Basu Dev Regmi School of Earth and Environment
|
|
|
- Marian Fleming
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Basu Dev Regmi School of Earth and Environment Basu was born and raised in the rural mountains of Nepal. He did undergraduate (B Sc. Ag) degree from Tribhuvan University, and M. Sc. (Agri. Systems) at Asian Institute of Technology, Bangkok, Thailand. Basu worked with agricultural research and development in Thailand and Nepal. He worked with the bilateral project funded by Swiss government and implemented by the Nepalese government for 5 and half years as theme leader of soil fertility and plant nutrition discipline before joining UWA. Having motivated to work in rural communities, he has seen and experienced the different dimensions of problems in these communities. His PhD research aims at investigating the dynamics of zinc (Zn) in biological and conventional farming systems, in WA. How best we can load the Zn into edible parts of the crops is the main interest of work.
2 Dynamics of zinc accumulation in wheat grains grown in the soils of conventional and biological farming systems Basu Dev Regmi School of Earth and Environment Soil Science and Plant Nutrition Supervisors: W/Prof Zed Rengel and Dr Hossein Khabaz-Saberi
3 Content 1. Background Role of Zn in plant Zinc in soil and its trend Global scenario of Zn (impact on human..) and role of Australia Zinc with respect to farming practice 2. Method and Materials 3. Results 4. Conclusion
4 Role of Zn in plant Stimulate germination in low Zn soils Involves many cellular process (enzyme activation...) production of auxin, an essential growth hormone regulates starch formation and proper root development biosynthesis of chlorophyll and carbohydrates enable plants to withstand lower air temperatures helps in the biosynthesis of cytochrome; a pigment, and maintains plasma membrane integrity, and synthesis of leaf cuticle... Cont Background
5 Effects of zinc deficiency on metabolic processes associated with growth Source: Mac Donald, Cont Background
6 Zn in soils Among micronutrients in soil, low Zn availability is most widespread Cereals growing areas are particularly affected by low Zn (Cakmak et al, 1998, Singh et al 2005) Among cereals, wheat is the most sensitive to Zn deficiency (Cakmak et al, 1998, Kabata-Pendias, 2001, Alvarez and Gonzalez, 2006) Post green revolution: increased crop production with increased use of mineral fertilizers Increased use of mineral fertilizers led to higher production hence depleted d inherent soil fertility (nutrient t mining) i Mostly macro-elements are taken into consideration (N P K) Imbalance among plant nutrients.. Cont Background
7 5 th out of 10 Risk Factors in Developing eloping Countries to Cause of Disease Burden (WHO, 2002) About 3 billion people e are affected by low Zn (Stein et al 2007) Over 1 million child death due to Zn with Vitamin A (The Lancet Maternal and Child Undernutrition Series January 2008) Zinc affects a range of functions: Immunity Growth Brain development Reproduction Sexual Formation
8 Current concentration of Zn in cereal grains mg/kg Phytate Phenolic compounds.. Required concentration of Zn in cereal grains mg/kg for human consumption Increasing micronutrient density in edible parts of plant highly desirable Zn ++ Cont Background
9 Zn Deficiency: Global Nutritional Problem in Soils Widespread Zn Deficiency Medium Zn Deficiency Alloway, IZA Publications, Brussels Cont Background
10 Countries at Risk of Zinc Deficiency in Children Black et al The Lancet Maternal and Child Undernutrition Series
11 Market destination of Australian bulk wheat exports (- 13 million t) Cont Background
12 Increasing on the awareness on soil health, environment,.. Organic farming and product are preferred Biological farming systems are not organic farming systems Biological farming systems (BF) is combination of orgainc and conventional, which aims to achieve optimum yield by balanced use of organic and mineral fertilizers. Conventional farming system (CF) aims to achieve highest possible yield through the use of mineral fertilizers and other external inputs. How farming practices impact the nutritional quality of grains, in particular grain Zn density? Cont Background
13 Aims Characterize the distribution of fzn fractions of soils (two farming systems) Characterize the concentration and content of Zn in shoot and seed of wheat grown in two soils
14 2. Method and Materials Identification of appropriate sites: - with history of conventional or biological farming - the same soil type, adjacent paddocks We identified Dalwallinu as an appropriate site for soil collection : Biological paddock: " S, " E Conventional paddock: " S, " E
15 History of biologically and conventionally managed soils in Dalwallinu Farming Crop rotation systems Biological Clover Brown Whe Wheat Green Wheat Wheat Green wheat Manure at Manure Manure Conventional Wheat Wheat Whe Wheat Wheat Wheat Oats Wheat Wheat at Source: Rob Harris, farmer, Dalwallinu Cont Method and Materials
16 Cont Method and Materials Soil Properties ph H 2 O (CaCl 2 ) 4.9 (5.7) Site OM (%) 0.9 NO 3 N (mg/kg) 9.5 NH 4 -N (mg/kg) 2 Phosphorous (mg/g) (5.9) (5.44) Soil Properties 2008 ph H 2 O (CaCl 2 ) 5.1 (5.4) OM (%) Dalwallinu (Lat ' 166 " S and Long ' 377 " E) Potassium (mg/g) 42 DTPA Zn (mg/kg) 0.36 Total Zn (mg/kg) 10 NO 3 N (mg/kg) 13 NH 4 -N (mg/kg) 2 Phosphorous (mg/g) 22 Potassium (mg/g) 60 DTPA Zn (mg/kg) 0.62 Total Zn (mg/kg) 12.5 Merredin (Lat ' 530 " S and Long ' 879 " E), Biological paddock
17 1. Characterization of soil Zn: Sequential fractionation as outlined by Iwasaki and Yoshikawa (1990, 1993). Total Zinc by aqua-regia DTPA - extractable Zn Cont Method and Materials
18 Sequential fractionations methods Fraction Chemicals/methods 1 Water soluble (WS) 2 Exchangeable (EX) Specifically adsorbed (SA) 1.5gm soils in 25mL MQ water shaken for 16 hours Wash with 10mL of MQ water and 25 ml of 0.5 M Calcium Nitrate Ca(NO 3 ) 2. 4H 2 O for 16 hours Wash with 10mL of MQ water and 25 ml of 0.05M Lead Nitrate Pb(NO 3 ) M Ammonium Acetate (CH 3 COONH 4 ) for 2 hours Wash with 10mL of MQ water and Acidsoluble (AS) 25 ml of 25mL Acetic Acid CH 3 COOH/LMQ water for 2 Manganese (Mn)-oxide-occluded (Mn-OX) 6 Organic matter occluded (OM) 7 amorphous iron (Fe)-oxide-bound (AFe-OX) crystalline Fe-oxide-bound (CFe-OX) hours Wash with 10mL of MQ water and 50 ml of 0.1 M Hydroxylamine Hydrochloride NH 2 OH.HCl for 30 min Wash with 10mL of MQ water and 50 ml of 0.1 M Potassium pyrophosphate K 4 P 2 O 7 for 2 hours Wash with 10mL of MQ water and 50 ml of 0.1M Oxalic acid (COOH) 2. 2H 2 O and 0.157M Ammonium Oxalate (NH 4 ) 2 C 2 O 4 for 4 hours Wash with 10mL of MQ water and 50 ml of ( 0.1 M Oxalic acid (COOH) 2. 2H 2 O, 0.175M 8 Ammonium Oxalate (NH 4 ) 2 C 2 O 4 01M 0.1 Ascorbic acid C 6 H 8 O 6 for 30 min boiling bath 9 Residual (RES) 10 Total (TZn) Total Zinc Sum of all fractions (as Alvaraz, et.al.,2006) Aqua-regia
19 2. Glasshouse experiment on Zn loading into wheat grains: Soils : Biological and Conventional Farming Systems Genotypes: Excalibur (Zn-efficient), and Kukri (Zn-inefficient) Zn fertilisation: 0, 0.1, and 1.0 mg/kg Zn source: ZnEDTA and ZnSO 4 Cont Method and Materials
20 Results Zinc in soils Fertilizers, OM decay... Total Residual Different fractions
21 Distribution ib ti of different fractions of Zn in soils Important to understand the Zn fractionation in soil for resources application (fertilizers) Previous studies: soil properties influence the transport of trace metals the soil-crop continuum. I looked at the fractions as influenced by farming practices
22 0.6 Distribution of differenct Zn fractions in soils of two farming systems, Dalwallinu CF BF 0.5 mg/kg g Zinc in WS EX SA AS Mn-OX OM AFe-OX CFe-OX Different Zn Fractions
