3-D Modified Proportional Navigation Guidance Law based on a Total Demand Vector Concept
|
|
|
- Kathlyn Richardson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Defence Science Journal, Vol. 55, No. 3, July 2005, pp O 2005, DESIDOC 3-D Modified Proportional Navigation Guidance Law based on a Total Demand Vector Concept P.K. Tiwari, Prashant Vora, S. Srinivasan and R.N. Bhattacharjee Defence Research & Development Laboratory, Hyderabad ABSTRACT Different proportional navigation (PN)-based guidance laws-pure proportional navigation (PPN), true proportional navigation (TPN), and proportional navigation with boost acceleration compensation generally used cannot maintain fundamental parameter of proportional navigation, viz., Navigation constant to the desired value in the presence of significantly high lead angles and missile longitudinal accelerations/decelerations. In a real-life situation with sensor noises and hardware constraints, this navigation constant should be maintained tightly at the selected value, which is generally between 3 and 4, for optimum performance. In this paper; a new 3-D modified PN guidance law based on a total demand vector concept is presented, which can maintain the navigation constant to the designer-selected value for any 3-D engagement scenario with associated lead angles and any velocity profile with missile longitudinal accelerations1 decelerations. Generality of this guidance law is brought out and superiority of this guidance law over the commonly used proportional navigation-based laws like PPN, TPN and PN with boost acceleration compensation has been demonstrated by applying it to the real-life 3-D engagement scenarios of different hypothetical missiles. Keywords: Proportional navigation, navigation guidance laws, pure proportional navigation, true proportional navigation, modified PN-based guidance NOMENCLATURE fzd Late'ral acceleration demand in light-of-sight frame Z-direction 8 Lead angle, angle between missile longitudinal axis and line-of-sight direction fxbd Lateral acceleration demand in missile body frame X-direction Vm Missile velocity vector V, Target velocity vector fybd Lateral acceleration demand in missile body frame Y-direction a Missile angle of attack fib, Lateral acceleration demand in missile body fxd Lateral acceleration demand in line-of-sight frame Z-direction frame X-direction N' Navigation constant Lateral acceleration demand in line-of-sight fyd frame Y-direction ax Missile longitudinal acceleration Received 15 November
2 DEF SCI J, VOL. 55, NO. 3, JULY 2005 Vc All he Neff Missile-target closing velocity Azimuth sight-line angle Elevation sight-line angle Realised navigation constant 1. INTRODUCTION For commonly used guidance laws based on proportional navigation theory like pure proportional navigation (PPN), true proportional navigation (TPN), etc, in the presence of lead angles (defined here as angle between the missile velocity vector and line-of-sight vector) and missile longitudinal acceleration1 deceleration generally present; the realised acceleration is different fi-om the one demanded by the proportional navigation law, in a plane perpendicular to line-ofsight vector. In other words, the effective or realised navigation constant is not the same as the desired one. For a practical system with sensor noises and hardware constraints, this navigation constant should be tightly maintained at the chosen value, which is generally between 3 and 4. However, in the presence of significant lead angles and missile longitudinal acceleration/deceleration, effective navigation constant can go up to fully unacceptable values, leading to fully unacceptable performance. It is, therefore, required to develop a guidance concept and law, which ensures that the realised navigation constant is the same as the one desired, even in the presence of real-life constraints, viz., in the presence of significant lead angles typical of 3-D interceptions and missile longitudinal acceleration1 deceleration. Such a concept is formulated and is visualised in 2-D scenario for the sake of understanding, and later extended to cater for a general 3-D interception scenario. Ultimately, it has been evolved as a 3-D guidance law in polar coordinates. The guidance law has been evaluated on a 6-DOF platform developed for a hypothetical surface-to-air missile with a 3-D interception scenario and also for an air-toair missile. The performance of the new guidance law is compared with the existing laws, viz., TPN, PPN and PN with boost acceleration compensation (BAC). It has been found that the performance of the new guidance law is appreciably better than the other guidancelaws listed above. The paper brings out the new guidance formulation and the significant performance improvement that can be achieved with the new guidance law. It is analytically shown that this new guidance law can tightly control the navigation constant to the desired value, whereas for TPN and PN with BAC; navigation constant can change considerably wrt the desired value set. 2. PROPORTIONAL NAVI'GATION GUIDANCE The problems associated with the existing PN guidance laws-tpn, PN with BAC, are highlighted. Also, the objective of the modified PN guidance, how these problems can be overcome in the new method, are discussed. To orient the missile flight path towards constant bearing collision course, the PN guidance generates commands perpendicular to the line-of-sight direction and an angle $m is generated by the guidance depending on Vm/V, speed ratio, target manoeuvres and errors/disturbances (Fig. 1). Guidance designer chooses an optimum navigation constant N depending on the target manoeuvres, noises in the system (ground radar, seeker, etc), errors and stability of missile guidance loop, including parasitic effects, etc. This generally vary between 3 to 4 for a reallife system. However, guidance commands can be applied only along body Y- and Z-axes (lateral plane) and those commands 4M,f,, can be considerably reduced wrt the required PN demands generated along the LOS frame Y- and Z-directions, ie,4,dlf,d, depending on lead angle = $m + a (angle between the LOS vector and the missile longitudinal axis) which is generally time varying. Thus, effective navigation constant, N varies due to the above en resolution error and deviates from the desired value. This deviation can be considerable in many cases, affecting performance appreciably. MISSILE Figure 1. Collision triangle
3 TIWARI, et al.: 3-D MODIFIED PROPORTIONAL NAVIGATION GUIDANCE LAW BASED ON A TOTAL DEMAND VECTOR CONCEPT 2.1 Proportional Navigation with Boost Acceleration Compensation In the process of transforming PN demands from the LOS frame to the body frame, a component of demand comes in body X, direction (longitudinal axis) also, which can be much different from the missile longitudinal acceleration, ax. Thus, effective lateral acceleration demands sent to the autopilot are either high or low in magnitude than the required acceleration and generated by the PN. In PN with BAC, the PN guidance commands have been improved through missile longitudinal acceleration compensation in the LOS frame by transforming acceleration ax along the directions perpendicular to LOS, ie, Y-LOS and Z-LOS and then reducinglincreasing the PN demands suitably by the transformed longitudinal acceleration commands. However, in the presence of significant lead angle, this compensation needs to be improved by correcting for the resolution error. 2.2 Modified PN Guidance To alleviate both resolution error and missile longitudinal acceleration constraints together, a unified, PN guidance design approach based on a total demand vector concept is formulated, which ensures full guidance demands as per PN guidance law, and is actually implemented through body plane commands in the presence of any propulsion and drag profile. However, in this implementation, in the case of accelerating thrust profile, closing velocity Vc would considerably increase and for deceleration phase, V, would decrease, while satisfying the full guidance requirement. With higherllower closing velocity, flight time and system coverage would change. In general, for any missile with both accelerating and decelerating velocity profiles, average closing velocity, Vc would be higher for the new method, leading to lower flight time and higher system coverage. 3. NAVIGATION GUIDANCE DEMANDS FORMULATION 3.1 PN Guidance Demands Formulation The proportional navigation guidance demands lateral accelerations, fy,, fid in the LOS frame, ie, along YLos, ZLos. The LOS frame X,,,, YLos, ZLos can be obtained from the launcher-fixed frame Xi, Y,, Z, by two successive rotations; first by an angle ha (azimuth sight-line angle) about 4 and then by an angle 90" - he (he = elevation sight-line angle) about newly obtained Y-axis, ie, Y-LOS (Fig. 2). The LOS rates about Y-LOS direction, 4 and same about Z-LOS direction, La cos he are used by PN guidance to generate latax demands Ld, & in LOS frame as per: fzd=~'vche, fm = N'v,~, cos he. These are transformed to body frame with the help of either lead angles or gimbal angles, depending on measurements available to Figure 2. Launcher-fixed frame the guidance system. For a homing missile system during mid-course, radar supplied target data and missile INS data can be used for the transformation, while in the terminal phase seeker, gimbal angles can be used for the transformation. 3.2 Modified PN Guidance Demands Formulation To realise PN componentsf, and f perpendicular u4 to the LOS fully in the presence of missile longitudinal acceleration/deceleration ax, consider a demand vector (Fig. 3) defined such that its component along body X, axis is ax and components perpendicular to LOS is fi,. This demand vector has a component along the LOS which is f,. From the definition, the demand vector in the LOS frame Lfr, fdr has a component ax in the X, direction. Therefore
4 fd DEF SCI J, VOL. 55, NO. 3, JULY 2005 [;]=[.I [;:I DEMAND VECTOR body +LOS fzhi Therefore Again, Figure 3. Modified PN formulation fzbd = fzd cos e - fxd sin 8 (3) which is the command sent to the autopilot Thus, the acceleration realised in the Z-LOS direction is (assuming an ideal autopilot): f,, cos 8 + a, sin 8 It is easy to see by substitution from Eqns (2) and (3) that the above expression equalsf,, implying that full latax demand as per the PN law is realised. The above concept can be extended to 3-D engagement scenario by considering the demand where vector in the LOS frame as [fxd fyd fzdlt 4, and jj, are the demands calculated as per PN law. Demands along Ybody, Zbody directions: fybd, A,, are calculated such that those realizedfybd, f,, along with actual missile longitudinal acceleration ax, when transformed from body frame to the LOS frame equals to the actual PN demands fs,, fy, perpendicular to the LOS and also a new demand along the LOS f,. Thus, fy,,, frbd are obtained from From the above Eqn (4), fxd = ax - T,2f,, T,l - T,3f?d is obtained. This demand along LOSf, along the with normal PN demands, fy,, fid constitute the complete demand vector in the LOS frame, which need to be transformed to body frame to obtain the required&,,,fr, satisfying the forward acceleration ax constraint. Therefore, putting the abovef, along with normal LOS frame, PN demands fyd, Ad in Eqn (4); body plane demands fy,, and fib, are I : [ obtained as [2]=[;; ; ;;I (5) fzd The transformations used for conversion between the LOS frame (seeker inner gimbal frame while homing) and the body frame can be obtained using the seeker gimbal angles in the homing phase. In the mid-course phase, above transformation matrix can be obtained as a product of rotation matrix from the LOS frame to launcher-fixed frame using the LOS angles and launcher-fixed body frame using INS Euler angles. Those body plane demands, 4,, frbd applied to autopilot would ensure full PN demands Ad, fid realised in the LOS frame, ie, perpendicular to X-LOS in the presence of any a, profile. Thus, desired navigation constant N' would be always maintained during the entire flight.
