Fusion 5 Light energy from Sun radiates across
Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition 1 Lecture 3 1. Introduction 2. Digestive System 3. Nutrition Basics 2 1 Introduction Some Ecology 3 Mr. Sun 4 2 Nuclear Fusion 5 Light energy from Sun radiates across
Digestive System. What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning?
 Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 15a Lab Activity
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 15a Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: The Digestive System Digestion is an important process that involves breaking down food and drink into small molecules that can
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 15a Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: The Digestive System Digestion is an important process that involves breaking down food and drink into small molecules that can
e. Undigested material is compacted and stored until the colon is full. When the colon is full, a signal to empty it is sent by sensors in the walls
 Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
10.2 The Human Digestive System (textbook p )
 10.2 The Human Digestive System (textbook p411 418) Learning Goal: Label and explain the anatomy of the Digestive System See text p411 Fig.10.6: Label "Organs of Digestive System": See text p411 Fig.10.6:
10.2 The Human Digestive System (textbook p411 418) Learning Goal: Label and explain the anatomy of the Digestive System See text p411 Fig.10.6: Label "Organs of Digestive System": See text p411 Fig.10.6:
Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1. BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
The Human Digestive Tract
 The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
Digestive System. Digestion Myths
 Digestive System Digestion Myths Myth # 1 Ulcers: Spicy food and stress cause stomach ulcers. Myth # 2 Heartburn: Smoking a cigarette helps relieve heartburn. Myth # 3 Celiac Disease: Celiac disease is
Digestive System Digestion Myths Myth # 1 Ulcers: Spicy food and stress cause stomach ulcers. Myth # 2 Heartburn: Smoking a cigarette helps relieve heartburn. Myth # 3 Celiac Disease: Celiac disease is
1 The Digestive System
 CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
Anatomy & Physiology Digestive System
 Anatomy & Physiology Digestive System I. Nutrition A. chemical substance that is needed by the body for normal growth, maintenance & repair. Two categories 1. needed in large amounts. Carbohydrates, Lipids
Anatomy & Physiology Digestive System I. Nutrition A. chemical substance that is needed by the body for normal growth, maintenance & repair. Two categories 1. needed in large amounts. Carbohydrates, Lipids
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 30 The Digestive System Lesson 2: Pathology of the Digestive System Lesson Objectives Upon completion
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 30 The Digestive System Lesson 2: Pathology of the Digestive System Lesson Objectives Upon completion
8 Digestive System. Anatomy and Physiology Overview
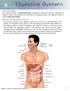 8 Digestive System Gastroenterology The medical practice of gastroenterology encompasses treatment of diseases affecting the digestive system. The physician who specializes in treating disorders of the
8 Digestive System Gastroenterology The medical practice of gastroenterology encompasses treatment of diseases affecting the digestive system. The physician who specializes in treating disorders of the
UNIT 5 MAINTENANCE SYSTEMS Digestive System Test Bank
 UNIT 5 MAINTENANCE SYSTEMS Digestive System Test Bank Objective 5.01 Describe the basic functions of the digestive system. 1. What is the main function of the digestive system? a. Hold and receive food
UNIT 5 MAINTENANCE SYSTEMS Digestive System Test Bank Objective 5.01 Describe the basic functions of the digestive system. 1. What is the main function of the digestive system? a. Hold and receive food
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM.
 1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
The Digestive System 1
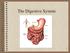 The Digestive System 1 Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases
The Digestive System 1 Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases
Bio 104 Digestive System
 13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
Digestion Introduction Lecture MMHS Science Chitraroff
 Digestion Introduction Lecture MMHS Science Chitraroff Digestion is the process that changes food into a form that is usable by your body. The Alimentary Canal The pathway of food from your mouth to your
Digestion Introduction Lecture MMHS Science Chitraroff Digestion is the process that changes food into a form that is usable by your body. The Alimentary Canal The pathway of food from your mouth to your
2.08 Understand the functions and disorders of the digestive system Essential questions
 2.08 Understand the functions and disorders of the digestive system Essential questions What are the functions of the digestive system? How do the functions of chemical and physical digestion interrelate?
2.08 Understand the functions and disorders of the digestive system Essential questions What are the functions of the digestive system? How do the functions of chemical and physical digestion interrelate?
The Digestive System. 1. The Mouth. 2. Epiglottis and Esophagus. 3. The Stomach. 4. The Small Intestine
 The Digestive System Name: The digestive system has 3 main functions. First, it breaks down food into smaller nutrients that the body can use. Secondly, these nutrients are absorbed into the blood. Thirdly,
The Digestive System Name: The digestive system has 3 main functions. First, it breaks down food into smaller nutrients that the body can use. Secondly, these nutrients are absorbed into the blood. Thirdly,
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION
 Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
General functions of digestive system. Ch. 15 The Digestive System. General histology of the wall of the digestive tract. Overview of digestive organs
 Overall idea: obtain nutrients from food (for energy and raw materials for synthesis), and defecate the leftover waste 2 types of organs involved: 1. Parts of the digestive tract (= a long muscular tube
Overall idea: obtain nutrients from food (for energy and raw materials for synthesis), and defecate the leftover waste 2 types of organs involved: 1. Parts of the digestive tract (= a long muscular tube