23 Residual and total Zn in mg/kg Zinc Res -Zn Total - Zn
24 Distribution of zinc fractions (%) in soils from the two different farming systems, Dalwallinu ---- Dalwallinu 100 Zinc fractions Conventional Biological i l Farming 90 CF BF Farming systems systems 80 cent Per WS EX SA AS Mn OX OM AFe OX CFe OX RES Total sum of total fraction Residual 100 Total 100
25 Correlation coefficient among different Zn fractions in soils WS Ex SA AS MnOx OM O AmFeOx Cr FeOx Res TZn WS Ex SA AS MnOx OM O AMFe ox CrFeO x Res TZn numbers with red marks are significant 0.05 probability levels
26 Zinc in vegetative tissues and grains
27 There is difference in growth No visible Zn deficiency symptoms appeared (4 th week) 0 mg/kg g.1 mg/kg 1 mg/kg ph 4.9 DTPA Zn 0.36 mg/kg Wheat (Kukri) grown in conventional soils, Dalwallinu
28 Zn concentration in wheat shoot grown in different soils for 7 weeks Zn concentr ration (mg/kg) 80 Zn 0 mg/kg soil Zn 0.1 mg/kg soil Zn 1mg/kg soil a 70 Zn 0 mg/kg soil Zn 0.1 mg/kg soil Zn 1mg/kg soil a b 40 bc b bc a a b b d d Zn SO4 ZnEDTA ZnSO4 ZnEDTA Zn concentr ration (mg/kg) 60 a 50 a a 40 b b 30 c c c 20 d d d d 10 0 Zn SO4 ZnEDTA ZnSO4 ZnEDTA Excalibur Kukri Excalibur Kukri Biological Farming Systems (Dalwillinu) Conventional Farming Systems (Dalwallinu ) Mean values with the same letters are not significantly different by Tukey s HSDα α = 0.05 Soils : Significant (Tukey s HSD α = 0.01 ) Zn level : Significant (Tukey s HSD α = 0.01 ) Zn Source : Significant (Tukey s HSD α = 0.05 ) Genotypes : Non-Significant
29 Concentration (mg/kg DW) of seed Zn Farming Wheat ZnSO 4 4( (mg/kg g soil) ZnEDTA(mg/kg g soil) Systems Genotypes Biological Excalibur 26c 26c 36a 26c 29b 36a Kukri 22cd 23d 32b 22cd 26c 31b Conventional Excalibur 21d 23cd 25c 22cd 26c 42a Kukri 21d 18d 20d 21cd 22cd 27b Mean values with the same letter are not significantly different by Tukey s HSD α = 0.05 Soils : Significant (Tukey s HSD α = 0.05 ) Zn level : Significant (Tukey s HSD α = 0.01 ) Zn Source : Significant (Tukey s HSD α = 0.05 ) Genotypes : Significant (Tukey s HSDα α = 0.05 )
30 Seed Zn content ent (µg/seed) Zn Conte Density of Zn is higher: Zn fertilizer level and sources (ZnEDTA doing better) Excalibur (Zn efficient genotypes) Biologically managed soils
31 Internal mobilization/translocation is better in Zn efficient Genotypes?? mg/kg mg/kg Excalibur (Zn-efficient) Kukri (Zn-inefficient) Critical Zn concentration in youngest leaf <15 mg/kg
32 Zinc fractions and their relative availability to plant SN Fractions Availabilit Sources ph, Clay content OM content Soil types.. h ( ) d b d ( ) Capacity of plant to solubalize inactive forms of Zn 1 Water soluble (WS) 5: Readily Davis and Leckie 2 Exchangeable (EX) 5: Readily 3 Specifically adsorbed (SA) 3: Available 4 Acid soluble (AS) 3: Available 5 Manganese (Mn)-oxide-occluded (Mn-OX) 2:Limited 6 organic matter occluded (OM) 3: Available 7 amorphous iron (Fe)-oxide-bound (AFe-OX) 0-2 limited 8 crystalline Fe-oxide-bound (CFe-OX) 0-2 limited 9 Residual (RES) 0-1 limited 10 Total 1 0 as least to 5 as very high y Nalovic 1978, Lindsay 1979 Liang et al 1990, Sharad et al 2001, Alvaraz, et.al.,2006 Adhikari et al 2007, Rico, et al 2008
33 Correlation coefficient among shoot and seed Zn concentration, and different Zn fractions in soils SN Fractions Shoot Zn Seed Zn 1 Water soluble (WS) 0.66* 0.71* 2 Exchangeable (EX) 0.55* 0.88** 3 Specifically adsorbed (SA) Acid soluble (AS) * 5 Manganese (Mn)-oxide-occluded (Mn-OX) * 6 organic matter occluded (OM) 0.75** 0.54* 7 amorphous iron (Fe)-oxide-bound (AFe OX) 8 crystalline Fe-oxide-bound (CFe-OX) Residual (RES) Total (TZn) 0.84** 0.37 * and ** are significant at 0.05 and 0.01 probability levels, respectively Harmsen 1977, Sharad et al 2001, Adhikari et al, 2007
34 Conclusions: Biologically managed soil has higher proportion of available and total Zn content than conventionally managed soils More inactive forms in conventional than biological soil (residual pool=85% vs 80%) Important fractions for crop nutrition i.e. water soluble, exchangeable, acid soluble and organically-occluded fractions are higher in biological than conventional soil Excalibur (Zn-efficient genotype) loaded significantly more Zn (31-85 mg/kg DW) into grains than Zn-inefficient Kukri (21-65 mg/kg DW) (translocation of shoot Zn into seed ) -- breeding ZnEDTA fertiliser was more effective than ZnSO 4, but relatively high cost limits the practical use of ZnEDTA Growing/promoting grain legumes or crops that can solubalize the inactive forms of Zn to plant (Biological farming approach to be promoted)
35 Acknowledgements UWA/IPRS scholarships ARC linkage project (with DAFWA and ERA sustainable) W/Prof. Z Rengel Hossein Saberi Paul Damon, Mike Smirk.. This is the way to my home
36 Conclusions: Biologically managed soil has higher proportion of available and total Zn content than conventionally managed soils More inactive forms in conventional than biological soil (residual pool=85% vs 80%) Important fractions for crop nutrition i.e. water soluble, exchangeable, acid soluble and organically-occluded fractions are higher in biological than conventional soil Excalibur (Zn-efficient genotype) loaded significantly more Zn (31-85 mg/kg DW) into grains than Zn-inefficient Kukri (21-65 mg/kg DW) (translocation of shoot Zn into seed ) -- breeding ZnEDTA fertiliser was more effective than ZnSO 4, but relatively high cost limits the practical use of ZnEDTA Growing/promoting grain legumes or crops that can solubalize the inactive forms of Zn to plant (Biological farming approach to be promoted)
Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils
 The Supply and Availability of Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Factors Controlling the Growth of Higher Plants 1. Light 2. Mechanical Support. Heat. Air 5. Water 6. Nutrients
The Supply and Availability of Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Factors Controlling the Growth of Higher Plants 1. Light 2. Mechanical Support. Heat. Air 5. Water 6. Nutrients
Basu Dev Regmi B.Sc. in Agriculture: 1998 (Tribhuvan University, Nepal) M.Sc. in Agri. Systems: 2001 (Asian Institute of Technology, Thailand)
 Dynamics of zinc accumulation in wheat grains grown in biological and conventional farming systems by Basu Dev Regmi B.Sc. in Agriculture: 1998 (Tribhuvan University, Nepal) M.Sc. in Agri. Systems: 2001
Dynamics of zinc accumulation in wheat grains grown in biological and conventional farming systems by Basu Dev Regmi B.Sc. in Agriculture: 1998 (Tribhuvan University, Nepal) M.Sc. in Agri. Systems: 2001
How to Develop a Balanced Program for Pecan and Chili. Robert R Smith
 Essential Plant Nutrients How to Develop a Balanced Program for Pecan and Chili Robert R Smith Nutrition Management Involves Knowledge of: Site/Soil characteristics and chemistry Plant requirements Cropping
Essential Plant Nutrients How to Develop a Balanced Program for Pecan and Chili Robert R Smith Nutrition Management Involves Knowledge of: Site/Soil characteristics and chemistry Plant requirements Cropping
Unit B: Seed Germination, Growth, and Development. Lesson 4: Determining Nutrient Functions and Utilization
 Unit B: Seed Germination, Growth, and Development Lesson 4: Determining Nutrient Functions and Utilization 1 Terms Denitrification Leach Macronutrient Micronutrient Nitrification Nitrogen cycle Nitrogen
Unit B: Seed Germination, Growth, and Development Lesson 4: Determining Nutrient Functions and Utilization 1 Terms Denitrification Leach Macronutrient Micronutrient Nitrification Nitrogen cycle Nitrogen
Terry Richmond s Fertilizer Package mentioned in the panel discussion March 14, 2013.