5 TIWARI, et al.: 3-D MODIFIED PROPORTIONAL NAVIGATION GUIDANCE LAW BASED ON A TOTAL DEMAND VECTOR CONCEPT 4. REALISED NAVIGATION CONSTANT It is shown above that for the modified PN, the guidance demand is met fully. The navigation constant actually realised. in other guidance schemes can be obtained by taking the component of total achieved acceleration in body frame into the plane perpendicular to the LOS vector, and thereafter, taking the ratio of that component with the product of sight-line rate vector magnitude and closing velocity V,. In other words, the components f $, f > Figure 4. Realised navigation constant (Ned calculation in the plane perpendicular to LOS, of the realised acceleration vector [ax, Abd, fibdit in the body plane are used for effective or realised navigation 2 constant N,// calculation. The corresponding LOS rates are ia cosheand i, (Fig. 2). Thus, total or resultant fir,,, (PN with BAC) realised navigation constant, Ng is obtained as = f, cos2 8, + ax cos 8, sin2 8, frms = Cfrr - ax cos 8,) cos 8, + ax cos 8, Thus, realised navigation constant, Ne, (PN It may be noted that the numerator term is the with BAC) can be given as total acceleration realised in the plane perpendicular to the LOS and V, is the closing velocity. To show how the above realised N' can go to a much different f zrms value from the desired value set in TPN and also V, in TPN with BAC, the above relation is expanded. In Fig. 4, a resultant latax demand vector fsr perpendicular to the LOS is defined based on latax demands along Z-LOS f, and Y-LOS Jd. Fzrb is the total or resultant latax demand achieved in the body frame lateral plane. 8, is the resolution error, between the PN demand vector in the LOS frame and acceleration achieved in the body lateral plane (which has been corrected in the modified guidance). [ fzr = N' cos2 8, + 1 L x cos 8, sin2 8, For planer case engagement; 8, = 90" - 8,, so the above expression reduces to N~~ (PN with BAC) = N' 4.1 Realised Navigation Constant for PN with BAC The acceleration demanded LOS lateral plane after missile longitudinal acceleration compensation = f, - a, cos 8,, assuming ideal autopilot-realised acceleration ierpendicular to the LOS 4.2 Realised Navigation Constant for TPN For TPN, realised acceleration in a plane perpendicular to the LOS (assuming ideal autopilot)
6 DEF SCI J, VOL. 55, NO. 3, JULY 2005 Thus I Again for the planer case engagement, Neg (TPN) = N' 8, = 90" - 8,, thus the realised navigation constant for planar engagement is where N' is the desired navigation constant set by the designer. It can be shown based on the above relations that effective navigation constant can go to a much different value from the desired value chosen N' even for resolution error of 20" and above. Nefl variation from desired N' depends on both the resolution error, 8, and the forward acceleration to resultant latax demand,lr ratio along with their signs. The effect of resolution error is more on the realised navigation constant, Neg in PN with BAC whereas Ng in TPN can get affected equally appreciably, both due to resolution error and axlfrr ratio. For example, with 8, = 30" and ax =fir; for planar case N~ (PN With BAC)= N I and With the same 8, = 30" and ax = -fir for planar case N~~(PN with BAC)= N', which islow, and ' which is unacceptably low, even for original N' = 4 choice of designer. Thus, simulation results presented in Section 5.1 for varying engagement scenarios, lead angles, and with accelerating/decelerating profilelphase of missile show wide variation in effective navigation ratios from the start of guidance to the end for both TPN and PN with BAC, whereas for modified scheme, it is held constant at the desired value. 5. PERFORMANCE OF GUIDANCE LAWS THROUGH 6-DOFS SIMULATION The performance improvement achievable with the new guidance law, vis-h-vis other PN laws can be best shown in the cases involving high lead angles and high missile longitudinal acceleration1 deceleration levels. For performance evaluation, modified PN and other PN-based guidance laws are applied to two different classes of missile systems. The TPN, PN with BAC, and modified PN were applied to a hypothetical surface-to-air missile with a boostcoast velocity profile, here Vm/V, < 1. The TPN, PPN, and the modified PN were also applied to an air-to-air missile which was also having a boostcoast velocity profile but with a velocity advantage, ie Vm/V, > 1. For a surface-to-air missile, different 3-D engagement scenarios were simulated to generate varying lead angle requirements. Tables 1 and 2 give comparison of performance of guidance laws for a surface-to-air missile. Results were generated by carrying out simulations on a 6-DOF platform for the hypothetical missile. Before sending the commands to autopilot, a time-varying latax limit was applied based on the minimum of latax limit coming due to (a, 6) deflection limit. In the mid-course guidance phase, the radar errors on target position and velocity were introduced in a way to give certain heading error at the start of homing phase. Here, the heading error is defined as an angle between the collision course velocity vector and thqe@al missile velocity vector (Fig. 1). In Table 1, the heading error settling characteristics of different guidance laws and the miss-distance are compared. In Table 2 for a different engagement scenario, the time for which the latax was saturated
7 TIWARI, el al.: 3-D MODIFIED PROPORTIONAL NAVIGATION GUIDANCE LAW BASED ON A TOTAL DEMAND VECTOR CONCEPT was compared, and was found to have a direct By analysing Tables 1 and 2 and the Figs 5 to 9, implication on the miss-distance. The variation of the following general conclusions can be drawn. effective navigation ratio is also tabulated. In Tables 3 and 4, the miss-distance comparison is done for It is seen that maximum heading error at the MPN and PPN and MPN and TPN, respectively end-phase is always less in modified PN compared for different missile-target heading angles. to other guidance laws (Tables 1 and 2). Table 1. Comparison of performance of TPN, PN with BAC, and modified PN guidance for a surface-to-air missile, N' = 4 Case Guidance type Height of kill (km) TF (s) Miss- Heading error distance (end-phase) (m) Elevation Azimuth I TPN PN + BAC OO Mod. PN I1 TPN PN + BAC Mod. PN TPN PN + BAC Mod. PN Table 2. Comparison of MAPN and TPN performance for a surface-to-air missile, N' = 3 - Case I I1 111 Guidance type Height Time of Miss- Time of latax of kill flight distance saturation N' variation (km) (4 (m) ' (end-phase) MAPN O TPN MAPN TPN OO MAPN TPN Table 3. Comparison of performance of PPN and MPN for an air-to-air missile, Vm = 520 mls, V, = 520 mls, h = 15 km, target manoeuvre nflflch = - 4 g (const) at 10 km range to go Guidance Modified PN Pure PN Time Miss- Time Miss- Heading angle of flight distance "- vat Range of flight distance "mu Vn.4 (dl (s) (m) (g) impact (km) (s) (m) (g) impact
8 DEF SCI J, VOL. 55, NO. 3, JULY 2005 Table 4. Comparison of performance of TPN and MPN for an air-to-air missile, Vm = 520 mls, V, = 520 mls, h = 15 km, target manoeuvre npiieh = - 4 g (const) at 10 km range to go Guidance MPN TPN Heading Time Miss- Time Missangle of flight distance vdv, Range nmax of flight distance nmax (d) (4 (m) (g) Impact (km) (4 (m) (g) VJV, Impact The heading error always settles to a low value at the end-phase for MPN (Figs 7 and 8). The phenomenon can be attributed to meeting the guidance demand completely. With low heading error at the end-phase, missile flight path is driven close to ideal collision course in MPN, which is reflected in low missdistance achieved in all cases of simulations (Tables 1 and 2). With appreciably higher heading error, the missdistance in other guidance laws is higher. It is also seen from Table 2 and Fig. 9 that the effective navigation constant in MPN is always maintained at the desired value set, whereas it can vary widely from the desired value in other guidance laws like TPN, etc. This is highly undesirable for any practical system where navigation constant is to be maintained generally between 3 and 4. TIME (s) Figure 5. Duration of saturation comparison, (Table 2, Case 1) TIME (s) Figure 6. Duration of saturation comparison, (Table 2, Case 2)
9 TIWARI, et al.: 3-D MODIFIED PROPORTIONAL NAVIGATION GUIDANCE LAW BASED ON A TOTAL DEMAND VECTOR CONCEPT TIME (s) TIME (s) Figure 7. Heading error settling comparison, (Table 2, Case 1) For air-to-air missile, several engagement simulations carried out with different heading angles (angle between the missile and the target velocity vector) varying from 180" to 0" and performance comparison between MPN, TPN, and PPN carried out in terms of miss-distance flight time, and V,/V, ratio (Tables 3 and 4). again shows that miss-distance is greatly reduced for MPN wrt both TPN and PPN, where missdistance goes to unacceptably high values in many cases. Figure 8. Heading error settling comparison, (Table 2, Case 2) that this new law can tightly control the navigation constant to the desired optimum value, whereas for the other PN-based laws commonly used, navigation constant can change appreciably wrt the desired value set. Superiority of the new modified PN guidance wrt other PN-based laws has been demonstrated by applying these to widely varying 3-.D engagement scenarios for different types of missile systems with boost-coast velocity profiles. In all the cases simulated, appreciable performance benefits have been obtained. Thus, this modified Summarising, it can be concluded that the new guidance law called modified PN, by maintaining the effective navigation constant to the desired value, gives better quality of guidance performance compared to the existing PN-based guidance laws in a general 3-D engagement scenario with both accelerating and decelerating velocity profiles of the missile. 6. CONCLUSION A new 3-D modified PN guidance law based on a total demand vector concept, has been presented. It ensures full guidance demands as per PN law implemented through body plane commands in the presence of any propulsion and drag profile, thereby maintaining the navigation constant to the desired value set. Derivation has been carried out to show TIME (s) Figure 9. Realised navigation constant Nla, (Table 2, Case 3)
10 DEF SCI J, VOL. 55, NO. 3, JULY 2005 PN guidance law is established as a general PN REFERENCES guidance law. 1. Shukla, U.S. & Mahapatra, P.R. The proportional ACKNOWLEDGEMENT navigation dilemma-pure or true, IEEE Trans. Aerospace Elec. Syst., 1990, 26(2). The authors like to express their deep sense of gratitude to Dr V.K. Saraswat, Shri Prahlada 2. Zarchan, Paul. Tactical and strategic missile and Shri N.V. Kadam for motivating and providing guidance, Vol In Progress in astronautics opportunity to work on this problem. The authors and aeronautics, AIAA, are also thankful to Wg Cmdr (Retd) A.S. Sharma, Shri. Surendra Kumar, Shri. N. Prabhakar and his 3. Garnell, P. & East, D.J. Guided weapon control systems. Pergamon Press, Oxford, team and other members of the Systems Engineering Committee for their useful suggestions and discussions from time to time. The authors are thankful to Dr Abhijit Bhattacharyya for all his technical input and suggestions while working on this problem.. Contributors Mr P.K. Tiwari obtained his MTech (Control & Guidance) from the Indian Institute Technology Bombay, Mumbai in Since then, he is working at the Defence Research & Development Laboratory (DRDL), Hyderabad. His areas of interest include: System simulation, missile guidance, and nonlinear control. Mr Prashant Vora obtained his MTech (Systems & Control) from the IIT Bombay, Mumbai in Since then, he is working at the DRDL, Hyderabad. His areas of interest include: System simulation, missile guidance, and nonlinear control.
An Introduction to Proportional Navigation
 Chapter 9 An Introduction to Proportional Navigation odule 8: Lecture 22 PPN; TPN; GTPN; IPN Keywords. Proportional Navigation, PPN, TPN, GTPN, IPN Proportional navigation is, by far, the most important
Chapter 9 An Introduction to Proportional Navigation odule 8: Lecture 22 PPN; TPN; GTPN; IPN Keywords. Proportional Navigation, PPN, TPN, GTPN, IPN Proportional navigation is, by far, the most important
Research on a Transmit-Receive Method of Ultrasonic Array for Planar Defects
 7 th Asia-Pacific Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring November 12-15, 2018 Hong Kong SAR, P.R. China Research on a Transmit-Receive Method of Ultrasonic Array for Planar Defects Zhenggan Zhou 1,2,3
7 th Asia-Pacific Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring November 12-15, 2018 Hong Kong SAR, P.R. China Research on a Transmit-Receive Method of Ultrasonic Array for Planar Defects Zhenggan Zhou 1,2,3
Threat Degree Analysis of the Multi-targets in Naval Gun
 MATEC Web of Conferences 22, 02013 ( 2015) DOI: 10.1051/ matecconf/ 20152202013 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2015 Threat Degree Analysis of the Multi-targets in Naval Gun Hao Sun
MATEC Web of Conferences 22, 02013 ( 2015) DOI: 10.1051/ matecconf/ 20152202013 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2015 Threat Degree Analysis of the Multi-targets in Naval Gun Hao Sun
An Evaluation of an Obstacle Avoidance Force Feedback Joystick
 An Evaluation of an Obstacle Avoidance Force Feedback Joystick James L. Protho, M.S. Edmund F. LoPresti, B.S. David M. Brienza, Ph.D. University of Pittsburgh Rehabilitation Science and Technology A Research
An Evaluation of an Obstacle Avoidance Force Feedback Joystick James L. Protho, M.S. Edmund F. LoPresti, B.S. David M. Brienza, Ph.D. University of Pittsburgh Rehabilitation Science and Technology A Research
Q: What is the relationship between muscle forces and EMG data that we have collected?
 FAQs ABOUT OPENSIM Q: What is the relationship between muscle forces and EMG data that we have collected? A: Muscle models in OpenSim generate force based on three parameters: activation, muscle fiber
FAQs ABOUT OPENSIM Q: What is the relationship between muscle forces and EMG data that we have collected? A: Muscle models in OpenSim generate force based on three parameters: activation, muscle fiber
Linear Ultrasonic Wave Propagation in Biological Tissues
 Indian Journal of Biomechanics: Special Issue (NCBM 7-8 March 29) Linear Ultrasonic Wave Propagation in Biological Tissues Narendra D Londhe R. S. Anand 2, 2 Electrical Engineering Department, IIT Roorkee,
Indian Journal of Biomechanics: Special Issue (NCBM 7-8 March 29) Linear Ultrasonic Wave Propagation in Biological Tissues Narendra D Londhe R. S. Anand 2, 2 Electrical Engineering Department, IIT Roorkee,
FUSE TECHNICAL REPORT
 FUSE TECHNICAL REPORT 1 / 16 Contents Page 3 Page 4 Page 8 Page 10 Page 13 Page 16 Introduction FUSE Accuracy Validation Testing LBD Risk Score Model Details FUSE Risk Score Implementation Details FUSE
FUSE TECHNICAL REPORT 1 / 16 Contents Page 3 Page 4 Page 8 Page 10 Page 13 Page 16 Introduction FUSE Accuracy Validation Testing LBD Risk Score Model Details FUSE Risk Score Implementation Details FUSE
Lect.6 Electrical axis and cardiac vector Cardiac vector: net result Vector that occurs during depolarization of the ventricles Figure:
 Lect.6 Electrical axis and cardiac vector Objectives: 1. State the relationship between the direction of cardiac vector with the direction (-ve, +ve) and amplitude of an ECG waves. 2. Draw diagram indicting