 Terry Richmond s Fertilizer Package mentioned in the panel discussion March 14, 2013. Roles of the 16 essential nutrients in plant development Sixteen plant food nutrients are essential for proper crop
Terry Richmond s Fertilizer Package mentioned in the panel discussion March 14, 2013. Roles of the 16 essential nutrients in plant development Sixteen plant food nutrients are essential for proper crop
Animal, Plant & Soil Science. D3-7 Characteristics and Sources of Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients
 Animal, Plant & Soil Science D3-7 Characteristics and Sources of Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients Interest Approach Obtain samples of minerals that serve as sources of calcium, magnesium, and sulfur
Animal, Plant & Soil Science D3-7 Characteristics and Sources of Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients Interest Approach Obtain samples of minerals that serve as sources of calcium, magnesium, and sulfur
Plant Food. Nitrogen (N)
 Plant Food Nitrogen (N) Functions: Promote plant growth Increase protein content of crops Improves quality of crop Makes plant more efficient with water Helps for stay green and dry down Plants take up
Plant Food Nitrogen (N) Functions: Promote plant growth Increase protein content of crops Improves quality of crop Makes plant more efficient with water Helps for stay green and dry down Plants take up
Total zinc was determined by digesting the soil ZnSO 4
 ADVANCE RESEARCH JOURNAL OF CROP IMPROVEMENT Volume 2 Issue 2 (December, 2011) Page : 203-207 Received : September, 2011; Revised : October, 2011; Accepted : November, 2011 Research Paper See end of the
ADVANCE RESEARCH JOURNAL OF CROP IMPROVEMENT Volume 2 Issue 2 (December, 2011) Page : 203-207 Received : September, 2011; Revised : October, 2011; Accepted : November, 2011 Research Paper See end of the
Chapter 1: Overview of soil fertility, plant nutrition, and nutrient management
 Chapter 1: Overview of soil fertility, plant nutrition, and nutrient management Agustin Pagani, John E. Sawyer, and Antonio P. Mallarino / Department of Agronomy, Iowa State University Developed in cooperation
Chapter 1: Overview of soil fertility, plant nutrition, and nutrient management Agustin Pagani, John E. Sawyer, and Antonio P. Mallarino / Department of Agronomy, Iowa State University Developed in cooperation
FROM SOIL ELEMENTS TO FOOD NUTRIENTS: Joyce Kinabo Dept. of Food Science and Technology, Sokoine University, Tanzania
 FROM SOIL ELEMENTS TO FOOD NUTRIENTS: Joyce Kinabo Dept. of Food Science and Technology, Sokoine University, Tanzania All forms of life are directly dependent on plants for food Plant foods contain almost
FROM SOIL ELEMENTS TO FOOD NUTRIENTS: Joyce Kinabo Dept. of Food Science and Technology, Sokoine University, Tanzania All forms of life are directly dependent on plants for food Plant foods contain almost
Use of Soil and Tissue Testing for Sustainable Crop Nutrient Programs
 Use of Soil and Tissue Testing for Sustainable Crop Nutrient Programs Kelly T. Morgan Soil and Water Science Department Southwest Florida Research and Education Center Immokalee 239 658 3400 conserv@ufl.edu
Use of Soil and Tissue Testing for Sustainable Crop Nutrient Programs Kelly T. Morgan Soil and Water Science Department Southwest Florida Research and Education Center Immokalee 239 658 3400 conserv@ufl.edu
Understanding your results Acidity... 3 Aluminium... 3 Base saturation... 3 Boron... 4 Bulk density... 4 Calcium... 4 Cations...
 Understanding your results Acidity... 3 Aluminium.... 3 Base saturation... 3 Boron... 4 Bulk density... 4 Calcium... 4 Cations... 4 CEC - Cation Exchange Capacity... 4 Copper... 5 Conductivity... 6 Deficiencies...
Understanding your results Acidity... 3 Aluminium.... 3 Base saturation... 3 Boron... 4 Bulk density... 4 Calcium... 4 Cations... 4 CEC - Cation Exchange Capacity... 4 Copper... 5 Conductivity... 6 Deficiencies...
Essential Soil Nutrients for Plant Growth and Development
 Essential Soil Nutrients for Plant Growth and Development Essential nutrients required by plants Role of nutrients within the plant Symptoms of deficiencies/toxicities 2 The basic soil components are:
Essential Soil Nutrients for Plant Growth and Development Essential nutrients required by plants Role of nutrients within the plant Symptoms of deficiencies/toxicities 2 The basic soil components are:
Interpreting Soils Report. Beyond N P K
 Interpreting Soils Report Beyond N P K What we will cover We will not discuss Macro Nutrients Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium. We will touch on Secondary Nutrients Magnesium, Calcium and Sulfur. We
Interpreting Soils Report Beyond N P K What we will cover We will not discuss Macro Nutrients Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium. We will touch on Secondary Nutrients Magnesium, Calcium and Sulfur. We
BOTANY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 9: PLANT NUTRITION. MACRONUTRIENTS Found in air and water carbon C oxygen hydrogen
 BOTANY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 9: PLANT NUTRITION Segment One Nutrient Listing Plants need 17 elements for normal growth. Carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen are found in air and water. Nitrogen, phosphorus,
BOTANY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 9: PLANT NUTRITION Segment One Nutrient Listing Plants need 17 elements for normal growth. Carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen are found in air and water. Nitrogen, phosphorus,
The effect of nano-micronutrients seed priming on germinability of Kabuli chickpea
 Current Opinion in Agriculture Curr. Opin. Agric. 2016 5(1), 24 30. The effect of nano-micronutrients seed priming on germinability of Kabuli chickpea Zahra Sayadiazar 1, Maryam Mohammadzadeh 1,Robab Morsali
Current Opinion in Agriculture Curr. Opin. Agric. 2016 5(1), 24 30. The effect of nano-micronutrients seed priming on germinability of Kabuli chickpea Zahra Sayadiazar 1, Maryam Mohammadzadeh 1,Robab Morsali
Sulphur Fertilizer Effect on Crop Development & Quality
 Sulphur Fertilizer Effect on Crop Development & Quality Sulphur Play a key role in: Chlorophyll (Photosynthesis) a key ingredient in the formation and sulphur deficient plants can be 40% lower in chlorophyll.
Sulphur Fertilizer Effect on Crop Development & Quality Sulphur Play a key role in: Chlorophyll (Photosynthesis) a key ingredient in the formation and sulphur deficient plants can be 40% lower in chlorophyll.
Markus Braaten. Elston D. Solberg. Director of Agri-Knowledge Agri-Trend. US Director of Agri-Knowledge Agri-Trend USA
 Water Drives Everything!! So Make Every Drop Count Elston D. Solberg Director of Agri-Knowledge Agri-Trend Markus Braaten US Director of Agri-Knowledge Agri-Trend USA Food, Fibre and Fuel Uptake (lbs/a)
Water Drives Everything!! So Make Every Drop Count Elston D. Solberg Director of Agri-Knowledge Agri-Trend Markus Braaten US Director of Agri-Knowledge Agri-Trend USA Food, Fibre and Fuel Uptake (lbs/a)
Greenhouse Horticulture
 Managing Nutrients in Greenhouse Horticulture Original content by Domenic Cavallaro Stoller Australia Pty Ltd Plant HORMONE PRODUCTION follows approx. cycles with changing NUTRIENT requirements Source:
Managing Nutrients in Greenhouse Horticulture Original content by Domenic Cavallaro Stoller Australia Pty Ltd Plant HORMONE PRODUCTION follows approx. cycles with changing NUTRIENT requirements Source:
The Effect of Boron (B) Application on the Growth and Nutrient Contents of Maize in Zinc (Zn) Deficient Soil
 387 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 12 (2006), 387-392 National Centre for Agrarian Sciences The Effect of Boron (B) Application on the Growth and Nutrient Contents of Maize in Zinc (Zn) Deficient
387 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 12 (2006), 387-392 National Centre for Agrarian Sciences The Effect of Boron (B) Application on the Growth and Nutrient Contents of Maize in Zinc (Zn) Deficient
IRON. AGRITOPIC August INTRODUCTION 2. IRON IN THE SOIL
 AGRITOPIC August 2015 IRON 1. INTRODUCTION Of all the elements plants derive from the soil, iron (Fe) is the most abundant. Yet, as far as plant nutrition is concerned, it is classified as a micronutrient,
AGRITOPIC August 2015 IRON 1. INTRODUCTION Of all the elements plants derive from the soil, iron (Fe) is the most abundant. Yet, as far as plant nutrition is concerned, it is classified as a micronutrient,
WHAT ARE FERTILIZERS
 FERTILIZER INDUSTRY WHAT ARE FERTILIZERS FERTILIZERS ARE COMPOUNDS GIVEN TO PLANTS WITH THE INTENTION OF PROMOTING GROWTH; THEY ARE USUALLY APPLIED EITHER VIA THE SOIL, FOR UPTAKE BY PLANT ROOTS, OR BY
FERTILIZER INDUSTRY WHAT ARE FERTILIZERS FERTILIZERS ARE COMPOUNDS GIVEN TO PLANTS WITH THE INTENTION OF PROMOTING GROWTH; THEY ARE USUALLY APPLIED EITHER VIA THE SOIL, FOR UPTAKE BY PLANT ROOTS, OR BY
Nitrophoska. Cereals, fodder beet, horticulture, maize and vegetables. Precise nutrition for superior plant performance
 Nitrophoska Cereals, fodder beet, horticulture, maize and vegetables Precise nutrition for superior plant performance Nitrophoska - The same composition of high-grade plant available nutrients in every
Nitrophoska Cereals, fodder beet, horticulture, maize and vegetables Precise nutrition for superior plant performance Nitrophoska - The same composition of high-grade plant available nutrients in every
Teff Compendium Nutrient deficiency symptoms SINCE
 Teff Compendium Nutrient deficiency symptoms SINCE Experimental design The experiment was conducted in a green house in 3 liter pots, filled with perlite. Each nutrient was tested in three levels: zero,
Teff Compendium Nutrient deficiency symptoms SINCE Experimental design The experiment was conducted in a green house in 3 liter pots, filled with perlite. Each nutrient was tested in three levels: zero,
Potassium and Phosphorus as Plant Nutrients. Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients. Potassium is required in large amounts by many crops
 Potassium and Phosphorus as Plant Nutrients Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients Potassium is required in large amounts by many crops Yield K 2 O taken up Crop level/ac in total crop, lb Alfalfa 8 tons
Potassium and Phosphorus as Plant Nutrients Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients Potassium is required in large amounts by many crops Yield K 2 O taken up Crop level/ac in total crop, lb Alfalfa 8 tons
Long term effect of cropping systems on the chemical fractions of zinc and copper in alluvial soils of north-west India
 An Asian Journal of Soil Science Volume 7 Issue June, 202 Research Article Long term effect of cropping systems on the chemical fractions of zinc and copper in alluvial soils of north-west India MEMBERS
An Asian Journal of Soil Science Volume 7 Issue June, 202 Research Article Long term effect of cropping systems on the chemical fractions of zinc and copper in alluvial soils of north-west India MEMBERS
There are six general classes of nutrients needed in the horse s diet: water carbohydrates fats protein minerals vitamins.
 HORSE NUTRITION Nutrients A nutrient is defined as any feed constituent that is necessary to support life. The following is a list of functions that nutrients perform in the horse's body: source of energy
HORSE NUTRITION Nutrients A nutrient is defined as any feed constituent that is necessary to support life. The following is a list of functions that nutrients perform in the horse's body: source of energy
Determining Nutrient Functions and Utilization
 Lesson C3 6 Determining Nutrient Functions and Utilization Unit C. Plant and Soil Science Problem Area 3. Seed Germination, Growth, and Development Lesson 6. Determining Nutrient Functions and Utilization
Lesson C3 6 Determining Nutrient Functions and Utilization Unit C. Plant and Soil Science Problem Area 3. Seed Germination, Growth, and Development Lesson 6. Determining Nutrient Functions and Utilization
Understanding a Soil Report
 Understanding a Soil Report AGRONOMY SOIL ANALYSIS 1. Soil ph Soil ph is a measure of the acidity in the soil. An acidic soil has a greater amount of hydrogen (H+) ions and a ph below 7.0. Values above
Understanding a Soil Report AGRONOMY SOIL ANALYSIS 1. Soil ph Soil ph is a measure of the acidity in the soil. An acidic soil has a greater amount of hydrogen (H+) ions and a ph below 7.0. Values above
REMEMBER as we go through this exercise: Science is the art of making simple things complicated!
 REMEMBER as we go through this exercise: Science is the art of making simple things complicated! Fertilization of Hops Ron Godin, Ph.D., Colorado State University Extension Fertilization of Hops - Care
REMEMBER as we go through this exercise: Science is the art of making simple things complicated! Fertilization of Hops Ron Godin, Ph.D., Colorado State University Extension Fertilization of Hops - Care
The effect of potassium nitrate on the uptake and translocation of foliar-applied nutrients in plants
 The effect of potassium nitrate on the uptake and translocation of foliar-applied nutrients in plants Harmen Tjalling HOLWERDA Agronomy Committee Potassium Nitrate Association (PNA) 1 Contents Trials about
The effect of potassium nitrate on the uptake and translocation of foliar-applied nutrients in plants Harmen Tjalling HOLWERDA Agronomy Committee Potassium Nitrate Association (PNA) 1 Contents Trials about
Assessment of Secondary and Micro Nutrient Status under Long-Term Fertilizer Experiment on Vertisol
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Joga Rao et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (4): 328-339 (2018) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.3068 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
Available online at www.ijpab.com Joga Rao et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (4): 328-339 (2018) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.3068 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
DOMOGRAN 45 ACTIVATING YOUR NUTRIENT POTENTIAL THE NITROGEN-SULFUR FERTILIZER FROM LEUNA
 DOMOGRAN 45 ACTIVATING YOUR NUTRIENT POTENTIAL THE NITROGEN-SULFUR FERTILIZER FROM LEUNA www.domogran.de DOMOGRAN 45 nitrogen and sulfur fertilizer for positive nutrient dynamics Because of its attraction
DOMOGRAN 45 ACTIVATING YOUR NUTRIENT POTENTIAL THE NITROGEN-SULFUR FERTILIZER FROM LEUNA www.domogran.de DOMOGRAN 45 nitrogen and sulfur fertilizer for positive nutrient dynamics Because of its attraction
Trace Yet Substantial
 Trace Yet Substantial ESSENTIAL MICRONUTRIENTS OF PECAN Joshua Sherman University of Arizona College of Agriculture and Life Sciences Cooperative Extension Commercial Horticulture, Area Assistant Agent
Trace Yet Substantial ESSENTIAL MICRONUTRIENTS OF PECAN Joshua Sherman University of Arizona College of Agriculture and Life Sciences Cooperative Extension Commercial Horticulture, Area Assistant Agent
Zinc in Fertilizers. Essential for Crops... Essential for Life!