Lect.6 Electrical axis and cardiac vector Objectives: 1. State the relationship between the direction of cardiac vector with the direction (-ve, +ve) and amplitude of an ECG waves. 2. Draw diagram indicting
Toward Meaningful Human Control of Autonomous Weapons Systems Through Function Allocation
 1 Toward Meaningful Human Control of Autonomous Weapons Systems Through Function Allocation Marc Canellas* (Presenter) and Rachel Haga Cognitive Engineering Center, School of Aerospace Engineering, Georgia
1 Toward Meaningful Human Control of Autonomous Weapons Systems Through Function Allocation Marc Canellas* (Presenter) and Rachel Haga Cognitive Engineering Center, School of Aerospace Engineering, Georgia
CONFORMANCE MONITORING APPROACHES IN CURRENT AND FUTURE AIR TRAFFIC CONTROL ENVIRONMENTS
 Submitted to 21 st Digital Avionics Systems Conference, Irvine, CA, 27-31 October 2002 The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2002 CONFORMANCE MONITORING APPROACHES IN CURRENT AND
Submitted to 21 st Digital Avionics Systems Conference, Irvine, CA, 27-31 October 2002 The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2002 CONFORMANCE MONITORING APPROACHES IN CURRENT AND
Artificial Intelligence Lecture 7
 Artificial Intelligence Lecture 7 Lecture plan AI in general (ch. 1) Search based AI (ch. 4) search, games, planning, optimization Agents (ch. 8) applied AI techniques in robots, software agents,... Knowledge
Artificial Intelligence Lecture 7 Lecture plan AI in general (ch. 1) Search based AI (ch. 4) search, games, planning, optimization Agents (ch. 8) applied AI techniques in robots, software agents,... Knowledge
of Olympic Weightlifters
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SPORT BIOMECHANICS, 1985, 1, 122-130 Biomechanical Profiles of Olympic Weightlifters John Garhammer St. Mary Medical Center, Long Beach, CA The heaviest successful snatch and clean
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SPORT BIOMECHANICS, 1985, 1, 122-130 Biomechanical Profiles of Olympic Weightlifters John Garhammer St. Mary Medical Center, Long Beach, CA The heaviest successful snatch and clean
Cars for Deaf People
 International Review of Applied Engineering Research. ISSN 2248-9967 Volume 4, Number 4 (2014), pp. 307-312 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/iraer.htm Cars for Deaf People Aniket
International Review of Applied Engineering Research. ISSN 2248-9967 Volume 4, Number 4 (2014), pp. 307-312 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/iraer.htm Cars for Deaf People Aniket
3-DOF Parallel robotics System for Foot Drop therapy using Arduino
 3-DOF Parallel robotics System for Foot Drop therapy using Arduino Prof. Dr. Bahaa I Kazem, Assist.Prof.Dr Ameer Morad, Kamal Mohammed Hasan Baghdad University, Baghdad, Iraq Abstract This paper discusses
3-DOF Parallel robotics System for Foot Drop therapy using Arduino Prof. Dr. Bahaa I Kazem, Assist.Prof.Dr Ameer Morad, Kamal Mohammed Hasan Baghdad University, Baghdad, Iraq Abstract This paper discusses
MODELING OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM AND ITS CONTROL MECHANISMS FOR THE EXERCISE SCENARIO
 MODELING OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM AND ITS CONTROL MECHANISMS FOR THE EXERCISE SCENARIO PhD Thesis Summary eng. Ana-Maria Dan PhD. Supervisor: Prof. univ. dr. eng. Toma-Leonida Dragomir The objective
MODELING OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM AND ITS CONTROL MECHANISMS FOR THE EXERCISE SCENARIO PhD Thesis Summary eng. Ana-Maria Dan PhD. Supervisor: Prof. univ. dr. eng. Toma-Leonida Dragomir The objective
Supplementary information for Effects of Stretching Speed on. Mechanical Rupture of Phospholipid/Cholesterol Bilayers: Molecular
 Supplementary information for Effects of Stretching Speed on Mechanical Rupture of Phospholipid/Cholesterol Bilayers: Molecular Dynamics Simulation Taiki Shigematsu, Kenichiro Koshiyama*, and Shigeo Wada
Supplementary information for Effects of Stretching Speed on Mechanical Rupture of Phospholipid/Cholesterol Bilayers: Molecular Dynamics Simulation Taiki Shigematsu, Kenichiro Koshiyama*, and Shigeo Wada
Papers Arising from the Vertebral Artery Study
 Papers Arising from the Vertebral Artery Study 1. Brief Introduction to quaternions and framed vectors and their application to the description of anatomical movements. The mathematical description of
Papers Arising from the Vertebral Artery Study 1. Brief Introduction to quaternions and framed vectors and their application to the description of anatomical movements. The mathematical description of
10/23/2018. Ishik University / Sulaimani. Architecture Department. Surveying ARCH 224 CHAPTER -3- Level and Leveling LEVEL AND LEVELING
 Ishik University - Sulaimani Architecture Department Surveying ARCH 224 CHAPTER -3- Level and Leveling 1 CHAPTER -3- LEVEL AND LEVELING 2 1 CONTENTS 1. Level instrument 2. Bubble 3. Tripod 4. Definitions
Ishik University - Sulaimani Architecture Department Surveying ARCH 224 CHAPTER -3- Level and Leveling 1 CHAPTER -3- LEVEL AND LEVELING 2 1 CONTENTS 1. Level instrument 2. Bubble 3. Tripod 4. Definitions
Functional and Biomechanical Assessment of Teres Major Tendon Transfer as Primary Treatment of Massive Rotator Cuff Tears
 Functional and Biomechanical Assessment of Teres Major Tendon Transfer as Primary Treatment of Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Reprinted with permission from Norris TR, Zuckerman JD, Warner JJP, Lee TQ (eds):
Functional and Biomechanical Assessment of Teres Major Tendon Transfer as Primary Treatment of Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Reprinted with permission from Norris TR, Zuckerman JD, Warner JJP, Lee TQ (eds):
Lecture 2 BME 599: Modeling & Simulation of Movement
 Simulation Lab #1 Lecture 2 Question of the Day How high can you jump without an approach or swinging your arms? How should you coordinate muscle forces to produce a maximum height jump? Outline for Today
Simulation Lab #1 Lecture 2 Question of the Day How high can you jump without an approach or swinging your arms? How should you coordinate muscle forces to produce a maximum height jump? Outline for Today
CFD ANALYSIS OF THE PERFORMANCE OF A FAST CATAMARAN WITH ROUGH SEA
 STAR EUROPEAN CONFERENCE 2011 Amsterdam, 22 23 March CFD ANALYSIS OF THE PERFORMANCE OF A FAST CATAMARAN WITH ROUGH SEA G. Lombardi, M. Maganzi Dept. of Aerospace Engineering of Pisa Italy The Problem
STAR EUROPEAN CONFERENCE 2011 Amsterdam, 22 23 March CFD ANALYSIS OF THE PERFORMANCE OF A FAST CATAMARAN WITH ROUGH SEA G. Lombardi, M. Maganzi Dept. of Aerospace Engineering of Pisa Italy The Problem
The challenge of deducing meaningful results from induced acceleration analyses. George Chen Oct. 24th, 2002 Honda Fundamental Research Lab
 The challenge of deducing meaningful results from induced acceleration analyses George Chen Oct. 24th, 2002 Honda Fundamental Research Lab Regarded as a powerful tool in the interpretation of muscle function
The challenge of deducing meaningful results from induced acceleration analyses George Chen Oct. 24th, 2002 Honda Fundamental Research Lab Regarded as a powerful tool in the interpretation of muscle function
National Exams November hours duration
 National Exams November 2012 3 hours duration 1. If doubt exists as to the interpretation of any question, the candidate is urged to include a clear statement of any assumptions made in the answer booklet.
National Exams November 2012 3 hours duration 1. If doubt exists as to the interpretation of any question, the candidate is urged to include a clear statement of any assumptions made in the answer booklet.