 Zinc in Fertilizers Essential for Crops... Essential for Life! Introduction Zinc deficiency, both in humans and in plants, has been known as a critical issue by nutritionists, medical scientists and agronomists
Zinc in Fertilizers Essential for Crops... Essential for Life! Introduction Zinc deficiency, both in humans and in plants, has been known as a critical issue by nutritionists, medical scientists and agronomists
Soil Program Recommendation
 Soil Program Recommendation Grower: G.C. Wynne Consultant: Bill Munton Doyle St Quirindi NSW 2343 Soil Test No: K6930ABC These comments and suggestions are based on our interpretation of soil analysis
Soil Program Recommendation Grower: G.C. Wynne Consultant: Bill Munton Doyle St Quirindi NSW 2343 Soil Test No: K6930ABC These comments and suggestions are based on our interpretation of soil analysis
Nutrition. Grain Legume Handbook
 Grain Legume Handbook Nutrition If the nutrients (phosphorus, nitrogen, zinc, etc.) removed as grain from the paddock are not replaced then crop yields and soil fertility will fall. This means that fertilizer
Grain Legume Handbook Nutrition If the nutrients (phosphorus, nitrogen, zinc, etc.) removed as grain from the paddock are not replaced then crop yields and soil fertility will fall. This means that fertilizer
to Plants Ross F. Brennan M.Sc. Agric. (Soil Science and Plant Nutrition) (UWA) B.Sc. Agric. (Hon.) (Soil Science and Plant Nutrition) (UWA)
 Zinc Application and Its Availability to Plants Ross F. Brennan M.Sc. Agric. (Soil Science and Plant Nutrition) (UWA) B.Sc. Agric. (Hon.) (Soil Science and Plant Nutrition) (UWA) This thesis is presented
Zinc Application and Its Availability to Plants Ross F. Brennan M.Sc. Agric. (Soil Science and Plant Nutrition) (UWA) B.Sc. Agric. (Hon.) (Soil Science and Plant Nutrition) (UWA) This thesis is presented
SOIL TEST INTERPRETATION JIM FASCHING Technical Field Representative
 SOIL TEST INTERPRETATION JIM FASCHING Technical Field Representative jfasching@midwestlabs.com 507 273-3339 TERMS ppm = parts per million 2 million pounds of soil represented by soil samples taken 6 inches
SOIL TEST INTERPRETATION JIM FASCHING Technical Field Representative jfasching@midwestlabs.com 507 273-3339 TERMS ppm = parts per million 2 million pounds of soil represented by soil samples taken 6 inches
May 2008 AG/Soils/ pr Understanding Your Soil Test Report Grant E. Cardon Jan Kotuby-Amacher Pam Hole Rich Koenig General Information
 May 2008 AG/Soils/2008-01pr Understanding Your Soil Test Report Grant E. Cardon, USU Extension Soil Specialist Jan Kotuby-Amacher, Coordinator for North American Proficiency Testing Program Pam Hole, Supervisor
May 2008 AG/Soils/2008-01pr Understanding Your Soil Test Report Grant E. Cardon, USU Extension Soil Specialist Jan Kotuby-Amacher, Coordinator for North American Proficiency Testing Program Pam Hole, Supervisor
TNPSC Chemistry Study Material Fertilizers
 TNPSC Chemistry Study Material A fertilizer is any material of natural or synthetic origin (other than liming materials) that is applied to soils or to plant tissues to supply one or more plant nutrients
TNPSC Chemistry Study Material A fertilizer is any material of natural or synthetic origin (other than liming materials) that is applied to soils or to plant tissues to supply one or more plant nutrients
Mineral Nutrients and their functions in plants
 Mineral Nutrients and their functions in plants PLANT NUTRITION The term "nutrition" refers to the interrelated steps by which a living organism assimilates food and uses it for growth and replacement
Mineral Nutrients and their functions in plants PLANT NUTRITION The term "nutrition" refers to the interrelated steps by which a living organism assimilates food and uses it for growth and replacement
Nutrients & Diagnosing Nutrient Needs. Carrie Laboski Dept. of Soil Science UW-Madison
 Nutrients & Diagnosing Nutrient Needs Carrie Laboski Dept. of Soil Science UW-Madison Sources of nutrients available for plant uptake Nutrients in the soil solution are: In ionic form At low concentration
Nutrients & Diagnosing Nutrient Needs Carrie Laboski Dept. of Soil Science UW-Madison Sources of nutrients available for plant uptake Nutrients in the soil solution are: In ionic form At low concentration
YaraVita PROCOTE. The colors of yield.
 YaraVita PROCOTE The colors of yield. Micronutrient Coating YaraVita PROCOTE is an innovative liquid technology developed by Yara for coating prilled and granular fertilizers with micronutrients. It allows
YaraVita PROCOTE The colors of yield. Micronutrient Coating YaraVita PROCOTE is an innovative liquid technology developed by Yara for coating prilled and granular fertilizers with micronutrients. It allows
Chapter 7: Micronutrient Management
 Chapter 7: Micronutrient Management Agustin Pagani, John E. Sawyer, and Antonio P. Mallarino / Department of Agronomy, Iowa State University Developed in cooperation with Lara Moody, TFI; John Davis, NRCS;
Chapter 7: Micronutrient Management Agustin Pagani, John E. Sawyer, and Antonio P. Mallarino / Department of Agronomy, Iowa State University Developed in cooperation with Lara Moody, TFI; John Davis, NRCS;
Early Detection of Nutrient Deficiencies and Toxicities
 Early Detection of Nutrient Deficiencies and Toxicities IPM Scout Training Program Andrew G. Ristvey Wye Research and Education Center University of Maryland Extension College of Agriculture and Natural
Early Detection of Nutrient Deficiencies and Toxicities IPM Scout Training Program Andrew G. Ristvey Wye Research and Education Center University of Maryland Extension College of Agriculture and Natural
International Zinc Association
 Outline IZA and Zinc Zinc and Human Health Zinc and Crops Zinc Nutrient Initiative Main End Uses of Zinc Other 3% Oxides & Chemicals 6% Die Casting Alloys 15% Brass 10% Galvanizing 60% Semis-Manufactured
Outline IZA and Zinc Zinc and Human Health Zinc and Crops Zinc Nutrient Initiative Main End Uses of Zinc Other 3% Oxides & Chemicals 6% Die Casting Alloys 15% Brass 10% Galvanizing 60% Semis-Manufactured
ABSTRACT. Keywords: Added Zn, Significant increase, Exchangeable Zn, Aerobic and Anaerobic Condition INTRODUCTION
 J. Sci. Foundation, 9(1&): 9-14, June-December 11 ISSN 178-7855 INCUBATION STUDIES ON EXCHANGEABLE Zn FOR VARYING LEVELS OF ADDED Zn UNDER AEROBIC AND ANAEROBIC CONDITIONS IN GREY TERRACE SOILS, NON CALCARIOUS
J. Sci. Foundation, 9(1&): 9-14, June-December 11 ISSN 178-7855 INCUBATION STUDIES ON EXCHANGEABLE Zn FOR VARYING LEVELS OF ADDED Zn UNDER AEROBIC AND ANAEROBIC CONDITIONS IN GREY TERRACE SOILS, NON CALCARIOUS
Visit For All NCERT solutions, CBSE sample papers, Question papers, Notes for Class 6 to 12. Chapter-12 MINERAL NUTRITION
 Chapter-12 MINERAL NUTRITION POINTS TO REMEMBER Autotroph : An organism that synthesize its required nutrients from simple and inorganic substances. Heterotroph : An organism that cannot synthesise its
Chapter-12 MINERAL NUTRITION POINTS TO REMEMBER Autotroph : An organism that synthesize its required nutrients from simple and inorganic substances. Heterotroph : An organism that cannot synthesise its
MICRONUTRIENT PRINCIPLES
 MICRONUTRIENT PRINCIPLES MGGA Convention Great Falls December 1, 2015 Clain Jones clainj@montana.edu 994-6076 MSU Soil Fertility Extension Clickers are better than cell phones because: A. You don t listen
MICRONUTRIENT PRINCIPLES MGGA Convention Great Falls December 1, 2015 Clain Jones clainj@montana.edu 994-6076 MSU Soil Fertility Extension Clickers are better than cell phones because: A. You don t listen
Raymond C. Ward Ward Laboratories, Inc Kearney, NE
 Raymond C. Ward Ward Laboratories, Inc Kearney, NE www.wardlab.com There is More Than N P K Major Nutrients N, P, and K Secondary Nutrients Calcium, Magnesium, and Sulfur Micro-Nutrients Zinc, Iron, Manganese,
Raymond C. Ward Ward Laboratories, Inc Kearney, NE www.wardlab.com There is More Than N P K Major Nutrients N, P, and K Secondary Nutrients Calcium, Magnesium, and Sulfur Micro-Nutrients Zinc, Iron, Manganese,
Mineral Nutrition. Criteria for Essentiality
 Mineral Nutrition Criteria for Essentiality The element is absolutely necessary for supporting normal growth and reproduction. In the absence of essential elements, plants cannot complete their life cycle
Mineral Nutrition Criteria for Essentiality The element is absolutely necessary for supporting normal growth and reproduction. In the absence of essential elements, plants cannot complete their life cycle
Table 1. Wheat grain nutrient concentrations (Norton, 2011) and critical nutrient concentrations (Reuter and Robinson, 1997)
 Trace Elements Importance Rob Norton 1, Jim Laycock 2, Charlie Walker 2 1. International Plant Nutrition Institute, 54 Florence St, Horsham, 3400. 2. Incitec Pivot Fertilizers, PO Box 54, Geelong North,
Trace Elements Importance Rob Norton 1, Jim Laycock 2, Charlie Walker 2 1. International Plant Nutrition Institute, 54 Florence St, Horsham, 3400. 2. Incitec Pivot Fertilizers, PO Box 54, Geelong North,
Mineral Nutrition in Plants. Plant nutrition: essentiality, mechanism of absorption, role in plant metabolism.