Noise Cancellation using Adaptive Filters Algorithms
 Noise Cancellation using Adaptive Filters Algorithms Suman, Poonam Beniwal Department of ECE, OITM, Hisar, bhariasuman13@gmail.com Abstract Active Noise Control (ANC) involves an electro acoustic or electromechanical
Noise Cancellation using Adaptive Filters Algorithms Suman, Poonam Beniwal Department of ECE, OITM, Hisar, bhariasuman13@gmail.com Abstract Active Noise Control (ANC) involves an electro acoustic or electromechanical
Biopac Student Lab Lesson 6 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) II Analysis Procedure. Rev
 42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 6 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) II Analysis Procedure Rev. 12292017 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University
42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 6 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) II Analysis Procedure Rev. 12292017 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University
NEURAL SYSTEMS FOR INTEGRATING ROBOT BEHAVIOURS
 NEURAL SYSTEMS FOR INTEGRATING ROBOT BEHAVIOURS Brett Browning & Gordon Wyeth University of Queensland Computer Science and Electrical Engineering Department Email: browning@elec.uq.edu.au & wyeth@elec.uq.edu.au
NEURAL SYSTEMS FOR INTEGRATING ROBOT BEHAVIOURS Brett Browning & Gordon Wyeth University of Queensland Computer Science and Electrical Engineering Department Email: browning@elec.uq.edu.au & wyeth@elec.uq.edu.au
CORESTA RECOMMENDED METHOD N 22
 CORESTA RECOMMENDED METHOD N 22 ROUTINE ANALYTICAL CIGARETTE-SMOKING MACHINE SPECIFICATIONS, DEFINITIONS AND STANDARD CONDITIONS (August 1991) 0. INTRODUCTION This CORESTA Recommended Method includes the
CORESTA RECOMMENDED METHOD N 22 ROUTINE ANALYTICAL CIGARETTE-SMOKING MACHINE SPECIFICATIONS, DEFINITIONS AND STANDARD CONDITIONS (August 1991) 0. INTRODUCTION This CORESTA Recommended Method includes the
Successful Splicing Made Easy
 Successful Splicing Made Easy Years ago fiber splicing was a difficult and finicky process that was left to the fiber guru. The splicers were expensive and temperamental. Nobody wanted to be the person
Successful Splicing Made Easy Years ago fiber splicing was a difficult and finicky process that was left to the fiber guru. The splicers were expensive and temperamental. Nobody wanted to be the person
Gender Discrimination Through Fingerprint- A Review
 Gender Discrimination Through Fingerprint- A Review Navkamal kaur 1, Beant kaur 2 1 M.tech Student, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala 2Assistant Professor,
Gender Discrimination Through Fingerprint- A Review Navkamal kaur 1, Beant kaur 2 1 M.tech Student, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala 2Assistant Professor,
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Technical Review Vol. 51 No. 1 (March 2014)
 The Challenge of Innovative Cancer Treatments Enabled by Vero4DRT -Development of High-precision Dose Delivery Features for Reducing Radiation Exposure of Healthy Tissue- 76 YASUNOBU SUZUKI *1 KUNIO TAKAHASHI
The Challenge of Innovative Cancer Treatments Enabled by Vero4DRT -Development of High-precision Dose Delivery Features for Reducing Radiation Exposure of Healthy Tissue- 76 YASUNOBU SUZUKI *1 KUNIO TAKAHASHI
ISE Italian School of Endoscopy Hysteroscopy lv.1 Salerno Jan , 2018 Ergonomics in Hysteroscopy
 ISE Italian School of Endoscopy Hysteroscopy lv.1 Salerno Jan. 27-28, 2018 Ergonomics in Hysteroscopy Luigi Fasolino, MD What is ergonomics? The term ergonomics is derived from the Greek words "ergon"
ISE Italian School of Endoscopy Hysteroscopy lv.1 Salerno Jan. 27-28, 2018 Ergonomics in Hysteroscopy Luigi Fasolino, MD What is ergonomics? The term ergonomics is derived from the Greek words "ergon"
Measurement Denoising Using Kernel Adaptive Filters in the Smart Grid
 Measurement Denoising Using Kernel Adaptive Filters in the Smart Grid Presenter: Zhe Chen, Ph.D. Associate Professor, Associate Director Institute of Cyber-Physical Systems Engineering Northeastern University
Measurement Denoising Using Kernel Adaptive Filters in the Smart Grid Presenter: Zhe Chen, Ph.D. Associate Professor, Associate Director Institute of Cyber-Physical Systems Engineering Northeastern University
Chapter 02. Basic Research Methodology
 Chapter 02 Basic Research Methodology Definition RESEARCH Research is a quest for knowledge through diligent search or investigation or experimentation aimed at the discovery and interpretation of new
Chapter 02 Basic Research Methodology Definition RESEARCH Research is a quest for knowledge through diligent search or investigation or experimentation aimed at the discovery and interpretation of new
Learning Classifier Systems (LCS/XCSF)
 Context-Dependent Predictions and Cognitive Arm Control with XCSF Learning Classifier Systems (LCS/XCSF) Laurentius Florentin Gruber Seminar aus Künstlicher Intelligenz WS 2015/16 Professor Johannes Fürnkranz
Context-Dependent Predictions and Cognitive Arm Control with XCSF Learning Classifier Systems (LCS/XCSF) Laurentius Florentin Gruber Seminar aus Künstlicher Intelligenz WS 2015/16 Professor Johannes Fürnkranz
How NDT will underpin the certification of greener aircraft
 How NDT will underpin the certification of greener aircraft Robert A Smith Professor of NDT and High Value manufacturing, University of Bristol. President British Institute of NDT Acknowledgements Prof
How NDT will underpin the certification of greener aircraft Robert A Smith Professor of NDT and High Value manufacturing, University of Bristol. President British Institute of NDT Acknowledgements Prof
DRIVER BEHAVIOUR STUDIES IN THE MOTORWAY OPERATIONS PLATFORM GRANT
 DRIVER BEHAVIOUR STUDIES IN THE MOTORWAY OPERATIONS PLATFORM GRANT Mark Brackstone and Mike McDonald Transportation Research Group Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of Southampton
DRIVER BEHAVIOUR STUDIES IN THE MOTORWAY OPERATIONS PLATFORM GRANT Mark Brackstone and Mike McDonald Transportation Research Group Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of Southampton
Persistent Visual Tracking and Accurate Geo-Location of Moving Ground Targets by Small Air Vehicles
 Persistent Visual Tracking and Accurate Geo-Location of Moving Ground Targets by Small Air Vehicles Michael Dille, Ben Grocholsky, Stephen Thomas Nuske EXTENDED ABSTRACT 1 Motivation, Problem Statement,
Persistent Visual Tracking and Accurate Geo-Location of Moving Ground Targets by Small Air Vehicles Michael Dille, Ben Grocholsky, Stephen Thomas Nuske EXTENDED ABSTRACT 1 Motivation, Problem Statement,
Parallel-Axis Gear Terminology
 Parallel-Axis Gear Terminology For more detailed coverage of this subject, consult ANSI/AGMA Standard 1012-F90; Gear Nomenclature, Definitions with Terms and Symbols Active Profile- that part of the gear
Parallel-Axis Gear Terminology For more detailed coverage of this subject, consult ANSI/AGMA Standard 1012-F90; Gear Nomenclature, Definitions with Terms and Symbols Active Profile- that part of the gear
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
LION. Application Note PRECISION. Linear Position Measurement with Eddy-Current Sensors. LA March, Applicable Equipment: Applications:
 LION PRECISION Application Note LA02-0061 March, 2013 Linear Position Measurement with Eddy-Current Sensors Position, Displacement Applicable Equipment: Eddy-Current position measurement systems. Applications:
LION PRECISION Application Note LA02-0061 March, 2013 Linear Position Measurement with Eddy-Current Sensors Position, Displacement Applicable Equipment: Eddy-Current position measurement systems. Applications:
CONTROL OF THE BOUNDARY CONDITIONS OF A DYNAMIC KNEE SIMULATOR
 CONTROL OF THE BOUNDARY CONDITIONS OF A DYNAMIC KNEE SIMULATOR J. Tiré 1, J. Victor 2, P. De Baets 3 and M.A. Verstraete 2 1 Ghent University, Belgium 2 Ghent University, Department of Physical Medicine
CONTROL OF THE BOUNDARY CONDITIONS OF A DYNAMIC KNEE SIMULATOR J. Tiré 1, J. Victor 2, P. De Baets 3 and M.A. Verstraete 2 1 Ghent University, Belgium 2 Ghent University, Department of Physical Medicine
Spreading of Epidemic Based on Human and Animal Mobility Pattern
 Spreading of Epidemic Based on Human and Animal Mobility Pattern Yanqing Hu, Dan Luo, Xiaoke Xu, Zhangang Han, Zengru Di Department of Systems Science, Beijing Normal University 2009-12-22 Background &
Spreading of Epidemic Based on Human and Animal Mobility Pattern Yanqing Hu, Dan Luo, Xiaoke Xu, Zhangang Han, Zengru Di Department of Systems Science, Beijing Normal University 2009-12-22 Background &
Experimental Prediction of Contact Area in Hip Replacement and Hemi- Arthroplasty
 Experimental Prediction of Contact Area in Hip Replacement and Hemi- Arthroplasty Qianqian Wang, John Fisher, Sophie Williams. Institute of Medical and Biological Engineering, School of Mechanical Engineering,
Experimental Prediction of Contact Area in Hip Replacement and Hemi- Arthroplasty Qianqian Wang, John Fisher, Sophie Williams. Institute of Medical and Biological Engineering, School of Mechanical Engineering,
The Technical Model: an Overview Explanation of the Technical Model
 A Technical Model for Pole Vault Success Michael A. Young Louisiana State University ****************This is a modified version of an article published in Track Coach Pole vaulting is perhaps the most
A Technical Model for Pole Vault Success Michael A. Young Louisiana State University ****************This is a modified version of an article published in Track Coach Pole vaulting is perhaps the most
Scientific Working Group on Digital Evidence
 Disclaimer: As a condition to the use of this document and the information contained therein, the SWGDE requests notification by e-mail before or contemporaneous to the introduction of this document, or
Disclaimer: As a condition to the use of this document and the information contained therein, the SWGDE requests notification by e-mail before or contemporaneous to the introduction of this document, or
Composite Structures. Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur
 Mechanics of Laminated Composite Structures Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture 20 Behavior of Short Fiber Composites V i V min and V crit for Short Fiber Composites The average
Mechanics of Laminated Composite Structures Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture 20 Behavior of Short Fiber Composites V i V min and V crit for Short Fiber Composites The average
On Signal Analysis of Three-Dimensional Nystagmus
 846 Medical Informatics in a United and Healthy Europe K.-P. Adlassnig et al. (Eds.) IOS Press, 29 29 European Federation for Medical Informatics. All rights reserved. doi:1.3233/978-1-675-44-5-846 On
846 Medical Informatics in a United and Healthy Europe K.-P. Adlassnig et al. (Eds.) IOS Press, 29 29 European Federation for Medical Informatics. All rights reserved. doi:1.3233/978-1-675-44-5-846 On
Noninvasive Blood Glucose Analysis using Near Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy. Abstract
 Progress Report No. 2-3, March 31, 1999 The Home Automation and Healthcare Consortium Noninvasive Blood Glucose Analysis using Near Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy Prof. Kamal Youcef-Toumi Principal Investigator
Progress Report No. 2-3, March 31, 1999 The Home Automation and Healthcare Consortium Noninvasive Blood Glucose Analysis using Near Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy Prof. Kamal Youcef-Toumi Principal Investigator
Unweaving the Web: Deception and Adaptation in Future Urban Operations
 SUMMARY Deception is widely appreciated as a powerful instrument of war, yet it is surprisingly understudied. There is much to be learned from the flexibility and innovation demonstrated at times by opposing
SUMMARY Deception is widely appreciated as a powerful instrument of war, yet it is surprisingly understudied. There is much to be learned from the flexibility and innovation demonstrated at times by opposing
A numerical 3D coronary tree model
 1 A numerical 3D coronary tree model Denis Sherknies a, Jean Meunier b a University of Montreal, sherknie@iro.umontreal.ca, b University of Montreal Abstract We present a method that defines a numerical
1 A numerical 3D coronary tree model Denis Sherknies a, Jean Meunier b a University of Montreal, sherknie@iro.umontreal.ca, b University of Montreal Abstract We present a method that defines a numerical
Muscle-Tendon Mechanics Dr. Ted Milner (KIN 416)
 Muscle-Tendon Mechanics Dr. Ted Milner (KIN 416) Muscle Fiber Geometry Muscle fibers are linked together by collagenous connective tissue. Endomysium surrounds individual fibers, perimysium collects bundles
Muscle-Tendon Mechanics Dr. Ted Milner (KIN 416) Muscle Fiber Geometry Muscle fibers are linked together by collagenous connective tissue. Endomysium surrounds individual fibers, perimysium collects bundles
GUIDANCE NOTE. Application of MEMS Ultrasonic Transducers to Flow Measurement.