 Mineral Nutrition in Plants Plant nutrition: essentiality, mechanism of absorption, role in plant metabolism. Mineral : An inorganic element Nutrient : A substance needed to survive or necessary for the
Mineral Nutrition in Plants Plant nutrition: essentiality, mechanism of absorption, role in plant metabolism. Mineral : An inorganic element Nutrient : A substance needed to survive or necessary for the
Figure 1. Location of 43 benchmark sites across Alberta.
 1.0 INTRODUCTION This report describes the micronutrient and trace element status of the AESA (Alberta Environmentally Sustainable Agriculture) Soil Quality Benchmark Sites. Previous reports completed
1.0 INTRODUCTION This report describes the micronutrient and trace element status of the AESA (Alberta Environmentally Sustainable Agriculture) Soil Quality Benchmark Sites. Previous reports completed
EconovaPlus Fertiliser
 EconovaPlus Fertiliser The complete plant growth fertiliser, bio-stimulater & carbon control solution. A bio-fertiliser based on the need for organic mineral complexes in the soil. Manufactured by building
EconovaPlus Fertiliser The complete plant growth fertiliser, bio-stimulater & carbon control solution. A bio-fertiliser based on the need for organic mineral complexes in the soil. Manufactured by building
Micronutrients What should you be doing? Rob Norton Regional Director IPNI ANZ
 Micronutrients What should you be doing? Rob Norton Regional Director IPNI ANZ Micronutrients ARE NOT miracle workers Follow the season Mg/Micros Assess N (& S) Look at P (& K) Get the soil right Clearly
Micronutrients What should you be doing? Rob Norton Regional Director IPNI ANZ Micronutrients ARE NOT miracle workers Follow the season Mg/Micros Assess N (& S) Look at P (& K) Get the soil right Clearly
MAGIC RECIPES? Strawberry Fertigation in the UK. John Atwood Senior Horticultural Consultant.
 MAGIC RECIPES? Strawberry Fertigation in the UK John Atwood Senior Horticultural Consultant www.adas.co.uk Strawberries in the UK Raised beds, polythene mulch, trickle line + fertigation Introduced 20
MAGIC RECIPES? Strawberry Fertigation in the UK John Atwood Senior Horticultural Consultant www.adas.co.uk Strawberries in the UK Raised beds, polythene mulch, trickle line + fertigation Introduced 20
SOIL AND PLANT NUTRITION
 SOIL AND PLANT NUTRITION 1.0 Introduction Plants need at least 16 elements for normal growth to be able to produce well. Some of the elements are needed in large quantities. Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
SOIL AND PLANT NUTRITION 1.0 Introduction Plants need at least 16 elements for normal growth to be able to produce well. Some of the elements are needed in large quantities. Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
By Andrew & Erin Oxford, Bethel
 Chemistry in Plant Nutrition & Growth Objectives Review elements of chemistry and apply them to plant nutrition and growth in an agricultural context. Suggested grade levels 9-12 Alaska Content Standards
Chemistry in Plant Nutrition & Growth Objectives Review elements of chemistry and apply them to plant nutrition and growth in an agricultural context. Suggested grade levels 9-12 Alaska Content Standards
Essential Elements. Original research don by Julius von Sachs 1860 using hydroponics
 Essential Elements Original research don by Julius von Sachs 1860 using hydroponics Using various solutions found ones that supported plant life Sachs found several elements that were needed in relatively
Essential Elements Original research don by Julius von Sachs 1860 using hydroponics Using various solutions found ones that supported plant life Sachs found several elements that were needed in relatively
Biofortified pearl millet cultivars to fight iron and zinc deficiencies in India
 Biofortified pearl millet cultivars to fight iron and zinc deficiencies in India Inadequate intake of energy-providing organic macronutrients (largely carbohydrate, followed by protein and fat, in that
Biofortified pearl millet cultivars to fight iron and zinc deficiencies in India Inadequate intake of energy-providing organic macronutrients (largely carbohydrate, followed by protein and fat, in that
Soil Nutrients and Fertilizers. Essential Standard Explain the role of nutrients and fertilizers.
 Soil Nutrients and Fertilizers Essential Standard 6.00- Explain the role of nutrients and fertilizers. Objective 6.01 Discuss macro and micro nutrients and the role they play in plant deficiencies. Macro
Soil Nutrients and Fertilizers Essential Standard 6.00- Explain the role of nutrients and fertilizers. Objective 6.01 Discuss macro and micro nutrients and the role they play in plant deficiencies. Macro
ANALYSIS OF RESPONSE OF DIFFERENT CHELATED ZINC SOURCES ON MICRO AND MACRO NUTRIENTS UPTAKE IN MOONG PLANT AND SEED (VIGNA RADIATA)
 ANALYSIS OF RESPONSE OF DIFFERENT CHELATED ZINC SOURCES ON MICRO AND MACRO NUTRIENTS UPTAKE IN MOONG PLANT AND SEED (VIGNA RADIATA) Jilani A A 1 1 Department of Chemistry, St. John s College, Agra-282003
ANALYSIS OF RESPONSE OF DIFFERENT CHELATED ZINC SOURCES ON MICRO AND MACRO NUTRIENTS UPTAKE IN MOONG PLANT AND SEED (VIGNA RADIATA) Jilani A A 1 1 Department of Chemistry, St. John s College, Agra-282003
Water Soluble Fertilizer for Foliar Application
 COMPO EXPERT EXPERTS FOR GROWTH Water Soluble Fertilizer for Foliar Application Highly efficient combination of macro and micro elements Fully chelated trace elements Fast and completely water soluble
COMPO EXPERT EXPERTS FOR GROWTH Water Soluble Fertilizer for Foliar Application Highly efficient combination of macro and micro elements Fully chelated trace elements Fast and completely water soluble
The role of water in the maintenance of life
 Inorganic compounds The role of water in the maintenance of life As mentioned in Table (Reference), up to 65% of our bodies are made up of water. Water is an inorganic compound made up of two hydrogen
Inorganic compounds The role of water in the maintenance of life As mentioned in Table (Reference), up to 65% of our bodies are made up of water. Water is an inorganic compound made up of two hydrogen
Plants Essential Elements. Macro and Micronutrients
 Plants Essential Elements Macro and Micronutrients Nutrients Are elements needed by a plant to promote healthy tissue, processes, and growth. When plants are lacking in nutrients have a deficiency and
Plants Essential Elements Macro and Micronutrients Nutrients Are elements needed by a plant to promote healthy tissue, processes, and growth. When plants are lacking in nutrients have a deficiency and
Enclosed are the tissue analysis results for the samples from the greens at Golf Club.