 GUIDANCE NOTE Application of MEMS Ultrasonic Transducers www.tuvnel.com Application of MEMS Ultrasonic Transducers Introduction This Guidance Note provides a review of the key issues associated with the
GUIDANCE NOTE Application of MEMS Ultrasonic Transducers www.tuvnel.com Application of MEMS Ultrasonic Transducers Introduction This Guidance Note provides a review of the key issues associated with the
FES Standing: The Effect of Arm Support on Stability and Fatigue During Sit-to-Stand Manoeuvres in SCI Individuals
 FES Standing: The Effect of Arm Support on Stability and Fatigue During Sit-to-Stand Manoeuvres in SCI Individuals Musfirah Abd Aziz and Nur Azah Hamzaid Abstract Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
FES Standing: The Effect of Arm Support on Stability and Fatigue During Sit-to-Stand Manoeuvres in SCI Individuals Musfirah Abd Aziz and Nur Azah Hamzaid Abstract Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
STPA-based Model of Threat and Error Management in Dual Flight Instruction
 STPA-based Model of Threat and Error Management in Dual Flight Instruction Ioana Koglbauer Graz University of Technology, Austria koglbauer@tugraz.at Threat and Error Management (TEM) Currently the Authorities
STPA-based Model of Threat and Error Management in Dual Flight Instruction Ioana Koglbauer Graz University of Technology, Austria koglbauer@tugraz.at Threat and Error Management (TEM) Currently the Authorities
The NHS Cancer Plan: A Progress Report
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH The NHS Cancer Plan: A Progress Report LONDON: The Stationery Office 9.25 Ordered by the House of Commons to be printed on 7 March 2005 REPORT BY THE COMPTROLLER AND AUDITOR GENERAL
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH The NHS Cancer Plan: A Progress Report LONDON: The Stationery Office 9.25 Ordered by the House of Commons to be printed on 7 March 2005 REPORT BY THE COMPTROLLER AND AUDITOR GENERAL
CKSS 2012 Exercise Science Section 1: The Anatomical Position An Introduction to Health and Physical Education
 CKSS 2012 Exercise Science Section 1: The Anatomical Position An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Text Books, Work Book and Reading List Introductions
CKSS 2012 Exercise Science Section 1: The Anatomical Position An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Text Books, Work Book and Reading List Introductions
Understanding cascade impaction and its importance for inhaler testing
 Understanding cascade impaction and its importance for inhaler testing Mark Copley, Technical Sales Manager Inhalation product development is an important area of activity for the pharmaceutical sector.
Understanding cascade impaction and its importance for inhaler testing Mark Copley, Technical Sales Manager Inhalation product development is an important area of activity for the pharmaceutical sector.
Characterizing Visual Attention during Driving and Non-driving Hazard Perception Tasks in a Simulated Environment
 Title: Authors: Characterizing Visual Attention during Driving and Non-driving Hazard Perception Tasks in a Simulated Environment Mackenzie, A.K. Harris, J.M. Journal: ACM Digital Library, (ETRA '14 Proceedings
Title: Authors: Characterizing Visual Attention during Driving and Non-driving Hazard Perception Tasks in a Simulated Environment Mackenzie, A.K. Harris, J.M. Journal: ACM Digital Library, (ETRA '14 Proceedings
EasyChair Preprint. Comparison between Epsilon Normalized Least means Square (-NLMS) and Recursive Least Squares (RLS) Adaptive Algorithms
 EasyChair Preprint 32 Comparison between Epsilon Normalized Least means Square (-NLMS) and Recursive Least Squares (RLS) Adaptive Algorithms Ali Salah Mahdi, Lwaa Faisal Abdulameer and Ameer Hussein Morad
EasyChair Preprint 32 Comparison between Epsilon Normalized Least means Square (-NLMS) and Recursive Least Squares (RLS) Adaptive Algorithms Ali Salah Mahdi, Lwaa Faisal Abdulameer and Ameer Hussein Morad
Developing a Game-Based Proprioception Reconstruction System for Patients with Ankle Sprain
 Developing a Game-Based Proprioception Reconstruction System for Patients with Ankle Sprain Yu-Cheng Lin, Chung Shan Medical University, Taiwan Tzu-Fang Sheu, Providence University, Taiwan Hsiao Ping Lee,
Developing a Game-Based Proprioception Reconstruction System for Patients with Ankle Sprain Yu-Cheng Lin, Chung Shan Medical University, Taiwan Tzu-Fang Sheu, Providence University, Taiwan Hsiao Ping Lee,
Automated ultrasonic testing of submerged-arc welded (SAW) pipes using phased-arrays
 18th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 16-20 April 2012, Durban, South Africa Automated ultrasonic testing of submerged-arc welded (SAW) pipes using phased-arrays 1 Jörg Ininger, 1 Ulrich Semmler,
18th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 16-20 April 2012, Durban, South Africa Automated ultrasonic testing of submerged-arc welded (SAW) pipes using phased-arrays 1 Jörg Ininger, 1 Ulrich Semmler,
Indirect retainers. 1 i
 8 1 i Indirect retainers Factors Influencing Effectiveness Indirect Retainers Auxiliary Functions Indirect Retainers Forms Indirect Retainers Auxiliary occlusal rest Canine extensions fiom occlusal rests
8 1 i Indirect retainers Factors Influencing Effectiveness Indirect Retainers Auxiliary Functions Indirect Retainers Forms Indirect Retainers Auxiliary occlusal rest Canine extensions fiom occlusal rests
Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Blalock-Taussig Shunt
 Washington University in St. Louis Washington University Open Scholarship Mechanical Engineering and Materials Science Independent Study Mechanical Engineering & Materials Science 12-23-2017 Computational
Washington University in St. Louis Washington University Open Scholarship Mechanical Engineering and Materials Science Independent Study Mechanical Engineering & Materials Science 12-23-2017 Computational
Fast Simulation of Arm Dynamics for Real-time, Userin-the-loop. Ed Chadwick Keele University Staffordshire, UK.
 Fast Simulation of Arm Dynamics for Real-time, Userin-the-loop Control Applications Ed Chadwick Keele University Staffordshire, UK. Acknowledgements Dimitra Blana, Keele University, Staffordshire, UK.
Fast Simulation of Arm Dynamics for Real-time, Userin-the-loop Control Applications Ed Chadwick Keele University Staffordshire, UK. Acknowledgements Dimitra Blana, Keele University, Staffordshire, UK.
THE DEVELOPMENT AND MANUFACTURE OF FIXED- ULTRASONIC INSPECTION REFERENCE REFLECTORS AND TRANSDUCERS FOR COMPRESSOR BLADE DOVETAILS
 International Workshop SMART MATERIALS, STRUCTURES & NDT in AEROSPACE Conference NDT in Canada 2011 2-4 November 2011, Montreal, Quebec, Canada THE DEVELOPMENT AND MANUFACTURE OF FIXED- ULTRASONIC INSPECTION
International Workshop SMART MATERIALS, STRUCTURES & NDT in AEROSPACE Conference NDT in Canada 2011 2-4 November 2011, Montreal, Quebec, Canada THE DEVELOPMENT AND MANUFACTURE OF FIXED- ULTRASONIC INSPECTION
Outline: Vergence Eye Movements: Classification I. Describe with 3 degrees of freedom- Horiz, Vert, torsion II. Quantifying units- deg, PD, MA III.
 Outline: Vergence Eye Movements: Classification I. Describe with 3 degrees of freedom- Horiz, Vert, torsion II. Quantifying units- deg, PD, MA III. Measurement of Vergence:- Objective & Subjective phoria
Outline: Vergence Eye Movements: Classification I. Describe with 3 degrees of freedom- Horiz, Vert, torsion II. Quantifying units- deg, PD, MA III. Measurement of Vergence:- Objective & Subjective phoria
A low supply voltage and wide-tuned CMOS Colpitts VCO
 This article has been accepted and published on J-STAGE in advance of copyediting. Content is final as presented. IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.* No.*,*-* A low supply voltage and wide-tuned CMOS Colpitts
This article has been accepted and published on J-STAGE in advance of copyediting. Content is final as presented. IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.* No.*,*-* A low supply voltage and wide-tuned CMOS Colpitts
Neuromorphic convolutional recurrent neural network for road safety or safety near the road
 Neuromorphic convolutional recurrent neural network for road safety or safety near the road WOO-SUP HAN 1, IL SONG HAN 2 1 ODIGA, London, U.K. 2 Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon,
Neuromorphic convolutional recurrent neural network for road safety or safety near the road WOO-SUP HAN 1, IL SONG HAN 2 1 ODIGA, London, U.K. 2 Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon,
Copenhagen, Denmark, September August Malaria
 Regional Committee for Europe 64th session EUR/RC64/Inf.Doc./5 Copenhagen, Denmark, 15 18 September 2014 21 August 2014 140602 Provisional agenda item 3 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Malaria Following the support
Regional Committee for Europe 64th session EUR/RC64/Inf.Doc./5 Copenhagen, Denmark, 15 18 September 2014 21 August 2014 140602 Provisional agenda item 3 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Malaria Following the support
Daniel P. Gillen Student, Air Force Institute of Technology, AFIT/ENY Wright Patterson Air Force Base, OH
 Chapter 1 COOPERATIVE BEHAVIOR SCHEMES FOR IMPROVING THE EFFECTIVENESS OF AUTONOMOUS WIDE AREA SEARCH MUNITIONS Λ Daniel P. Gillen Student, Air Force Institute of Technology, AFIT/ENY Wright Patterson
Chapter 1 COOPERATIVE BEHAVIOR SCHEMES FOR IMPROVING THE EFFECTIVENESS OF AUTONOMOUS WIDE AREA SEARCH MUNITIONS Λ Daniel P. Gillen Student, Air Force Institute of Technology, AFIT/ENY Wright Patterson
Inspection Qualification II
 Inspection Qualification II The Benefits of Technical Justification in the Inspection Qualification of Nozzle Inner Radius R. Martínez-Oña, J. Sánchez, R. Jiménez, Tecnatom, Spain INTRODUCTION Technical
Inspection Qualification II The Benefits of Technical Justification in the Inspection Qualification of Nozzle Inner Radius R. Martínez-Oña, J. Sánchez, R. Jiménez, Tecnatom, Spain INTRODUCTION Technical
Report 08 Salt observation 19jan13
 1 Standardization of test method for salt spreader: Air flow experiments Report 8: Observation of salt particle trajectory from spreader disc to road surface by Hisamitsu Takai, Consultant Aarhus University,
1 Standardization of test method for salt spreader: Air flow experiments Report 8: Observation of salt particle trajectory from spreader disc to road surface by Hisamitsu Takai, Consultant Aarhus University,
Image Enhancement and Compression using Edge Detection Technique
 Image Enhancement and Compression using Edge Detection Technique Sanjana C.Shekar 1, D.J.Ravi 2 1M.Tech in Signal Processing, Dept. Of ECE, Vidyavardhaka College of Engineering, Mysuru 2Professor, Dept.
Image Enhancement and Compression using Edge Detection Technique Sanjana C.Shekar 1, D.J.Ravi 2 1M.Tech in Signal Processing, Dept. Of ECE, Vidyavardhaka College of Engineering, Mysuru 2Professor, Dept.
EFFECTIVENESS ANALYSIS FOR WIDE AREA SEARCH MUNITIONS
 EFFECTIVEESS AALYSIS FOR WIDE AREA SEARCH MUITIOS David R. Jacques, Air Force Research Laboratory, Munitions Directorate 0 W. Eglin Blvd. Suite 348, Eglin Air Force Base, Florida 32542 jacques@eglin.af.mil
EFFECTIVEESS AALYSIS FOR WIDE AREA SEARCH MUITIOS David R. Jacques, Air Force Research Laboratory, Munitions Directorate 0 W. Eglin Blvd. Suite 348, Eglin Air Force Base, Florida 32542 jacques@eglin.af.mil
An architecture description method for Acknowledged System of Systems based on Federated Architecture
 An architecture description method for Acknowledged System of Systems based on Federated Architecture Jae-Hong Ahn 1, Yeunseung Ryu 2 and Doo-Kwon Baik 3 1 Agency for Defense Development, Korea koreaseman@daum.net
An architecture description method for Acknowledged System of Systems based on Federated Architecture Jae-Hong Ahn 1, Yeunseung Ryu 2 and Doo-Kwon Baik 3 1 Agency for Defense Development, Korea koreaseman@daum.net
Optimum Size Selection For Spring Loaded Detachable Canister Launch Vehicle Interface For Multistage Long Range System
 International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) Volume Number Nov Optimum Size Selection For Spring Loaded Detachable Canister Launch Vehicle Interface For Multistage Long Range System
International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) Volume Number Nov Optimum Size Selection For Spring Loaded Detachable Canister Launch Vehicle Interface For Multistage Long Range System
Adaptation in the development context
 Adaptation in the development context Anand Patwardhan University of Maryland, USA and Indian Institute of Technology-Bombay, India NAP Expo Bonn, August 2014 Shifts in the policy narrative Climate mitigation
Adaptation in the development context Anand Patwardhan University of Maryland, USA and Indian Institute of Technology-Bombay, India NAP Expo Bonn, August 2014 Shifts in the policy narrative Climate mitigation
Installation of force transducers
 Installation of force transducers Force transducers have reached a high technical standard in recent years. Transducers achieve part of their high accuracy due to improved possibilities for calibration.
Installation of force transducers Force transducers have reached a high technical standard in recent years. Transducers achieve part of their high accuracy due to improved possibilities for calibration.
Rotavirus Vaccine. Supply and Procurement Roadmap. The Market Shaping Goal. Public Summary. Rotavirus Supply and Procurement Roadmap UPDATE 2016
 The Market Shaping Goal Shape markets for vaccines and other immunisation products to achieve moderate or high levels of healthy markets dynamics. Supply and Procurement Roadmap Rotavirus Vaccine Public
The Market Shaping Goal Shape markets for vaccines and other immunisation products to achieve moderate or high levels of healthy markets dynamics. Supply and Procurement Roadmap Rotavirus Vaccine Public
Comparison of volume estimation methods for pancreatic islet cells
 Comparison of volume estimation methods for pancreatic islet cells Jiří Dvořák a,b, Jan Švihlíkb,c, David Habart d, and Jan Kybic b a Department of Probability and Mathematical Statistics, Faculty of Mathematics
Comparison of volume estimation methods for pancreatic islet cells Jiří Dvořák a,b, Jan Švihlíkb,c, David Habart d, and Jan Kybic b a Department of Probability and Mathematical Statistics, Faculty of Mathematics
The biomechanical design of a training aid for a backward handspring in gymnastics
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository The biomechanical design of a training aid for a backward handspring in gymnastics This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository
Loughborough University Institutional Repository The biomechanical design of a training aid for a backward handspring in gymnastics This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository
Best Practice: SPORTS
 Best Practice: SPORTS Go to the section that is most appropriate for you Key Points... 1 Introduction... 1 Preparation... 3 Novice Athletes... 4 Training Sessions with Larger Groups (e.g. 5 25)... 4 Training
Best Practice: SPORTS Go to the section that is most appropriate for you Key Points... 1 Introduction... 1 Preparation... 3 Novice Athletes... 4 Training Sessions with Larger Groups (e.g. 5 25)... 4 Training
Sterilization of health care products Radiation. Part 3: Guidance on dosimetric aspects of development, validation and routine control
 Provläsningsexemplar / Preview INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 11137-3 Second edition 2017-06 Sterilization of health care products Radiation Part 3: Guidance on dosimetric aspects of development, validation
Provläsningsexemplar / Preview INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 11137-3 Second edition 2017-06 Sterilization of health care products Radiation Part 3: Guidance on dosimetric aspects of development, validation
Design and Scaling of Versatile Quadruped Robots
 1 Design and Scaling of Versatile Quadruped Robots C. SEMINI, H. KHAN, M. FRIGERIO, T. BOAVENTURA, M. FOCCHI, J. BUCHLI and D. G. CALDWELL Department of Advanced Robotics, Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia
1 Design and Scaling of Versatile Quadruped Robots C. SEMINI, H. KHAN, M. FRIGERIO, T. BOAVENTURA, M. FOCCHI, J. BUCHLI and D. G. CALDWELL Department of Advanced Robotics, Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia
Application of ecological interface design to driver support systems
 Application of ecological interface design to driver support systems J.D. Lee, J.D. Hoffman, H.A. Stoner, B.D. Seppelt, and M.D. Brown Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, University of
Application of ecological interface design to driver support systems J.D. Lee, J.D. Hoffman, H.A. Stoner, B.D. Seppelt, and M.D. Brown Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, University of
Numerical analysis of the embedded abutments of integral bridges
 Numerical analysis of the embedded abutments of integral bridges Ming XU Researcher, Dept. of Civil & Env. Engrg., University of Southampton, UK Summary Alan G. BLOODWORTH Lecturer, Dept. of Civil & Env.