 Enclosed are the tissue analysis results for the samples from the greens at Golf Club. The results for nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur, and sodium are reported on a percent
Enclosed are the tissue analysis results for the samples from the greens at Golf Club. The results for nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur, and sodium are reported on a percent
Barley and Sugarbeet Symposium
 MICRONUTRIENT TESTING & MANAGEMENT IN BARLEY, CORN & PULSES Barley and Sugarbeet Symposium Billings, MT January 10, 2017 Clain Jones clainj@montana.edu 994-6076 MSU Soil Fertility Extension Goals Today
MICRONUTRIENT TESTING & MANAGEMENT IN BARLEY, CORN & PULSES Barley and Sugarbeet Symposium Billings, MT January 10, 2017 Clain Jones clainj@montana.edu 994-6076 MSU Soil Fertility Extension Goals Today
Multi-K. Potassium Nitrate Products For Healthy Crops
 Multi-K Potassium Nitrate Products For Healthy Crops Contents Potassium in the plant Multi-K and its advantages Nutrigation with Multi-K Foliar nutrition with Haifa Bonus Multi-K properties Multi-K products
Multi-K Potassium Nitrate Products For Healthy Crops Contents Potassium in the plant Multi-K and its advantages Nutrigation with Multi-K Foliar nutrition with Haifa Bonus Multi-K properties Multi-K products
PRIMARY (MACRO) NUTRIENTS
 Session 8 Earth: Fertility in the forest garden Lewis McNeill May 2014 Recap on nutrients Sixteen plant food nutrients are essential for proper plant and crop development. Each is equally important to
Session 8 Earth: Fertility in the forest garden Lewis McNeill May 2014 Recap on nutrients Sixteen plant food nutrients are essential for proper plant and crop development. Each is equally important to
Fertilizer. Fertilizers. (FAO press release, April 1990): Nutrient Depletion. Nutrient Depletion 4/16/2012
 Fertilizers Fertilizer Any organic or inorganic material of natural or synthetic origin which is added to a soil to supply elements essential to the growth of plants 1 2 (FAO press release, April 1990):
Fertilizers Fertilizer Any organic or inorganic material of natural or synthetic origin which is added to a soil to supply elements essential to the growth of plants 1 2 (FAO press release, April 1990):
Introduction to Soil Minerals
 Introduction to Soil Minerals 6th Annual Soil & Nutrition Conference 12/5/2016 David Forster Bionutrient Food Association, Agronomist Forster Soil Management, Owner agronomy@bionutrient.org (413) 570-0332
Introduction to Soil Minerals 6th Annual Soil & Nutrition Conference 12/5/2016 David Forster Bionutrient Food Association, Agronomist Forster Soil Management, Owner agronomy@bionutrient.org (413) 570-0332
The 1 th International and The 4 th National Congress on Recycling of Organic Waste in Agriculture April 2012 in Isfahan, Iran
 PERIODIC MUNICIPAL COMPOST AND SEWAGE SLUDGE APPLICATION ON ACCUMULATION OF HEAVY METALS IN SOIL AND PLANTS Ali R. Marjovvi 1,* and Moslehedin Rezaei 1 1 Soil and Water Department, Isfahan Agricultural
PERIODIC MUNICIPAL COMPOST AND SEWAGE SLUDGE APPLICATION ON ACCUMULATION OF HEAVY METALS IN SOIL AND PLANTS Ali R. Marjovvi 1,* and Moslehedin Rezaei 1 1 Soil and Water Department, Isfahan Agricultural
Incorporating Micronutrients to NPK Fertilizers
 Incorporating to NPK Fertilizers Presented at the 2006 IFA Agriculture Conference Jorge R. Polo Senior Technical Specialist IFDC How Plants Obtain Nutrients Nutrients Obtained from Air and Water Water,
Incorporating to NPK Fertilizers Presented at the 2006 IFA Agriculture Conference Jorge R. Polo Senior Technical Specialist IFDC How Plants Obtain Nutrients Nutrients Obtained from Air and Water Water,
Nutrient Recommendations Agronomic Crops Last Updated 12/1/16. Grain Corn. Crop Highlights Target ph: 6.0
 Nutrient Recommendations Agronomic Crops Last Updated 12/1/16 Crop Highlights Target ph: 6.0 Grain Corn Split N applications to increase N-use efficiency in corn. Apply a small amount (20-25%) at planting
Nutrient Recommendations Agronomic Crops Last Updated 12/1/16 Crop Highlights Target ph: 6.0 Grain Corn Split N applications to increase N-use efficiency in corn. Apply a small amount (20-25%) at planting
MICRO NUTRIENTS AND SECONDARY NUTRIENTS
 BR Global, LLC. P.O. Box 8164 Rocky Mount, NC 27804 Tel: 252-442-0700 / Fax: 252-442-0787 Sales@BRGLimited.com www.brglimited.com MICRO NUTRIENTS AND SECONDARY NUTRIENTS Trace elements or micronutrients
BR Global, LLC. P.O. Box 8164 Rocky Mount, NC 27804 Tel: 252-442-0700 / Fax: 252-442-0787 Sales@BRGLimited.com www.brglimited.com MICRO NUTRIENTS AND SECONDARY NUTRIENTS Trace elements or micronutrients
MULTI-NUTRIENT FERTILIZER DEMAND IN LATIN AMERICA
 MULTI-NUTRIENT FERTILIZER DEMAND IN LATIN AMERICA poly4.com siriusminerals.com MEETING THE CHALLENGE OF NUTRIENT DEFICIENCIE is a naturally-occurring, low-chloride, multi-nutrient fertilizer. It includes
MULTI-NUTRIENT FERTILIZER DEMAND IN LATIN AMERICA poly4.com siriusminerals.com MEETING THE CHALLENGE OF NUTRIENT DEFICIENCIE is a naturally-occurring, low-chloride, multi-nutrient fertilizer. It includes
Principles of Orchard Nutrition. Kevin Manning and Ross Wilson AgFirst
 Principles of Orchard Nutrition Kevin Manning and Ross Wilson AgFirst General Principles Nutrition is generally a very small proportion of production costs ( < 2%). Poor nutrition management can severely
Principles of Orchard Nutrition Kevin Manning and Ross Wilson AgFirst General Principles Nutrition is generally a very small proportion of production costs ( < 2%). Poor nutrition management can severely
What s new with micronutrients in our part of the world?
 2006 Integrated Crop Management Conference - Iowa State University 181 What s new with micronutrients in our part of the world? George Rehm, Professor, Soil, Water and Climate, University of Minnesota
2006 Integrated Crop Management Conference - Iowa State University 181 What s new with micronutrients in our part of the world? George Rehm, Professor, Soil, Water and Climate, University of Minnesota
Improving Micronutrient Fluid Fertilizers using Novel Chelating Agents
 Improving Micronutrient Fluid Fertilizers using Novel Chelating Agents Mike McLaughlin 12 1,2 and dsamuel lstacey 1 1 Earth and Environmental Sciences, The University of Adelaide, AUSTRALIA 2 CSIRO Land
Improving Micronutrient Fluid Fertilizers using Novel Chelating Agents Mike McLaughlin 12 1,2 and dsamuel lstacey 1 1 Earth and Environmental Sciences, The University of Adelaide, AUSTRALIA 2 CSIRO Land
Trends in Micro-Nutrient Soil Test Levels in Saskatchewan Pat Flaten, PAg 1, Brandon Green, PAg 2, Paul Routledge, PAg 3
 Trends in Micro-Nutrient Soil Test Levels in Saskatchewan Pat Flaten, PAg 1, Brandon Green, PAg 2, Paul Routledge, PAg 3 1 Enviro-Test Laboratories, 124 Veterinary Road, Saskatoon, SK, S7N 5E3 2 Enviro-Test
Trends in Micro-Nutrient Soil Test Levels in Saskatchewan Pat Flaten, PAg 1, Brandon Green, PAg 2, Paul Routledge, PAg 3 1 Enviro-Test Laboratories, 124 Veterinary Road, Saskatoon, SK, S7N 5E3 2 Enviro-Test
BIOZYME is a product in use by Latin American farmers in a wide range of crops to provide outstanding results for more than 18 years.
 BIOZYME BIOZYME TM is a unique formulation developed to enhance plant and crop performance. It influences plant nutrient uptake that enhances fruit set, fruit numbers, fruit quality and general crop performance.
BIOZYME BIOZYME TM is a unique formulation developed to enhance plant and crop performance. It influences plant nutrient uptake that enhances fruit set, fruit numbers, fruit quality and general crop performance.