Numerical analysis of the embedded abutments of integral bridges Ming XU Researcher, Dept. of Civil & Env. Engrg., University of Southampton, UK Summary Alan G. BLOODWORTH Lecturer, Dept. of Civil & Env.
Human Computer Interaction - An Introduction
 NPTEL Course on Human Computer Interaction - An Introduction Dr. Pradeep Yammiyavar Professor, Dept. of Design, IIT Guwahati, Assam, India Dr. Samit Bhattacharya Assistant Professor, Dept. of Computer
NPTEL Course on Human Computer Interaction - An Introduction Dr. Pradeep Yammiyavar Professor, Dept. of Design, IIT Guwahati, Assam, India Dr. Samit Bhattacharya Assistant Professor, Dept. of Computer
Definition 1: A fixed point iteration scheme to approximate the fixed point, p, of a function g, = for all n 1 given a starting approximation, p.
 Supplemental Material: A. Proof of Convergence In this Appendix, we provide a computational proof that the circadian adjustment method (CAM) belongs to the class of fixed-point iteration schemes (FPIS)
Supplemental Material: A. Proof of Convergence In this Appendix, we provide a computational proof that the circadian adjustment method (CAM) belongs to the class of fixed-point iteration schemes (FPIS)
week by week in the Training Calendar. Follow up graphics, sort, filter, merge, and split functions are also included.
 Firstbeat ATHLETE The story Firstbeat ATHLETE is one of the most advanced software tools for analyzing heart rate based training. It makes professional level training analysis available to all dedicated
Firstbeat ATHLETE The story Firstbeat ATHLETE is one of the most advanced software tools for analyzing heart rate based training. It makes professional level training analysis available to all dedicated
Estimation of the Upper Limb Lifting Movement Under Varying Weight and Movement Speed
 1 Sungyoon Lee, 1 Jaesung Oh, 1 Youngwon Kim, 1 Minsuk Kwon * Jaehyo Kim 1 Department of mechanical & control engineering, Handong University, qlfhlxhl@nate.com * Department of mechanical & control engineering,
1 Sungyoon Lee, 1 Jaesung Oh, 1 Youngwon Kim, 1 Minsuk Kwon * Jaehyo Kim 1 Department of mechanical & control engineering, Handong University, qlfhlxhl@nate.com * Department of mechanical & control engineering,
A contrast paradox in stereopsis, motion detection and vernier acuity
 A contrast paradox in stereopsis, motion detection and vernier acuity S. B. Stevenson *, L. K. Cormack Vision Research 40, 2881-2884. (2000) * University of Houston College of Optometry, Houston TX 77204
A contrast paradox in stereopsis, motion detection and vernier acuity S. B. Stevenson *, L. K. Cormack Vision Research 40, 2881-2884. (2000) * University of Houston College of Optometry, Houston TX 77204
Eindhoven University of Technology. Exam Modeling Cardiac Function (8W160)
 Eindhoven University of Technology department of Biomedical Engineering group Cardiovascular Biomechanics Exam Modeling Cardiac Function (8W160) January 21, 2011, 14.00 17.00 h This exam consists of 6
Eindhoven University of Technology department of Biomedical Engineering group Cardiovascular Biomechanics Exam Modeling Cardiac Function (8W160) January 21, 2011, 14.00 17.00 h This exam consists of 6
VIPR and Power plate EXERCISE - 1 EXERCISE Fitness Professionals Ltd 2011 Job No. 2968
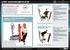 FIT FOR DAILY LIFE To be fit for daily life includes many movement abilities. Dynamic stability, co-ordination, balance, motor control, mobility and efficiency are all vital (including basic strength and
FIT FOR DAILY LIFE To be fit for daily life includes many movement abilities. Dynamic stability, co-ordination, balance, motor control, mobility and efficiency are all vital (including basic strength and
Aurora Police Department
 Aurora Police Department APDRecruiting@AuroraGov.org #JoinTheAPD 1.800.637.9963 Welcome to the Aurora Pre-Academy Fitness Guide. This guide is designed to give the reader better insight into the following
Aurora Police Department APDRecruiting@AuroraGov.org #JoinTheAPD 1.800.637.9963 Welcome to the Aurora Pre-Academy Fitness Guide. This guide is designed to give the reader better insight into the following
CERATIZIT 3X3. an intelligent combination
 CERATIZIT 3X3 an intelligent combination 2 \ CERATIZIT 3X3 INTRODUCTION The user-friendly concept CERATIZIT 3x3, an intelligent combination of grades and chip breaker, enable you to quickly choose the
CERATIZIT 3X3 an intelligent combination 2 \ CERATIZIT 3X3 INTRODUCTION The user-friendly concept CERATIZIT 3x3, an intelligent combination of grades and chip breaker, enable you to quickly choose the
Re: ENSC 370 Project Gerbil Functional Specifications
 Simon Fraser University Burnaby, BC V5A 1S6 trac-tech@sfu.ca February, 16, 1999 Dr. Andrew Rawicz School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University Burnaby, BC V5A 1S6 Re: ENSC 370 Project Gerbil Functional
Simon Fraser University Burnaby, BC V5A 1S6 trac-tech@sfu.ca February, 16, 1999 Dr. Andrew Rawicz School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University Burnaby, BC V5A 1S6 Re: ENSC 370 Project Gerbil Functional
Therapy Manual DO NOT PRINT
 Therapy Manual Contents 1. Shoulder 2. Shoulder and elbow a. Protraction: 1 DoF 1 b. Flexion: 1 DoF 1-6 c. Extension: 1 DoF 1-2 d. Abduction: 1 DoF 1-4 e. External rotation: 1 DoF 1-14 a. Combined shoulder
Therapy Manual Contents 1. Shoulder 2. Shoulder and elbow a. Protraction: 1 DoF 1 b. Flexion: 1 DoF 1-6 c. Extension: 1 DoF 1-2 d. Abduction: 1 DoF 1-4 e. External rotation: 1 DoF 1-14 a. Combined shoulder
Embracing Complexity in System of Systems Analysis and Architecting
 Embracing Complexity in System of Systems Analysis and Architecting Complex Adaptive System 2013 November 13-15, 2013, Baltimore, MA Cihan H. Dagli INCOSE and IIE Fellow Founder Director Systems Engineering
Embracing Complexity in System of Systems Analysis and Architecting Complex Adaptive System 2013 November 13-15, 2013, Baltimore, MA Cihan H. Dagli INCOSE and IIE Fellow Founder Director Systems Engineering
A STATISTICAL PATTERN RECOGNITION PARADIGM FOR VIBRATION-BASED STRUCTURAL HEALTH MONITORING
 A STATISTICAL PATTERN RECOGNITION PARADIGM FOR VIBRATION-BASED STRUCTURAL HEALTH MONITORING HOON SOHN Postdoctoral Research Fellow ESA-EA, MS C96 Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos, NM 87545 CHARLES
A STATISTICAL PATTERN RECOGNITION PARADIGM FOR VIBRATION-BASED STRUCTURAL HEALTH MONITORING HOON SOHN Postdoctoral Research Fellow ESA-EA, MS C96 Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos, NM 87545 CHARLES
Clinical experiences with a new device for fixed. orthodontic treatment of Angle classes 2 and 3
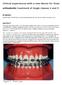 Clinical experiences with a new device for fixed orthodontic treatment of Angle classes 2 and 3 KEYWORDS Second Class; Therd Class; Fixed Connecting Device; New device, Herbst; Auxiliary arch. ABSTRACT
Clinical experiences with a new device for fixed orthodontic treatment of Angle classes 2 and 3 KEYWORDS Second Class; Therd Class; Fixed Connecting Device; New device, Herbst; Auxiliary arch. ABSTRACT