Zinc Fertilizer Overview
 Zinc Fact Sheet: Zinc Fertilizer Overview Introduction Zinc is an essential micronutrient for the growth and development of plants, animals and human beings. Zinc is required in small amounts but for very
Zinc Fact Sheet: Zinc Fertilizer Overview Introduction Zinc is an essential micronutrient for the growth and development of plants, animals and human beings. Zinc is required in small amounts but for very
Fertility Management for Corn on Corn Systems Kyle Freeman. The Mosaic Company
 Fertility Management for Corn on Corn Systems Kyle Freeman The Mosaic Company Safe Harbor Statement Certain statements contained herein constitute forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private
Fertility Management for Corn on Corn Systems Kyle Freeman The Mosaic Company Safe Harbor Statement Certain statements contained herein constitute forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private
Upper Tolerances for Micronutrients in Fertilizers
 2017 Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada (Canadian Food Inspection Agency), all rights reserved. Use without permission is prohibited. Upper Tolerances for Micronutrients in Fertilizers Program Objectives
2017 Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada (Canadian Food Inspection Agency), all rights reserved. Use without permission is prohibited. Upper Tolerances for Micronutrients in Fertilizers Program Objectives
Mineral Nutrition of Fruit & Nut Trees. Fruit & Nut Tree Nutrition 3/1/2013. Johnson - Nutrition 1
 Mineral Nutrition of Fruit & Nut Trees R. Scott Johnson Extension Pomologist UC Kearney Ag Center Fruit & Nut Tree Nutrition 1. Basic Principles 2. Sampling for Nutrients 3. Environmental Issues 4. BMPs
Mineral Nutrition of Fruit & Nut Trees R. Scott Johnson Extension Pomologist UC Kearney Ag Center Fruit & Nut Tree Nutrition 1. Basic Principles 2. Sampling for Nutrients 3. Environmental Issues 4. BMPs
C O P P E R. Technical Information. BMS Micro-Nutrients Cereals. Landamine Cu and Chelal Cu. More information >>>
 C O P P E R BMS Micro-Nutrients Cereals Technical Information Chelal Cu - Landamine Cu Since 1979 BMS Micro-Nutrients specialised itself in plant nutrition and developed an innovative product line based
C O P P E R BMS Micro-Nutrients Cereals Technical Information Chelal Cu - Landamine Cu Since 1979 BMS Micro-Nutrients specialised itself in plant nutrition and developed an innovative product line based
Rec Alkaline Presentation. Jarmo Pudas, Development Director
 Rec Alkaline Presentation Jarmo Pudas, Development Director Alkaline battery ingredients All types of batteries contain electrolysis main element allowing current to flow through the specific mixture.
Rec Alkaline Presentation Jarmo Pudas, Development Director Alkaline battery ingredients All types of batteries contain electrolysis main element allowing current to flow through the specific mixture.
Soils and Soil Fertility Management
 Soils and Soil Fertility Management Mark L. McFarland Professor and Soil Fertility Specialist Texas A&M AgriLife Extension Service College Station, Texas Four Principal Components of Soil Air Mineral Solid
Soils and Soil Fertility Management Mark L. McFarland Professor and Soil Fertility Specialist Texas A&M AgriLife Extension Service College Station, Texas Four Principal Components of Soil Air Mineral Solid
Vegetable Update 2013
 Vegetable Update 2013 Agenda 1) Foliar Feeding Is it beneficial? 2) WingP 2012 experiences 3) Clubroot update Foliar Feeding Is it Beneficial? Why do we foliar feed- deficiencies, improve colour / quality
Vegetable Update 2013 Agenda 1) Foliar Feeding Is it beneficial? 2) WingP 2012 experiences 3) Clubroot update Foliar Feeding Is it Beneficial? Why do we foliar feed- deficiencies, improve colour / quality
Investigating the probable cause of crop decline in central Oahu A.P. Pant, N.V. Hue, J. Uyeda, J. Sugano, and T. Radovich
 HanaiʻAi/The Food Provider June July August 2013 Investigating the probable cause of crop decline in central Oahu A.P. Pant, N.V. Hue, J. Uyeda, J. Sugano, and T. Radovich Summary Extension agents brought
HanaiʻAi/The Food Provider June July August 2013 Investigating the probable cause of crop decline in central Oahu A.P. Pant, N.V. Hue, J. Uyeda, J. Sugano, and T. Radovich Summary Extension agents brought
Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium deficiency on the uptake and mobilization of ions in Bengal gram (Cicer arietinum)
 J. Biosci., Vol. 3 Number 3, September 1981, pp. 249-257. Printed in India, Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium deficiency on the uptake and mobilization of ions in Bengal gram (Cicer arietinum)
J. Biosci., Vol. 3 Number 3, September 1981, pp. 249-257. Printed in India, Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium deficiency on the uptake and mobilization of ions in Bengal gram (Cicer arietinum)
Potash Phosphate Nitrogen
 Nutrients 160 140 120 100 Potash Phosphate Nitrogen 80 60 40 20 0 1961 1971 1981 1991 2001 2011 Year FAOSTAT 45,000,000 40,000,000 35,000,000 30,000,000 25,000,000 20,000,000 15,000,000 10,000,000 5,000,000
Nutrients 160 140 120 100 Potash Phosphate Nitrogen 80 60 40 20 0 1961 1971 1981 1991 2001 2011 Year FAOSTAT 45,000,000 40,000,000 35,000,000 30,000,000 25,000,000 20,000,000 15,000,000 10,000,000 5,000,000
SOLUFEED WATER SOLUBLE FERTILISERS
 WATER SOLUBLE FERTILISERS Standard water soluble fertilisers for crops grown in soil and artificial growing media. All containing magnesium (Mg) and premium levels of trace elements. water soluble fertilisers
WATER SOLUBLE FERTILISERS Standard water soluble fertilisers for crops grown in soil and artificial growing media. All containing magnesium (Mg) and premium levels of trace elements. water soluble fertilisers
Matrix Reference Materials - SCP SCIENCE
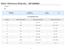 EnviroMAT SS-1 Catalogue No.: 140-025-001 EnviroMAT Contaminated Soil Lot No.: SC0063618 100 g TOTAL DIGESTION VALUES Elements Reference Value (mg/kg) Confidence Interval (mg/kg) Tolerance Interval (mg/kg)
EnviroMAT SS-1 Catalogue No.: 140-025-001 EnviroMAT Contaminated Soil Lot No.: SC0063618 100 g TOTAL DIGESTION VALUES Elements Reference Value (mg/kg) Confidence Interval (mg/kg) Tolerance Interval (mg/kg)
Application note. Determination of metals in soil by microwave plasma - atomic emission spectrometry (MP-AES) using DTPA extraction.
 Determination of metals in soil by microwave plasma - atomic emission spectrometry (MP-AES) using DTPA extraction Application note Agriculture Authors Marília S. Teodoro1, Daniela Schiavo2, Mônica Ferreira
Determination of metals in soil by microwave plasma - atomic emission spectrometry (MP-AES) using DTPA extraction Application note Agriculture Authors Marília S. Teodoro1, Daniela Schiavo2, Mônica Ferreira
Lesson 3 Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 3 Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance 1 Terms Balanced ration Carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates Disaccharides Essential nutrients Ether Fat Fat-soluble
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 3 Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance 1 Terms Balanced ration Carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates Disaccharides Essential nutrients Ether Fat Fat-soluble
CHELATES The most efficient solution to prevent and correct micronutrients deficiencies WHY TRADECORP UNCHELATED NUTRIENTS CHELATED NUTRIENTS
 chelates catalogue CHELATES The most efficient solution to prevent and correct micronutrients deficiencies WHY TRADECORP The use of EDTA / EDDHA chelates* is recognized as the most efficient way to prevent
chelates catalogue CHELATES The most efficient solution to prevent and correct micronutrients deficiencies WHY TRADECORP The use of EDTA / EDDHA chelates* is recognized as the most efficient way to prevent
Claire Mouquet-Rivier & Christèle Icard-Vernière UMR 204 NUTRIPASS, IRD, France
 Workshop: Improving the composition of plant foods for better mineral nutrition Food and Agriculture COST Action FA95: Mineral-improved crop production for healthy food and feed Claire Mouquet-Rivier &
Workshop: Improving the composition of plant foods for better mineral nutrition Food and Agriculture COST Action FA95: Mineral-improved crop production for healthy food and feed Claire Mouquet-Rivier &
